WO2020195595A1 - 服薬状況管理装置、方法およびプログラム - Google Patents
服薬状況管理装置、方法およびプログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2020195595A1 WO2020195595A1 PCT/JP2020/008797 JP2020008797W WO2020195595A1 WO 2020195595 A1 WO2020195595 A1 WO 2020195595A1 JP 2020008797 W JP2020008797 W JP 2020008797W WO 2020195595 A1 WO2020195595 A1 WO 2020195595A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- medication
- information
- declaration
- reliability
- period
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H15/00—ICT specially adapted for medical reports, e.g. generation or transmission thereof
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H20/00—ICT specially adapted for therapies or health-improving plans, e.g. for handling prescriptions, for steering therapy or for monitoring patient compliance
- G16H20/10—ICT specially adapted for therapies or health-improving plans, e.g. for handling prescriptions, for steering therapy or for monitoring patient compliance relating to drugs or medications, e.g. for ensuring correct administration to patients
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/48—Other medical applications
- A61B5/4833—Assessment of subject's compliance to treatment
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H10/00—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of patient-related medical or healthcare data
- G16H10/60—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of patient-related medical or healthcare data for patient-specific data, e.g. for electronic patient records
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H40/00—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices
- G16H40/60—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices for the operation of medical equipment or devices
- G16H40/67—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices for the operation of medical equipment or devices for remote operation
Definitions
- An embodiment of the present invention relates to a medication status management device, method and program used for managing the medication status by a user, for example.
- medication treatment As one of the treatment methods for diseases. In medication treatment, it is extremely important to comply with the medication prescribed by the doctor in order to obtain the desired therapeutic effect.
- the patient inputs declaration information indicating the medication status such as whether or not the patient has taken the medication, and based on this declaration information, the medication adherence indicating the status of compliance with the medication.
- declaration information indicating the medication status such as whether or not the patient has taken the medication
- the medication adherence indicating the status of compliance with the medication.
- medication managers such as doctors and pharmacists can accurately grasp the relationship between the patient's medication and the therapeutic effect, which is extremely effective. It also has the effect of being one of the motivations for patients to continue taking their own medication.
- the present invention was made by paying attention to the above circumstances, and is intended to provide a technique for providing information for more accurately managing the medication status.
- one aspect of the medication status management device or method acquires the user's medication declaration information, acquires the user's biometric information and stores it in a storage medium, and stores the storage. Based on the biometric information stored in the medium, the degree of dispersion of the biometric information acquired during the target period is calculated, and based on the degree of dispersion of the biometric information, the declaration information regarding the medication acquired during the target period is calculated. The reliability of the above is determined, and information indicating the determination result of the reliability is output.
- the degree of dispersion of biometric information is related to the compliance status of medication. For example, looking at the degree of dispersion of blood pressure values measured regularly every day during the target period of one week, the degree of dispersion of blood pressure values of patients who comply with medication is small, and conversely, the degree of dispersion of blood pressure values of patients who do not comply with medication is small. The degree of dispersion of blood pressure values tends to increase. Therefore, as in the first aspect of the present invention, the degree of dispersion of the measured values of biological information such as blood pressure during the target period is calculated, and the reliability of the medication declaration is determined and output based on this degree of dispersion. For example, a doctor or a pharmacist can accurately estimate the medication status of a user who is a patient and diagnose the effect of medication.
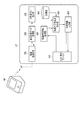
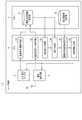
- FIG. 1 is a functional block diagram showing an application example of one of the medication status management devices according to the present invention.
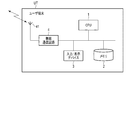
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing an overall configuration of a system including a mobile information terminal according to the first embodiment of the medication status management device according to the present invention.
- FIG. 3 is a diagram showing an example of the hardware configuration of the mobile information terminal shown in FIG.
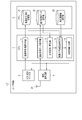
- FIG. 4 is a diagram showing an example of the software configuration of the mobile information terminal shown in FIG.
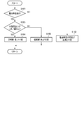
- FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing a procedure and processing contents of the medication status management process by the mobile information terminal shown in FIG.
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing an example of the procedure and processing contents of the medication declaration reliability determination process in the flowchart shown in FIG. FIG.
- FIG. 7 is a diagram showing an example of a software configuration of a mobile information terminal according to a second embodiment of the medication status management device according to the present invention.
- FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing a procedure and processing contents of the medication status management process by the mobile information terminal shown in FIG. 7.
- FIG. 9 is a flowchart showing an example of the procedure and processing contents of the medication declaration reliability determination process in the flowchart shown in FIG.
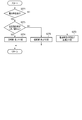
- FIG. 10 is a diagram showing an example of an input template displayed on the user terminal when inputting a medication report.
- FIG. 1 is a diagram for explaining this one application example, in which UT shows a user terminal and BP shows a sphygmomanometer.
- Sphygmomanometer BP is, for example, a stationary or upper arm-mounted blood pressure monitor that measures blood pressure by the oscillometric method, and is a wireless communication circuit that adopts a short-range wireless data communication standard such as Bluetooth (registered trademark) for blood pressure measurement data. Has a function of transmitting to the user terminal UT using.
- a wrist-type or wristwatch-type sphygmomanometer may be used in addition to the stationary type or the upper arm-mounted type in which the cuff is wrapped around the upper arm for measurement.
- a wristwatch-type sphygmomanometer can be used to measure blood pressure intermittently or automatically at a preset time.
- the user terminal UT is composed of a mobile information terminal such as a smartphone owned by a user who is a patient, and has an input / display device 100, a blood pressure measurement data acquisition unit 200, and a degree of dispersion as functions according to an application example of the present invention. It includes a calculation unit 300, a medication declaration information acquisition unit 400, a medication declaration reliability determination unit 500, a determination information output unit 600, and a wireless communication circuit 700.
- the blood pressure measurement data acquisition unit 200, the dispersion degree calculation unit 300, the medication declaration information acquisition unit 400, the medication declaration reliability determination unit 500, and the determination information output unit 600 are realized, for example, by causing a hardware processor to execute a program. Will be done.
- the input / display device 100 is a tablet-type device in which a capacitance type or pressure-sensitive input detection sheet is arranged on a liquid crystal or organic EL screen, and the medication declaration information input by the user's operation is acquired. Output to unit 400.
- the medication declaration information acquisition unit 400 takes in the medication declaration information output from the input / display device 100 and stores it in the memory in the user terminal UT.
- the wireless communication circuit 700 has a plurality of wireless interface functions for communicating with a wide area mobile communication network, a wireless LAN (Local Area Network), and Bluetooth (registered trademark), and in this example, the blood pressure monitor is described above. It is used to receive the blood pressure measurement data transmitted from the BP and to transmit the reliability determination information for the medication declaration information input by the user to the terminal of the medication manager such as a doctor or a pharmacist.
- a wireless LAN Local Area Network
- Bluetooth registered trademark
- the blood pressure measurement data acquisition unit 200 takes in the blood pressure measurement data received by the wireless communication circuit 700 and stores it in the memory in the user terminal UT.
- the variance degree calculation unit 300 reads the blood pressure measurement data measured in a preset target period (for example, one day or one week) from the memory, and reads the dispersion degree (for example, the degree of variation in the measured value or the change in the measured value). The degree of variation) is calculated.
- the medication declaration information acquisition unit 400 takes in the information input by the user in the input / display device 100 and declares the medication status during the medication period, and stores it in the memory in the user terminal UT.
- the medication declaration reliability determination unit 500 determines the reliability of the medication declaration information input by the user based on the variance degree of the blood pressure measurement data calculated by the dispersion degree calculation unit 300. The determination of the reliability is performed based on, for example, the number of times (timing) to be taken in a day and the content thereof specified by the prescription information.
- the prescription information is acquired from, for example, a terminal of a doctor or a pharmacist or an EMS server of a hospital and stored in a storage unit 800.
- the determination information output unit 600 sends, for example, a notification message for reporting the determination result of the reliability of the medication declaration information to the medication manager such as a doctor or a pharmacist based on the determination result of the reliability of the medication declaration information. It is generated and transmitted from the wireless communication circuit 700 to the terminal of a doctor or pharmacist.
- the determination information output unit 600 also has a function of generating, for example, a notification message urging the user to declare medication and displaying it on the input / display device 100.
- the determination information output unit 600 has a function of generating a contact message for a family member as a result of determining the reliability of the medication declaration information, for example, when the reliability is lower than the threshold value, and transmitting it from the wireless communication circuit 700. May have.
- the blood pressure measurement data acquisition unit 200 acquires the user's blood pressure measurement data together with the user's medication declaration information during the medication period by the medication declaration information acquisition unit 400. Then, based on the acquired blood pressure measurement data, the degree of dispersion of the blood pressure value or its change in the blood pressure measurement data during that period is calculated on a daily or weekly basis, and the degree of dispersion of the calculated blood pressure value is calculated. Based on this, the medication declaration reliability determination unit 500 determines the reliability of the user's medication declaration information during the same period, and the determination information indicating the determination result is output from the determination information output unit 600.
- the degree of dispersion of blood pressure values is related to the compliance status of medication. For example, looking at the degree of dispersion of blood pressure values measured regularly every day during the target period of one week, the degree of dispersion of blood pressure values of patients who comply with medication is small, and conversely, the degree of dispersion of blood pressure values of patients who do not comply with medication is small. The degree of dispersion of blood pressure values tends to increase.
- the medication manager such as a doctor or a pharmacist It is possible to accurately infer the medication status of the user who is the patient and diagnose the effect of the medication.
- the medication status management device acquires the declaration information acquisition unit that acquires the declaration information related to the user's medication and stores it in the storage medium, and acquires the biometric information of the user, and the biometric information is stored in the declaration information and the acquisition timing thereof. Based on the biometric information acquisition unit that stores the corresponding items in the storage medium in a state in which the corresponding ones can be associated with each other, and the declared information and biometric information stored in the storage medium in the first period in which the medication status is known.
- the prediction unit that calculates the predicted value of the biometric information in the second period for which the biometric information is monitored, and the living body acquired in the second period with respect to the calculated predicted value of the biometric information.
- a calculation unit that calculates the degree of deviation of the measured values of information, and a third unit before the second period that affects the change of the biological information in the second period based on the calculated degree of deviation. It includes a reliability determination unit that determines the reliability of the declaration information regarding the medication during the period, and an output unit that outputs information indicating the determination result of the reliability.
- the following actions and effects can be achieved. That is, in general, it is considered that the change in the measured value of the biometric information of the user who is observing the medication is small, so that the biometric information measured in the first period (prediction reference period) in which the medication status is known and the biometric information The degree of discrepancy between the predicted value of biometric information in the second period (monitoring period of biometric information) predicted from the medication declaration information and the measured value of biometric information actually measured in the second period becomes smaller. Tend.
- the biometric information in the second period as the monitoring period of the biometric information.
- the value of is predicted, and the change of the biometric information in the second period is affected based on the degree of deviation of the measured value of the biometric information actually measured with respect to the predicted value, before the second period.
- the degree of dispersion of the biological information or the degree of deviation of the measured value from the predicted value of the biological information calculated by the calculation unit by the reliability determination unit is higher or lower than the threshold value.
- the output unit generates a message prompting the user to correctly declare the medication or medication. Then, the message is output to at least one of the terminal of the user and the terminal of a related party having a predetermined relationship with the user.
- a message prompting the user to correctly declare the medication or medication is generated, and the user's terminal or the user's terminal or It is output to the terminal of a related person such as a family member who has a predetermined relationship with the user. Therefore, it is possible to more reliably enlighten the user to correctly declare the medication or medication.
- the medication status management device determines the medication rate, which represents the ratio of the number of times the medication is declared to the total number of medications declared during the period subject to the declaration of the medication, based on the declaration information regarding the medication, by the reliability determination unit. It is calculated, and the threshold value is set so that the lower the dose rate, the higher the value according to the calculated dose rate.
- the threshold value is set so that the lower the medication rate, the higher the threshold value. Therefore, when the user declares that he / she has "drinked” even though he / she has not actually taken it, a more accurate determination can be made.
- the medication status management device determines whether or not the declaration information has a deficiency in the medication-related declaration based on the declaration information regarding the medication by the reliability determination unit, and determines that the declaration is deficient. If this is the case, it is determined that it is necessary to prompt the user to declare the medication.
- the medication status management device when it is determined that it is necessary for the user to make a declaration regarding medication, the medication status management device outputs information prompting the user to make a declaration regarding medication, and presents information prompting the user to make a declaration regarding medication. It is determined whether or not there is a response from the user to the above, and if it is determined that there is no response, it is considered that there has been no declaration regarding the medication, and the determination process of the reliability of the declaration information is omitted.
- the medication status management device is a medication rate calculation unit that calculates the medication rate, which represents the ratio of the number of times the medication is declared to the total number of medications declared during the period subject to the declaration of the medication, based on the declaration information regarding the medication. Further, a correction unit for correcting the medication rate based on the determination result of the reliability of the declared information by the reliability determination unit is further provided.
- the medication rate is calculated from the medication declaration information. For example, by transmitting this medication rate to the terminal of the medication manager, the medication manager can change the user's medication status by the numerical value of the medication rate. It becomes possible to grasp. Moreover, since the above-mentioned medication rate is corrected based on the reliability of the declaration information, it is possible to recognize the accurate medication rate in consideration of the user's declaration error and false declaration.
- the medication status management device transmits information representing the determination result of the reliability to the terminal used by the medication manager for the user by the output unit.
- a medication manager such as a doctor or a pharmacist can automatically obtain the reliability of the user's medication declaration information, thereby, for example, the need to change the prescription. It can be useful for examinations.
- the reliability determination unit stores the obtained reliability determination result in the storage medium, and each time a new reliability determination result is obtained, the reliability stored in the storage medium is stored. Update the judgment result of the degree.
- the reliability of the medication declaration determined in the determination target period of the medication declaration reliability is provisionally continued until the reliability of the next medication declaration is determined, that is, the above determination target period. It will be retained for the period up to the present.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing an overall configuration of a system including a medication status management device according to the first embodiment of the present invention, in which UT is a user terminal as a medication status management device and BP is biometric information. The sphygmomanometer as a measuring device is shown respectively.
- the sphygmomanometer BP is, for example, a type of sphygmomanometer in which a cuff is wrapped around the user's upper arm to measure the blood pressure value by the oscillometric method, and the blood pressure measurement data is transmitted to the user via a short-range wireless network such as Bluetooth®. It has a function of transmitting to the terminal UT.
- a wrist-type or wristwatch-type sphygmomanometer may be used in addition to the type in which the cuff is wrapped around the upper arm for measurement.
- the wristwatch-type sphygmomanometer employs the oscillometric method or pulse wave velocity (PTT) as the measurement method, and can automatically measure blood pressure intermittently or at a preset time. It is possible. It is also possible to connect the sphygmomanometer BP and the user terminal UT via another wireless network such as a wireless LAN (Local Area Network) or a signal cable.
- PTT pulse wave velocity
- the user terminal UT can transmit data via the network NW between the administrator terminal MT used by a medication manager such as a doctor or a pharmacist and the family terminal FT used by the user's family.
- the network NW is composed of, for example, a wide area network centered on the Internet and an access network for connecting terminals to the wide area network.
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing an example of the hardware configuration of the user terminal UT.
- the user terminal UT is composed of a mobile information terminal such as a smartphone or a tablet terminal owned by a user who is a patient, for example.
- the user terminal UT has a hardware processor 1 (hereinafter, also simply referred to as a CPU) such as a CPU (Central Processing Unit), and a memory 2, an input / display device 3, and a wireless communication circuit 4 are bused to the CPU 1. It is connected via.
- a hardware processor 1 hereinafter, also simply referred to as a CPU
- a CPU Central Processing Unit
- the memory 2 for example, a non-volatile memory such as SSD (Solid State Drive) that can be written and read at any time and a volatile memory such as RAM (Random Access Memory) are used as a storage medium.
- the storage area includes a program storage area and a data storage area.
- the program storage area is used to store a middleware program that functions as an OS (Operation System) and various application programs.
- the data storage area is used to store various data used for determining the reliability of the medication declaration information.
- the input / display device 3 is composed of, for example, a tablet-type device in which a capacitive or pressure-sensitive input sheet is arranged on a display using a liquid crystal or an organic EL, and a user inputs operation information and displays information. Is used to display.
- the wireless communication circuit 4 wirelessly communicates with, for example, a short-range wireless network such as Bluetooth (registered trademark), a local wireless network in a home or a company such as a wireless LAN, and a public mobile communication network provided by a telecommunications carrier. It has multiple wireless interface functions for communication. Then, the blood pressure measurement data is received from the sphygmomanometer BP via the short-range wireless network, and the data is transmitted to and from the administrator terminal MT via the local wireless network or the public mobile communication network.
- the control of the wireless communication protocol and the like is usually performed by the CPU 1, but may be performed by the wireless communication circuit 4.
- Reference numeral 41 denotes an antenna.
- FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing the software configuration of the user terminal UT in association with the hardware configuration shown in FIG.
- the data storage area of the memory 2 is provided with a medication report information storage unit 21, a blood pressure measurement data storage unit 22, and a prescription information storage unit 23.
- the medication declaration information storage unit 21 stores input template data used when the user inputs medication declaration information. Further, in the medication declaration information storage unit 21, the medication declaration information input by the user by the input / display device 3 is stored in association with the information indicating the medication date and time according to the input template data.
- the blood pressure measurement data storage unit 22 stores the blood pressure measurement data transmitted from the sphygmomanometer BP in association with the information indicating the measurement date and time.
- the prescription information storage unit 23 stores the user's prescription information downloaded from the terminal MT or EMR (Electronic Medical Records) server of a medication manager such as a doctor or pharmacist.
- the CPU 1 includes a medication report information acquisition unit 11, a blood pressure measurement data acquisition unit 12, a dispersion degree calculation unit 13, a medication declaration reliability determination unit 14, and a determination information output. It has a part 15. All of these control units 11 to 15 are realized by causing the CPU 1 to execute an application program stored in the program storage area in the memory 2.
- the medication declaration information acquisition unit 11 is activated by, for example, an input request operation of the medication declaration by the user, reads input template data from the medication declaration information storage unit 21, and displays it on the input / display device 3. Then, the medication declaration information acquisition unit 11 receives the medication declaration information input by the user according to the guidance of the input template data from the input / display device 3, associates the declaration information with the information indicating the medication date and time, and stores the medication declaration information. The process of storing in the unit 21 is performed.
- the medication declaration information acquisition unit 11 may be activated, for example, in response to a user response operation to a message (reminder) prompting the medication declaration.
- the blood pressure measurement data acquisition unit 12 is activated by a data transmission request from the sphygmomanometer BP, and associates the blood pressure measurement data transmitted from the sphygmomanometer BP and received by the wireless communication circuit 4 with the information indicating the measurement date and time, and the blood pressure measurement data. A process of storing in the storage unit 22 is performed.
- the dispersion degree calculation unit 13 stores blood pressure measurement data including the measurement date and time in the determination target period every time a preset determination target period (for example, daily unit or weekly unit) elapses. Read from 22. Then, the dispersion degree calculation unit 13 performs a process of calculating the dispersion degree of the read blood pressure measurement data, for example, the degree of variation in the blood pressure measurement value or its change.
- a preset determination target period for example, daily unit or weekly unit
- the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14 performs a process of determining the reliability of the medication declaration information in the same period input by the user based on the calculation result of the variance degree of the blood pressure measurement data obtained by the dispersion degree calculation unit 13. Do. An example of reliability determination will be described later.
- the determination information output unit 15 generates notification information for notifying the medication manager, the user's family, or the user himself / herself of the determination result of the reliability of the medication declaration information by the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14, and the notification information. Is transmitted to the administrator terminal MT or the family terminal FT, or is displayed on the input / display device 3.
- the user terminal UT monitors the operation of the input request for medication declaration information in step S10 in the standby state. In this state, it is assumed that the user taps an icon to which the medication reporting function is assigned on the input / display device 3. Then, the user terminal UT activates the medication declaration information acquisition unit 11, and in step S11, first reads the input template data from the medication declaration information storage unit 21 and displays it on the input / display device 3.
- the input / display device 3 inputs information indicating whether or not the medicine is taken for each input meal. Received from, and stored in the medication declaration information storage unit 21. At this time, information indicating the date and time of filing is added to the information indicating the presence or absence of medication.
- the declared medication date and time will be different from the true medication date and time.
- check boxes 31a for inputting whether or not to take medication, correspond to each of the above-mentioned breakfast, lunch, and dinner for the non-input date and time 30.
- 32a, 33a and input fields 31b, 32b, 33b at the time of taking the drug are provided.
- the information indicating the presence or absence of medication and the information indicating the medication time entered in the corresponding check boxes 31a, 32a, 33a and the input fields 31b, 32b, 33b are used as medication declaration information. It is stored in the declaration information storage unit 21.
- the drug type 34 to be taken is displayed. By displaying the drug type, for example, a user who is taking a plurality of types of drugs can input the medication declaration information for each drug type without making a mistake.
- the user terminal UT After that, each time the user performs an input request operation for the medication declaration, the user terminal UT receives the above-mentioned medication declaration information and stores it in the medication declaration information storage unit 21 under the control of the medication declaration information acquisition unit 11. ..
- the user terminal UT monitors the request for transmission of blood pressure measurement data from the sphygmomanometer BP in step S12.
- the user terminal UT activates the blood pressure measurement data acquisition unit 12, and in step S13, it is transmitted from the sphygmomanometer BP and is transmitted by the wireless communication circuit 4.
- the received blood pressure measurement data is taken in from the wireless communication circuit 4, and the blood pressure measurement data is stored in the blood pressure measurement data storage unit 22.
- the user terminal UT stores the blood pressure measurement data in the blood pressure measurement data storage unit 22 in association with the measurement date and time.
- the user terminal UT After that, each time a transmission request is received from the sphygmomanometer BP, the user terminal UT performs the above-mentioned reception / storage processing of the blood pressure measurement data under the control of the blood pressure measurement data acquisition unit 12.
- the user terminal UT monitors the request for determining the reliability of the medication declaration in step S14 while performing the above-mentioned acquisition processing of the medication declaration information and the acquisition processing of the blood pressure measurement data.
- the user terminal UT activates the dispersion degree calculation unit 13.
- the blood pressure measurement data including the measurement date and time in the latest determination target period is read from the blood pressure measurement data storage unit 22, and each read blood pressure measurement data is also read. And the degree of dispersion of blood pressure measurement data is calculated.
- the degree of variance is, for example, the standard deviation or variance of all compression blood pressure values measured during the determination period, the difference between the highest and lowest values of all compression blood pressure values, and all compression blood pressure values. It can be obtained as the number or ratio of compression period blood pressure values that exceed the permissible blood pressure fluctuation range set around the average value of.
- the present invention is not limited to this, and when a determination request is sent from the terminal MT of a medication manager such as a doctor or pharmacist or the terminal FT of a family member and the determination request is received, a certain period (for example, one day or one day) before this point is received. The degree of dispersion of the blood pressure measurement value in 1 week) may be calculated.
- the user terminal UT subsequently activates the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14. Then, under the control of the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14, in step S16, the reliability of the medication declaration information stored in the medication declaration information storage unit 21 corresponding to the determination target period is determined.
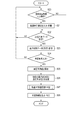
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing an example of the procedure and processing contents of the determination processing of the medication declaration reliability.
- the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14 first reads the medication declaration information corresponding to the determination target period from the medication declaration information storage unit 21 in step S161, and whether or not any medication declaration has been made based on the medication declaration information. Is determined. That is, it is determined whether or not the medication declaration is missing.
- the determination target period is one day
- the number of times of taking the medicine specified by the prescription information stored in the prescription information storage unit 23 is at least one time when the medicine is not declared, the medicine is taken on that day.
- Judge that there is no declaration For example, when the determination target period is one week, if there is one or more days or a predetermined number of days or more for which no medication declaration has been made, it is determined that there is no medication declaration for this week. Then, when it is determined that there is no medication declaration, the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14 considers this medication declaration information to be excluded from the determination of the medication declaration reliability, and in step S162, "a reminder for the user to take the medication declaration is required". The determination is made, and the determination result is passed to the determination information output unit 15.
- step S161 if it is determined in step S161 that there is a medication declaration, the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14 then in step S163, the variance degree of the blood pressure measurement data calculated by the dispersion degree calculation unit 13 is equal to or greater than the threshold value. It is determined whether or not it is. As a result of this determination, if the degree of dispersion is equal to or greater than the threshold value, the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14 determines in step S164 that the reliability of the medication declaration information in the determination target period is "low”. On the other hand, if the degree of dispersion is less than the threshold value, the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14 determines in step S165 that the reliability of the medication declaration information in the determination target period is “high”.
- the medication declaration information includes both information indicating whether or not there is a declaration, that is, both a declaration that "drinked” and a declaration that "did not take”. Therefore, the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14 calculates the medication rate (number of declarations of "drinking” / total number of declarations of medication (number of declarations of "drinking” + number of declarations of "did not take")). Then, a threshold value for determining the degree of dispersion is set for each calculated dose rate. That is, the determination threshold value is set so that the lower the medication rate, the higher the threshold value. By doing so, a more accurate determination can be made.
- the user terminal UT activates the determination information output unit 15. Then, under the control of the determination information output unit 15, in step S17, based on the determination result received from the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14, the determination result is obtained by the user himself / herself, a medication manager such as a doctor or a pharmacist. Alternatively, generate a notification message to notify the family. Then, the notification message for the user himself / herself is output to the input / display device 3 for display, and the notification message for the medication manager or family is output to the wireless communication circuit 4 from the wireless communication circuit 4 to the terminal of the medication manager. Send to MT or family terminal FT. In this case, the notification message for the user may include "a message urging the user to declare the medication correctly" and "a message urging the medication itself".
- the determination information of the reliability of the medication declaration is transmitted to the terminal MT of the medication manager or the terminal FT of the family.
- the user's medication declaration information is transmitted to the terminal MT of the medication manager or the terminal FT of the family by another process.
- the determination information of the reliability of the medication declaration is transmitted to the terminal MT of the medication manager or the terminal FT of the family, the blood pressure measurement value itself may be transmitted at the same time. By doing so, for example, it can be used as a reference when a doctor considers a change in prescription.
- the user's medication declaration information corresponding to the same determination target period may be transmitted to the terminal MT of the medication manager or the terminal FT of the family.
- the medication rate may be calculated from the medication declaration information, and the calculated medication rate may be transmitted together with the declaration information or instead of the declaration information to the terminal MT of the medication manager or the terminal FT of the family.
- the medication rate may be corrected (predicting the true medication rate) based on the determination result of the reliability of the medication declaration.
- a method of correction for example, it is conceivable to reduce the medication rate based on the declared information at a predetermined rate (for example, 70% of the declared value).
- the reliability determination process by the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14 is based on the declared medication rate, in addition to determining whether the variance is larger than the threshold value according to the declared medication rate. Regardless of the distance from the threshold value, that is, whether it is large or small, it is possible to judge only by the absolute value of the difference. By doing so, it can be judged that the reliability of the declaration is low even when the wrong declaration of "not drinking” is made even though the person is actually drinking.
- the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14 determines that "the user needs to be urged to declare medication" the following processing can be considered. That is, the determination information output unit 15 causes the user terminal UT to display a message prompting the user terminal UT to declare the medication. Then, the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14 determines whether or not the user responds to the transmission of the message prompting the medication declaration, that is, whether or not the user has performed the input operation of the medication declaration information, in the declaration information by the medication declaration information acquisition unit 11. Judgment is made based on the acquisition result, and if it is determined that the input operation of the declaration information is not performed, it is considered that there was no declaration regarding medication, and the reliability judgment processing for the declaration information is not performed. .. By doing so, the reliability determination process for the report information having a defect in the medication report is omitted, and the processing load of the user terminal UT can be reduced.
- the degree of dispersion of blood pressure values is related to the compliance status of medication. For example, looking at the degree of dispersion of blood pressure values measured regularly every day during the target period of one week, the degree of dispersion of blood pressure values of patients who comply with medication is small, and conversely, the degree of dispersion of blood pressure values of patients who do not comply with medication The degree of dispersion of blood pressure values tends to increase.
- the medication declaration information acquisition unit 11 accepts the input of the user's medication declaration information, and at the same time, the blood pressure measurement data acquisition unit 12 acquires the user's blood pressure measurement data from the sphygmomanometer BP.
- the dispersion degree calculation unit 13 calculates the dispersion degree of the blood pressure value in the determination target period based on the stored blood pressure measurement data, and the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14 is based on the dispersion degree of the blood pressure measurement value.
- the reliability of the medication declaration information declared during the same period is determined, and the determination result is transmitted to the terminal MT of the medication manager by the determination information output unit 15.
- a medication manager such as a doctor or a pharmacist can accurately estimate the medication status of a user who is a patient and judge the effect of medication.
- the reliability judgment result is sent to the terminal FT of the family, etc., the family can directly instruct the user himself / herself about the declaration of medication and confirm whether the medication is properly taken. Become. Further, for a user who tends to forget to declare the medication, by displaying a message urging the declaration of the medication on the input / display device 3, it is possible to increase the compliance rate of the medication declaration by the user.
- a subsequent change in blood pressure is predicted based on blood pressure measurement data obtained during a period in which the past medication status is known, and the predicted value of this blood pressure and the actual measurement are performed.
- the degree of deviation from the measured value of blood pressure is calculated, and the reliability of the medication declaration information during the medication period that affects the blood pressure value during the calculated period is determined.
- a period in which the medication rate is known or the medication rate is corrected based on the reliability is selected as the prediction reference period for blood pressure fluctuation (hereinafter, also referred to as the first period). Then, based on the blood pressure measurement data obtained in this first period, the subsequent blood pressure fluctuation is predicted, and the blood pressure predicted value and the actual blood pressure predicted value in the period to be monitored of the blood pressure value (hereinafter, also referred to as the second period). Calculate the degree of deviation from the measured blood pressure value measured in. Then, based on the degree of deviation of the calculated blood pressure value, the medication period (hereinafter also referred to as the third period) before the second period, which affects the blood pressure value in the second period (that is, the drug effect appears). ) To determine the reliability of the user's medication declaration information.
- the first period if the user has a period in which medication is accurately managed, such as an inpatient treatment period, this period may be selected as the first period.
- the third period which is the period for determining the reliability, is the target for monitoring the degree of divergence. It is also possible to set the same as the second period, which is a period.
- first period and the second or third period may not be continuous, but rather not continuous. This is because if the first period and the second or third period are continuous, it is expected that the degree of change or deviation of the blood pressure value is too small to be compared.
- first period and the second or third period are continuous, it is desirable to secure a certain length or more for each period. This is because the effects of natural blood pressure fluctuations and errors can be reduced by doing so.
- the second period it is theoretically possible to calculate the degree of divergence by using only the measured blood pressure value measured at a certain timing, but in order to eliminate the influence of natural blood pressure fluctuations and errors. It is desirable to include the measured blood pressure values for multiple times.
- FIG. 7 is a block diagram showing a software configuration of the user terminal UT.
- a medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61 and a prescription information storage unit 62 are provided in the data storage area of the memory 6.
- the medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61 stores input template data used when the user inputs medication declaration information. Further, the medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61 stores the medication declaration information input by the user based on the input template data in association with the information indicating the medication date and time. Further, the medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61 stores the blood pressure measurement data transmitted from the sphygmomanometer BP in association with the information indicating the measurement date and time.
- the prescription information storage unit 62 stores prescription information of the target user, for example, downloaded from the terminal MT of a medication manager such as a doctor or pharmacist or the EMR server of a medical institution or the like.
- the CPU 5 includes a medication report information acquisition unit 51, a blood pressure measurement data acquisition unit 52, a blood pressure change prediction unit 53, a blood pressure comparison unit 54, and a medication declaration reliability determination unit. It has 55 and a determination information output unit 56. All of these control units 51 to 56 are realized by causing the CPU 5 to execute an application program stored in the program storage area in the memory 6.
- the medication declaration information acquisition unit 51 is activated by the user's input request operation for the medication declaration, reads the input template data from the medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61, and displays it on the input / display device 3. Then, the medication declaration information acquisition unit 51 receives the medication declaration information input by the user according to the guidance of the input template data from the input / display device 3, and stores the declaration information in the medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61. Do.
- the medication declaration information includes, for example, information indicating the date and time of medication and information indicating the presence or absence of medication at the date and time.
- the information indicating the date and time of administration is represented by the information indicating the timing of administration, for example, when the timing of administration is specified by the prescription after breakfast, lunch, dinner, wake-up time, bedtime, or the like.
- the information indicating whether or not the drug is taken is input for each type of these drugs.
- the blood pressure measurement data acquisition unit 52 is activated by, for example, a data transmission request from the sphygmomanometer BP, and receives the blood pressure measurement data transmitted from the sphygmomanometer BP and received by the wireless communication circuit 4 together with the information indicating the measurement date and time, and the above-mentioned medication / blood pressure. A process of storing in the information storage unit 61 is performed. At that time, the blood pressure measurement data acquisition unit 52 stores the blood pressure measurement data and the medication declaration information in a state in which the measurement date and time and the medication date and time correspond to each other.
- the blood pressure change prediction unit 53 first selects a period in which the past medication status is known as a blood pressure fluctuation prediction reference period (first period). Then, the blood pressure measurement data obtained in the first period is read from the medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61, and a process of predicting a subsequent change in the blood pressure value from the blood pressure measurement data is performed.
- the blood pressure change prediction unit 53 reads, for example, the medication declaration information in the first period from the medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61, calculates the medication rate based on the medication declaration information, and calculates the medication rate. It is reflected in the predicted value of the above blood pressure value. That is, the process of correcting the predicted blood pressure value based on the medication rate in the first period is also performed.
- the blood pressure comparison unit 54 sets, for example, a period (second period) for monitoring the latest blood pressure value. Then, the blood pressure measurement data (measured value of blood pressure) obtained in the second period is read out from the medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61, and the blood pressure in the second period obtained by the blood pressure change prediction unit 53. The process of calculating the degree of deviation of the measured value of the blood pressure from the predicted value of is performed.
- the medication declaration reliability determination unit 55 Based on the degree of blood pressure divergence calculated by the blood pressure comparison unit 54, the medication declaration reliability determination unit 55, for example, takes the medication period before the drug effect appears in the blood pressure value in the second period (third period). Performs the process of determining the reliability of the medication declaration information in. An example of reliability determination will be described later.
- the determination information output unit 56 generates notification information for notifying the medication manager, the user's family, or the user himself / herself of the determination result of the reliability of the medication declaration information by the medication declaration reliability determination unit 55, and the notification information. Is transmitted to the administrator terminal MT or the family terminal FT, or is displayed on the input / display device 3.
- the user terminal UT monitors the operation of the input request for medication declaration information in step S20 in the standby state. In this state, it is assumed that the user taps an icon to which the medication reporting function is assigned on the input / display device 3. Then, the user terminal UT activates the medication report information acquisition unit 51, and in step S21, first reads the input template data from the medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61 and displays it on the input / display device 3.
- the input / display device 3 inputs information indicating whether or not the medicine is taken for each input meal. Received from, and stored in the medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61. At this time, information indicating the date and time of taking the drug or the date and time of taking the drug (hereinafter collectively referred to as the date and time of taking the drug) is added to the information indicating the presence or absence of the drug.
- the declared medication date and time will be different from the true medication date and time.
- check boxes 31a, 32a for inputting whether or not to take the medicine, correspond to each of the above-mentioned after breakfast, after lunch, and after dinner for the date and time not entered in the input template.
- 33a and input fields 31b, 32b, 33b for the time of taking the drug are provided.
- the information indicating the presence or absence of medication and the information indicating the medication time entered in the corresponding check boxes 31a, 32a, 33a and the input fields 31b, 32b, 33b are used as medication declaration information. It is stored in the declaration information storage unit 21.
- the user terminal UT After that, every time the user performs an input request operation for the medication declaration, the user terminal UT receives the above-mentioned medication declaration information and stores it in the medication declaration information storage unit 21 under the control of the medication declaration information acquisition unit 51. ..
- the user terminal UT monitors the request for transmission of blood pressure measurement data from the sphygmomanometer BP in step S52.
- the user terminal UT activates the blood pressure measurement data acquisition unit 52, and in step S23, the blood pressure measurement data is transmitted from the sphygmomanometer BP and is transmitted by the wireless communication circuit 4.
- the received blood pressure measurement data is taken in from the wireless communication circuit 4, and the blood pressure measurement data is stored in the medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61.
- the user terminal UT associates the blood pressure measurement data with the measurement date and time, and further associates the medication date and time with the corresponding medication declaration information to take the medication / blood pressure information. It is stored in the storage unit 61.
- the user terminal UT After that, each time a transmission request is received from the sphygmomanometer BP, the user terminal UT performs the above-mentioned reception / storage processing of the blood pressure measurement data under the control of the blood pressure measurement data acquisition unit 52.
- the user terminal UT monitors the request for determining the reliability of the medication declaration in step S24 while performing the acquisition processing of the medication declaration information and the acquisition processing of the blood pressure measurement data. In this state, when a determination request is received from the terminal MT of a medication manager such as a doctor or pharmacist or the terminal FT of a family member, the user terminal UT activates the blood pressure change prediction unit 53.
- the user terminal UT Under the control of the blood pressure change prediction unit 53, the user terminal UT first selects, for example, a period in which the past medication status is known as a blood pressure fluctuation prediction reference period (first period) in step S25. Then, the medication declaration information and the blood pressure measurement data in this first period (for example, one day or one week) are read out from the medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61. Then, for example, the medication rate in the above-mentioned medication period is calculated based on the medication declaration information, and the change in the blood pressure value after that is predicted from the blood pressure measurement data in the above-mentioned medication period in consideration of this medication rate. That is, based on the blood pressure value measured in the first period in which the medication rate is known, the change in the blood pressure value in the subsequent period is predicted.
- first period a blood pressure fluctuation prediction reference period
- the guideline data representing the change in the blood pressure value with respect to the standard patient dosage is acquired from a database such as an EMR (Electronic Medical Records) server, and the data of this guideline is referred to. Or, it is performed using a learning model in which changes in blood pressure are learned based on the user's past dosage and blood pressure fluctuation history. In addition, if there is a period in which it is clear that the patient was taking the drug reliably or the rate of medication is correct, for example, because he / she was undergoing hospitalization treatment, this period is described above. It may be used as a period of 1.
- the user terminal UT subsequently activates the blood pressure comparison unit 54, and under the control of the blood pressure comparison unit 54, in step S26, first, the latest blood pressure monitoring target period (for example, one day today). ) Is selected as the second period, and the blood pressure measurement data (measured value of blood pressure) in the second period is read out from the medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61. Then, among the predicted values of blood pressure obtained by the blood pressure change prediction unit 53, the degree of deviation (for example, difference) of the measured values of the blood pressure from the predicted blood pressure value obtained in the second period is calculated.
- the degree of deviation for example, difference
- the measured value of blood pressure at a certain point in time during the second period may be compared with the predicted value, but the measured blood pressure measured at a plurality of timings in the second period The average value of the values may be compared with the predicted value. In this way, the influence of temporary blood pressure fluctuation can be reduced.
- the user terminal UT subsequently activates the medication declaration reliability determination unit 55. Then, under the control of the medication declaration reliability determination unit 55, in step S27, the medication period (for example, yesterday or today) that affects the blood pressure value in the second period, that is, the drug effect appears, is set as the third period.
- the medication declaration information in this third period is read from the medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61. Then, the reliability of the read out medication declaration information in the third period is determined based on the degree of divergence of blood pressure in the second period calculated by the blood pressure comparison unit 54.
- FIG. 9 is a flowchart showing an example of the procedure and processing contents of the determination processing of the medication declaration reliability.
- the medication declaration reliability determination unit 55 first reads the medication declaration information in the third period from the medication / blood pressure information storage unit 61 in step S271, and whether or not any medication declaration has been made based on the medication declaration information. Is determined. That is, it is determined whether or not the medication declaration is missing.
- the third period is one day, if there is at least one medication timing for which the medication declaration has not been made among the medication timings specified by the prescription information stored in the prescription information storage unit 62, that day. Judges that there is no medication declaration. For example, if the medication timing is specified three times after breakfast, lunch, and dinner, and it is declared that the patient missed a dose (no medication) after dinner, it is determined that there is no medication declaration on this day. Further, for example, when the third period is one week, if there is one or more days or a predetermined number of days or more for which no medication declaration has been made, it is determined that there is no medication declaration for this week.
- the medication declaration reliability determination unit 55 considers that the medication declaration information in this third period is not subject to the determination of the medication declaration reliability, and in step S272, "the user is notified of the medication declaration. It is determined that "a reminder is required", and this determination result is passed to the determination information output unit 56.
- step S271 if it is determined in step S271 that there is a medication declaration, the medication declaration reliability determination unit 55 then in step S273, the degree of deviation of the blood pressure value calculated by the blood pressure comparison unit 54 (predicted value of blood pressure and actual measurement). Determine if the difference from the value) is greater than or equal to the threshold value.
- the medication declaration reliability determination unit 55 determines in step S274 that the reliability of the medication declaration information in the third period is "low”. ..
- the medication declaration reliability determination unit 55 determines in step S275 that the reliability of the medication declaration information in the third period is "high".
- the user terminal UT activates the determination information output unit 56. Then, under the control of the determination information output unit 56, in step S28, based on the determination result received from the medication declaration reliability determination unit 55, the determination result is obtained by the user himself / herself, a medication manager such as a doctor or a pharmacist. Alternatively, generate a notification message to notify the family. Then, the notification message for the user himself / herself is output to the input / display device 3 for display, and the notification message for the medication manager or family is output to the wireless communication circuit 4 from the wireless communication circuit 4 to the terminal of the medication manager. Send to MT or family terminal FT.
- the case where only the determination information of the reliability of the medication declaration is transmitted to the terminal MT of the medication manager or the terminal FT of the family is described. This is a case where it is premised that the user's medication declaration information is transmitted to the terminal MT of the medication manager or the terminal FT of the family by another process.
- the determination information of the reliability of the medication declaration is transmitted to the terminal MT of the medication manager or the terminal FT of the family
- the medication declaration information of the user corresponding to the same medication period (third period) is also transmitted. May be transmitted to the terminal MT of the medication manager or the terminal FT of the family.
- the medication rate may be calculated from the declaration information, and the calculated medication rate may be transmitted together with the declaration information or instead of the declaration information to the terminal MT of the medication manager or the terminal FT of the family.
- the medication rate may be corrected (predicting the true medication rate) based on the determination result of the reliability of the medication declaration.
- a method of correction for example, it is conceivable to reduce the medication rate based on the declared information at a predetermined rate (for example, 70% of the declared value).
- the reliability determination process by the medication declaration reliability determination unit 55 is performed according to the declared medication rate, in addition to determining whether the blood pressure deviation is larger than the threshold value according to the declared medication rate. Regardless of the distance from the threshold value, that is, whether it is large or small, it is possible to judge only by the absolute value of the difference. By doing so, it can be judged that the reliability of the declaration is low even when the wrong declaration of "not drinking” is made even though the person is actually drinking.
- the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14 determines that "a reminder for the medication declaration is required for the user"
- the determination information output unit 15 causes the user terminal UT to display a message prompting the user terminal UT to declare the medication.
- the medication declaration reliability determination unit 14 determines whether or not the user responds to the transmission of the message prompting the medication declaration, that is, whether or not the user has performed the input operation of the medication declaration information, in the declaration information by the medication declaration information acquisition unit 11. Judgment is made based on the acquisition result, and if it is determined that the input operation of the declaration information is not performed, it is considered that there was no declaration regarding medication, and the reliability judgment processing for the declaration information is not performed. .. In this way, the reliability determination process for the report information having a defect in the medication report is omitted, and the processing load of the user terminal UT can be reduced.
- the change in blood pressure in the second period) is predicted, and the degree of deviation between the predicted value of blood pressure and the actually measured value of blood pressure actually measured in the second period is calculated by the blood pressure comparison unit 54.
- the medication declaration reliability determination unit 55 affects the blood pressure value in the second period (the medicinal effect appears) and the previous medication period (third).
- the reliability of the medication declaration information in the period) is determined, and the information representing the determination result is output to the terminal MT of the medication manager by the determination information output unit 56.
- a medication manager such as a doctor or a pharmacist can more accurately estimate the medication status during the previous medication period that affects the blood pressure of the user who is the patient during the latest blood pressure monitoring period (the drug effect appears). , It becomes possible to judge the effect of medication.
- the determination result of the reliability of the medication declaration is sent to the terminal FT of the family, etc., the family can directly instruct the user about the medication declaration and confirm whether the medication is properly taken. It will be possible. Further, for a user who tends to forget to declare the medication, by displaying a message urging the declaration of the medication on the input / display device 3, it is possible to increase the compliance rate of the medication declaration by the user.
- the reliability of the medication declaration determined in the period for which the reliability of the medication declaration is determined is the reliability of the next medication declaration. It may be considered to be tentatively continued until the degree is determined, that is, to be retained for a period from the target period or the third period to the present including the second period in the second embodiment.
- the medication status management function according to the present invention is provided in the user terminal UT as an example.
- the present invention is not limited thereto.
- the medication status management function according to the present invention is provided in a server device operated by a medical institution such as a hospital or a pharmacy, or in a server device operated by a service provider related to medical care, medicine, nursing care, etc. You may.
- the server device When the server device is provided with a medication status management function in this way, for example, the medication declaration information input by the user on the user terminal and the biometric information measured by the blood pressure monitor are transmitted from the user terminal to the server device for a certain period of time. Then, the server device receives and stores the medication declaration information and the biometric information sent from the user terminal, and performs the first and second executions in response to the preset judgment timing or the input of the judgment request of the doctor or the like. It can be carried out by executing a series of processes described in the embodiment.
- the function of the medication status management device is provided in a mobile information terminal (user terminal) such as a smartphone owned by the user has been described as an example, but for example, the blood pressure measurement function has been described.
- the wearable terminal provided may be provided with the function of a medication status management device.
- the reliability of the medication declaration information is determined by comparing the degree of dispersion of the blood pressure value or the degree of deviation of the measured value with respect to the predicted blood pressure value with one threshold value. I tried to do it. However, not limited to this, for example, by setting a plurality of threshold values and comparing the degree of dispersion of the blood pressure value or the degree of deviation of the measured value with respect to the predicted blood pressure value with the above-mentioned multiple threshold values, the reliability of the medication declaration information can be obtained. The degree may be determined in multiple stages.
- the case of acquiring blood pressure measurement data as biological information has been described as an example, but in addition, the blood glucose level, uric acid level, creatinine level, cholesterol level, and blood oxygen saturation concentration ( SPO2) measurement data, as well as measurement data such as body weight, abdominal circumference, and body fat percentage are acquired, the degree of dispersion or the degree of deviation from the predicted value is calculated, and the reliability of medication declaration information is determined based on the results. It may be determined.
- SPO2 blood oxygen saturation concentration
- the method for selecting each of the third periods, the length thereof, and the like can also be variously modified and implemented without departing from the gist of the present invention.
- the present invention can form various inventions by appropriately combining a plurality of components disclosed in each of the above embodiments. For example, some components may be removed from all the components shown in each embodiment. In addition, components from different embodiments may be combined as appropriate.
- Appendix 1 A medication status management device equipped with a hardware processor and a storage medium.
- the hardware processor The process of acquiring the user's medication declaration information and The process of acquiring the biometric information of the user and storing it in the storage medium, A process of calculating the degree of dispersion of the biometric information acquired during the target period based on the biometric information stored in the storage medium, and A process of determining the reliability of the declaration information regarding the medication acquired during the target period based on the degree of dispersion of the biometric information.
- a medication status management device configured to execute a process of outputting information representing the reliability determination result.
- a medication status management device equipped with a hardware processor and a storage medium.
- the hardware processor The process of acquiring the user's medication declaration information and storing it in the storage medium, A process of acquiring the biometric information of the user and storing the biometric information in the storage medium in a state in which the declared information and the information corresponding to the acquisition timing can be associated with each other. Based on the declared information and biometric information stored in the storage medium in the first period in which the medication status is known, the predicted value of the biometric information in the second period in which the biometric information is monitored is calculated.
- a medication status management device configured to execute a process of outputting information representing the reliability determination result.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Medical Treatment And Welfare Office Work (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE112020000763.4T DE112020000763T5 (de) | 2019-03-25 | 2020-03-03 | Vorrichtung, verfahren und programm zur verwaltung des medikamenteneinnahmestatus |
| CN202080019506.0A CN113544791B (zh) | 2019-03-25 | 2020-03-03 | 服药情况管理装置、方法以及记录有程序的计算机可读记录介质 |
| US17/448,134 US12051493B2 (en) | 2019-03-25 | 2021-09-20 | Medication administration status management device, method, and non-transitory recording medium that records program |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019057045A JP7346868B2 (ja) | 2019-03-25 | 2019-03-25 | 服薬状況管理装置、方法およびプログラム |
| JP2019-057045 | 2019-03-25 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US17/448,134 Continuation US12051493B2 (en) | 2019-03-25 | 2021-09-20 | Medication administration status management device, method, and non-transitory recording medium that records program |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2020195595A1 true WO2020195595A1 (ja) | 2020-10-01 |
Family
ID=72608548
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2020/008797 Ceased WO2020195595A1 (ja) | 2019-03-25 | 2020-03-03 | 服薬状況管理装置、方法およびプログラム |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US12051493B2 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP7346868B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN113544791B (enExample) |
| DE (1) | DE112020000763T5 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2020195595A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7177540B1 (ja) | 2021-12-21 | 2022-11-24 | Essence research株式会社 | 血圧予測装置、血圧予測プログラム、及び、血圧予測方法 |
| JP7747562B2 (ja) * | 2022-03-23 | 2025-10-01 | 日本光電工業株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法およびプログラム |
| JP7421251B1 (ja) | 2023-06-29 | 2024-01-24 | 株式会社サンクスネット | リスク判定システム |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002183306A (ja) * | 2000-12-13 | 2002-06-28 | Mizu:Kk | 医薬分業に係る地域面分業ネットワークシステム |
| JP2018164601A (ja) * | 2017-03-28 | 2018-10-25 | 富士通株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラム、及び情報処理システム |
| WO2018235652A1 (ja) * | 2017-06-19 | 2018-12-27 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | 健康管理装置、健康管理方法、および健康管理プログラム |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007188149A (ja) * | 2006-01-11 | 2007-07-26 | Sharp Corp | 服薬情報提供システム、服薬情報提供サーバ、服用者端末、並びにプログラムおよび記録媒体 |
| US8872663B2 (en) * | 2010-01-19 | 2014-10-28 | Avery Dennison Corporation | Medication regimen compliance monitoring systems and methods |
| US20120157793A1 (en) * | 2010-12-20 | 2012-06-21 | General Electric Company | Medication intake analyzer |
| CN103473625A (zh) * | 2013-08-16 | 2013-12-25 | 上海华美络信息技术有限公司 | 一种慢性病管理系统 |
| CA2949449C (en) * | 2014-05-23 | 2021-05-25 | Dacadoo Ag | Automated health data acquisition, processing and communication system |
| CN104965966B (zh) * | 2014-12-31 | 2018-08-21 | 江苏财经职业技术学院 | 药物服用监控专家系统及其工作方法 |
| CN104966256A (zh) * | 2014-12-31 | 2015-10-07 | 江苏网泰信息技术有限公司 | 慢病药物服用监控专家系统及其工作方法 |
| CN105100181A (zh) * | 2015-01-19 | 2015-11-25 | 刘辉 | 一种基于大数据的监控系统及其工作方法 |
| US11039986B2 (en) * | 2016-02-25 | 2021-06-22 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Chronotherapeutic dosing of medication and medication regimen adherence |
| CN106726601A (zh) * | 2016-12-02 | 2017-05-31 | 重庆软汇科技股份有限公司 | 智能药盒系统 |
| JP6868423B2 (ja) | 2017-03-14 | 2021-05-12 | オムロン株式会社 | 投薬支援装置、方法及びプログラム |
| JP7124453B2 (ja) * | 2018-05-29 | 2022-08-24 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | 投薬管理装置、投薬管理方法及び投薬管理プログラム |
| KR101949102B1 (ko) * | 2018-10-08 | 2019-02-18 | 박기준 | 복약 보조 시스템 및 이를 이용한 복약 보조 방법 |
-
2019
- 2019-03-25 JP JP2019057045A patent/JP7346868B2/ja active Active
-
2020
- 2020-03-03 WO PCT/JP2020/008797 patent/WO2020195595A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2020-03-03 DE DE112020000763.4T patent/DE112020000763T5/de active Pending
- 2020-03-03 CN CN202080019506.0A patent/CN113544791B/zh active Active
-
2021
- 2021-09-20 US US17/448,134 patent/US12051493B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002183306A (ja) * | 2000-12-13 | 2002-06-28 | Mizu:Kk | 医薬分業に係る地域面分業ネットワークシステム |
| JP2018164601A (ja) * | 2017-03-28 | 2018-10-25 | 富士通株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラム、及び情報処理システム |
| WO2018235652A1 (ja) * | 2017-06-19 | 2018-12-27 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | 健康管理装置、健康管理方法、および健康管理プログラム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN113544791A (zh) | 2021-10-22 |
| DE112020000763T5 (de) | 2021-11-18 |
| JP2020160597A (ja) | 2020-10-01 |
| US20220005571A1 (en) | 2022-01-06 |
| JP7346868B2 (ja) | 2023-09-20 |
| US12051493B2 (en) | 2024-07-30 |
| CN113544791B (zh) | 2025-02-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8688467B2 (en) | Automated analysis of data collected by in-vivo devices | |
| US12213760B2 (en) | Physiological monitoring system | |
| CA2737086C (en) | Device, system and method for providing contextualized medical data | |
| US8945043B2 (en) | Medical device with contextual awareness | |
| US6612985B2 (en) | Method and system for monitoring and treating a patient | |
| US9183720B2 (en) | Interactive medical device monitoring and management system | |
| US20180189452A1 (en) | System and method for remote healthcare | |
| US12051493B2 (en) | Medication administration status management device, method, and non-transitory recording medium that records program | |
| CN110402465A (zh) | 给药辅助装置、方法以及程序 | |
| WO2018168803A1 (ja) | 投薬支援装置、方法およびプログラム | |
| US20240194314A1 (en) | Medical care assistance system, medical care assistance device, and program | |
| Haywood et al. | The promise and risks of mHealth in heart failure care | |
| US20210065856A1 (en) | Patient management based on sensed inputs | |
| US20170255750A1 (en) | System and method for recommending a discharge moment | |
| WO2014088933A1 (en) | Interactive medical device monitoring and management system | |
| JP2020160597A5 (enExample) | ||
| JP6911087B2 (ja) | 処方薬剤管理システム、処方薬剤管理方法および処方薬剤管理プログラム | |
| KR20210149929A (ko) | 복약관리장치 및 이를 이용한 복약관리방법 및 복약관리시스템 | |
| WO2020076273A2 (en) | Treatment recommendation generation system | |
| WO2020195597A1 (ja) | 服薬状況管理装置、方法およびプログラム | |
| Reamer et al. | Continuous remote patient monitoring in patients with heart failure (cascade study): protocol for a mixed methods feasibility study | |
| Lin et al. | Development and practice of a telehealthcare expert system (TES) | |
| Cafazzo et al. | The hospital at home: advances in remote patient monitoring | |
| Zasuwa et al. | Remote Monitoring of Sustained Low-Efficiency Dialysis (SLED) Machines in Intensive Care Unit | |
| US20240180438A1 (en) | Medical care assistance system, medical care assistance device, and recording medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 20775807 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 20775807 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWG | Wipo information: grant in national office |
Ref document number: 202080019506.0 Country of ref document: CN |