WO2014007071A1 - ペット用シート - Google Patents
ペット用シート Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2014007071A1 WO2014007071A1 PCT/JP2013/067009 JP2013067009W WO2014007071A1 WO 2014007071 A1 WO2014007071 A1 WO 2014007071A1 JP 2013067009 W JP2013067009 W JP 2013067009W WO 2014007071 A1 WO2014007071 A1 WO 2014007071A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- sheet
- pet
- absorption layer
- layer
- excrement
- Prior art date
Links
- 239000002250 absorbent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 90
- 230000002745 absorbent Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 80
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 51
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 49
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 49
- 239000003093 cationic surfactant Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 26
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 126
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims description 50
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 33
- 239000006096 absorbing agent Substances 0.000 claims description 15
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 15
- 238000004062 sedimentation Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 150000003242 quaternary ammonium salts Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 141
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 31
- 230000029142 excretion Effects 0.000 description 14
- 239000004745 nonwoven fabric Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000004831 Hot glue Substances 0.000 description 6
- -1 amine salts Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 5
- 210000002700 urine Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-GSVOUGTGSA-N (R)-(-)-Propylene glycol Chemical compound C[C@@H](O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-GSVOUGTGSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 230000000844 anti-bacterial effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 125000002091 cationic group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000003892 spreading Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 241000282472 Canis lupus familiaris Species 0.000 description 2
- 241000282326 Felis catus Species 0.000 description 2
- 239000004952 Polyamide Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 2
- JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyridine Chemical class C1=CC=NC=C1 JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium chloride Chemical compound [Na+].[Cl-] FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- UREZNYTWGJKWBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M benzethonium chloride Chemical class [Cl-].C1=CC(C(C)(C)CC(C)(C)C)=CC=C1OCCOCC[N+](C)(C)CC1=CC=CC=C1 UREZNYTWGJKWBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- CYDRXTMLKJDRQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzododecinium Chemical class CCCCCCCCCCCC[N+](C)(C)CC1=CC=CC=C1 CYDRXTMLKJDRQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000004693 imidazolium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002504 physiological saline solution Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920002647 polyamide Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920000915 polyvinyl chloride Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004800 polyvinyl chloride Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000247 superabsorbent polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 244000025254 Cannabis sativa Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000218631 Coniferophyta Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 208000003251 Pruritus Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229920001131 Pulp (paper) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000297 Rayon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 206010040880 Skin irritation Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000007792 addition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001768 cations Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012792 core layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012217 deletion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037430 deletion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004049 embossing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000003608 fece Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002209 hydrophobic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007803 itching Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000155 melt Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012856 packing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920000139 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000005020 polyethylene terephthalate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000002964 rayon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002940 repellent Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000005871 repellent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000036556 skin irritation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 231100000475 skin irritation Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 239000011780 sodium chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011122 softwood Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012085 test solution Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01K—ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; AVICULTURE; APICULTURE; PISCICULTURE; FISHING; REARING OR BREEDING ANIMALS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NEW BREEDS OF ANIMALS
- A01K1/00—Housing animals; Equipment therefor
- A01K1/01—Removal of dung or urine, e.g. from stables
- A01K1/0107—Cat trays; Dog urinals; Toilets for pets
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01K—ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; AVICULTURE; APICULTURE; PISCICULTURE; FISHING; REARING OR BREEDING ANIMALS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NEW BREEDS OF ANIMALS
- A01K1/00—Housing animals; Equipment therefor
- A01K1/01—Removal of dung or urine, e.g. from stables
- A01K1/0103—Removal of dung or urine, e.g. from stables of liquid manure
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01K—ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; AVICULTURE; APICULTURE; PISCICULTURE; FISHING; REARING OR BREEDING ANIMALS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NEW BREEDS OF ANIMALS
- A01K1/00—Housing animals; Equipment therefor
- A01K1/015—Floor coverings, e.g. bedding-down sheets ; Stable floors
- A01K1/0152—Litter
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01K—ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; AVICULTURE; APICULTURE; PISCICULTURE; FISHING; REARING OR BREEDING ANIMALS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NEW BREEDS OF ANIMALS
- A01K1/00—Housing animals; Equipment therefor
- A01K1/015—Floor coverings, e.g. bedding-down sheets ; Stable floors
- A01K1/0152—Litter
- A01K1/0155—Litter comprising organic material
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01K—ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; AVICULTURE; APICULTURE; PISCICULTURE; FISHING; REARING OR BREEDING ANIMALS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NEW BREEDS OF ANIMALS
- A01K1/00—Housing animals; Equipment therefor
- A01K1/015—Floor coverings, e.g. bedding-down sheets ; Stable floors
- A01K1/0157—Mats; Sheets
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a pet sheet used for treating the excrement of pets such as dogs and cats, and particularly to a pet sheet capable of suppressing the diffusion of excrement on the sheet surface.
- a pet sheet disclosed in Patent Document 1 is known as a pet sheet for treating excrement (particularly urine) of pets such as dogs and cats.
- the pet sheet disclosed in Patent Document 1 includes a liquid-permeable top sheet, a liquid-impermeable back sheet, and an absorber disposed between the top sheet and the back sheet.
- the absorber is formed of hydrophilic fibers such as pulp and a water-absorbing resin such as a superabsorbent polymer.
- an object of this invention is to provide the novel technique which can suppress the excretion absorbed by the absorption layer from diffusing to the sheet
- the pet sheet of the present invention includes a liquid-permeable top sheet, a liquid-impermeable back sheet, an absorbent body that is disposed between the top sheet and the back sheet, and absorbs excrement that has passed through the top sheet.
- the pet sheet of the present invention is configured such that the top sheet receives the excrement of the pet in a state where the back sheet is placed on a placement place such as a floor surface.
- the absorber has an absorption layer formed of hydrophilic fibers containing a cationic (cationic) surfactant.
- the hydrophilic fiber for example, pulp, rayon or the like is used.
- cationic surfactant for example, amine salts, quaternary ammonium salts, benzalkonium salts, benzethonium chloride salts, pyridinium salts, imidazolium salts, polyamide derivatives, and the like can be used.
- Hydrophilicity is imparted to the hydrophilic fiber by a cationic surfactant. Since the cationic surfactant is chemically bonded to the hydrophilic fiber, the excrement can prevent the cationic surfactant from being peeled off from the hydrophilic fiber.
- an absorption layer containing a water absorbent resin is used.
- the hydrophilic fiber since the cationic surfactant that imparts hydrophobicity to the hydrophilic fiber is not peeled off from the hydrophilic fiber by excrement, the hydrophilic fiber is maintained in a desired hydrophobic state for a long time. can do. Moreover, it is suppressed that the excretion absorbed in the absorption layer spreads (diffuses) in the absorption layer, and as a result, the excrement is suppressed from diffusing on the sheet surface.
- a quaternary ammonium salt is used as a cationic surfactant that imparts hydrophobicity to hydrophilic fibers.
- the pet sheet can have antibacterial properties.
- pulp is used as the hydrophilic fiber.
- the settling speed of the hydrophilic fibers forming the absorption layer is set to 5 seconds or more.
- the “sedimentation velocity” is a value of 10 mm above the water surface with a cylindrical body formed by using 5 g of a hydrophilic fiber containing a cationic surfactant and water placed in a container having a depth of 400 mm. It is expressed as the time from when the cylindrical body touches the water surface until it sinks below the water surface.
- the absorption layer is formed of hydrophilic fibers containing a cationic surfactant and a water absorbent resin.
- the absorption layer has a first absorption layer formed of hydrophilic fibers containing a cationic surfactant and a second absorption layer formed of water-absorbing fibers. Yes.
- the second absorbent layer is disposed closer to the surface sheet than the first absorbent layer.
- the second absorption layer When the absorption layer has a first absorption layer formed of hydrophilic fibers containing a cationic surfactant and a second absorption layer formed of a water absorbent resin, the second absorption layer is liquid-absorbing. A higher speed is preferred.
- the second absorption layer has a liquid absorption rate measured by vortex method set to 18 seconds or less.
- the second absorption layer can be formed of a water-absorbing resin having a desired liquid absorption rate, and the liquid absorption rate is such that the liquid absorption rate of the entire second absorption layer becomes the desired liquid absorption rate. It can also be formed by combining a plurality of different water-absorbing resins. In this embodiment, the diffusion of excrement on the sheet surface due to the diffusion of excrement in the first absorption layer can be further suppressed.
- the excrement absorbed in the absorption layer can be prevented from spreading (diffusing) in the absorption layer, and as a result, the excrement can be prevented from diffusing on the sheet surface.
- FIG. 2 is a sectional view taken along line II-II in FIG. It is a figure explaining the effect
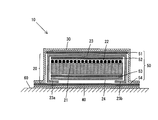
- FIG. 1 and FIG. 2 show a pet sheet 10 according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- 1 is a perspective view of the pet sheet 10 of the present embodiment
- FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view taken along the line II-II of FIG.
- the pet sheet 10 is formed in a rectangle having a long side along the longitudinal direction LD and a short side along the width direction WD, as shown in FIG.
- the pet sheet 10 can be formed in various shapes other than a rectangle.
- the pet sheet 10 includes an absorbent body 20, a top sheet 30, and a back sheet 40.
- the absorber 20 is disposed between the top sheet 30 and the back sheet 40 and is covered with the top sheet 30 and the back sheet 40.
- the back sheet 40 is mounted in the mounting location (for example, floor surface 60) so that the top sheet 30 may receive excrement. That is, the back sheet 40, the absorbent body 20, and the top sheet 30 are laminated in the vertical direction.
- the top sheet 30 has liquid permeability that allows liquid (such as urine) contained in excrement to pass therethrough.
- the surface sheet 30 should just have liquid permeability, for example, can be comprised with nonwoven fabrics, such as a thermal bond nonwoven fabric, a point bond nonwoven fabric, an air through nonwoven fabric, a spunlace nonwoven fabric, and a spun bond nonwoven fabric.
- the back sheet 40 has liquid impermeability or water repellency which prevents or suppresses permeation of the liquid contained in the excrement.
- the back sheet 40 should just have liquid impermeability, for example, can be comprised with the resin film formed with polyethylene, a polypropylene, a polyethylene terephthalate, etc.
- a polyethylene film having a basis weight of 17 [g / m 2 ] can be used.
- a non-woven fabric coated with a water repellent can be used as the back sheet 40.
- [g / m ⁇ 2 >] is a unit which shows a basis weight, and shows the weight (gram) per square meter.
- the top sheet 30 and the back sheet 40 are formed in a shape that can cover the absorber 20, and the peripheral portions are joined in a state of covering the absorber 20.
- the absorber 20 has an absorption layer, a front surface side covering sheet 23 and a back surface side covering sheet 24.
- the absorbent layer is a first absorbent layer (also referred to as “absorber core layer”) 21 formed of hydrophilic fibers and a second absorbent layer (also referred to as “dispersion layer”) formed of a water absorbent resin. ) 22.
- the second absorbent layer 22 is arranged on the top sheet 30 side (upper side) from the first absorbent layer 21.
- the first absorbent layer 21 is typically configured by laminating hydrophilic fibers so that the basis weight is 60 g / m 2 .
- the hydrophilic fiber for example, fluff pulp is used.
- the second absorption layer 22 is obtained by spraying a water-absorbing resin on the upper surface (surface on the surface sheet 30 side) of the first absorption layer 21 so that the basis weight is 40 [g / m 2 ]. Composed.
- a water absorbent resin for example, a super absorbent polymer (also referred to as “SAP”) is used.
- SAP super absorbent polymer
- water-absorbing resin is uniformly spread
- the absorbent layer 22 may not be completely separated.
- the absorbent layer is disposed between the front surface side covering sheet 23 and the back surface side covering sheet 24 and is covered with the front surface side covering sheet 23 and the back surface side covering sheet 24.
- the surface side coating sheet 23 is arrange
- the back surface side coating sheet 24 is arrange
- the front surface side covering sheet 23 and the back surface side covering sheet 24 are typically composed of a tissue made of softwood pulp (for example, a tissue having a basis weight of 12 to 25 [g / m 2 ]).
- both end portions 23 a and 23 b of the front surface side covering sheet 23 are below the both end portions of the back surface side covering sheet 24 ( It is folded on the back sheet 40 side.
- the 1st absorption layer 21 is formed with a pulp
- the 1st absorption layer 21 is comprised by laminating
- the excrement (urine) X that has permeated the top sheet and the top side covering sheet 323 is first absorbed in the second absorbent layer 322 with a high absorption rate. Absorbed by resin.
- the absorbent layer contains a hydrophobizing agent such as a higher aliphatic alcohol or higher fatty amine, which has a higher affinity for hydrophilic fibers than the water absorbent resin.
- a hydrophobizing agent such as a higher aliphatic alcohol or higher fatty amine, which has a higher affinity for hydrophilic fibers than the water absorbent resin. The excrement absorbed in the absorption layer is prevented from diffusing in the absorption layer.
- the first absorbent layer 21 is formed of a surfactant that imparts hydrophobicity to the hydrophilic fiber, in particular, a hydrophilic fiber containing a cationic (cation) surfactant. Since the cationic surfactant is chemically bonded to the hydrophilic fiber, the cationic surfactant is not peeled off from the hydrophilic fiber by excrement. Thereby, the state in which the hydrophilic fiber has the desired hydrophobicity can be maintained for a long time.
- a surfactant that imparts hydrophobicity to the hydrophilic fiber in particular, a hydrophilic fiber containing a cationic (cation) surfactant. Since the cationic surfactant is chemically bonded to the hydrophilic fiber, the cationic surfactant is not peeled off from the hydrophilic fiber by excrement. Thereby, the state in which the hydrophilic fiber has the desired hydrophobicity can be maintained for a long time.
- amine salts As the cationic surfactant, amine salts, quaternary ammonium salts, benzalkonium salts, benzethonium chloride salts, pyridinium salts, imidazolium salts, polyamide derivatives, and the like can be used.
- the antibacterial property of the quaternary ammonium salt can impart antibacterial properties to the pet sheet.
- hydrophilic fiber wood pulp from broad-leaved trees and conifers, pulp of grass plants, and the like can be used. Among these, it is preferable to use fluff pulp having a long fiber length.
- the first absorbent layer 21 is composed of treat pulp in which fluff pulp is uniformly laminated so as to have a basis weight of 60 [g / m 2 ] and includes a cationic surfactant.
- the sedimentation speed of the treat pulp (first absorption layer 21) is set to 5 seconds or more.
- the sedimentation rate is measured as follows. (1) A cylindrical body is formed by uniformly packing 5 g of treat pulp into a cylindrical shape. (2) Water is poured into a container such as a beaker so that the water depth is about 200 mm. (3) Lay the cylinder sideways and gently drop it from a height of 10m above the water surface.
- the sedimentation rate of the first absorption layer 21 is set to 5 seconds or more.
- the sedimentation speed of the first absorption layer 21 it is possible to effectively suppress the diffusion of excrement on the sheet surface due to the diffusion of excrement in the first water absorption layer. it can.
- the second absorbent layer 22 is formed by uniformly dispersing the water-absorbent resin on the upper surface of the first absorbent layer 21 so that the basis weight is 40 [g / m 2 ]. Yes.
- the operation of the pet sheet according to the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. (1)
- the excrement (urine) X that has passed through the top sheet 30 and the top side covering sheet 23 first has a high absorption rate in the second absorption layer 22. Absorbed by water absorbent resin.
- the excrement X that could not be absorbed by the water absorbent resin of the second absorption layer 22 moves to the first absorption layer 21.
- the hydrophilic property which forms the 1st absorption layer 21 is provided with hydrophobicity by the cationic surfactant.
- the excrement X transferred to the first absorption layer 21 is repelled by hydrophilic fibers to which hydrophobicity has been imparted, and the spread (diffusion) to the lower and outer sides in the first absorption layer 21 is suppressed.
- the excrement X transferred to the first absorption layer 21 is repelled by the hydrophilic fibers imparted with hydrophobicity and the spread to the lower and outer sides in the first absorption layer 21 is suppressed, the excrement X accumulates in one place.
- the accumulated excrement X continues to touch the user's body, causing skin irritation and itching. For this reason, such a method has not been used for an absorbent sheet used by being attached to the body.
- the pet sheet is not attached to the body, and is used by being placed horizontally (rarely used in a tilted state).
- a concavo-convex portion is formed in the joining region, and this concavo-convex portion causes a portion having a high fiber density (high density portion) and a portion having a low fiber density (low in the joining region). Density part) is formed.
- the excrement spreads (diffuses) along the high-density portion due to capillary action.
- excrement diffuses along the bonding region where the absorption layer (second absorption layer 21) and the surface-side coating sheet 23 are bonded, and the bonding region where the surface-side coating sheet 23 and the surface sheet 30 are bonded. The excreta will diffuse on the sheet surface.
- the surface sheet 30 and the surface side covering sheet 23, and the surface side covering sheet 23 and the absorbing layer (second absorbing layer 22) that is, the surface sheet 30 and the absorbing layer are the surface side covering sheet 23.
- the whole is joined using a heat-weldable adhesive (hot melt adhesive).
- a hot melt adhesive is an adhesive that liquefies by heating and melts and forms a joined state by cooling and solidifying.
- the hot melt adhesive a known one can be used.
- the absorbent layer (first absorbent layer 21) and the back surface side coated sheet 24, and the back surface side coated sheet 24 and the back surface sheet 40 are also bonded together using a hot melt adhesive. .
- the description “joined over the whole” is arranged so as to face each other along the stacking direction (vertical direction) among the surfaces of the surface sheet 30 and the surface side covering sheet 23 (the surface side covering sheet 23 and the absorption layer).
- the adhesive is applied evenly over the entire surface (entire surface) of at least one of the surfaces arranged facing the stacking direction (vertical direction), or at least one of the surfaces
- a mode in which the adhesive is applied to the entire surface in a non-continuous pattern such as a spiral shape, a lattice shape, a stripe shape, or a scattered dot shape is included.
- the joint portions 50 (51, 52, 53, 54) shown in FIG. 2 are respectively a surface sheet 30 and a surface side covering sheet 23, a surface side covering sheet 23 and an absorbing layer (second absorbing layer 22),
- the absorbent layer (first absorbent layer 21) and the back surface side coating sheet 24, and the back surface side coating sheet 24 and the back surface sheet 40 are joined by a hot melt adhesive.
- a heat welding adhesive By joining together using a heat welding adhesive, an absorber can be firmly fixed between the surface sheet 30 and the back surface sheet 40, and shape loss of an absorber can be prevented.
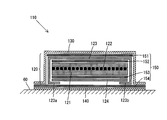
- FIG. 4 shows a cross-sectional view of a pet sheet 110 according to another embodiment of the present invention.
- the pet sheet 110 of the present embodiment is the same as the pet sheet 10 except for the configuration of the absorbent layer of the absorber 120. Therefore, only the configuration of the absorber 120 will be described.
- the absorber 120 has an absorbent layer 121, a front surface side covering sheet 123 and a back surface side covering sheet 124.
- the absorption layer 121 is formed of hydrophilic fibers, and a second absorption layer 122 formed of a water absorbent resin is provided in the first absorption layer 121.
- a hydrophilic fiber which forms the absorption layer 121 the same thing as the hydrophilic fiber which forms the 1st absorption layer 21 mentioned above can be used.
- the water absorbent resin forming the second absorbent layer 122 the same water absorbent resin as that forming the second absorbent layer 22 described above can be used.
- the pet sheet 110 of the present embodiment has the same effects as the pet sheet 10 described above.
- hydrophilic fibers containing a cationic surfactant and the liquid absorption rate of the water-absorbent resin were examined.
- the effect of suppressing the diffusion of excrement on the sheet surface was judged from the liquid diffusion area.
- the liquid absorption rate is measured by the following method (Vortex method).
- 2 g of water absorbent resin (SAP) is added, and the time for the liquid surface to become flat is measured.
- SAP water absorbent resin
- the liquid diffusion area is calculated by the following method.
- a polyvinyl chloride tube (outer diameter 66.6 mm, inner diameter 60.2 mm, height 53 mm) is arranged at a measurement location (apart from the crease) of the target sheet.
- a burette 40 cc / 6 seconds
- 40 cc of 0.9% physiological saline is dropped in 6 seconds from above 10 mm onto the center of the PVC pipe.
- the diffusion length in the MD direction (Machine Direction) of physiological saline and the diffusion length in the CD direction (Cross Direction) are measured.
- the liquid diffusion area (cm 2 ) is calculated using the measured MD direction diffusion length and CD direction diffusion length and the following calculation formula. [(MD direction diffusion length / 2) ⁇ (CD direction diffusion length / 2) ⁇ 3.14]
- the following sheets 1 to 8 were used as sheets having a first absorption layer and a second absorption layer disposed on the upper surface of the first absorption layer.
- Sheets 1 to 4 have fluff pulp uniformly laminated so that the basis weight is 60 [g / m 2 ], and a pulp (treat pulp) containing a cationic surfactant is used as the first absorbent layer.
- the sheets 5 to 8 use pulp (non-treat pulp) in which fluff pulp is uniformly laminated so as to have a basis weight of 60 [g / m 2 ] as the first absorbent layer.
- the water-absorbent resin is more expensive as the liquid absorption rate is faster.
- the water-absorbing resin has higher strength and lower rewet (an action in which excrement absorbed by the water-absorbing resin returns to the sheet surface side) when the liquid absorption rate is slower.
- the first absorbent layer is formed from treat pulp
- the second absorbent layer is formed from the water-absorbent resin, whereby the excrement absorbed in the absorbent layer returns to the sheet surface side. It can be understood that diffusion of excrement on the sheet surface can be effectively suppressed.
- the second absorption layer can be made of a water-absorbing resin having a desired liquid absorption rate, or the liquid absorption rate can be adjusted so that the liquid absorption rate of the entire second absorption layer becomes the desired liquid absorption rate.
- a plurality of water-absorbing resins having different speeds can be combined.
- the absorption layer is configured by the first absorption layer formed by the hydrophilic fiber containing the cationic surfactant and the second absorption layer formed by the water absorbent resin (SAP). It can also be composed of only one absorption layer.
- Various cationic surfactants that impart hydrophobicity to the hydrophilic fiber can be used.
- As the hydrophilic fiber various fibers other than pulp can be used. The arrangement position of the second absorption layer with respect to the first absorption layer and the number of the second absorption layers can be appropriately selected.
- positioned in the upper part and the lower part of a 1st absorption layer the aspect arrange
- a joining method a method other than a joining method using a heat-welding adhesive (hot melt adhesive) can also be used.
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Environmental Sciences (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Animal Husbandry (AREA)
- Biodiversity & Conservation Biology (AREA)
- Housing For Livestock And Birds (AREA)
Abstract
Description
このため、1枚のペット用シートで複数回の排泄を行うことができるようにするためには、ペット用シートに排泄された排泄物がシート表面に拡散するのを抑制する(拡散面積を狭める)ことが必要となる。
そこで、特許文献1に開示されているペット用シートでは、吸水性樹脂より親水性繊維に対して高い親和性を有する疎水化剤(高級脂肪族アルコールまたは高級脂肪アミン)を吸収層に含有させている。
これにより、特許文献1に開示されているペット用シートは、吸水性樹脂の吸収性を維持しながら、親水性繊維に疎水性を付与することができ、排泄物がシート表面に拡散するのを抑制することができる。
したがって、本発明は、吸収層に吸収された排泄物がシート表面側に拡散するのを抑制することができる新規な技術を提供することを目的とする。
本発明では、吸収体は、カチオン(陽イオン)系界面活性剤を含む親水性繊維により形成される吸収層を有している。親水性繊維としては、例えば、パルプ、レーヨン等が用いられる。カチオン系界面活性剤としては、例えば、アミン塩、第4級アンモニウム塩、ベンザルコニウム塩、塩化ベンゼトニウムン塩、ピリジニウム塩、イミダゾリウム塩、ポリアミド誘導体等を用いることができる。親水性繊維は、カチオン系界面活性剤によって疎水性が付与される。カチオン系界面活性剤は親水性繊維と化学的に結合するため、排泄物によって、カチオン系界面活性剤が親水性繊維から剥がれるのを防止することができる。なお、好適には、吸水性樹脂を含む吸収層が用いられる。
本発明では、親水性繊維に疎水性を付与するカチオン系界面活性剤が排泄物によって親水性繊維から剥がれることがないため、親水性繊維が所望の疎水性を有している状態を長い時間維持することができる。また、吸収層で吸収された排泄物が吸収層内で拡がる(拡散する)のが抑制され、結果として、排泄物がシート表面で拡散するのが抑制される。
「沈降速度」は、カチオン系界面活性剤を含む親水性繊維5gを用いて円筒体を形成し、深さ400mmの容器に水を入れた状態で、円筒体を横にして水面上10mmの高さから落とし、円筒体が水面に接してから水面下に沈むまでの時間で表される。
吸収層の沈降速度が5秒以上に設定されていることにより、吸収層内での排泄物の拡散に起因するシート表面での排泄物の拡散をより抑制することができる。
本発明のさらに他の形態では、第2の吸収層は、ボルテックス法を用いて測定した液体吸収速度が18秒以下に設定されている。
第2の吸収層は、所望の液体吸収速度を有する吸水性樹脂により形成することもできるし、第2の吸収層全体の液体吸収速度が所望の液体吸収速度となるように、液体吸収速度が異なる複数の吸水性樹脂を組み合わせて形成することもできる。
本形態では、第1の吸収層内での排泄物の拡散に起因するシート表面での排泄物の拡散をより抑制することができる。
なお、以下の詳細な説明は、本発明の好ましい適用例を実施するための詳細情報を当業者に教示するに留まり、本発明の技術的範囲は、当該詳細な説明によって制限されず、特許請求の範囲の記載に基づいて定められる。このため、以下の詳細な説明における各構成あるいは各方法は、広義の意味において、本発明を実施するのに全て必須であるというものではなく、本発明の代表的形態を開示するに留まるものである。
表面シート30と裏面シート40は、吸収体20を覆うことができる形状に形成されており、吸収体20を覆った状態で周縁部分が接合されている。
吸収層は、親水性繊維により形成されている第1の吸収層(「吸収体コア層」ともいう)21と、吸水性樹脂により形成されている第2の吸収層(「分散層」ともいう)22を有している。第2の吸収層22は、第1の吸収層21より表面シート30側(上側)に配置されている。
第1の吸収層21は、典型的には、親水性繊維を目付が60g/m2となるように積層して構成される。親水性繊維としては、例えば、フラッフパルプが用いられる。
第2の吸収層22は、典型的には、吸水性樹脂を目付が40[g/m2]となるように第1の吸収層21の上面(表面シート30側の表面)に散布して構成される。吸水性樹脂としては、例えば、高吸収性ポリマー(「SAP」ともいう)が用いられる。なお、親水性繊維により形成されている第1の吸収層21の上面に吸水性樹脂を均一に散布する場合、吸水性樹脂が親水性繊維の間に入り込み、第1の吸収層21と第2の吸収層22が完全に分離した状態とならないことがある。
表面側被覆シート23および裏面側被覆シート24は、典型的には、針葉樹パルプからなるティッシュ(例えば、目付が12~25[g/m2]のティッシュ)によって構成される。
本実施の形態では、表面側被覆シート23と裏面側被覆シート24によって吸収層を包み込むために、表面側被覆シート23の両端部23aおよび23bが、裏面側被覆シート24の両端部の下方側(裏面シート40側)に折り重ねられている。
カチオン系界面活性剤は、親水性繊維と化学的に結合するため、排泄物によってカチオン系界面活性剤が親水性繊維から剥がれることがない。これにより、親水性繊維が所望の疎水性を有している状態を長い時間維持することができる。
親水性繊維としては、広葉樹及び針葉樹からの木材パルプや草植物のパルプ等を用いることができる。この中でも、繊維長が長いフラッフパルプを用いるのが好ましい。
また、トリートパルプ(第1の吸収層21)の沈降速度が5秒以上に設定されている。
沈降速度は、以下のようにして測定する。
(1)トリートパルプ5gを円筒状に均一に詰めて円筒体を形成する。
(2)ビーカー等の容器に、水深約200mmとなるように水を注入する。
(3)円筒体を横にして、水面上10mの高さから静かに落とす。
(4)円筒体が水面に接してから水面下に沈むまでの時間を測定し、沈降速度とする。
好適には、第1の吸収層21の沈降速度は、5秒以上に設定される。第1の吸収層21の沈降速度を5秒以上に設定することにより、第1の吸水層内での排泄物の拡散に起因するシート表面での排泄物の拡散を効果的に抑制することができる。
なお、本実施の形態では、吸水性樹脂を目付が40[g/m2]となるように第1の吸収層21の上面に均一に散布することによって第2の吸収層22を形成している。
(1)ペット用シート10上でペットが排泄を行うと、表面シート30および表面側被覆シート23を透過した排泄物(尿)Xは、先ず、第2の吸収層22において、吸収速度が速い吸水性樹脂に吸収される。
(2)第2の吸収層22の吸水性樹脂で吸収することができなかった排泄物Xは、第1の吸収層21に移行する。ここで、本実施の形態では、第1の吸収層21を形成する親水性繊維は、カチオン系界面活性剤によって疎水性が付与されている。このため、第1の吸収層21に移行した排泄物Xは、疎水性が付与された親水性繊維によってはじかれ、第1の吸収層21内における下部・外側への拡がり(拡散)が抑制される。
(3)第1の吸収層21内において排泄物Xが下部・外側への拡がり(拡散)が抑制されている状態で、第2の吸収層22を形成している吸水性樹脂が排泄物Xを徐々に吸収する。これにより、排泄物Xがシート表面側に拡散するのを抑制することができる。
このため、1枚のシートでの排泄回数を増大させるためには、排泄物の漏れを防止することよりも、シート表面での排泄物の拡散を防止する方が有効である。
吸収層(第2の吸収層21)と表面側被覆シート23が接合されている接合領域、また、表面側被覆シート23と表面シート30が接合されている接合領域に沿って排泄物が拡散すると、排泄物がシート表面で拡散することになる。
なお、本実施の形態では、吸収層(第1の吸収層21)と裏面側被覆シート24、裏面側被覆シート24と裏面シート40も、全体にわたって、ホットメルト接着剤を用いて接合されている。
熱溶着接着剤を用いて、全体にわたって接合することにより、吸収体を表面シート30と裏面シート40の間に強固に固定することができ、吸収体の型崩れを防止することができる。
本発明の他の実施の形態のペット用シート110の断面図を図4に示す。
本実施の形態のペット用シート110は、吸収体120の吸収層の構成が異なるだけで、他の構成はペット用シート10と同じである。したがって、吸収体120の構成についてのみ説明する。
吸収層121は、親水性繊維により形成されているとともに、吸水性樹脂により形成される第2の吸収層122が第1の吸収層121内に設けられている。吸収層121を形成する親水性繊維としては、前述した第1の吸収層21を形成する親水性繊維と同じものを用いることができる。また、第2の吸収層122を形成する吸水性樹脂としては、前述した第2の吸収層22を形成する吸水性樹脂と同じものを用いることができる。
本実施の形態のペット用シート110は、前述したペット用シート10と同様の効果を有している。
(1)0.9%塩化ナトリウム水溶液を液温25℃に調整する。
(2)100mlビーカーに回転子を入れる。
(3)100mlビーカーに50gの試験液を注入するとともに、スターラーバー(攪拌子)を入れる。
(4)100mlビーカーをマグネットスターラー(磁気攪拌器)の上に置き、回転子を600rpmで回転させる。
(5)吸水性樹脂(SAP)を2g投入し、液表面がフラットになる時間を測定する。
(1)対象シートの測定箇所(折り目の部分は避ける)に塩ビ管(外径66.6mm、内径60.2mm、高さ53mm)を配置する。
(2)ビュレット(40cc/6秒)を用いて、10mm上方から塩ビ管中央に、0.9%生理食塩水40ccを6秒で滴下する。
(3)滴下してから5分経過した時点で、生理食塩水のMD方向(Machine Direction)の拡散長およびCD方向(Cross Direction)の拡散長を測定する。
(4)測定したMD方向拡散長およびCD方向拡散長と以下の計算式を用いて液体拡散面積(cm2)を算出する。
[(MD方向拡散長/2)×(CD方向拡散長/2)×3.14]
なお、シート1~4は、目付が60[g/m2]となるようにフラッフパルプが均一に積層され、カチオン系界面活性剤を含んでいるパルプ(トリートパルプ)を第1の吸収層として用いている。
また、シート5~8は、目付が60[g/m2]となるようにフラッフパルプが均一に積層されているパルプ(ノントリートパルプ)を第1の吸収層として用いている。
(第1の吸収層):目付が60[g/m2]となるようにフラッフパルプが均一に積層
されているとともにカチオン系界面活性剤を含んでおり、沈降速
度が5秒であるトリートパルプ
(第2の吸収層):目付が40[g/m2]であり、液体吸収速度が4秒である吸水性
樹脂(SAP)
[シート2]
(第1の吸収層):目付が60[g/m2]となるようにフラッフパルプが均一に積層
されているとともにカチオン系界面活性剤を含んでおり、沈降速
度が5秒であるトリートパルプ
(第2の吸収層):目付が40[g/m2]であり、液体吸収速度が10秒である吸
水性樹脂(SAP)
[シート3]
(第1の吸収層):[シート1]と同じトリートパルプ
(第2の吸収層):目付が40[g/m2]であり、液体吸収速度が18秒である
吸水性樹脂(SAP)
[シート4]
(第1の吸収層):[シート1]と同じトリートパルプ
(第2の吸収層):目付が40[g/m2]であり、液体吸収速度が35秒である
吸水性樹脂(SAP)
(第1の吸収層):目付が60[g/m2]となるようにフラッフパルプが均一に積層
されており、沈降速度が1秒であるノントリートパルプ
(第2の吸収層):目付が40[g/m2]であり、液体吸収速度が4秒である吸
水性樹脂(SAP)
[シート6]
(第1の吸収層):[シート4]と同じノントリートパルプ
(第2の吸収層):目付が40[g/m2]であり、液体吸収速度が10秒である吸
水性樹脂(SAP)
[シート7]
(第1の吸収層):[シート4]と同じノントリートパルプ
(第2の吸収層):目付が40[g/m2]であり、液体吸収速度が18秒である
吸水性樹脂(SAP)
[シート8]
(第1の吸収層):[シート4]と同じノントリートパルプ
(第2の吸収層):目付が40[g/m2]であり、液体吸収速度が35秒である
吸水性樹脂(SAP)
[シート1(トリートパルプ+液体吸収速度4秒)] :192cm2
[シート2(トリートパルプ+液体吸収速度10秒)] :245cm2
[シート3(トリートパルプ+液体吸収速度18秒)] :264cm2
[シート4(トリートパルプ+液体吸収速度35秒)] :281cm2
[シート5(ノントリートパルプ+液体吸収速度4秒)] :207cm2
[シート6(ノントリートパルプ+液体吸収速度10秒)]:270cm2
[シート7(ノントリートパルプ+液体吸収速度18秒)]:320cm2
[シート8(ノントリートパルプ+液体吸収速度35秒)]:341cm2
同じ液体吸収速度を有する吸水性樹脂を使用しているシートを比較すると、トリートパルプを使用しているシートの方が、液体拡散面積(シート表面での排泄物の拡散面積)が小さい。
例えば、液体吸収速度が18秒である吸水性樹脂を使用している[シート3]と[シート7]を比較すると、[シート3]では、液体拡散面積が264cm2であるのに対し、[シート7]では、液体拡散面積が320cm2である。
このことは、第1の吸収層をトリートパルプにより形成することにより、第1の吸収層をノントリートパルプにより形成する場合に比べて、液体吸収速度が遅い吸水性樹脂を使用することができることを示している。吸水性樹脂は、液体吸収速度が速いほど高価である。また、吸水性樹脂は、液体吸収速度が遅い方が、強度が高く、リウェット(吸水性樹脂で吸収した排泄物がシート表面側に戻る作用)が少ない。
以上のことから、第1の吸収層をトリートパルプにより形成し、第2の吸収層を吸水性樹脂により形成することにより、吸収層で吸収された排泄物がシート表面側に戻ることに起因するシート表面での排泄物の拡散を効果的に抑制することができることが理解できる。
すなわち、第1の吸収層をトリートパルプにより形成し、第2の吸収層を吸水性樹脂により形成する場合、液体吸収速度が18秒以下である吸水性樹脂を用いることによって、吸収層で吸収された排泄物がシート表面側に戻ることに起因するシート表面での排泄物の拡散を抑制することができる。
実施の形態では、吸収層を、カチオン系界面活性剤を含む親水性繊維により形成される第1の吸収層と吸水性樹脂(SAP)により形成される第2の吸収層により構成したが、第1の吸収層のみで構成することもできる。
親水性繊維に疎水性を付与するカチオン系界面活性剤としては、種々のものを用いることができる。
親水性繊維としては、パルプ以外の種々の繊維を用いることができる。
第2の吸収層の第1の吸収層に対する配置位置や第2の吸収層の数は、適宜選択することができる。例えば、第1の吸収層の上部と下部に配置する態様、第1の吸収層の上部と内部に配置する態様等を選択することができる。
接合方法としては、熱溶着性接着剤(ホットメルト接着剤)を用いた接合方法以外の方法を用いることもできる。
20、120 吸収体
21、121、321 第1の吸収層
22、122、322 第2の吸収層
23、123、323 表面側被覆シート
24、124、324 裏面側被覆シート
30、130 表面シート
40、140 裏面シート
50、51、52、53、54、150、151、152、153、153 接合部
60 載置面
Claims (9)
- 液透過性の表面シートと、液不透過性の裏面シートと、前記表面シートと前記裏面シートの間に配置され、前記表面シートを透過した排泄物を吸収する吸収体を備え、
前記表面シートは、前記裏面シートが載置箇所に載置されている状態で、ペットの排泄物を受けるように構成されているペット用シートであって、
前記吸収体は、カチオン系界面活性剤を含む親水性繊維により形成される吸収層を有していることを特徴とするペット用シート。 - 請求項1に記載のペット用シートであって、
前記カチオン系界面活性剤は、第4級アンモニウム塩であることを特徴とするペット用シート。 - 請求項1または2に記載のペット用シートであって、
前記親水性繊維としてパルプを用いていることを特徴とするペット用シート。 - 請求項1~3のうちのいずれか一項に記載のペット用シートであって、
前記吸収層を形成する親水性繊維は、沈降速度が5秒以上であることを特徴とするペット用シート。 - 請求項1~4のいずれか一項に記載のペット用シートであって、
前記吸収層は、カチオン系界面活性剤を含む親水性繊維と吸水性樹脂により形成されていることを特徴とするペット用シート。 - 請求項5に記載のペット用シートであって、
前記吸収層は、カチオン系界面活性剤を含む親水性繊維により形成される第1の吸収層と、前記吸水性樹脂により形成される第2の吸収層を有していることを特徴とするペット用シート。 - 請求項6に記載のペット用シートであって、
前記第2の吸収層は、前記第1の吸収層より前記表面シート側に配置されていることを特徴とするペット用シート。 - 請求項6または7に記載のペット用シートであって、
前記第2の吸収層を形成する吸水性樹脂は、ボルテックス法を用いて測定した液体吸収速度が18秒以下であることを特徴とするペット用シート。 - 請求項1~8のうちのいずれか一項に記載のペット用シートであって、
少なくとも、前記表面シートと前記吸収層は、全体にわたって熱溶着性接着剤を用いて接合されていることを特徴とするペット用シート。
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IN795DEN2015 IN2015DN00795A (ja) | 2012-07-06 | 2013-06-20 | |
| US14/412,970 US20150150212A1 (en) | 2012-07-06 | 2013-06-20 | Sheet for pets |
| EP13812738.6A EP2870865A4 (en) | 2012-07-06 | 2013-06-20 | FOIL FOR PETS |
| CN201380035999.7A CN104486941A (zh) | 2012-07-06 | 2013-06-20 | 宠物用片 |
| AU2013284679A AU2013284679A1 (en) | 2012-07-06 | 2013-06-20 | Sheet for pets |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012-153083 | 2012-07-06 | ||
| JP2012153083A JP6008625B2 (ja) | 2012-07-06 | 2012-07-06 | ペット用シート |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2014007071A1 true WO2014007071A1 (ja) | 2014-01-09 |
Family
ID=49881830
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/067009 WO2014007071A1 (ja) | 2012-07-06 | 2013-06-20 | ペット用シート |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20150150212A1 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2870865A4 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6008625B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN104486941A (ja) |
| AU (1) | AU2013284679A1 (ja) |
| IN (1) | IN2015DN00795A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2014007071A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6008623B2 (ja) * | 2012-07-06 | 2016-10-19 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | ペット用吸収性シート |
| JP6008622B2 (ja) * | 2012-07-06 | 2016-10-19 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | ペット用吸収性シート |
| NL2009780C2 (nl) * | 2012-11-09 | 2014-05-12 | Uniq Ag | Legnest met uitdrijfsysteem. |
| JP6359427B2 (ja) * | 2014-11-19 | 2018-07-18 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | ペット用吸収性シート |
| JP5728123B1 (ja) * | 2014-11-19 | 2015-06-03 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | ペット用吸収性シート |
| CN204259607U (zh) * | 2014-11-26 | 2015-04-15 | 江苏中恒宠物用品股份有限公司 | 快速吸收防侧漏宠物尿垫 |
| CN204317221U (zh) * | 2014-11-26 | 2015-05-13 | 江苏中恒宠物用品股份有限公司 | 一种防侧漏宠物尿垫 |
| JP6185042B2 (ja) | 2015-12-21 | 2017-08-23 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 動物用排泄物処理シート |
| JP5941234B1 (ja) * | 2016-01-29 | 2016-06-29 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | ペット用ベッドのベッドカバー |
| BR112019015456B1 (pt) | 2017-01-27 | 2023-02-23 | Ctb, Inc | Ninho de postura com sistema de expulsão de piso de acionamento de cremalheira |
| JP7079752B2 (ja) | 2019-05-20 | 2022-06-02 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | ペット用の吸収性シート |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005198598A (ja) * | 2004-01-16 | 2005-07-28 | Unicharm Petcare Corp | ペット用吸収シート |
| JP2008043243A (ja) * | 2006-08-14 | 2008-02-28 | Sanotec Co Ltd | ペット用吸収シート |
| JP2009232685A (ja) * | 2008-03-25 | 2009-10-15 | Lion Corp | ペット用吸収性物品 |
| JP2011205984A (ja) | 2010-03-30 | 2011-10-20 | Unicharm Corp | 動物用排泄物処理シート及びその製造方法 |
Family Cites Families (30)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3626899A (en) * | 1970-07-14 | 1971-12-14 | Spellman & Zenon Products Corp | Training pads for young dogs |
| US4622259A (en) * | 1985-08-08 | 1986-11-11 | Surgikos, Inc. | Nonwoven medical fabric |
| JPH0827942B2 (ja) * | 1987-11-30 | 1996-03-21 | コニカ株式会社 | 磁気記録媒体の製造方法 |
| US4961930A (en) * | 1988-04-29 | 1990-10-09 | Weyerhaeuser Company | Pet pad of thermoplastic containing materials with insecticide |
| JP2965467B2 (ja) * | 1994-08-23 | 1999-10-18 | ユニ・ハートス株式会社 | 愛玩動物用の排尿処理シート |
| US5609123A (en) * | 1995-08-17 | 1997-03-11 | Allied Colloids Limited | Animal litter compositions and processes for making them |
| SG73624A1 (en) * | 1998-03-24 | 2000-06-20 | Uni Heartous Corp | Household animal waste collection sheet |
| JP3753581B2 (ja) * | 1999-05-20 | 2006-03-08 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| DE60124962T2 (de) * | 2000-01-14 | 2007-03-08 | Kao Corp. | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Material für die Entsorgung von Exkrementen |
| JP3959339B2 (ja) * | 2002-11-12 | 2007-08-15 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2004321332A (ja) * | 2003-04-22 | 2004-11-18 | Kohjin Co Ltd | 消臭機能を有する材料及びその製造方法 |
| JP4570481B2 (ja) * | 2005-03-01 | 2010-10-27 | ユニ・チャームペットケア株式会社 | ペット用排泄物吸収シート |
| US7958846B2 (en) * | 2005-03-30 | 2011-06-14 | T.F.H. Publications, Inc. | Animal litter device |
| US20070179468A1 (en) * | 2006-01-30 | 2007-08-02 | Labelle Jeffery | Pet urine pad with vertical target and absorbent base |
| JP4986609B2 (ja) * | 2006-12-27 | 2012-07-25 | 花王株式会社 | ペット用シート |
| WO2008084565A1 (ja) * | 2006-12-27 | 2008-07-17 | Kao Corporation | ペット用シート |
| US20080236504A1 (en) * | 2007-03-28 | 2008-10-02 | Stephen Silverman | Pet waste collection pad |
| JP4996997B2 (ja) * | 2007-06-29 | 2012-08-08 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 動物用排泄物処理シート |
| JP5186141B2 (ja) * | 2007-06-29 | 2013-04-17 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 動物用排泄物処理シート |
| US9314544B2 (en) * | 2007-08-17 | 2016-04-19 | Kemal Vatansever Catalan | Durable hydrophilic coating compositions |
| US20120000428A1 (en) * | 2010-07-01 | 2012-01-05 | Georgia-Pacific Wood Products Llc | Small animal bedding system |
| JP6095265B2 (ja) * | 2011-12-21 | 2017-03-15 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | ペット用シート |
| JP5892866B2 (ja) * | 2012-05-31 | 2016-03-23 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 動物用排泄物処理シート |
| JP5952663B2 (ja) * | 2012-07-06 | 2016-07-13 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | ペットシートおよびペットシート包装体パッケージ |
| JP6008622B2 (ja) * | 2012-07-06 | 2016-10-19 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | ペット用吸収性シート |
| JP5956322B2 (ja) * | 2012-12-13 | 2016-07-27 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | ペット用吸収性シート |
| JP5557894B2 (ja) * | 2012-12-13 | 2014-07-23 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | ペット用吸収性シート |
| US20140261208A1 (en) * | 2013-03-15 | 2014-09-18 | The Clorox Company | Absorbent pet pad |
| JP6173770B2 (ja) * | 2013-05-17 | 2017-08-02 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | ペット用吸収性シート |
| JP6173769B2 (ja) * | 2013-05-17 | 2017-08-02 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | ペット用吸収性シート |
-
2012
- 2012-07-06 JP JP2012153083A patent/JP6008625B2/ja active Active
-
2013
- 2013-06-20 IN IN795DEN2015 patent/IN2015DN00795A/en unknown
- 2013-06-20 AU AU2013284679A patent/AU2013284679A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2013-06-20 CN CN201380035999.7A patent/CN104486941A/zh active Pending
- 2013-06-20 US US14/412,970 patent/US20150150212A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2013-06-20 WO PCT/JP2013/067009 patent/WO2014007071A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2013-06-20 EP EP13812738.6A patent/EP2870865A4/en not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005198598A (ja) * | 2004-01-16 | 2005-07-28 | Unicharm Petcare Corp | ペット用吸収シート |
| JP2008043243A (ja) * | 2006-08-14 | 2008-02-28 | Sanotec Co Ltd | ペット用吸収シート |
| JP2009232685A (ja) * | 2008-03-25 | 2009-10-15 | Lion Corp | ペット用吸収性物品 |
| JP2011205984A (ja) | 2010-03-30 | 2011-10-20 | Unicharm Corp | 動物用排泄物処理シート及びその製造方法 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP2870865A4 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| AU2013284679A1 (en) | 2015-02-26 |
| EP2870865A1 (en) | 2015-05-13 |
| CN104486941A (zh) | 2015-04-01 |
| JP6008625B2 (ja) | 2016-10-19 |
| JP2014014304A (ja) | 2014-01-30 |
| EP2870865A4 (en) | 2016-03-09 |
| US20150150212A1 (en) | 2015-06-04 |
| IN2015DN00795A (ja) | 2015-07-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6008625B2 (ja) | ペット用シート | |
| RU2660288C2 (ru) | Впитывающее изделие | |
| JP6411066B2 (ja) | 吸収体用の不織布シートを含む吸収性物品、及び当該吸収性物品に用いられる不織布シートの製造方法 | |
| JP5080606B2 (ja) | 動物用排泄物処理シート及びその製造方法 | |
| JP2008148950A (ja) | 使い捨ておむつ | |
| WO2012053482A1 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP5318747B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6008624B2 (ja) | ペット用シート | |
| JP6887443B2 (ja) | 動物用排泄物処理シート | |
| JP2007117727A (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| ES2606308T3 (es) | Estructura ondulada para un artículo absorbente | |
| JPWO2019167191A1 (ja) | 動物用排泄物処理シート | |
| JP6785726B2 (ja) | 動物用排泄物処理シート | |
| BR112020004299A2 (pt) | artigo absorvente tendo um sistema para manipulação de fluidos. | |
| JP7145810B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| TWI626882B (zh) | 動物用排泄物處理薄片 | |
| JP2021000376A (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JPWO2020008609A1 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| BR112020004015A2 (pt) | artigo absorvente tendo um sistema para manipulação de fluidos. | |
| TWM499922U (zh) | 吸收性用品 | |
| JP2012175981A (ja) | 動物用排泄物処理シート及びその製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13812738 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14412970 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2013812738 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2013812738 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2013284679 Country of ref document: AU Date of ref document: 20130620 Kind code of ref document: A |