WO2015099121A1 - 吸収性物品の製造方法 - Google Patents
吸収性物品の製造方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015099121A1 WO2015099121A1 PCT/JP2014/084507 JP2014084507W WO2015099121A1 WO 2015099121 A1 WO2015099121 A1 WO 2015099121A1 JP 2014084507 W JP2014084507 W JP 2014084507W WO 2015099121 A1 WO2015099121 A1 WO 2015099121A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- absorber
- recess
- absorbent
- sheet
- liquid
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/15577—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing
- A61F13/15804—Plant, e.g. involving several steps
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/15577—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing
- A61F13/15699—Forming webs by bringing together several webs, e.g. by laminating or folding several webs, with or without additional treatment of the webs
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/15577—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing
- A61F13/15707—Mechanical treatment, e.g. notching, twisting, compressing, shaping
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/15577—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing
- A61F13/15707—Mechanical treatment, e.g. notching, twisting, compressing, shaping
- A61F13/15747—Folding; Pleating; Coiling; Stacking; Packaging
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/45—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape
- A61F13/47—Sanitary towels, incontinence pads or napkins
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/51—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the outer layers of the pads
- A61F13/511—Topsheet, i.e. the permeable cover or layer facing the skin
- A61F13/51104—Topsheet, i.e. the permeable cover or layer facing the skin the top sheet having a three-dimensional cross-section, e.g. corrugations, embossments, recesses or projections
- A61F13/51108—Topsheet, i.e. the permeable cover or layer facing the skin the top sheet having a three-dimensional cross-section, e.g. corrugations, embossments, recesses or projections the top sheet having corrugations or embossments having one axis relatively longer than the other axis, e.g. forming channels or grooves in a longitudinal direction
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
- A61F13/534—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad
- A61F13/535—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad inhomogeneous in the plane of the pad, e.g. core absorbent layers being of different sizes
- A61F13/536—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having an inhomogeneous composition through the thickness of the pad inhomogeneous in the plane of the pad, e.g. core absorbent layers being of different sizes having discontinuous areas of compression
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C59/00—Surface shaping of articles, e.g. embossing; Apparatus therefor
- B29C59/007—Forming single grooves or ribs, e.g. tear lines, weak spots
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C59/00—Surface shaping of articles, e.g. embossing; Apparatus therefor
- B29C59/02—Surface shaping of articles, e.g. embossing; Apparatus therefor by mechanical means, e.g. pressing
- B29C59/022—Surface shaping of articles, e.g. embossing; Apparatus therefor by mechanical means, e.g. pressing characterised by the disposition or the configuration, e.g. dimensions, of the embossments or the shaping tools therefor
- B29C59/025—Fibrous surfaces with piles or similar fibres substantially perpendicular to the surface
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C65/00—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor
- B29C65/48—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor using adhesives, i.e. using supplementary joining material; solvent bonding
- B29C65/4805—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor using adhesives, i.e. using supplementary joining material; solvent bonding characterised by the type of adhesives
- B29C65/481—Non-reactive adhesives, e.g. physically hardening adhesives
- B29C65/4815—Hot melt adhesives, e.g. thermoplastic adhesives
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/15577—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing
- A61F13/15707—Mechanical treatment, e.g. notching, twisting, compressing, shaping
- A61F2013/15715—Shaping or making outer layers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29K—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASSES B29B, B29C OR B29D, RELATING TO MOULDING MATERIALS OR TO MATERIALS FOR MOULDS, REINFORCEMENTS, FILLERS OR PREFORMED PARTS, e.g. INSERTS
- B29K2105/00—Condition, form or state of moulded material or of the material to be shaped
- B29K2105/06—Condition, form or state of moulded material or of the material to be shaped containing reinforcements, fillers or inserts
- B29K2105/08—Condition, form or state of moulded material or of the material to be shaped containing reinforcements, fillers or inserts of continuous length, e.g. cords, rovings, mats, fabrics, strands or yarns
- B29K2105/0809—Fabrics
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29K—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASSES B29B, B29C OR B29D, RELATING TO MOULDING MATERIALS OR TO MATERIALS FOR MOULDS, REINFORCEMENTS, FILLERS OR PREFORMED PARTS, e.g. INSERTS
- B29K2995/00—Properties of moulding materials, reinforcements, fillers, preformed parts or moulds
- B29K2995/0037—Other properties
- B29K2995/0068—Permeability to liquids; Adsorption
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29L—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS B29C, RELATING TO PARTICULAR ARTICLES
- B29L2031/00—Other particular articles
- B29L2031/48—Wearing apparel
- B29L2031/4871—Underwear
- B29L2031/4878—Diapers, napkins
Definitions
- the present invention mainly relates to absorbent articles used for incontinence pads, sanitary napkins, vaginal sheets, medical pads, toiletries, disposable diapers, etc., and grooves along the longitudinal direction on the surface side of the absorbent body
- the present invention relates to a method for manufacturing an absorbent article in which is formed.
- an absorbent body is interposed between a liquid-impermeable back sheet such as a polyethylene sheet or a polyethylene sheet-laminated nonwoven fabric and a liquid-permeable surface sheet such as a nonwoven fabric or a liquid-permeable plastic sheet. It has been known.
- the middle and high portions formed by the lower layer absorber have a recess formed in the longitudinal direction formed on the skin contact surface side, and the recess is an opening penetrating the upper layer absorber, and the bottom surface of the opening
- An absorbent article is disclosed in which the lower layer absorber is positioned on the lower surface of the upper layer absorber.
- the embossing is formed along the three-dimensional gather near the inside of the three-dimensional gather of the absorber, and when the urine is absorbed, the three-dimensional gather near the absorbent polymer is formed.
- a female incontinence pad that can suppress swelling of an absorbent body is disclosed.
- a grooved center embossing provided on the absorbent body from the top surface of the liquid-permeable top sheet, which has a liquid-permeable top sheet made of a sheet having a large number of openings or a nonwoven fabric, and this center Side embossing exists on both sides of the embossing, the center embossing performs the side embossing processing, and the center embossing processing is performed in the subsequent process.
- An absorbent article is disclosed in which a concave groove is formed while the top sheet is stretched, and the center sheet embossed portion expands the opening of the top sheet or expands the fiber gap of the nonwoven fabric.
- JP 2009-112590 A Japanese Patent Laying-Open No. 2005-87655 Japanese Patent No. 4652626
- the upper absorbent body is laminated on the lower absorbent body, and a part of the surface side of the lower absorbent body (the bottom of the opening) is in close contact with the surface sheet directly at the opening. Has been. And at least one part of the opening part bottom face of this lower layer absorber is joined with a part of surface sheet introduced into the inside through the opening part by the melt-bonding method.
- a measure to enlarge the opening of the absorber in advance can be considered, but by increasing the opening, absorption around the opening can be compensated to compensate for the amount of absorption. It is necessary to increase the body weight, which may increase the thickness of the product and deteriorate the feeling of wearing.
- a liquid-permeable surface sheet is laminated on the surface side of the absorbent body, and embossing is performed by squeezing the inside of the concave groove from the surface side of the liquid-permeable surface sheet. If applied, the side wall of the groove may fall inward as the groove bottom is squeezed, thereby reducing the volume of the groove and reducing the amount of body fluid that can be stored. It was.
- the body fluid temporarily stored in the opening penetrates into the absorber also from the side wall of the opening.
- the body fluid is absorbed from the side wall of the opening.
- the bodily fluid that has penetrated into the body tends to stagnate, and the amount of water retained in the absorber may soon fill up, making it impossible to absorb more water.
- Patent Document 3 there has been a technique for enlarging a large number of openings formed in the liquid-permeable top sheet by performing embossing, but the technique was provided in the absorber. There has been no technique for enlarging the opening of the recess.
- the main problem of the present invention is to provide a method for manufacturing an absorbent article that makes it easy to process the groove, allows the groove to be formed cleanly, and improves the diffusibility of body fluids without deteriorating the wearing feeling. There is to do.
- a method for manufacturing an absorbent article provided with an embossed portion A first step of forming the absorber having the absorber recess, a second step of applying core embossing to at least both sides of the absorber recess by pressing from the skin contact surface side of the absorber, and the absorption And a third step of providing the embossed portion by laminating the liquid-permeable surface sheet on the surface side of the body.
- a groove-like or slit-like shape is obtained without squeezing.
- An absorbent article in which an absorbent body in which an absorbent body recess is formed is interposed, and an embossed portion is provided inside the absorbent body recess along the absorbent body recess by embossing from the surface side of the liquid-permeable surface sheet. It is a method for manufacturing.
- the absorbent recess when body fluid enters the absorbent recess and the polymer or pulp around the absorbent recess expands, the absorbent recess is formed in the absorber in advance, so that the polymer or The rise of the bottom surface of the absorber recess is suppressed to be extremely small compared to the pulp having a high density, and the liquid-permeable surface sheet is interposed in the absorber recess by the embossed portion.
- the expansion of the side surface of the can also be suppressed small. Accordingly, it is possible to prevent the absorbent recess from being blocked by the polymer or the pulp that has expanded during liquid absorption, thereby reducing the absorbability of the body fluid.
- the absorber recess when the absorber recess is formed in a slit shape, the absorber does not intervene on the bottom surface of the absorber recess so that the bottom surface does not expand.
- a first step of forming the absorbent body having the absorbent recess, and at least both sides of the absorbent recess from the skin contact surface side of the absorbent body is used.
- a manufacturing process including a second process of performing core embossing by pressing and a third process of stacking the liquid-permeable surface sheet on the surface side of the absorbent body and providing the embossed portion is used.
- the groove can be formed without increasing the opening size of the absorber recess, it is not necessary to increase the weight and thickness of the absorber, and the feeling of wearing the absorbent article can be maintained.
- the core embossing that is consolidated is provided around the absorber recess, when the bodily fluid temporarily stored in the absorber recess penetrates into the interior of the absorber, the body fluid is cored by the density gradient of the fibers. It becomes easy to be drawn into the embossed side, the diffusibility of body fluid is improved, and the water absorption performance is improved.
- the present invention according to claim 2, there is provided the method for producing an absorbent article according to claim 1, wherein the core embossing is applied in a range of 10 mm or more and 30 mm or less from the edge of the absorber recess. .
- the distance from the edge of the recess of the absorber is within a range of 10 mm or more and 30 mm or less as a position where the core emboss is provided.
- the core emboss is provided in a range closer than 10 mm, the height (depth) of the absorber concave portion is reduced by being dragged by the core emboss, and the volume of the concave groove may be reduced to reduce the absorption performance.
- it provides in the range far from 30 mm, since the effect of making the side wall of an absorber recessed part fall down outside cannot be expected so much, it is unpreferable.
- the planar shape of the core emboss is one or a plurality of continuous lines or discontinuous lines, dot-like or lattice-like patterns along the longitudinal direction of the absorbent article. 2.
- a method for producing an absorbent article according to any one of 2 is provided.
- the planar shape of the core embossing is preferably one or a plurality of continuous lines, discontinuous lines, dot-like or lattice-like patterns along the longitudinal direction of the absorbent article. ing.
- the continuous line or the discontinuous line may be a straight line or a curved line such as an arc.
- the core embossing is also applied to the front side and the rear side of the absorber concave portion, thereby improving the diffusibility of the body fluid permeating into the absorber from the concave groove to the front side and the rear side. And the absorption performance becomes even better.
- the core embossing is provided continuously or discontinuously from the absorber concave portion side toward the outer side in a plan view, and the outward pressing pressure is gradually increased.
- the outer pressing pressure is applied. Is set to gradually increase, the density gradient of the absorber gradually increases toward the outer side, so that the diffusibility of the body fluid is further increased and the absorption performance is improved.
- the groove can be easily processed, the groove can be formed cleanly, and the diffusibility of body fluid can be improved without deteriorating the wearing feeling.
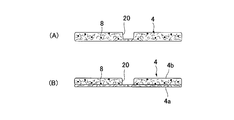
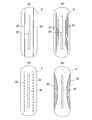
- FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view of the absorber 4.
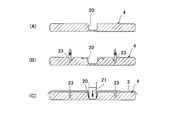
- FIGS. 4A to 4C are cross-sectional views showing the manufacturing process of the incontinence pad 1.
- 4 is a plan view of the absorber 4.
- FIG. (A) to (D) are plan views of the absorber 4.
- (A) to (D) are plan views of the absorber 4.
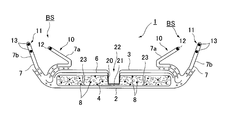
- an incontinence pad 1 includes a liquid-impervious back sheet 2 made of a polyethylene sheet and the like, a liquid-permeable front sheet 3 that allows urine to permeate quickly, and the like.
- An absorbent body 4 made of cotton-like pulp or synthetic pulp interposed between the two sheets 2 and 3 and a hydrophilic substance disposed between the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 and the absorbent body 4 as necessary.
- the outer edge with 3 is hot melt
- the liquid-impervious back sheet 2 and the side nonwoven fabric 7 which are bonded by an adhesive such as an adhesive or heat seal or the like and extend laterally from the absorbent body 4 at both side edges thereof are hot-melted. Are bonded by an adhesive such as an adhesive or heat seal.
- the absorbent body 4 can be surrounded by an encapsulating sheet made of crepe paper, non-woven fabric or the like in order to maintain shape and improve diffusibility.
- the liquid-impervious back sheet 2 is made of a sheet material having at least water-impervious properties such as polyethylene and polypropylene, but in addition to this, a non-woven sheet after securing a substantially liquid-impervious property through a waterproof film.
- a liquid-impervious back sheet is composed of the waterproof film and the nonwoven fabric.
- those having moisture permeability tend to be suitably used from the viewpoint of preventing stuffiness.
- the water- and moisture-permeable sheet material is a microporous material obtained by melting and kneading an inorganic filler in an olefin-based resin such as polyethylene or polypropylene to form a sheet, and then stretching in a uniaxial or biaxial direction.
- a sheet is preferably used.
- the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 is preferably a porous or non-porous nonwoven fabric or a porous plastic sheet.
- the material fibers constituting the nonwoven fabric include synthetic fibers such as polyethylene or polypropylene, synthetic fibers such as polyester and polyamide, recycled fibers such as rayon and cupra, and natural fibers such as cotton.
- a nonwoven fabric obtained by an appropriate processing method such as a lace method, a spun bond method, a thermal bond method, a melt blown method, or a needle punch method can be used. Among these processing methods, the spunlace method is excellent in terms of flexibility and drapeability, and the thermal bond method is excellent in terms of being bulky and soft.
- the absorbent body 4 is composed of, for example, absorbent fibers such as fluffy pulp and the superabsorbent polymer 8, and in the illustrated example, the planar shape is an oblong shape that is long in the longitudinal direction of the pad.
- the superabsorbent polymer 8 is, for example, granular powder, and is dispersed and mixed in the pulp constituting the absorber 4.
- the pulp examples include chemical fibers obtained from wood, cellulose fibers such as dissolved pulp, and artificial cellulose fibers such as rayon and acetate. Softwood pulp having a longer fiber length than hardwood pulp functions and It is preferably used in terms of price.
- the encapsulating sheet 5 is interposed between the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 and the absorbent body 4 as a result.
- the excellent encapsulating sheet 5 quickly diffuses body fluids and prevents the urine and the like from returning.
- the basis weight of the pulp is 100 g / m 2 to 600 g / m 2 , preferably 200 g / m 2 to 500 g / m 2 .
- the superabsorbent polymer 8 examples include a cross-linked polyacrylate, a self-crosslinked polyacrylate, a saponified acrylate-vinyl acetate copolymer cross-linked product, and a cross-linked isobutylene / maleic anhydride copolymer.
- a crosslinked polysulfonate, and a partially crosslinked water-swellable polymer such as polyethylene oxide and polyacrylamide.
- those based on acrylic acid or acrylate that are excellent in water absorption and water absorption speed are preferred.
- the water-absorbing polymer having the water-absorbing performance can be adjusted in water absorption (absorption capacity) and water absorption speed by adjusting the crosslinking density and the crosslinking density gradient in the production process.
- the basis weight of the polymer is 150 g / m 2 to 500 g / m 2 , preferably 200 g / m 2 to 450 g / m 2 .
- synthetic fibers may be mixed in the absorber 4.
- synthetic fiber for example, polyolefins such as polyethylene or polypropylene, polyesters such as polyethylene terephthalate and polybutylene terephthalate, polyamides such as nylon, and copolymers thereof can be used. It may be a mixture.
- a composite fiber such as a core-sheath fiber, a side-by-side fiber, or a split fiber having a fiber having a high melting point as a core and a fiber having a low melting point as a sheath can also be used.
- hydrophobic fiber it is desirable to use a synthetic fiber that has been surface-treated with a hydrophilizing agent so as to have an affinity for body fluids.
- the second sheet 6 only needs to be hydrophilic to body fluids. Specifically, by using recycled fibers such as rayon and cupra, natural fibers such as cotton, the material itself has hydrophilicity, or synthesis of olefins such as polyethylene or polypropylene, polyesters, polyamides, etc.
- the fiber which surface-treated with the hydrophilizing agent and provided the hydrophilic property can be used.
- the second sheet 6 may have a porous film layer on the back surface side (absorber 4 side) in order to give a firmness, and a material containing pulp may be used.
- Side nonwoven fabrics 7 and 7 are provided on both sides of the surface of the incontinence pad 1 along the longitudinal direction and over the entire length of the incontinence pad 1, and the outer portions of the side nonwoven fabrics 7 and 7 extend laterally.
- the liquid-impermeable back sheet 2 is laterally extended, and the side nonwoven fabric 7 portion and the liquid-impermeable back sheet 2 portion that are extended to the side are formed by a hot melt adhesive or the like. Joined to form side flaps.
- a water-repellent treated nonwoven fabric or a hydrophilic treated nonwoven fabric can be used from the viewpoint of important functions. For example, if importance is placed on functions such as preventing the penetration of urine, etc. or enhancing the feeling of touch, such as SSMS, SMS, and SMMS coated with a silicon-based, paraffin-based, alkylchromic chloride-based water repellent, etc.
- a water-repellent non-woven fabric It is desirable to use a water-repellent non-woven fabric, and if importance is attached to the absorbability of body fluids, a method of polymerizing a compound having a hydrophilic group, such as an oxidation product of polyethylene glycol, in the synthetic fiber production process, Treating with metal salt such as stannic, partially dissolving the surface to make it porous and making the synthetic fiber swell or porous by applying a metal hydroxide, etc., applying capillary action to impart hydrophilicity It is desirable to use a hydrophilic treated nonwoven fabric. As this side nonwoven fabric 7, what was formed by a proper processing method using natural fiber, synthetic fiber, regenerated fiber, etc. as a raw material can be used.
- a hydrophilic group such as an oxidation product of polyethylene glycol
- the side nonwoven fabrics 7 and 7 are appropriately folded, and a pair of left and right inner solid gathers 10 and 10 that stand on the skin side with the position near the side edge of the absorbent body 4 as a standing base end, and the inner side relatively
- a pair of left and right outer three-dimensional gathers 11 standing on the skin side formed by the liquid-impervious back sheet 2 and the side nonwoven fabric 7 that are located outside the three-dimensional gather 10 and extend laterally from the absorbent body 4, 11 is a three-dimensional gather BS having a double gather structure.
- the three-dimensional gather BS may have a single gather structure including only the inner three-dimensional gather 10 or the outer three-dimensional gather 11, or a three-dimensional gather standing up on the skin side simply by disposing the side nonwoven fabric 7. It does not have to be formed into a shape.
- the side nonwoven fabric 7 is folded back on both sides in the width direction toward the back side of the pad.
- one or a plurality of double sheet portions 7a and 7b are formed on the outer side, and both ends or appropriate positions in the longitudinal direction are fixed inside the double sheet portion 7a on the inner side in the width direction.
- One or a plurality of thread elastic elastic members 12 are arranged in the double sheet portion 7b on the outer side in the width direction, and two appropriate positions in the longitudinal direction are fixed.
- the base end portion of the double sheet portion 7 b on the outer side in the width direction extending laterally from the absorbent body 4.
- the inner solid gathers 10 standing on the skin side are formed by the double sheet portion 7a on the inner side in the width direction, and the skin is formed by the double sheet portion 7b on the outer side in the width direction.
- An outer three-dimensional gather 11 standing on the side is formed. As shown in FIG.
- the side nonwoven fabric 7 is not provided with the elastic elastic members 12 and 13 at both ends in the longitudinal direction of the pad, and the double sheet portion 7a on the inner side in the width direction is hot. It is joined to the absorber 4 side by a melt adhesive or the like.
- a body fluid inflow groove 22 is formed along the longitudinal direction on the surface side of the incontinence pad 1.
- the concave groove 22 receives body fluid discharged on the surface of the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3, temporarily stores the body fluid, induces diffusion of the body fluid in the front-rear direction, and absorbs the body fluid into the absorber 4. This is to increase the speed and prevent side leakage.
- the concave groove 22 is formed in advance in the absorbent body 4 along the longitudinal direction of the skin contact surface side including the body fluid discharge site, without forming the concave groove-shaped or slit-shaped absorbent concave portion 20 without squeezing.
- the embossing from the surface side (skin contact surface side) of the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 causes the inside of the absorbent body recess 20 to It is provided by forming an embossed portion 21 along the absorber recess 20.
- an absorbent body recess 20 is formed in advance before the embossed portion 21 is formed without being compressed.
- the absorbent body recess 20 is recessed from the periphery to the non-skin contact surface side (impermeable liquid back sheet 2 side) on the skin contact surface side (liquid permeable top sheet 3 side) of the absorber 4. Further, it is a non-penetrating concave groove portion having a bottom surface.
- the absorbent body recess 20 is formed by (A) stacking fiber, or (B) the lower layer absorbent body 4 a formed with the thickness of the bottom of the absorber recess 20, and A portion corresponding to the absorber recess 20 is formed by a laminated structure with the upper absorber 4b opened.
- the absorbent body recess 20 is formed in the pad width direction center portion corresponding to the body fluid discharge site H and only one strip in the longitudinal middle portion with respect to the absorbent body 4.
- the planar dimensions of the absorber recess 20 are preferably such that the length in the pad longitudinal direction is 100 to 180 mm and the groove width (bottom groove width) is 5 to 30 mm.
- the depth of the absorber recess 20 is preferably 50% or more of the thickness of the absorber 4.
- the absorbent 4 portion interposed in the bottom of the absorbent recess 20 has a pulp basis weight of 70 g / m 2 to 210 g / m 2 , preferably 90 g / m 2 to 190 g / m 2 is preferable, and the basis weight of the polymer is 60 g / m 2 to 200 g / m 2 , preferably 80 g / m 2 to 180 g / m 2 .
- the concave groove 22 is embossed from the skin contact surface side of the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3, and the embossed portion 21 extends along the absorber concave portion 20 inside the absorber concave portion 20. It is formed by providing.
- the embossed portion 21 is formed from the skin contact surface side of the liquid permeable surface sheet 3 in a state where the liquid permeable surface sheet 3 and, if necessary, the second sheet 6 are laminated on the skin contact surface side of the absorbent body 4. Is provided integrally with the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 and the second sheet 6.
- the said embossing part 21 surrounds the said absorber 4 with an enveloping sheet, after pressing the enveloping sheet only from the skin contact surface side of an encapsulating sheet in the state which surrounded the absorber 4 with the encapsulating sheet
- the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 and a second sheet 6 as needed are laminated, and the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 and the second sheet 6 are squeezed by pressing from the skin contact surface side of the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3.
- the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 and, if necessary, the second sheet 6 may be laminated with the absorbent body 4 surrounded by the encapsulating sheet, and the skin-contacting surface side of the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 may be provided. You may provide by squeezing the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3, the 2nd sheet
- the planar dimension of the embossed part 21 is preferably substantially the same as the dimension of the absorber recess 20.
- the width dimension of the embossed portion 21 is preferably set such that the difference from the groove width (bottom width dimension) of the absorber recess 20 is about 0 to ⁇ 2 mm.
- the longitudinal dimension of the embossed portion 21 varies greatly from machine to machine, it is preferable to shorten the longitudinal dimension of the embossed portion 21 by about 5 mm to 20 mm.
- a high-pressure squeezed portion squeezed deeper than the bottom surface of the peripheral concave groove 22 may be formed in an appropriate pattern.
- the concave groove 22 By providing the concave groove 22, the following effects can be obtained.
- the body fluid that has flowed into the concave groove 22 penetrates into the absorbent body 4 and the polymer and pulp around the absorbent body concave section 20 absorbs water and expands, by forming the absorbent body concave section 20 in the absorbent body 4 in advance,
- the rise of the bottom surface of the absorber recess 20 is suppressed to be extremely small as compared with the polymer or pulp having a high density by pressing, and the embossed portion 21 interposes the liquid-permeable surface sheet 3 in the absorber recess 20. Therefore, the expansion of the side surface of the absorber recess 20 is also suppressed to a low level.
- the absorbent body recess 20 it is possible to prevent the absorbent body recess 20 from being blocked by the polymer or pulp that has expanded during liquid absorption and thus reducing the absorbability of the body fluid.
- the absorber recess 20 is formed in a slit shape, the absorber does not intervene on the bottom surface of the absorber recess 20, so that the bottom surface does not expand during liquid absorption.
- the core embossing 23 is given by the predetermined pattern by the squeezing from the skin contact surface side of the absorber 4 at least on both sides of the absorber recessed part 20, respectively. .
- the core embossing 23 may be applied to the absorbent body 4 before surrounding the encapsulating sheet when the absorbent body 4 is surrounded by the encapsulating sheet, or to the absorbent body 4 surrounded by the encapsulating sheet, You may give by the pressing from the skin contact surface side of the covering sheet.
- the core emboss 23 can be provided in various forms. The core emboss 23 will be described in detail later.
- the fibers are pulled inside the core emboss 23.
- the opening of the absorber recess 20 is greatly opened.
- the tip of the embossing device when the embossed portion 21 is provided is an extra portion of the absorber 4. Without squeezing such a part, it becomes possible to enter the inside of the absorbent body recess 20 firmly. For this reason, alignment with the absorber 4 and an embossing apparatus becomes easy, it becomes easy to process the ditch
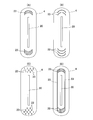
- the core emboss 23 is preferably disposed at a position away from the absorber recess 20 by a certain distance. Specifically, as shown in FIG. 6, the distance from the edge of the absorber recess 20 is 10 mm or more and 30 mm or less, preferably 10 mm or more and 25 mm or less.
- the core emboss 23 When the core emboss 23 is applied to a range where the distance from the absorber recess 20 is smaller than 10 mm, that is, the hatched range in the figure, the height of the side wall of the absorber recess 20 is dragged by the core emboss 23 (the absorber recess 20 Since the depth) is also reduced, the volume of the concave groove 22 may be reduced, and the body fluid absorption performance may be reduced.
- the distance from the edge of the absorber recess 20 is the length of the shortest linear distance from the edge of the core emboss 23 to the edge of the absorber recess 20.
- the planar shape of the core emboss 23 can be formed in various patterns.
- each of the absorber recesses 20 is formed in a continuous straight line pattern along the pad longitudinal direction including the range overlapping with the absorber recesses 20 in the pad width direction.
- the absorber recess 20 By forming the absorber recess 20 so as to have a length equal to or greater than the length of the absorber recess 20 including the range overlapping the absorbent recess 20 in the pad width direction, the absorber recess 20 opens in the entire length.
- the linear pattern extends to the middle in the longitudinal direction of the absorber 4, but it is also possible to provide the entire length of the absorber 4 as shown in FIG. This makes it possible to improve the diffusibility of body fluid from the central portion to the core emboss 23 side over the entire length of the absorbent body 4.
- one core emboss 23 is provided on each side of the absorber recess 20, but as shown in FIG. 7B, a plurality of core embosses 23 may be provided apart from each other in the pad width direction. . In the illustrated example, three lines are provided. When provided by a plurality of strips, they may all be formed with the same length, or the inner core embossing 23 may be provided so as to be gradually shortened in the front and rear as shown in the illustrated example. However, at least one core emboss 23 has a length that overlaps in the pad width direction over the entire length of the absorber recess 20.
- the absorbent body recess 20 can be opened more clearly, and the compacted region is formed over a wider range so that the diffusibility of body fluid can be further improved. become.
- the plurality of core embosses 23, 23,... May be squeezed at the same time, but in order to easily exert the effect of pulling the both side walls of the absorbent body recess 20 outward, they are positioned outside.
- One line may be provided inward from the core emboss 23 in order.
- the core emboss 23 can be provided in a discontinuous linear pattern in which a plurality of compressed parts and non-squeezed parts are alternately arranged in the pad longitudinal direction.
- this pattern although the effect of opening of the absorbent body recess 20 and body fluid diffusion due to squeezing is somewhat reduced, the increase in rigidity of the absorbent body by providing the core emboss 23 can be suppressed.
- the core emboss 23 can be provided in a curved pattern as shown in FIG. In the illustrated example, it is formed in an arc-shaped pattern that bulges inward. In the illustrated example, the region continuous to the end in the pad width direction is squeezed over the entire surface, but it may be formed with one or a plurality of curved patterns substantially along the pad longitudinal direction.
- the core emboss 23 can also squeeze the entire area extending to the end in the pad width direction. As a result, the effects of the core embossing 23 are more clearly exhibited, and both sides of the absorber 4 are thinned, so that the feeling of wearing is improved.
- the core embossing 23 is not shown, but in addition to this, a dot-like pattern in which a plurality of dots are given to a predetermined region, a grid-like pattern in which a plurality of pad longitudinal direction lines and pad width direction lines intersect, It can be provided in various patterns.
- the core emboss 23 can be applied not only on both sides of the absorber recess 20 but also on the front side and the rear side of the absorber recess 20 as shown in FIG.
- the core embossing 23 at the front and rear portions of the absorber recess 20 has a large machine feed variation with respect to the longitudinal direction of the pad when the machine flow direction is aligned with the longitudinal direction of the pad.
- the diffusivity in the front-rear direction of the absorber recess 20 is improved, and the entire absorber can be used efficiently, so that a large amount of body fluid can be absorbed with a smaller amount of pulp and polymer.
- the planar shape of the core emboss 23 provided in the front and rear portions of the absorber recess 20 is defined by (A) circular arcs in which front and rear end edges respectively bulge outward in the pad longitudinal direction. A pattern in which the formed region is squeezed over the entire surface, (B) a pattern composed of one or a plurality of curved lines that bulges outward in the longitudinal direction of the pad, substantially along the pad width direction, (C) A pattern in which a plurality of compressed portions are arranged in a zigzag or lattice pattern with an interval in the pad longitudinal direction and the width direction, (D) 2 along the pad width direction and bulges outward in the pad longitudinal direction A pattern in which a plurality of straight lines along the pad longitudinal direction are arranged in the pad width direction so as to straddle the two arcs in the pad width, and the like are arranged with the arc lines of the stripes spaced in the pad longitudinal direction. be able to.
- the core embosses 23 provided on the front and rear portions of the absorbent body recess 20 may be arranged so as to be continuous with the core embosses 23 provided on both sides of the absorbent body recess 20 (see FIG. 8D). You may arrange as follows.
- the pressing pressure of the core embossing 23 located on the outer side may be higher continuously or stepwise than the pressing pressure of the core embossing 23 positioned on the inner side. May be set.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Botany (AREA)
- Absorbent Articles And Supports Therefor (AREA)
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/106,362 US10596044B2 (en) | 2013-12-26 | 2014-12-26 | Method of manufacturing absorbent article |
| EP14875602.6A EP3087961B1 (en) | 2013-12-26 | 2014-12-26 | Method for producing absorbent article |
| CN201480070417.3A CN105828760B (zh) | 2013-12-26 | 2014-12-26 | 吸收性物品的制造方法 |
| KR1020167016567A KR102289775B1 (ko) | 2013-12-26 | 2014-12-26 | 흡수성 물품의 제조 방법 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013268306A JP6033765B2 (ja) | 2013-12-26 | 2013-12-26 | 吸収性物品の製造方法 |
| JP2013-268306 | 2013-12-26 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015099121A1 true WO2015099121A1 (ja) | 2015-07-02 |
Family
ID=53478960
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/084507 Ceased WO2015099121A1 (ja) | 2013-12-26 | 2014-12-26 | 吸収性物品の製造方法 |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10596044B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP3087961B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6033765B2 (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR102289775B1 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN105828760B (enExample) |
| TR (1) | TR201910477T4 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2015099121A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20160027008A (ko) * | 2013-06-28 | 2016-03-09 | 다이오 페이퍼 코퍼레이션 | 흡수성 물품 |
| CN107613933A (zh) * | 2015-07-31 | 2018-01-19 | 大王制纸株式会社 | 吸收性物品 |
| CN109310555A (zh) * | 2016-06-10 | 2019-02-05 | 尤妮佳股份有限公司 | 吸收性物品 |
| WO2025133064A1 (de) * | 2023-12-22 | 2025-06-26 | Paul Hartmann Ag | Inkontinenzartikel mit prägungselementen |
Families Citing this family (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015127289A1 (en) * | 2014-02-21 | 2015-08-27 | Attends Healthcare Products, Inc. | Absorbent article with fluid control features |
| JP6198076B2 (ja) | 2015-09-25 | 2017-09-20 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP6242423B2 (ja) * | 2016-03-29 | 2017-12-06 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP6346262B1 (ja) * | 2016-12-28 | 2018-06-20 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP6507193B2 (ja) * | 2017-03-30 | 2019-04-24 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| CN109893345B (zh) * | 2017-12-11 | 2022-04-12 | 花王株式会社 | 吸收性物品 |
| AT520852A1 (de) * | 2018-01-29 | 2019-08-15 | Lehner Andrea | Hygieneeinlage |
| JP6567713B1 (ja) * | 2018-03-05 | 2019-08-28 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP6605064B2 (ja) * | 2018-03-23 | 2019-11-13 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| WO2021015656A1 (en) * | 2019-07-19 | 2021-01-28 | Essity Hygiene And Health Aktiebolag | Absorbent article comprising a core comprising alternating high density and low density areas of absorbent material |
| US12285323B2 (en) * | 2019-07-19 | 2025-04-29 | Essity Hygiene And Health Aktiebolag | Absorbent article |
| KR102370317B1 (ko) * | 2020-01-07 | 2022-03-04 | 주식회사 보람씨앤에치 | 샘 방지 구조가 형성된 생리대 |
| CN217186765U (zh) * | 2021-01-26 | 2022-08-16 | 王子控股株式会社 | 吸收性物品的制造装置及吸收性物品 |
| US20230149223A1 (en) * | 2021-11-18 | 2023-05-18 | Judith Snyder | Waste collection device |
| AU2022464266A1 (en) * | 2022-06-22 | 2024-10-10 | Essity Hygiene And Health Aktiebolag | Absorbent article with embossed shaping elements |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005087655A (ja) | 2003-09-19 | 2005-04-07 | Daio Paper Corp | 女性用失禁パッド |
| JP2007089907A (ja) * | 2005-09-29 | 2007-04-12 | Kao Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2008080150A (ja) * | 2007-11-30 | 2008-04-10 | Daio Paper Corp | 吸収性物品およびその製造方法 |
| JP2009112590A (ja) | 2007-11-07 | 2009-05-28 | Kao Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP4652626B2 (ja) | 2001-07-16 | 2011-03-16 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品およびその製造方法 |
| JP2013075009A (ja) * | 2011-09-30 | 2013-04-25 | Daio Paper Corp | 吸収性物品 |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5435599B2 (enExample) * | 1974-04-01 | 1979-11-02 | ||
| JPS5648249Y2 (enExample) * | 1977-08-16 | 1981-11-11 | ||
| JPS5435599A (en) * | 1977-08-24 | 1979-03-15 | Toshiba Corp | Neutron detector |
| US6692603B1 (en) * | 1999-10-14 | 2004-02-17 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Method of making molded cellulosic webs for use in absorbent articles |
| US7037406B2 (en) | 1999-11-12 | 2006-05-02 | Fort James Corporation | Cross-machine direction embossing of absorbent paper products having an undulatory structure including ridges extending in the machine direction |
| JP3890313B2 (ja) * | 2003-03-31 | 2007-03-07 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP4683892B2 (ja) * | 2004-09-30 | 2011-05-18 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性パッド |
| JP4972335B2 (ja) * | 2006-02-09 | 2012-07-11 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収体物品 |
| JP5197147B2 (ja) * | 2008-05-15 | 2013-05-15 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
-
2013
- 2013-12-26 JP JP2013268306A patent/JP6033765B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2014
- 2014-12-26 EP EP14875602.6A patent/EP3087961B1/en active Active
- 2014-12-26 US US15/106,362 patent/US10596044B2/en active Active
- 2014-12-26 TR TR2019/10477T patent/TR201910477T4/tr unknown
- 2014-12-26 CN CN201480070417.3A patent/CN105828760B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2014-12-26 WO PCT/JP2014/084507 patent/WO2015099121A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2014-12-26 KR KR1020167016567A patent/KR102289775B1/ko active Active
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4652626B2 (ja) | 2001-07-16 | 2011-03-16 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品およびその製造方法 |
| JP2005087655A (ja) | 2003-09-19 | 2005-04-07 | Daio Paper Corp | 女性用失禁パッド |
| JP2007089907A (ja) * | 2005-09-29 | 2007-04-12 | Kao Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2009112590A (ja) | 2007-11-07 | 2009-05-28 | Kao Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2008080150A (ja) * | 2007-11-30 | 2008-04-10 | Daio Paper Corp | 吸収性物品およびその製造方法 |
| JP2013075009A (ja) * | 2011-09-30 | 2013-04-25 | Daio Paper Corp | 吸収性物品 |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20160027008A (ko) * | 2013-06-28 | 2016-03-09 | 다이오 페이퍼 코퍼레이션 | 흡수성 물품 |
| KR102313864B1 (ko) | 2013-06-28 | 2021-10-15 | 다이오 페이퍼 코퍼레이션 | 흡수성 물품 |
| CN107613933A (zh) * | 2015-07-31 | 2018-01-19 | 大王制纸株式会社 | 吸收性物品 |
| CN109310555A (zh) * | 2016-06-10 | 2019-02-05 | 尤妮佳股份有限公司 | 吸收性物品 |
| CN109310555B (zh) * | 2016-06-10 | 2019-11-26 | 尤妮佳股份有限公司 | 吸收性物品 |
| WO2025133064A1 (de) * | 2023-12-22 | 2025-06-26 | Paul Hartmann Ag | Inkontinenzartikel mit prägungselementen |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN105828760B (zh) | 2017-12-08 |
| TR201910477T4 (tr) | 2019-08-21 |
| JP2015123163A (ja) | 2015-07-06 |
| JP6033765B2 (ja) | 2016-11-30 |
| US10596044B2 (en) | 2020-03-24 |
| KR20160102423A (ko) | 2016-08-30 |
| KR102289775B1 (ko) | 2021-08-12 |
| EP3087961B1 (en) | 2019-06-19 |
| US20170027765A1 (en) | 2017-02-02 |
| EP3087961A1 (en) | 2016-11-02 |
| CN105828760A (zh) | 2016-08-03 |
| EP3087961A4 (en) | 2016-12-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6033765B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品の製造方法 | |
| JP5992381B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6031428B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6360540B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| KR101782763B1 (ko) | 흡수성 물품 | |
| JP6047606B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2015047432A5 (enExample) | ||
| JP2015089382A5 (enExample) | ||
| JP6484416B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| WO2019044966A1 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2016049199A (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6108435B2 (ja) | 表面シートの製造方法 | |
| JP6484417B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6326229B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6033612B2 (ja) | 吸収体及びこれを用いた吸収性物品 | |
| JP5957329B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6232482B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品及びその表面シート | |
| JP2016049312A (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2018149046A (ja) | 吸収性物品 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14875602 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2014875602 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15106362 Country of ref document: US Ref document number: 2014875602 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20167016567 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |