WO2019031167A1 - シールド導電路 - Google Patents
シールド導電路 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2019031167A1 WO2019031167A1 PCT/JP2018/026807 JP2018026807W WO2019031167A1 WO 2019031167 A1 WO2019031167 A1 WO 2019031167A1 JP 2018026807 W JP2018026807 W JP 2018026807W WO 2019031167 A1 WO2019031167 A1 WO 2019031167A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- shield
- conductor
- insulating
- conductive
- conductive path
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01B—CABLES; CONDUCTORS; INSULATORS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR CONDUCTIVE, INSULATING OR DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES
- H01B7/00—Insulated conductors or cables characterised by their form
- H01B7/17—Protection against damage caused by external factors, e.g. sheaths or armouring
- H01B7/18—Protection against damage caused by wear, mechanical force or pressure; Sheaths; Armouring
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R16/00—Electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for; Arrangement of elements of electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for
- B60R16/02—Electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for; Arrangement of elements of electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for electric constitutive elements
- B60R16/0207—Wire harnesses
- B60R16/0215—Protecting, fastening and routing means therefor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01B—CABLES; CONDUCTORS; INSULATORS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR CONDUCTIVE, INSULATING OR DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES
- H01B7/00—Insulated conductors or cables characterised by their form
- H01B7/0045—Cable-harnesses
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01B—CABLES; CONDUCTORS; INSULATORS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR CONDUCTIVE, INSULATING OR DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES
- H01B7/00—Insulated conductors or cables characterised by their form
- H01B7/02—Disposition of insulation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K9/00—Screening of apparatus or components against electric or magnetic fields
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a shielded conductive path.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a technique for connecting a battery and an inverter with a high-voltage wire harness in an electric car or a hybrid vehicle.
- the middle portion of the wire harness is housed in a metal shield pipe.
- the shield pipe is disposed under the floor of the vehicle and has a curved shape in the height direction and the vehicle width direction. Both ends of the wire harness are led out from both ends of the shield pipe and connected to the respective connectors.
- the parts of the wire harness which are led out from the shield pipe are respectively inserted into a flexible shield member (braided wire). One end of the braided wire is connected to both ends of the shield pipe, and the other end is connected to the connector.
- a wire harness is comprised by two or more multiple electric wires. These electric wires are collectively accommodated in the shield pipe and often arranged side by side in the vehicle width direction. As described above, in the related art, a relatively large space is created in the height direction in the shield pipe between the wire and the wire because a plurality of wires are collectively accommodated. For this reason, in the conventional case, there was a problem that it was bulky in the height direction.
- the fact that a large space is created in the shield pipe means that the contact area between the electric wire and the shield pipe is small. For this reason, even if heat is generated in the electric wire due to energization, the heat is likely to be dissipated in the shield pipe, and there is room for improvement from the viewpoint of heat dissipation.
- the present invention has been completed based on the above circumstances, and it is an object of the present invention to provide a shield conductive path which can improve the reduction in height and heat dissipation.
- the shield conductive path of the present invention is a shield conductive path formed by arranging in parallel a plurality of conductive members each having a conductor portion, an insulating portion, and a shield portion arranged from the central portion toward the outer peripheral side, At least one of the conductor portion, the insulating portion, and the shield portion is formed of a shape holding member capable of holding the conductive members in a set shape.
- the plurality of conductive members are not accommodated together by the shield part, but the conductive members are separately accommodated separately by the shield part. . Therefore, as in the conventional case, a large space is not generated inside the shield portion, and the contact area between the conductor portion side and the shield portion can be easily secured. Can be improved at the same time.
- the shield conductive path of the present invention is preferably configured such that the conductor portion is formed of a pipe made of a conductive metal and doubles as the shape holding member. According to such a configuration, the conductor portion can exhibit the shape holding function of the conductive member.
- the conductor portion can be crushed in the height direction. According to such a configuration, each conductive member can be further reduced in height.
- the insulating portion may be formed of a resin pipe that accommodates the conductor portion and also serves as the shape holding member. With such a configuration, the shape-retaining function of the conductive member can be exhibited by the insulating portion.
- the shield portion may be formed of a conductive metal pipe and also function as the shape holding member. With such a configuration, the shield portion can exhibit the shape holding function of the conductive member.
- Example 1 Hereinafter, a first embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to FIGS. 1 to 3.
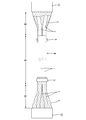
- the shield conductive path W in the first embodiment is provided at a front portion of the vehicle B and a device M1 such as a high voltage battery provided at the rear of the vehicle B, as shown in FIG. It is arranged along the floor of the vehicle B in order to connect with the device M2 such as the inverter or the fuse box which has been set via the connectors C1 and C2.
- a device M1 such as a high voltage battery provided at the rear of the vehicle B, as shown in FIG. It is arranged along the floor of the vehicle B in order to connect with the device M2 such as the inverter or the fuse box which has been set via the connectors C1 and C2.
- an intermediate portion in the front-rear direction of the vehicle B constitutes a rigid region R1 and both ends constitute a flexible region R2.
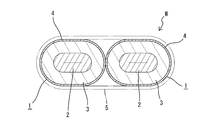
- the rigid region R1 is provided with two conductive members 1 each having a shape retention function, and is arranged in a contact state in which the under floor of the vehicle B is arranged in parallel in the vehicle width direction (see FIG. 3).
- the middle portion of the conductive member 1 is wired with a predetermined bending shape in the vehicle width direction and the height difference direction. The step of bending the conductive member 1 is performed after the conductive member 1 is assembled through the steps of inserting the conductor portion 2 and the like.
- the conductive members 1 of the first embodiment individually surround a plurality of (two in the first embodiment) conductor portions 2 with the shield portions 4 via the insulating portions 3 respectively. It is electromagnetically shielded.
- the conductor part 2 in the present Example 1 is comprised by the single core wire electric wire. That is, the conductor portion 2 in this embodiment is made of a long conductive metal pipe made of copper, copper alloy, aluminum or aluminum alloy. In the case of the first embodiment, the conductor portion 2 mainly functions as the shape holding member of the present invention.
- a cylindrical insulating portion 3 (insulating resin layer) is concentrically stacked on the entire outer peripheral surface of the conductor portion 2.
- the conductor portion 2 is crushed in the vehicle height direction together with the insulating portion 3 and has a shape (elliptical shape) extending flatly in the vehicle width direction over the entire length. As a result, the conductive member 1 is reduced in height in the vehicle height direction.
- the shield portion 4 is formed by winding a ribbon-like member made of a conductive metal foil spirally without gaps around the entire length and adhering it to the outer peripheral surface of the insulating portion 3.
- the winding step of the shield portion 4 may be performed after the bending step of the conductor portion 2 and the insulating portion 3 described above.
- a coating of a predetermined color for example, orange is applied to the entire surface of the shield portion 4 to alert the high voltage current and protect it from collision with foreign matter. You may make it plan.
- both conductive members 1 in the first embodiment are configured to be individually surrounded by the shield portion 4.
- the flexible region R2 is required to be able to be flexibly arranged because it is arranged in a relatively narrow space in the engine compartment or the passenger compartment. For this reason, in the present embodiment, the flexible region R2 adopts a configuration in which the two stranded wires 7 having flexibility are collectively surrounded by the braiding member 5.
- the insulation coating is peeled off at the end of the double stranded wire 7 to expose a core (not shown).
- both end portions of the conductor portion 2 project from the both ends of the insulating portion 3 and the shield portion 4 in the front-rear direction.
- the exposed core of the stranded wire 7 is connected to the upper surface or the lower surface of the crushed surface of the corresponding conductor 2 by welding or the like at both projecting ends of the conductor 2.
- a terminal fitting (not shown) is connected to the other end of the stranded wire 7 and the terminal fitting is accommodated in the connectors C1 and C2.
- the braid member 5 has a configuration in which a large number of conductive metal thin wires are tubularly knitted, and has excellent flexibility.
- the ends on the rigid region R1 side of the braided member 5 are collectively fitted to both the conductive members 1, are respectively clamped and fixed by the clamping members 6, and are electrically connected to the shield portion 4.
- the other end of the braided member 5 is electrically connected to a conductive metal shield member (not shown) attached to the corresponding connectors C1 and C2.
- the shield conductive path W in the first embodiment adopts a method in which shields for the respective conductive members 1 are separately surrounded. There is. That is, if the conductive members arranged in parallel in the vehicle width direction are collectively encircled by the shield portion having a circular cross section, empty spaces must be generated above and below the both conductive members in the shield portion. Conventionally, this has been a factor that prevents the reduction in height of the shield conductive path, but as in the first embodiment, if the form in which the shield portions 4 individually surround the conductor portions 2 and the insulating portions 3 is adopted.
- the shield portion 4 can surround the outer peripheral surface of the conductor portion 2 and the insulating portion 3 substantially in intimate contact. Therefore, unlike the prior art, since unnecessary empty spaces do not occur in the upper and lower portions in the shield portion 4, the height reduction of the shield conductive path W can be surely achieved.
- the conductor portion 2 is formed by crushing the metal pipe in the vehicle height direction, there is an effect that the height can be further improved.
- the conductive member 1 generates heat when it is energized
- the upper and lower spaces in the shield portion cause heat to be dissipated, which may lower the electrical characteristics of the conductor portion. I was concerned.
- the shield part 4 is enclosed in close contact with the insulating part 3, the heat generated in the conductor part 2 is smoothly dissipated to the outside by the heat radiation path formed by the conductor 2, the insulating part 3 and the shield part 4. Can be effective in maintaining the electrical characteristics of the conductor portion 2.
- the conductor portion 2 is constituted by a single cored wire obtained by processing a metal pipe, the conductor portion 2 can be mainly functioned as a shape holding member for holding a predetermined bending shape. ing. Therefore, it is not necessary to add a special member for shape retention, which also contributes to the reduction of the number of parts and the simplification of the configuration.
- FIG. 4 shows a conductive member 10 according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
- the conductor part 11 in the present Example 2 is comprised by the strand wire.
- the conductor portion 11 is composed of a core wire 11A in which a large number of thin wires are twisted in a spiral shape, and an insulating coating 11B surrounding the outer peripheral side thereof.
- the conductor portion 11 itself has flexibility and is in a so-called waistless state.
- the insulating portion 12 is made of a synthetic resin pipe having a circular cross section. In the second embodiment, the insulating portion 12 functions as the shape holding member of the present invention.
- the conductor portion 11 is loosely inserted from one end of the insulating portion 12 and surrounds the outer periphery of the conductor portion 11 substantially concentrically with a slight gap.
- the insulating portion 12 is formed through a bending process so as to have a predetermined bent shape after the conductor portion 11 is inserted.
- the insulating portion 12 is preferably bent in consideration of the amount of return after the bending process.
- the insulating portion 12 has a single-layer structure made of a synthetic resin material, and also has a multi-layer structure including a metal layer so that the shape retention function can be enhanced It is also conceivable to Both end portions of the conductor portion 11 project from the insulating portion 12 and the shield portion 13 described below in both the front and back directions of the vehicle, and are connected to the electric wire of the flexible region R2.
- the shield portion 13 is formed of a conductive metal layer laminated on the entire outer peripheral surface of the insulating portion 12. Therefore, the shield portion 13 is accommodated in a state in which the conductor portion 11 is surrounded substantially concentrically from the entire circumference.
- Both shield parts 13 in the rigid area R1 may be connected together with the braided member 5 in the flexible area R2, but without connecting both shield parts 13 from the rigid area R1 to the flexible area R2 It may be integrally extended as it is, and both may be connected to shield members (not shown) of the connectors C1 and C2.
- the shield portion 13 individually surrounds the conductor portion 11 and the insulating portion 12 and does not create a space in the height direction between them. , It is effective in height reduction and heat dissipation function.
- the shield portion 13 which is a metal member can protect the insulating portion 12 and the conductor portion 11. Further, by providing the shield portion 13, it is also expected that the spring back of the insulating portion 12 at the time of the bending process is alleviated, whereby the shape holding function of the insulating portion 12 can be enhanced.
- FIG. 5 shows a third embodiment of the present invention.
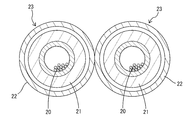
- the conductor part 20 in the present Example 3 is also comprised by the strand wire electric wire similarly to Example 2.
- the insulation part 21 of the present Example 3 is comprised by the insulation coating of a strand wire.
- the shield portion 22 is formed of a conductive metal pipe.
- the shield portion 22 functions as the shape holding member of the present invention.
- the conductor portion 20 and the insulating portion 21 are loosely inserted from one end side of the shield portion 22. Therefore, the conductor portion 20 and the insulating portion 21 in each conductive member 23 are individually surrounded by the shield portion 22.
- a proper gap necessary for the insertion work to the shield part 22 is kept, but this gap is only a small degree compared with the gap which has been generated conventionally. .
- the shield part 22 is made into a predetermined
- Both ends of the conductor portion 20 project in the front-rear direction from the shield portion 22 in a state in which the insulating coating is peeled off, and are connected to the wires of the flexible region R2.
- Both shield portions 22 in the rigid region R1 and the braided members 5 in the flexible region R2 are connected by the fastening member 6 in the same manner as in the first embodiment.
- the shield portion 22 individually surrounds the conductor portion 20 and the insulating portion 21 and generates an unnecessary space in the height direction between them. Because it does not let you do, it becomes effective in heightening the height and heat dissipation function.
- the insulating portion 21 performs the shape retention function, there is a concern about springback in the bending step.
- the third embodiment there is no such concern, so that the advantage of easy shape retention is obtained. is there.
- the shield part 22 is formed with a predetermined thickness in order to maintain its shape, the protective function for the conductor part 20 and the like is also high.
- the conductor portion 2 is formed of metal pipe material, but it may be replaced with a pipe material and replaced with a long flat plate, or a bar material having a circular cross section may be crushed from the height direction. You may.
- the method of manufacturing the shield portion 4 by spirally winding and bonding the ribbon-like member is described, but instead, metal foil is laminated on the entire outer peripheral surface of the insulating portion 3 Alternatively, the outer peripheral surface may be surrounded by laminating a protective layer made of a resin material.
- the shield conductive path W is formed of two conductive members. However, the number of conductive members is not limited as long as it is two or more.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Insulated Conductors (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Details Of Indoor Wiring (AREA)
- Shielding Devices Or Components To Electric Or Magnetic Fields (AREA)
Abstract
シールド導電路の低背化と放熱機能の向上を図る。 中心部から外周側に向けて導体部(2)、絶縁部(3)、シールド部(4)がそれぞれ配されてなる導電部材(1)を、複数本並列して配してなるシールド導電路(W)であって、導体部(2)、絶縁部(3)及びシールド部(4)のうち少なくとも一つが、各導電部材(1)を設定された形状に保持可能な形状保持部材にて形成されている。
Description
本発明は、シールド導電路に関するものである。
下記特許文献1には、電気自動車やハイブリッド車両において、バッテリとインバータとの間を高圧のワイヤハーネスによって接続する技術が開示されている。
ワイヤハーネスの中間部は金属製のシールドパイプ内に収容されている。シールドパイプは車両の床下に配され、高さ方向及び車幅方向に関して屈曲した形状となっている。ワイヤハーネスの両端部はシールドパイプの両端から導出され、それぞれコネクタに接続されている。ワイヤハーネスのうちシールドパイプから導出された部分は、可撓性を有するシールド部材(編組線)内にそれぞれ挿通されている。編組線の一端部はシールドパイプの両端部に、他端はコネクタ側にそれぞれ接続されている。
ところで、ワイヤハーネスは2本以上の複数本の電線によって構成されている。これら電線はシールドパイプ内に一括して収容され、車幅方向へ横並びに配置されることが多かった。このように、従来のものでは、複数の電線を一括して収容する関係上、シールドパイプ内では電線との間に比較的大きなスペースを高さ方向に生じさせていた。このため、従来の場合、高さ方向に嵩張る、という問題があった。
また、シールドパイプ内に大きなスペースが生じる、ということは電線とシールドパイプとの接触面積が小さいことを意味する。このため、通電によって電線に発熱が生じても、シールドパイプ内に熱が籠り易く放熱性の点からも改良の余地があった。
本発明は上記のような事情に基づいて完成されたものであって、低背化と放熱性を向上させうる、シールド導電路を提供することを目的とする。
本発明のシールド導電路は、中心部から外周側に向けて導体部、絶縁部、シールド部がそれぞれ配されてなる導電部材を、複数本並列して配してなるシールド導電路であって、前記導体部、前記絶縁部及び前記シールド部のうち少なくとも一つが、前記各導電部材を設定された形状に保持可能な形状保持部材にて形成されている。
本発明によれば、従来のように、複数本の導電部材がシールド部によって一括して収容される形態ではなく、各導電部材をシールド部によって別個独立して収容される形態としたものである。したがって、従来のように、シールド部の内部に大きなスペースを生じさせてしまうことがなく、また導体部側とシールド部との接触面積も確保しやすいため、シールド導電路として低背化と放熱性の向上を併せて図ることができる。
本発明における好ましい実施の形態を説明する。
(1)本発明のシールド導電路は、前記導体部が、導電金属製のパイプによって形成されて前記形状保持部材を兼ねた構成であると良い。
このような構成によれば、導体部によって導電部材の形状保持機能を発揮することができる。
(2)上記構成において、前記導体部が高さ方向に圧潰された構成とするのが好ましい。
このような構成によれば、各導電部材をより一層低背化することができる。
(3)前記絶縁部が、前記導体部を収容する樹脂パイプによって形成されて前記形状保持部材を兼ねた構成であってもよい。
このような構成であれば、絶縁部によって導電部材の形状保持機能を発揮することができる。
(4) 前記シールド部が、導電金属製のパイプによって形成されて前記形状保持部材を兼ねた構成であってもよい。
このような構成であれば、シールド部によって導電部材の形状保持機能を発揮することができる。
(1)本発明のシールド導電路は、前記導体部が、導電金属製のパイプによって形成されて前記形状保持部材を兼ねた構成であると良い。
このような構成によれば、導体部によって導電部材の形状保持機能を発揮することができる。
(2)上記構成において、前記導体部が高さ方向に圧潰された構成とするのが好ましい。
このような構成によれば、各導電部材をより一層低背化することができる。
(3)前記絶縁部が、前記導体部を収容する樹脂パイプによって形成されて前記形状保持部材を兼ねた構成であってもよい。
このような構成であれば、絶縁部によって導電部材の形状保持機能を発揮することができる。
(4) 前記シールド部が、導電金属製のパイプによって形成されて前記形状保持部材を兼ねた構成であってもよい。
このような構成であれば、シールド部によって導電部材の形状保持機能を発揮することができる。
次に、本発明のシールド導電路を具体化した実施例1乃至実施例3について、図面を参照しつつ説明する。
<実施例1>
以下、本発明を具体化した実施例1について、図1~図3を参照しつつ詳細に説明する。
以下、本発明を具体化した実施例1について、図1~図3を参照しつつ詳細に説明する。
本実施例1におけるシールド導電路Wは、ハイブリッド車等の車両Bにおいて、図1に示すように、例えば車両Bの後部に備えられた高圧バッテリ等の機器M1と、車両Bの前部に備えられたインバータやヒューズボックス等の機器M2とをコネクタC1、C2を介して接続するべく、車両Bの床下に沿って配索されるものである。
図2に示すように、本実施例1におけるシールド導電路Wは、車両Bの前後方向の中間部は剛体領域R1を構成し、その両端部はそれぞれ可撓領域R2を構成している。剛体領域R1は共に形状保機能を有する2本の導電部材1を備えていて、車両Bの床下を車幅方向に並列した接触状態で配索されている(図3参照2)。導電部材1の中間部は車幅方向及び高差方向に所定の屈曲形状をもって配索されている。なお、導電部材1を屈曲させる工程は、導体部2等を挿通させる等の工程を経て導電部材1を組み上げた後に行われる。
図3に示すように、本実施例1の導電部材1は、複数本(本実施例1では2本)の導体部2を、それぞれ絶縁部3を介してシールド部4によって個別に包囲して電磁シールドされている。
本実施例1における導体部2は単芯線電線によって構成されている。すなわち、この実施例における導体部2は銅あるいは銅合金、アルミあるいはアルミ合金によって形成された導電性を有する長尺の金属製パイプよりなる。本実施例1の場合、この導体部2が主として本発明の形状保持部材として機能する。導体部2の外周面の全面には筒状の絶縁部3(絶縁樹脂層)が同心で積層されている。導体部2は絶縁部3と共に車両高さ方向に圧潰されていて、全長に亘って車幅方向に平たく延びた形状(長円形)となっている。これによって、導電部材1は車両高さ方向に低背化が図られた形態となる。
また、両導電部材1における絶縁部3の外周面は、その全領域に亘りシールド部4によって包囲されている。具体的には、シールド部4は導電性の金属箔よりなるリボン状部材を、全長に亘って螺旋状に隙間なく巻き付けて絶縁部3の外周面に接着して形成されている。シールド部4の巻き付け工程は、前記した導体部2及び絶縁部3の屈曲工程を経た後に行われると良い。なお、上記したリボン状部材の巻き付け工程の後、シールド部4の全面に所定のカラー(例えばオレンジ色)の塗膜を施してこれを高圧電流に対する注意喚起と異物との衝突からの保護とを図るようにしてもよい。
かくして、本実施例1における両導電部材1は、従来と異なり、シールド部4によって個別に包囲された構成となる。
次に、可撓領域R2について説明する。可撓領域R2はエンジンルームや車室内の比較的狭いスペース内に配策される関係で、柔軟に配策できることが求められる。このため、本実施例では、可撓領域R2は、可撓性を有する2本の撚り線電線7を編組部材5によって一括して包囲する構成が採用されている。両撚り線電線7の端部では絶縁被覆が皮むきされて芯線(図示省略)が露出されている。一方、剛体領域R1における車両長さ方向の両端部においては、導体部2の両端部が絶縁部3及びシールド部4の両端から前後方向へ突出している。導体部2の突出した両端部においては、撚り線電線7の露出した芯線が、対応する導体部2の圧潰面の上面あるいは下面に溶着等によって接続されるようになっている。撚り線電線7の他方の端部には図示しない端子金具が接続され、端子金具はコネクタC1、C2内に収容されている。
編組部材5は多数本の導電金属製の細線を筒状に編成した構成であり、良好な可撓性を有している。編組部材5における剛体領域R1側の端部は、両導電部材1に一括して嵌め入れられ、それぞれ締め付け部材6によって締め付け固定されてシールド部4との電気的接続がとられている。編組部材5の他側の端部は、対応するコネクタC1、C2に装着された導電金属製のシールド部材(図示しない)との電気的接続がとられている。
次に、上記のように構成された本実施例1の作用効果を説明する。本実施例1におけるシールド導電路Wは、2本の導電部材を一括してシールド部によって包囲する従来方式に代えて、各導電部材1に対するシールドを個別に包囲することによって行う形式を採用している。すなわち、仮に車幅方向に並列する導電部材を断面円形のシールド部によって一括して包囲すると、シールド部内には両導電部材の上方と下方にそれぞれ空きスペースが生じざるを得ない。従来、このことがシールド導電路の低背化を妨げる要因となっていたが、本実施例1のように、各導体部2及び絶縁部3をシールド部4が個別に包囲する形式を採れば、シールド部4は導体部2及び絶縁部3の外周面をほぼ密着して包囲することが可能となる。したがって、従来とは異なり、シールド部4内の上下に無駄な空きスペースが生じることがないため、シールド導電路Wの低背化を確実に達成することができる。
特に、本実施例1では、導体部2を、金属パイプを車両高さ方向から圧潰して形成するようにしたことから低背化の一層の向上を図りうる効果がある。
また、導電部材1は通電に伴って発熱が生じるのであるが、従来の場合は、シールド部内の上下のスペースが熱を籠らせてしまい、導体部における電気的特性を低下させてしまうことが懸念された。しかし、本実施例1ではシールド部4内にスペースがほぼなく、つまり断熱層を形成することがない。かくして、シールド部4は絶縁部3とほぼ密着状態で包囲するため、導体部2、絶縁部3、シールド部4によって形成される放熱経路によって導体部2で生じた熱を外部に円滑に逃がすことができるため、導体部2における電気的特性の維持に有効となる。
さらに、本実施例1では導体部2を、金属パイプを加工することによって得た単芯線によって構成したため、主として導体部2を所定の屈曲形状を保持する形状保持部材として機能させることが可能となっている。したがって、形状保持のために特別な部材を追加する必要もなく、部品点数の軽減と構成の簡素化にも寄与する。
<実施例2>
図4は本発明の実施例2に係る導電部材10を示している。本実施例2における導体部11は撚り線電線によって構成されている。導体部11は多数本の細線を螺旋状に撚った芯線11Aと、その外周側を包囲する絶縁被覆11Bとから構成されている。導体部11自体は可撓性を有しており、いわゆる腰の無い状態となっている。
図4は本発明の実施例2に係る導電部材10を示している。本実施例2における導体部11は撚り線電線によって構成されている。導体部11は多数本の細線を螺旋状に撚った芯線11Aと、その外周側を包囲する絶縁被覆11Bとから構成されている。導体部11自体は可撓性を有しており、いわゆる腰の無い状態となっている。
絶縁部12は合成樹脂製の断面円形状のパイプ材によって構成されている。実施例2においては、この絶縁部12が本発明の形状保持部材として機能する。導体部11は絶縁部12における一方の端部から遊挿されて導体部11の外周を僅かな隙間を保有しつつ略同心で包囲している。
絶縁部12は、導体部11が挿通された後に所定の屈曲形状となるよう、曲げ工程を経て成形されている。絶縁部12は曲げ工程を経た後の復帰分を予め考慮して曲げがなされると良い。また、絶縁部12は本実施例2のように、合成樹脂材による単層構造で構成する他、金属層を含む複層構造とし、この金属層部分との協働で形状保持機能を高めるようにすることも考えられる。
なお、導体部11の両端部は絶縁部12及び次述するシールド部13から共に車両の前後両方向へ突出し、可撓領域R2の電線と接続される。
なお、導体部11の両端部は絶縁部12及び次述するシールド部13から共に車両の前後両方向へ突出し、可撓領域R2の電線と接続される。
シールド部13は、絶縁部12の外周面に全面に亘って積層された導電性の金属層によって形成されている。したがって、シールド部13は導体部11を全周から略同心で包囲した状態で収容している。剛体領域R1における両シールド部13は、可撓領域R2における編組部材5と一括して接続してもよいが、接続することなく、剛体領域R1から可撓領域R2に亘るまで両シールド部13をそのまま一体に延長し、共にコネクタC1、C2のシールド部材(図示しない)に接続するようにしてもよい。
上記のように構成された本実施例2のシールド導電路Wにおいても、シールド部13は導体部11及び絶縁部12を個別に包囲し、これらとの間に高さ方向に関してスペースを生じさせないから、低背化と放熱機能を高めることに有効となる。
また、形状保持機能をシールド部13の内側の絶縁部12が担うようにしたため、金属部材であるシールド部13によって絶縁部12や導体部11の保護を図りうる。また、シールド部13を設けたことによって曲げ工程時における絶縁部12のスプリングバックが緩和され、これによって絶縁部12の形状保持機能が高められることも期待できる。
<実施例3>
図5は本発明の実施例3を示している。本実施例3における導体部20も実施例2と同様、撚り線電線によって構成されている。本実施例3の絶縁部21は撚り線電線の絶縁被覆によって構成される。
図5は本発明の実施例3を示している。本実施例3における導体部20も実施例2と同様、撚り線電線によって構成されている。本実施例3の絶縁部21は撚り線電線の絶縁被覆によって構成される。
シールド部22は導電性の金属パイプによって形成されている。実施例3においては、このシールド部22が本発明の形状保持部材として機能する。導体部20および絶縁部21はシールド部22の一端部側から遊挿される。したがって、各導電部材23における導体部20及び絶縁部21はシールド部22によって個別に包囲される。シールド部22と絶縁部21との間には、シールド部22への挿通作業に必要な適度な隙間が保有されるが、この隙間は従来生じていた隙間に比較すれば僅かな程度に過ぎない。
なお、シールド部22は、導体部20及び絶縁部21が挿通された後に曲げ工程を経て所定の屈曲形状とされる。
なお、シールド部22は、導体部20及び絶縁部21が挿通された後に曲げ工程を経て所定の屈曲形状とされる。
導体部20の両端部は絶縁被覆が皮むきされた状態でシールド部22から前後方向へ突出し、可撓領域R2の電線と接続される。剛体領域R1における両シールド部22と可撓領域R2における編組部材5とは、締め付け部材6によって実施例1と同様の要領で接続される。
上記のように構成された本実施例3のシールド導電路Wにおいても、シールド部22は導体部20及び絶縁部21を個別に包囲し、これらとの間に高さ方向に関して無駄なスペースを生じさせないから、低背化と放熱機能を高めることに有効となる。
また、前記した実施例2では形状保持機能を絶縁部21が担うようにしたため、曲げ工程におけるスプリングバックが懸念されたが、本実施例3ではかかる懸念がないため、形状保持がし易い利点がある。さらに、シールド部22は形状保持のために、所定の肉厚をもって形成されるため、導体部20等に対する保護機能も高い。
<他の実施例>
本発明は上記記述及び図面によって説明した実施例に限定されるものではなく、例えば次のような実施例も本発明の技術的範囲に含まれる。
(1)上記実施例1では、導体部2を金属製のパイプ材によって形成したが、パイプ材にかえて長尺の平板に代えても良く、あるいは断面円形の棒材を高さ方向から圧潰しても良い。
(2)上記実施例1では、リボン状部材を螺旋状に巻き付けて接着することでシールド部4を製造する方式を示したが、これに代えて絶縁部3の外周面全面に金属箔を積層し、さらにその外周面を樹脂材による保護層を積層して包囲する方式としてもよい。
(3)いずれの実施例においても、シールド導電路Wを2本の導電部材によって構成される場合を説明したが、導電部材の本数は、2本以上であれば本数は問わない。
本発明は上記記述及び図面によって説明した実施例に限定されるものではなく、例えば次のような実施例も本発明の技術的範囲に含まれる。
(1)上記実施例1では、導体部2を金属製のパイプ材によって形成したが、パイプ材にかえて長尺の平板に代えても良く、あるいは断面円形の棒材を高さ方向から圧潰しても良い。
(2)上記実施例1では、リボン状部材を螺旋状に巻き付けて接着することでシールド部4を製造する方式を示したが、これに代えて絶縁部3の外周面全面に金属箔を積層し、さらにその外周面を樹脂材による保護層を積層して包囲する方式としてもよい。
(3)いずれの実施例においても、シールド導電路Wを2本の導電部材によって構成される場合を説明したが、導電部材の本数は、2本以上であれば本数は問わない。
1、10、23…導電部材
2、11、20…導体部
3、12、21…絶縁部
4、13、22…シールド部
W…シールド導電路
2、11、20…導体部
3、12、21…絶縁部
4、13、22…シールド部
W…シールド導電路
Claims (5)
- 中心部から外周側に向けて導体部、絶縁部、シールド部がそれぞれ配されてなる導電部材を、複数本並列して配してなるシールド導電路であって、
前記導体部、前記絶縁部及び前記シールド部のうち少なくとも一つが、前記各導電部材を設定された形状に保持可能な形状保持部材にて形成されているシールド導電路。 - 前記導体部は、導電金属製のパイプによって形成されて前記形状保持部材を兼ねた構成である請求項1記載のシールド導電路。
- 前記導体部は、高さ方向に圧潰されている請求項2記載のシールド導電路。
- 前記絶縁部は、前記導体部を収容する樹脂パイプによって形成されて前記形状保持部材を兼ねた構成である請求項1に記載のシールド導電路。
- 前記シールド部は、導電金属製のパイプによって形成されて前記形状保持部材を兼ねた構成であることを特徴とする請求項1に記載のシールド導電路。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201880048357.3A CN111052268B (zh) | 2017-08-08 | 2018-07-18 | 屏蔽导电路径 |
| US16/637,798 US10770200B2 (en) | 2017-08-08 | 2018-07-18 | Shielded conductive path |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017153013A JP2019032990A (ja) | 2017-08-08 | 2017-08-08 | シールド導電路 |
| JP2017-153013 | 2017-08-08 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2019031167A1 true WO2019031167A1 (ja) | 2019-02-14 |
Family
ID=65271263
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2018/026807 WO2019031167A1 (ja) | 2017-08-08 | 2018-07-18 | シールド導電路 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10770200B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP2019032990A (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN111052268B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2019031167A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7047649B2 (ja) * | 2018-07-30 | 2022-04-05 | 株式会社オートネットワーク技術研究所 | ワイヤハーネス |
| US20220108829A1 (en) * | 2019-02-15 | 2022-04-07 | Eaglerise Intelligent Device Corporation Ltd. | Wire for use in transformer winding and transformer |
| JP7392559B2 (ja) * | 2020-04-15 | 2023-12-06 | 株式会社オートネットワーク技術研究所 | ワイヤハーネス |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2013137230A1 (ja) * | 2012-03-14 | 2013-09-19 | 矢崎総業株式会社 | 同軸電線、及び同軸電線の製造方法 |
| JP2014123478A (ja) * | 2012-12-21 | 2014-07-03 | Auto Network Gijutsu Kenkyusho:Kk | 絶縁被覆電線及びその製造方法 |
| JP2015088251A (ja) * | 2013-10-28 | 2015-05-07 | 矢崎総業株式会社 | 回路導体、接続構造、及び回路導体の製造方法 |
| JP2016136460A (ja) * | 2015-01-23 | 2016-07-28 | 矢崎総業株式会社 | ワイヤハーネス |
| JP2017099155A (ja) * | 2015-11-25 | 2017-06-01 | 住友電装株式会社 | 電線外装材およびワイヤハーネス |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US1853677A (en) * | 1928-10-20 | 1932-04-12 | Siemensschuckertwerke Ag | Telephone cable |
| JP2006311699A (ja) | 2005-04-28 | 2006-11-09 | Auto Network Gijutsu Kenkyusho:Kk | シールド導電路 |
| US20080173464A1 (en) * | 2007-01-18 | 2008-07-24 | Rajendran Nair | Shielded flat pair cable with integrated resonant filter compensation |
| JP6281448B2 (ja) * | 2014-09-03 | 2018-02-21 | 住友電装株式会社 | 導電路 |
| US9875824B2 (en) * | 2014-12-24 | 2018-01-23 | Yazaki Corporation | Waterproofing structure, waterproofing method and wire harness |
| JP6657613B2 (ja) * | 2015-06-18 | 2020-03-04 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | 空気調和装置 |
-
2017
- 2017-08-08 JP JP2017153013A patent/JP2019032990A/ja active Pending
-
2018
- 2018-07-18 US US16/637,798 patent/US10770200B2/en active Active
- 2018-07-18 WO PCT/JP2018/026807 patent/WO2019031167A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2018-07-18 CN CN201880048357.3A patent/CN111052268B/zh active Active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2013137230A1 (ja) * | 2012-03-14 | 2013-09-19 | 矢崎総業株式会社 | 同軸電線、及び同軸電線の製造方法 |
| JP2014123478A (ja) * | 2012-12-21 | 2014-07-03 | Auto Network Gijutsu Kenkyusho:Kk | 絶縁被覆電線及びその製造方法 |
| JP2015088251A (ja) * | 2013-10-28 | 2015-05-07 | 矢崎総業株式会社 | 回路導体、接続構造、及び回路導体の製造方法 |
| JP2016136460A (ja) * | 2015-01-23 | 2016-07-28 | 矢崎総業株式会社 | ワイヤハーネス |
| JP2017099155A (ja) * | 2015-11-25 | 2017-06-01 | 住友電装株式会社 | 電線外装材およびワイヤハーネス |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN111052268B (zh) | 2022-03-15 |
| CN111052268A (zh) | 2020-04-21 |
| US20200258657A1 (en) | 2020-08-13 |
| US10770200B2 (en) | 2020-09-08 |
| JP2019032990A (ja) | 2019-02-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5986812B2 (ja) | ワイヤハーネス | |
| US10602647B2 (en) | Electromagnetic shield component and wire harness | |
| JP6002985B2 (ja) | ワイヤハーネス用中間部材及びワイヤハーネス | |
| WO2011078234A1 (ja) | ワイヤーハーネス | |
| JP6979957B2 (ja) | 電磁シールド構造およびワイヤハーネス | |
| WO2011158868A1 (ja) | 一体型シールドプロテクタ及びワイヤハーネス | |
| JP5830339B2 (ja) | 編組及びワイヤハーネス | |
| WO2019031167A1 (ja) | シールド導電路 | |
| JP2013099074A (ja) | ワイヤハーネス | |
| JP2016054030A (ja) | ワイヤハーネスおよびシールド導電路 | |
| CN107533887B (zh) | 导电部件 | |
| JP5884970B2 (ja) | ワイヤハーネスの製造方法及び製造配索方法 | |
| EP2738775A1 (en) | High-voltage conduction path and wiring harness | |
| US10596983B2 (en) | Wire harness | |
| JP2006269666A (ja) | シールド構造体 | |
| JP6819642B2 (ja) | ワイヤハーネス | |
| JP4820573B2 (ja) | シールド導電路 | |
| WO2020026885A1 (ja) | ワイヤハーネス | |
| WO2020026884A1 (ja) | ワイヤハーネス | |
| WO2020066587A1 (ja) | ワイヤハーネス | |
| JP2013165561A (ja) | ワイヤハーネス | |
| JP6700613B2 (ja) | 導電線 | |
| JP7160791B2 (ja) | 電線 | |
| JP5781289B2 (ja) | ワイヤハーネス配索構造 | |
| JP2013004275A (ja) | ワイヤハーネス |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 18844707 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 18844707 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |