EP2396484B1 - Utilisation d'un élément absorbant les sons comme une entretoise pour l'intégration dans une structure en béton, structure en béton avec un tel élément, et procédé de production d'une entretoise à effet acoustique - Google Patents
Utilisation d'un élément absorbant les sons comme une entretoise pour l'intégration dans une structure en béton, structure en béton avec un tel élément, et procédé de production d'une entretoise à effet acoustique Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2396484B1 EP2396484B1 EP10701830.1A EP10701830A EP2396484B1 EP 2396484 B1 EP2396484 B1 EP 2396484B1 EP 10701830 A EP10701830 A EP 10701830A EP 2396484 B1 EP2396484 B1 EP 2396484B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- concrete
- spacer
- concrete structure
- sound
- encasement
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004567 concrete Substances 0.000 title claims description 97
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 title claims description 94
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 7
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 title claims description 4
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 29
- 238000009415 formwork Methods 0.000 claims description 24
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 claims description 21
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims description 18
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 13
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000002787 reinforcement Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000011358 absorbing material Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000008187 granular material Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000011150 reinforced concrete Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000001913 cellulose Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920002678 cellulose Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000123 paper Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000004745 nonwoven fabric Substances 0.000 claims 2
- 238000004873 anchoring Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 description 10
- 230000003014 reinforcing effect Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000004568 cement Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229910052500 inorganic mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000011707 mineral Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000011210 fiber-reinforced concrete Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000011178 precast concrete Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000004927 clay Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000011148 porous material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000002557 mineral fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011490 mineral wool Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 235000019362 perlite Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011241 protective layer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005245 sintering Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000004793 Polystyrene Substances 0.000 description 1
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Carbonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002313 adhesive film Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012790 adhesive layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011449 brick Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005266 casting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000356 contaminant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009770 conventional sintering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011494 foam glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011888 foil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003562 lightweight material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007791 liquid phase Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011236 particulate material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035515 penetration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000010451 perlite Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011505 plaster Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002223 polystyrene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000019353 potassium silicate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012858 resilient material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003566 sealing material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010454 slate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010802 sludge Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000005361 soda-lime glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- NTHWMYGWWRZVTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N sodium silicate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-][Si]([O-])=O NTHWMYGWWRZVTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012798 spherical particle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004575 stone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003002 synthetic resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000000057 synthetic resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012549 training Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04C—STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS; BUILDING MATERIALS
- E04C5/00—Reinforcing elements, e.g. for concrete; Auxiliary elements therefor
- E04C5/16—Auxiliary parts for reinforcements, e.g. connectors, spacers, stirrups
- E04C5/20—Auxiliary parts for reinforcements, e.g. connectors, spacers, stirrups of material other than metal or with only additional metal parts, e.g. concrete or plastics spacers with metal binding wires
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04B—GENERAL BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS; WALLS, e.g. PARTITIONS; ROOFS; FLOORS; CEILINGS; INSULATION OR OTHER PROTECTION OF BUILDINGS
- E04B5/00—Floors; Floor construction with regard to insulation; Connections specially adapted therefor
- E04B5/16—Load-carrying floor structures wholly or partly cast or similarly formed in situ
- E04B5/32—Floor structures wholly cast in situ with or without form units or reinforcements
Definitions
- the present invention initially relates to a spacer made of a mineral material for integration into a concrete structure. Furthermore, the invention relates to a concrete structure, in particular a concrete ceiling with such a spacer. Finally, the invention relates to a method for producing such a spacer.
- Such spacers serve primarily the spacing of reinforcing elements during the manufacture of concrete structures, whereby on the one hand the desired distance between individual reinforcing bars or the like and on the other hand, the distance of these reinforcing elements is maintained by the formwork used in the manufacturing process.
- Such spacers consist for example of metal or plastic and can take over design tasks in addition to the spacing function itself, in particular serve as a reinforcement. Spacers have already become known in various respects. It is for example on the DE 36 24 447 A1 Reference is made, in which an insertable into concrete insert body is described, which has a chemically bonded to a base body coating, which is connectable to the surrounding concrete.
- Such spacers also made of mineral material, are used, for example, to carry reinforcing bars, which are subsequently poured over with concrete, to form, for example, a concrete ceiling.
- the mentioned coating in particular the connection between the insert body and the surrounding concrete is to be improved.
- the production cost of such insert body is high and it It must be checked on a case by case basis whether the applied coating is compatible with the respective ambient conditions.
- Concrete structures such as e.g. Concrete ceilings are used in residential, commercial and production areas. In addition to their static load-bearing function, such concrete structures must fulfill numerous other tasks. Frequent acoustic requirements exist that can not be met by smooth concrete surfaces, so that e.g. After production of the concrete slab, separate soundproofing panels must be installed, which usually span the entire concrete floor. The installation effort for such ceilings is significant.
- the DE 34 44 881 C2 shows a sound-absorbingschreibwand- or ceiling structure of joint-bumped mineral fiber boards, which are connected to a supporting structure.
- the mineral fiber boards are designed as prefabricated elements and have an adhesive layer on both sides.
- the DE 93 21 610 U1 is an acoustic ceiling of sound-absorbing lightweight panels described.
- the lightweight panels consist of interconnected by means of synthetic resin Blähglas-, Blähton- or similar particles.
- the insulating body has a hovwerksporige structure, which is formed from expanded glass granules in a stable binder framework.
- the DE 44 08 177 A1 shows a noise protection wall part, in which a wall element of solid concrete is provided on one side with an open-pore absorption layer.
- the absorption layer Contains mineral-silicate particulate material, in particular expanded clay or expandable slate.
- a molded body made of a lightweight material known which has sound insulating properties is a liquid phase sintering of a mixture of a lightweight aggregate and a soda water glass.
- the lightweight aggregate used are expanded glass, perlite and / or expanded clay.
- the lightweight aggregate particles are connected to form a soda-lime glass with this network. It is proposed to use the shaped body as an acoustic panel, in particular as a baffle, for which, however, no further instructions are given.
- the DE 100 20 955 A1 shows a shaped body which is formed exclusively of sintered together lightweight aggregates selected from expanded glass granules, expanded clay granules or thermally pre-expanded perlites.
- the GB 1 444 331 A discloses a method of manufacturing an envelope-containing acoustic spacer according to the preamble of claim 13 and a soundproofing body, its integration into a soundproofing block, and a wall of soundproofing blocks on an inclined surface.
- the soundproofing body itself consists of several layers, each containing spherical particles of different sizes.
- the CH 565 909 A5 shows a ceiling construction with a formwork, a cavity and a space-facing surface heating element, which covers the formwork body.
- Another object of the invention is to provide a concrete structure, in particular to provide a concrete floor, in which such a spacer is integrated and thereby has favorable acoustic properties.
- the spacer not only fulfills the mechanical spacing function for the positioning of the reinforcement but also comprises a sound absorbing material to permanently influence the acoustic properties of the concrete structure in which the spacer is installed, ie to act as a sound absorbing element.
- the spacer is preferably made of a glass-based, acoustically effective foam.
- the spacer adjoins the formwork during manufacture of the concrete structure with at least one absorption surface, so that this absorption surface is exposed after removal of the formwork from the concrete structure and can absorb sound.
- it is a mineral foam which may have high strength, such as a stone, brick or concrete block processed in construction.
- the foam is surrounded by at least one surface portion of the foam, namely the absorption surface releasing envelope.
- the foam has an angular structure in cross-section, in the simplest case a square or rectangular structure, the freed area section preferably corresponds to a total area which extends in cross-section from corner to corner.
- This released absorption surface is then the surface which, when installed, faces outwards, i. is exposed to the acoustically influencing space.
- the desired sound efficiency can be achieved particularly favorable by the foam.
- the foam is replaced by another suitable sound absorbing material.
- soft and possibly deformable materials e.g. Rock wool or mineral wool used for sound absorption.
- the wrapper is cement based.
- the sheath preferably has fiber portions, but the fiber portions may also be provided in the case of a sheath which is not cement-based.
- the spacers according to the invention are installed in the concrete structure such that at least one outer surface of the spacer is exposed in the finished concrete floor.
- spacers are connected by means of a surface element on which they are applied at a distance from one another.
- This summary several spacers allows it to easily comply with desired distances, especially regular distances, between the spacers in the course of preparation, for example.
- a concrete pavement or a precast concrete part In addition, they also allow easy handling, such as by unwinding the so summarized spacers.
- the summary of a plurality of spacers by means of a surface element possibly also in one of the further embodiments, in particular of the surface element as described below, also has independent significance. In particular, regardless of whether the spacer is constructed on a glass-based, acoustically effective foam.
- the surface element is a nonwoven, for example a cellulose-based nonwoven, or a cardboard or paper element.
- the binder can be a hydraulic, also be hydraulically setting binder. It is preferably a binder based on cement or ceramic. It is also expedient if the binder has a fiber content. Last but not least, such a fiber content can ensure the possibly desired diffusion openness or support it. Also, the fiber content can contribute to the acoustic effectiveness.
- the glass particles are preferably expanded glass granules which are compacted with the aid of the binder or else by a sintering process to form the acoustically effective foam.
- the spacer according to the invention preferably has a rectangular or square, possibly also trapezoidal or triangular cross-section.
- a cross-section forms a flat absorption surface, which can be integrated into the visible side or the outside of the concrete ceiling to be acoustically influenced.
- this absorption surface is not flat, but is characterized by the structure of the spacer material.
- the absorption surface which forms the visible side or is integrated into the outside of a concrete ceiling is also the surface which has no covering.
- the absorption surface of the acoustically acting spacer is covered by a self-adhesive film or similar protective layer.
- This protective layer protects the absorption surface from penetrating concrete sludge or other contaminants and can be removed after final completion of the structure.
- Another object of the invention is a concrete structure, preferably a concrete floor, in which in at least one outer surface partially exposed spacer made of acoustically active foam are embedded, preferably of a glass-based acoustically active foam.
- the spacers are exposed only in a direction parallel to the direction of extension of the concrete surface surface and specifically specifically only with an outer surface (namely, the absorption surface) of the spacer. Accordingly, viewed in cross-section, two or three further outer surfaces of the spacer in the concrete ceiling are covered by the concrete. Preferably, the faces of such a spacer are covered by concrete in the concrete floor. This overlap is also given by means of the already mentioned wrapping. The concrete then adheres to the outside of this enclosure.
- the adhesion of such a spacer to the concrete can be achieved partially or exclusively by mechanical attachment or clawing of the unevenly textured surfaces of the spacer.
- the spacer preferably has in its outer surfaces free-standing individual structures in the millimeter range, for example. In the size of 1 to 2 millimeters on. Integrated into an envelope, these may be spherical, glass-based or glass-like structures.
- the acoustically effective area of the concrete structure can be further processed later with conventional techniques.
- the area including the absorption surfaces of the spacers may be painted or coated with an open-pored plaster. It must be ensured that a coating remains acoustically transparent so that the sound absorbing properties of the absorption surfaces of the built-in spacers are maintained.
- the glass-based acoustically-effective foam may be produced by conventional sintering techniques.
- the wrapper can first be poured in a mold. Subsequently, the foam is placed in the freshly made wrapper and the wrapper is pressed in the not yet cured state to the inserted foam and fixed until the curing is done.
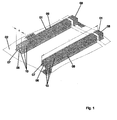
- Fig. 1 shows in a simplified perspective view of a first embodiment of two spacers 01 according to the invention, which are combined with a surface element 02, that in the exemplary embodiment is a non-woven.
- Each spacer has a preferably exposed absorption surface 06 and end faces 07, 08th
- each spacer 01 comprises a core 09 and a sheath 10.
- the core 09 is made of an acoustically effective, namely sound-absorbing material in the manner of a foam.
- it is a mineral material that forms a rigid foam.
- the core 09 is made of glass-based, acoustically active and diffusion-open foam. Individual glass particles are connected to each other by a concrete-like binder, which may also have a fiber content, to a bar structure shown in the figures.
- an edge length a of the illustrated latch structure for example. In Range of 2 to 8 cm are visible
- a square cross-section is selected.
- the length 1 can be approximately in the range of 0.5 to 3 m. It is understandable to the person skilled in the art that the dimensions and the shape of the spacers can be adapted almost arbitrarily to the respective application. Decisive for the invention is that the core 09 is made of a material which has a good sound-absorbing effect.
- the envelope 10 consists, for example, of a cement or cement-based substance or other hard material, which combines favorably with concrete.
- the envelope 10 serves on the one hand to protect and stabilize the core 09 and acts in the production as a lost form for the core 09, as long as it is not cured.
- the sheath 10 serves to connect the spacer to the surrounding concrete in the concrete structure to be created.
- the cover has a customized surface structure and is made of suitable material to ensure permanent attachment of the spacers in the concrete.
- the end faces 07, 08 of the spacers are preferably also surrounded by the sheath 10.
- the spacers 01 are glued to the surface element 02 or otherwise secured thereto. They can also be connected for example by the binder located in the spacers in the course of manufacturing immediately with the surface element 02.
- the surface element can also be in the form of individual Strip be formed, where adjacent spacers are strung chain-like.
- a strip-shaped fleece or a foil strip can be fastened to the spacers, for example with a lateral projection, the lateral projection serving for fixing on the formwork.
- the surface element can be dispensed with or its positioning function can be taken over by the formwork.
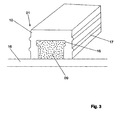
- Fig. 2 shows in cross section a concrete floor 03, in which the spacers 01 are integrated. It may also be, for example, a precast concrete or other concrete structure.
- reinforcing elements 04 eg steel bars
- the surface element 02 has been demolished in the example shown.
- an acoustically effective side 05 here the underside of the concrete floor 03
- an absorption surface 06 here formed by a longitudinal surface
- the sound reflectance of a concrete pavement can hereby be favorably influenced, namely lowered.
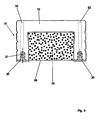
- Fig. 3 shows a modified embodiment of the spacer 01, which in turn has the core 09 and the sheath 10.
- the spacer 01 is in the drawn view on a formwork 16 and is not yet enclosed by concrete.
- the envelope 10 is designed as a U-shaped fiber reinforced concrete rail.
- profilings 17 are arranged, which serve to secure attachment in the concrete and the avoidance of Um Schaukeiten.
- sealing materials may be attached to the fiber concrete rail.
- On the inner sides of the fiber concrete rail 10 further profilings 18 are provided, which serve to fasten the core 09.
- an adhesive may be provided there if the core 09 is not formed in the envelope but is inserted into the envelope as an already hardened element.
- a tongue and groove connection or an undercut between the envelope and foam insert (core) is possible in order to achieve positive locking of these two parts.
- the fiber reinforced concrete rail for example, an H-shape or a dovetail shape own and / or be formed with non-profiled legs.
- a positive connection between core 09 and sheath 10 can be generated, for example, by tongue and groove training on the fiber reinforced concrete rail or the acoustically acting material of the core 09.
- the enclosure is structurally stable, so that it can take over additional reinforcement functions.
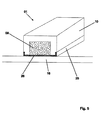
- Fig. 4 shows a further modified embodiment of the spacer 01 in cross section.
- the peculiarity here is firstly that at the free longitudinal edges of the U-shaped envelope 10 each sealing strip 20 are mounted from a resilient material.
- the sealing strips 20 are fastened, for example via dowels 21 in the wall of the enclosure 10.
- continuous rubber seals can be mounted in longitudinal grooves.
- mounting holes 22 are further arranged in the enclosure 10. Through this nails, screws or similar fasteners can be passed through to secure the sheath 10 and the core 09 therein to the formwork. Slipping of the spacer during the pouring with concrete is thus excluded.
- the fasteners may have a predetermined breaking point, which allows a rapid separation of the formwork after the manufacturing process, without causing the spacers are damaged.
- Modified mounting methods for the spacers can be achieved with metal brackets, nails or similar elements.
- metal straps can be placed with laterally projecting tabs on the sheath and nailed to the protruding tabs on the formwork with nails. Predetermined breaking points on the nails allow a simple separation of the formwork after the production of the concrete structure.
- adhesive strips can be attached to the spacer, which allow a fixation on the formwork. If a fixation on the formwork is not desired, holding clamps can be attached to the enclosure, which allows a fixation of the spacer to reinforcing bars.
- These retaining clips can be formed, for example, in one piece in the material of the envelope or attach as separate parts made of metal or plastic.
- Fig. 5 shows a further modified embodiment of the spacer 01 in cross section.
- the fixation of the spacer 01 takes place in this case via a holding profile 25, which is not a permanent part of the spacer but is attached to the formwork 16.
- the attachment takes place for example via a magnetic strip 26 which is integrated in the holding profile.
- the retaining profile 25 may include sealing lips, which bear tightly against the enclosure 10.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Architecture (AREA)
- Civil Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Building Environments (AREA)
- Road Paving Structures (AREA)
Claims (13)
- Utilisation d'un élément absorbant le bruit qui comprend un matériau (09) acoustiquement efficace, absorbant notamment le bruit avec une surface d'absorption (06), en tant qu'espaceur (01) pour intégration dans une structure en béton (03) armée coulée, pour laquelle la surface d'absorption (06) est dégagée dans la direction d'un côté (05) acoustiquement efficace de la structure en béton (03) et n'est pas également recouverte de béton après la coulée de l'espaceur, caractérisé en ce que l'espaceur sert à tenir à distance les armatures (04) des surfaces extérieures de la structure de béton et en ce que le matériau absorbant le bruit constitue un noyau (09) qui est entouré d'une enveloppe (10) laissant libre de toute façon la surface d'absorption (06).
- Utilisation d'un élément absorbant le bruit en tant qu'espaceur (01) selon la revendication 1, caractérisé en ce que le matériau absorbant e bruit est une mousse non ductile, en particulier une mousse à base de verre, qui comprend en particulier du granulat de verre expansé.
- Utilisation d'un élément absorbant le bruit en tant qu'espaceur (01) selon la revendication 1 ou 2, caractérisé en ce que l'enveloppe (10) est à base de ciment.
- Utilisation d'un élément absorbant le bruit en tant qu'espaceur (01) selon une quelconque des revendications 1 à 3, caractérisé en ce que l'enveloppe (10) contient des parties de fibres et/ou des armatures.
- Utilisation d'un élément absorbant le bruit en tant qu'espaceur (01) selon une quelconque des revendications 1 à 4, caractérisé en ce qu'il présente des éléments de fixation avec lesquels il est provisoirement fixé à un coffrage (16), est en même temps séparable du coffrage (16), après qu'il ait été fermement intégré dans la structure en béton (03).
- Structure en béton, en particulier revêtement en béton (03), avec des armatures (04) et des espaceurs scellées dans le béton (15), qui sont disposés au moins par sections entre l'armature (04) et une surface extérieure de la structure en béton, caractérisée en ce qu'au moins un élément absorbant le bruit est constitué comme espaceur (01) acoustiquement efficace pour laquelle l'espaceur comprend un matériau (09) acoustiquement efficace, absorbant notamment le bruit avec une surface d'absorption (06), pour laquelle cette surface d'absorption (06) étant dégagée dans la direction d'un côté (05) acoustiquement efficace de la structure en béton (03) et n'est pas recouverte de béton, pour laquelle le matériau absorbant le bruit constitue un noyau (09) et pour laquelle l'espaceur (01) acoustiquement efficace présente de toute façon une enveloppe (10) laissant libre la surface d'absorption (06) qui est encastré dans le béton (15) par complémentarité de forme.
- Structure en béton (03) selon la revendication 6, caractérisée en ce qu'elle comprend plusieurs espaceurs (01) acoustiquement efficaces qui sont reliés au moyen d'un élément en bandes ou plat (02) sur lequel ils sont montés à distance les uns des autres.
- Structure en béton (03) selon la revendication 7, caractérisée en ce que l'élément plat (02) est une nappe, en particulier une nappe à base de cellulose, un élément en carton ou papier.
- Structure en béton (03) selon une quelconque des revendications 6 à 8, caractérisée en ce que l'enveloppe (10) est un rail en béton fibreux avec une section ouverte unilatéralement.
- Structure en béton (03) selon la revendication 9, caractérisée en ce que le rail en béton fibreux est relié par force à l'armature (04).
- Structure en béton (03) selon une quelconque des revendications 6 à 10, caractérisée en ce que des profilages (17) et/ou des éléments de fixation sont disposés sur l'enveloppe (10) qui produisent un ancrage supplémentaire de l'espaceur (01) dans le béton (15).
- Structure en béton (03) selon une quelconque des revendications 6 à 11, caractérisée en ce que les surfaces d'absorption (06) de tous les espaceurs (01) acoustiquement efficaces se situent pour l'essentiel dans un plan avec le côté (05) acoustiquement efficace de la structure en béton (03) ou dans un plan parallèle à celui-ci.
- Procédé pour la fabrication d'un espaceur acoustiquement efficace présentant une enveloppe (10) qui comprend les étapes suivantes :- réalisation d'un noyau allongé (09) en matériau absorbant le bruit ;- réalisation de l'enveloppe (10) en matériau à base de ciment qui enserre le noyau (09) sur trois de ses côtés et laisse libre une surface d'absorption (06) allongée ;- encastrement du noyau (09) dans l'enveloppe (10) pas encore prise ;caractérisé en ce que le procédé comprend également la phase suivante :- application par pression et fixation de l'enveloppe au noyau jusqu'à la prise du noyau.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE200920001754 DE202009001754U1 (de) | 2009-02-12 | 2009-02-12 | Abstandshalter und Betondecke mit Abstandshalter |
| PCT/EP2010/050288 WO2010091911A1 (fr) | 2009-02-12 | 2010-01-12 | Écarteur destiné à être intégré dans une structure de béton, structure de béton avec un tel écarteur et procédé pour sa fabrication |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2396484A1 EP2396484A1 (fr) | 2011-12-21 |
| EP2396484B1 true EP2396484B1 (fr) | 2013-10-02 |
Family
ID=42079055
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP10701830.1A Active EP2396484B1 (fr) | 2009-02-12 | 2010-01-12 | Utilisation d'un élément absorbant les sons comme une entretoise pour l'intégration dans une structure en béton, structure en béton avec un tel élément, et procédé de production d'une entretoise à effet acoustique |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2396484B1 (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE202009001754U1 (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO2010091911A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2868637A1 (fr) | 2013-10-31 | 2015-05-06 | Construction Research & Technology GmbH | Formulation de mousse géopolymère |
| EP2868826A1 (fr) * | 2013-10-31 | 2015-05-06 | Basf Se | Élément de béton comprenant un absorbeur acoustique |
| EP2868638A1 (fr) | 2013-10-31 | 2015-05-06 | Construction Research & Technology GmbH | Composition de géopolymère automoussant contenant des scories d'aluminium |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE786543A (fr) | 1971-07-22 | 1973-01-22 | Williams Geoffrey M J C O Scot | Procede perfectionne pour la fabrication de structures en beton |
| AT332607B (de) | 1971-12-09 | 1976-10-11 | Katzenberger Helmut | Mehrlagige unterdecke mit heizelement |
| JPS49108808A (fr) | 1973-02-17 | 1974-10-16 | ||
| DE3624447A1 (de) | 1986-07-19 | 1988-01-21 | Betomax Kunststoff Metall | In beton einzubringender einsatzkoerper |
| GB9006795D0 (en) | 1990-03-27 | 1990-05-23 | Initiatives Dev Group Limited | Improvements in or relating to building and civil engineering |
| DE19712835C3 (de) | 1997-03-26 | 2002-05-08 | Fraunhofer Ges Forschung | Formkörper aus einem Leichtwerkstoff, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und ihre Verwendung |
| DE10020955A1 (de) | 2000-04-28 | 2001-11-22 | Fraunhofer Ges Forschung | Formkörper und Verfahren zur Herstellung |
| CZ297936B6 (cs) | 2005-02-22 | 2007-05-02 | Jasan@Petr | Stropní konstrukce a zpusob její výroby |
-
2009
- 2009-02-12 DE DE200920001754 patent/DE202009001754U1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2010
- 2010-01-12 WO PCT/EP2010/050288 patent/WO2010091911A1/fr active Application Filing
- 2010-01-12 EP EP10701830.1A patent/EP2396484B1/fr active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2396484A1 (fr) | 2011-12-21 |
| DE202009001754U1 (de) | 2010-07-15 |
| WO2010091911A1 (fr) | 2010-08-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2281964A1 (fr) | Élement moulé de paroi, de plancher ou de plafond et son procédé de fabrication | |
| EP2396484B1 (fr) | Utilisation d'un élément absorbant les sons comme une entretoise pour l'intégration dans une structure en béton, structure en béton avec un tel élément, et procédé de production d'une entretoise à effet acoustique | |
| EP2539518B1 (fr) | Construction contre le feu à base de plaques coupe-feu et d'éléments absorbeurs phoniques | |
| DE1946462A1 (de) | Isolierte Mauer fuer Gebaeudewaende | |
| EP1842984B1 (fr) | Plaque de coffrage profilée de bordure de dalle en béton | |
| WO1997040239A1 (fr) | Panneau mural servant a construire des murs | |
| DE2422192A1 (de) | Vorgefertigtes deckenbauelement | |
| DE19743883A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung industriell vorgefertigter Wandelemente und danach hergestelltes Wandelement | |
| DE3031276A1 (de) | Fertigteilhohldeckenelement und verfahren zu seiner herstellung | |
| DE2908995A1 (de) | Bauwerk mit plattenbalken | |
| DE871506C (de) | Nach Art eines Holzfachwerks aufgebaute Fachwerkwand aus Fertigteilen | |
| DE102012021213A1 (de) | Randschalungselement und Randschalungs-Verfahren | |
| EP2395164A2 (fr) | Composant pour un bâtiment, notamment composant de mur, de plafond ou de toit et procédé de fabrication associé | |
| EP1264943B1 (fr) | Elément de paroi, de plafond et d'isolation acoustique | |
| DE202010009045U1 (de) | Bauteil für ein Gebäude, insbesondere Wand-, Decken- oder Dachelementbauteil | |
| EP1905915B1 (fr) | Méthode de production d'une dalle de béton, et dalle de béton produite par cette méthode | |
| EP3524745B1 (fr) | Composant destiné à l'absorption de bruit | |
| EP1947256A2 (fr) | Dispositif de coffrage | |
| DE4414665A1 (de) | Schalungselement | |
| DE3914942A1 (de) | Bauelement fuer hochbauwerke | |
| WO1997026423A1 (fr) | Element de paroi | |
| DE10116976A1 (de) | Selbsttragendes Deckenelement und Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung | |
| DE924346C (de) | Schuettbauweise, insbesondere fuer eine nichttragende Aussenwand mit wetterfester Aussenverkleidung | |
| AT215128B (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von zweischaligen Decken u. dgl. Tragwerken | |
| DE9007194U1 (de) | Vorgefertigte, transportierbare, selbsttragende Fliesentrennwand |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20110908 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20120705 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20130502 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 634709 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20131015 Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502010004920 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20131205 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: FREI PATENTANWALTSBUERO AG, CH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: VDEP Effective date: 20131002 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140202 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140102 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140203 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502010004920 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: MAX FRANK G.M.B.H. & CO. KG Effective date: 20140131 Owner name: LIAVER G.M.B.H. & CO. KG Effective date: 20140131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140112 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20140703 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502010004920 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20140703 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20140930 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20140131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20140112 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20140131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140101 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140103 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20100112 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20131002 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PCAR Free format text: NEW ADDRESS: POSTFACH, 8032 ZUERICH (CH) |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20220125 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20230112 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20230112 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20240118 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20240125 Year of fee payment: 15 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20240202 Year of fee payment: 15 |