WO2018211815A1 - 暗号鍵の処理を行う車両用システム及び電子制御装置 - Google Patents
暗号鍵の処理を行う車両用システム及び電子制御装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2018211815A1 WO2018211815A1 PCT/JP2018/011269 JP2018011269W WO2018211815A1 WO 2018211815 A1 WO2018211815 A1 WO 2018211815A1 JP 2018011269 W JP2018011269 W JP 2018011269W WO 2018211815 A1 WO2018211815 A1 WO 2018211815A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- encryption key
- electronic control
- key
- unit
- control device
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0891—Revocation or update of secret information, e.g. encryption key update or rekeying
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0816—Key establishment, i.e. cryptographic processes or cryptographic protocols whereby a shared secret becomes available to two or more parties, for subsequent use
- H04L9/0819—Key transport or distribution, i.e. key establishment techniques where one party creates or otherwise obtains a secret value, and securely transfers it to the other(s)
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0894—Escrow, recovery or storing of secret information, e.g. secret key escrow or cryptographic key storage
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/14—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols using a plurality of keys or algorithms
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L2209/00—Additional information or applications relating to cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communication H04L9/00
- H04L2209/84—Vehicles
Definitions
- This disclosure relates to processing of encryption keys for ensuring security, and mainly relates to processing of encryption keys used by electronic control devices that constitute a vehicle system.
- a communication device installed in an automobile transmits and receives various information via a network.
- technology to collect and analyze vehicle conditions and road conditions acquired by in-vehicle sensors via a network, and autonomous driving vehicles that control traveling by sending and receiving commands via the network Development has become active.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a vehicle using a key management system that includes a management device mounted on a vehicle and a key management server device that is managed by a vehicle manufacturer and performs wireless communication with the management device on the vehicle side.
- a technology for improving the security of an automobile by generating and managing an encryption key used in the system and periodically updating the encryption key is disclosed.
- Automobiles are products that have a fostering second-hand market compared to home appliances, and it is not uncommon for owners to change. In addition, car users may frequently change in a short period of time, such as car rental and car sharing. However, if a malicious car owner or temporary user analyzes the vehicle's ECU and obtains an encryption key that is used to ensure message integrity and protect data, the next owner Alternatively, it is possible that the vehicle used by the user is illegally accessed by a malicious owner or the like and the ECU is illegally operated by inserting an illegal message.
- This disclosure is intended to realize a vehicle system that ensures security by changing an encryption key used in an automobile to a new encryption key when the owner of the vehicle is changed.
- the vehicle system includes a first electronic control device that manages an encryption key and a second electronic control device that uses the encryption key.
- the first electronic control device includes a key generation unit that generates an encryption key when the owner of the vehicle including the first and second electronic control devices is changed, and an encryption key for the second electronic control device.
- the second electronic control device includes a key holding unit that stores a first encryption key that is an encryption key in use, and a key reception unit that receives a second encryption key that is an encryption key output from the key distribution unit And a key update unit that updates the first encryption key stored in the key holding unit to the second encryption key.
- the electronic control device can communicate with another device using the encryption key stored in the storage unit, and the owner of the vehicle including the electronic control device has changed.
- a key generation unit that generates an encryption key
- a key distribution unit that outputs the encryption key to another device that updates the encryption key stored in the storage unit when the encryption key is received.
- the electronic control device can communicate with another device that generates an encryption key when the owner of the vehicle is changed, and uses the encryption key.
- the electronic control device includes a key holding unit that stores a first encryption key that is an encryption key in use, a key receiving unit that receives a second encryption key from another device, and a first key stored in the key holding unit.
- a key update unit that updates the first encryption key to the second encryption key.
- an encryption key generation / updating method is performed in a vehicle system including a first electronic control device that manages an encryption key and a second electronic control device that uses the encryption key. Is called.
- the encryption key generation / updating method generates the encryption key when the owner of the vehicle including the first and second electronic control devices changes, and the first electronic control Outputting the encryption key from the key distribution unit of the apparatus to the second electronic control unit; receiving the second encryption key that is the encryption key output from the key distribution unit in the second electronic control unit; And updating the first encryption key, which is the encryption key in use stored in the key holding unit of the second electronic control device, to the second encryption key.
- the encryption key generation method is performed in an electronic control device that can communicate with another device that uses the encryption key stored in the storage unit.
- the encryption key generation method generates an encryption key when the owner of the vehicle including the electronic control device is changed, and updates the encryption key stored in the storage unit when the encryption key is received. Output an encryption key.
- the encryption key update method is communicable with another device that generates an encryption key when the owner of the vehicle is changed, and is performed in an electronic control device that uses the encryption key. Is called.
- the second encryption key is received from another device, and the first encryption key that is being used and stored in the key holding unit is updated to the second encryption key. Including.
- an encryption key generation / update method an encryption key generation method, or a program for executing an encryption key update method.
- the encryption key used in the automobile can be changed to a new encryption key to ensure security.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram illustrating the configuration of the vehicle system according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 2 is a block diagram illustrating the configuration of the owner management device according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram illustrating the configuration of the key management device according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 4 is a block diagram illustrating the configuration of the vehicle control device of the first embodiment.
- FIG. 5 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the vehicle system according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 6A is a diagram illustrating a use state of an encryption key used by the vehicle control device of the first embodiment.
- FIG. 6B is a diagram illustrating the use state of the encryption key used by the vehicle control device of the first embodiment.
- FIG. 6C is a diagram illustrating a usage state of an encryption key used by the vehicle control device of the first embodiment.
- FIG. 7 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the vehicle system of the second embodiment.
- FIG. 1 shows a configuration of a vehicle system 100 according to the first embodiment.
- the vehicle system 100 of the present disclosure includes an owner management device 200, a key management device 300, and a plurality of vehicle control devices 400.
- the owner management device 200, the key management device 300, and the vehicle control device 400 are all electronic control devices (ECUs) for the vehicle, and the owner management device 200, the key management device 300, the key management device 300, and the vehicle control.
- Each of the devices 400 is connected via an in-vehicle network.
- the owner management device 200 corresponds to the third electronic control device of the present disclosure
- the key management device 300 corresponds to the first electronic control device of the present disclosure
- the vehicle control device 400 corresponds to the first electronic control device of the present disclosure. This corresponds to the second electronic control unit.
- the owner management device 200 is configured as a vehicle system mounted on a vehicle. However, the owner management device 200 is used as a server outside the vehicle so as to perform wired or wireless communication with the key management device 300. You may comprise.
- the owner management device 200 and the key management device 300 are configured as one electronic control device, the electronic control device having both functions of the owner management device 200 and the key management device 300 is configured as a server outside the vehicle. May be.
- the vehicle system 100 includes a description of each electronic control unit constituting the vehicle system 100.
- the first electronic control device, the second electronic control device, and the third electronic control device of the present disclosure need only be separable as functions, regardless of whether or not they are physically separated.
- the other device in the present disclosure corresponds to another electronic control device viewed from each electronic control device.
- the expression for vehicles of the present disclosure includes those that are pre-installed in the vehicle, those that are retrofitted to the vehicle, and those that output signals to an electronic control device mounted on the vehicle, for example, A server provided outside the vehicle, an electronic control device used at a dealer, and the like can be included.
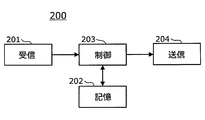
- the owner management device 200 is an electronic control device that manages information related to the vehicle owner, and includes a reception unit 201, a storage unit 202, a control unit 203, and a transmission unit 204, as shown in FIG.
- the owner management device 200 corresponds to the third electronic control device or the electronic control device of the present disclosure.
- the receiving unit 201 receives new owner information related to the owner of the vehicle.
- This owner information may be personal information about the vehicle owner entered via an interface such as a car navigation system installed in the vehicle or by wireless communication, for example, name, address, telephone number, email address, or Includes information such as driving position.
- the receiving unit 201 inputs the owner information to the control unit 203.
- the new owner information regarding the owner of the vehicle corresponds to the update information of the present disclosure.
- the owner described in the present disclosure includes an owner who owns the vehicle and a user who occupies the vehicle temporarily.
- the information about the owner includes information for identifying the owner, information associated with the owner, such as an attribute of the owner and an identification number.
- the old information related to the old owner described below includes information associated with the old owner such as the attribute and identification number of the old owner in addition to the information itself specifying the old owner.
- the storage unit 202 stores the owner information input to the receiving unit 201 in addition to the owner information related to the old owner stored from the beginning. Owner information stored in the storage unit 202 can be written, read, or erased based on an instruction from the control unit 203.
- the storage unit 202 includes, for example, a nonvolatile memory such as an EEPROM (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory), a flash ROM, or a hard disk.
- the owner information regarding the old owner stored from the beginning corresponds to the old information of the present disclosure.
- the control unit 203 reads the owner information related to the old owner stored in the storage unit 202 and compares it with the new owner information. Determine if there is a change in the owner of
- the control unit 203 determines that the owner of the vehicle has changed, the control unit 203 displays the owner change information indicating the change of the owner. Is input to the transmission unit 204.
- the control unit 203 further outputs a signal instructing the storage unit 202 to store new owner information.
- the transmission unit 204 outputs the owner change information to the key management apparatus 300 and notifies the key management apparatus 300 that the owner has changed.
- the criteria for judging whether or not the vehicle owner has changed can be arbitrarily set. For example, when the changed information is the name of the owner, the control unit 203 may determine that the owner has changed. In addition, the address, telephone number, and e-mail address may be changed even if they are the same owner. However, if two or more of these pieces of information are changed, the control unit 203 informs the owner. It may be determined that there has been a change. However, the criteria as to whether or not the owner has changed is not limited to this example.
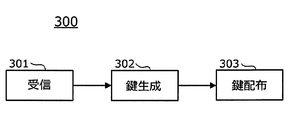
- the key management device 300 is an electronic control device that manages an encryption key used by the vehicle control device 400 to enhance security by ensuring message integrity, data protection, etc. As shown in FIG. A key generation unit 302 and a key distribution unit 303 are provided. The key management device 300 corresponds to the first electronic control device or the electronic control device of the present disclosure.
- the receiving unit 301 receives, from the transmission unit 204 of the owner management device 200, owner change information indicating that the vehicle owner has changed.
- the key generating unit 302 When the receiving unit 301 determines that the owner change information has been received, the key generating unit 302 generates, for example, a 128-bit encryption key. Then, the key generation unit 302 outputs the generated encryption key to the vehicle control device 400 via the key distribution unit 303.
- the expression “in the case of the present disclosure” includes a case where an encryption key is generated as soon as owner change information is received, and a case where an encryption key is generated when other conditions are further satisfied.
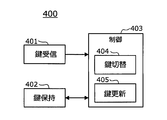
- Vehicle control device 400 is an electronic control device that controls a mechanism including an engine or the like mounted on the vehicle using a program and performs a desired operation. As illustrated in FIG. 4, a key receiving unit 401 and a key holding unit 402 are provided. And a control unit 403. The control unit 403 includes a key switching unit 404 and a key updating unit 405. As shown in FIG. 1, the vehicle control device 400 includes a drive system control device 411 that controls a drive mechanism, a vehicle body system control device 412 that controls opening and closing of a door, and a safety control system control that controls the operation of an airbag and the like. A device 413 and an arbitrary control device are included. The vehicle control device 400 corresponds to the second electronic control device or the electronic control device of the present disclosure.
- the key receiving unit 401 receives an encryption key from the key distribution unit 303 of the key management device 300.
- the received new encryption key is input to the control unit 403.
- the received new encryption key corresponds to the second encryption key of the present disclosure.
- the key holding unit 402 stores an encryption key used for encryption and decryption of a program or data that controls a mechanism such as an engine.
- the key holding unit 402 preferably stores two encryption keys. One of the two encryption keys is the encryption key K1 in use, and the other is not currently used, but is currently in use. Is the encryption key K2 used next to the encryption key K1.
- the key holding unit 402 includes a nonvolatile memory such as an EEPROM, a flash ROM, and a hard disk.
- the encryption key K1 corresponds to the first encryption key of the present disclosure
- the encryption key K2 corresponds to the third encryption key of the present disclosure.
- the initial encryption key K1 and encryption key K2 stored in the key holding unit 402 of the vehicle that is a new vehicle are written in a vehicle manufacturing factory, an ECU manufacturing factory, or the like before being shipped from the factory.
- the key switching unit 404 of the control unit 403 determines that the key receiving unit 401 has received a new encryption key, the key switching unit 404 changes the encryption key to be used from the encryption key K1 that is in use to the encryption key K2. Perform the switching process.
- the expression “in the case of the present disclosure” includes a case of performing a process of switching the encryption key immediately after receiving the second encryption key, and a case of performing a process of switching the encryption key after a predetermined time has elapsed.
- the key update unit 405 of the control unit 403 further rewrites the encryption key K1 stored in the key storage unit 402 with a new encryption key K3 input from the key reception unit 401, and stores it in the key storage unit 402. Update the encryption key.
- the key holding unit 402 may store only one encryption key K1.
- the encryption key to be used is switched from the encryption key K1 to the encryption key K3, and then stored in the key holding unit 402.
- the encryption key to be updated is updated from K1 to K3.
- the key update unit 405 can update the encryption key at an arbitrary timing. However, it is necessary to reliably rewrite the storage area accompanying the update of the encryption key. When rewriting is performed while the vehicle is running, for example, the ignition may be turned off by the owner during the rewriting process. Therefore, there is a possibility that a rewrite error occurs when the encryption key is rewritten from K1 to K3 and updated. In view of the above, it is desirable to update the encryption key while the operation of the key holding unit 402 is more stable, for example, when the ignition of the vehicle is turned on.
- the case where the ignition of the present disclosure is turned on from off includes the case where the ignition is turned on in a gasoline vehicle and the case where the power switch of an electric vehicle or a hybrid vehicle is turned on.
- FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing a series of operations performed in the vehicle system 100 from when new owner information is input until the encryption key is updated.
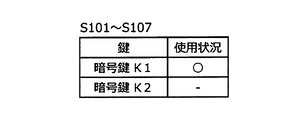
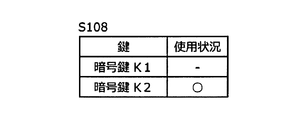
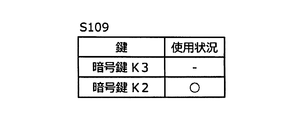
- FIGS. 6A, 6B, and 6C are vehicle control devices. 400 shows the use state of the encryption key stored in 400 and the encryption key to be used. 6A shows the usage status of the encryption key in S101 to S107, FIG. 6B shows the usage status of the encryption key in S108, and C in FIG. 6 shows the usage status of the encryption key in S109.
- the receiving unit 201 of the owner management apparatus 200 receives the new owner information as update information in S101, and the update information is stored in S102 in S102. 202.
- the control unit 203 of the owner management device 200 compares the owner information stored in the storage unit 202 with the update information, and determines whether or not the owner of the vehicle has changed. If it is determined that the owner of the vehicle has changed, the owner management device 200 outputs owner change information indicating the change of the owner to the key management device 300.
- the key generation unit 302 When the key management device 300 receives the owner change information from the owner management device 200 in S104, the key generation unit 302 generates the encryption key K3 in S105. In S ⁇ b> 106, the generated encryption key K ⁇ b> 3 is distributed from the receiving unit 301 to the vehicle control device 400 via the in-vehicle network.
- the vehicle control apparatus 400 receives the encryption key K3 from the key management apparatus 300 in S107, the currently used encryption key is switched from the encryption key K1 to the encryption key K2 in S108.
- the vehicle control device 400 uses the encryption key K1 as the encryption key. Then, as shown in FIG. 6B, the encryption key in use becomes the encryption key K2 by the processing of S108.
- the vehicle control device 400 switches the encryption key from the encryption key K1 to the encryption key K2 in S108, and then updates the encryption key K1 to the encryption key K3 received in S107 in S109 as shown in FIG. 6C.
- the process shown in FIG. 5 is performed each time new owner information is input. Therefore, when new owner information is input to the interface or the like again, and the owner management device 200 determines that the owner has changed, the key management device 300 newly starts based on the processing shown in FIG.
- the encryption key K4 is generated, and the encryption key K4 is distributed to the vehicle control device 400.
- the vehicle control device 400 switches the encryption key to be used from the encryption key K2 to the encryption key K3, and updates the encryption key K2 to the encryption key K4 received from the key management device 300.
- the owner management device 200 and the key management device 300 are configured as separate electronic control devices. However, the owner management device 200 and the key management device 300 may be configured as one electronic control device having both functions.
- the owner management device is also called an owner information management device.
- S104 in FIG. 5 is omitted.
- the key generation unit When the control unit determines that the owner of the vehicle has changed, the key generation unit generates a new encryption key.
- the expression “in the case of this disclosure” includes a case where an encryption key is generated as soon as it is determined that the owner has changed, and a case where an encryption key is generated when other conditions are further satisfied.
- the key holding unit 402 stores only one encryption key K1
- the encryption key currently used is the encryption key K1 in S108.
- the encryption key stored in the key holding unit 402 is updated from the encryption key K1 to the encryption key K3.
- the encryption key used by the vehicle control device can be updated.
- unauthorized access to the vehicle system by the previous owner, etc. Can be secured.
- the control part 203 of the owner management apparatus 200 compares the owner information memorize
- the control unit 203 may determine whether or not the owner has changed using a means other than the comparison.
- the control unit 203 when the new owner information is input and the receiving unit 201 of the owner management device 200 receives the new owner information as update information, the control unit 203 always changes the owner. You may judge.
- the control unit 203 may determine that the owner has changed.
- the case where it initializes may include the case where owner information is erase
- the encryption key is updated when there is a possibility that the owner of the vehicle may be changed, so that higher security can be ensured.
- the owner management device 200 when new owner information is input, the owner management device 200 confirms whether or not to update the encryption key to the owner of the vehicle, in other words, confirmation regarding necessity. And update the encryption key only when necessary.
- control unit 203 of the owner management device 200 in the second embodiment receives the new vehicle owner information input through the interface or the like as the update information, as in the first embodiment, To determine if the person has changed. If the control unit 203 determines in S103 that there is a high possibility that the owner has changed based on the input update information, should the encryption key be updated for the vehicle owner in S201? In order to confirm whether or not, for example, a message such as “Do you want to update the security of the vehicle? (Yes / No)” is displayed on an interface mounted on the vehicle. When the owner of the vehicle selects Yes in S202, control unit 203 outputs owner change information indicating the change of the owner to key management device 300. And the key management apparatus 300 which received owner change information produces
- the owner management device 200 confirms whether or not the encryption key needs to be updated with respect to the owner of the vehicle, and the owner of the key management device 300 based on the key update instruction.
- the change information is output.
- the key management device 300 may confirm whether or not the encryption key needs to be updated with respect to the owner of the vehicle, and may receive a key update instruction.
- the key management device 300 determines that the owner of the vehicle Displays a message on the interface confirming whether the encryption key needs to be updated.
- the receiving unit 301 of the key management device 300 receives an instruction to update the encryption key from the owner of the vehicle, the key management device 300 generates the encryption key K3.
- the encryption key can be manually updated every time the user changes, so the previous It becomes possible to prevent a user from gaining unauthorized access to the vehicle.
- the key management device 300 when the owner management device 200 determines that the owner of the vehicle has changed, the key management device 300 generates a new encryption key and the vehicle control device 400.
- the vehicle control device 400 updates the encryption key to be used.
- the encryption key is not necessarily generated in the vehicle system.
- the control unit 203 may notify the owner of the vehicle that security update is necessary. . Then, the owner who has received the notice may update the encryption key at the dealer by bringing the vehicle to the dealer.
- the expression for vehicles of the present disclosure includes those that are pre-installed in the vehicle, those that are retrofitted to the vehicle, and those that output a signal to an electronic control device mounted on the vehicle, for example, A server provided outside the vehicle and an electronic control unit used at a dealer are also included.
- the vehicle system according to the present disclosure includes a system constituted by an electronic control device mounted on a vehicle, and a system in which a part of the electronic control device of the system is provided outside the vehicle.
- S105, S106, S107, and S109 correspond to an example of the encryption key generation and update method of the present disclosure.
- S105 and S106 correspond to an example of the encryption key generation method of the present disclosure.
- S107 and S109 correspond to an example of the encryption key update method of the present disclosure.
- the vehicle system and the electronic control device including the owner management device, the key management device, and the vehicle control device in each embodiment of the present disclosure have been described.
- the operation of the electronic control device in each embodiment has also been described as a method description using a block diagram and a flowchart.
- a non-transitional tangible recording medium also called a computer-readable non-transitory storage medium
- a memory such as a RAM, a ROM, a flash memory (hereinafter referred to as a memory)
- It can also be realized as a combination of a program recorded on a recording medium such as a hard disk and a microcomputer having a dedicated or general-purpose CPU and memory for executing the program.
- the program can also be provided from a server via a communication line without going through a recording medium.
- the number of microcomputers may be one or more.
- the vehicle system and the electronic control device according to the present disclosure are mainly used to ensure the security of an automobile, but the security of a vehicle other than an automobile, for example, a motorcycle, an electrically assisted bicycle, a ship, an aircraft, etc. It may be used for securing. Further, the present disclosure is not limited to these applications.
- the electronic control device may be able to communicate with another device that uses or generates the encryption key.
- each step is expressed as S101, for example. Further, each step can be divided into a plurality of sub-steps, while a plurality of steps can be combined into one step.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Lock And Its Accessories (AREA)
- Stored Programmes (AREA)
Abstract
車両用システムは暗号鍵を管理する第1の電子制御装置(300)と、暗号鍵を使用する第2の電子制御装置(400)と、を備える。第1の電子制御装置(300)は、第1の電子制御装置及び第2の電子制御装置を備える車両の所有者に変更があった場合に暗号鍵を生成する鍵生成部(302)と、第2の電子制御装置に暗号鍵を出力する鍵配布部(303)と、を有し、第2の電子制御装置(400)は、使用中の暗号鍵である第1の暗号鍵を記憶する鍵保持部(402)と、鍵配布部から出力された暗号鍵である第2の暗号鍵を受信する鍵受信部(401)と、鍵保持部に記憶されている第1の暗号鍵を、第2の暗号鍵に更新する鍵更新部(405)と、を有する。
Description
本出願は、2017年5月16日に出願された日本国特許出願2017-97107号に基づくものであり、ここにその記載内容を参照により援用する。
本開示は、セキュリティを確保するための暗号鍵の処理に関し、主として車両用システムを構成する電子制御装置が使用する暗号鍵の処理に関する。
自動車に搭載される通信装置はネットワークを介して様々な情報を送受信している。近年では、無線通信の発達に伴い、ネットワークを介して車載センサで取得した車両の状態や道路状況を収集、分析する技術や、ネットワークを介してコマンドを送受信することにより走行を制御する自動運転車両の開発が活発になっている。
自動車をネットワークに接続する場合、車載装置が車外のネットワークからの不正アクセスによって影響を受ける可能性が高まる。特に、車両の駆動機構の動作を制御するECUについては、自動車の走行の安全性を担保すべく、高いセキュリティを確保する必要性が高まっている。
例えば、特許文献1には、自動車に搭載される管理装置と、自動車の製造会社にて管理され、自動車側の管理装置と無線通信を行う鍵管理サーバ装置とを有する鍵管理システムを用いて自動車で使用する暗号鍵の生成及び管理を行い、暗号鍵を定期的に更新することにより、自動車のセキュリティを高める技術が開示されている。
自動車は家電製品などと比較して中古市場が盛んな製品であり、所有者が代わることは珍しくない。また、レンタカーやカーシェアリングのように、自動車の利用者が短期間で頻繁に代わることもある。しかしながら、悪意を持った自動車の所有者又は一時的な利用者が車両のECUを解析して、メッセージの完全性確保やデータ保護に使用されている暗号鍵を入手された場合、次の所有者又は利用者が使用する車両が悪意を持った前所有者等によって不正にアクセスされ、不正メッセージの挿入等によりECUが不正操作されることが起こりうる。
本開示は、車両の所有者に変更があった場合に、自動車で使用する暗号鍵を新たな暗号鍵に変更してセキュリティを確保する車両用システムを実現することを目的とする。
本開示の一態様によると、車両用システムは、暗号鍵を管理する第1の電子制御装置と、暗号鍵を使用する第2の電子制御装置と、を備える。第1の電子制御装置は、第1及び第2の電子制御装置を備える車両の所有者に変更があった場合に暗号鍵を生成する鍵生成部と、第2の電子制御装置に暗号鍵を出力する鍵配布部と、を有する。第2の電子制御装置は、使用中の暗号鍵である第1の暗号鍵を記憶する鍵保持部と、鍵配布部から出力された暗号鍵である第2の暗号鍵を受信する鍵受信部と、鍵保持部に記憶されている第1の暗号鍵を、第2の暗号鍵に更新する鍵更新部と、を有する。
本開示の他の一態様によると、電子制御装置は、記憶部に記憶される暗号鍵を使用する他装置と通信可能であって、電子制御装置を備える車両の所有者に変更があった場合に暗号鍵を生成する鍵生成部と、暗号鍵を受信した場合に記憶部に記憶される暗号鍵を更新する他装置に対し、暗号鍵を出力する鍵配布部と、を備える。
本開示の他の一態様によると、電子制御装置は、車両の所有者に変更があった場合に暗号鍵を生成する他装置と通信可能であり、暗号鍵を使用する。電子制御装置は、使用中の暗号鍵である第1の暗号鍵を記憶する鍵保持部と、他装置から第2の暗号鍵を受信する鍵受信部と、鍵保持部に記憶されている第1の暗号鍵を、第2の暗号鍵に更新する鍵更新部と、を備える。
本開示の他の一態様によると、暗号鍵生成更新方法は、暗号鍵を管理する第1の電子制御装置と、暗号鍵を使用する第2の電子制御装置と、を備える車両用システムにおいて行われる。暗号鍵生成更新方法は、第1の電子制御装置において、第1及び第2の電子制御装置を備える車両の所有者に変更があった場合に暗号鍵を生成することと、第1の電子制御装置の鍵配布部から第2の電子制御装置に暗号鍵を出力することと、第2の電子制御装置において、鍵配布部から出力された暗号鍵である第2の暗号鍵を受信することと、第2の電子制御装置の鍵保持部に記憶されている使用中の暗号鍵である第1の暗号鍵を、第2の暗号鍵に更新することと、を含む。
本開示の他の一態様によると、暗号鍵生成方法は、記憶部に記憶される暗号鍵を使用する他装置と通信可能な電子制御装置において行われる。暗号鍵生成方法は、電子制御装置を備える車両の所有者に変更があった場合に暗号鍵を生成することと、暗号鍵を受信した場合に記憶部に記憶される暗号鍵を更新する他装置に対し、暗号鍵を出力することと、を含む。
本開示の他の一態様によると、暗号鍵更新方法は、車両の所有者に変更があった場合に暗号鍵を生成する他装置と通信可能であり、暗号鍵を使用する電子制御装置において行われる。暗号鍵更新方法は、他装置から第2の暗号鍵を受信することと、鍵保持部に記憶されている使用中の暗号鍵である第1の暗号鍵を、第2の暗号鍵に更新することと、を含む。
さらに本開示の他の態様によると、暗号鍵生成更新方法、暗号鍵生成方法、または暗号鍵更新方法を実行するプログラムが提供される。
本開示によれば、車両の所有者に変更があった場合に、自動車で使用する暗号鍵を新たな暗号鍵に変更して、セキュリティを確保することができる。
本開示についての上記および他の目的、特徴や利点は、添付図面を参照した下記詳細な説明から、より明確になる。添付図面において、
図1は、第1実施形態の車両用システムの構成を説明するブロック図であり、
図2は、第1実施形態の所有者管理装置の構成を説明するブロック図であり、
図3は、第1実施形態の鍵管理装置の構成を説明するブロック図であり、
図4は、第1実施形態の車両制御装置の構成を説明するブロック図であり、
図5は、第1実施形態の車両用システムの動作を説明するフローチャートであり、
図6Aは、第1実施形態の車両制御装置が使用する暗号鍵の使用状態を説明する図であり、
図6Bは、第1実施形態の車両制御装置が使用する暗号鍵の使用状態を説明する図であり、
図6Cは、第1実施形態の車両制御装置が使用する暗号鍵の使用状態を説明する図であり、
図7は、第2実施形態の車両用システムの動作を説明するフローチャートである。
以下に、 図面を参照しながら本開示を実施するための複数の実施形態を説明する。
(第1実施形態)
図1は、第1実施形態の車両用システム100の構成を示している。本開示の車両用システム100は、所有者管理装置200、鍵管理装置300、及び複数の車両制御装置400を備える。所有者管理装置200、鍵管理装置300、及び車両制御装置400はいずれも、車両用の電子制御装置(ECU)であり、所有者管理装置200と鍵管理装置300、鍵管理装置300と車両制御装置400はそれぞれ、車載ネットワークを介して接続されている。また、所有者管理装置200は、本開示の第3の電子制御装置に対応し、鍵管理装置300は、本開示の第1の電子制御装置に対応し、車両制御装置400は、本開示の第2の電子制御装置に対応する。
図1は、第1実施形態の車両用システム100の構成を示している。本開示の車両用システム100は、所有者管理装置200、鍵管理装置300、及び複数の車両制御装置400を備える。所有者管理装置200、鍵管理装置300、及び車両制御装置400はいずれも、車両用の電子制御装置(ECU)であり、所有者管理装置200と鍵管理装置300、鍵管理装置300と車両制御装置400はそれぞれ、車載ネットワークを介して接続されている。また、所有者管理装置200は、本開示の第3の電子制御装置に対応し、鍵管理装置300は、本開示の第1の電子制御装置に対応し、車両制御装置400は、本開示の第2の電子制御装置に対応する。
なお、第1実施形態では、所有者管理装置200は車両に搭載される車両用システムとして構成されているが、所有者管理装置200を車外サーバとして、鍵管理装置300と有線又は無線通信するように構成してもよい。また、所有者管理装置200及び鍵管理装置300を1つの電子制御装置として構成する場合には、所有者管理装置200及び鍵管理装置300の双方の機能を具備する電子制御装置を車外サーバとして構成してもよい。
なお、以下の記載は車両用システム100を説明するものであるが、車両用システム100を構成する各電子制御装置の説明を含んでいる。ここで、本開示の第1の電子制御装置、第2の電子制御装置、及び第3の電子制御装置は、機能として分離できればよく、物理的に分離するか否かは問わない。また、本開示における他装置とは、各電子制御装置から見た他の電子制御装置に該当する。
また、本開示の車両用という表現とは、車両に予め搭載されるもの、及び車両に後付けで搭載されるものや、車両に搭載された電子制御装置に対して信号を出力するもの、例えば、車外に設けられたサーバや、ディーラーにおいて使用される電子制御装置等を含むことができる。
また、本開示の車両用という表現とは、車両に予め搭載されるもの、及び車両に後付けで搭載されるものや、車両に搭載された電子制御装置に対して信号を出力するもの、例えば、車外に設けられたサーバや、ディーラーにおいて使用される電子制御装置等を含むことができる。
以下に、所有者管理装置200、鍵管理装置300、及び車両制御装置400の構成及び機能をそれぞれ説明する。
1.所有者管理装置200
所有者管理装置200は、車両の所有者に関する情報を管理する電子制御装置であり、図2に示すとおり、受信部201、記憶部202、制御部203、及び送信部204を備える。所有者管理装置200は、本開示の第3の電子制御装置又は電子制御装置に対応する。
所有者管理装置200は、車両の所有者に関する情報を管理する電子制御装置であり、図2に示すとおり、受信部201、記憶部202、制御部203、及び送信部204を備える。所有者管理装置200は、本開示の第3の電子制御装置又は電子制御装置に対応する。
受信部201は、車両の所有者に関する新たな所有者情報を受信する。この所有者情報は、車両に設置されたカーナビゲーションシステム等のインタフェースを介して、あるいは無線通信によって入力された車両の所有者に関する個人情報、例えば、氏名、住所、電話番号、メールアドレス、又は、ドライビングポジション等の情報を含む。受信部201は所有者情報を受信すると、当該所有者情報を制御部203に入力する。また、車両の所有者に関する新たな所有者情報とは、本開示の更新情報に対応する。
ここで、本開示に記載の所有者とは、車両を所有するオーナーや、一時的に車両を占有する使用者をも含む。また、所有者に関する情報とは、所有者を特定する情報や、所有者の属性、識別番号等、所有者に紐づけられる情報も含む。以下に記載する旧所有者に関する旧情報も同様に、旧所有者を特定する情報そのものの他、旧所有者の属性、識別番号等、旧所有者に紐づけられる情報も含む。
記憶部202は、元から記憶されている旧所有者に関する所有者情報に加えて、受信部201に入力された所有者情報を記憶する。記憶部202に記憶された所有者情報は、制御部203からの指示に基づいて、書き込み、読み出し、又は消去することができる。なお、記憶部202は、例えば、EEPROM(electrically erasable programmable read-only memory)、フラッシュROM、ハードディスク等の不揮発性メモリから構成される。また、元から記憶されている旧所有者に関する所有者情報とは、本開示の旧情報に対応する。
制御部203は、受信部201を介して新たな所有者情報が入力されると、記憶部202に記憶されている旧所有者に関する所有者情報を読み出して新たな所有者情報と比較し、車両の所有者に変更があるか否かを判断する。
新たな所有者情報と、記憶部202から読み出した所有者情報とを比較した結果、車両の所有者に変更があったと判断した場合、制御部203は、所有者の変更を示す所有者変更情報を送信部204に入力する。制御部203はさらに、記憶部202に対して新たな所有者情報を記憶することを指示する信号を出力する。
送信部204は、所有者変更情報を鍵管理装置300に出力し、所有者に変更があったことを鍵管理装置300に通知する。
なお、車両の所有者に変更があったか否かを判断する基準は、任意に設定することができる。例えば、変更された情報が所有者の氏名である場合には、制御部203は所有者に変更があったと判断してもよい。また、住所、電話番号、メールアドレスは、同一所有者であっても変更される可能性はあるが、これらの情報のうち2つ以上が変更された場合には、制御部203は所有者に変更があったと判断してもよい。しかしながら、所有者に変更があったか否かの基準は、この例に限定されるものではない。
2.鍵管理装置300
鍵管理装置300は、車両制御装置400がメッセージの完全性確保やデータ保護等により、セキュリティを高めるために使用する暗号鍵を管理する電子制御装置であり、図3に示すとおり、受信部301、鍵生成部302、及び鍵配布部303を備える。鍵管理装置300は、本開示の第1の電子制御装置又は電子制御装置に対応する。
鍵管理装置300は、車両制御装置400がメッセージの完全性確保やデータ保護等により、セキュリティを高めるために使用する暗号鍵を管理する電子制御装置であり、図3に示すとおり、受信部301、鍵生成部302、及び鍵配布部303を備える。鍵管理装置300は、本開示の第1の電子制御装置又は電子制御装置に対応する。
受信部301は、所有者管理装置200の送信部204から、車両の所有者に変更があったことを示す所有者変更情報を受信する。
鍵生成部302は、受信部301が所有者変更情報を受信したと判断した場合には、例えば、128ビットの暗号鍵を生成する。そして、鍵生成部302は、生成した暗号鍵を、鍵配布部303を介して車両制御装置400に出力する。
本開示の場合にとの表現は、所有者変更情報を受信すると直ちに暗号鍵の生成する場合や、その他の条件を更に満たしたときに暗号鍵を生成する場合を含む。
3.車両制御装置400
車両制御装置400は、プログラムを用いて車両に搭載されたエンジン等を含む機構を制御し、所望の動作をさせる電子制御装置であり、図4に示すとおり、鍵受信部401、鍵保持部402、及び制御部403を備える。また、制御部403は、鍵切替部404及び鍵更新部405を備える。この車両制御装置400は、図1に示すように、駆動機構を制御する駆動系制御装置411、ドアの開閉等を制御する車体系制御装置412、エアバッグ等の動作を制御する安全制御系制御装置413や、任意の制御装置を含む。車両制御装置400は、本開示の第2の電子制御装置又は電子制御装置に対応する。
車両制御装置400は、プログラムを用いて車両に搭載されたエンジン等を含む機構を制御し、所望の動作をさせる電子制御装置であり、図4に示すとおり、鍵受信部401、鍵保持部402、及び制御部403を備える。また、制御部403は、鍵切替部404及び鍵更新部405を備える。この車両制御装置400は、図1に示すように、駆動機構を制御する駆動系制御装置411、ドアの開閉等を制御する車体系制御装置412、エアバッグ等の動作を制御する安全制御系制御装置413や、任意の制御装置を含む。車両制御装置400は、本開示の第2の電子制御装置又は電子制御装置に対応する。
鍵受信部401は、鍵管理装置300の鍵配布部303から暗号鍵を受信する。受信した新たな暗号鍵は、制御部403に入力される。受信した新たな暗号鍵は、本開示の第2の暗号鍵に対応する。
鍵保持部402は、エンジン等の機構を制御するプログラムやデータ等の暗号化及び復号化に使用される暗号鍵を記憶している。鍵保持部402は2つの暗号鍵を記憶していることが望ましく、2つの暗号鍵のうち1つは使用中の暗号鍵K1であり、もう1つは現在使用されていないが、現在使用中の暗号鍵K1の次に使用される暗号鍵K2である。なお、鍵保持部402は、例えば、EEPROM、フラッシュROM、ハードディスク等の不揮発性メモリから構成される。暗号鍵K1は本開示の第1の暗号鍵に対応し、暗号鍵K2は本開示の第3の暗号鍵に対応する。
新車である車両の鍵保持部402に記憶される初期の暗号鍵K1及び暗号鍵K2は、工場から出荷される前に車両製造工場又はECU製造工場等において書き込まれる。
制御部403の鍵切替部404は、鍵受信部401が新たな暗号鍵を受信したと判断した場合には、使用する暗号鍵を、使用中の暗号鍵である暗号鍵K1から暗号鍵K2に切り替える処理を行う。
ここで、本開示の場合にとの表現は、第2の暗号鍵を受信すると直ちに暗号鍵を切り替える処理をする場合や、所定時間経過後に暗号鍵を切り替える処理を行う場合を含む。
制御部403の鍵更新部405はさらに、鍵保持部402に記憶されている暗号鍵K1を、鍵受信部401から入力された新たな暗号鍵K3に書き換えて、鍵保持部402に記憶されている暗号鍵を更新する。
なお、本実施形態では、鍵保持部402が2つの暗号鍵を記憶している例を記載しているが、鍵保持部402は1つの暗号鍵K1のみを記憶するものであってもよい。暗号鍵K1のみを記憶する場合、鍵受信部401が鍵配布部303から暗号鍵K3を受信すると、使用する暗号鍵を暗号鍵K1から暗号鍵K3へと切り替えた後、鍵保持部402に記憶される暗号鍵をK1からK3へと更新する。
鍵更新部405は、任意のタイミングで暗号鍵の更新を行うことができる。しかしながら、暗号鍵の更新に伴う記憶領域の書き換えは確実に行う必要がある。車両の走行中に書き換えを行う場合、例えば書き換え処理の途中で所有者によるイグニッションオフが行われる可能性がある。そのため、暗号鍵をK1からK3に書き換えて更新する際に、書き換えミスが発生するおそれがある。以上に照らせば、暗号鍵の更新は、鍵保持部402の動作がより安定している間、例えば、車両のイグニッションがオフからオンになったときに行うことが望ましい。
なお、本開示のイグニッションがオフからオンになる場合とは、ガソリン車においてイグニッションをオンにする場合や、電気自動車又はハイブリッド車のパワースイッチをオンにする場合をも含む。
以下に、図5、図6A、図6B、図6Cを参照して、本開示の車両用システム100の動作を説明する。
図5は、新たな所有者情報が入力されてから暗号鍵を更新するまでに車両用システム100において行われる一連の動作を示すフローチャートであり、図6A、図6B、図6Cは、車両制御装置400に記憶されている暗号鍵及び使用される暗号鍵の使用状態を示している。図6Aは、S101~S107における暗号鍵の使用状況を示し、図6Bは、S108における暗号鍵の使用状態を示し、図6のCはS109における暗号鍵の使用状態を示す。
まず、インタフェース等を介して新たな所有者情報が入力された場合、S101において所有者管理装置200の受信部201は新たな所有者情報を更新情報として受信し、S102で当該更新情報を記憶部202に記憶する。また、S103で所有者管理装置200の制御部203は、記憶部202に記憶されていた所有者情報と更新情報とを比較し、車両の所有者に変更があったかどうかを判断する。そして、車両の所有者に変更があったと判断した場合、所有者管理装置200は、鍵管理装置300に対して、所有者の変更を示す所有者変更情報を出力する。
鍵管理装置300は、S104において所有者管理装置200から所有者変更情報を受信すると、S105で鍵生成部302にて暗号鍵K3を生成する。そして、S106では、生成された暗号鍵K3は、受信部301から、車載ネットワークを介して車両制御装置400へと配布される。
次いで、S107において車両制御装置400が鍵管理装置300から暗号鍵K3を受信すると、S108で、現在使用されている暗号鍵を、暗号鍵K1から暗号鍵K2に切り替える。
ここで、図6Aに示すように、S101~S107の処理が行われている間、車両制御装置400は暗号鍵として暗号鍵K1を使用している。そして、図6Bに示すように、S108の処理により、使用中の暗号鍵は暗号鍵K2となる。
車両制御装置400は、S108にて暗号鍵を暗号鍵K1から暗号鍵K2に切り替えた後、図6Cに示すように、S109で、暗号鍵K1をS107にて受信した暗号鍵K3に更新する。
図5に示す処理は、新たな所有者情報が入力される度に行われる。したがって、新たな所有者情報が再度インタフェース等に入力され、所有者管理装置200が所有者に変更があったと判断した場合には、図5に示す処理に基づいて、鍵管理装置300は新たに暗号鍵K4を生成し、暗号鍵K4を車両制御装置400に配布する。また、車両制御装置400は、使用する暗号鍵を暗号鍵K2から暗号鍵K3に切り替えると共に、暗号鍵K2を鍵管理装置300から受信した暗号鍵K4に更新する。
なお、本実施形態では、所有者管理装置200と鍵管理装置300は別個の電子制御装置として構成されている。しかしながら、所有者管理装置200及び鍵管理装置300は、双方の機能を具備する1つの電子制御装置として構成してもよい。所有者管理装置は所有者情報管理装置とも呼ぶ。
この場合、図5におけるS104は省略される。そして、制御部が車両の所有者に変更があったことを判断した場合には、鍵生成部は新たな暗号鍵を生成する。
本開示の場合にとの表現は、所有者に変更があったことを判断すると直ちに暗号鍵の生成する場合や、その他の条件を更に満たしたときに暗号鍵を生成する場合を含む。
なお、鍵保持部402が1つの暗号鍵K1のみを記憶している場合は、S107にて車両制御装置400が暗号鍵K3を受信すると、S108において、現在使用されている暗号鍵を暗号鍵K1から暗号鍵K3に切り替える。その後、S109において、鍵保持部402に記憶される暗号鍵を暗号鍵K1から暗号鍵K3に更新する。
第1実施形態によれば、車両の所有者に変更があった場合には、車両制御装置が使用する暗号鍵を更新することができるため、以前の所有者による車両用システムへの不正アクセス等に対するセキュリティ確保が可能となる。
(第1変形例)
第1実施形態では、所有者管理装置200の制御部203は、記憶部202に記憶されている所有者情報と、新たな所有者情報である更新情報とを比較して、所有者に変更があったか否かを判断している。しかしながら、制御部203は、比較以外の手段を用いて所有者に変更があったか否かを判断してもよい。
第1実施形態では、所有者管理装置200の制御部203は、記憶部202に記憶されている所有者情報と、新たな所有者情報である更新情報とを比較して、所有者に変更があったか否かを判断している。しかしながら、制御部203は、比較以外の手段を用いて所有者に変更があったか否かを判断してもよい。
例えば、制御部203は、新たな所有者情報が入力され、所有者管理装置200の受信部201が新たな所有者情報を更新情報として受信した場合には常に、所有者に変更があったものと判断してもよい。あるいは、インタフェース等を介して記憶部202が初期化された場合には、制御部203は所有者に変更があったものと判断してもよい。また、初期化された場合とは、所有者情報が消去された場合を含んでもよい。
本変形例によれば、車両の所有者に変更がある可能性がある場合には暗号鍵が更新されるため、より高いセキュリティを確保することが可能となる。
(第2実施形態)
第1実施形態では、所有者管理装置200の制御部203が更新情報に基づいて所有者の変更があったと判断した場合には、自動的に、鍵管理装置300に所有者の変更を示す所有者変更情報を鍵管理装置300に入力している。しかしながら、例えば、引越により住所変更をした場合等のように、新たな所有者情報が入力された場合であっても車両の所有者に変更がないことがある。
第1実施形態では、所有者管理装置200の制御部203が更新情報に基づいて所有者の変更があったと判断した場合には、自動的に、鍵管理装置300に所有者の変更を示す所有者変更情報を鍵管理装置300に入力している。しかしながら、例えば、引越により住所変更をした場合等のように、新たな所有者情報が入力された場合であっても車両の所有者に変更がないことがある。
第2実施形態では、新たな所有者情報が入力された場合には、所有者管理装置200は、車両の所有者に対して暗号鍵を更新するかどうかの確認、言い換えれば、要否に関する確認を行い、必要な場合にのみ暗号鍵の更新を行う。
本開示の要否に関する確認という表現とは、暗号鍵を更新するか否かを直接的に確認することに限定されるものではなく、電子制御装置が暗号鍵を更新することが必要であるか否かを判断可能な内容、例えば、所有者に変更があったか否か、あるいは、システムのセキュリティをリセットするか否か等を間接的に確認するものであってもよい。
図7を参照して、第2実施形態の車両用システムの動作を以下に説明する。なお、第1実施形態との共通点については詳しい説明は省略し、第1実施形態との相違点を中心に説明する。
第2実施形態における所有者管理装置200の制御部203は、第1実施形態と同様、インタフェース等を介して入力された新たな車両の所有者情報を更新情報として受信した場合、S103において、所有者に変更があったかどうかを判断する。S103にて、制御部203が、入力された更新情報に基づいて所有者に変更があった可能性が高いと判断した場合、S201にて、車両の所有者に対して暗号鍵を更新すべきか否かを確認するために、例えば、車両に搭載されたインタフェースに「車両のセキュリティを更新しますか?(Yes/No)」といったメッセージを表示させる。S202にて、車両の所有者がYesを選択した場合、制御部203は、所有者の変更を示す所有者変更情報を鍵管理装置300に対して出力する。そして、所有者変更情報を受信した鍵管理装置300は、第1実施形態と同様、暗号鍵K3を生成する。
なお、第2実施形態では、所有者管理装置200が、車両の所有者に対して暗号鍵の更新の要否を確認すると共に、鍵更新の指示に基づいて鍵管理装置300に対して所有者変更情報を出力している。しかしながら、所有者管理装置200に代わり、鍵管理装置300が車両の所有者に対して暗号鍵の更新の要否を確認し、鍵更新の指示を受信してもよい。
この場合、所有者管理装置200が、S103にて車両の所有者に変更があったと判断し、鍵管理装置300に所有者変更情報が出力されると、鍵管理装置300は、車両の所有者に対して暗号鍵の更新の要否を確認するメッセージをインタフェースに表示させる。そして、鍵管理装置300の受信部301が車両の所有者から暗号鍵更新の指示を受信すると、鍵管理装置300は暗号鍵K3を生成する。
以上、第2実施形態によれば、車両の所有者に変更があったときにのみ暗号鍵を確実に更新することが可能となる。
(第2変形例)
第2実施形態では、所有者管理装置200の制御部203が、所有者に変更がある可能性が高いと判断した場合に、暗号鍵を更新することの要否に関する確認をインタフェースに表示して、車両の所有者から暗号鍵更新に関する指示を受けるように構成されている。しかしながら、制御部203が、車両の所有者に変更があると判断していない場合であっても、車両の所有者は任意のタイミングで、車両の所有者に変更があったことをインタフェースから入力してもよい。なお、車両の所有者に変更があったことをインタフェースから入力した場合も車両の所有者に変更があった場合に含まれる。
第2実施形態では、所有者管理装置200の制御部203が、所有者に変更がある可能性が高いと判断した場合に、暗号鍵を更新することの要否に関する確認をインタフェースに表示して、車両の所有者から暗号鍵更新に関する指示を受けるように構成されている。しかしながら、制御部203が、車両の所有者に変更があると判断していない場合であっても、車両の所有者は任意のタイミングで、車両の所有者に変更があったことをインタフェースから入力してもよい。なお、車両の所有者に変更があったことをインタフェースから入力した場合も車両の所有者に変更があった場合に含まれる。
本変形例によれば、レンタカーやカーシェアリングのように、車両の所有者自体に変更がない場合であっても、利用者が代わるごとに暗号鍵を手動で更新することができるため、前の利用者が車両に不正アクセスするのを防ぐことが可能となる。
(その他の実施形態)
第1実施形態、第2実施形態はいずれも、所有者管理装置200が車両の所有者に変更があったと判断した場合に、鍵管理装置300が新たな暗号鍵を生成して車両制御装置400に出力することにより、車両制御装置400は使用する暗号鍵を更新している。しかしながら、暗号鍵の生成は、必ずしも車両用システムにおいて行わなくてもよい。
第1実施形態、第2実施形態はいずれも、所有者管理装置200が車両の所有者に変更があったと判断した場合に、鍵管理装置300が新たな暗号鍵を生成して車両制御装置400に出力することにより、車両制御装置400は使用する暗号鍵を更新している。しかしながら、暗号鍵の生成は、必ずしも車両用システムにおいて行わなくてもよい。
例えば、所有者管理装置200が車両の所有者に変更があったと判断した場合には、制御部203は、車両の所有者に対して、セキュリティの更新が必要であることを通知してもよい。そして、その通知を受け取った所有者は、車両をディーラーに持ち込むことにより、ディーラーにて暗号鍵を更新してもよい。
なお、本開示の車両用という表現とは、車両に予め搭載されるもの、及び車両に後付けで搭載されるものや、車両に搭載された電子制御装置に対して信号を出力するもの、例えば、車外に設けられたサーバや、ディーラーにおいて使用される電子制御装置をも含む。また、本開示の車両用システムとは、車両に搭載されている電子制御装置から構成されるシステムや、当該システムの電子制御装置の一部が車外に設けられているものをも含む。S105,S106,S107,S109は本開示の暗号鍵生成更新方法の一例に相当する。S105,S106は本開示の暗号鍵生成方法の一例に相当する。S107,S109は本開示の暗号鍵更新方法の一例に相当する。
以上、本開示の各実施形態における車両用システム、及び、所有者管理装置、鍵管理装置、及び車両制御装置を含む電子制御装置について説明した。
各実施形態における電子制御装置の動作は、ブロック図及びフローチャートで方法の説明としても説明した。かかる方法は上述の物で実現できるだけでなく、非遷移的実体的記録媒体(コンピュータ読み取り可能な非一時的な記憶媒体ともよぶ)、例えば、RAM、ROM、フラッシュメモリ(以下、メモリとする)やハードディスク等の記録媒体に記録したプログラム、及びこれを実行する専用又は汎用CPU及びメモリ等を有するマイクロコンピュータとの組み合わせとしても実現できる。プログラムは、記録媒体を介さずにサーバから通信回線を経由して提供することもできる。これにより、プログラムのアップグレードを通じて常に最新の機能を提供することができる。また、マイクロコンピュータの数は1つでも複数でもよい。
本開示にかかる車両用システム及び電子制御装置は、主として自動車のセキュリティを確保するために用いられるものであるが、自動車以外の車両、例えば、二輪車、電動アシスト自転車や、船舶、航空機等のセキュリティを確保するために用いてもよい。さらに、本開示はこれらの用途に限られるものではない。また本開示において、電子制御装置は、暗号鍵を使用又は生成する他装置と通信可能であってもよい。
ここで、本出願に記載されるフローチャート、あるいは、フローチャートの処理は、複数のステップ(あるいはセクションと言及される)から構成され、各ステップは、たとえば、S101と表現される。さらに、各ステップは、複数のサブステップに分割されることができる、一方、複数のステップが合わさって一つのステップにすることも可能である。
以上、本開示の一態様に係る暗号鍵の処理を行う車両用システム及び電子制御装置の実施形態、構成、態様を例示したが、本開示に係る実施形態、構成、態様は、上述した各実施形態、各構成、各態様に限定されるものではない。例えば、異なる実施形態、構成、態様にそれぞれ開示された技術的部を適宜組み合わせて得られる実施形態、構成、態様についても本開示に係る実施形態、構成、態様の範囲に含まれる。
Claims (17)
- 暗号鍵を管理する第1の電子制御装置(300)と、
前記暗号鍵を使用する第2の電子制御装置(400)と、を備え、
前記第1の電子制御装置(300)は、
前記第1の電子制御装置及び前記第2の電子制御装置を備える車両の所有者に変更があった場合に前記暗号鍵を生成する鍵生成部(302)と、
前記第2の電子制御装置に前記暗号鍵を出力する鍵配布部(303)と、を有し、
前記第2の電子制御装置(400)は、
使用中の暗号鍵である第1の暗号鍵を記憶する鍵保持部(402)と、
前記鍵配布部から出力された前記暗号鍵である第2の暗号鍵を受信する鍵受信部(401)と、
前記鍵保持部に記憶されている前記第1の暗号鍵を、前記第2の暗号鍵に更新する鍵更新部(405)と、を有する、
車両用システム。 - 前記鍵保持部はさらに、第3の暗号鍵を記憶し、
前記第2の電子制御装置はさらに、前記第2の暗号鍵を受信した場合に、前記使用中の暗号鍵を前記第1の暗号鍵から前記第3の暗号鍵に切り替える鍵切替部(404)を備える、
請求項1記載の車両用システム。 - 前記車両の所有者に関する更新情報を受信する受信部(201)と、
前記更新情報を記憶する記憶部(202)と、
前記更新情報を受信したこと、前記記憶部を初期化したこと、又は、前記記憶部にさらに記憶された旧所有者に関する旧情報及び前記更新情報の内容に基づいて、前記車両の前記所有者に変更があったことを判断する処理部(203)と、
前記所有者に変更があったことを前記第1の電子制御装置に通知する送信部(204)と、
を有する第3の電子制御装置(200)をさらに備える、
請求項1記載の車両用システム。 - 記憶部に記憶される暗号鍵を使用する他装置と通信可能な電子制御装置であって、
前記電子制御装置を備える車両の所有者に変更があった場合に前記暗号鍵を生成する鍵生成部(302)と、
前記暗号鍵を受信した場合に前記記憶部に記憶される暗号鍵を更新する前記他装置に対し、前記暗号鍵を出力する鍵配布部(303)と、
を備える電子制御装置。 - 車両の所有者に変更があった場合に暗号鍵を生成する他装置と通信可能であり、前記暗号鍵を使用する電子制御装置であって、
使用中の暗号鍵である第1の暗号鍵を記憶する鍵保持部(402)と、
前記他装置から第2の暗号鍵を受信する鍵受信部(401)と、
前記鍵保持部に記憶されている前記第1の暗号鍵を、前記第2の暗号鍵に更新する鍵更新部(405)と、
を備える電子制御装置。 - 前記鍵保持部はさらに、第3の暗号鍵を記憶し、
前記電子制御装置はさらに、前記第2の暗号鍵を受信した場合に、前記使用中の暗号鍵を前記第1の暗号鍵から前記第3の暗号鍵に切り替える鍵切替部(404)を備える、
請求項5記載の電子制御装置。 - 前記車両は、前記所有者に暗号鍵更新の要否に関する確認を通知すると共に、前記所有者から前記暗号鍵更新の要否に関する指示を受信するインタフェースを備え、
前記鍵生成部は前記指示に基づいて前記暗号鍵を生成する、
請求項4記載の電子制御装置。 - 前記鍵更新部は、前記車両のイグニッションがオフからオンになったときに前記第1の暗号鍵を前記第2の暗号鍵に更新する、
請求項5記載の電子制御装置。 - 暗号鍵を管理する第1の電子制御装置(300)と、前記暗号鍵を使用する第2の電子制御装置(400)と、を備える車両用システム(100)において行われる暗号鍵生成更新方法であって、
前記第1の電子制御装置において、
前記第1の電子制御装置及び前記第2の電子制御装置を備える車両の所有者に変更があった場合に前記暗号鍵を生成することと、
前記第1の電子制御装置の鍵配布部から前記第2の電子制御装置に前記暗号鍵を出力することと、
前記第2の電子制御装置において、
前記鍵配布部から出力された前記暗号鍵である第2の暗号鍵を受信することと、
前記第2の電子制御装置の鍵保持部に記憶されている使用中の暗号鍵である第1の暗号鍵を、前記第2の暗号鍵に更新することと、
を含む、暗号鍵生成更新方法。 - 記憶部に記憶される暗号鍵を使用する他装置と通信可能な電子制御装置(300)において行われる暗号鍵生成方法であって、
前記電子制御装置を備える車両の所有者に変更があった場合に前記暗号鍵を生成することと、
前記暗号鍵を受信した場合に前記記憶部に記憶される暗号鍵を更新する前記他装置に対し、前記暗号鍵を出力することと、
を含む、暗号鍵生成方法。 - 車両の所有者に変更があった場合に暗号鍵を生成する他装置と通信可能であり、前記暗号鍵を使用する電子制御装置(400)において行われる暗号鍵更新方法であって、
前記他装置から第2の暗号鍵を受信することと、
鍵保持部に記憶されている使用中の暗号鍵である第1の暗号鍵を、前記第2の暗号鍵に更新することと、
を含む、暗号鍵更新方法。 - 暗号鍵を管理する第1の電子制御装置(300)と、前記暗号鍵を使用する第2の電子制御装置(400)と、を備える車両用システム(100)において行われる暗号鍵生成更新方法を実行するプログラムであって、
前記第1の電子制御装置において、
前記第1の電子制御装置及び前記第2の電子制御装置を備える車両の所有者に変更があった場合に前記暗号鍵を生成することと、
前記第1の電子制御装置の鍵配布部から前記第2の電子制御装置に前記暗号鍵を出力することと、
を実行する第1のプログラムと、
前記第2の電子制御装置において、
前記鍵配布部から出力された前記暗号鍵である第2の暗号鍵を受信することと、
前記第2の電子制御装置の鍵保持部に記憶されている使用中の暗号鍵である第1の暗号鍵を、前記第2の暗号鍵に更新することと、
を実行する第2のプログラムと、
を含む、暗号鍵生成更新プログラム。 - 記憶部に記憶される暗号鍵を使用する他装置と通信可能な電子制御装置(300)において行われる暗号鍵生成方法を実行するプログラムであって、
前記電子制御装置を備える車両の所有者に変更があった場合に前記暗号鍵を生成することと、
前記暗号鍵を受信した場合に前記記憶部に記憶される暗号鍵を更新する前記他装置に対し、前記暗号鍵を出力することと、
を含む、暗号鍵生成プログラム。 - 車両の所有者に変更があった場合に暗号鍵を生成する他装置と通信可能であり、前記暗号鍵を使用する電子制御装置(400)において行われる暗号鍵更新方法を実行するプログラムであって、
前記他装置から第2の暗号鍵を受信することと、
鍵保持部に記憶されている使用中の暗号鍵である第1の暗号鍵を、前記第2の暗号鍵に更新することと、
を含む、暗号鍵更新プログラム。 - 請求項12に記載の暗号鍵生成更新プログラムを記憶する、コンピュータ読み取り可能な非一時的な記憶媒体。
- 請求項13に記載の暗号鍵生成プログラムを記憶する、コンピュータ読み取り可能な非一時的な記憶媒体。
- 請求項14に記載の暗号鍵更新プログラムを記憶する、コンピュータ読み取り可能な非一時的な記憶媒体。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP18802621.5A EP3627756B1 (en) | 2017-05-16 | 2018-03-22 | Vehicular system for processing cipher key and electronic control device |
| US16/663,225 US11374747B2 (en) | 2017-05-16 | 2019-10-24 | Vehicular system for processing encryption key and electronic control device |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017097107A JP6855918B2 (ja) | 2017-05-16 | 2017-05-16 | 暗号鍵の処理を行う車両用システム及び電子制御装置 |
| JP2017-097107 | 2017-05-16 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/663,225 Continuation US11374747B2 (en) | 2017-05-16 | 2019-10-24 | Vehicular system for processing encryption key and electronic control device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2018211815A1 true WO2018211815A1 (ja) | 2018-11-22 |
Family
ID=64274237
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2018/011269 WO2018211815A1 (ja) | 2017-05-16 | 2018-03-22 | 暗号鍵の処理を行う車両用システム及び電子制御装置 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11374747B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP3627756B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6855918B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2018211815A1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113162959A (zh) * | 2020-01-23 | 2021-07-23 | 华为技术有限公司 | 车载设备的升级方法和装置 |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7111074B2 (ja) * | 2018-08-10 | 2022-08-02 | 株式会社デンソー | 車両用マスタ装置、セキュリティアクセス鍵の管理方法、セキュリティアクセス鍵の管理プログラム及び車両用電子制御システム |
| US11350256B2 (en) * | 2019-10-30 | 2022-05-31 | Aeris Communications, Inc. | Automated detection of change of ownership of assets |
| US20230188983A1 (en) * | 2020-04-30 | 2023-06-15 | Sensata Technologies, Inc. | Secure wireless protocol for wireless sensor networks |
| JP7380430B2 (ja) | 2020-06-01 | 2023-11-15 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、およびプログラム |
| JP7559415B2 (ja) * | 2020-08-06 | 2024-10-02 | 株式会社リコー | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラム、情報処理システム |
| WO2023000313A1 (zh) * | 2021-07-23 | 2023-01-26 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种密钥验证方法及相关装置 |
| EP4159555B1 (en) | 2021-09-29 | 2024-06-12 | Ningbo Geely Automobile Research & Development Co. Ltd. | Updating vehicle ownership authorizations |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005341528A (ja) * | 2004-04-28 | 2005-12-08 | Denso Corp | 通信システム、鍵配信装置、暗号処理装置、盗難防止装置 |
| JP2009182897A (ja) * | 2008-01-31 | 2009-08-13 | Sharp Corp | データ送信装置、通信システム、データ送信方法、通信プログラム、および該プログラムを記録する記録媒体 |
| JP2013138320A (ja) * | 2011-12-28 | 2013-07-11 | Denso Corp | 車載システム及び通信方法 |
| WO2016075869A1 (ja) * | 2014-11-13 | 2016-05-19 | パナソニック インテレクチュアル プロパティ コーポレーション オブ アメリカ | 鍵管理方法、車載ネットワークシステム及び鍵管理装置 |
| JP2016092811A (ja) | 2014-10-29 | 2016-05-23 | Kddi株式会社 | 鍵管理システム、鍵管理サーバ装置、管理装置、車両、鍵管理方法およびコンピュータプログラム |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4682903B2 (ja) | 2006-04-06 | 2011-05-11 | 株式会社デンソー | 車両用リモートサービスシステム |
| US8578153B2 (en) * | 2008-10-28 | 2013-11-05 | Telefonaktiebolaget L M Ericsson (Publ) | Method and arrangement for provisioning and managing a device |
| JP2011039712A (ja) * | 2009-08-07 | 2011-02-24 | Tokai Rika Co Ltd | カーシェアリングシステム |
| US9464905B2 (en) * | 2010-06-25 | 2016-10-11 | Toyota Motor Engineering & Manufacturing North America, Inc. | Over-the-air vehicle systems updating and associate security protocols |
| JP2012070167A (ja) * | 2010-09-22 | 2012-04-05 | Tokai Rika Co Ltd | 通信装置 |
| JP5703667B2 (ja) * | 2010-10-01 | 2015-04-22 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 認証システム及び認証方法 |
| EP2993608A1 (en) * | 2014-09-03 | 2016-03-09 | Gemalto Sa | A method for changing the ownership of a secure element |
| JP6183436B2 (ja) | 2015-10-08 | 2017-08-23 | 住友電気工業株式会社 | 車載機及び共通鍵の更新の契機を得る方法 |
| US20180012196A1 (en) * | 2016-07-07 | 2018-01-11 | NextEv USA, Inc. | Vehicle maintenance manager |
-
2017
- 2017-05-16 JP JP2017097107A patent/JP6855918B2/ja active Active
-
2018
- 2018-03-22 EP EP18802621.5A patent/EP3627756B1/en active Active
- 2018-03-22 WO PCT/JP2018/011269 patent/WO2018211815A1/ja unknown
-
2019
- 2019-10-24 US US16/663,225 patent/US11374747B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005341528A (ja) * | 2004-04-28 | 2005-12-08 | Denso Corp | 通信システム、鍵配信装置、暗号処理装置、盗難防止装置 |
| JP2009182897A (ja) * | 2008-01-31 | 2009-08-13 | Sharp Corp | データ送信装置、通信システム、データ送信方法、通信プログラム、および該プログラムを記録する記録媒体 |
| JP2013138320A (ja) * | 2011-12-28 | 2013-07-11 | Denso Corp | 車載システム及び通信方法 |
| JP2016092811A (ja) | 2014-10-29 | 2016-05-23 | Kddi株式会社 | 鍵管理システム、鍵管理サーバ装置、管理装置、車両、鍵管理方法およびコンピュータプログラム |
| WO2016075869A1 (ja) * | 2014-11-13 | 2016-05-19 | パナソニック インテレクチュアル プロパティ コーポレーション オブ アメリカ | 鍵管理方法、車載ネットワークシステム及び鍵管理装置 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP3627756A4 |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113162959A (zh) * | 2020-01-23 | 2021-07-23 | 华为技术有限公司 | 车载设备的升级方法和装置 |
| CN113162959B (zh) * | 2020-01-23 | 2023-06-30 | 华为技术有限公司 | 车载设备的升级方法和装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20200059359A1 (en) | 2020-02-20 |
| EP3627756A4 (en) | 2020-05-20 |
| EP3627756B1 (en) | 2021-12-29 |
| US11374747B2 (en) | 2022-06-28 |
| JP2018195932A (ja) | 2018-12-06 |
| EP3627756A1 (en) | 2020-03-25 |
| JP6855918B2 (ja) | 2021-04-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2018211815A1 (ja) | 暗号鍵の処理を行う車両用システム及び電子制御装置 | |
| US10592231B2 (en) | Vehicle information communication system | |
| CN106056702B (zh) | 用于移动电话遥控钥匙管理的系统和方法 | |
| WO2014148003A1 (ja) | 車載電子制御装置のプログラム書換システム及び車載中継装置 | |
| JP5886099B2 (ja) | 自動車用電子制御装置 | |
| WO2015080108A1 (ja) | プログラム更新システム及びプログラム更新方法 | |
| JP5900007B2 (ja) | 車両用データ通信認証システム及び車両用ゲートウェイ装置 | |
| US9672025B2 (en) | Encryption for telematics flashing of a vehicle | |
| CN107483393B (zh) | 车联网的通信方法、服务器及通信系统 | |
| JP6465258B1 (ja) | 制御装置、制御方法、およびコンピュータプログラム | |
| US11579865B2 (en) | Vehicle information communication system | |
| WO2017208890A1 (ja) | 制御装置、制御方法及びコンピュータプログラム | |
| WO2018230314A1 (ja) | 制御装置、制御方法、およびコンピュータプログラム | |
| JP6394678B2 (ja) | 制御装置、制御プログラムの更新可否の決定方法、及びコンピュータプログラム | |
| WO2018230084A1 (ja) | 更新制御装置、制御方法、およびコンピュータプログラム | |
| JP2002202895A (ja) | 車両基本機能制御プログラム更新装置 | |
| CN113645590B (zh) | 基于加密算法的远程控制车辆的方法、装置、设备及介质 | |
| CN115242634A (zh) | 软件升级方法、设备和存储介质 | |
| JP6274849B2 (ja) | 車両制御システム | |
| US10592457B2 (en) | Universal transponder interface with a databus docking station | |
| JP5783013B2 (ja) | 車載通信システム | |
| JP4798546B2 (ja) | 車載機器の設定システム | |
| JP6107716B2 (ja) | 車両制御装置及び車両用パスワード設定方法 | |
| JP2019074847A (ja) | 電子制御装置 | |
| JP2009033264A (ja) | 車両のデータ通信システム及び車両 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 18802621 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2018802621 Country of ref document: EP Effective date: 20191216 |