WO2013121950A1 - エアバッグ装置 - Google Patents
エアバッグ装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2013121950A1 WO2013121950A1 PCT/JP2013/052720 JP2013052720W WO2013121950A1 WO 2013121950 A1 WO2013121950 A1 WO 2013121950A1 JP 2013052720 W JP2013052720 W JP 2013052720W WO 2013121950 A1 WO2013121950 A1 WO 2013121950A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- airbag
- occupant
- exhaust state
- switching member
- state switching
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R21/00—Arrangements or fittings on vehicles for protecting or preventing injuries to occupants or pedestrians in case of accidents or other traffic risks
- B60R21/02—Occupant safety arrangements or fittings, e.g. crash pads
- B60R21/16—Inflatable occupant restraints or confinements designed to inflate upon impact or impending impact, e.g. air bags
- B60R21/26—Inflatable occupant restraints or confinements designed to inflate upon impact or impending impact, e.g. air bags characterised by the inflation fluid source or means to control inflation fluid flow
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R21/00—Arrangements or fittings on vehicles for protecting or preventing injuries to occupants or pedestrians in case of accidents or other traffic risks
- B60R21/02—Occupant safety arrangements or fittings, e.g. crash pads
- B60R21/16—Inflatable occupant restraints or confinements designed to inflate upon impact or impending impact, e.g. air bags
- B60R21/20—Arrangements for storing inflatable members in their non-use or deflated condition; Arrangement or mounting of air bag modules or components
- B60R21/205—Arrangements for storing inflatable members in their non-use or deflated condition; Arrangement or mounting of air bag modules or components in dashboards
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R21/00—Arrangements or fittings on vehicles for protecting or preventing injuries to occupants or pedestrians in case of accidents or other traffic risks
- B60R21/02—Occupant safety arrangements or fittings, e.g. crash pads
- B60R21/16—Inflatable occupant restraints or confinements designed to inflate upon impact or impending impact, e.g. air bags
- B60R21/23—Inflatable members
- B60R21/239—Inflatable members characterised by their venting means
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R21/00—Arrangements or fittings on vehicles for protecting or preventing injuries to occupants or pedestrians in case of accidents or other traffic risks
- B60R21/02—Occupant safety arrangements or fittings, e.g. crash pads
- B60R21/16—Inflatable occupant restraints or confinements designed to inflate upon impact or impending impact, e.g. air bags
- B60R21/26—Inflatable occupant restraints or confinements designed to inflate upon impact or impending impact, e.g. air bags characterised by the inflation fluid source or means to control inflation fluid flow
- B60R21/276—Inflatable occupant restraints or confinements designed to inflate upon impact or impending impact, e.g. air bags characterised by the inflation fluid source or means to control inflation fluid flow with means to vent the inflation fluid source, e.g. in case of overpressure
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R21/00—Arrangements or fittings on vehicles for protecting or preventing injuries to occupants or pedestrians in case of accidents or other traffic risks
- B60R21/02—Occupant safety arrangements or fittings, e.g. crash pads
- B60R21/16—Inflatable occupant restraints or confinements designed to inflate upon impact or impending impact, e.g. air bags
- B60R21/23—Inflatable members
- B60R21/231—Inflatable members characterised by their shape, construction or spatial configuration
- B60R21/2334—Expansion control features
- B60R21/2338—Tethers
- B60R2021/23382—Internal tether means
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an airbag device for protecting a vehicle occupant.
- Patent Document 1 discloses an airbag having a regulation means for regulating gas outflow from a vent hole.
- the restricting means includes a constricting member capable of confining the vent hole, and a connecting member provided so as to connect the constricting member and the occupant-facing surface of the airbag.
- the binding member is pulled through the connecting member to close the vent hole.
- the binding member is loosened and the vent hole is opened.
- Patent Document 2 As another conventional technique related to this case.
- Patent Document 1 Even in the technology disclosed in Patent Document 1, when the occupant is in an irregular posture, the occupant-facing surface and the occupant are in contact with each other before inflating, and the bent member is loosened and the vent hole is opened. It is expected that the state will be maintained to some extent. In this case, gas is discharged from the vent hole, and thereby, the airbag is suppressed to some extent from inflating rapidly.
- an appropriate gas discharge rate for gradually receiving the impact of the occupant after the airbag is inflated is different from an appropriate gas discharge rate as a countermeasure when the occupant is in an irregular posture.
- the gas is gradually discharged.
- the gas is rapidly discharged in order to prevent the airbag from hitting the occupant with a large force.
- the gas discharge speed is set so that the gas is gradually discharged assuming the former case. For this reason, even when the occupant is in an irregular posture, the gas is only gradually discharged, and thus the airbag may suddenly inflate.
- the present invention can discharge gas as quickly as possible when the occupant is in the non-regular posture state, and sudden discharge of gas when receiving the occupant in the normal posture state after inflation of the airbag.
- the purpose is to suppress.
- an airbag apparatus includes an airbag body having a gas supply port, an inflator for supplying gas into the airbag body through the gas supply port, and the airbag body.
- An exhaust state that is switched to a non-exhaust state that suppresses exhaust of the gas in the airbag body from an exhaust state that allows the gas in the airbag body to be exhausted when being drawn into the airbag body
- a switching member, and a connecting member that connects the exhaust state switching member and a part of the inner peripheral portion of the airbag main body, the disposition position of the exhaust state switching member, and the inner peripheral portion of the airbag main body
- the connecting position of the connecting member with respect to the connecting member and the passing line of the connecting member are the inflated forms of the airbag body, and the airbag body is in a normal posture state. It is provided in a portion avoiding the contact portion between the occupant when receiving the.
- a 2nd aspect is an airbag apparatus concerning a 1st aspect, Comprising: The arrangement
- the passage line is provided in a portion of the inflated form of the airbag body that avoids a portion that deforms when the airbag body receives an occupant in a normal posture state.
- a third aspect is an airbag apparatus according to the first or second aspect, wherein the exhaust state switching member is disposed, the connection position of the connection member with respect to the inner periphery of the airbag body,
- the connecting member passage line is provided in the front half of the inflated form of the airbag body that inflates from the vehicle assembled state.
- a fourth aspect is an airbag device according to any one of the first to third aspects, wherein the connecting member can be moved along the longitudinal direction on the inner peripheral portion of the inflated form of the airbag body.
- An annular relay portion is provided to support the airbag body, and the connecting member is arranged to bend via the annular relay portion in the inflated form of the airbag body.
- a fifth aspect is an airbag apparatus according to the fourth aspect, wherein the exhaust state switching member is provided on one side portion of the airbag body in an inflated form, and an upper part of the inflated form of the airbag body or
- the annular relay portion is provided at a front portion, one end portion of the connection member is connected to the exhaust state switching member, and the other end portion of the connection member is connected to the airbag main body via the annular relay portion. It connects with the inner peripheral part of the other side part of an expansion
- a sixth aspect is an airbag device according to any one of the first to fifth aspects, wherein the airbag body has an exhaust speed smaller than an exhaust speed of the exhaust state switching member in the exhaust state. A vent hole for discharging gas is formed.
- a seventh aspect is an airbag apparatus according to any one of the first to sixth aspects, wherein a base end portion is connected to an outer peripheral portion of the airbag body, and a distal end portion is the gas supply port. And a flap extending to cover the airbag body toward the opposite side.
- the inflated airbag when the inflated airbag receives the occupant in the normal posture state, the occupant abuts on the contact portion, so that the state in which the connecting member is pulled is maintained, and the exhaust state switching member is not turned on. Maintain exhaust conditions. Thereby, sudden discharge of gas can be controlled.
- the occupant when the occupant is in the non-regular posture state, the occupant abuts against a portion of the airbag body that avoids the contact portion with the occupant in the normal posture. Thereby, the slack state of the connecting member is maintained, and the exhaust state switching member maintains the exhaust state or is switched to the exhaust state. Thereby, gas can be discharged from the exhaust state switching member as rapidly as possible.
- the inflated airbag when the inflated airbag receives the occupant in the normal posture state, the state where the connecting member is pulled more reliably is maintained. Thereby, the sudden discharge
- the occupant when the occupant is in the non-regular posture state, the occupant reliably comes into contact with the portion of the airbag body where the connecting member is provided. Thereby, the state which the connection member slackened is maintained more reliably, and gas can be discharged from the exhaust state switching member as rapidly as possible.
- the third aspect when the inflated airbag receives the occupant in the normal posture state, the state where the connecting member is pulled more reliably is maintained. Thereby, the sudden discharge
- the occupant when the occupant is in the non-regular posture state, the occupant reliably comes into contact with the portion of the airbag body where the connecting member is provided. Thereby, the state which the connection member slackened is maintained more reliably, and gas can be discharged from the exhaust state switching member as rapidly as possible.
- the exhaust state switching member can be more securely pulled by pulling the connecting member more securely in the inflated form of the airbag. Fully retracted and more reliably switched to the non-exhaust state.
- the connecting member is disposed from one side portion to the other side portion of the inflated form of the airbag body via the upper or front annular relay portion.
- gas when the airbag body is normally inflated, gas can be discharged through the vent hole.
- the inflation of the airbag body is suppressed at that portion.
- the partial expansion of the airbag body it is possible to suppress the pulling of the connecting member and to suppress the exhaust state switching member from being switched to or maintained in the non-exhaust state.
- FIG. 11 is an explanatory diagram showing the operation of the airbag apparatus according to the modification when the occupant is in an irregular posture.
- FIG. 11 is an explanatory diagram showing the operation of the airbag apparatus according to the modification when the occupant is in an irregular posture.
- an occupant is in a normal posture, it is an explanatory view showing the operation of the airbag apparatus according to the modification.
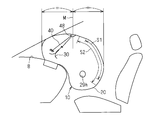
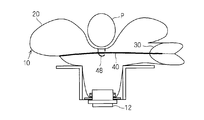
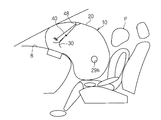
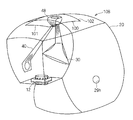
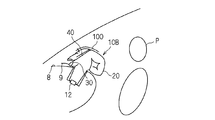
- FIG. 1 is a schematic perspective view showing an inflated form of the airbag device 10
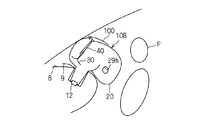
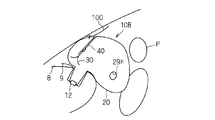
- FIG. 2 is a schematic side view showing an inflated form of the airbag device 10 attached to a dashboard.
- a partially transparent view is shown to show the internal structure of the airbag device 10.
- the airbag device 10 is a device that is incorporated in a dashboard in front of the passenger seat of the vehicle, deploys in front of the passenger in the passenger seat at the time of a vehicle collision, etc., receives the passenger in the passenger seat, and absorbs the impact.
- the airbag apparatus is not limited to the airbag apparatus for the passenger seat, but can be applied to an airbag for a driver's seat incorporated in the steering apparatus.
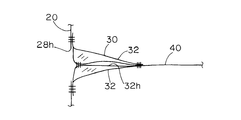
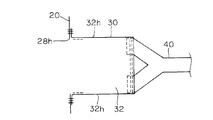
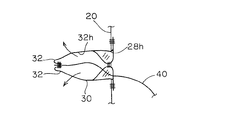
- the airbag device 10 includes an airbag body 20, an inflator 12, an exhaust state switching member 30, and a tether belt 40 as a connecting member.
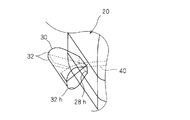
- the airbag body 20 is formed in an inflatable bag shape, and has a gas supply port 26h and at least one opening 28h.
- the airbag main body 20 is formed into a bag shape by the following configuration, for example. That is, the substantially cylindrical base fabric portion 22 is formed by joining the both edge portions of the substantially strip-shaped cloth by sewing or the like. Also, a pair of side cloth portions 24 having a widened shape capable of closing the side openings of the base cloth portion 22 are prepared, and the side cloth portions are respectively provided on the peripheral edge portions of the both side openings of the base cloth portion 22 formed in a substantially cylindrical shape. 24 edges are joined together by sewing. Thereby, the bag-shaped airbag main body 20 is formed.
- the airbag main body 20 is formed in a shape inflating from the upper side of the inflator 12 toward the occupant side (the rear side of the vehicle, the right side in FIG. 1) and inflating downward at the occupant side portion in a side view.
- the shape and combination of the base fabric for forming the airbag body 20 in a bag shape are not limited to the above example.
- swelling form of the airbag main body 20 is not restricted to the said example.
- the gas supply port 26h is formed at a portion facing the dashboard in an inflated form, more specifically, at a lower portion of the airbag body 20 on the front side of the vehicle (the side away from the passenger, the left side in FIG. 1).
- the inflator 12 is attached to the gas supply port 26h.
- the gas generated in the inflator 12 at the time of a vehicle collision or the like is introduced into the airbag body 20 through the gas supply port 26h.
- the opening 28h is a gas discharge hole.
- the opening 28h is formed in a portion away from the occupant in the inflated form of the airbag body 20, more specifically, at one side of the airbag body 20 in front of the vehicle.
- the opening 28h is formed in a long hole shape extending along the front-rear direction of the airbag body 20 or slightly obliquely from the front-rear direction.
- the opening 28h is not limited to a long hole shape, and may be formed in a circular hole shape, a polygonal hole shape, or a slit shape.
- a second vent hole 29h is formed in the airbag body 20 separately from the opening 28h.
- the second vent hole 29h is formed, for example, on one side or both sides of the airbag body 20 in an inflated form.
- the second vent hole 29h may be the side of the side facing the outside of the vehicle (that is, the door), or the vehicle interior. The side part facing inward may be sufficient.
- the second vent hole 29h is provided for the purpose of gradually discharging the internal air when the airbag body 20 receives an occupant in a normal posture in an inflated form. For this reason, the second vent hole 29h is provided in a portion that appears outside when the airbag main body 20 is inflated, for example, in a vehicle rear side portion (occupant side portion) in an expanded form of the airbag main body 20. Is preferred. Moreover, it is preferable that the gas discharge rate from the second vent hole 29h is such that the internal air can be gradually discharged so as to gradually receive the impact of the passenger.
- the second vent hole 29h is gas at an exhaust speed smaller than an exhaust speed (for example, an amount of gas discharged per unit time under a constant internal gas pressure condition) in an exhaust state of an exhaust state switching member 30 described later. It is preferable that it is set so that it can be discharged.
- the gas discharge speed from the second vent hole 29h is set by adjusting the size and the like.
- the various exhaust patterns can be set by combining the exhaust through the second vent hole 29h and the exhaust mode through the exhaust state switching member 30.
- the exhaust state switching member 30 is provided in the opening 28h, and is in an exhaust state in which the gas in the airbag body 20 can be exhausted before being drawn into the airbag body 20 (FIGS. 5 to 5). 7), when drawn into the airbag body 20, the exhaust state is switched to a non-exhaust state (see FIGS. 1 to 4) that suppresses the exhaust of gas in the airbag body 20. Yes. Then, the exhaust state switching member 30 changes the state between these two states in accordance with the pulling force by the tether belt 40 described later.
- the exhaust state switching member 30 has a pair of belt-like cloths 32.
- One end portions (base end portions) of the pair of belt-like cloths 32 are sewn so as to surround the peripheral edge portion of the opening 28 h in the airbag body 20.
- the exhaust state switching member 30 may be sewn to the airbag body 20 on the outer surface of the airbag body 20.
- the other end portions (tip portions) of the pair of belt-like cloths 32 are stitched together and joined substantially along the width direction.
- both side portions of the pair of belt-like cloths 32 are joined by stitching only their base end portions, and the other portions are in an open state where they are not stitched.
- the 1st vent hole 32h is comprised by the part enclosed by the non-sewing part among the both sides of a pair of strip
- the width dimension of the pair of belt-like cloths 32 is set larger than the width dimension of the opening 28h, and therefore the width dimension of the exhaust state switching member 30 is also set larger than the width dimension of the opening 28h. Yes.
- the exhaust state switching member 30 can pass through the opening 28h while being deformed so as to shrink in the width direction. Resistor is acting.
- the exhaust state switching member 30 is prevented from being inadvertently changed when, for example, a pull-in force by a tether belt 40, which will be described later, or an internal pressure exceeding a predetermined value is not applied to the airbag body 20.
- the exhaust state switching member 30 When the exhaust state switching member 30 is led out of the airbag body 20 together with the first vent hole 32h forming portion, the exhaust state switching member 30 is in an exhaust state in which the gas in the airbag body 20 can be exhausted through the first vent hole 32h. (See FIGS. 5, 6 and 7). On the other hand, when the exhaust state switching member 30 is introduced into the airbag main body 20 together with the first vent hole 32h forming portion, the exhaust state switching member 30 covers the opening 28h so as to block the gas exhaust in the airbag main body 20. (See FIGS. 1 to 4).
- the configuration of the exhaust state switching member 30 is not limited to the above example.
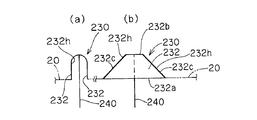
- the bottom side 232a that is the long side of the pair of substantially trapezoidal cloths 232 is sewn and attached to the opening 28h of the airbag body 20, and
- the upper sides 232b, which are the short sides of the trapezoidal cloth 232, are stitched together and joined.
- one end of the long tether belt 240 is connected to the joint portion of the upper side of the pair of substantially trapezoidal cloths 232.
- a pair of first vent holes 232 h are formed by the portions surrounded by the oblique sides 232 c of the pair of substantially trapezoidal cloths 232.
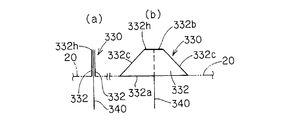
- the bottom side 332a that is the long side of the pair of substantially trapezoidal cloths 332 is sewn and attached to the opening 28h of the airbag body 20, and a pair of substantially Both oblique sides 332c of the trapezoidal cloth 332 are stitched together and joined.
- one end of a long tether belt 340 is connected to each upper side 332b of the pair of substantially trapezoidal cloths 332.
- a first vent hole 332h (refer to a thick line portion) is formed by a portion surrounded by the upper side 332b of the pair of substantially trapezoidal cloths 332.
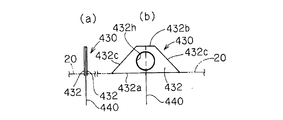
- the bottom side 432a which is the long side of the pair of substantially trapezoidal cloths 432 is sewn and attached to the opening 28h of the airbag body 20, and the pair of substantially trapezoidal cloths 432 Both oblique sides 432c and both upper sides 432b are sewn and joined. Then, one end of a long tether belt 440 is connected to each upper side of the pair of substantially trapezoidal cloths 432. Further, a hole is formed in one or both of the pair of substantially trapezoidal cloths 432, and this is used as a first vent hole 432h.
- the tether belt 40 is a member that connects the exhaust state switching member 30 and a part of the inner peripheral portion of the airbag body 20.
- the tether belt 40 receives the expansion force due to the gas supply from the inflator 12 and causes the exhaust state switching member 30 to move to the airbag main body 20. Pull it in to make it non-exhaust.
- the exhaust state switching member 30 is pulled by the tether belt 40. Is suppressed. As a result, the exhaust state switching member 30 is allowed to change to the exhaust state.
- the tether belt 40 is formed in an elongated band shape by a long member, here, cloth or the like.
- a connecting member a string-like member or the like may be used.
- the tether belt 40 is maintained in a slack state when the airbag body 20 is inflated, particularly when the airbag body 20 comes into contact with an occupant in a non-regular posture in the initial stage of inflation, and the airbag body 20 is in a regular posture in an inflated configuration.
- the tether belt 40 is arranged to be maintained in a pulled state.
- Normal posture means that the occupant seat is adjusted to the expected average position and posture of use, and the average skeleton, height and body occupant leans the torso against the backrest and the head axis is vertical.
- a posture that is like a posture As a normal posture, a state where an occupant wears a seat belt is assumed.
- An example of such a normal posture is FMVSS (Federal Motor Vehicle. Safety Standard) No. issued on August 29, 2011 and effective on December 27, 2011. Those defined in 208 “S7. Seat belt assembly requirements” and “S10. Method of placing test dummy” can be employed.
- the airbag main body 20 When the airbag main body 20 is inflated to receive the above-mentioned normal posture occupant (ie, inflated form), the occupant comes into contact with the rear portion (occupant side portion) of the airbag main body 20, and the airbag main body It sinks deeply into 20 gradually. For this reason, in the rear part of the airbag main body 20, the contact part S1 which the passenger
- the arrangement position of the exhaust state switching member 30 and the inner periphery of the airbag body 20 It is preferable that the connection position of the tether belt 40 with respect to the portion and the passage line of the tether belt 40 are provided in a portion of the inflated form of the airbag body 20 that avoids the contact portion S1.
- the disposition position of the exhaust state switching member 30, the connection position of the tether belt 40 with respect to the inner peripheral portion of the airbag body 20, and the tether belt 40 It is preferable that the passage line is provided at a portion of the inflated form of the airbag body 20 that avoids the deformed portion S2.
- the front half is a front half of the vehicle reference that is divided into two in the front-rear direction of the vehicle, assuming that the airbag body 20 is inflated from the dashboard 8 of the vehicle, and includes the boundary M of the two divisions.
- the position where the exhaust state switching member 30 is disposed, the connection position of the tether belt 40 with respect to the inner periphery of the airbag body 20, and the passage line of the tether belt 40 are defined as passengers whose airbag body 20 is in a normal posture. It is only necessary that the tether belt 40 be disposed in such a manner that the tether belt 40 is not loosened as much as possible.
- each part is disposed in the front part of the vehicle with respect to the deepest part when the occupant in the normal posture sinks deepest with respect to the inflated form of the airbag body 20, the dash
- the board 8 is disposed in the vehicle front side portion of the vehicle rear side portion (occupant side portion), or an inner side of the outer peripheral portion that is not visible to the passenger in the normal posture in the inflated form of the airbag body 20 It is only necessary that the air bag main body 20 is disposed in a portion that is in contact with the front window and in a portion that is disposed below the vicinity thereof in the inflated form of the airbag body 20.
- the passage line of the tether belt 40 is a line through which an intermediate portion of the tether belt 40 passes between connecting portions at both ends of the tether belt 40 in the inflated form of the airbag body 20.
- the straight line is a passing line of the tether belt 40.
- the bent line including the bent portion is the passing line of the tether belt 40.
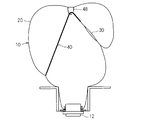
- the annular relay part 48 is provided in the inner peripheral part of the inflation form of the airbag body 20.
- the intermediate portion in the longitudinal direction of the tether belt 40 is supported so as to be movable along the longitudinal direction through the annular relay portion 48.
- the tether belt 40 is disposed so as to bend via the annular relay portion 48.
- the annular relay portion 48 is attached to the inner peripheral portion of the airbag body 20 within the restricted portion, so that the longitudinal intermediate portion of the tether belt 40 passes through the restricted portion. And bent at the annular relay portion 48.
- the center of the tether belt 40 is movably supported by the annular relay portion 48, but other portions, for example, a portion near one end of the tether belt is movably supported by the annular relay portion. Also good.
- the opening 28h is formed in one side of the front portion having a small vertical dimension in the inflated form of the airbag body 20, and the exhaust state switching member 30 is attached to the opening 28h. Accordingly, the exhaust state switching member 30 is provided on one side of the front portion of the airbag body 20 in an inflated form.
- one end of the tether belt 40 is connected to the exhaust state switching member 30.
- both end portions on the distal end side of the exhaust state switching member 30 are connected to the tether belt 40. That is, one end portion of the tether belt 40 is formed to have substantially the same width as the tip portion of the exhaust state switching member 30.
- the tip 52 of the tether belt 40 is formed in a shape that spreads in a Y shape. Then, both end portions extending in a substantially Y shape are sewn on both sides of the distal end portion of the exhaust state switching member 30.
- the tether belt 40 pulls the exhaust state switching member 30 into the airbag body 20 so as to pull both side portions on the distal end side of the exhaust state switching member 30.
- it is not essential that the tip portion of the tether belt 40 is formed in a Y-shaped shape as described above.
- the other end portion of the tether belt 40 is opposite to the other side portion of the front portion of the airbag body 20 in the inflated form, that is, the portion facing the exhaust state switching member 30 in the width direction of the airbag body 20. It is connected to.
- the other end of the tether belt 40 and the airbag body 20 are connected by sewing or the like.
- the annular relay portion 48 is a member formed of the same cloth as the airbag body 20, and is attached to the upper portion of the front portion of the airbag body 20 by sewing or the like so as to be formed in an annular shape. It has been.
- the location where the annular relay portion 48 is attached is a portion facing the inflator 12 or a portion on the rear side (occupant) side of the inflated form of the airbag body 20.
- the location where the annular relay part 48 is attached may be the front side (the side far from the occupant) of the airbag body 20 in the inflated form.
- the tether belt 40 can be disposed so as not to be directly exposed to the gas supplied from the inflator 12.
- it is not essential that the number of the annular relay portions is one, and a plurality of annular relay portions may be provided, and the tether belt may be disposed so as to be bent at each of the plurality of annular relay portions.
- the tether belt 40 is disposed in the front portion of the airbag body 20 in an inflated form so as to reach from the one side portion to the other side portion through the upper annular relay portion 48.
- the length of the tether belt 40 is set to a length dimension that satisfies the following conditions. That is, while the airbag main body 20 is inflating, the airbag main body 20 (particularly, the vicinity of the connection portion of the tether belt 40 and the portion via the annular relay portion 48) is the head or chest of an occupant in an irregular position.
- the length dimension of the tether belt 40 is It is longer than the sum of the distance connecting the opening 28 h of the bag body 20 and the annular relay part 48 and the distance connecting the annular relay part 48 and the connecting portion of the other end of the tether belt 40. Therefore, in this state, the tether belt 40 is loosened, and the exhaust state switching member 30 can be maintained or changed to the exhaust state.
- the airbag body 20 when the airbag body 20 is inflated to the assumed normal shape without being hindered by an occupant in a non-regular posture (hereinafter, the state in which the airbag is inflated to the greatest extent may be referred to as a deployed state 2),
- the sum is set to be larger than the length of the tether belt 40.
- the tether belt 40 receives an inflating force and is pulled between a part of the inner peripheral part of the airbag body 20 and the annular relay part 48 and between the opening 28h and the annular relay part 48 to be in an exhausted state.
- the switching member 30 is pulled into the airbag body 20 to switch to the non-exhaust state.
- the airbag device 10 is incorporated in the dashboard 8 of the vehicle as follows. That is, a lid portion 9 that is easily broken when the airbag body 20 is inflated is formed on the upward surface of the dashboard 8. A bracket or the like for attaching the airbag device 10 is attached to the inside of the lid portion 9 of the dashboard 8. The inflator 12 is attached to the bracket, and the airbag device 10 is attached to the inside of the upward surface of the dashboard 8 with the airbag body 20 folded. In a vehicle collision or the like, the gas generated in the inflator 12 is introduced into the airbag body 20 through the gas supply port 26h. Thereby, the airbag main body 20 is inflated, the lid portion 9 is opened, and the airbag 8 is inflated above the dashboard 8 and rearward of the vehicle (occupant side).
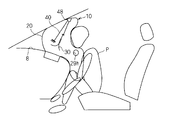
- the non-regular posture refers to one of postures that deviate from the normal posture and whose head is closer to the dashboard 8 side than the normal posture.
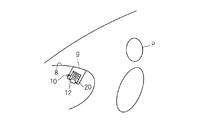
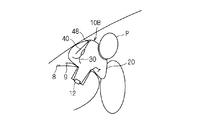
- the case where the head and the chest are positioned near the dashboard in front of the vehicle with the occupant P sitting on the occupant seat will be described as an irregular posture.
- the airbag main body 20 hits the head or chest of the occupant P at the initial stage when the airbag main body 20 is inflated.
- the airbag body 20 is prevented from expanding to the occupant side, the distance between the connecting portions on both ends of the tether belt 40 and the annular relay portion 48 is maintained relatively small, and a force that strongly pulls the tether belt 40 acts. It is hard to do.
- the tether belt 40 is in a slack state, and the exhaust state switching member 30 is in an exhaust state.
- the exhaust state switching member 30 may be in the exhaust state in the initial state, or the exhaust state switching member 30 is moved out of the airbag body 20 and switched to the exhaust state by the internal pressure of the airbag body 20. Also good.
- the gas in the airbag main body 20 passes through the exhaust state switching member 30 through the opening 28h and is discharged as quickly as possible from the first vent hole 32h, thereby suppressing rapid expansion and expansion of the airbag main body 20. Is done.
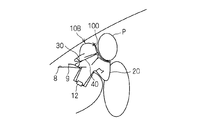
- the airbag body 20 is inflated toward the occupant side without being obstructed by the occupant P or the like.
- the airbag body 20 is inflated to some extent, the distance connecting the opening 28h of the airbag body 20 and the annular relay portion 48, and the connection between the annular relay portion 48 and the other end of the tether belt 40.
- the tether belt 40 is pulled.
- the exhaust state switching member 30 is pulled into the airbag body 20 by the pulling force of the tether belt 40 and switched to the non-exhaust state. For this reason, the airbag main body 20 is rapidly inflated in a state where the exhaust of the gas from the exhaust state switching member 30 is suppressed.
- the airbag body 20 receives the occupant P moving forward due to the impact of the vehicle collision, and absorbs the impact of the occupant P.
- the exhaust of gas through the exhaust state switching member 30 and the opening 28h is suppressed, but the gas is exhausted from the second vent hole 29h.
- the amount of gas discharged from the second vent hole 29h is set to such an extent that the impact of the passenger P can be gradually received as described above. For this reason, the impact of the occupant P is gradually received by the airbag body 20.
- the connecting portion of the exhaust state switching member 30 and the tether belt 40, the passage line, and the like are set to portions that do not deform when the occupant P is received in the inflated form of the airbag body 20.
- the tether belt 40 is maintained in the pulled state, and accordingly, the exhaust of gas through the exhaust state switching member 30 and the opening 28h is suppressed.
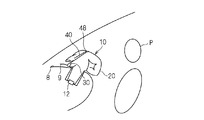
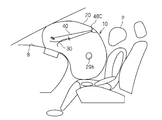
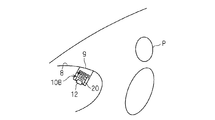
- FIG. 20 is a diagram assuming that the occupant P is in a normal posture but does not wear a seat belt. In this case, the occupant P sinks deeper into the airbag body 20.
- connection part and the passage line of the exhaust state switching member 30 and the tether belt 40 are portions that are not deformed even when the passenger P who is not wearing the seat belt is received in the inflated form of the airbag body 20, that is, the airbag body 20 It is preferable to set it in the more forward part of the expanded form. As a result, the tether belt 40 is maintained in a pulled state even while the occupant P who is not wearing the seat belt is being received, and therefore, gas discharge through the exhaust state switching member 30 and the opening 28h is suppressed.
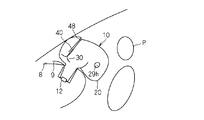
- FIGS. 21 and 22 show an example in which an annular relay part 48C corresponding to the annular relay part 48 is provided at the rear part (occupant side part) of the airbag body 20 as a comparative example.
- the tether belt 40 is loosened at a relatively initial stage, and gas is discharged from the exhaust state switching member 30.
- FIGS. 21 and 22 it is necessary to relatively reduce the exhaust speed of the gas from the exhaust state switching member 30. Then, as a countermeasure against the occupant P in the non-regular posture, the gas exhaust speed becomes insufficient, and another countermeasure needs to be taken.
- the airbag apparatus 10 configured as described above, when the inflated airbag body 20 receives the occupant P in the normal posture, the occupant P contacts the contact portion S1, and thus the tether belt 40 is pulled. Maintained. Thereby, the exhaust state switching member 30 maintains the non-exhaust state. Thereby, sudden discharge of gas can be suppressed and the impact of the passenger
- the occupant P is in the irregular posture state, the occupant P abuts against the airbag body 20 at a portion avoiding the contact portion S1 in the initial stage of inflation of the airbag body 20.
- the loose state of the tether belt 40 is maintained, and the exhaust state switching member 30 maintains the exhaust state or is switched to the exhaust state.
- gas can be discharged from the exhaust state switching member 30 as rapidly as possible, and the airbag main body 20 can be prevented from hitting the occupant P with as much force as possible.
- gas exhaust from the exhaust state switching member 30 can be suppressed even while the occupant P sinks into the airbag body 20, and the impact of the occupant P can be more reliably ensured. You can take it gradually.
- the occupant P comes into contact with the inflated form of the airbag body 20 from the rear (seat side), even if the occupant P is provided in the front half of the inflated form of the airbag body 20, the impact of the occupant P is gradually and more reliably. Can take it.
- the drawing amount of the tether belt 40 is provided. Can be made larger.
- the pull-in amount of the tether belt 40 is only about the difference in distance between the two points that are the connection destinations at both ends of the tether belt 40 between the deployed state 1 and the deployed state 2.
- the tether belt 40 is disposed so as to be bent via the annular relay portion 48 by providing the annular relay portion 48, the amount of the tether belt 40 retracted is between the deployed state 1 and the deployed state 2.
- the difference between the sum of the distance between one connection destination of the tether belt 40 and the annular relay portion 48 and the distance between the other connection destination of the tether belt 40 and the annular relay portion 48 is obtained. For this reason, the pull-in amount of the tether belt 40 for switching between the exhaust state and the non-exhaust state of the exhaust state switching member 30 between the deployed state 1 and the deployed state 2 is increased.
- the difference between the exhaust state and the non-exhaust state (that is, the difference in the degree of exhaust) can be increased, and a more complete non-exhaust state or exhaust state can be easily set.
- annular relay part 48 exists.
- an exhaust state switching member 30 is provided on one side of the inflated form of the airbag body 20, an annular relay part 48 is provided on the upper or front part of the inflated form of the airbag body 20, and one end of the tether belt 40 is In addition to being connected to the exhaust state switching member 30, the tether belt 40 is connected to the inner peripheral portion of the other side portion of the airbag body 20 via the annular relay portion 48, so that the airbag body 20 is inflated.
- the exhaust state switching member 30 can be pulled in more completely by pulling the tether belt 40 more surely and switched to the non-exhaust state more reliably.
- the air bag body 20 is provided with the second vent hole 29h for exhausting gas at an exhaust speed smaller than the exhaust speed of the exhaust state switching member 30 in the exhaust state, the exhaust state switching member 30 is in the exhaust state.
- the airbag main body 20 is normally inflated and catches the occupant P in the normal posture, the gas is gradually discharged from the second vent hole 29h to gradually impact the occupant P. Can take it.
- a switching type exhaust mechanism as shown in FIGS. 21 and 22 may be incorporated.
- the second vent hole 29h may be omitted.
- FIG. 23 is a schematic perspective view showing a modification of the embodiment.
- the flap 100 is provided in the airbag body 20 in the above embodiment.
- the flap 100 is a flexible sheet-like member formed of cloth or the like, and is formed in a square shape here.
- the flap 100 may be a polygon other than a square, a circle, or the like.
- the base end portion 101 (here, one side edge portion) of the flap 100 is connected to the outer peripheral portion of the airbag body 20 by sewing or the like. Further, the distal end portion 102 of the flap 100 opposite to the base end portion 101 covers the airbag body 20 from the initial stage of inflation of the airbag body 20 toward the opposite side of the gas supply port 26h during the inflation. So as to extend.
- the base end portion 101 of the flap 100 is more specifically on the gas supply port 26 h side than the attachment position of the annular relay portion 48 in the airbag body 20 on the outer periphery of the airbag body 20 viewed from the side.
- the airbag main body 20 it connects with the vehicle front side rather than the attachment location of the cyclic
- tip part 102 of the flap 100 has the attachment location of the cyclic
- the flap 100 is provided so as to cover the attachment portion of the annular relay portion 48 from the front portion of the vehicle toward the rear thereof in the airbag main body 20 during or after inflation.
- the airbag body 20 when the airbag body 20 is inflating and the head or chest of an occupant in a non-regular posture is present at a position from the occupant seat from above or above the inflator 12, the airbag 50 is being inflated. Between 20 and the passenger. Thereby, it can suppress that a part of airbag main body 20, especially the peripheral part of the attachment location of the cyclic
- the airbag main body 20 tries to inflate from the dashboard 8 upward and toward the rear of the vehicle (occupant P side).
- the peripheral portion of the airbag body 20 where the annular relay portion 48 is provided is closer to the front of the vehicle than the head or chest of the occupant P. Can be located.
- the flap 100 covers the airbag body 20 in the middle of inflation and faces the occupant P at the occupant P side portion behind the vehicle rather than the peripheral portion where the annular relay portion 48 is provided. For this reason, the flap 100 is sandwiched between the airbag body 20 and the occupant P in the middle of inflation. Since the airbag body 20 starts inflating from the folded state, the airbag body 20 remains in a state where it is folded to some extent in the middle of the inflation.
- the flap 100 when the flap 100 is sandwiched between the airbag body 20 in the middle of inflation and the occupant P, the force to be inflated is received by the flap 100 and the sandwiched portion. The expansion force is difficult to act on. For this reason, the airbag main body 20 is restrained from expanding at the inner portion of the flap 100 and the lower portion of the airbag main body 20 and the tether belt 40 is hardly pulled. As a result, the tether belt 40 is loosened, and the exhaust state switching member 30 is in the exhaust state.
- the gas in the airbag body 20 passes through the exhaust state switching member 30 through the opening 28h and is exhausted to the outside through the first vent hole 32h. Expansion and expansion are suppressed.
- the flap 100 When the occupant P is in the normal posture, as shown in FIGS. 27 to 30, the flap 100 is only covered over the airbag body 20 in the middle of inflation or in the inflated configuration. Do not touch. For this reason, it can expand
- FIG. 27 When the occupant P is in the normal posture, as shown in FIGS. 27 to 30, the flap 100 is only covered over the airbag body 20 in the middle of inflation or in the inflated configuration. Do not touch. For this reason, it can expand
- one of the connection destinations of the tether belt may be provided at a position from above the airbag body, and the flap may be provided so as to cover the connection portion.
- the flap 100 when the airbag body 20 is inflated for an occupant P in a non-regular posture, the flap 100 abuts on the occupant and is sandwiched between the occupant P and the airbag body 20.
- the partial inflation of the airbag main body 20 is suppressed inside the flap 100.
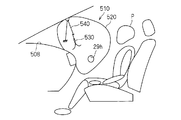
- the airbag apparatus 10 demonstrated in the example provided in the part which faces upwards among the dashboards 8, it corresponds to the airbag apparatus 10 as shown in FIG.31 and FIG.32.
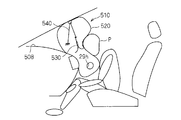
- the airbag device 510 that performs the above may be provided in a portion of the dashboard 508 that faces the occupant P side.
- the position of the exhaust state switching member 530 corresponding to the exhaust state switching member 30 the connection location of the tether belt 540 corresponding to the tether belt 40, the passing line, etc. Is set in the same manner as in the above embodiment, and the same effect as in the above embodiment can be obtained.
- an airbag device may be provided in the middle between the installation position of the above embodiment and the installation positions of FIGS. 31 and 32, that is, a portion facing diagonally rearward of the dashboard.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Air Bags (AREA)
Abstract
乗員が非正規姿勢状態である場合には、ガスをなるべく急に排出でき、かつ、エアバッグの膨張後に正規姿勢状態の乗員を受け止める場合には、ガスの急な排出を抑制することを目的とする。エアバッグ装置は、エアバッグ本体と、インフレータと、排気状態切替部材と、連結部材の一例としてのテザーベルトとを備える。排気状態切替部材は、エアバッグ本体内に引込まれることで、排気状態から非排気状態に切替えられる。テザーベルトは、排気状態切替部材とエアバッグ本体の内周部の一部とを連結する。排気状態切替部材の配設位置と、エアバッグ本体の内周部に対するテザーベルトの連結位置と、テザーベルトの通過ラインとが、エアバッグ本体が正規姿勢の乗員を受け止める際に、その乗員との接触部分を避けた部分に設けられている。
Description
この発明は、車両乗員を保護するためのエアバッグ装置に関する。
特許文献1は、ベントホールからのガスの流出を規制する規制手段を有するエアバッグを開示している。規制手段は、ベントホールを括ることが可能な括り部材と、括り部材とエアバッグの乗員対向面とを繋ぐように設けられた繋ぎ部材とを備える。そして、エアバッグの膨張時には、繋ぎ部材を介して括り部材が引っ張られてベントホールが閉じられる。一方、膨張したエアバッグに乗員が接触して乗員対向面が後退すると、括り部材が緩み、ベントホールが開かれる。
本件に関する他の従来技術として、特許文献2がある。
ところで、乗員が通常の乗車姿勢よりも前傾した姿勢等、非正規な姿勢をとっている場合(Out Of Position、略して、OOPといわれる場合がある)がある。この場合、エアバッグが乗員に対して大きい力で当らないようにするためには、エアバッグが急激に膨らむことを抑制することが好ましい。
特許文献1に開示の技術でも、乗員が非正規な姿勢をとっている場合に、膨張する前に乗員対向面と乗員とが接触して、括り部材が弛んだ状態及びベントホールが開かれた状態が維持されることがある程度期待される。この場合、ベントホールからガスが排出され、これにより、エアバッグが急激に膨らむことがある程度抑制される。
しかしながら、エアバッグ膨張後に乗員の衝撃を徐々に受け止めるために適切なガスの排出速度と、乗員が非正規な姿勢をとっている場合への対策として適切なガスの排出速度とは異なる。
例えば、エアバッグ膨張後に乗員の衝撃を徐々に受け止めるためには、ガスは徐々に排出されることが好ましい。一方、乗員が非正規な姿勢をとっている場合には、エアバッグが大きな力で乗員に当らないようにするため、ガスが急激に排出されることが好ましい。
特許文献1に開示の技術では、前者の場合を想定してガスが徐々に排出されるようにガス排出速度が設定されている。このため、乗員が非正規な姿勢をとっている場合にも、ガスは徐々に排出される程度であり、従って、エアバッグは急に膨張してしまうおそれがある。
そこで、この発明は、乗員が非正規姿勢状態である場合には、ガスをなるべく急に排出でき、かつ、エアバッグの膨張後に正規姿勢状態の乗員を受け止める場合には、ガスの急な排出を抑制することを目的とする。
上記課題を解決するため、第1の態様に係わるエアバッグ装置は、ガス供給口を有するエアバッグ本体と、前記ガス供給口を通じて前記エアバッグ本体内にガスを供給するインフレータと、前記エアバッグ本体に設けられ、前記エアバッグ本体内に引き込まれるときに、前記エアバッグ本体内のガスを排気可能にする排気状態から前記エアバッグ本体内のガスの排気を抑制する非排気状態に切り替えられる排気状態切替部材と、前記排気状態切替部材と前記エアバッグ本体の内周部の一部とを連結する連結部材とを備え、前記排気状態切替部材の配設位置と、前記エアバッグ本体の内周部に対する前記連結部材の連結位置と、前記連結部材の通過ラインとが、前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態のうち、そのエアバッグ本体が正規姿勢状態の乗員を受け止める際にその乗員との接触部分を避けた部分に設けられている。
第2の態様は、第1の態様に係わるエアバッグ装置であって、前記排気状態切替部材の配設位置と、前記エアバッグ本体の内周部に対する前記連結部材の連結位置と、前記連結部材の通過ラインとが、前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態のうち、そのエアバッグ本体が正規姿勢状態の乗員を受け止める際に変形する部分を避けた部分に設けられている。
第3の態様は、第1又は第2の態様に係わるエアバッグ装置であって、前記排気状態切替部材の配設位置と、前記エアバッグ本体の内周部に対する前記連結部材の連結位置と、前記連結部材の通過ラインとが、車両組付状態から膨張する前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態の前半部に設けられている。
第4の態様は、第1~第3のいずれか1つの態様に係わるエアバッグ装置であって、前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態の内周部に、前記連結部材を長手方向に沿って移動可能に支持する環状中継部が設けられ、前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態において、前記連結部材が前記環状中継部を経由して曲がるように配設されている。
第5の態様は、第4の態様に係わるエアバッグ装置であって、前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態の一側部に前記排気状態切替部材が設けられ、前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態の上部又は前部に前記環状中継部が設けられ、前記連結部材の一端部が前記排気状態切替部材に連結されると共に、前記連結部材の他端部が前記環状中継部を経由して前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態の他側部の内周部に連結されている。
第6の態様は、第1~第5のいずれか1つの態様に係わるエアバッグ装置であって、前記エアバッグ本体に、前記排気状態における前記排気状態切替部材の排気速度よりも小さい排気速度でガスを排出するベントホールが形成されている。
第7の態様は、第1~第6のいずれか1つの態様に係わるエアバッグ装置であって、基端部が前記エアバッグ本体の外周部に連結されると共に、先端部が前記ガス供給口とは反対側に向けて前記エアバッグ本体に覆い被さるように延在するフラップをさらに備える。
第1の態様によると、膨張したエアバッグが正規姿勢状態の乗員を受け止める場合には、乗員は前記接触部分に当接するため、連結部材の引っ張られた状態が維持され、排気状態切替部材は非排気状態を維持する。これにより、ガスの急な排出を抑制できる。一方、乗員が非正規姿勢状態である場合には、乗員は、エアバッグ本体に対して正規姿勢の乗員との接触部分を避けた部分に当接する。これにより、連結部材の弛んだ状態が維持され、排気状態切替部材が排気状態を維持し又は排気状態に切り替えられる。これにより、排気状態切替部材からガスをなるべく急に排出できる。
第2の態様によると、膨張したエアバッグが正規姿勢状態の乗員を受け止める場合に、より確実に連結部材が引っ張られた状態が維持される。これにより、ガスの急な排出をより確実に抑制できる。一方、乗員が非正規姿勢状態である場合には、乗員は、エアバッグ本体のうち連結部材が設けられた部分により確実に当接する。これにより、連結部材が弛んだ状態がより確実に維持され、排気状態切替部材からガスをなるべく急に排出できる。
第3の態様によると、膨張したエアバッグが正規姿勢状態の乗員を受け止める場合に、より確実に連結部材が引っ張られた状態が維持される。これにより、ガスの急な排出をより確実に抑制できる。一方、乗員が非正規姿勢状態である場合には、乗員は、エアバッグ本体のうち連結部材が設けられた部分により確実に当接する。これにより、連結部材が弛んだ状態がより確実に維持され、排気状態切替部材からガスをなるべく急に排出できる。
第4の態様によると、連結部材を、環状中継部を経由して曲がるように配設することで、エアバッグの膨張形態において、連結部材をより確実に引っ張ることにより、排気状態切替部材をより完全に引き込んでより確実に非排気状態に切り替えることができる。
第5の態様によると、連結部材は、前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態の一側部から他側部に向けて、その上方又は前部の環状中継部を経由して配設される。これにより、エアバッグの膨張形態において、連結部材をより確実に引っ張り、排気状態切替部材をより完全に引き込んでより確実に非排気状態に切り替えることができる。
第6の態様によると、エアバッグ本体が通常に膨張した場合には、前記ベントホールによってガスを排出することができる。
第7の態様によると、非正規姿勢時にエアバッグ本体が膨張しようとする際に、フラップが乗員に当接すると、その部分でエアバッグ本体の膨張が抑制される。エアバッグ本体の部分的な膨張を抑制することで、連結部材の引っ張りを抑制して、排気状態切替部材が非排気状態に切り替え又は維持されることを抑制できる。これにより、非正規姿勢時に、なるべく乗員の位置、姿勢に拘らず、エアバッグ本体の急な膨張を抑制できる。
以下、実施形態に係わるエアバッグ装置について説明する。図1はエアバッグ装置10の膨張形態を示す概略斜視図であり、図2はダッシュボードに取り付けられた状態でのエアバッグ装置10の膨張形態を示す概略側面図である。なお、図1ではエアバッグ装置10の内部構造を示すため、部分的に透過図となっている。
このエアバッグ装置10は、車両の助手席前方にあるダッシュボードに組み込まれ、車両の衝突時等に助手席乗員前方に展開して、助手席乗員を受け止めて衝撃を吸収する装置である。もちろん、本エアバッグ装置は、助手席用のエアバッグ装置に限らず、ステアリング装置に組み込まれる運転席用のエアバッグ等にも適用可能である。
本エアバッグ装置10は、エアバッグ本体20と、インフレータ12と、排気状態切替部材30と、連結部材としてのテザーベルト40とを備えている。
エアバッグ本体20は、膨張可能な袋状に形成されており、ガス供給口26hと、すくなくとも一つの開口部28hを有している。エアバッグ本体20は、例えば、次の構成によって袋状に形成される。すなわち、略帯状の布の両端縁部を縫い合せる等して接合することで略筒状の基布部22を形成する。また、基布部22の側方開口を閉塞可能な広がり形状を有する一対の側布部24を準備し、略筒状に形成された基布部22の両側開口周縁部に、それぞれ側布部24の縁部を縫いつける等して接合する。これにより、袋状のエアバッグ本体20が形成されている。ここでは、エアバッグ本体20は、側面視において、インフレータ12の上方から乗員側(車両後方、図1の右側)に向けて膨らみ、乗員側部分で下方に向けて膨らむ形状に形成されている。もちろん、エアバッグ本体20を袋状に形成するための基布の形状、組み合わせは上記例に限られない。また、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態は上記例に限られない。
ガス供給口26hは、膨張形態でダッシュボードに対向する部分、より具体的には、エアバッグ本体20の車両前方(乗員から離れる側、図1の左側)の下部に形成されている。このガス供給口26h部分にインフレータ12が取付けられる。そして、車両の衝突時等にインフレータ12で発生したガスがガス供給口26hを通ってエアバッグ本体20内に導入される構成となっている。
開口部28hは、ガス排出用の孔である。ここでは、開口部28hは、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態において乗員から離れる部分、より具体的には、エアバッグ本体20の車両前方の一側部に形成されている。ここでは、開口部28hは、エアバッグ本体20の前後方向或は当該前後方向からやや斜めに沿って延びる長孔状に形成されている。もっとも、開口部28hは、長孔状に限られず、円穴状、多角形孔状、或はスリット状に形成されていてもよい。
なお、上記エアバッグ本体20に、開口部28hとは別に、第2のベントホール29hが形成されている。この第2のベントホール29hは、例えば、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態の一方側の側部、或いは、両側部等に形成される。第2のベントホール29hがエアバッグ本体20の膨張形態の一方側の側部に形成される場合、車両外側を向く側部(つまり、ドア側)の側部であってもよいし、車室内側を向く側部であってもよい。
この第2のベントホール29hは、エアバッグ本体20が膨張形態で正規姿勢の乗員を受止める際に、内部のエアを徐々に排出する目的で設けられる。このため、第2のベントホール29hは、エアバッグ本体20が膨張した状態で外部に現れる部分、例えば、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態で車両後方側部分(乗員側部分)に設けられていることが好ましい。また、第2のベントホール29hからのガス排出速度は、乗員の衝撃を徐々に受け止めるように、内部のエアを徐々に排出できる程度であることが好ましい。従って、第2のベントホール29hは、後述する排気状態切替部材30の排気状態における排気速度(例えば、一定の内部ガス圧条件で単位時間当りに排出されるガス量)よりも小さい排気速度でガスを排出できることがように設定されていることが好ましい。なお、第2のベントホール29hからのガス排出速度は、その大きさ等を調整することで設定される。
この第2のベントホール29hによる排気と、排気状態切替部材30を介した排気態様との組み合わせによって、多彩な排気パターンの設定が可能となる。
排気状態切替部材30は、上記開口部28hに設けられており、エアバッグ本体20内に引き込まれる前の状態では、エアバッグ本体20内のガスを排気可能な排気状態とされ(図5~図7参照)、エアバッグ本体20内に引き込まれるときに、前記排気状態からエアバッグ本体20内のガスの排気を抑制する非排気状態(図1~図4参照)に切り替えられるように構成されている。そして、後述するテザーベルト40による引込力に応じて、排気状態切替部材30がこれらの両状態間で状態変更する。
より具体的に説明すると、排気状態切替部材30は、一対の帯状布32を有している。一対の帯状布32の一端部(基端部)は、エアバッグ本体20内で開口部28hの周縁部を囲むように縫いつけられている。なお、排気状態切替部材30は、エアバッグ本体20の外面で該エアバッグ本体20に縫いつけられていてもよい。また、一対の帯状布32の他端部(先端部)は、その幅方向に沿って略全体に亘って互いに縫い合わされて接合されている。さらに、一対の帯状布32の両側部は、その基端部だけ縫い合わされて接合されており、その他の部分は縫い合わされない開口状態となっている。そして、一対の帯状布32の両側部のうち非縫い合わせ部分で囲まれる部分をもって、第1のベントホール32hが構成されている。なお、一対の帯状布32の両側部の基端は所定長に亘って縫い合わされているため、開口部28hと第1のベントホール32hとは連続した位置関係にはなく、互いに離れた位置に形成されていることになる。
また、一対の帯状布32の幅寸法は、上記開口部28hの幅寸法よりも大きく設定されており、従って、排気状態切替部材30の幅寸法も開口部28hの幅寸法よりも大きく設定されている。そして、エアバッグ本体20の内部から外部へ又はその逆に移動する場合には、排気状態切替部材30がその幅方向に縮小するように変形しつつ開口部28h内をくぐり抜けるようになり、所定の抵抗が作用するようになっている。これにより、後述するテザーベルト40による引込力やエアバッグ本体20に所定以上の内圧が作用していない場合等に、排気状態切替部材30が不用意に状態変更することを抑制するようにしている。
この排気状態切替部材30は、第1のベントホール32h形成部分と共にエアバッグ本体20外に導出された状態では、第1のベントホール32hを通じてエアバッグ本体20内のガスを排気可能な排気状態となる(図5、図6及び図7参照)。一方、排気状態切替部材30は、第1のベントホール32h形成部分と共にエアバッグ本体20内に導入された状態では、開口部28hを閉塞するように覆ってエアバッグ本体20内のガス排気を抑制する非排気状態となる(図1~図4参照)。
排気状態切替部材30の構成は上記例に限られない。
例えば、図8に示す変形例に係わる排気状態切替部材230では、一対の略台形状布232の長辺側である底辺232aをエアバッグ本体20の開口部28hに縫いつけて取り付けると共に、一対の略台形状布232の短辺側である上辺232b同士を縫い合わせて接合している。そして、その一対の略台形状布232の上辺の接合部分に長尺状のテザーベルト240の一端部を連結している。また、一対の略台形状布232の斜辺232cで囲まれる部分により一対の第1のベントホール232h(太線部分参照)を形成している。
また、図9に示す変形例に係る排気状態切替部材330では、一対の略台形状布332の長辺側である底辺332aをエアバッグ本体20の開口部28hに縫いつけて取り付けると共に、一対の略台形状布332の両斜辺332c同士を縫い合わせて接合している。そして、その一対の略台形状布332の各上辺332bに長尺状のテザーベルト340の一端部を連結している。また、その一対の略台形状布332の上辺332bで囲まれる部分により、第1のベントホール332h(太線部分参照)を形成している。
図10に示す排気状態切替部材430では、一対の略台形状布432の長辺側である底辺432aをエアバッグ本体20の開口部28hに縫い付けて取り付けると共に、一対の略台形状布432の両斜辺432c同士及び両上辺432b同士を縫い合せて接合している。そして、その一対の略台形状布432の各上辺に長尺状のテザーベルト440の一端部を連結している。また、その一対の略台形状布432の一方又は双方に穴を形成してこれを第1のベントホール432hとしている。
これらの各変形例の場合でも、上記実施形態と同様にエアバッグ本体20内に導入され、又は、外に導出されることで、非排気、排気の状態が切り替えられる。
テザーベルト40は、上記排気状態切替部材30とエアバッグ本体20の内周部の一部とを連結する部材である。このテザーベルト40は、エアバッグ本体20が正規形状に膨張する際(図1及び図2参照)には、そのインフレータ12からのガス供給による膨張力を受けて排気状態切替部材30をエアバッグ本体20内に引き込んで、非排気状態にする。一方、エアバッグ本体20が膨張する途中でエアバッグ本体20が非正規姿勢の乗員に当接し、エアバッグ本体20の展開膨張が部分的に妨げられると、テザーベルト40による排気状態切替部材30の引張りが抑制される。これにより、排気状態切替部材30が排気状態に変更するのを許容された状態となる。
より具体的には、テザーベルト40は、長尺部材、ここでは、布等によって細長い帯状に形成されている。勿論、連結部材としては、その他、紐状の部材等を用いてもよい。
上記テザーベルト40は、エアバッグ本体20が膨張途中、特に、膨張初期段階で非正規姿勢の乗員に当接すると、テザーベルト40は弛んだ状態に維持され、エアバッグ本体20が膨張形態で正規姿勢の乗員を受止めた場合には、テザーベルト40は引っ張られた状態に維持される配設されている。
エアバッグ本体20が膨張形態で正規姿勢の乗員を受け止めた場合に、テザーベルト40が引っ張られた状態に維持されるようにするためには、次のようにするとよい。
まず、乗員が正規姿勢である場合を想定する。正規姿勢とは、乗員席を、想定される平均的な使用位置及び使用姿勢に調整し、平均的な骨格、身長及び体つきの乗員が、胴体を背もたれにもたれさせると共に、頭部の軸を鉛直姿勢にしたような姿勢をいう。ここでは、正規姿勢としては、乗員がシートベルトを着用した状態を想定している。かかる正規姿勢の一例は、2011年8月29日に発行され、2011年12月27日に有効となるFMVSS(Federal Motor Vehicle. Safety Standard)のNo.208の「S7.シートベルトアッセンブリ要件」及び「S10.テスト用ダミーの配置方法」等に規定されたものを採用することができる。
そして、エアバッグ本体20が膨張して、上記正規姿勢の乗員を受止める状態(つまり、膨張形態)になると、乗員はエアバッグ本体20の後方部分(乗員側部分)に当接し、エアバッグ本体20内に徐々に深く沈み込んでいく。このため、エアバッグ本体20の後方部分には、上記正規姿勢の乗員が接触する接触部分S1が存在する(図2及び図18参照)。また、エアバッグ本体20の後方部分のうち前記接触部分S1の周りには、乗員の沈み込みと共に変形していく変形部分S2が存在する(図2及び図18参照)。
エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態が、正規姿勢の乗員を受け止める際に、テザーベルト40の緩みを抑制するためには、まず、上記排気状態切替部材30の配設位置と、エアバッグ本体20の内周部に対するテザーベルト40の連結位置と、テザーベルト40の通過ラインとが、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態のうち、上記接触部分S1を避けた部分に設けられることが好ましい。また、上記場合に、より確実にテザーベルト40の緩みを抑制するためには、上記排気状態切替部材30の配設位置と、エアバッグ本体20の内周部に対するテザーベルト40の連結位置と、テザーベルト40の通過ラインとが、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態のうち、上記変形部分S2を避けた部分に設けられることが好ましい。
通常、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態において、乗員はエアバッグ本体20の後側部分(乗員側部分)に接触して沈みこんでいく。このため、上記排気状態切替部材30の配設位置と、エアバッグ本体20の内周部に対するテザーベルト40の連結位置と、テザーベルト40の通過ラインとは、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態の前半部に設けるとよいと捉えることもできる(図2参照)。この前半部は、エアバッグ本体20が車両のダッシュボード8から膨張した状態を想定し、車両の前後方向に2分割した車両基準の前半部分であり、その2分割の境界線M上を含む。
結局、上記排気状態切替部材30の配設位置と、エアバッグ本体20の内周部に対するテザーベルト40の連結位置と、テザーベルト40の通過ラインとは、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態が正規姿勢の乗員を受け止める際に、テザーベルト40がなるべく緩まないような態様で配設されればよい。そのような態様としては、上記各箇所が、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態に対して正規姿勢の乗員が最も深く沈み込んだ場合の最深部よりも車両前方側部分に配設される態様、ダッシュボード8の車両後方側部分(乗員側部分)よりも車両前方側部分に配設される態様、或いは、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態のうち正規姿勢の乗員から見えない外周部の内側に配設される態様、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態のうちフロントウインドウと接触する部分及びその近傍部分より下方部分に配設される態様、等に配設されていればよい。
なお、テザーベルト40の通過ラインとは、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態において、テザーベルト40の両端の連結部分間で、テザーベルト40の中間部が通過するラインである。テザーベルト40がエアバッグ本体20の膨張形態において直線状に配設される場合には、その直線状のラインがテザーベルト40の通過ラインである。テザーベルト40がエアバッグ本体20の膨張形態において曲げて配設される場合には、その曲がる箇所を含む曲げられたラインがテザーベルト40の通過ラインである。
ここでは、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態の内周部に環状中継部48が設けられている。テザーベルト40の長手方向中間部は、当該環状中継部48を通ってその長手方向に沿って移動可能に支持されている。そして、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態において、テザーベルト40は、環状中継部48を経由して曲がるように配設されている。ここでは、上記環状中継部48が上記制約された部分内で、エアバッグ本体20の内周部に取り付けられており、これにより、テザーベルト40の長手方向中間部が上記制約された部分内を通って環状中継部48で曲がって配設されている。なお、ここでは、テザーベルト40の中央付近が環状中継部48によって移動可能に支持されているが、その他の箇所、例えば、テザーベルトの一端側に近い箇所が環状中継部によって移動可能に支持されていてもよい。
排気状態切替部材30及びテザーベルト40の配設態様についてより具体的に説明する。
まず、上記開口部28hが、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態のうち上下方向の寸法が小さい前側部分の一側部に形成され、この開口部28hに排気状態切替部材30が取り付けられている。従って、排気状態切替部材30は、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態のうち上記前側部分の一側部に設けられている。
また、テザーベルト40の一端部は上記排気状態切替部材30に連結されている。ここでは、排気状態切替部材30の先端側両側部がテザーベルト40に連結されている。すなわち、テザーベルト40の一端部は、排気状態切替部材30の先端部と略同じ幅寸法に形成されている。ここでは、テザーベルト40の先端部52は、Y字状に広がる形状に形成されている。そして、その略Y字状に広がる両端部が、排気状態切替部材30の先端部の両側に縫いつけられている。これにより、テザーベルト40は、排気状態切替部材30の先端側両側部を引っ張るようにして、排気状態切替部材30をエアバッグ本体20内に引き込むようになっている。もっとも、テザーベルト40の先端部が上記のようにY字状に広がる形状に形成されていることは必須ではない。
また、テザーベルト40の他端部は、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態のうち上記前側部分の他側部に、即ち、上記排気状態切替部材30に対してエアバッグ本体20の幅方向に対向する部分に連結されている。テザーベルト40の他端部とエアバッグ本体20との連結は、縫い付け等により行われる。
また、環状中継部48は、エアバッグ本体20と同様の布等で形成された部材であり、環状に形成されるように、エアバッグ本体20の前記前側部分の上部に縫い付ける等して取り付けられている。ここでは、環状中継部48が取り付けられた箇所は、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態のうちインフレータ12に対向する部分或いはそれよりも後方側(乗員)側の部分である。環状中継部48が取り付けられる箇所は、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態のうち前側(乗員から遠い側)であってもよい。環状中継部48をこれらの位置に設定することで、テザーベルト40がインフレータ12から供給されるガスに直接的に直近で曝されないように配設することができる。また、環状中継部が1つであることは必須ではなく、複数の環状中継部が設けられ、テザーベルトが複数の環状中継部のそれぞれで曲がるように配設されていてもよい。
そして、テザーベルト40が、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態の上記前側部分において、その一側部から上方の環状中継部48を通ってその他側部に至るように配設される。
また、テザーベルト40の長さは、次の条件を満たす長さ寸法に設定されている。すなわち、エアバッグ本体20が膨張する途中で、エアバッグ本体20(特に、テザーベルト40の連結部分及び環状中継部48を経由する部分の近傍部位)が非正規姿勢の乗員の頭部或は胸部等に当接して排気状態切替部材30とテザーベルト40とが設けられた部分の膨張が部分的に妨げられた状態(以下、展開状態1という場合がある)において、テザーベルト40の長さ寸法は、エアバッグ本体20の開口部28hと環状中継部48とを結ぶ距離と、環状中継部48とテザーベルト40の他端部の連結部分とを結ぶ距離との和よりも長い。従って、この状態では、テザーベルト40は弛み、排気状態切替部材30が排気状態に維持又は変更できるようになる。一方、非正規姿勢の乗員によって膨張が妨げられないで、エアバッグ本体20が想定された正規形状に膨張する場合(以下、最も大きく膨張した状態を展開状態2という場合がある)には、上記展開状態1よりも大きく膨張する途中で、エアバッグ本体20の開口部28hと環状中継部48とを結ぶ距離と、環状中継部48とテザーベルト40の他端部の連結部分とを結ぶ距離との和は、テザーベルト40の長さ寸法よりも大きくなるように設定されている。これにより、テザーベルト40は、膨張力を受けてエアバッグ本体20内周部の一部と環状中継部48との間、及び、開口部28hと環状中継部48との間で引っ張られて排気状態切替部材30をエアバッグ本体20内に引込んで、非排気状態に切り替える。
上記エアバッグ装置10は、次のようにして車両のダッシュボード8に組み込まれる。すなわち、ダッシュボード8の上向き面には、エアバッグ本体20の膨張時に割れ容易な蓋部9が形成されている。ダッシュボード8のうち蓋部9の内側にエアバッグ装置10取付用のブラケット等が取り付けられている。インフレータ12が上記ブラケットに取り付けられると共に、エアバッグ本体20が折り畳まれた状態で、エアバッグ装置10がダッシュボード8の上向き面の内部に取り付けられている。そして、車両衝突時等には、インフレータ12で発生したガスがガス供給口26hを通ってエアバッグ本体20内に導入される。これにより、エアバッグ本体20が膨張し、上記蓋部9を割開いて、ダッシュボード8の上方及び車両後方側(乗員側)に膨張する。
まず、図11に示すように、乗員Pが非正規姿勢にある場合において、エアバッグ本体20の動作を説明する。なお、非正規姿勢とは、上記正規姿勢から外れた姿勢で、かつ、頭部が正規姿勢よりもダッシュボード8側に近い姿勢のうちの1つをいう。特に、ここでは、非正規姿勢として、乗員Pが乗員席に着座した状態で頭部及び胸部を車両前方のダッシュボード近くに位置させている場合を想定して説明する。
この場合、図12及び図13に示すように、エアバッグ本体20が膨張する初期段階で、エアバッグ本体20が乗員Pの頭部或は胸部に当る。これにより、エアバッグ本体20が乗員側へ膨張することが妨げられ、テザーベルト40の両端部連結箇所と環状中継部48との距離が比較的小さいままに維持され、テザーベルト40を強く引っ張る力が作用し難い。このため、テザーベルト40が弛んだ状態となり、排気状態切替部材30は排気状態となる。なお、排気状態切替部材30は、初期状態において排気状態であってもよいし、或いは、エアバッグ本体20の内圧によって排気状態切替部材30がエアバッグ本体20外に出て排気状態に切り替ってもよい。
これにより、エアバッグ本体20内のガスは開口部28hから排気状態切替部材30内を通って第1のベントホール32hから外部になるべく急に排出され、エアバッグ本体20の急激な展開膨張が抑制される。
次に、図14に示すように、乗員Pが正規姿勢にある場合において、エアバッグ本体20の動作を説明する。なお、乗員Pは、シートベルトを着用しているとする。
この場合、図15に示すように、エアバッグ本体20は、乗員P等に妨げられることなく乗員側に向けて膨張する。
そして、図16に示すように、エアバッグ本体20がある程度膨張し、エアバッグ本体20の開口部28hと環状中継部48とを結ぶ距離と、環状中継部48とテザーベルト40の他端部の連結部分とを結ぶ距離との和が、テザーベルト40の長さ寸法を超えると、テザーベルト40が引っ張られる。テザーベルト40の引っ張り力によって、排気状態切替部材30がエアバッグ本体20内に引き込まれ、非排気状態に切り替えられる。このため、排気状態切替部材30からガスの排気が抑制された状態で、エアバッグ本体20が迅速に膨張する。
そして、図17に示すように、エアバッグ本体20がほぼ完全に膨張すると、テザーベルト40が強く引っ張られて、排気状態切替部材30はエアバッグ本体20内に強く引張られた状態となり、エアバッグ本体20の内圧に抗して上記非排気状態にほぼ完全に維持される。
続いて、図18及び図19に示すように、このエアバッグ本体20が車両衝突の衝撃によって前方に移動する乗員Pを受け止め、乗員Pの衝撃を吸収する。この状態では、排気状態切替部材30及び開口部28hを介したガスの排出は抑制されているが、第2のベントホール29hからはガスが排出される。もっとも、第2のベントホール29hからのガス排出量は、上記したように、乗員Pの衝撃を徐々に受け止めることができる程度に設定されている。このため、乗員Pの衝撃はエアバッグ本体20によって徐々に受け止められる。
排気状態切替部材30及びテザーベルト40の連結箇所、通過ライン等を、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態のうち乗員Pを受け止めた場合に変形しない部分に設定することで、乗員Pを受止める途中でも上記テザーベルト40は引っ張られた状態に維持され、従って、排気状態切替部材30及び開口部28hを介したガスの排出は抑制される。
図20は、乗員Pは正規姿勢ではあるが、シートベルトを着用していない場合を想定した図である。この場合、乗員Pは、エアバッグ本体20に対してより深く沈み込む。
従って、排気状態切替部材30及びテザーベルト40の連結箇所、通過ラインは、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態のうちシートベルト非着用の乗員Pを受け止めた場合にも変形しない部分、即ち、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態のより前方の部分に設定することが好ましい。これにより、シートベルト非着用の乗員Pを受け止める途中でも上記テザーベルト40は引っ張られた状態に維持され、従って、排気状態切替部材30及び開口部28hを介したガスの排出は抑制される。
図21及び図22は比較例として、環状中継部48に対応する環状中継部48Cを、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態の後部(乗員側部分)に設けた例を示している。この場合、乗員Pが膨張したエアバッグ本体20に当接して沈み込んでいくと、比較的初期段階でテザーベルト40が緩んで、排気状態切替部材30からガスが排出されてしまう。このため、図21及び図22の場合には、排気状態切替部材30からのガスの排気速度を比較的小さくする必要がある。そうすると、上記非正規姿勢にある乗員P対策としては、ガスの排気速度が不十分となり、別の対策を講じる必要が生じる。
以上のように構成されたエアバッグ装置10によると、膨張したエアバッグ本体20が正規姿勢の乗員Pを受け止める場合には、乗員Pは接触部分S1に当接するため、テザーベルト40は引っ張られた状態に維持される。これにより、排気状態切替部材30は非排気状態を維持する。これにより、ガスの急な排出を抑制し、正規姿勢の乗員Pの衝撃を受け止めることができる。一方、乗員Pが非正規姿勢状態である場合には、エアバッグ本体20の膨張初期段階で、乗員Pは、エアバッグ本体20に対して上記接触部分S1を避けた部分に当接する。これにより、テザーベルト40の緩んだ状態が維持され、排気状態切替部材30が排気状態を維持し又は排気状態に切り替えられる。これにより、排気状態切替部材30からガスをなるべく急に排出することができ、エアバッグ本体20が乗員Pに対してなるべく大きい力で当らないようにすることができる。排気状態切替部材30の配設位置と、エアバッグ本体20の内周部に対するテザーベルト40の連結位置と、テザーベルト40の通過ラインとが、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態のうち、乗員Pを受け止める際の変形部分S2を避けた部分に設けられていると、乗員Pがエアバッグ本体20内に沈み込んでいく途中でも排気状態切替部材30からのガス排出を抑制でき、乗員Pの衝撃をより確実に徐々に受け止めることができる。
また、乗員Pはエアバッグ本体20の膨張形態に対して後方(席側)より当接するので、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態の前半部に設けることとしても、乗員Pの衝撃をより確実に徐々に受け止めることができる。
また、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態の内周部に、連結部材の長手方向中間部をその長手方向に沿って移動可能に支持する環状中継部48が設けられているため、テザーベルト40の引込量をより大きくすることができる。例えば、環状中継部48を省略した場合、テザーベルト40の引込量は、上記展開状態1と展開状態2との間における、テザーベルト40の両端の連結先である2点間の距離の差程度しかない。これに対して、環状中継部48を設けてテザーベルト40を、環状中継部48を経由して曲がるように配設すると、テザーベルト40の引込量は、上記展開状態1と展開状態2との間における、テザーベルト40の一方の連結先と環状中継部48との距離とテザーベルト40の他方の連結先と環状中継部48との距離との総和の差となる。このため、上記展開状態1と展開状態2との間で、排気状態切替部材30の排気状態と非排気状態との間で切り替えるためのテザーベルト40の引込量を大きくし、排気状態切替部材30の排気状態と非排気状態との差(つまり、排気される程度の差)を大きくすることができ、より完全な非排気状態又は排気状態に設定し易くすることができる。
もっとも、環状中継部48が存在することは必須ではない。
また、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態の一側部に排気状態切替部材30が設けられ、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態の上部又は前部に環状中継部48が設けられ、テザーベルト40の一端部が排気状態切替部材30に連結されると共に、テザーベルト40が環状中継部48を経由してエアバッグ本体20の膨張形態の他側部の内周部に連結されているため、エアバッグ本体20の膨張形態においてテザーベルト40をより確実に引っ張って、排気状態切替部材30をより完全に引き込んでより確実に非排気状態に切り替えることができる。
また、上記態様では、インフレータ12からのガスが直接的にテザーベルト40に吹き付けられ難いという利点もある。
また、エアバッグ本体20に、排気状態における排気状態切替部材30の排気速度よりも小さい排気速度でガスを排出する第2のベントホール29hが設けられているため、排気状態切替部材30が排気状態に切り替らない場合、即ち、エアバッグ本体20が通常に膨張して正規姿勢の乗員Pを受け止める場合にも、当該第2のベントホール29hからガスを徐々に排出して乗員Pの衝撃を徐々に受け止めることができる。
勿論、本第2ベントホール29hの代りに又はこれに加えて、図21及び図22に示すような、切替式の排気機構が組込まれていてもよい。また、第2のベントホール29hが省略されてもよい。
{変形例}
図23は、上記実施形態の変形例を示す概略斜視図である。
図23は、上記実施形態の変形例を示す概略斜視図である。
この変形例に係るエアバッグ装置10Bでは、上記実施形態におけるエアバッグ本体20に、フラップ100が設けられている。
フラップ100は、布等で形成された柔軟なシート状部材であり、ここでは、方形状に形成されている。もっとも、フラップ100は、方形以外の多角形、円形等であってもよい。
フラップ100の基端部101(ここでは、1つの側縁部)は、エアバッグ本体20の外周部に縫い合せ等によって連結されている。また、フラップ100のうち前記基端部101とは反対側の先端部102は、エアバッグ本体20の膨張初期から膨張途中においてガス供給口26hとは反対側に向けてエアバッグ本体20に覆い被さるように延在している。
ここでは、フラップ100の基端部101は、エアバッグ本体20を側方から視た外周りにおいて、エアバッグ本体20のうち環状中継部48の取付箇所よりもガス供給口26h側、より具体的には、エアバッグ本体20のうち環状中継部48の取付箇所よりも車両前方側に連結されている。また、フラップ100の先端部102は、エアバッグ本体20を側方から視た外周りにおいて、エアバッグ本体20のうち環状中継部48の取付箇所を、ガス供給口26hの反対側(車両前方、つまり、乗員側)に越えるように延在している。換言すれば、フラップ100は、膨張途中又は膨張完了後のエアバッグ本体20のうち環状中継部48の取付箇所を、車両前方部分からその後方に向けて被さるように設けられている。
これにより、エアバッグ本体20が膨張する途中で、インフレータ12の上方或は上方から乗員席よりの位置に非正規姿勢の乗員の頭部又は胸部が存在すると、フラップ50が膨張途中のエアバッグ本体20と乗員との間に挟まれる。これにより、エアバッグ本体20の一部分、特に、エアバッグ本体20のうち環状中継部48の取付箇所の周辺部分が、ダッシュボードと非正規姿勢の乗員との間を抜出てしまうことを抑制できる。
すなわち、乗員Pが上記実施形態で想定した非正規姿勢よりも正規姿勢よりの姿勢であり、かつ、フラップ100が無い場合を想定する。この場合、環状中継部48の位置設定等によっては、図24に示すように、エアバッグ本体20が膨張する途中で、環状中継部48の周辺部分がダッシュボード8と乗員Pとの間を抜出てしまう恐れがある。
これに対して、上記のようにフラップ100を設けると、エアバッグ本体20の環状中継部48の周辺部分が上記のように抜け出てしまうことを抑制できる。
すなわち、図25に示すように、エアバッグ本体20がダッシュボード8からその上方及び車両後方(乗員P側)に向けて膨張しようとする。
この際、乗員Pの頭部或は胸部が上記環状中継部48に設けられた付近に位置している場合には上記実施形態で説明した動作によってエアバッグ本体20の急な膨張が抑制される。
乗員Pが上記した姿勢よりも正規姿勢よりの姿勢である場合等には、エアバッグ本体20のうち環状中継部48が設けられた周辺部分は乗員Pの頭部或は胸部よりも車両前よりに位置することがあり得る。この際、フラップ100は、膨張途中のエアバッグ本体20の上方に覆い被さり、環状中継部48が設けられた周辺部分よりも車両後方の乗員P側部分で乗員Pに面する。このため、フラップ100は、膨張途中のエアバッグ本体20と乗員Pとの間に挟まれる。エアバッグ本体20は折り畳まれた状態から膨張を開始するため、膨張途中では、エアバッグ本体20は何らかの形態である程度折り畳まれた状態が残っている。しかしながら、上記のように、フラップ100が膨張途中のエアバッグ本体20と乗員Pとの間に挟まれると、膨張しようとする力がフラップ100及び前記挟込み部分によって受け止められるため、フラップ100の内側には膨張力が作用し難い。このため、エアバッグ本体20のうちフラップ100の内側の部分とそれよりも下方部分でエアバッグ本体20の膨張が抑制され、テザーベルト40が引っ張られ難くなる。これにより、テザーベルト40が弛んだ状態となり、排気状態切替部材30は排気状態となる。
これにより、図26に示すように、エアバッグ本体20内のガスは開口部28hから排気状態切替部材30内を通って第1のベントホール32hから外部に排気され、エアバッグ本体20の急激な展開膨張が抑制される。
なお、乗員Pが正規姿勢である場合、図27~図30に示すように、フラップ100は、膨張途中又は膨張形態のエアバッグ本体20の上方に被さっているだけであり、乗員Pには当接しない。このため、上記実施形態と同様に膨張して乗員Pを受け止めることができる。
なお、本変形例では、環状中継部48がある実施形態を想定して説明したが、環状中継部48が無い場合でも適用できる。
この場合、テザーベルトの連結先の一方がエアバッグ本体の上方よりの位置に設けられ、フラップが当該連結箇所に被さるように設けられていればよい。
この変形例によると、非正規姿勢の乗員Pに対してエアバッグ本体20が膨張使用とする際に、フラップ100が乗員に当接して乗員Pとエアバッグ本体20との間に挟まれることで、フラップ100の内側でエアバッグ本体20の部分的な膨張が抑制される。エアバッグ本体20の部分的な膨張を抑制することで、テザーベルト40の引っ張りを抑制して、排気状態切替部材30が非排気状態に切り替え又は維持されることを抑制できる。これにより、乗員Pが非正規姿勢である場合に、なるべく乗員Pの位置、姿勢に拘らず、エアバッグ本体20の急な膨張を抑制できる。
また、上記実施形態及び変形例では、エアバッグ装置10がダッシュボード8のうち上方を向く部分に設けられた例で説明したが、図31及び図32に示すように、エアバッグ装置10に対応するエアバッグ装置510が、ダッシュボード508のうち乗員P側を向く部分に設けられていてもよい。この場合、エアバッグ本体20に対応するエアバッグ本体520に対して、排気状態切替部材30に対応する排気状態切替部材530の位置、及び、テザーベルト40に対応するテザーベルト540の連結箇所、通過ライン等を、上記実施形態と同様に設定することで、上記実施形態と同様の作用効果を得ることができる。
勿論、上記実施形態の設置位置と図31及び図32の設置位置との中間、即ち、ダッシュボードの斜め後方を向く部分に、エアバッグ装置が設けられてもよい。
なお、上記実施形態及び各変形例で説明した各構成は、相互に矛盾しない限り適宜組み合わせることができる。
以上のようにこの発明は詳細に説明されたが、上記した説明は、すべての局面において、例示であって、この発明がそれに限定されるものではない。例示されていない無数の変形例が、この発明の範囲から外れることなく想定され得るものと解される。
Claims (7)
- ガス供給口を有するエアバッグ本体と、
前記ガス供給口を通じて前記エアバッグ本体内にガスを供給するインフレータと、
前記エアバッグ本体に設けられ、前記エアバッグ本体内に引込まれるときに、前記エアバッグ本体内のガスを排気可能にする排気状態から前記エアバッグ本体内のガスの排気を抑制する非排気状態に切り替えられる排気状態切替部材と、
前記排気状態切替部材と前記エアバッグ本体の内周部の一部とを連結する連結部材と、
を備え、
前記排気状態切替部材の配設位置と、前記エアバッグ本体の内周部に対する前記連結部材の連結位置と、前記連結部材の通過ラインとが、前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態のうち、そのエアバッグ本体が正規姿勢状態の乗員を受け止める際にその乗員との接触部分を避けた部分に設けられている、エアバッグ装置。 - 請求項1記載のエアバッグ装置であって、
前記排気状態切替部材の配設位置と、前記エアバッグ本体の内周部に対する前記連結部材の連結位置と、前記連結部材の通過ラインとが、前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態のうち、そのエアバッグ本体が正規姿勢状態の乗員を受け止める際に変形する部分を避けた部分に設けられている、エアバッグ装置。 - 請求項1又は請求項2記載のエアバッグ装置であって、
前記排気状態切替部材の配設位置と、前記エアバッグ本体の内周部に対する前記連結部材の連結位置と、前記連結部材の通過ラインとが、車両組付状態から膨張する前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態の前半部に設けられている、エアバッグ装置。 - 請求項1~請求項3のいずれか1つに記載のエアバッグ装置であって、
前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態の内周部に、前記連結部材を長手方向に沿って移動可能に支持する環状中継部が設けられ、前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態において、前記連結部材が前記環状中継部を経由して曲がるように配設されている、エアバッグ装置。 - 請求項4記載のエアバッグ装置であって、
前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態の一側部に前記排気状態切替部材が設けられ、前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態の上部又は前部に前記環状中継部が設けられ、前記連結部材の一端部が前記排気状態切替部材に連結されると共に、前記連結部材の他端部が前記環状中継部を経由して前記エアバッグ本体の膨張形態の他側部の内周部に連結されている、エアバッグ装置。 - 請求項1~請求項5のいずれか1つに記載のエアバッグ装置であって、
前記エアバッグ本体に、前記排気状態における前記排気状態切替部材の排気速度よりも小さい排気速度でガスを排出するベントホールが形成されている、エアバッグ装置。 - 請求項1~請求項6のいずれか1つに記載のエアバッグ装置であって、
基端部が前記エアバッグ本体の外周部に連結されると共に、先端部が前記ガス供給口とは反対側に向けて前記エアバッグ本体に覆い被さるように延在するフラップをさらに備えるエアバッグ装置。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14/379,034 US9187058B2 (en) | 2012-02-16 | 2013-02-06 | Airbag device |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012-031668 | 2012-02-16 | ||
| JP2012031668A JP5892807B2 (ja) | 2012-02-16 | 2012-02-16 | エアバッグ装置 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2013121950A1 true WO2013121950A1 (ja) | 2013-08-22 |
Family
ID=48984062
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/052720 WO2013121950A1 (ja) | 2012-02-16 | 2013-02-06 | エアバッグ装置 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9187058B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5892807B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2013121950A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6574554B2 (ja) * | 2014-06-26 | 2019-09-11 | 日本プラスト株式会社 | エアバッグ |
| US9199602B1 (en) * | 2014-07-23 | 2015-12-01 | Trw Vehicle Safety Systems Inc. | Passive air bag with slack creator |
| US9676364B2 (en) * | 2015-09-30 | 2017-06-13 | Autoliv Asp, Inc. | Airbag systems with passive venting control |
| US10099647B2 (en) | 2016-09-21 | 2018-10-16 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Airbag assembly |
| US10214174B2 (en) * | 2017-01-30 | 2019-02-26 | Toyoda Gosei Co., Ltd. | Vehicle airbag apparatus |
| US11254273B2 (en) * | 2018-10-19 | 2022-02-22 | Toyota Motor Engineering & Manufacturing North America, Inc. | Venting of airbag for adjustment of cushioning surface position |
| US11518335B2 (en) * | 2019-07-02 | 2022-12-06 | Joyson Safety Systems Acquisition Llc | Driver side airbag module |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008201214A (ja) * | 2007-02-19 | 2008-09-04 | Takata Corp | エアバッグ及びエアバッグ装置 |
| JP2009143483A (ja) * | 2007-12-17 | 2009-07-02 | Takata Corp | 助手席用エアバッグ、助手席用エアバッグ装置及び自動車 |
| JP2009196596A (ja) * | 2008-02-25 | 2009-09-03 | Takata Corp | エアバッグ及びエアバッグ装置 |
| JP2009196551A (ja) * | 2008-02-22 | 2009-09-03 | Toyota Motor Corp | 車両用エアバッグ装置 |
Family Cites Families (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7364192B2 (en) * | 2002-09-16 | 2008-04-29 | Trw Vehicle Safety Systems Inc. | Air bag module with locking member for locking the position of a vent member |
| US7347450B2 (en) * | 2004-10-06 | 2008-03-25 | Autoliv Asp, Inc. | Airbag cushion with cinch tube for reduced out-of-position effects |
| US7328915B2 (en) * | 2004-10-06 | 2008-02-12 | Autoliv Asp, Inc. | Airbag cushion with tether deactivated venting for reduced out-of-position effects |
| US7261319B2 (en) * | 2005-01-07 | 2007-08-28 | Autoliv Asp, Inc. | Airbag cushion with adaptive venting for reduced out-of-position effects |
| DE602006001275D1 (de) | 2005-08-24 | 2008-07-03 | Takata Corp | Gassack und Gassackeinrichtung |
| JP5045017B2 (ja) | 2005-08-24 | 2012-10-10 | タカタ株式会社 | エアバッグ及びエアバッグ装置 |
| JP2007099122A (ja) | 2005-10-05 | 2007-04-19 | Takata Corp | エアバッグ及びエアバッグ装置 |
| JP5053658B2 (ja) | 2007-02-23 | 2012-10-17 | 日本プラスト株式会社 | エアバッグ装置 |
| JP4992853B2 (ja) * | 2008-08-06 | 2012-08-08 | タカタ株式会社 | エアバッグ装置 |
| JP4666059B2 (ja) | 2008-11-12 | 2011-04-06 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 車両用エアバッグ装置 |
| US8590927B2 (en) * | 2010-04-19 | 2013-11-26 | Tk Holdings Inc. | Airbag module |
| US8684407B2 (en) * | 2010-10-27 | 2014-04-01 | Trw Vehicle Safety Systems Inc. | Air bag with height adaptive tether |
| US8684404B2 (en) * | 2010-10-27 | 2014-04-01 | Trw Vehicle Safety Systems Inc. | Air bag with variable venting |
| US8678431B2 (en) * | 2010-10-27 | 2014-03-25 | Trw Vehicle Safety Systems | Air bag with tether and pulley arrangement |
| US8696022B2 (en) * | 2010-10-27 | 2014-04-15 | Trw Vehicle Safety Systems Inc. | Air bag with variable venting |
| KR101438965B1 (ko) * | 2012-12-26 | 2014-09-11 | 현대자동차주식회사 | 차량의 에어백 장치 |
-
2012
- 2012-02-16 JP JP2012031668A patent/JP5892807B2/ja active Active
-
2013
- 2013-02-06 WO PCT/JP2013/052720 patent/WO2013121950A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2013-02-06 US US14/379,034 patent/US9187058B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008201214A (ja) * | 2007-02-19 | 2008-09-04 | Takata Corp | エアバッグ及びエアバッグ装置 |
| JP2009143483A (ja) * | 2007-12-17 | 2009-07-02 | Takata Corp | 助手席用エアバッグ、助手席用エアバッグ装置及び自動車 |
| JP2009196551A (ja) * | 2008-02-22 | 2009-09-03 | Toyota Motor Corp | 車両用エアバッグ装置 |
| JP2009196596A (ja) * | 2008-02-25 | 2009-09-03 | Takata Corp | エアバッグ及びエアバッグ装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20150084318A1 (en) | 2015-03-26 |
| JP5892807B2 (ja) | 2016-03-23 |
| US9187058B2 (en) | 2015-11-17 |
| JP2013166495A (ja) | 2013-08-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2013121950A1 (ja) | エアバッグ装置 | |
| EP2496446B1 (en) | Vehicle with a low-mount inflatable knee airbag having serial chambers | |
| JP4434193B2 (ja) | 車両用サイドエアバッグ装置 | |
| US7992897B2 (en) | Airbag device | |
| US8096578B2 (en) | Knee airbag | |
| US8517415B2 (en) | Airbag apparatus | |
| JP6939179B2 (ja) | エアバッグ及び乗員拘束装置 | |
| JP2008184159A (ja) | 乗員保護装置 | |
| EP2658748A1 (en) | Curtain airbag for a vehicle | |
| JP5491332B2 (ja) | 助手席用エアバッグ | |
| JP4781078B2 (ja) | エアバッグ装置 | |
| WO2019026538A1 (ja) | 乗員保護装置 | |
| WO2013038827A1 (ja) | 助手席用エアバッグ、助手席用エアバッグ装置及び車両 | |
| KR20230016684A (ko) | 에어백 장치 | |
| US11186249B2 (en) | Passenger airbag | |
| WO2021019842A1 (ja) | エアバッグ及びエアバッグ装置 | |
| JP4781077B2 (ja) | エアバッグ装置 | |
| JP2024522999A (ja) | 展開支援ラッパーを備えた前面エアバッグシステム | |
| JP5792601B2 (ja) | エアバッグ装置 | |
| EP3296161A1 (en) | Vehicular curtain air bag device | |
| JP4894283B2 (ja) | 乗員脚部拘束装置 | |
| JP4922796B2 (ja) | エアバッグ装置 | |
| JP2005313675A (ja) | エアバッグ装置 | |
| WO2018179844A1 (ja) | サイドエアバッグ装置 | |
| JP2005225463A (ja) | 乗員脚部保護装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13748951 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14379034 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 13748951 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |