EP1590423B1 - Verfahren zur hochtemperatur-kurzzeit-destillation von rückstandsöl - Google Patents
Verfahren zur hochtemperatur-kurzzeit-destillation von rückstandsöl Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1590423B1 EP1590423B1 EP03813544A EP03813544A EP1590423B1 EP 1590423 B1 EP1590423 B1 EP 1590423B1 EP 03813544 A EP03813544 A EP 03813544A EP 03813544 A EP03813544 A EP 03813544A EP 1590423 B1 EP1590423 B1 EP 1590423B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- oil
- gas
- column
- mixer
- fraction
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 21
- 238000004821 distillation Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 5
- 238000009835 boiling Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 25
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 claims description 62
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 claims description 52
- 239000000571 coke Substances 0.000 claims description 23
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical group [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000000428 dust Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910001385 heavy metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- LEONUFNNVUYDNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N vanadium atom Chemical compound [V] LEONUFNNVUYDNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000010426 asphalt Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000003208 petroleum Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000010791 quenching Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000356 contaminant Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 239000010779 crude oil Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 239000003027 oil sand Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 239000003344 environmental pollutant Substances 0.000 abstract description 17
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 abstract description 14
- 231100000719 pollutant Toxicity 0.000 abstract description 12
- 230000003197 catalytic effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 4
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 abstract description 4
- 229910052720 vanadium Inorganic materials 0.000 abstract description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 abstract 2
- UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1 UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 abstract 1
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000003502 gasoline Substances 0.000 description 11
- 239000000295 fuel oil Substances 0.000 description 10
- 238000005194 fractionation Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000009833 condensation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000005494 condensation Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005292 vacuum distillation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000010763 heavy fuel oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000004939 coking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000354 decomposition reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10G—CRACKING HYDROCARBON OILS; PRODUCTION OF LIQUID HYDROCARBON MIXTURES, e.g. BY DESTRUCTIVE HYDROGENATION, OLIGOMERISATION, POLYMERISATION; RECOVERY OF HYDROCARBON OILS FROM OIL-SHALE, OIL-SAND, OR GASES; REFINING MIXTURES MAINLY CONSISTING OF HYDROCARBONS; REFORMING OF NAPHTHA; MINERAL WAXES
- C10G9/00—Thermal non-catalytic cracking, in the absence of hydrogen, of hydrocarbon oils
- C10G9/28—Thermal non-catalytic cracking, in the absence of hydrogen, of hydrocarbon oils with preheated moving solid material
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10G—CRACKING HYDROCARBON OILS; PRODUCTION OF LIQUID HYDROCARBON MIXTURES, e.g. BY DESTRUCTIVE HYDROGENATION, OLIGOMERISATION, POLYMERISATION; RECOVERY OF HYDROCARBON OILS FROM OIL-SHALE, OIL-SAND, OR GASES; REFINING MIXTURES MAINLY CONSISTING OF HYDROCARBONS; REFORMING OF NAPHTHA; MINERAL WAXES
- C10G70/00—Working-up undefined normally gaseous mixtures obtained by processes covered by groups C10G9/00, C10G11/00, C10G15/00, C10G47/00, C10G51/00
- C10G70/04—Working-up undefined normally gaseous mixtures obtained by processes covered by groups C10G9/00, C10G11/00, C10G15/00, C10G47/00, C10G51/00 by physical processes
- C10G70/043—Working-up undefined normally gaseous mixtures obtained by processes covered by groups C10G9/00, C10G11/00, C10G15/00, C10G47/00, C10G51/00 by physical processes by fractional condensation
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10G—CRACKING HYDROCARBON OILS; PRODUCTION OF LIQUID HYDROCARBON MIXTURES, e.g. BY DESTRUCTIVE HYDROGENATION, OLIGOMERISATION, POLYMERISATION; RECOVERY OF HYDROCARBON OILS FROM OIL-SHALE, OIL-SAND, OR GASES; REFINING MIXTURES MAINLY CONSISTING OF HYDROCARBONS; REFORMING OF NAPHTHA; MINERAL WAXES
- C10G2300/00—Aspects relating to hydrocarbon processing covered by groups C10G1/00 - C10G99/00
- C10G2300/10—Feedstock materials
- C10G2300/107—Atmospheric residues having a boiling point of at least about 538 °C
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10G—CRACKING HYDROCARBON OILS; PRODUCTION OF LIQUID HYDROCARBON MIXTURES, e.g. BY DESTRUCTIVE HYDROGENATION, OLIGOMERISATION, POLYMERISATION; RECOVERY OF HYDROCARBON OILS FROM OIL-SHALE, OIL-SAND, OR GASES; REFINING MIXTURES MAINLY CONSISTING OF HYDROCARBONS; REFORMING OF NAPHTHA; MINERAL WAXES
- C10G2300/00—Aspects relating to hydrocarbon processing covered by groups C10G1/00 - C10G99/00
- C10G2300/10—Feedstock materials
- C10G2300/1077—Vacuum residues
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10G—CRACKING HYDROCARBON OILS; PRODUCTION OF LIQUID HYDROCARBON MIXTURES, e.g. BY DESTRUCTIVE HYDROGENATION, OLIGOMERISATION, POLYMERISATION; RECOVERY OF HYDROCARBON OILS FROM OIL-SHALE, OIL-SAND, OR GASES; REFINING MIXTURES MAINLY CONSISTING OF HYDROCARBONS; REFORMING OF NAPHTHA; MINERAL WAXES
- C10G2300/00—Aspects relating to hydrocarbon processing covered by groups C10G1/00 - C10G99/00
- C10G2300/20—Characteristics of the feedstock or the products
- C10G2300/30—Physical properties of feedstocks or products
- C10G2300/301—Boiling range
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10G—CRACKING HYDROCARBON OILS; PRODUCTION OF LIQUID HYDROCARBON MIXTURES, e.g. BY DESTRUCTIVE HYDROGENATION, OLIGOMERISATION, POLYMERISATION; RECOVERY OF HYDROCARBON OILS FROM OIL-SHALE, OIL-SAND, OR GASES; REFINING MIXTURES MAINLY CONSISTING OF HYDROCARBONS; REFORMING OF NAPHTHA; MINERAL WAXES
- C10G2400/00—Products obtained by processes covered by groups C10G9/00 - C10G69/14
- C10G2400/02—Gasoline
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10G—CRACKING HYDROCARBON OILS; PRODUCTION OF LIQUID HYDROCARBON MIXTURES, e.g. BY DESTRUCTIVE HYDROGENATION, OLIGOMERISATION, POLYMERISATION; RECOVERY OF HYDROCARBON OILS FROM OIL-SHALE, OIL-SAND, OR GASES; REFINING MIXTURES MAINLY CONSISTING OF HYDROCARBONS; REFORMING OF NAPHTHA; MINERAL WAXES
- C10G2400/00—Products obtained by processes covered by groups C10G9/00 - C10G69/14
- C10G2400/06—Gasoil
Definitions
- the invention relates to a method for high-temperature short-term distillation of a residual oil from the processing of petroleum, natural bitumen or oil sands, wherein the residual oil is mixed with granular, hot coke as a heat transfer medium in a mixer, converted into oil vapor, gas and coke and gases and Vapors from the mixer deducted largely separated from the granular coke, cools gases and vapors and produces a product oil as condensate and gas, and that is withdrawn from the mixer coke heated and recycled as a heat transfer medium in the mixer.
- a reduction of the pollutants can thus be done in principle by a subsequent vacuum distillation of over 360 ° C boiling product oil, in which a pollutant-containing vacuum residue (VR) and a largely pollutant-free vacuum gas oil (VGO) is obtained.
- VGO pollutant-containing vacuum residue
- VGO largely pollutant-free vacuum gas oil
- the present invention seeks to improve the process for high-temperature short-term distillation of residual oils to the effect that the smallest possible residue fraction can be obtained from the product oil in a technically simple manner in which the unwanted catalyst pollutants are largely concentrated.
- this object is achieved in that a pollutant-rich residue fraction of the vaporous product oil from the mixer after admixture of water vapor or gas to lower the partial pressure at temperatures below 450 ° C is condensed in a column and withdrawn separately from the residual product oil. Subsequently, the uncondensed product oil vapors from the column can be fed to a fractionation column where the remaining low-emission product oil is decomposed into a VGO and a gasoline / gas oil fraction.
- the invention makes use of the fact that the entire product oil is present in vapor form at the outlet of the mixing plant and can be separated into the desired fractions by a fractional condensation.
- the boiling cut between VGO and VR must be set as high as possible between 450 ° C and 650 ° C so that the separated VR fraction contains more than 60% of Conradson Carbon Residue (CCR ) contains more than 70% of the heavy metals nickel (Ni) and vanadium (V) still present in the product oil vapor and more than 80% of the asphaltenes still contained in the product oil vapor.
- CCR Conradson Carbon Residue
- the partial pressure of the oil fractions to be separated is reduced by adding water vapor or gas to the column, so that there is a heavy condensate at below 450 ° C. with a boiling point above 450 ° C condenses.
- the condensation of the low-pollutant VGO (boiling point about 360, boiling point 450 to 650 ° C) and the gasoline / gas oil fraction (boiling range C 5 - to about 360 ° C) can then take place in a second condensation stage at correspondingly lower temperatures.
- the low-pollutant VGO thus obtained can then be catalytically converted into gasoline and gas oil in a hydrocracker and the heavy condensate can either be returned to the mixing reactor or otherwise used, for example as heavy fuel oil.
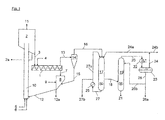
- residue oil having a temperature of from 100 ° C. to 400 ° C. is fed to the mixing reactor (1) through line (4).
- a conversion temperature of the mixture of 450 ° C to 600 ° C is established.
- the heat transfer coke in the mixing reactor (1) usually has a particle size in the range of 0.1 to 4 mm, so that a substantial separation of the coke from the gases and oil vapors formed in the mixer takes place at the mixer outlet.
- the mixer (1) has at least two intermeshing, co-rotating screws.
- the screws are designed in the manner of a screw conveyor and formed with coiled conveying blades.
- the hot, largely oil-free, granular coke leaves the mixing reactor (1) at the mixer outlet at a temperature of 450 to 600 ° C and falls through a channel (7) in a Nachentgasungsbunker (8) to which a stripping gas (9) supplied in the lower part can be. Residual gases and vapors can be withdrawn from the Nachentgasungsbunker (8) through the channel (7) upwards. Excess coke is withdrawn via line (2a), wherein a portion of the coke can alternatively be withdrawn via the lines (12a).
- the coke from line (12) passes via a pneumatic conveying path (10), which is supplied via line (5) combustion air and via line (6) fuel in the collection bunker (2). With the promotion by the pneumatic conveyor line (10) upwards a portion of the coke and / or the delivered fuel is burned at the same time.
- the coke heated in the pneumatic conveying section (10) passes into the collecting bunker (2), from which exhaust gas is removed through line (11).
- the coke in the collection bunker (2) has temperatures in the range of 500 to 700 ° C.
- the gaseous and vaporous products of the mixing reactor (1) are passed through the line (13) in a cyclone (14).
- a separation of fine coke particles instead, which are passed through line (15) in the Nachentgasungsbunker (8).
- the gaseous and vaporous products are quenched from the cyclone (14) via line (16) in a column (17) and thereby cooled from 450 to 600 ° C to 350 to 450 ° C.
- C 4- product gas from the container (23) or steam is introduced. This is the partial pressure of the vapor Lowered product oil so far that condenses there at 350 - 450 ° C, a heavy oil fraction with a boiling point between 450 and 650 ° C, in which almost all pollutants are concentrated. A decomposition or coking of the condensed oil is thus avoided.
- the column (17) is preferably a quench cooler with multiventuri scrubber connected downstream, in which the gases and vapors originating from the mixing reactor (1) are cooled very efficiently in the co-current method and residual coke dust is washed out with its own condensate.
- the boiling cut between VGO and VR is set to a temperature as high as possible in the range from 450 to 650 ° C. This is done by the application of gas or water vapor to the top of the column (17) via line (24a) and by the cooling of the gases and vapors by means of cooled heavy oil condensate from line (27a).
- the heavy oil condensate is withdrawn at a temperature of 350-450 ° C from the bottom of the column (17) through line (27), cooled in a heat exchanger (25) to the required temperature and partly as a cooling / washing medium the top of the column (17) fed again.
- the remaining part of the heavy oil Kondendates is withdrawn via line (27b) as a product.
- the heavy oil condensate from line (27b) can then either be returned to the mixing reactor (1) or otherwise used, eg as heavy fuel oil.
- the uncondensed gas / oil vapor mixture via line (18) is withdrawn. According to a further embodiment of the invention, it can be passed into a fractionation column (19).
- the remaining product oil is separated into low-emission VGO and a pollutant-free gasoline / gas oil fraction.
- the VGO with a boiling end of 450-650 ° C is withdrawn via line (21) from the bottom of the fractionation column (19).
- the VGO thus obtained can then be catalytically converted to gasoline and gas oil in a hydrocracker, not shown.
- the remaining gas / oil vapor mixture via line (20) in the condenser (22) is cooled and in the container (23) in a gasoline / gas oil fraction having a boiling range of, for example C 5 - 360 ° C and a C 4- gas separated.
- the gasoline / gas oil fraction is withdrawn via line (26) and partially recycled via line (26b) to the top of the fractionating column (19).
- the remaining gasoline / gas oil mixture is discharged via line (26a) as a product.
- the non-condensed C 4 gas is removed from the container (23) via line (24) upwards and partly through line (24 a) in the column (17) returned partly withdrawn as a product via line (24 b).
- 75 t / h of gas / oil vapor mixture at 550 ° C are passed through line (13) in a cyclone (14) for dedusting.
- the remaining 25 t / h coke are passed through line (7) together with the heat transfer coke in the Nachentgasungsbunker (8).
- the gas / oil vapor mixture is passed from the cyclone (14) via line (16) in a column (17), where it is diluted with gas and cooled from 550 ° C to 425 ° C.
- 65 t / h heavy oil condensate are withdrawn with a boiling point of 600 ° C via line (27) and cooled in a heat exchanger (25) from 425 ° C to 380 ° C.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Production Of Liquid Hydrocarbon Mixture For Refining Petroleum (AREA)
- Vaporization, Distillation, Condensation, Sublimation, And Cold Traps (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE10259450 | 2002-12-19 | ||
| DE10259450A DE10259450B4 (de) | 2002-12-19 | 2002-12-19 | Verfahren zur Hochtemperatur-Kurzzeit-Destillation von Rückstandsöl |
| PCT/EP2003/007377 WO2004056942A1 (de) | 2002-12-19 | 2003-07-09 | Verfahren zur hochtemperatur-kurzzeit-destillation von rückstandsöl |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1590423A1 EP1590423A1 (de) | 2005-11-02 |
| EP1590423B1 true EP1590423B1 (de) | 2007-02-21 |
Family
ID=32519110
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP03813544A Expired - Lifetime EP1590423B1 (de) | 2002-12-19 | 2003-07-09 | Verfahren zur hochtemperatur-kurzzeit-destillation von rückstandsöl |
Country Status (10)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7507330B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP1590423B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP4365788B2 (enExample) |
| AT (1) | ATE354625T1 (enExample) |
| AU (1) | AU2003250003B2 (enExample) |
| CA (1) | CA2511156C (enExample) |
| DE (2) | DE10259450B4 (enExample) |
| ES (1) | ES2282737T3 (enExample) |
| MX (1) | MXPA05006696A (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2004056942A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA2624746C (en) | 2007-03-12 | 2015-02-24 | Robert Graham | Methods and systems for producing reduced resid and bottomless products from heavy hydrocarbon feedstocks |
| CN107298988B (zh) * | 2016-04-14 | 2019-03-19 | 中国石油化工股份有限公司 | 一种炼化吸收稳定工艺及系统 |
| CN107298987B (zh) * | 2016-04-14 | 2019-03-19 | 中国石油化工股份有限公司 | 吸收稳定工艺及系统 |
| CN107298986B (zh) * | 2016-04-14 | 2019-05-21 | 中国石油化工股份有限公司 | 一种吸收稳定工艺方法 |
| CN107298989B (zh) * | 2016-04-14 | 2019-03-19 | 中国石油化工股份有限公司 | 一种吸收稳定工艺及系统 |
| CN107400538B (zh) * | 2016-05-21 | 2019-03-19 | 中国石油化工股份有限公司 | 一种焦化吸收稳定工艺和系统 |
| CN107400537B (zh) * | 2016-05-21 | 2019-03-19 | 中国石油化工股份有限公司 | 一种焦化吸收稳定工艺和装置 |
| CN107400536B (zh) * | 2016-05-21 | 2019-03-19 | 中国石油化工股份有限公司 | 焦化吸收稳定工艺和系统 |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4983278A (en) * | 1987-11-03 | 1991-01-08 | Western Research Institute & Ilr Services Inc. | Pyrolysis methods with product oil recycling |
| CA2314586C (en) | 1996-09-27 | 2006-11-14 | William Taciuk | Thermal apparatus and process for removing contaminants from oil |
| DE19724074C2 (de) | 1997-06-07 | 2000-01-13 | Metallgesellschaft Ag | Verfahren zur Hochtemperatur-Kurzzeit-Destillation von Rückstandsölen |
| DE19959587B4 (de) | 1999-12-10 | 2006-08-24 | Lurgi Lentjes Ag | Verfahren zur schonenden Kurzzeit-Destillation von Rückstandsölen |
-
2002
- 2002-12-19 DE DE10259450A patent/DE10259450B4/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2003
- 2003-07-09 MX MXPA05006696A patent/MXPA05006696A/es active IP Right Grant
- 2003-07-09 AU AU2003250003A patent/AU2003250003B2/en not_active Ceased
- 2003-07-09 JP JP2004561124A patent/JP4365788B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2003-07-09 WO PCT/EP2003/007377 patent/WO2004056942A1/de not_active Ceased
- 2003-07-09 CA CA2511156A patent/CA2511156C/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2003-07-09 EP EP03813544A patent/EP1590423B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2003-07-09 DE DE50306611T patent/DE50306611D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2003-07-09 AT AT03813544T patent/ATE354625T1/de active
- 2003-07-09 US US10/539,715 patent/US7507330B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2003-07-09 ES ES03813544T patent/ES2282737T3/es not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| MXPA05006696A (es) | 2006-03-30 |
| DE50306611D1 (de) | 2007-04-05 |
| CA2511156C (en) | 2012-04-03 |
| DE10259450B4 (de) | 2006-08-10 |
| CA2511156A1 (en) | 2004-07-08 |
| WO2004056942A1 (de) | 2004-07-08 |
| ES2282737T3 (es) | 2007-10-16 |
| AU2003250003A1 (en) | 2004-07-14 |
| JP4365788B2 (ja) | 2009-11-18 |
| JP2006510757A (ja) | 2006-03-30 |
| DE10259450A1 (de) | 2004-07-15 |
| US7507330B2 (en) | 2009-03-24 |
| EP1590423A1 (de) | 2005-11-02 |
| US20060138030A1 (en) | 2006-06-29 |
| ATE354625T1 (de) | 2007-03-15 |
| AU2003250003B2 (en) | 2006-12-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1009785B1 (de) | Verfahren zur hochtemperatur-kurzzeit-destillation von rückstandsölen | |
| DE69126638T2 (de) | Raffinierung von Schlamm-Schwerölfraktionen | |
| DE1119438B (de) | Verfahren zum Raffinieren von schwefelhaltigen schweren OElen | |
| EP1590423B1 (de) | Verfahren zur hochtemperatur-kurzzeit-destillation von rückstandsöl | |
| EP0138213B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Schwelung von Rückständen der Kohlehydrierung | |
| US5089114A (en) | Method for processing heavy crude oils | |
| DE2728455A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum pyrolysieren von kohlenstoffhaltigem material | |
| DE2914010A1 (de) | Verfahren zur umwandlung von hochsiedenden kohlenwasserstoffrueckstaenden | |
| CN106147879A (zh) | 一种快速热解油气处理系统及方法 | |
| DE3038951C2 (enExample) | ||
| DE2202526A1 (de) | Reinigungsverfahren fuer Kohlenwasserstoff-Einsatzmaterial u.dgl. sowie Verwendung der gereinigten Kohlenwasserstoffe zum katalytischen Cracken | |
| DE69826503T2 (de) | Katalytisches cracken von fluiden und integrierte wiederverwertung von rückständen | |
| JP2006510757A5 (enExample) | ||
| DE2803985C2 (de) | Verfahren zum Verflüssigen von Kohle | |
| JPS58176293A (ja) | 重質油の処理方法 | |
| DE1921917C3 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung schwefelarmer Heizöle aus Rückstandsölen mit hohem Schwefelgehalt | |
| JPH0689335B2 (ja) | デイレ−ドコ−キング方法 | |
| DE69723465T2 (de) | Two-stage process for obtaining significant olefin yields from residual feedstocks | |
| JP3187547B2 (ja) | 重質油の熱分解法 | |
| DD269857A5 (de) | Verfahren zur gewinnung von schweloel | |
| DE599629C (de) | Verfahren zur Behandlung von Destilaltionsprodukten fester Brennstoffe. | |
| EP4043539A1 (de) | Vorrichtung und verfahren zur reinigung und/oder kondensation von pyrolysegas | |
| DE2027600A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung schwefelarmer öle | |
| JPS6220588A (ja) | 分解生成油の処理方法 | |
| DE1036433B (de) | Verfahren zum Verkoken schwerer OEle |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20050611 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AT DE ES FR GB NL |
|
| GRAC | Information related to communication of intention to grant a patent modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCIGR1 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT DE ES FR GB NL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20070221 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 50306611 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20070405 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2282737 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20071122 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20130722 Year of fee payment: 11 Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20130729 Year of fee payment: 11 Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20130719 Year of fee payment: 11 Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20130711 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20130722 Year of fee payment: 11 Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20130719 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 50306611 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: V1 Effective date: 20150201 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 354625 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20140709 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20140709 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150201 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20150331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150203 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 50306611 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20150203 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20140709 Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20140731 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20140709 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20150828 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20140710 |