WO2011055722A1 - 情報端末装置、情報端末管理システム及びプログラムが格納された記憶媒体 - Google Patents
情報端末装置、情報端末管理システム及びプログラムが格納された記憶媒体 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2011055722A1 WO2011055722A1 PCT/JP2010/069496 JP2010069496W WO2011055722A1 WO 2011055722 A1 WO2011055722 A1 WO 2011055722A1 JP 2010069496 W JP2010069496 W JP 2010069496W WO 2011055722 A1 WO2011055722 A1 WO 2011055722A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- widget
- information terminal
- information
- terminal device
- state
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01C—MEASURING DISTANCES, LEVELS OR BEARINGS; SURVEYING; NAVIGATION; GYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS; PHOTOGRAMMETRY OR VIDEOGRAMMETRY
- G01C21/00—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00
- G01C21/26—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00 specially adapted for navigation in a road network
- G01C21/34—Route searching; Route guidance
- G01C21/36—Input/output arrangements for on-board computers
- G01C21/3667—Display of a road map
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01C—MEASURING DISTANCES, LEVELS OR BEARINGS; SURVEYING; NAVIGATION; GYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS; PHOTOGRAMMETRY OR VIDEOGRAMMETRY
- G01C21/00—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00
- G01C21/26—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00 specially adapted for navigation in a road network
- G01C21/34—Route searching; Route guidance
- G01C21/36—Input/output arrangements for on-board computers
- G01C21/3697—Output of additional, non-guidance related information, e.g. low fuel level
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a built-in device such as a mobile phone, a car navigation device, and a TV having a communication function and a function for handling position information, and a system using them.
- an application such as a widget displayed on the display device of the location information terminal can be used.
- “Widget” refers to a single-function application that is written in XML and script language and is constantly displayed on a part of the screen of the display device.
- the conventional location information terminal realizes comfortable operability while ensuring the safety of users on limited hardware resources (CPU performance, memory capacity, etc.)
- the installed functions are All are pre-configured, and the operation of each function is also strictly managed at the manufacturing stage, and often has a structure that suppresses the occurrence of malfunctions and the like as much as possible. Therefore, it is difficult to add functions after shipping the location information terminal necessary to realize the above (1) and (2) while ensuring safety and comfortable operability.
- a location information terminal having no hardware resources it is assumed that an added function and an existing function interfere with each other in an unexpected situation, resulting in unstable operation.
- Patent Document 1 separately manages screen data to be output to a display device by dividing it into drawing elements and animation methods thereof.
- the animation display method is changed only in accordance with predetermined state transition data. Therefore, even if the display device is managed in the same state, the situation other than the management of the state transition data such as the system load state is different. In this case, there is a problem that the animation display cannot be controlled dynamically.
- the reliability of elements (graphics elements and animation elements) dynamically added via a network or the like is increased.
- existing functions may interfere with functions added by users, etc., or the load of hardware resources may be excessive, which may cause unstable operation of the location information terminal.
- an original function for example, a map and a traveling direction display function
- the hardware resource required by the added function is large, the original function of the location information terminal is stopped or disabled in order to execute the added function. There was a risk of becoming stable.
- the present invention has been made in view of the above problems, and prevents functions such as widgets added by users and the like from interfering with the original functions of the location information terminal, thereby reducing the usability of the location information terminal.
- the purpose is to prevent. It is another object of the present invention to improve the reliability of a location information terminal by determining the reliability of a function such as a widget added by a user and eliminating an unauthorized additional function.
- a typical example of the invention disclosed in the present application is as follows. That is, an information terminal device that provides information for guiding to a set destination, a CPU that performs arithmetic processing, a memory that stores information, and a state of movement by detecting a current position
- a position information detection unit that detects position information, a navigation unit that calculates position information from the detected current position and map information, and calculates guidance information to a set destination, and the position information and the guidance information
- a communication unit that communicates via a network, and a widget management unit that manages execution of widget that is a single-function program that displays on the display unit, the widget management unit comprising: A policy determining unit that sets an operation policy including an operation restriction and priority related to a display state on the display device in the Widget, and a trust of the Widget A reliability determination unit that determines the operation of the widget, and the widget management unit restricts the operation of the widget according to the operation restriction and the reliability when the movement state is set in advance.
- the operation of the Widget can be limited according to the performance and the operation state of the information terminal device equipped with the Widget, the usability of the Widget and the information terminal device equipped with the Widget is reduced. Can be suppressed.
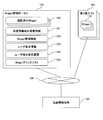
- FIGS. 1A and 1B are block diagrams showing an example of a location information terminal system to which the present invention is applied.
- the location information terminal shown in the figure has a configuration in which a user or the like can add a widget.
- the location information terminal 101 is connected to the Widget management portal 102 and the third party site 103 via the network 104.
- the location information terminal 101 includes a widget 110, a widget management unit 120, a navigation engine 127, a library group 128, an OS 129, hardware 130, and a recording device 140.
- Widget is a single-function application described in at least one of XML and script language, as described in the conventional example.
- the script language is assumed to be JavaScript, ActionScript, Ruby, Python, or the like.
- the location information terminal 101 is a device that identifies the current location and executes processing according to the identified current location.
- the location information terminal 101 is, for example, a navigation device set in a vehicle, a PND, or the like, and includes a widget 110, a widget management unit 120, a navigation engine 127, a library group 128, an OS 129, hardware 130, and a recording device 140.
- a case where the position information terminal 101 is a car navigation device will be described.
- Software such as the Widget 110, the Widget management unit 120, the navigation engine 127, the library group 128, and the OS 129 is stored in a recording device (storage device) 140 as a storage medium, and is loaded into the memory 132 and executed by the CPU 131. It is.
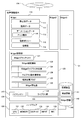
- Widget 110 is a single-function program having a display function composed of XML and script, and constantly displays still image data 111, animation data 113, moving image data, etc. on a part of the screen (display area) of the display device 133, It consists of an operation policy 115, reliability 116, and moving image data 112.
- the present invention can also be applied to a case where a program having a display function is used instead of Widget.
- the still image data 111 is still image data displayed on the display device 133 by the widget 110, and is, for example, a bitmap or a jpeg image.
- Animation data 113 is moving image data displayed on the display device 133 by the widget 110.
- Each animation data 113 is assigned an animation attribute 114 and is referred to by the widget management unit 120 for controlling animation according to the state of the location information terminal 101.
- the operation policy 115 is an operation standard of the widget 110 and is data in which an operation according to the control state of the location information terminal 101 is defined in advance.
- the widget management unit 120 determines an operation policy 115 for each widget 110.
- operation policy 115 for example, five types of states (normal time (stopped) / running / guidance / navigation high load / specific area entry) can be considered for the following parameters.
- the Widget execution priority is set by the Widget management unit 120 using the execution priority information of the Widget management information 142 as a basic value, and after the Widget 110 is downloaded to the location information terminal 101, it is already loaded on the location information terminal 101. It is changed based on the relationship between the reliability 116 of the Widget 110 and the reliability 116 of the downloaded Widget 110. For example, when a Widget 110 having higher reliability than the downloaded Widget 110 is loaded, the Widget management unit 120 lowers the execution priority of the Widget 110.
- the animation control policy is set with a basic value based on the load index of the widget management information 142, and after downloading the widget 110 to the location information terminal 101, the reliability 116 of the other widget 110 already loaded on the location information terminal 101 and the download Based on the relationship with the reliability 116 of the Widget 110 that has been changed.
- External information access is controlled according to the reliability 116 of the widget 110.
- control such as prohibition during guidance, prohibition during travel, and complete prohibition is performed.
- the navigation function access control is controlled according to the reliability of the widget.
- the reliability 116 falls below a predetermined reference value in several steps, control such as prohibition during guidance, prohibition during travel, and complete prohibition is performed.
- the execution priority 512 can be set according to the reliability. Specifically, if the reliability is high, the execution priority 512 can be set high, and if the reliability is low, the execution priority 512 can be set low.
- the setting timing of the operation policy 115 is set as a fixed value at the time of designing the Widget 110, or when the Widget management portal 154 sets based on the Widget management information 142 when the Widget 110 is downloaded to the location information terminal 101. , After the Widget 110 is downloaded to the location information terminal 101, the Widget management unit 120 may set.
- the widget management unit 120 is a function for managing the widget 110. Executes the start and end of the Widget 110, operation control, authentication using the credibility 116 of the Widget 110, and the like.
- the Widget authentication function 123 executes download of the Widget 110 and restriction of access from the Widget 110 to the inside of the location information terminal 101.
- a method for restricting access to the inside of the location information terminal 101 for example, a method of providing an access key for accessing internal information to a Widget 110 having a reliability 116 of a certain level or higher, or the Widget 110 uses an API (Application Program) from the OS 129.
- API Application Program
- the Widget library correspondence table 124 is a list of Widgets 110 that the location information terminal 101 is currently downloading from the Widget management portal 102 or the like.
- the Widget information 142 is Widget 110 information held by the location information terminal 101.
- the Widget blacklist 121 is a list for registering the Widget 110 (malicious widget) that may cause a disadvantage to the location information terminal 101 or the user, and the Widget blacklist owned by the Widget management portal 102 has a high priority.
- the information is recorded within the range allowed by the storage capacity of the location information terminal 101.
- the library operation history table 126 records a list of operation orders of native applications and a list of average loads of the CPU 131 to a certain number.
- the native application is an application installed in the location information terminal 101 at the time of manufacture.
- the terminal status flag 125 is data for managing the status of the location information terminal 101.
- This state three types of states are conceivable: a stopped state, a traveling state, and a guidance state.
- the stop state is considered to be a stop state where the place is not moved.
- the terminal state flag 125 compares the current position detected by the navigation engine 127 with the previous position, and determines whether the terminal is in a stopped state or a traveling state.
- the terminal state flag 125 indicates the guidance state. Become.
- the navigation engine 127 performs calculation of the current position of the position information terminal 101, generation of map data for display from the map information 141, guidance to a destination set by the user, and the like. For example, the navigation engine 127 receives a signal such as GPS, calculates a current position, calculates position information from the map information 141 and the current position, and outputs the position information to the display device 133.
- the position information includes map information 141 around the current position and a predetermined graphic (marker) indicating the current position.
- the navigation engine 127 includes an antenna and a receiver that receive signals such as GPS.
- the library group 128 is various libraries for destination search, audio reproduction, and the like, and those that need to be displayed on the display device 133 operate in cooperation with the Widget 110.
- OS 129 is basic software such as Linux and Windows.
- the hardware 130 is hardware necessary for operating the software of the location information terminal, and includes a CPU 131 that performs arithmetic processing, a memory 132 that stores data and programs, a display device 133 that displays location information, and the like.
- An input device 134 that accepts input from a user, and a communication interface 135 that communicates with a server such as a widget management portal (management server) 102 or a third party site (server installed by a third party) 103 via the network 104.
- a drawing function, a sound reproduction function, a position detection function, etc. are included.
- the recording device 140 stores data necessary for the operation of the location information terminal, and is configured by a nonvolatile storage medium such as a magnetic disk drive (HDD), a nonvolatile storage device (SSD), or an SD memory card.
- a nonvolatile storage medium such as a magnetic disk drive (HDD), a nonvolatile storage device (SSD), or an SD memory card.
- the program executed by the CPU 131 is provided to the location information terminal 101 via a non-volatile storage medium (CD-ROM, flash memory, etc.) or a network, stored in the storage device 140, and stored at the time of program execution. 132 is loaded. Therefore, the location information terminal 101 may include an interface for reading a storage medium.
- a non-volatile storage medium CD-ROM, flash memory, etc.
- the recording device 140 holds map information 141 and widget information 142.
- the map information 141 is map information used by the location information terminal 101.
- the Widget management table 122 is a list of Widgets currently downloaded from the management portal 102 or the like.
- the animation attribute 114 indicates an attribute of each moving image, and a value of either [required animation] or [direction animation] is assigned.
- the essential animation is an animation that is indispensable when the user operates, and is an animation expression that is essential for the function of the Widget 110.
- the essential animation suggests an operation instruction to the user, for example.
- the effect animation is a decorative animation, there is no instruction to the user, and execution may be suppressed when the load on the position information terminal 101 is high.
- the state of the position information terminal 101 the three states of the stop state, the traveling state, and the guidance state are shown, but other states necessary for control may be assigned.
- an attribute value for switching display may be assigned depending on whether or not the vehicle is running.
- the reliability 116 is data indicating the reliability of the widget 110.
- the reliability 116 means how much the Widget 110 is reliable for the user, that is, does not adversely affect the operation of the location information terminal 101.
- the following attributes can be considered.
- the reliability of the distribution source determined by the URL of the distribution source site of the Widget 110, that is, the reliability of the Widget.
- the reliability for each Widget 110 can be set as a numerical value by the above attribute. For example, if the distribution source URL is valid, 1 is added to the reliability, and if the distribution source URL is invalid, ⁇ 1 is added to the reliability 116. If the certificate added to the Widget 110 is valid, 1 is added to the reliability 116, and -1 is added to the reliability 116 if the certificate is invalid. Further, a predetermined numerical value is added to the reliability 116 for each use frequency of the user. As a result, the reliability 116 for each Widget 110 can be determined numerically. The reliability 116 may be determined by the widget management unit 120 or may be determined by another module executed on the OS 129.
- the reliability 116 may be a value indicating the validity of the Widget 110.
- the reliability 116 is set high as the highly reliable Widget 110, and the third party site 103 is set. Since there is a high possibility of a malicious or illegal Widget 110 downloaded from the unauthenticated Widget 110, the reliability 116 can be set low.
- the reliability 116 for each of the widgets 110 can be set by the widget management unit 120.
- the reliability 116 may be set by another module executed on the OS 129.
- the Widget management portal 102 is a portal site that distributes the Widget 110, and includes, for example, a Web server that stores distribution Widget data, and includes an authenticated Widget 150, location information terminal management information 151, Widget management information 152, User basic information 153, user terminal load history 154, and a Widget black list 155 are included.
- the Widget management portal 102 is a computer including a CPU, a memory, a storage device, and a network interface (not shown).
- the Widget management portal 102 may support secure communication such as SSL in order to enhance safety.
- Authenticated Widget 150 is a Widget 110 that is guaranteed to operate on the location information terminal 101 by the operator of the Widget management portal 102.
- the operator of the Widget management portal 102 confirms, for example, the internal structure of the Widget 110, the operation load on the location information terminal 101, and the competition state when operated simultaneously with other Widgets 110.
- the location information terminal management information 151 is information for managing the location information terminal 101 connected to the Widget management portal 102 as described later, and is referred to when the Widget 110 is distributed to the location information terminal 101.
- the Widget management information 152 manages information for each Widget 110 managed by the Widget management portal 102 as described later.
- the basic user information 153 is user management information of the location information terminal 101 connected to the Widget management portal 102.
- the user terminal load history 154 is load history information of the location information terminal 101 connected to the Widget management portal 102. Since the load state of the owned location information terminal 101 differs for each user, the user terminal load history 154 is referred to when distributing the Widget 110.
- the Widget black list 155 is a list in which unauthorized Widgets 110 and the like are registered. When checking whether or not the Widget 110 downloaded by the user to the location information terminal 101 is an unauthorized application, the Widget blacklist 155 is referred to.
- the third party site 103 is a site provided by a third party that provides a Widget 110 that can be executed on the location information terminal 101, and distributes the Widget 110 to the location information terminal 101.
- the network 104 is a network that connects devices, and is a LAN, the Internet, a wireless network, or the like.
- the moving image data 112 is moving image data displayed by the Widget 110, and for example, various moving image files such as WMV (Windows Media Video), MOV (QuickTime movie), FLV (Flash Video), and the like can be considered.
- FIGS. 2A to 2D are diagrams showing information managed by the Widget management portal 102.
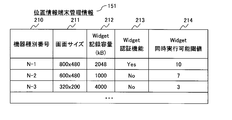
- FIG. FIG. 2A is an explanatory diagram showing an example of location information terminal management information 151 managed by the Widget management portal 102.
- the location information terminal management information 151 shown in FIG. 2A includes the device type number 210 of the location information terminal 101, the screen size 211 of the location information terminal 101, the Widget recording capacity (kB) 212 of the location information terminal 101, and the Widget of the location information terminal 101.
- the authentication function 213 and the location information terminal 101 Widget simultaneous execution threshold 214 are included.
- the device type number 210 is a number for identifying the model number of the location information terminal 101 and is different for each model.
- the screen size 211 is the resolution of the screen (display device 133) of the position information terminal 101 having the device type number 210.
- the Widget recording capacity (kB) 212 is the maximum capacity of the Widget storage area of the location information terminal 101 with the device type number 210.
- the Widget authentication function 213 stores the presence / absence of the authentication function of the Widget 110 of the location information terminal 101 of the device type number 210, where Yes indicates mounting and No indicates non-mounting.
- the widget simultaneous execution threshold 214 indicates a minimum load index required for the widget 110 to operate in the location information terminal 101 having the device type number 210.
- the simultaneous widgetable threshold value 214 is an upper limit threshold value of the total load index value when a plurality of widgets 110 are executed on the location information terminal 101.
- the load index is an index calculated based on a certain standard from the usage rate of the CPU 131 of the location information terminal 101 and the occupancy rate of the memory 132 when the Widget 110 operates. With this index as a guide, the operating condition of the Wideget 110 Judging.
- a method for calculating the load index for example, a method of obtaining the load index by (CPU usage rate (%) + memory occupation rate (%)) / 10 or the like can be considered.
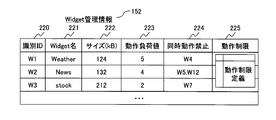
- FIG. 2B is an explanatory diagram showing an example of the Widget management information 152 managed by the Widget management portal 102.
- 2B includes an identification ID 220, a widget name 221, a size (kB) 222, an operation load value 223, a simultaneous operation prohibition 224, and an operation restriction 225.
- the Widget management information 152 is a table for managing features for each Widget 110.
- the identification ID 220 is a unique number that is different for each Widget 110.
- the size (kB) 222 is the size of the widget 110.
- the operation load value 223 is a load index indicating the size of the operation load when the location information terminal 101 executes the Widget 110.
- the simultaneous operation prohibition 224 is a list of Widgets 110 that interfere with the operation of the location information terminal 101 when the location information terminal 101 is operated simultaneously with the Widget 110.
- the operation restriction 225 indicates the definition of operation restriction when the Widget 110 is executed by the location information terminal 101, and stores the identification information (ID) of the operation restriction definition 204 shown in FIG. 2D.
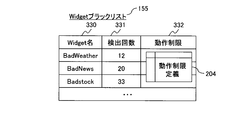
- FIG. 2C is an explanatory diagram showing an example of a Widget black list 155 managed by the Widget management portal 102.
- the Widget blacklist 155 shown in FIG. 2C includes a Widget name 230, a detection count 231, and an operation restriction 232.
- the Widget black list 155 is a list of Widgets 110 that may adversely affect the location information terminal 101 and the user.
- the number of detections 231 is the number detected from the list of Widgets 110 in the location information terminal 101 and is a value received from the location information terminal 101.
- the number of detections 231 is a measure of how much the Widget 110 is used in the location information terminal 101. For example, when a certain threshold value is exceeded, a notification to the administrator may be considered.
- the operation restriction 232 indicates an operation restriction on the widget 110 of the widget blacklist 155, and stores identification information (ID) of the operation restriction definition illustrated in FIG. 2D.
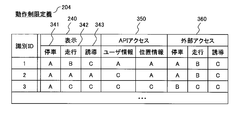
- FIG. 2D is an explanatory diagram illustrating an example of the operation restriction definition 204 managed by the Widget management portal 102.
- the operation restriction definition 204 shown in FIG. 2D includes a display 240, a stop 341, a travel 342, a guidance 343, an API access 350, and an external access 360.
- the operation restriction definition 204 is a table that predefines the contents of the operation restriction of the widget 110.
- a display 240 indicates display restrictions of the widget 110 in each state of the position information terminal 101. In this example, the following is determined as an example.
- a ... No limit B ... Animation prohibited C ... Display prohibited
- Stop 341 indicates a situation when the vehicle on which the location information terminal 101 is mounted is stopped or the location information terminal 101 is not moving.
- Guidance 243 indicates a situation in which the location information terminal 101 is conducting guidance to the destination designated by the user.
- working 242 shows the state in which the vehicle carrying the position information terminal 101 is moving.
- the API access 250 indicates access restriction to the API provided by the location information terminal 101. In this example, the following is determined as an example. A ... Access permitted C ... Access prohibited
- the external access 260 defines external access restrictions during the operation of the Widget 110. In this example, the following is determined as an example. A: Permits unlimited external access B: Permits only download sources
- FIGS. 3A and 3B are diagrams showing user information managed by the Widget management portal 102.
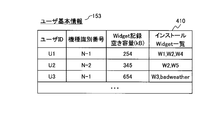
- FIG. 3A is an explanatory diagram illustrating an example of the user basic information 153 managed by the Widget management portal 102.
- a user ID for storing the identifier of the user of the location information terminal 101
- a model identification number for storing an identifier indicating the model of the location information terminal 101
- the location information terminal 101 can store the ID.
- One entry is composed of a Widget recording free capacity (kB) for storing the capacity of the large Widget 110 and an installation Widget 410 for storing a list of Widgets 110 already installed in the location information terminal 101.
- kB Widget recording free capacity
- User basic information 301 is basic information for each user who owns the location information terminal 101.
- the installation Widget 410 is a list of Widgets 110 installed in the location information terminal 101 owned by the user.
- the identification information (ID) of the Widget 110 is recorded in the installation Widget 410 and is not provided by the Widget management portal 102 (that is, downloaded from the third party site 103). Describes a name that can uniquely identify the widget 110.
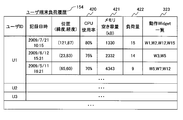
- FIG. 3B is an explanatory diagram showing an example of the user terminal load history 154 managed by the Widget management portal 102.
- the user terminal load history 154 shown in FIG. 3B is data in which a plurality of states when the maximum load is recorded in the position information terminal 101 owned by the user are recorded in order from the highest. These pieces of information are collected from the position information terminal 101 when the position information terminal 101 is connected to the widget management portal 102, and the user terminal load history 154 is updated.
- the maximum load indicates a maximum value within a predetermined time.
- the user ID for storing the identifier of the user of the position information terminal 101, the recording date and time for storing the date and time when the maximum load is updated, and the position for storing the lightness and latitude when the maximum load is updated ( Longitude, latitude), a CPU usage rate 420 for storing the usage rate of the CPU 131, a memory free space (kB) for storing the free space of the memory 132, a load amount 422 for storing a load index, and a maximum load.
- One entry is configured from the operation Widget list 323 that stores a list of Widgets 110 that have been operating.
- the load amount 422 is the total load index of the Widget 110 that was operating on the location information terminal 101 at the time of recording.
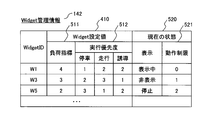
- FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the Widget management information 142 stored in the recording device 140 of the location information terminal 101.
- one entry is configured from the Widget ID, the Widget setting value 410, and the current state 520.
- the Widget ID an identifier of the Widget 110 is stored.
- the Widget setting value 410 includes a load index 511 and an execution priority 512 of the Widget 110.
- the current state 520 represents an operation restriction 521 for the widget 110 for display.
- the Widget setting value 410 is a basic attribute of the downloaded Widget 110.
- the basic attribute includes a load index 511 and an execution priority 512.
- the load index 511 is a load index necessary for the Widget 110 to operate.
- the execution priority 512 is the execution priority of the Widget 110, and the smaller the number, the higher the priority. When the load on the location information terminal 101 increases, the operation is restricted from the Widget 110 having the lowest execution priority 512. Further, different priorities may be assigned depending on the state of the location information terminal 101.
- a display state and an operation restriction state are recorded in the current state of each Widget 110.
- the following is considered as an example of the display state.
- the operation restriction 521 stores the contents of the operation restriction currently set in the Widget 110.
- the identification information (ID) of the Widget 110 is recorded in the Widget ID of the Widget management information 142, and in the case of the Widget 110 downloaded from the third party site 103, the Widget 110 can be uniquely identified. Name is described in WidgetID.
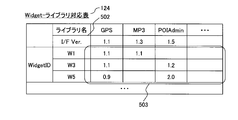
- FIG. 5 is an explanatory diagram showing the widget library correspondence table 124 of the location information terminal 101, and is an example of a table for managing the correspondence between the widget 110 and the library.
- the Widget library correspondence table 124 shows the relationship of the libraries existing in the location information terminal 101 used by each Widget 110 currently downloaded to the location information terminal 101.
- the library is an interface that provides each function of the location information terminal 101.
- the Widget library correspondence table 124 shows the Widget ID and I / F Ver. From 502, one entry is configured.
- Reference numeral 502 denotes an I / F version of each library. Also, as shown in an area 503, when the widget 110 uses a library, the version number of the library corresponding to the widget 110 is set. If the I / F version of each library is different from the version of the library corresponding to the Widget 110, the library cannot be used. When the version numbers are different, for example, a method of displaying a warning to the user can be considered.
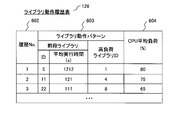
- FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram showing the library operation history table 126 of the location information terminal 101.
- the library operation history table 126 holds the identifier of the library and the identifier of the library executed immediately before the library in order from the highest average load of the CPU 131 when the library is operated on the position information terminal 101.
- the widget 110 management unit 120 uses the library operation history table 126 to predict the load on the location information terminal 101 and restricts the operation of the widget 110.
- the library operation history table 126 shown in FIG. 6 includes a history number 602 for storing a history identifier, a library operation pattern 603 for storing the operation state of the library, and a CPU average load 604 for storing the average load (%) of the CPU 131. Thus, one entry is constructed.
- the library operation pattern 603 indicates the relevance of the library operation order, and includes a high load library ID that stores an identifier of a library having a high usage rate (load) of the CPU 131, and a library ID that was executed immediately before the high load library ID. And the average execution time.
- the CPU average load (%) 604 is an average value of the usage rate of the CPU 131 within a certain period.
- the execution time can be monitored, and when the average execution time is exceeded, the operation of the widget 110 can be limited. As a result, it is possible to prevent a situation where a shortage of resources occurs in the location information terminal 101 when the high-load library starts to operate.
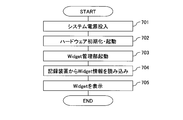
- FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing processing at the time of starting the location information terminal 101.
- Step 701 is a process of turning on the power of the location information terminal 101.
- Step 702 is a process of initializing the hardware 130 of the location information terminal 101 and starting the OS 129, the navigation engine 127, and the library group 128.
- Step 703 is a process for starting the Widget management unit 120.
- Step 704 is a process of reading the widget information 142 from the recording device 140.
- Step 705 is a process for displaying the Widget 110 on the display device 133.
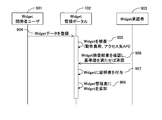
- FIG. 8 is a sequence diagram showing an example of a procedure for registering the Widget 110 created by the developer in the Widget management portal 102.
- the developer user 901 of the Widget 110 operates a computer (not shown) and connects to the Widget management portal 102 via the network 104.
- the registered widget approver 903 approves the widget 110 registered in the widget management portal 102.
- the Widget developer user 901 transmits the data of the Widget 110 to the Widget management portal 102 and registers it in the Widget management portal 102 (step 904).
- the Widget management portal 102 performs a process of inspecting the registered Widget 110 (verification of operation load, access destination API, etc.) (Step 905).
- the registered widget approver 903 connects to the widget management portal 102 via a network 104 from a computer (not shown), checks the inspection result of the widget 110, and approves if a predetermined reference value is satisfied (step 906).
- the Widget management portal 102 performs processing for assigning a certificate to the Widget 110 (Step 907). Finally, the Widget management portal 102 performs processing for adding the Widget 110 to the Widget management table (Step 908).
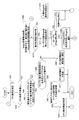
- FIG. 9 is a sequence diagram showing a flow when installing the widget 110 from the widget management portal 102 to the location information terminal 101 via the network.
- reference numeral 1003 denotes a user.
- reference numeral 102 is a Widget management portal
- reference numeral 101 is a location information terminal
- reference numeral 1003 is a user.
- the user 1003 transmits an instruction to acquire a list of Widgets 110 that can be installed in the location information terminal 101 to the location information terminal 101 (step 1004).
- the location information terminal 101 checks the Widget management table 122 (Step 1005), checks the capacity of the recording device 140 (Step 1006), and checks the Widget library correspondence table 124 (Step 1007).
- the location information terminal 101 transmits terminal information such as the terminal 101 identifier, user ID, load history, and the widget management table 122 to the widget management portal 102 and requests the widget management portal 102 for a list of downloadable widgets 110. (Step 1008).
- the Widget management portal 102 updates the user terminal load history 154 based on the load history received from the location information terminal 101 (step 1009).
- the Widget management portal 102 refers to the Widget management table 122 included in the received request, and selects a list of Widgets 110 that can be used by the location information terminal 101 (Step 1010).
- the Widget management portal 102 transmits a list of Widgets 110 that can be downloaded by the location information terminal 101 to the location information terminal 101 (step 1011).
- the location information terminal 101 displays a list of downloadable widgets 110 received from the widget management portal 102 on the display device 133 (step 1012).
- the user 1003 selects the widget 110 to be downloaded on the location information terminal 101 (step 1013).
- the location information terminal 101 refers to the widget management information 152 of the widget management portal 102 and determines whether or not the operation restriction 225 is set for the widget 110 to be downloaded. When there is a restriction on the operation of the Widget 110, the location information terminal 101 warns the user of the restriction on the operation (step 1014). Then, the user 1003 executes an operation of downloading the selected Widget 110 from the Widget management portal 102 on the location information terminal 101 (Step 1015).
- the Widget management portal 102 transmits the data of the specified Widget 110 to the location information terminal 101 (Step 1016).
- the location information terminal 101 stores the data of the widget 110 received from the widget management portal 102 in the memory 132 or the recording device 140 (step 1017). Next, the location information terminal 101 adds the information of the downloaded Widget 110 and updates the Widget management table 122 and the Widget management information 142 (Step 1018). The location information terminal 101 activates the last downloaded Widget 110 (step 1019). When starting the Widget 110, the location information terminal 101 adds an entry of the Widget 110 to the Widget management information 142 and sets the execution priority 512 and the operation restriction 521 based on the operation policy 115.
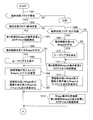
- FIG. 10A and FIG. 10B are flowcharts showing a flow in which the location information terminal 101 downloads the Widget 110 from the third party providing site.
- the location information terminal 101 downloads a list of Widgets 110 from a third party site (step 1101).
- the third party site 103 and the Widget management portal 102 can be distinguished by a URL or an IP address.
- the location information terminal 101 checks whether or not the user-designated widget 110 can be downloaded (step 1103). For example, the location information terminal 101 determines whether or not the free capacity of the recording device 140 storing the widget 110 is larger than the designated widget 110 capacity. judge. If the specified Widget 110 can be downloaded, the process proceeds to Step 1004. On the other hand, if the designated widget 110 is not downloadable, the process is terminated.
- step 1104 It is determined whether or not the location information terminal 101 has the authentication function of the widget 110 (step 1104). If the location information terminal 101 has the authentication function of the widget 110, the process proceeds to step 1105. On the other hand, if the location information terminal 101 does not have the authentication function of the Widget 110, this process ends.
- step 1105 it is determined whether or not the location information terminal 101 can be connected to the network 104. If the location information terminal 101 can be connected to the network 104, the process proceeds to step 1106. On the other hand, if the location information terminal 101 is not connectable to the network 104, the process proceeds to step 1112.
- step 1106 the location information terminal 101 transmits the list information of the Widget 110 received from the third party site 103 to the Widget management portal 102.
- the widget management portal 102 compares the list information of the widget 110 of the third party site 103 received from the location information terminal 101 with the widget blacklist 155 (step 1107).
- the Widget management portal 102 determines whether or not the Widget 110 on the Widget black list 155 exists in the list information of the Widget 110 of the third party site 103 (Step 1108). If there is a widget 110 on the widget blacklist 155 in the widget 110 list information of the third party site 103, the process proceeds to step 1109. On the other hand, if the list information of the widget 110 of the third party site 103 does not exist in the list information of the widget 110 of the third party site 103, the process proceeds to step 1111.
- step 1109 the widget management portal 102 gives information indicating that the widget 110 has been registered in the black list to the reliability 116 of the corresponding widget 110.
- the Widget management portal 102 adds 1 to the number of times the corresponding part of the Widget black list 155 is detected (step 1110).
- Step 1111 the Widget management portal 102 transmits a comparison result between the Widget 110 list information of the third party site 103 and the Widget black list 155 to the location information terminal 101.
- step 1112 it is determined whether or not the location information terminal 101 is provided with the Widget black list 121. If the location information terminal 101 has the Widget blacklist 121, the process proceeds to step 1113. On the other hand, if the location information terminal 101 does not include the Widget blacklist 121, the process proceeds to step 1116.
- step 1113 the location information terminal 101 determines whether or not the Widget 110 included in the Widget blacklist 121 exists in the Widget 110 list information received from the third party site 103. If there is a Widget 110 on the Widget black list 121 in the Widget 110 list information received from the third party site 103, the process proceeds to Step 1114. On the other hand, if there is no widget 110 on the black list in the list information of the widget 110 received from the third party site 103, the process proceeds to step 1116.
- step 1114 information indicating that the blacklist has been registered is assigned to the reliability 116 of the corresponding widget 110.
- the location information terminal 101 adds 1 to the number of times of detection of the corresponding part of the Widget blacklist 121 (step 1115).
- step 1116 the location information terminal 101 outputs a list of the Widgets 110 of the third party site 103 to the display device 133, and the user selects the Widget 110 to be downloaded on the display device 133.
- Step 1117 it is determined whether or not there is an operation restriction on the widget 110 from which the location information terminal 101 is downloaded. If there is an operation restriction on the downloaded Widget 110, the process proceeds to Step 1118. On the other hand, if there is no operation restriction item in the downloaded Widget 110, this process is terminated.
- step 1118 the location information terminal 101 displays a warning to the user that there is an operation restriction item on the download target widget 110.
- the location information terminal 101 determines whether or not the user has accepted the warning (step 1119). If the user accepts the warning, go to step 1120. On the other hand, if the user warning is not accepted, this process is terminated.
- step 1120 the location information terminal 101 downloads data of the target Widget 110 from the third party site 103.
- the location information terminal 101 stores the downloaded data of the widget 110 in the recording device 140 (step 1117).
- the location information terminal 101 adds the downloaded information about the widget 110 and updates the widget management table 122 of the widget management unit 120 (step 1122).
- the location information terminal 101 downloads the Widget 110 from the third party site 103
- the location information terminal 101 or the Widget blacklist of the Widget management portal 102 is referenced to detect an unauthorized Widget 110. Then, since the operation restriction is given to the unauthorized Widget 110 by the Widget blacklist, it is possible to notify the user that the operation is restricted by notifying the user that the operation is restricted.
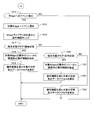
- FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing an example of the operation restriction of the widget 110 according to the state of the location information terminal 101. This process is executed when the Widget 110 to which the operation restriction is given is executed.
- the location information terminal 101 measures the load on the CPU 131 (step 1201).
- the location information terminal 101 determines whether or not the load on the CPU 131 is equal to or greater than a threshold value (step 1202). If the measured load on the CPU 131 is equal to or greater than the threshold, the process proceeds to step 1209. On the other hand, if the load on the CPU 131 is not greater than or equal to the threshold, the process proceeds to step 1203.
- the threshold value for example, a fixed value can be set for each model of the location information terminal 101 or can be dynamically changed according to the installation state of the library and the widget 110.
- a value acquired from the Widget simultaneous executable threshold value 214 of the location information terminal management information 151 of the Widget management portal 102 can be used. The acquisition of the widget simultaneous executable threshold 214 may be acquired when the location information terminal 101 is connected to the widget management portal 102.
- step 1203 it is determined whether or not the library currently operating on the location information terminal 101 exists in the preceding application ID of the library operation history table 126 (step 1203). If the currently operating library has already been registered in the preceding library ID of the library operation history table 126, the process proceeds to step 1204. On the other hand, if the currently operating library is not registered in the preceding library ID of the library operation history table 126, the process proceeds to step 1206.
- step 1204 it is determined whether or not the execution time of the library corresponding to the preceding library ID has exceeded the average execution time of the library operation history table 126. If the execution time of the library corresponding to the preceding library ID exceeds the average execution time of the library operation history table 126, the process proceeds to step 1205. Otherwise, this process is terminated.
- step 1205 the load threshold of the CPU 131 is reduced.
- a fixed value is set for each model of the location information terminal 101 as a load threshold of the CPU 131, and the load of the CPU 131 including the library being executed satisfies a predetermined value (for example, 10%) within a range that satisfies the load threshold. ) There are ways to lower it.
- step 1206 the location information terminal 101 determines whether the library with the high load library ID in the library operation history table 126 is operating. If the library with the high load library ID is operating, the process proceeds to step 1207. If the library with the high load library ID is not in operation, the process proceeds to step 1208.
- step 1207 the location information terminal 101 reduces the load threshold of the CPU 131. This process can be performed in the same manner as in step 1205 above.
- step 1208 the load threshold of the CPU 131 is set to a default value.
- the location information terminal 101 refers to the widget management information 142 and acquires the operation limit value 521 of the widget 110 that is currently operating and has the lowest execution priority 512.
- step 1210 it is checked whether or not the operation limit value 521 is the maximum value at the location information terminal 101 (step 1210). If the operation limit value 521 is the maximum value, the process proceeds to step 1211. On the other hand, if the operation limit value 521 is not the maximum value, the process proceeds to step 1215.
- step 1211 a warning for stopping the widget 110 having the lowest execution priority 512 is displayed to the user.
- step 1212 it is determined whether or not the user has permitted the stop of the Widget 110 having the lowest execution priority 512. If the user permits the stop of the Widget 110 having the lowest execution priority 512, the process proceeds to Step 1213. On the other hand, if the user does not permit the stop of the widget 110 having the lowest execution priority 512, the process proceeds to step 1214.
- step 1213 the Widget 110 having the lowest execution priority 512 is stopped.
- Step 1214 the Widget 110 having the second lowest priority is selected after the Widget 110 stopped by the location information terminal 101.
- step 1215 1 is added to the operation limit value of the widget 110 acquired in step 1209.
- the Widget 110 having a low execution priority can be stopped sequentially, and the Widget process having a high execution priority 512 can be reliably executed.
- FIG. 12A and FIG. 12B are flowcharts showing the processing of the widget 110 executed by the location information terminal 101, and show the flow of the processing of the widget 110 operation according to the state of the location information terminal.
- a change in the terminal status flag 125 is determined (step 1301). If the value of the terminal status flag 125 has changed, the process proceeds to step 1302. On the other hand, if the value of the terminal state flag 125 has not changed, this process is terminated.
- step 1302 it is determined whether or not the terminal state flag 125 is in the guidance state (step 1302). If the value of the terminal state flag 125 is the guidance state, the process proceeds to step 1303. On the other hand, if the value of the terminal state flag 125 is not the guiding state, the process proceeds to step 1308.
- step 1303 display change of the Widget 110 (third party provided Widget) downloaded from the third party site 103 and access restriction to the API are started.
- Step 1304 it is determined whether or not there is a Widget 110 subject to operation restriction. If there is a Widget 110 subject to the operation restriction, the process proceeds to Step 1305. On the other hand, if there is no widget 110 subject to the operation restriction, the process proceeds to step 1306.
- step 1305 the user is warned that there is a Widget 110 subject to the operation restriction.
- step 1306 the arrangement or layout of the widget 110 is changed so that the guidance information is visible to the user on the display device 133.
- the display position of the widget 110 is changed to a position that does not overlap the guidance information.
- the display size of the widget 110 is changed to a size that does not overlap the guidance information.
- the guidance information is information that suggests the traveling direction that the navigation engine 127 outputs to the display device 133 together with the map information 141, and is information that guides the destination set by the user.
- the widget 110 having a low reliability 116 and the widget 110 whose display prohibition attribute is set to the operation restriction 521 during guidance are iconified and hidden according to the operation policy 115.
- the display prohibition attribute may be determined by referring to the operation restriction 521 and the operation restriction definition 204 of the widget management information 142 and the attribute of the widget 110 currently being executed.
- the operation restriction definition 204 may be acquired when the location information terminal 101 connects to the widget management portal 102.
- step 1308 it is determined whether or not the terminal state flag 125 is in the traveling state. If the value of the terminal state flag 125 is the traveling state, the process proceeds to step 1309. On the other hand, if the value of the terminal state flag 125 is not the running state, the process proceeds to step 1313.
- step 1309 it is determined whether or not there is a Widget 110 subject to operation restriction. If there is a Widget 110 subject to the operation restriction, the process proceeds to Step 1310. If there is no Widget 110 subject to the operation restriction, the process proceeds to Step 1311.
- step 1310 the user is warned that there is a Widget 110 subject to the operation restriction.
- step 1311 the display change of the Widget 110 provided by the third party site 103 and the access restriction on the API are started.
- the widget 110 having a low reliability 116 and the widget 110 having the display prohibition attribute during guidance are iconified or hidden (step 1312).
- step 1313 when the terminal state flag 125 is stopped, the display position of the Widget 110 is returned, and the display change of the Widget 110 and the access restriction to the API provided by the third party are released.
- the location information terminal 101 determines whether or not an event for the widget 110 has been detected (step 1314). If an event to Widget 110 is detected, the process proceeds to step 1315. If no event to Widget 110 is detected, this process ends.
- step 1315 an event is notified to the Widget 110 that is the display change target.
- Step 1316 it is determined from the Widget library correspondence table 124 whether or not there is an operation restriction on the Widget 110 that is the display change target.
- step 1317 if the terminal state flag 125 is in the guidance state as a result of the determination in step 1316, the process proceeds to step 1318. On the other hand, if the terminal state flag 125 is not the guiding state, the process proceeds to step 1320.
- step 1318 the operation restriction at the time of guidance is extracted from the operation policy 115 of the Widget 110 that is a display change target.
- the operation policy 115 can refer to the operation restriction 521 of the Widget management information 142.
- step 1320 it is determined whether or not the terminal state flag 125 is in the traveling state. If the terminal state flag 125 is in the traveling state, the process proceeds to step 1321. If the terminal state flag 125 is not in the running state, the process proceeds to step 1323.
- step 1321 the operation restriction at the time of guidance is extracted from the operation policy 115 of the target Widget 110.
- step 1322 display switching and data access that satisfy the operation restrictions of the Widget 110 are executed.
- step 1323 display switching and data access satisfying the condition of operation restriction of Widget 110 are executed.
- the navigation engine 127 when the navigation engine 127 is in a guidance state displaying guidance information, the widget 110 is hidden or iconified or the display position of the widget 110 is changed based on the operation restriction of the widget management information 142 to guide the navigation. Information can be reliably presented to the user.
- the navigation engine 127 when the navigation engine 127 is in a traveling state in which the map information 141 and the current position are displayed, the current position can be accurately presented to the user by changing the display of the Widget 110 downloaded from the third party site 103. Further, by restricting access to the API of the Widget 110 during the guidance state or the traveling state, the CPU 131 can be prevented from being overloaded, and the information necessary for the user such as the map information 141 is reliably presented. be able to.
- the Widget 110 displayed in the running state allows the Widget 110 downloaded from the Widget management portal 102 that has been authenticated, and the Widget 110 downloaded from the third party site 103 that has not been authenticated.
- By restricting the URL it is possible to prevent the Widget 110 downloaded from the third party site 103 whose behavior is unknown from overlapping with the information required by the user such as the map information 141 and the current position, and to ensure the reliability of the location information terminal 101 can do.
- FIG. 13 is a flowchart showing processing when updating the Widget 110 and the library.
- the location information terminal 101 obtains a list of libraries accessed by the update target Widget 110 from the library group 128 (step 1401).
- the Widget library correspondence table 124 is checked and the i / FVer. 502 is acquired (step 1402).
- step 1403 it is determined whether or not there is an inconsistency in the I / F version of the library accessed by the update target Wideget 110 (step 1403). If the I / F version is inconsistent, the process proceeds to step 1404. On the other hand, if the I / F version matches, the process proceeds to step 1407.
- step 1404 there is an I / F version inconsistency, and thus operation restriction occurs when the Widget 110 is executed. For this reason, the contents of the operation restriction and a warning are displayed to the user.
- step 1405 it is determined whether or not the user acknowledges the warning and the content and permits the update. If the user permits the update, the process proceeds to step 1406. On the other hand, if the update is not permitted by the user, the process proceeds to step 1407.
- Step 1406 the target Wideget 110 is updated.
- the location information terminal 101 acquires an update program for the Widget 110 from the Widget management portal 102 and executes the acquired update program.
- Step 1407 is a process of checking the list of Widgets 110 using the library to be updated with reference to the Widget library correspondence table 124.
- step 1408 it is a process of determining whether or not there is a Widget 110 in which an I / F version mismatch occurs (step 1408). If an I / F mismatch has occurred, the process proceeds to step 1409. On the other hand, if no I / F mismatch has occurred, the process proceeds to step 1412.
- step 1409 since there is an I / F version inconsistency, an operation restriction occurs when the Widget 110 is executed, so the contents of the operation restriction and a warning are displayed to the user.
- step 1410 it is determined whether or not the user has accepted the warning. If the user accepts the operation restriction warning, the process proceeds to step 1411. On the other hand, if the user does not approve the operation restriction warning, the process is terminated.
- step 1411 the Widget 110 that uses the library to be updated is updated. This process can be performed in the same manner as in step 1406 above.
- step 1412 the library is updated, and the Widget library correspondence table 124 is updated.
- FIG. 14 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of changing the display method when the position information terminal 101 changes state.
- the stationary screen 1501 shown in FIG. 14 includes an authenticated Widget 1510, a Widget 1511 provided by a third party, and a Widget 1512 provided by a third party.
- the stopped screen 1501 transitions to a traveling screen 1503 by the travel start 1520. Further, the stopped screen 1501 transitions between the guiding screens 1504 via a warning display screen 1502 including a warning display 1530.
- This warning display screen 1502 includes a warning display 1530, and the guiding screen 1504 includes an iconized Widget 1540.
- the terminal state flag 125 changes to the running state, reads the setting at the time of the running state from the operation policy 115 of each widget 110, and performs display control according to the operation policy 115. Further, while traveling, the widget 1511 near the center of the screen is converted into an icon and automatically moved to the end of the screen so that the map information can be easily seen by the user. In this example, Widget 1550 is moved to the edge of the screen.
- the content of the display control is displayed as a warning 1530 before the position information terminal 101 enters the guidance state.
- Widget 3 is not displayed during guidance, and a warning indicating that Widget 2 is iconized is displayed to widen the display range.
- An expression method such as not displaying a warning after the second time may be used.
- FIG. 15 is an explanatory diagram showing a display example when the operation load of the location information terminal 101 is high.
- the screen (a) 1601 is displayed during normal operation. If the load on the location information terminal 101 exceeds the threshold value, the screen branches to either the warning screen 1 (1602) or the warning screen 2 (1603).
- the branching criterion can be determined by the amount by which the load on the CPU 131 exceeds the threshold.
- Warning screen 1 (1602) includes a warning 1604 when the operation of Widget 3 is stopped.
- Warning screen 2 (1603) includes a warning 1605 for restricting the animation operations of Widgets 2 and 3.
- the screen transitions from the warning screen 1 (1602) to the operation restriction screen 1 (1606), and from the warning screen 2 (1603) to the operation restriction screen 2 (1607).
- FIG. 16 is an example of a download selection screen 1701 of the Widget 110 that is browsed when the user downloads the Widget 110 on the location information terminal 101. Depending on the service, this screen may be browsed on a computer (not shown) and the selected widget 110 may be downloaded to the location information terminal 101.
- the load 1721 is the maximum load when the Wideget 110 is executed, and is expressed by a load index.
- the rate 1622 is an evaluation value of the widget 110, and the higher the value, the higher the evaluation.
- the warning 1730 is displayed when the Widget 110 registered in the Widget blacklist 155 is found on the location information terminal 101 owned by the user.
- this Widget selection screen 1701 wants to delete the target Widget 110, the Widget 110 is deleted from the position information terminal 101 by operating the delete button 1732.
- the Widget 110 when the Widget 110 is operated on the location information terminal 101 that does not have the resources of the hardware 130 that operates the Widget 110 sufficiently, Since the operation can be limited, the appearance and usability of the Widget 110 can be suppressed from decreasing. In addition, since the display and operation of the Widget 110 are automatically controlled according to the state of the location information terminal 110 (guidance state, running state, stop state), the safety at the time of destination guidance for the user and the operability of the Widget 110 Can be automatically balanced. Furthermore, since the Widget itself has the operation policy 115 and the reliability parameter 116, it is possible to prevent an illegal operation of the Widget 110 on the location information terminal 101, and to ensure the reliability of the information terminal device.
- the widget 110 is controlled according to the state of the navigation, but it is also possible to add another state as a condition, such as when the navigation is heavily loaded or when entering a specific area.
- the present invention can be applied to a location information terminal that can reproduce a Widget added by a user or the like, and reproduces the Widget 110 in a limited range that reflects the intention of the Widget creator even on a location information terminal with particularly few hardware resources. It becomes possible to do.
- it is equipped with a delete function of Widget 110 added by a user or the like, and can be applied to a position information terminal and a control program for the position information terminal that require reliability.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Navigation (AREA)
- User Interface Of Digital Computer (AREA)
- Information Transfer Between Computers (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201080050080.1A CN102667405B (zh) | 2009-11-05 | 2010-11-02 | 信息终端装置、信息终端管理系统及保存有程序的存储介质 |
| US13/508,239 US8825385B2 (en) | 2009-11-05 | 2010-11-02 | Information terminal device, information terminal management system, and storage medium in which program is stored |
| EP10828282.3A EP2498054B1 (en) | 2009-11-05 | 2010-11-02 | Information terminal device, information terminal management system, and storage medium in which program is stored |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009253971A JP5252352B2 (ja) | 2009-11-05 | 2009-11-05 | 情報端末装置、情報端末管理システム及びプログラム |
| JP2009-253971 | 2009-11-05 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2011055722A1 true WO2011055722A1 (ja) | 2011-05-12 |
Family
ID=43969960
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2010/069496 Ceased WO2011055722A1 (ja) | 2009-11-05 | 2010-11-02 | 情報端末装置、情報端末管理システム及びプログラムが格納された記憶媒体 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8825385B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP2498054B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP5252352B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN102667405B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2011055722A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8938706B2 (en) * | 2010-11-23 | 2015-01-20 | Red Hat, Inc. | Providing customized visualization of application binary interface/application programming interface-related information |
| KR101810882B1 (ko) * | 2011-04-01 | 2017-12-20 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 엠펙 2 계층을 이용한 위젯 정보를 제공하기 위한 방법 및 장치 |
| US20120272167A1 (en) * | 2011-04-20 | 2012-10-25 | Nokia Corporation | Methods, apparatuses and computer program products for providing a mechanism for same origin widget interworking |
| FR2974647B1 (fr) * | 2011-04-26 | 2013-04-26 | Bull Sas | Dispositif de reperage pour reperer une armoire informatique parmi une pluralite d'armoires informatiques |
| JP5300938B2 (ja) * | 2011-08-24 | 2013-09-25 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | 輻輳検出方法及び輻輳制御方法 |
| JP5862643B2 (ja) * | 2013-02-20 | 2016-02-16 | 株式会社デンソー | 車載装置 |
| US20140344728A1 (en) * | 2013-05-17 | 2014-11-20 | Here Global B.V. | Method and apparatus for generating context-based functional icons |
| JP2015001817A (ja) * | 2013-06-14 | 2015-01-05 | ソニー株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、及びプログラム |
| US9710484B2 (en) | 2013-09-17 | 2017-07-18 | Here Global B.V. | Method and apparatus for associating physical locations to online entities |
| JP6134369B2 (ja) * | 2015-10-28 | 2017-05-24 | 株式会社オプティム | 端末管理システム及び端末管理方法。 |
| US20170337027A1 (en) * | 2016-05-17 | 2017-11-23 | Google Inc. | Dynamic content management of a vehicle display |
| KR20180106196A (ko) * | 2017-03-17 | 2018-10-01 | 현대자동차주식회사 | 네비게이션의 성능 최적화 장치 및 방법 |
| JP6859870B2 (ja) * | 2017-06-28 | 2021-04-14 | 株式会社リコー | サーバ、システムおよび情報処理方法 |
| CN109462769B (zh) * | 2018-10-30 | 2021-03-16 | 武汉斗鱼网络科技有限公司 | 直播间挂件显示方法、装置、终端及计算机可读介质 |
| JP2023119757A (ja) * | 2022-02-17 | 2023-08-29 | 三菱ロジスネクスト株式会社 | 遠隔操作システム |
| CN119522420A (zh) * | 2022-07-21 | 2025-02-25 | 住友电气工业株式会社 | 车载装置、服务器装置、资源控制方法、资源控制辅助方法及计算机程序 |
| CN116244002B (zh) * | 2022-12-23 | 2025-09-12 | 神策网络科技(北京)有限公司 | 资源处理方法、装置、终端设备及计算机可读存储介质 |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001075772A (ja) | 1999-06-29 | 2001-03-23 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 画像表示装置および画像表示方法 |
| JP2003307422A (ja) * | 2002-04-15 | 2003-10-31 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 車載情報端末 |
| JP2004251738A (ja) * | 2003-02-20 | 2004-09-09 | Hitachi Ltd | 車載情報表示装置 |
| JP2005106651A (ja) * | 2003-09-30 | 2005-04-21 | Mazda Motor Corp | 車両用情報提供装置 |
| JP2006023171A (ja) * | 2004-07-07 | 2006-01-26 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 車載情報端末 |
| JP2007045168A (ja) * | 2005-08-05 | 2007-02-22 | Aisin Aw Co Ltd | 車両用情報処理装置 |
| JP2007114402A (ja) * | 2005-10-19 | 2007-05-10 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 表示処理装置 |
| JP2008186208A (ja) * | 2007-01-30 | 2008-08-14 | Hitachi Ltd | Cpu負荷低減方法および監視/制御サーバ |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1098244A3 (en) * | 1999-11-02 | 2001-06-13 | CANAL + Société Anonyme | Graphical user interface |
| US6574531B2 (en) * | 2001-07-25 | 2003-06-03 | Visteon Global Technologies, Inc. | Method and apparatus for providing information to an occupant of a vehicle |
| DE602004014674D1 (de) * | 2003-05-09 | 2008-08-14 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co Ltd | Videowiedergabesystem und Fahrzeugnavigationsvorrichtung in einem Fahrzeug |
| JP2005016651A (ja) | 2003-06-27 | 2005-01-20 | Yachiyo Industry Co Ltd | シール部材 |
| JP4508728B2 (ja) * | 2004-06-07 | 2010-07-21 | アルパイン株式会社 | 車載用電子機器およびその機器におけるディジタル放送の表示方法 |
| US7490295B2 (en) * | 2004-06-25 | 2009-02-10 | Apple Inc. | Layer for accessing user interface elements |
| WO2007030503A2 (en) * | 2005-09-06 | 2007-03-15 | Pattern Intelligence, Inc. | Graphical user interfaces |
| JP5147352B2 (ja) * | 2007-10-16 | 2013-02-20 | 株式会社日立製作所 | データ処理装置の情報提供方法 |
| DE102008051757A1 (de) * | 2007-11-12 | 2009-05-14 | Volkswagen Ag | Multimodale Benutzerschnittstelle eines Fahrerassistenzsystems zur Eingabe und Präsentation von Informationen |
| US8242884B2 (en) * | 2008-09-24 | 2012-08-14 | Denso International America, Inc. | Car finder by cell phone |
| KR101531192B1 (ko) * | 2008-11-14 | 2015-06-25 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 이동 단말기 및 이를 이용한 맵 표시 방법 |
| US20110109472A1 (en) * | 2009-07-30 | 2011-05-12 | Google Inc. | Resource monitoring on a mobile device |
| JP2011075772A (ja) | 2009-09-30 | 2011-04-14 | Seiko Epson Corp | プロジェクター |
| US20110099507A1 (en) * | 2009-10-28 | 2011-04-28 | Google Inc. | Displaying a collection of interactive elements that trigger actions directed to an item |
-
2009
- 2009-11-05 JP JP2009253971A patent/JP5252352B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2010
- 2010-11-02 CN CN201080050080.1A patent/CN102667405B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2010-11-02 EP EP10828282.3A patent/EP2498054B1/en not_active Not-in-force
- 2010-11-02 WO PCT/JP2010/069496 patent/WO2011055722A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2010-11-02 US US13/508,239 patent/US8825385B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001075772A (ja) | 1999-06-29 | 2001-03-23 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 画像表示装置および画像表示方法 |
| JP2003307422A (ja) * | 2002-04-15 | 2003-10-31 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 車載情報端末 |
| JP2004251738A (ja) * | 2003-02-20 | 2004-09-09 | Hitachi Ltd | 車載情報表示装置 |
| JP2005106651A (ja) * | 2003-09-30 | 2005-04-21 | Mazda Motor Corp | 車両用情報提供装置 |
| JP2006023171A (ja) * | 2004-07-07 | 2006-01-26 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 車載情報端末 |
| JP2007045168A (ja) * | 2005-08-05 | 2007-02-22 | Aisin Aw Co Ltd | 車両用情報処理装置 |
| JP2007114402A (ja) * | 2005-10-19 | 2007-05-10 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 表示処理装置 |
| JP2008186208A (ja) * | 2007-01-30 | 2008-08-14 | Hitachi Ltd | Cpu負荷低減方法および監視/制御サーバ |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP2498054A4 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2498054B1 (en) | 2018-05-09 |
| EP2498054A1 (en) | 2012-09-12 |
| US20120253662A1 (en) | 2012-10-04 |
| CN102667405B (zh) | 2015-03-18 |
| JP2011099739A (ja) | 2011-05-19 |
| US8825385B2 (en) | 2014-09-02 |
| EP2498054A4 (en) | 2014-07-02 |
| CN102667405A (zh) | 2012-09-12 |
| JP5252352B2 (ja) | 2013-07-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5252352B2 (ja) | 情報端末装置、情報端末管理システム及びプログラム | |
| US8739298B2 (en) | Method and system for enforcing a license dependency rule for a software application | |
| US8990561B2 (en) | Pervasive package identifiers | |
| US9317681B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and computer program product | |
| US8316120B2 (en) | Applicability detection using third party target state | |
| CN102804133B (zh) | 一种用于管理系统可扩展性的方法和设备 | |
| JP5027807B2 (ja) | 信頼される環境をサポートするコンピュータ可読コンポーネントの自動更新 | |
| US8380751B2 (en) | Abstraction layer for online/offline resource access | |
| KR20140061448A (ko) | 선언 및 동의에 기초하는 액세스 중개 | |
| US7779427B2 (en) | Automated application configuration using device-provided data | |
| US20130031512A1 (en) | Method and system for providing web content on a mobile device | |
| KR101977428B1 (ko) | 애플리케이션용 콘텐츠 핸들링 기법 | |
| CN113792328A (zh) | 权限管理方法、用户界面及电子设备 | |
| US10303462B2 (en) | Windows support of a pluggable ecosystem for universal windows application stores | |
| JP5444563B2 (ja) | 計算機システム、サーバ装置、端末装置及びソフトウェアアップデート方法 | |
| US8006281B2 (en) | Network accessible trusted code | |
| CN119989388B (zh) | 权限校验方法、过滤器、前端服务器及存储介质 | |
| KR102870234B1 (ko) | 실시간 사용자-서비스 상호작용 및 장애대응 방법 및 시스템 | |
| CN119089434B (zh) | 一种权限数据处理方法、系统和存储介质 | |
| KR20100069229A (ko) | 컨텐츠 바로가기 서비스 제공 시스템 및 방법 | |
| KR101086166B1 (ko) | 웹 기반의 어플리케이션 제어 시스템 및 방법 | |
| CN118567681A (zh) | 数据更新方法、装置、设备以及存储介质 | |
| CN120166062A (zh) | 基于业务角色的路由管理方法、存储介质及程序产品 | |
| CN120560735A (zh) | 应用程序功能配置方法、装置、电子设备及存储介质 | |
| CN119127278A (zh) | 参数管理方法、装置、设备、存储介质及程序产品 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 201080050080.1 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 10828282 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2010828282 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 13508239 Country of ref document: US |