WO2017110884A1 - 超音波センサ - Google Patents
超音波センサ Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017110884A1 WO2017110884A1 PCT/JP2016/088130 JP2016088130W WO2017110884A1 WO 2017110884 A1 WO2017110884 A1 WO 2017110884A1 JP 2016088130 W JP2016088130 W JP 2016088130W WO 2017110884 A1 WO2017110884 A1 WO 2017110884A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- elastic member
- ultrasonic sensor
- main body
- bezel
- gap
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S7/00—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00
- G01S7/52—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00 of systems according to group G01S15/00
- G01S7/521—Constructional features
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R11/00—Arrangements for holding or mounting articles, not otherwise provided for
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R19/00—Wheel guards; Radiator guards, e.g. grilles; Obstruction removers; Fittings damping bouncing force in collisions
- B60R19/02—Bumpers, i.e. impact receiving or absorbing members for protecting vehicles or fending off blows from other vehicles or objects
- B60R19/48—Bumpers, i.e. impact receiving or absorbing members for protecting vehicles or fending off blows from other vehicles or objects combined with, or convertible into, other devices or objects, e.g. bumpers combined with road brushes, bumpers convertible into beds
- B60R19/483—Bumpers, i.e. impact receiving or absorbing members for protecting vehicles or fending off blows from other vehicles or objects combined with, or convertible into, other devices or objects, e.g. bumpers combined with road brushes, bumpers convertible into beds with obstacle sensors of electric or electronic type
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S15/00—Systems using the reflection or reradiation of acoustic waves, e.g. sonar systems
- G01S15/88—Sonar systems specially adapted for specific applications
- G01S15/93—Sonar systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes
- G01S15/931—Sonar systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes of land vehicles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R11/00—Arrangements for holding or mounting articles, not otherwise provided for
- B60R2011/0042—Arrangements for holding or mounting articles, not otherwise provided for characterised by mounting means
- B60R2011/0043—Arrangements for holding or mounting articles, not otherwise provided for characterised by mounting means for integrated articles, i.e. not substantially protruding from the surrounding parts
- B60R2011/0045—Arrangements for holding or mounting articles, not otherwise provided for characterised by mounting means for integrated articles, i.e. not substantially protruding from the surrounding parts with visible part, e.g. flush mounted
- B60R2011/0047—Arrangements for holding or mounting articles, not otherwise provided for characterised by mounting means for integrated articles, i.e. not substantially protruding from the surrounding parts with visible part, e.g. flush mounted using hidden fastening means
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S15/00—Systems using the reflection or reradiation of acoustic waves, e.g. sonar systems
- G01S15/88—Sonar systems specially adapted for specific applications
- G01S15/93—Sonar systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes
- G01S15/931—Sonar systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes of land vehicles
- G01S2015/937—Sonar systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes of land vehicles sensor installation details
- G01S2015/938—Sonar systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes of land vehicles sensor installation details in the bumper area
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an ultrasonic sensor.
- JP 2013-107493 A discloses an ultrasonic sensor as described above.
- the ultrasonic sensor includes a vibration body having a transmission / reception surface for transmitting and receiving ultrasonic waves, a cylindrical elastic member surrounding an outer surface of the vibration body, a main body portion including a housing portion for housing the vibration body and the elastic member, and an elastic member.
- An annular body that is provided so as to surround the member and is assembled to the main body in a state of being in contact with the front side of the attachment object, and is attached to the attachment object in a state of penetrating the attachment object.
- a vehicle equipped with the ultrasonic sensor described in Patent Document 1 may be washed using a high-pressure washing machine. At this time, water may enter the inside of the main body portion between the housing portion and the elastic member or between the elastic member and the vibrating body due to water pressure. At this time, the water pressure inside the main body portion increases, and the vibration body may be pushed out of the housing portion by the water pressure.
- the present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems, and a main object thereof is to provide an ultrasonic sensor that suppresses the intrusion of water into the main body.
- the present invention relates to an ultrasonic sensor that is attached to an attachment object in a state of passing through the attachment object, and includes a vibrating body having a transmission / reception surface that transmits and receives ultrasonic waves, and a vibration body that extends from the transmission / reception surface in a thickness direction.
- a cylindrical elastic member that surrounds the outer side surface and the inner side surface abuts on the outer side surface, and has a bottomed accommodating portion that accommodates the vibrating body and the elastic member except for some protruding portions on the transmission / reception surface side.
- a main body, and an annular body that is provided so as to surround the protruding portion of the elastic member and is assembled to the main body in a state of being in contact with the front side of the object to be attached.
- a gap is provided between the inner surface of the annular body facing the side surface.
- FIG. 1 It is a side view which shows the state which attached the ultrasonic sensor to the bumper.
- (a) is a front view of a sensor main body.
- (b) is a right side view of the sensor body.
- (c) is a top view of the sensor body.
- (d) is a rear view of the sensor body. It is AA sectional drawing of Fig.2 (a). It is sectional drawing of a vibrating body.
- (a) is a front view of a bezel.
- (b) is a left side view of the bezel.
- (c) is a rear view of a bezel.
- (d) is a top view of the bezel.
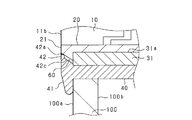
- (e) is a bottom view of the bezel. It is an expanded sectional view of the front end part of a bezel.
- the ultrasonic sensor according to the first embodiment will be described.
- the ultrasonic sensor is attached to a bumper of a vehicle and is used to detect an object around the vehicle.
- FIG. 1 is a side view of the ultrasonic sensor of the present embodiment attached to a bumper 100 that is an attachment object.
- FIG. 1 shows only the bumper 100 in cross section.
- the ultrasonic sensor is fixed in the hole 101 of the bumper 100.
- the ultrasonic sensor has a sensor body 200 and an annular bezel 40.
- the ultrasonic sensor is fixed to the bumper 100 by inserting the bezel 40 into the hole 101 from the front side 100 a of the bumper 100 and then inserting the sensor body 200 into the bezel 40 from the back side 100 b of the bumper 100.
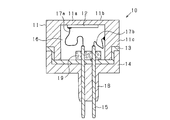
- the sensor body 200 of the ultrasonic sensor has a body 30 in which the vibrating body 10 is housed.
- the vibrating body 10 includes a housing 11, a piezoelectric element 12, a spacer 13, a base 14, and a connection pin 15.
- the housing 11 is made of a conductive material, has a bottomed cylindrical shape, and an internal space 16 is formed therein.
- a piezoelectric element 12 is attached to the inner surface of the bottom 11 a of the housing 11.
- the outer surface of the bottom 11a is a transmission / reception surface 11b.
- Aluminum is used as the conductive material of the housing 11.
- the transmission / reception surface 11b is circular.
- the piezoelectric element 12 is made of piezoelectric ceramics, for example, lead zirconate titanate ceramics, and has electrodes on both front and back surfaces.
- One electrode of the piezoelectric element 12 is electrically connected to one of the pair of connection pins 15 by a lead 17a.
- the other electrode of the piezoelectric element 12 is attached to the bottom 11a of the housing 11 with a conductive adhesive, for example, and connected to the lead 17b through the housing 11, and then electrically connected to the other of the pair of connection pins 15.
- the internal space 16 of the housing 11 is filled with a vibration isolating material, for example, silicone rubber, so that unnecessary vibration transmitted from the transmission / reception surface 11b to the connection pin 15 is suppressed.
- the spacer 13 is disposed between the opening of the housing 11 and the base 14.
- the spacer 13 is an elastic body for suppressing unnecessary vibration generated in the cylindrical portion 11 c of the housing 11 due to vibration of the bottom 11 a of the housing 11 from being transmitted to the base 14 to which the connection pin 15 is fixed.
- it is made of silicone rubber.
- the base 14 is fitted to the outer peripheral surface on the opening side of the housing 11 via a spacer 13 and is fixed to the housing 11.
- the base 14 is made of an insulating material, for example, a synthetic resin such as ABS resin.
- the base 14 is provided with a protection portion 18 for covering the connection pin 15 so as to protrude toward the circuit board 32, and the connection pin 15 is disposed so as to penetrate the protection portion 18.
- the connection pin 15 is insert-molded so that a part of the connection pin 15 is embedded and fixed in the base 14.
- connection pin 15 is made of a conductive material mainly composed of copper, for example, and is composed of a rod having a thickness of 0.5 mm ⁇ , for example.
- the vibrating body 10 is provided with a foamed elastic body 19 made of, for example, foamed silicone.
- the foamed elastic body 19 is for suppressing transmission of vibration to the base 14, and the connection pin 15 is disposed so as to penetrate the foamed elastic body 19.
- the housing 11, the spacer 13, the base 14, and the foamed elastic body 19 are bonded to each other with an adhesive, for example, a silicone-based adhesive, so that the vibration body 10 having an integral structure is configured.
- the vibrating body 10 configured as described above is assembled into a hollow main body 30 made of synthetic resin, with the elastic member 20 covering a part of the side surface and the bottom surface.
- the elastic member 20 is made of an elastic resin, for example, silicone rubber.
- the elastic member 20 has a cylindrical shape, and an enlarged flange portion 21 is formed at the front end which is one end of the length.
- a narrowed bottom 22 is formed at the rear end, which is the other end of the length.
- the outer peripheral surface of the flange portion 21 is formed as a tapered surface whose outer dimension, that is, the diameter gradually decreases toward the end surface of the front end portion. That is, the shape of the flange portion 21 can be said to be tapered. Further, the surface opposite to the front end portion of the flange portion 21 is formed perpendicular to the outer surface of the elastic member 20.
- the diameter of the inner surface of the elastic member 20 is the same as the outer diameter of the housing 11 of the vibrating body 10.
- the vibrating body 10 is accommodated in the cylinder of the elastic member 20, and the outer surface of the vibrating body 10, that is, the outer surface of the housing 11 abuts on the inner surface of the elastic member 20. Further, the bottom surface of the vibrating body 10 abuts on the bottom 22 of the elastic member 20.
- the diameter of the inner surface of the elastic member 20 may be smaller than the outer diameter of the housing 11 of the vibrating body 10. By doing so, the contact force between the elastic member 20 and the vibrating body 10 when the vibrating body 10 is accommodated can be improved.
- the length from the front end portion of the elastic member 20 to the inner surface of the bottom 22 is equal to the length from the transmission / reception surface 11b of the vibrating body 10 to the bottom surface. Therefore, when the vibrating body 10 is accommodated in the elastic member 20, the transmission / reception surface 11 b of the vibrating body 10 and the front end portion of the elastic member 20 are substantially flush with each other.
- the main body 30 is a hollow, substantially rectangular parallelepiped.
- a cylindrical side wall portion 31 having an open upper end is provided on one surface of the main body 30, and the inside of the side wall portion 31 functions as a housing portion 31 a for the vibrating body 10 and the elastic member 20.
- the inner diameter of the side wall portion 31 is equal to the outer diameter of the elastic member 20.
- the outer diameter of the side wall portion 31 is larger than the maximum diameter of the flange portion 21.
- the length from the opening surface of the side wall portion 31 to the inner bottom surface is equal to the length from the surface opposite to the front end portion of the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 to the bottom surface.
- the surface opposite to the front end portion of the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 abuts on the upper end of the side wall portion 31. Is in contact with the inner bottom surface of the side wall portion 31.
- the inner side surface of the side wall portion 31 is in contact with the outer side surface of the elastic member 20. At this time, a part of the upper end of the side wall portion 31 is covered with the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20.
- the inner diameter of the side wall 31 may be smaller than the outer diameter of the elastic member 20 and larger than the outer diameter of the housing 11 of the vibrating body 10. By doing so, the contact force between the side wall 31 and the elastic member 20 when the vibrating body 10 and the elastic member 20 are accommodated in the side wall 31 can be improved.
- the main body 30 is provided with a guide 33 for positioning the connection pin 15 with respect to the connection position of the circuit board 32.
- the guide 33 is configured in a plate shape that divides the internal space of the main body 30 into an arrangement space for the vibrating body 10 and an arrangement space for the circuit board 32, and a positioning hole 33 a into which the connection pin 15 and the protection portion 18 are inserted. Is provided.
- the elastic body 20 has an elastic member 20 in contact with the outer peripheral surface thereof, and a foamed elastic body 34 serving as an elastic body that suppresses vibration is disposed below the base 14 and is assembled to the main body 30.
- connection pin 15 is inserted into the positioning hole 33 a of the guide 33, and the tip of the connection pin 15 is inserted into the circuit board 32. Then, the electrical connection between the tip of the connection pin 15 and the circuit board 32 is made by soldering or the like.
- the transmission / reception surface 11 b of the vibrating body 10 is exposed from the side wall portion 31 of the main body 30, and the ultrasonic wave emitted from the vibrating body 10 is transmitted to the outside of the main body 30.
- the foamed elastic body 34 is made of foamed silicone, similar to the foamed elastic body 19 disposed in the housing 11 of the vibrating body 10, and the connection pin 15 and the protection portion 18 penetrate therethrough.
- the foamed elastic body 34 is provided with a cut, and the protection portion 18 can be inserted into the cut.
- the base 14, the elastic member 20, and the foamed elastic body 34 of the vibrating body 10 are bonded and fixed to each other with a silicone-based adhesive.
- a moisture-proof member 35 is filled in a hollow portion where the circuit board 32 is arranged in the main body 30 partitioned by the guide 33.
- a silicone resin or a urethane resin can be applied as the moisture-proof member 35.
- a silicone resin is applied as the moisture-proof member 35.
- an external output terminal 36 for outputting from the circuit board 32 to the outside is provided, and one end side of the external output terminal 36 is exposed from a connector 37 formed on one surface of the main body 30. It is said that.
- a locking portion 38 is provided on the upper surface of the main body 30, and a receiving portion 39 is provided on the bottom surface thereof.
- the locking portion 38 is formed so as to protrude from the upper surface of the main body 30 in the same direction as the side wall portion 31, and is used for fixing to the bezel 40.
- the locking portion 38 has a so-called snap-fit configuration having a rod-like portion 38a and a claw portion 38b.
- the rod-shaped portion 38a is projected from the upper surface of the main body 30 in the same direction as the side wall portion 31, and a claw portion 38b is formed on the side wall portion 31 side at the tip position of the rod-shaped portion 38a.
- the receiving portion 39 has a frame shape provided so as to protrude from the main body 30, and this is also used for fixing to the bezel 40.
- the protruding direction of the side wall 31 is the direction in which the sensor main body 200 is inserted into the bezel 40.
- FIGS. 5A to 5D show the structure of the bezel 40
- FIG. 6 shows an enlarged cross section of the front end portion of the bezel 40.
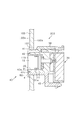
- the bezel 40 is made of a substantially cylindrical member made of synthetic resin or the like, for example.
- the shape and size of the hollow cylindrical portion 40a of the bezel 40 correspond to the shape of the side wall portion 31 in the sensor body 200, and the side wall portion 31 is inserted into the hollow portion.
- An outer flange 41 having an enlarged diameter is formed on the outer peripheral surface of the front end which is one end of the bezel 40 in the axial direction.
- a narrow inner flange 42 is formed on the inner peripheral surface of the front end.
- the outer peripheral surface of the outer flange 41 is formed so that its diameter gradually increases from the end surface of the front end portion. That is, the outer flange 41 can be said to be tapered.
- the inner flange 42 includes an outer surface portion 42a in which the diameter of the inner peripheral surface is constant in the axial direction, and a tapered portion 42b in which the diameter gradually increases from the front end side and the inner peripheral surface is a tapered surface. Is done.
- the angle formed between the inner peripheral surface of the tapered portion 42b and the central axis is equal to the angle formed between the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 and the central axis. That is, on the plane passing through the central axis, the inner peripheral surface of the tapered portion 42 b and the outer peripheral surface of the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 are formed in parallel.
- concave portions 42c and convex portions 42d are alternately formed in the circumferential direction, thereby forming a rectangular wave-shaped inner peripheral surface.
- the diameter between the opposing convex portions 42 d is formed to be equal to the outer diameter of the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20. That is, when the side wall portion 31 is inserted into the bezel 40, the convex portion 42 d of the bezel 40 and the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 come into contact with each other, and the space between the outer surface portion 42 a of the bezel 40 and the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20.
- a gap 60 is formed between the concave portion 42 c of the bezel 40 and the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20.
- the other end of the bezel 40 in the axial direction is provided with a locking portion 43 that protrudes from the cylindrical portion.
- the locking portion 43 is a so-called snap fit, and has a claw portion 43 a formed at the tip, and is engaged with the receiving portion 39 by being inserted into the hole of the receiving portion 39 of the main body 30.
- a locking hole 44 is formed on the upper surface of the bezel 40.
- the locking hole 44 has a rectangular shape when viewed from the front, and is for inserting the claw portion 38b of the locking portion 38 provided in the main body 30 described above. When the claw portion 38 b of the locking portion 38 is inserted into the locking hole 44, the claw portion 38 b is caught on the inner wall of the locking hole 44.
- the left and right sides of the bezel 40 are provided with anti-falling claws 45.
- the removal preventing claw 45 is formed at a position considering the thickness of the bumper 100 and is provided at a position spaced from the end face of the outer flange 41 by the thickness of the bumper 100 or slightly larger than that.
- the removal prevention claw 45 is provided to prevent the bezel 40 from coming off the bumper 100.
- a plurality of, for example, four metal springs 50 are arranged on the bezel 40 at equal intervals.
- the shape of the metal spring 50 is a convex shape toward the radially outer side of the bezel 40. That is, when stress is applied to the metal spring 50 from the radially outer side of the bezel 40, the metal spring 50 is elastically deformed and applies stress to the inner surface of the bezel 40.
- the bezel 40 is inserted into the hole 101 of the bumper 100 from one side of the bumper 100, that is, from the front side 100 a of the bumper 100.
- the removal preventing claw 45 is inserted until it enters the back side 100 b of the bumper 100.
- the opening end of the hole 101 of the bumper 100 and the metal spring 50 come into contact with each other.
- the metal spring 50 is elastically deformed and bent by the opening end of the hole 101 of the bumper 100, and stress is applied to the inner surface of the bezel 40.
- the side wall portion 31 of the main body 30 is inserted into the hollow portion of the bezel 40 from the opposite side of the bumper 100, that is, from the back side 100b of the bumper 100.
- the claw portion 43 a comes into contact with the inner wall of the receiving portion 39 and is elastically deformed and inserted into the receiving portion 39.
- the claw portion 43a and the receiving portion 39 are engaged, and the assembly is completed.
- the claw portion 38b of the locking portion 38 contacts the outer wall surface of the bezel 40, and the rod-like portion 38a is elastically deformed.
- the elastically deformed portion returns to the original state, and the locking portion 38 engages with the locking hole 44.
- FIG. 8 shows a cross-sectional view of the ultrasonic sensor thus attached to the bumper 100
- FIG. 9 shows an enlarged cross-sectional view of the vicinity of the front end portion.
- the outer flange 41 of the bezel 40 contacts the bumper 100
- the inner flange 42 of the bezel 40 contacts the upper end of the side wall portion 31 of the main body 30.
- the inner diameter of the outer surface portion 42 a of the inner flange 42 of the bezel 40 is constant, and the inner diameter of the concave portion 42 c of the inner flange 42 of the bezel 40 is larger than the outer diameter of the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20. Therefore, a gap 60 is generated between the inner flange 42 of the bezel 40 and the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20. Further, as described above, the angle between the taper portion 42b of the inner flange 42 of the bezel 40 and the central axis is equal to the angle between the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 and the central axis.
- the width of the gap 60 formed between the tapered portion 42b and the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 is constant in the central axis direction.
- the inner diameter of the convex portion 42d of the inner flange 42 of the bezel 40 is made equal to the outer diameter of the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20, the convex portion 42d and the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 come into contact with each other. It will be.
- FIG. 10 shows a flow path when water is discharged from the front side 100a of the bumper 100 to the ultrasonic sensor attached to the bumper 100 in this way.
- the flow paths are indicated by arrows.
- Water enters the gap 60 between the outer surface portion 42 a and the flange portion 21, and the water pressure causes at least one of deformation of the flange portion 21 and displacement of the entire sensor body 200, and water enters the gap 60.
- the side wall 31 of the main body 30 is pushed toward the inner side of the bumper 100 by water pressure, and the inner flange 42 of the bezel 40 and the upper end of the side wall 31 of the main body 30 are separated from each other. Therefore, water passes between the inner flange 42 of the bezel 40 and the side wall portion 31 of the main body 30 through the gap 60 and flows out of the main body 30.
- the water pressure is applied not only to the side wall portion 31 but also to the elastic member 20.
- the contact force between the elastic member 20 and the vibrating body 10 is increased by the water pressure, and water can be prevented from entering between the vibrating body 10 and the elastic member 20.
- the contact force between the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 and the upper end of the side wall portion 31 is also increased, and water can be prevented from entering between the elastic member 20 and the main body 30.
- the housing 11 of the vibrating body 10 is chamfered at the connecting portion between the end portion of the bottom 11a and the end portion of the cylindrical portion 11c to form an arc shape.
- a gap may be formed between the vibrating body 10 and the elastic member 20, and water may enter the main body 30 through the gap.
- the gap 60 between the inner flange 42 of the bezel 40 and the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 in the radial direction of the vibrating body 10, the elastic member 20, and the bezel 40 that is, the contact direction, 10 and the gap between the elastic member 20.
- the ultrasonic sensor according to this embodiment has the following effects.
- the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 is tapered, when the water pressure is applied to the gap 60, the elastic member 20 is pressed against the vibrating body 10 by the water pressure. Therefore, it is possible to further suppress the intrusion of water between the vibrating body 10 and the elastic member 20.
- a gap 60 can be formed by the concave portions 42c between the convex portions 42d.
- the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 is tapered so that the inner dimension increases as the distance from the transmission / reception surface 11b increases, and the inner flange 42 of the bezel 40 increases as the outer dimension increases as the distance from the transmission / reception surface 11b increases. Accordingly, the gap 60 functioning as a water flow path serves as a flow path that guides water to the outside of the main body 30, and thus can more suitably prevent water from entering the main body 30.
- the bezel 40 is attached to the bumper 100 from the front side 100a, and the main body 30 is attached from the back side 100b. In this case, if the main body 30 is removed, the inside of the bezel 40 can be exposed, and even if a foreign object or the like enters the gap 60, it can be easily removed.
- the bezel 40 is integrated with the main body 30 by the tube portion 40a being assembled to the side wall portion 31 of the main body 30, and thereby, rattling with respect to the main body 30 is suppressed in the radial direction.
- the portion of the elastic member 20 facing the bezel 40 has a small dimension in the thickness direction of the sensor, but a uniform gap 60 is formed in the circumferential direction by the coupling of the cylindrical portion 40a and the side wall portion 31. it can.
- the concave portion 42c and the convex portion 42d are alternately provided on the inner flange 42 of the bezel 40 so that the convex portion 42d and the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 are in contact with each other. It is not necessary to provide the concave portion 42c and the convex portion 42d.
- the gap 60 is between the bezel 40 and the elastic member 20. May be formed.
- the gap 60 is formed between the bezel 40 and the elastic member 20 by providing the front end portion of the bezel 40 with a concave portion 42c and a convex portion 42d having a rectangular wave shape in the circumferential direction.
- the uneven shape is not limited to this, and any shape may be used as long as the gap 60 is generated between the bezel 40 and the elastic member 20 when the case is assembled to the bezel 40.
- triangular wave irregularities may be provided in the circumferential direction.
- the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 and the inner flange 42 of the bezel 40 are both tapered, but only one of the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 and the inner flange 42 of the bezel 40 may be tapered. . Further, none of them may be tapered.
- the concave portions 42c and the convex portions 42d are alternately provided on the inner flange 42 of the bezel 40, but the concave portions and the convex portions may be alternately provided on the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20. Further, the inner flange 42 of the bezel 40 and the flange portion 21 of the elastic member 20 may be provided with recesses and protrusions alternately.
- the ultrasonic sensor is attached to the bumper 100 of the vehicle, but the attachment target of the ultrasonic sensor is not limited to the bumper 100, and may be attached to other parts of the vehicle. Further, the attachment object may be other than the vehicle.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Acoustics & Sound (AREA)
- Measurement Of Velocity Or Position Using Acoustic Or Ultrasonic Waves (AREA)
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2018127140A RU2696405C1 (ru) | 2015-12-25 | 2016-12-21 | Ультразвуковой датчик |
| DE112016005983.3T DE112016005983B4 (de) | 2015-12-25 | 2016-12-21 | Ultraschallsensor |
| US16/064,681 US11156703B2 (en) | 2015-12-25 | 2016-12-21 | Ultrasonic sensor |
| CN201680075252.8A CN108431627B (zh) | 2015-12-25 | 2016-12-21 | 超声波传感器 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015254447A JP6443322B2 (ja) | 2015-12-25 | 2015-12-25 | 超音波センサ |
| JP2015-254447 | 2015-12-25 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017110884A1 true WO2017110884A1 (ja) | 2017-06-29 |
Family
ID=59089457
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2016/088130 Ceased WO2017110884A1 (ja) | 2015-12-25 | 2016-12-21 | 超音波センサ |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11156703B2 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6443322B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN108431627B (enExample) |
| DE (1) | DE112016005983B4 (enExample) |
| RU (1) | RU2696405C1 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2017110884A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102015212599B3 (de) * | 2015-07-06 | 2016-06-23 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Ultraschallsensorvorrichtung zur Anordnung an einem Verkleidungsbauteil eines Fahrzeugs |
| JP6443322B2 (ja) | 2015-12-25 | 2018-12-26 | 株式会社デンソー | 超音波センサ |
| JP6611992B2 (ja) * | 2017-05-16 | 2019-11-27 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 超音波センサ装置及び障害物検知装置 |
| JP6870594B2 (ja) | 2017-11-28 | 2021-05-12 | 株式会社デンソー | 超音波センサ |
| JP7024662B2 (ja) * | 2018-08-24 | 2022-02-24 | 株式会社デンソー | リテーナ部材 |
| DE102018127418A1 (de) * | 2018-11-02 | 2020-05-07 | Brose Fahrzeugteile Se & Co. Kommanditgesellschaft, Bamberg | Traganordnung für eine Steuerung eines Kraftfahrzeugs |
| JP7230453B2 (ja) * | 2018-11-20 | 2023-03-01 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 車両用センサの搭載構造 |
| CN110673149A (zh) * | 2019-10-22 | 2020-01-10 | 江苏理工学院 | 一种基于电动汽车辅助驾驶用雷达测距报警装置 |
| DE102020002912B4 (de) | 2020-05-14 | 2022-01-27 | Daimler Ag | Sensoranordnung zum Selbstpositionieren eines Sensors in einem Bauteil eines Fahrzeugs und Verfahren zur Montage des Sensors |
| US11884223B2 (en) * | 2021-12-01 | 2024-01-30 | Google Llc | Ground vehicle bumper system |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007284035A (ja) * | 2006-03-23 | 2007-11-01 | Denso Corp | 超音波センサ |
| US20130009528A1 (en) * | 2011-01-28 | 2013-01-10 | Zhitao Li | Reversing Radar Sensor Component |
| JP2014098579A (ja) * | 2012-11-13 | 2014-05-29 | Panasonic Corp | 超音波センサ |
| EP2869081A1 (en) * | 2013-11-04 | 2015-05-06 | Tung Thih Electronic Co., Ltd. | Parking sensor device |
Family Cites Families (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3850326A (en) * | 1973-01-11 | 1974-11-26 | Medical Plastics Pty Ltd | Safety closure |
| US8060282B2 (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 2011-11-15 | Automotive Technologies International, Inc. | Vehicle component control methods and systems based on vehicle stability |
| US20080046149A1 (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 2008-02-21 | Automotive Technologies International, Inc. | Vehicle Component Control Methods and Systems Based on Vehicle Stability |
| US20080161989A1 (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 2008-07-03 | Automotive Technologies International, Inc. | Vehicle Diagnostic or Prognostic Message Transmission Systems and Methods |
| US5729077A (en) * | 1995-12-15 | 1998-03-17 | The Penn State Research Foundation | Metal-electroactive ceramic composite transducer |
| CN1779482B (zh) * | 2004-11-26 | 2010-04-21 | 中国船舶重工集团公司第七一五研究所 | 水声超宽带组合声阵与发射的方法及其装置 |
| JP4438667B2 (ja) | 2005-03-29 | 2010-03-24 | 株式会社デンソー | 超音波センサ及び超音波振動子 |
| CN2802519Y (zh) * | 2005-07-06 | 2006-08-02 | 中国科学院声学研究所 | 一种小型压电陶瓷水听器 |
| HK1117990A2 (zh) * | 2007-10-25 | 2009-01-23 | The Sunrider Corporation | 安全密封的貯存室蓋 |
| DE102009046972A1 (de) * | 2009-11-23 | 2011-05-26 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Ultraschallsensor |
| CN102156277A (zh) | 2011-01-28 | 2011-08-17 | 广东铁将军防盗设备有限公司 | 倒车雷达传感器组件 |
| JP5804907B2 (ja) | 2011-11-21 | 2015-11-04 | 日本セラミック株式会社 | 超音波送受信器 |
| WO2013100142A1 (ja) * | 2011-12-28 | 2013-07-04 | パナソニック株式会社 | 超音波センサ |
| DE102012002760A1 (de) * | 2012-02-11 | 2013-08-14 | Volkswagen Aktiengesellschaft | Anordnung an einem Bauteil eines Kraftfahrzeuges |
| CN104198593B (zh) * | 2014-08-26 | 2016-06-29 | 中国船舶重工集团公司第七一五研究所 | 一种高静水压低频校准腔体及测试方法 |
| JP6443322B2 (ja) | 2015-12-25 | 2018-12-26 | 株式会社デンソー | 超音波センサ |
-
2015
- 2015-12-25 JP JP2015254447A patent/JP6443322B2/ja active Active
-
2016
- 2016-12-21 RU RU2018127140A patent/RU2696405C1/ru active
- 2016-12-21 WO PCT/JP2016/088130 patent/WO2017110884A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2016-12-21 US US16/064,681 patent/US11156703B2/en active Active
- 2016-12-21 DE DE112016005983.3T patent/DE112016005983B4/de active Active
- 2016-12-21 CN CN201680075252.8A patent/CN108431627B/zh active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007284035A (ja) * | 2006-03-23 | 2007-11-01 | Denso Corp | 超音波センサ |
| US20130009528A1 (en) * | 2011-01-28 | 2013-01-10 | Zhitao Li | Reversing Radar Sensor Component |
| JP2014098579A (ja) * | 2012-11-13 | 2014-05-29 | Panasonic Corp | 超音波センサ |
| EP2869081A1 (en) * | 2013-11-04 | 2015-05-06 | Tung Thih Electronic Co., Ltd. | Parking sensor device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20190004161A1 (en) | 2019-01-03 |
| RU2696405C1 (ru) | 2019-08-01 |
| US11156703B2 (en) | 2021-10-26 |
| CN108431627A (zh) | 2018-08-21 |
| JP6443322B2 (ja) | 2018-12-26 |
| DE112016005983T5 (de) | 2018-09-20 |
| DE112016005983B4 (de) | 2021-04-22 |
| JP2017116478A (ja) | 2017-06-29 |
| CN108431627B (zh) | 2021-12-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6443322B2 (ja) | 超音波センサ | |
| JP4893322B2 (ja) | 超音波センサ | |
| US11474239B2 (en) | Ultrasonic wave sensor | |
| JP4742924B2 (ja) | 超音波センサ | |
| JP4720587B2 (ja) | 超音波センサ | |
| CN1841087B (zh) | 超声传感器 | |
| US20090223296A1 (en) | Attachment structure for ultrasonic sensor | |
| US10288730B2 (en) | Ultrasonic sensor | |
| JP4742923B2 (ja) | 超音波センサ | |
| CN107367732B (zh) | 超声波传感器 | |
| JP5195572B2 (ja) | 超音波センサ | |
| JP5984082B2 (ja) | 超音波センサ | |
| US7628076B2 (en) | Ultrasound sensor | |
| JP4640223B2 (ja) | 超音波センサ | |
| JP2012181147A (ja) | 超音波センサ | |
| WO2018164153A1 (ja) | 超音波センサ | |
| KR20150058895A (ko) | 차량용 초음파 센서 | |
| KR20180055172A (ko) | 차량용 감지센서 | |
| KR20160013683A (ko) | 차량용 감지센서 | |
| US11049483B2 (en) | Acoustic sensor having a housing and a diaphragm element situated on this housing | |
| KR102326056B1 (ko) | 차량용 감지센서 | |
| JP2013024846A (ja) | 超音波センサ | |
| KR20240152383A (ko) | 차량용 초음파 센서 | |
| WO2019131663A1 (ja) | 液面検出装置 | |
| JP2019117183A (ja) | 液面検出装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16878771 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 112016005983 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 16878771 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |