EP1347145A2 - Dämmstoffplatte zur Wärme-und/oder Schalldämmung sowie Dämmschicht - Google Patents
Dämmstoffplatte zur Wärme-und/oder Schalldämmung sowie Dämmschicht Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1347145A2 EP1347145A2 EP03004361A EP03004361A EP1347145A2 EP 1347145 A2 EP1347145 A2 EP 1347145A2 EP 03004361 A EP03004361 A EP 03004361A EP 03004361 A EP03004361 A EP 03004361A EP 1347145 A2 EP1347145 A2 EP 1347145A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- fire protection
- cavities
- protection element
- element according
- insulation board
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 30
- 239000011490 mineral wool Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 229910052602 gypsum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 8
- 239000010440 gypsum Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 8
- VTHJTEIRLNZDEV-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium dihydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[OH-].[Mg+2] VTHJTEIRLNZDEV-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 239000000347 magnesium hydroxide Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 229910001862 magnesium hydroxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 229940024548 aluminum oxide Drugs 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 239000000378 calcium silicate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 229910052918 calcium silicate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- OYACROKNLOSFPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N calcium;dioxido(oxo)silane Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-][Si]([O-])=O OYACROKNLOSFPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 claims description 51
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 18
- 239000004575 stone Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 210000002268 wool Anatomy 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 5
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 3
- CPLXHLVBOLITMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium oxide Chemical compound [Mg]=O CPLXHLVBOLITMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WNROFYMDJYEPJX-UHFFFAOYSA-K aluminium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[OH-].[OH-].[Al+3] WNROFYMDJYEPJX-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 2
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003292 glue Substances 0.000 description 2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-M hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-] XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 239000012774 insulation material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000035515 penetration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 235000019353 potassium silicate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- RMAQACBXLXPBSY-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicic acid Chemical compound O[Si](O)(O)O RMAQACBXLXPBSY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NTHWMYGWWRZVTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N sodium silicate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-][Si]([O-])=O NTHWMYGWWRZVTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920001807 Urea-formaldehyde Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000004026 adhesive bonding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000004649 carbonic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000018044 dehydration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006297 dehydration reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003063 flame retardant Substances 0.000 description 1
- LCDFWRDNEPDQBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N formaldehyde;phenol;urea Chemical compound O=C.NC(N)=O.OC1=CC=CC=C1 LCDFWRDNEPDQBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000395 magnesium oxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010327 methods by industry Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003973 paint Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011837 pasties Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011505 plaster Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011265 semifinished product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003980 solgel method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002344 surface layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920001187 thermosetting polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04B—GENERAL BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS; WALLS, e.g. PARTITIONS; ROOFS; FLOORS; CEILINGS; INSULATION OR OTHER PROTECTION OF BUILDINGS
- E04B1/00—Constructions in general; Structures which are not restricted either to walls, e.g. partitions, or floors or ceilings or roofs
- E04B1/62—Insulation or other protection; Elements or use of specified material therefor
- E04B1/92—Protection against other undesired influences or dangers
- E04B1/94—Protection against other undesired influences or dangers against fire
- E04B1/941—Building elements specially adapted therefor
- E04B1/942—Building elements specially adapted therefor slab-shaped
Definitions
- the invention relates to a fire protection element, in particular for fire protection doors, consisting of at least one mineral wool, in particular stone wool insulation board with two large ones, spaced apart and parallel to each other large surfaces that are substantially perpendicular to the four large surfaces and mutually extending side surfaces are connected, and from at least one water-releasing fire protection material.
- the invention also relates to a method for producing such a fire protection element.
- steel doors according to DIN 18082, part 1 or part 3 apply are, for example, self-closing doors, flaps and gates that are intended to be installed in accordance with the definition of the standard the passage of fire through openings in walls and ceilings hinder.
- the fire resistance of these internals is based on the time in which these prevent the fire from passing through.
- the fire resistance period is according to DIN 4102-4 tested. It becomes the essential test criterion the duration measured up to which the surface temperature of the side facing away from the fire Door element, for example, remains ⁇ 180 ° C.
- Fire resistance classes T 30, T 60, T 90, T 120 and T 180 corresponds to the fire resistance duration in minutes.
- Fire Barriers according to DIN 18082 hereinafter generally only as fire protection doors referred to consist of sheet metal structures, in the so-called Fire protection elements are inserted. Assembling the fire doors takes place in a very short time on efficient production lines, so that the fire protection elements for handling when manufacturing the doors should be as light as possible. At the same time, the holding elements the doors and the frames are dimensioned smaller.
- the fire protection element must be for normal use, especially against vibrations have sufficient internal rigidity. To fire resistance To achieve, the fire protection element must be dimensionally stable even in the event of a fire remain and have low thermal conductivity at high temperatures.
- Fire protection elements made of mineral wool, in particular stone wool insulation panels have proven their worth for doors with a low fire resistance.
- These mineral wool, in particular stone wool insulation boards have a bulk density of over 100 kg / m 3 and are usually bound with small amounts of a thermosetting phenol-formaldehyde-urea resin. Since the organic components naturally contribute to an energy transfer to the side facing away from the fire, their proportion in the fire protection element must be as small as possible.
- the fire protection element should absorb energy and therefore contain temperature-reducing substances. Hydrate compounds are often used for this purpose used where significant amounts of thermal energy are required are to warm these substances up to the dehydration temperatures, break the chemical bond and evaporate the water. additional For example, carbonates or suitable for hydrosilicate compounds.
- Such compounds can be used alone or in mixtures in the fiber mass Insulation boards are evenly distributed. The effectiveness can also be seen through the concentration of the surcharges or part of them in the central zones of the fire protection element can be influenced.
- DE 295 07 498 U1 describes the process engineering in particular Disadvantages in the manufacture of such fire protection elements highlighted.
- the Improvement according to DE 295 07 498 U1 is that the naturally wet Do not mix directly onto the surfaces of the mineral wool insulation boards apply and glue two panels together to form a fire protection element, but in the production of a separate plate as a semi-finished product.
- This The plate consists preferably of 50 to 90% by mass of aluminum hydroxide and 10 up to 50 mass% water glass and is on both large surfaces with a glass fabric covered, depending on the embodiment also silica sol or magnesia binder be used.
- the thickness of this separate plate is preferably 4 to 5 mm, with side lengths of the plates of, for example, 50 to 100 cm x 150 up to 200 cm.
- the invention has for its object to simplify the manufacture of such fire protection elements and to make them more cost-effective, in particular to create such a fire protection element that has very good fire protection properties, can be adapted in a simple manner to the requirements of the individual case and in particular avoids moisture penetration of the insulation board.
- the insulation board has at least one, preferably several cavities which are open at least on one side and into which elements made of water-releasing material are inserted.
- the fire protection element thus consists of only one insulation board, preferably made of rock wool, so that the gluing of several insulation boards to a sandwich-like unit and glue can be avoided can, the classification of such a fire protection element in higher Fire protection classes difficult.
- Another advantage of this fire protection element is that about the size and number of elements made from water-releasing Material, the required amount of this material can be set very precisely can, the heat and / or sound insulation of the fire protection element is also optimized in that a fire protection element for the application coordinated water-splitting material with the maximum possible Insulation material portion is provided, so that with full-surface layers made of fire protection material sometimes poor insulation properties can be.
- the fire protection element according to the invention despite the stiff water-splitting material, at least limited bendability.
- the elements preferably extend from water-splitting material over the entire length or the entire width of the insulation board to be in each Section of the fire protection element to an optimal fire resistance value achieve.
- the elements can be made of water-releasing Material be made relatively narrow, which the bending ability of the Fire protection element significantly improved.
- the elements rod-shaped and separated from each other by mineral wool bridges are. This configuration simplifies the production of the Fire protection element achieved, the fire protection element very good heat and / or Has soundproofing properties, because on a flat, continuous, rigid body is dispensed within the fire protection element.
- the cross sections of the cavities are preferably symmetrical, in particular rotationally symmetrical are designed so that the fire protection element is independent of direction can be installed.
- the cavities are arranged at a uniform distance from each other, whereby the distance between adjacent cavities is essentially the width or corresponds to the diameter of a cavity, so that over the entire Volume of the fire protection element homogeneous fire resistance properties be achieved.
- the cavities are preferably cut out of the insulation board, in particular milled or sawn out.
- a CNC saw can be used, which enables the cavities to be formed precisely and in terms of position.
- the insulation board has incisions through which the cavities are connected to a large surface of the insulation board. The saw blade is guided through the incisions.
- the incisions in the finished fire protection element can increase the bendability, so that the fire protection element can also be used advantageously in curved components.
- the elements made of water-separating fire protection material are after one Another feature of the invention designed as a hardened molded body and in the cavities are inserted.
- the elements made of water-separating fire protection material are thus prefabricated and only after they have hardened as Shaped body inserted into the cavities. This results in moisture penetration the insulation board avoided and the fire protection element can be done without expensive Storage for drying the water-releasing fire protection material in very be produced in a short time, so that the production is very cost-effective can.
- different elements are processed to different properties of the fire protection element To be able to offer.
- the fire protection element according to the invention thus has a high variability with low cost producibility.
- the cavities can also be granulated with a water-binding hydroxide be filled, the front openings with a closure are closed. It can also pasty or gel-like substances in the Cavities are introduced.
- an element is arranged in each cavity. ever but depending on the application and the required fire resistance class be provided that elements are arranged in part of the cavities.
- the elements made of water-releasing material are preferably made of plaster and / or gypsum materials, such as gypsum plasterboard, gypsum plasterboard or fiber-reinforced gypsum boards, especially with calcium silicate, aluminum or Magnesium hydroxide.
- the elements have a slight excess compared to the clear dimension of the cavities.
- the insulation board has an outer contour that has a cavity in a door leaf of a fire door.
- the invention Fire protection element in a simple manner as the only plate in the Cavity can be inserted and it is no longer necessary to add several panels process, at least some of which must be cut.
- the insulation board has a bulk density between 80 and 180 kg / m 3 .
- the method according to the invention for producing a previously described Fire protection element provides that in an insulation board at least on one side open cavities are worked into which elements are then made water-splitting fire protection material.
- the cavities are preferably cut from the Sawed out insulation board. Alternatively, it can be provided that the cavities of the insulation board. Depending on the tool, the incisions can then be made to be dispensed with
- the mineral wool, in particular stone wool insulation boards have bulk densities ⁇ approx. 100 kg / m 3 to approx. 200 kg / m 3 , preferably approx. 150-170 kg / m 3 .
- the content of organic components is less than approx. 3% by mass.
- the fire protection element according to the invention can accordingly the processor, especially the manufacturer of fire protection doors in his Components are made available.
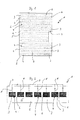
- a fire protection element 1 according to FIGS. 1 and 2 is particularly suitable for fire protection doors determined and consists of a stone wool insulation board 2 and therein arranged elements 3 made of a water-releasing fire protection material, such as magnesium hydroxide.
- the Insulation board 2 For receiving the elements 3, the Insulation board 2 a number of cavities corresponding to the number of elements 3 4, into which the elements 3 are inserted.
- the cavities 4 are aligned transversely to the longitudinal axis direction of the insulation board 2 and open in the area of a long side 5 of the insulation board 2.
- the cavities 4 extend over almost the entire width of the insulation board 2, so that the length of the elements 3 essentially match the width of the insulation board 2.
- FIG. 2 shows an embodiment in which the The width of the webs 6 is less than the width of the elements 3.
- the cavities 4 and the elements 3 are square in cross section, wherein the clear width of the cavities 4 is made slightly smaller than that Dimensions of the elements 3, so that the elements 3 non-positively in the cavities 4 are held.
- the elements 3 are designed as shaped bodies and are prefabricated and cured before they are inserted into the cavities 4.
- the insulation board 2 is processed with a raw density of 100 kg / m 3 up to 200 kg / m 3 over a large surface 7 with a CNC saw. With the saw, an incision 8 is sawn into the insulation board 2 for each cavity 4, which cuts into the area of the cavity 4 to be cut out. The cavity 4 is then sawed over this incision 8, the insulation material of the insulation board 2 arranged in the cavity 4 being pulled out of the insulation board 2 via the longitudinal side 5.
- the fire protection element 1 according to Figure 1 has an outer contour that with a cavity in a door leaf of a fire door, not shown matches, so that the fire protection element 1 completely this cavity fills. Accordingly, a recess in the fire protection element 1 is closed in FIG recognize which is arranged in the area of a lock case of the door leaf.
- the stone wool insulation board can have bulk densities ⁇ approx. 100 kg / m 3 to approx. 200 kg / m 3 , a bulk density of approx. 150 to 170 kg / m 3 proving to be advantageous in numerous applications Has.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Architecture (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Civil Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Special Wing (AREA)
- Building Environments (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Bei dieser Ausbildung weist die Dämmplatte Einschnitte auf, über die die Hohlräume mit einer großen Oberfläche der Dämmplatte verbunden sind. Durch die Einschnitte wird das Sägeblatt geführt. Die Einschnitte können beim fertigen Brandschutzelement die Biegefähigkeit erhöhen, so dass das Brandschutzelement auch in gebogenen Bauteilen vorteilhaft eingesetzt werden kann.
- 1
- Brandschutzelement
- 2
- Dämmplatte
- 3
- Element
- 4
- Hohlraum
- 5
- Längsseite
- 6
- Steg
- 7
- Oberfläche
- 8
- Einschnitt
- 9
- Punklinie
Claims (20)
- Brandschutzelement, insbesondere für Feuerschutztüren, bestehend aus zumindest einer Mineralwolle-, insbesondere Steinwolle-Dämmplatte mit zwei großen, im Abstand zueinander und parallel verlaufend angeordnet große Oberflächen, die über vier im wesentlichen rechtwinklig zu den großen Oberflächen und zueinander verlaufenden Seitenflächen verbunden sind, und aus zumindest einem wasserabspaltenden Brandschutzmaterial,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Dämmplatte (2) zumindest einen,(vorzugsweise mehrere zumindest einseitig) offene Hohlräume (4) aufweist, in die Elemente (3) aus wasserabspaltendem Material eingesetzt sind. - Brandschutzelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Elemente (3) stabförmig ausgebildet und durch Stege (6) aus Mineralwolle voneinander getrennt sind. - Brandschutzelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass sich die Hohlräume (4) im wesentlichen über die gesamte Länge oder die gesamte Breite der Dämmplatte (2) erstrecken. - Brandschutzelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Hohlräume (4) im Querschnitt symmetrisch, insbesondere rotationssymmetrisch ausgebildet sind. - Brandschutzelement nach Anspruch 4,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Hohlräume (4) im Querschnitt quadratisch ausgebildet sind. - Brandschutzelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Hohlräume (4) in gleichmäßigem Abstand zueinander angeordnet sind, wobei der Abstand zwischen benachbarten Hohlräumen (4) im wesentlichen der Breite oder dem Durchmesser eines Hohlraums (4) entspricht. - Brandschutzelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Hohlräume (4) aus der Dämmplatte (2) ausgeschnitten, insbesondere ausgefräst oder ausgesägt sind. - Brandschutzelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Dämmplatte (2) Einschnitte (8) aufweist, über die die Hohlräume (4) mit einer großen Oberfläche (7) der Dämmplatte (2) verbunden sind. - Brandschutzelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Elemente (3) aus wasserabspaltendem Brandschutzmaterial als ausgehärtete Formkörper ausgebildet und in die Hohlräume (4) eingesetzt sind. - Brandschutzelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass in jedem Hohlraum (4) ein Element (3) angeordnet ist. - Brandschutzelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass in einem Teil der Hohlräume (4) Elemente (3) angeordnet sind. - Brandschutzelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Elemente (3) aus wasserabspaltendem Material aus Gips oder Gipswerkstoffen, Kalziumsilikat, Aluminium- oder Magnesiumhydroxid bestehen. - Brandschutzelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Elemente (3) ein gegenüber dem lichten Maß der Hohlräume (4) geringes Übermaß aufweisen. - Brandschutzelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Hohlräume (4) und die darin eingeschobenen Elemente (3) aus wasserabspaltendem Brandschutzmaterial rechtwinklig zur Längsrichtung der Dämmplatte (2) angeordnet sind. - Brandschutzelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Dämmplatte (2) eine äußere Kontur aufweist, die mit einem Hohlraum (4) in einem Türblatt einer Feuerschutztür übereinstimmt. - Brandschutzelement nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Dämmplatte (2) eine Rohdichte zwischen 80 und 200 kg/m3 aufweist. - Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Brandschutzelementes nach einem der Ansprüche 1bis 16,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass in eine Dämmplatte (2) zumindest einseitig offene Hohlräume (4) eingearbeitet werden, in die anschließend Elemente (3) aus wasserabspaltendem Brandschutzmaterial eingeschoben werden. - Verfahren nach Anspruch 17,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Hohlräume (4) über jeweils einen Einschnitt (8) aus der Dämmplatte (2) ausgesägt werden. - Verfahren nach Anspruch 17,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Hohlräume (4) aus der Dämmplatte (2) ausgefräst werden. - Verfahren nach Anspruch 17,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Elemente (3) aus wasserabspaltendem Material in rigider, insbesondere ausgehärteter Form in die Hohlräume (4) eingeschoben werden.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE10212331 | 2002-03-20 | ||
| DE2002112331 DE10212331A1 (de) | 2002-03-20 | 2002-03-20 | Brandschutzelement, insbesondere für Feuerschutztüren |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1347145A2 true EP1347145A2 (de) | 2003-09-24 |
| EP1347145A3 EP1347145A3 (de) | 2004-01-28 |
Family
ID=27771444
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP03004361A Withdrawn EP1347145A3 (de) | 2002-03-20 | 2003-03-03 | Dämmstoffplatte zur Wärme-und/oder Schalldämmung sowie Dämmschicht |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1347145A3 (de) |
| DE (1) | DE10212331A1 (de) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2236282A1 (de) * | 2009-03-31 | 2010-10-06 | IKJ S.a.r.l. | Brandschutzplatte sowie Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung einer Brandschutzplatte |
| EP1680372B1 (de) | 2003-10-06 | 2015-08-19 | Saint-Gobain Isover | Feuerschutzt re und feuerschutzeinlage hierfür |
| EP3412858A1 (de) * | 2017-06-07 | 2018-12-12 | Knauf Insulation SPRL | Isolierplatte aus mineralwolle und methode zur herstellung einer solchen isolierplatte |
| EP4477812A1 (de) * | 2023-06-02 | 2024-12-18 | vanDockumGROUP v/Charlotte van Dockum Davidsen | Schall- und feuerhemmende isolierplatte und verfahren zur herstellung einer schall- und feuerhemmenden isolierplatte |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10354221C5 (de) † | 2003-11-20 | 2011-05-12 | Hörmann KG Freisen | Feuerabschlusselement und Verfahren zur Herstellung |
| DE10356889A1 (de) * | 2003-12-05 | 2005-07-14 | Saint-Gobain Isover G+H Ag | Geteilte Feuerschutztüreinlage |
| EP2816188B1 (de) | 2013-06-17 | 2019-12-11 | Rockwool International A/S | Feuerbarriere für ein Gebäude und Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Dämmelements für eine Feuerbarriere eines Gebäudes |
| DE102015108567A1 (de) * | 2015-05-29 | 2016-12-01 | Novoferm Riexinger Türenwerke GmbH | Brandschutzeinrichtung |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3824598A1 (de) | 1988-07-19 | 1990-01-25 | Gruenzweig & Hartmann | Einlage fuer feuerschutztueren mit kieselsol |
| DE29507498U1 (de) | 1995-05-05 | 1995-07-13 | SAINT-GOBAIN ISOVER G+H AG, 67059 Ludwigshafen | Brandschutzelement mit Schichtstruktur, insbesondere als Einlage für Feuerschutztüren, sowie Halbzeug hierfür |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3411296C2 (de) * | 1984-03-27 | 1995-07-06 | Brandschutz Indverband | Wärmedämmittel zum Einbau in Hohlprofile von Brandschutzkonstruktionen |
| SE8504028D0 (sv) * | 1985-08-29 | 1985-08-29 | Laxa Bruks Ab | Brandskyddskropp |
| WO1990002855A1 (en) * | 1987-03-17 | 1990-03-22 | Combal & Co. A/S | Fire retardant wall/roofing element |
-
2002
- 2002-03-20 DE DE2002112331 patent/DE10212331A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
2003
- 2003-03-03 EP EP03004361A patent/EP1347145A3/de not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3824598A1 (de) | 1988-07-19 | 1990-01-25 | Gruenzweig & Hartmann | Einlage fuer feuerschutztueren mit kieselsol |
| DE29507498U1 (de) | 1995-05-05 | 1995-07-13 | SAINT-GOBAIN ISOVER G+H AG, 67059 Ludwigshafen | Brandschutzelement mit Schichtstruktur, insbesondere als Einlage für Feuerschutztüren, sowie Halbzeug hierfür |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1680372B1 (de) | 2003-10-06 | 2015-08-19 | Saint-Gobain Isover | Feuerschutzt re und feuerschutzeinlage hierfür |
| EP2236282A1 (de) * | 2009-03-31 | 2010-10-06 | IKJ S.a.r.l. | Brandschutzplatte sowie Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung einer Brandschutzplatte |
| EP3412858A1 (de) * | 2017-06-07 | 2018-12-12 | Knauf Insulation SPRL | Isolierplatte aus mineralwolle und methode zur herstellung einer solchen isolierplatte |
| EP3412858B1 (de) | 2017-06-07 | 2022-10-19 | Knauf Insulation SPRL | Gebäudestruktur mit einer isolierplatte aus mineralwolle und methode zur herstellung derselben |
| EP4477812A1 (de) * | 2023-06-02 | 2024-12-18 | vanDockumGROUP v/Charlotte van Dockum Davidsen | Schall- und feuerhemmende isolierplatte und verfahren zur herstellung einer schall- und feuerhemmenden isolierplatte |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1347145A3 (de) | 2004-01-28 |
| DE10212331A1 (de) | 2003-10-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2025484B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Formkörpers, insbesondere für die Bau- oder Möbelindustrie | |
| DE4310191C2 (de) | Laminierte Holzfaserplatte | |
| EP2666625B1 (de) | Wandaufbau und Wärmedämmplatte | |
| EP1097807B1 (de) | Gebundenes Mineralwolleprodukt mit Feuerschutzfunktion sowie Brandschutzelement mit dem gebundenen Mineralwolleprodukt | |
| EP2208594B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung einer brandhemmenden Holzwerkstoffplatte | |
| EP0960251A1 (de) | Feuerwiderstandsfähiger öffnungsverschluss | |
| EP3129564B1 (de) | Leichtbauelement, herstellungsverfahren dafür, verwendung desselben, sowie leichtbauplatte und dämmstoff | |
| DE29507498U1 (de) | Brandschutzelement mit Schichtstruktur, insbesondere als Einlage für Feuerschutztüren, sowie Halbzeug hierfür | |
| EP1347145A2 (de) | Dämmstoffplatte zur Wärme-und/oder Schalldämmung sowie Dämmschicht | |
| EP1538297B2 (de) | Geteilte Feuerschutztüreinlage | |
| DE2635736C2 (de) | Feuerhemmende Platte | |
| DE19952072A1 (de) | Fertigverbundbauelement | |
| WO2003023161A1 (de) | Brandschutzelement, verfahren zu dessen herstellung und brandschutzgesichertes rahmenwerk für ein gebäudeteil, wie für eine gebäudefassade oder dgl. | |
| EP1239093A2 (de) | Brandschutzelement, insbesondere für Feuerschutztüren | |
| EP1347144A2 (de) | Brandschutzelement, insbesondere für Feuerschutztüren | |
| EP0947638B1 (de) | Dämmplatte zur Verwendung an Aussenfassaden von Häusern | |
| DE3202488C2 (de) | ||
| DE69109205T2 (de) | Mischung für den Kern einer Gipsplatte. | |
| DE2548210A1 (de) | Bauplatte aus hydraulischem bindemittelzement, organischen fasern, spaenen o.dgl., mineralisierungsmittel und wasser sowie verfahren zu deren herstellung | |
| DE69922502T2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Türblattes | |
| DE102005008200A1 (de) | Schaumglasverbundelement | |
| DE20119043U1 (de) | Brandschutzelement, insbesondere für Feuerschutztüren | |
| DE2323659B2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Schallabsorptionstafeln, -brettern, -platten oder anderen -formkörpern | |
| DE10226784B4 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Bauelements oder einer Schicht eines Verbundelementes | |
| EP1247916A1 (de) | Dämmformkörper, insbesondere Dämmplatte, aus Holzfaserstoff sowie dessen Herstellung und Verwendung |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: 7E 06B 5/16 B Ipc: 7E 04B 1/94 A |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: 8566 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 20040729 |