JP5524468B2 - Game machine - Google Patents
Game machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5524468B2 JP5524468B2 JP2008288818A JP2008288818A JP5524468B2 JP 5524468 B2 JP5524468 B2 JP 5524468B2 JP 2008288818 A JP2008288818 A JP 2008288818A JP 2008288818 A JP2008288818 A JP 2008288818A JP 5524468 B2 JP5524468 B2 JP 5524468B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- effect
- display
- big hit
- state
- variation
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Description
本発明は、パチンコ遊技機およびコイン遊技機等の遊技機に関し、特に、各々が識別可能な複数種類の識別情報の変動表示を行ない表示結果を導出表示する複数の変動表示領域を有する変動表示手段を備え、該変動表示手段に特定表示結果が導出表示されたときに遊技者にとって有利な特定遊技状態に制御する遊技機に関する。 The present invention relates to a gaming machine such as a pachinko gaming machine and a coin gaming machine, and in particular, a variable display means having a plurality of variable display areas for performing variable display of a plurality of types of identification information each identifiable and deriving and displaying a display result. And a gaming machine that controls to a specific gaming state advantageous to the player when the specific display result is derived and displayed on the variation display means.
この種の遊技機として一般的に知られているものとしては、たとえば、パチンコ遊技機のように、各々が識別可能な複数種類の識別情報(図柄)の変動表示を行ない表示結果を導出表示する複数の変動表示領域を有する変動表示手段(画像表示装置等)を備え、該変動表示手段に特定表示結果(大当り表示結果)が導出表示されたときに遊技者にとって有利な特定遊技状態(大当り遊技状態)に制御し、予め定められた特別状態発生条件が成立(確変大当り種別に決定した)ときに前記特定遊技状態よりも遊技者に有利な特別状態を付与する特別遊技状態(確変状態)に制御するものがあった。 As what is generally known as this type of gaming machine, for example, as in a pachinko gaming machine, a plurality of types of identification information (symbols) each identifiable are displayed in a variable manner, and the display result is derived and displayed. There is provided a variable display means (image display device or the like) having a plurality of variable display areas, and a specific game state (big hit game) that is advantageous to the player when a specific display result (big hit display result) is derived and displayed on the variable display means To a special gaming state (probability variation state) that gives a special state more advantageous to the player than the specific gaming state when a predetermined special state occurrence condition is established (determined as a probability variation big hit type) There was something to control.
このような遊技機としては、変動表示手段の変動表示においてリーチ演出状態となったときに、当該リーチ演出中において、次のリーチパターンが予告されて別のリーチ演出に切替える制御が行なわれるように構成された遊技機があった(特許文献1)。
しかし、前述のような従来の遊技機では、切替え先のリーチ演出を予告する一定の演出が繰返される等、遊技の演出の進行が単調であるため、遊技者が演出に飽きてしまい、遊技の興趣が著しく減退するおそれがあった。 However, in the conventional gaming machine as described above, since the progress of the game effect is monotonous, such as a certain effect of notifying the reach effect of the switching destination is repeated, the player gets bored with the effect, and the game There was a risk that interest would decline significantly.
本発明は、かかる実情に鑑み考え出されたものであり、その目的は、リーチ演出における遊技の興趣を向上させることができる遊技機を提供することである。 The present invention has been conceived in view of such circumstances, and an object thereof is to provide a gaming machine capable of improving the interest of a game in reach production.
(1) 各々が識別可能な複数種類の識別情報の変動表示を行ない表示結果を導出表示する複数の変動表示領域(「左」、「中」、「右」の各図柄表示エリア9L、9C、9R)を有する変動表示手段(演出表示装置9)を備え、該変動表示手段に特定表示結果(大当り表示結果)が導出表示されたときに遊技者にとって有利な特定遊技状態(大当り遊技状態)に制御する遊技機(パチンコ遊技機1)であって、
前記特定遊技状態に制御するか否かを、前記識別情報の表示結果が導出表示される以前に決定する事前決定手段(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560、図28のS62)と、
該事前決定手段による決定に基づいて、前記複数の変動表示領域において前記識別情報が前記特定表示結果の一部を構成しているが少なくとも一部の変動表示領域が変動表示中であるリーチ状態とするリーチ演出を行なうリーチ変動表示パターンを含む複数種類の変動表示パターンの中から1つの変動表示パターンを選択する変動表示パターン選択手段(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560、図29のS101〜S105)と、
該変動表示パターン選択手段が選択した変動表示パターンに基づいて、前記変動表示手段における前記識別情報の変動表示の制御を行なう演出制御手段(演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100、図39のS801〜S803)とを含み、
前記リーチ変動表示パターンには、予め定められた通常のリーチ演出(ノーマルリーチ)を行なう通常リーチ変動表示パターンと、前記通常のリーチ演出が行なわれた後に当該通常のリーチ演出と比べて前記特定遊技状態となるときに実行される割合が高い特別なリーチ演出(スーパーリーチA,B)を行なう特別リーチ変動表示パターンとを含む複数種類のリーチ変動表示パターンが設けられ、
リーチ演出を実行して前記特定表示結果とならない状態で一旦停止した後に、所定の演出パターン(図12の煽り演出および発展演出)を実行する発展演出実行手段(演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100、図39のS801,S802、図45のS845)をさらに含み、
該発展演出実行手段における前記演出パターンには、実行中の変動表示が継続するか否かを報知する発展可否演出を前記演出装置により行なった後に前記特別なリーチ演出(スーパーリーチA,B)に発展する第1の発展演出パターンと、前記発展可否演出を行なった後に前記特定表示結果とならない状態で前記識別情報の変動表示を停止する第2の発展演出パターンとを含む複数種類の演出パターンが設けられ、
前記発展可否演出には、第1表示態様のキャラクタ画像が表示される第1発展可否演出と、第2表示態様のキャラクタ画像が表示される第2発展可否演出とを含む複数種類の発展可否演出が設けられ、
前記特別なリーチ演出には、第1特別リーチ演出と、当該第1特別リーチ演出よりも前記特定遊技状態となるときに実行される割合が高い第2特別リーチ演出とを含む複数種類の特別なリーチ演出が設けられ、
前記発展演出実行手段は、前記第1の発展演出パターンおよび前記第2の発展演出パターンをそれぞれ異なる割合で実行し、
前記第1の発展演出パターンにおいては、前記第1発展可否演出が行なわれた後には前記第2発展可否演出が行なわれた後よりも高い割合で前記第1特別リーチ演出に発展し、前記第2発展可否演出が行なわれた後には前記第1発展可否演出が行なわれた後よりも高い割合で前記第2特別リーチ演出に発展し、さらに、前記第1発展可否演出が行なわれた後に前記第2特別リーチ演出に発展したときには、前記第2発展可否演出が行なわれた後に前記第1特別リーチ演出に発展したときよりも高い割合で前記特定遊技状態となる。
(1) A plurality of variable display areas (“left”, “middle”, and “right”
Predetermining means (
Based on the determination by the pre-determining means, a reach state in which the identification information forms part of the specific display result in the plurality of variable display areas, but at least some of the variable display areas are in variable display A variation display pattern selection means (
Production control means (
The reach variation display pattern includes a normal reach variation display pattern for performing a predetermined normal reach effect (normal reach), and the specific game state compared to the normal reach effect after the normal reach effect is performed. A plurality of types of reach variation display patterns including a special reach variation display pattern for performing a special reach effect (super reach A and B) that is executed at a high rate when
After performing the reach effect and temporarily stopping in a state where the specific display result is not obtained, the development effect execution means (the
In the production pattern in the development production execution means, the special reach production (super reach A, B) is performed after the production device performs a development possibility production to notify whether or not the variable display during execution is continued. There are a plurality of types of production patterns including a first development production pattern that develops and a second development production pattern that stops the change display of the identification information in a state in which the specific display result is not obtained after performing the development propriety production. Provided,
The development propriety effect includes a plurality of types of development propriety effects including a first development propriety effect in which a character image in a first display mode is displayed and a second development propriety effect in which a character image in a second display mode is displayed. Is provided,
The special reach production includes a plurality of types of special reach production including a first special reach production and a second special reach production that is executed at a higher rate when the specific gaming state is set than the first special reach production. Reach production is provided,
The development effect execution means executes the first development effect pattern and the second development effect pattern at different ratios,
In the first development effect pattern, after the first development propriety effect is performed, the first development effect pattern is developed at a higher rate than after the second development propriety effect is performed. After the second development propriety effect is performed, the second special reach production is developed at a higher rate than after the first development propriety effect is performed , and further after the first development propriety effect is performed. When the second special reach effect is developed, the specific gaming state is set at a higher rate than when the second special reach effect is developed after the second development possibility effect is performed.
このような構成によれば、リーチ変動表示パターンにおいて、リーチ演出を実行して特定表示結果とならない状態で一旦停止した後に、実行中の変動表示が継続するか否かを報知する発展可否演出が行なわれる。そして、所定の発展演出が複数種類設けられ、発展可否演出において表示されるキャラクタ画像の表示態様に応じて発展先の特別なリーチ演出の割合が異なるので、特定表示結果とならない状態で一旦停止した後、キャラクタ画像の表示態様に応じて、発展先の特別なリーチ演出への発展を煽ることにより、変動表示の演出進行のバリエーションを豊富化することができる。これにより、遊技者がリーチ演出に飽きてしまわないようにすることができ、リーチ演出における遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。
(2) 前記発展可否演出は、複数種類の所定演出のうち何れかが実行され、
前記第1の発展演出パターンは、前記第2の発展演出パターンよりも高い割合で、前記発展可否演出において前記所定演出のうち特定演出が実行される。
According to such a configuration, in the reach variation display pattern, after the reach effect is executed and temporarily stopped in a state where the specific display result is not obtained, the development propriety effect informing whether or not the variation display being executed continues is performed. Done. A plurality of types of predetermined development effects are provided, and the ratio of the special reach effects at the development destination varies depending on the display mode of the character image displayed in the development permission / prohibition effect. Later, depending on the display mode of the character image, the development of the special reach effect at the development destination can be encouraged to enrich the variation in the effect display effect. Thereby, it is possible to prevent the player from getting bored with the reach production, and to improve the interest of the game in the reach production.
(2) One of a plurality of types of predetermined effects is executed as the development propriety effect,
The first development effect pattern is executed at a higher rate than the second development effect pattern, and the specific effect is executed among the predetermined effects in the development propriety effect.
以下、本発明の実施の形態を、図面を参照して説明する。なお、遊技機の一例としてパチンコ遊技機を示すが、本発明はパチンコ遊技機に限られず、コイン遊技機およびスロットマシン等のその他の遊技機であってもよく、各々が識別可能な複数種類の識別情報の変動表示を行ない表示結果を導出表示する複数の変動表示領域を有する変動表示手段を備え、該変動表示手段に特定表示結果が導出表示されたときに遊技者にとって有利な特定遊技状態に制御する遊技機であれば、どのような遊技機であってもよい。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. Note that a pachinko gaming machine is shown as an example of a gaming machine, but the present invention is not limited to a pachinko gaming machine, and may be other gaming machines such as a coin gaming machine and a slot machine. A variation display means having a plurality of variation display areas for performing a variation display of the identification information and deriving and displaying the display result is provided. Any gaming machine may be used as long as it is a gaming machine to be controlled.
〔第1実施形態〕
まず、遊技機の一例であるパチンコ遊技機1の全体の構成について説明する。図1はパチンコ遊技機1を正面からみた正面図である。
[First Embodiment]
First, the overall configuration of a
パチンコ遊技機1は、遊技用媒体としての遊技球を遊技領域7に打込んで所定の遊技が行なわれる遊技機である。縦長の方形状に形成された外枠(図示せず)と、外枠の内側に開閉可能に取付けられた遊技枠とで構成される。また、パチンコ遊技機1は、遊技枠に開閉可能に設けられている額縁状に形成されたガラス扉枠2を有する。遊技枠は、外枠に対して開閉自在に設置される前面枠(図示せず)と、機構部品等が取付けられる機構板(図示せず)と、それらに取付けられる種々の部品(後述する遊技盤6を除く)とを含む構造体である。
The
ガラス扉枠2の下部表面には打球供給皿(上皿)3がある。打球供給皿3の下部には、打球供給皿3に収容しきれない遊技球を貯留する余剰球受皿4や、打球を発射する打球操作ハンドル(操作ノブ)5が設けられている。また、ガラス扉枠2の背面には、遊技盤6が着脱可能に取付けられている。なお、遊技盤6は、それを構成する板状体と、その板状体に取付けられた種々の部品とを含む構造体である。また、遊技盤6の前面には、打込まれた遊技球が流下可能な遊技領域7が形成されている。
On the lower surface of the
遊技領域7の中央付近には、液晶表示装置(LCD)で構成された演出表示装置9が設けられている。演出表示装置9の表示画面には、後述する第1特別図柄表示器8aでの第1特別図柄、および、第2特別図柄表示器8bでの第2特別図柄のそれぞれの変動表示に同期した演出図柄の変動表示を行なう演出図柄表示領域がある。演出表示装置9は、各々が識別可能な複数種類の識別情報としての演出図柄の変動表示を行なう変動表示装置(変動表示部)に相当する。演出図柄表示領域には、たとえば「左」、「中」、「右」の3つの装飾用(演出用)の識別情報を変動表示する図柄表示エリアがある。図柄表示エリアには「左」、「中」、「右」の各図柄表示エリア9L、9C、9Rがあるが、図柄表示エリア9Aの位置は、演出表示装置9の表示画面において固定的でなくてもよいし、図柄表示エリア9L、9C、9Rの3つの領域が離れていてもよい。第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄のそれぞれは、主基板に搭載されている遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータによって制御される。演出表示装置9は、演出制御基板に搭載されている演出制御用マイクロコンピュータによって制御される。第1特別図柄表示器8aで第1特別図柄の変動表示が実行されているときに、その変動表示に伴って演出表示装置9で演出表示を実行させ、第2特別図柄表示器8bで第2特別図柄の変動表示が実行されているときに、その変動表示に伴って演出表示装置で演出表示を実行させるので、遊技の進行状況を把握しやすくすることができる。
An
なお、本実施の形態においては、演出表示装置9は、液晶表示装置を用いた例について説明するが、これに限らず、CRT、プラズマ表示やエレクトロルミネセンスあるいはドットマトリックス表示を利用したもの等、その他の画像表示式のものであってもよい。
In the present embodiment, the
遊技盤6における下部の左側には、各々が識別可能な複数種類の識別情報としての第1特別図柄を変動表示する第1特別図柄表示器(第1変動表示部)8aが設けられている。この実施の形態では、第1特別図柄表示器8aは、0〜9の数字を変動表示可能な簡易で小型の表示器(たとえば7セグメントLED)で実現されている。すなわち、第1特別図柄表示器8aは、0〜9の数字(または、記号)を変動表示するように構成されている。遊技盤6における下部の右側には、各々が識別可能な複数種類の識別情報としての第2特別図柄を変動表示する第2特別図柄表示器(第2変動表示部)8bが設けられている。第2特別図柄表示器8bは、0〜9の数字を変動表示可能な簡易で小型の表示器(たとえば7セグメントLED)で実現されている。すなわち、第2特別図柄表示器8bは、0〜9の数字(または、記号)を変動表示するように構成されている。
On the left side of the lower part of the
なお、本実施の形態においては、第1特別図柄表示器8aおよび第2特別図柄表示器8bは、7セグメントLEDを用いた例について説明するが、これに限らず、液晶表示装置、CRT、プラズマ表示やエレクトロルミネセンスあるいはドットマトリックス表示を利用したもの等、画像表示式のものであってもよい。また、特別図柄表示器8は、回転ドラム式の表示装置等、機械式のものであってもよい。
In the present embodiment, the first
小型の表示器は、たとえば方形状に形成されている。また、この実施の形態では、第1特別図柄の種類と第2特別図柄の種類とは同じ(たとえば、ともに0〜9の数字)であるが、種類が異なっていてもよい。また、第1特別図柄表示器8aおよび第2特別図柄表示器8bは、それぞれ、たとえば、00〜99の数字(または、2桁の記号)を変動表示するように構成されていてもよい。
The small indicator is formed in, for example, a square shape. In this embodiment, the type of the first special symbol and the type of the second special symbol are the same (for example, both 0 to 9), but the types may be different. Further, the first
以下、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄とを特別図柄と総称することがあり、第1特別図柄表示器8aと第2特別図柄表示器8bとを特別図柄表示器(変動表示部)と総称することがある。
Hereinafter, the first special symbol and the second special symbol may be collectively referred to as a special symbol, and the first
第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄の変動表示は、変動表示の実行条件である第1始動条件(遊技球が第1始動入賞口13に入賞したこと)または第2始動条件(遊技球が第2始動入賞口14に入賞したこと)が成立した後、変動表示の開始条件(たとえば、保留記憶数が0でない場合であって、第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄の変動表示が実行されていない状態であり、かつ、大当り遊技が実行されていない状態)が成立したことに基づいて開始され、変動表示時間が経過すると表示結果(停止図柄)を導出表示する。始動条件は成立しているが開始条件が成立していない変動表示に関するデータは、開始条件が成立するまで保留記憶データとして保留して記憶される。具体的に、保留記憶データは、後述する遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のRAM55の所定領域に記憶される。
The variation display of the first special symbol or the second special symbol is the first start condition (that the game ball has won the first start winning opening 13) or the second start condition (the game ball is the first one) After the 2
入賞とは、入賞口等の予め入賞領域として定められている領域に遊技球が入ったことであり、当該領域を遊技球が通過したことを含む概念である。始動条件(第1始動条件,第2始動条件)は、少なくとも、遊技球が始動領域(第1始動入賞口13,第2始動入賞口14)を遊技球が通過したことに基づいて成立するものであればよい。つまり、始動条件は、第1始動入賞口13,第2始動入賞口14の構成のような通過した遊技球が始動領域内部に取込まれる構成における遊技球の当該通過に基づいて成立するものであってもよく、通過ゲートのような通過した遊技球が内部に取込まれずに遊技領域7を流下する構成における遊技球の当該通過に基づいて成立するものであってもよい。また、表示結果を導出表示するとは、図柄(識別情報の例)を停止表示させることである(いわゆる再変動の前の停止を除く。)。また、この実施の形態では、第1始動入賞口13への入賞と第2始動入賞口14への入賞とのうち第2始動入賞口14への入賞を優先させ、変動表示の開始条件を成立させる。たとえば第2始動入賞口14への入賞を優先させる場合には、第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄の変動表示が実行されていない状態であり、かつ、大当り遊技が実行されていない状態であれば、第1保留記憶数が0でない場合でも、第2保留記憶数が0になるまで、第2特別図柄の変動表示を続けて実行する。なお第1始動入賞口13への入賞を優先させ、変動表示の開始条件を成立させるようにしてもよい。また、第1始動入賞口13への入賞および第2始動入賞口14への入賞に関わりなく、始動入賞が生じた順に変動表示の開始条件を成立させるようにしてもよい。
Winning is a concept including that a game ball has entered a predetermined area such as a prize opening and that has passed through the area. The start condition (first start condition, second start condition) is established based on at least the game ball passing through the start area (the first
第1特別図柄表示器8aの近傍には、第1特別図柄表示器8aによる第1特別図柄の変動表示時間中に、装飾用(演出用)の図柄としての第1飾り図柄の変動表示を行なう第1飾り図柄表示器9aが設けられている。この実施の形態では、第1飾り図柄表示器9aは、2つのLEDで構成されている。第1飾り図柄表示器9aは、演出制御基板に搭載されている演出制御用マイクロコンピュータによって制御される。また、第2特別図柄表示器8bの近傍には、第2特別図柄表示器8bによる第2特別図柄の変動表示時間中に、装飾用(演出用)の図柄としての第2飾り図柄の変動表示を行なう第2飾り図柄表示器9bが設けられている。第2飾り図柄表示器9bは、2つのLEDで構成されている。第2飾り図柄表示器9bは、演出制御基板に搭載されている演出制御用マイクロコンピュータによって制御される。
In the vicinity of the first
なお、第1飾り図柄と第2飾り図柄とを、飾り図柄と総称することがある。また、第1飾り図柄表示器9aと第2飾り図柄表示器9bとを、飾り図柄表示器と総称することがある。 In addition, a 1st decorative design and a 2nd decorative design may be named generically. Further, the first decorative symbol display 9a and the second decorative symbol display 9b may be collectively referred to as a decorative symbol display.
飾り図柄の変動(変動表示)は、2つのLEDが交互に点灯する状態を継続することによって実現される。第1特別図柄表示器8aにおける第1特別図柄の変動表示と、第1飾り図柄表示器9aにおける第1飾り図柄の変動表示とは同期している。第2特別図柄表示器8bにおける第2特別図柄の変動表示と、第2飾り図柄表示器9bにおける第2飾り図柄の変動表示とは同期している。同期とは、変動表示の開始時点および終了時点が同じであって、変動表示の期間が同じであることをいう。また、第1特別図柄表示器8aにおいて大当り図柄が停止表示されるときには、第1飾り図柄表示器9aにおいて大当りを想起させる側のLEDが点灯されたままになる。第2特別図柄表示器8bにおいて大当り図柄が停止表示されるときには、第2飾り図柄表示器9bにおいて大当りを想起させる側のLEDが点灯されたままになる。なお、第1飾り図柄表示器9aおよび第2飾り図柄表示器9bの機能を、演出表示装置9で実現するようにしてもよい。すなわち、第1飾り図柄および第2飾り図柄が、演出表示装置9の表示画面において画像として変動表示されるように制御してもよい。
The variation of the decorative pattern (variable display) is realized by continuing the state where the two LEDs are alternately lit. The fluctuation display of the first special symbol on the first
演出表示装置9の下方には、第1始動入賞口13を有する入賞装置が設けられている。第1始動入賞口13に入賞した遊技球は、遊技盤6の背面に導かれ、第1始動口スイッチ13aによって検出される。
A winning device having a first
また、第1始動入賞口(第1始動口)13を有する入賞装置の下方には、遊技球が入賞(通過)可能な第2始動入賞口(第2始動口)14を有する可変入賞球装置15が設けられている。第2始動入賞口14に入賞した遊技球は、遊技盤6の背面に導かれ、第2始動口スイッチ14aによって検出される。可変入賞球装置15は、ソレノイド16によって開状態とされる。可変入賞球装置15が開状態になることによって、遊技球が第2始動入賞口14に入賞可能になり(始動入賞し易くなり)、遊技者にとって有利な状態(第1状態)になる。可変入賞球装置15が開状態になっている状態では、第1始動入賞口13よりも、第2始動入賞口14に遊技球が入賞しやすい。また、可変入賞球装置15が閉状態になっている状態は、遊技者にとって不利な状態(第2状態)であり、遊技球が第2始動入賞口14に入賞しない。したがって、可変入賞球装置15が閉状態になっている状態では、第2始動入賞口14よりも、第1始動入賞口13に遊技球が入賞しやすい。なお、可変入賞球装置15が閉状態になっている状態において、入賞はしづらいものの、入賞することは可能である(すなわち、遊技球が入賞しにくい)ように構成されていてもよい。
A variable winning ball apparatus having a second starting winning port (second starting port) 14 through which a game ball can win (pass) is provided below the winning device having the first starting winning port (first starting port) 13. 15 is provided. The game ball that has won the second
以下、第1始動入賞口13と第2始動入賞口14とを総称して始動入賞口または始動口ということがある。
Hereinafter, the first
可変入賞球装置15が開放状態に制御されているときには、可変入賞球装置15に向かう遊技球は第2始動入賞口14に極めて入賞しやすい。そして、第1始動入賞口13は演出表示装置9の直下に設けられているが、第2始動入賞口14の入賞率の方を第1始動入賞口13の入賞率よりもより高くするようにしてもよい。具体的には、演出表示装置9の下端と第1始動入賞口13との間の間隔をさらに狭めたり、第1始動入賞口13の周辺で釘を密に配置したり、第1始動入賞口13の周辺での釘配列を遊技球を第1始動入賞口13に導きづらくして、第2始動入賞口14の入賞率の方を第1始動入賞口13の入賞率よりもより高くするようにしてもよい。
When the variable winning
なお、この実施の形態では、図1に示すように、第2始動入賞口14に対してのみ開閉動作を行なう可変入賞球装置15が設けられているが、第1始動入賞口13および第2始動入賞口14のいずれについても開閉動作を行なう可変入賞球装置が設けられている構成であってもよい。
In this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 1, the variable winning
第1飾り図柄表示器9aの側方には、第1始動入賞口13に入った有効入賞球数すなわち第1保留記憶数(保留記憶を、始動記憶または始動入賞記憶ともいう。)を表示する4つの表示器からなる第1特別図柄保留記憶表示器18aが設けられている。第1特別図柄保留記憶表示器18aは、有効始動入賞がある毎に、点灯する表示器の数を1増やす。そして、第1特別図柄表示器8aでの変動表示が開始される毎に、点灯する表示器の数を1減らす。
On the side of the first decorative symbol display 9a, the number of effective winning balls that have entered the first
第2飾り図柄表示器9bの側方には、第2始動入賞口14に入った有効入賞球数すなわち第2保留記憶数を表示する4つの表示器からなる第2特別図柄保留記憶表示器18bが設けられている。第2特別図柄保留記憶表示器18bは、有効始動入賞がある毎に、点灯する表示器の数を1増やす。そして、第2特別図柄表示器8bでの変動表示が開始される毎に、点灯する表示器の数を1減らす。
On the side of the second decorative symbol display 9b is a second special symbol reserved memory display 18b comprising four indicators for displaying the number of effective winning balls that have entered the second
また、演出表示装置9の表示画面には、第1保留記憶数と第2保留記憶数との合計である合計数(合算保留記憶数)を表示する領域(以下、合算保留記憶表示部18cという。)が設けられている。合計数を表示する合算保留記憶表示部18cが設けられているので、変動表示の開始条件が成立していない実行条件の成立数の合計を把握しやすくすることができる。なお、合算保留記憶表示部18cが設けられているので、第1特別図柄保留記憶表示器18aおよび第2特別図柄保留記憶表示器18bは、設けられていなくてもよい。
In addition, the display screen of the
演出表示装置9は、第1特別図柄表示器8aによる第1特別図柄の変動表示時間中、および第2特別図柄表示器8bによる第2特別図柄の変動表示時間中に、装飾用(演出用)の図柄としての演出図柄の変動表示を行なう。第1特別図柄表示器8aにおける第1特別図柄の変動表示と、それに対応した演出表示装置9における演出図柄の変動表示とは同期して行なわれる。また、第2特別図柄表示器8bにおける第2特別図柄の変動表示と、それに対応した演出表示装置9における演出図柄の変動表示とは同期して行なわれる。また、第1特別図柄表示器8aにおいて大当り図柄が停止表示されるときと、第2特別図柄表示器8bにおいて大当り図柄が停止表示されるときとには、演出表示装置9において大当りを想起させるような特定表示結果としての演出図柄の組合せが停止表示される。
The
また、演出表示装置9の周囲の飾り部において、上側には、回転動作をする星形状の可動部材84が設けられている。可動部材84は、演出表示装置9の周囲の飾り部というような遊技者に視認可能な位置に設けられ、後述する可動部材予告のような所定の演出に応じて動作する部材である。より具体的に、可動部材84は、モータ88の回転軸に取付けられ、モータ88が回転することにしたがって駆動され、回転動作をする。可動部材84は、予め定められた動作条件が成立したときに動作させられる。
In addition, a star-shaped
演出表示装置9の周囲の飾り部において、右側には、上演出LED85a、中演出LED85bおよび下演出LED85cが設けられている。上演出LED85a、中演出LED85bおよび下演出LED85cは、特定演出としての擬似連の演出(1回の変動期間中におけるそれぞれの再変動期間(初回変動の期間も含む。)において関連する表示演出が実行されるような演出)が実行されるときに点滅する。ここで、擬似連とは、本来は1つの保留記憶に対応する1回の変動であるものの複数の保留記憶に対応する複数回の変動が連続して行なわれているように見せる演出表示である擬似連続変動を示す略語である。
On the right side of the decorative portion around the
また、擬似連とは、1の始動入賞に対して、あたかも複数回の図柄の変動表示(可変表示)が実行されたかのように見せるために、1の始動入賞に対して決定された変動時間内にて、全部の図柄列(左,中,右)について仮停止と、再変動とを所定回数実行する特殊な変動パターン(変動表示パターンともいう)のことを指す。たとえば、再変動の繰返し実行回数(初回変動およびその後の再変動を含む合計の変動回数であり、擬似連変動回数ともいう)が多い程、大当りとなる信頼度(大当りとなるときとはずれとなるときとを含むすべての選択割合に対して大当りとなるときに選択される割合の度合い、大当りとなる割合の程度、すなわち、大当りとなる信頼性の度合い)が高くなる。より具体的には、大当りと決定されたときに選択される割合が高くなる。擬似連の変動パターンにおいては、演出表示装置9において仮停止される図柄の組合せが、仮停止図柄の組合せと呼ばれる。仮停止図柄の組合せは、大当り図柄の組合せ以外の図柄の組合せよりなる複数種類のチャンス目(以下、擬似連チャンス目という)のうちからいずれかの擬似連チャンスに決定される。また、擬似連変動を実行した場合には、必ず最終的にリーチ状態として何らかのリーチ演出を実行するようにしてもよい。
In addition, the pseudo-ream is within the variation time determined with respect to one start winning prize in order to make it appear as if multiple symbols of variable display (variable display) have been executed for one starting winning prize. In this case, a special variation pattern (also referred to as a variation display pattern) in which temporary stop and re-variation are executed a predetermined number of times for all the symbol strings (left, middle, right). For example, the greater the number of repeated re-executions (the total number of changes including the initial change and subsequent re-changes, also referred to as the pseudo-variable number of times), the greater the reliability of the big hit (the difference from the big hit) The ratio of the ratio that is selected when the jackpot is large, the ratio of the ratio that is jackpot, that is, the degree of reliability that is the jackpot) is increased. More specifically, the ratio selected when it is determined that the jackpot is high. In the pseudo-continuous variation pattern, a combination of symbols temporarily stopped in the
ここで、リーチ状態は、演出表示装置9の表示領域において停止表示された演出図柄が大当り組合せの一部を構成しているときに未だ停止表示されていない演出図柄の変動が継続している表示状態、または、全部もしくは一部の演出図柄が大当り組合せの全部または一部を構成しながら同期して変動している表示状態である。言い換えると、リーチとは、複数の変動表示領域において識別情報が特定表示結果を構成しているが少なくとも一部の変動領域領域が変動表示中である状態をいう。この実施形態において、リーチ状態は、たとえば、左,右の図柄表示エリア9L,9Rで同じ図柄が停止し、中の図柄表示エリア9Cで図柄が停止していない状態で形成される。リーチ状態が形成されるときの左,右の図柄表示エリア9L,9Rで停止された図柄は、リーチ形成図柄、または、リーチ図柄と呼ばれる。
Here, in the reach state, when the effect symbols that are stopped and displayed in the display area of the
そして、リーチ状態における表示演出が、リーチ演出表示(リーチ演出)である。また、リーチの際に、通常と異なる演出がランプや音で行なわれることがある。この演出をリーチ演出という。また、リーチの際に、キャラクタ(人物等を模した演出表示であり、図柄(演出図柄等)とは異なるもの)を表示させたり、演出表示装置9の背景画像の表示態様(たとえば、色等)を変化させたりすることがある。このキャラクタの表示や背景の表示態様の変化をリーチ演出表示という。また、リーチの中には、それが出現すると、通常のリーチに比べて、大当りが発生しやすいように設定されたものがある。このような特別(特定)のリーチをスーパーリーチという。さらに、擬似連変動を実行した場合は、再変動の繰返し実行回数(擬似連変動回数)によって演出の発生割合が変化するものでもよい。たとえば、再変動の実行回数が2回まで行くと「リーチ確定」、再変動の実行回数が3回まで行くと「スーパーリーチ確定」、再変動の実行回数が4回まで行くと「大当り確定」となるようなものでもよい。
The display effect in the reach state is reach effect display (reach effect). In addition, during the reach, an unusual performance may be performed with a lamp or sound. This production is called reach production. Further, in the case of reach, a character (an effect display imitating a person or the like, which is different from a design (effect design etc.)) or a display mode (for example, a color etc.) of the background image of the
擬似連において仮停止する図柄としては、たとえば、「1」「3」「5」の奇数目、「3」「4」「5」の並び目のようにゾロ目ではないが特徴のある出目よりなる仮停止図柄が選択される。このような仮停止図柄を表示することにより、遊技者に擬似連をアピールすることができ、仮停止する際、および、または、再変動する際に擬似連をアピールすることができる。 As a symbol that temporarily stops in the quasi-ream, for example, odd numbers of “1”, “3”, and “5”, and features that are not double-thick like “3”, “4”, and “5” are characteristic A temporary stop symbol is selected. By displaying such a temporary stop symbol, it is possible to appeal the pseudo-ream to the player, and it is possible to appeal the pseudo-ream when temporarily stopping and / or changing again.
また、演出表示装置9の周囲の飾り部において、左側には、モータ86の回転軸に取付けられ、モータ86が回転すると移動する可動部材78が設けられている。可動部材78は、擬似連の演出が実行されるときに動作する。なお、上演出LED85a、中演出LED85bおよび下演出LED85cの近傍には、各LEDの取付部分を振動させる振動モータ(図示せず)が設けられている。
In addition, in the decorative portion around the
また、図1に示すように、可変入賞球装置15の下方には、ソレノイド21によって開閉される開閉板を用いた特別可変入賞球装置20が設けられている。特別可変入賞球装置20は、開閉板によって開閉される大入賞口が設けられている。特別可変入賞球装置20は、第1特別図柄表示器8aに特定表示結果(大当り図柄)が導出表示されたときと、第2特別図柄表示器8bに特定表示結果(大当り図柄)が導出表示されたときとにそれぞれ生起する特定遊技状態としての大当り遊技状態において、開閉板が遊技者にとって有利な開状態(第1の状態)に制御され、大当り遊技状態以外の状態において開閉板が遊技者にとって不利な閉状態(第2の状態)に制御される。大入賞口に入賞した遊技球はカウントスイッチ23で検出される。
As shown in FIG. 1, a special variable winning
遊技領域6には、遊技球の入賞に基づいて予め決められている所定数の景品遊技球(賞球)の払出を行なうための入賞口(普通入賞口)29,30,33,39も設けられている。入賞口29,30,33,39に入賞した遊技球は、入賞口スイッチ29a,30a,33a,39aで検出される。
The
遊技盤6の右側方には、普通図柄表示器10が設けられている。普通図柄表示器10は、普通図柄と呼ばれる複数種類の識別情報(たとえば、「○」および「×」)を変動表示する。
A
遊技球がゲート32を通過しゲートスイッチ32aで検出されると、普通図柄表示器10での変動表示が開始される。この実施の形態では、上下のランプ(点灯時に図柄が視認可能になる)が交互に点灯することによって変動表示が行なわれ、たとえば、変動表示の終了時に下側のランプが点灯すれば当りとなる。そして、普通図柄表示器10における停止図柄が所定の図柄(当り図柄)である場合に、可変入賞球装置15が所定回数、所定時間だけ開状態になる。すなわち、可変入賞球装置15の状態は、普通図柄の停止図柄が当り図柄である場合に、遊技者にとって不利な状態から有利な状態(第2始動入賞口14に遊技球が入賞可能な状態)に変化する。普通図柄表示器10の近傍には、ゲート32を通過した入賞球数を表示する4つのLEDによる表示部を有する普通図柄保留記憶表示器41が設けられている。ゲート32への遊技球の通過がある毎に、すなわちゲートスイッチ32aによって遊技球が検出される毎に、普通図柄保留記憶表示器41は点灯するLEDを1増やす。そして、普通図柄表示器10の変動表示が開始される毎に、点灯するLEDを1減らす。さらに、通常状態に比べて大当りとすることに決定される確率が高い状態である確変状態では、普通図柄表示器10における停止図柄が当り図柄になる確率が高められるとともに、可変入賞球装置15の開放時間と開放回数とが高められる。また、確変状態ではないが特別図柄の変動時間が短縮される時短状態(特別図柄の変動表示時間が短縮される遊技状態)にする制御を行なうようにしてもよく、そのような場合に、可変入賞球装置15の開放時間と開放回数とが高められるようにしてもよい。
When the game ball passes through the
遊技盤6の遊技領域7の左右周辺には、遊技中に点滅表示される装飾LED25が設けられている。遊技盤6の遊技領域7の下部には、入賞しなかった打球が取り込まれるアウト口26が設けられている。また、遊技領域7の外側の左右上部には、所定の音声出力として効果音や音声を発声する2つのスピーカ27が設けられている。遊技領域7の外周には、前面枠に設けられた枠LED28が設けられている。
On the left and right sides of the
打球供給皿3の上面における手前側の中央位置といった、パチンコ遊技機1の遊技機用枠における所定位置には、押下操作等により遊技者が操作可能な操作ボタン130が設置されている。なお、操作ボタン130は、押下操作が可能なものに限定されず、たとえば回転型セレクタのような回転操作が可能なものであってもよいし、タッチパネルのように接触操作や押圧操作が可能なものであってもよいし、レバー型スイッチのような傾動操作が可能なものであってもよい。また、操作ボタン130に代えて、たとえば赤外線センサやCCDセンサ、CMOSセンサのように、遊技者による所定の操作行為を検出できるセンサを用いてもよい。すなわち、操作ボタン130は、遊技者による所定の操作行為を、機械的、電気的、あるいは、電磁的に、検出できるものであればよい。
At predetermined positions in the gaming machine frame of the
パチンコ遊技機1には、遊技者が打球操作ハンドル5を操作することに応じて駆動モータを駆動し、駆動モータの回転力を利用して遊技球を遊技領域7に発射する打球発射装置(図示せず)が設けられている。打球発射装置から発射された遊技球は、遊技領域7を囲むように円形状に形成された打球レールを通って遊技領域7に入り、その後、遊技領域7を下りてくる。遊技球が第1始動入賞口13に入り第1始動口スイッチ13aで検出されると、第1特別図柄の変動表示を開始できる状態であれば(たとえば、特別図柄の変動表示が終了し、第1特別図柄の変動表示を開始させるための第1の開始条件が成立したこと)、第1特別図柄表示器8aにおいて第1特別図柄の変動表示(変動)が開始されるとともに、第1飾り図柄表示器9aにおいて第1飾り図柄の変動表示が開始され、演出表示装置9において演出図柄の変動表示が開始される。すなわち、第1特別図柄、第1飾り図柄および演出図柄の変動表示は、第1始動入賞口13への入賞に対応する。第1特別図柄の変動表示を開始できる状態でなければ、第1保留記憶数が上限値に達していないことを条件として、第1保留記憶数を1増やす。
The
遊技球が第2始動入賞口14に入り第2始動口スイッチ14aで検出されると、第2特別図柄の変動表示を開始できる状態であれば(たとえば、特別図柄の変動表示が終了し、第2特別図柄の変動表示を開始させるための第2の開始条件が成立したこと)、第2特別図柄表示器8bにおいて第2特別図柄の変動表示(変動)が開始されるとともに、第2飾り図柄表示器9bにおいて第2飾り図柄の変動表示が開始され、演出表示装置9において演出図柄の変動表示が開始される。すなわち、第2特別図柄、第2飾り図柄および演出図柄の変動表示は、第2始動入賞口14への入賞に対応する。第2特別図柄の変動表示を開始できる状態でなければ、第2保留記憶数が上限値に達していないことを条件として、第2保留記憶数を1増やす。
When the game ball enters the second
図2は、主基板(遊技制御基板)31における回路構成の一例を示すブロック図である。なお、図2は、払出制御基板37および演出制御基板80等も示されている。主基板31には、プログラムにしたがってパチンコ遊技機1を制御する遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ(遊技制御手段に相当)560が搭載されている。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ゲーム制御(遊技進行制御)用のプログラム等を記憶するROM54、ワークメモリとして使用される記憶手段としてのRAM55、プログラムにしたがって制御動作を行なうCPU56およびI/Oポート部57を含む。この実施の形態では、ROM54およびRAM55は遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に内蔵されている。すなわち、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、1チップマイクロコンピュータである。1チップマイクロコンピュータには、少なくともCPU56のほかRAM55が内蔵されていればよく、ROM54は外付けであっても内蔵されていてもよい。また、I/Oポート部57は、外付けであってもよい。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560には、さらに、ハードウェア乱数(ハードウェア回路が発生する乱数)を発生する乱数回路503が内蔵されている。
FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing an example of the circuit configuration of the main board (game control board) 31. FIG. 2 also shows a
また、RAM55は、その一部または全部が電源基板910において作成されるバックアップ電源によってバックアップされている不揮発性記憶手段としてのバックアップRAMである。すなわち、パチンコ遊技機1に対する電力供給が停止しても、所定期間(バックアップ電源としてのコンデンサが放電してバックアップ電源が電力供給不能になるまで)は、RAM55の一部または全部の内容は保存される。特に、少なくとも、遊技状態すなわち遊技制御手段の制御状態に応じたデータ(特別図柄プロセスフラグ等)と未払出賞球数を示すデータは、バックアップRAMに保存される。遊技制御手段の制御状態に応じたデータとは、停電等が生じた後に復旧した場合に、そのデータに基づいて、制御状態を停電等の発生前に復旧させるために必要なデータである。また、制御状態に応じたデータと未払出賞球数を示すデータとを遊技の進行状態を示すデータと定義する。なお、この実施の形態では、RAM55の全部が、電源バックアップされているとする。
The
なお、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560においてCPU56がROM54に格納されているプログラムにしたがって制御を実行するので、以下、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(またはCPU56)が実行する(または、処理を行なう)ということは、具体的には、CPU56がプログラムにしたがって制御を実行することである。このことは、主基板31以外の他の基板に搭載されているマイクロコンピュータについても同様である。
In the
乱数回路503は、特別図柄の変動表示の表示結果により大当りとするか否か判定するための判定用の乱数を発生するために用いられるハードウェア回路である。乱数回路503は、初期値(たとえば、0)と上限値(たとえば、65535)とが設定された数値範囲内で、数値データを、設定された更新規則にしたがって更新し、ランダムなタイミングで発生する始動入賞時が数値データの読出(抽出)時であることに基づいて、読出される数値データが乱数値となる乱数発生機能を有する。
The
乱数回路503は、数値データの更新範囲の選択設定機能(初期値の選択設定機能、および、上限値の選択設定機能)、数値データの更新規則の選択設定機能、および数値データの更新規則の選択切替え機能等の各種の機能を有する。このような機能によって、生成する乱数のランダム性を向上させることができる。
The
また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、乱数回路503が更新する数値データの初期値を設定する機能を有している。たとえば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ROM54等の所定の記憶領域に記憶された遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のIDナンバ(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560の各製品ごとに異なる数値で付与されたIDナンバ)を用いて所定の演算を行なって得られた数値データを、乱数回路503が更新する数値データの初期値として設定する。そのような処理を行なうことによって、乱数回路503が発生する乱数のランダム性をより向上させることができる。
Further, the
また、ゲートスイッチ32a、第1始動口スイッチ13a、第2始動口スイッチ14a、カウントスイッチ23、入賞口スイッチ29a,30a,33a,39aからの検出信号を遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に与える入力ドライバ回路58も主基板31に搭載されている。また、可変入賞球装置15を開閉するソレノイド16、および大入賞口を形成する特別可変入賞球装置20を開閉するソレノイド21を遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560からの指令にしたがって駆動する出力回路59も主基板31に搭載されている。
Also, an input driver circuit for supplying detection signals from the gate switch 32a, the first
また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、特別図柄を変動表示する第1特別図柄表示器8a、第2特別図柄表示器8b、普通図柄を変動表示する普通図柄表示器10、第1特別図柄保留記憶表示器18a、第2特別図柄保留記憶表示器18bおよび普通図柄保留記憶表示器41の表示制御を行なう。
Further, the
なお、大当り遊技状態の発生を示す大当り情報等の情報出力信号をホールコンピュータ等の外部装置に対して出力する情報出力回路(図示せず)も主基板31に搭載されている。
An information output circuit (not shown) that outputs an information output signal such as jackpot information indicating the occurrence of a jackpot gaming state to an external device such as a hall computer is also mounted on the
この実施の形態では、演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御手段としての(後述する演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100)が、中継基板77を介して遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から演出内容を指示する演出制御コマンドを受信し、飾り図柄を変動表示する第1飾り図柄表示器9aおよび第2飾り図柄表示器9bの表示制御と、演出図柄を変動表示する演出表示装置9の表示制御とを行なう。また、演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御手段は、操作ボタン130からの操作検出信号が入力され、その信号に応じて、後述する予告演出等の各種演出を行なう。
In this embodiment, the effect control means (
また、演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御手段が、ランプドライバ基板35を介して、遊技盤6に設けられている装飾LED25、および枠側に設けられている枠LED28の表示制御を行なうとともに、音声出力基板70を介してスピーカ27からの音出力の制御を行なう。
Further, the effect control means mounted on the
第1特別図柄表示器8aおよび第2特別図柄表示器8bにおける特別図柄の変動表示は、変動表示が行なわれるごとに設定された変動表示時間が経過したときに停止する。大当りにすることに決定されている場合には、特定の特別図柄(たとえば、「1」、「3」、または、「7」というような大当り図柄)が停止表示される。そのときには、演出表示装置9において、特定の演出図柄の組合せ(「左」,「中」,「右」の演出図柄として、後述する突確大当りを除く大当りの種別については、たとえば、「7,7,7」というようなゾロ目となる大当り図柄の組合せ、また、突確大当りの種別については、たとえば、「1,2,3」というようなチャンス目となる突確大当り図柄の組合せ)が停止表示される。また、はずれにすることに決定されている場合には、大当り図柄以外の特別図柄(たとえば、「−」というはずれ図柄)が停止表示される。そのときには、演出表示装置9において、大当りの演出図柄の組合せ以外の演出図柄の組合せが停止表示される。
The variation display of the special symbol in the first
変動表示の停止時の第1,第2特別図柄(停止図柄)が特定表示結果としての大当り図柄(大当り表示結果ともいう)であると、大当りとなり、遊技者にとって有利な特定遊技状態としての大当り遊技状態に移行する。大当り遊技状態においては、特別可変入賞球装置20が、所定の開放終了条件が成立するまで開放する。そして、開放終了条件が成立すると、継続権が発生し、特別可変入賞球装置20の開放が再度行なわれる。継続権の発生は、大当り遊技状態における開放回数が予め定められた上限値に達するまで繰返される。このように特別可変入賞球装置20の開放が繰返し継続される制御は、繰返し継続制御と呼ばれる。繰返し継続制御において、特別可変入賞球装置20が開放されている状態がラウンドと呼ばれる。継続権が発生する開放回数の上限値は、大当りの種類により異なり、たとえば15ラウンドまたは2ラウンドのような所定回数に設定されている。
If the first and second special symbols (stop symbol) when the variable display is stopped is a big hit symbol (also called a big hit display result) as a specific display result, it will be a big hit, and a big hit as a specific gaming state advantageous to the player Transition to gaming state. In the big hit gaming state, the special variable winning
この実施の形態の場合は、大当りの種類として、第15ラウンドを最終ラウンドとして第15ラウンドとなるまで継続権が成立する15ラウンド大当り(以下、15R大当りという場合がある)と、第2ラウンドを最終ラウンドとして第2ラウンドとなるまで継続権が成立する2ラウンド大当り(以下、2R大当りという場合がある)とが設けられている。これにより、15R大当りの場合は、特別可変入賞球装置20が必ず15回開放される制御が行なわれ、2R大当りの場合は、特別可変入賞球装置20が必ず2回開放される制御が行なわれることとなる。ただし、15R大当りのときの開放終了条件は、開放してから29秒間(所定時間)経過するまで、または、10個(所定個数)の遊技球が入賞するまでという2つの条件のうちいずれかが成立したときに成立する。また、2R大当りのときの開放終了条件は、開放してから0.5秒間(所定時間)経過するまで、または、10個(所定個数)の遊技球が入賞するまでという2つの条件のうちいずれかが成立したときに成立する。
In the case of this embodiment, as the types of jackpots, the 15th round jackpot (hereinafter sometimes referred to as 15R jackpot) in which continuation rights are established until the 15th round is the final round, and the second round is As the final round, there is provided a 2-round jackpot (hereinafter sometimes referred to as 2R jackpot) in which the continuation right is established until the second round. Thus, in the case of 15R big hit, the special variable winning
第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bでの変動表示の停止時における第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄の表示結果が、大当り図柄のうち予め定められた特別な大当り図柄としての確変図柄(たとえば、「7」)である場合には、大当り遊技状態に制御されることに加え、大当り遊技状態終了後に、遊技者にとって有利な特別遊技状態として、大当り遊技状態後に大当りになる確率が、大当り遊技状態と異なる通常状態である通常遊技状態(後述する低確低ベース状態)よりも高くなる確率変動状態(以下、確変状態と呼ぶ)という遊技者にとって有利な状態になる。15R大当りのうち、大当り遊技状態の終了後に確変状態となるものは、確変大当りと呼ばれる。以下、確変状態は、高確率状態(高確状態と略称で呼ぶ場合もある)ともいう。また、非確変状態(確変状態以外の状態)は、低確率状態(低確状態と略称で呼ぶ場合もある)ともいう。確変状態は、たとえば、次に変動表示結果として大当り図柄が導出表示されるまで継続する。また、大当り遊技状態に制御されたり、確変状態に制御されたりするような遊技者にとって有利な状態にされることは、遊技価値を付与するとも呼ばれる。遊技価値とは、たとえば、遊技機の遊技領域に設けられた可変入賞球装置の状態が打球が入賞しやすい遊技者にとって有利な状態になることや、所定の入賞が発生しやすい遊技者にとって有利な状態になることや、遊技者にとって有利な状態になるための権利を発生させたりすることや、遊技者にとって有利な大当り遊技状態になるための確率を向上させたりする(確変状態にする)ことや、遊技媒体の払出の条件が成立しやすくなる状態になることである。
The display result of the first special symbol or the second special symbol when the variable display on the first
なお、特別遊技状態は、次のような遊技状態であってもよい。a第1,第2特別図柄の変動時間短縮制御(変動開始から表示結果の導出表示までの時間が変動時間短縮制御状態以外の通常状態での当該時間よりも短縮される制御)が行なわれる状態、b普通図柄の変動時間短縮制御が行なわれる状態、c普通図柄の当りの発生確率を向上させる制御が行なわれる状態、d普通図柄が当りとなったときに可変入賞球装置15が開放される回数を増加させる開放回数増加制御が行なわれる状態、e可変入賞球装置15の1回の開放時間を延長させる開放時間延長制御。特別遊技状態としては、確変状態および前記a〜前記eのうちのいずれかの単独制御、または、確変状態および前記a〜eのうちから2つ〜5つの状態が適宜組合わされた制御でもよい。つまり、前述したような制御を実行する対象となる特別遊技状態としては、予め定められた特別遊技状態発生条件が成立したときに特定遊技状態に加えて遊技者に有利な特別状態を付与する特別遊技状態であれば、どのような特別遊技状態であってもよい。
The special gaming state may be the following gaming state. a State in which the fluctuation time reduction control of the first and second special symbols (control in which the time from the start of fluctuation to the derivation and display of the display result is shorter than the corresponding time in the normal state other than the fluctuation time reduction control state) is performed , B Normal symbol variation time shortening control is performed, c Normal symbol hitting probability is improved Control probability, d When the normal symbol hits, the variable winning
15R大当りのうち、第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bでの変動表示の停止時における第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄の表示結果が、大当り図柄のうち予め定められた通常図柄(たとえば、「3」)である場合には、大当り遊技状態後に大当りになる確率が、確変状態とならない。このような15R大当りの大当り遊技状態の終了後に確変状態とならないものは、通常大当りと呼ばれる。以下の説明においては、大当りの種類を特定せずに単に「大当り」と示すときは、これら複数種類の大当りを代表して示す場合である。
Among the 15R jackpots, the display result of the first special symbol or the second special symbol when the variable display on the first
また、第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bでの変動表示の停止時における第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄の表示結果が、大当り図柄のうち予め定められた突確図柄(たとえば、「1」)である場合には、大当り遊技状態後に大当りになる確率が確変状態となる2R大当りとなる。このように、大当り遊技状態の終了後に確変状態となるものは、突確大当りと呼ばれる。突確大当りの大当り遊技状態では、大入賞口は2回開放状態になるが、開放時間は極めて短い(たとえば、0.5秒)。よって、遊技者は、大当りが発生したことを感じずに、あたかも、突然に遊技状態が確変状態になったかのように感じる。したがって、このような2R大当りが、突確大当りと呼ばれるのである。
In addition, the display result of the first special symbol or the second special symbol when the variable display on the first
また、15ラウンドの大当りの遊技状態および突確大当りの遊技状態が終了した後には、所定期間に亘り、遊技状態が時短状態に制御される。時短状態では、通常状態(確変状態や時短状態ではない状態)に比べて普通図柄の変動表示における普通図柄の変動時間が短縮される。 In addition, after the 15-round big hit gaming state and the probable big hit gaming state are finished, the gaming state is controlled to the short-time state for a predetermined period. In the short time state, the variation time of the normal symbol in the normal symbol variation display is shortened compared to the normal state (the state that is not the probability variation state or the short time state).
時短状態とは、通常遊技状態(後述する低確低ベース状態)に比べて、普通図柄表示器10の変動表示時間(変動開始時から表示結果の導出表示時までの時間)を短縮して早期に表示結果を導出表示させる制御状態をいう。言い換えると、時短状態は、通常遊技状態(低確低ベース状態)に比べて、可変入賞球装置15に遊技球が進入する可能性を高めた、遊技者にとって始動条件が成立しやすくなることで遊技者にとって有利となる制御が行なわれることを指す。さらに、時短状態中には、普通図柄表示器10における停止図柄が当り図柄になる確率が高められるとともに、可変入賞球装置15の開放時間が長くされ、開放回数が増加させられる。また、時短状態においては、普通図柄表示器10の変動表示時間を短縮する制御に、普通図柄が当り図柄になる確率が高められる制御、可変入賞球装置15の開放時間を長くする制御、および、可変入賞球装置15の開放回数を増加させる制御のうちのいずれか1つまたは複数を組合せた制御を、付加して行なうようにしてもよく、これらの制御を行なわないようにしてもよい。また、このような、普通図柄が当り図柄になる確率が高められる制御、可変入賞球装置15の開放時間を長くする制御、可変入賞球装置15の開放回数を増加させる制御、および、特別図柄の変動表示時間を短縮する制御は、普通図柄表示器10の変動表示時間を短縮する制御に代えて、単独で実行するようにしてもよい。
The short time state means that the fluctuation display time of the normal symbol display 10 (the time from the start of fluctuation until the display result is derived and displayed) is shortened compared to the normal gaming state (the low probability low base state described later). A control state in which the display result is derived and displayed. In other words, the short-time state increases the possibility that a game ball will enter the variable winning
なお、時短状態としては、普通図柄表示器10の変動表示時間を短縮する時間状態の代わりに、第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bおよび演出表示装置9での図柄(特別図柄および演出図柄)の変動表示時間を通常遊技状態よりも短縮する制御を行なうようにしてもよい。そのようにすれば、第1特別図柄または第2特特別図柄の変動表示時間が短縮されるので、保留記憶数が早期に消化され、第1保留記憶数および第2保留記憶数のそれぞれの上限(たとえば「4」)を超えて発生した始動入賞が無効になってしまう状態を減少でき、短期間に頻繁に表示結果を導出表示して早期に大当り表示結果を導出表示しやすくなるので、時間効率的な観点で変動表示の表示結果が大当り図柄の表示結果となりやすくなり、遊技者にとって有利な遊技状態となる。また、時短状態としては、第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bおよび演出表示装置9での図柄(特別図柄および演出図柄)の変動表示時間を短縮する制御を行なうときには、普通図柄表示器10の変動表示時間を短縮する制御、普通図柄が当り図柄になる確率が高められる制御、可変入賞球装置15の開放時間を長くする制御、および、可変入賞球装置15の開放回数を増加させる制御のうちのいずれか1つまたは複数を組合せた制御を、付加して行なうようにしてもよく、これらの制御を行なわないようにしてもよい。
In addition, as the time-short state, instead of the time state in which the variable display time of the
また、入賞に応じた遊技球の払出しの面から考えると、15ラウンドの大当り遊技状態が終了した後の時短状態は、非時短状態と比べて、普通図柄の変動表示時間が短縮され、普通図柄表示器10における停止図柄が当り図柄になる確率が高められ、当り時における可変入賞球装置15の開放時間が長くされ、当り時における可変入賞球装置15の1度の開放回数が多くされることに基づいて、通常遊技状態と比べて可変入賞球装置15が開放状態となりやすい。したがって、時短状態では、第2始動入賞口14への入賞(始動入賞が有効である場合と無効である場合との両方を含む)が生じやすくなるため、遊技領域7へ打込んだ遊技球数(打込球数)に対して、入賞に応じた賞球として払出される遊技球数(払出球数)の割合が、通常遊技状態と比べて多くなる。一般的に、発射球数に対する入賞による払出球数の割合は、「ベース」と呼ばれる。たとえば、100球の打込球数に対して40球の払出球数があったときには、ベースは40(%)となる。この実施の形態の場合では、たとえば通常遊技状態のような非時短状態よりもベースが高い時短状態を高ベース状態と呼び、逆に、そのような高ベース状態と比べてベースが低い通常遊技状態のような非時短状態を低ベース状態と呼ぶ。
Also, considering the payout of game balls in accordance with winnings, the short time state after the 15-round jackpot game state has ended, the normal symbol variation display time is shortened compared to the non-short time state, and the normal symbol The probability that the stop symbol on the
時短状態に制御される所定期間は、たとえば、所定回数(たとえば、100回)の特別図柄の変動表示が実行されること、および、変動表示結果が「大当り」となることのうち、いずれかの条件が先に成立したときに終了する。なお、大当り状態が終了した後に、時短状態にせずに通常状態になるようにしてもよい。 The predetermined period controlled to the short-time state is, for example, any one of executing a predetermined symbol variable display for a predetermined number of times (for example, 100 times) and the variable display result being “big hit”. End when the condition is met first. In addition, after the big hit state is ended, the normal state may be set instead of the time reduction state.
なお、15R大当りは、特別可変入賞球装置20を所定期間(29秒間)開状態に変化させることを所定回数(15回)行なうことにより終了し、大当り遊技状態終了後、通常遊技状態または確変状態に制御される第1遊技状態として定義した場合、突確大当りは、次のように定義される。
The 15R big hit is ended by changing the special variable winning
第2遊技状態としての突確大当りは、特別可変入賞球装置20を所定期間(29秒間)よりも短い期間(0.5秒間)および所定回数(15回)よりも少ない回数(2回)の少なくともいずれかで開状態に変化させることにより終了し、大当り遊技状態終了後、確変状態に制御されるものであればよい。つまり、第2遊技状態は、第1遊技状態に対して、特別可変入賞球装置20の1回の開放時間が短いことと、特別可変入賞球装置20の合計開放回数とが少ないこととの少なくともいずれかで、特別可変入賞球装置20が開状態に制御されるものであればよい。
The big hit as the second gaming state is at least a period (0.5 seconds) shorter than a predetermined period (29 seconds) and a number (2 times) less than a predetermined number (15 times). Any one may be used as long as it is terminated by changing to an open state, and is controlled to a probable change state after the big hit gaming state. That is, in the second gaming state, at least one special opening time of the special variable winning
突確大当りは、大当り遊技状態が、特別可変入賞球装置20の開放動作を0.5秒間という短期間の開放を2回という少ない回数行なうものであり、遊技者にとっては大当りとなったことが認識しにくい。
It is recognized that the big hit game state is a big hit for the player because the special
確変状態ではなく、かつ、時短状態ではない状態は、低確率状態かつ低ベース状態であり、低確低ベース状態と呼ばれる。確変大当りは、大当り遊技状態の終了後に確変状態になり、かつ、時短状態になることにより、高確率状態、かつ、高ベース状態となる大当りである。このような、高確率状態かつ高ベース状態となった状態は、高確高ベース状態と呼ばれる。通常大当りは、大当り遊技状態の終了後に確変状態にならず、かつ、時短状態になる大当りである。このような、低確率状態かつ高ベース状態となった状態は、低確高ベース状態と呼ばれる。突確大当りは、大当り遊技状態の終了後に確変状態になり、かつ、時短状態にならない大当りである。このような、高確率状態かつ低ベース状態となった状態は、高確低ベース状態と呼ばれる。確変大当りおよび通常大当りのような15R大当りとなったときには、前述したように、大当り遊技状態の終了後に所定回数(100回)の変動表示が行なわれるまで、時短状態となることに基づいて高ベース状態となる。 A state that is not a probability variation state and is not a time-short state is a low probability state and a low base state, and is called a low probability low base state. The probable big hit is a big win that becomes a high probability state and a high base state by being in a probable change state after the big hit gaming state is finished and being in a short time state. Such a state with a high probability state and a high base state is referred to as a highly accurate high base state. Usually, the big hit is a big hit that does not enter a certain change state after the end of the big hit gaming state and becomes a short time state. Such a state having a low probability state and a high base state is referred to as a low probability high base state. The sudden hit big hit is a big hit that is in a probable change state after the end of the big hit gaming state and does not become a short-time state. Such a state having a high probability state and a low base state is referred to as a high probability low base state. When the 15R big hit such as the probable big hit and the normal big hit, as described above, the high base is based on the fact that the short time state is displayed until the predetermined number of times (100 times) is displayed after the big hit gaming state ends. It becomes a state.
確変状態(高確率状態)と非確変状態(低確率状態)とのどちらの状態であるかは、確変状態においてセットされるフラグである確変フラグがセットされているか否かに基づいて判断される。また、時短状態(高ベース状態)と非時短状態(低ベース状態)とのどちらの状態であるかは、時短状態においてセットされるフラグである時短フラグがセットされているか否かに基づいて判断される。 Whether the probability variation state (high probability state) or the non-probability variation state (low probability state) is determined based on whether or not the probability variation flag, which is a flag set in the probability variation state, is set. . Also, whether the time-short state (high base state) or the non-time-short state (low base state) is determined based on whether or not the time-short flag, which is a flag set in the time-short state, is set. Is done.
演出表示装置9において変動表示される演出図柄は、第1特別図柄表示器8aおよび第2特別図柄表示器8bにおける第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄の変動表示の装飾効果を高めるために、第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄のそれぞれの変動表示と所定の関係を有して変動表示される装飾的な意味合いがある図柄である。このような図柄についての所定の関係には、たとえば、第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bでの第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄の変動表示が開始されたときに演出図柄の変動表示が開始する関係、および、第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄の変動表示の終了時に第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄の表示結果が導出表示されるときに演出図柄の表示結果が導出表示されて演出図柄の変動表示が終了する関係等が含まれる。第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bにより予め定められた大当り図柄が表示結果として導出表示されるときには、演出表示装置9により、左,中,右図柄がゾロ目(15R大当りのとき)、または、ゾロ目以外の図柄の組合せにより構成されたチャンス目(突確大当りのとき)となる大当り図柄の組合せが表示結果として導出表示される。ここで、チャンス目は、前述したゾロ目以外の図柄の組合せにより構成される図柄の組合せであり、遊技者にチャンスをもたらす表示結果として予め定められている。このような特別図柄による大当り図柄の表示結果および演出図柄による大当り図柄の組合せの表示結果は、大当り表示結果という。
In order to enhance the decorative effect of the variable display of the first special symbol and the second special symbol on the first
第1特別図柄表示器8aおよび第2特別図柄表示器8bと演出表示装置9とは変動表示結果が前述したような対応関係になるため、以下の説明においては、これらをまとめて変動表示部と呼ぶ場合がある。
The first special
また、演出表示装置9については、大当りを発生させる契機となる変動表示において、大当りとなることを報知する予告演出である大当り予告が行なわれる場合がある。
In addition, for the
図3は、中継基板77、演出制御基板80、ランプドライバ基板35および音声出力基板70の回路構成例を示すブロック図である。なお、図3に示す例では、ランプドライバ基板35および音声出力基板70には、マイクロコンピュータは搭載されていないが、マイクロコンピュータを搭載してもよい。また、ランプドライバ基板35および音声出力基板70を設けずに、演出制御に関して演出制御基板80のみを設けてもよい。
FIG. 3 is a block diagram illustrating a circuit configuration example of the
演出制御基板80は、演出制御用CPU101、および演出図柄プロセスフラグ等の演出に関する情報を記憶するRAMを含む演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100を搭載している。なお、RAMは外付けであってもよい。この実施の形態では、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100におけるRAMは電源バックアップされていない。演出制御基板80において、演出制御用CPU101は、内蔵または外付けのROM(図示せず)に格納されたプログラムにしたがって動作し、中継基板77を介して入力される主基板31からの取込信号(演出制御INT信号)に応じて、入力ドライバ102および入力ポート103を介して演出制御コマンドを受信する。また、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御コマンドに基づいて、VDP(ビデオディスプレイプロセッサ)109に演出表示装置9の表示制御を行なわせる。
The
また、操作ボタン130からの操作信号が、入力ポート107を介して演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に入力される。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、後述するように、操作ボタン130からの操作信号に基づいて、たとえば予告演出等の遊技の演出を行なう。
An operation signal from the
この実施の形態では、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100と共動して演出表示装置9の表示制御を行なうVDP109が演出制御基板80に搭載されている。VDP109は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100とは独立したアドレス空間を有し、そこにVRAMをマッピングする。VRAMは、画像データを展開するためのバッファメモリである。そして、VDP109は、VRAM内の画像データをフレームメモリを介して演出表示装置9に出力する。
In this embodiment, a
演出制御用CPU101は、受信した演出制御コマンドにしたがってCGROM(図示せず)から必要なデータを読出すための指令をVDP109に出力する。CGROMは、演出表示装置9に表示されるキャラクタ画像データや動画像データ、具体的には、人物、文字、図形や記号等(演出図柄を含む)、および背景画像のデータを予め格納しておくためのROMである。VDP109は、演出制御用CPU101の指令に応じて、CGROMから画像データを読出す。そして、VDP109は、読出した画像データに基づいて表示制御を実行する。
The
演出制御コマンドおよび演出制御INT信号は、演出制御基板80において、まず、入力ドライバ102に入力する。入力ドライバ102は、中継基板77から入力された信号を演出制御基板80の内部に向かう方向にしか通過させない(演出制御基板80の内部から中継基板77への方向には信号を通過させない)信号方向規制手段としての単方向性回路でもある。
The effect control command and the effect control INT signal are first input to the input driver 102 on the
中継基板77には、主基板31から入力された信号を演出制御基板80に向かう方向にしか通過させない(演出制御基板80から中継基板77への方向には信号を通過させない)信号方向規制手段としての単方向性回路74が搭載されている。単方向性回路として、たとえばダイオードやトランジスタが使用される。図3には、ダイオードが例示されている。また、単方向性回路は、各信号毎に設けられる。さらに、単方向性回路である出力ポート571を介して主基板31から演出制御コマンドおよび演出制御INT信号が出力されるので、中継基板77から主基板31の内部に向かう信号が規制される。すなわち、中継基板77からの信号は主基板31の内部(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560側)に入り込まない。なお、出力ポート571は、図2に示されたI/Oポート部57の一部である。また、出力ポート571の外側(中継基板77側)に、さらに、単方向性回路である信号ドライバ回路が設けられていてもよい。
As a signal direction regulating means, the signal inputted from the
また、演出制御用CPU101は、出力ポート106を介して、可動部材78を動作させるためにモータ86を駆動する。また、演出制御用CPU101は、上演出LED85a、中演出LED85bおよび下演出LED85cの近傍に設けられ、各LEDの取付部分を振動させる振動モータ87a,87b,87cを出力ポート106を介して駆動する。振動モータ87aは、上演出LED85aを振動させる。振動モータ87bは、中演出LED85bを振動させ、振動モータ87cは下演出LED85cを振動させる。また、演出制御用CPU101は、出力ポート106を介して、可動部材84を動作させるためにモータ88を駆動する。
The
さらに、演出制御用CPU101は、出力ポート105を介してランプドライバ基板35に対してLEDを駆動する信号を出力する。また、演出制御用CPU101は、出力ポート104を介して音声出力基板70に対して音番号データを出力する。
Further, the
ランプドライバ基板35において、LEDを駆動する信号は、入力ドライバ351を介してLEDドライバ352に入力される。LEDドライバ352は、LEDを駆動する信号に基づいて枠LED28等の枠側に設けられている発光体に電流を供給する。また、遊技盤側に設けられている装飾LED25、上演出LED85a、中演出LED85bおよび下演出LED85cに電流を供給する。
In the
音声出力基板70において、音番号データは、入力ドライバ702を介して音声合成用IC703に入力される。音声合成用IC703は、音番号データに応じた音声や効果音を発生し増幅回路705に出力する。増幅回路705は、音声合成用IC703の出力レベルを、ボリューム706で設定されている音量に応じたレベルに増幅した音声信号をスピーカ27に出力する。音声データROM704には、音番号データに応じた制御データが格納されている。音番号データに応じた制御データは、所定期間(たとえば演出図柄の変動期間)における効果音または音声の出力態様を時系列的に示すデータの集まりである。
In the
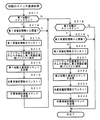
次に、パチンコ遊技機1の動作について説明する。図4は、主基板31における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が実行するメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。パチンコ遊技機1に対して電源が投入され電力供給が開始されると、リセット信号が入力されるリセット端子の入力レベルがハイレベルになる。そして、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(具体的には、CPU56)は、プログラムの内容が正当か否か確認するための処理であるセキュリティチェック処理を実行した後、ステップS(以下、単にSと呼ぶ)1以降のメイン処理を開始する。メイン処理において、CPU56は、まず、必要な初期設定を行なう。
Next, the operation of the
初期設定処理において、CPU56は、まず、割込禁止に設定する(S1)。次に、割込モードを割込モード2に設定し(S2)、スタックポインタにスタックポインタ指定アドレスを設定する(S3)。そして、内蔵デバイスの初期化(内蔵デバイス(内蔵周辺回路)であるCTC(カウンタ/タイマ)およびPIO(パラレル入出力ポート)の初期化等)を行なった後(S4)、RAM55をアクセス可能状態に設定する(S5)。なお、割込モード2は、CPU56が内蔵する特定レジスタ(Iレジスタ)の値(1バイト)と内蔵デバイスが出力する割込ベクタ(1バイト:最下位ビット0)とから合成されるアドレスが、割込番地を示すモードである。
In the initial setting process, the
次いで、CPU56は、入力ポートを介して入力されるクリアスイッチ(たとえば、電源基板に搭載されている。)の出力信号の状態を確認する(S6)。その確認においてオンを検出した場合には、CPU56は、通常の初期化処理を実行する(S10〜S15)。
Next, the
クリアスイッチがオンの状態でない場合には、パチンコ遊技機1への電力供給が停止したときにバックアップRAM領域のデータ保護処理(たとえばパリティデータの付加等の電力供給停止時処理)が行なわれたか否か確認する(S7)。そのような保護処理が行なわれていないことを確認したら、CPU56は初期化処理を実行する。バックアップRAM領域にバックアップデータがあるか否かは、たとえば、電力供給停止時処理においてバックアップRAM領域に設定されるバックアップフラグの状態によって確認される。
If the clear switch is not in an on state, whether or not data protection processing for the backup RAM area (for example, power supply stop processing such as addition of parity data) has been performed when power supply to the
電力供給停止時処理が行なわれたことを確認したら、CPU56は、バックアップRAM領域のデータチェックを行なう(S8)。この実施の形態では、データチェックとしてパリティチェックを行なう。よって、S8では、算出したチェックサムと、電力供給停止時処理で同一の処理によって算出され保存されているチェックサムとを比較する。不測の停電等の電力供給停止が生じた後に復旧した場合には、バックアップRAM領域のデータは保存されているはずであるから、チェック結果(比較結果)は正常(一致)になる。チェック結果が正常でないということは、バックアップRAM領域のデータが、電力供給停止時のデータとは異なっていることを意味する。そのような場合には、内部状態を電力供給停止時の状態に戻すことができないので、電力供給の停止からの復旧時でない電源投入時に実行される初期化処理を実行する。
When it is confirmed that the power supply stop process has been performed, the
チェック結果が正常であれば、CPU56は、遊技制御手段の内部状態と演出制御手段等の電気部品制御手段の制御状態とを電力供給停止時の状態に戻すための遊技状態復旧処理(S41〜S43の処理)を行なう。具体的には、ROM54に格納されているバックアップ時設定テーブルの先頭アドレスをポインタに設定し(S41)、バックアップ時設定テーブルの内容を順次作業領域(RAM55内の領域)に設定する(S42)。作業領域はバックアップ電源によって電源バックアップされている。バックアップ時設定テーブルには、作業領域のうち初期化してもよい領域についての初期化データが設定されている。S41およびS42の処理によって、作業領域のうち初期化してはならない部分については、保存されていた内容がそのまま残る。初期化してはならない部分とは、たとえば、電力供給停止前の遊技状態を示すデータ(特別図柄プロセスフラグ、確変フラグ、時短フラグ等)、出力ポートの出力状態が保存されている領域(出力ポートバッファ)、未払出賞球数を示すデータが設定されている部分等である。
If the check result is normal, the
また、CPU56は、電力供給復旧時に、電力供給が復旧したことを示すコマンドとしての停電復旧指定コマンド(停電復旧1指定コマンド)を演出制御基板80に送信する(S43)。そして、S14に移行する。
In addition, when the power supply is restored, the
なお、この実施の形態では、バックアップフラグとチェックデータとの双方を用いてバックアップRAM領域のデータが保存されているか否か確認しているが、いずれか一方のみを用いてもよい。すなわち、バックアップフラグとチェックデータとのいずれかを、遊技状態復旧処理を実行するための契機としてもよい。 In this embodiment, it is confirmed whether the data in the backup RAM area is stored using both the backup flag and the check data. However, only one of them may be used. That is, either the backup flag or the check data may be used as an opportunity for executing the game state restoration process.
初期化処理では、CPU56は、まず、RAMクリア処理を行なう(S10)。なお、RAMクリア処理によって、所定のデータ(たとえば大当り判定用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値のデータ)は0に初期化されるが、任意の値または予め決められている値に初期化するようにしてもよい。また、RAM55の全領域を初期化せず、所定のデータ(たとえば大当り判定用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値のデータ)をそのままにしてもよい。また、ROM54に格納されている初期化時設定テーブルの先頭アドレスをポインタに設定し(S11)、初期化時設定テーブルの内容を順次RAM55における作業領域に設定する(S12)。
In the initialization process, the
S11およびS12の処理によって、特別図柄プロセスフラグ等制御状態に応じて選択的に処理を行なうためのフラグに初期値が設定される。 By the processing of S11 and S12, an initial value is set to a flag for selectively performing processing according to a control state such as a special symbol process flag.
また、CPU56は、サブ基板(主基板31以外のマイクロコンピュータが搭載された基板。)を初期化するための初期化指定コマンド(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が初期化処理を実行したことを示すコマンドでもある。)を演出制御基板80に送信する(S13)。たとえば、演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、初期化指定コマンドを受信すると、演出表示装置9において、パチンコ遊技機1の制御の初期化がなされたことを報知するための画面表示、すなわち初期化報知を行なう。なお、初期化処理において、CPU56は、客待ちデモンストレーション指定(デモ指定)コマンドも送信する。
Further, the
また、CPU56は、乱数回路503を初期設定する乱数回路設定処理を実行する(S14)。CPU56は、たとえば、乱数回路設定プログラムにしたがって処理を実行することによって、乱数回路503に大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)の値を更新させるための設定を行なう。
Further, the
そして、CPU56は、所定時間(たとえば2ms)毎に定期的にタイマ割込がかかるように遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に内蔵されているCTCのレジスタの設定を行なう(S15)。すなわち、初期値としてたとえば2msに相当する値が所定のレジスタ(時間定数レジスタ)に設定される。この実施の形態では、2ms毎に定期的にタイマ割込がかかるとする。
Then, the
初期化処理の実行(S10〜S15)が完了すると、CPU56は、メイン処理で、表示用乱数更新処理(S17)および初期値用乱数更新処理(S18)を繰返し実行する。表示用乱数更新処理および初期値用乱数更新処理を実行するときには割込禁止状態に設定し(S16)、表示用乱数更新処理および初期値用乱数更新処理の実行が終了すると割込許可状態に設定する(S19)。この実施の形態では、表示用乱数とは、変動パターン等を決定するための乱数であり、表示用乱数更新処理とは、表示用乱数を発生するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する処理である。また、初期値用乱数更新処理とは、初期値用乱数を発生するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する処理である。この実施の形態では、初期値用乱数とは、普通図柄の当りとするか否か決定するための乱数を発生するためのカウンタ(普通図柄当り判定用乱数発生カウンタ)等のカウント値の初期値を決定するための乱数である。後述する遊技の進行を制御する遊技制御処理(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が、パチンコ遊技機1に設けられている変動表示装置、可変入賞球装置、球払出装置等の遊技用の装置を、自身で制御する処理、または他のマイクロコンピュータに制御させるために指令信号を送信する処理、遊技装置制御処理ともいう)において、普通図柄当り判定用乱数発生カウンタ等のカウント値が1周(乱数の取りうる値の最小値から最大値までの間の数値の個数分歩進したこと)すると、そのカウンタに初期値が設定される。
When the execution of the initialization process (S10 to S15) is completed, the
なお、本実施の形態における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560においては、大当り判定用乱数発生カウンタとして、内蔵されている乱数回路503によるハードウェア乱数を用いる。したがって、大当り判定用乱数については、このような初期値の設定は行なわれない。ただし、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が大当り判定用乱数発生カウンタとしてソフトウェア乱数を用いる場合には、当該カウンタについて、前述のような初期値用乱数を用いた初期値の設定を行なうようにしてもよい。このようにした場合には、大当り判定用乱数発生カウンタが最大値まで歩進した後の初期値がランダムな値となるので、大当りの判定値と同じ乱数値を不正に狙って取出して大当りを発生させる不正行為が行なわれにくくなるようにすることができる。
In the
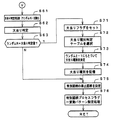
タイマ割込が発生すると、CPU56は、図5に示すS20〜S34のタイマ割込処理を実行する。タイマ割込処理において、まず、電源断信号が出力されたか否か(オン状態になったか否か)を検出する電源断検出処理を実行する(S20)。電源断信号は、たとえば電源基板に搭載されている電源監視回路920が、パチンコ遊技1に供給される電源の電圧の低下を検出した場合に出力する。そして、電源断検出処理において、CPU56は、電源断信号が出力されたことを検出したら、必要なデータをバックアップRAM領域に保存するための電力供給停止時処理を実行する。次いで、入力ドライバ回路58を介して、ゲートスイッチ32a、第1始動口スイッチ13a、第2始動口スイッチ14a、カウントスイッチ23、および入賞口スイッチ29a,30a,33a,39aの検出信号を入力し、それらの状態判定を行なうスイッチ処理を実行する(S21)。
When the timer interrupt occurs, the
次に、CPU56は、第1特別図柄表示器8a、第2特別図柄表示器8b、普通図柄表示器10、第1特別図柄保留記憶表示器18a、第2特別図柄保留記憶表示器18b、普通図柄保留記憶表示器41の表示制御を行なう表示制御処理を実行する(S22)。第1特別図柄表示器8a、第2特別図柄表示器8bおよび普通図柄表示器10については、S32,S33で設定される出力バッファの内容に応じて各表示器に対して駆動信号を出力する制御を実行する。
Next, the
また、遊技制御に用いられる普通当り図柄決定用の乱数等の各判定用乱数を生成するための各カウンタのカウント値を更新する判定用乱数更新処理を行なう(S23)。CPU56は、さらに、初期値用乱数および表示用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する初期値用乱数更新処理(S24)および表示用乱数更新処理(S25)を実行する。
Also, a determination random number update process is performed to update the count value of each counter for generating each determination random number such as a random number for determining a normal winning symbol used for game control (S23). The
さらに、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセス処理を行なう(S26)。特別図柄プロセス処理では、第1特別図柄表示器8a、第2特別図柄表示器8bおよび大入賞口を所定の順序で制御するための特別図柄プロセスフラグにしたがって該当する処理を実行する。CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を、遊技状態に応じて更新する。
Further, the
次いで、普通図柄プロセス処理を行なう(S27)。普通図柄プロセス処理では、CPU56は、普通図柄表示器10の表示状態を所定の順序で制御するための普通図柄プロセスフラグにしたがって該当する処理を実行する。CPU56は、普通図柄プロセスフラグの値を、遊技状態に応じて更新する。
Next, the normal symbol process is performed (S27). In the normal symbol process, the
また、CPU56は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に演出制御コマンドを送出する演出制御コマンド制御処理を行なう(S28)。
Further, the
さらに、CPU56は、たとえばホール管理用コンピュータに供給される大当り情報、始動情報、確率変動情報等のデータを出力する情報出力処理を行なう(S29)。
Further, the
また、CPU56は、第1始動口スイッチ13a、第2始動口スイッチ14a、カウントスイッチ23および入賞口スイッチ29a,30a,33a,39aの検出信号に基づく賞球個数の設定等を行なう賞球処理を実行する(S30)。具体的にCPU56は、第1始動口スイッチ13a、第2始動口スイッチ14a、カウントスイッチ23および入賞口スイッチ29a,30a,33a,39aのいずれかがオンしたことに基づく入賞検出に応じて、払出制御基板37に搭載されている払出制御用マイクロコンピュータに賞球個数を示す払出制御コマンド(賞球個数信号)を出力する。払出制御用マイクロコンピュータは、賞球個数を示す払出制御コマンドに応じて球払出装置97を駆動する。
Further, the
この実施の形態では、出力ポートの出力状態に対応したRAM領域(出力ポートバッファ)が設けられているのであるが、CPU56は、出力ポートの出力状態に対応したRAM領域におけるソレノイドのオン/オフに関する内容を出力ポートに出力する出力処理を実行する(S31)。
In this embodiment, a RAM area (output port buffer) corresponding to the output state of the output port is provided. However, the
また、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値に応じて特別図柄の演出表示を行なうための特別図柄表示制御データを特別図柄表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファに設定する特別図柄表示制御処理を行なう(S32)。CPU56は、たとえば、特別図柄プロセス処理でセットされる開始フラグがセットされると終了フラグがセットされるまで、変動速度が1コマ/0.2秒であれば、0.2秒が経過する毎に、出力バッファに設定される表示制御データの値を+1する。また、CPU56は、出力バッファに設定された表示制御データに応じて、S22において駆動信号を出力することによって、第1特別図柄表示器8aおよび第2特別図柄表示器8bにおける第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄の変動表示を実行する。
Further, the
なお、S32において、開始フラグがセットされたことに基づいて特別図柄の変動を開始するのではなく、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が変動パターン決定後の特別図柄変動中処理を示す値(具体的には3)となった(または、表示結果特定コマンド送信処理を示す値(具体的には2)となった)ことに基づいて、特別図柄の変動を開始するようにしてもよい。そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が特別図柄停止処理を示す値(具体的には4)となったことに基づいて、特別図柄の変動を停止するようにしてもよい。そのようにすれば、開始フラグおよび終了フラグを不要とすることができ、RAM55の必要容量を低減することができる。
In S32, instead of starting the variation of the special symbol based on the start flag being set, the value of the special symbol process flag is a value indicating the special symbol variation processing after the variation pattern is determined (specifically, 3) (or a value indicating the display result specifying command transmission process (specifically, 2)), the special symbol may be changed. Then, based on the fact that the value of the special symbol process flag becomes a value indicating the special symbol stop process (specifically, 4), the variation of the special symbol may be stopped. By doing so, the start flag and the end flag can be eliminated, and the required capacity of the
さらに、CPU56は、普通図柄プロセスフラグの値に応じて普通図柄の演出表示を行なうための普通図柄表示制御データを普通図柄表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファに設定する普通図柄表示制御処理を行なう(S33)。CPU56は、たとえば、普通図柄の変動に関する開始フラグがセットされると終了フラグがセットされるまで、普通図柄の変動速度が0.2秒ごとに表示状態(「○」および「×」)を切替えるような速度であれば、0.2秒が経過する毎に、出力バッファに設定される表示制御データの値(たとえば、「○」を示す1と「×」を示す0)を切替える。また、CPU56は、出力バッファに設定された表示制御データに応じて、S22において駆動信号を出力することによって、普通図柄表示器10における普通図柄の演出表示を実行する。
Further, the
なお、S33において、開始フラグがセットされたことに基づいて普通図柄の変動を開始するのではなく、普通図柄プロセスフラグの値が普通図柄変動中処理を示す値となったことに基づいて、普通図柄の変動を開始するようにしてもよい。そして、普通図柄プロセスフラグの値が普通図柄停止処理を示す値となったことに基づいて、普通図柄の変動を停止するようにしてもよい。そのようにすれば、開始フラグおよび終了フラグを不要とすることができ、RAM55の必要容量を低減することができる。その後、割込許可状態に設定し(S34)、処理を終了する。
In S33, the normal symbol change is not started based on the start flag being set, but the normal symbol process flag value becomes a value indicating the normal symbol changing process. You may make it start the fluctuation | variation of a symbol. Then, based on the fact that the value of the normal symbol process flag becomes a value indicating the normal symbol stop process, the variation of the normal symbol may be stopped. By doing so, the start flag and the end flag can be eliminated, and the required capacity of the
以上の制御によって、この実施の形態では、遊技制御処理は2ms毎に起動されることになる。なお、遊技制御処理は、タイマ割込処理におけるS21〜S33(S29を除く。)の処理に相当する。また、この実施の形態では、タイマ割込処理で遊技制御処理が実行されているが、タイマ割込処理ではたとえば割込が発生したことを示すフラグのセットのみがなされ、遊技制御処理はメイン処理において実行されるようにしてもよい。 With the above control, in this embodiment, the game control process is started every 2 ms. The game control process corresponds to the processes of S21 to S33 (excluding S29) in the timer interrupt process. In this embodiment, the game control process is executed by the timer interrupt process. However, in the timer interrupt process, for example, only a flag indicating that an interrupt has occurred is set, and the game control process is performed by the main process. May be executed.
図6は、遊技制御に用いる乱数を示す説明図である。各乱数は、以下のように使用される。ランダム2−1(MR2−1)は、大当りの種別(確変大当り、突然確変大当り、通常大当り)を決定する大当り種別判定用の乱数を発生するためのランダムカウンタにより生成される乱数である。ランダム2−2(MR2−2)は、 リーチとするか否か決定するリーチ判定用の乱数を発生するためのランダムカウンタにより生成される乱数である。ランダム3(MR3)は、変動パターンの種別(種類)を決定する変動パターン種別判定用の乱数を発生するためのランダムカウンタにより生成される乱数である。ランダム4(MR4)は、変動パターン(変動時間)を決定する変動パターン判定用の乱数を発生するためのランダムカウンタにより生成される乱数である。ランダム5(MR5)は、普通図柄に基づく当りを発生させるか否か決定する普通図柄当り判定用の乱数を発生するためのランダムカウンタにより生成される乱数である。ランダム6(MR6)は、ランダム5の初期値を決定するランダム5初期値決定用の乱数を発生するためのランダムカウンタにより生成される乱数である。 FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram showing random numbers used for game control. Each random number is used as follows. Random 2-1 (MR2-1) is a random number generated by a random counter for generating a big hit type determination random number for determining a big hit type (probability big hit, sudden probability change big hit, or normal big hit). Random 2-2 (MR2-2) is a random number generated by a random counter for generating a random number for reach determination that determines whether or not to reach. Random 3 (MR3) is a random number generated by a random counter for generating a random number for determining the variation pattern type that determines the type (type) of the variation pattern. Random 4 (MR4) is a random number generated by a random counter for generating a random number for determining a variation pattern that determines a variation pattern (variation time). Random 5 (MR5) is a random number generated by a random counter for generating a random number for normal symbol determination that determines whether or not to generate a hit based on the normal symbol. Random 6 (MR6) is a random number generated by a random counter for generating a random 5 initial value determining random number for determining a random 5 initial value.
図5に示された遊技制御処理におけるS23では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、(ランダム2−1)の大当り種別判定用乱数、および(ランダム5)の普通図柄当り判定用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウントアップ(1加算)を行なう。すなわち、それらが判定用乱数であり、それら以外の乱数が表示用乱数(ランダム2−2、ランダム3、ランダム4)または初期値用乱数(ランダム6)である。なお、遊技効果を高めるために、上記の乱数以外の乱数も用いてもよい。また、この実施の形態では、大当り判定用乱数として、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に内蔵されたハードウェア(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560の外部のハードウェアでもよい。)が生成する乱数を用いる。また、大当り種別判定用乱数についても、前述のような初期値用乱数を用いた初期値の設定を行なうようにしてもよい。このようにした場合には、大当り種別判定用乱数発生カウンタが最大値まで歩進した後の初期値がランダムな値となるので、確変となる大当り種別の判定値と同じ乱数値を不正に狙って取出し、確変となる種別の大当りを発生させる不正行為が、行なわれにくくなるようにすることができる。
In S23 in the game control process shown in FIG. 5, the
なお、変動パターン種別判定用乱数(ランダム3)や変動パターン判定用乱数(ランダム4)を更新する場合に、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が搭載する乱数回路503が発生するハードウェア乱数の値を用いて加算値を決定し、決定した加算値を加算することによって変動パターン種別判定用乱数(ランダム3)と変動パターン判定用乱数(ランダム4)との少なくとも一方を更新してもよい。そのようにすれば、変動パターン種別判定用乱数(ランダム3)と変動パターン判定用乱数(ランダム4)との少なくとも一方を更新するための加算値用のソフトウェア乱数を発生させる等の処理を不要とすることができる。そのため、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560の処理負担を増大させることなく、変動パターン種別判定用乱数(ランダム3)や変動パターン判定用乱数(ランダム4)をランダムに更新することができる。ここで、変動パターン種別とは、変動パターンを種類によって区別すること、または、その区別をいい、本実施の形態では、予め定められた条件に基づいて、変動パターンの種類をいくつかのグループに分けた区別をいい、変動パターンの大まかな振分けを示すものである。より具体的に、本実施の形態では、変動パターンを、たとえば、リーチの種類(ノーマルリーチ、スーパーリーチ等)、特殊演出(擬似連、滑り)の有無等の変動表示の種類によって区別した変動パターン種別を用いている。
In addition, when updating the random number for variation pattern type determination (random 3) and the random number for variation pattern determination (random 4), the value of the hardware random number generated by the
図7は、大当り判定テーブル、および、大当り種別判定テーブル等の各種判定テーブルを示す説明図である。図7において、(A)は、大当り判定テーブルを示す説明図である。大当り判定テーブルとは、ROM54に記憶されているデータの集まりであって、ランダムRと比較される大当り判定値が設定されているテーブルである。大当り判定テーブルには、通常状態(確変状態でない遊技状態)において用いられる通常時大当り判定テーブルと、確変状態において用いられる確変時大当り判定テーブルとがある。通常時大当り判定テーブルには、図7(A)の左欄に記載されている各数値が大当り判定値として設定され、確変時大当り判定テーブルには、図7(A)の右欄に記載されている各数値が大当り判定値として設定されている。なお、図7(A)においては、通常時と確変時とで大当り判定値の数値範囲の最初の数値が異なっている例が示されているが、当該最初の値は、同じ数値であってもよい。
FIG. 7 is an explanatory diagram showing various determination tables such as a jackpot determination table and a jackpot type determination table. In FIG. 7, (A) is an explanatory diagram showing a jackpot determination table. The jackpot determination table is a collection of data stored in the
CPU56は、所定の時期に、乱数回路503のカウント値を抽出して抽出値を大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)の値とするのであるが、大当り判定用乱数値が図7(A)に示すいずれかの大当り判定値に一致すると、特別図柄に関して大当り(通常大当り、確変大当りまたは突確大当り)にすることに決定する。なお、図7(A)に示す「確率」は、大当りになる確率(割合)を示す。また、大当りにするか否か決定するということは、大当り遊技状態に移行させるか否か決定するということであるが、第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bにおける停止図柄を大当り図柄にするか否か決定するということでもある。
The
図7(B)は、ROM54に記憶されている第1特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルを示す説明図である。大当り種別判定テーブルは、第1特別図柄の変動表示結果を大当り図柄にする旨の判定がなされたときに、大当り種別判定用の乱数(ランダム2−1)に基づいて、大当りの種別を「通常大当り」、「確変大当り」、「突確大当り」のうちのいずれかに決定するために参照されるテーブルである。第1特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルには、ランダム2−1の値と比較される数値であって、「通常大当り」、「確変大当り」、「突確大当り」のそれぞれに対応した判定値(大当り種別判定値)が設定されている。CPU56は、ランダム2−1の値が大当り種別判定値のいずれかに一致した場合に、大当りの種別を、一致した大当り種別判定値に対応する種別に決定する。
FIG. 7B is an explanatory diagram showing a first special symbol jackpot type determination table stored in the
図7(C)は、ROM54に記憶されている第2特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルを示す説明図である。大当り種別判定テーブルは、第2特別図柄の変動表示結果を大当り図柄にする旨の判定がなされたときに、大当り種別判定用の乱数(ランダム2−1)に基づいて、大当りの種別を「通常大当り」、「確変大当り」のうちのいずれかに決定するために参照されるテーブルである。第2特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルには、ランダム2−1の値と比較される数値であって、「通常大当り」、「確変大当り」のそれぞれに対応した判定値(大当り種別判定値)が設定されている。CPU56は、ランダム2−1の値が大当り種別判定値のいずれかに一致した場合に、大当りの種別を、一致した大当り種別判定値に対応する種別に決定する。
FIG. 7C is an explanatory diagram showing a second special symbol jackpot type determination table stored in the
第2特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルにおいては、第1特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルと異なり、「突確大当り」に対応した判定値が設定されていない。したがって、第2特別図柄の変動表示結果に基づいて大当りとなるときには、「突確大当り」の大当り種別が選択されず、「突確大当り」に制御される場合がない。これにより、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄とでは、変動表示結果に応じて制御される大当りの種別が一部異なる。このように第2特別図柄の変動表示において「突確大当り」が生じないようにすることにより、確変状態(時短状態)である場合には、可変入賞球装置15が設けられている第2始動入賞口14に始動入賞して第2特別図柄の変動表示が実行される頻度が高くなるのであるから、15ラウンドの大当りとなる確率を高めることができ、出球率が向上し、遊技に対する興趣を向上させることができる。
In the second special symbol jackpot type judgment table, unlike the first special symbol jackpot type judgment table, a judgment value corresponding to “sudden big hit” is not set. Therefore, when the big hit is made based on the fluctuation display result of the second special symbol, the big hit type of the “surprise big hit” is not selected, and there is no case where the “big hit big hit” is controlled. As a result, the type of jackpot controlled according to the variation display result is partially different between the first special symbol and the second special symbol. In this way, by preventing the occurrence of the “probable big hit” in the variation display of the second special symbol, the second start winning prize provided with the variable winning
なお、第1特別図柄の変動表示を行なう場合と第2特別図柄の変動表示を行なう場合とで、同じ大当り種別判定テーブルを用い、第1特別図柄の変動表示と第2特別図柄の変動表示とのそれぞれにおいて、通常大当り、確変大当りおよび突確大当りを大当り種別として決定するようにしてもよい。 The first special symbol variation display and the second special symbol variation display are used for the first special symbol variation display and the second special symbol variation display using the same jackpot type determination table. In each of these, the normal big hit, the probability variation big hit and the sudden big hit may be determined as the big hit types.
図8は、ROM54に記憶されているリーチ判定テーブルを示す説明図である。リーチ判定テーブルは、変動表示結果をはずれにする旨の判定がなされたときに、リーチ判定用の乱数(ランダム2−2)に基づいて、リーチとするか否かを決定するために参照されるテーブルである。リーチ判定テーブルは、(A)に示す通常時リーチ判定テーブルと、(B)に示す確変・時短時リーチ判定テーブルとを含む。
FIG. 8 is an explanatory diagram showing a reach determination table stored in the
(A)に示す通常時リーチ判定テーブルは、遊技状態が通常遊技状態であるときにリーチ判定のために用いられる。また、(B)に示す確変・時短時リーチ判定テーブルは、遊技状態が確変状態であるとき、および、時短状態であるときにリーチ判定のために用いられる。 The normal-time reach determination table shown in (A) is used for reach determination when the gaming state is the normal gaming state. Further, the probability change / short time reach determination table shown in (B) is used for reach determination when the gaming state is the probability change state and when the game state is the short time state.
通常時リーチ判定テーブルおよび確変・時短時リーチ判定テーブルにおいては、ランダム2−2の値に基づいてリーチとする決定をする値(リーチあり)と、ランダム2−2の値に基づいてリーチとしない決定をする値(リーチなし)とが設定されている。CPU56は、ランダム2−2の値を抽出し、そのランダム2−2の抽出値がリーチとする決定をする値とリーチとしない決定をする値とのどちらに該当するかに基づいて、リーチとするか否かの決定を行なう。
In the normal time reach determination table and the probability change / short time reach determination table, a value for determining reach based on the value of random 2-2 (with reach) and no reach based on the value of random 2-2 A value to decide (no reach) is set. The
なお、リーチ判定テーブルとしては、保留記憶数別にリーチ判定テーブルを設ける等、保留記憶数に応じてリーチとする決定をする割合が異なる(たとえば、保留記憶数が多い程リーチとする決定をする割合が低くなる等)ようにデータが設定されたテーブルを用いてもよい。具体的には、保留記憶数に応じて、リーチとする決定をする判定値の数が異なるようにデータを設定すればよい。また、保留記憶数に応じてリーチとする決定をする判定値の数を異ならせるときの保留記憶数の閾値(たとえば、保留記憶数が所定個以上で判定値を異ならせるときの所定値)を、遊技状態に応じて異ならせるようにしてもよい。たとえば、保留記憶数が所定数以上のときにリーチとする決定をする割合を低くするテーブルについて、確変状態においては、非確変状態よりも少ない保留記憶数が当該閾値となるように設定してもよい。 In addition, as a reach determination table, the ratio of determining reach according to the number of reserved memories is different, such as providing a reach determination table for each number of reserved memories (for example, the ratio of determining reach as the number of reserved memories increases) It is also possible to use a table in which data is set so that the data becomes lower. Specifically, the data may be set so that the number of determination values for determining reach varies depending on the number of reserved memories. Further, a threshold value of the number of reserved memories when the number of determination values for determining reach according to the number of reserved memories (for example, a predetermined value when the number of reserved memories is equal to or more than a predetermined value and the determination value is different) is set. Depending on the gaming state, it may be made different. For example, with respect to a table that reduces the ratio of the reach determination when the number of reserved memories is equal to or greater than a predetermined number, in the probability variation state, a smaller number of retention memories may be set as the threshold value than in the non-probability variation state. Good.
次に、複数種類設けられた大当りについて、それぞれの特徴を説明する。図9は、各種の大当りのそれぞれの特徴を表形式で示す図である。 Next, the characteristics of the jackpot provided in plural types will be described. FIG. 9 is a diagram showing the characteristics of various jackpots in a tabular format.
通常大当りについては、演出図柄の表示結果を、通常大当り表示結果用のゾロ目の組合せ(たとえば、左,中,右が「2,2,2」というようないずれかの偶数図柄の組合せ)とすることが決定される。通常大当りとなったときには、大当り遊技状態終了後に、低確高ベース状態に制御される。通常大当りとなったときの特別可変入賞球装置20の開放回数は15回である。高ベース状態は、特別図柄の変動表示が100回実行された後に終了し、低ベース状態に移行する。
For normal jackpots, the display result of the production symbol is combined with a combination of doubles for the normal jackpot display result (for example, any combination of even symbols such as “2, 2, 2” on the left, middle and right). It is decided to do. Normally, when the big hit is made, the low probability and high base state is controlled after the big hit gaming state. Normally, the special variable winning
確変大当りについては、演出図柄の表示結果を、確変大当り表示結果用のゾロ目の組合せ(たとえば、左,中,右が「7,7,7」というようないずれかの奇数図柄の組合せ)とすることが決定される。確変大当りとなったときには、大当り遊技状態終了後に、高確高ベース状態に制御される。確変大当りとなったときの特別可変入賞球装置20の開放回数は15回である。高ベース状態は、特別図柄の変動表示が100回実行された後に終了し、低ベース状態に移行する。確変大当りとなったときには、大当り遊技状態終了後に、確変状態である旨を報知する演出が行なわれる。
For the probable big hit, the display result of the production symbol is combined with a combination of double eyes for the probable big hit display result (for example, any odd symbol combination such as “7, 7, 7” for the left, middle, and right). It is decided to do. When the probable big hit is reached, after the big hit gaming state is finished, the high probable high base state is controlled. The number of times the special variable winning
突確大当りについては、演出図柄の表示結果を、たとえば左,中,右が「1,2,3」または「3,2,1」というような突確大当り表示結果用のチャンス目として予め定められた複数のチャンス目のうちいずれかとすることが決定される。突確大当りとなったときには、大当り遊技状態終了後に、高確高ベース状態に制御される。突確大当りとなったときの特別可変入賞球装置20の開放回数は2回である。
For the surprise big hit, the display result of the production symbol is determined in advance as a chance item for the sudden big hit display result such as “1, 2, 3” or “3, 2, 1” on the left, middle, and right, for example. It is determined to be one of a plurality of chances. When a big hit hit is achieved, the high hit high base state is controlled after the big hit gaming state. The number of times that the special variable winning
次に、擬似連の変動表示の変動パターンについて説明する。図10は、擬似連の変動表示の変動パターンの一例を示すタイミングチャートである。図10においては、一例として、再変動が3回行なわれる擬似連の変動パターンが示されている。 Next, a variation pattern of pseudo-variable variation display will be described. FIG. 10 is a timing chart showing an example of a variation pattern of pseudo-variable variation display. FIG. 10 shows, as an example, a quasi-continuous variation pattern in which re-variation is performed three times.
擬似連の変動パターンにおいては、変動表示の開始時が初回変動の開始時である。そして、1回の仮停止が行なわれた後、1回目の再変動が行なわれる。仮停止時には、演出表示装置9において、前述の擬似連チャンス目を形成する仮停止図柄の組合せが仮停止される。そして、たとえば、変動パターンにおいて設定された回数分の仮停止および再変動が行なわれ、最後の再変動の終了時には、演出表示装置9において、前述の大当り判定の判定結果に応じ、最終停止図柄(確定停止図柄)として、大当り図柄の組合せ、または、はずれ図柄の組合せが停止表示される。また、リーチとなる変動パターンのときには、最後の再変動時において、演出表示装置9で、リーチ図柄が表示されてリーチ状態となり、リーチ演出が行なわれる。なお、リーチ演出は、最後の再変動時以外の再変動時に行なうようにしてもよい。
In the pseudo-continuous variation pattern, the start of variation display is the start of the first variation. Then, after one temporary stop is performed, the first re-variation is performed. At the time of temporary stop, the
このようなパチンコ遊技機1では、リーチとなる変動パターンにおいて、リーチ演出を実行して大当り表示結果とならない状態(リーチはずれ表示結果)で演出図柄を一旦停止した後に、実行中の変動表示が継続するか否かを報知する発展可否演出が行なわれるときがある。発展可否演出は、スーパーリーチ以外のリーチ演出の態様からスーパーリーチの演出に発展する発展演出、スーパーリーチの演出に発展することを煽る煽り演出、発展可否演出後に突確大当りに発展することを報知する突確移行演出、および、変動表示の進行が終了する進行終了演出を含み、これらの演出が行なわれることにより実行中の変動表示が継続するか否かを報知する演出である。発展可否演出が行なわれるときの演出表示装置9での画像による演出を説明する。図11および図12は、発展可否演出が行なわれるときの演出表示装置9での画像による演出の一例を示す表示画面図である。
In such a
パチンコ遊技機1において、発展可否演出としては、複数種類の演出のうちいずれかを実行可能である。図11および図12においては、キャラクタの動作に応じて、スーパーリーチの発展先が異なる発展可否演出を一例として示す。図11を参照して、変動表示の開始条件が成立すると、図11の(A)に示すように、特別図柄の変動表示における特別図柄の変動開始等に対応して、「左」、「中」、「右」の図柄表示エリア9L、9C、9Rの全部で演出図柄の変動が開始される。そして、図11の(B)に示すように、「左」、「中」、「右」の図柄表示エリア9L、9C、9Rにおいて、リーチ図柄の組合せ(左,右の図柄が一致したリーチ図柄の組合せ)が表示され、図11の(C)に示すように、後述するキャラクタaまたはbよりなり遊技者の味方となる味方キャラクタ91と、味方キャラクタ91に敵対する第1の敵キャラクタ99とが、武器92(たとえば剣等)を用いて1回または2回戦う演出であるバトルリーチ演出が行なわれる。たとえば、これらキャラクタが1回戦う演出のときには1段階目の演出でリーチ演出が終了し、これらキャラクタが2回戦う演出のときには1段階目の演出の後、2段階目の演出が行なわれることによりリーチ演出が終了する。
In the
バトルリーチ演出では、変動表示の結果として15R大当り(通常大当り、確変大当り)となるときに、味方キャラクタ91が最終的に勝利し、変動表示の結果はずれとなるときに、敵キャラクタ99が勝利し、変動表示の結果突確大当りとなるときに、武器92等の所定の画像が、後述する図12に示すような特定の表示態様で表示される演出が行なわれる。また、武器92等の所定の画像を表示する演出は、スーパーリーチに発展するときと、表示結果がはずれとなるときとにも行なわれる場合がある。また、変動表示の結果として15R大当り(通常大当り、確変大当り)となるときには、発展可否演出中に突然15R大当りの表示結果が表示される場合もある。
In battle reach production, when the variation display results in 15R big hit (ordinary big hit, probable big hit), the
バトルリーチ演出の演出パターンには、複数種類の演出パターンがある。バトルリーチ演出の演出パターンのうち、主なものを以下に示す。 There are a plurality of types of effect patterns for the battle reach effect. Among the production patterns of battle reach production, the main ones are shown below.
第1の演出パターンは、図11の(D),(E)に示すように、1回目の戦いに味方キャラクタ91が勝利して演出図柄が大当りの表示結果となる演出パターンである。第2の演出パターンは、図11の(F),(G)に示すように1回目の戦いに味方キャラクタ91が敗北して(味方キャラクタ91が倒れて武器92が地面に突刺さる)演出図柄が一旦はずれの表示結果となった後、図12の(H)に示すような第1煽り演出が行なわれ、図12の(J)に示すように味方キャラクタ91が第1の態様(起き上がって前進する態様)で復活して第1の敵キャラクタとは異なる第2の敵キャラクタと2回目の戦いを行なうスーパーリーチAの演出に発展して中図柄が再変動し、2回目の戦いにおいて味方キャラクタ91が勝利して大当りの表示結果となる発展演出を行なう演出パターンである。ここで、第1煽り演出は、前向きの味方キャラクタ91が振動することによりスーパーリーチAへの発展を煽る動作をするとともに、武器92が振動することにより突確大当り移行への発展を煽る動作をする演出であり、このような発展がされないときにはずれとなることを示す演出である。なお、第1煽り演出については、前向きの味方キャラクタ91が振動すること、および、武器92が振動することの演出全体により、スーパーリーチAへの発展、および、突確大当り移行への発展、および、はずれとなることのいずれかとなることを示す演出として実行するようにしてもよい。
As shown in FIGS. 11D and 11E, the first effect pattern is an effect pattern in which the
第3の演出パターンは、図11の(F),(G)に示すように1回目の戦いに味方キャラクタ91が敗北した後、第1煽り演出が行なわれ、図12の(J)に示すように第2の敵キャラクタと2回目の戦いを行なうスーパーリーチAの演出に発展して中図柄が再変動し、2回目の戦いにおいて味方キャラクタ91が敗北してはずれの表示結果となる発展演出を行なう演出パターンである。なお、ここでは、2回目の戦いとして、1回目の戦いと異なる第2の敵キャラクタと戦う演出を行なう例を示したが、これに限らず、2回目の戦いとしては、1回目の戦いと同じ第1の敵キャラクタと再度戦う演出を行なうようにしてもよい。
As shown in FIGS. 11 (F) and 11 (G), the third effect pattern is the first beat effect after the
第4の演出パターンは、図11の(F),(G)に示すように1回目の戦いに味方キャラクタ91が敗北した後、図12の(H)に示すように第1煽り演出が行なわれ、図12の(L)に示すように武器92が所定の表示態様で動作(剣が倒れる動作)することにより突確大当りに移行する旨を報知して突確大当りの表示結果となる(左,中,右図柄が(L)に示す段階で突確大当り図柄に切替る。なお、(H)に示す段階で突確大当り図柄に切替るようにしてもよい。)突確移行演出を行なう演出パターンである。第5の演出パターンは、図11の(F),(G)に示すように1回目の戦いに味方キャラクタ91が敗北した後、図12の(H)に示すように第1煽り演出が行なわれ、図12の(K)に示すように武器92が所定の表示態様で動作せず(剣が倒れない)に振動が停止することにより変動表示の進行が終了する進行終了演出を行なう演出パターンである。進行終了演出を行なれると、当該変動パターンにおける変動表示が終了する。第6の演出パターンは、図11の(F),(G)に示すように1回目の戦いに味方キャラクタ91が敗北した後、第1煽り演出が行なわれ、その第1煽り演出の最中に爆弾が爆発して画面が切替り、突然に大当りの表示結果が表示されることにより大当り遊技状態に移行することを示す移行演出としての突然切替演出を行なう演出パターンである。
In the fourth effect pattern, after the
第7の演出パターンは、図11の(F),(G)に示すように1回目の戦いに味方キャラクタ91が敗北した後、図12の(I)に示すように第2煽り演出が行なわれ、図12の(M)に示すように味方キャラクタ91が第2の態様(それ場で起き上がる態様)で復活して第1の敵キャラクタおよび第2の敵キャラクタとは異なる第3の敵キャラクタと2回目の戦いを行なうスーパーリーチBの演出に発展し、2回目の戦いにおいて味方キャラクタ91が勝利して大当りの表示結果となる発展演出を行なう演出パターンである。ここで、第2煽り演出は、後向きの味方キャラクタ91が振動することによりスーパーリーチBへの発展を煽る動作をするとともに、武器92が振動することにより突確大当り移行への発展を煽る動作をする演出であり、このような発展がされないときにはずれとなることを示す演出である。なお、第2煽り演出については、前向きの味方キャラクタ91が振動すること、および、武器92が振動することの演出全体により、スーパーリーチBへの発展、および、突確大当り移行への発展、および、はずれとなることのいずれかとなることを示す演出として実行するようにしてもよい。
In the seventh effect pattern, after the
第8の演出パターンは、図11の(F),(G)に示すように1回目の戦いに味方キャラクタ91が敗北した後、図12の(I)に示すように第2煽り演出が行なわれ、図12の(M)に示すように第3の敵キャラクタと2回目の戦いを行なうスーパーリーチBの演出に発展し、2回目の戦いにおいて味方キャラクタ91が敗北してはずれの表示結果となる発展演出を行なう演出パターンである。なお、ここでは、2回目の戦いとして、1回目の戦いと異なる第3の敵キャラクタと戦う演出を行なう例を示したが、これに限らず、2回目の戦いとしては、1回目の戦いと同じ第1の敵キャラクタと再度戦う演出を行なうようにしてもよい。
In the eighth effect pattern, after the
第9の演出パターンは図11の(F),(G)に示すように、1回目の戦いに味方キャラクタ91が敗北した後、図12の(I)に示すように第2煽り演出が行なわれ、(L)に示すように武器92が所定の表示態様で動作(剣が倒れる動作)することにより突確大当りに移行する旨を報知して突確大当りの表示結果となる(左,中,右図柄が(L)に示す段階で突確大当り図柄に切替る。なお、(I)に示す段階で突確大当り図柄に切替るようにしてもよい。)突確移行演出を行なう演出パターンである。第10の演出パターンは、図11の(F),(G)に示すように1回目の戦いに味方キャラクタ91が敗北した後、図12の(I)に示すように第2煽り演出が行なわれ、図12の(K)に示すように武器92が所定の表示態様で動作せず(剣が倒れない)に振動が停止することにより変動表示の進行が終了する進行終了演出を行なう演出パターンである。第11の演出パターンは、図11の(F),(G)に示すように1回目の戦いに味方キャラクタ91が敗北した後、第2煽り演出が行なわれ、その第2煽り演出の最中に爆弾が爆発して画面が切替り、突然に大当りの表示結果が表示されることにより大当り遊技状態に移行することを示す移行演出としての突然切替演出を行なう演出パターンである。
In the ninth effect pattern, as shown in FIGS. 11F and 11G, after the
このようなキャラクタaを用いた発展可否演出については、煽り演出が行なわれるときのキャラクタaの動作、すなわち、前向きで動作するか、後向きで操作するかに応じて、スーパーリーチの発展先が異なるように制御される。なお、キャラクタの動作に限らず、キャラクタの色変化等、キャラクタの画像による演出態様に応じて、スーパーリーチの発展先が異なるように制御すればよい。このようにすれば、変動表示の演出進行のバリエーションを豊富化することができる。これにより、遊技者がリーチ演出に飽きてしまわないようにすることができ、リーチ演出における遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 With regard to such an advancement / prohibition effect using the character a, the development destination of the super reach differs depending on the action of the character a when the roaring effect is performed, that is, whether to operate forward or backward. To be controlled. It should be noted that control may be performed so that the development destination of the super reach differs depending on the effect mode by the character image such as the color change of the character as well as the motion of the character. In this way, it is possible to enrich the variation of the effect display of the variable display. Thereby, it is possible to prevent the player from getting bored with the reach production, and to improve the interest of the game in the reach production.
以上に示したキャラクタ画像を用いた発展可否演出は、キャラクタaと異なるキャラクタbについても同様に行なわれる。つまり、キャラクタ画像を用いた発展可否演出としてキャラクタaの代わりにキャラクタbを用いた発展可否演出が行なわれる場合もある。 The development permission / prohibition effect using the character image described above is similarly performed for the character b different from the character a. That is, there is a case where the development propriety effect using the character b instead of the character a is performed as the development propriety effect using the character image.
また、この実施の形態では、キャラクタa,b以外のキャラクタc,dを用いて、前述したようなキャラクタa,bを用いた発展可否演出と種類が異なる発展可否演出が行なわれる場合がある。キャラクタa,bを用いた発展可否演出が1つのキャラクタが表示されたときの発展先のスーパーリーチがスーパーリーチA,Bの複数であるのに対し、キャラクタc,dを用いた発展可否演出は、1つのキャラクタが表示されたときの発展先のスーパーリーチがスーパーリーチAまたはスーパーリーチBのどちらか1つに設定されている。キャラクタc,dを用いた発展可否演出は、次のように行なわれる。 Further, in this embodiment, there may be a case where the development propriety effect different from the development propriety effect using the characters a and b as described above is performed using the characters c and d other than the characters a and b. The development possibility using the characters a and b is a plurality of super reach A and B, and the development possibility using the characters c and d when one character is displayed. The super-reach of the development destination when one character is displayed is set to one of super-reach A and super-reach B. The development propriety effect using the characters c and d is performed as follows.
キャラクタcを用いた発展可否演出は、スーパーリーチの発展先が複数の選択先から選択されずスーパーリーチAのみであり、変動表示の結果突確大当りとなるときには実行されない。具体的に、キャラクタcを用いた発展可否演出では、キャラクタcが図11のような味方キャラクタ91として表示され、前述したキャラクタa,bを用いた発展可否演出と同様に第1の敵キャラクタ99と戦い、変動表示の結果として15R大当り(通常大当り、確変大当り)となるときに、味方キャラクタが勝利し、変動表示の結果はずれとなるときに、敵キャラクタが勝利する。キャラクタcを用いた発展可否演出は、変動表示の結果突確大当りとなるときには実行されない。キャラクタcを用いた発展可否演出では、スーパーリーチAの演出に発展することを煽る第3煽り演出、スーパーリーチAの演出に発展する発展演出、変動表示の進行が終了する進行終了演出とのいずれかが行なわれる。
The development possibility effect using the character c is not executed when the development destination of the super reach is not selected from a plurality of selection destinations, and only the super reach A is obtained, and as a result of the variable display, a sudden big hit is obtained. Specifically, in the development propriety effect using the character c, the character c is displayed as a
キャラクタcを用いた発展可否演出では、味方キャラクタ91が第1の敵キャラクタ99に敗北したときに、味方キャラクタ91が武器92を持った状態で倒れる表示が行なわれ、武器92が地面に突刺さる状態が表示されない。キャラクタcを用いた発展可否演出では、突確移行演出が行なわれないので、キャラクタa,bを用いた発展可否演出のように、武器92が地面に突刺さる状態は表示されない。前述のキャラクタcを用いた発展可否演出では後に行なわれる煽り演出として、図12の(H),(I)に示すような第1、第2煽り演出の代わりに、第3煽り演出が行なわれる。第3煽り演出は、味方キャラクタ91としてのキャラクタcが上向きに倒れた状態で振動することによりスーパーリーチAへの発展を煽る動作が行なわれる演出であり、このような発展がされないときにはずれとなることを示す演出である。第3煽り演出においては、前述のような突確移行演出が行なわれない。
In the development propriety effect using the character c, when the
キャラクタcを用いた発展可否演出では、味方キャラクタ91としてのキャラクタcの振動を停止させることにより、変動表示の進行が終了する進行終了演出が行なわれる。また、キャラクタcを用いた発展可否演出で、スーパーリーチAに発展する演出を行なうときには、味方キャラクタ91が第3の態様(起き上がってジャンプする態様)で復活して第2の敵キャラクタと2回目の戦いを行なうスーパーリーチAの演出に発展して中図柄が再変動し、2回目の戦いにおいて味方キャラクタ91が勝利して大当りの表示結果となる発展演出を行なう演出パターンと、同様にスーパーリーチAの演出に発展して、2回目の戦いにおいて味方キャラクタ91が敗北してはずれの表示結果となる発展演出を行なう演出パターンとのいずれかが、大当り判定の結果に応じて選択される。
In the development propriety effect using the character c, by stopping the vibration of the character c as the
また、キャラクタcを用いた発展可否演出では、図11の(F),(G)に示すように1回目の戦いに味方キャラクタ91が敗北した後、第3煽り演出が行なわれ、その第3煽り演出の最中に爆弾が爆発して画面が切替り、突然に大当りの表示結果が表示される突然切替演出を行なう演出パターンが行なわれる。
Moreover, in the development propriety effect using the character c, after the
なお、ここでは、2回目の戦いとして、1回目の戦いと異なる第2の敵キャラクタと戦う演出を行なう例を示したが、これに限らず、2回目の戦いとしては、1回目の戦いと同じ第1の敵キャラクタと再度戦う演出を行なうようにしてもよい。 In addition, although the example which performs the effect which fights the 2nd enemy character different from the 1st battle was shown here as a 2nd battle, not only this but as the 2nd battle, You may make it perform the effect which fights again with the same 1st enemy character.
このように、キャラクタcを用いた発展可否演出は、キャラクタcが表示されたときの発展先のスーパーリーチがスーパーリーチAに限定されている。 As described above, in the development availability effect using the character c, the super-reach of the development destination when the character c is displayed is limited to the super-reach A.
また、キャラクタdを用いた発展可否演出は、スーパーリーチの発展先が複数の選択先から選択されずスーパーリーチBのみであり、変動表示の結果突確大当りとなるときには実行されない。具体的に、キャラクタdを用いた発展可否演出では、キャラクタdが図11のような味方キャラクタ91として表示され、前述したキャラクタa,bを用いた発展可否演出と同様に第1の敵キャラクタ99と戦い、変動表示の結果として15R大当り(通常大当り、確変大当り)となるときに、味方キャラクタが勝利し、変動表示の結果がはずれとなるときに、敵キャラクタが勝利する。キャラクタdを用いた発展可否演出は、変動表示の結果突確大当りとなるときには実行されない。キャラクタdを用いた発展可否演出では、スーパーリーチBの演出に発展することを煽る第4煽り演出、スーパーリーチBの演出に発展する発展演出、変動表示の進行が終了する進行終了演出とのいずれかが行なわれる。
Further, the development possibility effect using the character d is not executed when the super reach development destination is not selected from a plurality of selection destinations, and only the super reach B is obtained, and as a result of the variable display, it becomes a big hit. Specifically, in the development propriety effect using the character d, the character d is displayed as a
キャラクタdを用いた発展可否演出では、味方キャラクタ91が第1の敵キャラクタ99に敗北したときに、味方キャラクタ91が武器92を持った状態で倒れる表示が行なわれ、武器92が地面に突刺さる状態が表示されない。キャラクタdを用いた発展可否演出では、突確移行演出が行なわれないので、キャラクタa,bを用いた発展可否演出のように、武器92が地面に突刺さる状態は表示されない。前述のキャラクタdを用いた発展可否演出では後に行なわれる煽り演出として、図12の(H),(I)に示すような第1、第2煽り演出の代わりに、第4煽り演出が行なわれる。第4煽り演出は、味方キャラクタ91としてのキャラクタdが下向きに倒れた状態で振動することによりスーパーリーチBへの発展を煽る動作が行なわれる演出であり、このような発展がされないときにはずれとなることを示す演出である。第4煽り演出においては、前述のような突確移行演出が行なわれない。
In the development propriety effect using the character d, when the
キャラクタdを用いた発展可否演出では、味方キャラクタ91としてのキャラクタdの振動を停止させることにより、変動表示の進行が終了する進行終了演出が行なわれる。また、キャラクタdを用いた発展可否演出で、スーパーリーチBに発展する演出を行なうときには、味方キャラクタ91が第4の態様で復活して第3の敵キャラクタと2回目の戦いを行なうスーパーリーチBの演出に発展して中図柄が再変動し、2回目の戦いにおいて味方キャラクタ91が勝利して大当りの表示結果となる発展演出を行なう演出パターンと、同様にスーパーリーチBの演出に発展して、2回目の戦いにおいて味方キャラクタ91が敗北してはずれの表示結果となる発展演出を行なう演出パターンとのいずれかが、大当り判定の結果に応じて選択される。
In the development propriety effect using the character d, by stopping the vibration of the character d as the
また、キャラクタdを用いた発展可否演出では、図11の(F),(G)に示すように1回目の戦いに味方キャラクタ91が敗北した後、第4煽り演出が行なわれ、その第4煽り演出の最中に爆弾が爆発して画面が切替り、突然に大当りの表示結果が表示される突然切替演出を行なう演出パターンが行なわれる。
Further, in the development propriety effect using the character d, as shown in FIGS. 11 (F) and 11 (G), after the
なお、ここでは、2回目の戦いとして、1回目の戦いと異なる第3の敵キャラクタと戦う演出を行なう例を示したが、これに限らず、2回目の戦いとしては、1回目の戦いと同じ第1の敵キャラクタと再度戦う演出を行なうようにしてもよい。 In addition, although the example which performs the effect which fights with the 3rd enemy character different from the 1st battle was shown here as a 2nd battle, not only this but as the 2nd battle, You may make it perform the effect which fights again with the same 1st enemy character.
このように、キャラクタdを用いた発展可否演出は、キャラクタdが表示されたときの発展先のスーパーリーチがスーパーリーチBに限定されている。 As described above, in the development availability effect using the character d, the superreach of the development destination when the character d is displayed is limited to the superreach B.
このようなキャラクタc,dを用いた発展可否演出では、キャラクタが表示されたときの発展先のスーパーリーチは、1種類のスーパーリーチに限定されているので、キャラクタが表示された段階で、キャラクタ自体によりスーパーリーチに発展したときの発展先のスーパーリーチの種類を容易に把握することができる。なお、キャラクタ自体に限らず、キャラクタ自体とキャラクタの色との組合せ等、キャラクタの画像による演出態様に応じて、スーパーリーチの発展先が異なるように制御すればよい。このようにすれば、変動表示の演出進行のバリエーションを豊富化することができる。これにより、遊技者がリーチ演出に飽きてしまわないようにすることができ、リーチ演出における遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 In such a development possibility using characters c and d, since the super-reach of the development destination when the character is displayed is limited to one type of super-reach, the character is displayed when the character is displayed. By itself, it is possible to easily grasp the type of superreach of the development destination when it has evolved into superreach. It should be noted that control is not limited to the character itself, and the super reach development destination may be controlled to be different depending on the effect mode by the character image, such as a combination of the character itself and the character color. In this way, it is possible to enrich the variation of the effect display of the variable display. Thereby, it is possible to prevent the player from getting bored with the reach production, and to improve the interest of the game in the reach production.
なお、前述したキャラクタc,dを用いた発展可否演出では、キャラクタa,bを用いた発展可否演出と別の演出表示態様で、突確移行演出を行なうようにしてもよく、キャラクタa,bを用いた発展可否演出の場合と同様に、煽り演出を行なわずに突確移行演出を行なうようにしてもよい。また、キャラクタa,bを用いた発展可否演出では、キャラクタc,dを用いた発展可否演出と同様に、突確移行演出を行なわないようにしてもよい。 It should be noted that in the above-described development propriety effect using the characters c and d, the sudden transition effect may be performed in an effect display manner different from the development propriety effect using the characters a and b. As in the case of the used development propriety effect, the sudden transition effect may be performed without performing the roaring effect. Further, in the development propriety effect using the characters a and b, the sudden transition effect may not be performed as in the development propriety effect using the characters c and d.
このような発展可否演出は、擬似連とならない変動パターンでの変動表示において行なわれる場合と、擬似連となる変動パターンでの変動表示において行なわれる場合とがある。擬似連となる変動パターンでの変動表示において発展可否演出が行なわれるときには、擬似連において最終的な表示結果を導出表示する前の再変動の回(最後の再変動の回)の変動表示時において、発展可否演出が行なわれる。 Such development propriety effect may be performed in a variation display with a variation pattern that does not become a pseudo-continuous, or in a variation display with a variation pattern that becomes a pseudo-continuous. When a changeable display is performed in a variation display with a variation pattern that becomes a pseudo-continuous, during the variation display of the re-variation times (the last re-variation times) before the final display result is derived and displayed in the pseudo-ream , The development propriety effect is performed.
なお、発展可否演出は、実行中の変動表示が継続するか否かを報知する演出であればよく、少なくとも図12の(H),(I)に示すような煽り演出を含んでいるものであればよい。したがって、発展可否演出としては、煽り演出に、その後行なわれるスーパーリーチの演出に発展する発展演出と、突確大当りに発展することを報知する突確移行演出と、変動表示の進行が終了する進行終了演出とがそれぞれ加えられた演出が該当してもよい。そして、発展可否演出としては、煽り演出に、その後行なわれるこのような発展演出と、突確移行演出と、進行終了演出とがそれぞれ加えられない演出(これら発展演出、突確移行演出、進行終了演出が含まれない演出)が該当してもよい。つまり、発展可否演出としては、発展可否演出が行なわれた後に、変動表示が終了するのか、その発展可否演出に続く演出が行なわれるのかを煽る演出であればよい。 It should be noted that the development propriety effect may be any effect that informs whether or not the variable display during execution is continued, and includes at least a turn effect as shown in (H) and (I) of FIG. I just need it. Therefore, as the propriety effect, the development effect that develops into the super-reaching effect that is performed thereafter, the sudden transition effect that informs that it will develop into a sudden big hit, and the end-of-progress effect that the progress of the variable display ends. A production in which and are added may be applicable. And, as the propriety development effect, such an effect that the development effect, the sudden transition effect, and the progress end effect that are performed afterwards are not added respectively (the development effect, the sudden transition effect, and the progress end effect are not included). Production not included) may be applicable. That is, the development propriety effect may be any effect that indicates whether the change display ends after the development propriety effect is performed or whether an effect following the development propriety effect is performed.
また、発展可否演出については、煽り演出後に、スーパーリーチの演出に発展するか、突確大当りに移行するか、そのままはずれとなるかにより、複数種類の敵キャラクタから選択される割合が高い敵キャラクタが異なるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、たとえ煽り演出前の1段階目の演出において味方キャラクタが負けても、煽り演出後の2段階目の演出に発展することについての遊技者の期待感を生じさせることができる。また、煽り演出前の1段階目の演出においてそのままはずれとなる割合が高く設定された敵キャラクタが表示されたときには、そのままはずれとなってしまうかどうか遊技者の興味を引くようにすることができ、1段階目の演出について、遊技者の期待感を生じさせることができる。これらにより、遊技者の興趣を向上させることができる。また、煽り演出前の1段階目の演出において、煽り演出後の2段階目の演出に発展しやすいキャラクタが味方キャラクタとして表示されたときには、煽り演出前の1段階目の演出と、煽り演出後の2段階目の演出への発展との両方について、遊技者の期待感を生じさせることができる。 Also, with regard to the development propriety effect, there is an enemy character that has a high ratio of being selected from a plurality of types of enemy characters depending on whether it develops into a super-reaching effect, shifts to a sudden big hit, or goes off as it is after the roaring effect. It may be different. In this way, even if the ally character loses in the first stage production before the roaring effect, it is possible to generate a player's expectation about developing into the second stage production after the roaring effect. . In addition, when an enemy character that is set with a high percentage of divergence is displayed in the first stage stage before the squealing stage, it is possible to attract the player's interest as to whether or not it will be lost. A player's expectation can be generated for the first stage effect. Thereby, the interest of the player can be improved. In addition, in the first stage production before the roaring effect, when a character that is likely to develop into the second stage production after the roaring effect is displayed as an ally character, the first stage effect before the roaring effect and after the roaring effect It is possible to generate a player's expectation for both of the development to the second stage production.
次に、特別図柄および演出図柄の変動パターンを選択決定するために用いる変動パターンテーブルについて説明する。変動パターンテーブルとしては、ROM54に、非リーチはずれ時判定テーブル、非確変状態リーチはずれ時判定テーブル、確変状態リーチはずれ時判定テーブル、非確変状態通常大当り時判定テーブル、確変状態通常大当り時判定テーブル、非確変状態確変大当り時判定テーブル、確変状態確変大当り時判定テーブル、非確変状態突確大当り時判定テーブル、および、確変状態突確大当り時判定テーブルが記憶されており、選択的に用いられる。
Next, the variation pattern table used for selecting and determining the variation pattern of the special symbol and the effect symbol will be described. As the variation pattern table, in the
非リーチはずれ時判定テーブルは、大当り判定によりはずれとすることが決定され、かつ、リーチ判定によりリーチとしないことが決定されたとき、すなわち「非リーチはずれ」とすることが決定されたときに用いられる変動パターンテーブルである。非確変状態リーチはずれ時判定テーブルは、非確変状態において大当り判定によりはずれとすることが決定され、かつ、リーチ判定によりリーチとすることが決定されたとき、すなわち非確変状態において「リーチはずれ」とすることが決定されたときに用いられる変動パターンテーブルである。確変状態リーチはずれ時判定テーブルは、確変状態において大当り判定によりはずれとすることが決定され、かつ、リーチ判定によりリーチとすることが決定されたとき、すなわち確変状態において「リーチはずれ」とすることが決定されたときに用いられる変動パターンテーブルである。 The non-reach deviation determination table is used when it is determined that a hit is determined by a big hit determination, and when it is determined that a reach is not determined by a reach determination, that is, when it is determined that a “non-reach shift” is determined. It is a fluctuation pattern table to be obtained. The non-probability change state reach-off determination table is set to “reach out” in the non-probability change state when it is determined to be out of the jackpot determination in the non-probability change state and is determined to be reach through the reach determination. It is a fluctuation pattern table used when it is decided to do. The probability variation state reach failure determination table may be “reach loss” in the probability variation state when it is determined that the hit is determined by the big hit determination and the reach determination is determined by the reach determination, that is, in the probability variation state. It is a fluctuation pattern table used when it is determined.
非確変状態通常大当り時判定テーブルは、非確変状態において大当り判定により大当りとすることが決定され、かつ、大当り種別判定により通常大当りとすることが決定されたときに用いられる変動パターンテーブルである。確変状態通常大当り時判定テーブルは、確変状態において大当り判定により大当りとすることが決定され、かつ、大当り種別判定により通常大当りとすることが決定されたときに用いられる変動パターンテーブルである。 The non-probability change state normal big hit determination table is a variation pattern table used when it is determined that the big hit is determined by the big hit determination in the non-probable change state and the normal big hit is determined by the big hit type determination. The probability variation state normal big hit determination table is a variation pattern table used when it is determined that the big hit is determined by the big hit determination in the probability varying state and the normal big hit is determined by the big hit type determination.
非確変状態確変大当り時判定テーブルは、非確変状態において大当り判定により大当りとすることが決定され、かつ、大当り種別判定により確変大当りとすることが決定されたときに用いられる変動パターンテーブルである。確変状態確変大当り時判定テーブルは、確変状態において大当り判定により大当りとすることが決定され、かつ、大当り種別判定により確変大当りとすることが決定されたときに用いられる変動パターンテーブルである。 The non-probability variation state probability variation big hit determination table is a variation pattern table used when it is determined that the big hit is determined by the big hit determination in the non-probable variation state, and the probability variation big hit is determined by the big hit type determination. The probability variation state probability variation big hit determination table is a variation pattern table used when it is determined that the big hit is determined by the big hit determination in the probability variation state and the probability variation big hit is determined by the big hit type determination.
非確変状態突確大当り時判定テーブルは、非確変状態において大当り判定により大当りとすることが決定され、かつ、大当り種別判定により突確大当りとすることが決定されたときに用いられる変動パターンテーブルである。確変状態突確大当り時判定テーブルは、確変状態において大当り判定により大当りとすることが決定され、かつ、大当り種別判定により突確大当りとすることが決定されたときに用いられる変動パターンテーブルである。 The non-probability variation state sudden hit big hit determination table is a variation pattern table used when it is determined that the big hit is determined by the big hit determination in the non-probability variable state and the sudden hit big hit is determined by the big hit type determination. The probability variation state sudden hit big hit determination table is a variation pattern table used when it is determined that the big hit is determined by the big hit determination in the probability changed state and the sudden hit big hit is determined by the big hit type determination.
図13は、非リーチはずれ時判定テーブルを示す説明図である。図14は、非確変状態リーチはずれ時判定テーブルを示す説明図である。図15は、確変状態リーチはずれ時判定テーブルを示す説明図である。非リーチはずれ時判定テーブル、非確変状態リーチはずれ時判定テーブル、および、確変状態リーチはずれ時判定テーブルのそれぞれは、ランダム3と変動パターン種別との関係を示す変動パターン種別判定テーブルと、各変動パターン種別についてランダム4と各種別に属する変動パターンとの関係を示す変動パターン判定テーブルとを含む。 FIG. 13 is an explanatory diagram of a determination table for non-reach deviation. FIG. 14 is an explanatory diagram of a non-probability change state reach determination table. FIG. 15 is an explanatory diagram of a probability variation state reach determination table. Each of the non-reach deviation determination table, the non-probability change state reach deviation determination table, and the probability change state reach deviation determination table includes a variation pattern type determination table indicating the relationship between random 3 and the variation pattern type, and each variation pattern. It includes a variation pattern determination table showing the relationship between random 4 and variation patterns belonging to various types.
非リーチはずれ時判定テーブルにおいては、変動パターン種別により、変動パターンにおける特殊演出の有無等変動パターンの大分類(種別)が特定される。非確変状態リーチはずれ時判定テーブル、および、確変状態リーチはずれ時判定テーブルのそれぞれにおいては、変動パターン種別により、変動パターンにおけるリーチの種類等変動パターンの大分類(種別)が特定される。このように、変動パターンは、変動パターンの演出の態様に基づいて複数種類の変動パターン種別に分類されている。 In the non-reach out-of-reach determination table, a large classification (type) of a variation pattern such as the presence or absence of special effects in the variation pattern is specified by the variation pattern type. In each of the non-probability change state reach-off determination table and the probability change state reach-out determination table, the large classification (type) of the change pattern such as the type of reach in the change pattern is specified by the change pattern type. In this way, the variation patterns are classified into a plurality of types of variation patterns based on the variation pattern effects.
図13〜図15のテーブルでの変動パターンの欄において、「擬似連なし」は、擬似連が行なわれない変動パターンである。「通常」はリーチとならずはずれとなる変動表示を示している。「滑り」は左,中,右図柄を変動させてから、2つ以上の図柄を仮停止表示させた後、その仮停止表示した図柄のうち所定数の図柄を再び変動させた後に停止表示させることによって、図柄が滑って停止表示するように演出図柄を変更させる演出表を行なう変動表示を示している。 In the variation pattern column in the tables of FIGS. 13 to 15, “no quasi-continuation” is a variation pattern in which quasi-continuation is not performed. “Normal” indicates a variable display that does not become reach but shifts. “Slip” is to change the left, middle and right symbols, then temporarily stop and display two or more symbols, and then change the number of symbols temporarily displayed and then stop and display them again. Thus, a variable display is shown in which an effect table for changing the effect symbol so that the symbol slides and stops is displayed.
また、「ノーマル」は変動中にリーチになるものの特別なリーチ演出が行なわれることなく停止する変動パターンとしてのノーマルリーチを示している。「バトルA」は、キャラクタa,bを用いた発展可否演出を行ない、第1煽り演出または第2煽り演出を経て進行終了演出によりリーチはずれ図柄を停止表示するリーチ演出としてのバトルAリーチを示している。「バトルB」は、キャラクタc,dを用いた発展可否演出を行ない、キャラクタに応じて第3煽り演出または第4煽り演出を経て進行終了演出によりリーチはずれ図柄を停止表示するリーチ演出としてのバトルリーチBを示している。 “Normal” indicates normal reach as a variation pattern in which the reach is reached during the variation but stops without performing a special reach performance. “Battle A” indicates a battle A reach as a reach effect in which a character “a” or “b” is used as a development effect, and a reach off effect is stopped by a progress end effect after the first or second turn effect. ing. “Battle B” is a battle effect as a reach effect in which the development is performed using the characters c and d, and the reach off symbol is stopped and displayed by the progress end effect through the third or fourth turn effect depending on the character. Reach B is shown.
「スーパーA」は、キャラクタを用いた発展可否演出を行ない、発展演出によりスーパーリーチAに発展し、リーチはずれ図柄を停止表示するリーチ演出としてのスーパーリーチAを示している。スーパーリーチAには、キャラクタa,bのいずれかを用いた発展可否演出を行ない、キャラクタを用いた第1煽り演出を経て発展演出によりスーパーリーチAに発展するリーチ演出が含まれている。また、スーパーリーチAには、キャラクタcを用いた発展可否演出を行ない、キャラクタを用いた第3煽り演出を経て発展演出によりスーパーリーチAに発展するリーチ演出が含まれている。「スーパーB」は、キャラクタを用いた発展可否演出を行ない、発展演出によりスーパーリーチBに発展し、リーチはずれ図柄を停止表示するリーチ演出としてのスーパーリーチBを示している。スーパーリーチBには、キャラクタa,bのいずれかを用いた発展可否演出を行ない、キャラクタを用いた第2煽り演出を経て発展演出によりスーパーリーチBに発展するリーチ演出が含まれている。また、スーパーリーチBには、キャラクタdを用いた発展可否演出を行ない、キャラクタを用いた第4煽り演出を経て発展演出によりスーパーリーチBに発展するリーチ演出が含まれている。 “Super A” indicates a super reach A as a reach effect in which a character is used to develop or not, develops to a super reach A by the development effect, and stops reaching and displaying the symbols that are out of reach. Super reach A includes a reach effect that develops whether or not development is possible using either character a or b, and develops into super reach A by the development effect through the first roll effect using the character. In addition, the super reach A includes a reach effect that develops whether or not the character c is used and develops to a super reach A by the development effect through the third turning effect using the character. “Super B” indicates a super reach B as a reach effect in which a character is used to develop or not, develops to a super reach B by the development effect, and stops reaching and displaying the symbols that are out of reach. Super reach B includes a reach effect that develops whether or not to develop using either character a or b, and develops to super reach B by the development effect through a second turn effect using the character. In addition, the super reach B includes a reach effect that develops whether or not the character d is used and develops into a super reach B by the development effect through the fourth turning effect using the character.
キャラクタa,bについては、スーパーリーチの演出に関し、第1煽り演出を経てスーパーリーチAに発展する「スーパーA」と、第2煽り演出を経てスーパーリーチBに発展する「スーパーB」とが実行可能であるので、図11および図12に示したような、発展可否演出におけるキャラクタa,bの動作が第1煽りの動作か第2煽りの動作かで発展先のスーパーリーチが異なる演出を行なうことができる。また、キャラクタc,dについては、スーパーリーチの演出に関し、キャラクタcが第3煽り演出を経てスーパーリーチAに発展する「スーパーA」のみが実行可能であり、キャラクタdが第4煽り演出を経てスーパーリーチBに発展する「スーパーB」のみが実行可能であるので、発展可否演出において表示されるキャラクタ自体で発展先のスーパーリーチが異なる演出を行なうことができる。なお、キャラクタを用いたスーパーリーチの演出としては、発展可否演出におけるキャラクタの動作態様に応じて発展先のスーパーリーチが異なる演出のみが選択可能となるように設定してもよく、発展可否演出において表示されるキャラクタ自体で発展先のスーパーリーチが異なる演出のみが選択可能となるように設定してもよい。 For characters a and b, with regard to the production of super reach, “Super A”, which develops into Super Reach A through the first turn production, and “Super B”, which develops into Super Reach B through the second production production, are executed. Since it is possible, as shown in FIGS. 11 and 12, the development of the super reach of the development destination is different depending on whether the movement of the characters a and b in the development permission / prohibition is the first or second movement. be able to. As for characters c and d, only the “super A” that character c progresses to super reach A through the third turn production can be executed, and the character d goes through the fourth turn production. Since only “Super B”, which develops into Super Reach B, can be executed, it is possible to produce an effect in which the developed Super Reach is different in the character itself displayed in the development possible / impossible effect. In addition, as the effect of the super reach using the character, it may be set so that only the effect in which the super reach of the development destination is different can be selected in accordance with the action mode of the character in the development possible / impossible effect. It may be set so that only the effects in which the developed super reach differs depending on the displayed character itself can be selected.
なお、この実施の形態では、第1煽り演出をしたときにのみスーパーリーチAに発展可能であり、第2煽り演出をしたときにのみスーパーリーチBに発展可能である例を示した。しかし、これに限らず、第1煽り演出をしたときにスーパーリーチAとスーパーリーチBとの両方に発展可能であり、第2煽り演出をしたときにスーパーリーチAとスーパーリーチBとの両方に発展可能であるようにしてもよい。その場合には、たとえば、第1煽り演出をしたときにスーパーリーチAに発展する割合がスーパーリーチBに発展する割合よりも高くなるように選択割合を設定し、第2煽り演出をしたときにスーパーリーチBに発展する割合がスーパーリーチAに発展する割合よりも高くなるように選択割合を設定すればよい。このように設定すれば、煽り演出の種類と、発展先のスーパーリーチの種類との関係の選択肢が豊富化し、発展可否演出の面白みを向上させることができる。また、キャラクタbが表示されたときにはキャラクタaが表示されたときよりも大当りとなる割合が高く、スーパーリーチBに発展したときにはスーパーリーチAに発展したときよりも大当りとなる割合が高く、キャラクタaが表示されたときにスーパーリーチBよりもスーパーリーチAに発展する割合が高く、および、キャラクタbが表示されたときにスーパーリーチAよりもスーパーリーチBに発展する割合が高くなるような設定された場合において、キャラクタaからスーパーリーチBに発展したときに、キャラクタbからスーパーリーチAに発展したときよりも大当りとなる割合が高くなるようにデータを設定して変動パターンを選択するようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、たとえば、キャラクタa単体ではキャラクタb単体と比べて、表示されたときに大当りとなる割合が低いが、キャラクタaとスーパーリーチBとの組合せによりキャラクタbが表示されたときよりも大当りとなる割合が高くなるので、キャラクタの種類と発展先のスーパーリーチの種類との組合せに応じて大当りとなる割合が異なるようになる。これにより、キャラクタ画像を表示するだけで遊技者が特定遊技状態への期待感を持てなくなることが防がれ、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 In this embodiment, an example has been shown in which it can be developed to Super Reach A only when the first roll production is performed, and can be developed to Super Reach B only when the second roll production is performed. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and it is possible to develop both Super Reach A and Super Reach B when the first hit production is performed, and to both Super Reach A and Super Reach B when the second strike production is performed. It may be possible to develop. In this case, for example, when the selection ratio is set so that the ratio of development to super reach A is higher than the ratio of development to super reach B when the first roll production is performed, and the second roll production is performed. The selection ratio may be set so that the ratio of developing to super reach B is higher than the ratio of developing to super reach A. By setting in this way, the options of the relationship between the type of squealing effect and the type of super-reach at the development destination are abundant, and it is possible to improve the fun of the development availability effect. Further, when character b is displayed, the ratio of winning big hits is higher than when character a is displayed, and when developing to super reach B, the ratio of winning big hits is higher than when developing to super reach A. Is set such that the rate of development to super reach A is higher than that of super reach B when the character is displayed, and the rate of development to super reach B is higher than that of super reach A when the character b is displayed. In this case, when the character a is developed to the super reach B, the data is set so that the ratio of the big hit is higher than that when the character b is developed to the super reach A, and the variation pattern is selected. Also good. In this way, for example, the character a alone has a lower percentage of big hits when displayed than the character b alone, but the character b is displayed by the combination of the character a and the super reach B. Since the ratio of winning big hits increases, the ratio of winning big hits differs depending on the combination of the character type and the type of super-reach at the development destination. As a result, it is possible to prevent the player from having a sense of expectation for the specific gaming state simply by displaying the character image, and to improve the interest of the game.
「擬似連1回」は、擬似連で再変動が1回行なわれる変動パターンである。「擬似連2回」は、擬似連で再変動が2回行なわれる変動パターンである。「擬似連3回」は、擬似連で再変動が3回行なわれる変動パターンである。「擬似連4回」は、擬似連で再変動が4回行なわれる変動パターンである。「はずれ」は、変動表示の最終的な表示結果が「はずれ」の表示結果となる変動パターンである。
The “pseudo sequence once” is a variation pattern in which re-variation is performed once in the pseudo sequence. “Pseudo-continuous twice” is a variation pattern in which re-variation is performed twice in the pseudo-continuous. The “
「キャラクタa」〜「キャラクタd」は、キャラクタa〜dを用いたリーチ演出が行なわれる変動パターンであることを示している。「第1煽り」〜「第4煽り」は、第1煽り演出〜第4煽り演出が行なわれる変動パターンであることを示している。「発展無」は、スーパーリーチへの発展演出および突確大当りへの移行演出が行なわれない変動パターン、すなわち、「進行終了演出」が行なわれる変動パターンであることを示している。「発展有」は、スーパーリーチへの発展演出が行なわれる変動パターンであることを示している。 “Character a” to “Character d” indicate a variation pattern in which a reach effect using the characters a to d is performed. “First turn” to “fourth turn” indicate a variation pattern in which a first turn effect to a fourth turn effect are performed. “No development” indicates a variation pattern in which a development effect to super reach and a transition effect to a sudden big hit are not performed, that is, a variation pattern in which “progress end effect” is performed. “Developed” indicates that the pattern is a variation pattern in which development for super reach is performed.
これらの情報に基づいて、たとえば、「擬似連なし スーパーA はずれ キャラクタa 第1煽り 発展有」という変動パターンは、「擬似連とならないキャラクタaを用いた変動表示において、第1煽り演出を経てスーパーリーチAに発展した後、はずれ表示結果となる変動パターン」であることが示される。 Based on these pieces of information, for example, a variation pattern of “no super-continuous super A out-of-order character a first inflection present” is displayed in a variation display using a character a that does not become a pseudo-continuum through a first inflection effect. After the development to reach A, it is indicated that the pattern is a variation pattern resulting in a loss display result.
図13〜図15のテーブルにおいて、「ランダム3範囲」および「変動パターン種別」という記載がされた欄は、「ランダム3範囲」と「変動パターン種別」との関係を示す変動パターン種別判定テーブルを示す欄である。たとえば、図14を例にとれば、「ノーマルリーチ」、「バトルリーチA」、「バトルリーチB」、「スーパーリーチA」、「スーパーリーチB」というような複数の変動パターン種別のそれぞれに、ランダム3(0〜109)のすべての値が、r3で示される数値範囲、r4で示される数値範囲、r5で示される数値範囲、r6で示される数値範囲、および、r7で示されるの数値範囲のような複数の数値範囲で割振られている。たとえば、所定のタイミングで抽出したランダム3の値がr6の数値範囲のいずれかの数値と一致すると、変動パターン種別として「スーパーリーチA」とすることが決定される。
In the tables of FIG. 13 to FIG. 15, the columns labeled “
図13〜図15のそれぞれのテーブルにおいて、「ランダム4範囲」および「変動パターン」という記載がされた欄は、「ランダム4範囲」と「変動パターン」との関係を示す変動パターン判定テーブルを示す欄である。変動パターン種別判定テーブルの各種別に対応して示されている変動パターンが、各種別に属する変動パターンである。たとえば、図14を例にとれば、「ノーマルリーチ」の種別に属する変動パターンは、「擬似連なしノーマルはずれ」、「擬似連1回ノーマルはずれ」、「擬似連2回ノーマルはずれ」、および、「滑り」である。各変動パターン種別に対応する複数の変動パターンのそれぞれに、ランダム4(0〜99)のすべての値が、たとえばr3〜r7というような複数の数値範囲で割振られている。たとえば、「スーパーリーチA」の変動パターン種別とすることが決定されたときに、所定のタイミングで抽出したランダム4の値に応じて、「擬似連なし スーパーA はずれ キャラa 第1煽り 発展有」等の当該種別に属する変動パターンが選択決定される。
In each of the tables of FIGS. 13 to 15, the columns labeled “
図13の非リーチはずれ時判定テーブルにおいては、変動パターン種別として「特殊演出なし通常」と「特殊演出あり通常」との種別が設定されている。ここで、「特殊演出」は、擬似連の演出と、滑りの演出とを含む。また、「通常」は、リーチとならない通常変動となる変動パターンを示している。したがって、非リーチはずれとなるときには、「特殊演出なし通常」と「特殊演出あり通常」とのいずれかの種別に属する変動パターンが選択される。 In the non-reach deviation determination table of FIG. 13, types of “normal with no special effect” and “normal with a special effect” are set as the variation pattern types. Here, the “special effect” includes a pseudo-ream effect and a slip effect. Further, “normal” indicates a fluctuation pattern that is a normal fluctuation that does not result in reach. Therefore, when the non-reach is lost, a variation pattern belonging to one of the types “normal with no special effect” and “normal with a special effect” is selected.
図14の非確変状態リーチはずれ時判定テーブルでの「変動パターン種別」の欄において、「ノーマルリーチ」の種別は、ノーマルリーチの変動パターンが属する変動パターン種別である。また、「バトルリーチA」の種別は、バトルリーチAの変動パターンが属する変動パターン種別である。「バトルリーチB」の種別は、バトルリーチBの変動パターンが属する変動パターン種別である。 In the “variation pattern type” column of the non-probability change state reach determination table in FIG. 14, the type of “normal reach” is the change pattern type to which the change pattern of the normal reach belongs. The type of “battle reach A” is a variation pattern type to which the variation pattern of battle reach A belongs. The type of “battle reach B” is a variation pattern type to which the variation pattern of battle reach B belongs.
また、「スーパーリーチA」の種別は、スーパーリーチAの変動パターンが属する変動パターン種別である。スーパーリーチBの変動パターンが属する変動パターン種別である。 The type of “super reach A” is the variation pattern type to which the variation pattern of super reach A belongs. This is the variation pattern type to which the variation pattern of Super Reach B belongs.
「スーパーリーチA,B」のうち、「スーパーリーチA」の種別は、「スーパーリーチB」の種別と比べて、大当りとなるときに選択される割合が高く設定されている。また、「スーパーリーチA,B」のそれぞれにおいて、キャラクタa,bを用いた発展可否演出を行なう変動パターンは、キャラクタc,dを用いた発展可否演出を行なう変動パターンよりも、大当りとなるときに選択される割合が高く設定されている。 Of “Super Reach A, B”, the type of “Super Reach A” is set to be higher when compared to the type of “Super Reach B”. Further, in each of “Super Reach A, B”, when the variation pattern that performs the development propriety effect using the characters a and b is larger than the variation pattern that performs the development propriety effect using the characters c and d. The percentage selected for is set high.
「スーパーリーチA」の種別に属する変動パターンで実行される発展可否演出は、キャラクタa,bの場合に、第1煽り演出が行なわれた後に、スーパーリーチAに発展し、キャラクタcの場合に、第3煽り演出が行なわれた後に、スーパーリーチAに発展する。「スーパーリーチB」の種別に属する変動パターンで実行される発展可否演出は、キャラクタa,bの場合に、第2煽り演出が行なわれた後に、スーパーリーチBに発展し、キャラクタdの場合に、第4煽り演出が行なわれた後に、スーパーリーチBに発展する。 In the case of the characters a and b, the development permission / inhibition effect executed with the variation pattern belonging to the type of “super reach A” is developed into the super reach A after the first turn effect, and in the case of the character c. After the third hit production, it will evolve into Super Reach A. In the case of the characters a and b, the development propriety effect executed with the variation pattern belonging to the type of “super reach B” is developed into the super reach B after the second turning effect is performed, and in the case of the character d. Then, after the fourth hit production is performed, it develops into Super Reach B.
なお、この実施の形態では、発展可否演出が、演出表示装置9においてキャラクタ画像を用いた画像表示を用いて行なわれるが、発展可否演出は、演出表示装置9においてキャラクタ画像以外の画像を用いた画像表示で行なうようにしてよく、また、各種発光体による発光パターンまたはスピーカ27から出力する音声等の演出表示装置9以外の演出装置を用いた演出で行なうようにしてもよい。
In this embodiment, the development availability effect is performed using an image display using a character image in the
図15においては、確変状態で用いられる変動パターンであり、次のような理由により、キャラクタaまたはキャラクタbを用いて発展可否演出を行なう変動パターンが選択されないように、各変動パターン種別に属する変動パターンが設定されている。図7(B),(C)で第1特別図柄については、突確大当りとする決定がされるが、第2特別図柄については、突確大当りとする決定がされないので、第2特別図柄表示器8bにおいて表示結果が大当り表示結果となったときには突確大当り遊技状態に制御されない。特に確変状態においては、突確大当りとなっても特に遊技状態が大きく変わるわけではないので、突確大当り遊技状態に制御される可能性がないにも関わらず無駄な発展可否演出が行なわれずに済むように、突確大当りへの移行演出を含むキャラクタaまたはキャラクタbを用いて発展可否演出を行なう変動パターンが選択されないようにデータテーブルのデータが設定されている。 In FIG. 15, the variation pattern used in the probability variation state, the variation belonging to each variation pattern type is selected so that the variation pattern for performing the development propriety effect using the character a or the character b is not selected for the following reason. A pattern is set. In FIGS. 7B and 7C, the first special symbol is determined to be a big hit, but the second special symbol is not decided to be a big hit, so the second special symbol display 8b. When the display result is a big hit display result, the sudden big hit gaming state is not controlled. Especially in the probable change state, even if it becomes a sudden big hit, the game state does not change significantly, so that there is no possibility that it will be controlled to the big hit game state, so that it will not be possible to perform a useless development propriety effect. In addition, the data in the data table is set so that the variation pattern for performing the development propriety effect using the character a or the character b including the transition effect to the sudden hit is not selected.
具体的に、図15においては、図14と比べて、「バトルリーチA」の変動パターン種別が設けられていない。さらに、「スーパーリーチA,B」の変動パターン種別については、キャラクタaまたはキャラクタbを用いて発展可否演出を行なう変動パターンが属さないように変動パターンのデータが設定されている。 Specifically, in FIG. 15, the variation pattern type of “Battle Reach A” is not provided as compared to FIG. 14. Furthermore, with respect to the variation pattern type of “super reach A, B”, variation pattern data is set so that the variation pattern for performing the development propriety effect using the character a or the character b does not belong.
図16は、非確変状態通常大当り時判定テーブルを示す説明図である。図17は、確変状態通常大当り時判定テーブルを示す説明図である。図18は、非確変状態確変大当り時判定テーブルを示す説明図である。図19は、確変状態確変大当り時判定テーブルを示す説明図である。 FIG. 16 is an explanatory diagram of a non-probability change state normal big hit determination table. FIG. 17 is an explanatory diagram showing a probability variation state normal big hit determination table. FIG. 18 is an explanatory diagram of a non-probability variation state probability variation big hit determination table. FIG. 19 is an explanatory diagram of a probability variation state probability variation big hit determination table.
非確変状態通常大当り時判定テーブル、確変状態通常大当り時判定テーブル、非確変状態確変大当り時判定テーブル、および、確変状態確変大当り時判定テーブルは、15R大当りとなるときに選択される判定テーブルであることで共通する。これら大当り時判定テーブルについては、ランダム3と変動パターン種別との関係を示す変動パターン種別判定テーブルと、各変動パターン種別についてランダム4と各種別に属する変動パターンとの関係を示す変動パターン判定テーブルとを含む。これら大当り時判定テーブルにおけるランダム3と変動パターン種別との対応関係、および、ランダム4と変動パターンとの対応関係は、図14および図15に示すリーチはずれ時判定テーブルの場合と同様である。 Non-probability change normal big hit decision table, Probability change normal big hit decision table, Non-probability change state probable big hit decision table, and Probability change probable big hit decision table are decision tables that are selected when 15R big hit. It is common in that. For these big hit determination tables, there are a variation pattern type determination table showing the relationship between the random 3 and the variation pattern type, and a variation pattern determination table showing the relationship between the random 4 and the variation patterns belonging to each type for each variation pattern type. Including. The correspondence relationship between the random 3 and the variation pattern type and the correspondence relationship between the random 4 and the variation pattern in these big hit determination tables are the same as those in the reach failure determination tables shown in FIGS. 14 and 15.
図16および図18に示すように、非確変状態通常大当り時判定テーブルおよび非確変状態確変大当り時判定テーブルのそれぞれに設定された変動パターン種別は、図14の非確変状態リーチはずれ時判定テーブルに設定された変動パターン種別と同様である。図17および図19に示すように、確変状態通常大当り時判定テーブルおよび確変状態確変大当り時判定テーブルのそれぞれに設定された変動パターン種別は、図15の確変状態リーチはずれ時判定テーブルに設定された変動パターン種別と同様である。 As shown in FIGS. 16 and 18, the variation pattern types set in the non-probability change state normal big hit determination table and the non-probability change state positive change big hit determination table are the non-probability change state reach determination table in FIG. This is the same as the set variation pattern type. As shown in FIGS. 17 and 19, the variation pattern types set in the probability variation state normal jackpot determination table and the probability variation status probability variation jackpot determination table are set in the probability variation state reach misalignment determination table of FIG. 15. This is the same as the variation pattern type.
また、図16〜図19に示すように、通常大当り時判定テーブルおよび確変大当り判定テーブルに設定された変動パターンは、図14および図15のリーチはずれ時判定テーブルに設定された変動パターンと比べて次の点が異なる。 Further, as shown in FIGS. 16 to 19, the fluctuation patterns set in the normal big hit determination table and the probability variation big hit determination table are compared with the fluctuation patterns set in the reach deviation determination tables of FIGS. The following points are different.
「通常大当り」における「ノーマルリーチ」の変動パターン種別には、「擬似連3回ノーマル大当り」という擬似連3回の変動パターンが含まれている。「確変大当り」における「ノーマルリーチ」の変動パターン種別には、「擬似連4回ノーマル大当り」という擬似連4回の変動パターンが含まれている。「スーパーリーチA,B」のそれぞれの変動パターン種別には、擬似連1回〜3回の場合と同様のキャラクタを用いた発展可否演出を行なう擬似連4回の変動パターンが含まれている。 The variation pattern type of “normal reach” in “normal jackpot” includes a variation pattern of three times of pseudo-continuous “normal three-time big hit”. The variation pattern type of “normal reach” in “probable variation big hit” includes a variation pattern of four pseudo runs “pseudo continuous big hit”. Each variation pattern type of “Super Reach A, B” includes a variation pattern of four pseudo-reams that perform development propriety using the same characters as those of the first to third pseudo-reams.
図17の確変状態通常大当り時判定テーブルにおいては、確変状態で用いられる変動パターンであり、図16に対して、前述の図15の場合と同様の理由により、キャラクタaまたはキャラクタbを用いて発展可否演出を行なう変動パターンが選択されないように、各変動パターン種別に属する変動パターンが設定されている。また、図19の確変状態通常大当り時判定テーブルにおいては、確変状態で用いられる変動パターンであり、図18に対して、前述の図15の場合と同様の理由により、キャラクタaまたはキャラクタbを用いて発展可否演出を行なう変動パターンが選択されないように、各変動パターン種別に属する変動パターンが設定されている。 The probability variation state normal big hit determination table of FIG. 17 is a variation pattern used in the probability variation state, and is developed using the character a or the character b for the same reason as in FIG. The variation patterns belonging to each variation pattern type are set so that the variation pattern that performs the propriety effect is not selected. Further, in the probability variation state normal big hit determination table of FIG. 19, it is a variation pattern used in the probability variation state, and the character a or the character b is used for the same reason as in FIG. Thus, the variation patterns belonging to each variation pattern type are set so that the variation patterns for performing the development allowance effect are not selected.
このように、通常大当りの「ノーマルリーチ」の変動パターン種別において擬似連3回の変動パターンが含まれ、確変大当りのそれぞれの「ノーマルリーチ」の変動パターン種別において擬似連4回の変動パターンが含まれている。したがって、擬似連においてノーマルリーチとなるときには、擬似連での再変動回数が3回のような所定回数以上になると所定回数未満のときよりも大当りになる割合が高く(たとえば、100%)、かつ、擬似連での再変動回数が4回のような予め定められた回数になると所定回数未満のときよりも確変状態になる割合が高く(たとえば、100%)なるようにデータが設定されている。なお、擬似連においてノーマルリーチとなるときには、擬似連での再変動回数が多い程、大当りになる割合が高く、かつ、確変状態になる割合が高くなるようにデータを設定してもよい。 As described above, the variation pattern type of “normal reach” for the normal jackpot includes a variation pattern of three pseudo-continuations, and the variation pattern type of each “normal reach” for a probability variation jack includes a variation pattern of four pseudo-continuations. Yes. Therefore, when normal reach is reached in the pseudo-ream, when the number of re-variations in the pseudo-ream is greater than or equal to a predetermined number such as 3, the percentage of big hits is higher than when it is less than the predetermined number (for example, 100%), and The data is set such that when the number of re-variations in the quasi-continuous number is a predetermined number such as four, the rate of the probability variation state is higher (for example, 100%) than when it is less than the predetermined number. Note that when normal reach is reached in the quasi-ream, data may be set such that the greater the number of re-variations in the quasi-ream, the higher the percentage of big hits and the higher the percentage of probability variation.
図13〜図21の変動パターンの欄において、「ノーマル」、「バトルA」「バトルB」、「スーパーA」および「スーパーB」のように、同じ変動パターン名の変動パターンは、同じ変動態様で変動表示が実行される変動パターンである。これにより、大当りとなるときも、はずれとなるときも、変動表示が実行されるときにおいて、ある程度の時間が経過するまでは、同様の変動態様で変動表示が行なわれるので、はずれとなることが早々と遊技者に知られてしまわないようにすることができる。 In the variation pattern columns of FIGS. 13 to 21, variation patterns having the same variation pattern names such as “Normal”, “Battle A”, “Battle B”, “Super A”, and “Super B” have the same variation mode. This is a variation pattern in which variation display is executed. As a result, even when a big hit or a loss occurs, the variation display is performed in the same variation manner until a certain amount of time elapses when the variation display is executed. It is possible to prevent the player from being informed immediately.
また、図16〜図21のそれぞれの変動パターンの欄において、「擬似連4回」が特定された変動パターンは、大当りとなるときにのみ選択される変動パターンである(はずれとなるときの最大の擬似連回数は3回)。したがって、変動表示において擬似連の再変動が4回実行されたときには、必ず大当りとなる。これにより、擬似連における再変動の回数が多いほど大当りとなりやすくなるように設定することができる。
In addition, in each of the variation pattern columns of FIGS. 16 to 21, the variation pattern in which “
図16〜図19においては、大当り時に用いられる変動パターンであるので、「スーパーリーチA」および「スーパーリーチB」のようなスーパーリーチとなる変動パターン種別が選択される割合の方が、「ノーマルリーチ」、「バトルA」および「バトルB」の変動パターン種別が選択される割合よりも高くなるように変動パターン種別判定値が割振られている。また、大当り時に用いられる変動パターンであるので、「スーパーリーチ」の変動パターン種別については、「スーパーリーチA」が選択される割合の方が「スーパーリーチB」が選択される割合よりも高くなるように変動パターン種別判定値が割振られている。このように大当りとなるときには、はずれとなるときと比べて、「スーパーリーチ」となる変動パターンが選択される割合が高いので、「スーパーリーチ」となる変動パターンで変動表示が実行されることにより、遊技者の大当りへの期待感を高めることができる。 In FIG. 16 to FIG. 19, since the fluctuation pattern is used at the time of big hit, the ratio of the fluctuation pattern types that become super reach such as “super reach A” and “super reach B” is selected as “normal reach”. ”,“ Battle A ”, and“ Battle B ”are assigned the variation pattern type determination values so as to be higher than the selected ratio. Further, since the variation pattern is used at the time of big hit, for the variation pattern type of “super reach”, the ratio of selecting “super reach A” is higher than the ratio of selecting “super reach B”. As described above, variation pattern type determination values are assigned. In this way, when a big hit is made, the rate of selection of a variation pattern that becomes “super reach” is higher than when a loss occurs, so that variation display is executed with a variation pattern that becomes “super reach”. , It can increase the player's sense of expectation for jackpot.
また、図16〜図21においては、大当り時に用いられる変動パターンであるので、「擬似連1回」〜「擬似連4回」のような擬似連となる変動パターンが選択される割合の方が、「擬似連なし」のような擬似連とならない変動パターンが選択される割合よりも高くなるように変動パターン判定値が割振られている。一方、図13〜図15に示すようなはずれ時に用いられる変動パターンでは、擬似連とならない変動パターンが選択される割合の方が、擬似連となる変動パターンが選択される割合よりも高くなるように変動パターン判定値が割振られている。また、擬似連の変動パターンについては、再変動回数が多い程、選択される割合が高くなるように変動パターン判定値が割振られている。一方、図13〜図15に示すようなはずれ時に用いられる変動パターンでは、擬似連について、再変動回数が少ない程、選択される割合が高くなるように変動パターン判定値が割振られている。これにより、擬似連の変動パターンが実行されたときに、遊技者の大当りへの期待感を高め、さらに、擬似連での再変動回数が多くなるほど、遊技者の大当りへの期待感をより一層高めることができる。 In addition, in FIGS. 16 to 21, since the variation pattern is used at the time of the big hit, the ratio at which the variation pattern that becomes a pseudo sequence such as “1 pseudo sequence” to “4 pseudo sequence” is selected. The variation pattern determination value is assigned so as to be higher than the rate at which variation patterns that do not become pseudo-continuous such as “no pseudo-continuous” are selected. On the other hand, in the variation pattern used at the time of deviation as shown in FIGS. 13 to 15, the rate at which the variation pattern that does not become a pseudo-continuous is selected is higher than the rate at which the variation pattern that becomes a pseudo-continuous is selected. Fluctuation pattern judgment values are assigned to. In addition, for the variation pattern of the pseudo-continuous, the variation pattern determination value is assigned such that the greater the number of re-variations, the higher the selected ratio. On the other hand, in the variation pattern used at the time of deviation as shown in FIG. 13 to FIG. 15, the variation pattern determination value is assigned so that the selected ratio becomes higher as the number of re-variations is smaller. This increases the player's expectation for the big hit when the fluctuation pattern of the pseudo-ream is executed, and further increases the player's expectation for the big hit as the number of re-variations in the pseudo-ream increases. Can be increased.
なお、図14〜図19のテーブルにおいては、スーパーリーチに関し、擬似連なし、擬似連1回、擬似連2回、擬似連3回というような擬似連の有無および擬似連での再変動回数に応じて、変動パターン種別を類別し、各種別ごとに、スーパーAのリーチおよびスーパーBのリーチが属するように設定してもよい。 In addition, in the tables of FIGS. 14 to 19, regarding the super reach, the presence / absence of the pseudo-series such as no pseudo-series, one pseudo-series, two pseudo-series, and three pseudo-series, and the number of re-variations in the pseudo-series Accordingly, the variation pattern types may be classified and set so that the reach of Super A and the reach of Super B belong to each type.
図20は、非確変状態突確大当り時判定テーブルを示す説明図である。図21は、確変状態突確大当り時判定テーブルを示す説明図である。 FIG. 20 is an explanatory diagram of a non-probability change state sudden big hit determination table. FIG. 21 is an explanatory diagram of a probability variation state sudden large hit determination table.
非確変状態突確大当り時判定テーブル、および、確変状態突確大当り時判定テーブルは、突確大当りとなるときに用いられる判定テーブルである。これら突確大当り時判定テーブルについては、ランダム3と変動パターン種別との関係を示す変動パターン種別判定テーブルと、各変動パターン種別についてランダム4と各種別に属する変動パターンとの関係を示す変動パターン判定テーブルとを含む。これら突確大当り時判定テーブルにおけるランダム3と変動パターン種別との対応関係、および、ランダム4と変動パターンとの対応関係は、図14〜図19に示す判定テーブルの場合と同様である。
The non-probability change state sudden hit big hit determination table and the probability change state sudden hit big hit determination table are determination tables used when a sudden hit big hit. As for these sudden hit determination tables, a variation pattern type determination table showing the relationship between the random 3 and the variation pattern type, a variation pattern determination table showing the relationship between the
図20のテーブルでの変動パターンの欄において、「通常突確」は、リーチとならず突確大当りとなる変動表示を示している。「第1突確移行有」は、前述のような第1煽り演出を経て突確大当りとなる変動表示を示している。「第2突確移行有」は、前述のような第2煽り演出を経て突確大当りとなる変動表示を示している。 In the column of the fluctuation pattern in the table of FIG. 20, “normal accuracy” indicates a fluctuation display that is not reach but is a big hit. “With first-accuracy transition” indicates a variation display that is a large-accuracy big hit through the first squealing effect as described above. “With second-accuracy transition” indicates a fluctuation display that is a big hit after the second turning effect as described above.
このような情報に基づいて、たとえば、「擬似連なし リーチ 大当り キャラクタa 第1煽り 第1突確移行有」という変動パターンは、「擬似連とならないキャラクタaを用いた変動表示において、第1煽り演出を経て突確移行演出を行なって、突確表示結果となる変動パターン」であることが示される。 Based on such information, for example, a variation pattern of “no pseudo-ream reach big hit character a 1st beat first transition transition presence” is “the first turn effect in the variation display using the character“ a ”that is not a pseudo-ream. After that, it is shown that the variation pattern is a result of the accuracy display by performing the accuracy transition effect.
図20において、「特殊演出なし通常突確」、「特殊演出あり通常突確」、および、「突確移行」というような複数の変動パターン種別のそれぞれに、ランダム3(0〜109)のすべての値が、r30で示される数値範囲、r31で示される数値範囲、および、r32で示されるの数値範囲のような複数の数値範囲で割振られている。たとえば、所定のタイミングで抽出したランダム3の値がr32の数値範囲のいずれかの数値と一致すると、変動パターン種別として「突確移行」とすることが決定される。したがって、突確大当りとなるときには、「特殊演出なし通常突確」、「特殊演出あり通常突確」、および、「突確移行」のいずれかの種別に属する変動パターンが選択される。 In FIG. 20, all the values of random 3 (0 to 109) are included in each of a plurality of variation pattern types such as “normal accuracy without special effect”, “normal accuracy with special effect”, and “transition of accuracy”. , R30, a numerical range indicated by r31, and a numerical range indicated by r32. For example, when the random 3 value extracted at a predetermined timing matches any numerical value in the numerical value range of r32, it is determined that the variation pattern type is “susceptibility transition”. Therefore, when the hit is a big hit, a variation pattern belonging to any of the types of “normal hit without special effects”, “normal hit with special effects”, and “transition of hit accuracy” is selected.
図20において、「特殊演出なし通常突確」の種別は、擬似連等のような特殊演出が行なわれずに突確大当りとなる変動パターンが属する変動パターン種別である。「特殊演出あり通常突確」の種別は、擬似連および滑りのような特殊演出が行なわれて突確大当りとなる変動パターンが属する変動パターン種別である。「突確移行」の種別は、擬似連が行なわれないか、または、擬似連が行なわれ、リーチ演出が行なわれて突確大当りとなる変動パターンが属する変動パターン種別である。 In FIG. 20, the type of “normal success without special effects” is a variation pattern type to which a variation pattern that is a big hit without any special effects such as pseudo-ream belongs. The type of “ordinary accuracy with special effects” is a variation pattern type to which a variation pattern that is a special hit such as a pseudo-ream and a slip and that is a sudden hit is a belonging. The type of “accuracy transfer” is a variation pattern type to which a variation pattern that is not a pseudo-ream, or a pseudo-ream is performed and a reach effect is performed to become a decisive big hit.
図21の確変状態突確大当り時判定テーブルにおいては、確変状態で用いられる変動パターンであり、図20に対して、前述の図15の場合と同様の理由により、キャラクタaまたはキャラクタbを用いて発展可否演出を行なう変動パターンが選択されないように、各変動パターン種別に属する変動パターンが設定されている。 21 is a variation pattern used in the probability variation state, and is developed using the character a or the character b for the same reason as in FIG. 15 described above. The variation patterns belonging to each variation pattern type are set so that the variation pattern that performs the propriety effect is not selected.
図16〜図19においては、大当り時に用いられる変動パターンであるので、「スーパーリーチA」および「スーパーリーチB」のようなスーパーリーチとなる変動パターン種別が選択される割合の方が、「ノーマルリーチ」、「バトルA」および「バトルB」の変動パターン種別が選択される割合よりも高くなるように変動パターン種別判定値が割振られている。また、大当り時に用いられる変動パターンであるので、「スーパーリーチ」の変動パターン種別については、「スーパーリーチA」が選択される割合の方が「スーパーリーチB」が選択される割合よりも高くなるように変動パターン種別判定値が割振られている。このように大当りとなるときには、はずれとなるときと比べて、「スーパーリーチ」となる変動パターンが選択される割合が高いので、「スーパーリーチ」となる変動パターンで変動表示が実行されることにより、遊技者の大当りへの期待感を高めることができる。さらに、大当りとなるときには、はずれとなるときと比べて、「スーパーリーチA」となる変動パターンが選択される割合が高いので、「スーパーリーチ」となる変動パターンのうち、「スーパーリーチA」となる変動パターンで変動表示が実行されることにより、遊技者の大当りへの期待感をより一層高めることができる。なお、大当りとなるときには、「スーパーリーチA」となる変動パターンよりも「スーパーリーチB」となる変動パターンが選択される割合が高くなるように設定し、はずれとなるときには、「スーパーリーチB」となる変動パターンよりも「スーパーリーチA」となる変動パターンが選択される割合が高くなるように設定してもよい。その場合においては、変動表示においてキャラクタbが表示されるときの方が、変動表示においてキャラクタaが表示されるときよりも、突確大当りを含む大当りとなる割合が高くなるように設定する。 In FIG. 16 to FIG. 19, since the fluctuation pattern is used at the time of big hit, the ratio of the fluctuation pattern types that become super reach such as “super reach A” and “super reach B” is selected as “normal reach”. ”,“ Battle A ”, and“ Battle B ”are assigned the variation pattern type determination values so as to be higher than the selected ratio. Further, since the variation pattern is used at the time of big hit, for the variation pattern type of “super reach”, the ratio of selecting “super reach A” is higher than the ratio of selecting “super reach B”. As described above, variation pattern type determination values are assigned. In this way, when a big hit is made, the rate of selection of a variation pattern that becomes “super reach” is higher than when a loss occurs, so that variation display is executed with a variation pattern that becomes “super reach”. , It can increase the player's sense of expectation for jackpot. Furthermore, since the rate of selection of the variation pattern that becomes “Super Reach A” is higher when it is a big hit than the case of a loss, “Super Reach A” among the variation patterns that become “Super Reach” By executing the variation display with the variation pattern as described above, it is possible to further increase the player's expectation for the jackpot. It should be noted that when the winning pattern is a big hit, the ratio of the variation pattern that becomes “Super Reach B” is selected to be higher than the variation pattern that becomes “Super Reach A”. It may be set such that the rate at which the variation pattern that becomes “super reach A” is selected is higher than the variation pattern that becomes. In this case, the ratio of the big hit including the sudden hit is set higher when the character b is displayed in the variable display than when the character a is displayed in the variable display.
図14〜図20においては、第1煽り演出〜第4煽り演出のそれぞれで、発展演出ありの変動パターンの選択割合と、突確移行演出の変動パターンの選択割合とが異なるように、変動パターン判定値が割振られている。 14 to 20, the variation pattern determination is performed so that the selection ratio of the variation pattern with the development effect differs from the selection ratio of the variation pattern of the sudden transition effect in each of the first to fourth production effects. The value is assigned.
図14〜図20において、大当りとなるときに選択される変動パターンの割合がキャラクタa>b、かつ、はずれとなるときに選択される変動パターンの割合がキャラクタb>aであり、大当りとなるときに選択されるスーパーリーチ種類の割合がスーパーリーチA>B、かつ、はずれとなるときに選択されるスーパーリーチ種類の割合がスーパーリーチB>Aであり、キャラクタの種類と発展先のスーパーリーチの種類との組合せに応じて大当りとなる割合が異なる。 14 to 20, the ratio of the variation pattern selected when the big hit is the character a> b, and the proportion of the variation pattern selected when the loss occurs is the character b> a, which is the big hit. The ratio of the super reach type that is sometimes selected is super reach A> B, and the ratio of the super reach type that is selected when it is off is super reach B> A. Depending on the combination with the type, the ratio of jackpot will vary.
また、図20および図21においては、突確大当り時に用いられる変動パターンであるので、「擬似連1回」〜「擬似連4回」のような擬似連となる変動パターンが選択される割合の方が、「擬似連なし」のような擬似連とならない変動パターンが選択される割合よりも高くなるように変動パターン判定値が割振られている。また、擬似連の変動パターンについては、再変動回数が多い程、選択される割合が高くなるように変動パターン判定値が割振られている。これにより、擬似連の変動パターンが実行されたときに、遊技者の大当りへの期待感を高め、さらに、擬似連での再変動回数が多くなるほど、遊技者の大当りへの期待感をより一層高めることができる。
20 and FIG. 21, since the variation pattern is used at the time of sudden hit, the ratio of the variation pattern that becomes a pseudo sequence such as “pseudo sequence once” to “
なお、図20および図21のテーブルにおいては、「特殊演出あり突確通常」および「突確移行」の変動パターン種別に属する変動パターンに関し、擬似連なし、擬似連1回、擬似連2回、擬似連3回というような擬似連の有無および擬似連での再変動回数に応じて、変動パターン種別を類別し、このような各種別ごとに、変動パターンが属するように設定してもよい。 In the tables of FIG. 20 and FIG. 21, regarding the variation patterns belonging to the variation pattern types of “probability normal with special effects” and “transition of sudden accuracy”, there is no pseudo-continuation, one pseudo-continuous, two pseudo-continuous, pseudo-continuous. The variation pattern type may be classified according to the presence / absence of the pseudo-continuation such as three times and the number of re-variations in the pseudo-continuation, and the variation pattern may be set to belong to each of the various types.
また、図13に示す非リーチはずれ時判定テーブルとしては、図14〜図21に示すその他の判定テーブルと同様に、確変状態に用いるデータテーブルと、非確変状態に用いるデータテーブルとを設け、確変状態であるか否かに基づいて、使い分けるようにしてもよい。 In addition, as the non-reach deviation determination table shown in FIG. 13, similarly to the other determination tables shown in FIGS. 14 to 21, a data table used for the probability variation state and a data table used for the non-probability variation state are provided. You may make it use properly based on whether it is in a state.
また、図13〜図21に示す変動パターンテーブルとしては、保留記憶数別にテーブルを設ける等、保留記憶数に応じて変動パターン種別を決定をする割合が異なる(たとえば、保留記憶数が多い程変動時間が長い変動パターン種別とする決定をする割合が低くなる等)ようにデータが設定されたテーブルを用いてもよい。具体的には、保留記憶数に応じて、変動パターン種別を決定をする判定値の数が異なるようにデータを設定すればよい。また、保留記憶数に応じて変動パターン種別を決定する判定値の数を異ならせるときの保留記憶数の閾値(たとえば、保留記憶数が所定個以上で判定値を異ならせるときの所定値)を、遊技状態に応じて異ならせるようにしてもよい。たとえば、保留記憶数が所定数以上のときに変動時間が長い変動パターン種別とする決定をする割合を低くするテーブルについて、確変状態においては、非確変状態よりも少ない保留記憶数が当該閾値となるように設定してもよい。 In addition, as the variation pattern tables shown in FIGS. 13 to 21, the ratio of determining the variation pattern type varies depending on the number of reserved memories, such as providing a table for each number of reserved memories (for example, the larger the number of reserved memories, the more variable It is also possible to use a table in which data is set so that the rate of determination as a variation pattern type with a long time is reduced. Specifically, the data may be set so that the number of determination values for determining the variation pattern type differs according to the number of reserved storage. Further, a threshold value for the number of reserved memories when changing the number of determination values for determining the variation pattern type according to the number of reserved memories (for example, a predetermined value when the number of reserved memories is equal to or more than a predetermined value and the determination value is different). Depending on the gaming state, it may be made different. For example, with respect to a table that lowers the ratio of determining a variation pattern type with a long variation time when the number of reserved memories is equal to or greater than a predetermined number, the number of reserved memories that is less than the non-probable variation state is the threshold value in the probability variation state. You may set as follows.
この実施の形態では、発展可否演出の種類(たとえば、表示するキャラクタの種類)の決定を、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560側で行なう例を示した。しかし、これに限らず、発展可否演出の種類(たとえば、表示するキャラクタの種類)の決定は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100側で行なうようにしてもよい。その場合には、たとえば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560側では、発展可否演出を行なうか否かを決定して変動パターンコマンドによりその旨を示し、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100側では、発展可否演出を行なうことが示された変動パターンコマンドを受信したときに、発展可否演出の種類を決定して実行すればよい。
In this embodiment, an example is shown in which the type of development propriety effect (for example, the type of character to be displayed) is determined on the
図22は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が送信する演出制御コマンドの内容の一例を示す説明図である。図22に示す例において、コマンド80XX(H)は、特別図柄の変動表示に対応して演出表示装置9において変動表示される演出図柄の変動パターンを指定する演出制御コマンド(変動パターンコマンド)である(それぞれ変動パターンXXに対応)。つまり、図13〜図21に示された使用されうる変動パターンのそれぞれに対して一意な番号を付した場合に、その番号で特定される変動パターンのそれぞれに対応する変動パターンコマンドがある。なお、「(H)」は16進数であることを示す。また、変動パターンを指定する演出制御コマンドは、変動開始を指定するためのコマンドでもある。したがって、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、コマンド80XX(H)を受信すると、第1飾り図柄表示器9aまたは第2飾り図柄表示器9bにおいて飾り図柄変動表示を開始するように制御し、演出表示装置9において演出図柄の変動表示を開始するように制御する。
FIG. 22 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of the contents of the effect control command transmitted by the
コマンド8C01(H)〜8C04(H)は、大当りとするか否か、および大当り遊技の種類を示す演出制御コマンドである。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、コマンド8C01(H)〜8C04(H)の受信に応じて飾り図柄および演出図柄の表示結果を決定するので、コマンド8C01(H)〜8C04(H)を表示結果特定コマンドという。
Commands 8C01 (H) to 8C04 (H) are effect control commands indicating whether or not to make a big hit and the type of the big win game. The
コマンド8D01(H)は、第1特別図柄の変動表示(変動)を開始することを示す演出制御コマンド(第1図柄変動指定コマンド)である。コマンド8D02(H)は、第2特別図柄の変動表示(変動)を開始することを示す演出制御コマンド(第2図柄変動指定コマンド)である。第1図柄変動指定コマンドと第2図柄変動指定コマンドとを特別図柄特定コマンド(または図柄変動指定コマンド)と総称することがある。なお、第1特別図柄の変動表示を開始するのか第2特別図柄の変動表示を開始するのかを示す情報を、変動パターンコマンドに含めるようにしてもよい。 The command 8D01 (H) is an effect control command (first symbol variation designation command) indicating that the variation display (variation) of the first special symbol is started. Command 8D02 (H) is an effect control command (second symbol variation designation command) indicating that the variation display (variation) of the second special symbol is started. The first symbol variation designation command and the second symbol variation designation command may be collectively referred to as a special symbol specifying command (or symbol variation designation command). Note that information indicating whether to start the variable display of the first special symbol or the variable display of the second special symbol may be included in the variable pattern command.
コマンド8F00(H)は、演出図柄(および飾り図柄)の変動表示(変動)を終了して表示結果(停止図柄)を導出表示することを示す演出制御コマンド(図柄確定指定コマンド)である。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、図柄確定指定コマンドを受信すると、演出図柄および飾り図柄の変動表示(変動)を終了して表示結果を導出表示する。
The command 8F00 (H) is an effect control command (symbol determination designation command) indicating that the display (change) of the effect symbol (and decoration symbol) is terminated and the display result (stop symbol) is derived and displayed. When receiving the symbol confirmation designation command, the
コマンド9000(H)は、遊技機に対する電力供給が開始されたときに送信される演出制御コマンド(初期化指定コマンド:電源投入指定コマンド)である。コマンド9200(H)は、遊技機に対する電力供給が再開されたときに送信される演出制御コマンド(停電復旧指定コマンド)である。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、遊技機に対する電力供給が開始されたときに、バックアップRAMにデータが保存されている場合には、停電復旧指定コマンドを送信し、そうでない場合には、初期化指定コマンドを送信する。
Command 9000 (H) is an effect control command (initialization designation command: power-on designation command) transmitted when power supply to the gaming machine is started. Command 9200 (H) is an effect control command (power failure recovery designation command) transmitted when power supply to the gaming machine is resumed. When the power supply to the gaming machine is started, the
コマンド9F00(H)は、客待ちデモンストレーションを指定する演出制御コマンド(客待ちデモ指定コマンド)である。 Command 9F00 (H) is an effect control command (customer waiting demonstration designation command) for designating a customer waiting demonstration.
コマンドA001〜A003(H)は、ファンファーレ画面を表示すること、すなわち大当り遊技の開始を指定する演出制御コマンド(大当り開始指定コマンド:ファンファーレ指定コマンド)である。大当り開始指定コマンドには、大当りの種類に応じた大当り開始1指定コマンド、大当り開始指定2指定コマンドおよび突確開始指定コマンドがある。コマンドA1XX(H)は、XXで示す回数目(ラウンド)の大入賞口開放中の表示を示す演出制御コマンド(大入賞口開放中指定コマンド)である。A2XX(H)は、XXで示す回数目(ラウンド)の大入賞口閉鎖を示す演出制御コマンド(大入賞口開放後指定コマンド)である。
The commands A001 to A003 (H) are effect control commands for displaying the fanfare screen, that is, designating the start of the big hit game (big hit start designation command: fanfare designation command). The jackpot start designation command includes a
コマンドA301(H)は、大当り終了画面を表示すること、すなわち大当り遊技の終了を指定するとともに、非確変大当り(通常大当り)であったことを指定する演出制御コマンド(大当り終了1指定コマンド:エンディング1指定コマンド)である。コマンドA302(H)は、大当り終了画面を表示すること、すなわち大当り遊技の終了を指定するとともに、確変大当りであったことを指定する演出制御コマンド(大当り終了2指定コマンド:エンディング2指定コマンド)である。コマンドA303(H)は、突然確変の遊技の終了を指定する演出制御コマンド(突確終了指定コマンド:エンディング3指定コマンド)である。
Command A301 (H) displays a jackpot end screen, that is, specifies the end of the jackpot game and an effect control command (
コマンドC000(H)は、第1始動入賞があったことを指定する演出制御コマンド(第1始動入賞指定コマンド)である。コマンドC100(H)は、第2始動入賞があったことを指定する演出制御コマンド(第2始動入賞指定コマンド)である。第1始動入賞指定コマンドと第2始動入賞指定コマンドとを、始動入賞指定コマンドと総称することがある。 The command C000 (H) is an effect control command (first start winning designation command) that designates that the first start winning has been won. The command C100 (H) is an effect control command (second start winning designation command) for designating that the second starting win has been won. The first start prize designation command and the second start prize designation command may be collectively referred to as a start prize designation command.
コマンドC2XX(H)は、第1保留記憶数と第2保留記憶数との合計である合計数(合算保留記憶数)を指定する演出制御コマンド(合算保留記憶数指定コマンド)である。コマンドC2XX(H)における「XX」が、合算保留記憶数を示す。コマンドC300(H)は、合算保留記憶数を1減算することを指定する演出制御コマンド(合算保留記憶数減算指定コマンド)である。この実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、合算保留記憶数を減算する場合には合算保留記憶数減算指定コマンドを送信するが、合算保留記憶数減算指定コマンドを使用せず、合算保留記憶数を減算するときに、減算後の合算保留記憶数を合算保留記憶数指定コマンドで指定するようにしてもよい。
The command C2XX (H) is an effect control command (total pending storage number designation command) that designates the total number (total pending storage number) that is the sum of the first reserved memory number and the second reserved memory number. “XX” in the command C2XX (H) indicates the total pending storage number. The command C300 (H) is an effect control command (total pending storage count subtraction designation command) that designates that the total pending storage count is decremented by one. In this embodiment, the
演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100(具体的には、演出制御用CPU101)は、主基板31に搭載されている遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から上述した演出制御コマンドを受信すると、図22に示された内容に応じて演出表示装置9の表示状態を変更したり、ランプの表示状態を変更したり、音声出力基板70に対して音番号データを出力したりする。
The effect control microcomputer 100 (specifically, the effect control CPU 101) mounted on the
たとえば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、始動入賞があり第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bにおいて特別図柄の変動表示が開始される度に、演出図柄の変動パターンを指定する変動パターンコマンドおよび表示結果特定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する。
For example, the
この実施の形態では、演出制御コマンドは2バイト構成であり、1バイト目はMODE(コマンドの分類)を表し、2バイト目はEXT(コマンドの種類)を表す。MODEデータの先頭ビット(ビット7)は必ず「1」に設定され、EXTデータの先頭ビット(ビット7)は必ず「0」に設定される。なお、そのようなコマンド形態は一例であって他のコマンド形態を用いてもよい。たとえば、1バイトや3バイト以上で構成される制御コマンドを用いてもよい。 In this embodiment, the presentation control command has a 2-byte structure, the first byte represents MODE (command classification), and the second byte represents EXT (command type). The first bit (bit 7) of the MODE data is always set to “1”, and the first bit (bit 7) of the EXT data is always set to “0”. Note that such a command form is an example, and other command forms may be used. For example, a control command composed of 1 byte or 3 bytes or more may be used.
なお、演出制御コマンドの送出方式として、演出制御信号CD0〜CD7の8本のパラレル信号線で1バイトずつ主基板31から中継基板77を介して演出制御基板80に演出制御コマンドデータを出力し、演出制御コマンドデータの他に、演出制御コマンドデータの取込を指示するパルス状(矩形波状)の取込信号(演出制御INT信号)を出力する方式を用いる。演出制御コマンドの8ビットの演出制御コマンドデータは、演出制御INT信号に同期して出力される。演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、演出制御INT信号が立ち上がったことを検知して、割込処理によって1バイトのデータの取り込み処理を開始する。
In addition, as the transmission method of the effect control command, the effect control command data is output from the
図22に示す例では、変動パターンコマンドおよび表示結果特定コマンドを、第1特別図柄表示器8aでの第1特別図柄の変動に対応した演出図柄の変動表示(変動)と第2特別図柄表示器8bでの第2特別図柄の変動に対応した演出図柄の変動表示(変動)とで共通に使用でき、第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄の変動表示に伴なって演出を行なう演出表示装置9等の演出用部品を制御する際に、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信されるコマンドの種類を増大させないようにすることができる。
In the example shown in FIG. 22, the variation pattern command and the display result specifying command are displayed as the variation display (variation) of the effect symbol corresponding to the variation of the first special symbol on the first
なお、コマンド8D01(H)(第1図柄変動指定コマンド)およびコマンド8D02(H)(第2図柄変動指定コマンド)は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が、第1特別図柄表示器8aによる第1特別図柄の変動表示時間中に装飾用(演出用)の図柄としての第1飾り図柄の変動表示を行なう第1飾り図柄表示器9aにおいて飾り図柄の変動を行なうのか、第2特別図柄表示器8bによる第2特別図柄の変動表示時間中に第2飾り図柄の変動表示を行なう第2飾り図柄表示器9bにおいて飾り図柄の変動を行なうのかを判定するために使用される。
Note that the command 8D01 (H) (first symbol variation designation command) and the command 8D02 (H) (second symbol variation designation command) are executed by the
図23は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が用いる乱数を示す説明図である。図23には、一例として、演出図柄の左停止図柄決定用のSR1−1、演出図柄の中停止図柄決定用のSR1−2、演出図柄の右停止図柄決定用のSR1−3、各種の演出決定用のSR2、滑り時仮停止図柄決定用のSR3、擬似連時第1仮停止図柄決定用のSR4−1、擬似連時第2仮停止図柄決定用のSR4−2、擬似連時第3仮停止図柄決定用のSR4−3、および、擬似連時第4仮停止図柄決定用のSR4−4が示されている。
FIG. 23 is an explanatory diagram showing random numbers used by the
SR1−1,SR1−2,SR1−3は、演出図柄の左,中,右の停止図柄(仮停止図柄を除く最終的な停止図柄)をランダムに決定するために用いられる。SR2は、演出表示装置9で表示される画像による演出内容等の各種の演出内容をランダムに決定するために用いられる。SR3は、前述したような滑り演出が行なわれるときの仮停止図柄をランダムに決定するために用いられる。擬似連時第1仮停止図柄決定用のSR4−1〜擬似連時第4仮停止図柄決定用のSR4−4のそれぞれは、前述したような擬似連の演出が行なわれるときの第1回目の仮停止時の仮停止図柄〜第4回目の仮停止時の仮停止図柄を決定するために用いられる。
SR1-1, SR1-2, and SR1-3 are used for randomly determining the left, middle, and right stop symbols (final stop symbols excluding temporary stop symbols) of the effect symbols. SR2 is used for randomly determining various contents of effects such as effects produced by an image displayed on the
このような乱数SR1−1〜SR4−4のそれぞれは、ソフトウェアによりカウント値を更新するランダムカウンタのカウントにより生成されるものであり、図23において対応付けられた範囲内でそれぞれ巡回更新され、それぞれについて定められたタイミングで抽出されることにより乱数として用いられる。 Each of such random numbers SR1-1 to SR4-4 is generated by counting of a random counter that updates the count value by software, and is cyclically updated within the range associated in FIG. Is used as a random number by being extracted at a predetermined timing.
図24は、主基板31に搭載される遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(具体的には、CPU56)が実行する特別図柄プロセス処理(S26)のプログラムの一例を示すフローチャートである。上述したように、特別図柄プロセス処理では第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bおよび大入賞口を制御するための処理が実行される。特別図柄プロセス処理において、CPU56は、第1始動入賞口13に遊技球が入賞したことを検出するための第1始動口スイッチ13aまたは第2始動入賞口14に遊技球が入賞したことを検出するための第2始動口スイッチ14aがオンしていたら、すなわち始動入賞が発生していたら、始動口スイッチ通過処理を実行する(S311,S312)。そして、S300〜S307のうちのいずれかの処理を行なう。第1始動入賞口スイッチ13aまたは第2始動口スイッチ14aがオンしていなければ、内部状態に応じて、S300〜S307のうちのいずれかの処理を行なう。
FIG. 24 is a flowchart showing an example of a special symbol process (S26) program executed by the game control microcomputer 560 (specifically, the CPU 56) mounted on the
S300〜S307の処理は、以下のような処理である。
特別図柄通常処理(S300):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が0であるときに実行される。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、特別図柄の変動表示が開始できる状態になると、保留記憶数バッファに記憶される数値データの記憶数(合計保留記憶数)を確認する。保留記憶数バッファに記憶される数値データの記憶数は合計保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値により確認できる。また、合計保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値が0でなければ、第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄の変動表示の表示結果を大当りとするか否かを決定する。大当りとする場合には大当りフラグをセットする。そして、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をS301に応じた値(この例では1)に更新する。なお、大当りフラグは、大当り遊技が終了するときにリセットされる。
The processing of S300 to S307 is as follows.
Special symbol normal processing (S300): Executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is zero. When the
変動パターン設定処理(S301):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が1であるときに実行される。また、変動パターンを決定し、その変動パターンにおける変動時間(変動表示時間:変動表示を開始してから表示結果を導出表示(停止表示)するまでの時間)を特別図柄の変動表示の変動時間とすることに決定する。また、特別図柄の変動時間を計測する変動時間タイマをスタートさせる。そして、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をS302に対応した値(この例では2)に更新する。 Fluctuation pattern setting process (S301): This process is executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 1. Also, the variation pattern is determined, and the variation time in the variation pattern (variation display time: the time from the start of the variation display until the display result is derived and displayed (stopped display)) is the variation time of the variation display of the special symbol Decide to do. Also, a variable time timer for measuring the special symbol variable time is started. Then, the internal state (special symbol process flag) is updated to a value corresponding to S302 (2 in this example).
表示結果特定コマンド送信処理(S302):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が2であるときに実行される。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に、表示結果特定コマンドを送信する制御を行なう。そして、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をS303に対応した値(この例では3)に更新する。
Display result specifying command transmission process (S302): This process is executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 2. Control for transmitting a display result specifying command to the
特別図柄変動中処理(S303):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が3であるときに実行される。変動パターン設定処理で選択された変動パターンの変動時間が経過(S301でセットされる変動時間タイマがタイムアウトすなわち変動時間タイマの値が0になる)すると、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をS304に対応した値(この例では4)に更新する。 Special symbol changing process (S303): This process is executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 3. When the variation time of the variation pattern selected in the variation pattern setting process elapses (the variation time timer set in S301 times out, that is, the variation time timer value becomes 0), the internal state (special symbol process flag) is set to S304. Update to the corresponding value (4 in this example).
特別図柄停止処理(S304):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が4であるときに実行される。第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bにおける変動表示を停止して停止図柄を導出表示させる。また、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に、図柄確定指定コマンドを送信する制御を行なう。そして、大当りフラグがセットされている場合には、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をS305に対応した値(この例では5)に更新する。大当りフラグがセットされていない場合には、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をS300に対応した値(この例では0)に更新する。なお、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が送信する図柄確定指定コマンドを受信すると演出表示装置9において演出図柄が停止じ、および飾り図柄が停止されるように制御する。
Special symbol stop process (S304): Executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 4. The variable display on the first
大入賞口開放前処理(S305):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が5であるときに実行される。大入賞口開放前処理では、大入賞口を開放する制御を行なう。具体的には、カウンタ(たとえば、大入賞口に入った遊技球数をカウントするカウンタ)等を初期化するとともに、ソレノイド21を駆動して大入賞口を開放状態にする。また、タイマによって大入賞口開放中処理の実行時間を設定し、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をS306に対応した値(この例では6)に更新する。なお、大入賞口開放前処理は各ラウンド毎に実行されるが、第1ラウンドを開始する場合には、大入賞口開放前処理は大当り遊技を開始する処理でもある。
Preliminary winning opening opening process (S305): This is executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 5. In the pre-opening process for the big prize opening, control for opening the big prize opening is performed. Specifically, a counter (for example, a counter that counts the number of game balls that have entered the big prize opening) is initialized, and the
大入賞口開放中処理(S306):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が6であるときに実行される。大当り遊技状態中のラウンド表示の演出制御コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御や大入賞口の閉成条件の成立を確認する処理等を行なう。大入賞口の閉成条件が成立し、かつ、まだ残りラウンドがある場合には、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をS305に対応した値(この例では5)に更新する。また、すべてのラウンドを終えた場合には、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をS307に対応した値(この例では7)に更新する。
Large winning opening open process (S306): This process is executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 6. A control for transmitting an effect control command for round display during the big hit gaming state to the
大当り終了処理(S307):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が7であるときに実行される。大当り遊技状態が終了したことを遊技者に報知する表示制御を演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に行なわせるための制御を行なう。また、遊技状態を示すフラグ(たとえば、確変フラグや時短フラグ)をセットする処理を行なう。そして、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をS300に対応した値(この例では0)に更新する。
Big hit end process (S307): This process is executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 7. Control for causing the
図25は、S312の始動口スイッチ通過処理を示すフローチャートである。第1始動口スイッチ13aと第2始動口スイッチ14aとのうちの少なくとも一方がオン状態の場合に実行される始動口スイッチ通過処理において、CPU56は、第1始動口スイッチ13aがオンした否かを確認する(S211)。第1始動口スイッチ13aがオンしていなければ、後述するS218に進む。一方、第1始動口スイッチ13aがオンしていれば、CPU56は、第1保留記憶数カウンタの値が4(上限値)であるか否かを確認する(S212)。第1保留記憶数カウンタは、第1始動入賞口13に始動入賞した第1保留記憶数をカウントするためのカウンタである。
FIG. 25 is a flowchart showing the start port switch passing process in S312. In the start port switch passing process that is executed when at least one of the first
S212において第1保留記憶数カウンタの値が4であれば、S218に進む。一方、第1保留記憶数カウンタの値が4でなければ、CPU56は第1保留記憶数カウンタの値を1増やす(S213)。
If the value of the first reserved storage number counter is 4 in S212, the process proceeds to S218. On the other hand, if the value of the first reserved memory number counter is not 4, the
図26は、保留記憶に対応する乱数等を保存する領域(保留記憶バッファ)の構成例を示す説明図である。図26に示すように、第1保留記憶バッファには、第1保留記憶数の上限値(この例では4)に対応した保存領域が確保されている。また、第2保留記憶バッファには、第2保留記憶数の上限値(この例では4)に対応した保存領域が確保されている。なお、第1保留記憶バッファおよび第2保留記憶バッファは、RAM55に形成されている。
FIG. 26 is an explanatory diagram showing a configuration example of an area (holding storage buffer) for storing random numbers and the like corresponding to holding storage. As shown in FIG. 26, a storage area corresponding to the upper limit value (4 in this example) of the first reserved storage number is secured in the first reserved storage buffer. In addition, a storage area corresponding to the upper limit value of the second reserved storage number (4 in this example) is secured in the second reserved storage buffer. The first reserved storage buffer and the second reserved storage buffer are formed in the
次に、始動口スイッチ通過処理において、CPU56は、乱数回路503やソフトウェア乱数を生成するためのカウンタから値を抽出し、それらを、第1保留記憶バッファにおける保存領域に格納する処理を実行する(S214)。なお、S214の処理では、ランダムR(大当り判定用乱数)およびソフトウェア乱数であるランダム2−1(図6参照)が、保存領域に格納される。
Next, in the start port switch passing process, the
次いで、CPU56は、第1始動入賞指定コマンドを送信する制御を行なう(S215)。また、CPU56は、第1保留記憶数と第2保留記憶数との合計である合計保留記憶数を示す合算保留記憶数カウンタの値を1増やす(S216)。そして、CPU56は、合算保留記憶数カウンタの値に基づいて、合算保留記憶数を示す合算保留記憶数指定コマンドを送信する制御を行なう(S218)。なお、合算保留記憶数指定コマンドを、第1始動入賞指定コマンドの前に送信してもよい。
Next, the
また、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に演出制御コマンドを送信する場合には、CPU56は、演出制御コマンドに応じたコマンド送信テーブル(予めROMにコマンド毎に設定されている)のアドレスをポインタにセットする。そして、演出制御コマンドに応じたコマンド送信テーブルのアドレスをポインタにセットして、演出制御コマンド制御処理(S29)において演出制御コマンドを送信する。そして、S218に進む。
When transmitting an effect control command to the
S218に進んだときは、CPU56は、第2始動口スイッチ14aがオンした否かを確認する(S218)。第2始動口スイッチ14aがオンしていなければ、処理を終了する。一方、第2始動口スイッチ14aがオンしていれば、CPU56は、第2保留記憶数カウンタの値が4(上限値)であるか否かを確認する(S219)。第2保留記憶数カウンタは、第2始動入賞口14に始動入賞した第2保留記憶数をカウントするためのカウンタである。
When the process proceeds to S218, the
S218において第2保留記憶数カウンタの値が4であれば、S219に進む。一方、第2保留記憶数カウンタの値が4でなければ、CPU56は第2保留記憶数カウンタの値を1増やす(S220)。
If the value of the second reserved memory number counter is 4 in S218, the process proceeds to S219. On the other hand, if the value of the second reserved memory number counter is not 4, the
次に、CPU56は、乱数回路503やソフトウェア乱数を生成するためのカウンタから値を抽出し、それらを、第2保留記憶バッファにおける保存領域に格納する処理を実行する(S221)。なお、S220の処理では、ランダムR(大当り判定用乱数)およびソフトウェア乱数であるランダム2−1(図6参照)が、保存領域に格納される。
Next, the
次いで、CPU56は、第2始動入賞指定コマンドを送信する制御を行なう(S222)。また、CPU56は、合算保留記憶数カウンタの値を1増やす(S223)。そして、CPU56は、合算保留記憶数カウンタの値に基づいて、合算保留記憶数を示す合算保留記憶数指定コマンドを送信する制御を行なう(S224)。なお、合算保留記憶数指定コマンドを、第2始動入賞指定コマンドの前に送信してもよい。
Next, the
このように始動口スイッチ通過処理の1回のルーチン内で第1始動口スイッチ13aと第2始動口スイッチ14aとのそれぞれへの入賞に応じた処理を行なうことにより、第1始動口スイッチ13aと第2始動口スイッチ14aとが同じタイミングでオンした場合に、正確なタイミングで乱数値を抽出して保留記憶数バッファに保存することができる。
In this way, by performing a process corresponding to the winning of each of the first
図27および図28は、特別図柄プロセス処理における特別図柄通常処理(S300)を示すフローチャートである。特別図柄通常処理において、CPU56は、合算保留記憶数の値を確認する(S51)。具体的には、合算保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値を確認する。合算保留記憶数が0であれば処理を終了する。
27 and 28 are flowcharts showing the special symbol normal process (S300) in the special symbol process. In the special symbol normal process, the
合算保留記憶数が0でなければ、CPU56は、第2保留記憶バッファ(図26参照)に保留記憶データがあるか否か確認する(S52)。第2保留記憶バッファ(図26参照)に保留記憶データがあれば、特別図柄ポインタ(第1特別図柄について特別図柄プロセス処理を行なっているのか第2特別図柄について特別図柄プロセス処理を行なっているのかを示すフラグ)に「第2」を示すデータを設定する(S54)。一方、第2保留記憶バッファに保留記憶データがなければ、特別図柄ポインタに「第1」を示すデータを設定する(S53)。
If the total pending storage number is not 0, the
この実施の形態では、以下、特別図柄ポインタに「第1」を示すデータが設定されたか「第2」を示すデータが設定されたかに応じて、第1特別図柄表示器8aにおける第1特別図柄の変動表示と、第2特別図柄表示器8bにおける第2特別図柄の変動表示とを、共通の処理ルーチンを用いて実行する。特別図柄ポインタに「第1」を示すデータが設定されたときには、第1保留記憶バッファに記憶された保留記憶データに基づいて、第1特別図柄表示器8aにおける第1特別図柄の変動表示が行なわれる。一方、特別図柄ポインタに「第2」を示すデータが設定されたときには、第2保留記憶バッファに記憶された保留記憶データに基づいて、第2特別図柄表示器9aにおける第2特別図柄の変動表示が行なわれる。なお、ここでいう「共通の処理ルーチン」とは、ある特定の一連の処理を実現するためのプログラムであり、この実施の形態では、第1特別図柄や第2特別図柄の変動表示を行なう一連の処理を実現するためのプログラムを指している。この実施の形態において、「共通の処理ルーチン」には、後述する特別図柄通常処理におけるS55〜S76の処理、S301の変動パターン設定処理、S302の表示結果特定コマンド送信処理、S303の特別図柄変動中処理およびS304の特別図柄停止処理が含まれる。
In this embodiment, hereinafter, the first special symbol on the first
S52〜S54の制御により、第2保留記憶バッファ内に第2保留記憶のデータが1つでも存在すれば、その第2保留記憶のデータに基づいた第2特別図柄表示器8bの変動表示が第1保留記憶のデータに基づいた第1特別図柄表示器8aの変動表示に優先して実行される。
If there is at least one second reserved memory data in the second reserved memory buffer under the control of S52 to S54, the variable display of the second special symbol display unit 8b based on the second reserved memory data is displayed in the second. This is executed in preference to the variable display of the first
CPU56は、RAM55において、特別図柄ポインタが示す方の保留記憶数=1に対応する保存領域に格納されている各乱数値を読出してRAM55の乱数バッファ領域に格納する(S55)。具体的には、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが「第1」を示している場合には、第1保留記憶数バッファにおける第1保留記憶数=1に対応する保存領域に格納されている各乱数値を読出してRAM55の乱数バッファ領域に格納する。また、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが「第2」を示している場合には、第2保留記憶数バッファにおける第2保留記憶数=1に対応する保存領域に格納されている各乱数値を読出してRAM55の乱数バッファ領域に格納する。
In the
そして、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが示す方の保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値を1減算し、かつ、各保存領域の内容をシフトする(S56)。具体的には、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが「第1」を示している場合には、第1保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値を1減算し、かつ、第1保留記憶数バッファにおける各保存領域の内容をシフトする。また、特別図柄ポインタが「第2」を示している場合に、第2保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値を1減算し、かつ、第2保留記憶数バッファにおける各保存領域の内容をシフトする。
Then, the
すなわち、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが「第1」を示している場合に、RAM55の第1保留記憶数バッファにおいて第1保留記憶数=n(n=2,3,4)に対応する保存領域に格納されている各乱数値を、第1保留記憶数=n−1に対応する保存領域に格納する。また、特別図柄ポインタが「第2」を示す場合に、RAM55の第2保留記憶数バッファにおいて第2保留記憶数=n(n=2,3,4)に対応する保存領域に格納されている各乱数値を、第2保留記憶数=n−1に対応する保存領域に格納する。
That is, when the special symbol pointer indicates “first”, the
よって、各第1保留記憶数(または、各第2保留記憶数)に対応するそれぞれの保存領域に格納されている各乱数値が抽出された順番は、常に、第1保留記憶数(または、第2保留記憶数)=1,2,3,4の順番と一致するようになっている。 Therefore, the order in which each random value stored in each storage area corresponding to each first reserved memory number (or each second reserved memory number) is extracted is always the first reserved memory number (or (Second reserved storage number) = 1, 2, 3, 4 in order.
そして、CPU56は、合算保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値をRAM55の所定の領域に保存した後(S57)、合算保留記憶数の値を1減らす。すなわち、合算保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値を1減算する(S58)。なお、CPU56は、合算保留記憶数に応じて、特別図柄の変動表示時間を短縮する制御(たとえば、合算保留記憶数が所定数以上になると変動表示時間を短縮する制御)を行なう等、合算保留記憶数の値に基づいて所定の制御を行なうときには、S58でカウント値が1減算される前の合算保留記憶数カウンタの値をRAM55の所定の領域に保存し、保存したカウンタ値を用いて当該制御を行なうようにしてもよい。
Then, the
特別図柄通常処理では、最初に、第1始動入賞口13を対象として処理を実行することを示す「第1」を示すデータすなわち第1特別図柄を対象として処理を実行することを示す「第1」を示すデータ、または第2始動入賞口14を対象として処理を実行することを示す「第2」を示すデータすなわち第2特別図柄を対象として処理を実行することを示す「第2」を示すデータが、特別図柄ポインタに設定される。そして、特別図柄プロセス処理における以降の処理では、特別図柄ポインタに設定されているデータに応じた処理が実行される。よって、S300〜S307の処理を、第1特別図柄を対象とする場合と第2特別図柄を対象とする場合とで共通化することができる。
In the special symbol normal process, first, data indicating “first” indicating that the process is executed for the first
次いで、CPU56は、乱数バッファ領域からランダムR(大当り判定用乱数)を読出し(S61)、大当り判定モジュールを実行する(S62)。大当り判定モジュールは、予め決められている大当り判定値(図7参照)と大当り判定用乱数とを比較し、それらが一致したら大当りとすることに決定する処理を実行するプログラムである。すなわち、大当り判定の処理を実行するプログラムである。
Next, the
大当り判定の処理では、遊技状態が確変状態(高確率状態)の場合は、遊技状態が非確変状態(通常遊技状態および時短状態)の場合よりも、大当りとなる確率が高くなるように構成されている。具体的には、予め大当り判定値の数が多く設定されている確変時大当り判定テーブル(ROM54における図7(A)の右側の数値が設定されているテーブル)と、大当り判定値の数が確変大当り判定テーブルよりも少なく設定されている通常時大当り判定テーブル(ROM54における図7(A)の左側の数値が設定されているテーブル)とが設けられている。そして、CPU56は、遊技状態が確変状態であるか否かを確認し、遊技状態が確変状態であるときは、確変時大当り判定テーブルを使用して大当りの判定の処理を行ない、遊技状態が通常遊技状態であるときは、通常時大当り判定テーブルを使用して大当りの判定の処理を行なう。すなわち、CPU56は、大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)の値が図7(A)に示すいずれかの大当り判定値に一致すると、特別図柄に関して大当り(確変大当りまたは通常大当り)とすることに決定する。大当りとすることに決定した場合には(S63のY)、S71に移行する。なお、大当りとするか否か決定するということは、大当り遊技状態に移行させるか否か決定するということであるが、特別図柄表示器における停止図柄を大当り図柄とするか否か決定するということでもある。
The jackpot determination process is configured such that when the gaming state is a probable change state (high probability state), the probability of a big hit is higher than when the gaming state is a non-probability change state (normal game state and short-time state). ing. Specifically, a jackpot determination table (a table in which the numerical value on the right side of FIG. 7A in the
なお、現在の遊技状態が確変状態であるか否かの確認は、確変フラグがセットされているか否かにより行なわれる。確変フラグは、遊技状態を確変状態に移行するときにセットされ、確変状態を終了するときにリセットされる。具体的に、確変フラグは、確変大当りまたは突然確変大当りとすることに決定されたときに、大当り遊技を終了する処理においてセットされ、次の大当りが発生したときの大当り遊技の開始時においてリセットされる(次の大当りが確変となる大当りであっても、大当り遊技の開始時に一旦リセットされる)。 Note that whether or not the current gaming state is the probability variation state is determined by whether or not the probability variation flag is set. The probability variation flag is set when the gaming state is shifted to the probability variation state, and is reset when the probability variation state is terminated. Specifically, the probability change flag is set in the process of ending the big hit game when it is determined to be the probability change big hit or suddenly the probability change big hit, and is reset at the start of the big hit game when the next big hit occurs. (Even if the next big hit is a promising big hit, it is reset once at the start of the big hit game).
ランダムRの値が大当り判定値のいずれにも一致しない場合には、そのままS75に移行する。一方、一致した場合には、S71に移行する。 If the value of the random R does not match any of the big hit determination values, the process proceeds to S75 as it is. On the other hand, if they match, the process proceeds to S71.
S71では、CPU56は、大当りフラグをセットする。そして、大当り種別を複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定するために使用するテーブルとして、図7(C)に示す大当り種別判定テーブルを選択する(S72)。乱数バッファ領域に格納された大当り種別判定用の乱数(ランダム2−1)の値と一致する値に対応した種別(「通常」、「確変」または「突確」)を大当りの種別に決定する(S73)。また、決定した大当りの種別を示すデータをRAM55における大当り種別バッファに設定する(S74)。たとえば、大当り種別が「通常」の場合には大当り種別を示すデータとして「01」が設定され、大当り種別が「確変」の場合には大当り種別を示すデータとして「02」が設定され、大当り種別が「突確」の場合には大当り種別を示すデータとして「03」が設定される。
In S71, the
前述したように、可変入賞球装置15が設けられている第2始動入賞口14に対応する第2特別図柄については、大当り種別のうち、「突確」を割振らないように設定されている。そして、第2特別図柄について「確変」(「突確」は選択されない)の大当り種別が選択される割合と、第1特別図柄について「確変」および「突確」を合せた大当り種別が選択される割合とが等しくなるような設定がされている。これにより、第2始動入賞口14への始動入賞については15R大当りが発生しやすくなり、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。なお、可変入賞球装置15が設けられていない第1始動入賞口13に対応する第1特別図柄については、大当り種別のうち、「突確」を割振らないようにしてもよい。その場合には、第1特別図柄について「確変」(「突確」は選択されない)の大当り種別が選択される割合と、第2特別図柄について「確変」および「突確」を合せた大当り種別が選択される割合とが等しくなるような設定を行なう。このようにすれば、第1始動入賞口13への始動入賞について、15R大当りが発生しやすくなり、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。
As described above, the second special symbol corresponding to the second
次いで、CPU56は、特別図柄の停止図柄を決定する(S75)。具体的には、大当りフラグがセットされていない場合には、はずれ図柄となる「−」を特別図柄の停止図柄に決定する。大当りフラグがセットされている場合には、大当り種別の決定結果に応じて、大当り図柄となる「1」、「3」、「7」のいずれかを特別図柄の停止図柄に決定する。すなわち、大当り種別を「突確」に決定した場合には、2ラウンド大当り図柄となる「1」を特別図柄の停止図柄に決定する。大当り種別を「通常」に決定した場合には、「3」を特別図柄の停止図柄に決定する。大当り種別を「確変」に決定した場合には、「7」を特別図柄の停止図柄に決定する。
Next, the
そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を変動パターン設定処理(S301)に対応した値に更新する(S76)。 Then, the value of the special symbol process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the variation pattern setting process (S301) (S76).
図29は、特別図柄プロセス処理における変動パターン設定処理(S301)を示すフローチャートである。変動パターン設定処理において、CPU56は、大当りフラグがセットされているか否か確認する(S91)。
FIG. 29 is a flowchart showing the variation pattern setting process (S301) in the special symbol process. In the variation pattern setting process, the
大当りフラグがセットされている場合には、変動パターン種別を複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定するために使用するテーブルとして、S74で記憶された大当り種別に関する情報と、現在が確変状態であるか否かの情報(確変フラグがセットされているときに確変状態であると判断する)とに基づいて、図16〜図21に示す変動パターン種別判定テーブルのうちから、決定された大当り種別および確変状態の有無に対応する変動パターン種別判定テーブルを選択する(S92)。そして、S101に移行する。たとえば、大当り種別判定結果により通常大当りとすることが決定されたときには、非確変状態であれば図16の非確変状態通常大当り時判定テーブルにおける変動パターン種別判定テーブルを選択し、確変状態であれば図17の確変状態通常大当り時判定テーブルにおける変動パターン種別判定テーブルを選択する。また、大当り種別判定結果により確変大当りとすることが決定されたときには、非確変状態であれば図18の非確変状態確変大当り時判定テーブルにおける変動パターン種別判定テーブルを選択し、確変状態であれば図19の確変状態確変大当り時判定テーブルにおける変動パターン種別判定テーブルを選択する。また、大当り種別判定結果により突確大当りとすることが決定されたときには、非確変状態であれば図20の非確変状態突確大当り時判定テーブルにおける変動パターン種別判定テーブルを選択し、確変状態であれば図21の確変状態突確大当り時判定テーブルにおける変動パターン種別判定テーブルを選択する。 When the big hit flag is set, as the table used to determine the variation pattern type as one of a plurality of types, information on the big hit type stored in S74 and whether the current state is a probable change state Based on the information on whether or not (determined that the probability variation state is present when the probability variation flag is set), it is determined from the variation pattern type determination table shown in FIGS. A variation pattern type determination table corresponding to the presence / absence of a state is selected (S92). Then, the process proceeds to S101. For example, when it is determined that the normal big hit is determined based on the big hit type determination result, if the non-probability change state, the variation pattern type determination table in the non-probability change state normal big hit determination table of FIG. 16 is selected. The variation pattern type determination table in the probability variation state normal big hit determination table of FIG. 17 is selected. Also, when it is determined that the probability variation big hit is based on the big hit type determination result, if it is a non-probability variation state, the variation pattern type determination table in the non-probability variation state certain variation big hit determination table of FIG. 18 is selected. The variation pattern type determination table in the probability variation state probability variation big hit determination table of FIG. 19 is selected. Further, when it is determined that the big hit type judgment result is the big hit type determination result, if it is in a non-probable variation state, the variation pattern type determination table in the non-probable variation state sudden big hit determination table in FIG. 20 is selected. The variation pattern type determination table in the probability variation state sudden probability big hit determination table of FIG. 21 is selected.
大当りフラグがセットされていない場合には、パチンコ遊技機1における遊技状態が通常状態、確変状態および時短状態のいずれであるかに基づいて、前述したようなリーチ判定テーブル選択規則にしたがって、遊技状態別に設けられた図9のような複数のリーチ判定テーブルのうちいずれかを選択する(S95)。CPU56は、遊技状態を、確変フラグおよび時短フラグの状態によって判定できる。たとえば、図9のように通常状態用のテーブルと、確変・時短状態用のテーブルとを設けたときには、通常状態用のテーブルは、低確低ベースの状態であるとき、すなわち、確変フラグがリセット状態かつ時短フラグがリセット状態のときに選択される。また、確変・時短状態用のテーブルは、高確高ベース、高確低ベース、低確高ベースのうちのいずれかの状態であるとき、すなわち、確変フラグがセット状態かつ時短フラグがセット状態、確変フラグがセット状態かつ時短フラグがリセット状態、および、確変フラグがリセット状態かつ時短フラグがセット状態のうちのいずれかのときに選択される。したがって、突確大当りのときには、確変・時短状態用のテーブルが用いられる。なお、リーチ判定テーブルは、通常状態、確変状態、および、時短状態(高確低ベース状態も含む)の3つの状態別に設けてもよい。
If the big hit flag is not set, the gaming state according to the reach determination table selection rule as described above based on whether the gaming state in the
ここで、図9のように、リーチ判定テーブルは、ランダム2−2の値に基づいて飾り図柄の変動表示状態をリーチ状態とするか否かを判定するために使用するテーブルであって、ランダム2−2の値のそれぞれについて、リーチ状態とするか否かが予め定められたテーブルである。このようなリーチ判定テーブルは、図9のように、遊技状態別に設けられたテーブルの相互間でリーチ状態にすると判定する割合が異なる。なお、リーチ判定テーブルは、リーチ判定を行なうときの保留記憶数によってもリーチ状態にすると判定する割合が異なるようにしてもよい。 Here, as shown in FIG. 9, the reach determination table is a table used to determine whether or not the decorative symbol variation display state is set to the reach state based on the random value 2-2. It is a table in which whether or not to reach each of the values of 2-2 is determined in advance. As shown in FIG. 9, such reach determination tables have different ratios for determining to reach a reach state between tables provided for each gaming state. In the reach determination table, the ratio of determining to reach the reach state may be different depending on the number of reserved memories when the reach determination is performed.
また、ランダム2−2を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を抽出することによってランダム2−2を抽出する(S96)。そして、CPU56は、S95で選択したリーチ判定テーブルにおいて、ランダム2−2の値と一致する値に対応したリーチ状態の有無を示すデータによって、リーチ状態にするか否かを決定する(S97)。
Further, random 2-2 is extracted by extracting the count value of the counter for generating random 2-2 (S96). Then, the
そして、S97による決定において、リーチ状態にすることに決定したか否かを判定する(S98)。リーチ状態にすることに決定した場合には、現在が確変状態であるか否かの情報(確変フラグがセットされているときに確変状態であると判断する)に基づいて、図14および図15に示すリーチはずれ時用(リーチ用)の変動パターン種別判定テーブルのうちから、確変状態の有無に対応する変動パターン種別判定テーブルを選択する(S99)。そして、S101に移行する。たとえば、非確変状態であれば図14の非確変状態リーチはずれ時判定テーブルにおける変動パターン種別判定テーブルを選択し、確変状態であれば図15の確変状態リーチはずれ時判定テーブルにおける変動パターン種別判定テーブルを選択する。 Then, in the determination at S97, it is determined whether or not it has been determined to reach the reach state (S98). 14 and 15 based on information indicating whether or not the current state is the probability variation state (determined that the probability variation state is present when the probability variation flag is set). The variation pattern type determination table corresponding to the presence / absence of a probable variation state is selected from the variation pattern type determination table for reach deviation (for reach) (S99). Then, the process proceeds to S101. For example, if the state is an uncertain change state, the variation pattern type determination table in the non-probability change state reach determination table of FIG. 14 is selected. If the state of change is the probability change state, the change pattern type determination table of FIG. Select.
一方、S97による決定において、リーチ状態にしないことに決定した場合には、図13に示す非リーチはずれ用時判定テーブルから、変動パターン種別判定テーブルを選択する(S100)。そして、S101に移行する。 On the other hand, when it is determined in S97 that the reach state is not set, a variation pattern type determination table is selected from the non-reach deviation determination table shown in FIG. 13 (S100). Then, the process proceeds to S101.
S101では、CPU56は、ランダム3を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を抽出することによってランダム3の値を抽出する。そして、抽出したランダム3の値に基づいて、S92、S99またはS100の処理で選択した変動パターン種別判定テーブルを参照することによって、変動パターン種別を複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定する(S102)。
In S101, the
次いで、CPU56は、S102の変動パターン種別の決定結果に基づいて、変動パターンを複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定するために使用するテーブルとして、S102で決定された変動パターン種別等の変動パターン種別に対応する変動パターン判定テーブルを選択する(S103)。
Next, the
たとえば、非確変状態での確変大当り時に「スーパーリーチA」の種別に決定されたときには、図18に示すような「スーパーリーチA」の変動パターン種別に対応する変動パターン判定テーブルを選択する。また、確変状態での確変大当り時に「スーパーリーチA」の種別に決定されたときには、図19に示すような「スーパーリーチA」の変動パターン種別に対応する変動パターン判定テーブルを選択する。 For example, when the type of “super reach A” is determined at the probability variation big hit in the non-probability variation state, the variation pattern determination table corresponding to the variation pattern type of “super reach A” as shown in FIG. 18 is selected. Further, when the probability variation big hit in the probability variation state is determined as the type of “super reach A”, the variation pattern determination table corresponding to the variation pattern type of “super reach A” as shown in FIG. 19 is selected.
次に、ランダム4を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を抽出することによってランダム4の値を抽出する(S104)。そして、抽出したランダム4の値に基づいて、S103の処理で選択した変動パターン判定テーブルを参照することによって、変動パターンを複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定する(S105)。
Next, the value of random 4 is extracted by extracting the count value of the counter for generating random 4 (S104). Based on the extracted
次いで、決定した変動パターンに対応する演出制御コマンド(変動パターンコマンド)を、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行なう(S106)。 Next, an effect control command (variation pattern command) corresponding to the determined variation pattern is transmitted to the effect control microcomputer 100 (S106).
また、特別図柄の変動を開始する(S107)。たとえば、S33の特別図柄表示制御処理で参照される特別図柄に対応した開始フラグをセットする。また、RAM55に形成されている変動時間タイマに、選択された変動パターンに対応した変動時間に応じた値を設定する(S108)。そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を表示結果特定コマンド送信処理(S302)に対応した値に更新する(S109)。 Also, the special symbol change is started (S107). For example, the start flag corresponding to the special symbol referred to in the special symbol display control process of S33 is set. Further, a value corresponding to the variation time corresponding to the selected variation pattern is set in the variation time timer formed in the RAM 55 (S108). Then, the value of the special symbol process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the display result specifying command transmission process (S302) (S109).
なお、この実施の形態では、擬似連用の変動パターンを決定する場合に、予め再変動回数およびリーチ種類が指定された変動パターンをS105で最終決定することによって、再変動回数およびリーチ種類を同時決定する場合を示すが、再変動回数とリーチ種類とを別々に2段階に決定するようにしてもよい。この場合、たとえば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、まず擬似連における再変動回数を決定した後に、リーチ種類を決定するようにしてもよい。また、たとえば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、まずリーチ種類を決定した後に、擬似連における再変動回数を決定するようにしてもよい。
In this embodiment, when the fluctuation pattern for pseudo continuous use is determined, the fluctuation pattern for which the number of re-variations and the reach type are specified in advance is finally determined in S105, so that the number of re-variations and the reach type are simultaneously determined. However, the number of re-variations and the reach type may be determined separately in two stages. In this case, for example, the
表示結果特定コマンド送信処理(S302)において、CPU56は、決定されている大当りの種別、はずれに応じて、表示結果1指定〜表示結果4指定のいずれかの演出制御コマンド(図25参照)を送信する制御を行なう。具体的には、CPU56は、まず、大当りフラグがセットされており、大当りの種別が確変大当りであるときには、確変大当りを示す表示結果3指定コマンドを送信する処理を行なう。一方、大当りの種別が確変大当りでなく、突確大当りであるときには、突確大当りであることを示す表示結果4指定コマンドを送信する処理を行なう。大当りの種別が確変大当りでも突確大当りでもないときには、通常大当りを示す表示結果2指定コマンドを送信する制御を行なう。また、大当りフラグがセットされていないときには、はずれを示す表示結果1指定コマンドを送信する処理を行なう。そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を特別図柄変動中処理(S303)に対応した値に更新する(S109)。
In the display result specifying command transmission process (S302), the
特別図柄変動中処理において、CPU56は、特別図柄変動中処理が実行されるごとに、前述のS108によりセットされた変動時間タイマの値を1ずつ減算し、変動時間タイマの値が0になってタイムアウトしたら、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を特別図柄停止処理(S304)に対応した値に更新する。
In the special symbol changing process, every time the special symbol changing process is executed, the
図30は、特別図柄プロセス処理における特別図柄停止処理(S304)を示すフローチャートである。特別図柄停止処理において、CPU56は、S32の特別図柄表示制御処理で参照される終了フラグをセットして特別図柄の変動を終了させ、第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bに停止図柄を導出表示する制御を行なう(S131)。なお、特別図柄ポインタに「第1」を示すデータが設定されている場合には第1特別図柄表示器8aでの第1特別図柄の変動を終了させ、特別図柄ポインタに「第2」を示すデータが設定されている場合には第2特別図柄表示器8bでの第2特別図柄の変動を終了させる。また、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に図柄確定指定コマンドを送信する制御を行なう(S132)。そして、大当りフラグがセットされていない場合には、S139に移行する(S133)。
FIG. 30 is a flowchart showing the special symbol stop process (S304) in the special symbol process. In the special symbol stop process, the
大当りフラグがセットされている場合には、CPU56は、確変フラグおよび時短フラグをリセットし(S134)、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に大当り開始指定コマンドを送信する制御を行なう(S135)。具体的には、大当りの種別が確変大当りである場合には大当り開始2指定コマンドを送信する。大当りの種別が突確大当りである場合には突確開始指定コマンドを送信する。そうでない場合には大当り開始1指定コマンドを送信する。なお、大当りの種別が確変大当りまたは突確大当りであるか否かは、RAM55に記憶されている大当り種別を示すデータ(大当り種別バッファに記憶されているデータ)に基づいて判定される。
If the big hit flag is set, the
また、大当り表示時間タイマに大当り表示時間(大当りが発生したことをたとえば、演出表示装置9において報知する時間)に相当する値を設定する(S136)。また、大入賞口開放回数カウンタに開放回数(たとえば、通常大当りおよび確変大当り(15ラウンド大当り)の場合には15回。突確(2ラウンド大当り)の場合には2回。)をセットする(S137)。そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を大入賞口開放前処理(S305)に対応した値に更新する(S138)。 Further, a value corresponding to the big hit display time (time for notifying the occurrence of the big hit, for example, in the effect display device 9) is set in the big hit display time timer (S136). In addition, the number of times of opening (for example, 15 times in the case of a normal big hit and a probable big hit (15 round big hit), 2 times in the case of a sudden hit (2 round big hit)) is set in the big prize opening number counter (S137). ). Then, the value of the special symbol process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the special winning opening opening pre-processing (S305) (S138).
S139では、CPU56は、時短状態であることを示す時短フラグがセットされているか否か確認する。時短フラグがセットされている場合には、時短状態における特別図柄の変動可能回数を示す時短回数カウンタの値を−1する(S140)。そして、時短回数カウンタの値が0になった場合には、時短フラグをリセットする(S142)。そして、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を特別図柄通常処理(S300)に対応した値に更新する(S148)。
In S139, the
図31は、特別図柄プロセス処理における大入賞口開放前処理(S305)を示すフローチャートである。大入賞口開放前処理において、CPU56は、大入賞口制御タイマの値を−1する(S401)。そして、大入賞口制御タイマの値が0であるか否かを確認し(S402)、大入賞口制御タイマの値が0になっていなければ、処理を終了する。
FIG. 31 is a flowchart showing the pre-opening process for the special winning opening in the special symbol process (S305). In the pre-opening process for the big winning opening, the
大入賞口制御タイマの値が0になっている場合には、CPU56は、大入賞口の開放中(ラウンド中)におけるラウンド数に応じた表示状態を指定する大入賞口開放中指定コマンド(A1XX(H))を演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行なう(S403)。なお、CPU56は、ラウンド数を、大当り遊技中のラウンド数をカウントするための開放回数カウンタの値を確認することにより認識する。そして、CPU56は、ソレノイド21を駆動して大入賞口(特別可変入賞球装置20)を開放する制御を行なうとともに(S404)、開放回数カウンタの値を−1する(S405)。
When the value of the big prize opening control timer is 0, the
また、大入賞口制御タイマに、各ラウンドにおいて大入賞口が開放可能な最大時間に応じた値を設定する(S406)。たとえば、15ラウンド大当りの場合には最大時間は29秒であり、突確大当りの場合には最大時間は0.5秒である。そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値をステップ大入賞口開放中処理(S306)に応じた値に更新する(S415)。 In addition, a value corresponding to the maximum time that the big prize opening can be opened in each round is set in the big prize opening control timer (S406). For example, in the case of 15 round big hits, the maximum time is 29 seconds, and in the case of sudden hit big hits, the maximum time is 0.5 seconds. Then, the value of the special symbol process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the step large winning opening opening process (S306) (S415).
図32および図33は、特別図柄プロセス処理における大入賞口開放中処理(S306)を示すフローチャートである。大入賞口開放中処理において、CPU56は、大入賞口制御タイマの値を−1する(S420)。
FIG. 32 and FIG. 33 are flowcharts showing the special winning opening opening process (S306) in the special symbol process. In the special prize opening opening process, the
そして、CPU56は、大入賞口制御タイマの値が0になったか否か確認する(S421)。大入賞口制御タイマの値が0になっていないときは、カウントスイッチ23がオンしたか否か確認し(S432)、カウントスイッチ23がオンしていなければ、処理を終了する。カウントスイッチ23がオンした場合には、大入賞口への遊技球の入賞個数をカウントするための入賞個数カウンタの値を+1する(S433)。そして、CPU56は、入賞個数カウンタの値が所定数(たとえば10)になっているか否か確認する(S434)。入賞個数カウンタの値が所定数になっていなければ、処理を終了する。なお、S421とS432との判定順は逆でもよい。
Then, the
大入賞口制御タイマの値が0になっているとき、または入賞個数カウンタの値が所定数になっているときには、CPU56は、ソレノイド21を駆動して大入賞口を閉鎖する制御を行なう(S435)。そして、入賞個数カウンタの値をクリアする(0にする)(S436)。
When the value of the big prize opening control timer is 0 or when the value of the winning number counter is a predetermined number, the
次いで、CPU56は、開放回数カウンタの値を確認する(S438)。開放回数カウンタの値が0でない場合には、CPU56は、大入賞口の開放後(ラウンドの終了後)におけるラウンド数に応じた表示状態を指定する大入賞口開放後指定コマンド(A2XX(H))を演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行なう(S439)。そして、大入賞口制御タイマに、ラウンドが終了してから次のラウンドが開始するまでの時間(インターバル期間)に相当する値を設定し(S440)、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を大入賞口開放前処理(S305)に応じた値に更新する(S441)。なお、インターバル期間は、たとえば5秒である。突確大当りのときは15R大当りより短い期間としてもよい。
Next, the
開放回数カウンタの値が0である場合には、CPU56は、大当り種別を示すデータが確変大当りを示すデータであるときに、大当り終了2指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行なう(S442,S447)。なお、S442で確変大当りであるか否かは、具体的には、S74でRAM55における大当り種別バッファに設定した大当り種別を示すデータが確変大当りを示す値(本例では「02」)であるか否かを確認することにより判定できる。そして、CPU56は、大入賞口制御タイマに大当り終了時間(大当り遊技が終了したことをたとえば、演出表示装置9において報知する時間)に相当する値を設定し(S449)、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を大当り終了処理(S307)に応じた値に更新する(S450)。
When the value of the number-of-releases counter is 0, the
CPU56は、大当り種別を示すデータが確変大当りを示すデータでなく、突確大当りを示すデータである場合には、突確終了指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行なう(S443,S444)。なお、S443で突確大当りであるか否かは、具体的には、S74でRAM55における大当り種別バッファに設定した大当り種別を示すデータが突確大当りを示す値(本例では「03」)であるか否かを確認することにより判定できる。大当り種別を示すデータが突確大当りを示すデータでもないときには、大当り終了1指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行なう(S445)。そして、S449に移行する。
If the data indicating the big hit type is not the data indicating the probability variation big hit but the data indicating the sudden big hit, the
図34は、特別図柄プロセス処理における大当り終了処理(S307)を示すフローチャートである。大当り終了処理において、CPU56は、大当り終了表示タイマが設定されているか否か確認し(S150)、大当り終了表示タイマが設定されている場合には、S154に移行する。大当り終了表示タイマが設定されていない場合には、大当りフラグをリセットし(S151)、大当り終了指定コマンドを送信する制御を行なう(S152)。ここで、確変大当りであった場合には大当り終了2指定コマンドを送信し、突確大当りであった場合には突確終了指定コマンドを送信し、いずれでもない場合には大当り終了1指定コマンドを送信する。そして、大当り終了表示タイマに、演出表示装置9において大当り終了表示が行なわれている時間(大当り終了表示時間)に対応する表示時間に相当する値を設定し(S153)、処理を終了する。
FIG. 34 is a flowchart showing the jackpot end process (S307) in the special symbol process. In the jackpot end process, the
S154では、大当り終了表示タイマの値を1減算する。そして、CPU56は、大当り終了表示タイマの値が0になっているか否か、すなわち大当り終了表示時間が経過したか否か確認する(S155)。経過していなければ処理を終了する。経過していれば、大当りの種別が確変大当りまたは突確大当りであったか否か確認する(S158)。S158では、大当り種別の決定に応じて大当り種別バッファに設定された大当りの種別を示すデータに基づいて、確変大当りまたは突確大当りであったか否かを確認する。大当り種別バッファに設定された大当りの種別を示すデータは、後述するS162が実行された後、クリアされる。
In S154, 1 is subtracted from the value of the big hit end display timer. Then, the
大当りの種別が確変大当りまたは突確大当りであった場合には、確変フラグをセットして遊技状態を確変状態に移行させる(S161)。そして、S162に移行する。確変大当りでも突確大当りでもない場合には、そのままS162に移行する。そして、S162では、時短フラグをセットし(S162)、時短回数カウンタにたとえば100をセットする(S163)。これにより、大当り遊技状態の終了後には、必ず時短状態に制御されることとなる。そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を特別図柄通常処理(S300)に対応した値に更新する(S164)。 If the big hit type is a probable big hit or a sudden big hit, the probability change flag is set and the gaming state is shifted to the probability change state (S161). Then, the process proceeds to S162. If there is neither a probable big hit nor a sudden big hit, the process proceeds to S162. In S162, the time reduction flag is set (S162), and for example, 100 is set in the time reduction counter (S163). As a result, after the big hit gaming state is ended, the time-saving state is always controlled. Then, the value of the special symbol process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the special symbol normal process (S300) (S164).
次に、演出制御手段としての演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100の動作を説明する。図35は、演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100(具体的には、演出制御用CPU101)が実行するメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。演出制御用CPU101は、電源が投入されると、メイン処理の実行を開始する。メイン処理では、まず、RAM領域のクリアや各種初期値の設定、また演出制御の起動間隔(たとえば、2ms)を決めるためのタイマの初期設定等を行なうための初期化処理を行なう(S701)。その後、演出制御用CPU101は、タイマ割込フラグの監視(S702)を行なうループ処理に移行する。タイマ割込が発生すると、演出制御用CPU101は、タイマ割込処理においてタイマ割込フラグをセットする。メイン処理において、タイマ割込フラグがセットされていたら、演出制御用CPU101は、そのフラグをクリアし(S703)、S704〜S709の演出制御処理を実行する。
Next, the operation of the
演出制御処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、まず、受信した演出制御コマンドを解析し、受信した演出制御コマンドに応じたフラグをセットする処理等を行なう(コマンド解析処理:S704)。次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御プロセス処理を行なう(S705)。演出制御プロセス処理では、制御状態に応じた各プロセスのうち、現在の制御状態(演出制御プロセスフラグ)に対応した処理を選択して演出表示装置9の表示制御を実行する。
In the effect control process, the
次いで、第1飾り図柄表示制御処理を行なう(S706)。第1飾り図柄表示制御処理では、第1飾り図柄表示器9aの表示制御を実行する。また、第2飾り図柄表示制御処理を行なう(S707)。第2飾り図柄表示制御処理では、第2飾り図柄表示器9bの表示制御を実行する。また、合算保留記憶表示部18cの表示状態の制御を行なう保留記憶表示制御処理を実行する(S708)。さらに、演出の態様等を決定するために用いられる乱数を生成するためのカウンタ(ランダムカウンタ)のカウント値を更新する乱数更新処理を実行する(S709)。その後、S702に移行する。なお、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が実行する特別図柄プロセス処理のように、第1飾り図柄表示制御処理と第2飾り図柄表示制御処理とを共通化して、すなわち一つのプログラムモジュールで実現するようにして、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が実行するプログラム容量を減らすようにしてもよい。
Next, a first decorative symbol display control process is performed (S706). In the first decorative symbol display control process, display control of the first decorative symbol display 9a is executed. Further, a second decorative symbol display control process is performed (S707). In the second decorative symbol display control process, display control of the second decorative symbol display 9b is executed. Further, a hold storage display control process for controlling the display state of the combined hold
図36および図37は、コマンド解析処理(S704)の具体例を示すフローチャートである。主基板31から受信された演出制御コマンドは受信コマンドバッファに格納されるが、コマンド解析処理では、演出制御用CPU101は、コマンド受信バッファに格納されているコマンドの内容を確認する。
36 and 37 are flowcharts showing a specific example of the command analysis process (S704). The effect control command received from the
コマンド解析処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、まず、RAMに形成されているコマンド受信バッファに受信コマンドが格納されているか否か確認する(S611)。格納されているか否かは、コマンド受信個数カウンタの値と読出ポインタとを比較することによって判定される。両者が一致している場合が、受信コマンドが格納されていない場合である。コマンド受信バッファに受信コマンドが格納されている場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、コマンド受信バッファから受信コマンドを読出す(S612)。なお、読出したら読出ポインタの値を+2しておく(S613)。+2するのは2バイト(1コマンド)ずつ読出すからである。
In the command analysis process, the
コマンド受信バッファとして、たとえば、2バイト構成の演出制御コマンドを6個格納可能なリングバッファ形式のコマンド受信バッファが用いられる。したがって、コマンド受信バッファは、受信コマンドバッファ1〜12の12バイトの領域で構成される。そして、受信したコマンドをどの領域に格納するのかを示すコマンド受信個数カウンタが用いられる。コマンド受信個数カウンタは、0〜11の値をとる。なお、必ずしもリングバッファ形式でなくてもよい。
As the command receiving buffer, for example, a ring buffer type command receiving buffer capable of storing six 2-byte effect control commands is used. Therefore, the command reception buffer is configured by a 12-byte area of
なお、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から送信された演出制御コマンドは、演出制御INT信号に基づく割込処理で受信されコマンド受信バッファに保存されている。コマンド解析処理では、バッファ領域に保存されている演出制御コマンドがどのコマンド(図22参照)であるのか解析する。
The effect control command transmitted from the
受信した演出制御コマンドが変動パターンコマンドであれば(S614)、演出制御用CPU101は、その変動パターンコマンドを、RAMに形成されている変動パターンコマンド格納領域に格納する(S615)。そして、変動パターンコマンド受信フラグをセットする(S616)。
If the received effect control command is a variation pattern command (S614), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが表示結果特定コマンドであれば(S617)、演出制御用CPU101は、その表示結果特定コマンド(表示結果1指定コマンド〜表示結果4指定コマンドのいずれか)を、RAMに形成されている表示結果特定コマンド格納領域に格納する(S618)。
If the received effect control command is a display result specifying command (S617), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが図柄確定指定コマンドであれば(S621)、演出制御用CPU101は、確定コマンド受信フラグをセットする(S622)。
If the received effect control command is a symbol confirmation designation command (S621), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが大当り開始1指定コマンドまたは大当り開始2指定コマンドであれば(S623)、演出制御用CPU101は、大当り開始1指定コマンド受信フラグまたは大当り開始2指定コマンド受信フラグをセットする(S624)。受信した演出制御コマンドが突確開始指定コマンドであれば(S625)、演出制御用CPU101は、突確開始指定コマンド受信フラグをセットする(S626)。
If the received effect control command is a
受信した演出制御コマンドが第1図柄変動指定コマンドであれば(S627)、第1図柄変動指定コマンド受信フラグをセットする(S628)。受信した演出制御コマンドが第2図柄変動指定コマンドであれば(S629)、第2図柄変動指定コマンド受信フラグをセットする(S630)。 If the received effect control command is the first symbol variation designation command (S627), the first symbol variation designation command reception flag is set (S628). If the received effect control command is the second symbol variation designation command (S629), the second symbol variation designation command reception flag is set (S630).
受信した演出制御コマンドが電源投入指定コマンド(初期化指定コマンド)であれば(S631)、演出制御用CPU101は、初期化処理が実行されたことを示す初期画面を演出表示装置9に表示する制御を行なう(S632)。初期画面には、予め決められている演出図柄の初期表示が含まれる。
If the received production control command is a power-on designation command (initialization designation command) (S631), the
また、受信した演出制御コマンドが停電復旧指定コマンドであれば(S633)、予め決められている停電復旧画面(遊技状態が継続していることを遊技者に報知する情報を表示する画面)を表示する制御を行なう(S634)。 If the received effect control command is a power failure recovery designation command (S633), a predetermined power failure recovery screen (screen for displaying information notifying the player that the gaming state is continuing) is displayed. Control is performed (S634).
受信した演出制御コマンドが大当り終了1指定コマンドまたは大当り終了2指定コマンドであれば(S641)、演出制御用CPU101は、大当り終了1指定コマンド受信フラグまたは大当り終了2指定コマンド受信フラグをセットする(S642)。受信した演出制御コマンドが突確終了指定コマンドであれば(S643)、演出制御用CPU101は、突確終了指定コマンド受信フラグをセットする(S644)。
If the received effect control command is a
受信した演出制御コマンドが大入賞口開放中指定コマンドであれば(S645)、演出制御用CPU101は、大入賞口開放中フラグをセットする(S646)。また、受信した演出制御コマンドが大入賞口開放後指定コマンドであれば(S647)、演出制御用CPU101は、大入賞口開放後フラグをセットする(S648)。
If the received effect control command is a special winning opening open designation command (S645), the
受信した演出制御コマンドがその他のコマンドであれば、演出制御用CPU101は、受信した演出制御コマンドに応じたフラグをセットする(S649)。そして、S611に移行する。
If the received effect control command is another command, the
図38は、飾り図柄(第1飾り図柄および第2飾り図柄)の変動表示の態様の一例を示す説明図である。この実施の形態では、第1飾り図柄表示器9aおよび第2飾り図柄表示器9bは、2つのLEDで構成されている。そして、図38に示すように、所定時間(たとえば、0.5秒)毎に交互に点灯する。特別図柄の表示結果を大当り図柄にする場合には、大当りを想起させる飾り図柄の表示結果として、上側のLEDが点灯している状態にする(図38(A)参照)。また、特別図柄の表示結果をはずれ図柄にする場合には、はずれを想起させる飾り図柄の表示結果として、下側のLEDが点灯している状態にする(図38(B)参照)。 FIG. 38 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of a variation display mode of decorative symbols (first decorative symbol and second decorative symbol). In this embodiment, the first decorative symbol display 9a and the second decorative symbol display 9b are composed of two LEDs. And as shown in FIG. 38, it lights alternately every predetermined time (for example, 0.5 second). When the display result of the special symbol is a jackpot symbol, the upper LED is turned on as a display result of a decorative symbol reminiscent of the jackpot (see FIG. 38A). Further, when the display result of the special symbol is changed to the off symbol, the lower LED is turned on as the display result of the decorative symbol reminiscent of the loss (see FIG. 38B).
図39は、図35に示されたメイン処理における演出制御プロセス処理(S705)を示すフローチャートである。演出制御プロセス処理では、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御プロセスフラグの値に応じてS800〜S807のうちのいずれかの処理を行なう。各処理において、以下のような処理を実行する。
FIG. 39 is a flowchart showing the effect control process (S705) in the main process shown in FIG. In the effect control process, the
変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(S800):遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から変動パターンコマンドを受信しているか否か確認する。具体的には、コマンド解析処理でセットされる変動パターンコマンド受信フラグがセットされているか否か確認する。変動パターンコマンドを受信していれば、変動パターンコマンド受信フラグをリセットし、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動開始処理(S801)に対応した値に変更する。
Fluctuation pattern command reception waiting process (S800): It is confirmed whether or not a variation pattern command has been received from the
演出図柄変動開始処理(S801):演出図柄および飾り図柄の変動が開始されるように制御する。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動中処理(S802)に対応した値に更新する。 Production symbol variation start processing (S801): Control is performed so that variation of the production symbol and the decoration symbol is started. Then, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the effect symbol changing process (S802).
演出図柄変動中処理(S802):変動パターンを構成する各変動状態(変動速度)の切替えタイミング等を制御するとともに、変動時間の終了を監視する。そして、変動時間が終了したら、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動停止処理(S803)に対応した値に更新する。 Production symbol variation processing (S802): Controls the switching timing of each variation state (variation speed) constituting the variation pattern and monitors the end of the variation time. Then, when the variation time ends, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the effect symbol variation stop process (S803).
演出図柄変動停止処理(S803):全図柄停止を指示する演出制御コマンド(図柄確定指定コマンド)を受信したことに基づいて、演出図柄(および飾り図柄)の変動を停止し表示結果(停止図柄)を導出表示する制御を行なう。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を大当り表示処理(S804)または変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(S800)に対応した値に更新する。 Effect symbol variation stop processing (S803): Based on the reception of the effect control command (design determination designation command) instructing all symbols to stop, the variation of the effect symbol (and the decorative symbol) is stopped and the display result (stop symbol) Control to derive and display. Then, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the jackpot display process (S804) or the variation pattern command reception waiting process (S800).
大当り表示処理(S804):変動時間の終了後、演出表示装置9に大当りの発生を報知するための画面を表示する制御を行なう。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値をラウンド中処理(S805)に対応した値に更新する。
Big hit display process (S804): After the end of the variation time, control is performed to display a screen for notifying the
ラウンド中処理(S805):ラウンド中の表示制御を行なう。また、いわゆる確変昇格演出を実行する遊技機では、確変昇格演出の実行を示す確変昇格演出実行中フラグがセットされている場合には確変昇格演出を実行する。そして、ラウンド終了条件が成立したら、最終ラウンドが終了していなければ、演出制御プロセスフラグの値をラウンド後処理(S806)に対応した値に更新する。最終ラウンドが終了していれば、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を大当り終了処理(S807)に対応した値に更新する。 In-round processing (S805): Display control during round is performed. In addition, in a gaming machine that executes a so-called probability change promotion effect, a probability change promotion effect is executed when the flag of the probability change promotion effect execution flag indicating execution of the probability change promotion effect is set. If the round end condition is satisfied, if the final round has not ended, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the post-round processing (S806). If the final round has ended, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the big hit end process (S807).
ラウンド後処理(S806):ラウンド間の表示制御を行なう。そして、ラウンド開始条件が成立したら、演出制御プロセスフラグの値をラウンド中処理(S805)に対応した値に更新する。 Post-round processing (S806): Display control between rounds is performed. If the round start condition is satisfied, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the in-round processing (S805).
大当り終了処理(S807):演出表示装置9において、大当り遊技状態が終了したことを遊技者に報知する表示制御を行なう。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(S800)に対応した値に更新する。
Big hit end processing (S807): In the
図40は、図39に示された演出制御プロセス処理における演出図柄変動開始処理(S801)を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 40 is a flowchart showing the effect symbol variation start process (S801) in the effect control process shown in FIG.
演出図柄変動開始処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、はずれとすることに決定されているか否か確認する(S501)。はずれとすることに決定されているか否かは、たとえば、表示結果特定コマンド格納領域に表示結果1指定コマンドが格納されているか否かによって判定される。なお、はずれとすることに決定されているか否かは、大当りとするか否かを特定可能な変動パターンコマンドに基づいて、確認するようにしてもよい。はずれとすることに決定されている場合には、変動パターンコマンドとして、非リーチ変動パターンに対応したコマンドを受信したか否か確認する(S502)。非リーチ変動パターンに対応したコマンドを受信したか否かは、たとえば、変動パターンコマンド格納領域に格納されているデータによって判定される。
In the effect symbol variation start process, the
非リーチ変動パターンに対応したコマンドを受信したと判定した場合、演出制御用CPU101は、予め定められたはずれ図柄決定用データテーブルを用いて、演出図柄のリーチにならないはずれの停止図柄を決定し(S503)、S514へ進む。はずれ図柄決定用データテーブルでは、複数種類の演出図柄のそれぞれに、SR1−1〜SR1−3のそれぞれの数値データが対応付けられている。S503の処理では、所定のタイミングでSR1−1〜SR1−3のそれぞれから数値データ(乱数)を抽出し、ROM82に記憶されたはずれ図柄決定用データテーブルを用い、抽出した乱数に対応する図柄がそれぞれ左,中,右の演出図柄の変動表示結果となる停止図柄の組合せとして決定される。このように非リーチはずれの図柄の組合せを決定する場合において、抽出された乱数に対応する停止図柄が偶然大当り図柄の組合せ(確変大当り図柄の組合せ、通常大当り図柄の組合せ、突確大当り図柄の組合せ)と一致する場合には、はずれ図柄の組合せとなるように補正(たとえば、右図柄を1図柄ずらす補正)して各停止図柄が決定される。また、抽出された乱数に対応する停止図柄が偶然リーチ図柄となってしまう場合には、非リーチはずれ図柄の組合せとなるように補正(たとえば、右図柄を1図柄ずらす補正)して各停止図柄が決定される。
When it is determined that the command corresponding to the non-reach variation pattern has been received, the
S502の処理で非リーチ変動パターンではないと判定した場合(リーチ変動パターンであると判定した場合)に、演出制御用CPU101は、リーチの組合せを構成する演出図柄の停止図柄を決定し(S504)、S514へ進む。S504の処理では、所定のタイミングでSR1−1〜SR1−3のそれぞれから数値データ(乱数)を抽出し、はずれ図柄決定用データテーブルを用い、SR1−1から抽出された乱数に対応する図柄がリーチ状態を形成する左,右の各演出図柄の停止図柄として決定され、SR1−2から抽出されたカウンタの値と一致する乱数に対応する図柄が中図柄の停止図柄として決定される。また、この場合も、偶然大当り図柄の組合せとなってしまうときには、はずれ図柄の組合せとなるように補正(たとえば、中図柄を1図柄ずらす補正)して各停止図柄が決定される。
When it is determined in step S502 that the pattern is not a non-reach variation pattern (when it is determined that the pattern is a reach variation pattern), the
はずれとすることに決定されていない場合に(S501)、演出制御用CPU101は、突確大当りに決定されているか否かを判定する(S505)。突確大当りに決定されているか否かは、たとえば、表示結果特定コマンド格納領域に表示結果4指定コマンド(図22参照)が格納されているか否かによって判定される。なお、突確大当りに決定されているか否かは、突確大当りであるかを特定可能な変動パターンコマンドに基づいて判定するようにしてもよい。
When it is not determined to be out of place (S501), the
突確大当りに決定されていない場合(S505N)、すなわち確変大当りまたは通常大当りに決定されている場合には、大当りの組合せの演出図柄の最終停止図柄を決定する(S506)。S506の処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、確変大当りにすることに決定されている場合に、確変大当り図柄決定用テーブルを用いて、確変大当り図柄の組合せ(たとえば、左,中,右が「7,7,7」というようないずれかの奇数図柄の組合せ)を選択決定する。確変大当り図柄決定用テーブルは、予め定められた複数種類の確変大当り図柄のそれぞれに、SR1−1のそれぞれの数値データが対応付けられている。S506の処理では、所定のタイミングでSR1−1から数値データ(乱数)を抽出し、確変大当り図柄決定用データテーブルを用い、抽出した乱数に対応する図柄を、確変大当り図柄の組合せを構成する左,中,右の演出図柄の停止図柄の組合せとして決定する。S506で決定された図柄が大当り遊技状態に制御される前の変動表示結果である最終停止図柄として用いられる。また、演出制御用CPU101は、通常大当りにすることに決定されている場合に、通常大当り図柄決定用テーブルを用いて、通常大当り図柄の組合(たとえば、左,中,右が「2,2,2」というようないずれかの偶数図柄のゾロ目の組合せ)を選択決定する。通常大当り図柄決定用テーブルは、予め定められた複数種類の通常大当り図柄のそれぞれに、SR1−1のそれぞれの数値データが対応付けられている。S506の処理では、所定のタイミングでSR1−1から数値データ(乱数)を抽出し、通常大当り図柄決定用データテーブルを用い、抽出した乱数に対応する図柄を、通常大当り図柄の組合せを構成する左,中,右の演出図柄の停止図柄の組合せとして決定する。
If it is not determined to be a big hit (S505N), that is, if it is decided to be a promising big hit or a normal big hit, the final stop symbol of the combination symbol of the big hit is determined (S506). In the processing of S506, when it is determined that the probability variation big hit is made, the
また、突確大当りに決定されている場合には(S505Y)、突確大当り図柄の組合せとして予め定められた演出図柄の最終停止図柄を決定し(S507)、S514に進む。S507の処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、突確図柄決定用テーブルを用いて、突確大当り図柄の組合せを選択決定する。突確図柄決定用テーブルは、複数種類の突確図柄の組合せのそれぞれに、SR1−1のそれぞれの数値データが対応付けられている。S507の処理では、所定のタイミングでSR1−1から数値データ(乱数)を抽出し、突確図柄決定用データテーブルを用い、抽出した乱数に対応する図柄の組合せが突確図柄の組合せを構成する左,中,右の演出図柄の停止図柄の組合せとして決定される。
If it is determined that the winning big hit is determined (S505Y), the final stop symbol of the production symbol predetermined as a combination of the big winning hit symbol is determined (S507), and the process proceeds to S514. In the process of S507, the
S514では、特定演出設定処理を実行する。ここで、図41を用いて、特定演出設定処理について説明する。図41は、特定演出設定処理を示すフローチャートである。 In S514, a specific effect setting process is executed. Here, the specific effect setting process will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 41 is a flowchart showing the specific effect setting process.
特定演出設定処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、「擬似連」、「滑り」、および、「スーパーリーチA,B」のような仮停止図柄(一旦停止図柄)を決定する必要がある演出としての特定演出が行なわれるか否かを判定し、演出種類に応じて、演出中に必要となる仮停止図柄を決定する処理を行なう。
In the specific effect setting process, the
演出制御用CPU101は、「滑り」の演出が行なわれるか否かを判定する(S1550)。「滑り」の演出が行なわれるか否かは、受信した変動パターンコマンドにより「滑り」であることが示されているか否かに応じて判断する。「滑り」の演出が行なわれるときには、次のように仮停止図柄を決定し(S1551)、処理を終了する。S1551において、演出制御用CPU101は、滑り時仮停止図柄決定用の乱数SR3の値を抽出して、抽出した乱数SR3の値に基づいて仮停止図柄を決定する。
The
「滑り」の演出が行なわれないときに、演出制御用CPU101は、「擬似連」の演出が行なわれるか否かを判定する(S1552)。「擬似連」の演出が行なわれるか否かは、受信した変動パターンコマンドにより「擬似連」であることが示されているか否かに応じて判断する。「擬似連」の演出が行なわれないときには、後述するS1554に進む。一方、「擬似連」の演出が行なわれるときには、次のように仮停止図柄を決定し(S1553)、後述するS1554に進む。
When the “slip” effect is not performed, the
S1553の処理において擬似連チャンス目を決定するときに、演出制御用CPU101は、ROM82に記憶された擬似連時仮停止図柄決定用テーブルを用いて、仮停止図柄の組合せを決定する。擬似連時仮停止図柄決定用テーブルは、予め定められた複数種類の仮停止図柄の組合せのそれぞれに、SR4−1〜SR4−4のそれぞれの数値データが対応付けられている。SR4−1から抽出された数値データに基づいて決定された仮停止図柄が擬似連時第1仮停止図柄として決定される。SR4−2から抽出された数値データに基づいて決定された仮停止図柄が擬似連時第2仮停止図柄として決定される。SR4−3から抽出された数値データに基づいて決定された仮停止図柄が擬似連時第3仮停止図柄として決定される。SR4−4から抽出された数値データに基づいて決定された仮停止図柄が擬似連時第4仮停止図柄として決定される。
When determining the quasi-continuous chance item in the process of S1553, the
具体的に、「擬似連」の演出である場合には、擬似連のたとえば、擬似連3回の変動パターンのときには、擬似連時第1仮停止図柄決定用乱数SR4−1〜擬似連時第3仮停止図柄決定用乱数SR4−3を選択し、それぞれの乱数を抽出して、第1回目仮停止時の仮停止図柄〜第2回目仮停止時の仮停止図柄のそれぞれを決定する。 Specifically, in the case of the production of “pseudo-continuous”, the pseudo-continuous first temporary stop symbol determining random number SR4-1 to the pseudo-continuous The 3 temporary stop design determining random numbers SR4-3 are selected, the respective random numbers are extracted, and the temporary stop symbols at the time of the first temporary stop to the temporary stop symbols at the time of the second temporary stop are determined.
次に、S1555〜S1558により、前述したように一旦リーチはずれの図柄が仮停止した後、スーパーリーチへの発展演出、突確大当りへの移行演出、または、バトルリーチで突然切替演出が行なわれるときにおいて仮停止表示するリーチはずれ図柄を決定する処理が行なわれる。このようなリーチはずれ図柄を仮停止する発展演出、移行演出、および、突然切替演出を行なう変動パターンとしては、大当りまたははずれとなるときの「スーパーリーチA,B」、「第1,第2突確移行」、または、「バトルリーチA,Bで突然切替」を実行する変動パターンが該当する。つまり、表示結果がスーパーリーチA,B以外の変動パターンでリーチはずれとなるときには、決定したリーチはずれ図柄の組合せをそのまま仮停止表示した後、仮停止表示したリーチはずれ図柄を最終的な表示結果として表示すれば、最終的にリーチはずれ図柄を表示結果として表示することができるので、仮停止表示するリーチはずれ図柄を別途決定する必要がない。一方、表示結果がスーパーリーチA,Bの変動パターンでリーチはずれとなるときには、最終的な表示結果として決定したリーチはずれ図柄の組合せをそのまま仮停止表示すれば仮停止図柄と最終的な表示結果とが同じリーチはずれ図柄になってしまうので、これを防ぐためには、仮停止表示するリーチはずれ図柄を別途決定する必要がある。したがって、表示結果がスーパーリーチA,Bの変動パターンでリーチはずれとなるときには、決定したリーチはずれ図柄の組合せを最終的な表示結果として用い、別途決定したリーチはずれ図柄を、仮停止表示するリーチはずれ図柄として用いる。また、表示結果が大当りとなるときには、最終的な表示結果として決定した大当り図柄の組合せをそのまま仮停止表示すると大当りとなることが確定した表示が行なわれることとなるので、仮停止表示するリーチはずれ図柄を別途決定する必要がある。表示結果が大当りとなるときには、決定した大当り図柄の組合せを最終的な表示結果として用い、別途決定したリーチはずれ図柄を、仮停止表示するリーチはずれ図柄として用いる。なお、表示結果がスーパーリーチA,Bの変動パターンでリーチはずれとなるときには、最終的な表示結果として決定したリーチはずれ図柄の組合せを仮停止図柄として用いて仮停止表示するようにしてもよい。その場合には、仮停止図柄を別途決定する処理負担を軽減することができる。 Next, in S1555 to S1558, as described above, after the reach-removed symbol is temporarily stopped, the development effect to super reach, the transition effect to sudden hit, or the sudden change effect in battle reach is performed. A process of determining a detachable symbol for temporary stop display is performed. Such development patterns, transition effects, and sudden change effects that temporarily stop the out-of-reach symbols are included in the variation patterns of “Super Reach A, B”, “First and Second Sustainability”. Transition patterns for executing “transition” or “sudden switching at battle reach A and B” are applicable. In other words, when the display result is a fluctuation pattern other than the super reach A and B, the reach is shifted. After the determined reach shift pattern combination is temporarily stopped and displayed, the temporarily stopped display reach shift pattern is used as the final display result. If displayed, the reach-removed symbol can be finally displayed as the display result, so that it is not necessary to separately determine the reach-removed symbol for temporary stop display. On the other hand, when the display result is a variation in the reach pattern of super reach A and B, the reach is shifted. If the combination of the reach lost pattern determined as the final display result is displayed as a temporary stop, the temporary stop pattern and the final display result are displayed. However, in order to prevent this, it is necessary to separately determine the reach deviating symbol for temporary stop display. Therefore, when the display result is the reach variation due to the variation pattern of super reach A and B, the combination of the decided reach deviation design is used as the final display result, and the reach decision symbol that is determined separately is not used for the temporary stop display. Use as a symbol. In addition, when the display result is a big hit, if the combination of the big hit symbols determined as the final display result is displayed as a temporary stop as it is, a display that is determined to be a big hit will be performed. It is necessary to determine the design separately. When the display result is a big hit, the determined combination of big hit symbols is used as the final display result, and the separately determined reach-off symbol is used as the reach-off symbol for temporary stop display. In addition, when the display result is a reach deviation due to the variation pattern of the super reach A and B, a temporary stop display may be performed using the combination of the reach failure symbols determined as the final display result as a temporary stop symbol. In that case, it is possible to reduce the processing load for separately determining the temporary stop symbol.
S1555においては、「第1または第2突確移行」の演出が行なわれるか否かを判定する(S1555)。「第1または第2突確移行」の演出が行なわれるか否かは、受信した変動パターンコマンドにより「第1または第2突確移行」であることが示されているか否かに応じて判断する。 In S1555, it is determined whether or not an effect of “first or second sudden transition” is performed (S1555). Whether or not the effect of “first or second suspicion shift” is performed is determined depending on whether or not the received variation pattern command indicates “first or second susceptibility transition”.
S1555において、「第1または第2突確移行」の演出が行なわれると判断したときは後述するS1558に進み、「第1または第2突確移行」の演出が行なわれないと判断したときは、大当りとなるときまたははずれとなるときの「スーパーリーチAまたはB」の演出が行なわれるか否かを判定する(S1556)。大当りとなるときまたははずれとなるときの「スーパーリーチAまたはB」の演出が行なわれるか否かは、受信した変動パターンコマンドにより「スーパーリーチAまたはB」であることが示されているか否かに応じて判断する。S1556において「スーパーリーチAまたはB」の演出が行なわれると判断したときは、後述するS1558に進む。一方、S1556において「スーパーリーチAまたはB」の演出が行なわれないと判断したときは、「バトルリーチAまたはBで突然切替」の演出が行なわれるか否かを判定する(S1557)。「バトルリーチAまたはBで突然切替」の演出が行なわれるか否かは、受信した変動パターンコマンドにより「バトルリーチAまたはBで突然切替」であることが示されているか否かに応じて判断する。「バトルリーチAまたはBで突然切替」の演出が行なわれると判断したときは、後述するS1558に進む。一方、S1557において「バトルリーチAまたはBで突然切替」の演出が行なわれないと判断したときは、処理を終了する。 In S1555, if it is determined that the “first or second sudden transition” effect is performed, the process proceeds to S1558 described later. If it is determined that the “first or second sudden transition” effect is not performed, the big hit It is determined whether or not an effect of “super reach A or B” is performed when it becomes or becomes out of step (S1556). Whether or not the effect of “super reach A or B” at the time of a big hit or a loss is performed indicates whether or not “super reach A or B” is indicated by the received variation pattern command. Judge according to. If it is determined in S1556 that the effect of “super reach A or B” is performed, the process proceeds to S1558 described later. On the other hand, if it is determined in S1556 that the effect of “super reach A or B” is not performed, it is determined whether or not the effect of “sudden switching in battle reach A or B” is performed (S1557). Whether or not the effect of “sudden switching at battle reach A or B” is performed is determined based on whether or not the received variation pattern command indicates “sudden switching at battle reach A or B”. To do. If it is determined that the effect of “sudden switching at battle reach A or B” is performed, the process proceeds to S1558 described below. On the other hand, when it is determined in S1557 that the effect of “sudden switching at battle reach A or B” is not performed, the process ends.
前述したS1555、S1556、S1557のうち、いずれかの演出に該当すると判断したときは、S1558により、一旦リーチはずれの図柄が仮停止した後、スーパーリーチへの発展演出、突確大当りへの移行演出、または、15R大当りへの突然切替演出が行なわれるときにおいて仮停止表示するリーチはずれ図柄を決定する処理が行なわれ、処理を終了する。 When it is determined that any one of the above-described S1555, S1556, and S1557 is applicable, in S1558, after the reach-removed symbol is temporarily stopped, the development effect to super reach, the transition effect to sudden hit, Alternatively, when a sudden switching effect to 15R big hit is performed, a process of determining a reach-off symbol for temporary stop display is performed, and the process ends.
S1558では、リーチはずれの仮停止時の仮停止図柄を決定する。具体的にS1558では、前述した演出図柄変動開始処理において決定された演出図柄の最終的な表示結果となる図柄の組合せとの関係を考慮して、次のような場合分けに基づいて、仮停止リーチはずれ図柄を決定する。 In S1558, a temporary stop symbol at the time of temporary stop of reach is determined. Specifically, in S1558, a temporary stop is performed based on the following case classification in consideration of the relationship with the combination of symbols that will be the final display result of the effect symbols determined in the effect symbol variation start process described above. Reach out of design.
大当りとなるときに「スーパーリーチAまたはB」に発展する演出が行なわれるとき、および、「バトルリーチAまたはBで突然切替」する演出が行なわれるときには、仮停止リーチはずれ図柄の組合せのうち、リーチ図柄を形成する左,右図柄として、S506で決定した大当り図柄の左図柄,右図柄に基づいてリーチ図柄を決定する。そして、中図柄としては、S506での図柄の決定に用いられなかったSR1−3から数値データ(乱数)を抽出し、抽出した乱数に基づき、はずれ図柄決定用データテーブルを用いて決定する。抽出された乱数に対応する停止図柄が偶然リーチ図柄と同じ図柄となってしまう場合には、リーチはずれ図柄の組合せとなるように中図柄を1図柄ずらす補正をすることにより、中図柄が決定される。「スーパーリーチAまたはB」に発展する演出が行なわれて大当りとなるときには、このように決定された仮停止リーチはずれ図柄が一旦停止された後、「スーパーリーチAまたはB」に発展し、中図柄が再変動した後、S506で決定した大当り図柄の組合せが最終的な表示結果として表示される。また、「バトルリーチAまたはBで突然切替」する演出が行なわれて大当りとなるときには、このように決定された仮停止リーチはずれ図柄が一旦停止された後、煽り演出中に15R大当りの演出に突然切替る突然切替演出が行なわれ、仮停止リーチはずれ図柄がS506で決定した大当り図柄の組合せに切替えられ、その大当り図柄の組合せが最終的な表示結果として表示される。 When an effect that develops to “Super Reach A or B” is performed when a big hit is made, and when an effect that “suddenly switches with Battle Reach A or B” is performed, among the combinations of symbols that are temporarily stopped reach, Reach symbols are determined based on the left symbol and right symbol of the jackpot symbol determined in S506 as the left and right symbols forming the reach symbol. Then, as the middle symbol, numerical data (random number) is extracted from SR1-3 that was not used for the symbol determination in S506, and based on the extracted random number, it is determined using the outlier symbol determination data table. If the stop symbol corresponding to the extracted random number accidentally becomes the same symbol as the reach symbol, the middle symbol is determined by correcting the middle symbol by one symbol so that it becomes a combination of the reach symbol. The When an effect that develops to "Super Reach A or B" is performed and a big hit is made, after the temporary stop reach failure symbol determined in this way is temporarily stopped, it is developed to "Super Reach A or B" After the symbols have changed again, the jackpot symbol combination determined in S506 is displayed as the final display result. In addition, when an effect of “suddenly switching with Battle Reach A or B” is performed and a big hit is made, the temporary stop reach failure symbol determined in this way is temporarily stopped, and then the 15R big hit effect is given during the turn effect. A sudden switching effect is performed in which the temporary stop reach failure symbol is switched to the jackpot symbol combination determined in S506, and the jackpot symbol combination is displayed as a final display result.
はずれとなるときに「スーパーリーチAまたはB」に発展する演出が行なわれるときには、仮停止リーチはずれ図柄の組合せのうち、リーチ図柄を形成する左,右図柄として、S504で決定したリーチはずれ図柄の左図柄,右図柄に基づいてリーチ図柄を決定する。そして、中図柄としては、S504での図柄の決定に用いられなかったSR1−3から数値データ(乱数)を抽出し、抽出した乱数に基づき、はずれ図柄決定用データテーブルを用いて決定する。抽出された乱数に対応する停止図柄が偶然リーチ図柄と同じ図柄となってしまう場合には、リーチはずれ図柄の組合せとなるように中図柄を1図柄ずらす補正をすることにより、中図柄が決定される。「スーパーリーチAまたはB」に発展する演出が行なわれてはずれとなるときには、このように決定された仮停止リーチはずれ図柄が一旦停止された後、「スーパーリーチAまたはB」に発展し、中図柄が再変動した後、S504で決定したリーチはずれ図柄の組合せが最終的な表示結果として表示される。 When an effect that develops to “Super Reach A or B” is performed at the time of a loss, the reach determination symbol determined in S504 is used as the left and right symbols forming the reach symbol among the combinations of temporary stop reach failure symbols. The reach symbol is determined based on the left symbol and the right symbol. Then, as the middle symbol, numerical data (random number) is extracted from SR1-3 that was not used for the symbol determination in S504, and based on the extracted random number, the symbol symbol determination data table is used for determination. If the stop symbol corresponding to the extracted random number accidentally becomes the same symbol as the reach symbol, the middle symbol is determined by correcting the middle symbol by one symbol so that it becomes a combination of the reach symbol. The When an effect that develops to “Super Reach A or B” is performed and the result is a deviation, the temporary stop reach failure symbol determined in this way is temporarily stopped and then developed to “Super Reach A or B”. After the symbols have changed again, the reach-removed symbol combination determined in S504 is displayed as the final display result.
「第1,第2突確移行」となるときにおいては、最終的な表示結果が突確大当り図柄の組合せであるチャンス目の組合せとなる。したがって、「第1,第2突確移行」となるときにおいては、S504の場合と同様に、SR1−1〜SR1−3から抽出した乱数に基づき、はずれ図柄決定用データテーブルを用いてリーチはずれ図柄を決定することにより、仮停止リーチはずれ図柄の組合せを決定する。「第1,第2突確移行」の演出が行なわれるときには、このように決定された仮停止リーチはずれ図柄が一旦停止された後、最終的な表示結果として、停止図柄を、S507で決定されたチャンス目の図柄の組合せに差替える制御が行なわれる。 In the case of “first and second sudden transition”, the final display result is a combination of chance chances, which is a combination of the sudden winning symbols. Therefore, when the “first and second sudden transition” is performed, as in the case of S504, based on the random numbers extracted from SR1-1 to SR1-3, the reach failure symbol is determined using the loss symbol determination data table. Is determined, the combination of symbols for temporary stop reach is determined. When the “first and second collision probability transition” effects are performed, after the temporary stop reach failure symbol determined in this way is temporarily stopped, the stop symbol is determined in S507 as the final display result. Control is performed to replace the combination of symbols of chance.
たとえば、擬似連の変動パターンの場合には、最終の停止図柄を停止表示するときの再変動を行なう期間において、決定されたリーチはずれ図柄が仮停止され、前述したような演出が行なわれる。したがって、たとえば、擬似連ありで、かつ、スーパーリーチAを行なう変動パターンでの変動表示が実行されるときには、S1553で擬似連の仮停止図柄が決定され、かつ、S1558でリーチはずれ図柄の仮停止図柄が決定され、このように決定された擬似連チャンス目よりなる仮停止図柄を用いて擬似連での再変動が行なわれ、かつ、このように決定されたリーチはずれ図柄よりなる仮停止図柄を用いてスーパーリーチAが実行されることとなる。そして、「第1,第2突確移行」の演出が行なわれるときには、このように決定された仮停止リーチはずれ図柄が、突確大当り図柄の組合せとしてのチャンス目の図柄の組合せに差替えられる。 For example, in the case of a quasi-continuous variation pattern, the determined reach-off symbol is temporarily stopped during the period of re-variation when the last stop symbol is stopped and displayed, and the effect as described above is performed. Therefore, for example, when there is a quasi-continuation and a variation display is performed with a variation pattern in which super reach A is performed, a quasi-continuous temporary stop symbol is determined in S1553, and in S1558, the reach-out symbol is temporarily stopped. The symbol is determined, and the temporary stop symbol consisting of the pseudo-stop chance determined in this way is used to re-variate in the pseudo-continuous sequence, and the temporary stop symbol consisting of the out-of-reach symbol determined in this way is used. The super reach A will be executed. Then, when the effect of “first and second suspicious transition” is performed, the temporary stop reach out symbol determined in this way is replaced with a symbol combination of chances as a combination of the swift large hit symbol.
なお、「第1,第2突確移行」の演出が行なわれるときには、リーチはずれ図柄を、チャンス目の図柄の組合せに差替えず、そのまま最終停止させるようにしてもよい。そのようにする場合には、特定のリーチはずれ図柄の組合せ(たとえば、左,右図柄により形成されるリーチ図柄と、中図柄との図柄差が所定数の図柄の組合せ)を突確大当り図柄として定めておき、「第1,第2突確移行」の演出が行なわれるときにおいて、リーチはずれ図柄をそのような特定のリーチはずれ図柄の組合せに決定し、特定のリーチはずれ図柄の組合せが突確大当り図柄として扱われるようにすればよい。 In addition, when the effect of “first and second sudden transition” is performed, the reach failure symbol may be finally stopped without being replaced with the combination of symbols of chance. In such a case, a specific combination of symbols that are out of reach (for example, a combination of a symbol having a predetermined number of symbol differences between a symbol symbol formed by the left and right symbols and a symbol symbol) is determined as a random hit symbol. In addition, when the performance of “first and second suspicious transition” is performed, the reach losing symbol is determined to be a combination of such specific reach losing symbols, and the combination of the specific reach detaching symbols is used as the probability big hit symbol. It should be handled.
次いで、図40を参照して、演出制御用CPU101は、S515で選択した演出制御パターンに応じたプロセステーブルを選択する(S516)。そして、選択したプロセステーブルのプロセスデータ1におけるプロセスタイマ(演出設定プロセスタイマ)をスタートさせる(S517)。
Next, with reference to FIG. 40, the
ここで、図42および図43を用いてプロセステーブルについて説明する。図42は、プロセステーブルの構成例を示す説明図である。プロセステーブルとは、演出制御用CPU101が演出装置の制御を実行する際に参照するプロセスデータが設定されたテーブルである。すなわち、演出制御用CPU101は、プロセステーブルに設定されているプロセスデータにしたがって演出表示装置9等の演出装置(演出用部品)の制御を行なう。
Here, the process table will be described with reference to FIGS. FIG. 42 is an explanatory diagram of a configuration example of the process table. The process table is a table in which process data referred to when the
プロセステーブルは、プロセスタイマ設定値と表示制御実行データ、ランプ制御実行データ、および、音番号データの組合せが複数集まったデータとしてのプロセスデータにより構成されている。表示制御実行データには、演出図柄の変動表示の変動表示時間(変動時間)中の変動態様を構成する各変動の態様を示すデータ等(演出図柄の表示態様の他に演出表示装置9の表示画面における演出図柄以外の演出態様を含む。)が記載されている。具体的には、演出表示装置9の表示画面の変更に関わるデータが記載されている。
The process table includes process data as data obtained by collecting a plurality of combinations of process timer set values, display control execution data, lamp control execution data, and sound number data. The display control execution data includes, for example, data indicating each variation mode constituting the variation mode during the variation display time (variation time) of the variation display of the effect symbol (display of the
また、プロセスタイマ設定値には、その演出態様での演出時間が設定されている。演出制御用CPU101は、プロセステーブルを参照し、プロセスタイマ設定値に設定されている時間だけ表示制御実行データに設定されている態様で演出図柄を表示させるとともに表示画面に表示されるキャラクタ画像や背景を表示させる制御を行なう。
Further, the production time in the production mode is set in the process timer set value. The
また、演出制御用CPU101は、ランプ制御実行データおよび音番号データに設定されている態様で発光体の点滅を制御するとともに、スピーカ27からの音出力を制御する。
In addition, the
図42に示すプロセステーブルは、演出制御基板80におけるROM82に格納されている。また、プロセステーブルは、各演出制御パターンに応じて用意されている。
The process table shown in FIG. 42 is stored in the ROM 82 of the
図43は、プロセステーブルの内容にしたがって実行される演出を説明するための説明図である。演出制御用CPU101は、プロセステーブルにおける演出制御実行データにしたがって表示制御を実行する。すなわち、プロセスタイマ設定値に設定されたタイマ値に応じた時間が経過すると、プロセステーブルにおける次の演出制御実行データにしたがって、演出表示装置9、LED等の発光体、スピーカ27、可動部材78,84、および、振動モータ87a,87b,87cを制御する処理を繰返すことによって、1回の演出図柄の変動における演出が実現される。なお、変動期間中に制御対象にならない演出用部品に対応するデータ(たとえば、可動部材制御データ)には、ダミーデータ(制御を指定しないデータ)が設定されている。
FIG. 43 is an explanatory diagram for explaining effects performed according to the contents of the process table. The
図40を参照して、演出制御用CPU101は、S517の処理を実行したら、プロセスデータ1の内容(表示制御実行データ1、ランプ制御実行データ1、音番号データ1、可動部材制御データ1)にしたがって演出装置(演出用部品としての演出表示装置9、演出用部品としての各種ランプ、演出用部品としてのスピーカ27、および演出用部品としての可動部材78,84と振動モータ87a,87b,87c)の制御を開始する(S518)。たとえば、表示制御実行データにしたがって、演出表示装置9において変動パターンに応じた画像(演出図柄を含む。)を表示させるために、VDP109に指令を出力する。また、各種ランプを点灯/消灯制御を行なわせるために、ランプドライバ基板35に対して制御信号(ランプ制御実行データ)を出力する。また、スピーカ27からの音声出力を行なわせるために、音声出力基板70に対して制御信号(音番号データ)を出力する。また、可動部材制御データにしたがって、可動部材78,84と振動モータ87a,87b,87cを動作させるための駆動信号を出力する。
Referring to FIG. 40, when the
また、図44は、擬似連演出の変動パターンを実現する際の変動期間とプロセステーブルとの関係を示す説明図である。図44に示す例では、一例として、2回の仮停止期間が設けられ、3回の変動(初回変動も含めて)が実行される場合の例が示されている。図44に示すように、変動開始時から初回の仮停止時までの演出制御は、初回演出のプロセステーブルに設定されている演出制御実行データに基づいて実行され、初回の仮停止時から2回目の仮停止時までの演出制御は、2回目演出のプロセステーブルに設定されている演出制御実行データに基づいて実行され、2回目の仮停止時から図柄の最終停止時までの演出制御は、3回目演出のプロセステーブルに設定されている演出制御実行データに基づいて実行される。 FIG. 44 is an explanatory diagram showing the relationship between the variation period and the process table when realizing the variation pattern of the pseudo-continuous effect. The example shown in FIG. 44 shows an example in which two temporary stop periods are provided and three changes (including the initial change) are executed. As shown in FIG. 44, the production control from the start of the fluctuation to the first temporary stop is executed based on the production control execution data set in the process table of the first production, and the second time from the first temporary stop. The production control until the temporary stop is executed based on the production control execution data set in the process table of the second production, and the production control from the second temporary stop to the final stop of the symbol is 3 This is executed based on the production control execution data set in the process table of the second production.
なお、擬似連演出の変動表示が行なわれる場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、S516において、1回目の変動に応じたプロセステーブルを選択する。
In addition, when the fluctuating display of the pseudo-continuous effect is performed, the
図40を参照して、演出制御用CPU101は、変動時間タイマに、変動パターンコマンドで特定される変動時間に相当する値を設定する(S519)。なお、変動時間タイマは、演出図柄の変動を開始してから最終停止図柄を停止表示するまでの変動時間を計測するためのタイマである。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動中処理(S802)に対応した値にし(S520)、処理を終了する。
Referring to FIG. 40,
図45は、演出制御プロセス処理における演出図柄変動中処理(S802)を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 45 is a flowchart showing the effect symbol changing process (S802) in the effect control process.
演出図柄変動中処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、プロセスタイマの値を1減算するとともに(S841)、変動時間タイマの値を1減算する(S842)。そしてプロセスタイマがタイムアウトしているか否かを判断する(S843)。
In the effect symbol variation processing, the
プロセスタイマがタイムアウトするまで(S843N)は、S846に進む。S843においてプロセスタイマがタイムアウトしたと判断したときは(S843Y)、プロセスデータの切替えを行なう(S844)。すなわち、プロセステーブルにおける次に設定されているプロセスタイマ設定値をプロセスタイマに設定することによってプロセスタイマをあらためてスタートさせる(S844)。また、その次に設定されている表示制御実行データ、ランプ制御実行データ、音番号データおよび可動部材制御データ等のプロセスデータに基づいて演出装置(演出用部品)に対する制御状態を変更する等、次のプロセスデータの内容にしたがって、演出装置を制御する(S845)。これにより、決定された予告パターンによる予告演出を実行することができる。 Until the process timer times out (S843N), the process proceeds to S846. If it is determined in S843 that the process timer has timed out (S843Y), the process data is switched (S844). That is, the process timer is started again by setting the process timer set value set next in the process table in the process timer (S844). In addition, the control state for the effect device (effect parts) is changed based on process data such as display control execution data, lamp control execution data, sound number data, and movable member control data set next. The rendering device is controlled in accordance with the contents of the process data (S845). Thereby, the notice effect by the decided notice pattern can be executed.
このように、プロセスタイマを用いて時間管理を行なって、プロセスデータを順次切替えていくことにより、図43および図44に示すような変動表示制御を含む各種演出制御が行なわれる。 In this way, by performing time management using the process timer and sequentially switching the process data, various effect controls including variable display control as shown in FIGS. 43 and 44 are performed.
S846においては、操作ボタン130の操作に応じて演出をする操作演出処理が行なわれる。S847で、演出制御用CPU101は、変動時間タイマの値に基づいて、変動時間タイマがタイムアウトしたか否かを確認する(S847)。変動時間タイマがタイムアウトしていれば(S847でY)、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動停止処理(S803)に応じた値に更新する(S849)。一方、変動時間タイマがタイムアウトしていないときは(S847でN)、図柄確定指定コマンドを受信したことを示す確定コマンド受信フラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(S848)。確定コマンド受信フラグがセットされていないときは(S848でN)、演出図柄変動中処理が終了する。一方、確定コマンド受信フラグがセットされているときは(S848でY)、S849に移行する。変動時間タイマがタイムアウトしていなくても(S848でN)、図柄確定指定コマンドを受信したら変動を停止させる制御に移行するので、たとえば、基板間でのノイズ等に起因して長い変動時間を示す変動パターンコマンドを受信したような場合でも、正規の変動時間経過時(特別図柄の変動終了時)に、演出図柄の変動を終了させることができる。
In S846, an operation effect process is performed in which an effect is generated according to the operation of the
なお、「擬似連」の演出を含む変動パターンに基づいてS841〜S845の処理を実行する部分は、再変動演出を実行する再変動演出制御処理に相当する。 In addition, the part which performs the process of S841-S845 based on the fluctuation pattern containing the effect of a "pseudo ream" is equivalent to the re-change effect control process which performs a re-change effect.
図46は、演出制御プロセス処理における演出図柄変動停止処理(S803)を示すフローチャートである。演出図柄変動停止処理において、まず、演出制御用CPU101は、演出図柄の停止図柄を表示していることを示す停止図柄表示フラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(S880)。停止図柄表示フラグがセットされていれば、S887に移行する。この実施の形態では、演出図柄の停止図柄として大当り図柄を表示した場合には、S886で停止図柄表示フラグがセットされる。そして、ファンファーレ演出を実行するときに停止図柄表示フラグがリセットされる。従って、停止図柄表示フラグがセットされているということは、大当り図柄を停止表示したがファンファーレ演出をまだ実行していない段階であるので、S881〜S886の演出図柄の停止図柄を表示する処理を実行することなく、S887に移行する。
FIG. 46 is a flowchart showing the effect symbol variation stop process (S803) in the effect control process. In the effect symbol variation stop process, first, the
停止図柄表示フラグがセットされていない場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、演出図柄の変動停止を指示する演出制御コマンド(図柄確定指定コマンド)を受信したことを示す確定コマンド受信フラグがセットされているか否か確認する(S881)。確定コマンド受信フラグがセットされている場合には、決定されている停止図柄(はずれ図柄または大当り図柄)を停止表示させる制御を行なう(S882)。
When the stop symbol display flag is not set, the
なお、この実施の形態では、演出制御用CPU101が、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から図柄確定指定コマンドを受信したことに応じて演出図柄を停止表示する制御を行なうが、変動時間タイマがタイムアップしたことに基づいて演出図柄を停止表示するようにしてもよい。
In this embodiment, the
S882の処理で大当り図柄を表示しなかった場合(すなわち、はずれ図柄を表示した場合)には(S883)、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(S800)に応じた値に更新する(S884)。
When the jackpot symbol is not displayed in the processing of S882 (that is, when the loss symbol is displayed) (S883), the
S882の処理で大当り図柄を停止表示した場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、停止図柄表示フラグをセットし(S886)、大当り開始指定コマンドを受信したことを示す大当り開始指定コマンド受信フラグ(大当り開始1指定コマンド受信フラグまたは大当り開始2指定コマンド受信フラグ)または突確開始指定コマンドを受信したことを示す突確開始指定コマンド受信フラグがセットされているか否か確認する(S887)。大当り開始指定コマンド受信フラグまたは突確開始指定コマンド受信フラグがセットされている場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、停止図柄表示フラグをリセットし(S888)、ファンファーレ演出に応じたプロセステーブルを選択する(S889)。
When the jackpot symbol is stopped and displayed in the process of S882, the
なお、演出制御用CPU101は、大当り開始指定コマンド受信フラグまたは突確開始指定コマンド受信フラグがセットされていた場合には、セットされていたフラグをリセットする。また、S889の処理では、演出制御用CPU101は、通常大当りまたは確変大当りに決定されているとき(具体的には、表示結果2指定コマンドまたは表示結果3指定コマンドを受信しているとき)には、「15回開放遊技開始報知」に対応するプロセステーブルを選択し、突確大当りに決定されているとき(具体的には、表示結果4指定コマンドを受信しているとき)は、「2回開放遊技開始報知」に対応するプロセステーブルを選択する。そして、プロセスタイマ設定値をプロセスタイマに設定することによってプロセスタイマをスタートさせ(S890)、プロセスデータ1の内容(表示制御実行データ1、ランプ制御実行データ1、音番号データ1、可動部材制御データ1)に従って演出装置(演出用部品としての演出表示装置9、演出用部品としての各種ランプ、演出用部品としてのスピーカ27、および演出用部品としての可動部材78,84、振動モータ87a,87b,87c)の制御を実行する(S891)。その後、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を大当り表示処理(S804)に応じた値に更新する(S892)。
When the big hit start designation command reception flag or the sudden start designation command reception flag is set, the
なお、上記の実施の形態では、変動表示部として2つの特別図柄表示器(第1特別図柄表示器8aおよび第2特別図柄表示器8b)を備えた遊技機を例にしたが、1つの特別図柄表示器が設けられた遊技機にも本発明を適用することができる。
In the above embodiment, a gaming machine provided with two special symbol indicators (first
また、上記の実施の形態では、演出装置を制御する回路が搭載された基板として、演出制御基板80、音声出力基板70およびランプドライバ基板35が設けられているが、演出装置を制御する回路を1つの基板に搭載してもよい。さらに、演出表示装置9等を制御する回路が搭載された第1の演出制御基板(表示制御基板)と、その他の演出装置(ランプ、LED、スピーカ27等)を制御する回路が搭載された第2の演出制御基板との2つの基板を設けるようにしてもよい。
In the above-described embodiment, the
また、上記の実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して直接コマンドを送信していたが、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が他の基板(たとえば、図3に示す音声出力基板70やランプドライバ基板35等、または音声出力基板70に搭載されている回路による機能とランプドライバ基板35に搭載されている回路による機能とを備えた音/ランプ基板)に演出制御コマンドを送信し、他の基板を経由して演出制御基板80における演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信されるようにしてもよい。その場合、他の基板においてコマンドが単に通過するようにしてもよいし、音声出力基板70、ランプドライバ基板35、音/ランプ基板にマイクロコンピュータ等の制御手段を搭載し、制御手段がコマンドを受信したことに応じて音声制御やランプ制御に関わる制御を実行し、さらに、受信したコマンドを、そのまま、またはたとえば、簡略化したコマンドに変更して、演出表示装置9を制御する演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信するようにしてもよい。その場合でも、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、上記の実施の形態における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から直接受信した演出制御コマンドに応じて表示制御を行なうのと同様に、音声出力基板70、ランプドライバ基板35または音/ランプ基板から受信したコマンドに応じて表示制御を行なうことができる。
In the above-described embodiment, the
〔第2実施形態〕
次に、第2実施形態を説明する。第2実施形態においては、図11および図12に示したような煽り演出、発展演出、および、突確移行演出のような発展可否演出を、可動部材により行なう例を説明する。可動部材としては、具体的に可動部材84が用いられる。
[Second Embodiment]
Next, a second embodiment will be described. In the second embodiment, an example will be described in which a development effect is produced by a movable member, such as a turning effect, a development effect, and a sudden transition effect as shown in FIGS. Specifically, the
図47は、可動部材84により発展可否演出を行なうときの可動部材84の演出動作例を示す説明図である。図47では、(A)〜(C)に、発展可否演出を行なうときの可動部材84の演出動作の状態が示されている。図47において、演出表示装置9の周囲の飾り部については、可動部材78、上演出LED85a、中演出LED85bおよび下演出LED85cの図示を省略している。
FIG. 47 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of the operation of the
図47を参照して、可動部材84は、可動部材予告が行なわれるときに、(A)に示すような可動部材動作Aと、(B)に示すような可動部材動作Bと、(C)に示すような可動部材動作Cとのいずれかの動作態様で動作させられる。(A)に示す可動部材動作Aは、第1回転速度としての低速度で回転動作する演出動作パターンである。(B)に示す可動部材動作Bは、第2回転速度としての中速度(第1回転速度よりも高速度)で回転動作する演出動作パターンである。(C)に示す可動部材動作Cは、第3回転速度としての高速度(第2回転速度よりも高速度)で回転動作する演出動作パターンである。
Referring to FIG. 47, the
可動部材84は、可動部材動作A〜Cのような回転動作を図47のような右方向の回転(右回転)と、その逆方向の左方向の回転(左回転)とを行なうことが可能である。図11の(C)〜(G)のようなリーチ演出が行なわれているときには、可動部材84が停止させられている。可動部材84を左回転させることにより、図12の(H),(J),(K),(L)のようなスーパーリーチAに関する発展可否演出が行なわれる。また、可動部材84を右回転させることにより、図12の(I),(M),(K),(L)のようなスーパーリーチBに関する発展可否演出が行なわれる。
The
スーパーリーチAに関する発展可否演出は、次のように行なわれる。図12の(H)に示す第1煽り演出として、可動部材84の低速の可動部材動作Aを左回転で実行させる。その後、図12の(J)のようにスーパーリーチAへの発展演出を行なうときには、可動部材84の高速の可動部材動作Cを左回転で実行させる。また、図12の(L)のように第1突確移行演出を行なうときには、可動部材84の中速の可動部材動作Bを左回転で実行させる。また、図12の(K)のように進行終了演出を行なうときには、可動部材84の動作を停止させる。また、突然切替演出を行なうときには、低速の可動部材動作Aの途中で可動部材84を逆回転させる。
The development propriety effect regarding Super Reach A is performed as follows. As the first roaring effect shown in FIG. 12H, the low-speed movable member operation A of the
スーパーリーチBに関する発展可否演出は、次のように行なわれる。図12の(I)に示す第2煽り演出として、可動部材84の低速の可動部材動作Aを右回転で実行させる。その後、図12の(M)のようにスーパーリーチBへの発展演出を行なうときには、可動部材84の高速の可動部材動作Cを右回転で実行させる。また、図12の(L)のように第2突確移行演出を行なうときには、可動部材84の中速の可動部材動作Bを右回転で実行させる。また、図12の(K)のように進行終了演出を行なうときには、可動部材84の動作を停止させる。また、突然切替演出を行なうときには、低速の可動部材動作Aの途中で可動部材84を逆回転させる。
The development propriety effect regarding Super Reach B is performed as follows. As the second turning effect shown in (I) of FIG. 12, the low-speed movable member operation A of the
このような可動部材84を用いた発展可否演出は、前述の演出制御プロセス処理において用いるプロセステーブルに、このような可動部材84の動作制御を実行する演出制御実行データを設定しておき、その演出制御実行データに基づいて、演出制御用CPU101が、演出制御プロセス処理において、前述のように可動部材84を制御することにより実現される。このような可動部材84を用いた発展可否演出は、第1実施形態に示したような演出表示装置9での画像を用いた発展可否演出の代わりに実行される。このようにすれば、演出のバリエーションを豊富化することができる。なお、このような可動部材84を用いた発展可否演出は、第1実施形態に示したような演出表示装置9での画像を用いた発展可否演出と並行して実行するようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、画像と可動部材とを組合せた演出により、演出に遊技者の注目を集めることができ、演出の面白みを向上させることができる。
For the development availability effect using such a
なお、第2実施形態で説明した可動部材を用いた発展可否演出は、1つの可動部材で行なわずに複数の可動部材を用いて行なうようにしてもよい。たとえば、第1の可動部材をスーパーリーチAに関する発展可否演出を行なうために設けるとともに、第2の可動部材をスーパーリーチBに関する発展可否演出を行なうために設け、これら2つの可動部材で、スーパーリーチAに関する発展可否演出と、スーパーリーチBに関する発展可否演出とを区別して実行するように制御すればよい。 In addition, the development propriety effect using the movable member described in the second embodiment may be performed using a plurality of movable members instead of using one movable member. For example, a first movable member is provided for performing the possibility of development regarding Super Reach A, and a second movable member is provided for performing the possibility of development regarding Super Reach B. With these two movable members, What is necessary is just to control so that the development propriety effect regarding A and the development propriety effect regarding the super reach B may be distinguished and executed.
また、第2実施形態で説明した発展可否演出に用いる可動部材は、回転動作をするものに限らず、振動、揺動、摺動等、一般的な可動部材が動作しうる動作態様であれば、どのような動作態様で動作する可動部材を用いてもよい。 Moreover, the movable member used for the development propriety described in the second embodiment is not limited to a rotating operation, and any operation mode in which a general movable member can operate, such as vibration, swinging, and sliding. A movable member that operates in any operation mode may be used.
次に、前述した実施の形態により得られる主な効果を説明する。
(1) 図11および図12に示すように、リーチ変動パターンにおいて、リーチ演出を実行してリーチはずれの表示結果で一旦停止した後に、実行中の変動表示が継続するか否かを報知する発展可否演出が行なわれる。発展可否演出としては、図12に示すように、ノーマルリーチと比べて15R大当りとなるときに実行される割合が高いスーパーリーチA,Bに発展することを報知する第1の発展演出(スーパーリーチA,Bの発展演出)を行なうことが可能であるので、リーチはずれの表示結果で一旦停止した後スーパーリーチへの発展を煽ることにより、遊技者の大当りへの期待感を高めることができる。さらに、図12に示すように、発展可否演出としては、単にリーチ演出がスーパーリーチに発展するか否かの演出に留まらず、発展可否演出後に突確大当りに移行することを報知する第2の発展演出(突確移行演出)も行なうことが可能であるので、演出に意外性が生じ、スーパーリーチへの移行を煽ることにより、遊技者の大当りへの期待感を高めることができる。このようにリーチ演出において遊技状態への期待感を高めることにより、リーチ演出における遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。
Next, main effects obtained by the embodiment described above will be described.
(1) As shown in FIG. 11 and FIG. 12, in the reach variation pattern, after the reach effect is executed and temporarily stopped with the display result of losing reach, it is notified whether or not the variation display being executed continues. A propriety effect is performed. As shown in FIG. 12, the first development effect (Super Reach A) that informs the development of Super Reach A and B, which is executed at a rate of 15R big hit as compared to Normal Reach, as shown in FIG. , B development effect), it is possible to increase the player's sense of expectation for a big hit by temporarily stopping with the display result of out-of-reach and encouraging the development to super reach. Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 12, the development possibility / prohibition effect is not limited to the effect of whether or not the reach effect is developed into a super reach, but the second development for notifying that a sudden big hit is made after the effect of development / impossibility. Since it is also possible to produce an effect (progressive transition effect), the production is unexpected, and the player's sense of expectation for a big hit can be enhanced by encouraging the transition to super reach. Thus, the interest of the game in the reach production can be improved by increasing the expectation to the gaming state in the reach production.
(2) このような構成によれば、図11および図12に示すように、リーチ変動パターンにおいて、リーチ演出を実行して特定表示結果とならない状態で一旦停止した後に、実行中の変動表示が継続するか否かを報知する発展可否演出が行なわれる。そして、図12に示すように、スーパーリーチの演出がスーパーリーチA,Bのように複数種類設けられ、発展可否演出において表示されるキャラクタa〜dの画像による表示態様(キャラクタa,bのようにキャラクタの動作が異なる演出、キャラクタc,dのように表示されるキャラクタ自体が異なる演出)に応じて発展先のスーパーリーチの種類が異なるので、リーチはずれの表示結果で一旦停止した後、キャラクタの画像による表示態様に応じて、発展先の特別なリーチ演出への発展を煽ることにより、変動表示の演出進行のバリエーションを豊富化することができる。これにより、遊技者がリーチ演出に飽きてしまわないようにすることができ、リーチ演出における遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 (2) According to such a configuration, as shown in FIGS. 11 and 12, in the reach variation pattern, after the reach effect is executed and the specific display result is not temporarily stopped, the variation display being executed is performed. A development propriety effect informing whether or not to continue is performed. Then, as shown in FIG. 12, there are provided a plurality of types of super reach effects such as super reach A and B, and display modes (such as characters a and b) of characters a to d displayed in the development propriety effect. Since the type of super-reach at the development destination is different depending on the effect of the character's movement and the effect of the characters c and d displayed in different characters), Depending on the display mode of the image, the development of a special reach production at the development destination can be encouraged to enrich the variation in the production progress of the variable display. Thereby, it is possible to prevent the player from getting bored with the reach production, and to improve the interest of the game in the reach production.
(3) 図14〜図20において、大当りとなるときに選択される変動パターンの割合がキャラクタa>b、かつ、はずれとなるときに選択される変動パターンの割合がキャラクタb>aであり、大当りとなるときに選択されるスーパーリーチ種類の割合がスーパーリーチA>B、かつ、はずれとなるときに選択されるスーパーリーチ種類の割合がスーパーリーチB>Aであり、キャラクタの種類と発展先のスーパーリーチの種類との組合せに応じて大当りとなる割合が異なるので、キャラクタの画像により大当りへの期待が異なるため、表示されたキャラクタの画像に基づいて遊技者の期待感を高めることができる。また、キャラクタ画像を表示するだけで遊技者が大当りへの期待感を持てなくなることが防がれる。これにより、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 (3) In FIGS. 14 to 20, the ratio of the variation pattern selected when the big hit is the character a> b, and the ratio of the variation pattern selected when the loss occurs is the character b> a. The ratio of the super reach type selected when the big hit is super reach A> B, and the ratio of the super reach type selected when the hit is lost is super reach B> A. Since the ratio of winning big hits differs depending on the combination with the type of super reach, the expectation for big hits differs depending on the character image, so that the player's expectation can be enhanced based on the displayed character image . Further, it is possible to prevent the player from having a sense of expectation for the big hit only by displaying the character image. Thereby, the interest of a game can be improved.
(4) 図29のS101,S102と、S104,S105とに示すように、変動パターンを選択するための手段が、変動パターン種別を決定する手段と、決定された変動パターン種別に属する変動パターンのうちから実行する変動パターンを決定する手段とに分けられている。これにより、変動パターン種別を決定する手段により決定可能な変動パターン種別の数と、変動パターンを決定する手段により決定可能な変動表示パターン数との組合せにより、多種類の変動パターンを設定して選択的に用いることができるようになる。また、変動パターン種別を決定する手段における種別決定の割合を変更するだけで、各変動パターン種別に属する各変動表示パターンを選択する割合を変更しなくても、変動パターン種別ごとの変動パターンの出現割合を変更することができるようになる。これにより、変動パターンに関し、実行可能とする変動パターン数の変更設定、および、変動パターンの出現割合の変更設定が容易になる。 (4) As shown in S101, S102 and S104, S105 of FIG. 29, the means for selecting a fluctuation pattern includes a means for determining a fluctuation pattern type, and a change pattern belonging to the determined fluctuation pattern type. It is divided into means for determining a variation pattern to be executed from inside. As a result, various types of variation patterns can be set and selected by a combination of the number of variation pattern types that can be determined by means for determining the variation pattern type and the number of variation display patterns that can be determined by the unit for determining variation patterns. Can be used automatically. In addition, the appearance of the variation pattern for each variation pattern type can be changed without changing the proportion for selecting each variation display pattern belonging to each variation pattern type only by changing the proportion of the type determination in the means for determining the variation pattern type. You will be able to change the percentage. Thereby, regarding the variation pattern, the change setting of the number of variation patterns that can be executed and the change setting of the appearance ratio of the variation pattern become easy.
(5) 図13〜図21に示すように、大当りに制御する決定がされたときに加えて、大当りに制御しない決定がされ、かつ、リーチ演出を実行しないときに、擬似連の演出を含む変動パターンの種別を選択可能であるので、変動表示の演出のバリエーションを豊富化することができるが、図29のS101,S102と、S104,S105とに示すように、変動パターンを選択するための手段が、変動パターン種別を決定する手段と、決定された変動パターン種別に属する変動パターンのうちから実行する変動パターンを決定する手段とに分けられていることにより、パチンコ遊技機1の設計段階において、変動表示の演出の設定変更時における処理負担を増大させることなく、変動表示の演出のバリエーションを豊富化することができる。
(5) As shown in FIG. 13 to FIG. 21, in addition to when the decision to control the big hit is made, when the decision not to control the big hit is made and the reach production is not executed, the pseudo-continuous production is included. Since the type of variation pattern can be selected, variations in the effects of variation display can be enriched. However, as shown in S101, S102 and S104, S105 of FIG. 29, the variation pattern can be selected. In the design stage of the
(6) 図16、図18等に示すように、発展可否演出は、複数段階で発展するリーチ演出のうち第2段階目の演出が実行される以前に、大当り遊技状態に移行することを示す移行演出としての突然切替演出を含むことにより、複数段階で発展するリーチ演出の途中の段階で大当り遊技状態への移行演出が行なわれることとなるので、意外性がある演出により遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 (6) As shown in FIG. 16, FIG. 18, etc., the development allowance / prohibition effect indicates a transition to the big hit game state before the second stage effect is executed among the reach effects that develop in a plurality of stages. By including a sudden switching effect as a transition effect, the transition effect to the big hit gaming state will be performed in the middle of the reach effect that develops in multiple stages, so the fun of the game is improved by an unexpected effect Can be made.
(7) 図14〜図20において、第1煽り演出〜第4煽り演出のそれぞれで、発展演出ありの変動パターンの選択割合と、突確移行演出の変動パターンの選択割合とが異なることを示したように、発展可否演出は、発展演出ありの変動パターンの実行割合と、突確移行演出の変動パターンの実行割合とが、発展可否演出の種類に応じて異なる。これにより、発展可否演出の種類ごとに演出の実行割合が一定ではないことに基づいて、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。 (7) In FIGS. 14 to 20, it is shown that the selection ratio of the variation pattern with the development effect is different from the selection ratio of the variation pattern of the sudden transition effect in each of the first to fourth production effects. In this way, in the development availability effect, the execution rate of the variation pattern with the development effect and the execution rate of the variation pattern of the sudden transition effect differ depending on the type of the development availability effect. Thereby, the interest of the game can be improved based on the fact that the execution ratio of the effect is not constant for each type of the development possibility effect.
(8) 図7(B),(C)で第1特別図柄について突確大当りとする決定がされるが、第2特別図柄については、突確大当りとする決定がされないので、第2特別図柄表示器8bにおいて表示結果が大当り表示結果となるときには突確大当り遊技状態に制御されない。そして、図13〜図21で、非確変時に用いる変動パターンの判定テーブルでは、発展演出および突確移行演出を実行する変動パターンが選択されるが、確変時に用いる変動パターンの判定テーブルでは、発展演出または突確移行演出を実行する変動パターンが選択されないようにデータが設定されているので、確変状態でないときにおいて発展可否演出が実行され、確変状態であるときにおいて発展可否演出が実行されない。これにより、確変状態において、突確大当り遊技状態に制御される可能性がないにも関わらず無駄な発展可否演出が行なわれずに済むようにするこができ、現実性がない発展可否演出により遊技者の不快感を誘発するおそれが生じないようにすることができる。 (8) In FIGS. 7B and 7C, the first special symbol is determined to be a big hit, but the second special symbol is not decided to be a big hit, so the second special symbol indicator When the display result becomes the big hit display result in 8b, the game is not controlled to the sudden big hit gaming state. In FIG. 13 to FIG. 21, the variation pattern for executing the development effect and the sudden transition effect is selected in the variation pattern determination table used at the time of non-probability change. Since the data is set so that the variation pattern for executing the sudden transition effect is not selected, the development propriety effect is executed when not in the probability variation state, and the development propriety effect is not executed in the probability variation state. As a result, in the probability variation state, it is possible to prevent the useless development propriety effect from being performed in spite of the possibility that the game state is not controlled suddenly. It is possible to prevent the possibility of causing discomfort.
(9) 図47に示すように、発展可否演出が、可動部材84を動作させることにより行なわれるので、演出表示装置9における変動表示の表示状態に影響を受けることなく発展可否演出を行なうことができるため、発展可否演出による演出効果を向上させることができる。
(9) As shown in FIG. 47, the development propriety effect is performed by operating the
次に、以上に説明した実施の形態の変形例や特徴点等を以下に列挙する。
(1) 上記の各実施の形態では、演出装置を制御する回路が搭載された基板として、演出制御基板80、音声出力基板70およびランプドライバ基板35が設けられているが、演出装置を制御する回路を1つの基板に搭載してもよい。さらに、演出表示装置9等を制御する回路が搭載された第1の演出制御基板(表示制御基板)と、その他の演出装置(ランプ、LED、スピーカ27など)を制御する回路が搭載された第2の演出制御基板との2つの基板を設けるようにしてもよい。
Next, modifications, feature points, and the like of the embodiment described above are listed below.
(1) In each of the above embodiments, the
(2) 上記の各実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して直接コマンドを送信していたが、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が他の基板(たとえば、図3に示す音声出力基板70やランプドライバ基板35など、または音声出力基板70に搭載されている回路による機能とランプドライバ基板35に搭載されている回路による機能とを備えた音/ランプ基板)に演出制御コマンドを送信し、他の基板を経由して演出制御基板80における演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信されるようにしてもよい。その場合、他の基板においてコマンドが単に通過するようにしてもよいし、音声出力基板70、ランプドライバ基板35、音/ランプ基板にマイクロコンピュータ等の制御手段を搭載し、制御手段がコマンドを受信したことに応じて音声制御やランプ制御に関わる制御を実行し、さらに、受信したコマンドを、そのまま、またはたとえば簡略化したコマンドに変更して、演出表示装置9および飾り図柄表示器9a,9bを制御する演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信するようにしてもよい。その場合でも、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、上記の各実施の形態における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から直接受信した演出制御コマンドに応じて表示制御を行なうのと同様に、音声出力基板70、ランプドライバ基板35または音/ランプ基板から受信したコマンドに応じて表示制御を行なうことができる。
(2) In each of the embodiments described above, the
(3) 演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560からの変動パターンコマンドに基づいて、演出用部品としての演出表示装置9で、図柄変動指定コマンドで特定される特別図柄表示器に対応した予告演出を実行するように構成されているので、2つの特別図柄表示器(特別図柄表示器8a、特別図柄表示器8b)が設けられていても、遊技者に、遊技の進行状況(いずれの変動表示手段における変動表示に対応する演出が行なわれているのか等)を把握させやすくすることができる。
(3) Based on the variation pattern command from the
(4) 演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560からの変動パターンコマンドに基づいて、演出用部品としての演出表示装置9で、図柄変動指定コマンドで特定される特別図柄表示器に対応した変動態様による変動表示演出を実行するように構成されているので、2つの特別図柄表示器(第1特別図柄表示器8a、第2特別図柄表示器8b)が設けられていても、遊技者に、遊技の進行状況(いずれの特別図柄表示器における変動表示に対応する演出が行なわれているのか等)を把握させやすくすることができるとともに、遊技のバリエーションを豊富にすることができる。
(4) Based on the variation pattern command from the
(5) 上記の各実施の形態では、飾り図柄表示器として2つのLEDからなる表示器が用いられていたが、飾り図柄表示器は、そのような構成のものに限られない。たとえば、1つ以上の7セグメントLEDで構成してもよい。また、飾り図柄表示器が設けられていない遊技機も、本発明を適用可能である。 (5) In each of the above-described embodiments, a display composed of two LEDs is used as a decorative symbol display. However, the decorative symbol display is not limited to such a configuration. For example, you may comprise one or more 7 segment LED. In addition, the present invention can also be applied to a gaming machine that is not provided with a decorative symbol display.
(6) 前述した実施の形態は、入賞球の検出に応答して所定数の賞球を払い出す払出式遊技機に限定されるものではなく、遊技球を封入し入賞球の検出に応答して得点を付与する封入式遊技機にも適用することができる。 (6) The embodiment described above is not limited to a payout type gaming machine that pays out a predetermined number of prize balls in response to detection of a winning ball, but responds to detection of a winning ball by enclosing a gaming ball. It can also be applied to enclosed game machines that give points.
(7) 前述した実施の形態は、パチンコ遊技機1の動作をシミュレーションするゲーム機などの装置にも適用することができる。前述した実施の形態を実現するためのプログラム及びデータは、コンピュータ装置等に対して、着脱自在の記録媒体により配布・提供される形態に限定されるものではなく、予めコンピュータ装置等の有する記憶装置にプリインストールしておくことで配布される形態を採っても構わない。さらに、本発明を実現するためのプログラム及びデータは、通信処理部を設けておくことにより、通信回線等を介して接続されたネットワーク上の、他の機器からダウンロードすることによって配布する形態を採っても構わない。そして、ゲームの実施形態も、着脱自在の記録媒体を装着することにより実行するものだけではなく、通信回線等を介してダウンロードしたプログラム及びデータを、内部メモリ等に一旦格納することにより実行可能とする形態、通信回線等を介して接続されたネットワーク上における、他の機器側のハードウェア資源を用いて直接実行する形態としてもよい。さらには、他のコンピュータ装置等とネットワークを介してデータの交換を行なうことによりゲームを実行するような形態とすることもできる。
(7) The above-described embodiment can also be applied to an apparatus such as a game machine that simulates the operation of the
(8) なお、前述したように特別図柄プロセス処理において始動口スイッチ通過処理を第1特別図柄用の処理と第2特別図柄用の処理とに分けて設けるときには、たとえば大当り判定をする処理等の一部の処理については、共通の処理ルーチンを実行することにより共通化するようにしてもよい。 (8) As described above, in the special symbol process, when the start port switch passing process is provided separately for the first special symbol process and the second special symbol process, for example, a process for determining a big hit Some processes may be made common by executing a common process routine.
(9) 前述した実施の形態においては、第1特別図柄表示器8aと第2特別図柄表示器8bとを同じ種類の表示器(7セグメントLED)で構成する例を示した。しかし、これに限らず、第1特別図柄表示器8aと第2特別図柄表示器8bとは、異なる種類の表示器で構成するようにしてもよい。具体的には、第1特別図柄表示器8aと第2特別図柄表示器8bとは、一方を7セグメント表示器で構成し、他方をドットマトリックス表示器で構成してもよい。また、第1特別図柄表示器8aと第2特別図柄表示器8bとは、一方を7セグメント表示器で構成し、他方を前述の飾り図柄表示器9a,9bのようなLED表示器で構成してもよい。
(9) In embodiment mentioned above, the example which comprises the 1st
(10) 前述した実施の形態においては、遊技球がゲート32を通過したことが検出されたときに変動表示される普通図柄表示器10における変動表示の表示結果が所定の表示結果(当り図柄)となったときに可変入賞球装置15が開状態に制御される例を示した。しかし、これに限らず、普通図柄表示器10を設けず、遊技球がゲート32を通過したことが検出されたときに、可変入賞球装置15が、開状態に制御されるようにしてもよい。
(10) In the above-described embodiment, the display result of the variable display on the
(11) 前述した実施の形態においては、遊技球がゲート32を通過したことが検出されたときに変動表示される普通図柄表示器10における変動表示の表示結果が所定の表示結果(当り図柄)となったときに可変入賞球装置15が開状態に制御される例を示した。しかし、これに限らず、普通図柄表示器10を設けず、遊技球がゲート32を通過したことが検出されたときに、可変入賞球装置15が、開状態に制御されるようにしてもよい。
(11) In the embodiment described above, the display result of the variable display on the
(12) 前述した実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が、擬似連の具体的な変動パターン(変動回数等の変動に関する情報を特定する変動パターン)を決定して演出制御コマンドでその変動パターンを指示し、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が、その演出制御コマンドに基づいて擬似連の具体的な変動パターン(変動回数等の変動に関する情報を特定する変動パターン)を認識し、擬似連の変動パターンでの変動表示を実行する例を示した。しかし、これに限らず、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が、擬似連の具体的な変動パターン(再変動の報知演出を含む演出パターン)を決定するようにしてもよい。たとえば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560の側において、決定した変動パターンを示す変動パターンコマンドを送信し、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100の側で、受信した変動パターンコマンドと対応して記憶された擬似連の有無、および、擬似連での変動回数の情報に基づいて、擬似連の具体的な変動パターンを決定すればよい。
(12) In the above-described embodiment, the
(13) 前述した実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が擬似連の変動回数を決定する例を示したが、これに限らず、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が擬似連の変動回数を決定するようにしてもよい。たとえば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が、擬似連を実行するか否かを特定可能な変動パターンコマンドを送信し、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が、擬似連を実行することが特定された変動パターンコマンドを受信したときに、擬似連の変動回数を決定する。
(13) In the above-described embodiment, an example in which the
(14) 前述した実施の形態では、識別情報としての図柄を変動表示する表示装置として、特別図柄の表示装置、飾り図柄の表示装置、および、演出図柄の表示装置の3種類の表示装置を設けた例を示した。しかし、これに限らず、識別情報としての図柄を変動表示する表示装置として、前述した演出図柄を表示する演出表示装置9のような画像を表示する1つの表示装置のみを設け、その表示装置により、前述したような特別図柄、飾り図柄、および、演出図柄を1種類の図柄に統一して、当該図柄の変動表示および各種の演出画像の表示を行なうようにしてもよい。
(14) In the embodiment described above, three types of display devices, a special symbol display device, a decorative symbol display device, and an effect symbol display device, are provided as display devices for variably displaying symbols as identification information. An example was given. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and only one display device for displaying an image, such as the
(15) 前記キャラクタ画像は、複数種類(キャラクタa〜d)用意され、
前記キャラクタ画像のキャラクタの種類と発展先の前記特別なリーチ演出の種類との組合せに応じて、前記特定遊技状態となる割合が異なる(図14〜図20において、大当りとなるときに選択される変動パターンの割合がキャラクタa>b、かつ、はずれとなるときに選択される変動パターンの割合がキャラクタb>aであり、大当りとなるときに選択されるスーパーリーチ種類の割合がスーパーリーチA>B、かつ、はずれとなるときに選択されるスーパーリーチ種類の割合がスーパーリーチB>Aであり、キャラクタの種類と発展先のスーパーリーチの種類との組合せに応じて大当りとなる割合が異なる)。
このような構成によれば、キャラクタ画像のキャラクタの種類と発展先の特別なリーチ演出の種類との組合せに応じて、特定遊技状態となる割合が異なるので、キャラクタ画像により特定遊技状態への期待が異なるため、表示されたキャラクタ画像に基づいて遊技者の期待感を高めることができる。また、キャラクタ画像を表示するだけで遊技者が特定遊技状態への期待感を持てなくなることが防がれる。これにより、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。
(16) 前記変動表示手段は、遊技球を遊技領域(遊技領域7)に打込んで遊技を行なうことが可能であり、当該遊技領域に設けられた始動領域(第1始動入賞口13、第2始動入賞口14)を遊技球が通過したことに基づいて変動表示が行なわれ、
予め定められた特別状態発生条件が成立(確変大当り種別に決定)したときに前記特定遊技状態とは異なる遊技者に有利な特別状態を付与する特別遊技状態(確変状態)に制御され、
前記遊技領域に設けられ、遊技球が通過可能な第1状態(開状態)と該第1状態に比べて遊技球が通過しにくいまたは通過しない第2状態(閉状態)とに変化可能であり、前記特定遊技状態に制御されたときに当該第1状態に制御される可変入賞装置(特別
可変入賞球装置20)と、
前記特定遊技状態として、前記可変入賞装置を所定期間前記第1状態に変化させることを所定回数(15回)行なうことにより終了し、前記特定遊技状態終了後、通常遊技状態または前記特別遊技状態に制御される第1遊技状態(15Rの通常大当り、15Rの確変大当り)に制御する第1遊技状態制御手段(図24のS305〜S307、図28のS71,S74、図30のS138、図34のS161)と、
前記特定遊技状態として、前記可変入賞装置を前記所定期間よりも短い期間および前記所定回数よりも少ない回数(2回)の少なくともいずれかで前記第1状態に変化させることにより終了し、前記特定遊技状態終了後、前記特別遊技状態に制御される第2遊技状態(突確大当り)に制御する第2遊技状態制御手段(図24のS305〜S307、図28のS71,S74、図30のS138、図34のS161)とをさらに含み、
前記事前決定手段は、前記特定遊技状態に制御すると決定するときに、前記第1遊技状態、または、前記第2遊技状態とするか否かを決定し(図28のS73)、
前記発展演出実行手段により実行される前記発展可否演出は、該発展可否演出後に前記発展演出としての第1の発展演出(スーパーリーチA,Bの発展演出)と、前記発展可否演出後に前記第2遊技状態に移行することを報知する第2の発展演出(突確移行演出)とを含む。
このような構成によれば、発展可否演出としては、該発展可否演出後に第1の発展演出と、第2遊技状態に移行することを報知する第2の発展演出とを含むので、特定表示結果とならない状態で一旦停止した後特別なリーチ演出への発展を煽ることにより、遊技者の特定状態への期待感を高めることができる。さらに、発展可否演出としては、単にリーチ演出が特別なリーチ演出に発展するか否かの演出に留まらず、発展可否演出後に第2遊技状態に移行することを報知する演出も行なうことが可能であるので、演出に意外性が生じ、特別遊技状態への移行を煽ることにより、遊技者の特定状態への期待感を高めることができる。このようにリーチ演出において遊技状態への期待感を高めることにより、リーチ演出における遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。
(17) 前記変動表示パターン選択手段は、
前記変動表示の態様に基づいて分類された複数種類の変動表示パターン種別(図13〜図21の変動パターン種別)のうちいずれの変動表示パターン種別に属する変動表示パターン(図13〜図21の変動パターン)を実行するかを決定する変動表示パターン種別決定手段(図29のS101,S102)と、
該変動表示パターン種別決定手段により決定された変動表示パターン種別に属する変動表示パターンのうちから実行する変動表示パターンを決定する変動パターン決定手段(図29のS104,S105)とを含む。
このような構成によれば、変動表示パターンを選択するための手段が、変動表示パターン種別を決定する手段と、決定された変動表示演出種別に属する変動表示パターンのうちから実行する変動表示パターンを決定する手段とに分けられている。これにより、変動表示パターン種別を決定する手段により決定可能な変動表示パターン種別の数と、変動表示パターンを決定する手段により決定可能な変動表示パターン数との組合せにより、多種類の変動表示パターンを設定して選択的に用いることができるようになる。また、変動表示パターン種別を決定する手段における種別決定の割合を変更するだけで、各変動表示パターン種別に属する各変動表示パターンを選択する割合を変更しなくても、変動表示パターン種別ごとの変動表示パターンの出現割合を変更することができるようになる。これにより、変動表示パターンに関し、実行可能とする変動表示パターン数の変更設定、および、変動表示パターンの出現割合の変更設定が容易になる。
(18) 前記複数種類の変動表示パターン種別は、前記変動表示手段において、前記識別情報の変動表示が開始されてから表示結果が導出表示されるまでに一旦非特定表示結果となる特殊表示結果(擬似連チャンス目等の仮停止図柄)を仮停止させた後に、すべての変動表示領域において変動表示を再度実行する再変動を1回または複数回実行する再変動表示を行なう再変動表示パターン(擬似連の演出を含む変動パターン)が属する再変動表示パターン種別(スーパーリーチE,Fの種別)を含み(図13〜図21)、
前記変動表示パターン種別決定手段は、前記事前決定手段により前記特定遊技状態に制御する決定がされたときと、前記事前決定手段により前記特定遊技状態に制御しない決定がされ、かつ、リーチ演出を実行しないときに、前記再変動表示パターン種別を選択可能である(図13〜図21)。
このような構成によれば、特定遊技状態に制御する決定がされたときに加えて、特定遊技状態に制御しない決定がされ、かつ、リーチ演出を実行しないときに、再変動表示パターン種別を選択可能であるので、変動表示の演出のバリエーションを豊富化することができるが、変動表示パターンを選択するための手段が、変動表示パターン種別を決定する手段と、決定された変動表示演出種別に属する変動表示パターンのうちから実行する変動表示パターンを決定する手段とに分けられていることにより、遊技機の設計段階において、設定変更者の処理負担を増大させることなく、変動表示の演出のバリエーションを豊富化することができる。
(19) 前記発展可否演出は、複数段階で発展するリーチ演出(スーパーリーチA,B)のうちの第2段階目の演出(煽り演出後のスーパーリーチA,Bの演出)が実行される以前に、前記第1遊技状態に移行することを示す移行演出(突然切替演出)を行なう発展演出(バトルリーチA,Bの突然切替演出)を含む(図16、図18等)。
このような構成によれば、発展可否演出は、複数段階発展するリーチ演出のうちの第2段階目の演出が実行される以前に、第1遊技状態に移行することを示す移行演出を行なう発展演出を含むことにより、複数段階で発展するリーチ演出の途中の段階で第1遊技状態への移行演出が行なわれることとなるので、意外性がある演出により遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。
(20) 前記発展可否演出は、複数種類設けられ(煽り演出が第1煽り演出〜第4煽り演出の複数設けられている)、前記第1の発展演出と前記第2の発展演出との実行割合が、前記発展可否演出の種類に応じて異なる(図14〜図20において、第1煽り演出〜第4煽り演出のそれぞれで、発展演出ありの変動パターンの選択割合と、突確移行演出の変動パターンの選択割合とが異なる)。
このような構成によれば、発展可否演出が行われるときにおいて、第1の発展演出と第2の発展演出との実行割合が発展可否演出の種類に応じて異なるので、発展可否演出の種類ごとに演出の実行割合が一定ではないことに基づいて、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。
(21) 各々が識別可能な複数種類の第1情報を変動表示する第1変動表示手段(第1特別図柄表示器8a)と、
各々が識別可能な複数種類の第2情報を変動表示する第2変動表示手段(第2特別図柄表示器8b)とを備え、
前記変動表示手段は、前記第1変動表示手段における前記第1情報の変動表示、および、前記第2変動表示手段における前記第2情報の変動表示に対応して前記識別情報の変動表示を行なうものであり、
当該第1変動表示手段または第2変動表示手段に導出表示された識別情報の表示結果が予め定められた特定表示結果となったときに、前記特定遊技状態に制御され(図28のS62)、
前記第2遊技状態は、前記第1の変動表示手段において、前記表示結果が前記特定表示結果となるときに制御可能であり(図7(B),(C)の大当り種別判定テーブルは、第1特別図柄について突確大当りとする決定がされるが、第2特別図柄については、突確大当りとする決定がされない。)、
前記発展演出実行手段は、前記特別遊技状態であるときにおいて、前記発展可否演出を実行しない(図13〜図21で、非確変時に用いる変動パターンの判定テーブルでは、発展演出および第1,2突確移行を実行する変動パターンが選択されるが、確変時に用いる変動パターンの判定テーブルでは、発展演出または突確移行演出を実行する変動パターンが選択されないようにデータが設定されている。)。
このような構成によれば、第1の変動表示手段において表示結果が特定表示結果となるときに第2遊技状態に制御可能である。そして、特別遊技状態であるときにおいて発展可否演出が実行されない。これにより、特別遊技状態において、第2の変動表示手段における表示結果に基づいて第2遊技状態に制御される可能性がないにも関わらず無駄な発展可否演出が行なわれずに済むようにすることができ、現実性がない発展可否演出により遊技者の不快感を誘発するおそれが生じないようにすることができる。
(22) 前記演出装置は、可動部材(可動部材84)を含み、
前記発展可否演出は、前記可動部材を動作させることにより行なわれる(図47)。
このような構成によれば、発展可否演出が、可動部材を動作させることにより行なわれるので、変動表示の表示状態に影響を受けることなく発展可否演出を行なうことができるため、発展可否演出による演出効果を向上させることができる。
(23) なお、今回開示された実施の形態はすべての点で例示であって制限的なものではないと考えられるべきである。本発明の範囲は上記した説明ではなく特許請求の範囲によって示され、特許請求の範囲と均等の意味および範囲内でのすべての変更が含まれることが意図される。
(15) A plurality of types of character images (characters a to d) are prepared,
Depending on the combination of the character type of the character image and the type of the special reach effect at the development destination, the proportion of the specific gaming state varies (in FIGS. 14 to 20, it is selected when it is a big hit. The ratio of the variation pattern is selected when the character a> b, and the variation pattern selected when the variation is out of character is the character b> a, and the proportion of the super reach type selected when the big hit is the super reach A>. B and the ratio of the super reach type selected when it is out of place is super reach B> A, and the ratio of the big hit depends on the combination of the character type and the developed super reach type) .
According to such a configuration, the ratio of the specific game state varies depending on the combination of the character type of the character image and the type of special reach performance of the development destination. Therefore, the player's expectation can be enhanced based on the displayed character image. Further, it is possible to prevent the player from having a sense of expectation for the specific gaming state simply by displaying the character image. Thereby, the interest of a game can be improved.
(16) The variation display means can play a game ball by hitting a game ball into the game area (game area 7), and a start area (first
It is controlled to a special gaming state (probability variation state) that gives a special state advantageous to a player different from the specific gaming state when a predetermined special state occurrence condition is established (determined as a probability variation big hit type),
A first state (open state) that is provided in the gaming area and allows a game ball to pass through and can be changed between a first state (open state) and a second state (closed state) in which the game ball is less likely to pass or does not pass. , A variable winning device (special) controlled to the first state when controlled to the specific gaming state
Variable winning ball apparatus 20),
As the specific gaming state, the variable winning device is ended by changing the variable winning device to the first state for a predetermined period of time (15 times), and after the specific gaming state, the normal gaming state or the special gaming state is entered. First gaming state control means (S305 to S307 in FIG. 24, S71 and S74 in FIG. 28, S138 in FIG. 30, S138 in FIG. 34) to be controlled to the first gaming state to be controlled (ordinary big hit of 15R, probable big hit of 15R) S161),
The specific game state is ended by changing the variable prize apparatus to the first state at least one of a period shorter than the predetermined period and a number (twice) less than the predetermined number of times, and the specific game is ended. After the completion of the state, the second gaming state control means (S305 to S307 in FIG. 24, S71 and S74 in FIG. 28, S138 in FIG. 30, FIG. 34 S161),
The pre-determining means determines whether to set the first gaming state or the second gaming state when determining to control to the specific gaming state (S73 in FIG. 28),
The development propriety effect executed by the development effect execution means includes the first development effect (the development effect of super reach A and B) as the development effect after the development propriety effect and the second after the development propriety effect. And a second development effect (abrupt transition effect) for notifying the transition to the gaming state.
According to such a configuration, the development propriety effect includes the first development effect after the development propriety effect and the second development effect informing that the transition to the second gaming state has occurred. It is possible to increase a player's sense of expectation for a specific state by encouraging the development to a special reach production after stopping in a state that does not become. In addition, the development availability effect is not limited to simply whether or not the reach production is developed into a special reach production, but it is also possible to provide an effect to notify the transition to the second gaming state after the development availability production. As a result, unexpected effects occur in the performance, and the player's sense of expectation for the specific state can be enhanced by encouraging the transition to the special game state. Thus, the interest of the game in the reach production can be improved by increasing the expectation to the gaming state in the reach production.
(17) The variable display pattern selection means includes:
The variation display patterns belonging to any variation display pattern type (variations in FIGS. 13 to 21) among a plurality of types of variation display pattern types (variation pattern types in FIGS. 13 to 21) classified based on the variation display mode. A variable display pattern type determining means (S101, S102 in FIG. 29) for determining whether to execute (pattern);
And variation pattern determination means (S104, S105 in FIG. 29) for determining a variation display pattern to be executed from among the variation display patterns belonging to the variation display pattern type determined by the variation display pattern type determination means.
According to such a configuration, the means for selecting the variable display pattern includes a means for determining the variable display pattern type and a variable display pattern to be executed from among the variable display patterns belonging to the determined variable display effect type. It is divided into the means to decide. Thus, a variety of variable display patterns can be obtained by combining the number of variable display pattern types that can be determined by the means for determining the variable display pattern type and the number of variable display patterns that can be determined by the means for determining the variable display pattern. It can be set and used selectively. In addition, the change for each variable display pattern type can be changed without changing the ratio for selecting each variable display pattern belonging to each variable display pattern type only by changing the type determination ratio in the means for determining the variable display pattern type. The appearance ratio of the display pattern can be changed. This facilitates the change setting of the number of variable display patterns that can be executed and the change setting of the appearance ratio of the change display pattern with respect to the change display pattern.
(18) The plurality of types of variable display pattern types include special display results that are temporarily non-specific display results from the start of variable display of the identification information until display results are derived and displayed in the variable display means. After temporarily stopping a temporary stop symbol such as a pseudo-continuous chance), a re-variable display pattern (pseudo) for performing re-variable display for executing re-variation once or a plurality of times for re-execution of variable display in all the variable display areas Including the re-variable display pattern type (type of super reach E and F) to which the re-variable display pattern belongs) (FIGS. 13 to 21),
The variable display pattern type determining means is determined to be controlled to the specific gaming state by the prior determining means, and determined not to be controlled to the specific gaming state by the preliminary determining means, and reach effect When the operation is not executed, the re-variable display pattern type can be selected (FIGS. 13 to 21).
According to such a configuration, in addition to the decision to control to the specific gaming state, the re-variable display pattern type is selected when the decision not to control to the specific gaming state is made and the reach effect is not executed. Since it is possible, it is possible to enrich the variation display effect variations, but the means for selecting the variable display pattern belongs to the means for determining the variable display pattern type and the determined variable display effect type It is divided into means for determining the variable display pattern to be executed from among the variable display patterns, so that variations in the effects of variable display can be achieved without increasing the processing burden on the setting changer at the design stage of the gaming machine. Can be enriched.
(19) The development propriety effect is performed before the second stage effect (the effect of super reach A and B after the roaring effect) of the reach effect (super reach A and B) that develops in a plurality of stages. In addition, a development effect (sudden switching effect of battle reach A, B) that performs a transition effect (sudden switching effect) indicating the transition to the first gaming state is included (FIGS. 16, 18, etc.).
According to such a configuration, the advancement / prohibition effect is a development in which a transition effect indicating a transition to the first gaming state is performed before the second-stage effect among the reach effects that develop in a plurality of stages is executed. By including the effect, the transition effect to the first game state is performed at a stage in the middle of the reach effect that develops in a plurality of stages, so that the entertainment of the game can be improved by the unexpected effect.
(20) A plurality of types of development allowance / prohibition effects are provided (a plurality of turn effects are provided from a first turn effect to a fourth turn effect), and execution of the first development effect and the second development effect is performed. The ratio varies depending on the type of the development possibility effect (in FIGS. 14 to 20, the variation ratio of the variation pattern with the development effect and the variation of the sudden transition effect in each of the first to fourth production effects) The pattern selection ratio is different.)
According to such a configuration, when the development propriety effect is performed, the execution ratio of the first development effect and the second development effect varies depending on the type of the development propriety effect. Based on the fact that the performance execution ratio is not constant, it is possible to improve the interest of the game.
(21) first fluctuation display means (first
A second variation display means (second special symbol display 8b) for variably displaying a plurality of types of second information, each of which can be identified;
The fluctuation display means performs fluctuation display of the identification information corresponding to the fluctuation display of the first information in the first fluctuation display means and the fluctuation display of the second information in the second fluctuation display means. And
When the display result of the identification information derived and displayed on the first variation display means or the second variation display means is a predetermined specific display result, the specific gaming state is controlled (S62 in FIG. 28),
The second gaming state can be controlled in the first variation display means when the display result becomes the specific display result (the jackpot type determination table in FIGS. 1 special symbol is determined to be a big hit, but the second special symbol is not decided to be a big hit).
The development effect executing means does not execute the development propriety effect when in the special gaming state (in the variation pattern determination table used in the case of uncertain change in FIGS. The variation pattern for executing the transition is selected, but in the variation pattern determination table used at the time of the probability variation, data is set so that the variation pattern for executing the development effect or the sudden transition effect is not selected.
According to such a configuration, it is possible to control to the second gaming state when the display result becomes the specific display result in the first variation display means. And the development propriety effect is not executed in the special game state. As a result, in the special gaming state, it is possible to avoid the useless development propriety effect although there is no possibility of being controlled to the second gaming state based on the display result in the second variation display means. It is possible to prevent the player from feeling uncomfortable due to the development feasibility without reality.
(22) The rendering device includes a movable member (movable member 84),
The development propriety effect is performed by operating the movable member (FIG. 47).
According to such a configuration, the development propriety effect is performed by operating the movable member, and therefore the development propriety effect can be performed without being affected by the display state of the variable display. The effect can be improved.
( 23 ) It should be understood that the embodiment disclosed this time is illustrative in all respects and not restrictive. The scope of the present invention is defined by the terms of the claims, rather than the description above, and is intended to include any modifications within the scope and meaning equivalent to the terms of the claims.
7 遊技領域、13 第1始動入賞口、9L,9C,9R 図柄表示エリア、9 演出表示装置、84 可動部材、1 パチンコ遊技機、14 第2始動入賞口、560 遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ、100 演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ。 7 gaming area, 13 first start winning opening, 9L, 9C, 9R symbol display area, 9 presentation display device, 84 movable member, 1 pachinko gaming machine, 14 second starting winning opening, 560 microcomputer for game control, 100 presentation Control microcomputer.
Claims (2)
前記特定遊技状態に制御するか否かを、前記識別情報の表示結果が導出表示される以前に決定する事前決定手段と、
該事前決定手段による決定に基づいて、前記複数の変動表示領域において前記識別情報が前記特定表示結果の一部を構成しているが少なくとも一部の変動表示領域が変動表示中であるリーチ状態とするリーチ演出を行なうリーチ変動表示パターンを含む複数種類の変動表示パターンの中から1つの変動表示パターンを選択する変動表示パターン選択手段と、
該変動表示パターン選択手段が選択した変動表示パターンに基づいて、前記変動表示手段における前記識別情報の変動表示の制御を行なう演出制御手段とを含み、
前記リーチ変動表示パターンには、予め定められた通常のリーチ演出を行なう通常リーチ変動表示パターンと、前記通常のリーチ演出が行なわれた後に当該通常のリーチ演出と比べて前記特定遊技状態となるときに実行される割合が高い特別なリーチ演出を行なう特別リーチ変動表示パターンとを含む複数種類のリーチ変動表示パターンが設けられ、
リーチ演出を実行して前記特定表示結果とならない状態で一旦停止した後に、所定の演出パターンを実行する発展演出実行手段をさらに含み、
該発展演出実行手段により実行される前記演出パターンには、実行中の変動表示が継続するか否かを報知する発展可否演出を行なった後に前記特別なリーチ演出に発展する第1の発展演出パターンと、前記発展可否演出を行なった後に前記特定表示結果とならない状態で前記識別情報の変動表示を停止する第2の発展演出パターンとを含む複数種類の演出パターンが設けられ、
前記発展可否演出には、第1表示態様のキャラクタ画像が表示される第1発展可否演出と、第2表示態様のキャラクタ画像が表示される第2発展可否演出とを含む複数種類の発展可否演出が設けられ、
前記特別なリーチ演出には、第1特別リーチ演出と、当該第1特別リーチ演出よりも前記特定遊技状態となるときに実行される割合が高い第2特別リーチ演出とを含む複数種類の特別なリーチ演出が設けられ、
前記発展演出実行手段は、前記第1の発展演出パターンおよび前記第2の発展演出パターンをそれぞれ異なる割合で実行し、
前記第1の発展演出パターンにおいては、前記第1発展可否演出が行なわれた後には前記第2発展可否演出が行なわれた後よりも高い割合で前記第1特別リーチ演出に発展し、前記第2発展可否演出が行なわれた後には前記第1発展可否演出が行なわれた後よりも高い割合で前記第2特別リーチ演出に発展し、さらに、前記第1発展可否演出が行なわれた後に前記第2特別リーチ演出に発展したときには、前記第2発展可否演出が行なわれた後に前記第1特別リーチ演出に発展したときよりも高い割合で前記特定遊技状態となる、遊技機。 A variable display means having a plurality of variable display areas for performing a variable display of a plurality of types of identification information each identifiable and deriving and displaying a display result, and when a specific display result is derived and displayed on the variable display means A gaming machine that controls a specific gaming state that is advantageous to the player,
Pre-decision means for deciding whether to control to the specific gaming state before the display result of the identification information is derived and displayed;
Based on the determination by the pre-determining means, a reach state in which the identification information forms part of the specific display result in the plurality of variable display areas, but at least some of the variable display areas are in variable display A variation display pattern selecting means for selecting one variation display pattern from a plurality of types of variation display patterns including a reach variation display pattern for performing a reach effect;
Production control means for controlling the fluctuation display of the identification information in the fluctuation display means based on the fluctuation display pattern selected by the fluctuation display pattern selection means,
The reach variation display pattern includes a normal reach variation display pattern for performing a predetermined normal reach effect, and a state in which the specific game state is achieved after the normal reach effect is performed as compared to the normal reach effect. A plurality of types of reach fluctuation display patterns including a special reach fluctuation display pattern for performing a special reach production with a high ratio of
And further comprising a development effect execution means for executing a predetermined effect pattern after executing a reach effect and temporarily stopping in a state where the specific display result is not obtained.
The development pattern executed by the development production execution means includes a first development production pattern that develops to the special reach production after performing the development possibility production informing whether or not the variable display being executed continues. And a plurality of types of production patterns including a second development production pattern that stops the variation display of the identification information in a state where the specific display result is not obtained after performing the development propriety production,
The development propriety effect includes a plurality of types of development propriety effects including a first development propriety effect in which a character image in a first display mode is displayed and a second development propriety effect in which a character image in a second display mode is displayed. Is provided,
The special reach production includes a plurality of types of special reach production including a first special reach production and a second special reach production that is executed at a higher rate when the specific gaming state is set than the first special reach production. Reach production is provided,
The development effect execution means executes the first development effect pattern and the second development effect pattern at different ratios,
In the first development effect pattern, after the first development propriety effect is performed, the first development effect pattern is developed at a higher rate than after the second development propriety effect is performed. After the second development propriety effect is performed, the second special reach production is developed at a higher rate than after the first development propriety effect is performed , and further after the first development propriety effect is performed. A gaming machine that, when developed into a second special reach production, enters the specific gaming state at a higher rate than when developed into the first special reach production after the second development availability effect .
前記第1の発展演出パターンは、前記第2の発展演出パターンよりも高い割合で、前記発展可否演出において前記所定演出のうち特定演出が実行される、請求項1に記載の遊技機。 The development propriety effect is one of a plurality of types of predetermined effects,
The gaming machine according to claim 1, wherein the first development effect pattern is executed at a higher rate than the second development effect pattern, and the specific effect is executed out of the predetermined effects in the development propriety effect.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008288818A JP5524468B2 (en) | 2008-11-11 | 2008-11-11 | Game machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008288818A JP5524468B2 (en) | 2008-11-11 | 2008-11-11 | Game machine |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012134875A Division JP5588479B2 (en) | 2012-06-14 | 2012-06-14 | Game machine |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010115249A JP2010115249A (en) | 2010-05-27 |
| JP2010115249A5 JP2010115249A5 (en) | 2012-08-02 |
| JP5524468B2 true JP5524468B2 (en) | 2014-06-18 |
Family
ID=42303313
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008288818A Active JP5524468B2 (en) | 2008-11-11 | 2008-11-11 | Game machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5524468B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017070730A (en) * | 2016-09-07 | 2017-04-13 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
Families Citing this family (42)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5771954B2 (en) * | 2009-12-25 | 2015-09-02 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Game machine |
| JP5376529B2 (en) * | 2010-06-21 | 2013-12-25 | サミー株式会社 | Bullet ball machine |
| JP5250593B2 (en) * | 2010-09-01 | 2013-07-31 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP5594605B2 (en) * | 2011-04-19 | 2014-09-24 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP5307910B2 (en) * | 2012-02-21 | 2013-10-02 | 株式会社藤商事 | Game machine |
| JP5470413B2 (en) * | 2012-03-06 | 2014-04-16 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP5898594B2 (en) * | 2012-09-05 | 2016-04-06 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP5859415B2 (en) * | 2012-11-02 | 2016-02-10 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP5534479B2 (en) * | 2012-12-27 | 2014-07-02 | サミー株式会社 | Bullet ball machine |
| JP5647287B2 (en) * | 2013-04-02 | 2014-12-24 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP5555352B2 (en) * | 2013-04-02 | 2014-07-23 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP5876006B2 (en) * | 2013-04-19 | 2016-03-02 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP6278657B2 (en) * | 2013-10-17 | 2018-02-14 | 株式会社オリンピア | Game machine and game system |
| JP2016195705A (en) * | 2015-04-06 | 2016-11-24 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP5938120B2 (en) * | 2015-04-16 | 2016-06-22 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP6169640B2 (en) * | 2015-04-17 | 2017-07-26 | 株式会社ニューギン | Game machine |
| JP2016019785A (en) * | 2015-09-25 | 2016-02-04 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Game machine |
| JP2016019784A (en) * | 2015-09-25 | 2016-02-04 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Game machine |
| JP6190860B2 (en) * | 2015-10-09 | 2017-08-30 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP6294361B2 (en) * | 2016-01-06 | 2018-03-14 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP6277217B2 (en) * | 2016-03-30 | 2018-02-07 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP2017035598A (en) * | 2016-11-22 | 2017-02-16 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP2017035599A (en) * | 2016-11-22 | 2017-02-16 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP2017035597A (en) * | 2016-11-22 | 2017-02-16 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP6580616B2 (en) * | 2017-02-24 | 2019-09-25 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP6580614B2 (en) * | 2017-02-24 | 2019-09-25 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP6580615B2 (en) * | 2017-02-24 | 2019-09-25 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP6917729B2 (en) * | 2017-02-28 | 2021-08-11 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Pachinko machine |
| JP2018139807A (en) * | 2017-02-28 | 2018-09-13 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP6917730B2 (en) * | 2017-02-28 | 2021-08-11 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Pachinko machine |
| JP2018139806A (en) * | 2017-02-28 | 2018-09-13 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP6825938B2 (en) * | 2017-03-01 | 2021-02-03 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP6912222B2 (en) * | 2017-03-01 | 2021-08-04 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Pachinko machine |
| JP6689770B2 (en) * | 2017-03-01 | 2020-04-28 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Amusement machine |
| JP6912221B2 (en) * | 2017-03-01 | 2021-08-04 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Pachinko machine |
| JP7046022B2 (en) * | 2019-02-05 | 2022-04-01 | 株式会社ユニバーサルエンターテインメント | Pachinko machine |
| JP6873575B2 (en) * | 2019-04-05 | 2021-05-19 | 株式会社ユニバーサルエンターテインメント | Pachinko machine |
| JP2019115791A (en) * | 2019-04-24 | 2019-07-18 | 株式会社ユニバーサルエンターテインメント | Game machine |
| JP7362571B2 (en) * | 2020-08-27 | 2023-10-17 | 株式会社三共 | gaming machine |
| JP7362572B2 (en) * | 2020-08-27 | 2023-10-17 | 株式会社三共 | gaming machine |
| JP7381082B2 (en) * | 2020-10-01 | 2023-11-15 | 株式会社サンセイアールアンドディ | gaming machine |
| JP7410071B2 (en) * | 2021-03-19 | 2024-01-09 | 株式会社三共 | gaming machine |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002136716A (en) * | 2000-10-30 | 2002-05-14 | Aruze Corp | Game machine |
| JP2002346127A (en) * | 2001-05-28 | 2002-12-03 | Aruze Corp | Game machine |
| JP2008099771A (en) * | 2006-10-18 | 2008-05-01 | Abilit Corp | Game machine |
-
2008
- 2008-11-11 JP JP2008288818A patent/JP5524468B2/en active Active
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017070730A (en) * | 2016-09-07 | 2017-04-13 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2010115249A (en) | 2010-05-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5524468B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5479717B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5266555B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5234786B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5329074B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2010154921A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2010154927A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5588480B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2009195492A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5329073B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2011218045A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2010154923A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2010162160A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5332024B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2010154925A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2012161669A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5332023B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2015120068A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5301713B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5362316B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5735066B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5778201B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5588479B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5603460B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5778202B2 (en) | Game machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110902 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120614 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20121113 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130110 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130205 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130319 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20130423 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130710 |
|
| A911 | Transfer of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20130718 |
|
| A912 | Removal of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A912 Effective date: 20130809 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140410 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5524468 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |