WO2020183736A1 - コンプレッサホイール装置および過給機 - Google Patents
コンプレッサホイール装置および過給機 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2020183736A1 WO2020183736A1 PCT/JP2019/010716 JP2019010716W WO2020183736A1 WO 2020183736 A1 WO2020183736 A1 WO 2020183736A1 JP 2019010716 W JP2019010716 W JP 2019010716W WO 2020183736 A1 WO2020183736 A1 WO 2020183736A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- compressor wheel
- sleeve portion
- hub
- wheel device
- sleeve
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04D—NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04D17/00—Radial-flow pumps, e.g. centrifugal pumps; Helico-centrifugal pumps
- F04D17/08—Centrifugal pumps
- F04D17/10—Centrifugal pumps for compressing or evacuating
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04D—NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04D29/00—Details, component parts, or accessories
- F04D29/05—Shafts or bearings, or assemblies thereof, specially adapted for elastic fluid pumps
- F04D29/051—Axial thrust balancing
- F04D29/0513—Axial thrust balancing hydrostatic; hydrodynamic thrust bearings
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04D—NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04D29/00—Details, component parts, or accessories
- F04D29/06—Lubrication
- F04D29/063—Lubrication specially adapted for elastic fluid pumps
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04D—NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04D29/00—Details, component parts, or accessories
- F04D29/08—Sealings
- F04D29/10—Shaft sealings
- F04D29/12—Shaft sealings using sealing-rings
- F04D29/122—Shaft sealings using sealing-rings especially adapted for elastic fluid pumps
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04D—NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04D29/00—Details, component parts, or accessories
- F04D29/26—Rotors specially for elastic fluids
- F04D29/28—Rotors specially for elastic fluids for centrifugal or helico-centrifugal pumps for radial-flow or helico-centrifugal pumps
- F04D29/284—Rotors specially for elastic fluids for centrifugal or helico-centrifugal pumps for radial-flow or helico-centrifugal pumps for compressors
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to a compressor wheel device including a compressor wheel and a thrust collar, and a supercharger equipped with the compressor wheel device.
- Some compressor wheels mounted on a turbocharger include a hub and a plurality of blades provided on the outer peripheral surface of the hub, and have through holes formed through the hub in the axial direction.
- the compressor wheel has a so-called through-bore structure in which a rotary shaft is inserted through a through hole and a nut is screwed into a protruding portion protruding from the front edge of the wheel of the rotary shaft to be mechanically connected to the rotary shaft. It has become.
- a stress concentration portion is generated on the inner peripheral surface of the through hole.
- the stress concentration portion is generated near the maximum outer diameter portion.
- a compressor mounted on a commercial vehicle or an industrial supercharger is required to have a high pressure ratio, but since the outlet temperature of the compressor rises as the pressure ratio increases, the creep strength in the stress concentration portion is a problem. Will be. Adopting a high-strength material such as titanium for the compressor wheel in order to secure creep strength is not preferable because it leads to an increase in cost.
- compressor wheels include a wheel body member including the hub and the blade, and a cylindrical sleeve member (see Patent Document 1).
- the shaft end surface of the sleeve member is brought into contact with the central portion of the back surface of the wheel body member, and the contact portion is melted by the heat generated by rotating the sleeve member, so that the wheel body member and the sleeve member are formed.
- a fixed compressor wheel is disclosed.
- the compressor wheel is mechanically connected to the rotating shaft by screwing the tip of the rotating shaft into the female threaded portion formed on the inner peripheral surface of the sleeve member, so-called boreless. The structure is disclosed.
- the occurrence of the stress concentration portion can be suppressed by providing the female screw portion on the back side of the vicinity of the maximum outer diameter portion, it is necessary to increase the creep strength as compared with the through bore structure.
- the material cost can be reduced because there is no material.
- the length of the compressor wheel in the axial direction is longer by the length of the sleeve member than in the through-bore structure. Therefore, not only the size of the compressor is increased, but also the shaft vibration is increased and the critical speed is increased. There is a risk of deterioration.
- the thrust collar attached to the rotating shaft on the back side of the compressor wheel it is conceivable to make the thrust collar attached to the rotating shaft on the back side of the compressor wheel larger than the sleeve member and arrange it so as to cover the sleeve member. There is a risk that the thrust color will become complicated and the manufacturing cost of the supercharger will increase.
- an object of at least one embodiment of the present invention is to provide a compressor wheel device capable of preventing complication of structure and reducing manufacturing cost.
- the compressor wheel device is A compressor wheel that can be attached to a rotating shaft
- a wheel body including a hub and at least one blade provided on the outer peripheral surface of the hub, and a tubular sleeve portion protruding along the axial direction from the back surface of the hub on the outer peripheral surface.
- One surface that includes the contact surface that comes into contact with the end surface of the sleeve portion and extends along the radial direction Including a sliding contact surface that is in sliding contact with a thrust bearing that supports the rotating shaft in the thrust direction, and another surface that extends along the radial direction.
- the wheel body portion and the sleeve portion are integrally formed of the same material.
- the wheel body and sleeve are separate, it will be necessary to assemble the wheel body and sleeve.
- the configuration of (2) above since the wheel main body and the sleeve are integrally formed of the same material, the assembling property is improved as compared with the case where the wheel main body and the sleeve are separate bodies. It is good. Further, since the processing of integrally forming the wheel body portion and the sleeve portion is not difficult, there is no possibility that the workability is deteriorated. Therefore, according to the above configuration, the manufacturing cost of the compressor wheel device can be further reduced.
- the bottom surface of the seal groove is the inner peripheral surface of the seal member supported by the housing accommodating the compressor wheel. It was configured to form a clearance between them.
- a low-strength material such as aluminum or an aluminum alloy may be used as the material of the compressor wheel.
- the sleeve portion may be a low-strength material.
- the bottom surface of the seal groove is configured so that a clearance is formed between the bottom surface of the seal groove and the inner peripheral surface of the seal member supported by the housing, so that the seal groove of the sleeve portion is formed. , It is possible to prevent the seal member from sliding and being worn or damaged.
- At least one of hardness and slidability is improved in a portion of the sleeve portion including the seal groove. Surface processing was applied.
- connection position between the wheel body and the sleeve is outside the maximum of the hub.
- the diameter is D, it is configured to be 0.03D or more away from the maximum outer diameter position of the hub in the axial direction.
- Centrifugal stress becomes maximum near the maximum outer diameter position of the hub in the axial direction.
- the connection position between the wheel body and the sleeve is 0.03D or more in the axial direction from the maximum outer diameter of the hub, where D is the maximum outer diameter of the hub. Since it is configured as such, the centrifugal stress applied to the connection position can be reduced. By reducing the centrifugal stress applied to the connection position, the outer diameter of the sleeve portion can be reduced, so that it is possible to prevent the peripheral length of the seal mechanism portion of the turbocharger from increasing.
- connection portion between the wheel body portion and the sleeve portion is formed in an arc shape that is concave inside the compressor wheel in the cross section including the axial direction of the rotating shaft. It is possible to prevent stress concentration from occurring at the connection portion. By preventing stress concentration from occurring in the connection portion, the outer diameter of the sleeve portion can be reduced, so that it is possible to prevent the peripheral length of the seal mechanism portion of the turbocharger from increasing.
- the sleeve portion is formed with a screw groove into which the rotating shaft is screwed. It has an inner peripheral surface.
- the compressor wheel rotates by screwing the rotary shaft into the screw groove formed on the inner peripheral surface of the sleeve portion located at a position away from the maximum outer diameter position of the hub. It has a so-called boreless structure that is mechanically connected to the shaft. According to the above configuration, the generation of the stress concentration portion can be suppressed, and the material cost of the wheel body portion can be reduced because it is not necessary to increase the creep strength of the wheel body portion as compared with the through-bore structure. it can.
- the sleeve portion is press-fitted into the recess formed on the back surface of the hub to form the wheel main body portion. It has one end that is configured to be solidified, and is made of a material that has higher wear resistance than the wheel body.
- the wheel body portion and the sleeve portion are integrated, so that the work of assembling the wheel body portion and the sleeve portion is easy. .. Further, since the wheel body portion and the sleeve portion can be assembled to the turbocharger in an integrated state, the assembling property is good. Therefore, according to the above configuration, it is possible to suppress an increase in manufacturing cost due to the separate wheel body and sleeve. Further, since the sleeve portion having the seal groove is formed of a material having higher wear resistance than the wheel main body portion, it is possible to prevent the seal groove from being worn or damaged.
- the tip of the one end portion is located on the back side of the compressor wheel with respect to the maximum outer diameter position of the hub. It is composed of.
- the tip of one end of the sleeve portion is configured to be located on the back side of the compressor wheel rather than the maximum outer diameter position of the hub, so that the wheel is different from the through-bore structure. It is possible to suppress the occurrence of a stress concentration portion in the main body portion. Therefore, it is not necessary to increase the creep strength of the wheel body, so that the material cost of the wheel body can be reduced.
- the compressor wheel device according to (8) or (9) above the sleeve portion has an inner circumference in which a screw groove into which the rotating shaft is screwed is formed. Has a face.
- the compressor wheel is mechanically connected to the rotary shaft by screwing the rotary shaft into the screw groove formed on the inner peripheral surface of the sleeve portion. Since the sleeve portion having the screw groove is made of a material having higher wear resistance than the wheel body portion, the screw fastening between the rotary shaft and the compressor wheel can be strengthened.
- the turbocharger according to at least one embodiment of the present invention is With a rotating shaft
- the compressor wheel device according to any one of (1) to (10) above, A housing configured to house the compressor wheel device, It is provided with a seal member that is supported by the housing and is configured to form a seal mechanism portion with the seal groove.
- the supercharger includes a compressor wheel device including a sleeve portion having a seal groove, a seal member supported by the housing and forming a seal mechanism portion between the seal groove, and a seal member. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the peripheral length of the seal mechanism portion from becoming large, and it is possible to prevent the seal mechanism portion from becoming complicated. Therefore, according to the above configuration, it is possible to prevent the supercharger from becoming complicated and reduce the manufacturing cost of the supercharger.
- a compressor wheel device capable of preventing structural complications and reducing manufacturing costs.
- expressions such as “same”, “equal”, and “homogeneous” that indicate that things are in the same state not only represent exactly the same state, but also have tolerances or differences to the extent that the same function can be obtained. It shall also represent the state of existence.
- an expression representing a shape such as a quadrangular shape or a cylindrical shape not only represents a shape such as a quadrangular shape or a cylindrical shape in a geometrically strict sense, but also an uneven portion or chamfering within a range in which the same effect can be obtained.
- the shape including the part and the like shall also be represented.
- the expression “comprising”, “including”, or “having” one component is not an exclusive expression excluding the existence of another component.
- the same reference numerals may be given to the same configurations, and the description thereof may be omitted.
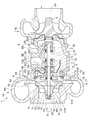
- FIG. 1 is a schematic cross-sectional view along the axis of a turbocharger including the compressor wheel device according to the embodiment.
- the arrow in FIG. 1 indicates the direction in which the combustion gas (air) and the exhaust gas flow.
- the compressor wheel device 3 according to some embodiments has a compressor wheel 4 attached to a rotating shaft 2 extending along the axis LA and a back surface 54 side of the compressor wheel 4 (in the drawing). Includes a thrust collar 7 attached to the rotating shaft 2 on the right side).
- the compressor wheel device 3 is mounted on the supercharger 1 as shown in FIG.
- the turbocharger 1 is configured to accommodate the rotary shaft 2, the compressor wheel device 3, the rotary shaft 2 and the compressor wheel device 3, as shown in FIG. It includes a housing 8.
- the booster 1 includes a turbine wheel 9 attached to the rotary shaft 2 and a thrust bearing 10 configured to support the rotary shaft 2 in the thrust direction, as shown in FIG. ,
- the journal bearings 11 and 12 configured to support the rotary shaft 2 in the radial direction, the thrust collar 13 on the other side, the insert 14, the oil deflector 15, the snap ring 16, and the seal member 17. It consists of a turbocharger for automobiles.
- Each of the thrust bearing 10 and the journal bearings 11 and 12 rotatably supports the rotary shaft 2.
- the housing 8 is configured to accommodate a compressor housing 8A configured to accommodate the compressor wheel 4, thrust bearings 10 and journal bearings 11 and 12, as shown in FIG.
- a bearing housing 8B and a turbine housing 8C configured to accommodate the turbine wheel 9.
- the bearing housing 8B is arranged between the compressor housing 8A and the turbine housing 8C in the axial direction.
- the bearing housing 8B is connected and fixed to the compressor housing 8A by a fastening device (not shown), and the other end is connected and fixed to the turbine housing 8C.
- the fastening device include bolts, nuts, and V-clamps.
- the supercharger 1 rotates the turbine wheel 9 by exhaust gas introduced into the turbine housing 8C from an internal combustion engine such as an engine, and is mechanically connected to the turbine wheel 9 via a rotating shaft 2. It is configured to rotate the compressor wheel 4.
- the supercharger 1 rotates the compressor wheel 4 to compress the combustion gas (air) introduced into the compressor housing 8A to generate compressed air and send it to the internal combustion engine described above. It is configured in.
- the turbine housing 8C is such that the exhaust gas is introduced from the outside in the radial direction and the exhaust gas obtained by rotating the turbine wheel 9 is discharged to the outside along the axial direction, as shown in FIG. It is configured in.
- the compressor housing 8A is such that air is introduced from the outside in the axial direction and the combustion gas that has passed through the compressor wheel 4 and the diffuser flow path is discharged to the outside along the radial direction. It is configured.
- the bearing housing 8B has an internal space 81 configured to allow the rotating shaft 2 to be inserted along the axial direction, and an internal space 81 from the outside of the bearing housing 8B.
- An oil supply flow path 82 for flowing lubricating oil is defined inside.
- a thrust collar 7 In the internal space 81, as shown in FIG. 1, a thrust collar 7, a thrust bearing 10, journal bearings 11 and 12, a thrust collar 13 on the other side, an insert 14, an oil deflector 15, and a snap ring 16 are provided. And the seal member 17 are arranged.
- the journal bearing 11 is arranged on one side of the journal bearing 12 and on the other side of the thrust collar 13 on the other side.
- the bearing housing 8B includes a refueling inlet 821 formed on the outer surface 83 of the bearing housing 8B, a thrust side outlet 822 formed on the stepped surface 84 of the bearing housing 8B, and an inner surface of the bearing housing 8B.
- the journal side outlets 823 and 824 formed at 85 are formed. A part of the lubricating oil introduced from the lubrication inlet 821 to the lubrication flow path 82 passes through the journal side outlets 823 and 824 and lubricates the journal bearings 11 and 12.
- the thrust bearing 10 internally defines a lubrication introduction path 101 for flowing lubricating oil.
- the thrust bearing 10 is formed with a refueling contact port 102 communicating with the thrust side outlet 822 and a discharge port 103 for discharging the lubricating oil flowing through the refueling introduction path 101 to the outside.
- a part of the lubricating oil introduced from the refueling inlet 821 to the refueling flow path 82 passes through the thrust side outlet 822 and the refueling communication port 102, is introduced into the refueling introduction path 101, and then passes through the discharge port 103 to the thrust bearing 10. It is discharged to the outside of the thrust collar 7 and introduced into the gap between the thrust collar 7 and the thrust collar 13 on the other side and the thrust bearing 10.
- the compressor wheel 4 includes a wheel body 5 including at least one blade 53 provided on the hub 51 and the outer peripheral surface 52 of the hub 51, and the compressor wheel 4 along the axial direction from the back surface 54 of the hub 51.
- a protruding tubular sleeve portion 6 The sleeve portion 6 has at least one seal groove 62 extending along the circumferential direction on the outer peripheral surface 61.
- the wheel body portion 5 and the sleeve portion 6 are configured to rotate integrally with the rotating shaft 2.
- the at least one blade 53 includes a plurality of blades 53 provided at intervals in the circumferential direction of the hub 51.
- the sleeve portion 6 is provided coaxially with the hub 51, and protrudes from the center of the back surface 54 of the hub 51.
- the hub 51 includes a disc portion 51A extending along the radial direction, and a nose portion 51B provided on one side of the disc portion 51A and having a diameter smaller than that of the disc portion 51A.
- the sleeve portion 6 is configured to have a smaller diameter than the disc portion 51A of the hub 51.
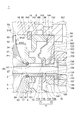
- FIG. 2 is a schematic partially enlarged cross-sectional view showing the vicinity of the sleeve portion of the compressor wheel device shown in FIG. 1 in an enlarged manner.
- FIG. 3 is a schematic partially enlarged cross-sectional view corresponding to FIG. 2 of the compressor wheel device according to another embodiment.
- the thrust collar 7 has one surface 71 located at one end (one side) in the thickness direction (axial direction) and extending along the radial direction, and the other end in the thickness direction. It has a disk shape including an other surface 72 located on (the other side) and extending along the radial direction.
- One surface 71 includes a contact surface 71A that abuts the end surface 63 of the sleeve portion 6, as shown in FIGS.
- the other surface 72 includes a sliding contact surface 72A that is in sliding contact with the end surface 104 of the thrust bearing 10 described above, as shown in FIGS.
- the thrust collar 7 is formed with a through hole 73 penetrating along the thickness direction, and the rotary shaft 2 is inserted through the through hole 73.
- the thrust collar 7 is configured to rotate integrally with the rotating shaft 2.
- the thrust collar 7 is arranged on the one side of the thrust collar 13 on the other side.
- the other side thrust collar 13 has a cylindrical body portion 131 having a through hole 132 through which the rotating shaft 2 is inserted, and a radial body portion 131 from the other side outer peripheral edge portion of the body portion 131. Includes a flange 133 that projects along the line.
- the other side thrust collar 13 is configured to rotate integrally with the rotating shaft 2.
- the body portion 131 has an end surface 134 located on one side thereof, and has an end surface 134 extending along the radial direction and abutting on the other surface 72 of the thrust collar 7. ..
- the other surface 72 of the thrust collar 7 includes a collar contact surface 72B provided radially inside the sliding contact surface 72A and in contact with the end surface 134 of the other side thrust collar 13.
- the flange portion 133 is a stepped surface 135 located on one side thereof, and is a stepped surface extending along the radial direction and in sliding contact with the end surface 105 of the thrust bearing 10 described above. Has 135.
- the thrust bearing 10 is formed in a plate shape extending along the radial direction, and extends along the axial direction to form a body portion 131 of the thrust collar 13 on the other side.
- An insertion hole 106 is formed so as to be loosely inserted.
- the thrust bearing 10 is located on one side of the thrust bearing 10 and extends along the radial direction, and is located on the other side of the thrust bearing 10 and extends along the radial direction. Includes the above-mentioned end face 105 extending.
- the thrust bearing 10 has an inner peripheral edge portion 107 arranged in a gap between the sliding contact surface 72A of the thrust collar 7 in the axial direction and the stepped surface 135 of the thrust collar 13 on the other side.
- the thrust bearing 10 causes the rotary shaft 2 to slide in the thrust direction by causing the end surface 104 to slide in contact with the sliding contact surface 72A or the end surface 105 in sliding contact with the stepped surface 135.
- the inner surface of the insertion hole 106 of the thrust bearing 10 is configured to be in sliding contact with the outer peripheral surface 136 of the body portion 131 of the thrust collar 13 on the other side as the rotating shaft 2 rotates.
- the above-mentioned refueling connection port 102 is formed on the end surface 105
- the above-mentioned discharge port 103 is formed on the inner surface of the insertion hole 106.
- the lubricating oil discharged from the discharge port 103 is between the inner surface of the insertion hole 106 of the thrust bearing 10 and the outer peripheral surface 136 of the thrust collar 13 on the other side, the end surface 104 of the thrust bearing 10 and the sliding contact surface 72A of the thrust collar 7. It is introduced between the space and between the end surface 105 of the thrust bearing 10 and the stepped surface 135 of the thrust collar 13 on the other side to form a liquid film as the rotating shaft 2 rotates.
- the insert 14 is an annular member having a through hole 141 penetrating along the axial direction, and is configured such that the sleeve portion 6 is loosely inserted into the through hole 141. ..
- the insert 14 is arranged so that the inner surface of the through hole 141 faces the outer peripheral surface 61 including the seal groove 62 with a gap.
- the insert 14 has a protruding portion 142 protruding from the outer peripheral portion toward the thrust bearing 10 side along the axial direction.
- the tip 144 protruding from the stepped surface 143 on the other side extending along the radial direction of the protruding portion 142 is in contact with the outer peripheral edge of the end surface 104 of the thrust bearing 10.
- the bearing housing 8B has a covering portion 86 extending along the axial direction so as to cover the outer peripheral side of the thrust bearing 10 and the insert 14, and the other side of the thrust bearing 10 in the axial direction.
- the inwardly projecting portion 87 has the stepped surface 84 that abuts on the end surface 105 of the thrust bearing 10.
- the rear end surface 145 of the protrusion 142 on the one side of the insert 14 is an arc-shaped snap fitted in the inner peripheral groove 88 formed in the covering portion 86 of the bearing housing 8B. It is in contact with the ring 16 (movement restricting member).
- the insert 14 is pressed against the thrust bearing 10 side by the snap ring 16.
- each of the thrust bearing 10 and the insert 14 has its outer peripheral edge sandwiched between the inwardly projecting portion 87 and the snap ring 16 of the bearing housing 8B. That is, the thrust bearing 10 and the insert 14 are supported on the outer peripheral side of the rotating shaft 2 by the bearing housing 8B (housing 8).
- the oil deflector 15 extends along the radial direction, and the outer peripheral edge portion 152 thereof has a stepped surface 143 of the insert 14 and an outer peripheral edge of the end surface 104 of the thrust bearing 10. It is sandwiched between. That is, the oil deflector 15 is supported on the outer peripheral side of the rotary shaft 2 by the bearing housing 8B (housing 8) via the thrust bearing 10 and the insert 14. Further, the oil deflector 15 is configured such that the inner peripheral edge 153 of the other side surface is in sliding contact with one surface 71 of the thrust collar 7.
- the one surface 71 includes a sliding contact surface 71B provided on the outer side in the radial direction from the contact surface 71A and in sliding contact with the inner peripheral edge 153 of the oil deflector 15. That is, as shown in FIGS. 2 and 3, the thrust collar 7 has a protruding portion 74 that protrudes radially outward from the outer peripheral surface 61 of the sleeve portion 6, and the one side surface of the protruding portion 74 is the above. It becomes the sliding contact surface 71B.
- the seal member 17 is configured to form a seal mechanism portion 18 with the seal groove 62 of the sleeve portion 6.
- the seal member 17 is supported on the outer peripheral side of the rotary shaft 2 by the bearing housing 8B (housing 8) via the insert 14.
- the compressor wheel 4 in the embodiment shown in FIGS. 1 and 2 has a so-called through-bore structure.
- the compressor wheel 4 is formed on the outer peripheral surface of the tip portion 23 of the rotary shaft 2 in the screw groove 65 (female screw portion) formed on the inner peripheral surface 64A of the sleeve portion 6.
- the screwed portion 24 male screw portion
- the compressor wheel 4 in the embodiment shown in FIG. 3 has a so-called boreless structure.
- the compressor wheel device 3 includes the above-mentioned compressor wheel 4 and the above-mentioned thrust collar 7.
- the compressor wheel 4 includes the wheel body portion 5 described above and the sleeve portion 6 having the seal groove 62 described above, and the thrust collar 7 includes the one surface 71 including the contact surface 71A and the sliding contact surface 72A. It has a disk shape including the other surface 72 described above.
- the compressor wheel device 3 includes a compressor wheel 4 having a wheel main body portion 5 and a sleeve portion 6, and a thrust collar 7.
- the thrust collar 7 includes the contact surface 71A that comes into contact with the end surface 63 of the sleeve portion 6 and is in sliding contact with the above-mentioned one surface 71 that extends along the radial direction and the thrust bearing 10 that supports the rotary shaft 2 in the thrust direction. Since it has a disk shape including the sliding contact surface 72A and the above-mentioned other surface 72 extending along the radial direction, it has a simple structure and is easy to manufacture.
- the thrust collar 7 can be assembled to the turbocharger 1 without distinguishing between the one side 71 and the other side 72, the assembling property is good. Therefore, according to the above configuration, it is possible to prevent the structure of the compressor wheel device 3 from becoming complicated and reduce the manufacturing cost of the compressor wheel device 3.
- the lubricating oil is likely to leak by that amount, which causes the seal mechanism portion 18 to become complicated in order to prevent the leakage of the lubricating oil. There is a risk.
- the sleeve portion 6 since the sleeve portion 6 has the seal groove 62, it is possible to prevent the peripheral length of the seal mechanism portion 18 of the turbocharger 1 including the seal groove 62 from becoming large. This makes it possible to prevent the seal mechanism portion 18 from becoming complicated. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the supercharger 1 on which the compressor wheel device 3 is mounted from becoming complicated, and to reduce the manufacturing cost of the supercharger 1.
- the above-mentioned wheel body portion 5 and the above-mentioned sleeve portion 6 are integrally formed of the same material. If the wheel body 5 and the sleeve 6 are separate bodies, it is necessary to assemble the wheel body 5 and the sleeve 6. According to the above configuration, since the wheel main body 5 and the sleeve 6 are integrally formed of the same material, the wheel main body 5 and the sleeve 6 can be assembled as compared with the case where the wheel main body 5 and the sleeve 6 are separate bodies. Is good.
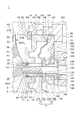
- FIG. 4 is a schematic partial enlarged cross-sectional view of the vicinity of the seal mechanism portion of the supercharger including the compressor wheel device according to the embodiment.
- FIG. 5 is a schematic view of the seal member in one embodiment.
- the wheel body 5 described above and the sleeve portion 6 described above are integrally formed of the same material.
- the bottom surface 621 of the seal groove 62 described above is configured such that a clearance C is formed between the bottom surface 621 of the seal groove 62 described above and the inner peripheral surface 171 of the seal member 17 supported by the housing 8.
- the seal member 17 is formed in an arc shape having an arc angle of 180 degrees or more.
- the sealing member 17 has flexibility and extends along the circumferential direction in the through hole 141 of the insert 14 in a state of being bent so that one arc end 173 and the other arc end 174 come close to each other. It is fitted in the seal groove 146.
- the seal member 17 is supported by the insert 14 by pressing the bottom surface of the seal groove 146 with a restoring force acting to expand the outer peripheral surface 172 of the seal member 17 radially outward.
- the seal member 17 is supported on the outer peripheral side of the rotary shaft 2 by the bearing housing 8B (housing 8) via the insert 14.
- the sleeve portion 6 may be a low-strength material.
- the bottom surface 621 of the seal groove 62 is configured such that a clearance C is formed between the bottom surface 621 of the seal groove 62 and the inner peripheral surface 171 of the seal member 17 supported by the housing 8, so that the sleeve portion 6 It is possible to prevent the seal groove 62 of the above from sliding with respect to the seal member 17 and being worn or damaged.
- the seal groove 62 may be configured to form the clearance C described above when the wheel body portion 5 and the sleeve portion 6 are separate bodies.
- the wheel body 5 described above and the sleeve portion 6 described above are integrally formed of the same material.
- the portion of the sleeve portion 6 including the seal groove 62 is subjected to a surface processing treatment for improving at least one of hardness and slidability.
- the surface processing treatment includes at least one of chemical conversion treatment, plating treatment, alumite treatment, Teflon (registered trademark) processing treatment, Teflon impregnation treatment, or a combination thereof.
- the plating treatment include nickel plating, zinc plating, electroless nickel plating for improving hardness, caniflon plating (Teflon composite electroless nickel plating) for improving hardness and slidability, and electroless nickel boron plating for improving hardness. Be done.
- the sleeve portion 6 As mentioned above, aluminum or an aluminum alloy may be used for the sleeve portion 6.
- these materials are used for the seal groove 62 which may slide with other members, wear or damage may easily progress due to insufficient hardness, or the slidability may be poor and galling may easily occur. There is.
- the portion of the sleeve portion 6 including the seal groove 62 is subjected to a surface processing treatment for improving at least one of hardness and slidability, the seal groove 62 is worn or damaged due to insufficient hardness. It is possible to prevent the occurrence of galling.
- the wheel body 5 described above and the sleeve portion 6 described above are integrally formed of the same material.
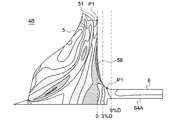
- the connection position P1 between the wheel body portion 5 and the sleeve portion 6 described above is in the axial direction from the maximum outer diameter position P2 of the hub 51 when the maximum outer diameter of the hub 51 described above is D (see FIG. 1). It is configured to be separated by 0.03D (3% D) or more.
- the maximum outer diameter position P2 is located on the other side edge of the disc portion 51A. In other words, the maximum outer diameter position P2 is located on the outer peripheral edge of the back surface 54 of the wheel body 5.
- connection position P1 is configured to be within 0.09D (9% D) in the axial direction from the maximum outer diameter position P2 of the hub 51. In this case, it is possible to prevent the length of the compressor wheel 4 in the axial direction from becoming long.
- a hole 57A (corresponding to a through hole 57) is formed inside the maximum outer diameter position P2 in the radial direction, and the inner peripheral side is near the inner peripheral surface of the hole 57A.
- the stress concentration portion 56 is generated.
- the hole 57A is not formed inside the maximum outer diameter position P2 in the radial direction, the stress concentration portion 56 on the inner peripheral side is not generated.
- Centrifugal stress becomes maximum near the maximum outer diameter position P2 of the hub 51 in the axial direction.
- the connection position P1 between the wheel body 5 and the sleeve 6 is 0.03D in the axial direction from the maximum outer diameter position P2 of the hub 51 when the maximum outer diameter of the hub 51 is D. Since it is configured to be separated from each other as described above, the centrifugal stress applied to the connection position P1 can be reduced. By reducing the centrifugal stress applied to the connection position P1, the outer diameter of the sleeve portion 6 can be reduced, so that it is possible to prevent the peripheral length of the seal mechanism portion 18 of the turbocharger 1 from increasing.
- the above-mentioned wheel body portion 5 and the above-mentioned sleeve portion 6 are integrally formed of the same material.
- the connection portion 41 between the wheel body portion 5 described above and the sleeve portion 6 described above is formed in an arc shape that is concave inside the compressor wheel 4 in a cross section including the axial direction of the rotating shaft 2.
- the connecting portion 41 between the wheel body portion 5 and the sleeve portion 6 is formed in an arc shape that is concave inside the compressor wheel 4 in the cross section including the axial direction of the rotating shaft 2. , It is possible to prevent stress concentration from occurring in the connecting portion 41. By preventing stress concentration from occurring in the connecting portion 41, the outer diameter of the sleeve portion 6 can be reduced, so that it is possible to prevent the peripheral length of the sealing mechanism portion 18 of the turbocharger 1 from increasing.
- the rotary shaft 2 is screwed into the screw groove 65 formed on the inner peripheral surface 64A of the sleeve portion 6 located at a position away from the maximum outer diameter position P2 of the hub 51.
- it has a so-called boreless structure that is mechanically connected to the rotating shaft 2.
- it is possible to suppress the occurrence of the stress concentration portion 56 (stress concentration portion) on the inner peripheral side described above, and it is not necessary to increase the creep strength of the wheel body portion 5 as compared with the through-bore structure. , The material cost of the wheel body 5 can be reduced.
- the wheel body 5 and the sleeve 6 are integrally formed of the same material, but in some other embodiments, the wheel body 5 and the sleeve 6 are It may be a separate body, and each of the wheel body portion 5 and the sleeve portion 6 may be formed of different materials.
- the sleeve portion 6 described above is consolidated into the wheel body portion 5 by being press-fitted into the recess 55 formed in the back surface 54 of the hub 51. It is made of a material that has one end portion 66 and has a higher wear resistance than the wheel main body portion 5. In the illustrated embodiment, one end 66 has an outer peripheral surface having a diameter smaller than the outer peripheral surface 61 on which the seal groove 62 of the sleeve portion 6 is formed, as shown in FIG.
- the wheel body 5 and the sleeve 6 are integrated, so that the wheel body 5 and the sleeve 6 are assembled.
- the work is easy.
- the wheel main body portion 5 and the sleeve portion 6 are assembled to the turbocharger 1 in an integrated state, the assembling property is good. Therefore, according to the above configuration, it is possible to suppress an increase in manufacturing cost due to the separate body of the wheel body 5 and the sleeve 6.
- the sleeve portion 6 having the seal groove 62 is made of a material having higher wear resistance than the wheel main body portion 5, it is possible to prevent the seal groove 62 from being worn or damaged.
- the tip 661 of one end 66 of the sleeve 6 is configured to be located on the back surface 54 side of the compressor wheel 4 with respect to the maximum outer diameter position P2 of the hub 51, and thus has a through-bore structure.
- the wheel body 5 and the sleeve 6 are separate bodies, as shown in FIG.
- the sleeve portion 6 described above has an inner peripheral surface 64A in which a screw groove 65 into which the rotating shaft 2 is screwed is formed.
- the compressor wheel 4 is mechanically connected to the rotary shaft 2 by screwing the rotary shaft 2 into the screw groove 65 formed on the inner peripheral surface 64A of the sleeve portion 6. Since the sleeve portion 6 having the screw groove 65 is made of a material having higher wear resistance than the wheel main body portion 5, the screw fastening between the rotary shaft 2 and the compressor wheel 4 can be strengthened. it can.
- the supercharger 1 is configured to accommodate the above-mentioned rotating shaft 2, the above-mentioned compressor wheel device 3, and the above-mentioned compressor wheel device 3. It includes the housing 8 and the above-mentioned sealing member 17 which is supported by the housing 8 and is configured to form a sealing mechanism portion 18 between the housing 8 and the sealing groove 62.
- the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and includes a modification of the above-described embodiment and a combination of these embodiments as appropriate.
- a turbocharger including a compressor wheel 4 and a turbine wheel 9 as the supercharger 1 has been described as an example, but the supercharger 1 is not limited to the turbocharger.
- the supercharger 1 may be a supercharger other than the turbocharger.
- the supercharger 1 may be configured not to include the above-mentioned turbine wheel 9.
- Examples of the turbocharger 1 not provided with the turbine wheel 9 include an electric compressor configured to rotate the compressor wheel 4 by an electric motor (not shown).
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Structures Of Non-Positive Displacement Pumps (AREA)
- Supercharger (AREA)
Abstract
コンプレッサホイール装置は、回転シャフトに取り付けられるコンプレッサホイールと、コンプレッサホイールの背面側にて回転シャフトに取り付けられるスラストカラーと、を備える。コンプレッサホイールは、ハブ及びハブの外周面に設けられた少なくとも一つにブレードを含むホイール本体部と、ハブの背面から軸方向に沿って突出する筒状のスリーブ部であって、外周面に周方向に沿って延在するシール溝を有するスリーブ部と、を含む。スラストカラーは、スリーブ部の端面と当接する当接面を含むとともに径方向に沿って延在する一面と、回転シャフトをスラスト方向に支持するスラスト軸受と摺接する摺接面を含むとともに前記径方向に沿って延在する他面と、を含む円板形状を有する。
Description
本開示は、コンプレッサホイールおよびスラストカラーを備えるコンプレッサホイール装置、該コンプレッサホイール装置を備える過給機に関する。
過給機に搭載されるコンプレッサホイールには、ハブおよび該ハブの外周面に設けられた複数のブレードを含み、ハブを軸方向に貫通する貫通孔が形成されたものがある。上記コンプレッサホイールは、貫通孔に回転シャフトが挿通されて、回転シャフトのホイール前縁端から突出した突出部にナットを螺合することで、回転シャフトに機械的に連結される、いわゆるスルーボア構造となっている。
上記スルーボア構造では、上記貫通孔の内周面に応力集中部が発生することが知られている。応力集中部は最大外径部近傍に発生する。例えば、商用車や産業用過給機などに搭載されるコンプレッサは、高圧力比が求められるが、高圧力比化に伴いコンプレッサの出口温度が上昇するため、上記応力集中部におけるクリープ強度が問題となる。クリープ強度を確保するためにコンプレッサホイールにチタンなどの高強度材を採用することは、コスト増加に繋がるので好ましくはない。
また、コンプレッサホイールには、上記ハブと上記ブレードとを含むホイール本体部材と、円筒状のスリーブ部材と、を備えるものがある(特許文献1参照)。特許文献1には、ホイール本体部材の裏面中央部にスリーブ部材の軸端面を接触させ、スリーブ部材を回転させることにより発生する熱で接触部が溶融することで、ホイール本体部材とスリーブ部材とが固着されたコンプレッサホイールが開示されている。また、特許文献1には、スリーブ部材の内周面に形成された雌ネジ部に、回転シャフトの先端部を螺合することで、コンプレッサホイールが回転シャフトに機械的に連結される、いわゆるボアレス構造が開示されている。
上記ボアレス構造では、上記雌ネジ部を最大外径部近傍よりも背面側に設けることにより、応力集中部の発生を抑制することができるので、上記スルーボア構造に比べて、クリープ強度を高くする必要がない分、材料コストを低減させることができる。
しかし、上記ボアレス構造では、上記スルーボア構造に比べて、コンプレッサホイールの軸方向における長さがスリーブ部材の長さ分だけ長くなるので、コンプレッサの大型化だけでなく、軸振動の増加や危険速度の低下を招く虞がある。コンプレッサの軸方向における長さを短くするために、コンプレッサホイールの背面側にて回転シャフトに取り付けられるスラストカラーをスリーブ部材より大径にして、スリーブ部材に被せるように配置することが考えられるが、スラストカラーの複雑化を招き、過給機の製造コストの増大を招く虞がある。
上述した事情に鑑みて、本発明の少なくとも一実施形態の目的は、構造の複雑化を防止して、製造コストを低減させることができるコンプレッサホイール装置を提供することにある。
(1)本発明の少なくとも一実施形態にかかるコンプレッサホイール装置は、
回転シャフトに取り付けられるコンプレッサホイールであって、
ハブと、上記ハブの外周面に設けられた少なくとも一つにブレードと、を含むホイール本体部、及び
上記ハブの背面から軸方向に沿って突出する筒状のスリーブ部であって、外周面に周方向に沿って延在するシール溝を有するスリーブ部、
を含むコンプレッサホイールと、
上記コンプレッサホイールの背面側にて上記回転シャフトに取り付けられるスラストカラーであって、
上記スリーブ部の端面と当接する当接面を含むとともに径方向に沿って延在する一面と、
上記回転シャフトをスラスト方向に支持するスラスト軸受と摺接する摺接面を含むとともに上記径方向に沿って延在する他面と、
を含む円板形状を有するスラストカラーと、を備える。
回転シャフトに取り付けられるコンプレッサホイールであって、
ハブと、上記ハブの外周面に設けられた少なくとも一つにブレードと、を含むホイール本体部、及び
上記ハブの背面から軸方向に沿って突出する筒状のスリーブ部であって、外周面に周方向に沿って延在するシール溝を有するスリーブ部、
を含むコンプレッサホイールと、
上記コンプレッサホイールの背面側にて上記回転シャフトに取り付けられるスラストカラーであって、
上記スリーブ部の端面と当接する当接面を含むとともに径方向に沿って延在する一面と、
上記回転シャフトをスラスト方向に支持するスラスト軸受と摺接する摺接面を含むとともに上記径方向に沿って延在する他面と、
を含む円板形状を有するスラストカラーと、を備える。
上記(1)の構成によれば、コンプレッサホイール装置は、ホイール本体部およびスリーブ部を有するコンプレッサホイールと、スラストカラーと、を備える。スラストカラーは、スリーブ部の端面と当接する当接面を含むとともに径方向に沿って延在する一面と、回転シャフトをスラスト方向に支持するスラスト軸受と摺接する摺接面を含むとともに径方向に沿って延在する他面と、を含む円板形状であるため、簡単な構造であり、製造が容易である。また、スラストカラーは、過給機に対して一面と他面とを区別することなく組付け可能であるため、組付け性が良好である。よって、上記の構成によれば、コンプレッサホイール装置の構造の複雑化を防止して、コンプレッサホイール装置の製造コストを低減させることができる。
仮に過給機のシール機構部の周長が長いものであると、その分だけ潤滑油が漏洩し易くなるので、潤滑油の漏洩を防止するために、シール機構部の複雑化を招く虞がある。上記(1)の構成によれば、スリーブ部にシール溝を有しているので、上記シール溝を含んで構成される過給機のシール機構部の周長が大きくなるのを防止することができ、シール機構部の複雑化を防止することができる。このため、コンプレッサホイール装置が搭載される過給機の複雑化を防止して、過給機の製造コストを低減させることができる。
(2)幾つかの実施形態では、上記(1)に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置であって、上記ホイール本体部と上記スリーブ部とは、同じ材料により一体的に形成されている。
仮にホイール本体部とスリーブ部が別体であると、ホイール本体部とスリーブ部を組付ける作業が必要となる。上記(2)の構成によれば、ホイール本体部とスリーブ部とが同じ材料により一体的に形成されているので、ホイール本体部とスリーブ部が別体である場合に比べて、組付け性が良好である。また、ホイール本体部とスリーブ部とを一体的に形成する加工は、困難ではないため、加工性が低下する虞はない。よって、上記の構成によれば、コンプレッサホイール装置の製造コストをより低減させることができる。
(3)幾つかの実施形態では、上記(2)に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置であって、上記シール溝の底面は、上記コンプレッサホイールを収容するハウジングに支持されたシール部材の内周面との間にクリアランスが形成されるように構成された。
一般的に、コンプレッサホイールの軽量化を図るために、コンプレッサホイールの材料としてアルミニウムやアルミニウム合金のような低強度材料が用いられることがある。ホイール本体部とスリーブ部とが一体的に形成されている場合には、スリーブ部が低強度材料となる可能性がある。上記(3)の構成によれば、シール溝の底面は、ハウジングに支持されたシール部材の内周面との間にクリアランスが形成されるように構成されているので、スリーブ部のシール溝が、シール部材に対して摺動して摩耗や損傷することを防止することができる。
(4)幾つかの実施形態では、上記(2)又は(3)に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置であって、上記スリーブ部の上記シール溝を含む部分に硬度又は摺動性の少なくとも一方を向上させる表面加工処理が施された。
上述したように、スリーブ部にアルミニウムやアルミニウム合金が用いられる可能性がある。これらの材料を他部材と摺動する可能性があるシール溝に採用した場合には、硬度不足により摩耗や損傷が進展し易かったり、摺動性が悪くカジリが発生し易かったりする可能性がある。上記(4)の構成によれば、スリーブ部のシール溝を含む部分に硬度又は摺動性の少なくとも一方を向上させる表面加工処理が施されているので、シール溝が硬度不足による摩耗や損傷することや、カジリの発生を防止することができる。
(5)幾つかの実施形態では、上記(2)~(4)の何れかに記載のコンプレッサホイール装置であって、上記ホイール本体部と上記スリーブ部との接続位置は、上記ハブの最大外径をDとしたときに、上記ハブの最大外径位置から上記軸方向において0.03D以上離れるように構成された。
軸方向におけるハブの最大外径位置近傍において遠心応力が極大となる。上記(5)の構成によれば、ホイール本体部とスリーブ部との接続位置は、ハブの最大外径をDとしたときに、ハブの最大外径位置から上記軸方向において0.03D以上離れるように構成されているので、上記接続位置にかかる遠心応力を小さなものにすることができる。上記接続位置にかかる遠心応力を小さくすることで、スリーブ部の外径を小さくできるため、過給機のシール機構部の周長が大きくなるのを防止することができる。
(6)幾つかの実施形態では、上記(2)~(5)の何れかに記載のコンプレッサホイール装置であって、上記ホイール本体部と上記スリーブ部との接続部は、上記回転シャフトの軸線方向を含む断面において、上記コンプレッサホイールの内側に凹となる円弧状に形成されている。
上記(6)の構成によれば、ホイール本体部とスリーブ部との接続部は、回転シャフトの軸線方向を含む断面において、コンプレッサホイールの内側に凹となる円弧状に形成されているので、上記接続部に応力集中が生じるのを防止することができる。上記接続部に応力集中が生じるのを防止することで、スリーブ部の外径を小さくできるため、過給機のシール機構部の周長が大きくなるのを防止することができる。
(7)幾つかの実施形態では、上記(1)~(6)の何れかに記載のコンプレッサホイール装置であって、上記スリーブ部は、上記回転シャフトが螺合される螺合溝が形成された内周面を有する。
上記(7)の構成によれば、コンプレッサホイールは、ハブの最大外径位置から離れた位置にあるスリーブ部の内周面に形成された螺合溝に回転シャフトを螺合させることで、回転シャフトに機械的に連結される、いわゆるボアレス構造となっている。上記の構成によれば、応力集中部の発生を抑制することができ、スルーボア構造に比べて、ホイール本体部のクリープ強度を高くする必要がない分、ホイール本体部の材料コストを低減させることができる。
(8)幾つかの実施形態では、上記(1)に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置であって、上記スリーブ部は、上記ハブの上記背面に形成された凹部に圧入されることで上記ホイール本体部に固結されるように構成される一端部を有し、且つ、上記ホイール本体部よりも耐摩耗性が高い材料により形成されている。
上記(8)の構成によれば、スリーブ部の一端部をハブの凹部に圧入すれば、ホイール本体部とスリーブ部が一体となるので、ホイール本体部とスリーブ部を組付ける作業は容易である。また、ホイール本体部とスリーブ部とが一体になった状態で過給機に組付けられるので、組付け性が良好である。よって、上記の構成によれば、ホイール本体部とスリーブ部とを別体にしたことによる製造コストの増加を抑えることができる。また、シール溝を有するスリーブ部がホイール本体部よりも耐摩耗性が高い材料により形成されているので、シール溝の摩耗や損傷を防止することができる。
(9)幾つかの実施形態では、上記(8)に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置であって、上記一端部の先端は、上記ハブの最大外径位置よりも上記コンプレッサホイールの背面側に位置するように構成される。
上記(9)の構成によれば、スリーブ部の一端部の先端は、ハブの最大外径位置よりもコンプレッサホイールの背面側に位置するように構成されているので、スルーボア構造とは異なり、ホイール本体部における応力集中部の発生を抑制することができる。このため、ホイール本体部のクリープ強度を高くする必要がない分、ホイール本体部の材料コストを低減させることができる。
(10)幾つかの実施形態では、上記(8)又は(9)に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置であって、上記スリーブ部は、上記回転シャフトが螺合される螺合溝が形成された内周面を有する。
上記(10)の構成によれば、コンプレッサホイールは、スリーブ部の内周面に形成された螺合溝に回転シャフトを螺合させることで、回転シャフトに機械的に連結される。螺合溝を有するスリーブ部は、ホイール本体部よりも耐摩耗性が高い材料により形成されているので、回転シャフトとコンプレッサホイールとの螺合締結を強固なものにすることができる。
(11)本発明の少なくとも一実施形態にかかる過給機は、
回転シャフトと、
上記(1)~(10)の何れかに記載のコンプレッサホイール装置と、
上記コンプレッサホイール装置を収容するように構成されたハウジングと、
上記ハウジングに支持されるとともに、上記シール溝との間にシール機構部を形成するように構成されたシール部材と、を備える。
回転シャフトと、
上記(1)~(10)の何れかに記載のコンプレッサホイール装置と、
上記コンプレッサホイール装置を収容するように構成されたハウジングと、
上記ハウジングに支持されるとともに、上記シール溝との間にシール機構部を形成するように構成されたシール部材と、を備える。
上記(11)の構成によれば、過給機は、シール溝を有するスリーブ部を含むコンプレッサホイール装置と、ハウジングに支持されるとともにシール溝との間にシール機構部を形成するシール部材と、を備えるので、シール機構部の周長が大きくなるのを防止することができ、シール機構部の複雑化を防止することができる。よって、上記の構成によれば、過給機の複雑化を防止して、過給機の製造コストを低減させることができる。
本発明の少なくとも一実施形態によれば、構造の複雑化を防止して、製造コストを低減させることができるコンプレッサホイール装置が提供される。
以下、添付図面を参照して本発明の幾つかの実施形態について説明する。ただし、実施形態として記載されている又は図面に示されている構成部品の寸法、材質、形状、その相対的配置等は、本発明の範囲をこれに限定する趣旨ではなく、単なる説明例にすぎない。
例えば、「ある方向に」、「ある方向に沿って」、「平行」、「直交」、「中心」、「同心」或いは「同軸」等の相対的或いは絶対的な配置を表す表現は、厳密にそのような配置を表すのみならず、公差、若しくは、同じ機能が得られる程度の角度や距離をもって相対的に変位している状態も表すものとする。
例えば、「同一」、「等しい」及び「均質」等の物事が等しい状態であることを表す表現は、厳密に等しい状態を表すのみならず、公差、若しくは、同じ機能が得られる程度の差が存在している状態も表すものとする。
例えば、四角形状や円筒形状等の形状を表す表現は、幾何学的に厳密な意味での四角形状や円筒形状等の形状を表すのみならず、同じ効果が得られる範囲で、凹凸部や面取り部等を含む形状も表すものとする。
一方、一の構成要素を「備える」、「含む」、又は、「有する」という表現は、他の構成要素の存在を除外する排他的な表現ではない。
なお、同様の構成については同じ符号を付し説明を省略することがある。
例えば、「ある方向に」、「ある方向に沿って」、「平行」、「直交」、「中心」、「同心」或いは「同軸」等の相対的或いは絶対的な配置を表す表現は、厳密にそのような配置を表すのみならず、公差、若しくは、同じ機能が得られる程度の角度や距離をもって相対的に変位している状態も表すものとする。
例えば、「同一」、「等しい」及び「均質」等の物事が等しい状態であることを表す表現は、厳密に等しい状態を表すのみならず、公差、若しくは、同じ機能が得られる程度の差が存在している状態も表すものとする。
例えば、四角形状や円筒形状等の形状を表す表現は、幾何学的に厳密な意味での四角形状や円筒形状等の形状を表すのみならず、同じ効果が得られる範囲で、凹凸部や面取り部等を含む形状も表すものとする。
一方、一の構成要素を「備える」、「含む」、又は、「有する」という表現は、他の構成要素の存在を除外する排他的な表現ではない。
なお、同様の構成については同じ符号を付し説明を省略することがある。
図1は、一実施形態にかかるコンプレッサホイール装置を備える過給機の軸線に沿った概略断面図である。図1中矢印は、燃焼用気体(空気)や排ガスの流れる方向を示している。
幾つかの実施形態にかかるコンプレッサホイール装置3は、図1に示されるように、軸線LAに沿って延在する回転シャフト2に取り付けられるコンプレッサホイール4と、コンプレッサホイール4の背面54側(図中右側)にて回転シャフト2に取り付けられるスラストカラー7と、を含む。コンプレッサホイール装置3は、図1に示されるように過給機1に搭載される。
幾つかの実施形態にかかるコンプレッサホイール装置3は、図1に示されるように、軸線LAに沿って延在する回転シャフト2に取り付けられるコンプレッサホイール4と、コンプレッサホイール4の背面54側(図中右側)にて回転シャフト2に取り付けられるスラストカラー7と、を含む。コンプレッサホイール装置3は、図1に示されるように過給機1に搭載される。
幾つかの実施形態にかかる過給機1は、図1に示されるように、上記回転シャフト2と、上記コンプレッサホイール装置3と、回転シャフト2およびコンプレッサホイール装置3を収容するように構成されたハウジング8と、を備える。
図示される実施形態では、過給機1は、図1に示されるように、回転シャフト2に取り付けられるタービンホイール9と、回転シャフト2をスラスト方向に支持するように構成されたスラスト軸受10と、回転シャフト2をラジアル方向に支持するように構成されたジャーナル軸受11、12と、他方側スラストカラー13と、インサート14と、オイルディフレクタ15と、スナップリング16と、シール部材17と、をさらに備える自動車用のターボチャージャからなる。スラスト軸受10およびジャーナル軸受11、12の夫々は、回転シャフト2を回転可能に支持している。
タービンホイール9は、図1に示されるように、スラストカラー7に対してコンプレッサホイール4とは反対側にて回転シャフト2に取り付けられる。以下、軸線LAが延在する方向を単に軸方向とし、軸線LAに直交する方向を単に径方向とし、軸方向においてコンプレッサホイール4が位置する側(図中左側)を一方側とし、軸方向においてタービンホイール9が位置する側(図中右側)を他方側とする。
図示される実施形態では、ハウジング8は、図1に示されるように、コンプレッサホイール4を収容するように構成されたコンプレッサハウジング8Aと、スラスト軸受10およびジャーナル軸受11、12を収容するように構成された軸受ハウジング8Bと、タービンホイール9を収容するように構成されたタービンハウジング8Cと、を含む。
軸受ハウジング8Bは、図1に示されるように、軸方向におけるコンプレッサハウジング8Aとタービンハウジング8Cとの間に配置されている。軸受ハウジング8Bは、不図示の締結装置によって、上記一方側の端部がコンプレッサハウジング8Aに連結固定され、上記他方側の端部がタービンハウジング8Cに連結固定されている。締結装置としては、ボルトやナット、Vクランプなどが挙げられる。
軸受ハウジング8Bは、図1に示されるように、軸方向におけるコンプレッサハウジング8Aとタービンハウジング8Cとの間に配置されている。軸受ハウジング8Bは、不図示の締結装置によって、上記一方側の端部がコンプレッサハウジング8Aに連結固定され、上記他方側の端部がタービンハウジング8Cに連結固定されている。締結装置としては、ボルトやナット、Vクランプなどが挙げられる。
過給機1(ターボチャージャ)は、エンジンなどの内燃機関からタービンハウジング8C内に導入された排ガスにより、タービンホイール9を回転させ、回転シャフト2を介してタービンホイール9に機械的に連結されたコンプレッサホイール4を回転させるように構成されている。過給機1(ターボチャージャ)は、コンプレッサホイール4を回転させることで、コンプレッサハウジング8A内に導入された燃焼用気体(空気)を圧縮して圧縮空気を生成して上述した内燃機関に送るように構成されている。
図示される実施形態では、タービンハウジング8Cは、図1に示されるように、径方向の外側から排ガスが導入されて、タービンホイール9を回転させた排ガスを軸方向に沿って外側に排出するように構成されている。また、コンプレッサハウジング8Aは、図1に示されるように、軸方向外側から空気が導入されて、コンプレッサホイール4やディフューザ流路を通過した燃焼用気体を径方向に沿って外側に排出するように構成されている。
図示される実施形態では、軸受ハウジング8Bは、図1に示されるように、回転シャフト2を軸方向に沿って挿通可能に構成された内部空間81と、軸受ハウジング8Bの外部から内部空間81に潤滑油を流すための給油流路82と、を内部に画定している。
内部空間81には、図1に示されるように、スラストカラー7と、スラスト軸受10と、ジャーナル軸受11、12と、他方側スラストカラー13と、インサート14と、オイルディフレクタ15と、スナップリング16と、シール部材17と、が配置されている。ジャーナル軸受11は、ジャーナル軸受12より上記一方側に配置され、且つ、他方側スラストカラー13よりも上記他方側に配置されている。
軸受ハウジング8Bは、図1に示されるように、軸受ハウジング8Bの外面83に形成された給油入口821と、軸受ハウジング8Bの段差面84に形成されたスラスト側出口822と、軸受ハウジング8Bの内面85に形成されたジャーナル側出口823、824と、が形成されている。給油入口821から給油流路82に導入された潤滑油の一部は、ジャーナル側出口823、824を通り、ジャーナル軸受11、12を潤滑している。
スラスト軸受10は、図1に示されるように、潤滑油を流すための給油導入路101を内部に画定している。スラスト軸受10は、図1に示されるように、スラスト側出口822に連通する給油連絡口102と、給油導入路101を流れる潤滑油を外部に排出するための排出口103と、が形成されている。給油入口821から給油流路82に導入された潤滑油の一部は、スラスト側出口822および給油連絡口102を通り、給油導入路101に導入された後、排出口103を通ってスラスト軸受10の外部に排出され、スラストカラー7および他方側スラストカラー13の夫々と、スラスト軸受10との隙間に導入される。
コンプレッサホイール4は、図1に示されるように、ハブ51およびハブ51の外周面52に設けられた少なくとも一つのブレード53を含むホイール本体部5と、ハブ51の背面54から軸方向に沿って突出する筒状のスリーブ部6と、を含む。スリーブ部6は、外周面61に周方向に沿って延在する少なくとも一つのシール溝62を有する。ホイール本体部5およびスリーブ部6は、回転シャフト2と一体的に回転するように構成されている。
図示される実施形態では、図1に示されるように、上記少なくとも一つのブレード53は、ハブ51の周方向に互いに間隔をあけて設けられた複数のブレード53を含む。また、スリーブ部6は、ハブ51と同軸上に設けられており、ハブ51の背面54における中央から突出している。ハブ51は、径方向に沿って延在するディスク部51Aと、ディスク部51Aより上記一方側に設けられ、ディスク部51Aより小径のノーズ部51Bと、を含む。スリーブ部6は、ハブ51のディスク部51Aより小径になるように構成されている。
図2は、図1に示すコンプレッサホイール装置のスリーブ部近傍を拡大して示す概略部分拡大断面図である。図3は、他の一実施形態にかかるコンプレッサホイール装置の図2に相当する概略部分拡大断面図である。
スラストカラー7は、図2、3に示されるように、厚さ方向(軸方向)における一端(一方側)に位置して径方向に沿って延在する一面71と、厚さ方向における他端(他方側)に位置して径方向に沿って延在する他面72と、を含む円板形状を有する。
一面71は、図2、3に示されるように、スリーブ部6の端面63と当接する当接面71Aを含む。他面72は、図2、3に示されるように、上述したスラスト軸受10の端面104と摺接する摺接面72Aを含む。
一面71は、図2、3に示されるように、スリーブ部6の端面63と当接する当接面71Aを含む。他面72は、図2、3に示されるように、上述したスラスト軸受10の端面104と摺接する摺接面72Aを含む。
図2、3に示されるように、スラストカラー7は、厚さ方向に沿って貫通する貫通孔73が形成されており、上記貫通孔73に回転シャフト2が挿通される。スラストカラー7は、回転シャフト2と一体的に回転するように構成されている。スラストカラー7は、他方側スラストカラー13より上記一方側に配置されている。
他方側スラストカラー13は、図2、3に示されるように、回転シャフト2が挿通される貫通孔132を有する円筒状の胴体部131と、胴体部131の他方側外周縁部から径方向に沿って突出する鍔部133と、を含む。他方側スラストカラー13は、回転シャフト2と一体的に回転するように構成されている。
胴体部131は、図2、3に示されるように、上記一方側に位置する端面134であって、径方向に沿って延在してスラストカラー7の他面72に当接する端面134を有する。換言すると、スラストカラー7の他面72は、摺接面72Aより径方向内側に設けられ、且つ、他方側スラストカラー13の端面134に当接するカラー当接面72Bを含む。
鍔部133は、図2、3に示されるように、上記一方側に位置する段差面135であって、径方向に沿って延在して上述したスラスト軸受10の端面105と摺接する段差面135を有する。
鍔部133は、図2、3に示されるように、上記一方側に位置する段差面135であって、径方向に沿って延在して上述したスラスト軸受10の端面105と摺接する段差面135を有する。
スラスト軸受10は、図2、3に示されるように、径方向に沿って延在する板状に形成されており、軸方向に沿って延在して他方側スラストカラー13の胴体部131を緩く挿通させるように構成された挿通孔106が形成されている。また、スラスト軸受10は、図2、3に示されるように、上記一方側に位置して径方向に沿って延在する上述した端面104と、上記他方側に位置して径方向に沿って延在する上述した端面105と、を含む。
スラスト軸受10は、軸方向におけるスラストカラー7の摺接面72Aと、他方側スラストカラー13の段差面135との隙間に配置される内周縁部107を有する。
スラスト軸受10は、回転シャフト2にスラスト力が作用した際に、端面104が摺接面72Aに摺接したり、端面105が段差面135に摺接したりすることで、回転シャフト2をスラスト方向に支持している。また、スラスト軸受10の挿通孔106の内面は、回転シャフト2の回転に伴い、他方側スラストカラー13の胴体部131の外周面136に摺接するように構成されている。
スラスト軸受10は、回転シャフト2にスラスト力が作用した際に、端面104が摺接面72Aに摺接したり、端面105が段差面135に摺接したりすることで、回転シャフト2をスラスト方向に支持している。また、スラスト軸受10の挿通孔106の内面は、回転シャフト2の回転に伴い、他方側スラストカラー13の胴体部131の外周面136に摺接するように構成されている。
図示される実施形態では、図2、3に示されるように、上述した給油連絡口102は、端面105に形成され、上述した排出口103は、挿通孔106の内面に形成されている。排出口103から排出された潤滑油は、スラスト軸受10の挿通孔106の内面と他方側スラストカラー13の外周面136との間、スラスト軸受10の端面104とスラストカラー7の摺接面72Aとの間、およびスラスト軸受10の端面105と他方側スラストカラー13の段差面135との間に導入されて、回転シャフト2の回転に伴い液膜を形成する。
インサート14は、図2、3に示されるように、軸方向に沿って貫通する貫通孔141を有する環状部材であり、上記貫通孔141にスリーブ部6が緩く挿通されるように構成されている。インサート14は、貫通孔141の内面が、シール溝62を含む外周面61に対して隙間を有して対向するように配置されている。
インサート14は、図2、3に示されるように、外周部から軸方向に沿ってスラスト軸受10側に突出する突出部142を有する。突出部142の径方向に沿って延在する他方側の段差面143から突出した先端144が、スラスト軸受10の端面104の外周縁に当接している。
軸受ハウジング8Bは、図2、3に示されるように、スラスト軸受10およびインサート14の外周側を覆うように軸方向に沿って延在する被覆部86と、軸方向におけるスラスト軸受10より上記他方側の位置で径方向内側に突出し、径方向に沿って延在する内方突出部87と、を含む。内方突出部87は、スラスト軸受10の端面105に当接する上記段差面84を有する。
インサート14の突出部142の上記一方側の後端面145は、図2、3に示されるように、軸受ハウジング8Bの被覆部86に形成された内周溝88に嵌合された円弧状のスナップリング16(移動規制部材)と当接している。インサート14は、スナップリング16により、スラスト軸受10側に押し付けられている。換言すると、スラスト軸受10およびインサート14の夫々は、各々の外周縁部が軸受ハウジング8Bの内方突出部87およびスナップリング16に挟持されている。つまり、スラスト軸受10およびインサート14は、軸受ハウジング8B(ハウジング8)により、回転シャフト2の外周側に支持されている。
オイルディフレクタ15は、図2、3に示されるように、インサート14より上記他方側に配置されている。オイルディフレクタ15は、軸方向に沿って貫通する貫通孔151を有する環状部材であり、上記貫通孔151にスリーブ部6が緩く挿通されるように構成されている。
オイルディフレクタ15は、図2、3に示されるように、径方向に沿って延在しており、その外周縁部152がインサート14の段差面143と、スラスト軸受10の端面104の外周縁と、の間に挟持されている。つまり、オイルディフレクタ15は、スラスト軸受10およびインサート14を介して、軸受ハウジング8B(ハウジング8)により、回転シャフト2の外周側に支持されている。また、オイルディフレクタ15は、上記他方側の面の内周縁153がスラストカラー7の一面71に摺接するように構成されている。
上記一面71は、当接面71Aより径方向外側に設けられ、且つ、オイルディフレクタ15の内周縁153に摺接する摺接面71Bを含む。つまり、スラストカラー7は、図2、3に示されるように、スリーブ部6の外周面61よりも径方向外側に突出する突出部74を有し、突出部74の上記一方側の面が上記摺接面71Bとなる。
シール部材17は、図2、3に示されるように、スリーブ部6のシール溝62との間にシール機構部18を形成するように構成されている。シール部材17は、インサート14を介して、軸受ハウジング8B(ハウジング8)により、回転シャフト2の外周側に支持されている。
図1、2に示される実施形態では、コンプレッサホイール4には、回転シャフト2が軸方向に沿って挿通可能な貫通孔40が形成されている。貫通孔40は、図1に示されるように、ホイール本体部5を軸方向に沿って貫通する貫通孔57と、貫通孔57に連通するとともにスリーブ部6を軸方向に沿って貫通する貫通孔64と、を含む。コンプレッサホイール4は、貫通孔40に回転シャフト2が挿通されて、回転シャフト2のホイール前縁端から突出した突出部21の外周面に形成された螺合部22(雄ネジ部)に、ナット部材19の内周面に形成された螺合溝191(雌ネジ部)を螺合することで、回転シャフト2に機械的に連結固定されている。つまり、図1、2に示される実施形態におけるコンプレッサホイール4は、いわゆるスルーボア構造となっている。
図3に示される実施形態では、コンプレッサホイール4は、スリーブ部6の内周面64Aに形成された螺合溝65(雌ネジ部)に、回転シャフト2の先端部23の外周面に形成された螺合部24(雄ネジ部)を螺合することで、回転シャフト2に機械的に連結固定されている。つまり、図3に示される実施形態におけるコンプレッサホイール4は、いわゆるボアレス構造となっている。
幾つかの実施形態にかかるコンプレッサホイール装置3は、図2、3に示されるように、上述したコンプレッサホイール4と、上述したスラストカラー7と、を備える。コンプレッサホイール4は、上述したホイール本体部5と、上述したシール溝62を有するスリーブ部6と、を含み、スラストカラー7は、当接面71Aを含む上述した一面71と、摺接面72Aを含む上述した他面72と、を含む円板形状を有する。
上記の構成によれば、コンプレッサホイール装置3は、ホイール本体部5およびスリーブ部6を有するコンプレッサホイール4と、スラストカラー7と、を備える。スラストカラー7は、スリーブ部6の端面63と当接する当接面71Aを含むとともに径方向に沿って延在する上述した一面71と、回転シャフト2をスラスト方向に支持するスラスト軸受10と摺接する摺接面72Aを含むとともに径方向に沿って延在する上述した他面72と、を含む円板形状であるため、簡単な構造であり、製造が容易である。また、スラストカラー7は、過給機1に対して一面71と他面72とを区別することなく組付け可能であるため、組付け性が良好である。よって、上記の構成によれば、コンプレッサホイール装置3の構造の複雑化を防止して、コンプレッサホイール装置3の製造コストを低減させることができる。
仮に過給機1のシール機構部18の周長が長いものであると、その分だけ潤滑油が漏洩し易くなるので、潤滑油の漏洩を防止するために、シール機構部18の複雑化を招く虞がある。上記の構成によれば、スリーブ部6にシール溝62を有しているので、シール溝62を含んで構成される過給機1のシール機構部18の周長が大きくなるのを防止することができ、シール機構部18の複雑化を防止することができる。このため、コンプレッサホイール装置3が搭載される過給機1の複雑化を防止して、過給機1の製造コストを低減させることができる。
幾つかの実施形態では、図2、3に示されるように、上述したホイール本体部5と上述したスリーブ部6とは、同じ材料により一体的に形成されている。仮にホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6が別体であると、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6を組付ける作業が必要となる。上記の構成によれば、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6とが同じ材料により一体的に形成されているので、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6が別体である場合に比べて、組付け性が良好である。また、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6とを一体的に形成する加工は、困難ではないため、加工性が低下する虞はない。よって、上記の構成によれば、コンプレッサホイール装置3の製造コストをより低減させることができる。
図4は、一実施形態にかかるコンプレッサホイール装置を備える過給機のシール機構部近傍を拡大する概略部分拡大断面図である。図5は、一実施形態におけるシール部材の概略図である。
幾つかの実施形態では、図4に示されるように、上述したホイール本体部5と上述したスリーブ部6とは、同じ材料により一体的に形成されている。上述したシール溝62の底面621は、ハウジング8に支持された上述したシール部材17の内周面171との間にクリアランスCが形成されるように構成された。
幾つかの実施形態では、図4に示されるように、上述したホイール本体部5と上述したスリーブ部6とは、同じ材料により一体的に形成されている。上述したシール溝62の底面621は、ハウジング8に支持された上述したシール部材17の内周面171との間にクリアランスCが形成されるように構成された。
図示される実施形態では、図5に示されるように、シール部材17は、円弧角度が180度以上の円弧状に形成されている。シール部材17は、可撓性を有しており、一方の円弧端173と他方の円弧端174とが近付くように撓ませた状態で、インサート14の貫通孔141に周方向に沿って延在するシール溝146に嵌入されている。シール部材17は、シール部材17の外周面172を径方向外側に広げるように作用する復元力により、シール溝146の底面を押圧することで、インサート14に支持されている。換言すると、シール部材17は、図4に示されるように、インサート14を介して、軸受ハウジング8B(ハウジング8)により、回転シャフト2の外周側に支持されている。
図示される実施形態では、図4に示されるように、スリーブ部6は、外周面61とインサート14の貫通孔141とに隙間が形成されるように構成されている。また、スリーブ部6のシール溝62は、他方側に位置する側壁622とシール部材17の他方側に位置する側壁175との間に隙間が形成されるように構成されている。また、スリーブ部6のシール溝62は、一方側に位置する側壁623とシール部材17の一方側に位置する側壁176との間に隙間が形成されるように構成されている。
一般的に、コンプレッサホイール4の軽量化を図るために、コンプレッサホイール4の材料としてアルミニウムやアルミニウム合金のような低強度材料が用いられることがある。ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6とが一体的に形成されている場合には、スリーブ部6が低強度材料となる可能性がある。上記の構成によれば、シール溝62の底面621は、ハウジング8に支持されたシール部材17の内周面171との間にクリアランスCが形成されるように構成されているので、スリーブ部6のシール溝62が、シール部材17に対して摺動して摩耗や損傷することを防止することができる。
なお、他の幾つかの実施形態では、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6とが別体である場合において、シール溝62は、上述したクリアランスCが形成されるように構成されていてもよい。
幾つかの実施形態では、図4に示されるように、上述したホイール本体部5と上述したスリーブ部6とは、同じ材料により一体的に形成されている。上述したスリーブ部6のシール溝62を含む部分には、硬度又は摺動性の少なくとも一方を向上させる表面加工処理が施されている。
幾つかの実施形態では、図4に示されるように、上述したホイール本体部5と上述したスリーブ部6とは、同じ材料により一体的に形成されている。上述したスリーブ部6のシール溝62を含む部分には、硬度又は摺動性の少なくとも一方を向上させる表面加工処理が施されている。
上記表面加工処理には、化成処理、メッキ処理、アルマイト処理、テフロン(登録商標)加工処理、テフロン含侵処理、又はこれらの組み合わせの少なくとも一つが含まれる。
メッキ処理としては、硬度を向上させるニッケルメッキ、亜鉛メッキ、無電解ニッケルメッキ、又は、硬度および摺動性を向上させるカニフロンメッキ(テフロン複合無電解ニッケルメッキ)、無電解ニッケルホウ素メッキなどが挙げられる。
メッキ処理としては、硬度を向上させるニッケルメッキ、亜鉛メッキ、無電解ニッケルメッキ、又は、硬度および摺動性を向上させるカニフロンメッキ(テフロン複合無電解ニッケルメッキ)、無電解ニッケルホウ素メッキなどが挙げられる。
上述したように、スリーブ部6にアルミニウムやアルミニウム合金が用いられる可能性がある。これらの材料を他部材と摺動する可能性があるシール溝62に採用した場合には、硬度不足により摩耗や損傷が進展し易かったり、摺動性が悪くカジリが発生し易かったりする可能性がある。上記の構成によれば、スリーブ部6のシール溝62を含む部分に硬度又は摺動性の少なくとも一方を向上させる表面加工処理が施されているので、シール溝62が硬度不足による摩耗や損傷することや、カジリの発生を防止することができる。
幾つかの実施形態では、図2、3に示されるように、上述したホイール本体部5と上述したスリーブ部6とは、同じ材料により一体的に形成されている。上述したホイール本体部5と上述したスリーブ部6との接続位置P1は、上述したハブ51の最大外径をD(図1参照)としたときに、ハブ51の最大外径位置P2から軸方向において0.03D(3%D)以上離れるように構成されている。
図示される実施形態では、図2、3に示されるように、最大外径位置P2は、ディスク部51Aの他方側縁に位置している。換言すると、最大外径位置P2は、ホイール本体部5の背面54の外周縁に位置している。また、図示される実施形態では、接続位置P1は、ハブ51の最大外径位置P2から軸方向において0.09D(9%D)以内になるように構成されている。この場合には、コンプレッサホイール4の軸方向における長さが長くなることを防止することができる。
図示される実施形態では、図2、3に示されるように、最大外径位置P2は、ディスク部51Aの他方側縁に位置している。換言すると、最大外径位置P2は、ホイール本体部5の背面54の外周縁に位置している。また、図示される実施形態では、接続位置P1は、ハブ51の最大外径位置P2から軸方向において0.09D(9%D)以内になるように構成されている。この場合には、コンプレッサホイール4の軸方向における長さが長くなることを防止することができる。
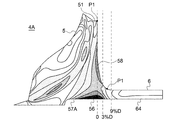
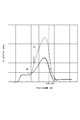
図6は、スルーボア構造のコンプレッサホイールのミーゼス応力分布を示す図である。図7は、ボアレス構造のコンプレッサホイールのミーゼス応力分布を示す図である。図8は、スルーボア構造およびボアレス構造のコンプレッサホイールの中心軸上のミーゼス応力分布を示すグラフである。図6~8の夫々は、強度解析結果により得られたものである。
図6に示されるように、スルーボア構造のコンプレッサホイール4Aは、最大外径位置P2の径方向内側に孔57A(貫通孔57に相当)が形成され、孔57Aの内周面近傍に内周側応力集中部56が生じている。
図7に示されるように、ボアレス構造のコンプレッサホイール4Bは、最大外径位置P2の径方向内側に孔57Aが形成されていないので、上記内周側応力集中部56が生じていない。
図7に示されるように、ボアレス構造のコンプレッサホイール4Bは、最大外径位置P2の径方向内側に孔57Aが形成されていないので、上記内周側応力集中部56が生じていない。
また、図6、7に示されるように、コンプレッサホイール4A、4Bの夫々は、最大外径位置P2の径方向内側に位置する背面54近傍に背面側応力集中部58が生じている。上記背面側応力集中部58は、ハブ51の最大外径位置P2から軸方向において0.03D(3%D)以上離れた位置には生じていない。
図8に示されるように、最大外径位置P2で発生する応力(ピーク応力)に対して、ハブ51の最大外径位置P2から軸方向において0.03D(3%D)離れた位置における応力は、上記ピーク応力の50%以下となっている。
軸方向におけるハブ51の最大外径位置P2近傍において遠心応力が極大となる。上記の構成によれば、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6との接続位置P1は、ハブ51の最大外径をDとしたときに、ハブ51の最大外径位置P2から軸方向において0.03D以上離れるように構成されているので、接続位置P1にかかる遠心応力を小さなものにすることができる。接続位置P1にかかる遠心応力を小さくすることで、スリーブ部6の外径を小さくできるため、過給機1のシール機構部18の周長が大きくなるのを防止することができる。
幾つかの実施形態では、図2、3に示されるように、上述したホイール本体部5と上述したスリーブ部6とは、同じ材料により一体的に形成されている。上述したホイール本体部5と上述したスリーブ部6との接続部41は、回転シャフト2の軸線方向を含む断面において、コンプレッサホイール4の内側に凹となる円弧状に形成されている。
上記の構成によれば、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6との接続部41は、回転シャフト2の軸線方向を含む断面において、コンプレッサホイール4の内側に凹となる円弧状に形成されているので、接続部41に応力集中が生じるのを防止することができる。接続部41に応力集中が生じるのを防止することで、スリーブ部6の外径を小さくできるため、過給機1のシール機構部18の周長が大きくなるのを防止することができる。
上述したように、幾つかの実施形態では、上述したスリーブ部6は、図3に示されるように、回転シャフト2が螺合される螺合溝65が形成された内周面64Aを有する。
上記の構成によれば、コンプレッサホイール4は、ハブ51の最大外径位置P2から離れた位置にあるスリーブ部6の内周面64Aに形成された螺合溝65に、回転シャフト2を螺合させることで、回転シャフト2に機械的に連結される、いわゆるボアレス構造となっている。上記の構成によれば、上述した内周側応力集中部56(応力集中部)の発生を抑制することができ、スルーボア構造に比べて、ホイール本体部5のクリープ強度を高くする必要がない分、ホイール本体部5の材料コストを低減させることができる。
上述した幾つかの実施形態では、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6とは、同じ材料により一体的に形成されていたが、他の幾つかの実施形態では、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6は別体であってもよく、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6の夫々は、別々の材料により形成されていてもよい。
図9は、他の一実施形態にかかるコンプレッサホイール装置の図2に相当する概略部分拡大断面図である。
幾つかの実施形態では、図9に示されるように、上述したスリーブ部6は、ハブ51の背面54に形成された凹部55に圧入されることで、ホイール本体部5に固結されるように構成される一端部66を有し、且つ、ホイール本体部5よりも耐摩耗性が高い材料により形成されている。
図示される実施形態では、一端部66は、図9に示されるように、スリーブ部6のシール溝62が形成された外周面61より小径の外周面を有する。
図示される実施形態では、一端部66は、図9に示されるように、スリーブ部6のシール溝62が形成された外周面61より小径の外周面を有する。
上記の構成によれば、スリーブ部6の一端部66をハブ51の凹部55に圧入すれば、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6が一体となるので、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6を組付ける作業は容易である。また、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6とが一体になった状態で過給機1に組付けられるので、組付け性が良好である。よって、上記の構成によれば、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6とを別体にしたことによる製造コストの増加を抑えることができる。また、シール溝62を有するスリーブ部6がホイール本体部5よりも耐摩耗性が高い材料により形成されているので、シール溝62の摩耗や損傷を防止することができる。
幾つかの実施形態では、図9に示されるように、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6とが別体である。上述した一端部66の先端661は、ハブ51の最大外径位置P2よりもコンプレッサホイール4の背面54側(上記他方側)に位置するように構成される。
図示される実施形態では、上述した一端部66の先端661は、ハブ51の最大外径位置P2から軸方向において0.03D(3%D)以上離れるように構成されている。また、図示される実施形態では、先端661は、ハブ51の最大外径位置P2から軸方向において0.09D(9%D)以内になるように構成されている。この場合には、コンプレッサホイール4の軸方向における長さが長くなることを防止することができる。
図示される実施形態では、上述した一端部66の先端661は、ハブ51の最大外径位置P2から軸方向において0.03D(3%D)以上離れるように構成されている。また、図示される実施形態では、先端661は、ハブ51の最大外径位置P2から軸方向において0.09D(9%D)以内になるように構成されている。この場合には、コンプレッサホイール4の軸方向における長さが長くなることを防止することができる。
上記の構成によれば、スリーブ部6の一端部66の先端661は、ハブ51の最大外径位置P2よりもコンプレッサホイール4の背面54側に位置するように構成されているので、スルーボア構造とは異なり、ホイール本体部5における上述した内周側応力集中部56(応力集中部)の発生を抑制することができる。このため、ホイール本体部5のクリープ強度を高くする必要がない分、ホイール本体部5の材料コストを低減させることができる。
幾つかの実施形態では、図9に示されるように、ホイール本体部5とスリーブ部6とが別体である。上述したスリーブ部6は、回転シャフト2が螺合される螺合溝65が形成された内周面64Aを有する。
上記の構成によれば、コンプレッサホイール4は、スリーブ部6の内周面64Aに形成された螺合溝65に回転シャフト2を螺合させることで、回転シャフト2に機械的に連結される。螺合溝65を有するスリーブ部6は、ホイール本体部5よりも耐摩耗性が高い材料により形成されているので、回転シャフト2とコンプレッサホイール4との螺合締結を強固なものにすることができる。
幾つかの実施形態にかかる過給機1は、図1に示されるように、上述した回転シャフト2と、上述したコンプレッサホイール装置3と、コンプレッサホイール装置3を収容するように構成された上述したハウジング8と、ハウジング8に支持されるとともに、シール溝62との間にシール機構部18を形成するように構成された上述したシール部材17と、を備える。
上記の構成によれば、過給機1は、シール溝62を有するスリーブ部6を含むコンプレッサホイール装置3と、ハウジング8に支持されるとともにシール溝62との間にシール機構部18を形成するシール部材17と、を備えるので、シール機構部18の周長が大きくなるのを防止することができ、シール機構部18の複雑化を防止することができる。よって、上記の構成によれば、過給機1の複雑化を防止して、過給機1の製造コストを低減させることができる。
本発明は上述した実施形態に限定されることはなく、上述した実施形態に変形を加えた形態や、これらの形態を適宜組み合わせた形態も含む。
上述した幾つかの実施形態では、過給機1としてコンプレッサホイール4と、タービンホイール9とを備えるターボチャージャを例に説明したが、過給機1は、ターボチャージャに限定されるものではなく、種々の変更が可能である。例えば、過給機1は、ターボチャージャ以外の過給機であってもよい。また、過給機1は、上述したタービンホイール9を備えない構成にしてもよい。タービンホイール9を備えない過給機1としては、不図示の電動機によりコンプレッサホイール4を回転させるように構成された電動コンプレッサなどが挙げられる。
1 過給機
2 回転シャフト
3 コンプレッサホイール装置
4,4A,4B コンプレッサホイール
5 ホイール本体部
6 スリーブ部
7 スラストカラー
8 ハウジング
8A コンプレッサハウジング
8B 軸受ハウジング
8C タービンハウジング
9 タービンホイール
10 スラスト軸受
11,12 ジャーナル軸受
13 タービン側スラストカラー
14 インサート
15 オイルディフレクタ
16 スナップリング
17 シール部材
18 シール機構部
19 ナット部材
21 突出部
22,24 螺合部
23 先端部
40 貫通孔
41 接続部
51 ハブ
51A ディスク部
51B ノーズ部
52 外周面
53 ブレード
54 背面
55 凹部
56 内周側応力集中部
57 貫通孔
57A 孔
58 背面側応力集中部
61 外周面
62 シール溝
63 端面
64 貫通孔
64A 内周面
65 螺合溝
66 一端部
71 一面
71A,72B 当接面
71B,72A 摺接面
72 他面
73 貫通孔
74 突出部
81 内部空間
82 給油流路
83 外面
84 段差面
85 内面
86 被覆部
87 内方突出部
88 内周溝
C クリアランス
LA 軸線
P1 接続位置
P2 最大外径位置
2 回転シャフト
3 コンプレッサホイール装置
4,4A,4B コンプレッサホイール
5 ホイール本体部
6 スリーブ部
7 スラストカラー
8 ハウジング
8A コンプレッサハウジング
8B 軸受ハウジング
8C タービンハウジング
9 タービンホイール
10 スラスト軸受
11,12 ジャーナル軸受
13 タービン側スラストカラー
14 インサート
15 オイルディフレクタ
16 スナップリング
17 シール部材
18 シール機構部
19 ナット部材
21 突出部
22,24 螺合部
23 先端部
40 貫通孔
41 接続部
51 ハブ
51A ディスク部
51B ノーズ部
52 外周面
53 ブレード
54 背面
55 凹部
56 内周側応力集中部
57 貫通孔
57A 孔
58 背面側応力集中部
61 外周面
62 シール溝
63 端面
64 貫通孔
64A 内周面
65 螺合溝
66 一端部
71 一面
71A,72B 当接面
71B,72A 摺接面
72 他面
73 貫通孔
74 突出部
81 内部空間
82 給油流路
83 外面
84 段差面
85 内面
86 被覆部
87 内方突出部
88 内周溝
C クリアランス
LA 軸線
P1 接続位置
P2 最大外径位置
Claims (11)
- 回転シャフトに取り付けられるコンプレッサホイールであって、
ハブと、前記ハブの外周面に設けられた少なくとも一つにブレードと、を含むホイール本体部、及び
前記ハブの背面から軸方向に沿って突出する筒状のスリーブ部であって、外周面に周方向に沿って延在するシール溝を有するスリーブ部、
を含むコンプレッサホイールと、
前記コンプレッサホイールの背面側にて前記回転シャフトに取り付けられるスラストカラーであって、
前記スリーブ部の端面と当接する当接面を含むとともに径方向に沿って延在する一面と、
前記回転シャフトをスラスト方向に支持するスラスト軸受と摺接する摺接面を含むとともに前記径方向に沿って延在する他面と、
を含む円板形状を有するスラストカラーと、を備える
コンプレッサホイール装置。 - 前記ホイール本体部と前記スリーブ部とは、同じ材料により一体的に形成されている
請求項1に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置。 - 前記シール溝の底面は、前記コンプレッサホイールを収容するハウジングに支持されたシール部材の内周面との間にクリアランスが形成されるように構成された
請求項2に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置。 - 前記スリーブ部の前記シール溝を含む部分に硬度又は摺動性の少なくとも一方を向上させる表面加工処理が施された
請求項2又は3に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置。 - 前記ホイール本体部と前記スリーブ部との接続位置は、前記ハブの最大外径をDとしたときに、前記ハブの最大外径位置から前記軸方向において0.03D以上離れるように構成された
請求項2乃至4の何れか1項に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置。 - 前記ホイール本体部と前記スリーブ部との接続部は、前記回転シャフトの軸線方向を含む断面において、前記コンプレッサホイールの内側に凹となる円弧状に形成されている
請求項2乃至5の何れか1項に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置。 - 前記スリーブ部は、前記回転シャフトが螺合される螺合溝が形成された内周面を有する
請求項1乃至6の何れか1項に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置。 - 前記スリーブ部は、前記ハブの前記背面に形成された凹部に圧入されることで前記ホイール本体部に固結されるように構成される一端部を有し、且つ、前記ホイール本体部よりも耐摩耗性が高い材料により形成されている
請求項1に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置。 - 前記一端部の先端は、前記ハブの最大外径位置よりも前記コンプレッサホイールの背面側に位置するように構成される
請求項8に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置。 - 前記スリーブ部は、前記回転シャフトが螺合される螺合溝が形成された内周面を有する
請求項8又は9に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置。 - 回転シャフトと、
請求項1乃至10の何れか1項に記載のコンプレッサホイール装置と、
前記コンプレッサホイール装置を収容するように構成されたハウジングと、
前記ハウジングに支持されるとともに、前記シール溝との間にシール機構部を形成するように構成されたシール部材と、を備える
過給機。
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021505480A JP7187668B2 (ja) | 2019-03-14 | 2019-03-14 | コンプレッサホイール装置および過給機 |
| PCT/JP2019/010716 WO2020183736A1 (ja) | 2019-03-14 | 2019-03-14 | コンプレッサホイール装置および過給機 |
| DE112019006752.4T DE112019006752T5 (de) | 2019-03-14 | 2019-03-14 | Kompressorradvorrichtung und lader |
| CN201980093828.7A CN113557362B (zh) | 2019-03-14 | 2019-03-14 | 压缩机叶轮装置以及增压器 |
| US17/432,621 US11585348B2 (en) | 2019-03-14 | 2019-03-14 | Compressor wheel device and supercharger |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2019/010716 WO2020183736A1 (ja) | 2019-03-14 | 2019-03-14 | コンプレッサホイール装置および過給機 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2020183736A1 true WO2020183736A1 (ja) | 2020-09-17 |
Family
ID=72426994
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2019/010716 WO2020183736A1 (ja) | 2019-03-14 | 2019-03-14 | コンプレッサホイール装置および過給機 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11585348B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP7187668B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN113557362B (ja) |
| DE (1) | DE112019006752T5 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2020183736A1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024150387A1 (ja) * | 2023-01-13 | 2024-07-18 | 三菱重工エンジン&ターボチャージャ株式会社 | ターボチャージャ用ハウジング、及びターボチャージャ |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5225562B2 (ja) * | 1973-04-06 | 1977-07-08 | ||
| US5176497A (en) * | 1991-01-22 | 1993-01-05 | Allied-Signal Inc. | Boreless hub compressor wheel assembly for a turbocharger |
| JP2009208138A (ja) * | 2008-03-06 | 2009-09-17 | Ihi Corp | 異種金属の接合方法及び過給機 |
| JP2016500140A (ja) * | 2012-11-28 | 2016-01-07 | ネーピア・ターボチャージャーズ・リミテッド | 熱膨張を適応する構成を有するシャフトにねじ込まれたターボチャージャー・インペラー |
Family Cites Families (24)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5826616B2 (ja) | 1975-08-21 | 1983-06-03 | イケガミ ヒデツグ | タキヨクジバソウチ |
| US4340317A (en) * | 1981-05-07 | 1982-07-20 | Northern Research & Engineering Corp. | Splineless coupling means |
| US4705463A (en) * | 1983-04-21 | 1987-11-10 | The Garrett Corporation | Compressor wheel assembly for turbochargers |
| DE3464644D1 (en) | 1983-04-21 | 1987-08-13 | Garrett Corp | Compressor wheel assembly |
| EP0138516A1 (en) * | 1983-10-07 | 1985-04-24 | Household Manufacturing, Inc. | Centrifugal compressor wheel and its mounting on a shaft |
| US4749334A (en) * | 1984-12-06 | 1988-06-07 | Allied-Signal Aerospace Company | Ceramic rotor-shaft attachment |
| US4986733A (en) * | 1989-10-30 | 1991-01-22 | Allied-Signal, Inc. | Turbocharger compressor wheel assembly with boreless hub compressor wheel |
| US5193989A (en) * | 1991-07-19 | 1993-03-16 | Allied-Signal Inc. | Compressor wheel and shaft assembly for turbocharger |
| EP0903465B1 (de) * | 1997-09-19 | 2003-09-03 | ABB Turbo Systems AG | Verdichterradbefestigung für schnellaufende Turbomaschinen |
| AU2001221812A1 (en) * | 2000-11-30 | 2002-06-11 | Honeywell Garrett Sa | Variable geometry turbocharger with sliding piston |
| CN1329629C (zh) * | 2002-05-06 | 2007-08-01 | Abb涡轮系统有限公司 | 将工作轮固定在轴上的固定装置 |
| GB0224727D0 (en) * | 2002-10-24 | 2002-12-04 | Holset Engineering Co | Compressor wheel assembly |
| GB0224721D0 (en) * | 2002-10-24 | 2002-12-04 | Holset Engineering Co | Compressor wheel assembly |
| US6845617B1 (en) * | 2003-12-20 | 2005-01-25 | Honeywell International Inc | Center housing design for electric assisted turbocharger |
| JP2005330816A (ja) * | 2004-05-18 | 2005-12-02 | Komatsu Ltd | ターボ機械およびターボ機械のコンプレッサインペラ |
| WO2006043556A1 (ja) * | 2004-10-19 | 2006-04-27 | Komatsu Ltd. | ターボ機械、ターボ機械に用いられるコンプレッサインペラ、及びターボ機械の製造方法 |
| GB0714929D0 (en) * | 2007-08-01 | 2007-09-12 | Cummins Turbo Tech Ltd | A turbocharger bearing assembly and lubrication thereof |
| JP5589889B2 (ja) * | 2011-02-21 | 2014-09-17 | 株式会社Ihi | ターボ機械 |
| DE102013015563A1 (de) * | 2013-09-20 | 2015-03-26 | Abb Turbo Systems Ag | Abgasturbolader |
| CN106795808B (zh) * | 2014-11-17 | 2019-11-05 | 三菱重工发动机和增压器株式会社 | 涡轮机械 |
| JP6288516B2 (ja) * | 2014-12-03 | 2018-03-07 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | インペラ、及び回転機械 |
| US10550849B2 (en) * | 2016-12-12 | 2020-02-04 | Garrett Transportation I Inc. | Turbocharger assembly |
| JP6795973B2 (ja) | 2016-12-28 | 2020-12-02 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | ウィンドファーム並びにその運転方法、制御装置及び運転制御プログラム |
| JP6920852B2 (ja) * | 2017-03-29 | 2021-08-18 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 遠心圧縮機用インペラ及び電動式遠心圧縮機 |
-
2019
- 2019-03-14 US US17/432,621 patent/US11585348B2/en active Active
- 2019-03-14 JP JP2021505480A patent/JP7187668B2/ja active Active
- 2019-03-14 WO PCT/JP2019/010716 patent/WO2020183736A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2019-03-14 DE DE112019006752.4T patent/DE112019006752T5/de active Pending
- 2019-03-14 CN CN201980093828.7A patent/CN113557362B/zh active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5225562B2 (ja) * | 1973-04-06 | 1977-07-08 | ||
| US5176497A (en) * | 1991-01-22 | 1993-01-05 | Allied-Signal Inc. | Boreless hub compressor wheel assembly for a turbocharger |
| JP2009208138A (ja) * | 2008-03-06 | 2009-09-17 | Ihi Corp | 異種金属の接合方法及び過給機 |
| JP2016500140A (ja) * | 2012-11-28 | 2016-01-07 | ネーピア・ターボチャージャーズ・リミテッド | 熱膨張を適応する構成を有するシャフトにねじ込まれたターボチャージャー・インペラー |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024150387A1 (ja) * | 2023-01-13 | 2024-07-18 | 三菱重工エンジン&ターボチャージャ株式会社 | ターボチャージャ用ハウジング、及びターボチャージャ |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN113557362B (zh) | 2023-09-05 |
| US11585348B2 (en) | 2023-02-21 |
| CN113557362A (zh) | 2021-10-26 |
| DE112019006752T5 (de) | 2021-11-04 |
| JP7187668B2 (ja) | 2022-12-12 |
| US20220145891A1 (en) | 2022-05-12 |
| JPWO2020183736A1 (ja) | 2020-09-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US6499884B1 (en) | Bearing/seal member/assembly and mounting | |
| US8714556B2 (en) | Pump seal | |
| EP3026225A1 (en) | Variable geometry exhaust turbocharger and method of manufacturing | |
| US10197065B2 (en) | Centrifugal compressor, turbocharger provided with the centrifugal compressor, and method for producing the centrifugal compressor | |
| US10677287B2 (en) | Bearing structure and turbocharger | |
| JP6177421B2 (ja) | シール構造及び該シール構造を備える過給機 | |
| US20170130646A1 (en) | Variable nozzle unit and variable geometry system turbocharger | |
| JP2013002466A (ja) | スラスト軸受構造及び過給機 | |
| US20150110607A1 (en) | Variable nozzle unit and variable geometry system turbocharger | |
| JP6396512B2 (ja) | 過給機 | |
| WO2020183736A1 (ja) | コンプレッサホイール装置および過給機 | |
| US11530706B2 (en) | Rotating body, turbocharger, and rotating body manufacturing method | |
| CN109563772B (zh) | 电动增压器 | |
| CN210122936U (zh) | 涡轮增压器 | |
| US10753367B2 (en) | Mounting structure and turbocharger | |
| WO2018012540A1 (ja) | シール構造および過給機 | |
| US11841028B2 (en) | Thrust bearing device and turbocharger | |
| US11739659B2 (en) | Supercharging device | |
| WO2022264313A1 (ja) | コンプレッサホイールの取付構造および過給機 | |
| WO2022168897A1 (ja) | スラスト軸受装置及びターボチャージャ | |
| JP7341218B2 (ja) | 浮動ブッシュ軸受および過給機 | |
| WO2020144851A1 (ja) | 過給機および過給機用のスラスト軸受 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 19918976 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2021505480 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 19918976 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |