EP1213628A1 - Verfahren zur Regulierung der Schwingungsfrequenz einer Unruhspiralfeder für eine mechanische Uhr - Google Patents
Verfahren zur Regulierung der Schwingungsfrequenz einer Unruhspiralfeder für eine mechanische Uhr Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1213628A1 EP1213628A1 EP00204369A EP00204369A EP1213628A1 EP 1213628 A1 EP1213628 A1 EP 1213628A1 EP 00204369 A EP00204369 A EP 00204369A EP 00204369 A EP00204369 A EP 00204369A EP 1213628 A1 EP1213628 A1 EP 1213628A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- hairspring
- oscillation
- frequency
- machining
- balance
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 230000010355 oscillation Effects 0.000 title claims description 23
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 22
- 238000003754 machining Methods 0.000 claims description 23
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 3
- 241000287828 Gallus gallus Species 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005021 gait Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008439 repair process Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G04—HOROLOGY
- G04D—APPARATUS OR TOOLS SPECIALLY DESIGNED FOR MAKING OR MAINTAINING CLOCKS OR WATCHES
- G04D7/00—Measuring, counting, calibrating, testing or regulating apparatus
- G04D7/10—Measuring, counting, calibrating, testing or regulating apparatus for hairsprings of balances
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G04—HOROLOGY
- G04B—MECHANICALLY-DRIVEN CLOCKS OR WATCHES; MECHANICAL PARTS OF CLOCKS OR WATCHES IN GENERAL; TIME PIECES USING THE POSITION OF THE SUN, MOON OR STARS
- G04B17/00—Mechanisms for stabilising frequency
- G04B17/04—Oscillators acting by spring tension
- G04B17/06—Oscillators with hairsprings, e.g. balance
- G04B17/066—Manufacture of the spiral spring
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a frequency adjustment method of a balance spring fitted to a mechanical timepiece.
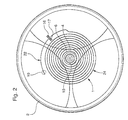
- the regulator assembly of a watch movement will be briefly described below in using Figures 1 and 2 attached.
- this regulator assembly includes a balance spring 1 associated with a balance 2.
- the balance spring is connected to axis 4 of the balance by means of a ferrule 6.
- the outer end 8 of the hairspring is fixed to a stud 10 secured to the balance bridge 12 (rooster).
- the balance-spring oscillation is maintained by the escape wheel 14 engaged with the train of the movement.
- the object of the present invention is to overcome the drawbacks mentioned above by proposing a method for adjusting the frequency of a balance spring efficient, inexpensive and simplifying the construction of the assembly regulator.
- the invention relates to a method for adjusting the frequency of oscillation of a balance-spring according to the steps mentioned in claim 1, in which we use laser machining of the balance spring to reduce the torque elasticity of the latter until reaching a reference elastic torque substantially corresponding to the reference frequency for the oscillation of the sprung balance.
- knowledge of the elastic reference torque is not necessary since the adjustment can be done in one or more successive steps by measuring the frequency of the assembled balance spring.
- the hairspring ready for mounting for a given length between the points of attachment to the ferrule 6 and to the pin 10 has an elastic torque greater than the reference elastic torque above.
- laser machining has the effect of reducing the elastic torque of the spiral, as will be explained below in more detail.
- the adjustment of the oscillation frequency of the balance spring can be carried out during a preliminary stage, preceding the mounting of this balance spring in a watch movement.
- a presetting can be carried out according to the invention in this preliminary step and a fine adjustment, also to using a laser beam, is carried out once the balance spring is mounted in the watch movement to allow precise adjustment of the oscillation frequency of this balance spring in real operating conditions and thus ensure a exact movement of the watch movement.
- the regulator assembly preferably no longer comprises pins racket.
- the problems of gait variation according to the position of the movement, due to the passage of the outer spiral spiral between the pins, are eliminated.
- the present invention is particularly suitable for factory or watch workshop adjustment and may prove to be complex for implementation by an after-sales service workshop carrying out the traditional checks and necessary repairs following possible damage caused to the timepiece.
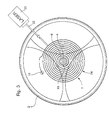
- the balance spring 1, 2 is assembled and the outer end 22 of the balance spring is attached to a stud 10 of a watch movement (not shown).
- the assembled balance spring can be mounted in a device specifically used to the process of the invention. In the latter case, the stud 10 belongs to the device specific or is replaced by an equivalent fixing means.
- the hairspring is produced with an elastic torque greater than one reference elastic torque corresponding to a reference frequency for the oscillation of the balance-spring.
- the frequency is measured of balance-spring oscillation, this frequency then being greater than the frequency reference.
- a laser device 30 providing a laser beam 32 for machining or processing the hairspring 1.
- the adjustment of the frequency of the regulator assembly is adjusted neither using racket pins, nor using screws or small masses arranged on the balance 2.
- the present invention does not exclude the possibility of providing means for variation of the balance inertia to allow fine adjustments after adjustment initial in the factory by means of the method according to the invention. According to this process, laser machining of hairspring 1 so as to reduce its elastic torque until that it is substantially equal to the above-mentioned reference elastic torque.
- the oscillation frequency is finely adjusted to using the laser device 30 as a function of one or more frequency measurements oscillation.
- the program for controlling the laser device 30 and its movement relative to the balance spring can include a single step of machining or processing based on an initial frequency measurement, using an algorithm based on an analytical or empirical model, or a combination both.
- numerous control variants of the laser device within the framework of the implementation of the method according to the invention are possible.
- the laser beam 32 to modify at least superficially the structure of hairspring 1 in at least one of its parts, in particular on a section of its external turn 24.
- This machining has firstly, the function of varying the elastic modulus E of the balance spring by lowering it up to a value for which the elastic torque of this hairspring corresponds to the value reference. Indeed, the oscillation frequency being proportional to the root square of the elastic torque M of the hairspring, and this torque being proportional to the modulus elasticity E, a reduction in this modulus therefore makes it possible to decrease the frequency oscillation of the regulator assembly.
- laser machining can also be carried out on several spiral turns, along sections of varying sizes defined in particular according to the access to these turns by the laser beam.
- a second embodiment of the method shown schematically in Figure 4, it is planned to partially decrease the height H of the ribbon 36 forming this hairspring.
- This decrease in height is expected only along of sections L1, L2 of the ribbon 36, which defines open cutouts 40 along the upper or lower edge of this ribbon. These cuts can vary in length and in number.
- the elastic torque of hairspring 1 being proportional to the height of the ribbon 36, an at least partial reduction in this height makes it possible to reduce this torque and therefore the frequency of oscillation of the balance spring.
- laser machining is therefore used primarily to remove material and provision is made to focus the beam 32 on the region of machining of the ribbon 36.
- the laser is arranged so that the beam 32 is substantially perpendicular to the general plane of the hairspring allowing machining either the upper surface, that is, the lower surface of the hairspring.
- This last variant makes it possible to act over a larger area for the laser beam, but has the disadvantage that the laser beam can also reach the turn preceding that which is being machined.
- This second mode of implementation of the method easily makes it possible to machine several spiral turns, in particular in the preferred variant.
- the thickness of the ribbon 36 forming the hairspring 1 is planned to at least partially reduce the thickness of the ribbon 36 forming the hairspring 1.
- This reduction in thickness in the zones 44 is carried out using of a laser beam.
- This laser machining is preferably carried out on the turn 24 of the balance spring, but it is also possible to machine other turns by orienting this laser beam obliquely relative to the plane of the balance spring.
- the zones 44 pass through from top to bottom. Their width can be variable, as can the number of machined zones provided. It is also possible to provide a succession of machining of lines operated by paths along a vertical axis of the laser beam. The decrease in frequency comes from the fact that the elastic torque of the balance spring varies according to the cube thickness (e 3 ) of the ribbon forming the balance spring.
- Figures 6 and 7 show two machining variants on the face lateral 46 of the hairspring 1.
- the area 48 is oblong. This zone 48 forms a recess in the tape 36 without reaching the upper and lower surfaces of this one. Thus, the appearance of the hairspring seen from above is not affected.
- the areas 50 form a succession of circular recesses.
- laser machining may create through openings.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Springs (AREA)
- Laser Beam Processing (AREA)
- Micromachines (AREA)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP00204369A EP1213628A1 (de) | 2000-12-07 | 2000-12-07 | Verfahren zur Regulierung der Schwingungsfrequenz einer Unruhspiralfeder für eine mechanische Uhr |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP00204369A EP1213628A1 (de) | 2000-12-07 | 2000-12-07 | Verfahren zur Regulierung der Schwingungsfrequenz einer Unruhspiralfeder für eine mechanische Uhr |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1213628A1 true EP1213628A1 (de) | 2002-06-12 |
Family
ID=8172390
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP00204369A Withdrawn EP1213628A1 (de) | 2000-12-07 | 2000-12-07 | Verfahren zur Regulierung der Schwingungsfrequenz einer Unruhspiralfeder für eine mechanische Uhr |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1213628A1 (de) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012007460A1 (fr) * | 2010-07-16 | 2012-01-19 | Eta Sa Manufacture Horlogère Suisse | Procédé d'ajustement de fréquence d'oscillation, d'inertie ou d'équilibrage d'un composant mobile de mouvement d'horlogerie, ou d'un ensemble balancier-spiral d'horlogerie |
| CN102528282A (zh) * | 2010-12-08 | 2012-07-04 | 上海康比利仪表有限公司 | 一种激光游丝焊接仪 |
| EP3181940A1 (de) * | 2015-12-18 | 2017-06-21 | CSEM Centre Suisse d'Electronique et de Microtechnique SA - Recherche et Développement | Herstellungsverfahren einer spiralfeder mit einer vorbestimmten steifigkeit durch lokalisierte wegnahme von material |
| EP3181938A1 (de) * | 2015-12-18 | 2017-06-21 | CSEM Centre Suisse d'Electronique et de Microtechnique SA - Recherche et Développement | Herstellungsverfahren einer spiralfeder mit einer vorbestimmten steifigkeit durch wegnahme von material |
| EP3181939A1 (de) * | 2015-12-18 | 2017-06-21 | CSEM Centre Suisse d'Electronique et de Microtechnique SA - Recherche et Développement | Herstellungsverfahren einer spiralfeder mit einer vorbestimmten steifigkeit durch zugabe von material |
| EP3416001B1 (de) * | 2017-06-13 | 2022-04-13 | Patek Philippe SA Genève | Herstellungsverfahren eines oszillators mit flexiblem zapfen |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3673376A (en) * | 1968-08-26 | 1972-06-27 | Jean Claude Kullmann | Method for attaching the inner end of a balance spring to its collet |
| CH1283368A4 (fr) * | 1968-08-27 | 1972-10-31 | Fabriques De Spiraux Reunis So | Procédé pour l'obtention d'un ensemble oscillant balancier-spiral de fréquence désirée |
-
2000
- 2000-12-07 EP EP00204369A patent/EP1213628A1/de not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3673376A (en) * | 1968-08-26 | 1972-06-27 | Jean Claude Kullmann | Method for attaching the inner end of a balance spring to its collet |
| CH1283368A4 (fr) * | 1968-08-27 | 1972-10-31 | Fabriques De Spiraux Reunis So | Procédé pour l'obtention d'un ensemble oscillant balancier-spiral de fréquence désirée |
Cited By (26)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012007460A1 (fr) * | 2010-07-16 | 2012-01-19 | Eta Sa Manufacture Horlogère Suisse | Procédé d'ajustement de fréquence d'oscillation, d'inertie ou d'équilibrage d'un composant mobile de mouvement d'horlogerie, ou d'un ensemble balancier-spiral d'horlogerie |
| CN103003760A (zh) * | 2010-07-16 | 2013-03-27 | Eta瑞士钟表制造股份有限公司 | 用于调节可动时计机芯构件或时计游丝摆轮组件的振荡频率和/或调节其惯性和/或平衡的方法 |
| JP2013542402A (ja) * | 2010-07-16 | 2013-11-21 | ウーテーアー・エス・アー・マニファクチュール・オロロジェール・スイス | 時計ムーブメントの可動構成要素又は時計のばね−テンプ組立体の、発振周波数調整及び/又は慣性調整及び/又はバランス修正のための方法 |
| CN103003760B (zh) * | 2010-07-16 | 2015-04-15 | Eta瑞士钟表制造股份有限公司 | 用于调节可动时计机芯构件或时计游丝摆轮组件的振荡频率和/或调节其惯性和/或平衡的方法 |
| RU2556322C2 (ru) * | 2010-07-16 | 2015-07-10 | Эта Са Мануфактюр Орложэр Сюис | Способ регулирования частоты колебаний и/или регулирования момента инерции и/или балансировки подвижного компонента механизма хронометра или узла баланс-спираль хронометра |
| US9436162B2 (en) | 2010-07-16 | 2016-09-06 | Eta Sa Manufacture Horlogere Suisse | Method for adjusting the oscillation frequency and/or adjusting the inertia and/or balancing of a movable timepiece movement component or of a timepiece spring balance assembly |
| CN102528282A (zh) * | 2010-12-08 | 2012-07-04 | 上海康比利仪表有限公司 | 一种激光游丝焊接仪 |
| CN102528282B (zh) * | 2010-12-08 | 2014-04-09 | 上海康比利仪表有限公司 | 一种激光游丝焊接仪 |
| CN106896700A (zh) * | 2015-12-18 | 2017-06-27 | 瑞士电子显微技术研究与开发中心股份有限公司 | 通过局部去除材料来制造预定刚度的游丝的方法 |
| EP3181938B1 (de) | 2015-12-18 | 2019-02-20 | CSEM Centre Suisse d'Electronique et de Microtechnique SA - Recherche et Développement | Herstellungsverfahren einer spiralfeder mit einer vorbestimmten steifigkeit durch wegnahme von material |
| EP3181939A1 (de) * | 2015-12-18 | 2017-06-21 | CSEM Centre Suisse d'Electronique et de Microtechnique SA - Recherche et Développement | Herstellungsverfahren einer spiralfeder mit einer vorbestimmten steifigkeit durch zugabe von material |
| US20170176941A1 (en) * | 2015-12-18 | 2017-06-22 | Csem Centre Suisse D'electronique Et De Microtechnique Sa - Recherche Et Developpement | Method for fabrication of a balance spring of a predetermined stiffness by local removal of material |
| EP3181940A1 (de) * | 2015-12-18 | 2017-06-21 | CSEM Centre Suisse d'Electronique et de Microtechnique SA - Recherche et Développement | Herstellungsverfahren einer spiralfeder mit einer vorbestimmten steifigkeit durch lokalisierte wegnahme von material |
| CN106896708A (zh) * | 2015-12-18 | 2017-06-27 | 瑞士电子显微技术研究与开发中心股份有限公司 | 用于通过去除材料制造预定刚度的游丝的方法 |
| CN106997170A (zh) * | 2015-12-18 | 2017-08-01 | 瑞士电子显微技术研究与开发中心股份有限公司 | 用于通过增加材料制造预定厚度的游丝的方法 |
| EP3181940B1 (de) | 2015-12-18 | 2019-02-06 | CSEM Centre Suisse d'Electronique et de Microtechnique SA - Recherche et Développement | Herstellungsverfahren einer spiralfeder mit einer vorbestimmten steifigkeit durch lokalisierte wegnahme von material |
| EP3181939B1 (de) | 2015-12-18 | 2019-02-20 | CSEM Centre Suisse d'Electronique et de Microtechnique SA - Recherche et Développement | Herstellungsverfahren einer spiralfeder mit einer vorbestimmten steifigkeit durch zugabe von material |
| EP3181938A1 (de) * | 2015-12-18 | 2017-06-21 | CSEM Centre Suisse d'Electronique et de Microtechnique SA - Recherche et Développement | Herstellungsverfahren einer spiralfeder mit einer vorbestimmten steifigkeit durch wegnahme von material |
| US10324418B2 (en) | 2015-12-18 | 2019-06-18 | CSEM Centre Suisse d'Electronique et de Microtechnique SA-Recherche et Développement | Method for fabrication of a balance spring of predetermined thickness through the addition of material |
| US10324417B2 (en) | 2015-12-18 | 2019-06-18 | CSEM Centre Suisse d'Electronique et de Microtechnique SA-Recherche et Développement | Method for fabrication of a balance spring of a predetermined stiffness by removal of material |
| US10338528B2 (en) | 2015-12-18 | 2019-07-02 | Csem Centre Suisse D'electronique Et De Microtechnique Sa—Recherche Et Developpement | Method for fabrication of a balance spring of a predetermined stiffness by local removal of material |
| CN106896700B (zh) * | 2015-12-18 | 2019-10-15 | 瑞士电子显微技术研究与开发中心股份有限公司 | 通过局部去除材料来制造预定刚度的游丝的方法 |
| CN106896708B (zh) * | 2015-12-18 | 2019-10-15 | 瑞士电子显微技术研究与开发中心股份有限公司 | 用于通过去除材料制造预定刚度的游丝的方法 |
| CN106997170B (zh) * | 2015-12-18 | 2019-10-15 | 瑞士电子显微技术研究与开发中心股份有限公司 | 用于通过增加材料制造预定厚度的游丝的方法 |
| CN110376871A (zh) * | 2015-12-18 | 2019-10-25 | 瑞士电子显微技术研究与开发中心股份有限公司 | 用于通过去除材料制造预定刚度的游丝的方法 |
| EP3416001B1 (de) * | 2017-06-13 | 2022-04-13 | Patek Philippe SA Genève | Herstellungsverfahren eines oszillators mit flexiblem zapfen |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3502788B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur selbstregulierung der aktiven länge einer spirale | |
| EP2275879B1 (de) | Einsatzhemmung | |
| WO2012066094A2 (fr) | Procede d'ajustement de frequence d'oscillation d'un sous-ensemble d'horlogerie | |
| CH703935A2 (fr) | Organe régulateur balancier-spiral. | |
| EP3227754B1 (de) | Spiralunruh-einheit für uhrwerk | |
| CH700260B1 (fr) | Balancier spiral sans élément de réglage. | |
| JP2002214368A (ja) | 機械式時計用のスプリング・バランスの振動周波数を調整する方法 | |
| EP1213628A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Regulierung der Schwingungsfrequenz einer Unruhspiralfeder für eine mechanische Uhr | |
| WO2016016456A2 (fr) | Dispositif d'assemblage et de reglage d'un spiral | |
| EP4286962A1 (de) | Regulierorgan für uhr, das eine rückervorrichtung umfasst, die mit verriegelungsmitteln ausgestattet ist | |
| EP3430479B1 (de) | Vorrichtung für eine uhr, uhrwerk und uhr mit solch einer vorrichtung | |
| EP2917792B1 (de) | Verfahren zur auswuchten einer spiralunruh-einheit für uhrwerk | |
| CH713409B1 (fr) | Balancier pour balancier-spiral du type thermocompensé, balancier-spiral du type thermocompensé, mouvement et pièce d'horlogerie. | |
| FR3048792B1 (fr) | Dispositif pour piece d'horlogerie, mouvement horloger et piece d'horlogerie comprenant un tel dispositif | |
| CH715513A2 (fr) | Balancier d'une pièce d'horlogerie. | |
| EP3391154B1 (de) | Schwingsystem für eine uhr | |
| WO2018015071A1 (fr) | Procede de reglage de la marche d'une piece d'horlogerie | |
| EP1079284A1 (de) | Uhrwerk | |
| EP3647883A1 (de) | Unruh einer uhr | |
| CH720580A2 (fr) | Dispositif de réglage autonome de la longueur active d'un spiral | |
| CH703605B1 (fr) | Oscillateur pour pièce d'horlogerie, balancier pour équiper un tel oscillateur et mouvement de montre équipé d'un tourbillon comportant un tel balancier. | |
| WO2024141600A1 (fr) | Système réglant pour mouvement horloger | |
| CH704149A2 (fr) | Procédé d'appairage et d'ajustement d'un sous-ensemble d'horlogerie. | |
| CH713791B1 (fr) | Micro mécanisme à réglage de position, mouvement horloger et pièce d'horlogerie comprenant un tel mécanisme. | |
| CH720774A2 (fr) | Mouvement horloger mécanique comprenant un mobile portant un organe d'affichage et muni d'un dispositif de freinage |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20021212 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): CH DE LI |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN WITHDRAWN |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: ETA SA MANUFACTURE HORLOGERE SUISSE |
|
| 18W | Application withdrawn |
Effective date: 20030227 |