JP5795835B2 - Game machine - Google Patents
Game machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5795835B2 JP5795835B2 JP2007154573A JP2007154573A JP5795835B2 JP 5795835 B2 JP5795835 B2 JP 5795835B2 JP 2007154573 A JP2007154573 A JP 2007154573A JP 2007154573 A JP2007154573 A JP 2007154573A JP 5795835 B2 JP5795835 B2 JP 5795835B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- effect
- symbol
- command
- display
- big hit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Pinball Game Machines (AREA)
- Display Devices Of Pinball Game Machines (AREA)
Description
本発明は、各々を識別可能な複数種類の識別情報の可変表示を行い表示結果を導出表示する演出表示装置を備え、演出表示装置に特定表示結果が導出表示されたときに遊技者にとって有利な特定遊技状態に移行させ、特別条件が成立したときに遊技者にとって有利な特定遊技状態に移行させるとともに特定遊技状態が終了した後に通常状態に比べて特定遊技状態に移行しやすい状態である特別遊技状態に移行させる遊技機パチンコ遊技機等の遊技機に関する。 The present invention is provided with an effect display device that variably displays a plurality of types of identification information that can identify each of them and derives and displays a display result, and is advantageous for a player when a specific display result is derived and displayed on the effect display device. A special game in which a transition is made to a specific gaming state, a transition to a specific gaming state advantageous to the player when a special condition is established, and a transition to the specific gaming state is easier than the normal state after the specific gaming state has ended. The present invention relates to a gaming machine such as a pachinko gaming machine to be shifted to a state.
遊技機として、遊技球などの遊技媒体を発射装置によって遊技領域に発射し、遊技領域に設けられている入賞口などの入賞領域に遊技媒体が入賞すると、所定個の賞球が遊技者に払い出されるものがある。さらに、識別情報を可変表示(「変動」ともいう。)可能な可変表示装置が設けられ、可変表示装置において識別情報の可変表示の表示結果が特定表示結果となった場合に遊技者にとって有利な特定遊技状態に制御可能になるように構成されたものがある。 As a gaming machine, a game medium such as a game ball is launched into a game area by a launching device, and when a game medium wins a prize area such as a prize opening provided in the game area, a predetermined number of prize balls are paid out to the player. There is something to be. Furthermore, a variable display device capable of variably displaying the identification information (also referred to as “fluctuation”) is provided, which is advantageous to the player when the display result of the variable display of the identification information becomes the specific display result in the variable display device. Some are configured to be controllable to a specific gaming state.
特定遊技状態とは、所定の遊技価値が付与された遊技者にとって有利な状態を意味する。具体的には、特定遊技状態は、例えば特別可変入賞装置の状態を打球が入賞しやすい遊技者にとって有利な状態(大当り遊技状態)、遊技者にとって有利な状態になるための権利が発生した状態、景品遊技媒体払出の条件が成立しやすくなる状態などの所定の遊技価値が付与された状態である。 The specific game state means a state advantageous for a player who is given a predetermined game value. Specifically, the specific game state is, for example, a state in which a special variable winning device is advantageous for a player who is likely to win a ball (a big hit game state), or a state in which a right to be advantageous for a player has occurred. In this state, a predetermined game value such as a state where conditions for paying out premium game media are easily established is given.
そのような遊技機では、識別情報としての図柄を表示する可変表示装置の表示結果があらかじめ定められた特定の表示態様の組合せ(特定表示結果)になることを、通常、「大当り」という。大当りが発生すると、例えば、大入賞口が所定回数開放して打球が入賞しやすい大当り遊技状態に移行する。そして、各開放期間において、所定個(例えば10個)の大入賞口への入賞があると大入賞口は閉成する。そして、大入賞口の開放回数は、所定回数(例えば15ラウンド)に固定されている。なお、各開放について開放時間(例えば29.5秒)が決められ、入賞数が所定個に達しなくても開放時間が経過すると大入賞口は閉成する。また、大入賞口が閉成した時点で所定の条件(例えば、大入賞口内に設けられているVゾーンへの入賞)が成立していない場合には、大当り遊技状態は終了する。 In such a gaming machine, the fact that the display result of the variable display device that displays the symbol as identification information is a combination of specific display modes (specific display result) determined in advance is generally referred to as “big hit”. When the big hit occurs, for example, the big winning opening is opened a predetermined number of times, and the game shifts to a big hit gaming state where the hit ball is easy to win. And in each open period, if there is a prize for a predetermined number (for example, 10) of the big prize opening, the big prize opening is closed. And the number of times the special winning opening is opened is fixed to a predetermined number (for example, 15 rounds). An opening time (for example, 29.5 seconds) is determined for each opening, and even if the number of winnings does not reach a predetermined number, the big winning opening is closed when the opening time elapses. Further, when a predetermined condition (for example, winning in the V zone provided in the big prize opening) is not established at the time when the big prize opening is closed, the big hit gaming state is ended.
さらに、可変表示装置において識別情報の可変表示の表示結果が特定表示結果のうちの特別な特定表示結果(特別表示結果)になる等の特別の条件が成立すると、大当り遊技状態の終了後に、大当りが発生する確率が高くなる高確率状態(確変状態ともいう。)に移行する遊技機がある。 Furthermore, if a special condition is established such that the display result of the variable display of the identification information becomes a special specific display result (special display result) of the specific display results in the variable display device, the big hit is made after the end of the big hit gaming state. There is a gaming machine that shifts to a high-probability state (also referred to as a probabilistic change state) in which the probability of occurrence of is high.
そのような遊技機において、識別情報の可変表示が行われているときや大当り遊技中に、可変表示装置を含む演出装置において、確変状態に移行することを遊技者に報知する演出を行う遊技機がある(例えば、特許文献1,2参照。)。
In such a gaming machine, when the variable display of the identification information is being performed or during the big hit game, the gaming machine that performs the effect of notifying the player that the state is to be changed to the probable change state in the effect device including the variable display device (For example, see
特許文献1に記載された遊技機では、識別情報の可変表示中に特定のキャラクタ画像を可変表示装置に表示することによって、大当り遊技状態の終了後に確変状態に移行することを報知する。
In the gaming machine described in
特許文献2に記載された遊技機では、大当り遊技中に特定のキャラクタ画像を可変表示装置に表示することによって、大当り遊技状態の終了後に確変状態に移行することを報知する。すなわち、識別情報の可変表示の表示結果(停止図柄)によって遊技者は大当り遊技状態に移行することを把握できるが、確変状態に移行するか否か把握できない。そして、大当り遊技中に実行される演出によって確変状態に移行することを把握できる。以下、識別情報の可変表示の表示結果によって確変状態に移行するか否か把握できない場合に、その後に実行される演出であって遊技者に確変状態に移行することを把握させるための演出を昇格演出という。
In the gaming machine described in
しかし、特許文献1に記載されている遊技機では、識別情報の可変表示が終了する前に確変状態に移行することが報知されるので、識別情報の可変表示中において確変状態に関する遊技者の興味を引きつけることができるが、昇格演出の演出態様は単調である。また、特許文献2に記載されている遊技機では、大当り遊技中に昇格演出が実行されるので大当り遊技中において確変状態に関する遊技者の興味を引きつけることができるが、昇格演出の演出態様はやはり単調である。
However, in the gaming machine described in
そこで、本発明は、昇格演出の演出態様に変化を付けて遊技の興趣をより高めることができる遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION An object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine that can enhance the entertainment of a game by changing the effect mode of the promotion effect.
本発明による遊技機は、各々を識別可能な複数種類の識別情報の可変表示を行い表示結果を導出表示する演出表示装置(例えば、特別図柄表示器8や演出表示装置9)を備え、該演出表示装置に特定表示結果(例えば、大当り図柄)が導出表示されたときに遊技者にとって有利な特定遊技状態(例えば、大当り遊技状態)に移行させ、特別条件が成立したときに遊技状態を遊技者にとって有利な特定遊技状態に移行させるとともに該特定遊技状態が終了した後に通常の遊技状態(例えば、特別遊技状態でない状態)に比べて特定表示結果が導出表示されやすい状態である確変状態に移行させる遊技機であって、識別情報の可変表示の表示結果を特定表示結果とするか否かと、特別条件を成立させるか否かとを、可変表示の表示結果を導出表示する前に決定する事前決定手段(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560において、ステップS61〜S63の処理を実行する部分)と、第1演出(例えば、キャラクタP(9p)を用いた演出、キャラクタQ(9q)を用いた演出、キャラクタR(9r)を用いた演出、キャラクタS(9s)を用いた演出)および該第1演出とは異なる第2演出(例えば、キャラクタA(9a)を用いた演出、キャラクタB(9b)を用いた演出、キャラクタC(9c)を用いた演出)を、それぞれ、複数種類のうちから選択する演出選択手段(例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100において、ステップS825〜S826の処理、およびS911〜S912の処理を実行する部分)と、演出選択手段が選択した第1演出を識別情報の可変表示中に演出表示装置において実行し、演出選択手段が選択した第2演出を当該識別情報の可変表示が終了した後に移行される特定遊技状態中に演出表示装置において実行する演出実行手段(例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100において、ステップS840,S845〜S847の処理を実行する部分)とを備え、演出選択手段は、事前決定手段が特別条件を成立させることに決定したときには、表示結果を特定表示結果とするとともに特別条件を成立させないことに決定したときに比べて、第1演出として特定第1演出(例えば、キャラクタR)を選択した場合に高い割合で第2演出として特定第2演出(例えば、キャラクタC)を選択し、第1演出として所定第1演出(例えば、キャラクタQ)を選択した場合に高い割合で第2演出として所定第2演出(例えば、キャラクタA)を選択することを特徴とする。
The gaming machine according to the present invention includes an effect display device (for example, a special
演出実行手段は、識別情報の可変表示が行われているときに第1演出を実行し、当該第1演出を実行した後の当該識別情報の可変表示中において第2演出を実行し(例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が、まず、ステップS833の処理にもとづいてステップS840,S845〜S847の処理を実行し、次いで、ステップS912の処理にもとづいてステップS840,S845〜S847の処理を実行)、演出選択手段は、事前決定手段が識別情報の可変表示の表示結果を特定表示結果とすることに決定したときと特定表示結果としないことに決定したときとで、複数種類のうちの少なくとも一の第1演出の選択割合を異ならせる(図30参照)ように構成されていてもよい。
The effect execution means executes the first effect when the variable display of the identification information is performed, and executes the second effect during the variable display of the identification information after executing the first effect (for example, The
演出実行手段は、特定遊技状態中において第1演出を実行し、当該第1演出を実行した後の当該特定遊技状態中において第2演出を実行する(例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が、まず、図59に示すステップS871の処理にもとづいて図60に示すステップS883〜S886の処理を実行し、次いで、図61に示すステップS912の処理にもとづいてステップS883〜S886の処理を実行する)ように構成されていてもよい。
The effect execution means executes the first effect in the specific game state, and executes the second effect in the specific game state after executing the first effect (for example, the
演出実行手段は、特定遊技状態の終了後に第1演出を実行し、当該第1演出を実行した後の当該特定遊技状態の終了後において第2演出を実行する(例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が、まず、図71に示すステップS936の処理にもとづいて図43に示すステップS840,S845〜S847の処理を実行し、次いで、図44に示すステップS912の処理にもとづいてステップS840,S845〜S847の処理を実行する)ように構成されていてもよい。 The effect execution means executes the first effect after the end of the specific game state, and executes the second effect after the end of the specific game state after executing the first effect (for example, the effect control microcomputer 100). First, the processes of steps S840 and S845 to S847 shown in FIG. 43 are executed based on the process of step S936 shown in FIG. 71, and then the steps S840 and S845 to S847 are executed based on the process of step S912 shown in FIG. May be configured to execute the process (1).
演出選択手段は、第1演出の種類を選択する第1演出種類選択手段(例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100において、ステップS825〜S826の処理を実行する部分)と、第1演出種類選択手段が選択した第1演出の種類と、特別条件が成立するか否かとにもとづいて第2演出の種類を選択する第2演出選択手段(例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100において、ステップS911〜S912の処理を実行する部分)とを含むように構成されていてもよい。 The effect selecting means includes a first effect type selecting means (for example, a portion for executing the processing of steps S825 to S826 in the effect control microcomputer 100) and a first effect type selecting means. Second effect selection means for selecting the type of the second effect based on the type of the selected first effect and whether or not the special condition is satisfied (for example, the processing of steps S911 to S912 in the effect control microcomputer 100) And a portion for executing the above.
演出選択手段は、第1演出種類選択手段が選択した第1演出の種類を特定可能なデータを演出種類記憶手段(例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100におけるRAM112における第1演出キャラクタバッファ112a)に設定する第1演出種類保存手段(例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100において、ステップS827の処理を実行する部分)を含み、第2演出選択手段は、演出種類記憶手段に設定されているデータにもとづいて第2演出の種類を選択する(例えば、ステップS912の処理で第1演出キャラクタバッファ112aに記憶されているデータを使用する)ように構成されていてもよい。
The effect selecting means sets data capable of specifying the type of the first effect selected by the first effect type selecting means in the effect type storage means (for example, the first
遊技の進行を制御する遊技制御手段(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560)と、遊技制御手段が出力したコマンドにもとづいて、演出表示装置の表示状態を制御する演出制御手段(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から演出制御コマンドを受信する演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100や他の基板を経由して遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から演出制御コマンドを受信する演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100)とを備え、事前決定手段は、遊技制御手段に含まれ、演出選択手段は、演出制御手段に含まれ、遊技制御手段は、所定の時期に、事前決定手段が特別条件を成立させることに決定したことを特定可能な特別条件特定コマンド(例えば、演出図柄指定コマンド(8C01(H)〜8C03(H))や背景指定コマンド(9500(H)〜9502(H))を出力するコマンド出力手段(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560において、ステップS119,S125の処理を実行する部分)を含み、第1演出種類選択手段は、特別条件特定コマンドにもとづいて第1演出を選択し(例えば、ステップS826の処理)、第2演出種類選択手段は、第1演出種類選択手段が選択した第1演出の種類と特別条件特定コマンドとにもとづいて第2演出を選択する(例えば、ステップS912の処理)ように構成されていてもよい。
Game control means (for example, a game control microcomputer 560) for controlling the progress of the game, and effect control means (for example, for game control) for controlling the display state of the effect display device based on the command output by the game control means. An
コマンド出力手段は、特別条件特定コマンドとして、第1演出種類選択手段が第1演出の種類を選択する時期と第2演出種類選択手段が第2演出の種類を選択する時期のそれぞれにおいて、事前決定手段の決定結果にもとづく識別情報の可変表示の表示結果を特定可能な表示結果特定コマンド(例えば、演出図柄指定コマンド)を出力し(例えば、ステップS826,S912の処理)、第1演出種類選択手段は、表示結果特定コマンドにもとづいて第1演出の種類を選択し(例えば、ステップS826の処理)、第2演出種類選択手段は、第1演出種類選択手段が選択した第1演出の種類と表示結果特定コマンドとにもとづいて第2演出の種類を選択する(例えば、ステップS912の処理)ように構成されていてもよい。 The command output means is determined in advance as a special condition specifying command at each of the time when the first effect type selecting means selects the first effect type and the second effect type selecting means selecting the second effect type. A display result specifying command (for example, an effect symbol designating command) that can specify a display result of variable display of identification information based on the determination result of the means is output (for example, processing in steps S826 and S912), and first effect type selecting means Selects the type of the first effect based on the display result specifying command (for example, the process of step S826), and the second effect type selecting means displays the type and the display of the first effect selected by the first effect type selecting means. The type of the second effect may be selected based on the result specifying command (for example, the process of step S912).
コマンド出力手段は、特別条件特定コマンドとして、識別情報の可変表示が行われるときに、演出表示装置の表示画面における背景部を特別遊技状態または非特別遊技状態に対応する態様にすることを指定する背景指定コマンドを出力する背景指定コマンド出力手段(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560において、ステップS107の処理を実行する部分)を含み、第1演出種類選択手段と第2演出種類選択手段の少なくとも一方は、背景指定コマンドにもとづいて演出の種類を選択する(図72に示すステップS936Bの処理や、図73に示すステップS912Aの処理)ように構成されていてもよい。 The command output means designates that the background portion on the display screen of the effect display device is in a mode corresponding to the special gaming state or the non-special gaming state when the identification information is variably displayed as the special condition specifying command. It includes a background designation command output means for outputting a background designation command (for example, a part for executing the processing of step S107 in the game control microcomputer 560), and at least one of the first effect type selection means and the second effect type selection means. May be configured to select the type of effect based on the background designation command (the process in step S936B shown in FIG. 72 or the process in step S912A shown in FIG. 73).
請求項1記載の発明では、遊技機が、第1演出および該第1演出とは異なる第2演出を、それぞれ、複数種類のうちから選択する演出選択手段と、前記演出選択手段が選択した第1演出を識別情報の可変表示中に前記演出表示装置において実行し、前記演出選択手段が選択した第2演出を当該識別情報の可変表示が終了した後に移行される特定遊技状態中に前記演出表示装置において実行する演出実行手段とを備え、前記演出選択手段は、前記事前決定手段が前記特別条件を成立させることに決定したときには、表示結果を特定表示結果とするとともに前記特別条件を成立させないことに決定したときに比べて、第1演出として特定第1演出を選択した場合に高い割合で第2演出として特定第2演出を選択し、第1演出として所定第1演出を選択した場合に高い割合で第2演出として所定第2演出を選択するように構成されているので、確変状態に移行することの報知が第1演出と第2演出との組み合わせで実現され、特別遊技状態に移行することの報知演出の演出態様に変化が付いて遊技の興趣をより高めることができる効果がある。 In the first aspect of the present invention, the gaming machine selects a first effect and a second effect different from the first effect from among a plurality of types , respectively, and an effect selection unit selected by the effect selection unit. The effect display device executes one effect during the variable display of the identification information, and the effect display is performed during the specific game state to which the second effect selected by the effect selection means is transferred after the variable information is displayed. And an effect executing means that executes in the apparatus, and the effect selecting means sets the display result as the specific display result and does not satisfy the special condition when the pre-decision means determines to establish the special condition. When the specific first effect is selected as the first effect, the specific second effect is selected as the second effect at a high rate, and the predetermined first effect is selected as the first effect. Since the second effect at a high rate when-option is configured to select a predetermined second effect, the notification of moving to probability variation state is realized by the combination of the first effect and the second effect, a special There is an effect that the entertainment aspect of the game can be further enhanced by changing the effect mode of the notification effect of transitioning to the gaming state.
演出実行手段が、識別情報の可変表示が行われているときに第1演出を実行し、当該第1演出を実行した後の当該識別情報の可変表示中において第2演出を実行し、演出選択手段が、事前決定手段が識別情報の可変表示の表示結果を特定表示結果とすることに決定したときと特定表示結果としないことに決定したときとで、複数種類のうちの少なくとも一の第1演出の選択割合を異ならせるように構成されている場合には、実行される第1演出の種類を、特別遊技状態に移行する期待度の高低に加えて、演出表示装置に特定表示結果が導出表示される期待度の高低に対応させることができる。また、第1演出と第2演出の特定の組み合わせによって特別条件が成立することの期待度を高くしつつ、表示結果が特定表示結果になる期待度を低くするといった種々の演出を実行することができ、遊技の興趣をさらに向上させることができる。 Starring out executing means executes a first effect when the variable display of the identification information is being performed, perform a second effect on the variable display in the the identification information after performing the first effect, effect When the selection means decides that the display result of the variable display of the identification information is the specific display result, and when the selection means decides not to use the specific display result, at least one of the plurality of types is selected. In the case where the selection ratio of one effect is made different, the specific display result is displayed on the effect display device in addition to the level of expectation to shift to the special gaming state as the type of the first effect to be executed. It is possible to correspond to the degree of expectation that is derived and displayed. In addition, various effects such as lowering the expectation that the display result becomes the specific display result while increasing the expectation that the special condition is satisfied by a specific combination of the first effect and the second effect may be executed. And can further enhance the fun of the game.
演出実行手段が、特定遊技状態中において第1演出を実行し、当該第1演出を実行した後の当該特定遊技状態中において第2演出を実行するように構成されている場合には、特別遊技状態に移行することの報知が特定遊技状態において実行される第1演出と第2演出との組み合わせで実現され、特別遊技状態に移行することの報知演出の演出態様に変化が付いて遊技の興趣をより高めることができる。 Starring out executing means executes a first effect in a particular game state, if it is configured to perform a second effect in the in the specific game state after executing the first effect is a special Notification of the transition to the gaming state is realized by a combination of the first effect and the second effect executed in the specific gaming state, and the effect mode of the notification effect of transitioning to the special gaming state is changed, and the game It can enhance the interest.
演出実行手段が、特定遊技状態の終了後に第1演出を実行し、当該第1演出を実行した後の当該特定遊技状態の終了後において第2演出を実行するように構成されている場合には、特別遊技状態に移行することの報知が特定遊技状態後において実行される第1演出と第2演出との組み合わせで実現され、特別遊技状態に移行することの報知演出の演出態様に変化が付いて遊技の興趣をより高めることができる。 If Starring out executing means executes a first effect after completion of the specific gaming state, it is configured to perform a second effect after completion of the specific game state after executing the first effect Is realized by a combination of the first effect and the second effect that are executed after the specific game state, and the effect state of the notification effect that changes to the special game state is changed. Along with this, it is possible to further enhance the interest of the game.
演出選択手段が、第1演出の種類を選択する第1演出種類選択手段と、第1演出種類選択手段が選択した第1演出の種類と、特別条件が成立するか否かとにもとづいて第2演出の種類を選択する第2演出選択手段とを含むように構成されている場合には、選択された第1演出の種類に応じた第2演出の種類を柔軟に選択することができる。例えば、第1演出の種類と特別条件が成立することの期待度との間に相関があるようにした場合に、期待度が低い第1演出に対して、特別条件が成立することの期待度が高い第1演出と第2演出の組み合わせになるように第2演出の種類を選択することによって、第1演出の実行中では期待度は低いが第2の演出の実行が開始されると期待度が高くなるといった演出を実行することができる。 Starring output selection means, first based on the first effect type selecting means and the type of the first effect of the first effect type selecting means has selected, and whether special condition is met for selecting the type of the first effect In the case of including the second effect selecting means for selecting the type of the second effect, the type of the second effect corresponding to the selected type of the first effect can be flexibly selected. For example, when there is a correlation between the type of the first effect and the expectation that the special condition will be established, the expectation that the special condition will be established for the first effect with a low expectation By selecting the type of the second effect so that the combination of the first effect and the second effect is high, the expectation is low while the first effect is being executed, but the second effect is expected to start. It is possible to execute an effect such as increasing the degree.
演出選択手段が、第1演出種類選択手段が選択した第1演出の種類を特定可能なデータを演出種類記憶手段に設定する第1演出種類保存手段を含み、第2演出選択手段が、演出種類記憶手段に設定されているデータにもとづいて第2演出の種類を選択するように構成されている場合には、選択された第1演出の種類に応じた第2演出の種類を柔軟に選択することができる。 Starring output selection means includes a first effect type storage means for setting to the effect type memory means capable of identifying data of the first rendition of the selected type is first effect type selecting means, the second effect selecting means, effect if on the basis of the data set in the type storage unit is configured to select the type of the second effect is flexibly select the type of second effect corresponding to the type of the first effect that is selected can do.
演出制御手段における第1演出種類選択手段が、特別条件特定コマンドにもとづいて第1演出の種類を選択し、演出制御手段における第2演出種類選択手段が、第1演出種類選択手段が選択した第1演出の種類と特別条件特定コマンドとにもとづいて第2演出を選択するように構成されている場合には、遊技制御手段の昇格演出に関する処理負担を軽減できる。 Starring output control means first directing type selection means in selects the first effect of the kind based on the special condition specifying command, the second effect type selecting means in the performance control unit, the first effect type selecting means selects if it is configured to select the second effect based on the and special conditions specific command type of the first effect can reduce the processing load related to the promotion effect of the game controller.
コマンド出力手段が、特別条件特定コマンドとして、第1演出種類選択手段が第1演出の種類を選択する時期と第2演出種類選択手段が第2演出の種類を選択する時期のそれぞれにおいて、事前決定手段の決定結果にもとづく識別情報の可変表示の表示結果を特定可能な表示結果特定コマンドを出力し、第1演出種類選択手段が、表示結果特定コマンドにもとづいて第1演出の種類を選択し、第2演出種類選択手段が、第1演出種類選択手段が選択した第1演出の種類と表示結果特定コマンドとにもとづいて第2演出の種類を選択するように構成されている場合には、演出選択手段は、最初に遊技制御手段から出力された表示結果特定コマンドを保存しておく必要はなく、演出制御手段の処理が簡略化される。また、最初に遊技制御手段から出力された表示結果特定コマンドが受信されなかったような場合でも、第2演出の種類を選択する時期に出力された表示結果特定コマンドにもとづいて第2演出を開始することができるようになる。 Is command output means, as a special condition specifying command, at each time when the first effect type selecting means when and second effect type selecting means for selecting the type of the first effect to select the type of the second effect, pre A display result specifying command capable of specifying the display result of the variable display of the identification information based on the determination result of the determining means is output, and the first effect type selecting means selects the type of the first effect based on the display result specifying command. , when the second effect type selecting means is configured to select the first effect of the type and display result specific commands and type of the second effect based on the first effect type selecting means has selected, The effect selection means does not need to store the display result specifying command output from the game control means first, and the processing of the effect control means is simplified. Even when the display result specifying command output from the game control means is not received first, the second effect is started based on the display result specifying command output at the time of selecting the type of the second effect. Will be able to.
コマンド出力手段が、特別条件特定コマンドとして、識別情報の可変表示が行われるときに、演出表示装置の表示画面における背景部を特別遊技状態または非特別遊技状態に対応する態様にすることを指定する背景指定コマンドを出力する背景指定コマンド出力手段を含み、第1演出種類選択手段と第2演出種類選択手段の少なくとも一方は、背景指定コマンドにもとづいて演出の種類を選択するように構成されている場合には、遊技制御手段から出力されるコマンドの種類を増やすことなく、第1演出と第2演出とによる上記の効果を得ることができる。また、特定遊技状態終了後に第2演出が実行され、次の識別情報の可変表示開始後に第2演出の種類を選択するように構成されている場合には、表示結果特定コマンドにもとづいて第2演出の種類を選択する場合に比べて選択制御が容易になる。表示結果特定コマンドにもとづいて第2演出の種類を選択する場合には、特定遊技状態が開始される前の可変表示に関わる表示結果特定コマンドにもとづいて第2演出の種類を選択すべきであるから、次の識別情報の可変表示に関わる表示結果特定コマンドにもとづいて第2演出の種類を選択しないようにする制御が必要になるからである。 Is command output means, as a special condition specifying command, specify when the variable display of the identification information is, to the manner in which the corresponding background portion of the display screen of the effect display device in a special game state or a non-special game state Background designation command output means for outputting a background designation command to be performed, and at least one of the first effect type selection means and the second effect type selection means is configured to select an effect type based on the background designation command. If there is , the above-described effects of the first effect and the second effect can be obtained without increasing the types of commands output from the game control means. Further, when the second effect is executed after the end of the specific gaming state and the type of the second effect is selected after the start of variable display of the next identification information, the second effect is based on the display result specifying command. Selection control is easier than when selecting the type of effect. When the type of the second effect is selected based on the display result specifying command, the type of the second effect should be selected based on the display result specifying command related to the variable display before the specific game state is started. This is because it is necessary to control not to select the type of the second effect based on the display result specifying command related to the variable display of the next identification information.
実施の形態1.
以下、本発明の実施形態を図面を参照して説明する。
まず、遊技機の一例であるパチンコ遊技機の全体の構成について説明する。図1はパチンコ遊技機を正面からみた正面図である。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
First, the overall configuration of a pachinko gaming machine that is an example of a gaming machine will be described. FIG. 1 is a front view of a pachinko gaming machine as viewed from the front.
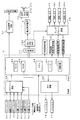
パチンコ遊技機1は、縦長の方形状に形成された外枠(図示せず)と、外枠の内側に開閉可能に取り付けられた遊技枠とで構成される。また、パチンコ遊技機1は、遊技枠に開閉可能に設けられている額縁状に形成されたガラス扉枠2を有する。遊技枠は、外枠に対して開閉自在に設置される前面枠(図示せず)と、機構部品等が取り付けられる機構板と、それらに取り付けられる種々の部品(後述する遊技盤を除く。)とを含む構造体である。
The
図1に示すように、パチンコ遊技機1は、額縁状に形成されたガラス扉枠2を有する。ガラス扉枠2の下部表面には打球供給皿(上皿)3がある。打球供給皿3の下部には、打球供給皿3に収容しきれない遊技球を貯留する余剰球受皿4と遊技球を発射する打球操作ハンドル(操作ノブ)5が設けられている。ガラス扉枠2の背面には、遊技盤6が着脱可能に取り付けられている。なお、遊技盤6は、それを構成する板状体と、その板状体に取り付けられた種々の部品とを含む構造体である。また、遊技盤6の前面には遊技領域7が形成されている。
As shown in FIG. 1, the
遊技領域7の中央付近には、複数種類の演出用の飾り図柄を可変表示する可変表示装置としての演出表示装置(画像表示装置)9が設けられている。演出表示装置9には、例えば「左」、「中」、「右」の3つの装飾用(演出用)の図柄を可変表示する図柄表示エリア9Aがある。演出表示装置9は、特別図柄表示器8による特別図柄の可変表示期間中に、装飾用(演出用)の図柄としての飾り図柄の可変表示を行う。飾り図柄の可変表示を行う演出表示装置9は、演出制御基板に搭載されている演出制御用マイクロコンピュータによって制御される。なお、図柄表示エリア9Aの位置は、演出表示装置9の表示画面において固定的でなくてもよいし、「左」、「中」、「右」の3つ領域が離れてもよい。
In the vicinity of the center of the
演出表示装置9の上部には、識別情報としての特別図柄を可変表示する特別図柄表示器(特別図柄表示装置)8が設けられている。この実施の形態では、特別図柄表示器8は、例えば0〜9の数字を可変表示可能な簡易で小型の表示器(例えば7セグメントLED)で実現されている。特別図柄表示器8は、遊技者に特定の停止図柄を把握しづらくさせるために、0〜99など、より多種類の数字を可変表示するように構成されていてもよい。また、演出表示装置9は、特別図柄表示器8による特別図柄の可変表示期間中に、飾り図柄の可変表示を行う。
A special symbol display (special symbol display device) 8 that variably displays a special symbol as identification information is provided on the top of the
演出表示装置9の下部には、始動入賞口13に入った有効入賞球数すなわち保留記憶(始動記憶または始動入賞記憶ともいう。)数を表示する4つの表示器からなる特別図柄保留記憶表示器18が設けられている。有効始動入賞がある毎に、1つの表示器の表示色を変化させる。そして、特別図柄表示器8の可変表示が開始される毎に、1つの表示器の表示色をもとに戻す。なお、演出表示装置9の表示領域内に、保留記憶数を表示する4つの表示領域からなる特別図柄保留記憶表示領域を設けるようにしてもよい。また、この実施の形態では、保留記憶数の上限値を4とするが、上限値をより大きい値にしてもよい。さらに、上限値を、遊技状態に応じて変更可能であるようにしてもよい。
At the bottom of the
演出表示装置9の下方には、始動入賞口13を形成する可変入賞球装置15が設けられている。可変入賞球装置15は、ソレノイド16によって開放状態とされ、開放状態になると、始動入賞口13への遊技球の入賞が容易になる。始動入賞口13に入賞した遊技球は、遊技盤6の背面に導かれ、始動口スイッチ13aによって検出される。
Below the
可変入賞球装置15の下部には、特別可変入賞球装置20が設けられている。特別可変入賞球装置20は開閉板を備え、特定遊技状態(大当り状態)においてソレノイド21によって開閉板が開放状態に制御されることによって入賞領域となる大入賞口が開放状態になる。大入賞口に入賞した入賞球はカウントスイッチ23で検出される。
A special variable winning
ゲート32に遊技球が入賞しゲートスイッチ32aで検出されると、普通図柄表示器10の表示の可変表示が開始される。この実施の形態では、左右のランプ(点灯時に図柄が視認可能になる)が交互に点灯することによって可変表示が行われ、例えば、可変表示の終了時に右側のランプが点灯すれば当りになる。そして、普通図柄表示器10における停止図柄が所定の図柄(当り図柄)である場合に、可変入賞球装置15が所定回数、所定時間だけ開放状態になる。普通図柄表示器10の近傍には、ゲート32に入った入賞球数を表示する4つのLEDによる表示部を有する普通図柄始動記憶表示器41が設けられている。ゲート32への入賞がある毎に、普通図柄始動記憶表示器41は点灯するLEDを1増やす。そして、普通図柄表示器10の可変表示が開始される毎に、点灯するLEDを1減らす。
When a game ball wins the
遊技盤6には、複数の入賞口(普通入賞口)29,30,33,39が設けられ、遊技球の入賞口29,30,33,39への入賞は、それぞれ入賞口スイッチ29a,30a,33a,39aによって検出される。各入賞口29,30,33,39は、遊技媒体を受け入れて入賞を許容する領域として遊技盤6に設けられる入賞領域を構成している。なお、始動入賞口13や大入賞口も、遊技媒体を受け入れて入賞を許容する入賞領域を構成する。また、それぞれの入賞口29,30,33,39に入賞した遊技球を1つのスイッチで検出するようにしてもよい。
The
遊技領域7の左右周辺には、遊技中に点滅表示される装飾LED25が設けられ、下部には、入賞しなかった遊技球を吸収するアウト口26がある。また、遊技領域7の外側の左右上部には、効果音を発する2つのスピーカ27が設けられている。遊技領域7の外周には、天枠LED28a、左枠LED28bおよび右枠LED28cが設けられている。さらに、遊技領域7における各構造物(演出表示装置9等)の周囲には装飾LEDが設置されている。天枠LED28a、左枠LED28b、右枠LED28cおよび装飾用LEDは、遊技機に設けられている装飾発光体の一例である。
A
打球発射装置から発射された遊技球は、打球レールを通って遊技領域7に入り、その後、遊技領域7を下りてくる。遊技球が始動入賞口13に入り始動口スイッチ13aで検出されると、図柄の可変表示を開始できる状態であれば、特別図柄表示器8において特別図柄が可変表示(変動)を始めるとともに、演出表示装置9において飾り図柄が可変表示(変動)を始める。図柄の可変表示を開始できる状態でなければ、始動入賞記憶数を1増やす。
The game balls launched from the hit ball launching device enter the
特別図柄表示器8における特別図柄の可変表示、および演出表示装置9における飾り図柄の可変表示は、所定時間が経過したときに停止する。停止時の特別図柄(停止図柄)が大当り図柄(特定表示結果:例えば「0」〜「9」のうちの「7」の図柄)であると、大当り遊技状態に移行する。すなわち、特別可変入賞球装置20が、所定時間(例えば、29秒)が経過するまで、または、所定個数(例えば10個)の遊技球が入賞するまで開放する。
The variable display of the special symbol on the
遊技球がゲート32に入賞すると、普通図柄表示器10において普通図柄(例えば、「○」および「×」)が可変表示される状態になる。また、普通図柄表示器10における停止図柄が所定の図柄(当り図柄:例えば「○」)である場合に、可変入賞球装置15が所定時間だけ開放状態になる。さらに、確変状態では、普通図柄表示器10における停止図柄が当り図柄になる確率が高められるとともに、可変入賞球装置15の開放時間と開放回数が高められる。また、時短状態(特別図柄の可変表示時間が短縮される遊技状態)において、可変入賞球装置15の開放時間と開放回数が高められるようにしてもよい。
When the game ball wins the
そして、この例では、左枠LED28bの近傍に、賞球払出中に点灯する賞球LED51が設けられ、右枠LED28cの近傍に、補給球が切れたときに点灯する球切れLED52が設けられている。上記のように、この実施の形態のパチンコ遊技機1には、発光体が各所に設けられている。さらに、プリペイドカードが挿入されることによって球貸しを可能にするプリペイドカードユニット(以下、単に「カードユニット」ともいう。)が、パチンコ遊技機1に隣接して設置される(図示せず)。
In this example, a prize ball LED 51 that is lit during award ball payout is provided in the vicinity of the
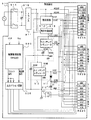
図2は、主基板(遊技制御基板)31における回路構成の一例を示すブロック図である。なお、図2は、払出制御基板37および演出制御基板80等も示されている。主基板31には、プログラムに従ってパチンコ遊技機1を制御する遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ(遊技制御手段に相当)560が搭載されている。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ゲーム制御(遊技進行制御)用のプログラム等を記憶するROM54、ワークメモリとして使用される記憶手段としてのRAM55、プログラムに従って制御動作を行うCPU56およびI/Oポート部57を含む。この実施の形態では、ROM54およびRAM55は遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に内蔵されている。すなわち、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、1チップマイクロコンピュータである。1チップマイクロコンピュータには、少なくともCPU56のほかRAM55が内蔵されていればよく、ROM54は外付けであっても内蔵されていてもよい。また、I/Oポート部57は、外付けであってもよい。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560には、さらに、ハードウェア乱数(ハードウェア回路が発生する乱数)を発生する乱数回路503が内蔵されている。
FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing an example of the circuit configuration of the main board (game control board) 31. FIG. 2 also shows a payout control board 37, an
なお、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560においてCPU56がROM54に格納されているプログラムに従って制御を実行するので、以下、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(またはCPU56)が実行する(または、処理を行う)ということは、具体的には、CPU56がプログラムに従って制御を実行することである。このことは、主基板31以外の他の基板に搭載されているマイクロコンピュータについても同様である。
In the
乱数回路503は、特別図柄の可変表示の表示結果により大当りとするか否か判定するための判定用の乱数を発生するために用いられるハードウェア回路である。乱数回路503は、初期値(例えば、0)と上限値(例えば、65535)とが設定された数値範囲内で、数値データを、設定された更新規則に従って更新し、ランダムなタイミングで発生する始動入賞時が数値データの読出(抽出)時であることにもとづいて、読出される数値データが乱数値となる乱数発生機能を有する。
The
乱数回路503は、数値データの更新範囲の選択設定機能(初期値の選択設定機能、および、上限値の選択設定機能)、数値データの更新規則の選択設定機能、および数値データの更新規則の選択切換え機能等の各種の機能を有する。このような機能によって、生成する乱数のランダム性を向上させることができる。
The
また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、乱数回路503が更新する数値データの初期値を設定する機能を有している。例えば、ROM54等の所定の記憶領域に記憶された遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のIDナンバ(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560の各製品ごとに異なる数値で付与されたIDナンバ)を用いて所定の演算を行なって得られた数値データを、乱数回路503が更新する数値データの初期値として設定する。そのような処理を行うことによって、乱数回路503が発生する乱数のランダム性をより向上させることができる。
Further, the
また、ゲートスイッチ32a、始動口スイッチ13a、カウントスイッチ23、入賞口スイッチ29a,30a,33a,39aからの検出信号を遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に与える入力ドライバ回路58も主基板31に搭載されている。また、可変入賞球装置15を開閉するソレノイド16、および大入賞口を形成する特別可変入賞球装置20を開閉するソレノイド21を遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560からの指令に従って駆動する出力回路59も主基板31に搭載されている。
Further, an input driver circuit 58 for supplying detection signals from the
また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、特別図柄を可変表示する特別図柄表示器8、普通図柄を可変表示する普通図柄表示器10、特別図柄保留記憶表示器18および普通図柄保留記憶表示器41の表示制御を行う。
In addition, the
なお、大当り遊技状態の発生を示す大当り情報等の情報出力信号をホールコンピュータ等の外部装置に対して出力する情報出力回路(図示せず)も主基板31に搭載されている。 An information output circuit (not shown) that outputs an information output signal such as jackpot information indicating the occurrence of a jackpot gaming state to an external device such as a hall computer is also mounted on the main board 31.
この実施の形態では、演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御手段(演出制御用マイクロコンピュータで構成される。)が、中継基板77を介して遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560からの演出制御コマンドを受信し、飾り図柄を可変表示する演出表示装置9の表示制御を行う。
In this embodiment, the effect control means (configured by the effect control microcomputer) mounted on the
また、演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御手段が、ランプドライバ基板35を介して、遊技盤に設けられている装飾LED25の表示制御を行うとともに、枠側に設けられている天枠LED28a、左枠LED28b、右枠LED28c、賞球ランプ51および球切れランプ52の表示制御を行うとともに、音声出力基板70を介してスピーカ27からの音出力の制御を行う。
Further, the effect control means mounted on the
図3は、中継基板77、演出制御基板80、ランプドライバ基板35および音声出力基板70の回路構成例を示すブロック図である。なお、図3に示す例では、ランプドライバ基板35および音声出力基板70には、マイクロコンピュータは搭載されていないが、マイクロコンピュータを搭載してもよい。また、ランプドライバ基板35および音声出力基板70を設けずに、演出制御に関して演出制御基板80のみを設けてもよい。
FIG. 3 is a block diagram illustrating a circuit configuration example of the
演出制御基板80は、演出制御用CPU101、および演出図柄プロセスフラグ等の演出に関する情報を記憶するRAM112を含む演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100を搭載している。なお、RAM112は外付けであってもよい。演出制御基板80において、演出制御用CPU101は、内蔵または外付けのROM111に格納されたプログラムに従って動作し、中継基板77を介して入力される主基板31からの取込信号(演出制御INT信号)に応じて、入力ドライバ102および入力ポート103を介して演出制御コマンドを受信する。また、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御コマンドにもとづいて、VDP(ビデオディスプレイプロセッサ)109に演出表示装置9の表示制御を行わせる。
The
この実施の形態では、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100と共動して演出表示装置9の表示制御を行うVDP109が演出制御基板80に搭載されている。VDP109は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100とは独立したアドレス空間を有し、そこにVRAMをマッピングする。VRAMは、画像データを展開するためのバッファメモリである。そして、VDP109は、VRAM内の画像データをフレームメモリを介して演出表示装置9に出力する。
In this embodiment, a
演出制御用CPU101は、受信した演出制御コマンドに従ってCGROM(図示せず)から必要なデータを読み出すための指令をVDP109に出力する。CGROMは、演出表示装置9に表示されるキャラクタ画像データや動画像データ、具体的には、人物、文字、図形や記号等(飾り図柄を含む)、および背景画像のデータをあらかじめ格納しておくためのROMである。VDP109は、演出制御用CPU101の指令に応じて、CGROMから画像データを読み出す。そして、VDP109は、読み出した画像データにもとづいて表示制御を実行する。
The
演出制御コマンドおよび演出制御INT信号は、演出制御基板80において、まず、入力ドライバ102に入力する。入力ドライバ102は、中継基板77から入力された信号を演出制御基板80の内部に向かう方向にしか通過させない(演出制御基板80の内部から中継基板77への方向には信号を通過させない)信号方向規制手段としての単方向性回路でもある。
The effect control command and the effect control INT signal are first input to the
中継基板77には、主基板31から入力された信号を演出制御基板80に向かう方向にしか通過させない(演出制御基板80から中継基板77への方向には信号を通過させない)信号方向規制手段としての単方向性回路74が搭載されている。単方向性回路として、例えばダイオードやトランジスタが使用される。図3には、ダイオードが例示されている。また、単方向性回路は、各信号毎に設けられる。さらに、単方向性回路である出力ポート571を介して主基板31から演出制御コマンドおよび演出制御INT信号が出力されるので、中継基板77から主基板31の内部に向かう信号が規制される。すなわち、中継基板77からの信号は主基板31の内部(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560側)に入り込まない。なお、出力ポート571は、図2に示されたI/Oポート部57の一部である。また、出力ポート571の外側(中継基板77側)に、さらに、単方向性回路である信号ドライバ回路が設けられていてもよい。
As a signal direction regulating means, the signal inputted from the main board 31 is allowed to pass through the
さらに、演出制御用CPU101は、出力ポート105を介してランプドライバ基板35に対してLEDを駆動する信号を出力する。また、演出制御用CPU101は、出力ポート104を介して音声出力基板70に対して音番号データを出力する。
Further, the
ランプドライバ基板35において、LEDを駆動する信号は、入力ドライバ351を介してLEDドライバ352に入力される。LEDドライバ352は、LEDを駆動する信号にもとづいて天枠LED28a、左枠LED28b、右枠LED28cなどの枠側に設けられている各LEDに電流を供給する。また、枠側に設けられている装飾LED25に電流を供給する。
In the
音声出力基板70において、音番号データは、入力ドライバ702を介して音声合成用IC703に入力される。音声合成用IC703は、音番号データに応じた音声や効果音を発生し増幅回路705に出力する。増幅回路705は、音声合成用IC703の出力レベルを、ボリューム706で設定されている音量に応じたレベルに増幅した音声信号をスピーカ27に出力する。音声データROM704には、音番号データに応じた制御データが格納されている。音番号データに応じた制御データは、所定期間(例えば飾り図柄の変動期間)における効果音または音声の出力態様を時系列的に示すデータの集まりである。
In the
次に、電源基板910の構成を図4のブロック図を参照して説明する。電源基板910には、遊技機内の各電気部品制御基板や機構部品への電力供給を許可したり遮断したりするための電源スイッチ914が設けられている。なお、電源スイッチ914は、遊技機において、電源基板910の外に設けられていてもよい。電源スイッチ914が閉状態(オン状態)では、交流電源(AC24V)がトランス911の入力側(一次側)に印加される。トランス911は、交流電源(AC24V)と電源基板910の内部とを電気的に絶縁するためのものであるが、その出力電圧もAC24Vである。また、トランス911の入力側には、過電圧保護回路としてのバリスタ918が設置されている。
Next, the configuration of the
電源基板910は、電気部品制御基板(主基板31、払出制御基板37および演出制御基板80等)と独立して設置され、遊技機内の各基板および機構部品が使用する電圧を生成する。この例では、AC24V、VSL(DC+30V)、VLP(DC+24V)、VDD(DC+12V)およびVCC(DC+5V)を生成する。また、バックアップ電源(VBB)すなわちバックアップRAMに記憶内容を保持させるための記憶保持手段となるコンデンサ916は、DC+5V(VCC)すなわち各基板上のIC等を駆動する電源のラインから充電される。また、+5Vラインとバックアップ+5V(VBB)ラインとの間に、逆流防止用のダイオード917が挿入される。なお、VSLは、整流平滑回路915において、整流素子でAC24Vを整流昇圧することによって生成される。VSLは、ソレノイド駆動電源になる。また、VLPは、ランプ点灯用の電圧であって、整流回路912において、整流素子でAC24Vを整流することによって生成される。
The
電源電圧生成手段としてのDC−DCコンバータ913は、1つまたは複数のスイッチングレギュレータ(図4では2つのレギュレータIC924A,924Bを示す。)を有し、VSLにもとづいてVDDおよびVCCを生成する。レギュレータIC(スイッチングレギュレータ)924A,924Bの入力側には、比較的大容量のコンデンサ923A,923Bが接続されている。従って、外部からの遊技機に対する電力供給が停止したときに、VSL、VDD、VCC等の直流電圧は、比較的緩やかに低下する。
The DC-
図4に示すように、トランス911から出力されたAC24Vは、そのままコネクタ922Bに供給される。また、VLPは、コネクタ922Cに供給される。VCC、VDDおよびVSLは、コネクタ922A,922B,922Cに供給される。
As shown in FIG. 4, AC24V output from the transformer 911 is supplied to the
コネクタ922Aに接続されるケーブルは、主基板31に接続される。また、コネクタ922Bに接続されるケーブルは、払出制御基板37に接続される。従って、コネクタ922Aには、VBBも供給されている。例えば、コネクタ922Cに接続されるケーブルは、ランプドライバ基板35に接続される。なお、演出制御基板80には、ランプドライバ基板35を経由して各電圧が供給される。
The cable connected to the
また、電源基板910には、押しボタン構造のクリアスイッチ921が搭載されている。クリアスイッチ921が押下されるとローレベル(オン状態)のクリア信号が出力され、コネクタ922Aを介して主基板31に出力される。また、クリアスイッチ921が押下されていなければハイレベル(オフ状態)の信号が出力される。なお、クリアスイッチ921は、押しボタン構造以外の他の構成であってもよい。また、クリアスイッチ921は、遊技機において、電源基板910以外に設けられていてもよい。
In addition, a
さらに、電源基板910には、電気部品制御基板に搭載されているマイクロコンピュータに対するリセット信号を作成するとともに、電源断信号を出力する電源監視回路920と、電源監視回路920からのリセット信号を増幅してコネクタ922A,922B,922Cに出力するとともに、電源断信号を増幅してコネクタ922Bに出力する出力ドライバ回路925が搭載されている。なお、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータに対するリセット信号は、ランプドライバ基板35を経由して演出制御基板80に伝達される。また、リセット回路をそれぞれの電気部品制御基板に搭載した場合に、リセット信号をハイレベルにすることになる電圧値を異ならせるようにしてもよい(例えば、主基板31における場合を最も高くして、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に対するリセット信号がハイレベルになるタイミングを最も遅くする。)。
Further, the
電源監視回路920からの電源断信号すなわち電源監視手段からの検出信号は、主基板31に搭載されている入力ポートを介して遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に入力される。すなわち、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、入力ポートの入力信号を監視することによって遊技機への電力供給の停止の発生を確認することができる。
A power-off signal from the
次に、遊技機の動作について説明する。図5は、主基板31における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が実行するメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。遊技機に対して電源が投入され電力供給が開始されると、リセット信号が入力されるリセット端子の入力レベルがハイレベルになり、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(具体的には、CPU56)は、プログラムの内容が正当か否か確認するための処理であるセキュリティチェック処理を実行した後、ステップS1以降のメイン処理を開始する。メイン処理において、CPU56は、まず、必要な初期設定を行う。
Next, the operation of the gaming machine will be described. FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing main processing executed by the
初期設定処理において、CPU56は、まず、割込禁止に設定する(ステップS1)。次に、割込モードを割込モード2に設定し(ステップS2)、スタックポインタにスタックポインタ指定アドレスを設定する(ステップS3)。そして、内蔵デバイスの初期化(内蔵デバイス(内蔵周辺回路)であるCTC(カウンタ/タイマ)およびPIO(パラレル入出力ポート)の初期化など)を行った後(ステップS4)、RAM55をアクセス可能状態に設定する(ステップS5)。なお、割込モード2は、CPU56が内蔵する特定レジスタ(Iレジスタ)の値(1バイト)と内蔵デバイスが出力する割込ベクタ(1バイト:最下位ビット0)とから合成されるアドレスが、割込番地を示すモードである。
In the initial setting process, the CPU 56 first sets the interrupt prohibition (step S1). Next, the interrupt mode is set to interrupt mode 2 (step S2), and a stack pointer designation address is set to the stack pointer (step S3). Then, after initialization of the built-in device (CTC (counter / timer) and PIO (parallel input / output port) which are built-in devices (built-in peripheral circuits)) is performed (step S4), the
次いで、CPU56は、入力ポートを介して入力されるクリアスイッチ(例えば、電源基板に搭載されている。)の出力信号の状態を確認する(ステップS6)。その確認においてオンを検出した場合には、CPU56は、通常の初期化処理を実行する(ステップS10〜S15)。 Next, the CPU 56 checks the state of the output signal of the clear switch (for example, mounted on the power supply board) input via the input port (step S6). When the on-state is detected in the confirmation, the CPU 56 executes normal initialization processing (steps S10 to S15).
クリアスイッチがオンの状態でない場合には、遊技機への電力供給が停止したときにバックアップRAM領域のデータ保護処理(例えばパリティデータの付加等の電力供給停止時処理)が行われたか否か確認する(ステップS7)。そのような保護処理が行われていないことを確認したら、CPU56は初期化処理を実行する。バックアップRAM領域にバックアップデータがあるか否かは、例えば、電力供給停止時処理においてバックアップRAM領域に設定されるバックアップフラグの状態によって確認される。 If the clear switch is not on, check whether data protection processing of the backup RAM area (for example, power supply stop processing such as addition of parity data) was performed when power supply to the gaming machine was stopped (Step S7). When it is confirmed that such protection processing is not performed, the CPU 56 executes initialization processing. Whether there is backup data in the backup RAM area is confirmed, for example, by the state of the backup flag set in the backup RAM area in the power supply stop process.
電力供給停止時処理が行われたことを確認したら、CPU56は、バックアップRAM領域のデータチェックを行う(ステップS8)。この実施の形態では、データチェックとしてパリティチェックを行う。よって、ステップS8では、算出したチェックサムと、電力供給停止時処理で同一の処理によって算出され保存されているチェックサムとを比較する。不測の停電等の電力供給停止が生じた後に復旧した場合には、バックアップRAM領域のデータは保存されているはずであるから、チェック結果(比較結果)は正常(一致)になる。チェック結果が正常でないということは、バックアップRAM領域のデータが、電力供給停止時のデータとは異なっていることを意味する。そのような場合には、内部状態を電力供給停止時の状態に戻すことができないので、電力供給の停止からの復旧時でない電源投入時に実行される初期化処理を実行する。 When it is confirmed that the power supply stop process has been performed, the CPU 56 performs data check of the backup RAM area (step S8). In this embodiment, a parity check is performed as a data check. Therefore, in step S8, the calculated checksum is compared with the checksum calculated and stored by the same process in the power supply stop process. When the power supply is stopped after an unexpected power failure or the like, the data in the backup RAM area should be saved, so the check result (comparison result) is normal (matched). That the check result is not normal means that the data in the backup RAM area is different from the data when the power supply is stopped. In such a case, since the internal state cannot be returned to the state when the power supply is stopped, an initialization process that is executed when the power is turned on is not performed when the power supply is stopped.
チェック結果が正常であれば、CPU56は、遊技制御手段の内部状態と演出制御手段等の電気部品制御手段の制御状態を電力供給停止時の状態に戻すための遊技状態復旧処理(ステップS41〜S44の処理)を行う。具体的には、ROM54に格納されているバックアップ時設定テーブルの先頭アドレスをポインタに設定し(ステップS41)、バックアップ時設定テーブルの内容を順次作業領域(RAM55内の領域)に設定する(ステップS42)。作業領域はバックアップ電源によって電源バックアップされている。バックアップ時設定テーブルには、作業領域のうち初期化してもよい領域についての初期化データが設定されている。ステップS41およびS42の処理によって、作業領域のうち初期化してはならない部分については、保存されていた内容がそのまま残る。初期化してはならない部分とは、例えば、電力供給停止前の遊技状態を示すデータ(特別図柄プロセスフラグ、確変フラグ、時短フラグなど)、出力ポートの出力状態が保存されている領域(出力ポートバッファ)、未払出賞球数を示すデータが設定されている部分などである。
If the check result is normal, the CPU 56 restores the game state recovery process (steps S41 to S44) for returning the internal state of the game control means and the control state of the electrical component control means such as the effect control means to the state when the power supply is stopped. Process). Specifically, the start address of the backup setting table stored in the
また、CPU56は、電力供給復旧時の初期化コマンドとしての停電復旧指定コマンドを演出制御基板80に送信する(ステップS43)。さらに、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の停止図柄を特定可能な演出図柄指定コマンドを演出制御基板80に送信する(ステップS44)。なお、送信する演出図柄指定コマンドは、バックアップRAM領域に保存されていた演出図柄指定コマンド(電力供給が停止する前において最後に送信した演出図柄指定コマンド)を示すデータにもとづく演出図柄指定コマンドである。また、CPU56は、背景指定コマンドも送信する。そして、ステップS14に移行する。 Further, the CPU 56 transmits a power failure recovery designation command as an initialization command at the time of power supply recovery to the effect control board 80 (step S43). Furthermore, an effect designating command capable of specifying a stop symbol of the effect design (decorative design) is transmitted to the effect control board 80 (step S44). The effect symbol designation command to be transmitted is an effect symbol designation command based on data indicating the effect symbol designation command (the effect symbol designation command transmitted last before the power supply is stopped) stored in the backup RAM area. . The CPU 56 also transmits a background designation command. Then, the process proceeds to step S14.
なお、この実施の形態では、バックアップフラグとチェックデータとの双方を用いてバックアップRAM領域のデータが保存されているか否か確認しているが、いずれか一方のみを用いてもよい。すなわち、バックアップフラグとチェックデータとのいずれかを、遊技状態復旧処理を実行するための契機としてもよい。 In this embodiment, it is confirmed whether the data in the backup RAM area is stored using both the backup flag and the check data. However, only one of them may be used. That is, either the backup flag or the check data may be used as an opportunity for executing the game state restoration process.
初期化処理では、CPU56は、まず、RAMクリア処理を行う(ステップS10)。なお、RAMクリア処理によって、所定のデータ(例えば大当り判定用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値のデータ)は0に初期化されるが、任意の値またはあらかじめ決められている値に初期化するようにしてもよい。また、RAM55の全領域を初期化せず、所定のデータ(例えば大当り判定用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値のデータ)をそのままにしてもよい。また、ROM54に格納されている初期化時設定テーブルの先頭アドレスをポインタに設定し(ステップS11)、初期化時設定テーブルの内容を順次RAM55における作業領域に設定する(ステップS12)。
In the initialization process, the CPU 56 first performs a RAM clear process (step S10). The RAM clear process initializes predetermined data (for example, count value data of a counter for generating a big hit determination random number) to 0, but is initialized to an arbitrary value or a predetermined value. You may make it do. Alternatively, the entire area of the
ステップS11およびS12の処理によって、特別図柄プロセスフラグなど制御状態に応じて選択的に処理を行うためのフラグに初期値が設定される。 By the processing in steps S11 and S12, an initial value is set to a flag for selectively performing processing according to the control state, such as a special symbol process flag.
また、CPU56は、サブ基板(主基板31以外のマイクロコンピュータが搭載された基板。)を初期化するための初期化指定コマンド(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が初期化処理を実行したことを示すコマンドでもある。)を演出制御基板80に送信する(ステップS13)。例えば、演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、初期化指定コマンドを受信すると、演出表示装置9において、遊技機の制御の初期化がなされたことを報知するための画面表示、すなわち初期化報知を行う。なお、初期化処理において、CPU56は、客待ちデモンストレーション指定(デモ指定)コマンドおよび背景指定コマンドも送信する。
Further, the CPU 56 initializes a sub board (a board on which a microcomputer other than the main board 31 is mounted) (a command indicating that the
また、CPU56は、乱数回路503を初期設定する乱数回路設定処理を実行する(ステップS14)。CPU56は、例えば、乱数回路設定プログラムに従って処理を実行することによって、乱数回路503にランダムRの値を更新させるための設定を行う。
Further, the CPU 56 executes a random number circuit setting process for initial setting of the random number circuit 503 (step S14). For example, the CPU 56 performs setting according to the random number circuit setting program to cause the
そして、CPU56は、所定時間(例えば2ms)毎に定期的にタイマ割込がかかるように遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に内蔵されているCTCのレジスタの設定を行なう(ステップS15)。すなわち、初期値として例えば2msに相当する値が所定のレジスタ(時間定数レジスタ)に設定される。この実施の形態では、2ms毎に定期的にタイマ割込がかかるとする。
Then, the CPU 56 sets a CTC register built in the
初期化処理の実行(ステップS10〜S15)が完了すると、CPU56は、メイン処理で、表示用乱数更新処理(ステップS17)および初期値用乱数更新処理(ステップS18)を繰り返し実行する。表示用乱数更新処理および初期値用乱数更新処理を実行するときには割込禁止状態に設定し(ステップS16)、表示用乱数更新処理および初期値用乱数更新処理の実行が終了すると割込許可状態に設定する(ステップS19)。この実施の形態では、表示用乱数とは、変動パターン等を決定するための乱数であり、表示用乱数更新処理とは、表示用乱数を発生するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する処理である。また、初期値用乱数更新処理とは、初期値用乱数を発生するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する処理である。この実施の形態では、初期値用乱数とは、普通図柄の当りとするか否か決定するための乱数を発生するためのカウンタ(普通図柄当り判定用乱数発生カウンタ)等のカウント値の初期値を決定するための乱数である。後述する遊技の進行を制御する遊技制御処理(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が、遊技機に設けられている可変表示装置、可変入賞球装置、球払出装置等の遊技用の装置を、自身で制御する処理、または他のマイクロコンピュータに制御させるために指令信号を送信する処理、遊技装置制御処理ともいう)において、大当り判定用乱数発生カウンタ等のカウント値が1周(乱数の取りうる値の最小値から最大値までの間の数値の個数分歩進したこと)すると、そのカウンタに初期値が設定される。
When the execution of the initialization process (steps S10 to S15) is completed, the CPU 56 repeatedly executes the display random number update process (step S17) and the initial value random number update process (step S18) in the main process. When executing the display random number update process and the initial value random number update process, the interrupt disabled state is set (step S16). When the display random number update process and the initial value random number update process are finished, the interrupt enabled state is set. Set (step S19). In this embodiment, the display random number is a random number for determining a variation pattern or the like, and the display random number update process is a process for updating the count value of the counter for generating the display random number. . The initial value random number update process is a process for updating the count value of the counter for generating the initial value random number. In this embodiment, the initial value random number is an initial value of a count value such as a counter for generating a random number for determining whether or not to hit a normal symbol (normal symbol determination random number generation counter). It is a random number for determining. A game control process for controlling the progress of the game, which will be described later (the
タイマ割込が発生すると、CPU56は、図6に示すステップS20〜S34のタイマ割込処理を実行する。タイマ割込処理において、まず、電源断信号が出力されたか否か(オン状態になったか否か)を検出する電源断検出処理を実行する(ステップS20)。電源断信号は、例えば電源基板に搭載されている電源監視回路920が、遊技機に供給される電源の電圧の低下を検出した場合に出力する。そして、電源断検出処理において、CPU56は、電源断信号が出力されたことを検出したら、必要なデータをバックアップRAM領域に保存するための電力供給停止時処理を実行する。次いで、入力ドライバ回路58を介して、ゲートスイッチ32a、始動口スイッチ13a、カウントスイッチ23、および入賞口スイッチ29a,30a,33a,39aの検出信号を入力し、それらの状態判定を行う(スイッチ処理:ステップS21)。
When the timer interrupt occurs, the CPU 56 executes the timer interrupt process in steps S20 to S34 shown in FIG. In the timer interrupt process, first, a power-off detection process for detecting whether or not a power-off signal is output (whether or not an on-state is turned on) is executed (step S20). The power-off signal is output, for example, when the
次に、CPU56は、特別図柄表示器8、普通図柄表示器10、特別図柄保留記憶表示器18、普通図柄保留記憶表示器41の表示制御を行う表示制御処理を実行する(ステップS22)。特別図柄表示器8および普通図柄表示器10については、ステップS32,S33で設定される出力バッファの内容に応じて各表示器に対して駆動信号を出力する制御を実行する。
Next, the CPU 56 executes display control processing for performing display control of the
また、遊技制御に用いられる普通当り図柄決定用の乱数等の各判定用乱数を生成するための各カウンタのカウント値を更新する処理を行う(判定用乱数更新処理:ステップS23)。CPU56は、さらに、初期値用乱数および表示用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する処理を行う(初期値用乱数更新処理,表示用乱数更新処理:ステップS24,S25)。 Further, a process of updating the count value of each counter for generating each random number for determination such as a random number for determining a normal winning symbol used for game control is performed (determination random number update process: step S23). The CPU 56 further performs a process of updating the count value of the counter for generating the initial value random number and the display random number (initial value random number update process, display random number update process: steps S24 and S25).
図7は、各乱数を示す説明図である。各乱数を示す説明図である。各乱数は、以下のように使用される。
(1)ランダム1:特別図柄のはずれ図柄を決定する(はずれ図柄判定用)
(2)ランダム2:特別図柄の大当り図柄を決定する(大当り図柄判定用)
(3)ランダム3:リーチとするか否か決定する(リーチ決定用)
(4)ランダム4:大当り図柄および飾り図柄の変動パターン(変動時間)を決定する(変動パターン決定用)
(5)ランダム5:普通図柄にもとづく当りを発生させるか否か決定する(普通図柄当り判定用)
(6)ランダム6:昇格演出における第1演出を実行するか否か決定する(演出実行決定用)
(7)ランダム7:ランダム5の初期値を決定する(ランダム5初期値決定用)
FIG. 7 is an explanatory diagram showing each random number. It is explanatory drawing which shows each random number. Each random number is used as follows.
(1) Random 1: Determine a special symbol's off symbol (for off symbol determination)
(2) Random 2: Determine the special symbol jackpot symbol (for jackpot symbol determination)
(3) Random 3: Determine whether or not to reach (for reach determination)
(4) Random 4: Determines the variation pattern (variation time) of the jackpot symbol and the decorative symbol (for variation pattern determination)
(5) Random 5: Determines whether or not to generate a hit based on a normal symbol (for normal symbol hit determination)
(6) Random 6: Decide whether or not to execute the first effect in the promotion effect (for effect execution determination)
(7) Random 7: Determine the initial value of random 5 (for determining the random 5 initial value)
図6に示された遊技制御処理におけるステップS23では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、(2)の大当り図柄決定用乱数、および(5)の普通図柄当り判定用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウントアップ(1加算)を行う。すなわち、それらが判定用乱数であり、それら以外の乱数が表示用乱数または初期値用乱数である。なお、遊技効果を高めるために、上記(1)〜(7)の乱数以外の乱数も用いるようにしてもよい。また、この実施の形態では、大当り判定用乱数は遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に内蔵されたハードウェア(乱数回路503)が生成する乱数であるが、大当り判定用乱数として、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560によってプログラムにもとづいて生成されるソフトウェア乱数を用いてもよい。
In step S23 in the game control process shown in FIG. 6, the
さらに、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセス処理を行う(ステップS26)。特別図柄プロセス処理では、特別図柄表示器8および大入賞口を所定の順序で制御するための特別図柄プロセスフラグに従って該当する処理を実行する。CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を、遊技状態に応じて更新する。
Further, the CPU 56 performs special symbol process processing (step S26). In the special symbol process, the corresponding symbol is executed in accordance with a special symbol process flag for controlling the
次いで、普通図柄プロセス処理を行う(ステップS27)。普通図柄プロセス処理では、CPU56は、普通図柄表示器10の表示状態を所定の順序で制御するための普通図柄プロセスフラグに従って該当する処理を実行する。CPU56は、普通図柄プロセスフラグの値を、遊技状態に応じて更新する。
Next, normal symbol process processing is performed (step S27). In the normal symbol process, the CPU 56 executes the corresponding process according to the normal symbol process flag for controlling the display state of the
また、CPU56は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に演出制御コマンドを送出する処理を行う(演出制御コマンド制御処理:ステップS28)。 Further, the CPU 56 performs a process of sending an effect control command to the effect control microcomputer 100 (effect control command control process: step S28).
さらに、CPU56は、例えばホール管理用コンピュータに供給される大当り情報、始動情報、確率変動情報などのデータを出力する情報出力処理を行う(ステップS29)。 Further, the CPU 56 performs information output processing for outputting data such as jackpot information, start information, probability variation information supplied to the hall management computer, for example (step S29).
また、CPU56は、始動口スイッチ13a、カウントスイッチ23および入賞口スイッチ29a,30a,33a,39aの検出信号にもとづく賞球個数の設定などを行う賞球処理を実行する(ステップS30)。具体的には、始動口スイッチ13a、カウントスイッチ23および入賞口スイッチ29a,30a,33a,39aのいずれかがオンしたことにもとづく入賞検出に応じて、払出制御基板37に搭載されている払出制御用マイクロコンピュータに賞球個数を示す払出制御コマンド(賞球個数信号)を出力する。払出制御用マイクロコンピュータは、賞球個数を示す払出制御コマンドに応じて球払出装置97を駆動する。
Further, the CPU 56 executes prize ball processing for setting the number of prize balls based on detection signals from the
この実施の形態では、出力ポートの出力状態に対応したRAM領域(出力ポートバッファ)が設けられているのであるが、CPU56は、出力ポートの出力状態に対応したRAM領域におけるソレノイドのオン/オフに関する内容を出力ポートに出力する(ステップS31:出力処理)。 In this embodiment, a RAM area (output port buffer) corresponding to the output state of the output port is provided. However, the CPU 56 relates to on / off of the solenoid in the RAM area corresponding to the output state of the output port. The contents are output to the output port (step S31: output process).
また、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値に応じて特別図柄の演出表示を行うための特別図柄表示制御データを特別図柄表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファに設定する特別図柄表示制御処理を行う(ステップS32)。CPU56は、例えば、特別図柄プロセス処理でセットされる開始フラグがセットされると終了フラグがセットされるまで、変動速度が1コマ/0.2秒であれば、0.2秒が経過する毎に、出力バッファに設定される表示制御データの値を+1する。また、CPU56は、出力バッファに設定された表示制御データに応じて、ステップS22において駆動信号を出力することによって、特別図柄表示器8における特別図柄の可変表示を実行する。
Further, the CPU 56 performs special symbol display control processing for setting special symbol display control data for effect display of the special symbol in the output buffer for setting the special symbol display control data according to the value of the special symbol process flag ( Step S32). For example, if the variation speed is 1 frame / 0.2 seconds until the end flag is set when the start flag set in the special symbol process is set, the CPU 56, for example, every 0.2 seconds passes. Then, the value of the display control data set in the output buffer is incremented by one. Further, the CPU 56 performs variable display of the special symbol on the
さらに、CPU56は、普通図柄プロセスフラグの値に応じて普通図柄の演出表示を行うための普通図柄表示制御データを普通図柄表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファに設定する普通図柄表示制御処理を行う(ステップS33)。CPU56は、例えば、普通図柄の変動に関する開始フラグがセットされると終了フラグがセットされるまで、普通図柄の変動速度が0.2秒ごとに表示状態(「○」および「×」)を切り替えるような速度であれば、0.2秒が経過する毎に、出力バッファに設定される表示制御データの値(例えば、「○」を示す1と「×」を示す0)を切り替える。また、CPU56は、出力バッファに設定された表示制御データに応じて、ステップS22において駆動信号を出力することによって、普通図柄表示器10における普通図柄の演出表示を実行する。
Further, the CPU 56 performs a normal symbol display control process for setting normal symbol display control data for effect display of the normal symbol in the output buffer for setting the normal symbol display control data according to the value of the normal symbol process flag ( Step S33). For example, when the start flag related to the variation of the normal symbol is set, the CPU 56 switches the display state (“◯” and “×”) for the variation rate of the normal symbol every 0.2 seconds until the end flag is set. With such a speed, the value of the display control data set in the output buffer (for example, 1 indicating “◯” and 0 indicating “x”) is switched every 0.2 seconds. Further, the CPU 56 outputs a normal signal on the
その後、割込許可状態に設定し(ステップS34)、処理を終了する。 Thereafter, the interrupt permission state is set (step S34), and the process is terminated.
以上の制御によって、この実施の形態では、遊技制御処理は2ms毎に起動されることになる。なお、遊技制御処理は、タイマ割込処理におけるステップS21〜S33(ステップS29を除く。)の処理に相当する。また、この実施の形態では、タイマ割込処理で遊技制御処理が実行されているが、タイマ割込処理では例えば割込が発生したことを示すフラグのセットのみがなされ、遊技制御処理はメイン処理において実行されるようにしてもよい。 With the above control, in this embodiment, the game control process is started every 2 ms. The game control process corresponds to the processes in steps S21 to S33 (excluding step S29) in the timer interrupt process. In this embodiment, the game control process is executed by the timer interrupt process. However, in the timer interrupt process, for example, only a flag indicating that an interrupt has occurred is set, and the game control process is performed by the main process. May be executed.
図8は、大当り判定テーブルを示す説明図である。大当り判定テーブルとは、ランダムRと比較される大当り判定値が設定されているテーブルである。大当り判定テーブルには、通常状態(確変状態でない遊技状態)において用いられる通常時大当り判定テーブル(図8(A)参照)と、確変状態において用いられる確変時大当り判定テーブル(図8(B)参照)とがある。図8(A),(B)の左欄に記載されている数値が大当り判定値である。CPU56は、所定の時期に、乱数回路503のカウント値を抽出して抽出値を大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)の値とするのであるが、大当り判定用乱数値が図8に示すいずれかの大当り判定値に一致すると、特別図柄に関して大当り(確変大当りまたは通常大当り)とすることに決定する。なお、図8に示す「確率」は、通常大当り、確変大当り、はずれになる確率(割合)を示す。また、大当りとするか否か決定するということは、大当り遊技状態に移行させるか否か決定するということであるが、特別図柄表示器8における停止図柄を大当り図柄とするか否か決定するということでもある。
FIG. 8 is an explanatory diagram showing a jackpot determination table. The jackpot determination table is a table in which a jackpot determination value to be compared with the random R is set. The jackpot determination table includes a normal jackpot determination table (see FIG. 8 (A)) used in a normal state (a gaming state that is not a probability change state) and a probability change jackpot determination table (see FIG. 8 (B)) used in a probability change state. ) The numerical values described in the left column of FIGS. 8A and 8B are jackpot determination values. The CPU 56 extracts the count value of the
また、確変大当りとは、大当り遊技後の遊技状態を、通常状態に比べて大当りとすることに決定される確率が高い状態である確変状態に移行させるような大当りである。通常大当りとは、大当り遊技後の遊技状態を確変状態ではない通常状態に移行させるような、または通常状態を維持させるような大当りである。 The probable big hit is a big hit that shifts the gaming state after the big hit game to a probable state where there is a high probability of being determined to be a big hit compared to the normal state. The normal big hit is a big hit that causes the game state after the big hit game to shift to a normal state that is not a probable change state or that maintains the normal state.
図9は、演出実行判定テーブルを示す説明図である。演出実行判定テーブルは、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560におけるROM54に格納され、CPU56が、ランダム6(演出実行決定用乱数)の値と比較する演出実行判定値が設定されている。CPU56は、抽出したランダム6が演出実行判定値のいずれかと一致すると、昇格演出における第1演出を実行することに決定する。なお、この実施の形態では、大当りとするか否か、および大当りとする場合に確変大当りとするか否かに関わらず、同じ割合で第1演出を実行することに決定されるが、大当りとするか否か、および大当りとする場合に確変大当りとするか否かに応じて、第1演出を実行する割合を変えるようにしてもよい。
FIG. 9 is an explanatory diagram of an effect execution determination table. The effect execution determination table is stored in the
図10は、特別図柄の停止図柄(最終停止図柄)と、その後に制御される遊技状態との関係の一例を示す説明図である。図10に示す例では、停止図柄が偶数の図柄である場合には、はずれとなり、奇数の図柄である場合には、大当りとなり、特別図柄の変動終了後に大当り遊技状態に移行する。なお、この実施の形態では、確変大当りと通常大当りとで特別図柄の停止図柄を分けていない。よって、遊技者は停止図柄から遊技状態の変化を把握することができない。なお、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、所定の時期に、遊技機に設けられている電気部品によって確変大当りの報知のための昇格演出を行う。よって、遊技者は昇格演出によって初めて遊技状態の変更を把握することができるので遊技の興趣が向上する。ただし、特別図柄の停止図柄を、確変大当りであるのか通常大当りであるのかを遊技者が判別することは難しい態様ではあるが区別して表示するようにしてもよい。その場合、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の停止図柄を、確変大当りであるのか通常大当りであるのか判別不能であるようにしてもよい。
FIG. 10 is an explanatory diagram illustrating an example of a relationship between a special symbol stop symbol (final stop symbol) and a gaming state controlled thereafter. In the example shown in FIG. 10, when the stop symbol is an even symbol, the game is out of the game. When the stop symbol is an odd symbol, it is a big hit, and after the end of the change of the special symbol, the game shifts to the big hit game state. In this embodiment, the special symbol stop symbol is not divided into the probability variation big hit and the normal big hit. Therefore, the player cannot grasp the change of the gaming state from the stop symbol. The
図11は、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の停止図柄(最終停止図柄)の一例を示す説明図である。図11に示す例では、大当りの場合には、左中右の演出図柄の停止図柄として図柄が揃った組み合わせ(一致した図柄の組み合わせ)が演出表示装置9に停止表示され、大当りとはしないがリーチする場合には、左中右の演出図柄の停止図柄として左右図柄のみが揃った組み合わせが演出表示装置9に停止表示される。はずれとする場合であってリーチにもしないときには、左中右の演出図柄の停止図柄として左右図柄が一致しない組み合わせが演出表示装置9に停止表示される。演出表示装置9において可変表示および停止表示される演出図柄(飾り図柄)は、数字、アルファベット、キャラクタ状の図柄、キャラクタ状の表示物の中に数字等が表示されている図柄、その他どのような図柄であってもよい。なお、確変大当りと通常大当りとで演出図柄(飾り図柄)の停止図柄を分けていないことは、特別図柄の場合と同様である。
FIG. 11 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of the stop symbol (final stop symbol) of the effect symbol (decorative symbol). In the example shown in FIG. 11, in the case of a big hit, a combination of symbols (matched symbol combination) is stopped and displayed on the
図12は、この実施の形態で用いられる特別図柄および演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動パターン(変動時間)の一例を示す説明図である。なお、変動パターンは、特別図柄および演出図柄の変動時間等を示すものであるが、演出図柄の変動は特別図柄の変動と同期しているので、以下、単に、特別図柄の変動パターン、演出図柄の変動パターンのように表現することがある。 FIG. 12 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of the variation pattern (variation time) of the special symbol and the effect symbol (decoration symbol) used in this embodiment. The variation pattern indicates the variation time of the special symbol and the production symbol, but since the variation of the production symbol is synchronized with the variation of the special symbol, hereinafter, the variation pattern of the special symbol and the production symbol are simply described below. It may be expressed as a variation pattern.
図12に示すように、この実施の形態では、変動パターン#1(変動時間22秒)、変動パターン#2(変動時間22秒)、変動パターン#3(変動時間11秒)、変動パターン#4(変動時間11秒)の前半の4秒間では高速変動(表示される図柄の切り替えタイミングが短いこと)が行われる。変動開始から4秒が経過したときに、左右の演出図柄(飾り図柄)として同じ図柄が停止表示され、以後、中図柄が変動する。その間、演出表示装置9では、図柄以外のキャラクタ画像等によってリーチ演出が実行されるとともに、演出用のLED等の発光体およびスピーカ27によって、演出表示装置9における演出に同期したリーチ演出が実行される。
As shown in FIG. 12, in this embodiment, variation pattern # 1 (variation time 22 seconds), variation pattern # 2 (variation time 22 seconds), variation pattern # 3 (
また、変動パターン#2および変動パターン#4では、リーチ演出の期間において、第1演出のみ、または第1演出および第2演出が実行される。なお、この実施の形態では、高速変動の期間では第1演出や第2演出が実行されないが、第1演出や第2演出を高速変動の期間において開始してもよい。
In the
変動パターン#5は、4秒間の高速変動のみが実行される変動パターンである。変動開始から4秒が経過したときに、左中右の演出図柄(飾り図柄)が停止表示される。変動パターン#5は、停止図柄を大当り図柄にしないことに決定されているときに用いられる。
The
変動パターン#6は、2秒間の高速変動のみが実行される変動パターンである。変動開始から2秒が経過したときに、左中右の演出図柄(飾り図柄)が停止表示される。変動パターン#6は、遊技状態が時短状態であるときの変動パターンとして用いられる。
The
図13は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が送信する演出制御コマンドの内容の一例を示す説明図である。図13に示す例において、コマンド8001(H)〜8006(H)は、特別図柄の可変表示に対応して演出表示装置9において可変表示される演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動パターンを指定する演出制御コマンド(変動パターンコマンド)である(それぞれ変動パターン#1〜#6に対応)。なお、「(H)」は16進数であることを示す。また、変動パターンを指定する演出制御コマンドは、変動開始を指定するためのコマンドでもある。従って、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、コマンド8001(H)〜8006(H)のいずれかを受信すると、演出表示装置9において演出図柄(飾り図柄)の可変表示を開始するように制御する。
FIG. 13 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of the contents of the effect control command transmitted by the
コマンド8C01(H)〜8C03(H)は、大当りとするか否か、および大当り遊技の種類を示す演出制御コマンドである。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、コマンド8C01(H)〜8C03(H)の受信に応じて演出図柄(飾り図柄)の表示結果を決定するので、コマンド8C01(H)〜8C03(H)を演出図柄指定コマンドまたは表示結果特定コマンドという。ただし、上述したように、この実施の形態では、通常大当りとする場合と確変大当りとする場合とで演出図柄(飾り図柄)の表示結果を区別しない。
The commands 8C01 (H) to 8C03 (H) are effect control commands indicating whether or not to make a big hit and the type of the big hit game. The
コマンド8F00(H)は、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の可変表示(変動)を終了して表示結果(停止図柄)を導出表示することを示す演出制御コマンド(図柄確定指定コマンド)である。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、図柄確定指定コマンドを受信すると、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の可変表示(変動)を終了して表示結果を導出表示する。
Command 8F00 (H) is an effect control command (symbol confirmation designation command) indicating that the variable display (fluctuation) of the effect symbol (decoration symbol) is terminated and the display result (stop symbol) is derived and displayed. When receiving the symbol confirmation designation command, the
コマンド9000(H)は、遊技機に対する電力供給が開始されたときに送信される演出制御コマンド(初期化指定コマンド:電源投入指定コマンド)である。コマンド9200(H)〜9202(H)は、遊技機に対する電力供給が再開されたときに送信される演出制御コマンド(停電復旧指定コマンド)である。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、遊技機に対する電力供給が開始されたときに、バックアップRAMにデータが保存されている場合(バックアップフラグがセットされていた場合でもよい。)には、停電復旧指定コマンドを送信し、そうでない場合には、初期化指定コマンドを送信する。
Command 9000 (H) is an effect control command (initialization designation command: power-on designation command) transmitted when power supply to the gaming machine is started. Commands 9200 (H) to 9202 (H) are production control commands (power failure recovery designation commands) transmitted when power supply to the gaming machine is resumed. When the power supply to the gaming machine is started, the
遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、電力供給が停止したときの状態に応じて異なる停電復旧指定コマンドを送信する。すなわち、図5に示されたステップS43の処理において、バックアップRAMに保存されていたデータ(例えば、特別図柄プロセスフラグ)にもとづいて特別図柄の変動中であったと判断される場合にはコマンド9201(H)の停電復旧指定コマンドを送信する。特別図柄の変動中であった場合にはコマンド9202(H)の停電復旧指定コマンドを送信する。
The
なお、停電復旧指定コマンドという名称を用いているが、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、遊技機に対して電力供給が開始されたときにバックアップRAMにデータが保存されている場合には、停電から復旧したときに限らず、停電復旧指定コマンドを送信する。
Although the name of the power failure recovery designation command is used, the
コマンド9500(H)は、遊技状態が通常状態であることを示す演出制御コマンド(通常時背景指定コマンド)である。コマンド9501(H)は、遊技状態が時短状態であることを示す演出制御コマンド(時短時背景指定コマンド)である。コマンド9502(H)は、遊技状態が確変状態であることを示す演出制御コマンド(確変時背景指定コマンド)である。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、それら背景指定コマンド(遊技状態指定コマンド)の受信に応じて、演出表示装置9の表示画面における背景を、背景指定コマンドが示す遊技状態に対応する背景にする。
Command 9500 (H) is an effect control command (normal background designation command) indicating that the gaming state is the normal state. The command 9501 (H) is an effect control command (short time background designation command) indicating that the gaming state is the short time state. Command 9502 (H) is an effect control command (probability change background designation command) indicating that the gaming state is a probability change state. In response to receiving these background designation commands (game state designation commands), the
コマンド9F00(H)は、客待ちデモンストレーションを指定する演出制御コマンド(客待ちデモ指定コマンド)である。 Command 9F00 (H) is an effect control command (customer waiting demonstration designation command) for designating a customer waiting demonstration.
コマンドA001(H)は、ファンファーレ画面を表示すること、すなわち大当り遊技の開始を指定する演出制御コマンド(大当り開始指定コマンド:ファンファーレコマンド)である。コマンドA1XX(H)は、XXで示す回数目(ラウンド)の大入賞口開放中の表示を示す演出制御コマンド(大入賞口開放中指定コマンド)である。A2XX(H)は、XXで示す回数目(ラウンド)の大入賞口閉鎖を示す演出制御コマンド(大入賞口開放後指定コマンド)である。 The command A001 (H) is an effect control command for displaying the fanfare screen, that is, designating the start of the big hit game (big hit start designation command: fanfare command). The command A1XX (H) is an effect control command (special command during opening of a big winning opening) indicating a display during the opening of the big winning opening for the number of times (round) indicated by XX. A2XX (H) is an effect control command (designation command after opening the big winning opening) indicating the closing of the big winning opening for the number of times (round) indicated by XX.
コマンドA301(H)は、大当り終了画面を表示すること、すなわち大当り遊技の終了を指定することを指定する演出制御コマンド(大当り終了指定コマンド:エンディングコマンド)である。 Command A301 (H) is an effect control command (a jackpot end designation command: an ending command) that designates displaying a jackpot end screen, that is, designating the end of the jackpot game.
図14および図15は、演出制御コマンドの送信タイミングの例を示す説明図である。図14(A)に示すように、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、変動開始時に、背景指定コマンド、変動パターンコマンド、および演出図柄指定コマンド(演出図柄1指定コマンド、演出図柄2指定コマンドまたは演出図柄3指定コマンド)を送信する。そして、可変表示時間(変動時間)が経過すると、図柄確定指定コマンドを送信する。
14 and 15 are explanatory diagrams illustrating an example of the transmission timing of the effect control command. As shown in FIG. 14 (A), the
なお、この実施の形態では、第2演出の開始タイミングで、演出図柄指定コマンドを送信する。また、変動開始時には演出図柄指定コマンドを送信せず、第1演出の開始タイミングにおいて演出図柄指定コマンドを送信するようにしてもよい。 In this embodiment, an effect designating command is transmitted at the start timing of the second effect. In addition, the effect designating command may be transmitted at the start timing of the first effect without transmitting the effect designating command at the start of variation.
図14(B)には、大当り遊技における例が示されている。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、大当り遊技の開始時に、大当り開始指定コマンドを送信し、各ラウンドの開始時に大入賞口開放中指定コマンドを送信し、各ラウンドの終了時に大入賞口開放後指定コマンドを送信し、大当り遊技の終了時に、大当り終了指定コマンドを送信する。
FIG. 14B shows an example in the big hit game. The
図15(A)には、電力供給が開始されたとき(電源投入時)の例が示されている。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、電源投入指定コマンドおよび背景指定コマンドを送信した後、客待ちデモ指定コマンドを送信する。
FIG. 15A shows an example when power supply is started (when power is turned on). The
図15(B)は、電力供給が再開されたとき(停電復旧時)の例を示す。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、電源投入指定コマンド背景指定コマンドを送信した後、バックアップRAM領域に保存されていた演出図柄指定コマンド(電力供給が停止する前において最後に送信した演出図柄指定コマンド)を示すデータにもとづく演出図柄指定コマンドを送信する。
FIG. 15B shows an example when power supply is resumed (when power failure is restored). After transmitting the power-on designation command background designation command, the
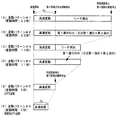
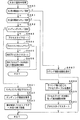
図16は、主基板31に搭載される遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(具体的には、CPU56)が実行する特別図柄プロセス処理(ステップS26)のプログラムの一例を示すフローチャートである。上述したように、特別図柄プロセス処理では特別図柄表示器8および大入賞口を制御するための処理が実行される。特別図柄プロセス処理において、CPU56は、始動入賞口13に遊技球が入賞したことを検出するための始動口スイッチ13aがオンしていたら、すなわち始動入賞が発生していたら、始動口スイッチ通過処理を実行する(ステップS311,S312)。そして、ステップS300〜S307のうちのいずれかの処理を行う。
FIG. 16 is a flowchart illustrating an example of a special symbol process (step S26) program executed by the game control microcomputer 560 (specifically, the CPU 56) mounted on the main board 31. As described above, in the special symbol process, a process for controlling the
ステップS300〜S307の処理は、以下のような処理である。 The processes in steps S300 to S307 are as follows.
特別図柄通常処理(ステップS300):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が0であるときに実行される。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、特別図柄の可変表示が開始できる状態になると、保留記憶数(始動入賞記憶数)を確認する。保留記憶数は保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値により確認できる。保留記憶数が0でない場合には、大当りとするか否か決定する。大当りとしないことに決定したときには、特別図柄表示器8の停止図柄としてはずれ図柄を決定する。大当りとすることに決定したときには、大当り図柄を決定する。そして、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS301に対応した値(この例では1)に更新する。
Special symbol normal processing (step S300): Executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is zero. When the
変動パターン設定処理(ステップS301):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が1であるときに実行される。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、変動パターンを決定し、その変動パターンにおける変動時間(可変表示時間:可変表示を開始してから表示結果が導出表示(停止表示)するまでの時間)を特別図柄の可変表示の変動時間とすることに決定する。また、第1演出を実行するか否かを決定する。そして、特別図柄の変動時間を計測する変動時間タイマをスタートさせる。その後、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS302に対応した値(この例では2)に更新する。
Fluctuation pattern setting process (step S301): This process is executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 1. The
演出図柄指定コマンド送信処理(ステップS302):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が2であるときに実行される。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に、演出図柄指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う。大当りとしないことに決定したときは、はずれを指定する演出図柄1指定コマンドを送信する。通常大当りとすることに決定したときは、通常大当りを指定する演出図柄2指定コマンドを送信する。確変大当りとすることに決定したときは、確変大当りを指定する演出図柄3指定コマンドを送信する。そして、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS303に対応した値(この例では3)に更新する。
Production symbol designation command transmission processing (step S302): This is executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 2. Control for transmitting an effect designating command to the
特別図柄変動中処理(ステップS303):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が3であるときに実行される。変動パターン設定処理で選択された変動パターンの変動時間が経過(ステップS301でセットされる変動時間タイマがタイムアウトすなわち変動時間タイマの値が0になる)すると、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS304に対応した値(この例では4)に更新する。 Special symbol changing process (step S303): This process is executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 3. When the variation time of the variation pattern selected in the variation pattern setting process elapses (the variation time timer set in step S301 times out, that is, the variation time timer value becomes 0), the internal state (special symbol process flag) is stepped. Update to a value corresponding to S304 (4 in this example).
特別図柄停止処理(ステップS304):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が4であるときに実行される。特別図柄表示器8における可変表示を停止して停止図柄を導出表示させる。また、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に、図柄確定指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う。そして、大当りフラグがセットされている場合には、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS305に対応した値(この例では5)に更新する。大当りフラグがセットされていない場合には、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS300に対応した値(この例では0)に更新する。なお、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が送信する図柄確定指定コマンドを受信すると演出表示装置9において演出図柄(飾り図柄)が停止されるように制御する。
Special symbol stop process (step S304): executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 4. The variable display on the
大入賞口開放前処理(ステップS305):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が5であるときに実行される。大入賞口開放前処理では、大入賞口を開放する制御を行う。具体的には、カウンタ(例えば大入賞口に入った遊技球数をカウントするカウンタ)などを初期化するとともに、ソレノイド21を駆動して大入賞口を開放状態にする。また、タイマによって大入賞口開放中処理の実行時間を設定し、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS306に対応した値(この例では6)に更新する。なお、大入賞口開放前処理は各ラウンド毎に実行されるが、第1ラウンドを開始する場合には、大入賞口開放前処理は大当り遊技を開始する処理でもある。
Preliminary winning opening opening process (step S305): This is executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 5. In the pre-opening process for the big prize opening, control for opening the big prize opening is performed. Specifically, a counter (for example, a counter that counts the number of game balls that have entered the big prize opening) is initialized, and the
大入賞口開放中処理(ステップS306):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が6であるときに実行される。大当り遊技状態中のラウンド表示の演出制御コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御や大入賞口の閉成条件の成立を確認する処理等を行う。大入賞口の閉成条件が成立し、かつ、まだ残りラウンドがある場合には、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS305に対応した値(この例では5)に更新する。また、全てのラウンドを終えた場合には、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS307に対応した値(この例では7)に更新する。
Large winning opening opening process (step S306): This process is executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 6. A control for transmitting a presentation control command for round display during the big hit gaming state to the
大当り終了処理(ステップS307):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が7であるときに実行される。大当り遊技状態が終了したことを遊技者に報知する表示制御を演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に行わせるための制御を行う。また、遊技状態を示すフラグ(例えば、確変フラグ)をセットする処理を行う。そして、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS300に対応した値(この例では0)に更新する。
Big hit end process (step S307): executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 7. Control is performed to cause the
図17は、ステップS312の始動口スイッチ通過処理を示すフローチャートである。始動口スイッチ通過処理において、CPU56は、保留記憶数が上限値である4になっているか否か確認する(ステップS211)。保留記憶数が4になっている場合には、処理を終了する。 FIG. 17 is a flowchart showing the start port switch passing process in step S312. In the start port switch passing process, the CPU 56 checks whether or not the reserved storage number is 4 which is the upper limit value (step S211). If the number of reserved memories is 4, the process is terminated.
保留記憶数が4になっていない場合には、保留記憶数を示す保留記憶数カウンタの値を1増やす(ステップS212)。また、CPU56は、ソフトウェア乱数(大当り図柄決定用乱数等を生成するためのカウンタの値等)およびランダムR(大当り判定用乱数)を抽出し、それらを、抽出した乱数値として保留記憶数カウンタの値に対応する保留記憶バッファにおける保存領域に格納する処理を実行する(ステップS213)。ステップS213では、CPU56は、ソフトウェア乱数としてランダム1〜4,6(図7参照)の値を抽出する。また、保留記憶バッファにおいて、保存領域は、保留記憶数の上限値と同数確保されている。また、大当り図柄決定用乱数等を生成するためのカウンタや保留記憶バッファは、RAM55に形成されている。「RAMに形成されている」とは、RAM内の領域であることを意味する。
If the number of reserved memories is not 4, the value of the reserved memory number counter indicating the number of reserved memories is incremented by 1 (step S212). Further, the CPU 56 extracts software random numbers (counter value for generating a big hit symbol determination random number, etc.) and random R (big hit determination random number), and uses them as an extracted random number value of the reserved memory number counter. A process of storing in the storage area in the storage buffer corresponding to the value is executed (step S213). In step S213, the CPU 56 extracts
図18および図19は、特別図柄プロセス処理における特別図柄通常処理(ステップS300)を示すフローチャートである。特別図柄通常処理において、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、CPU56は、保留記憶数の値を確認する(ステップS51)。具体的には、保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値を確認する。保留記憶数が0であれば処理を終了する。
18 and 19 are flowcharts showing the special symbol normal process (step S300) in the special symbol process. In the special symbol normal process, the
保留記憶数が0でなければ、CPU56は、RAM55の保留記憶数バッファにおける保留記憶数=1に対応する保存領域に格納されている各乱数値を読み出してRAM55の乱数バッファ領域に格納する(ステップS52)。そして、保留記憶数の値を1減らし(保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値を1減算し)、かつ、各保存領域の内容をシフトする(ステップS53)。すなわち、RAM55の保留記憶数バッファにおいて保留記憶数=n(n=2,3,4)に対応する保存領域に格納されている各乱数値を、保留記憶数=n−1に対応する保存領域に格納する。よって、各保留記憶数に対応するそれぞれの保存領域に格納されている各乱数値が抽出された順番は、常に、保留記憶数=1,2,3,4の順番と一致するようになっている。
If the reserved memory number is not 0, the CPU 56 reads out each random number value stored in the storage area corresponding to the reserved memory number = 1 in the reserved memory number buffer of the
そして、CPU56は、乱数バッファ領域から大当り判定用乱数を読み出し(ステップS61)、大当り判定の処理を実行する(ステップS62)。大当り判定の処理では、遊技状態が確変状態(高確率状態)の場合は、遊技状態が非確変状態(通常遊技状態および時短状態)の場合よりも、大当りとなる確率が高くなるように構成されている。具体的には、あらかじめ大当り判定値の数が多く設定されている確変時大当り判定テーブル(図8(B)参照)と、大当り判定値の数が確変大当り判定テーブルよりも少なく設定されている通常時大当り判定テーブル(図8(A)参照)とが設けられている。そして、CPU56は、遊技状態が確変状態であるか否かを確認し、遊技状態が確変状態であるときは、確変時大当り判定テーブルを使用して大当りの判定の処理を行い、遊技状態が通常遊技状態であるときは、通常時大当り判定テーブルを使用して大当りの判定の処理を行う。すなわち、CPU56は、大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)の値が図8に示すいずれかの大当り判定値に一致すると、特別図柄に関して大当り(確変大当りまたは通常大当り)とすることに決定する。 Then, the CPU 56 reads the big hit determination random number from the random number buffer area (step S61), and executes the big hit determination process (step S62). The jackpot determination process is configured such that when the gaming state is a probable change state (high probability state), the probability of a big hit is higher than when the gaming state is a non-probability change state (normal game state and short-time state). ing. Specifically, the probability change jackpot determination table (see FIG. 8 (B)) in which a large number of jackpot determination values are set in advance and the number of jackpot determination values are set to be smaller than those in the probability variation jackpot determination table. An hourly big hit determination table (see FIG. 8A) is provided. Then, the CPU 56 checks whether or not the gaming state is a probability variation state. If the gaming state is a probability variation state, the jackpot determination process is performed using the probability variation jackpot determination table, and the gaming state is normal. When in the gaming state, the big hit determination process is performed using the normal big hit determination table. That is, when the value of the big hit determination random number (random R) matches any of the big hit determination values shown in FIG. 8, the CPU 56 determines that the special symbol is a big hit (probability big hit or normal big hit).
なお、現在の遊技状態が確変状態であるか否かの確認は、確変フラグがセットされているか否かにより行われる。確変フラグは、遊技状態を確変状態に移行するときにセットされ、確変状態を終了するときにリセットされる。具体的には、確変図柄で大当りとなって、その大当り遊技を終了する処理においてセットされ、非確変図柄で大当りとなって、その大当り遊技を終了する処理においてリセットされる。 Note that whether or not the current gaming state is the probability variation state is determined by whether or not the probability variation flag is set. The probability variation flag is set when the gaming state is shifted to the probability variation state, and is reset when the probability variation state is terminated. Specifically, it is set in a process for ending a big hit game with a probable change symbol, and is set in a process for ending the big hit game with a non-probable change symbol.
大当り判定処理で大当りとすることに決定した場合には(ステップS63)、CPU56は、大当りフラグをセットする(ステップS71)。次いで、CPU56は、乱数バッファ領域から大当り図柄決定用乱数の値を読み出し(ステップS72)、大当り図柄決定用乱数の値にもとづいて停止図柄を決定する(ステップS73)。また、大当りの種別として、確変大当りにすると決定されたか否か確認し(ステップS74)、確変大当りにすると決定したときは、確変大当りフラグをセットし(ステップS75)、ステップS70に移行する。 When it is determined to be a big hit in the big hit determination process (step S63), the CPU 56 sets a big hit flag (step S71). Next, the CPU 56 reads the value of the jackpot symbol determining random number from the random number buffer area (step S72), and determines the stop symbol based on the value of the jackpot symbol determining random number (step S73). In addition, it is confirmed whether or not it is determined to be a probability variation big hit as the type of jackpot (step S74). If it is determined to be a probability variation big hit, a probability variation big hit flag is set (step S75), and the process proceeds to step S70.
大当りとしないことに決定した場合には、CPU56は、乱数バッファ領域からはずれ図柄決定用乱数の値を読み出し(ステップS64)、はずれ図柄決定用乱数の値にもとづいて停止図柄を決定する(ステップS65)。 If it is decided not to win the game, the CPU 56 reads out the value of the random symbol for determining the out-of-sequence from the random number buffer area (step S64), and determines the stop symbol based on the value of the random number for determining out-of-sequence (step S65). ).
さらに、時短状態であることを示す時短フラグがセットされている場合には(ステップS66)、時短状態における特別図柄の変動可能回数を示す時短回数カウンタの値を−1する(ステップS67)。そして、時短回数カウンタの値が0になった場合には、可変表示が終了したときに遊技状態を非時短状態に移行させるために時短終了フラグをセットする(ステップS68,S69)。そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を変動パターン設定処理(ステップS301)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS70)。 Further, when the time reduction flag indicating the time reduction state is set (step S66), the value of the time reduction counter indicating the number of possible changes of the special symbol in the time reduction state is decremented by 1 (step S67). When the value of the time reduction counter becomes 0, a time reduction end flag is set in order to shift the gaming state to the non-time reduction state when the variable display ends (steps S68 and S69). Then, the value of the special symbol process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the variation pattern setting process (step S301) (step S70).
図20は、特別図柄プロセス処理における変動パターン設定処理(ステップS301)を示すフローチャートである。変動パターン設定処理において、CPU56は、大当りフラグがセットされているか否か確認し(ステップS100)、大当りフラグがセットされていない場合には、乱数バッファ領域からリーチ判定用乱数の値を読み出し(ステップS103)、リーチ判定用乱数の値にもとづいてリーチするか否か決定する(ステップS104)。なお、ステップS103の処理では、リーチ判定用乱数の値があらかじめ定められているリーチ判定値のいずれかと一致したらリーチすることに決定する。そして、リーチするか否かを示すデータをRAM55に格納する。その後、ステップS105に移行する。
FIG. 20 is a flowchart showing the variation pattern setting process (step S301) in the special symbol process. In the variation pattern setting process, the CPU 56 checks whether or not the big hit flag is set (step S100), and if the big hit flag is not set, reads the value of the reach determination random number from the random number buffer area (step S100). S103), it is determined whether or not to reach based on the value of the reach determination random number (step S104). In the process of step S103, if the value of the reach determination random number matches any of the predetermined reach determination values, it is determined to reach. Then, data indicating whether or not to reach is stored in the
大当りフラグがセットされている場合には、乱数バッファ領域から演出実行決定用乱数の値を読み出し(ステップS101)、演出実行決定用乱数の値にもとづいて第1演出を実行するか否か決定する(ステップS105)。具体的には、演出実行決定用乱数の値が図9に示された演出実行判定値のいずれかと一致したら第1演出を実行することに決定する。そして、第1演出を実行するか否かを示すデータをRAM55に格納する。その後、ステップS105に移行する。
When the big hit flag is set, the value of the random number for effect execution determination is read from the random number buffer area (step S101), and it is determined whether or not to execute the first effect based on the value of the random number for effect execution determination. (Step S105). Specifically, when the value of the random number for effect execution determination matches one of the effect execution determination values shown in FIG. 9, it is determined to execute the first effect. Then, data indicating whether or not to execute the first effect is stored in the
なお、変動パターン設定処理においてステップS101,S102の処理を実行せず、第1演出の開始タイミングにおいてステップS101,S102の処理を実行するようにしてもよい。 Note that the processing of steps S101 and S102 may be executed at the start timing of the first effect without executing the processing of steps S101 and S102 in the variation pattern setting processing.
ステップS105では、CPU56は、乱数バッファ領域から変動パターン決定用乱数の値を読み出す。そして、変動パターン決定用乱数の値にもとづいて、使用する変動パターンを決定する(ステップS106)。 In step S105, the CPU 56 reads the value of the random number for determining the variation pattern from the random number buffer area. Then, the variation pattern to be used is determined based on the value of the variation pattern determination random number (step S106).
具体的には、大当りフラグがセットされていない場合には、リーチすることに決定されていないときには、図12に例示された変動パターン#5または変動パターン#6に決定する。リーチすることに決定されているときには、はずれ時変動パターンテーブルを用いて変動パターンを決定する。はずれ時変動パターンテーブルはROM54に記憶され、はずれ時変動パターンテーブルには、変動パターン#1〜#4のそれぞれに対応した変動パターン判定値が設定されている。CPU56は、変動パターン決定用乱数の値に一致する変動パターン判定値に対応した変動パターンを決定する。なお、はずれ時変動パターンテーブルにおいて、変動パターン#2または#4が図9に示された確率(9/179)で選択されるように、変動パターン判定値が設定されている。
Specifically, when the big hit flag is not set, when it is not determined to reach, the
また、大当りフラグがセットされている場合には、第1演出を実行することに決定されているときには、大当り時第1演出変動パターンテーブルを用いて変動パターンを決定する。大当り時第1演出変動パターンテーブルはROM54に記憶され、大当り時第1演出変動パターンテーブルには、変動パターン#2に対応した変動パターン判定値と変動パターン#4に対応した変動パターン判定値とが設定されている。CPU56は、変動パターン決定用乱数の値に一致する変動パターン判定値に対応した変動パターンを決定する。第1演出を実行することに決定されていないときには、大当り時リーチ変動パターンテーブルを用いて変動パターンを決定する。大当り時リーチ変動パターンテーブルはROM54に記憶され、大当り時リーチ変動パターンテーブルには、変動パターン#1に対応した変動パターン判定値と変動パターン#3に対応した変動パターン判定値とが設定されている。CPU56は、変動パターン決定用乱数の値に一致する変動パターン判定値に対応した変動パターンを決定する。
In addition, when the big hit flag is set, when it is decided to execute the first effect, the fluctuation pattern is determined using the first effect change pattern table at the big hit. The first effect variation pattern table for the big hit is stored in the
そして、CPU56は、遊技状態に応じた背景指定コマンド(図13参照)を演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS107)。具体的には、CPU56は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に演出制御コマンドを送信する際に、演出制御コマンドに応じたコマンド送信テーブル(あらかじめROM54にコマンド毎に設定されている)のアドレスをポインタにセットする。そして、演出制御コマンドに応じたコマンド送信テーブルのアドレスをポインタにセットして、演出制御コマンド制御処理(ステップS28)において演出制御コマンドを送信する。なお、CPU56は、遊技状態を、確変フラグや時短フラグがセットされているか否かによって判定する。すなわち、確変フラグがセットされている場合には確変状態であって、確変時背景指定コマンドを送信し、時短フラグがセットされている場合には時短状態であって、時短時背景指定コマンドを送信し、それ以外の場合には通常時背景指定コマンドを送信する。
And CPU56 performs control which transmits the background designation | designated command (refer FIG. 13) according to a game state to the
また、CPU56は、ステップS106で選択した変動パターンに応じた変動パターンコマンド(図13参照)を演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS108)。また、送信した変動パターンコマンドを示すデータをRAM55に設定(書き込むこと)する(ステップS109)。なお、第1演出を伴う変動パターンコマンドを送信した場合には、第1演出中フラグをRAM55の所定領域に設定する。すなわち、遊技制御手段におけるコマンド出力手段は、第1演出を実行することを特定可能な演出制御コマンドを出力し、遊技制御手段は、コマンド出力手段が当該演出制御コマンドを出力したときに第1演出を実行することを示すデータを記憶手段に記憶するようにしてもよい。そのような構成によれば、記憶手段に記憶されたデータにもとづいて、第2演出を実行するのか否かを直ちに判定できる。
Further, the CPU 56 performs control to transmit a variation pattern command (see FIG. 13) corresponding to the variation pattern selected in step S106 to the effect control microcomputer 100 (step S108). Further, data indicating the transmitted variation pattern command is set (written) in the RAM 55 (step S109). When a variation pattern command with the first effect is transmitted, the first effect flag is set in a predetermined area of the
この実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して、変動パターンコマンドによって第1演出を実行するか否か指定することになる。しかし、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、変動パターンコマンドとは別のコマンド(例えば、第1演出の実行を指定する演出制御コマンド)によって第1演出を実行するか否か指定するようにしてもよい。
In this embodiment, the
そして、特別図柄の変動を開始する(ステップS110)。例えば、ステップS33の特別図柄表示制御処理で参照される開始フラグをセットする。また、RAM55に形成されている変動時間タイマに、選択された変動パターンに対応した変動時間(図12参照)に応じた値を設定する(ステップS111)。その後、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄指定コマンド送信処理(ステップS302)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS112)。 Then, the variation of the special symbol is started (step S110). For example, a start flag referred to in the special symbol display control process in step S33 is set. Further, a value corresponding to the variation time (see FIG. 12) corresponding to the selected variation pattern is set in the variation time timer formed in the RAM 55 (step S111). Thereafter, the value of the special symbol process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the effect symbol designation command transmission process (step S302) (step S112).
図21は、演出図柄指定コマンド送信処理(ステップS302)を示すフローチャートである。演出図柄指定コマンド送信処理において、CPU56は、決定されている大当りの種類等に応じて、8C01(H)〜8C03(H)のいずれかの演出制御コマンド(図13参照)を送信する制御を行う。具体的には、CPU56は、まず、大当りフラグがセットされているか否か確認する(ステップS114)。セットされていない場合には、演出図柄1指定コマンド(はずれ指定コマンド)を送信する制御を行う(ステップS115)。そして、ステップS119に移行する。
FIG. 21 is a flowchart showing the effect symbol designation command transmission process (step S302). In the effect symbol designation command transmission processing, the CPU 56 performs control to transmit any effect control command (see FIG. 13) of 8C01 (H) to 8C03 (H) according to the determined type of jackpot. . Specifically, the CPU 56 first checks whether or not the big hit flag is set (step S114). If it is not set, control is performed to transmit a
大当りフラグがセットされている場合、確変大当りフラグがセットされているときには、演出図柄3指定コマンド(確変大当り指定コマンド)を演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS116,S118)。確変大当りフラグがセットされていないときには、演出図柄2指定コマンド(通常大当り指定コマンド)を演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS116,S117)。そして、ステップS119に移行する。以上のように、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、確変大当りとすることに事前決定した場合には、演出図柄3指定コマンドを送信し、それ以外の場合には、演出図柄1指定コマンドまたは演出図柄2指定コマンドを送信する。従って、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、受信した演出図柄指定コマンド(演出図柄1指定コマンド、演出図柄2指定コマンドまたは演出図柄3指定コマンド)にもとづいて、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が確変大当りとすることに事前決定したことを特定できる。
When the big hit flag is set, when the probability variation big hit flag is set, control is performed to transmit the
ステップS119では、CPU56は、ステップS115,S117,S118の処理で送信した演出図柄指定コマンドを示すデータをRAM55に設定し、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)を特別図柄変動中処理(ステップS303)に応じた値に更新する(ステップS120)。
In step S119, the CPU 56 sets the data indicating the effect symbol designation command transmitted in the processing of steps S115, S117, and S118 in the
図22は、特別図柄プロセス処理における特別図柄変動中処理(ステップS303)を示すフローチャートである。特別図柄変動中処理において、CPU56は、変動時間タイマを1減算し(ステップS121)、変動時間タイマがタイムアウトしたら(ステップS122)、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を特別図柄停止処理(ステップS304)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS123)。変動時間タイマがタイムアウトしていない場合には、変動時間タイマの値があらかじめ決められている第2演出の開始タイミングに相当する値になると、演出図柄指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う(ステップS124,S125)。なお、第2演出の開始タイミングは、第1演出が終了した後に到来する。また、ステップS125の処理で送信する演出図柄指定コマンドは、ステップS119の処理でRAM55に格納された演出図柄指定コマンドである。
FIG. 22 is a flowchart showing the special symbol changing process (step S303) in the special symbol process. In the special symbol changing process, the CPU 56 decrements the variable time timer by 1 (step S121), and when the variable time timer times out (step S122), the value of the special symbol process flag corresponds to the special symbol stop process (step S304). The updated value is updated (step S123). If the variable time timer has not timed out, control is performed to transmit an effect symbol designation command when the value of the variable time timer becomes a value corresponding to a predetermined start timing of the second effect (step S124, S125). Note that the start timing of the second effect arrives after the first effect ends. The effect symbol designation command transmitted in the process of step S125 is the effect symbol designation command stored in the
なお、この実施の形態では、変動開始時に演出図柄1指定コマンド(はずれ指定コマンド)を送信したときにも遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、第2演出の開始のタイミングにおいて再度演出図柄指定コマンドを送信するが、変動開始時に演出図柄1指定コマンド(はずれ指定コマンド)を送信した場合には第2演出は実行されないので、変動開始時に演出図柄1指定コマンド(はずれ指定コマンド)を送信したときに第2演出の開始のタイミングにおいて演出図柄指定コマンドを送信しないように構成してもよい。
In this embodiment, the
図23は、特別図柄プロセス処理における特別図柄変動停止処理(ステップS304)を示すフローチャートである。特別図柄変動停止処理において、CPU56は、特別図柄表示器8における特別図柄の変動を止めて、停止図柄を導出表示する(ステップS130)。また、CPU56は、演出表示装置9における飾り図柄の変動の停止を指定する図柄確定指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS131)。そして、大当りフラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS132)。大当りフラグがセットされていなければ、ステップS141に移行する(ステップS133)。
FIG. 23 is a flowchart showing the special symbol variation stop process (step S304) in the special symbol process. In the special symbol variation stop process, the CPU 56 stops the variation of the special symbol in the
大当りフラグがセットされている場合には、CPU56は、確変フラグをリセットし(ステップS133)、大当り開始指定コマンド(ファンファーレコマンド)を送信する制御を行う(ステップS134)。 When the big hit flag is set, the CPU 56 resets the probability variation flag (step S133), and performs control to transmit a big hit start designation command (fanfare command) (step S134).
また、大当り表示時間タイマに大当り表示時間(大当りが発生したことを例えば演出表示装置9において報知する時間)に相当する値を設定する(ステップS136)。そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を大入賞口開放前処理(ステップS305)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS137)。 Also, a value corresponding to the big hit display time (time for notifying the fact that the big hit has occurred, for example, in the effect display device 9) is set in the big hit display time timer (step S136). Then, the value of the special symbol process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the pre-winner opening pre-processing (step S305) (step S137).
ステップS141では、CPU56は、時短終了フラグがセットされているか否か確認する。時短終了フラグがセットされている場合には、時短終了フラグをリセットするとともに、時短フラグをリセットする(ステップS142,S143)。そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を特別図柄通常処理(ステップS300)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS144)。 In step S141, the CPU 56 checks whether or not the time reduction end flag is set. If the time reduction end flag is set, the time reduction end flag is reset and the time reduction flag is reset (steps S142 and S143). Then, the value of the special symbol process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the special symbol normal process (step S300) (step S144).
大入賞口開放前処理では、CPU56は、大当り表示時間タイマが設定されている場合には、大当り表示時間タイマがタイムアウトしたら、大入賞口を開放する制御を行うとともに、大入賞口開放時間タイマに開放時間(例えば、29秒)に相当する値を設定し、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を大入賞口開放中処理(ステップS306)に対応した値に更新する。なお、大当り表示時間タイマが設定されている場合とは、第1ラウンドの開始前の場合である。インターバルタイマ(ラウンド間のインターバル時間を決めるためのタイマ)が設定されている場合には、インターバルタイマがタイムアウトしたら、大入賞口を開放する制御を行うとともに、大入賞口開放時間タイマに開放時間に相当する値を設定し、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を大入賞口開放中処理(ステップS306)に対応した値に更新する。 In the big winning opening opening pre-processing, when the big hit display time timer is set, the CPU 56 controls to open the big winning opening when the big hit display time timer times out, and sets the big winning opening opening time timer. A value corresponding to the opening time (for example, 29 seconds) is set, and the value of the special symbol process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the special winning opening opening process (step S306). The case where the big hit display time timer is set is the case before the start of the first round. If an interval timer (a timer for determining the interval time between rounds) is set, when the interval timer times out, control is performed to open the grand prize opening, and the opening time is set to the big prize opening time timer. A corresponding value is set, and the value of the special symbol process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the special winning opening opening process (step S306).
大入賞口開放中処理では、CPU56は、大入賞口開放時間タイマがタイムアウトするか、または大入賞口への入賞球数が所定数(例えば10個)に達したら、最終ラウンドが終了していない場合には、大入賞口を閉鎖する制御を行うとともに、インターバルタイマにインターバル時間に相当する値を設定し、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を大入賞口開放前処理(ステップS305)に対応した値に更新する。最終ラウンドが終了した場合には、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を大当り終了処理(ステップS307)に対応した値に更新する。 In the process during opening of the big prize opening, the CPU 56 does not finish the final round when the big prize opening time timer times out or the number of winning balls to the big prize opening reaches a predetermined number (for example, 10). In this case, control for closing the special winning opening is performed, a value corresponding to the interval time is set in the interval timer, and the value of the special symbol process flag is set to a value corresponding to the pre-opening process for the special winning opening (step S305). Update. When the final round is completed, the value of the special symbol process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the jackpot end process (step S307).
図24は、特別図柄プロセス処理における大当り終了処理(ステップS307)を示すフローチャートである。大当り終了処理において、CPU56は、大当り終了表示タイマが設定されているか否か確認し(ステップS170)、大当り終了表示タイマが設定されている場合には、ステップS181に移行する。大当り終了表示タイマが設定されていない場合には、遊技状態を時短状態に移行させるために時短フラグをセットして(ステップS171)、時短回数カウンタに100を設定する(ステップS172)。 FIG. 24 is a flowchart showing the jackpot end process (step S307) in the special symbol process. In the jackpot end process, the CPU 56 checks whether or not the jackpot end display timer is set (step S170). If the jackpot end display timer is set, the process proceeds to step S181. If the big hit end display timer is not set, a time reduction flag is set to shift the gaming state to the time reduction state (step S171), and 100 is set in the time reduction counter (step S172).
また、大当りフラグをリセットし(ステップS173)、大当り終了指定コマンド(エンディングコマンド)を送信する制御を行う(ステップS174)。さらに、確変大当りフラグがセットされている場合には、確変大当りフラグをリセットするとともに(ステップS176,S177)、遊技状態を確変状態に移行させるために確変フラグをセットする(ステップS178)。そして、大当り終了表示タイマに、演出表示装置9において大当り終了表示が行われている時間(大当り終了表示時間)に対応する表示時間に相当する値を設定し(ステップS179)、処理を終了する。 Further, the big hit flag is reset (step S173), and a control for transmitting a big hit end designation command (ending command) is performed (step S174). If the probability variation jackpot flag is set, the probability variation jackpot flag is reset (steps S176 and S177), and the probability variation flag is set to shift the gaming state to the probability variation state (step S178). Then, a value corresponding to the display time corresponding to the time during which the big hit end display is performed in the effect display device 9 (big hit end display time) is set in the big hit end display timer (step S179), and the processing is ended.
ステップS181では、大当り終了表示タイマの値を1減算する。そして、CPU56は、大当り終了表示タイマの値が0になっているか否か、すなわち大当り終了表示時間が経過したか否か確認する(ステップS182)。経過していなければ処理を終了する。経過していれば、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を特別図柄通常処理(ステップS300)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS183)。 In step S181, 1 is subtracted from the value of the big hit end display timer. Then, the CPU 56 checks whether or not the value of the jackpot end display timer is 0, that is, whether or not the jackpot end display time has elapsed (step S182). If not, the process ends. If it has elapsed, the value of the special symbol process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the special symbol normal process (step S300) (step S183).
次に、演出制御手段の動作を説明する。図25は、演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御手段としての演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100(具体的には、演出制御用CPU101)が実行するメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。演出制御用CPU101は、電源が投入されると、メイン処理の実行を開始する。メイン処理では、まず、RAM領域のクリアや各種初期値の設定、また演出制御の起動間隔(例えば、2ms)を決めるためのタイマの初期設定等を行うための初期化処理を行う(ステップS701)。その後、演出制御用CPU101は、タイマ割込フラグの監視(ステップS702)を行うループ処理に移行する。タイマ割込が発生すると、演出制御用CPU101は、タイマ割込処理においてタイマ割込フラグをセットする。メイン処理において、タイマ割込フラグがセットされていたら、演出制御用CPU101は、そのフラグをクリアし(ステップS703)、以下の演出制御処理を実行する。
Next, the operation of the effect control means will be described. FIG. 25 is a flowchart showing main processing executed by the effect control microcomputer 100 (specifically, effect control CPU 101) as effect control means mounted on the
演出制御処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、まず、受信した演出制御コマンドを解析し、受信した演出制御コマンドに応じたフラグをセットする処理等を行う(コマンド解析処理:ステップS704)。次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御プロセス処理を行う(ステップS705)。演出制御プロセス処理では、制御状態に応じた各プロセスのうち、現在の制御状態(演出制御プロセスフラグ)に対応した処理を選択して演出表示装置9の表示制御を実行する。
In the effect control process, the
次いで、停止図柄決定用乱数、第1演出種類選択用乱数、第2演出種類選択用乱数等の乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する乱数更新処理を実行する(ステップS706)。その後、ステップS702に移行する。 Next, a random number update process for updating the count value of a counter for generating random numbers such as a stop symbol determination random number, a first effect type selection random number, a second effect type selection random number, or the like is executed (step S706). Thereafter, the process proceeds to step S702.
図26は、主基板31の遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から受信した演出制御コマンドを格納するためのコマンド受信バッファの一構成例を示す説明図である。この例では、2バイト構成の演出制御コマンドを6個格納可能なリングバッファ形式のコマンド受信バッファが用いられる。従って、コマンド受信バッファは、受信コマンドバッファ1〜12の12バイトの領域で構成される。そして、受信したコマンドをどの領域に格納するのかを示すコマンド受信個数カウンタが用いられる。コマンド受信個数カウンタは、0〜11の値をとる。なお、必ずしもリングバッファ形式でなくてもよい。
FIG. 26 is an explanatory diagram showing a configuration example of a command reception buffer for storing the effect control command received from the
なお、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から送信された演出制御コマンドは、演出制御INT信号にもとづく割込処理で受信され、RAM112に形成されているバッファ領域に保存されている。コマンド解析処理では、バッファ領域に保存されている演出制御コマンドがどのコマンド(図13参照)であるのか解析する。
The effect control command transmitted from the
図27は、ステップS701の初期化処理を示すフローチャートである。初期化処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100におけるRAM112の内容を初期化する(ステップS711)。次いで、ROM111に格納されている初期化時設定テーブルの先頭アドレスをポインタに設定し(ステップS712)、初期化時設定テーブルの内容を順次RAM112における作業領域に設定する(ステップS713)。ステップS712およびS713の処理によって、演出制御に必要なデータの初期値が設定されるが、特に、RAM112における第1演出キャラクタバッファ112a(図3参照)にキャラクタPを示すデータが設定され、第2演出キャラクタバッファ112b(図3参照)にキャラクタAを示すデータが設定される。次いで、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に内蔵されている回路の初期化を行う(ステップS714)。特に、所定時間(例えば2ms)毎に定期的にタイマ割込がかかるように演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に内蔵されているタイマ回路の初期設定を行なう。また、VDP109を初期化する(ステップS715)。
FIG. 27 is a flowchart showing the initialization process in step S701. In the initialization process, the
初期化処理において、第1演出キャラクタバッファ112aおよび第2演出キャラクタバッファ112bに初期値としてのデータを設定することによって、例えば、演出図柄指定コマンドが受信できなかったような場合に、第1演出キャラクタバッファ112aおよび第2演出キャラクタバッファ112bに設定されているデータにもとづいて第1演出や第2演出を実行することが可能になる。
In the initialization process, by setting data as the initial value in the first
図28および図29は、コマンド解析処理(ステップS704)の具体例を示すフローチャートである。主基板31から受信された演出制御コマンドは受信コマンドバッファに格納されるが、コマンド解析処理では、演出制御用CPU101は、コマンド受信バッファに格納されているコマンドの内容を確認する。
28 and 29 are flowcharts showing a specific example of the command analysis processing (step S704). The effect control command received from the main board 31 is stored in the reception command buffer, but in the command analysis process, the
コマンド解析処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、まず、コマンド受信バッファに受信コマンドが格納されているか否か確認する(ステップS611)。格納されているか否かは、コマンド受信個数カウンタの値と読出ポインタとを比較することによって判定される。両者が一致している場合が、受信コマンドが格納されていない場合である。コマンド受信バッファに受信コマンドが格納されている場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、コマンド受信バッファから受信コマンドを読み出す(ステップS612)。なお、読み出したら読出ポインタの値を+2しておく(ステップS613)。+2するのは2バイト(1コマンド)ずつ読み出すからである。
In the command analysis process, the
受信した演出制御コマンドが背景指定コマンドであれば(ステップS614)、演出制御用CPU101は、その背景指定コマンドを、RAM112に形成されている背景指定コマンド格納領域に格納する(ステップS615)。
If the received effect control command is a background designation command (step S614), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが変動パターンコマンドであれば(ステップS616)、演出制御用CPU101は、その変動パターンコマンドを、RAM112に形成されている変動パターンコマンド格納領域に格納する(ステップS617)。そして、変動パターンコマンド受信フラグをセットする(ステップS618)。
If the received effect control command is a variation pattern command (step S616), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが演出図柄指定コマンドであれば(ステップS619)、演出制御用CPU101は、その演出図柄指定コマンド(演出図柄1指定コマンド、演出図柄2指定コマンドまたは演出図柄3指定コマンド)を、RAM112に形成されている演出図柄指定コマンド格納領域に格納する(ステップS620)。
If the received effect control command is an effect symbol designation command (step S619), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが図柄確定指定コマンドであれば(ステップS621)、演出制御用CPU101は、確定コマンド受信フラグをセットする(ステップS622)。
If the received effect control command is a symbol confirmation designation command (step S621), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが大当り開始指定コマンド(ファンファーレコマンド)であれば(ステップS623)、演出制御用CPU101は、ファンファーレコマンド受信フラグをセットする(ステップS624)。
If the received effect control command is a jackpot start designation command (fanfare command) (step S623), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが電源投入指定コマンド(初期化指定コマンド)であれば(ステップS631)、演出制御用CPU101は、初期化処理が実行されたことを示す初期画面を演出表示装置9に表示する制御を行う(ステップS632)。初期画面には、あらかじめ決められている演出図柄の初期表示が含まれる。
If the received effect control command is a power-on specification command (initialization specification command) (step S631), the
また、受信した演出制御コマンドが停電復旧指定コマンドであれば(ステップS633)、あらかじめ決められている停電復旧画面(遊技状態が継続していることを遊技者に報知する情報を表示する画面)を表示する制御を行い(ステップS634)、受信した停電復旧指定コマンドをRAM112に形成されている停電復旧指定コマンド格納領域に格納する(ステップS635)。 If the received effect control command is a power failure recovery designation command (step S633), a predetermined power failure recovery screen (screen for displaying information notifying the player that the gaming state is continuing) is displayed. Display control is performed (step S634), and the received power failure recovery designation command is stored in the power failure recovery designation command storage area formed in the RAM 112 (step S635).
また、受信した停電復旧指定コマンドが変動中であったことを指定するコマンド(9201(H):図13参照)であった場合には、演出図柄プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動開始処理に対応した値に設定する(ステップS636,S637)。また、受信した停電復旧指定コマンドが大当り遊技中であったことを指定するコマンド(9202(H):図13参照)であった場合には、演出図柄プロセスフラグの値を大当り遊技中処理に対応した値に設定する(ステップS638,S639)。 Further, when the received power failure recovery designation command is a command for designating that it is fluctuating (9201 (H): see FIG. 13), the value of the production symbol process flag corresponds to the production symbol variation start process. The set value is set (steps S636 and S637). Also, if the received power failure recovery designation command is a command designating that a big hit game is being played (9202 (H): see FIG. 13), the value of the production symbol process flag corresponds to the big hit game process. The set value is set (steps S638 and S639).
また、受信した演出制御コマンドが大当り終了指定コマンド(エンディングコマンド)であれば(ステップS645)、演出制御用CPU101は、エンディングコマンド受信フラグをセットする(ステップS646)。
If the received effect control command is a jackpot end designation command (ending command) (step S645), the
演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100におけるRAM112は電源バックアップされていない。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560におけるRAM55は電源バックアップされ、停電等からの復旧時に、RAM55の記憶内容が停電等が生ずる前の状態に保存されていたときには、RAM55に保存されていた遊技状態を示すデータ(例えば、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値)に応じた種類の停電復旧指定コマンドを送信する(図5におけるステップS43参照)。そして、ステップS636〜S639の処理によって、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100の制御状態も、停電等が生ずる前の状態に復旧される。
The
次に、昇格演出(第1演出および第2演出)を説明する。図30は、第1演出の種類の選択に関する説明図である。図31は、第2演出の種類の選択に関する説明図であって、第1演出の種類のそれぞれ、および第1演出の種類と第2演出の種類の組み合わせの期待度を示す説明図である。図32は、第1演出の種類および第2演出の種類を示す説明図である。 Next, the promotion effects (first effect and second effect) will be described. FIG. 30 is an explanatory diagram regarding selection of the type of the first effect. FIG. 31 is an explanatory diagram regarding the selection of the type of the second effect, and is an explanatory diagram showing the expectation of each type of the first effect and the combination of the type of the first effect and the type of the second effect. FIG. 32 is an explanatory diagram showing the type of the first effect and the type of the second effect.
図30は、具体的には、第1演出種類選択用乱数の値と比較される判定値であって第1演出の種類のそれぞれに応じた判定値を示す説明図である。この実施の形態では、第1演出の種類として、キャラクタP〜Qのそれぞれを使用する4種類がある。ただし、図30には、具体的な判定値ではなく、判定値の個数が示されている。判定値は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100のROM111にテーブルとして設定されている。テーブルは、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が決定した結果(事前決定手段の決定結果)に応じて設けられている。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560における事前決定手段が決定した結果を、受信した演出図柄指定コマンド(識別情報の可変表示の表示結果を特定可能なコマンドの一例)で判定することができる。
Specifically, FIG. 30 is an explanatory diagram showing determination values that are compared with the value of the first effect type selection random number and that correspond to the first effect type. In this embodiment, there are four types that use each of the characters P to Q as the types of first effects. However, FIG. 30 shows the number of determination values, not specific determination values. The determination values are set as a table in the
図30に示す例では、はずれとすることに決定されている場合には、大当りとすることに決定されている場合に比べて、キャラクタR(鮫)が高い割合で選択され、キャラクタQ(鶏)およびキャラクタS(蟹)が選択される割合は低い。また、大当りとすることに決定されている場合に、確変大当りとすることに決定されているときには、通常大当りとすることに決定されているときに比べて、キャラクタS(蟹)が選択される割合が高い。すなわち、キャラクタP〜Qのそれぞれは、大当りの期待度と確変昇格の期待度との双方に応じて選択される。換言すれば、キャラクタP〜Qのそれぞれは、大当りの期待度と確変昇格の期待度との双方を示す。 In the example shown in FIG. 30, when it is determined to be out of play, the character R (選 択) is selected at a higher rate than when it is determined to be a big hit, and the character Q (chicken) ) And the character S (蟹) are selected at a low rate. In addition, when it is determined to be a big hit, when it is determined to be a probable big hit, the character S (蟹) is selected compared to when it is normally determined to be a big hit. The ratio is high. That is, each of the characters P to Q is selected according to both the degree of expectation of jackpot and the degree of expectation of probability variation promotion. In other words, each of the characters P to Q shows both the jackpot expectation and the probability variation promotion expectation.
図31は、具体的には、第2演出種類選択用乱数の値と比較される判定値であって第2演出の種類のそれぞれに応じた判定値を示す説明図である。この実施の形態では、第2演出の種類として、キャラクタA〜Cのそれぞれを使用する3種類がある。ただし、図31には、具体的な判定値ではなく、判定値の個数が示されている。判定値は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100のROM111にテーブルとして設定されている。また、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、通常大当りに決定されている場合には、図31(A)に例示するテーブルを使用し、確変大当りに決定されている場合には、図31(B)に例示するテーブルを使用する。
Specifically, FIG. 31 is an explanatory diagram showing determination values that are compared with the value of the second effect type selection random number and that correspond to each of the second effect types. In this embodiment, there are three types of characters that are used for the characters A to C as the types of second effects. However, FIG. 31 shows the number of determination values, not specific determination values. The determination values are set as a table in the
キャラクタA〜Cのそれぞれに対する判定値の割り当ては、第1演出の種類に応じて異なる。つまり、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、第1演出の種類と事前決定手段の決定結果(確変大当りとするか通常大当りとするか)とにもとづいて第2演出の種類を決定する。
The determination value is assigned to each of the characters A to C in accordance with the type of the first effect. In other words, the
また、例えば、キャラクタQとキャラクタAの組み合わせやキャラクタRとキャラクタCの組み合わせは、通常大当りに決定されている場合には選択されない。換言すれば、確変大当りとすることに決定されている場合には、キャラクタQとキャラクタAの組み合わせやキャラクタRとキャラクタCの組み合わせが高い割合(この例では、100%)で選択される。 Further, for example, the combination of character Q and character A and the combination of character R and character C are not selected when the jackpot is normally determined. In other words, when it is determined to be a probable big hit, the combination of the character Q and the character A or the combination of the character R and the character C is selected at a high rate (100% in this example).
図32(A)には、図8に示す大当り確率、図9に示す第1演出実行確率、および図30に示す判定値数の割合にもとづく第1演出の種類の大当り信頼度が示されている。つまり、キャラクタP〜Sのそれぞれを用いた第1演出が実行されたときに大当りとなる割合が示されている。図32(A)に示すように、キャラクタQ,Sの大当り信頼度は、キャラクタP,Rの大当り信頼度よりも高い。換言すれば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、大当りとする(識別情報の可変表示の表示結果を特定表示結果とすることに対応)ことに決定されているときと大当りとしないことに決定されているときとで、複数種類の各々の第1演出の選択割合を異ならせるのであるが、大当りとすることに決定されているときには、キャラクタP,RよりもキャラクタQ,Sを高い割合で選択する。
FIG. 32A shows the jackpot reliability of the type of first effect based on the jackpot probability shown in FIG. 8, the first effect execution probability shown in FIG. 9, and the ratio of the number of determination values shown in FIG. Yes. That is, the ratio that is a big hit when the first effect using each of the characters P to S is executed is shown. As shown in FIG. 32A, the jackpot reliability of the characters Q and S is higher than the jackpot reliability of the characters P and R. In other words, the
図32(B)には、図8に示す大当り確率、図9に示す第1演出実行確率、および図30に示す判定値数の割合にもとづく第1演出の種類の昇格信頼度が示されている。つまり、キャラクタP〜Sのそれぞれを用いた第1演出が実行されたときに確変大当りとなる割合が示されている。図32(B)に示すように、キャラクタR,Sの昇格信頼度は、キャラクタP,Qの大当り信頼度よりも高い。換言すれば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、確変大当りとすることに決定されているときと通常大当りとすることに決定されているときとで、複数種類の各々の第1演出の選択割合を異ならせるのであるが、確変大当りとすることに決定されているときには、キャラクタP,QよりもキャラクタR,Sを高い割合で選択する。なお、確変大当りとなる割合は、昇格演出(具体的には第2演出)において、確変大当りの報知がなされる割合(昇格成功の割合)に相当する。また、昇格演出において確変大当りの報知がなされないことを、昇格失敗ということがある。
FIG. 32B shows the promotion reliability of the type of the first effect based on the jackpot probability shown in FIG. 8, the first effect execution probability shown in FIG. 9, and the ratio of the number of determination values shown in FIG. Yes. That is, the ratio of the probability variation big hit when the first effect using each of the characters P to S is executed is shown. As shown in FIG. 32B, the promotion reliability of the characters R and S is higher than the big hit reliability of the characters P and Q. In other words, the
図32(C)には、図8に示す大当り確率、図9に示す第1演出実行確率、および図30に示す判定値数の割合にもとづく第1演出の種類と第2演出の種類との組み合わせの昇格信頼度が示されている。つまり、第1演出の種類と第2演出の種類との組み合わせのそれぞれを用いた昇格演出が実行されたときに確変大当りとなる割合が示されている。図32(C)に示すように、キャラクタQとキャラクタAの組み合わせ、およびキャラクタRとキャラクタCの組み合わせの昇格信頼度は最も高く、キャラクタQとキャラクタCの組み合わせ、およびキャラクタRとキャラクタBの組み合わせの昇格信頼度は2番目に高い。 FIG. 32C shows the types of the first effect and the second effect based on the jackpot probability shown in FIG. 8, the first effect execution probability shown in FIG. 9, and the ratio of the number of determination values shown in FIG. The promotion confidence of the combination is shown. That is, the ratio of the probable big hit when the promotion effect using each combination of the first effect type and the second effect type is executed is shown. As shown in FIG. 32C, the combination of character Q and character A, and the combination of character R and character C have the highest promotion reliability, and the combination of character Q and character C, and the combination of character R and character B Has the second highest reliability of promotion.
図33には、第1演出の種類(キャラクタP〜Q)が「第1演出キャラ」として示され、第2演出の種類(キャラクタA〜C)が「第2演出キャラ」として示されている。キャラクタP〜Q(キャラクタ9p、キャラクタq、キャラクタrおよびキャラクタs)およびキャラクタA〜C(キャラクタ9a、キャラクタ9bおよびキャラクタ9c)は、演出表示装置9に表示されるキャラクタ画像である。
In FIG. 33, the type of the first effect (characters P to Q) is shown as “first effect character”, and the type of the second effect (characters A to C) is shown as “second effect character”. . Characters P to Q (
なお、この実施の形態では、キャラクタP〜Qのそれぞれについて演出の種類は1つなのでキャラクタP〜Qのそれぞれを第1演出の種類としているが、すなわち第1演出の種類を4としているが、キャラクタP〜Qのそれぞれについて演出の種類が複数ある場合には、第1演出の種類の数は、4(キャラクタP〜Qのそれぞれ)×(キャラクタP〜Qのそれぞれにの演出の種類の数)になる。 In this embodiment, since there is only one kind of effect for each of the characters P to Q, each of the characters P to Q is set as the type of the first effect, that is, the type of the first effect is set as 4. When there are a plurality of types of effects for each of the characters P to Q, the number of types of first effects is 4 (each of the characters P to Q) × (the number of types of effects for each of the characters P to Q). )become.
また、キャラクタA〜Cのそれぞれについて演出の種類は1つなのでキャラクタA〜Cのそれぞれを第2演出の種類としているが、厳密には、キャラクタP〜Qのそれぞれを用いたキャラクタA〜Cのそれぞれによる演出が実行されるので、第2演出の種類の数は図32(C)に示されたように12である。ただし、実行されない組み合わせ(判定値の個数0に対応した組み合わせ)が設けられている。また、キャラクタA〜Cのそれぞれについて演出の種類が複数ある場合には、第2演出の種類の数はさらに多くなる。 Further, since each character A to C has one type of production, each of the characters A to C is set as the type of the second production. Strictly speaking, the characters A to C using the characters P to Q respectively. Since each effect is executed, the number of types of second effects is 12, as shown in FIG. However, combinations that are not executed (combinations corresponding to the number of determination values 0) are provided. In addition, when there are a plurality of types of effects for each of the characters A to C, the number of types of second effects is further increased.
次に、第1演出および第2演出の具体例を、図34〜図37の説明図を参照して説明する。図34に示す例では、演出表示装置9に表示画面において、左中右の演出図柄(飾り図柄)が変動し(図34(A)参照)、リーチになると(図34(B)参照)、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動中にキャラクタ9p(豚)を用いた第1演出が実行されている(図34(C)〜(E)参照)。主人公キャラクタ9eによるハンマー9fによってキャラクタ9pが倒れるような表示演出がなされると(図34(F)参照)、図34(G)に示すように大当りになることを報知する表示がなされた後、大当り遊技中において、第2演出が実行される(図34(H)〜(J)参照)。なお、図34に示すような演出は、図12における変動パターン#2または#4の演出に相当する。なお、図34において、演出表示装置9における表示状態は、(A)に示す状態から順次(J)に示す状態に向かって遷移する。図35〜図37についても同様である。
Next, specific examples of the first effect and the second effect will be described with reference to the explanatory diagrams of FIGS. In the example shown in FIG. 34, on the display screen of the
また、第1演出が終了するときに左中右の飾り図柄は揃った状態で変動する(図34(F),(G)参照)。さらに、第2演出の実行中では、図柄表示エリア9Aにおいて、左中右の飾り図柄は揃った状態で高速変動する、いわゆる全回転リーチ態様になる。
Also, when the first effect ends, the left, middle, and right decorative symbols change in a uniform state (see FIGS. 34 (F) and (G)). Further, during the execution of the second effect, in the
図34に示す例では、キャラクタ9bを用いた第2演出が実行されている(図34(I),(J)参照)。なお、図34(J)に示す状態は、第2演出の中途の状態である。また、第2演出では、第1演出において用いられたキャラクタ(図34に示す例ではキャラクタ9p)が用いられる。
In the example shown in FIG. 34, the second effect using the
図35(K)〜(P)には、図34(J)に示す状態における演出に続く演出を示し、昇格成功の場合の第2演出が示されている。図35に示す例では、キャラクタ9b(西洋料理人)とは異なる他のキャラクタ(主人公キャラクタ9e)が、キャラクタ9pを食材とした料理を完成させた状態が示されている(図35(K)参照)。さらに、キャラクタ9bが、キャラクタ9pを食材とした料理を完成させた状態が示されている(図35(L)参照)。そして、試食者9gが、主人公キャラクタ9eが完成させた料理とキャラクタ9bが完成させた料理とを試食し(図35(M)参照)、試食者9gが主人公キャラクタ9eに高得点を与え、主人公キャラクタ9eが勝利して昇格成功した演出が示されている(図35(N)〜(P)参照)。
35 (K) to (P) show the effects following the effects in the state shown in FIG. 34 (J), and show the second effects in the case of successful promotion. In the example shown in FIG. 35, the
図36(K)〜(P)には、図34(J)に示す状態における演出に続く演出を示し、昇格失敗の場合の第2演出が示されている。図36に示す例では、主人公キャラクタ9eが、キャラクタ9pを食材とした料理を完成させた状態が示されている(図36(K)参照)。さらに、キャラクタ9bが、キャラクタ9pを食材とした料理を完成させた状態が示されている(図36(L)参照)。そして、試食者が、主人公キャラクタ9eが完成させた料理とキャラクタ9bが完成させた料理とを試食し(図36(M)参照)、試食者9gがキャラクタ9bに高得点を与え、キャラクタ9bが勝利して昇格失敗した演出が示されている(図36(M)〜(P)参照)。すなわち、通常大当りであったことを報知する表示演出を行う(図36(P)参照)。
36 (K) to (P) show the effects following the effects in the state shown in FIG. 34 (J), and show the second effects in the case of promotion failure. In the example shown in FIG. 36, a state in which the
図37には、演出表示装置9に表示画面において、左中右の演出図柄(飾り図柄)が変動し(図37(A)参照)、リーチになると(図37(B)参照)、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動中にキャラクタ9pを用いた第1演出が実行される例が示されている(図37(C)〜(E)参照)。そして、主人公キャラクタ9eによるハンマー9fによってキャラクタ9pが倒れなかったような表示演出がなされ(図37(F)参照)、図37(G)に示すように、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の停止図柄(最終停止図柄)として、はずれ図柄が表示される。なお、図37に示すような演出は、はずれとすることに決定されているがリーチすることに決定された場合であって第1演出を実行することに決定されたときの変動パターンの演出に相当する。すなわち、図12における変動パターン#2または#4の演出に相当する。また、図37に示された例では、第2演出は実行されない。
In FIG. 37, on the display screen of the
なお、図34〜図37に示す例では、第1演出および第2演出における演出表示装置9において、第1演出および第2演出は、時間的に継続して表示されているが、一時的に表示したり間欠的に表示するようにしてもよい。例えば、短期間(一例として数秒間)だけ表示演出を行ったり、短期間の表示演出が、表示演出がなされない期間をおいて複数回実行されるようにしてもよい。
In the examples shown in FIGS. 34 to 37, in the
また、図34〜図37には、キャラクタ9pとキャラクタ9bとを用いた演出が例示されているが、その他のキャラクタの組み合わせ(キャラクタ9pと9a,9cとの組み合わせ、およびキャラクタ9q,9r,9sのいずれかとキャラクタ9a,9b,9cのいずれかとの組み合わせの全て)を用いた演出も用意されている。
34 to 37 illustrate an effect using the
図34(E)および図37(E),(F)には、主人公キャラクタ9eがハンマー9fを有する演出例が示されたが、ハンマー9fに代えて剣や槍などによる演出を実行してもよい。また、ハンマー、剣、槍等と第1演出におけるキャラクタとの組み合わせに応じて大当り期待度や確変昇格期待度を変えるようにしてもよい。ハンマー、剣、槍等を用いる演出を第3演出とすると、第1〜第3演出の組み合わせによって期待度を報知してもよい。
FIGS. 34 (E) and 37 (E), (F) show examples of effects in which the
次に、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100とによる第1演出および第2演出の処理の流れを説明する。図38に示すように、遊技制御手段としての遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、変動開始時に、演出制御手段としての演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して変動パターンコマンドおよび演出図柄指定コマンドを送信するが(図20におけるステップS109および図21におけるステップS115,S117,S118参照)、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、変動パターンコマンドによって第1演出を実行することが指定されると、受信した演出図柄指定コマンド(演出図柄1指定コマンド(はずれ指定コマンド)、演出図柄2指定コマンド(通常大当り指定コマンド)または演出図柄3指定コマンド(確変大当り指定コマンド))にもとづいて第1演出の種類を決定する。具体的には、図30に示された3つのテーブル(はずれの列、通常大当りの列、確変大当りの列に相当)のうち演出図柄指定コマンドに応じたテーブルを選択し、第1演出種類選択用乱数を生成するためのカウント値を抽出して第1演出種類選択用乱数の値とし、第1演出の種類として、第1演出種類選択用乱数の値と一致する判定値に対応したキャラクタを選択する。また、第1演出の種類を示すデータをRAM112における第1演出キャラクタバッファ112aに設定する。
Next, the flow of processing of the first effect and the second effect by the
変動中に、具体的には第2演出を開始するタイミングにおいて、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して演出図柄指定コマンド(演出図柄1指定コマンド(はずれ指定コマンド)、演出図柄2指定コマンド(通常大当り指定コマンド)または演出図柄3指定コマンド(確変大当り指定コマンド))を送信する(図22におけるステップS124,S125参照)。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、演出図柄指定コマンドを受信すると、受信した演出図柄指定コマンドおよびRAM112に記憶されている第1演出の種類を示すデータとにもとづいて第2演出の種類を決定する。具体的には、受信した演出図柄指定コマンドに応じて図31(A)に示されたテーブルまたは図31(B)に示されたテーブルを選択し、第2演出種類選択用乱数を生成するためのカウント値を抽出して第2演出種類選択用乱数の値とし、第2演出の種類として、選択したテーブルにおいて第2演出種類選択用乱数の値と一致する判定値に対応したキャラクタを選択する。
During the change, specifically, at the timing of starting the second effect, the
なお、第2演出では、第1演出で用いたキャラクタを使用するので、第2演出の種類を決定することによって、第1演出の種類と第2演出の種類との組み合わせも決定されたことになる。また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が第2演出を開始するタイミングにおいて送信する演出図柄指定コマンドの種類(演出図柄1指定コマンド(はずれ指定コマンド)、演出図柄2指定コマンド(通常大当り指定コマンド)または演出図柄3指定コマンド(確変大当り指定コマンド)は、変動開始時に送信した演出図柄指定コマンドの種類と同じである。また、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、第2演出を開始するタイミングにおいて演出図柄1指定コマンド(はずれ指定コマンド)を受信した場合には、第2演出を実行しない。
Since the character used in the first effect is used in the second effect, the combination of the type of the first effect and the type of the second effect is determined by determining the type of the second effect. Become. Also, the type of effect symbol designation command (the
第2演出を開始するときに遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が演出図柄指定コマンドを送信し、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、演出図柄指定コマンドを受信すると、受信した演出図柄指定コマンドにもとづいて第2演出を実行するか否か決定するとともに、演出図柄指定コマンドを実行する場合には第2演出の種類を決定する。従って、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、第2演出を開始するタイミングを管理しなくてもよい。また、第2演出を開始するときに送信される演出制御コマンドは、本来、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の停止図柄を特定するための演出制御コマンドであるから、演出制御コマンドの種類を増加させずに、第2演出を開始するときに遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して第2演出を開始するタイミングを知らせることができる。
When the second effect is started, the
図39は、図25に示されたメイン処理における演出制御プロセス処理(ステップS705)を示すフローチャートである。演出制御プロセス処理では、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御プロセスフラグの値に応じてステップS800〜S806のうちのいずれかの処理を行う。各処理において、以下のような処理を実行する。
FIG. 39 is a flowchart showing the effect control process (step S705) in the main process shown in FIG. In the effect control process, the
変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(ステップS800):遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から変動パターンコマンドを受信しているか否か確認する。具体的には、コマンド解析処理でセットされる変動パターンコマンド受信フラグがセットされているか否か確認する。変動パターンコマンドを受信していれば、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動開始処理(ステップS801)に対応した値に変更する。
Fluctuation pattern command reception waiting process (step S800): It is confirmed whether or not a variation pattern command has been received from the
演出図柄変動開始処理(ステップS801):演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動が開始されるように制御する。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動中処理(ステップS802)に対応した値に更新する。 Effect symbol variation start processing (step S801): Control is performed so that the variation of the effect symbol (decoration symbol) is started. Then, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the effect symbol changing process (step S802).
演出図柄変動中処理(ステップS802):変動パターンを構成する各変動状態(変動速度)の切替タイミング等を制御するとともに、変動時間の終了を監視する。そして、変動時間が終了したら、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動停止処理(ステップS803)に対応した値に更新する。 Production symbol variation processing (step S802): Controls the switching timing of each variation state (variation speed) constituting the variation pattern and monitors the end of the variation time. When the variation time ends, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the effect symbol variation stop process (step S803).
演出図柄変動停止処理(ステップS803):全図柄停止を指示する演出制御コマンド(図柄確定指定コマンド)を受信したことにもとづいて、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動を停止し表示結果(停止図柄)を導出表示する制御を行う。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を大当り表示処理(ステップS804)または変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(ステップS800)に対応した値に更新する。 Effect symbol variation stop processing (step S803): Based on the reception of the effect control command (design determination designation command) for instructing all symbols to stop, the variation of the effect symbol (decoration symbol) is stopped and the display result (stop symbol) Control to derive and display. Then, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the jackpot display process (step S804) or the variation pattern command reception waiting process (step S800).
大当り表示処理(ステップS804):変動時間の終了後、演出表示装置9に大当りの発生を報知するための画面を表示する制御を行う。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を大当り遊技中処理(ステップS805)に対応した値に更新する。
Big hit display process (step S804): After the end of the variation time, control is performed to display a screen for notifying the
大当り遊技中処理(ステップS805):大当り遊技中の制御を行う。例えば、大入賞口開放中指定コマンドや大入賞口開放後指定コマンドを受信したら、演出表示装置9におけるラウンド数の表示制御等を行う。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を大当り終了処理(ステップS806)に対応した値に更新する。
Big hit game processing (step S805): Control during big hit game is performed. For example, when a special winning opening opening designation command or a special winning opening open designation command is received, display control of the number of rounds in the
大当り終了処理(ステップS806):演出表示装置9において、大当り遊技状態が終了したことを遊技者に報知する表示制御を行う。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(ステップS800)に対応した値に更新する。
Big hit end processing (step S806): In the
図40は、図39に示された演出制御プロセス処理における変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(ステップS800)を示すフローチャートである。変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、変動パターンコマンド受信フラグがセットされているか否か確認する(ステップS811)。変動パターンコマンド受信フラグがセットされていれば、変動パターンコマンド受信フラグをリセットする(ステップS812)。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動開始処理(ステップS801)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS813)。
FIG. 40 is a flowchart showing a variation pattern command reception waiting process (step S800) in the effect control process shown in FIG. In the variation pattern command reception waiting process, the
図41は、図39に示された演出制御プロセス処理における演出図柄変動開始処理(ステップS801)を示すフローチャートである。演出図柄変動開始処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、変動パターンコマンド格納領域(受信した変動パターンコマンドが格納されている。)から変動パターンコマンドを読み出し、受信した変動パターンの種類を確認する(ステップS824)。変動パターンコマンドが第1演出を伴う変動パターンコマンドではなかった場合には、ステップS831に移行する。
FIG. 41 is a flowchart showing the effect symbol variation start process (step S801) in the effect control process shown in FIG. In the effect symbol variation start process, the
変動パターンコマンドが第1演出を伴う変動パターンコマンドであった場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、第1演出種類選択用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を読み出し、読み出した値を第1演出種類選択用乱数値とする。すなわち、第1演出種類選択用乱数を抽出する。そして、第1演出種類選択用乱数値と受信している演出図柄指定コマンド(演出図柄1指定コマンド、演出図柄2指定コマンドまたは演出図柄3指定コマンド)とにもとづいて第1演出の種類を決定する(ステップS826)。具体的には、受信した演出図柄指定コマンド(識別情報の可変表示の表示結果を特定可能なコマンドの一例)に応じて図30に示されたテーブルのうち、はずれ、通常大当りまたは確変大当りの部分を選択し、第1演出種類選択用乱数値と一致する判定値に応じたキャラクタを第1演出の種類として選択する。
When the variation pattern command is a variation pattern command with the first effect, the
そして、選択した第1演出の種類を、RAM112における第1演出キャラクタバッファ112aに格納する(ステップS827)。また、第1演出実行フラグをセットする(ステップS828)。その後、ステップS831に移行する。
Then, the selected type of the first effect is stored in the first
ステップS831では、演出制御用CPU101は、演出図柄指定コマンド格納領域に格納されているデータ(すなわち、受信した表示結果特定コマンド)に応じて演出図柄(飾り図柄)の表示結果(停止図柄)を決定する(ステップS831)。演出制御用CPU101は、停止図柄を決定したら、演出図柄指定コマンド格納領域の内容をクリアする(ステップS832)。
In step S831, the
なお、演出制御用CPU101は、停止図柄を決定する際に、停止図柄決定用乱数を抽出し、演出図柄の組合せを示すデータと判定値とが対応付けられている停止図柄決定テーブルを用いて、演出図柄の停止図柄を決定する。すなわち、抽出した停止図柄決定用乱数値に一致する判定値に対応する演出図柄の組合せを示すデータを選択することによって、図11に例示されたように停止図柄を決定する。なお、リーチありか否かは、例えば、受信した変動パターンコマンドで判定される。また、演出制御用CPU101は、決定した演出図柄の停止図柄を示すデータを演出図柄表示結果格納領域に格納する。
When determining the stop symbol, the
また、演出図柄についても、大当りを想起させるような停止図柄を大当り図柄という。また、はずれを想起させるような停止図柄をはずれ図柄という。 Also, with regard to the production symbol, a stop symbol that recalls a big hit is called a big hit symbol. In addition, a stop symbol that recalls a loss is called a loss symbol.
次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、変動パターンおよび第1演出の種類に応じたプロセステーブルを選択する(ステップS833)。そして、演出制御用CPU101は、プロセスデータ1の内容(表示制御実行データ1、ランプ制御実行データ1、音番号データ1)に従って演出装置(演出用部品としての演出表示装置9、演出用部品としての各種LEDおよび演出用部品としてのスピーカ27など)の制御を実行する(ステップS834)。例えば、演出表示装置9において変動パターンに応じた画像を表示させるために、VDP109に指令を出力する。また、各種ランプを点灯/消灯制御を行わせるために、ランプドライバ基板35に対して制御信号(ランプ制御実行データ)を出力する。また、スピーカ27からの音声出力を行わせるために、音声出力基板70に対して制御信号(音番号データ)を出力する。また、選択したプロセステーブルのプロセスデータ1におけるプロセスタイマをスタートさせる(ステップS835)。
Next, the
図42は、プロセステーブルの構成例を示す説明図である。プロセステーブルとは、演出制御用CPU101が演出装置の制御を実行する際に参照するプロセスデータが設定されたテーブルである。すなわち、演出制御用CPU101は、プロセステーブルに設定されているプロセスデータに従って演出表示装置9等の演出装置(演出用部品)の制御を行う。プロセスデータは、プロセスタイマ設定値と表示制御実行データ、ランプ制御実行データおよび音番号データの組み合わせが複数集まったデータで構成されている。表示制御実行データには、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の可変表示の可変表示時間(変動時間)中の変動態様を構成する各変動の態様を示すデータ等が記載されている。また、第1演出を行う場合に選択されるプロセステーブルには、演出態様を構成するデータ等が記載されている。具体的には、演出表示装置9の表示画面の変更に関わるデータ等が記載されている。また、プロセスタイマ設定値には、その変動の態様での変動時間が設定されている。演出制御用CPU101は、プロセステーブルを参照し、プロセスタイマ設定値に設定されている時間だけ表示制御実行データに設定されている変動の態様で演出図柄を表示させる制御を行う。
FIG. 42 is an explanatory diagram of a configuration example of the process table. The process table is a table in which process data referred to when the
また、演出制御用CPU101は、表示制御実行データにもとづく制御と同様に、プロセスタイマ設定値に設定されている時間だけランプ制御実行データにもとづいて各種LEDの点灯状態を制御し、音番号データを音声出力基板70に出力する。
In addition, similar to the control based on the display control execution data, the
演出制御用CPU101は、プロセステーブルにおけるプロセスデータに従って演出装置を制御することによって、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動態様と、それに同期した発光体の点灯状態および音出力とを実現する。また、プロセステーブルにおけるプロセスデータに従って演出装置を制御することによって、演出表示装置9における第1演出の表示状態と、それに同期した発光体の点灯状態および音出力とを実現する。
The
図42に示すプロセスデータは、演出制御基板80におけるROM111に格納されている。また、プロセステーブルは、各変動パターンと第1演出の種類との組み合わせのそれぞれに応じて用意されている。さらに、各変動パターンと第2演出の種類との組み合わせのそれぞれに応じて用意されている。
The process data shown in FIG. 42 is stored in the
なお、リーチ演出を伴う変動パターンについて演出制御を実行する場合に用いられるプロセステーブルには、変動開始から所定時間が経過したときに左図柄を停止表示させ、さらに所定時間が経過すると右図柄を停止表示させることを示すプロセスデータが設定されている。 In addition, in the process table used when effect control is executed for a variation pattern with reach effect, the left symbol is stopped when a predetermined time has elapsed from the start of the variation, and the right symbol is stopped when a predetermined time further elapses. Process data indicating that it is to be displayed is set.
その後、演出制御用CPU101は、演出表示装置9の表示画面における背景部の色を、受信した背景指定コマンド(通常時背景指定コマンド、確変時背景指定コマンドまたは時短時背景指定コマンド)に応じた色にする制御を行う(ステップS836)。また、変動時間タイマに、変動パターンコマンドで特定される変動時間に相当する値を設定し(ステップS837)、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動中処理(ステップS802)を示す値に更新する(ステップS838)。
Thereafter, the
図43は、演出制御プロセス処理における演出図柄変動中処理(ステップS802)を示すフローチャートである。演出図柄変動中処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、プロセスタイマの値を1減算するとともに(ステップS840)、変動時間タイマの値を1減算する(ステップS841)。
FIG. 43 is a flowchart showing the effect symbol changing process (step S802) in the effect control process. In the effect symbol changing process, the
演出制御用CPU101は、第1演出を実行していることを示す第1演出実行中フラグがセットされている場合には、演出図柄指定コマンドを受信したか否か確認する(ステップS842,S843)。演出図柄指定コマンドを受信したか否かは、演出図柄指定コマンド格納領域に有意な値(クリアされた値である0でない値)が設定されているか否かによって判定される。演出図柄指定コマンドを受信している場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、第2演出設定処理を実行する(ステップS844)。
When the first effect execution flag indicating that the first effect is being executed is set, the
また、演出制御用CPU101は、プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしたら(ステップS845)、プロセスデータの切替を行う。すなわち、プロセステーブルにおける次に設定されているプロセスタイマ設定値をプロセスタイマに設定する(ステップS846)。また、その次に設定されている表示制御実行データ、ランプ制御実行データおよび音番号データにもとづいて演出装置に対する制御状態を変更する(ステップS847)。
In addition, when the process timer times out (step S845), the
また、変動時間タイマがタイムアウトしていれば(ステップS848)、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動停止処理(ステップS803)に応じた値に更新する(ステップS850)。変動時間タイマがタイムアウトしていなくても、図柄確定指定コマンドを受信したことを示す確定コマンド受信フラグがセットされていたら(ステップS849)、ステップS850に移行する。変動時間タイマがタイムアウトしていなくても図柄確定指定コマンドを受信したら変動を停止させる制御に移行するので、例えば、基板間でのノイズ等に起因して長い変動時間を示す変動パターンコマンドを受信したような場合でも、正規の変動時間経過時(特別図柄の変動終了時)に、演出図柄の変動を終了させることができる。 If the variation time timer has timed out (step S848), the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the effect symbol variation stop process (step S803) (step S850). Even if the variable time timer has not timed out, if the confirmation command reception flag indicating that the symbol confirmation designation command has been received is set (step S849), the process proceeds to step S850. Even if the variation time timer has not timed out, if the symbol confirmation designation command is received, the process shifts to control to stop variation.For example, a variation pattern command indicating a long variation time due to noise between substrates is received. Even in such a case, it is possible to end the variation of the effect symbol when the regular variation time has elapsed (when the variation of the special symbol ends).
なお、プロセステーブルにおける各プロセスデータに従って制御を実行する(ステップS840,S845〜S847の処理により制御を実行する)ことによって、変動パターンや第1演出に応じた演出制御が実現される。特に、第1演出に応じた演出制御を実行することによって、例えば、図34(A)〜(F)に例示された演出を実現することができる。また、ステップS844の第2演出設定処理を実行した後では、変動パターンや第2演出に応じた演出制御が実現される。特に、第2演出に応じた演出制御を実行することによって、例えば、図34(J)〜(J)および図35に例示された演出、または図34(J)〜(J)および図36に例示された演出を実現することができる。 In addition, by executing control according to each process data in the process table (control is executed by the processing of steps S840, S845 to S847), the effect control according to the variation pattern and the first effect is realized. In particular, by performing the effect control according to the first effect, for example, the effects illustrated in FIGS. 34 (A) to (F) can be realized. In addition, after the second effect setting process in step S844 is performed, effect control according to the variation pattern and the second effect is realized. In particular, by performing effect control according to the second effect, for example, the effects illustrated in FIGS. 34 (J) to (J) and FIG. 35, or FIGS. 34 (J) to (J) and FIG. The illustrated effects can be realized.
図44は、ステップS844の第2演出設定処理を示すフローチャートである。第2演出設定処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、受信した演出図柄指定コマンドが演出図柄1指定コマンド(はずれ指定コマンド)であるか否か確認する(ステップS910)。演出図柄1指定コマンドであれば処理を終了する。演出図柄1指定コマンドでない場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、第2演出種類選択用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を読み出し、読み出した値を第2演出種類選択用乱数値とする。すなわち、第2演出種類選択用乱数を抽出する(ステップS911)。そして、第2演出種類選択用乱数値と、第1演出キャラクタバッファ112aに記憶されているデータが示す第1演出の種類と、受信した演出図柄指定コマンド(演出図柄2指定コマンドまたは演出図柄3指定コマンド)とにもとづいて第2演出の種類を決定し、第2演出の種類を示すデータを第2演出キャラクタバッファ112bに設定する(ステップS912)。具体的には、受信した演出図柄指定コマンド(識別情報の可変表示の表示結果を特定可能なコマンドの一例)に応じて図31(A)に示されたテーブルまたは図31(B)に示されたテーブルを選択し、第2演出の種類として、第2演出種類選択用乱数の値と一致する判定値(図31において、第1演出の種類に応じた行に対応した判定値)に対応したキャラクタを選択する。
FIG. 44 is a flowchart showing the second effect setting process in step S844. In the second effect setting process, the
そして、演出制御用CPU101は、第1演出実行フラグをリセットするとともに第2演出実行フラグをセットする(ステップS913)。また、変動パターンと第2演出の種類に応じたプロセステーブルを選択し(ステップS914)、プロセスデータ1の内容(表示制御実行データ1、ランプ制御実行データ1、音番号データ1)に従って演出装置の制御を実行する(ステップS915)。例えば、演出表示装置9において変動パターンに応じた画像を表示させるために、VDP109に指令を出力する。また、各種ランプを点灯/消灯制御を行わせるために、ランプドライバ基板35に対して制御信号(ランプ制御実行データ)を出力する。また、スピーカ27からの音声出力を行わせるために、音声出力基板70に対して制御信号(音番号データ)を出力する。また、選択したプロセステーブルのプロセスデータ1におけるプロセスタイマをスタートさせる(ステップS916)。
Then, the
図45は、演出制御プロセス処理における演出図柄変動停止処理(ステップS803)を示すフローチャートである。演出図柄変動停止処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、確定コマンド受信フラグがセットされているか否か確認する(ステップS851)、確定コマンド受信フラグがセットされている場合には、確定コマンド受信フラグをリセットし(ステップS852)、演出図柄表示結果格納領域に格納されているデータ(停止図柄を示すデータ)に従って停止図柄を導出表示する制御を行う(ステップS853)。また、飾り図柄変動終了フラグをセットする(ステップS854)。そして、演出制御用CPU101は、大当りとすることに決定されているか否か確認する(ステップS855)。大当りとすることに決定されているか否かは、例えば、決定されている停止図柄によって、大当りとすることに決定されているか否か判定される。
FIG. 45 is a flowchart showing the effect symbol variation stop process (step S803) in the effect control process. In the effect symbol variation stop process, the
大当りとすることに決定されている場合には、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を大当り表示処理(ステップS804)に応じた値に更新する(ステップS856)。 If it is determined to be a big hit, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the big hit display process (step S804) (step S856).
大当りとしないことに決定されている場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(ステップS800)に応じた値に更新する(ステップS857)。
If it is determined not to win, the
なお、この実施の形態では、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、図柄確定指定コマンドを受信したことを条件に、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動(可変表示)を終了させる(ステップS851,S853参照)。しかし、受信した変動パターンコマンドにもとづく変動時間タイマがタイムアウトしたら、図柄確定指定コマンドを受信しなくても、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動を終了させるように制御してもよい。その場合、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、可変表示の終了を指定する図柄確定指定コマンドを送信しないようにしてもよい。
In this embodiment, the
図46は、演出制御プロセス処理における大当り表示処理(ステップS804)を示すフローチャートである。大当り表示処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、大当り表示時間タイマが設定されているか否か確認する(ステップS861)。大当り表示時間タイマが設定されている場合には、ステップS862に移行する。大当り表示時間タイマが設定されていない場合には、大当り開始指定コマンド(ファンファーレコマンド)を受信したことを示すファンファーレコマンド受信フラグがセットされているか否か確認する(ステップS865)。ファンファーレコマンド受信フラグがセットされている場合には、ファンファーレコマンド受信フラグをリセットし(ステップS866)、大当り表示時間タイマに大当り表示時間に相当する値を設定して(ステップS867)、ファンファーレ画面(大当り遊技の開始を報知する画面)を演出表示装置9表示する制御を行う(ステップS868)。具体的には、VDP109に、ファンファーレ画面を表示させるための指示を与える。
FIG. 46 is a flowchart showing the jackpot display process (step S804) in the effect control process. In the jackpot display process, the
また、演出制御用CPU101は、第2演出を実行した場合には、第2演出実行中フラグをリセットする(ステップS869,S870)。
In addition, when the second effect is executed, the
ステップS862では、演出制御用CPU101は、大当り表示時間タイマの値を1減算する。そして、大当り表示時間タイマの値が0になっているか否か、すなわち大当り表示時間が経過したか否か確認する(ステップS863)。経過していなければ処理を終了する。大当り表示時間が経過している場合には、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を大当り遊技中処理(ステップS805)に応じた値に更新する(ステップS864)。
In step S862, the
図47は、演出制御プロセス処理における大当り遊技中処理(ステップS805)を示すフローチャートである。大当り遊技中処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御用CPU101は、大入賞口開放後コマンドを受信した場合には、ラウンド間表示画面(大当り遊技中のラウンド間を報知する画面)を演出表示装置9に表示する制御を行う(ステップS880,S887)。また、大入賞口開放中コマンドを受信した場合には(ステップS881)、ラウンド数に応じたプロセステーブルを選択し(ステップS888)、プロセスデータ1の内容(表示制御実行データ1、ランプ制御実行データ1、音番号データ1)に従って演出装置の制御を実行する(ステップS889)。例えば、演出表示装置9において変動パターンに応じた画像を表示させるために、VDP109に指令を出力する。また、各種ランプを点灯/消灯制御を行わせるために、ランプドライバ基板35に対して制御信号(ランプ制御実行データ)を出力する。また、スピーカ27からの音声出力を行わせるために、音声出力基板70に対して制御信号(音番号データ)を出力する。また、選択したプロセステーブルのプロセスデータ1におけるプロセスタイマをスタートさせる(ステップS890)。
FIG. 47 is a flowchart showing the big hit game processing (step S805) in the effect control process. In the process during the big hit game, the
また、大当り終了指定コマンド(エンディングコマンド)を受信したことを示すエンディングコマンド受信フラグがセットされている場合には、エンディングコマンド受信フラグをリセットし(ステップS882,S891)、エンディング画面(大当り遊技の終了を報知する画面)を演出表示装置9表示する制御を行う(ステップS892)。具体的には、VDP109に、エンディング画面を表示させるための指示を与える。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を大当り終了処理(ステップS806)に応じた値に更新する(ステップS893)。
When the ending command reception flag indicating that the jackpot end designation command (ending command) has been received is set, the ending command reception flag is reset (steps S882 and S891), and the ending screen (end of jackpot game) Is displayed on the effect display device 9 (step S892). Specifically, an instruction for displaying the ending screen is given to the
大当り終了処理では、大当り遊技の終了を報知する時間が経過すると、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(ステップS800)に対応した値に更新する。
In the big hit end process, when the time for notifying the end of the big hit game has elapsed, the
エンディングコマンド受信フラグがセットされていない場合には、プロセスタイマの値を1減算し(ステップS881)、プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしたら(ステップS884)、プロセスデータの切替を行う。すなわち、プロセステーブルにおける次に設定されているプロセスタイマ設定値をプロセスタイマに設定する(ステップS885)。また、その次に設定されている表示制御実行データ、ランプ制御実行データおよび音番号データにもとづいて演出装置に対する制御状態を変更する(ステップS886)。 If the ending command reception flag is not set, the process timer value is decremented by 1 (step S881), and when the process timer times out (step S884), the process data is switched. That is, the process timer setting value set next in the process table is set in the process timer (step S885). Further, the control state for the effect device is changed based on the display control execution data, lamp control execution data, and sound number data set next (step S886).
以上のような処理によって、特別図柄および演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動が行われているときに第1演出を実行し、第1演出の実行が終了した後に第2演出を実行する制御を実現することができる。この実施の形態では、特別図柄および演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動が行われているときに第1演出を実行し、その後に、第1演出に関連する第2演出を実行するので、確変状態に移行することの報知演出の演出態様に変化が付いて遊技の興趣をより高めることができる。また、確変状態に関する遊技者の興味を長期間に亘って持続させ、遊技の興趣をより高めることができる。 Through the processing described above, the first effect is executed when the special symbol and the effect symbol (decoration symbol) are changed, and the second effect is executed after the execution of the first effect is completed. can do. In this embodiment, the first effect is executed when the special symbol and the effect symbol (decoration symbol) are changed, and then the second effect related to the first effect is executed. There is a change in the production mode of the notification effect of the transition to the game, and the entertainment of the game can be further enhanced. In addition, the player's interest in the probabilistic state can be maintained for a long period of time, and the interest of the game can be further enhanced.
また、可変表示の表示結果を大当り図柄にすることに決定したときと、大当り図柄にしないことに決定したときとで、第1演出の選択割合を異ならせるので(図30参照)、実行される第1演出の種類を、昇格期待度(昇格信頼度)の高低に加えて、演出表示装置9に大当り図柄が導出表示される期待度(大当り信頼度)の高低に対応させることができる。
Further, the selection ratio of the first effect is different depending on whether the display result of variable display is decided to be a big hit symbol or not decided to be a big hit symbol (see FIG. 30). In addition to the level of promotion expectation (elevation reliability), the type of the first effect can be made to correspond to the level of expectation (hit reliability) at which the jackpot symbol is derived and displayed on the
実施の形態2.
第1の実施の形態では、特別図柄および演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動が行われているときに第1演出と第2演出とをともに実行したが、第1演出の実行時期および第2演出の実行時期を他の時期にしてもよい。
In the first embodiment, the first effect and the second effect are executed together when the special symbol and the effect symbol (decorative symbol) are changed. However, the execution time and the second effect of the first effect are executed. The execution time of may be set to another time.
第2の実施の形態(実施の形態2)では、大当り遊技中に第1演出と第2演出とをともに実行する。 In the second embodiment (Embodiment 2), both the first effect and the second effect are executed during the big hit game.
図48〜図51は、この実施の形態における第1演出および第2演出の具体例を示す説明図である。図48に示す例では、演出表示装置9に表示画面において、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動後に大当り表示(ファンファーレ表示)がなされた後(図48(A),(B)参照)、大当り遊技中にキャラクタ9p(豚)を用いた第1演出が実行されている(図48(C)〜(E)参照)。そして、キャラクタPが倒れるような表示演出がなされると(図48(F)参照)、大当り遊技中において、第2演出が実行される(図48(G)〜(J)参照)。なお、図48において、演出表示装置9における表示状態は、(A)に示す状態から順次(J)に示す状態に向かって遷移する。図49〜図51についても同様である。
48 to 51 are explanatory diagrams showing specific examples of the first effect and the second effect in this embodiment. In the example shown in FIG. 48, after the jackpot display (fanfare display) is made on the display screen of the
図48に示す例およびそれに続く図49に示す例では、キャラクタ9bを用いた第2演出が実行されている(図48(H),(I)や図49(M)参照)。なお、第2演出では、第1演出において用いられたキャラクタ(図48および図49に示す例ではキャラクタ9p)が用いられる。
In the example shown in FIG. 48 and the example shown in FIG. 49 subsequent thereto, the second effect using the
図49(K)〜(P)には、昇格成功の場合の第2演出が示されている。すなわち、キャラクタ9b(西洋料理人)とは異なる他のキャラクタ(主人公キャラクタ9e)が、キャラクタ9pを食材とした料理を完成させた状態が示された後(図48(J)参照)、キャラクタ9bが、キャラクタ9pを食材とした料理を完成させた状態が示され(図49(K)参照)、試食者9gが、主人公キャラクタ9eが完成させた料理とキャラクタ9bが完成させた料理とを試食し(図48(L)参照)、試食者9gが主人公キャラクタ9eに高得点を与え、主人公キャラクタ9eが勝利して昇格成功した演出が示されている(図49(M)〜(P)参照)。
49 (K) to 49 (P) show the second performance in the case of successful promotion. That is, after the
図50(K)〜(P)には、図48(J)に示す状態における演出に続く演出が示され、昇格失敗の場合の第2演出が示されている。すなわち、主人公キャラクタ9eが、キャラクタ9pを食材とした料理を完成させた状態が示された後(図48(J)参照)。また、キャラクタ9bが、キャラクタ9pを食材とした料理を完成させた状態が示され(図50(K)参照)、試食者9gが、主人公キャラクタ9eが完成させた料理とキャラクタ9bが完成させた料理とを試食し(図50(L)参照)、試食者9gがキャラクタ9bに高得点を与え、キャラクタ9bが勝利して昇格失敗した演出が示されている(図50(M)〜(P)参照)。なお、この実施の形態では、大当り遊技が終了したら遊技状態が時短状態に制御されるので、図50(P)に示されたような表示演出を行う。
50 (K) to (P) show the effects following the effects in the state shown in FIG. 48 (J), and show the second effects in the case of promotion failure. That is, after the
なお、昇格失敗の場合には、大当り遊技中において、第1演出のみを実行してもよい。図51には、演出表示装置9に表示画面において、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動後に大当り表示(ファンファーレ表示)がなされた後(図51(A),(B)参照)、大当り遊技中にキャラクタ9p(豚)を用いた第1演出が実行されている例が示されている(図51(C)〜(E)参照)。そして、キャラクタ9pが倒れなかったような表示演出がなされ(図51(F)参照)、図37(E)に示すようにはずれ表示がなされる。この場合には、第1演出が終了しても、第2演出は実行されない(図51(G)〜(H)参照)。
In the case of a promotion failure, only the first effect may be executed during the big hit game. In FIG. 51, after the big hit display (fanfare display) is made on the display screen of the
また、図48〜図50には、キャラクタ9pとキャラクタ9bとを用いた演出が例示されているが、その他のキャラクタの組み合わせ(キャラクタ9pと9a,9cとの組み合わせ、およびキャラクタ9q,9r,9sのいずれかとキャラクタ9a,9b,9cのいずれかとの組み合わせの全て)を用いた演出も用意されている。
48 to 50 exemplify effects using the
図52は、この実施の形態で用いられる特別図柄および演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動パターン(変動時間)の一例を示す説明図である。図12に示された第1の実施の形態における各変動パターンとは異なり、この実施の形態では、変動パターン#1〜#2において、第1演出や第2演出の態様は含まれていない。
FIG. 52 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of the variation pattern (variation time) of the special symbol and the effect symbol (decoration symbol) used in this embodiment. Unlike the variation patterns in the first embodiment shown in FIG. 12, in this embodiment, the
図53は、この実施の形態における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が送信する演出制御コマンドの内容の一例を示す説明図である。図13に示された第1の実施の形態における演出制御コマンドと異なる点は、大当り開始指定コマンド(ファンファーレコマンド)として、第1演出を実行することを指定する大当り開始1指定コマンドと、第1演出を実行しないことを指定する大当り開始2指定コマンドとがあることである。
FIG. 53 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of the contents of the effect control command transmitted by the
すなわち、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ファンファーレコマンドとして、第1演出を行うことに決定されている場合にはA001(H)の演出制御コマンド(大当り開始1指定コマンド)を送信し、第1演出を行うことに決定されていない場合にはA002(H)の演出制御コマンド(大当り開始2指定コマンド)を送信する。
That is, the
図54は、この実施の形態における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560におけるCPU56が実行する変動パターン設定処理を示すフローチャートである。この実施の形態では、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動中には昇格演出(第1演出および第2演出)を実行しないので、CPU56は、第1の実施の形態では実行していたステップS101,S102の処理を実行しない。その他の処理は第1の実施の形態の場合と同様である。
FIG. 54 is a flowchart showing a variation pattern setting process executed by the CPU 56 in the
なお、CPU56は、ステップS106の処理で、乱数バッファ領域から変動パターン決定用乱数の値を読み出し、変動パターン決定用乱数の値にもとづいて、使用する変動パターンを決定するのであるが、大当りフラグがセットされていない場合には、リーチすることに決定されていないときには、図52に例示された変動パターン#3または変動パターン#4に決定する。リーチすることに決定されているときには、はずれ時変動パターンテーブルを用いて変動パターンを決定する。はずれ時変動パターンテーブルはROM54に記憶され、はずれ時変動パターンテーブルには、変動パターン#1または変動パターン#2に対応した変動パターン判定値が設定されている。CPU56は、変動パターン決定用乱数の値に一致する変動パターン判定値に対応した変動パターンを決定する。また、大当りフラグがセットされている場合には、大当り時変動パターンテーブルを用いて変動パターンを決定する。大当り時変動パターンテーブルはROM54に記憶され、大当り時変動パターンテーブルには、変動パターン#1または変動パターン#2に対応した変動パターン判定値(それぞれの判定値数は、はずれ時変動パターンテーブルにおける判定値数とは異なる。)が設定されている。CPU56は、変動パターン決定用乱数の値に一致する変動パターン判定値に対応した変動パターンを決定する。
The CPU 56 reads the value of the variation pattern determination random number from the random number buffer area in the process of step S106, and determines the variation pattern to be used based on the value of the variation pattern determination random number. When it is not set, when it is not determined to reach, it is determined as the
なお、この実施の形態では、図柄の変動中に第1演出および第2演出を実行しないので、特別図柄変動中処理(図22参照)においてステップS124,S125の処理は実行されない。 In this embodiment, since the first effect and the second effect are not executed during the change of the symbol, the processes of steps S124 and S125 are not executed in the special symbol changing process (see FIG. 22).
図55は、この実施の形態における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560におけるCPU56が実行する特別図柄停止処理を示すフローチャートである。この実施の形態では、大当りフラグがセットされている場合には(ステップS132、CPU56は、確変フラグをリセットするが(ステップS133)、次いで、乱数バッファ領域から演出実行決定用乱数の値を読み出し(ステップS134A)、演出実行決定用乱数の値にもとづいて第1演出を実行するか否か決定する(ステップS134B)。具体的には、演出実行決定用乱数の値が図9に示された演出実行判定値のいずれかと一致したら第1演出を実行することに決定する。そして、第1演出を実行するか否かを示すデータをRAM55に格納する。
FIG. 55 is a flowchart showing special symbol stop processing executed by CPU 56 in
次いで、ファンファーレコマンドとして、第1演出を実行することに決定された場合には大当り開始1指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信し、第1演出を実行しないことに決定された場合には大当り開始2指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS134C)。また、演出図柄指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行い(ステップS135A)、第1演出中フラグをセットする(ステップS135B)。なお、ステップS135Aの処理で送信する演出図柄指定コマンドの種類(演出図柄1指定コマンド(はずれ指定コマンド)、演出図柄2指定コマンド(通常大当り指定コマンド)または演出図柄3指定コマンド(確変大当り指定コマンド)は、変動開始時に送信した演出図柄指定コマンドの種類と同じである。その他の処理は、第1の実施の形態における処理(図23参照)と同じである。
Next, when it is decided to execute the first effect as a fanfare command, a big hit start 1 designation command is transmitted to the
図56は、この実施の形態における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560におけるCPU56が実行する大当り遊技中処理を示すフローチャートである。大当り遊技中処理において、CPU56は、ラウンド時間が経過したか否か判定する(ステップS190)。ラウンド時間は、1ラウンドの許容時間(例えば29秒)である。例えば、大入賞口開放前処理(ステップS305)でRAM55に形成されているタイマに許容時間に相当する値が設定され、大当り遊技中処理において−1され(図56において図示せず)、タイマの値が0になったときにラウンド時間が経過したと判定される。ラウンド時間が経過した場合には、ステップS193に移行する。
FIG. 56 is a flowchart showing the big hit game processing executed by the CPU 56 in the
ラウンド時間が経過していない場合には、大入賞口へ遊技球の入賞を検出するカウントスイッチ23から、オンした(遊技球を検出した)ことを示す検出信号を入力すると、RAM55に形成されている大入賞口入賞個数カウンタのカウント値を+1する(ステップS191)。大入賞口入賞個数カウンタのカウント値が1ラウンドの入賞許容数(例えば10)になったらステップS193に移行する。カウント値が1ラウンドの入賞許容数に達していない場合には処理を終了する。なお、大入賞口入賞個数カウンタのカウント値は、例えば、大入賞口開放前処理(ステップS305)で0に初期化される。
If the round time has not elapsed, a detection signal indicating that the game ball has been turned on (the game ball has been detected) is input from the
ステップS193では、CPU56は、最終ラウンドであったか否か確認する。最終ラウンドであった場合には、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を大当り終了前処理(ステップS307)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS196)。最終ラウンドであったか否か確認するために、例えば、大入賞口開放前処理(ステップS305)で、大当り遊技中処理に移行するときに、RAM55に形成されている開放回数カウンタの値が+1される。
In step S193, the CPU 56 checks whether or not it was the final round. If it is the final round, the value of the special symbol process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the pre-hit end pre-processing (step S307) (step S196). In order to confirm whether or not it is the final round, for example, in the big winning opening opening pre-processing (step S305), the value of the number-of-opening counter formed in the
最終ラウンドでなかった場合には、CPU56は、第2演出を開始するラウンド(例えば、第4ラウンド)としてあらかじめ決められているラウンドであったか否か確認する(ステップS194)。第2演出を開始するラウンドであれば、演出図柄指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS195)。その後、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を大入賞口開放前処理(ステップS305)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS196)。なお、ステップS195の処理で送信する演出図柄指定コマンドは、ステップS135Aの処理でRAM55に格納された演出図柄指定コマンドである。
If it is not the final round, the CPU 56 checks whether or not the round is predetermined as a round (for example, the fourth round) for starting the second effect (step S194). If it is the round which starts the 2nd production, control which transmits a production design designation command to
第2演出を開始するときに遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が演出図柄指定コマンドを送信し、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、演出図柄指定コマンドを受信すると、受信した演出図柄指定コマンドにもとづいて第2演出を実行するか否か決定するとともに、演出図柄指定コマンドを実行する場合には第2演出の種類を決定する。従って、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、第2演出を開始するタイミングを管理しなくてもよい。また、第2演出を開始するときに送信される演出制御コマンドは、本来、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の停止図柄を特定するための演出制御コマンドであるから、演出制御コマンドの種類を増加させずに、第2演出を開始するときに遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して第2演出を開始するタイミングを知らせることができる。
When the second effect is started, the
なお、この実施の形態では、変動開始時に演出図柄1指定コマンド(はずれ指定コマンド)を送信したときにも遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、第2演出の開始のタイミングにおいて再度演出図柄指定コマンドを送信するが、変動開始時に演出図柄1指定コマンド(はずれ指定コマンド)を送信した場合には第2演出は実行されないので、変動開始時に演出図柄1指定コマンド(はずれ指定コマンド)を送信したときに第2演出の開始のタイミングにおいて演出図柄指定コマンドを送信しないように構成してもよい。
In this embodiment, the
また、この実施の形態では、大当り遊技中の所定のラウンドが終了したときに演出図柄指定コマンドが演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信されるが、大当り遊技中の所定のラウンドを開始するときに、CPU56が、演出図柄指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行うようにしてもよい。さらに、所定のラウンド間のインターバル期間や、所定のラウンド中において、CPU56が、演出図柄指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行うようにしてもよい。
Further, in this embodiment, when the predetermined round during the big hit game ends, the production symbol designation command is transmitted to the
次に、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100とによる第1演出および第2演出の処理の流れを説明する。図57に示すように、遊技制御手段としての遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、変動終了時に、演出制御手段としての演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対してファンファーレコマンドおよび演出図柄指定コマンドを送信するが(図55におけるステップS134C,S135参照)、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、ファンファーレコマンドによって第1演出を実行することが指定されると、受信した演出図柄指定コマンド(この場合には、演出図柄2指定コマンド(通常大当り指定コマンド)または演出図柄3指定コマンド(確変大当り指定コマンド))にもとづいて第1演出の種類を決定する。具体的には、図30に示された3つのテーブルのうち演出図柄指定コマンドに応じたテーブルである「通常大当り」に対応するテーブルまたは「確変大当り」に対応するテーブルを選択し、第1演出種類選択用乱数を生成するためのカウント値を抽出して第1演出種類選択用乱数の値とし、第1演出の種類として、第1演出種類選択用乱数の値と一致する判定値に対応したキャラクタを選択する。また、第1演出の種類を示すデータをRAM112における第1演出キャラクタバッファ112aに設定する。
Next, the flow of processing of the first effect and the second effect by the
大当り遊技中に、具体的には、大当り遊技中の所定ラウンドにおいて、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して演出図柄指定コマンド(演出図柄2指定コマンド(通常大当り指定コマンド)または演出図柄3指定コマンド(確変大当り指定コマンド))を送信する(図56におけるステップS194,S195参照)。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、演出図柄指定コマンドを受信すると、受信した演出図柄指定コマンドおよびRAM112に記憶されている第1演出の種類を示すデータとにもとづいて第2演出の種類を決定する。具体的には、受信した演出図柄指定コマンドに応じて図31(A)に示されたテーブルまたは図31(B)に示されたテーブルを選択し、第2演出種類選択用乱数を生成するためのカウント値を抽出して第2演出種類選択用乱数の値とし、第2演出の種類として、第2演出種類選択用乱数の値と一致する判定値に対応したキャラクタを選択する。なお、第2演出では、第1演出で用いたキャラクタを使用するので、第2演出の種類を決定することによって、第1演出の種類と第2演出の種類との組み合わせも決定されたことになる。
During the jackpot game, specifically, in a predetermined round during the jackpot game, the
以下、この実施の形態における演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が実行する第1演出および第2演出の制御を説明する。
Hereinafter, the control of the 1st effect and the 2nd effect which the
図58は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100における演出制御用CPU101が実行する演出図柄プロセス処理(図39参照)における演出図柄変動開始処理(ステップS801)を示すフローチャートである。
FIG. 58 is a flowchart showing the effect symbol variation start process (step S801) in the effect symbol process (see FIG. 39) executed by the
この実施の形態では、演出図柄変動開始処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から受信した変動パターンコマンドが記憶されている変動パターンコマンドから変動パターンコマンドを読み出す(ステップS831A)。そして、図41に示された第1の実施の形態におけるステップS831以降の処理と同じ処理を実行する。なお、この実施の形態では、図41に示されたステップS824〜S828の処理は実行されない。また、第1の実施の形態ではステップS833の処理で変動パターンおよび第1演出の種類に応じたプロセステーブルを選択したが、この実施の形態では、変動パターンに応じたに応じたプロセステーブルが選択される(ステップS833A)。すなわち、ステップS833Aの処理において第1演出は考慮されない。
In this embodiment, in the effect symbol variation start process, the
また、この実施の形態では、演出図柄変動中処理において、図43に示されたステップS842〜S844の処理は実行されない。 Moreover, in this embodiment, the processing in steps S842 to S844 shown in FIG. 43 is not executed in the effect symbol variation processing.
図59は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100における演出制御用CPU101が実行する演出図柄プロセス処理(図39参照)における大当り表示処理(ステップS804)を示すフローチャートである。
FIG. 59 is a flowchart showing the jackpot display process (step S804) in the effect symbol process (see FIG. 39) executed by the
この実施の形態では、大当り表示処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、ファンファーレコマンドによって第1演出を実行することが指定されたとき(大当り開始2指定コマンド(図53参照)を受信している場合)に(ステップS869A)、第1演出種類選択用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を読み出し、読み出した値を第1演出種類選択用乱数値とする。すなわち、第1演出種類選択用乱数を抽出する(ステップS869B)。そして、第1演出種類選択用乱数値と受信している演出図柄指定コマンド(この場合には、演出図柄2指定コマンドまたは演出図柄3指定コマンド)とにもとづいて第1演出の種類を決定する(ステップS871)。具体的には、受信した演出図柄指定コマンド(識別情報の可変表示の表示結果を特定可能なコマンドの一例)に応じて図30に示されたテーブルのうち、通常大当りまたは確変大当りの部分を選択し、第1演出種類選択用乱数値と一致する判定値に応じたキャラクタを第1演出の種類として選択する。
In this embodiment, in the jackpot display process, the
そして、選択した第1演出の種類を、RAM112における第1演出キャラクタバッファ112aに格納する(ステップS872)。また、第1演出実行フラグをセットする(ステップS873)。その他の処理は、第1の実施の形態の場合と同じである(図46参照)。
Then, the selected type of the first effect is stored in the first
図60は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100における演出制御用CPU101が実行する演出制御プロセス処理における大当り遊技中処理(ステップS805)を示すフローチャートである。この実施の形態では、大当り遊技中処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、第1演出を実行していることを示す第1演出実行中フラグがセットされている場合には(ステップS888A)、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ100から演出図柄指定コマンドを受信したときに第2演出選択処理(図61参照)を実行する(ステップS888B,S888C)。
FIG. 60 is a flowchart showing the big hit game processing (step S805) in the effect control process executed by the
また、第1の実施の形態では、大入賞口開放中コマンドを受信したときに、ラウンド数のみに応じたプロセステーブルを選択したが(図47におけるステップS888参照)、この実施の形態では、第1演出の実行中には、ラウンド数および第1演出の種類に応じたプロセステーブルを選択し、第2演出の実行中には、ラウンド数および第2演出の種類に応じたプロセステーブルを選択する(ステップS888D)。その他の処理は、第1の実施の形態の場合(図47参照)と同じである。 Further, in the first embodiment, when a command for opening a big prize opening is received, a process table corresponding to only the number of rounds is selected (see step S888 in FIG. 47). During execution of one effect, a process table corresponding to the number of rounds and the type of first effect is selected, and during execution of the second effect, a process table according to the number of rounds and the type of second effect is selected. (Step S888D). Other processes are the same as those in the first embodiment (see FIG. 47).
また、プロセステーブルにおける各プロセスデータに従って制御を実行する(ステップS883〜S886の処理により制御を実行する)ことによって、第1演出および第2演出に応じた演出制御が実現される。例えば、図48(C)〜(F)に例示された第1演出、図48(G)〜(J)および図49に例示された第2演出、図48(G)〜(J)および図50に例示された第2演出、図51に示された演出を実現することができる。 Further, by performing control according to each process data in the process table (execution of control by the processing of steps S883 to S886), effect control according to the first effect and the second effect is realized. For example, the first effect illustrated in FIGS. 48C to 48F, the second effect illustrated in FIGS. 48G to 48J and FIG. 49, and FIGS. 48G to 48J and FIG. The second effect illustrated in FIG. 50 and the effect shown in FIG. 51 can be realized.
図61は、ステップS888Cの第2演出選択処理を示すフローチャートである。第2演出設定処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、受信した演出図柄指定コマンドが演出図柄1指定コマンド(はずれ指定コマンド)であるか否か確認する(ステップS910)。演出図柄1指定コマンドであれば処理を終了する。演出図柄1指定コマンドでない場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、第2演出種類選択用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を読み出し、読み出した値を第2演出種類選択用乱数値とする。すなわち、第2演出種類選択用乱数を抽出する(ステップS911)。そして、第2演出種類選択用乱数値と、第1演出キャラクタバッファ112aに記憶されているデータが示す第1演出の種類と、受信した演出図柄指定コマンド(演出図柄2指定コマンドまたは演出図柄3指定コマンド)とにもとづいて第2演出の種類を決定し、第2演出の種類を示すデータを第2演出キャラクタバッファ112bに設定する(ステップS912)。具体的には、受信した演出図柄指定コマンド(識別情報の可変表示の表示結果を特定可能なコマンドの一例)に応じて図31(A)に示されたテーブルまたは図31(B)に示されたテーブルを選択し、第2演出の種類として、第2演出種類選択用乱数の値と一致する判定値(図31において、第1演出の種類に応じた行に対応した判定値)に対応したキャラクタを選択する。
FIG. 61 is a flowchart showing the second effect selection process in step S888C. In the second effect setting process, the
そして、演出制御用CPU101は、第1演出実行フラグをリセットするとともに第2演出実行フラグをセットする(ステップS913)。また、実行中のラウンド数と第2演出の種類に応じたプロセステーブルを選択し(ステップS914A)、プロセスデータ1の内容(表示制御実行データ1、ランプ制御実行データ1、音番号データ1)に従って演出装置の制御を実行する(ステップS915)。例えば、演出表示装置9においてラウンド数に応じた画像を表示させるために、VDP109に指令を出力する。また、各種ランプを点灯/消灯制御を行わせるために、ランプドライバ基板35に対して制御信号(ランプ制御実行データ)を出力する。また、スピーカ27からの音声出力を行わせるために、音声出力基板70に対して制御信号(音番号データ)を出力する。また、選択したプロセステーブルのプロセスデータ1におけるプロセスタイマをスタートさせる(ステップS916)。
Then, the
以上のような処理によって、大当り遊技中に、第1演出を実行し、第1演出が終了した後に第2演出を実行する制御が実現される。この実施の形態では、大当り遊技中に第1演出および第2演出を実行するので、確変状態に移行することの報知演出の演出態様に変化が付いて遊技の興趣をより高めることができる。また、大当り遊技状態中の期間において確変状態等の特別遊技状態に関する遊技者の興味を持続させ、遊技の興趣をより高めることができる。 Through the processing as described above, the control for executing the first effect during the big hit game and executing the second effect after the first effect is completed is realized. In this embodiment, since the first effect and the second effect are executed during the big hit game, the effect mode of the notification effect indicating the transition to the probable change state is changed, and the interest of the game can be further enhanced. In addition, it is possible to maintain the player's interest regarding the special game state such as the probable change state during the big hit game state, and to enhance the interest of the game.
実施の形態3.
第1の実施の形態では、特別図柄および演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動が行われているときに第1演出と第2演出とをともに実行し、第2の実施の形態では、大当り遊技中に第1演出と第2演出とをともに実行したが、第3の実施の形態(実施の形態3)では、大当り遊技が終了した後に第1演出と第2演出とをともに実行する。
In the first embodiment, the first effect and the second effect are executed together when the special symbol and the effect symbol (decoration symbol) are changed. In the second embodiment, the big hit game is being played. Both the first effect and the second effect are executed, but in the third embodiment (Embodiment 3), both the first effect and the second effect are executed after the big hit game is finished.
図62〜図66は、この実施の形態における第1演出および第2演出の具体例を示す説明図である。図62に示す例では、演出表示装置9に表示画面において、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動後に大当り表示(ファンファーレ表示)がなされた、大当り遊技が実行された後大当り終了(エンディング表示)がなされた後(図62(A),(B),(C),(D)参照)、キャラクタ9p(豚)を用いた第1演出が実行されている(図62(E)〜(G)参照)。そして、主人公キャラクタ9eによるハンマー9fによってキャラクタ9pが倒れるような表示演出がなされると(図62(H)参照)、第2演出が実行される(図62(I),(J)参照)。なお、図62において、演出表示装置9における表示状態は、(A)に示す状態から順次(J)に示す状態に向かって遷移する。図63〜図66についても同様である。
62 to 66 are explanatory diagrams showing specific examples of the first effect and the second effect in this embodiment. In the example shown in FIG. 62, on the display screen of the
図62に示す例およびそれに続く図63に示す例では、キャラクタ9b(西洋料理人)を用いた第2演出が実行されている(図62(J)や図63(K)参照)。なお、第2演出では、第1演出において用いられたキャラクタ(図62および図63に示す例ではキャラクタ9p)が用いられる。
In the example shown in FIG. 62 and the subsequent example shown in FIG. 63, the second effect using the
図63(K)〜(Q)には、昇格成功の場合の第2演出が示されている。すなわち、キャラクタ9bとは異なる他のキャラクタ(主人公キャラクタ9e)が、キャラクタ9pを食材とした料理を完成させた状態が示された後(図63(L)参照)、キャラクタ9bが、キャラクタ9pを食材とした料理を完成させた状態が示され(図63(M)参照)、試食者9gが、9pが完成させた料理とキャラクタ9bが完成させた料理とを試食し(図63(N)参照)、試食者9gが主人公キャラクタ9eに高得点を与え、主人公キャラクタ9eが勝利して昇格成功した演出が示されている(図63(O)〜(Q)参照)。
63 (K) to (Q) show the second effect in the case of successful promotion. That is, after another character (the
図64(K)〜(P)には、図62(J)に示す状態における演出に続く演出が示され、昇格失敗の場合の第2演出が示されている。すなわち、主人公キャラクタ9eが、キャラクタ9pを食材とした料理を完成させた状態が示された後(図64(L)参照)。また、キャラクタ9bが、キャラクタ9pを食材とした料理を完成させた状態が示され(図64(M)参照)、試食者9gが、主人公キャラクタ9eが完成させた料理とキャラクタ9bが完成させた料理とを試食し(図64(N)参照)、試食者9gがキャラクタ9bに高得点を与え、キャラクタ9bが勝利して昇格失敗した演出が示されている(図64(O)〜(P)参照)。なお、図64には、昇格失敗後に、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動が開始された様子も示されている(図64(Q)参照)。
FIGS. 64 (K) to (P) show the effects following the effects in the state shown in FIG. 62 (J), and show the second effects in the case of promotion failure. That is, after the
図63および図64に示すように、時短残り回数(時短状態における可変表示の実行可能回数)が少なくなるに従って第2演出の演出内容は変化し、時短残り回数が極めて少なくなると(この例では10回)、図63(O)や図64(O)に示されたように、キャラクタA〜C(この例ではキャラクタB(9b))と主人公キャラクタ9eとの判定の演出に到達し、時短残り回数が0になると、昇格成功または昇格失敗の報知画面が演出表示装置9に表示される。
As shown in FIGS. 63 and 64, the content of the effect of the second effect changes as the number of remaining time reductions (the number of times variable display can be performed in the time reduction state) decreases, and when the remaining number of time reductions becomes extremely small (in this example, 10 63), as shown in FIG. 63 (O) and FIG. 64 (O), the character A to C (character B (9b) in this example) and the
なお、この実施の形態では、確変大当りに決定されているときと通常大当りに決定されているときとで演出図柄(飾り図柄)の停止図柄を分けていないので、遊技者は、第2演出が終了するまで、確変大当りであったのか通常大当りであったのかを判別できない。つまり、第2演出が終了するまで、遊技者の確変大当りに対する期待感を維持できる。 In this embodiment, since the stop symbols of the production symbols (decoration symbols) are not divided between when the probability variation jackpot is determined and when the normal jackpot is determined, the player can perform the second performance. Until it is finished, it cannot be determined whether it was a probable big hit or a normal big hit. In other words, the player's sense of expectation for the probable big hit can be maintained until the second performance is completed.
そのような効果をさらに効果的にするために、すなわち、確変大当りであったのか通常大当りであったのか不明であることをより強調するために、第2演出の期間において、キャラクタA〜Cを用いる演出とは異なる演出を行うようにしてもよい。 In order to make such an effect more effective, that is, to further emphasize that it is unknown whether it was a promiscuous big hit or a normal big hit, the characters A to C are used during the second stage. An effect different from the effect to be used may be performed.
例えば、図65の説明図に示すように、キャラクタA〜Cとは異なる他のキャラクタ(主人公キャラクタ9e)を表示し(図65(C)等参照)、第1演出で用いられるキャラクタを再度得ることが可能なような演出(図65(F)〜(H)参照)を行って、確変大当りであったのか通常大当りであったのか不明であることをより強調する。
For example, as shown in the explanatory diagram of FIG. 65, another character (the
また、この実施の形態では、大当り遊技終了後のあらかじめ決められている所定回(回数は可変であってもよい。)の演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動に亘って第1演出および第2演出が実行されるが、所定回の変動が完了する前に次の大当りが発生する可能性がある。その場合には、大当りの演出が第1演出または第2演出に優先して実行される。図66には、例えば、大当り遊技終了後の60回の演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動に亘って第1演出および第2演出が実行されることになっている場合に、35回の変動が残っている状態で大当りが発生したときの例が示されている。その場合には、大当り遊技終了後に再度第1演出が開始される(図66(N)〜(R)参照)。 Further, in this embodiment, the first effect and the second effect are produced over a predetermined number of times (the number of times may be variable) after the jackpot game ends, over a variation of the effect symbol (decorative symbol). Is executed, but the next jackpot may occur before the predetermined number of changes are completed. In that case, the jackpot effect is executed with priority over the first effect or the second effect. In FIG. 66, for example, in the case where the first effect and the second effect are to be executed over the variation of the effect symbol (decoration symbol) 60 times after the end of the big hit game, there are 35 variations. An example is shown when a big hit occurs in the remaining state. In that case, the first effect is started again after the end of the big hit game (see FIGS. 66N to 66R).
図67は、この実施の形態における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が送信する演出制御コマンドの内容の一例を示す説明図である。図13に示された第1の実施の形態における演出制御コマンドと異なる点は、大当り終了指定コマンド(エンディングコマンド)として、第1演出を実行することを指定する大当り終了1指定コマンドと、第1演出を実行しないことを指定する大当り終了2指定コマンドとがあることである。
FIG. 67 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of the contents of the effect control command transmitted by the
すなわち、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、エンディングコマンドとして、第1演出を行うことに決定されている場合にはA301(H)の演出制御コマンド(大当り終了1指定コマンド)を送信し、第1演出を行うことに決定されていない場合にはA302(H)の演出制御コマンド(大当り終了2指定コマンド)を送信する。
That is, when it is determined to perform the first effect as the ending command, the
なお、この実施の形態で用いられる特別図柄および演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動パターン(変動時間)は、第2の実施の形態の場合と同じである(図52参照)。 Note that the variation pattern (variation time) of the special symbol and the effect symbol (decoration symbol) used in this embodiment is the same as that in the second embodiment (see FIG. 52).
図68は、この実施の形態における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560におけるCPU56が実行する特別図柄プロセス処理における大当り終了処理(ステップS307)を示すフローチャートである。この実施の形態では、CPU56は、エンディングコマンドを送信する際に、乱数バッファ領域から演出実行決定用乱数の値を読み出し(ステップS174A)、演出実行決定用乱数の値にもとづいて第1演出を実行するか否か決定する(ステップS174B)。具体的には、演出実行決定用乱数の値が図9に示された演出実行判定値のいずれかと一致したら第1演出を実行することに決定する。そして、第1演出を実行するか否かを示すデータをRAM55に格納する。
FIG. 68 is a flowchart showing a jackpot end process (step S307) in the special symbol process executed by the CPU 56 in the
次いで、エンディングコマンドとして、第1演出を実行することに決定された場合には大当り終了1指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信し、第1演出を実行しないことに決定された場合には大当り終了2指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS174C)。また、演出図柄指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS174D)。なお、ステップS174D)の処理で送信する演出図柄指定コマンドの種類(演出図柄1指定コマンド(はずれ指定コマンド)、演出図柄2指定コマンド(通常大当り指定コマンド)または演出図柄3指定コマンド(確変大当り指定コマンド)は、変動開始時に送信した演出図柄指定コマンドの種類と同じである。その他の処理は、第1の実施の形態における処理(図24参照)と同じである。
Next, when it is decided to execute the first effect as an ending command, a
次に、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100とによる第1演出および第2演出の処理の流れを説明する。図69に示すように、遊技制御手段としての遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、大当り遊技の終了時に、演出制御手段としての演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対してエンディングコマンドおよび演出図柄指定コマンドを送信するが(図68におけるステップS174C,S174D参照)、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、エンディングコマンドによって第1演出を実行することが指定されると、受信した演出図柄指定コマンド(この場合には、演出図柄2指定コマンド(通常大当り指定コマンド)または演出図柄3指定コマンド(確変大当り指定コマンド))にもとづいて第1演出の種類を決定する。具体的には、図30に示された3つのテーブルのうち演出図柄指定コマンドに応じたテーブルである「通常大当り」に対応するテーブルまたは「確変大当り」に対応するテーブルを選択し、第1演出種類選択用乱数を生成するためのカウント値を抽出して第1演出種類選択用乱数の値とし、第1演出の種類として、第1演出種類選択用乱数の値と一致する判定値に対応したキャラクタを選択する。また、第1演出の種類を示すデータをRAM112における第1演出キャラクタバッファ112aに設定する。
Next, the flow of processing of the first effect and the second effect by the
また、大当り遊技の終了後であって第2演出の開始時に、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、受信している演出図柄指定コマンド(演出図柄2指定コマンド(通常大当り指定コマンド)または演出図柄3指定コマンド(確変大当り指定コマンド))およびRAM112に記憶されている第1演出の種類を示すデータとにもとづいて第2演出の種類を決定する。具体的には、受信した演出図柄指定コマンドに応じて図31(A)に示されたテーブルまたは図31(B)に示されたテーブルを選択し、第2演出種類選択用乱数を生成するためのカウント値を抽出して第2演出種類選択用乱数の値とし、第2演出の種類として、第2演出種類選択用乱数の値と一致する判定値に対応したキャラクタを選択する。なお、第2演出では、第1演出で用いたキャラクタを使用するので、第2演出の種類を決定することによって、第1演出の種類と第2演出の種類との組み合わせも決定されたことになる。
In addition, at the start of the second effect after the end of the jackpot game, the
また、この実施の形態では、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が独自に第2演出の開始タイミングを決定しているが、第1の実施の形態および第2の実施の形態の場合と同様に、第2演出の開始タイミングにおいて、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に演出図柄指定コマンドを送信するようにしてもよい。
In this embodiment, the
以下、この実施の形態における演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が実行する第1演出および第2演出の制御を説明する。なお、以下の説明では、第1演出および第2演出は、大当り遊技終了後の演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動中に実行されるが、変動中でないときにおいて、または変動中と変動中でないときの双方において第2演出を実行するようにしてもよい。
Hereinafter, the control of the 1st effect and the 2nd effect which the
図70は、この実施の形態における演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が実行する演出制御プロセス処理における演出図柄変動開始処理(ステップS801)を示すフローチャートである。この実施の形態では、演出制御用CPU101は、第2演出開始タイミングになると(図69参照)、図44に示された第2演出設定処理を実行する(ステップS833B,S833D)。
FIG. 70 is a flowchart showing an effect symbol variation start process (step S801) in the effect control process executed by the
また、プロセステーブルを選択する際に、演出制御用CPU101は、変動パターンと第1演出の種類または第2演出の種類とに応じたプロセステーブルを選択する(ステップS833E)。すなわち、第1演出実行中フラグがセットされている場合には、変動パターンと第1演出とに応じたプロセステーブルを選択し、第2演出実行中フラグがセットされている場合には、変動パターンと第2演出とに応じたプロセステーブルを選択する。なお、第1演出実行中フラグも第2演出実行中フラグもセットされていない場合には、第1演出および第2演出を考慮しない。つまり、変動パターンに応じたプロセステーブルを選択する。また、演出制御用CPU101は、第2演出実行中フラグを、例えば第2演出の終了時にリセットする。
When selecting the process table, the
また、この実施の形態では、第2演出中でないことを条件として、すなわち、第2演出実行フラグがセットされていないときに、演出表示装置9の表示画面における背景色を、背景指定コマンド格納領域に記憶されている背景指定コマンドに対応する色(遊技状態に対応した色)に設定する制御を行う(ステップS835D,S836)。その他の処理は、第1の実施の形態および第2の実施の形態の場合と同じである。
In this embodiment, on the condition that the second effect is not being performed, that is, when the second effect execution flag is not set, the background color on the display screen of the
なお、第2演出実行フラグがセットされているときに背景色を変更しないのは、背景色を変更したのでは確変状態に移行したのかしないのかを遊技者に報知することになり、確変状態に移行するか否かを報知するための演出である昇格演出の効果が薄れてしまうからである。 Note that the background color is not changed when the second effect execution flag is set. This is because the player is notified whether the background color has been changed or has changed to the probability change state. This is because the effect of the promotion effect, which is an effect for notifying whether or not to shift, will fade.
また、ステップS833Eの処理において、第1演出の種類や第2演出の種類も対象にするのは、大当り遊技の終了後に実行される第1演出および第2演出を実現するためである。つまり、第1の実施の形態の場合と同様に実行される演出図柄変動中処理(図43参照)では、第1の実施の形態の場合と同様にプロセステーブルにおけるプロセスデータに従って演出制御が実行されるが、第1演出を実行している場合には、第1演出の種類に応じたプロセステーブルを使用することによって、大当り遊技終了後の演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動中に、図62(E)〜(H)に例示されたような第1演出が実行される。また、第2演出を実行している場合には、第2演出の種類に応じたプロセステーブルを使用することによって、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動中に、図62(I)〜(J)、図63〜図66に例示されたような第2演出が実行される。なお、この実施の形態では、第2演出は複数回の演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動に亘って実行されている。また、この実施の形態では、演出図柄変動中処理(図43参照)において、ステップS842〜S844の処理は実行されない。 In addition, in the process of step S833E, the type of the first effect and the type of the second effect are also targeted in order to realize the first effect and the second effect that are executed after the end of the big hit game. In other words, in the effect symbol variation processing (see FIG. 43) executed as in the case of the first embodiment, effect control is executed according to the process data in the process table as in the case of the first embodiment. However, when the first effect is being executed, by using a process table corresponding to the type of the first effect, during the change of the effect symbol (decoration symbol) after the big hit game, FIG. The first effects as exemplified in E) to (H) are executed. In addition, when the second effect is being executed, the process table corresponding to the type of the second effect is used, so that during the change of the effect symbol (decorative symbol), FIGS. 62 (I) to (J). The second effect as illustrated in FIGS. 63 to 66 is executed. In this embodiment, the second effect is executed over a plurality of variations of the effect symbol (decoration symbol). Further, in this embodiment, the processing in steps S842 to S844 is not executed in the effect symbol changing process (see FIG. 43).
また、変動中でないときにおいて、または変動中と変動中でないときの双方において第1演出および第2演出を実行する場合には、例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560を、演出制御プロセス処理における変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理において、ステップS831A〜S835の処理を実行してプロセステーブルを選択するとともに、プロセステーブルにおけるプロセスデータに従って演出制御を実行するように構成すればよい。なお、例えば、変動中でないときに第1演出や第2演出を実行する場合には、変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理において実行されるステップS833Aの処理で、変動パターンを考慮せず、第1演出の種類または第2演出の種類のみにもとづいてプロセステーブルを選択する。
Further, when the first effect and the second effect are executed when not changing, or both when changing and not changing, for example, the
図71は、この実施の形態における演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100における演出制御用CPU101が実行する演出制御プロセス処理における大当り終了処理(ステップS806)を示すフローチャートである。大当り終了処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、大当り終了演出タイマが設定されているか否か確認する(ステップS930)。大当り終了演出タイマが設定されている場合には、ステップS932に移行する。
FIG. 71 is a flowchart showing a jackpot end process (step S806) in the effect control process executed by the
大当り終了演出タイマが設定されていない場合には、大当り終了演出タイマに大当り終了表示時間に相当する値を設定する(ステップS931)。 If the jackpot end effect timer is not set, a value corresponding to the jackpot end display time is set in the jackpot end effect timer (step S931).
ステップS932では、大当り終了演出タイマの値を−1し、大当り終了演出タイマがタイムアウトしていなければ処理を終了する(ステップS933)。大当り終了演出タイマがタイムアウトしていたら、大当り終了指定コマンド(エンディングコマンド)として第1演出ありのコマンドを受信しているか否か確認する(ステップS934)。第1演出なしのエンディングコマンド(大当り終了2指定コマンド)を受信していたら、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(ステップS800)に応じた値に更新する(ステップS939)。
In step S932, the value of the jackpot end effect timer is decremented by 1. If the jackpot end effect timer has not timed out, the process ends (step S933). If the jackpot end effect timer has timed out, it is confirmed whether or not a command with the first effect is received as a jackpot end designation command (ending command) (step S934). If an ending command without first effect (a
そして、第1演出ありのエンディングコマンド(大当り終了1指定コマンド)を受信していたら、演出制御用CPU101は、第1演出種類選択用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を読み出し、読み出した値を第1演出種類選択用乱数値とする。すなわち、第1演出種類選択用乱数を抽出する(ステップS935)。そして、第1演出種類選択用乱数値と受信している演出図柄指定コマンド(この場合には、演出図柄2指定コマンドまたは演出図柄3指定コマンド)とにもとづいて第1演出の種類を決定する(ステップS936)。具体的には、受信した演出図柄指定コマンド(識別情報の可変表示の表示結果を特定可能なコマンドの一例)に応じて図30に示されたテーブルのうち、通常大当りまたは確変大当りの部分を選択し、第1演出種類選択用乱数値と一致する判定値に応じたキャラクタを第1演出の種類として選択する。
Then, if the ending command with the first effect (a
そして、選択した第1演出の種類を、RAM112における第1演出キャラクタバッファ112aに格納する(ステップS937)。また、第1演出実行フラグをセットする(ステップS938)。その後、ステップS939に移行する。
Then, the selected type of the first effect is stored in the first
なお、この実施の形態では、次の演出図柄(飾り図柄)の可変表示の開始時に、第1演出キャラクタバッファ112aに記憶されている第1演出の種類を示すデータ等を用いて第1演出が開始される(図70におけるステップS833E,S834,S835参照)。
In this embodiment, at the start of variable display of the next effect symbol (decoration symbol), the first effect is generated using data indicating the type of the first effect stored in the first
以上のような処理によって、大当り遊技終了後に、第1演出を実行し、第1演出が終了した後に第2演出を実行する制御が実現される。この実施の形態では、大当り遊技後に所定期間に亘って第1演出および第2演出を実行するので、確変状態等の特別遊技状態に関する遊技者の興味を長期間に亘って持続させ、遊技の興趣をより高めることができる。 By the process as described above, the control for executing the first effect after the end of the big hit game and executing the second effect after the end of the first effect is realized. In this embodiment, since the first effect and the second effect are executed for a predetermined period after the big hit game, the player's interest regarding the special game state such as the probability change state is maintained for a long period of time, and the game is interesting. Can be further enhanced.
実施の形態4.
上記の各の実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が送信した演出図柄指定コマンドにもとづいて第1演出および第2演出の種類を決定したが、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が送信する他のコマンドにもとづいて第1演出および第2演出の種類を決定するようにしてもよい。
In each of the embodiments described above, the types of the first effect and the second effect are determined based on the effect designating command transmitted by the
第4の実施の形態(実施の形態4)では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が送信した背景指定コマンドにもとづいて第1演出および第2演出の種類を決定する。なお、ここでは、第3の実施の形態の変形例としての実施の形態を説明する。
In the fourth embodiment (Embodiment 4), the types of the first effect and the second effect are determined based on the background designation command transmitted by the
図72この実施の形態における演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100における演出制御用CPU101が実行する演出制御プロセス処理における大当り終了処理(ステップS806)を示すフローチャートである。この実施の形態では、演出制御用CPU101は、第1演出種類選択用乱数値と受信している背景指定コマンド(識別情報の可変表示の表示結果を特定可能なコマンドの一例)とにもとづいて第1演出の種類を決定する(ステップS936A)。具体的には、受信した背景指定コマンドに応じたテーブルである「通常大当り」に対応するテーブルまたは「確変大当り」に対応するテーブルを選択し、第1演出種類選択用乱数値と一致する判定値に応じたキャラクタを第1演出の種類として選択する(図30参照)。
FIG. 72 is a flowchart showing a jackpot end process (step S806) in the effect control process executed by the
なお、演出制御用CPU101は、受信している背景指定コマンドが、通常時背景指定コマンドと時短時背景指定コマンドと確変時背景指定コマンドとのうちのいずれであるのかを、受信した背景指定コマンドを格納する背景指定コマンド格納領域に記憶されているデータにもとづいて判定する。そして、受信している背景指定コマンドが確変時背景指定コマンドである場合には「確変大当り」に対応するテーブルを選択し、その他の背景指定コマンドである場合には「通常大当り」に対応するテーブルを選択する。その他の処理は、第3の実施の形態の場合と同じである。なお、図13に示すように、背景指定コマンド(通常時背景指定コマンド、時短時背景指定コマンドおよび確変時背景指定コマンド)は、遊技状態が確変状態であるのか否かを特定可能なコマンドである。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、確変大当りとすることに事前決定した場合には、大当り遊技状態の終了後に、遊技状態を、通常状態から確変状態に移行させる。そして、その後の確変状態において、確変時背景指定コマンド(図13参照)を送信する。従って、背景指定コマンドは、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が確変大当りとすることに事前決定したことを特定可能な演出制御コマンドである。
The
また、この実施の形態では、演出図柄変動開始処理は第3の実施の形態の場合と同様に実行されるが(図70参照)、ステップS833Dの第2演出設定処理では、図73のフローチャートに示す処理が実行される。 In this embodiment, the effect symbol variation start process is executed in the same manner as in the third embodiment (see FIG. 70), but in the second effect setting process in step S833D, the flowchart of FIG. The processing shown is executed.
第3の実施の形態では、演出制御用CPU101は、図44に示された第2演出設定処理を実行するので、第2演出種類選択用乱数値と、第1演出キャラクタバッファ112aに記憶されているデータが示す第1演出の種類と、受信している演出図柄指定コマンドとにもとづいて第2演出の種類を決定した(図44におけるステップS912参照)。この実施の形態では、第2演出種類選択用乱数値と、第1演出キャラクタバッファ112aに記憶されているデータが示す第1演出の種類と、受信した背景指定コマンドとにもとづいて第2演出の種類を決定する(ステップS912A)。具体的には、受信した背景指定コマンドに応じて図31(A)に示されたテーブルまたは図31(B)に示されたテーブルを選択し、第2演出の種類として、第2演出種類選択用乱数の値と一致する判定値(図31において、第1演出の種類に応じた行に対応した判定値)に対応したキャラクタを選択する。
In the third embodiment, the
なお、演出制御用CPU101は、受信している背景指定コマンドが確変時背景指定コマンドである場合には図31(B)に示されたテーブルを選択し、その他の背景指定コマンドである場合には図31(A)に示されたテーブルを選択する。その他の処理は、第3の実施の形態の場合と同じである。
The
また、この実施の形態では、背景指定コマンドにもとづいて第1演出および第2演出の種類を決定したが、いずれか一方を背景指定コマンドにもとづいて決定し、他方を他の演出制御コマンド(例えば、演出図柄指定コマンド)にもとづいて決定するようにしてもよい。 In this embodiment, the type of the first effect and the second effect is determined based on the background designation command, but either one is determined based on the background designation command and the other is controlled by another effect control command (for example, , A design symbol designation command) may be determined.
また、この実施の形態では、第3の実施の形態、すなわち大当り遊技の終了後に第1演出および第2演出を実行する形態について、演出図柄制御コマンドに代えて背景指定コマンドを用いるようにしたが、第1または第2の実施の形態について、演出図柄制御コマンドに代えて背景指定コマンドを用いるようにしてもよい。 In this embodiment, the background designating command is used in place of the effect design control command in the third embodiment, that is, in the form of executing the first effect and the second effect after the end of the big hit game. In the first or second embodiment, a background designation command may be used instead of the effect symbol control command.
その場合にも、背景指定コマンドにもとづいて第1演出および第2演出の種類を決定するのではなく、いずれか一方を背景指定コマンドにもとづいて決定し、他方を他の演出制御コマンド(例えば、演出図柄指定コマンド)にもとづいて決定するようにしてもよい。例えば、第1演出を演出図柄指定コマンドにもとづいて決定し、第2演出の種類を背景指定コマンドにもとづいて決定する。 Even in this case, instead of determining the type of the first effect and the second effect based on the background designation command, either one is determined based on the background designation command, and the other is controlled by another effect control command (for example, It may be determined on the basis of a design symbol designation command). For example, the first effect is determined based on the effect designating command, and the type of the second effect is determined based on the background specifying command.
また、図20に示されたステップS107の処理では、背景指定コマンドを送信するときの遊技状態に応じた種類の背景指定コマンドを送信したが、ステップS107の処理で、事前決定手段の決定結果に応じた背景指定コマンドを送信するようにしてもよい。すなわち、図19に示されたステップS62の処理で確変大当りとすることに決定されている場合には確変時背景指定コマンドを送信し、通常大当りとすることに決定されている場合には通常時背景指定コマンドを送信する。そのように構成した場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、背景指定コマンドにもとづいて事前決定手段の決定結果を反映した決定を行うことができる。
Further, in the process of step S107 shown in FIG. 20, a background designation command of a type corresponding to the gaming state at the time of transmitting the background designation command is transmitted. A corresponding background designation command may be transmitted. That is, when it is determined that the probability change big hit is determined in the processing of step S62 shown in FIG. 19, a probability change background designation command is transmitted. Send a background specification command. In the case of such a configuration, the
なお、上記の各実施の形態では、通常状態に比べて大当り遊技状態に移行しやすい状態である特別遊技状態として確変状態を例にしたが、特別遊技状態を他の遊技状態にしてもよい。例えば、可変表示時間が短縮されることによって所定時間あたりの可変表示回数が増加し、その結果大当りの判定が実施される間隔が短くなって、結果として大当り遊技状態に移行しやすくなる時短状態を、特別遊技状態にしてもよい。 In each of the above-described embodiments, the probability variation state is taken as an example of the special gaming state in which the transition to the big hit gaming state is easier than in the normal state. However, the special gaming state may be changed to another gaming state. For example, when the variable display time is shortened, the number of variable displays per predetermined time increases, and as a result, the interval at which the determination of jackpot is performed is shortened, and as a result, the time-short state that makes it easier to shift to the jackpot gaming state. The special game state may be set.
また、上記の実施の形態では、演出装置を制御する回路が搭載された基板として、演出制御基板80、音声出力基板70およびランプドライバ基板35が設けられているが、演出装置を制御する回路を1つの基板に搭載してもよい。さらに、演出表示装置9等を制御する回路が搭載された第1の演出制御基板(表示制御基板)と、その他の演出装置(ランプ、LED、スピーカ27R,27Lなど)を制御する回路が搭載された第2の演出制御基板との2つの基板を設けるようにしてもよい。
In the above-described embodiment, the
また、上記の実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して直接コマンドを送信していたが、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が他の基板(例えば、図3に示す音声出力基板70やランプドライバ基板35など、または音声出力基板70に搭載されている回路による機能とランプドライバ基板35に搭載されている回路による機能とを備えた音/ランプ基板)に演出制御コマンドを送信し、他の基板を経由して演出制御基板80における演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信されるようにしてもよい。その場合、他の基板においてコマンドが単に通過するようにしてもよいし、音声出力基板70、ランプドライバ基板35、音/ランプ基板にマイクロコンピュータ等の制御手段を搭載し、制御手段がコマンドを受信したことに応じて音声制御やランプ制御に関わる制御を実行し、さらに、受信したコマンドを、そのまま、または例えば簡略化したコマンドに変更して、演出表示装置9を制御する演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信するようにしてもよい。その場合でも、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、上記の実施の形態における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から直接受信した演出制御コマンドに応じて表示制御を行うのと同様に、音声出力基板70、ランプドライバ基板35または音/ランプ基板から受信したコマンドに応じて表示制御を行うことができる。
In the above-described embodiment, the
また、上記の実施の形態のパチンコ遊技機は、主として、始動入賞にもとづいて可変表示部に可変表示される特別図柄の停止図柄が所定の図柄になると所定の遊技価値が遊技者に付与可能になるパチンコ遊技機であったが、始動入賞にもとづいて開放する電動役物の所定領域への入賞があると所定の遊技価値が遊技者に付与可能になるパチンコ遊技機や、始動入賞にもとづいて可変表示される図柄の停止図柄が所定の図柄の組み合わせになると開放する所定の電動役物への入賞があると所定の権利が発生または継続するパチンコ遊技機であっても、本発明を適用できる。さらに、遊技メダルを投入して賭け数を設定し遊技を行うスロット機や、遊技メダルではなく遊技球を投入して賭け数を設定し遊技を行う遊技機などにも本発明を適用できる。 In addition, the pachinko gaming machine of the above embodiment can be given a predetermined game value to a player mainly when the special symbol stop symbol variably displayed on the variable display unit based on the start winning prize becomes a predetermined symbol. A pachinko machine that can be given a predetermined gaming value to a player when there is a prize in a predetermined area of an electric game that is released based on a start prize, or a start prize The present invention can be applied even to a pachinko gaming machine in which a predetermined right is generated or continued when a winning is given to a predetermined electric combination that is released when a stop symbol of a variably displayed symbol becomes a predetermined symbol combination . Furthermore, the present invention can be applied to a slot machine that inserts game medals and sets a bet number and plays a game, or a game machine that inserts game balls instead of game medals and sets a bet number and plays a game.
本発明は、パチンコ遊技機などの遊技機に適用可能であり、遊技状態が確変状態等の特別な遊技状態に制御可能な遊技機に適用可能である。 The present invention can be applied to a gaming machine such as a pachinko gaming machine, and can be applied to a gaming machine in which the gaming state can be controlled to a special gaming state such as a probability change state.
1 パチンコ遊技機
8 特別図柄表示器
9 演出表示装置
13 始動入賞口
20 可変入賞球装置
31 遊技制御基板(主基板)
56 CPU
80 演出制御基板
100 演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ
101 演出制御用CPU
109 VDP
560 遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ
DESCRIPTION OF
56 CPU
80
109 VDP
560 Microcomputer for game control
Claims (2)
識別情報の可変表示の表示結果を前記特定表示結果とするか否かと、前記特別条件を成立させるか否かとを、可変表示の表示結果を導出表示する前に決定する事前決定手段と、
第1演出および該第1演出とは異なる第2演出を、それぞれ、複数種類のうちから選択する演出選択手段と、
前記演出選択手段が選択した前記第1演出を識別情報の可変表示中に前記演出表示装置において実行し、前記演出選択手段が選択した前記第2演出を当該識別情報の可変表示が終了した後に移行される前記特定遊技状態中に前記演出表示装置において実行する演出実行手段とを備え、
前記演出選択手段は、前記事前決定手段が前記特別条件を成立させることに決定したときには、表示結果を前記特定表示結果とするとともに前記特別条件を成立させないことに決定したときに比べて、前記第1演出として特定第1演出を選択した場合に高い割合で前記第2演出として特定第2演出を選択し、前記第1演出として所定第1演出を選択した場合に高い割合で前記第2演出として所定第2演出を選択する
ことを特徴とする遊技機。 Provided with an effect display device that variably displays a plurality of types of identification information that can be distinguished from each other and derives and displays the display result, and the game state is advantageous to the player when the specific display result is derived and displayed on the effect display device Transition to a specific gaming state, when the special condition is satisfied, shift to the specific gaming state that is advantageous to the player, and after the specific gaming state is finished, the specific display result is derived and displayed as compared with the normal gaming state It is a gaming machine that shifts to a probable state, which is an easy state,
Predetermining means for deciding whether to display the variable information display result of the identification information as the specific display result and whether to establish the special condition before deriving and displaying the variable display display result;
An effect selecting means for selecting a first effect and a second effect different from the first effect from a plurality of types , respectively ;
The first effect selected by the effect selection means is executed in the effect display device during variable display of identification information, and the second effect selected by the effect selection means is shifted to after the variable display of the identification information ends. Effect execution means for executing in the effect display device during the specific gaming state to be performed,
When the predetermining means decides to establish the special condition, the effect selection means is configured to make the display result the specific display result and not to establish the special condition, When the specific first effect is selected as the first effect, the specific second effect is selected as the second effect at a high rate, and when the predetermined first effect is selected as the first effect, the second effect is at a high rate. A predetermined second production is selected as a gaming machine.
請求項1記載の遊技機。 The effect selecting means includes at least one of a plurality of types when the pre-deciding means decides to use the display result of variable display of identification information as the specific display result and not to use the specific display result. The gaming machine according to claim 1, wherein the selection ratio of the first effect is different.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007154573A JP5795835B2 (en) | 2007-06-11 | 2007-06-11 | Game machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007154573A JP5795835B2 (en) | 2007-06-11 | 2007-06-11 | Game machine |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008302150A JP2008302150A (en) | 2008-12-18 |
| JP2008302150A5 JP2008302150A5 (en) | 2011-05-06 |
| JP5795835B2 true JP5795835B2 (en) | 2015-10-14 |
Family
ID=40231371
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007154573A Expired - Fee Related JP5795835B2 (en) | 2007-06-11 | 2007-06-11 | Game machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5795835B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5594605B2 (en) * | 2011-04-19 | 2014-09-24 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP6133235B2 (en) * | 2014-05-22 | 2017-05-24 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP6084956B2 (en) * | 2014-10-07 | 2017-02-22 | 株式会社平和 | Pachinko machine |
| JP2016083253A (en) * | 2014-10-28 | 2016-05-19 | 株式会社平和 | Game machine |
| JP6978030B2 (en) * | 2017-02-27 | 2021-12-08 | 株式会社サンセイアールアンドディ | Pachinko machine |
| JP6503564B2 (en) * | 2018-03-29 | 2019-04-24 | 株式会社サンセイアールアンドディ | Gaming machine |
| JP6929553B2 (en) * | 2018-08-29 | 2021-09-01 | 株式会社サンセイアールアンドディ | Pachinko machine |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002085705A (en) * | 2000-09-12 | 2002-03-26 | Snk Corp | Game machine |
| JP2002113194A (en) * | 2000-10-04 | 2002-04-16 | Aruze Corp | Game machine |
| JP4723073B2 (en) * | 2000-11-02 | 2011-07-13 | 株式会社平和 | Game machine |
| JP2002204865A (en) * | 2001-01-11 | 2002-07-23 | Maruhon Ind Co Ltd | Pattern display system for game machine |
| JP2005328920A (en) * | 2004-05-18 | 2005-12-02 | Aruze Corp | Game machine and simulation program of the game machine |
| JP4711220B2 (en) * | 2005-05-20 | 2011-06-29 | 奥村遊機株式会社 | Game machine |
-
2007
- 2007-06-11 JP JP2007154573A patent/JP5795835B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2008302150A (en) | 2008-12-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5468192B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6867755B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5795835B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5548369B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6279876B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5236211B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4327010B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5026135B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4499068B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6158157B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4519145B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5995898B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5995896B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6711561B2 (en) | Amusement machine | |
| JP5931675B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5931674B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4451419B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5995897B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4680843B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2006020963A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6391635B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6391636B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4668325B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2014158818A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2015080634A (en) | Game machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100524 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110322 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20111130 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120124 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120322 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130122 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130321 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20131203 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140225 |
|
| A911 | Transfer of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20140305 |
|
| A912 | Removal of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A912 Effective date: 20140418 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150428 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20150817 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5795835 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |