WO2015037305A1 - 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム - Google Patents
情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015037305A1 WO2015037305A1 PCT/JP2014/066839 JP2014066839W WO2015037305A1 WO 2015037305 A1 WO2015037305 A1 WO 2015037305A1 JP 2014066839 W JP2014066839 W JP 2014066839W WO 2015037305 A1 WO2015037305 A1 WO 2015037305A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- odds
- race
- information
- skill level
- history
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07F—COIN-FREED OR LIKE APPARATUS
- G07F17/00—Coin-freed apparatus for hiring articles; Coin-freed facilities or services
- G07F17/32—Coin-freed apparatus for hiring articles; Coin-freed facilities or services for games, toys, sports, or amusements
- G07F17/3225—Data transfer within a gaming system, e.g. data sent between gaming machines and users
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/10—Office automation; Time management
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q50/00—Information and communication technology [ICT] specially adapted for implementation of business processes of specific business sectors, e.g. utilities or tourism
- G06Q50/34—Betting or bookmaking, e.g. Internet betting
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07F—COIN-FREED OR LIKE APPARATUS
- G07F17/00—Coin-freed apparatus for hiring articles; Coin-freed facilities or services
- G07F17/32—Coin-freed apparatus for hiring articles; Coin-freed facilities or services for games, toys, sports, or amusements
- G07F17/3244—Payment aspects of a gaming system, e.g. payment schemes, setting payout ratio, bonus or consolation prizes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07F—COIN-FREED OR LIKE APPARATUS
- G07F17/00—Coin-freed apparatus for hiring articles; Coin-freed facilities or services
- G07F17/32—Coin-freed apparatus for hiring articles; Coin-freed facilities or services for games, toys, sports, or amusements
- G07F17/3286—Type of games
- G07F17/3288—Betting, e.g. on live events, bookmaking
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07F—COIN-FREED OR LIKE APPARATUS
- G07F17/00—Coin-freed apparatus for hiring articles; Coin-freed facilities or services
- G07F17/32—Coin-freed apparatus for hiring articles; Coin-freed facilities or services for games, toys, sports, or amusements
- G07F17/3286—Type of games
- G07F17/3295—Games involving skill, e.g. dexterity, memory, thinking
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a technical field that provides information about a race.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a technology in which a user sets necessary information among various pieces of information related to horse racing, and a server distributes only information required by the user.
- the information necessary to purchase voting tickets for public competitions and the timing when information is required may vary depending on the user. However, it is troublesome for the user to set information required by the user. Some users do not even know what information they need.
- the present invention has been made in view of the above points, and an information processing apparatus, an information processing method, and an information processing apparatus capable of automatically providing appropriate information according to the user without increasing the user's trouble
- An object is to provide an information processing program.
- the invention according to claim 1 is characterized in that a history of operations for one or more races by a predetermined user is stored from storage means for storing a history of operations for purchasing voting tickets for public competitions.
- An obtaining means for obtaining, a judging means for judging a proficiency level of the predetermined user for the purchase of the voting ticket based on the status of the operation specified from the history obtained by the obtaining means, and the judging means Control means for controlling display of race information in response to a request from the predetermined user according to the determined skill level.
- the information processing apparatus determines the skill level of a predetermined user based on a history of operations for purchasing a voting ticket.
- the information processing apparatus controls display of race information in response to a request from a predetermined user according to the skill level. Therefore, appropriate information can be automatically provided according to the user without increasing the user's trouble.
- the acquisition means indicates an operation of updating the odds to the latest odds when the odds of the voting ticket are displayed.
- a history is acquired, and the determination unit determines that the skill level is higher as the frequency of the operation of updating the odds is higher.
- the skill level can be determined appropriately. The reason is that a user with a higher skill level tends to consider the odds in detail, and a user with a higher skill level tends to desire the latest odds.
- the acquisition unit includes the history indicating an operation for displaying information related to a race object participating in the race, and the race.
- the history indicating an operation for displaying the prediction information of the result of the determination is obtained, and the determination means increases the ratio of the display time of the information related to the race object to the display time of the prediction information, Is determined to be high.
- the skill level can be determined appropriately.
- the reason for this is that users with a high level of skill tend to consider information about the race in detail and decide which voting ticket to purchase, and users with a high level of skill tend to not rely on other people's expectations. is there.
- the acquisition unit displays the history indicating an operation for displaying information on a race object participating in the race. And acquiring at least one of the history indicating an operation for displaying the odds information of the voting ticket and the history indicating an operation for displaying information on the prediction of the result of the race, and the determination unit includes: After the information about the race object is displayed, when either the odds information or the prediction information is displayed next, it is determined that the skill level is lower as the display time of the information about the race object is shorter It is characterized by doing.
- the skill level can be determined appropriately. The reason is that users with lower skill levels tend to look at the odds information and other people's expectations immediately without looking at the details about the race object.
- the acquisition unit acquires the history indicating the purchase operation of the voting ticket
- the determination unit includes: The skill level is determined to be higher as the number of race objects and / or frames voted among the race objects participating in the race increases.
- the skill level can be determined appropriately. The reason is that users with higher skill levels tend to purchase voting tickets with more complicated purchases. The more voting races or frames, the more complex the buy.
- the control means is odds of a voting ticket for a race in response to a request from the predetermined user.
- the odds stored in the odds storage means for storing the odds updated at a predetermined timing are displayed, the display of the odds is periodically performed based on the latest odds stored in the odds storage means. The period for updating the display of the odds is shortened as the skill level determined by the determination means is higher.
- the odds can be automatically updated at an appropriate cycle according to the skill level.
- the period at which the odds display is updated becomes longer. Therefore, the processing load of the information processing apparatus due to the update of the display of odds can be reduced.
- a seventh aspect of the present invention is the information processing apparatus according to any one of the first to sixth aspects, wherein the control means is odds of a voting ticket for a race in response to a request from the predetermined user.
- the control means is odds of a voting ticket for a race in response to a request from the predetermined user.
- the odds stored in the odds storage means for storing odds updated at a predetermined timing are displayed, only when the skill level determined by the determination means is equal to or higher than a predetermined skill level, The display of the odds is periodically updated based on the latest odds stored in the odds storage means.
- the odds display is not automatically updated for users with low skill levels. Therefore, the processing load of the information processing apparatus due to the update of the display of odds can be reduced.
- the invention according to claim 8 is the information processing apparatus according to any one of claims 1 to 7, wherein the control means stores information on a race object participating in a race in response to a request from the predetermined user.
- the amount of information related to the race object is increased as the skill level determined by the determination means is higher.
- the determination unit is configured to purchase the voting ticket out of the history stored in the storage unit.
- the skill level is determined based on the history stored so far.
- the information processing apparatus can acquire an appropriate history as an operation history for purchasing a voting ticket for a race.
- the invention according to claim 10 is an information processing method executed by a computer, and from a storage means for storing a history of operations for purchasing voting tickets for public competitions, one or more races by a predetermined user
- the invention according to claim 11 is an acquisition means for acquiring an operation history for one or more races by a predetermined user from a storage means for storing an operation history for purchasing a voting ticket for a public competition. Based on the status of the operation specified from the history acquired by the acquisition means, a determination means for determining the skill level of the predetermined user regarding the purchase of the voting ticket, and the skill determined by the determination means Depending on the degree, it is executed as a control means for controlling display of race information in response to a request from the predetermined user.
- the information processing apparatus determines the skill level of a predetermined user based on a history of operations for purchasing a voting ticket.
- the information processing apparatus controls display of race information in response to a request from a predetermined user according to the skill level. Therefore, appropriate information can be automatically provided according to the user without increasing the user's trouble.
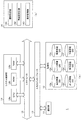
- FIG. 1 It is a figure showing an example of outline composition of information processing system S concerning one embodiment. It is a figure which shows the example of a display of a racecard page.
- A is a figure which shows the example of a display of the odds page which displays odds of a win and a win
- (b) is a figure which shows the example of a display of an anticipation list page.
- (A) is a block diagram which shows an example of schematic structure of the betting ticket sale agency server 1 which concerns on one Embodiment
- (b) is a figure which shows an example of the functional block of the betting ticket sale agency server 1 which concerns on one Embodiment. It is.
- (A) is a figure which shows an example of the content registered into member information DB12a
- (b) is a figure which shows an example of the content registered into race information DB12b
- (c) is a betting ticket information DB12c.
- (D) is a figure which shows an example of the content registered into odds information DB12d
- (e) is an example of the content registered into operation history DB12e.
- (F) is a figure which shows an example of the content which detailed information contains when an operation division is "browsing”, (g) is detailed when an operation division is "manual update”.
- (A) is a flowchart which shows an example of the 3rd determination process by the system control part 14 of the betting ticket sale agency server 1 which concerns on one Embodiment
- (b) is the system of the betting ticket sale agency server 1 which concerns on one Embodiment
- 12 is a flowchart illustrating an example of a fourth determination process performed by the control unit 14.
- Horse racing is an example of a race in the present invention.
- a racehorse participating in a race is an example of a race object in the present invention.
- a betting ticket is an example of a voting ticket in the present invention.
- the race to which the present invention is applicable is not limited to horse racing.
- the present invention can be applied to any race where voting tickets can be purchased. Examples of such races include public competitions such as bicycle races, boat races, and auto races.
- FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating an example of a schematic configuration of an information processing system S according to the present embodiment.
- the information processing system S includes a betting ticket release agency server 1, a sponsor server 2, and a plurality of user terminals 3.
- the betting ticket sale agency server 1, the sponsor server 2, and each user terminal 3 can transmit and receive data to and from each other using, for example, TCP / IP as a communication protocol via the network NW.
- the network NW is constructed by, for example, the Internet, a dedicated communication line (for example, a CATV (CommunityCommunAntenna Television) line), a mobile communication network (including a base station, etc.), a gateway, and the like.
- the betting ticket release agency server 1 is a server device that performs various processes related to a horse racing site for selling betting tickets on behalf of a horse race organizer.
- the betting ticket sale agency server 1 is an example of an information processing apparatus according to the present invention.
- the betting ticket sales agency server 1 acquires information on the race announced by the organizer from the organizer server 2.
- the betting ticket sale agency server 1 transmits a web page in response to a request from the user terminal 3. Thereby, the betting ticket sale agency server 1 provides information on the race. Examples of race information to be provided include race tables, odds, predictions, race results, and the like.
- the betting ticket sale agency server 1 performs, for example, a process of accepting purchase of a betting ticket or a process of refunding a hit betting ticket.
- a user of a horse racing site selects a purchase eye, the number of purchases, and the like.
- Buy eyes include racehorses or frames subject to voting and voting.
- the racehorse or frame to be voted is specified by a horse number or a frame number.
- the purchase order includes the order of arrival for the racehorses to be voted on.
- the betting ticket release agency server 1 accepts a prediction of a race by the user based on a request from the user terminal 3. When posting the prediction, the user selects a favorite, a rival, a single hole (dark) horse), and a descendant (lower level) as a racehorse that predicts that the arrival order is higher.
- the betting ticket sales agency server 1 determines the skill level of each user regarding the purchase of betting tickets.
- the betting ticket release agency server 1 controls display of information regarding the race according to the determined skill level. Thereby, betting ticket sale representation server 1 can provide appropriate information to each user.
- the skill level indicates, for example, how familiar the user is with purchasing a betting ticket. That is, the skill level indicates the degree to which the user is used to voting for racehorses.
- the betting ticket sales agency server 1 uses a history of operations for purchasing betting tickets. This history is called an operation history. A skill level determination method and information display control method will be described later.
- the user terminal 3 is a terminal device of a user who uses the horse racing site.
- the user terminal 3 receives and displays a web page from the betting ticket sales agency server 1 by accessing the betting ticket sales agency server 1 based on an operation from the user.
- Software such as a browser and an e-mail client is incorporated in the user terminal 3.
- the race table page is a web page that displays information on racehorses that participate in the race designated by the user. Information about racehorses is called racehorse information.
- the racehorse information is an example of information related to the race subject of the present invention.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a display example of a racecard page. In FIG. 2, only the racehorse information of one racehorse is displayed, but actually the racehorse information of all racehorses participating in the race is displayed. As shown in FIG.
- the displayed horse information includes frame number, horse number, racehorse basic attributes, racehorse attributes, horse weight at the time of pairing, increase / decrease in horse weight, and information on the last five races.
- the basic attributes of a racehorse include the name of the racehorse father, the name of the racehorse, the name of the racehorse mother, the odds of the racehorse win, the date of birth, the name of the owner, and the name of the ranch that produced the racehorse.
- the racehorse attributes of the racehorse include age, coat color, weight, jockey name, and trainer name.
- Information on the last 5 races is arrival order, race condition, number of runners, venue, date, race name, grade, distance, whether the course is clockwise or counterclockwise, type of race, popularity, jockey Name, burden weight, running time, time difference with 1st or 2nd racehorse, remaining 600 emails running time, horse weight, starting gate number, ranking when passing the corner, 1st or 2nd racehorse Includes name.
- Past results include results of all races, results at the racetrack where the race corresponding to the race table page is held, results at the same distance as the race corresponding to the race table page, races corresponding to the race table page Includes results from courses held by, and results by distance.
- the odds page is a web page that displays the odds for the race specified by the user. There is an odds page for each formula (voting method), for example.
- FIG. 3A is a diagram illustrating a display example of an odds page displaying odds of winning and winning.
- the odds page includes a list 110 and an update link 120.
- the list 110 includes frame numbers, horse numbers, racehorse names, odds areas 111, and the like.
- odds area 111 for example, odds for each purchase of a single win and a double win are displayed.
- the odds page is displayed, the odds displayed in the odds area 111 are updated to the latest odds every predetermined period. Updating the odds at a predetermined cycle is called automatic update.
- the odds displayed in the odds area 111 are updated to the latest odds when the operation is performed. Updating the odds by a user operation is called manual update. Note that the odds page need not be automatically updated. And only the manual update of odds may be possible.
- the prediction list page is a web page that displays a list of predictions in the race specified by the user.
- the prediction list page is an example of information on prediction of the result of the race of the present invention.
- FIG. 3B is a diagram illustrating a display example of the prediction list page.
- the expected list page displays the horse number of the favorite, the counter horse number, the single hole horse number, the horse number of the legion, the nickname of the predictor, the predictive predictive value, the expected recovery rate, etc. Is done.
- FIG. 4A is a block diagram showing an example of a schematic configuration of the betting ticket sale agency server 1 according to the present embodiment.
- the betting ticket release agency server 1 includes a communication unit 11, a storage unit 12, an input / output interface 13, and a system control unit 14.
- the system control unit 14 and the input / output interface 13 are connected via a system bus 15.
- the communication unit 11 is connected to the network NW and controls the communication state with the user terminal 3 and the like.
- the storage unit 12 is an example of a storage unit and an odds storage unit of the present invention.
- the storage unit 12 is configured by, for example, a hard disk drive.
- databases such as a member information DB 12a, a race information DB 12b, a betting ticket information DB 12c, an odds information DB 12d, an operation history DB 12e, and an expected information DB 12f are constructed.
- DB is an abbreviation for database.
- FIG. 5A is a diagram showing an example of contents registered in the member information DB 12a.
- member information regarding users who are registered as members of the horse racing site is registered for each user. Specifically, a user ID, password, nickname, name, date of birth, sex, zip code, address, telephone number, e-mail address, etc. are registered in association with the member information DB 12a.
- FIG. 5B is a diagram showing an example of contents registered in the race information DB 12b.
- race information related to the race is registered for each race.
- information such as a race ID, a race name, a grade, a racetrack name, a date, a start time, a race number, and a racehorse information are registered in association with each other.
- the race ID is race identification information.
- the starting horse information includes frame number, horse number, basic attributes, race attributes, horse weight at the time of pairing, increase / decrease in horse weight, information on the latest five races, and past results.
- the racehorse information is registered for each racehorse.
- FIG.5 (c) is a figure which shows an example of the content registered into betting ticket information DB12c.
- betting ticket information related to betting tickets to be sold is registered for each betting ticket.
- race IDs, betting ticket IDs, expressions, numbers for voting, and the like are associated and registered.
- the betting ticket ID is identification information of the betting ticket.
- the race ID indicates which race the betting ticket indicated by the betting ticket ID is.
- the number to be voted is a horse number or a frame number.
- One or a plurality of voting target numbers are registered depending on the formula. The combination of the expression type and the voting target number indicates a purchase.
- FIG. 5D is a diagram showing an example of contents registered in the odds information DB 12d.
- odds information related to betting ticket odds is registered for each betting ticket at predetermined time intervals. Specifically, a race ID, a betting ticket ID, an update date and time, odds, and the like are registered in the odds information DB 12d in association with each other.
- the sponsoring server 2 transmits odds information to the betting ticket sales agency server 1 at a predetermined time interval (for example, every minute).
- the system control unit 14 registers the received odds information in the odds information DB 12d.
- the update date and time indicates the date and time when the betting ticket odds indicated by the betting ticket ID are updated by the sponsor server 2.
- FIG. 5E is a diagram showing an example of contents registered in the operation history DB 12e.
- the operation history DB 12e a user's operation history at the horse racing site is registered.
- the user terminal 3 transmits a request corresponding to the operation to the betting ticket sale agency server 1.
- the system control unit 14 registers an operation history every time a request is received. Specifically, a user ID, operation date and time, detailed information, and the like are registered in the operation history DB 12e.
- the user ID indicates the user who performed the operation.
- the operation date / time indicates the date / time when the operation was performed. More specifically, the operation date and time is the date and time when the operation history is registered in the operation history DB 12e.
- Detailed information is detailed information regarding the operation.
- the detailed information may be a URL (Uniform (Resource Locator) included in the request transmitted from the user terminal 3, for example.
- URL Uniform (Resource Locator
- the detailed information includes at least the operation category.
- Examples of the operation category include “view”, “manual update”, “purchase”, and the like.
- “Browse” indicates an operation of displaying a web page.
- An operation history when the operation classification is “browsing” is referred to as a browsing history.
- the operation date and time when the operation category is “browsing” is referred to as “browsing date”.
- FIG. 5F is a diagram illustrating an example of the contents included in the detailed information when the operation category is “browse”.
- the detailed information further includes a race ID, a page type, and the like.
- the race ID indicates which race the browsed web page is related to.
- the page type indicates the type of the browsed web page.
- the types of web pages include a runner table page, an odds page, and a forecast list page.
- “Manual update” indicates an operation for manually updating the odds.
- An operation history when the operation classification is “manual update” is referred to as a manual update history.
- FIG. 5G is a diagram illustrating an example of the contents included in the detailed information when the operation classification is “manual update”.
- the detailed information further includes a race ID and the like. The race ID indicates a race in which the odds are manually updated.
- FIG. 5H is a diagram illustrating an example of contents included in the detailed information when the operation classification is “purchase”.
- the detailed information further includes a race ID, a betting ticket ID, a formula, a vote target number, the number of purchases, and the like.
- the betting ticket ID indicates a betting ticket purchased by the user.
- the combination of the race ID, the betting ticket ID, the type and the number to be voted is the same as the combination of the race ID, betting ticket ID, the type and the number to be voted registered in the betting ticket information DB 12c.
- FIG. 5I is a diagram showing an example of contents registered in the prediction information DB 12f.
- prediction information indicating the prediction of the race by the user is registered every time the betting ticket release agency server 1 receives the prediction.
- a user ID indicates the user who made the prediction.
- the posting date / time indicates the date / time when the prediction was posted.
- the race ID indicates which race the accepted prediction is for.
- the storage unit 12 stores various data such as an HTML document, an XML (Extensible Markup Language) document, image data, text data, and an electronic document for displaying a web page.
- the storage unit 12 stores various set values, threshold values, constants, and the like.
- the storage unit 12 stores various programs such as an operating system, a WWW (World Wide Web) server program, a DBMS (Database Management System), and a betting ticket issuing agency management program.
- the betting ticket issuing agency management program is a program for executing processing such as acceptance of purchase of betting tickets, determination of skill level, and control of display of a web page.
- the betting ticket issuing agency management program is an example of an information processing program in the present invention.
- the various programs may be acquired from other server devices or the like via the network NW, or may be recorded on a recording medium such as a DVD (Digital Versatile Disc) and read via the drive device. You may do it.
- the betting ticket issuing agency management program may be a program product.
- the input / output interface 13 performs interface processing between the communication unit 11 and the storage unit 12 and the system control unit 14.
- the system control unit 14 includes a CPU 14a, a ROM (Read Only Memory) 14b, a RAM (Random Access Memory) 14c, and the like.
- the CPU 14a reads out and executes various programs, thereby executing various processes related to the horse racing site.
- the betting ticket sale agency server 1 may be configured by a plurality of server devices.
- a server device that performs processing such as a server device that performs processing such as acceptance of purchase of a betting ticket, a server device that determines skill level, a server device that transmits a web page in response to a request from the user terminal 3, and a database Server devices to be managed may be connected to each other via a LAN or the like.
- FIG. 4B is a diagram illustrating an example of functional blocks of the betting ticket release agency server 1 according to the present embodiment.
- the system control unit 14 By reading and executing various programs stored in the storage unit 12, the system control unit 14 functions as a history acquisition unit 141, a skill level determination unit 142, a display control unit 143, and the like, as shown in FIG. 4B.
- the history acquisition unit 141 is an example of an acquisition unit in the present invention.
- the skill level determination unit 142 is an example of a determination unit in the present invention.
- the display control unit 143 is an example of a control unit in the present invention.
- the history acquisition unit 141 acquires an operation history of a predetermined user in at least one race from the operation history DB 12e.
- the operation history acquired by the history acquisition unit 141 includes, for example, a race history page browsing history, an odds page browsing history, a prediction list page browsing history, an odds manual update history, and a purchase history.
- the operation for displaying the racecard page is an operation for purchasing a betting ticket.
- the odds are not known, the user cannot determine which racehorse or frame is appropriate for voting. Therefore, the operation for displaying the odds page and the operation for manually updating the odds are operations for purchasing a betting ticket.
- a user may determine the racehorse or frame to vote with reference to others' expectation. Therefore, the operation for displaying the prediction list page is an operation for purchasing a betting ticket.
- the skill level determination unit 142 determines the skill level of a predetermined user based on the operation status specified from the operation history acquired by the history acquisition unit 141.
- FIG. 6A is a diagram illustrating an example of a skill level determination method.
- FIG. 6A shows methods 1 to 4 as examples of the determination method.
- the history acquisition unit 141 acquires a manual update history of odds.
- the skill level determination unit 142 calculates the frequency with which the manual update of the odds when the odds page is displayed. This frequency is called manual update frequency.
- the skill level determination unit 142 determines that the skill level is higher as the manual update frequency is higher. The reason is that users with higher skill levels tend to consider the odds in detail. Therefore, users with higher skill levels tend to want the latest odds.
- the odds are periodically updated in the odds page.
- the user feels that the period at which the odds are updated is long for the user, the user performs a manual update operation.
- users with low skill levels tend not to stick to fine odds numbers. For this reason, the frequency of manual update operations is lower for users with lower skill levels.
- the history acquisition unit 141 acquires the browsing history of the racecard page and the browsing history of the forecast list page.
- the skill level determination unit 142 calculates a display time ratio.
- the display time ratio is a ratio of the display time of the race table page to the display time of the expected list page.
- the skill level determination unit 142 determines that the skill level is higher as the display time ratio is higher. The reason for this is that users with higher skill levels tend to consider running horse information in detail and purchase betting tickets without relying on other people's expectations. Therefore, the higher the skill level, the longer the time for the user to browse the race table page and the shorter the time to browse the expected list page.
- a user with low level of skill tend to rely on other people's predictions without much consideration of racehorse information.
- a user with low skill level may not know how to use for determination of a racehorse to vote or a frame for some information in the racehorse information.
- the history acquisition unit 141 acquires the browsing history of the racecard page, the browsing history of the odds page, and the browsing history of the forecast list page.
- the skill level determination unit 142 determines whether the user has next viewed either the odds page or the prediction list page.
- the skill level determination unit 142 calculates the display time of the racecard page. The skill level determination unit 142 determines that the skill level is lower as the display time is shorter. The reason is that a user with a low skill level tends to browse odds and other people's predictions immediately without considering the racehorse information.
- the history acquisition unit 141 acquires a purchase history.
- the skill level determination unit 142 calculates the number of racehorses and frames that the user has voted for by purchasing a betting ticket. This number is called the number of votes.
- the skill level determination unit 142 determines that the skill level is higher as the number of votes is larger. The reason is that users with higher skill levels tend to purchase betting tickets with more complicated purchases. The larger the number of votes, the more complicated the purchase.
- the skill level determination unit 142 may specify the number of votes based on, for example, the betting ticket formula. Depending on the formula, the number of racehorses to be voted on or the number of frame numbers is determined. The number of horse numbers and the number of frame numbers are the number of votes for one voting ticket.
- a single winning type for example, there are a single winning type, a double winning type, a frame number consecutive winning double type, a normal horse number consecutive winning double type, a frame number consecutive winning single type, a horse number consecutive winning single type, a wide, a horse number three consecutive winning single type, and a horse number three consecutive winning single type.
- the number of voting objects for the single and double wins is one.
- the number of voting objects for the number consecutive winning combination, the normal horse number consecutive winning, the frame number consecutive winning, the horse number consecutive winning, and the wide is two.
- the number of voting objects of the horse number 3 consecutive winning combination and the horse number 3 consecutive winning single is 3.
- a user may purchase a plurality of betting tickets for one race. For example, the user may purchase a formation or a box.
- the skill level determination unit 142 may use, for example, the number of horse numbers and the number of frame numbers in a plurality of betting tickets as the number of votes. For example, it is assumed that the user purchases 1-2, 2-3, and 3-1 betting tickets as horse number single winning betting tickets. In this case, the user has voted for the racehorses whose horse numbers are 1, 2 and 3. Therefore, the number of votes is 3.
- the skill level determination unit 142 may determine the skill level based only on the operation history registered up to the time of purchase of the betting ticket among the operation history of a predetermined user in any race. The reason is that when a user who has purchased a betting ticket performs some operation on the horse racing site, there is a probability that the user is performing an operation without aiming to purchase a betting ticket. In this case, the skill level determination unit 142 determines the skill level without using the operation history of the race in which the predetermined user did not purchase the betting ticket. The reason for this is that there is a probability that the user did not intend to purchase a betting ticket for a race in which the user did not purchase a betting ticket.
- the skill level determination unit 142 may determine the skill level using only one of the methods 1 to 4. For example, when only method 1 is used, the skill level determination unit 142 may use the manual update frequency as the skill level. When only method 2 is used, the skill level determination unit 142 may use the display time ratio as the skill level. When only method 3 is used, the skill level determination unit 142 may use the display time ratio of the racecard page as the skill level. When only method 4 is used, the skill level determination unit 142 may use the number of votes as a skill level. The skill level determination unit 142 may determine the skill level using a plurality of methods 1 to 4. When using a plurality of methods, the skill level determination unit 142 may calculate points by each method.
- the skill level determination unit 142 may determine the skill level based on the points calculated by each method.
- the skill level determination unit 142 may calculate a representative value such as a total value or an average value of points calculated by each method, and use the representative value as the skill level.
- the skill level determination unit 142 uses all the methods 1 to 4 and calculates points by each method. Then, the skill level determination unit 142 determines the skill level based on the calculated points. The skill level determination unit 142 determines whether the user is a beginner or an expert as an example of the skill level. The skill level may be three or more levels.
- the display control unit 143 controls the display of information related to the race according to the skill level determined by the skill level determination unit 142.
- FIG. 6B is a diagram illustrating an example of a method for controlling display of information related to a race.
- FIG. 6A shows controls 1 to 3 as examples of the control method.
- the web page to be controlled is an odds page.
- the display control unit 143 controls the cycle of automatic update of odds. This cycle is called an update cycle.
- the display control unit 143 shortens the update cycle as the skill level increases. The reason is that, as described above, a user with a higher skill level tends to desire the latest odds.
- the web page to be controlled is an odds page.
- the display control unit 143 controls whether or not the odds are automatically updated. Specifically, the display control unit 143 controls to automatically update the odds only when the skill level is equal to or higher than the predetermined skill level, and automatically updates the odds when the skill level is less than the predetermined skill level. Control not to. The reason is the same as in the case of the control 1.
- the display control unit 143 may combine the controls 1 and 2. For example, it is assumed that there are beginner, intermediate, and advanced levels of skill. The display control unit 143 does not automatically update if it is a beginner level, and automatically updates if it is an intermediate level or an advanced level. The display control unit 143 sets the update cycle for the advanced level to be shorter than the update cycle for the intermediate level.
- the web page to be controlled is the race page.
- the display control unit 143 controls the information amount of the running horse information. Specifically, the display control unit 143 increases the amount of information as the skill level increases. The reason is that as described above, a user with a higher skill level tends to consider a betting ticket to be purchased based on more information. Therefore, it is better to display detailed information for a user with a higher skill level. On the other hand, even if detailed information is displayed, a user with a low skill level tends to consider a betting ticket to be purchased based on only a part of the displayed information. Therefore, if the amount of information is large, a large amount of information that is not used by the user is displayed, which may be annoying for users with low skill levels. In addition, it is difficult for users with low skill levels to find necessary information. Therefore, the display control unit 143 decreases the amount of information as the skill level is lower.
- the skill level determination unit 142 determines whether the user is a beginner or an expert. In the case of a skilled person, the skill level determination unit 142 performs control so that, for example, a race guide page shown in FIG. 2 is displayed.
- FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating a display example of a racecard page when the user is a beginner. In the case of a beginner, the skill level determination unit 142 performs control so that, for example, a race guide page shown in FIG. 7 is displayed. As shown in FIG. 7, among the basic attributes of the racehorse, the name of the owner and the name of the ranch are not displayed.
- the display control unit 143 may perform control so that, for example, the race table page illustrated in FIG. 2 is displayed.
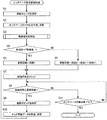
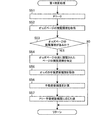
- FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing an example of the odds page display control process by the system control unit 14 of the betting ticket release agency server 1 according to the present embodiment.
- the user performs an operation of displaying an odds page of a desired race.
- the user terminal 3 transmits an odds page request to the betting ticket release agency server 1.
- the odds page request includes a user ID and a race ID.
- the user ID indicates a user who has performed an operation for displaying a web page.
- the user who performed the operation is referred to as a target user.
- the target user is an example of the predetermined user of the present invention.
- the race ID indicates the race in which the web page is displayed.
- a race in which a web page is displayed is called a target race.
- the target race is an example of a race according to a request from a predetermined user of the present invention.
- the display control unit 143 obtains the latest odds information (step S1). Specifically, the display control unit 143 searches the odds information DB 12d for odds information corresponding to the race ID of the target race included in the request. Next, the display control unit 143 acquires the odds information with the latest update date / time among the searched odds information.
- the display control unit 143 transmits the HTML page of the odds page (step S2). Specifically, the display control unit 143 acquires the odds included in the acquired odds information. Next, the display control unit 143 generates an HTML page including the acquired odds. Then, the display control unit 143 transmits the generated HTML page to the user terminal 3 that has transmitted the request. The user terminal 3 displays an odds page (for example, FIG. 3A) on the screen based on the received HTML page.
- an odds page for example, FIG. 3A
- the display control unit 143 executes skill level determination processing (step S3).
- the skill level determination unit 142 determines “expert” or “beginner” as the skill level of the target user. Details of the skill level determination unit 142 will be described later.
- the skill level determination unit 142 determines the skill level when transmitting a web page whose display is controlled. However, the skill level determination unit 142 may determine the skill level at a timing different from that when the web page is transmitted. For example, the skill level determination unit 142 may periodically determine the skill level of each user.
- the skill level determination unit 142 may determine the skill level of the user who performed the operation indicated by the registered operation history when an operation history such as a purchase history is registered in the operation history DB 12e.
- step S4 determines whether or not the skill level determined in the skill level determination process is “expert” (step S4). At this time, if the display control unit 143 determines that the skill level is “expert” (step S4: YES), the display control unit 143 proceeds to step S5. In step S ⁇ b> 5, the display control unit 143 sets the update cycle to the cycle 1 stored in advance in the storage unit 12. On the other hand, if the display control unit 143 determines that the skill level is not “expert” (step S4: NO), the process proceeds to step S6. In step S ⁇ b> 6, the display control unit 143 sets the update cycle to the cycle 2 stored in advance in the storage unit 12. Period 2 is longer than period 1. After completing step S5 or S6, the display control unit 143 proceeds to step S7.
- step S7 the display control unit 143 resets the elapsed time to zero. And the display control part 143 starts measurement of the elapsed time from the present.
- step S8 determines whether or not the elapsed time is equal to or longer than the update period (step S8). At this time, if the display control unit 143 determines that the elapsed time is not equal to or longer than the update period (step S8: NO), the display control unit 143 proceeds to step S11. On the other hand, if the display control unit 143 determines that the elapsed time is equal to or longer than the update period (step S8: YES), the display control unit 143 proceeds to step S9.
- step S9 the display control unit 143 acquires the latest odds information.
- the process of step S9 is the same as that of step S1.
- the display control unit 143 generates odds update data based on the latest odds information (step S10).
- the odds update data is data for the user terminal 3 to update the odds displayed on the odds page.
- the display control unit 143 may generate HTML format data corresponding to the odds area 111 of the odds page.
- the display control unit 143 puts the odds included in the latest odds information in the odds update data.
- the display control unit 143 transmits the generated odds update data to the user terminal 3 that has transmitted the request.
- the display control unit 143 proceeds to step S7.
- the user terminal 3 rewrites the HTML document of the odds page displayed on the screen based on the odds update data. Thereby, the user terminal 3 displays the latest odds in the odds page.
- step S11 the display control unit 143 determines whether or not the display of the odds page is finished. For example, when the betting ticket sale agency server 1 receives a request for another web page from the user terminal 3, the display control unit 143 determines that the display of the odds page has ended. At this time, if the display control unit 143 determines that the display of the odds page has not ended (step S11: NO), the display control unit 143 proceeds to step S8. On the other hand, if the display control unit 143 determines that the display of the odds page has ended (step S11: YES), the display control unit 143 ends the odds page display control process.
- step S4 NO
- the odds page display control process may be terminated. .
- the target user is a beginner
- the user terminal 3 does not execute the automatic update of the odds on the odds page.
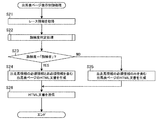
- FIG. 9 is a flowchart showing an example of a horse race table page display control process by the system control unit 14 of the betting ticket release agency server 1 according to the present embodiment.
- the user performs an operation of displaying a race table page of a desired race.
- the user terminal 3 transmits a request for a horse race table page to the betting ticket release agency server 1.
- the request for the racecard page includes the user ID of the target user and the race ID of the target race.
- the system control unit 14 starts the race table page display control process.
- the display control unit 143 acquires race information corresponding to the race ID of the target race included in the request from the race information DB 12b (step S21). Next, the display control unit 143 executes skill level determination processing (step S22). Next, the display control unit 143 determines whether or not the skill level determined in the skill level determination process is “expert” (step S23). At this time, if the display control unit 143 determines that the skill level is “expert” (step S23: YES), the display control unit 143 proceeds to step S24. On the other hand, if the display control unit 143 determines that the skill level is not “expert” (step S23: NO), the display control unit 143 proceeds to step S25.
- step S24 the display control unit 143 generates an HTML document of the racecard page corresponding to the expert based on the race information. At this time, the display control unit 143 acquires the entire racehorse information including essential information and non-essential information from the racehorse information included in the race information. Then, the display control unit 143 generates an HTML document including essential information. Next, the display control unit 143 proceeds to step S26.
- step S25 the display control unit 143 generates an HTML document of the racecard page corresponding to the beginner based on the race information. At this time, the display control unit 143 acquires only essential information from the race information. And the display control part 143 produces
- step S26 the display control unit 143 transmits the generated HTML page to the user terminal 3 that has transmitted the request.
- the display control unit 143 ends the horse race table page display control process.
- the user terminal 3 displays a race page (for example, FIG. 2 or FIG. 7) on the screen based on the received HTML page.
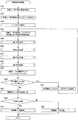
- FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing an example of skill level determination processing by the system control unit 14 of the betting ticket release agency server 1 according to the present embodiment.
- the history acquisition unit 141 searches the operation history DB 12e for a purchase history including the user ID of the target user (step S31).
- the history acquisition unit 141 may perform a search from a purchase history that does not include the race ID of the target race, for example.
- the history acquisition unit 141 can determine what operation history the operation history is by referring to the operation classification included in the operation history.
- the history acquisition unit 141 identifies the race in which the target user has purchased the betting ticket based on the searched purchase history (step S32).
- the history acquisition unit 141 acquires a race ID from the purchase history.
- the identified race is an example of one or more races of the present invention.
- the history acquisition unit 141 may limit the race to be specified.
- the history acquisition unit 141 may determine the date and time before the preset time from the current time as the reference date and specify only races that are held after the reference date and time.
- the history acquisition unit 141 can acquire the date of the event and the start time from the race information DB as the date of the event.
- the skill level determination unit 142 selects one of the identified races (step S33).
- the history acquisition unit 141 searches the operation history DB 12e for an operation history including the user ID of the target user and the race ID of the selected race (step S34).
- the skill level determination unit 142 sequentially executes a first determination process, a second determination process, a third determination process, and a fourth determination process (steps S35 to S38).
- the first to fourth determination processes are processes corresponding to the methods 1 to 4 shown in FIG.
- FIG. 11 is a flowchart illustrating an example of a first determination process performed by the system control unit 14 of the betting ticket release agency server 1 according to the present embodiment.
- the skill level determination unit 142 calculates a point P1 corresponding to the method 1.
- the skill level determination unit 142 sets the point P1 to 0 (step S51). In Method 1, when the point P1 is greater than 0, the target user is an expert, and when the point P1 is less than 0, the target user is a beginner.
- the history acquisition unit 141 acquires the browsing history of the odds page from the operation history searched in step S34 (step S52).
- the history acquisition unit 141 can determine what web page history the browsing history is by referring to the page type included in the browsing history.
- the skill level determination unit 142 determines whether or not there is an odds page browsing history in the searched operation history (step S53). At this time, when it is determined that there is no browsing history of the odds page (step S53: NO), the skill level determination unit 142 ends the first determination process. In this case, since the target user is not browsing the odds page, the skill level determination unit 142 cannot determine whether the target user is an expert or a beginner.
- step S53 the skill level determination unit 142 determines that there is a browsing history of the odds page (step S53: YES)
- the process proceeds to step S54.
- step S54 the history acquisition unit 141 specifies the browsing history of the web page browsed next to the odds page by the target user. Specifically, the history acquisition unit 141 extracts the browsing history of the web page from the operation history searched in step S34. Next, the history acquisition unit 141 acquires the browsing time of the odds page from the browsing history of the odds page. Next, the history acquisition unit 141 acquires the browsing time from each browsing history of the extracted web page.
- the history acquisition unit 141 determines a browsing time that is later than the browsing time of the odds page and closest to the browsing time of the odds page among the acquired browsing times. Then, the history acquisition unit 141 identifies the browsing history including the determined browsing time as the browsing history of the web page that the target user browsed next to the odds page.
- the history acquisition unit 141 acquires a manual update history of odds from the operation history searched in step S34.
- the skill level determination unit 142 calculates a manual update frequency (step S56). Specifically, the skill level determination unit 142 subtracts the browsing time included in the browsing history of the odds page from the browsing time included in the browsing history of the web page browsed next to the odds page to display the odds page. Calculate time. When there are a plurality of browsing histories of the odds page, the skill level determination unit 142 calculates a display time for each browsing history and calculates a total value of the display times. Next, the skill level determination unit 142 calculates the manual update frequency by dividing the number of manual update histories by the display time.
- the skill level determination unit 142 sets the point P1 to a value corresponding to the manual update frequency (step S57). At this time, the skill level determination unit 142 increases the point P1 as the manual update frequency increases. For example, the skill level determination unit 142 may calculate the point P1 using a predetermined calculation formula. Further, for example, the storage unit 12 may store a table indicating the correspondence relationship between the manual update frequency and the points. In this case, the skill level determination unit 142 may acquire points corresponding to the manual update frequency from the table. The skill level determination unit 142 ends the first determination process when step S57 is completed.
- FIG. 12 is a flowchart showing an example of the second determination process by the system control unit 14 of the betting ticket release agency server 1 according to this embodiment.
- the skill level determination unit 142 calculates a point P2 corresponding to the method 2.
- the skill level determination unit 142 sets the point P2 to 0 (step S61).
- the history acquisition unit 141 acquires the browsing history of the racecard page from the operation history searched in step S34 (step S62).
- step S63 determines whether there is a race history page browsing history in the searched operation history. At this time, if the skill level determination unit 142 determines that there is a viewing history of the racecard page (step S63: YES), the process proceeds to step S66. On the other hand, if the skill level determination unit 142 determines that there is no browsing history of the racecard page (step S63: NO), the process proceeds to step S64.
- step S64 the skill level determination unit 142 determines whether or not the operation history searched in step S34 has a browsing history of the expected list page. At this time, if the skill level determination unit 142 determines that there is a browsing history of the expected list page (step S64: YES), the process proceeds to step S65. In step S ⁇ b> 65, the skill level determination unit 142 acquires the minimum value of the point P ⁇ b> 2 from the storage unit 12. Then, the skill level determination unit 142 sets the point P2 to the minimum value. The skill level determination unit 142 ends the second determination process when step S65 is completed.
- step S64 determines that there is no browsing history of the prediction list page.
- the second determination process is terminated. In this case, since the target user is not browsing any of the race table page and the forecast list page, the skill level determination unit 142 cannot determine whether the target user is a skilled user or a beginner.
- step S66 the history acquisition unit 141 identifies the browsing history of the web page browsed by the target user next to the race table page.
- the method for specifying the browsing history of the next viewed web page is the same as step S54 of the first determination process.
- the skill level determination unit 142 subtracts the browsing time included in the browsing history of the race table page from the browsing time included in the browsing history of the web page browsed next to the race table page, and The display time is calculated (step S67).
- the skill level determination unit 142 calculates a display time for each browsing history, and calculates a total value of the display times.
- step S68 acquires the browsing history of the expected list page from the operation history searched in step S34 (step S68).
- the skill level determination unit 142 determines whether or not there is a browsing history of the expected list page in the searched operation history (step S69). At this time, if the skill level determination unit 142 determines that there is no browsing history of the prediction list page (step S69: NO), the process proceeds to step S70.
- step S ⁇ b> 70 the skill level determination unit 142 acquires the maximum value of the points P ⁇ b> 2 from the storage unit 12. Then, the skill level determination unit 142 sets the point P2 to the maximum value.
- the skill level determination unit 142 ends the second determination process after step S70.
- step S69 determines that there is a browsing history of the forecast list page (step S69: YES)
- step S71 the history acquisition unit 141 identifies the browsing history of the web page browsed next by the target user after the prediction list page.
- step S ⁇ b> 71 the history acquisition unit 141 identifies the browsing history of the web page browsed next by the target user after the prediction list page.
- step S ⁇ b> 71 the history acquisition unit 141 identifies the browsing history of the web page browsed next by the target user after the prediction list page.
- the skill level determination unit 142 subtracts the browsing time included in the browsing history of the prediction list page from the browsing time included in the browsing history of the web page browsed next to the prediction list page, and The display time is calculated (step S72).
- the skill level determination unit 142 calculates a display time for each browsing history and calculates a total value of the display times.
- the skill level determination unit 142 calculates the display time ratio by dividing the display time of the racecard page by the display time of the expected list page (step S73).
- the skill level determination unit 142 sets the point P2 to a value corresponding to the display time ratio (step S74).
- the skill level determination unit 142 increases the point P2 as the display time ratio increases.
- the skill level determination unit 142 may calculate the point P2 using a predetermined calculation formula, or may acquire a point corresponding to the display time ratio from the table stored in the storage unit 12. .
- the skill level determination unit 142 ends the second determination process when step S74 is completed.
- FIG. 13A is a flowchart showing an example of the third determination process by the system control unit 14 of the betting ticket release agency server 1 according to the present embodiment.
- the skill level determination unit 142 calculates a point P3 corresponding to the method 3.
- the skill level determination unit 142 sets the point P3 to 0 (step S81).
- the history acquisition unit 141 acquires the browsing history of the racecard page from the operation history searched in step S34 (step S82).
- the skill level determination unit 142 determines whether or not the race history page browsing history is included in the searched operation history (step S83). At this time, if the skill level determination unit 142 determines that there is no browsing history of the racecard page (step S83: NO), the third determination process ends. In this case, since the target user is not browsing the racecard page, the skill level determination unit 142 cannot determine whether the target user is a skilled user or a beginner.
- step S83 determines that there is a viewing history of the racecard page.
- step S84 the history acquisition unit 141 specifies the browsing history of the web page that the target user browses next to the racecard page.
- the skill level determination unit 142 determines, based on the page type included in the specified browsing history, whether the web page browsed next to the race page is an odds page or an expected list page. (Step S85). At this time, if the skill level determination unit 142 determines that the next viewed web page is neither an odds page nor an expected list page (step S85: NO), the third determination process ends.
- step S 85 the skill level determination unit 142 determines that the next viewed web page is either an odds page or an expected list page (step S85: YES)
- the process proceeds to step S86.
- step S ⁇ b> 86 the skill level determination unit 142 calculates the display time of the racecard page.
- the display time calculation method is the same as that in step S67 of the second determination process.
- the skill level determination unit 142 sets the point P3 to a value corresponding to the display time (step S87).
- the skill level determination unit 142 increases the point P3 as the display time is longer.
- the skill level determination unit 142 may calculate the point P3 using a predetermined calculation formula, or may acquire a point corresponding to the display time from a table stored in the storage unit 12.
- the skill level determination unit 142 ends the third determination process after step S87.
- FIG. 13B is a flowchart illustrating an example of a fourth determination process performed by the system control unit 14 of the betting ticket release agency server 1 according to the present embodiment.
- the skill level determination unit 142 calculates a point P4 corresponding to the method 4.
- the history acquisition unit 141 acquires a purchase history from the operation history searched in step S34 (step S91).
- the skill level determination unit 142 determines the number of votes based on the searched purchase history (step S92). For example, the skill level determination unit 142 may determine the number of voting objects corresponding to each formula included in the purchase history. Further, the skill level determination unit 142 may acquire the horse number and the frame number from the purchase history.
- the skill level determination unit 142 may determine the number of horse numbers and frame numbers as the number of votes. At this time, when there are a plurality of the same horse number or frame number, for example, the skill level determination unit 142 assigns 1 as the number of votes to the plurality of numbers or frame numbers.
- the skill level determination unit 142 sets the point P4 to a value according to the number of votes (step S93). At this time, the skill level determination unit 142 increases the point P4 as the number of voting objects increases. For example, the skill level determination unit 142 may calculate the point P4 using a predetermined calculation formula, or may acquire a point corresponding to the display time from a table stored in the storage unit 12. The skill level determination unit 142 ends the fourth determination process when step S93 is completed.
- the skill level determination unit 142 calculates the total value of the points P1 to P4 calculated in the first to fourth determination processes (step S39). Then, the skill level determination unit 142 determines the total value as a skill point of the selected race. Next, the skill level determination unit 142 determines whether there is a race that has not yet been selected among the identified races (step S40). At this time, if the skill level determination unit 142 determines that there is a race that has not yet been selected (step S40: YES), the process proceeds to step S41. In step S41, the skill level determination unit 142 selects one of the races that have not yet been selected. Next, the skill level determination unit 142 proceeds to step S34.
- step S40 determines that all races have been selected.
- step S40 determines that all races have been selected.
- step S42 the skill level determination unit 142 calculates the average value of skill points calculated in step S39.
- step S43 the threshold value stored in the storage unit 12
- step S44 the skill level determination unit 142 sets the skill level to “expert”.
- step S43 determines that the average value is not equal to or greater than the threshold value (step S43: NO)
- step S45 the skill level determination unit 142 sets the skill level to “beginner”.
- the skill level determination unit 142 ends the skill level determination process when step S44 or S45 is completed.
- the system control unit 14 acquires the operation history of the target user in the specified race from the storage unit 12. Moreover, the system control unit 14 determines the skill level of the target user regarding the purchase of the betting ticket based on the operation status specified from the acquired operation history. And the system control part 14 controls the display with respect to the object user of the information of an object race according to skill level. Therefore, appropriate information can be automatically provided according to the user without increasing the user's trouble.
- the system control unit 14 acquires the manual update history of the specified race and calculates the manual update frequency. Then, the system control unit 14 determines that the skill level is higher as the manual update frequency is higher. Further, the system control unit 14 obtains the browsing history of the race table page of the specified race and the browsing history of the prediction list page, and calculates the display time ratio. Then, the system control unit 14 determines that the skill level is higher as the display time ratio is higher. In addition, the system control unit 14 acquires the browsing history of the race page specified for the specified race, and acquires at least one of the browsing history of the odds page and the browsing history of the prediction list page.
- the system control unit 14 determines that the skill level is lower as the display time of the race table page is shorter. To do. In addition, the system control unit 14 acquires the purchase history of the specified race and determines the number of votes. Then, the system control unit 14 determines that the skill level is higher as the number of votes is larger. Thus, the skill level can be appropriately determined.
- the system control unit 14 when the odds stored in the storage unit 12 are displayed on the screen of the user terminal 3, the system control unit 14 periodically displays the odds based on the latest odds stored in the storage unit 12. Update. And the system control part 14 shortens the period which updates the display of odds, so that skill level is high. Therefore, the odds can be automatically updated at an appropriate cycle according to the skill level. In addition, for users with a low skill level, the period in which the odds are updated becomes longer. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the processing load of the betting ticket release agency server 1 by updating the odds.
- the system control unit 14 periodically updates the odds display based on the latest odds stored in the storage unit 12 only when the skill level is equal to or higher than the predetermined skill level. Therefore, it is possible to appropriately control whether or not the odds are automatically updated according to the skill level. Also, odds are not automatically updated for users with low skill levels. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the processing load of the betting ticket release agency server 1 by updating the odds.
- the system control unit 14 displays the race table page by the user terminal 3, and the higher the skill level, the larger the information amount of the race horse information included in the race table page. Therefore, it is possible to provide information regarding the racehorses participating in the race with an appropriate amount of information according to the skill level. In addition, the amount of information can be reduced as compared to displaying a race page with a large amount of information for all users. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the processing load of the betting ticket sale agency server 1 and the communication load of the network.
- the system control unit 14 determines the skill level based on the operation history stored up to the purchase of the specified race betting ticket among the operation histories stored in the storage unit 12. Therefore, the betting ticket sale agency server 1 can acquire an appropriate operation history as an operation history for purchasing a betting ticket.
- the betting ticket release agency server 1 controls the display of information about the race using the skill level.
- the betting ticket release agency server 1 may control the update cycle when the odds are automatically updated according to the manual update frequency of the odds.
- the betting ticket release agency server 1 calculates the manual update frequency based on the manual update history, and shortens the update cycle as the manual update frequency increases.
- the betting ticket sale agency server 1 may control whether or not the odds are automatically updated according to the manual update frequency of the odds.
- the betting ticket sale agency server 1 automatically updates the odds when the manual update frequency is greater than or equal to a predetermined value, and does not automatically update the odds when the manual update frequency is less than the predetermined value.
- the betting ticket release agency server 1 may perform control so that the data of the horse race table can be downloaded at the horse racing site.
- the format of the data in the racecard may be PDF, for example.
- the race table data is stored in the storage unit 12 of the betting ticket sale agency server 1.
- the race table data for example, there are detailed version of race table data and simplified version of race table data.
- the amount of information in the detailed version of the racecard data is larger than the amount of information in the simplified version of the racecard data.
- the content of the detailed version of the race table data is the same as the content of the race table page shown in FIG. 2, and the content of the simple version of the race table data is the same as the content of the race table page shown in FIG. Also good.
- the betting ticket release agency server 1 generates the racecard data based on the race information DB 12b.
- the betting ticket sales agency server 1 transmits a download page in response to a request from the user terminal 3.
- the download page is a web page for downloading the racecard data.
- On the download page for example, a link for downloading the detailed version of the racecard data and a link for downloading the simple version of the racecard data are displayed.
- the betting ticket release agency server 1 may control the arrangement order of the links on the download page according to the skill level. Specifically, when the betting ticket release agency server 1 determines that the proficiency level of the target user is equal to or higher than a predetermined skill level, a link for downloading the detailed version of the race table data is displayed as a simplified version of the race table.
- the betting ticket release agency server 1 determines that the proficiency level of the target user is less than the predetermined proficiency level, the link for downloading the simplified version of the racecard data is displayed as a detailed version of the racecard data. Send a download page that appears above the download link.
- the present invention is applied to the race.
- the present invention may be applied to matters other than races.
- this invention may be applied to the technique which determines a user's skill level regarding the matter.
- a web page that displays a manual of a product such as an electrical appliance on a predetermined website.
- the manual consists of several chapters.
- the information processing apparatus records a browsing history of web pages on a predetermined website in a database.
- the information processing apparatus determines the skill level of the target user based on the browsing status of the web page specified by the browsing history.
- the information processing apparatus may determine that the skill level of the product is high when only a predetermined chapter of the manual is viewed in a pinpoint manner. The reason is that it is considered that there is no hesitation for the user before reaching the target information. When in doubt, the user browses various chapters to arrive at the desired information. For example, the information processing apparatus calculates the number of manual browsing times for each chapter. Then, for example, the information processing apparatus may calculate a ratio of the number of times of browsing other chapters to the number of times of browsing a predetermined chapter. Then, the information processing apparatus may determine that the skill level is higher as the calculated ratio is smaller. The information processing apparatus may control the display of information on a predetermined website based on the skill level, or may use the skill level for another purpose.
- the information processing apparatus of the present invention is applied to a server apparatus in a client server system.
- the information processing apparatus of the present invention may be applied to an information processing apparatus other than the server apparatus.
- the information processing apparatus of the present invention may be applied to the user terminal 3 or the like.
- the information processing apparatus may store an operation history, for example, or may acquire an operation history from a predetermined server device.
- the control unit included in the information processing apparatus functions as a unit in the present invention, so that the control unit may control display of information by a display unit such as a display.
- the display means may be provided in the information processing apparatus.
- the display unit may be a separate device from the information processing device.
Landscapes
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Human Resources & Organizations (AREA)
- Tourism & Hospitality (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Operations Research (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Social Psychology (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14/917,187 US9934649B2 (en) | 2013-09-13 | 2014-06-25 | Information processing device, information processing method, and information processing program |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013191073A JP5923471B2 (ja) | 2013-09-13 | 2013-09-13 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム |
| JP2013-191073 | 2013-09-13 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015037305A1 true WO2015037305A1 (ja) | 2015-03-19 |
Family
ID=52665429
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/066839 Ceased WO2015037305A1 (ja) | 2013-09-13 | 2014-06-25 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9934649B2 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP5923471B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2015037305A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10970459B2 (en) | 2017-12-07 | 2021-04-06 | Paypal, Inc. | Dynamic web content based on contextual profile |
| JP7281719B2 (ja) * | 2018-08-17 | 2023-05-26 | 株式会社Mixi | 情報処理装置、投票受付方法及び投票受付プログラム |
| JP6886122B1 (ja) * | 2020-05-29 | 2021-06-16 | 株式会社ミクシィ | 情報処理システム、情報処理方法及びプログラム |
| US11410502B2 (en) | 2020-09-24 | 2022-08-09 | Adrenalineip | Method of rewarding non-dangerous behavior |
| JP7534639B2 (ja) * | 2021-03-23 | 2024-08-15 | 株式会社Mixi | 情報処理装置、コンピュータプログラムおよび情報処理方法 |
| JP7422113B2 (ja) * | 2021-08-20 | 2024-01-25 | Lineヤフー株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法および情報処理プログラム |
| JP7231705B1 (ja) * | 2021-12-28 | 2023-03-01 | 楽天グループ株式会社 | 投票券販売装置、投票券販売方法、投票券販売プログラム、及び投票券販売システム |
| JP7629886B2 (ja) * | 2022-03-17 | 2025-02-14 | 富士通フロンテック株式会社 | 出走表表示装置、出走表表示プログラムおよび出走表表示方法 |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012014407A (ja) * | 2010-06-30 | 2012-01-19 | Terumo Corp | 医療機器情報提供装置、医療機器情報提供システム及び医療機器情報提供方法 |
| JP2013037584A (ja) * | 2011-08-09 | 2013-02-21 | Sumitomo Electric Ind Ltd | 情報提供装置、コンピュータプログラム及び情報提供方法 |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3488525B2 (ja) * | 1994-12-13 | 2004-01-19 | 富士通株式会社 | ヘルプ画面表示方法およびヘルプ画面表示装置 |
| US5963910A (en) * | 1996-09-20 | 1999-10-05 | Ulwick; Anthony W. | Computer based process for strategy evaluation and optimization based on customer desired outcomes and predictive metrics |
| NZ521635A (en) * | 2000-04-05 | 2004-03-26 | Ods Properties Inc | Interactive wagering systems and methods for restricting wagering access |
| JP2001357292A (ja) * | 2000-06-14 | 2001-12-26 | Koji Matsumura | 電子マニュアル配信システム |
| AU2002322835A1 (en) * | 2001-08-01 | 2003-02-17 | Kim Updike | Methods and apparatus for fairly placing players in bet positions |
| US8734226B2 (en) * | 2001-12-12 | 2014-05-27 | Bgc Partners, Inc. | Systems and methods for assisting in game play and wagering |
| US20070106553A1 (en) * | 2004-09-15 | 2007-05-10 | Jordan Richard J | Pari-mutuel betting with bonus feature |
| JP2007087328A (ja) * | 2005-09-26 | 2007-04-05 | Toshiba Solutions Corp | 競馬情報配信システム |
| JP2008033539A (ja) * | 2006-07-27 | 2008-02-14 | Nihon Unica Corp | 電子投票システム |
-
2013
- 2013-09-13 JP JP2013191073A patent/JP5923471B2/ja active Active
-
2014
- 2014-06-25 WO PCT/JP2014/066839 patent/WO2015037305A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2014-06-25 US US14/917,187 patent/US9934649B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012014407A (ja) * | 2010-06-30 | 2012-01-19 | Terumo Corp | 医療機器情報提供装置、医療機器情報提供システム及び医療機器情報提供方法 |
| JP2013037584A (ja) * | 2011-08-09 | 2013-02-21 | Sumitomo Electric Ind Ltd | 情報提供装置、コンピュータプログラム及び情報提供方法 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| KOSUKE NONAKA: "Otegaru Keiba Apuri 'Daimajin' wa Sugokatta!! Ninkiusu no Anauma mo Hirotte 3 Rentan Tekichu no Jitsuryoku o Hakki", 15 March 2013 (2013-03-15), Retrieved from the Internet <URL:http://keiba.nifty.com/cs/column-detail/pdetail/daimajin20130315/1.htm> [retrieved on 20140731] * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US9934649B2 (en) | 2018-04-03 |
| JP5923471B2 (ja) | 2016-05-24 |
| JP2015056165A (ja) | 2015-03-23 |
| US20160217651A1 (en) | 2016-07-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5923471B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム | |
| JP5373956B1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム | |
| JP5870084B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラム及び情報処理システム | |
| JP5124680B1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラム及び記録媒体 | |
| JP5702422B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム | |
| JP5156123B1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラム、及び記録媒体 | |
| JP5740536B1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム | |
| US9542077B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, information processing program, and recording medium | |
| JP2013167917A (ja) | サーバ装置、表示制御方法、表示制御プログラム及び記録媒体 | |
| JP5386660B1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、及び情報処理プログラム | |
| JP5506104B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、及び情報処理プログラム | |
| JP5827710B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラム及び情報処理システム | |
| JP6539772B1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、プログラム、記憶媒体 | |
| JP2016071753A (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム | |
| JP5827676B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラム及び情報処理システム | |
| JP6462297B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム | |
| JP5760158B1 (ja) | 投票券情報提供装置、投票券情報提供方法、および、投票券情報提供装置用プログラム | |
| JP6497866B2 (ja) | 懸賞情報提供サーバ、懸賞情報提供方法及び懸賞情報提供サーバ用プログラム | |
| JP2012083904A (ja) | サーバ装置、情報処理方法、情報処理プログラム及び記録媒体 | |
| JP5839765B1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム | |
| JP7553109B2 (ja) | 釣果情報に基づいたアプリケーションの提供方法 | |
| JP2012079018A (ja) | サーバ装置、抽籤方法、抽籤プログラム及び記録媒体 | |
| JP2012079019A (ja) | サーバ装置、抽籤方法、抽籤プログラム及び記録媒体 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14843494 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14917187 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 14843494 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |