JP4593179B2 - Display device - Google Patents
Display device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4593179B2 JP4593179B2 JP2004179165A JP2004179165A JP4593179B2 JP 4593179 B2 JP4593179 B2 JP 4593179B2 JP 2004179165 A JP2004179165 A JP 2004179165A JP 2004179165 A JP2004179165 A JP 2004179165A JP 4593179 B2 JP4593179 B2 JP 4593179B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- transistor
- wiring
- emitting element
- pixel
- light
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 72
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 claims description 26
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 78
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 75
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 35
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 32
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 27
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 27
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 23
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 description 15
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 14
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 10
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 9
- 229910021417 amorphous silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 8
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 7
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 239000008186 active pharmaceutical agent Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000011368 organic material Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000005281 excited state Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000005669 field effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000005283 ground state Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000002161 passivation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 150000003222 pyridines Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 4
- BCMCBBGGLRIHSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-benzoxazole Chemical class C1=CC=C2OC=NC2=C1 BCMCBBGGLRIHSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910010272 inorganic material Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000011147 inorganic material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000004020 luminiscence type Methods 0.000 description 3
- SLIUAWYAILUBJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N pentacene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC3=CC4=CC5=CC=CC=C5C=C4C=C3C=C21 SLIUAWYAILUBJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229920000553 poly(phenylenevinylene) Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 3
- STTGYIUESPWXOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,9-dimethyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline Chemical compound C=12C=CC3=C(C=4C=CC=CC=4)C=C(C)N=C3C2=NC(C)=CC=1C1=CC=CC=C1 STTGYIUESPWXOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920001609 Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 150000001340 alkali metals Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910052784 alkaline earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 150000001342 alkaline earth metals Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000620 organic polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 2
- -1 pentacene Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 2
- LLHKCFNBLRBOGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N propylene glycol methyl ether acetate Chemical compound COCC(C)OC(C)=O LLHKCFNBLRBOGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052723 transition metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 150000003624 transition metals Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- QTWJRLJHJPIABL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylphenol;3-methylphenol;4-methylphenol Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1.CC1=CC=CC(O)=C1.CC1=CC=CC=C1O QTWJRLJHJPIABL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241001270131 Agaricus moelleri Species 0.000 description 1
- WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lithium Chemical compound [Li] WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N acrylic acid group Chemical group C(C=C)(=O)O NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001408 amides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- PMHQVHHXPFUNSP-UHFFFAOYSA-M copper(1+);methylsulfanylmethane;bromide Chemical compound Br[Cu].CSC PMHQVHHXPFUNSP-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229930003836 cresol Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005525 hole transport Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007972 injectable composition Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052744 lithium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Al]O[Al]=O TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000123 polythiophene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003384 small molecules Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004528 spin coating Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Electroluminescent Light Sources (AREA)
- Devices For Indicating Variable Information By Combining Individual Elements (AREA)
Description
本発明は、自発光型の発光素子と非晶質半導体又は有機半導体でチャネル部を形成するトランジスタを含む表示装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a display device including a self-luminous light emitting element and a transistor in which a channel portion is formed using an amorphous semiconductor or an organic semiconductor.
近年、発光素子を有する表示装置の開発が活発に進められている。この表示装置は、既存の液晶表示装置がもつ利点の他、応答速度が速く動画表示に優れ、なおかつ視野角が広いなどの特徴を有し、次世代のフラットパネルディスプレイとして大きく注目されている。 In recent years, development of display devices having light-emitting elements has been actively promoted. In addition to the advantages of existing liquid crystal display devices, this display device has features such as a high response speed, excellent video display, and a wide viewing angle, and has attracted much attention as a next-generation flat panel display.
表示装置は、発光素子と少なくとも2つのトランジスタを具備した画素を複数有し、画素において発光素子と直列に接続されたトランジスタは、発光素子の発光又は非発光を制御する。トランジスタは、その高い電界効果移動度から結晶質半導体(ポリシリコン)を用いることが多い。また、発光素子は、2つの電極間に電界発光層が挟まれた構造を有し、パターン加工された第1の導電膜(第1の電極)上に電界発光層を形成し、該電界発光層上の全面を覆うように第2の導電膜(第2の電極)を形成する。 The display device includes a plurality of pixels each including a light emitting element and at least two transistors, and the transistor connected in series with the light emitting element in the pixel controls light emission or non-light emission of the light emitting element. A transistor often uses a crystalline semiconductor (polysilicon) because of its high field effect mobility. The light-emitting element has a structure in which an electroluminescent layer is sandwiched between two electrodes. The electroluminescent layer is formed on a patterned first conductive film (first electrode), and the electroluminescent layer is formed. A second conductive film (second electrode) is formed so as to cover the entire surface of the layer.
発光素子を制御するトランジスタとしてアモルファスシリコンTFTを用いるものがある(例えば、特許文献1参照)。
ポリシリコンを用いたトランジスタは、結晶粒界に形成される欠陥に起因してその特性にバラツキが生じやすい。従って、トランジスタのドレイン電流にバラツキが生じていた場合、入力された信号電圧が同じであっても、そのドレイン電流が画素毎に異なってしまい、結果的に輝度ムラが生じてしまう。 A transistor using polysilicon is likely to have variations in characteristics due to defects formed in crystal grain boundaries. Therefore, when there is variation in the drain current of the transistor, even if the input signal voltage is the same, the drain current varies from pixel to pixel, resulting in luminance unevenness.
上記の実情を鑑み、本発明は、トランジスタの特性バラツキにより生じる輝度ムラが抑制された表示装置を提供することを課題とする。 In view of the above circumstances, it is an object of the present invention to provide a display device in which unevenness in luminance caused by variation in transistor characteristics is suppressed.
また、電界発光層上に形成された第2の導電膜(第2の電極)は、熱処理を施すことにより低抵抗化を図ることが好適である。しかしながら、電界発光層は耐熱性が低く、高温の熱処理を行うことができない。従って、抵抗値の相違により、端部と中心部とで両電極間に印加される電圧値が異なり、そのために画質不良が生じる場合がある。 In addition, it is preferable that the second conductive film (second electrode) formed over the electroluminescent layer be subjected to heat treatment to reduce resistance. However, the electroluminescent layer has low heat resistance and cannot be subjected to high-temperature heat treatment. Therefore, due to the difference in resistance value, the voltage value applied between the electrodes at the end and the center is different, which may cause poor image quality.
上記の実情を鑑み、本発明は、抵抗値の相違に起因した画質不良が抑制された表示装置を提供することを課題とする。 In view of the above circumstances, an object of the present invention is to provide a display device in which image quality defects due to a difference in resistance value are suppressed.
上述した従来技術の課題を解決するために、本発明は以下の手段を講じる。 In order to solve the above-described problems of the prior art, the present invention takes the following measures.
本発明は、発光素子を駆動するトランジスタとして、非晶質半導体(代表的にはアモルファスシリコン、a-Si:H)、又は有機半導体でチャネル部を形成するトランジスタを用いることを特徴とする。前記トランジスタは、電界効果移動度などの特性にバラツキが少ない。従って、トランジスタの特性バラツキにより生じる輝度ムラを改善した表示装置を提供することができる。また、非晶質半導体を用いる本発明は、数インチから数十インチの大型のパネルを作製する場合に大変有効であり、また結晶化の工程が不要でマスク数が少なくて済むので、作製費用を低減することができる。 The present invention is characterized in that a transistor in which a channel portion is formed using an amorphous semiconductor (typically amorphous silicon, a-Si: H) or an organic semiconductor is used as a transistor for driving a light-emitting element. The transistor has little variation in characteristics such as field effect mobility. Therefore, a display device in which luminance unevenness caused by variation in transistor characteristics is improved can be provided. In addition, the present invention using an amorphous semiconductor is very effective when manufacturing a large panel of several inches to several tens of inches, and since the crystallization process is unnecessary and the number of masks is small, the manufacturing cost is low. Can be reduced.
本発明は、電界発光層上に積層される導電膜に、補助的な導電膜(配線)を接続することにより、該導電膜の低抵抗化を図ることを特徴とする。上記特徴により、熱処理を施すことなく、前記導電膜の低抵抗化を図ることができ、画質不良が抑制された表示装置を提供することができる。本特徴は、数十インチの大型のパネルを作製する場合に大変有効であり、これは、パネルのインチ数が大きくなる程、その抵抗値が問題になるためである。 The present invention is characterized in that an auxiliary conductive film (wiring) is connected to the conductive film laminated on the electroluminescent layer to reduce the resistance of the conductive film. With the above characteristics, it is possible to provide a display device in which the resistance of the conductive film can be reduced without performing heat treatment and image quality defects are suppressed. This feature is very effective in manufacturing a large panel of several tens of inches, because the resistance value becomes a problem as the number of inches of the panel increases.
本発明は、一対の電極間に発光材料を含む発光素子と、非晶質半導体でチャネル部を形成するトランジスタが複数配置された画素部及び該画素部の周辺に配置された駆動回路を含む基板と、前記基板に張り合わされたドライバICとを有する。基板上に形成された駆動回路は、非晶質半導体でチャネル部を形成するN型トランジスタ(以下a-Si:HTFTと表記することがある)と、有機半導体でチャネル部を形成するP型トランジスタ(以下有機TFTと表記することがある)を含むことを特徴とする。有機TFTは、ペンタセンなどの有機低分子、PEDOT(ポリチオフェン系)やPPV(ポリフェニレンビニレン)などの有機高分子などを含むトランジスタに相当する。このa-Si:HTFTと有機TFTは、画素部と共に同一基板上に作製することが可能であり、このCMOS回路を1つの単位回路として、シフトレジスタやバッファなどを構成することができる。また、N型トランジスタのみ、P型トランジスタのみで駆動回路を構成することも可能であり、その場合は、a-Si:HTFTのみ、有機TFTのみで駆動回路を構成することができる。 The present invention relates to a light emitting element including a light emitting material between a pair of electrodes, a pixel portion in which a plurality of transistors that form a channel portion using an amorphous semiconductor are disposed, and a substrate including a driver circuit disposed around the pixel portion. And a driver IC attached to the substrate. The driving circuit formed on the substrate includes an N-type transistor (hereinafter sometimes referred to as a-Si: HTFT) in which a channel portion is formed of an amorphous semiconductor and a P-type transistor in which a channel portion is formed of an organic semiconductor. (Hereinafter sometimes referred to as organic TFT). The organic TFT corresponds to a transistor including an organic small molecule such as pentacene, an organic polymer such as PEDOT (polythiophene) or PPV (polyphenylene vinylene). The a-Si: HTFT and the organic TFT can be manufactured on the same substrate together with the pixel portion, and a shift register, a buffer, or the like can be configured using this CMOS circuit as one unit circuit. It is also possible to configure a drive circuit with only N-type transistors and only P-type transistors. In that case, a drive circuit can be configured with only a-Si: HTFT and only organic TFT.
本発明は、アノード線に接続された第1の電極と、カソード線に接続された第2の電極間に発光材料を含む発光素子と、非晶質半導体でチャネル部を形成するトランジスタとを有し、前記アノード線と前記カソード線の電位を反転させて、前記発光素子に逆方向バイアスを印加する逆方向バイアス印加回路を有することを特徴とする。上記構成により、発光素子の経時劣化が抑制され、信頼性を向上させた表示装置を提供することができる。 The present invention includes a first electrode connected to the anode line, a light-emitting element including a light-emitting material between the second electrodes connected to the cathode line, and a transistor in which a channel portion is formed using an amorphous semiconductor. And a reverse bias applying circuit for applying a reverse bias to the light emitting element by inverting the potentials of the anode line and the cathode line. With the above structure, it is possible to provide a display device in which deterioration of the light-emitting element over time is suppressed and reliability is improved.
本発明は、一対の電極間に発光材料を含む発光素子と、電位が一定に保たれた第1の電源にゲート電極が接続された第1のトランジスタと、信号線にゲート電極が接続された第2のトランジスタとを有し、前記発光素子並びに前記第1及び前記第2のトランジスタは、低電位電圧と同電位である第2の電源と、高電位電圧と同電位である第3の電源との間に直列に接続される。そして、前記第1及び前記第2のトランジスタは、非晶質半導体でチャネル部を形成することを特徴とする表示装置を提供する。
上記構成において、第2のトランジスタは線形領域で動作するために、第1のトランジスタのVGSの僅かな変動は発光素子の電流値に影響を及ぼさない。つまり、発光素子の電流値は、飽和領域で動作する第1のトランジスタにより決定される。従って、上記構成を有する本発明は、トランジスタの特性バラツキに起因した発光素子の輝度ムラを改善して画質を向上させた表示装置を提供することができる。
In the present invention, a light-emitting element including a light-emitting material between a pair of electrodes, a first transistor having a gate electrode connected to a first power source whose potential is kept constant, and a gate electrode connected to a signal line A second power source having the same potential as the low potential voltage, and a third power source having the same potential as the high potential voltage, and the light emitting element and the first and second transistors. Connected in series. In addition, the display device is characterized in that the first and second transistors form a channel portion with an amorphous semiconductor.
In the above structure, since the second transistor operates in a linear region, a slight change in V GS of the first transistor does not affect the current value of the light emitting element. That is, the current value of the light emitting element is determined by the first transistor operating in the saturation region. Therefore, the present invention having the above structure can provide a display device in which luminance unevenness of a light-emitting element due to variation in transistor characteristics is improved and image quality is improved.
上記構成を有する本発明は、トランジスタの特性バラツキにより生じる輝度ムラを改善した表示装置を提供することができる。また、熱処理を施すことなく、前記導電膜の低抵抗化を図ることができ、画質不良が抑制された表示装置を提供することができる。さらに、非晶質半導体をチャネル部とするトランジスタを含む本発明は、安価で大型の表示装置を提供することができる。 The present invention having the above structure can provide a display device in which luminance unevenness caused by variation in transistor characteristics is improved. Further, the resistance of the conductive film can be reduced without performing heat treatment, and a display device in which image quality defects are suppressed can be provided. Further, the present invention including a transistor including an amorphous semiconductor as a channel portion can provide an inexpensive and large display device.
(実施の形態1)
本発明の実施の形態について、図面を用いて詳細に説明する。但し、本発明は以下の説明に限定されず、本発明の趣旨及びその範囲から逸脱することなくその形態及び詳細を様々に変更し得ることは当業者であれば容易に理解される。従って、本発明は以下に示す実施の形態の記載内容に限定して解釈されるものではない。なお、以下に説明する本発明の構成において、同じものを指す符号は異なる図面間で共通して用いる。
(Embodiment 1)
Embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. However, the present invention is not limited to the following description, and it is easily understood by those skilled in the art that modes and details can be variously changed without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention. Therefore, the present invention should not be construed as being limited to the description of the embodiments below. Note that in the structures of the present invention described below, the same reference numerals are used in common in different drawings.
まず、パネルにおける配線の配置、特に高電位電圧VDDと同電位である電源線(以下アノード線と表記)と、低電位電圧VSSと同電位である電源線(以下カソード線と表記)の配置について、図4を用いて説明する。なお、図4では、画素部104において列方向に配置される配線のみを図示する。
First, the arrangement of wirings in the panel, particularly the arrangement of a power supply line (hereinafter referred to as an anode line) having the same potential as the high potential voltage VDD and a power supply line (hereinafter referred to as a cathode line) having the same potential as the low potential voltage VSS. This will be described with reference to FIG. Note that FIG. 4 illustrates only wirings arranged in the column direction in the
図4(A)はパネルの上面図を示したものであり、基板100上に、マトリクス状に複数の画素105が配置された画素部104、該画素部104の周辺に信号線駆動回路101、走査線駆動回路102、103が配置される。これらの駆動回路の個数は特に限定されず、画素105の構成に応じて適宜変更すればよい。また基板100上に一体形成せずに、COG法などを用いてドライバICを貼り合わせてもよい。
4A is a top view of the panel. A
画素部104内において列方向に配置された信号線111は、信号線駆動回路101と接続する。同様に、列方向に配置された電源線112〜114は、アノード線107〜109のいずれかと接続する。また同様に、列方向に配置された補助配線110は、カソード線106と接続する。アノード線107〜109及びカソード線106は、画素部104とその周辺に配置された駆動回路の周りを囲むように引き回して、FPCの端子と接続する。
The
アノード線107〜109は、RGBのいずれかの色に対応したものである。これは、各アノード線107〜109の電位を変えることで、各色間で生じる輝度バラツキの補正を目的としたものである。つまり、発光素子の電界発光層の電流密度が各色で異なるために、同じ電流値を流しても各色で輝度が異なってしまう問題を改善するものである。なお、ここでは、RGBで電界発光層を塗り分ける場合を想定しているが、カラー化の方法として、白色を発光する発光素子とカラーフィルタを用いる方法など、各色での電流密度の相違が問題とならない方法を採用した場合やモノクロ表示を行う場合には、アノード線を複数本設けなくてもよい。
The
図4(B)はマスクレイアウト図を簡単に示したものであり、信号線駆動回路101の周囲にアノード線107〜109、カソード線106が配置され、アノード線107〜109は、画素部104内において列方向に配置された電源線112〜114と接続する。図示するように、カソード線106と補助配線110は同じレイヤーの導電体により形成される。
FIG. 4B simply shows a mask layout diagram. The anode lines 107 to 109 and the
そして、カソード線106及び補助配線110を形成後、発光素子の第1の導電膜(第1の電極)が形成され、その後絶縁膜(土手ともよばれる)が形成される。次に、カソード線106及び補助配線110の上方に位置する絶縁膜には開口部が形成される。前記開口部の形成により、カソード線106と補助配線110は露出した状態となり、この状態で、電界発光層が形成される。電界発光層は、カソード線106及び補助配線110の上方に形成された開口部には積層されないように塗り分けが行われる。次に、第2の導電膜(第2の電極)が全面に形成され、この際、該第2の導電膜は、電界発光層、カソード線106及び補助配線110上に積層して形成される。上記工程により、第2の導電膜は、カソード線106及び補助配線110と電気的に接続し、本実施の形態では、この構成を大きな特徴とする。本特徴により、電界発光層を覆うように形成される第2の導電膜の低抵抗化を図ることができるため、この第2の導電膜の抵抗値に起因した画質不良を改善することができる。本特徴は、数十インチの大型のパネルを作製する場合に大変有効であり、これは、パネルのインチ数が大きくなる程、その抵抗値が問題になるためである。
After the
なお、本実施の形態では、第2の導電膜がカソード線に接続された場合を例に挙げるが、本発明はこれに限定されない。第2の導電膜は、アノード線に接続してもよく、この場合は、発光素子の対向電極が陽極となるように設定する。 Note that although a case where the second conductive film is connected to the cathode line is given as an example in this embodiment, the present invention is not limited to this. The second conductive film may be connected to the anode line. In this case, the second conductive film is set so that the counter electrode of the light emitting element serves as an anode.
また、補助配線110を形成する層は、図4に示すように列方向に配置される信号線と同じ層の導電体に限らず、行方向に配置される走査線と同じ層の導電膜を用いてもよい。また、補助配線110と第2の導電膜とのコンタクト(接続)は、列方向に線状に設けてもよいし、点状に設けてもよいし、それらを組み合わせてもよい。また行方向に線状に設けてもよいし、点状に設けてもよいし、それらを組み合わせてもよい。そこで、以下には、いくつかの場合を例に挙げて、そのマスクレイアウト図について、図5〜図7を用いて説明する。なお、図5〜図7は簡略化した図面であり、画素105内には画素電極のみを図示する。また、電源線112の図示は省略する。
The layer for forming the
まず、補助配線110と信号線111を同じ層の導電体で形成し、線状に形成された開口部を介して、補助配線110と第2の導電膜が接続する場合について図5を用いて説明する。図5において、画素部104には複数の画素105がマトリクス状に配置され、またこの画素部104には列方向に信号線111と補助配線110、行方向に走査線128が配置される。この補助配線110はカソード線106と接続される。なお、補助配線110とカソード線106は、同じレイヤーの導電体により形成される配線であるが、ここでは、画素部104内に配置される配線を補助配線110とよび、それ以外の領域に配置される配線をカソード線106とよぶ。
First, a case where the
そして、カソード線106と補助配線110の上方には線状の開口部120が形成され、この開口部120を介して、補助配線110及びカソード線106と、第2の導電膜とが接続する。この場合、補助配線110は、線状に形成された開口部120を介して、第2の導電膜と接続する。
A
次いで、カソード線106の上方に線状の開口部122が形成され、補助配線110上に点状の開口部123が形成された場合について、図6を用いて説明する。この場合、補助配線110は、点状に形成された開口部123を介して、第2の導電膜と接続する。それ以外は、図5の構成と同じである。
Next, the case where the
最後に、補助配線124と走査線128を同じレイヤーの導電体で形成し、点状に形成された開口部を介して、補助配線124と第2の導電膜が接続する場合について図7を用いて説明する。図7において、画素部104には複数の画素105がマトリクス状に配置され、またこの画素部104には列方向に信号線111、行方向に走査線128と補助配線124が配置される。この補助配線124は、カソード線126と接続される。補助配線124とカソード線126は、別のレイヤーの導電体により形成され、コンタクトホールを介して接続される。
Finally, the case where the
そして、カソード線126の上方に線状の開口部125が形成され、補助配線124の上方に点状の開口部127が形成され、これらの開口部を介して、カソード線126及び補助配線124と、第2の導電膜とが接続する。この場合、補助配線124は、点状に形成された開口部127を介して、第2の導電膜と接続する。
A linear opening 125 is formed above the
このように、補助配線は、列方向に配置される配線(例えば信号線)と同じ層の導電体で形成する方法(図5、6)と、行方向に配置される配線(例えば走査線)と同じ層の導電体で形成する方法(図7)が主な方法として挙げられ、これらの方法は、新たにマスクなどを作製する必要がない。従って、マスクの増加に伴う作製費用の上昇や信頼性の低減といった問題を回避することができる。また、補助配線と第2の導電膜とのコンタクトを点状に設けた場合、該コンタクトの形成箇所を画素の端部に配置すると、開口部の低減を抑制することができ、より明るい画像を提供することができる。 As described above, the auxiliary wiring is formed using a conductor in the same layer as the wiring (for example, signal line) arranged in the column direction (FIGS. 5 and 6), and the wiring (for example, scanning line) arranged in the row direction. The main method is a method of forming a conductor of the same layer (FIG. 7), and these methods do not require a new mask or the like. Therefore, problems such as an increase in manufacturing cost and a decrease in reliability due to an increase in masks can be avoided. Further, in the case where the contact between the auxiliary wiring and the second conductive film is provided in a dot shape, if the contact formation portion is arranged at the end portion of the pixel, reduction of the opening can be suppressed, and a brighter image can be obtained. Can be provided.
続いて、絶縁表面を有する基板上に、駆動用トランジスタ、発光素子及び補助配線を設けたときの断面構造とそのマスクレイアウト図について、図1〜3を用いて説明する。 Subsequently, a cross-sectional structure and a mask layout diagram thereof when a driving transistor, a light emitting element, and an auxiliary wiring are provided over a substrate having an insulating surface will be described with reference to FIGS.
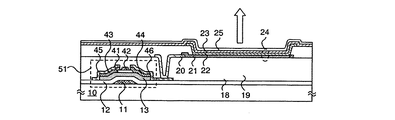
図1(C)は、1画素分のマスクレイアウトを示したものであり、列方向に電源線として機能する導電体16、信号線として機能する導電体26、補助配線として機能する導電体27が配置され、行方向に走査線として機能する導電体28が配置される。また、スイッチング用トランジスタ29と、駆動用トランジスタ30が設けられる。
FIG. 1C shows a mask layout for one pixel. A
図1(A)は、図1(C)のマスクレイアウト図のA-B-Cにおける断面構造を示す図に相当する。絶縁表面を有する基板10上に、ゲート電極11、該ゲート電極11上にゲート絶縁膜12が形成される。次に、非晶質半導体、N型半導体、導電体が積層して形成され、それらを同時にパターン加工して、非晶質半導体13、N型半導体14、15、導電体16、17が形成される。次に絶縁体18、19を形成し、導電体17の一部が露出するように所定の領域に開口部を形成後、導電体20が形成される。その後、導電体20と電気的に接続するように、導電体(第1の電極、画素電極)21、電界発光層22及び導電体(第2の電極、対向電極)23が形成される。この導電体21、電界発光層22及び導電体23の積層体が発光素子24に相当する。次に、保護膜25が全面に形成される。
FIG. 1A corresponds to a diagram showing a cross-sectional structure taken along ABC in the mask layout diagram of FIG. A
なお、導電体16、17が形成される際、導電体26、27が同時に形成される。導電体26は信号線に相当し、導電体27は補助配線に相当する。導電体(第2の電極、対向電極)23を成膜する前に、導電体27を露出させた状態にしておくことで、導電体23と導電体27は積層して形成され、導電体23の低抵抗化が実現される。なお、図1(A)に示す断面構造では、補助配線として機能する導電体27は、導電体16、17と同じ層の導電体で形成されている。
When the
図1(B)は、駆動用トランジスタ50と発光素子24の断面構造を示す。絶縁表面を有する基板10上に、ゲート電極11、該ゲート電極11上にゲート絶縁膜12が形成される。次に非晶質半導体13が形成され、次にエッチングストッパとなる絶縁体31が形成され、続いて、N型半導体、導電体が積層して形成され、それらを同時にパターン加工して、N型半導体32、33、導電体34、35が形成される。次に絶縁体18、5070、5080を形成し、導電体35の一部が露出するように所定の領域に開口部を形成後、導電体からなる接続配線5060が形成される。その後、導電体21、電界発光層22及び導電体23を含む発光素子24が形成され、その後保護膜25が形成される。
FIG. 1B shows a cross-sectional structure of the driving
なお、導電体34、35が形成される際、導電体26が同時に形成され、また、導電体20が形成される際、導電体36が同時に形成される。導電体26は信号線に相当し、導電体36は補助配線に相当する。導電体(対向電極)23を成膜する前に、導電体36を露出させた状態にしておくことで、導電体36と導電体23は積層して形成され、導電体23の低抵抗化が実現される。なお図1(B)に示す断面構造では、補助配線として機能する導電体36は、導電体20と同じ層の導電体で形成されている。
When the
図2は、駆動用トランジスタ51と発光素子24の断面構造を示す。絶縁表面を有する基板10上に、ゲート電極11、該ゲート電極11にゲート絶縁膜12が形成される。次に非晶質半導体13が形成され、次にエッチングストッパとなる絶縁体41が形成され、ゲート電極42が形成される。続いて、N型半導体、導電体が積層して形成され、それらを同時にパターン加工して、N型半導体43、44、導電体45、46が形成される。次に絶縁体18、19を形成し、導電体46の一部が露出するように所定の領域に開口部を形成後、導電体20が形成される。その後、導電体21、電界発光層22及び導電体23を含む発光素子24が形成され、その後保護膜25が形成される。また、補助配線として機能する導電体36は、導電体23と電気的に接続される。
FIG. 2 shows a cross-sectional structure of the driving
図3(A)は、駆動用トランジスタ431と発光素子438の断面構造を示す。絶縁表面を有する基板430上に、駆動用トランジスタ431が形成され、該駆動用トランジスタ431上に絶縁体440が形成され、所定の箇所に開口部が形成された後、該絶縁体440上に導電体433、434が形成される。続いて、画素電極に相当する導電体435が形成され、次に、絶縁体442が形成される。絶縁体441、442の所定の箇所に開口部439が形成された後、該絶縁体442上に電界発光層436、該電界発光層436上に、対向電極に相当する導電体437が形成される。このように、図3(A)に示す構成では、4層の絶縁体を積層した構成となっている。
FIG. 3A illustrates a cross-sectional structure of the driving
図3(B)は、駆動用トランジスタ431と発光素子459の断面構造を示す。絶縁表面を有する基板430上に、駆動用トランジスタ431が形成され、該駆動用トランジスタ431と電気的に接続された配線460、補助配線452が形成される。その後、絶縁体453が形成され、該絶縁体453の所定の箇所に開口部が形成される。続いて、画素電極に相当する導電体454が形成され、該導電体454上に絶縁体458が形成され、該絶縁体458の所定の箇所に開口部が形成される。次に、導電体454上に電界発光層455、456、該電界発光層455、456上に対向電極に相当する導電体457が形成される。導電体454、電界発光層455及び導電体457の積層体が発光素子459に相当する。
FIG. 3B illustrates a cross-sectional structure of the driving
図3(B)に示す構成では、補助配線452上の電界発光層456の膜厚は薄く、また蒸着法で形成されるため、補助配線452の側面までには形成されない。本構成はその点を活用しており、そのために、補助配線452の側面と導電体457とは電気的に接続される。
In the structure illustrated in FIG. 3B, the
図1〜図3に図示したように、本発明は、非晶質半導体を有するトランジスタと、発光素子を具備する。そして、発光素子と直列に接続された駆動用トランジスタは、電流能力の向上から、チャネル幅W/チャネル長L=1〜100(好ましくは5〜20)に設定することが好適である。具体的には、チャネル長を5〜15μm、チャネル幅Wを20〜1200μm(好ましくは40〜600μm)に設定することが好適である。なお、チャネル幅Wとチャネル長を上記のように設定すると、画素内におけるトランジスタの占有面積が大きくなってしまう。従って、発光素子は基板と反対の方向に出射する上面出射を行うことが好ましい。 As shown in FIGS. 1 to 3, the present invention includes a transistor having an amorphous semiconductor and a light emitting element. The driving transistor connected in series with the light emitting element is preferably set to channel width W / channel length L = 1 to 100 (preferably 5 to 20) in order to improve current capability. Specifically, it is preferable to set the channel length to 5 to 15 μm and the channel width W to 20 to 1200 μm (preferably 40 to 600 μm). Note that when the channel width W and the channel length are set as described above, the area occupied by the transistor in the pixel increases. Therefore, it is preferable that the light emitting element emits a top surface that is emitted in a direction opposite to the substrate.
非晶質半導体でチャネル部を形成するトランジスタは、大別して、チャネルエッチ型(図1(A)、図3(A)(B))、チャネル保護型(図1(B))、デュアルゲート型(図2)が挙げられ、本発明ではいずれを用いても構わない。 Transistors in which a channel portion is formed using an amorphous semiconductor are roughly classified into a channel etch type (FIGS. 1A, 3A and 3B), a channel protection type (FIG. 1B), and a dual gate type. (FIG. 2) is mentioned, and any of them may be used in the present invention.
発光素子を構成する一対の電極は、一方は陽極、他方は陰極に相当する。陽極及び陰極には、金属、合金、電気伝導体化合物及びこれらの混合物といった材料を用いることが好ましく、陽極には仕事関数の大きい材料、陰極には仕事関数の小さい材料を用いる。陽極と陰極の間に挟まれる電界発光層は、有機材料、無機材料の広汎に渡る材料により形成され、この電界発光層におけるルミネッセンスには、一重項励起状態から基底状態に戻る際の発光(蛍光)と、三重項励起状態から基底状態に戻る際の発光(リン光)とが含まれる。 One of the pair of electrodes included in the light-emitting element corresponds to an anode and the other corresponds to a cathode. It is preferable to use materials such as metals, alloys, electrical conductor compounds, and mixtures thereof for the anode and the cathode. A material having a high work function is used for the anode, and a material having a low work function is used for the cathode. The electroluminescent layer sandwiched between the anode and the cathode is formed of a wide variety of materials such as an organic material and an inorganic material. The luminescence in the electroluminescent layer includes luminescence (fluorescence when returning from a singlet excited state to a ground state). ) And light emission (phosphorescence) when returning from the triplet excited state to the ground state.
また、絶縁膜には、有機材料、無機材料のいずれの材料を用いてもよい。但し、有機材料は、その吸湿性に問題があるため、窒化珪素膜などのバリア膜を設けるとよい。有機材料のうち、レジスト材料は、アクリルやポリイミドといった他の有機材料よりも低コストで、コンタクトホールの径が小さく、且つ吸湿性が低いため、バリア膜を必要としないため、用いることが好適である。しかし、レジスト材料は有色であるため、上面出射型の表示装置に用いることが好適である。具体的なレジスト材料としては、クレゾール樹脂等を溶媒(プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテルアセテート;PGMEA)を溶かした溶液が挙げられ、該溶液をスピンコート法により塗布して形成する。 In addition, any material of an organic material and an inorganic material may be used for the insulating film. However, since an organic material has a problem in its hygroscopicity, a barrier film such as a silicon nitride film is preferably provided. Among organic materials, resist materials are preferable because they are less expensive than other organic materials such as acrylic and polyimide, have a small contact hole diameter, and have a low hygroscopic property, so that a barrier film is not necessary. is there. However, since the resist material is colored, it is preferably used for a top emission display device. Specific examples of the resist material include a solution in which a cresol resin or the like is dissolved in a solvent (propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate; PGMEA), and the solution is formed by applying the solution by a spin coating method.
上記構成を有する本発明は、トランジスタの特性にバラツキが少ないため、該トランジスタの特性バラツキにより生じる輝度ムラを改善した表示装置を提供することができる。また、非晶質半導体を用いる本発明は、数インチから数十インチの大型のパネルの作製に好適である。これは、結晶化の工程が不要であり、またマスク数も少なくて済むので、作製費用を抑制することができるためである。さらに、工程における熱処理温度にもよるが、非晶質半導体は、プラスチックなどの軽量、薄型、安価の可撓性基板上に作製することができるため、表示装置の用途を広げることができる。 The present invention having the above structure can provide a display device in which luminance unevenness caused by variation in characteristics of the transistor is improved because variation in characteristics of the transistor is small. In addition, the present invention using an amorphous semiconductor is suitable for manufacturing a large panel of several inches to several tens of inches. This is because a crystallization step is unnecessary and the number of masks is small, so that manufacturing costs can be suppressed. Further, although depending on the heat treatment temperature in the process, the amorphous semiconductor can be manufactured over a lightweight, thin, and inexpensive flexible substrate such as a plastic, so that the application of the display device can be expanded.
また、補助配線の配置により、第2の導電膜の抵抗値を低減することができ、その結果消費電力の低減が実現する。さらに、配線抵抗による信号の書き込み不良や階調不良などの防止や、電圧降下の発生が抑制され、発光素子に対して均一な電圧を印加することができる。従って、画像品質を向上させた表示装置を提供することができる。本構成は、数十インチの大型のパネルを作製する場合に大変有効であり、これは、パネルのインチ数が大きくなる程、その抵抗値が問題になるためである。 In addition, the auxiliary wiring can reduce the resistance value of the second conductive film, resulting in a reduction in power consumption. Further, signal writing failure and gradation failure due to wiring resistance can be prevented, and the occurrence of voltage drop can be suppressed, so that a uniform voltage can be applied to the light emitting element. Therefore, a display device with improved image quality can be provided. This configuration is very effective in manufacturing a large panel of several tens of inches, because the resistance value becomes a problem as the number of inches of the panel increases.
(実施の形態2)
本発明の実施の形態について図面を用いて説明する。
(Embodiment 2)
Embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
図8(A)はパネルの上面図を示したものであり、絶縁表面を有する基板200上に、マトリクス状に配置された複数の画素201を含む画素部202と走査線駆動回路203を有する。前記基板200には複数のドライバIC205が貼り付けられ、この複数のドライバIC205は信号線駆動回路204に相当する。走査線駆動回路203及び信号線駆動回路204は、電源回路206とコントローラ207に接続する。
FIG. 8A shows a top view of a panel, which includes a
電源回路206は、パネルに電源を供給するものであり、具体的には、画素部202内に配置された電源線と接続する。この電源線はアノード線又はカソード線ともよばれ、該アノード線は高電位電圧VDDと同電位、該カソード線は低電位電圧VSSと同電位である。コントローラ207は、クロック、クロックバック、スタートパルス及びビデオ信号を信号線駆動回路204及び走査線駆動回路203に供給する役割を担う。また、本パネルのように、信号線駆動回路204として複数のドライバIC205を具備する場合には、どのドライバICにどのビデオ信号を供給するのかを決定する役割、つまり信号を振り分ける役割もある。
The
なお図8(A)には、走査線側の駆動回路のみ基板上に一体形成する場合を示したが、本発明はこれに限定されず、その駆動回路の動作周波数によっては、同一基板上に信号線側の駆動回路も形成してもよい。但し、好適には、走査線側の駆動回路は基板上に一体形成し、信号線側の駆動回路はドライバICを用いるとよい。これは、走査線駆動回路と信号線駆動回路の各々の要求に応えるものであり、信号線駆動回路は、周波数50MHz以上(例えば65MHz以上)で駆動し、走査線駆動回路は、信号線駆動回路と比較するとその駆動周波数は約100分の1となる100kMHz程度で駆動するためである。このように、各々の駆動回路の動作周波数に応じて、基板上に集積された駆動回路を用いる方法か、ドライバICを貼り合わせる方法のどちらかを選択するとよい。 Note that FIG. 8A shows the case where only the driving circuit on the scanning line side is formed over the substrate; however, the present invention is not limited to this, and depending on the operating frequency of the driving circuit, the driving circuit on the same substrate is used. A driver circuit on the signal line side may also be formed. However, preferably, the driver circuit on the scanning line side is formed over the substrate and the driver circuit on the signal line side is a driver IC. This meets the demands of each of the scanning line driving circuit and the signal line driving circuit. The signal line driving circuit is driven at a frequency of 50 MHz or more (for example, 65 MHz or more), and the scanning line driving circuit is a signal line driving circuit. This is because the driving frequency is about 100 kHz, which is about 1/100. As described above, it is preferable to select either a method using a drive circuit integrated on a substrate or a method of attaching a driver IC in accordance with the operating frequency of each drive circuit.
図8(B)はパネルの上面図を示したものであり、絶縁表面を有する基板200上に、マトリクス状に配置された複数の画素201を含む画素部202を有する。また、COG方式により貼り付けられた信号線側のドライバIC209と、走査線側のドライバIC208を有する。これらのドライバIC208、209は、接続配線210により、外部入力端子211に接続される。そして、外部入力端子211を介して、電源回路206とコントローラ207に接続する。なお図8(B)には、COG方式により貼り付けられた場合を示したが、本発明はこれに限定されず、TAB方式や、基板上に貼り付けずにFPCを介してドライバICと接続させてもよい。また実装するドライバICの長辺、短辺の長さやその個数も特に限定されない。
FIG. 8B is a top view of the panel, which includes a
両パネルが有する各画素201は、一対の電極間に発光材料を含む発光素子と、非晶質半導体又は有機半導体でチャネル部を形成するトランジスタを有する。発光素子の第1の電極はアノード線、第2の電極はカソード線に接続され、本発明では、発光素子が発光していない期間に、アノード線とカソード線の電位を入れ替えて、該発光素子に逆方向バイアスを印加することを特徴とする。発光素子に逆方向バイアスを印加するタイミングは、コントローラ207から、所定の信号を電源回路206に供給することで行うことで決定される。従って、本発明では電源回路206とコントローラ207とをあわせて逆方向バイアス印加回路とよぶ。
Each
ところで、本発明の表示装置を用いて多階調の画像を表示する場合、時間階調方式を用いることが好適である。これは、発光素子が発光しない期間に逆方向バイアスを印加するように設定すれば、階調表示に影響を及ぼすことなく、逆方向バイアスを印加することができるためである。 By the way, when displaying a multi-tone image using the display device of the present invention, it is preferable to use a time gray scale method. This is because if the reverse bias is set to be applied during a period in which the light emitting element does not emit light, the reverse bias can be applied without affecting the gradation display.
また、通常、アノード線及びカソード線の一方の配線は、全ての画素に共通で接続されている。そのため、逆方向バイアスを印加するタイミングは、全ての画素で同時に行う必要が生じる。従って、逆方向バイアスを発光素子に印加するために、新たに半導体素子を配置してもよい。この半導体素子とは、トランジスタ又はダイオードに相当し、この半導体素子を用いることで、画素毎又はライン毎などの任意の画素毎に逆バイアスを印加することが出来るようにする。具体的には、前記半導体素子が導通状態になると同時に、発光素子に逆方向バイアスが印加されるようにする。つまり前記半導体素子が導通状態になると、ある配線と発光素子とが電気的に接続される状態になるようにする。このとき、このある配線の電位を発光素子の対向電位よりも低くしておくことで、発光素子に逆方向バイアスが印加されるようにする。逆方向バイアスを印加すると、発光素子は必然的に非発光となるが、上記構成を有する場合は、任意の画素に任意のタイミングで逆方向バイアスを印加することができるため、階調表示に影響を及ぼすことはない。この方法は、時間階調方式だけでなく、多階調を表現する方法として、アナログ駆動などの他の方式を用いた場合にも好適な方法である。 In general, one wiring of the anode line and the cathode line is commonly connected to all the pixels. Therefore, it is necessary to apply the reverse bias at the same time for all the pixels. Therefore, a new semiconductor element may be disposed in order to apply a reverse bias to the light emitting element. This semiconductor element corresponds to a transistor or a diode. By using this semiconductor element, a reverse bias can be applied to any pixel such as every pixel or every line. Specifically, a reverse bias is applied to the light emitting element at the same time as the semiconductor element becomes conductive. That is, when the semiconductor element becomes conductive, a certain wiring and a light emitting element are electrically connected. At this time, the reverse bias is applied to the light emitting element by setting the potential of the wiring lower than the counter potential of the light emitting element. When a reverse bias is applied, the light emitting element inevitably emits no light. However, in the case of the above structure, the reverse bias can be applied to an arbitrary pixel at an arbitrary timing, which affects gradation display. Will not affect. This method is suitable not only for the time gray scale method but also when other methods such as analog driving are used as a method for expressing multiple gray scales.
上記構成を有する本発明は、発光素子の経時劣化を抑制することができ、信頼性の向上や素子の長寿命化を実現した表示装置を提供することができる。本実施の形態は、上記の実施の形態と自由に組み合わせることができる。 The present invention having the above structure can provide a display device that can suppress deterioration over time of a light-emitting element and can improve reliability and extend the life of the element. This embodiment mode can be freely combined with the above embodiment modes.
(実施の形態3)
本実施の形態では、非晶質半導体でチャネル部を形成するN型トランジスタと、有機半導体でチャネル部を形成するP型トランジスタを含むCMOS回路の断面構造について、図10を用いて説明する。
(Embodiment 3)
In this embodiment mode, a cross-sectional structure of a CMOS circuit including an N-type transistor whose channel portion is formed using an amorphous semiconductor and a P-type transistor whose channel portion is formed using an organic semiconductor will be described with reference to FIGS.
図10(A)は等価回路図であり、P型トランジスタ221とN型トランジスタ222が直列に接続され、一端はVDD、他端はVSSと同電位に設定されている。図10(B)は、これらのトランジスタの断面構造を示したものであり、基板200上に導電体231、232が設けられ、該導電体231、232上に窒化シリコン233が設けられる。次に、窒化シリコン233上に非晶質半導体234が設けられ、該非晶質半導体234上に再度窒化シリコン241が設けられる。次に、窒化シリコン241上にN型半導体と導電体が積層して設けられ、これらを同時にパターン加工して、N型半導体235、242、電極236、237が設けられる。その後、電極238、239が設けられ、続いて、チャネル層となる有機半導体240を設けられる。有機半導体240としては、ペンタセンなどの有機低分子、PEDOTやPPVなどの有機高分子などを用いればよく、ペンタセンのパターン加工には、蒸着法にメタルマスクを併用する方法を用いるとよい。このようにして、非晶質半導体234でチャネル部を形成するN型トランジスタと、有機半導体240でチャネル部を形成するP型トランジスタを含むCMOS回路が完成する。
FIG. 10A is an equivalent circuit diagram in which a P-
このCMOS回路は、シフトレジスタやバッファなどを構成するクロックドインバータ等の単位回路となるため、駆動回路に用いてもよいし、また画素回路に用いてもよい。また本構成は、その動作周波数から、走査線側の駆動回路に用いることが好適である。具体的には、図8(A)に示すように、走査線側の駆動回路を本構成のCMOS回路で形成し、信号線側の駆動回路としてドライバICを用いることが好適である。なお本実施の形態では、CMOS回路で駆動回路を構成する場合を説明したが、本発明はこれに限定されない。勿論、N型トランジスタ(a-Si:HTFT)のみ、P型トランジスタ(有機TFT)のみで駆動回路を構成しても構わない。 Since this CMOS circuit is a unit circuit such as a clocked inverter that constitutes a shift register, a buffer, or the like, it may be used for a driver circuit or a pixel circuit. In addition, this configuration is preferably used for a driving circuit on the scanning line side because of its operating frequency. Specifically, as illustrated in FIG. 8A, it is preferable that the driver circuit on the scanning line side is formed using a CMOS circuit of this structure and a driver IC is used as the driver circuit on the signal line side. In this embodiment mode, the case where the driver circuit is formed using a CMOS circuit has been described, but the present invention is not limited to this. Of course, the drive circuit may be configured with only an N-type transistor (a-Si: HTFT) and only a P-type transistor (organic TFT).
本実施の形態は、上記の実施の形態と自由に組み合わせることができる。 This embodiment mode can be freely combined with the above embodiment modes.
(実施の形態4)
本発明は、一対の電極間に発光材料を含む発光素子と、非晶質半導体、又は有機半導体でチャネル部を形成するトランジスタを含む画素を複数有する表示装置を提供するものであり、ここでは、該画素の構成について、図11を用いて説明する。
(Embodiment 4)
The present invention provides a display device including a plurality of pixels each including a light-emitting element including a light-emitting material between a pair of electrodes and a transistor in which a channel portion is formed using an amorphous semiconductor or an organic semiconductor. The configuration of the pixel will be described with reference to FIG.
図11(A)に示す画素は、列方向に信号線310及び電源線311〜313、行方向に走査線314が配置される。また、スイッチング用のトランジスタ301、駆動用のトランジスタ303、電流制御用のトランジスタ304、容量素子302及び発光素子305を有する。
In the pixel shown in FIG. 11A, a
図11(C)に示す画素は、トランジスタ303のゲート電極が、行方向に配置された電源線313に接続される点が異なっており、それ以外は図11(A)に示す画素と同じ構成である。つまり、図11(A)(C)に示す両画素は、同じ等価回路図を示す。しかしながら、行方向に電源線312が配置される場合(図11(A))と、列方向に電源線312が配置される場合(図11(C))では、各電源線は異なる層の導電体で形成される。ここでは、トランジスタ303のゲート電極が接続される配線に注目し、これらを作製する層が異なることを表すために、図11(A)(C)として分けて記載する。
The pixel shown in FIG. 11C is different from the pixel shown in FIG. 11A except that the gate electrode of the
図11(A)(C)に示す画素の特徴として、画素内にトランジスタ303、304が直列に接続されており、トランジスタ303のチャネル長L3、チャネル幅W3、トランジスタ304のチャネル長L4、チャネル幅W4は、L3/W3:L4/W4=5〜6000:1を満たすように設定される点が挙げられる。6000:1を満たす場合の一例としては、L3が500μm、W3が3μm、L4が3μm、W4が100μmの場合がある。
As a feature of the pixel shown in FIGS. 11A and 11C,
なお、トランジスタ303は、飽和領域で動作し発光素子305に流れる電流値を制御する役目を有し、トランジスタ304は線形領域で動作し発光素子305に対する電流の供給を制御する役目を有する。両トランジスタは同じ導電型を有していると作製工程上好ましい。またトランジスタ303には、エンハンスメント型だけでなく、ディプリーション型のトランジスタを用いてもよい。上記構成を有する本発明は、トランジスタ304が線形領域で動作するために、トランジスタ304のVGSの僅かな変動は発光素子305の電流値に影響を及ぼさない。つまり、発光素子305の電流値は、飽和領域で動作するトランジスタ303により決定される。上記構成を有する本発明は、トランジスタの特性バラツキに起因した発光素子の輝度ムラを改善して画質を向上させた表示装置を提供することができる。
Note that the
図11(A)〜(D)に示す画素において、トランジスタ301は、画素に対するビデオ信号の入力を制御するものであり、トランジスタ301がオンして、画素内にビデオ信号が入力されると、容量素子302にそのビデオ信号が保持される。なお図11(A)(C)には、容量素子302を設けた構成を示したが、本発明はこれに限定されず、ビデオ信号を保持する容量がゲート容量などでまかなうことが可能な場合には、明示的に容量素子302を設けなくてもよい。
In the pixel illustrated in FIGS. 11A to 11D, the
発光素子305は、2つの電極間に電界発光層が挟まれた構造を有し、順バイアス方向の電圧が印加されるように、画素電極と対向電極の間(陽極と陰極の間)に電位差が設けられる。電界発光層は有機材料や無機材料等の広汎に渡る材料により構成され、この電界発光層におけるルミネッセンスには、一重項励起状態から基底状態に戻る際の発光(蛍光)と、三重項励起状態から基底状態に戻る際の発光(リン光)とが含まれる。
The light-emitting
図11(B)に示す画素は、トランジスタ306と走査線315を追加している以外は、図11(A)に示す画素構成と同じである。同様に、図11(D)に示す画素は、トランジスタ306と走査線315を追加している以外は、図11(C)に示す画素構成と同じである。
The pixel illustrated in FIG. 11B has the same pixel structure as that illustrated in FIG. 11A except that a
トランジスタ306は、新たに配置された走査線315によりオン又はオフが制御される。トランジスタ306がオンになると、容量素子302に保持された電荷は放電し、トランジスタ306がオフする。つまり、トランジスタ306の配置により、強制的に発光素子305に電流が流れない状態を作ることができる。従って、図11(B)(D)の構成は、全ての画素に対する信号の書き込みを待つことなく、書き込み期間の開始と同時又は直後に点灯期間を開始することができるため、デューティ比を向上することが可能となる。
The
図11(E)に示す画素は、列方向に信号線350、電源線351、352、行方向に走査線353が配置される。また、スイッチング用トランジスタ341、駆動用トランジスタ343、容量素子342及び発光素子344を有する。図11(F)に示す画素は、トランジスタ345と走査線354を追加している以外は、図11(E)に示す画素構成と同じである。なお、図11(F)の構成も、トランジスタ345の配置により、デューティ比を向上することが可能となる。
In the pixel shown in FIG. 11E, a
本実施の形態は、上記の実施の形態と自由に組み合わせることができる。 This embodiment mode can be freely combined with the above embodiment modes.
本発明の必須の構成要素として、一対の電極間に発光材料を含む発光素子と、非晶質半導体又は有機半導体を含むトランジスタが挙げられ、該発光素子と該トランジスタは各画素に具備されている。このように、非晶質半導体を含むトランジスタを各画素に含む場合、多くの場合において、ドライバICをCOG方式やTAB方式により実装したり、FPCを介して接続したりする。本実施例では、矩形上の基板に複数のドライバICを形成し、該ドライバICを実装する実施例について説明する。 As essential components of the present invention, a light-emitting element including a light-emitting material between a pair of electrodes and a transistor including an amorphous semiconductor or an organic semiconductor can be given, and the light-emitting element and the transistor are included in each pixel. . As described above, when a transistor including an amorphous semiconductor is included in each pixel, in many cases, a driver IC is mounted by a COG method or a TAB method, or connected through an FPC. In the present embodiment, an embodiment in which a plurality of driver ICs are formed on a rectangular substrate and the driver ICs are mounted will be described.
図9(A)に示すパネルの上面図は、走査線側と信号線側の各々に1つのドライバIC251、252が設けられている。それ以外の構成は、図8(B)に示すパネルと同じであるため、ここでは説明を省略する。
In the top view of the panel shown in FIG. 9A, one
図9(B)は、基板にドライバICを貼り付ける様子を示した斜視図である。基板253上には、複数の駆動回路と該複数の駆動回路を接続する入出力端子が設けられる。各駆動回路と、当該駆動回路に対応した入力出力端子を1つのユニットとして、基板253を短冊状又は矩形状に分断すると、複数のドライバICが得られる。そして、このドライバICを基板200に貼り合わせると、表示装置が完成する。図9(B)では、走査線駆動回路に相当するドライバIC252と、信号線駆動回路に相当するドライバIC251が実装された形態を示す。
FIG. 9B is a perspective view showing a state where the driver IC is attached to the substrate. On the
信号線及び走査線のピッチは、ドライバICの出力端子のピッチと合わせることが好適である。そうすると、画素部202の端部で数ブロック毎に区分して引出線を形成する必要がなく、プロセス上、歩留まりよく作製することができる。また、これらのドライバICは、矩形状の基板200上に複数個作り込むと、大量に形成することができるため、生産性を向上させる観点から好ましい。従って、基板200として、大面積の基板を用いることが好ましく、例えば、一辺が300mmから1000mm程度の大面積の基板を用いることが好ましい。これは、円形のシリコンウエハからICチップを取り出す場合と比較すると、大きな優位点である。さらに、切り出す際、ドライバICの長辺の長さを、画素部202の縦方向又は横方向の長さと同じ長さにすると、貼り付けるドライバICの個数が減少させることが可能となり、信頼性が向上する。
The pitch of the signal lines and the scanning lines is preferably matched with the pitch of the output terminals of the driver IC. Then, it is not necessary to form the leader line by dividing into several blocks at the end portion of the
また、これらのドライバICは結晶質半導体により形成されることが好適であり、前記結晶質半導体は連続発振のレーザ光を照射することで形成されることが好適である。従って、当該レーザ光を発生させる発振器としては、連続発振の固体レーザ又は気体レーザを用いることが好適である。これは、連続発振のレーザ光を照射すると、その走査方向に、結晶粒界が延びることを活用するものであり、結晶粒界が延びた方向とチャネル長方向とが平行になるように、半導体層をパターン加工すると、十分な電気的特性が得られた結晶質半導体を活性層として用いた薄膜トランジスタを形成することができるためである。 These driver ICs are preferably formed of a crystalline semiconductor, and the crystalline semiconductor is preferably formed by irradiating continuous wave laser light. Therefore, it is preferable to use a continuous wave solid-state laser or a gas laser as an oscillator for generating the laser light. This utilizes the fact that crystal grain boundaries extend in the scanning direction when irradiated with continuous-wave laser light, and the semiconductor extends so that the direction in which the crystal grain boundaries extend and the channel length direction are parallel to each other. This is because when a layer is patterned, a thin film transistor using a crystalline semiconductor with sufficient electrical characteristics as an active layer can be formed.
ドライバICの構成は、走査線側と信号線側で異なる構成であることが好適である。具体的には、信号線側に配置する駆動回路と、走査線側に配置する駆動回路とで、薄膜トランジスタのゲート絶縁膜の膜厚を変えることが好適である。これは、信号線(データ線)側と走査線側の各々の要求に応えるものであり、具体的には、信号線駆動回路を構成する薄膜トランジスタのゲート絶縁膜の厚さは20〜70nm、チャネル長は0.3〜1μmに設定する。一方、走査線駆動回路を構成する薄膜トランジスタのゲート絶縁膜の厚さは150〜250nm、チャネル長は1〜2μmに設定する。上記構成により、各々の駆動回路の動作周波数に応じたドライバICを有する表示装置を提供することができる。本実施例は、上記の実施の形態、実施例と自由に組み合わせることができる。 The configuration of the driver IC is preferably different between the scanning line side and the signal line side. Specifically, it is preferable to change the film thickness of the gate insulating film of the thin film transistor between the driver circuit arranged on the signal line side and the driver circuit arranged on the scanning line side. This meets the requirements of the signal line (data line) side and the scanning line side. Specifically, the thickness of the gate insulating film of the thin film transistor constituting the signal line driving circuit is 20 to 70 nm, and the channel The length is set to 0.3-1 μm. On the other hand, the thickness of the gate insulating film of the thin film transistor constituting the scanning line driving circuit is set to 150 to 250 nm, and the channel length is set to 1 to 2 μm. With the above structure, a display device having a driver IC corresponding to the operating frequency of each driving circuit can be provided. This embodiment can be freely combined with the above embodiment modes and embodiments.
本発明の必須の構成要素として、一対の電極間に発光材料を含む発光素子と、非晶質半導体又は有機半導体を含むトランジスタが挙げられ、該発光素子と該トランジスタは各画素に具備される。このような、非晶質半導体を含むトランジスタは、その電気特性(しきい値電圧、電界効果移動度等)が経時的に変化する性質を有する。そこで、ここでは、しきい値電圧に注目し、しきい値補正回路について説明する。 As essential components of the present invention, a light-emitting element including a light-emitting material between a pair of electrodes and a transistor including an amorphous semiconductor or an organic semiconductor can be given, and the light-emitting element and the transistor are included in each pixel. Such a transistor including an amorphous semiconductor has a property that its electrical characteristics (threshold voltage, field-effect mobility, and the like) change with time. Therefore, here, the threshold voltage correction circuit will be described by focusing on the threshold voltage.
まず、しきい値補正回路について、図17(A)〜(D)を用いて説明する。図17(A)は等価回路図を示し、トランジスタ等からなるスイッチ531、532、トランジスタ533、容量素子534を有する。この回路の動作について、以下に簡単に説明する。
First, the threshold correction circuit will be described with reference to FIGS. FIG. 17A shows an equivalent circuit diagram, which includes
まず、スイッチ531、532をオンにする(図17(A))。そうすると、スイッチ531からトランジスタ533の方向と、スイッチ531から容量素子534の方向に向かって電流IDSが流れる。このとき、電流IDSはI1とI2に分かれて流れ、IDS=I1+I2を満たす。電流が流れ始めた瞬間には、容量素子534に電荷は保持されず、トランジスタ533はオフである。従って、I2=0、IDS=I1である。しかしながら、徐々に容量素子534に電荷が蓄積されて、容量素子534の両電極間に電位差が生じ始める。両電極間の電位差がVTHになると、トランジスタ554がオンになり、I2>0となる。このとき、IDS=I1+I2を満たすので、I1は次第に減少するが、以前電流は流れている。そして、容量素子534では、その両電極間の電位差がVDDになるまで、電荷の蓄積が続けられる。容量素子534の両電極間の電位差がVDDになると、I2は流れなくなり、トランジスタ533はオンであるため、IDS=I1となる(図17(C)(D)、A点)。
First, the
続いて、スイッチ531をオフにする(図17(B))。そうすると、容量素子534に保持された電荷は、スイッチ532を介してトランジスタ533の方向に流れていき、放電する。この動作は、トランジスタ533がオフになるまで行われる。つまり、容量素子534に保持された電荷が、トランジスタ533のしきい値電圧と同じ値になるまで電荷が保持される(図17(C)(D)、B点)。
Subsequently, the
このようにすると、容量素子の両電極間の電位差を、あるトランジスタのしきい値電圧と同じ値になるように設定することができる。そして、トランジスタのVGSをそのまま保持して、該トランジスタのゲート電極に信号電圧を入力する。そうすると、トランジスタのゲート電極には、容量素子に保持されているVGSに加えて、前記信号電圧を上乗せした値が入力される。つまり、トランジスタ間のしきい値電圧にバラツキが生じていても、信号電圧が入力されるトランジスタは、常に該トランジスタのしきい値電圧と信号電圧を足した値が入力される。従って、トランジスタ間のしきい値電圧のバラツキの影響を抑制することができる。 In this way, the potential difference between both electrodes of the capacitor can be set to the same value as the threshold voltage of a certain transistor. Then, while keeping V GS of the transistor as it is, a signal voltage is input to the gate electrode of the transistor. Then, in addition to V GS held in the capacitor, a value obtained by adding the signal voltage is input to the gate electrode of the transistor. That is, even if the threshold voltage between transistors varies, a transistor to which a signal voltage is input always receives a value obtained by adding the threshold voltage of the transistor and the signal voltage. Therefore, the influence of the variation in threshold voltage between transistors can be suppressed.
しきい値補正回路を設けることで、発光素子を駆動する駆動用トランジスタのしきい値電圧のバラツキを抑制することができ、これらのバラツキに起因した輝度ムラを改善して、高画質の画像を表示する表示装置を提供することができる。なお、本実施例で示したしきい値補正回路は、図11に図示した画素回路にも適用することができる。その際、ゲート電極に信号電圧が入力される駆動用トランジスタのしきい値電圧を補正できるように、本しきい値補正回路を設けるとよい。 By providing the threshold correction circuit, variations in threshold voltage of the driving transistor for driving the light emitting element can be suppressed, and luminance unevenness caused by these variations can be improved, resulting in high-quality images. A display device for displaying can be provided. Note that the threshold correction circuit shown in this embodiment can also be applied to the pixel circuit shown in FIG. At this time, this threshold value correction circuit may be provided so that the threshold voltage of the driving transistor in which the signal voltage is input to the gate electrode can be corrected.
なお本実施例では、しきい値電圧の補正手段を例示したが、他の電気特性の補正手段を有していてもよく、例えば、電界効果移動度の補正手段を設けてもよい。本実施例は、上記の実施の形態、実施例と自由に組み合わせることができる。 In the present embodiment, the threshold voltage correcting means is exemplified, but other electric characteristic correcting means may be provided, for example, a field effect mobility correcting means may be provided. This embodiment can be freely combined with the above embodiment modes and embodiments.
発光素子は、正孔注入層、正孔輸送層、正孔阻止層(ホールブロッキング層)、電子輸送層等が適宜組み合わされて形成される。但し、電子注入層は、電子のみの輸送性に優れた材料として知られているバソキュプロイン(BCP)にリチウム(Li)をドーピングした場合に電極からの電子注入性を著しく向上させることができるため、そのような材料を用いるとよい。 The light-emitting element is formed by appropriately combining a hole injection layer, a hole transport layer, a hole blocking layer (hole blocking layer), an electron transport layer, and the like. However, since the electron injection layer can significantly improve the electron injection property from the electrode when lithium (Li) is doped into bathocuproin (BCP), which is known as a material excellent in the transport property of only electrons, Such a material may be used.
また、ベンゾオキサゾール誘導体(BzOS)、又はピリジン誘導体が、優れた電子輸送性を有し、かつ成膜した場合に結晶化しにくい材料であり、さらにアルカリ金属、アルカリ土類金属、または遷移金属のうちの少なくとも一種を含むことにより電子注入性に優れた層を形成する。そこで、一対の電極間に発光物質を含む層を有する発光素子において、発光物質を含む層の一部にベンゾオキサゾール誘導体、又はピリジン誘導体を用いることが好適である。 In addition, a benzoxazole derivative (BzOS) or a pyridine derivative is a material that has excellent electron transporting properties and is difficult to crystallize when formed, and among alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, and transition metals By including at least one of the above, a layer having excellent electron injectability is formed. Therefore, in a light-emitting element having a layer containing a light-emitting substance between a pair of electrodes, it is preferable to use a benzoxazole derivative or a pyridine derivative for part of the layer containing a light-emitting substance.
つまり、ベンゾオキサゾール誘導体、又はピリジン誘導体と、アルカリ金属、アルカリ土類金属、または遷移金属のうちの少なくとも一種とを含む発光素子用電子注入性組成物を用いて電子注入層を形成することにより、陰極として機能する電極からの電子注入性を高めることができる。さらに、ピリジン誘導体は成膜した場合に結晶化しにくい材料であることから、従来よりも素子特性に優れ、素子寿命の長い発光素子、およびそれを用いた表示装置を提供することができる。本実施例は、上記の実施の形態、実施例と自由に組み合わせることができる。 That is, by forming an electron injection layer using a benzoxazole derivative or a pyridine derivative and an electron injectable composition for a light-emitting element containing at least one of an alkali metal, an alkaline earth metal, or a transition metal, Electron injection from the electrode functioning as the cathode can be improved. Furthermore, since a pyridine derivative is a material that is difficult to crystallize when deposited, a light-emitting element that has superior element characteristics and a longer element lifetime than conventional ones, and a display device using the light-emitting element can be provided. This embodiment can be freely combined with the above embodiment modes and embodiments.
本実施例では、発光素子の積層構造について説明する。ここでは、図1(B)において、破線5700、5710で囲んだ部分の拡大図を用いて説明する。なお、図18(A)(C)、図19(A)は、破線5700で囲んだ部分の拡大図に相当し、図18(B)(D)、図21(B)は、破線5710で囲んだ部分の拡大図に相当する。なお、図1(B)の断面構造と、図18、19に示す断面構造とは、絶縁膜5070、パッシべーション膜5080、接続配線5060及び画素電極5100が形成されている点は同じであるが、それ以外の構造は異なっており、以下には、異なる符号を用いて説明する。
In this embodiment, a stacked structure of light emitting elements will be described. Here, description is made using an enlarged view of a portion surrounded by
図18(A)(B)において、絶縁膜5070上にパッシべーション膜5080が形成され、該パッシべーション膜5080上に接続配線5060が形成される。この接続配線5060は、駆動用トランジスタのソース電極又はドレイン電極と電気的に接続されている。また、パッシべーション膜5080上には、接続配線5060と共通の導電体をパターン加工することで得られた補助配線5200が形成される。そして接続配線5060に接続するように画素電極5100が形成され、該画素電極5100上に正孔注入層5110、発光層5120、電子注入層5130が順に積層される。最後に、保護膜5240が形成される。画素電極5100、正孔注入層5110、発光層5120及び電子注入層5130との積層体が発光素子5140に相当する。
18A and 18B, a
この発光層5120は、開口部を完全に覆わず、補助配線5200の一部を露出させるように、メタルマスクを用いて形成する。従って、開口部においては、補助配線5200上に、正孔注入層5110、電子注入層5130が順に積層されている。なお、本発明はこれに限定されず、正孔注入層5110及び発光層5120を、メタルマスクを用いて形成することで、補助配線5200上に電子注入層5130のみが形成された構成としてもよい。
The
また、図18(A)(B)では、発光素子5140から発せられる光が基板側に出射する構成を示すが、光が基板側とは反対側に向かう構造を有していてもよい。
18A and 18B illustrate a structure in which light emitted from the light-emitting
図18(C)(D)に示す断面構造は、接続配線5060と接続するように、画素電極5100が形成され、該画素電極5100上に正孔注入層5110、発光層5120、電子注入層5130、透明導電膜5800が順に積層される。最後に保護膜5240が形成される。電子注入層5130に接するように透明導電膜5800を形成することで、対向電極として機能する電子注入層5130自体の抵抗が高まっても、電位降下を抑えることができる。
18C and 18D, a
この発光層5120は、開口部を完全に覆わず、補助配線5200の一部を露出させるように、メタルマスクを用いて形成する。従って、開口部においては、補助配線5200上に、正孔注入層5110、電子注入層5130、透明導電膜5800が順に積層されている。なお、本発明はこれに限定されず、正孔注入層5110及び発光層5120を、メタルマスクを用いて形成することで、補助配線5200上に電子注入層5130及び透明導電膜5800のみが形成された構成としてもよい。また、正孔注入層5110、発光層5120及び電子注入層5130を、メタルマスクを用いて形成することで、補助配線5200上に透明導電膜5800のみが形成された構成としてもよい。
The
なお、図18(A)(B)において、保護膜5240は、無機絶縁膜と有機絶縁膜の積層構造を有していてもよく、そのときの断面構造について、図19(A)(B)を用いて説明する。
18A and 18B, the
図19(A)(B)において、保護膜5240は積層構造を有しており、電子注入層5130に接するように無機絶縁膜5240a、該無機絶縁膜5240a上に有機樹脂膜5240b、該有機樹脂膜5240b上に無機絶縁膜5240cが形成される。無機絶縁膜5240a、5240cとしては、窒化珪素、窒化酸化珪素、酸化アルミニウム、窒化アルミニウム等を用いることで、発光素子5140に対する水分や酸素の劣化を促進させる物質の侵入を防止することができる。また、無機絶縁膜5240aと無機絶縁膜5240cとの間に、内部応力が小さい有機樹脂膜5240bを設けることで、保護膜5240が応力によって剥離することを防止することができる。この有機樹脂膜5240bとしては、ポリイミド、ポリアミド、ポリイミドアミド等を用いることができる。
19A and 19B, the
この発光層5120は、開口部を完全に覆わず、補助配線5200の一部を露出させるように、メタルマスクを用いて形成する。従って、開口部においては、補助配線5200上に、正孔注入層5110、電子注入層5130、無機絶縁膜5240a、有機樹脂膜5240b及び無機絶縁膜5240cが順に積層されている。なお、本発明はこれに限定されず、正孔注入層5110及び発光層5120を、メタルマスクを用いて形成することで、補助配線5200上に電子注入層5130、無機絶縁膜5240a、有機樹脂膜5240b及び無機絶縁膜5240cが順に形成された構成としてもよい。本実施例は、上記の実施の形態、実施例と自由に組み合わせることができる。
The
本発明の必須の構成要素として、一対の電極間に発光材料を含む発光素子と、非晶質半導体又は有機半導体を含むトランジスタが挙げられ、該発光素子と該トランジスタは各画素に具備される。このようなトランジスタを各画素に含む場合、同一基板上に形成する駆動回路も非晶質半導体又は有機半導体を含むトランジスタにより形成することが好適である。但し、非晶質半導体を含むトランジスタはN型トランジスタしか形成できない。そこで、本実施例では、N型トランジスタのみでシフトレジスタを構成する例について説明する。 As essential components of the present invention, a light-emitting element including a light-emitting material between a pair of electrodes and a transistor including an amorphous semiconductor or an organic semiconductor can be given, and the light-emitting element and the transistor are included in each pixel. In the case where such a transistor is included in each pixel, a driver circuit formed over the same substrate is preferably formed using a transistor including an amorphous semiconductor or an organic semiconductor. However, only an N-type transistor can be formed as a transistor including an amorphous semiconductor. Therefore, in this embodiment, an example in which a shift register is configured with only N-type transistors will be described.
図12(A)において、400で示すブロックが1段分のサンプリングパルスを出力するパルス出力回路に相当し、シフトレジスタはn個のパルス出力回路により構成される。図12(B)は、パルス出力回路400の具体的な構成を示したものであり、N型のトランジスタ401〜406と、容量素子407を有する。このパルス出力回路は、ブートストラップ法を応用することで、N型トランジスタのみでの構成が可能となった回路である。詳しい動作については、特開2002-335153号公報に記載されているため、本公報を参考にするとよい。
In FIG. 12A, a block denoted by 400 corresponds to a pulse output circuit that outputs a sampling pulse for one stage, and the shift register includes n pulse output circuits. FIG. 12B shows a specific structure of the
なお本実施例では、N型トランジスタのみで構成する例を示したが、本発明はこれに限定されない。チャネル部に有機半導体を含むP型トランジスタで駆動回路を構成してもよい。本実施例は、上記の実施の形態、実施例と自由に組み合わせることができる。 In this embodiment, an example in which only an N-type transistor is used is shown, but the present invention is not limited to this. The driver circuit may be formed of a P-type transistor including an organic semiconductor in the channel portion. This embodiment can be freely combined with the above embodiment modes and embodiments.
本発明の表示装置をデジタル駆動する場合、多階調の画像を表現するためには時間階調方式を用いることが好適である。本実施例は時間階調方式について説明するものであり、図13(A)は、縦軸は走査線、横軸は時間のときのタイミングチャートを示し、図13(B)はj行目の走査線のタイミングチャートを示す。 When the display device of the present invention is digitally driven, it is preferable to use a time gray scale method in order to express a multi-tone image. This embodiment describes a time gray scale method. FIG. 13A shows a timing chart when the vertical axis indicates a scanning line and the horizontal axis indicates time, and FIG. 13B shows the j-th row. A timing chart of a scanning line is shown.
表示装置は、そのフレーム周波数を通常60Hz程度とする。つまり、1秒間に60回程度の画面の描画が行われ、画面の描画を1回行う期間を1フレーム期間と呼ぶ。時間階調方式では、1フレーム期間を複数のサブフレーム期間に分割する。このときの分割数は、階調ビット数に等しい場合が多く、ここでは簡単のために、分割数が階調ビット数に等しい場合を示す。つまり本実施例では5ビット階調を例示しているので、5つのサブフレーム期間SF1〜SF5に分割した例を示す。各サブフレーム期間は、画素にビデオ信号を書き込むアドレス期間Taと、画素が点灯又は非点灯するサステイン期間Tsを有する。サステイン期間Ts1〜Ts5は、その長さの比をTs1:・・・:Ts5=16:8:4:2:1とする。つまり、nビット階調を表現する場合、n個のサステイン期間は、その長さの比を2(n-1):2(n-2):・・・:21:20とする。 The display device normally has a frame frequency of about 60 Hz. In other words, a screen drawing is performed about 60 times per second, and a period in which the screen is drawn once is referred to as one frame period. In the time gray scale method, one frame period is divided into a plurality of subframe periods. In many cases, the number of divisions at this time is equal to the number of gradation bits. Here, for the sake of simplicity, the case where the number of divisions is equal to the number of gradation bits is shown. In other words, since the 5-bit gradation is illustrated in the present embodiment, an example in which it is divided into five subframe periods SF1 to SF5 is shown. Each sub-frame period has an address period Ta in which a video signal is written to the pixel and a sustain period Ts in which the pixel is lit or not lit. In the sustain periods Ts1 to Ts5, the ratio of the lengths is Ts1:...: Ts5 = 16: 8: 4: 2: 1. That is, when expressing n-bit gradation, the length ratio of n sustain periods is 2 (n-1) : 2 (n-2) :...: 2 1 : 2 0 .
そして、書き込み期間よりも短い点灯期間を有するサブフレーム期間(ここではサブフレーム期間SF5が該当)は消去期間Te5を有する。消去期間Te5は、画素に書き込まれたビデオ信号をリセットし、発光素子が強制的にリセットされる期間であり、点灯期間の終了後、直ちに次の期間が開始しないようにする。 A subframe period (here, the subframe period SF5 corresponds) having a lighting period shorter than the writing period has an erasing period Te5. The erasing period Te5 is a period in which the video signal written in the pixel is reset and the light emitting element is forcibly reset, and the next period does not start immediately after the lighting period ends.
なお、表示階調数を増やしたい場合は、サブフレーム期間の分割数を増やせば良い。また、サブフレーム期間の順序は、必ずしも上位ビットから下位ビットといった順序である必要はなく、1フレーム期間中、ランダムに並んでいても良い。さらにフレーム期間毎に、その順序が変化してもよい。本実施例は、上記の実施の形態、実施例と自由に組み合わせることができる。 Note that in order to increase the number of display gradations, the number of subframe periods may be increased. Further, the order of the subframe periods does not necessarily have to be the order from the upper bit to the lower bit, and may be arranged at random during one frame period. Furthermore, the order may change for each frame period. This embodiment can be freely combined with the above embodiment modes and embodiments.
本実施例では、信号線駆動回路と走査線駆動回路の構成の一例について、図14を用いて説明する。 In this embodiment, an example of a structure of a signal line driver circuit and a scan line driver circuit will be described with reference to FIGS.
図14(A)に示すように、信号線駆動回路は、シフトレジスタ3021、第1のラッチ回路3022及び第2のラッチ回路3023を有する。また、図14(B)に示すように、走査線駆動回路は、シフトレジスタ3024、バッファ3025を有する。但し図示する構成はあくまで一例であり、例えば、信号線駆動回路にレベルシフタやバッファを新たに配置した構成にしたり、走査線駆動回路において、シフトレジスタ3024とバッファ3025の間にレベルシフタを配置した構成にしたりしてもよい。レベルシフタを配置すると、ロジック回路部とバッファ部の電圧振幅を変えることが出来る。本実施例は、上記の実施の形態、実施例と自由に組み合わせることができる。 As shown in FIG. 14A, the signal line driver circuit includes a shift register 3021, a first latch circuit 3022, and a second latch circuit 3023. In addition, as illustrated in FIG. 14B, the scan line driver circuit includes a shift register 3024 and a buffer 3025. However, the illustrated configuration is merely an example. For example, a configuration in which a level shifter and a buffer are newly arranged in the signal line driver circuit, or a level shifter is arranged between the shift register 3024 and the buffer 3025 in the scanning line driver circuit. Or you may. When the level shifter is arranged, the voltage amplitude of the logic circuit portion and the buffer portion can be changed. This embodiment can be freely combined with the above embodiment modes and embodiments.
本発明を適用して作製される電子機器の一例として、ビデオカメラ、デジタルカメラ、ゴーグル型ディスプレイ、ナビゲーションシステム、カーオーディオなどの音響再生装置、ノート型パーソナルコンピュータ、ゲーム機器、携帯情報端末(モバイルコンピュータ、携帯電話、携帯型ゲーム機又は電子書籍等)、家庭用ゲーム機などの記録媒体を備えた画像再生装置(具体的にはDVD等の記録媒体を再生し、その画像を表示しうるディスプレイを備えた装置)などが挙げられる。それら電子機器の具体例を図15、16に示す。 As an example of an electronic device manufactured by applying the present invention, a video camera, a digital camera, a goggle type display, a navigation system, a sound reproducing device such as a car audio, a notebook type personal computer, a game device, a portable information terminal (mobile computer) , Mobile phones, portable game machines, electronic books, etc.), image playback devices equipped with recording media such as home game machines (specifically, displays that can play back recording media such as DVDs and display the images) And the like). Specific examples of these electronic devices are shown in FIGS.
図15(A)は、携帯端末であり、本体9301、音声出力部9302、音声入力部9303、表示部9304及び操作スイッチ9305等を含む。図15(B)はPDAであり、本体9101、スタイラス9102、表示部9103、操作ボタン9104及び外部インターフェース9105等を含む。図15(C)は、携帯型ゲーム機器であり、本体9201、表示部9202及び操作ボタン9203等を含む。図15(D)は、ゴーグル型ディスプレイであり、本体9501、表示部9502及びアーム部9503等を含む。
FIG. 15A illustrates a portable terminal, which includes a
図16(A)は、40インチ程度の大型の液晶テレビであり、表示部9401、筐体9402及び音声出力部9403等を含む。図16(B)は、モニターであり、筐体9601、音声出力部9602及び表示部9603等を含む。図16(C)は、デジタルビデオカメラであり、表示部9701、9702等を含む。図16(D)は、ノートパソコンであり、筐体9801、表示部9802及びキーボード9803等を含む。
FIG. 16A illustrates a large liquid crystal television of about 40 inches, which includes a display portion 9401, a housing 9402, an
上記に挙げた電子機器において、表示部9304、9103、9202、9502、9401、9603、9701、9702及び9802を含むパネルには、本発明の表示装置を用いることが好適である。本実施例は、上記の実施の形態、実施例と自由に組み合わせることができる。
In the electronic device described above, the display device of the present invention is preferably used for a panel including the
本実施例では、実施の形態4で説明した画素回路のレイアウト例について説明する。これから説明するレイアウト例では、発光素子が含む画素電極と、当該画素電極の端部を囲む絶縁層までを形成した場合を示す。また、図21〜23で示すレイアウト例では、隣接する3つの画素を示し、1つの画素はトランジスタと容量素子までを形成したときのレイアウト、1つの画素は画素電極までを形成したときのレイアウト、1つの画素は隔壁層として機能する絶縁層までを形成したときのレイアウトを示す。 In this example, a layout example of the pixel circuit described in Embodiment Mode 4 will be described. The layout example to be described below shows a case where a pixel electrode included in a light emitting element and an insulating layer surrounding an end portion of the pixel electrode are formed. In the layout examples shown in FIGS. 21 to 23, three adjacent pixels are shown, one pixel is a layout when a transistor and a capacitor are formed, and one pixel is a layout when a pixel electrode is formed. One pixel shows a layout when an insulating layer functioning as a partition layer is formed.
1つ目のレイアウト例と2つ目のレイアウト例は、1つの画素に3つのトランジスタが設けられた場合(3TFT/Cell)であり、スイッチング用のトランジスタ601、駆動用のトランジスタ602、消去用のトランジスタ603、容量素子604、列方向に配置された信号線609と補助配線610、行方向に配置された走査線607、608が設けられる(図20、21参照)。また、発光素子が含む画素電極605と絶縁層606が設けられる。
絶縁層606は、隣接する画素電極605の間に設けられている。また、絶縁層606には、補助配線610と画素電極605が露出するように、開口部が設けられている。絶縁層606に設けられた開口部を介して、補助配線610と対向電極とが接続する。また、絶縁層606に設けられた開口部を介して、画素電極605と接するように電界発光層が設けられ、当該電界発光層と接するように対向電極が設けられる。
The first layout example and the second layout example are in the case where three transistors are provided in one pixel (3 TFT / Cell). The switching
The insulating
なお、図20に示すレイアウト例では、上面出射、下面出射、両面出射のいずれの方式を用いてもよい。一方、図21に示すレイアウト例では、画素電極605は、トランジスタ601〜603の上方に設けられているため、上面出射の方式を採用するとよい。但し、図21に示すレイアウト例では、両面出射の方式を採用しても構わないが、その場合は、トランジスタ601〜603に光が当たらないように、絶縁層606は、遮光性を有する材料で形成するとよい。
In the layout example shown in FIG. 20, any of top emission, bottom emission, and dual emission may be used. On the other hand, in the layout example shown in FIG. 21, since the
3つ目のレイアウト例と4つ目のレイアウト例は、1つの画素に4つのトランジスタが設けられた場合(4TFT/Cell)であり、スイッチング用のトランジスタ611、駆動用のトランジスタ619、電流制御用のトランジスタ620、消去用のトランジスタ613、容量素子614、列方向に配置された信号線612と補助配線621、行方向に配置された走査線617、618が設けられる(図22、23参照)。また、発光素子が含む画素電極605と、絶縁層616が設けられる。
絶縁層616には、補助配線621と画素電極615が露出するように、開口部が設けられている。絶縁層616に設けられた開口部を介して、補助配線621と対向電極とが接続する。また、絶縁層616に設けられた開口部を介して、画素電極615と接するように電界発光層が設けられ、当該電界発光層と接するように対向電極が設けられる。
図示する構成によると、画素電極615は、トランジスタ611、613、619、620の上方に設けられており、開口率を向上させることができる。従って、この構成では、上面出射の方式を採用するとよい。なお、図22に示すレイアウト例では、両面出射の方式を採用してもよいが、その場合は、トランジスタ611、613、619、620に光が当たらないように、絶縁層616は遮光性を有する材料で形成するとよい。
The third layout example and the fourth layout example are cases where four transistors are provided in one pixel (4 TFT / Cell), and are a switching
An opening is provided in the insulating
According to the structure shown in the drawing, the
なお、上記構成において、トランジスタ601〜603、611、613、619、620は、非晶質半導体又は有機半導体でチャネル部を形成するトランジスタである。また、補助配線610、621は、トランジスタ601〜603、611、613、619、620のゲート電極と同じ層、トランジスタ601〜603、611、613、619、620のソース電極又はドレイン電極に接続する接続配線と同じ層、又は画素電極605、615と同じ層に設けられる。
Note that in the above structure, the
Claims (6)
前記第1のトランジスタのソース又はドレインの一方に電気的に接続された接続配線と、A connection wiring electrically connected to one of a source or a drain of the first transistor;
前記接続配線上に設けられた第1の絶縁層と、A first insulating layer provided on the connection wiring;
前記第1の絶縁層に設けられた第1の開口部と、A first opening provided in the first insulating layer;
前記第1の絶縁層上に設けられ、前記第1の開口部内において前記接続配線と電気的に接続する第1の電極と、A first electrode provided on the first insulating layer and electrically connected to the connection wiring in the first opening;
前記第1の電極上に設けられた第2の絶縁層と、A second insulating layer provided on the first electrode;
前記第2の絶縁層に設けられた第2の開口部と、A second opening provided in the second insulating layer;
前記第2の絶縁層上に設けられ、前記第2の開口部内において前記第1の電極と電気的に接続する電界発光層と、An electroluminescent layer provided on the second insulating layer and electrically connected to the first electrode in the second opening;
前記電界発光層上に設けられた第2の電極と、を有し、A second electrode provided on the electroluminescent layer,
前記第1の絶縁層には、第3の開口部が設けられており、The first insulating layer is provided with a third opening,
前記第2の絶縁層には、第4の開口部が設けられており、The second insulating layer is provided with a fourth opening,
前記第3の開口部内及び前記第4の開口部内には、補助配線が設けられており、An auxiliary wiring is provided in the third opening and in the fourth opening,
前記補助配線の上面には前記電界発光層が設けられているとともに、前記補助配線の側面において前記補助配線と前記第2の電極とが電気的に接続していることを特徴とする表示装置。The display device, wherein the electroluminescent layer is provided on an upper surface of the auxiliary wiring, and the auxiliary wiring and the second electrode are electrically connected on a side surface of the auxiliary wiring.
前記第1のトランジスタは、非晶質半導体又は有機半導体を含むことを特徴とする表示装置。The display device, wherein the first transistor includes an amorphous semiconductor or an organic semiconductor.
前記第1の電極と前記電界発光層と前記第2の電極とから構成される発光素子と、前記第1のトランジスタと、第2のトランジスタと、第3のトランジスタと、第4のトランジスタと、容量素子と、第1の配線と、第2の配線と、第3の配線と、第4の配線と、第5の配線と、を画素内に有し、A light-emitting element composed of the first electrode, the electroluminescent layer, and the second electrode, the first transistor, the second transistor, the third transistor, and the fourth transistor; A capacitor having a capacitor, a first wiring, a second wiring, a third wiring, a fourth wiring, and a fifth wiring;
前記第1のトランジスタのソース又はドレインの他方は、前記第2のトランジスタのソース又はドレインの一方に電気的に接続されており、The other of the source and the drain of the first transistor is electrically connected to one of the source and the drain of the second transistor;
前記第1のトランジスタのゲートは、前記第1の配線に電気的に接続されており、A gate of the first transistor is electrically connected to the first wiring;
前記第2のトランジスタのソース又はドレインの他方は、前記第2の配線に電気的に接続されており、The other of the source and the drain of the second transistor is electrically connected to the second wiring;
前記第2のトランジスタのゲートは、前記第3のトランジスタのソース又はドレインの一方と、前記第4のトランジスタのソース又はドレインの一方と、前記容量素子の有する一対の電極の一方と、に電気的に接続されており、The gate of the second transistor is electrically connected to one of a source or a drain of the third transistor, one of a source or a drain of the fourth transistor, and one of a pair of electrodes of the capacitor. Connected to
前記第3のトランジスタのソース又はドレインの他方は、前記第3の配線に電気的に接続されており、The other of the source and the drain of the third transistor is electrically connected to the third wiring,
前記第3のトランジスタのゲートは、前記第4の配線に電気的に接続されており、A gate of the third transistor is electrically connected to the fourth wiring;
前記第4のトランジスタのソース又はドレインの他方は、前記第2の配線と、前記容量素子の有する一対の電極の他方と、に電気的に接続されており、The other of the source and the drain of the fourth transistor is electrically connected to the second wiring and the other of the pair of electrodes of the capacitor,
前記第4のトランジスタのゲートは、前記第5の配線に電気的に接続されていることを特徴とする表示装置。A display device, wherein a gate of the fourth transistor is electrically connected to the fifth wiring.
前記第1のトランジスタは飽和領域で動作し、The first transistor operates in a saturation region;
前記第2のトランジスタは線形領域で動作することを特徴とする表示装置。The display device, wherein the second transistor operates in a linear region.
前記第1の電極は、前記第1乃至第4のトランジスタの上方に設けられているとともに、前記第1乃至第4のトランジスタと重なるように設けられており、The first electrode is provided above the first to fourth transistors, and is provided to overlap the first to fourth transistors,
前記発光素子は、上面出射の方式であることを特徴とする表示装置。The display device is characterized in that the light emitting element is a top emission type.
前記第2乃至第4のトランジスタは、非晶質半導体又は有機半導体を含むことを特徴とする表示装置。The display device, wherein the second to fourth transistors include an amorphous semiconductor or an organic semiconductor.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004179165A JP4593179B2 (en) | 2003-06-17 | 2004-06-17 | Display device |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003172009 | 2003-06-17 | ||
| JP2004179165A JP4593179B2 (en) | 2003-06-17 | 2004-06-17 | Display device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005031651A JP2005031651A (en) | 2005-02-03 |
| JP2005031651A5 JP2005031651A5 (en) | 2007-04-19 |
| JP4593179B2 true JP4593179B2 (en) | 2010-12-08 |
Family
ID=34219920
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004179165A Expired - Fee Related JP4593179B2 (en) | 2003-06-17 | 2004-06-17 | Display device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4593179B2 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101754533B1 (en) | 2007-02-14 | 2017-07-05 | 소니 주식회사 | Display device |
| US11171195B2 (en) | 2018-01-19 | 2021-11-09 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Display device including a power supply line that overlaps a driving circuit |
Families Citing this family (30)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100589376B1 (en) * | 2003-11-27 | 2006-06-14 | 삼성에스디아이 주식회사 | Light emitting display device using demultiplexer |
| EP1760776B1 (en) * | 2005-08-31 | 2019-12-25 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Manufacturing method for semiconductor device with flexible substrate |
| JP2007108469A (en) * | 2005-10-14 | 2007-04-26 | Seiko Epson Corp | Method of manufacturing organic el device, organic el device, and electronic apparatus |
| KR101274037B1 (en) * | 2006-09-25 | 2013-06-12 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | Display apparatus |
| JP5401784B2 (en) * | 2007-02-08 | 2014-01-29 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Light emitting device |
| JP4403430B2 (en) * | 2007-03-14 | 2010-01-27 | ソニー株式会社 | Display panel and electronic equipment |
| KR100875102B1 (en) | 2007-09-03 | 2008-12-19 | 삼성모바일디스플레이주식회사 | Organic light emitting display apparatus |
| JP2009122652A (en) | 2007-10-23 | 2009-06-04 | Sony Corp | Display device and electronic apparatus |
| WO2009110186A1 (en) * | 2008-03-04 | 2009-09-11 | パナソニック株式会社 | Light-emitting element and display device |
| KR100908236B1 (en) * | 2008-04-24 | 2009-07-20 | 삼성모바일디스플레이주식회사 | Organic light emitting display apparatus and method of manufacturing the same |
| JP5256863B2 (en) * | 2008-06-06 | 2013-08-07 | ソニー株式会社 | ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING ELEMENT, MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF, AND DISPLAY DEVICE |
| WO2010070798A1 (en) * | 2008-12-18 | 2010-06-24 | パナソニック株式会社 | Organic electroluminescent display device and method for manufacturing same |
| WO2010125622A1 (en) * | 2009-04-30 | 2010-11-04 | シャープ株式会社 | Method for manufacturing a display device, and display device manufactured using said method |
| KR102575653B1 (en) | 2009-05-02 | 2023-09-07 | 가부시키가이샤 한도오따이 에네루기 켄큐쇼 | Display device |
| KR101576834B1 (en) * | 2009-09-29 | 2015-12-11 | 엘지디스플레이 주식회사 | Organic electro-luminescence device and method for fabricating of the same |
| JP5953923B2 (en) * | 2012-05-15 | 2016-07-20 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus |
| JP6217161B2 (en) * | 2013-06-19 | 2017-10-25 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE |
| CN103700694B (en) * | 2013-12-31 | 2016-02-03 | 京东方科技集团股份有限公司 | AMOLED array basal plate and display unit |
| CN104600200B (en) | 2014-12-26 | 2017-07-28 | 上海天马微电子有限公司 | Array substrate and display panel |
| KR102578834B1 (en) * | 2015-11-30 | 2023-09-15 | 엘지디스플레이 주식회사 | Organic Light Emitting Display Device |
| KR102606279B1 (en) | 2016-04-04 | 2023-11-27 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | Display apparatus |
| KR102642198B1 (en) | 2016-04-04 | 2024-03-05 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | Organic light-emitting display apparatus |
| KR102404573B1 (en) | 2016-05-27 | 2022-06-03 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | Display device |
| KR102717808B1 (en) * | 2016-11-30 | 2024-10-15 | 엘지디스플레이 주식회사 | Display device having a plurality of insulating layer disposed between two electrodes |
| KR20180068549A (en) * | 2016-12-14 | 2018-06-22 | 엘지디스플레이 주식회사 | Organic light emitting display device and method for fabricating the same |
| JP7046627B2 (en) * | 2018-02-06 | 2022-04-04 | 株式会社ジャパンディスプレイ | Display device |
| KR102638296B1 (en) | 2018-03-19 | 2024-02-20 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | Organic light-emitting display apparatus |
| US10943526B2 (en) | 2018-07-31 | 2021-03-09 | Innolux Corporation | Display device, backlight module and electronic device |
| JP7411554B2 (en) | 2018-08-29 | 2024-01-11 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | Display panel, display device, input/output device, information processing device |
| KR20210053610A (en) * | 2019-11-04 | 2021-05-12 | 엘지디스플레이 주식회사 | Flexible display device |
Citations (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH06250211A (en) * | 1993-02-23 | 1994-09-09 | Hitachi Ltd | Liquid crystal display substrate and its production |
| JPH09199732A (en) * | 1996-01-16 | 1997-07-31 | Lucent Technol Inc | Product comprising transistors |
| JPH113048A (en) * | 1997-06-10 | 1999-01-06 | Canon Inc | Electroluminescent element and device and their production |
| JP2000347621A (en) * | 1999-06-09 | 2000-12-15 | Nec Corp | Method and device for image display |
| JP2001109395A (en) * | 1999-10-01 | 2001-04-20 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | El display device |
| JP2002318556A (en) * | 2001-04-20 | 2002-10-31 | Toshiba Corp | Active matrix type planar display device and manufacturing method therefor |
| JP2003059660A (en) * | 2001-08-17 | 2003-02-28 | Toshiba Corp | Manufacturing method of self-luminescence display |
| JP2003069022A (en) * | 2001-08-16 | 2003-03-07 | Internatl Business Mach Corp <Ibm> | Thin-film transistor and manufacturing method thereof, array substrate including it, display device and driving system therefor |
| JP2003084683A (en) * | 2001-09-10 | 2003-03-19 | Semiconductor Energy Lab Co Ltd | Light emitting apparatus and its manufacturing method |
| JP2003131593A (en) * | 2001-10-26 | 2003-05-09 | Sharp Corp | Active matrix driven organic led panel |
| JP2003303687A (en) * | 2002-02-06 | 2003-10-24 | Hitachi Ltd | Organic luminous display device |
| JP2004139970A (en) * | 2002-09-25 | 2004-05-13 | Seiko Epson Corp | Electro-optical device, matrix substrate, and electronic equipment |
-
2004
- 2004-06-17 JP JP2004179165A patent/JP4593179B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH06250211A (en) * | 1993-02-23 | 1994-09-09 | Hitachi Ltd | Liquid crystal display substrate and its production |
| JPH09199732A (en) * | 1996-01-16 | 1997-07-31 | Lucent Technol Inc | Product comprising transistors |
| JPH113048A (en) * | 1997-06-10 | 1999-01-06 | Canon Inc | Electroluminescent element and device and their production |
| JP2000347621A (en) * | 1999-06-09 | 2000-12-15 | Nec Corp | Method and device for image display |
| JP2001109395A (en) * | 1999-10-01 | 2001-04-20 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | El display device |
| JP2002318556A (en) * | 2001-04-20 | 2002-10-31 | Toshiba Corp | Active matrix type planar display device and manufacturing method therefor |
| JP2003069022A (en) * | 2001-08-16 | 2003-03-07 | Internatl Business Mach Corp <Ibm> | Thin-film transistor and manufacturing method thereof, array substrate including it, display device and driving system therefor |
| JP2003059660A (en) * | 2001-08-17 | 2003-02-28 | Toshiba Corp | Manufacturing method of self-luminescence display |
| JP2003084683A (en) * | 2001-09-10 | 2003-03-19 | Semiconductor Energy Lab Co Ltd | Light emitting apparatus and its manufacturing method |
| JP2003131593A (en) * | 2001-10-26 | 2003-05-09 | Sharp Corp | Active matrix driven organic led panel |
| JP2003303687A (en) * | 2002-02-06 | 2003-10-24 | Hitachi Ltd | Organic luminous display device |
| JP2004139970A (en) * | 2002-09-25 | 2004-05-13 | Seiko Epson Corp | Electro-optical device, matrix substrate, and electronic equipment |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101754533B1 (en) | 2007-02-14 | 2017-07-05 | 소니 주식회사 | Display device |
| US11171195B2 (en) | 2018-01-19 | 2021-11-09 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Display device including a power supply line that overlaps a driving circuit |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2005031651A (en) | 2005-02-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4593179B2 (en) | Display device | |
| US9887241B2 (en) | Display device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP4574130B2 (en) | Semiconductor devices, electronic equipment | |
| TWI814595B (en) | Semiconductor device, display device, and electronic device | |
| US7623099B2 (en) | Display device | |
| US7283111B2 (en) | Display device and method of driving thereof | |
| US8736522B2 (en) | Display device with threshold correction | |
| US8581805B2 (en) | Display device and driving method thereof | |
| KR20010104294A (en) | Light-Emitting Device and Electric Appliance | |
| JP2008072064A (en) | Display unit | |
| KR20090106162A (en) | Organic light emitting display apparatus and driving method thereof | |
| KR100646935B1 (en) | Light emitting display | |
| JP2009122196A (en) | Active matrix display device and its driving method | |
| JP2005215609A (en) | Unit circuit, electro-optical device, and electronic equipment | |
| JP4879515B2 (en) | Display device and electronic device | |
| JP4556957B2 (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus | |
| KR20100029811A (en) | Organic light emitting display apparatus and driving method thereof | |
| JP2010117722A (en) | Electro-optical device and electronic equipment |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20041203 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070307 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070307 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20100624 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100629 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100817 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20100914 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20100915 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130924 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4593179 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130924 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |