RU2560366C1 - Peat sorbent and preparation method thereof - Google Patents
Peat sorbent and preparation method thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2560366C1 RU2560366C1 RU2014112717/05A RU2014112717A RU2560366C1 RU 2560366 C1 RU2560366 C1 RU 2560366C1 RU 2014112717/05 A RU2014112717/05 A RU 2014112717/05A RU 2014112717 A RU2014112717 A RU 2014112717A RU 2560366 C1 RU2560366 C1 RU 2560366C1
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- peat
- sorbent
- drying
- separation
- fed
- Prior art date
Links
Abstract
Description
Изобретение относится к средствам борьбы с загрязнениями объектов окружающей среды нефтью и нефтепродуктами и может быть использовано для сбора нефтепродуктов, масел, других жидких материалов с техногенно загрязненной поверхности (асфальт, почва, водная поверхность и другие), а также, например, при ликвидации последствий нефтяных разливов.The invention relates to a means of combating pollution of environmental objects with oil and oil products and can be used to collect oil products, oils, other liquid materials from anthropogenic contaminated surfaces (asphalt, soil, water surface and others), as well as, for example, in eliminating the effects of oil spills.
Известен способ получения гидрофобного сорбента, в котором фрезерный торф малой степени разложения, предварительно высушенный с 60 до 23-25% влажности и спрессованный под давлением 14,0-15,0 МПа в брикеты, пропитывают водонерастворимыми углеродсодержащими веществами, выделяющимися вместе с водой из твердого органического вещества торфа при его термообработке при температуре 270-300°C без доступа воздуха до влажности 2,5-10% (см. патент РФ 2116128, В 01 J 20/24, 1998).A known method of producing a hydrophobic sorbent in which milled peat of low decomposition, pre-dried from 60 to 23-25% humidity and compressed under pressure of 14.0-15.0 MPa into briquettes, is impregnated with water-insoluble carbon-containing substances released together with water from solid organic matter of peat during its heat treatment at a temperature of 270-300 ° C without air access to a moisture content of 2.5-10% (see RF patent 2116128, 01 J 20/24, 1998).
Недостатками способа являются значительные нарушения структуры торфа при воздействии выбранных давлений, пропитка торфа водонерастворимыми продуктами предыдущего возгона является малоэффективной вследствие того, что эти продукты опять перейдут полностью в газовую фазу при последующей термообработке.The disadvantages of the method are significant violations of the structure of peat when exposed to selected pressures, impregnation of peat with water-insoluble products of the previous sublimation is ineffective due to the fact that these products again go completely into the gas phase during subsequent heat treatment.
Известен способ очистки водоемов от нефти органоминеральным нефтяным сорбентом "СОРБОНАФТ" (ТУ 0392-001-55763877-2003). Сорбент, состоящий из торфа, который предварительно модифицируют путем высушивания при 100-120°C до образования необратимого коллоида (см. патент РФ №2214859, по кл. МПК С02С 1/28, 2003).A known method of cleaning water from oil using an organomineral oil sorbent "SORBONAFT" (TU 0392-001-55763877-2003). Sorbent consisting of peat, which is pre-modified by drying at 100-120 ° C to form an irreversible colloid (see RF patent No. 2214859, according to IPC С02С 1/28, 2003).
Основным недостатком этого способа является то, что сорбент, насыщенный нефтью, теряет гидрофобность. Кроме того, существует необходимость утилизации адсорбированной нефти и нефтепродуктов, что приводит к накоплению отходов.The main disadvantage of this method is that the sorbent saturated with oil loses hydrophobicity. In addition, there is a need for disposal of adsorbed oil and oil products, which leads to the accumulation of waste.
Известен также способ получения гидрофобного сорбента, включающего сушку верхового торфа, термообработку без доступа воздуха по крайней мере в две стадии в герметичной емкости, на первой стадии при 120-150°C, на второй при 250-300°C с охлаждением выделяющейся газовой фазы с раздельным сбором образующегося конденсата и несконденсированных газов, охлаждение торфа в той же емкости до 50-100°C по окончании последней стадии термообработки при подаче в емкость несконденсированных газов до компенсации падения давления в емкости при охлаждении торфа, при этом каждую стадию термообработки проводят в течение времени, после которого фиксируется снижение скорости конденсации газовой фазы при охлаждении. Дополнительно можно провести третью стадию термообработки при 340-350°C. Предпочтительно провести предварительное уплотнение торфа до уменьшения его объема не более чем в три раза и уложить в емкость послойно (см. патент РФ №.2185236, по кл. МПК B01J 20/24,2002).There is also a known method of producing a hydrophobic sorbent, including drying peat, heat treatment without air access in at least two stages in a sealed container, in the first stage at 120-150 ° C, in the second at 250-300 ° C with cooling of the evolved gas phase with separate collection of condensate and non-condensed gases, cooling of peat in the same tank to 50-100 ° C at the end of the last heat treatment stage when non-condensed gases are fed into the tank to compensate for the pressure drop in the tank when peat is cooled, etc. and each stage of the heat treatment is carried out for a time after which a decrease in the rate of condensation of the gas phase upon cooling is recorded. Additionally, you can carry out the third stage of heat treatment at 340-350 ° C. It is preferable to pre-compact peat to reduce its volume by no more than three times and lay it in a layer-by-layer layer (see RF patent No. 2185236, class IPC B01J 20 / 24,2002).
Недостатками данного способа являются цикличность данного способа производства сорбента, требующая различных условий работы установки (температуры и давления), кроме того, непроизводительная трата энергии, направленной на разогрев и охлаждение установки в каждом цикле, и времени.The disadvantages of this method are the cyclical nature of this method of sorbent production, which requires different operating conditions of the installation (temperature and pressure), in addition, unproductive waste of energy aimed at heating and cooling the installation in each cycle, and time.
Наиболее близким по технической сущности к заявляемому техническому решению является способ непрерывного производства торфоминерального гидрофобного нефтяного сорбента, включающий предварительную подготовку торфа, его подачу на гидрофобизацию, осуществляемую при пиролизе торфа в атмосфере выделившихся из него газов и летучих смол без внешнего доступа воздуха, и охлаждение полученного сорбента. Предварительную подготовку торфа производят путем сепарирования с выделением частиц с размерами 1-3 мм, которые загружают в бункер-дозатор колбы гидрофобизации, пиролиз проводят при равномерном перемещении частиц торфа от бункера-дозатора вращающейся колбы к узлу выгрузки в течение 40-60 мин, при температуре 250÷300°C и давлении 0,8÷1 атм, а охлаждение полученного сорбента осуществляют после его выгрузки из колбы (см. патент РФ №2336125, по кл. МПК B01J 20/24, 2008).The closest in technical essence to the claimed technical solution is a method for the continuous production of peat mineral hydrophobic oil sorbent, including preliminary preparation of peat, its submission to hydrophobization, carried out by pyrolysis of peat in the atmosphere of gases and volatile resins released from it without external air access, and cooling the resulting sorbent . Preliminary preparation of peat is carried out by separation with the separation of particles with sizes of 1-3 mm, which are loaded into the hopper-batcher of the hydrophobization flask, pyrolysis is carried out with a uniform movement of peat particles from the hopper-batcher of the rotating flask to the discharge unit for 40-60 minutes, at a temperature 250 ÷ 300 ° C and a pressure of 0.8 ÷ 1 atm, and the cooling of the obtained sorbent is carried out after it is unloaded from the flask (see RF patent No. 2336125, class IPC B01J 20/24, 2008).
Недостатком данного способа является сложность производства сорбента, и как следствие, сорбент получается дорогостоящим.The disadvantage of this method is the complexity of the production of the sorbent, and as a result, the sorbent is expensive.
Заявленное техническое решение направлено на создание сорбента, менее затратного за счет снижения трудоемкости его получения, но эффективного при его использовании.The claimed technical solution is aimed at creating a sorbent, less expensive by reducing the complexity of its production, but effective in its use.
Поставленная задача решается тем, что сорбент торфяной содержит торфяную основу, подвергшуюся предварительной обработке и модифицированию путем высушивания. В качестве торфяной основы использован верховой сфагновый слаборазложившийся торф мохового типа, степенью разложения не более 20%, зольностью не более 10%, обработанный сепарированием с отделением от древесных и других включений, высушенный до влажности 18-24%, измельченный до фракции 0,5-10 мм.The problem is solved in that the peat sorbent contains a peat base, subjected to pre-treatment and modification by drying. As a peat base, we used high-level sphagnum poorly decomposed peat of a moss type, with a decomposition degree of not more than 20%, an ash content of not more than 10%, processed by separation with separation from wood and other inclusions, dried to a moisture content of 18-24%, crushed to a fraction of 0.5- 10 mm.
Для получения указанного сорбента торфяного проводят предварительную подготовку торфа, модифицирование путем высушивания. В качестве торфяной основы используют верховой сфагновый слаборазложившийся торф мохового типа, степенью разложения не более 20%, зольностью не более 10%, обрабатывают сепарированием с отделением от древесных и других включений. Затем непрерывным потоком торф подают в сушильный барабан, причем температура теплоносителя на входе 350-500°C, на выходе 60-110°C, контролируют влажность, после сушки до влажности 18-24% измельчают до фракции 0,5-10 мм.To obtain the indicated peat sorbent, preliminary preparation of peat is carried out, modification by drying. As a peat base, sphagnum poorly decomposed peat of a moss type is used, with a degree of decomposition of not more than 20%, an ash content of not more than 10%, it is processed by separation with separation from wood and other inclusions. Then, a continuous stream of peat is fed into the dryer drum, and the temperature of the coolant at the inlet of 350-500 ° C, at the outlet of 60-110 ° C, the humidity is controlled, after drying to a moisture content of 18-24% it is crushed to a fraction of 0.5-10 mm
При использовании торфа влажностью 55-65% сушку осуществляют в сушильном барабане в одну стадию.When using peat with a moisture content of 55-65%, drying is carried out in a drying drum in one stage.
При использовании торфа влажностью 65-70% сушку осуществляют в две стадии: сначала торф подают непрерывным потоком в один сушильный барабан, после контроля влажности торф подают во второй сушильный барабан, причем барабаны установлены последовательно.When using peat with a humidity of 65-70%, drying is carried out in two stages: first, peat is fed in a continuous stream to one dryer drum, after controlling the moisture, peat is fed to the second dryer drum, and the drums are installed in series.
При испытаниях, которые проводились на предприятии ОАО «Соколагрохимия» и ОАО ВНИИТП, было определено, что:During the tests that were carried out at the enterprise OJSC Sokolagrokhimiya and OJSC VNIITP, it was determined that:
- при использовании торфа степени разложения более 20% получается более мелкая фракция после сушки, которая имеет меньшую площадь контакта с нефтепродуктами и обладает меньшей плавучестью;- when using peat decomposition degree of more than 20%, a finer fraction is obtained after drying, which has a smaller contact area with oil products and has less buoyancy;
- при использовании торфа зольности более 10% - уменьшается нефтепоглощение и плавучесть сорбента;- when using ash peat more than 10% - oil absorption and sorbent buoyancy are reduced;
- при влажности торфа менее 18% - большая плавучесть, но удорожание процесса сушки;- when the humidity of the peat is less than 18% - great buoyancy, but the cost of the drying process;
- при влажности более 24% получается сорбент с меньшей плавучестью и снижается срок хранения за счет биопроцессов.- at a moisture content of more than 24%, a sorbent with less buoyancy is obtained and the shelf life is reduced due to bioprocesses.
Фракция торфяной основы должна быть 0,5-10 мм, при которой достигается наибольшее соприкосновение с нефтепродуктами и наибольшее нефтепоглощение, т.к. при фракции менее 0,5 мм фракция сорбента получается пылевидной, уменьшается нефтепоглощение и плавучесть, а при фракции более 10 мм наблюдается рыхлость сорбента, что уменьшает нефтепоглощаемость сорбента.The peat base fraction should be 0.5-10 mm, at which the greatest contact with oil products and the greatest oil absorption are achieved, because when the fraction is less than 0.5 mm, the sorbent fraction is dusty, oil absorption and buoyancy are reduced, and when the fraction is more than 10 mm, the sorbent friability is observed, which reduces the oil absorption of the sorbent.
Торф поступает в зону обработки, где предварительно производят отделение крупных пней и кусков мерзлоты до засоренности не более 10%. После чего торф поступает на сепаратор. Предварительно обработанный торф подают конвейером на магнитный сепаратор, затем далее на сито для отделения от древесных и других включений. Затем непрерывным потоком торф подают в сушильный барабан АВМ - 0,65, причем температура теплоносителя на входе 350-500°C, на выходе 60-110°C. При выходе из сушильного барабана контролируют влажность. После сушки до влажности 18-24% измельчают. При использовании торфа влажностью 55-65% сушку осуществляют в сушильном барабане в одну стадию, а при использовании торфа влажностью 65-70% сушку осуществляют в две стадии: сначала торф подают непрерывным потоком в один сушильный барабан, после контроля влажности торф подают во второй сушильный барабан, причем барабаны установлены последовательно. Выходящий из сушильного барабана сухой торф подают в циклон-осадитель, затем торф измельчают до фракции 0,5-10 мм. Полученные фракции торфа менее 0,5 мм и более 10 мм отделяют и могут быть направлены в бункер-сборник и затем в теплогенератор сушильного барабана. Готовый сорбент поступает на упаковку.Peat enters the processing zone where large stumps and pieces of permafrost are preliminarily separated to no more than 10% contamination. After that, peat enters the separator. Pre-processed peat is conveyed to a magnetic separator, then to a sieve to separate it from wood and other inclusions. Then a continuous stream of peat is fed into the drying drum ABM - 0.65, and the temperature of the coolant at the inlet is 350-500 ° C, at the outlet 60-110 ° C. Upon exiting the dryer drum, humidity is controlled. After drying to a moisture content of 18-24% is crushed. When using peat with a humidity of 55-65%, drying is carried out in a drying drum in one stage, and when using peat with a humidity of 65-70%, drying is carried out in two stages: first, peat is fed in a continuous stream to one drying drum, after controlling the moisture, peat is fed to the second drying drum, and the drums are installed in series. The dry peat coming out of the dryer drum is fed to a cyclone precipitator, then the peat is ground to a fraction of 0.5-10 mm. The resulting peat fractions of less than 0.5 mm and more than 10 mm are separated and can be sent to the collection hopper and then to the heat generator of the drying drum. Ready sorbent is delivered to the packaging.
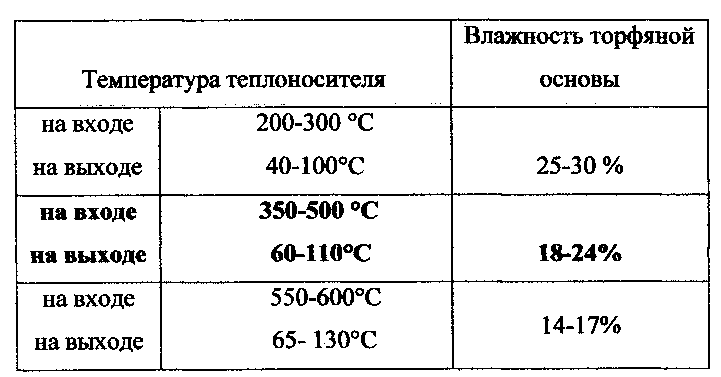
Торф подвергается сушке при заданных режимах в зависимости от влажности. Температура теплоносителя на входе 350-500°C, на выходе 60-110°C для получения требуемой влажности торфяной основы 18-24% выбрана экспериментально, как видно из таблицы.Peat is dried under specified conditions depending on humidity. The temperature of the coolant at the inlet is 350-500 ° C, at the outlet 60-110 ° C in order to obtain the required moisture content of the peat base 18-24% is chosen experimentally, as can be seen from the table.
Пример 1 осуществления процесса сушки.Example 1 of the drying process.
Торф влажностью до 61,1% поступает на сушку. Температура теплоносителя на входе 390°C, а температура теплоносителя на выходе -91,2°C, получаемая влажность торфа на выходе - 18,1%.Peat with humidity up to 61.1% goes to drying. The temperature of the coolant at the inlet is 390 ° C, and the temperature of the coolant at the outlet is -91.2 ° C, the resulting humidity of peat at the outlet is 18.1%.
Пример 2 осуществления процесса сушки.Example 2 of the drying process.
Торф влажностью до 65,1% поступает на сушку. Температура теплоносителя на входе 420,6°C, а температура теплоносителя на выходе -92,4°C, получаемая влажность торфа на выходе 20,6%.Peat with humidity up to 65.1% goes to drying. The temperature of the coolant at the inlet is 420.6 ° C, and the temperature of the coolant at the outlet is -92.4 ° C, the resulting humidity of peat at the outlet is 20.6%.
Пример осуществления способа получения сорбента торфяного.An example of the method of producing peat sorbent.
Для получения сорбента используют фрезерный торф верхового типа сфагновой (моховой группы) степенью разложения не более 20%, зольностью не более 10%, добываемый на месторождении «Алексеевское -1» Сокольского района Вологодской области (Инструкция производства сорбента торфяного «Норд» ТУ 0391-008-00611034-2013).To obtain the sorbent, milling peat of the upper type of sphagnum (moss group) decomposition degree of not more than 20%, ash content of not more than 10%, extracted at the Alekseevskoye-1 deposit in the Sokolsky district of the Vologda region is used (Production instruction for the Nord sorbent TU 0391-008 -00611034-2013).
Верховой слаборазложившийся сфагновый торф со степенью разложения 15-20%, зольностью 2-5%, влажностью 63,3% поступает в зону обработки, где предварительно производят отделение крупных пней и кусков мерзлоты до засоренности не более 10%. После чего торф поступает на сепаратор. Предварительно обработанный торф подают конвейером на магнитный сепаратор и далее на сито для отделения от древесных и других включений. Непрерывным потоком торф подают в сушильный барабан АВМ- 0,65, температура теплоносителя на входе - 408,3°C, на выходе - 93,6°C. При выходе из сушильного барабана получаем торф влажностью 19,4%. Выходящий из сушильного барабана сухой торф подают в циклон-осадитель, затем торф измельчают до фракции 0,5-10 мм. Полученные фракции торфа менее 0, 5 мм и более 10 мм отделяют. Готовый сорбент поступает на упаковку.Slightly decomposed sphagnum peat with a decomposition degree of 15–20%, an ash content of 2–5%, and a moisture content of 63.3% enters the treatment zone, where large stumps and pieces of permafrost are preliminarily separated to no more than 10% infestation. After that, peat enters the separator. Pre-processed peat is conveyed to a magnetic separator and then to a sieve for separation from wood and other inclusions. A continuous stream of peat is fed into the drying drum ABM-0.65, the temperature of the coolant at the inlet is 408.3 ° C, and the outlet is 93.6 ° C. Upon exiting the dryer drum, we obtain peat with a moisture content of 19.4%. The dry peat coming out of the dryer drum is fed to a cyclone precipitator, then the peat is ground to a fraction of 0.5-10 mm. The resulting peat fractions of less than 0.5 mm and more than 10 mm are separated. Ready sorbent is delivered to the packaging.
В результате предложенного способа получаем новый сорбент торфяной «Норд» (испытания были проведены ОАО ВНИИ111):As a result of the proposed method, we obtain a new sorbent peat "Nord" (tests were carried out by JSC VNII111):
В результате за счет снижения трудоемкости технологии получаем дешевый сорбент, а за счет снижения удельного расхода сорбента торфяного при очистке для сбора нефтепродуктов, масел, других жидких материалов с техногенно загрязненной поверхности получаем более экономичный процесс очистки.As a result, by reducing the complexity of the technology, we obtain a cheap sorbent, and by reducing the specific consumption of peat sorbent during cleaning to collect oil products, oils, and other liquid materials from technologically contaminated surfaces, we obtain a more economical cleaning process.
Указанный сорбент, попадая на поверхность разлитой маслянистой жидкости, впитывает ее и удерживает в своем объеме, предотвращая ее дальнейшее распространение. Для покрытия поверхности, загрязненной нефтепродуктами, используют механические и пневматические разбрасыватели. Возможно ручное нанесение сорбента. Потребное количество сорбента (по объему) определяется из условия, что толщина слоя сорбента, нанесенного на нефтепродукт, должна быть в 3-4 раза больше толщины слоя нефтепродукта. Сбор смеси сорбента с нефтепродуктом (или маслом) проводится нефтемусоросборщиком или вручную скребковыми лопатами или другими средствами с затариванием собранной смеси в полиэтиленовые мешки или другие емкости с последующей сдачей на очистные сооружения, котельные установки или площадки для сжигания отходов.The specified sorbent, getting on the surface of the spilled oily liquid, absorbs it and holds in its volume, preventing its further spread. Mechanical and pneumatic spreaders are used to cover a surface contaminated with oil products. Manual application of the sorbent is possible. The required amount of sorbent (by volume) is determined from the condition that the thickness of the sorbent layer deposited on the oil product should be 3-4 times greater than the thickness of the oil product layer. A mixture of the sorbent with the oil product (or oil) is collected by an oil picker or manually using scraper shovels or other means with packing the collected mixture in plastic bags or other containers, followed by delivery to treatment plants, boiler plants or waste incinerators.
Применение торфяного сорбента более предпочтительно по сравнению с аналогами, так как является более эффективным и менее затратным за счет снижения удельного расхода сорбента и снижения трудоемкости его получения.The use of peat sorbent is more preferable in comparison with analogues, since it is more efficient and less costly due to a decrease in the specific consumption of the sorbent and a decrease in the laboriousness of its production.
Кроме того, использование предлагаемого торфяного сорбента «Норд» имеет ряд преимуществ перед другими видами сорбентов. Во-первых, он обладает способностью биологического разложения поглощенных углеводов при хранении отсорбированной массы, снижая ее степень загрязнения, не имеет повторного загрязнения, работает в любых погодных условиях при низких отрицательных температурах. Во-вторых, он является экологически безопасным для окружающей среды, животных и людей; имеет высокую степень очистки воды. Сорбент может быть компактно упакован, удобен для хранения и перевозки. Он может применяться на водных объектах и на суше, при хранении не слеживается и не теряет качественных показателей. По окончании срока годности его можно использовать в сельском хозяйстве, садоводстве, огородничестве.In addition, the use of the proposed peat sorbent "Nord" has several advantages over other types of sorbents. Firstly, it has the ability to biodegrade the absorbed carbohydrates during storage of the sorbed mass, reducing its degree of contamination, does not have re-contamination, and works in all weather conditions at low freezing temperatures. Secondly, it is environmentally friendly for the environment, animals and people; has a high degree of water purification. The sorbent can be compactly packed, convenient for storage and transportation. It can be used on water bodies and on land; during storage, it does not cake and does not lose quality indicators. At the end of its shelf life, it can be used in agriculture, horticulture, gardening.
Claims (4)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2014112717/05A RU2560366C1 (en) | 2014-04-01 | 2014-04-01 | Peat sorbent and preparation method thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2014112717/05A RU2560366C1 (en) | 2014-04-01 | 2014-04-01 | Peat sorbent and preparation method thereof |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2560366C1 true RU2560366C1 (en) | 2015-08-20 |
Family
ID=53880626
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2014112717/05A RU2560366C1 (en) | 2014-04-01 | 2014-04-01 | Peat sorbent and preparation method thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2560366C1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2786981C1 (en) * | 2022-05-25 | 2022-12-27 | Публичное акционерное общество "Газпром" | Activated complex sorbent |
Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2102319C1 (en) * | 1995-06-27 | 1998-01-20 | Владимир Иванович Суворов | Method for producing peat-based adsorbent |
| RU10164U1 (en) * | 1998-12-17 | 1999-06-16 | Гамаюнов Сергей Николаевич | SORBENT BASED ON PEAT "GRANULATED" |
| RU2173578C1 (en) * | 2000-12-22 | 2001-09-20 | Острецов Валерий Иванович | Method of preparing sorbent for removing oil from water and solid surfaces |
| RU2185236C1 (en) * | 2001-10-29 | 2002-07-20 | Дружинин Вадим Леонидович | Hydrophobic sorbent preparation method |
| RU2191066C1 (en) * | 2001-04-20 | 2002-10-20 | Хохлов Антон Львович | Method of preparing sorbent for cleaning solid surfaces from crude oil and petroleum products |
| RU2191067C1 (en) * | 2001-04-20 | 2002-10-20 | Хохлов Антон Львович | Method of preparing sorbent for cleaning solid surfaces from crude oil and petroleum products |
| RU2214859C1 (en) * | 2002-09-11 | 2003-10-27 | Гридин Олег Михайлович | Hydrophobic sorbent preparation method |
| US6890631B2 (en) * | 2002-06-10 | 2005-05-10 | International Business Machines Corporation | Dual-surface flexible magnetic tape |
| RU2318529C1 (en) * | 2006-09-25 | 2008-03-10 | ГУ Научно-исследовательский институт фармакологии Томского научного центра Сибирского отделения Российской академии медицинских наук (ГУ НИИ фармакологии ТНЦ СО РАМН) | Means for preventing and correcting spermatogenesis disorders caused by cytostatic treatment |
| RU2336125C1 (en) * | 2007-01-09 | 2008-10-20 | Закрытое Акционерное Общество "Маркетинг-Бюро" | Method of continuous production of peat-mineral hydrophobic oil sorbent |
-
2014
- 2014-04-01 RU RU2014112717/05A patent/RU2560366C1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2102319C1 (en) * | 1995-06-27 | 1998-01-20 | Владимир Иванович Суворов | Method for producing peat-based adsorbent |
| RU10164U1 (en) * | 1998-12-17 | 1999-06-16 | Гамаюнов Сергей Николаевич | SORBENT BASED ON PEAT "GRANULATED" |
| RU2173578C1 (en) * | 2000-12-22 | 2001-09-20 | Острецов Валерий Иванович | Method of preparing sorbent for removing oil from water and solid surfaces |
| RU2191066C1 (en) * | 2001-04-20 | 2002-10-20 | Хохлов Антон Львович | Method of preparing sorbent for cleaning solid surfaces from crude oil and petroleum products |
| RU2191067C1 (en) * | 2001-04-20 | 2002-10-20 | Хохлов Антон Львович | Method of preparing sorbent for cleaning solid surfaces from crude oil and petroleum products |
| RU2185236C1 (en) * | 2001-10-29 | 2002-07-20 | Дружинин Вадим Леонидович | Hydrophobic sorbent preparation method |
| US6890631B2 (en) * | 2002-06-10 | 2005-05-10 | International Business Machines Corporation | Dual-surface flexible magnetic tape |
| RU2214859C1 (en) * | 2002-09-11 | 2003-10-27 | Гридин Олег Михайлович | Hydrophobic sorbent preparation method |
| RU2318529C1 (en) * | 2006-09-25 | 2008-03-10 | ГУ Научно-исследовательский институт фармакологии Томского научного центра Сибирского отделения Российской академии медицинских наук (ГУ НИИ фармакологии ТНЦ СО РАМН) | Means for preventing and correcting spermatogenesis disorders caused by cytostatic treatment |
| RU2336125C1 (en) * | 2007-01-09 | 2008-10-20 | Закрытое Акционерное Общество "Маркетинг-Бюро" | Method of continuous production of peat-mineral hydrophobic oil sorbent |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2786981C1 (en) * | 2022-05-25 | 2022-12-27 | Публичное акционерное общество "Газпром" | Activated complex sorbent |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Abdin et al. | Competitive sorption and availability of coexisting heavy metals in mining-contaminated soil: Contrasting effects of mesquite and fishbone biochars | |
| Thines et al. | Effect of process parameters for production of microporous magnetic biochar derived from agriculture waste biomass | |
| AlOthman et al. | Valorization of two waste streams into activated carbon and studying its adsorption kinetics, equilibrium isotherms and thermodynamics for methylene blue removal | |
| US3681851A (en) | Novel production and waste treatment process for producing said product | |
| Hameed et al. | Equilibrium modeling and kinetic studies on the adsorption of basic dye by a low-cost adsorbent: Coconut (Cocos nucifera) bunch waste | |
| AU2011201612B2 (en) | Method to transform bulk material | |
| Berrazoum et al. | Bioadsorption of a reactive dye from aqueous solution by municipal solid waste | |
| Said et al. | Investigation of hydrochar derived from male oil palm flower: characteristics and application for dye removal | |
| RU2560366C1 (en) | Peat sorbent and preparation method thereof | |
| DE2833191A1 (en) | Biological earth filter for removing odours and toxic waste gas - has layer of expanded aluminosilicate supported over gas distribution pipe | |
| US7128109B2 (en) | Essential oil reclaim apparatus, and method of use | |
| CN101165029A (en) | Method for extracting benzene-like compounds from flammable explosive gas of benzene-containing compounds | |
| Aikpokpodion Paul et al. | Studies on adsorption mechanism and kinetics of magnesium in selected cocoa growing soils in Nigeria | |
| RU2116128C1 (en) | Method of preparing sorbent for removing oil from solid and water surfaces | |
| Babakhouya et al. | Kinetics and thermodynamics of Cd (II) ions sorption on mixed sorbents prepared from olive stone and date pit from aqueous solution | |
| US20160237378A1 (en) | A filter medium for the filtration of olive oil, in particular for the filtration of extra virgin olive oil, and the filtration process of the olive oil, in particular of the filtration of the extra virgin olive oil | |
| Thines et al. | Production of magnetic biochar derived from durian’s rind at vacuum condition for removal of methylene blue pigments from aqueous solution | |
| Malovanyy et al. | The strategy of environmental danger minimization from poultry farms waste | |
| Aksas et al. | Kinetics and thermodynamics of Cr ions sorption on mixed sorbents prepared from olive stone and date pit from aqueous solution | |
| Latif et al. | Removal of cadmium (II) and lead (II) from water by chemically treated Citrullus lanatus peels as biosorbent in cost effective way | |
| RU2185236C1 (en) | Hydrophobic sorbent preparation method | |
| KR100400873B1 (en) | Manufacturing method of organic fertilizer using food waste | |
| Nikolaeva et al. | Complex use of waste in wastewater and circulating water treatment from oil in heat power stations | |
| Ayuba et al. | Adsorption and kinetics study for the removal of pendimethalin from aqueous solution using activated carbon prepared from agricultural waste | |
| Nasri et al. | Equilibrium and kinetic studies of benzene and toluene adsorption onto microwave irradiated-coconut shell activated carbon |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM4A | The patent is invalid due to non-payment of fees |
Effective date: 20170402 |