EP1088945A2 - Elément d'isolation d'une façade - Google Patents
Elément d'isolation d'une façade Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1088945A2 EP1088945A2 EP00118845A EP00118845A EP1088945A2 EP 1088945 A2 EP1088945 A2 EP 1088945A2 EP 00118845 A EP00118845 A EP 00118845A EP 00118845 A EP00118845 A EP 00118845A EP 1088945 A2 EP1088945 A2 EP 1088945A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- insulation
- insulating element
- element according
- markings
- depressions
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 182
- 239000011505 plaster Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 23
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 13
- 239000012774 insulation material Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000002557 mineral fiber Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000003475 lamination Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000011490 mineral wool Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000003973 paint Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 abstract 1
- 229910052500 inorganic mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000003550 marker Substances 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000011707 mineral Substances 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 22
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000004793 Polystyrene Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229920002223 polystyrene Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 239000012790 adhesive layer Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000006735 deficit Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000004575 stone Substances 0.000 description 3
- 210000002268 wool Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004567 concrete Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003292 glue Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001788 irregular Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002023 wood Substances 0.000 description 2
- KXGFMDJXCMQABM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methoxy-6-methylphenol Chemical compound [CH]OC1=CC=CC([CH])=C1O KXGFMDJXCMQABM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920005830 Polyurethane Foam Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000004026 adhesive bonding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002969 artificial stone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004568 cement Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005253 cladding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005056 compaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002657 fibrous material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010304 firing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011494 foam glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005187 foaming Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920001568 phenolic resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000005011 phenolic resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011496 polyurethane foam Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003014 reinforcing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000013589 supplement Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008093 supporting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920001169 thermoplastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004416 thermosoftening plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009423 ventilation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000007 visual effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011179 visual inspection Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04B—GENERAL BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS; WALLS, e.g. PARTITIONS; ROOFS; FLOORS; CEILINGS; INSULATION OR OTHER PROTECTION OF BUILDINGS
- E04B1/00—Constructions in general; Structures which are not restricted either to walls, e.g. partitions, or floors or ceilings or roofs
- E04B1/62—Insulation or other protection; Elements or use of specified material therefor
- E04B1/74—Heat, sound or noise insulation, absorption, or reflection; Other building methods affording favourable thermal or acoustical conditions, e.g. accumulating of heat within walls
- E04B1/76—Heat, sound or noise insulation, absorption, or reflection; Other building methods affording favourable thermal or acoustical conditions, e.g. accumulating of heat within walls specifically with respect to heat only
- E04B1/762—Exterior insulation of exterior walls
- E04B1/7629—Details of the mechanical connection of the insulation to the wall
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04B—GENERAL BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS; WALLS, e.g. PARTITIONS; ROOFS; FLOORS; CEILINGS; INSULATION OR OTHER PROTECTION OF BUILDINGS
- E04B1/00—Constructions in general; Structures which are not restricted either to walls, e.g. partitions, or floors or ceilings or roofs
- E04B1/62—Insulation or other protection; Elements or use of specified material therefor
- E04B1/74—Heat, sound or noise insulation, absorption, or reflection; Other building methods affording favourable thermal or acoustical conditions, e.g. accumulating of heat within walls
- E04B1/76—Heat, sound or noise insulation, absorption, or reflection; Other building methods affording favourable thermal or acoustical conditions, e.g. accumulating of heat within walls specifically with respect to heat only
- E04B1/762—Exterior insulation of exterior walls
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04B—GENERAL BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS; WALLS, e.g. PARTITIONS; ROOFS; FLOORS; CEILINGS; INSULATION OR OTHER PROTECTION OF BUILDINGS
- E04B1/00—Constructions in general; Structures which are not restricted either to walls, e.g. partitions, or floors or ceilings or roofs
- E04B1/62—Insulation or other protection; Elements or use of specified material therefor
- E04B1/74—Heat, sound or noise insulation, absorption, or reflection; Other building methods affording favourable thermal or acoustical conditions, e.g. accumulating of heat within walls
- E04B1/76—Heat, sound or noise insulation, absorption, or reflection; Other building methods affording favourable thermal or acoustical conditions, e.g. accumulating of heat within walls specifically with respect to heat only
- E04B1/762—Exterior insulation of exterior walls
- E04B1/7629—Details of the mechanical connection of the insulation to the wall
- E04B1/7633—Dowels with enlarged insulation retaining head
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04B—GENERAL BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS; WALLS, e.g. PARTITIONS; ROOFS; FLOORS; CEILINGS; INSULATION OR OTHER PROTECTION OF BUILDINGS
- E04B1/00—Constructions in general; Structures which are not restricted either to walls, e.g. partitions, or floors or ceilings or roofs
- E04B1/62—Insulation or other protection; Elements or use of specified material therefor
- E04B1/74—Heat, sound or noise insulation, absorption, or reflection; Other building methods affording favourable thermal or acoustical conditions, e.g. accumulating of heat within walls
- E04B2001/741—Insulation elements with markings, e.g. identification or cutting template
Definitions
- the invention relates to an insulation element for the insulation of external facades on buildings, especially as part of a composite thermal insulation system, which is plate-shaped and for receiving a plaster job suitable and attachable to the outer facade using retaining elements is.
- Insulation materials made of fiber insulation materials, polystyrene, phenolic resin, rigid polyurethane foam, Foam glass or light aerated concrete is used.
- This Insulation materials differ primarily in their mechanical properties.
- the insulation materials are in layers of insulation on the outer facade arranged and with ventilated cladding or covers for example sheets, fiber cement panels, wood, wood materials, natural and artificial stones, concrete or the like covered.
- ventilated cladding or covers for example sheets, fiber cement panels, wood, wood materials, natural and artificial stones, concrete or the like covered.
- the insulation of such Insulation layers become low due to their own weight and are insignificant burdened by wind suction. There is therefore the possibility of such Insulation layers made of flexible and easily compressible fiber insulation materials train low to medium bulk density.
- thermal insulation composite systems insulated.
- plaster layers are applied directly to the insulation boards, so that the Insulation layer due to its own weight, wind suction and the cleaning movements induced constraint stresses.
- thermal insulation composite systems have proven insulation boards that are stiff in themselves are trained.
- the insulation elements are generally laid in a group and held on the facade with the help of insulation plates and dowels anchored in the facade.
- the insulation plate is here with the dowels connected by a shaft and form a unit.
- the Unit made of insulation plate and dowels called insulation holder.
- the insulation elements are used in the usual way of processing only fixed with the help of the insulation holder.
- the insulation holder is pressed firmly against the insulation in order to close it to enable a corresponding power transmission.
- Compressible Insulation elements are clearly compressed at these points and stretch in the areas between the insulation holders in unfavorable Cases even out.
- a necessary ventilation gap which is usually has a depth of 2 to 4 cm, not to narrow, the insulation elements especially at the edges. Furthermore have protruding edges when the insulation layer is still unprotected for rain on. To avoid these disadvantages, it is from the State of the art, the insulation holder in the joint area adjacent Arrange insulation elements.
- insulation holders are also necessary which are arranged in the area of the large surfaces of an insulation element are.
- Such an, as a rule, arbitrarily chosen arrangement of Insulation holders result in a very high demand for insulation holders, although with this procedure, unevenness of the facade surface can be compensated in the area of the insulation elements.
- Such insulation holders are preferably used, their insulation plates have a diameter of approx. 90 mm.
- the insulation material holder in the joint area between adjacent insulation elements arranged so can hardly an essential holding effect the insulation holder can be achieved.
- the required number of insulation holders per insulation element depending on the dead weight of the insulation element or the plaster layers attached to it, their dimensions, the flow resistance and the wind suction load, i.e. the position and height the wall surface to be insulated.
- Stone wool insulation elements also feature sufficient rigidity and point load capacity.
- the rigidity and Point load capacity increases with increasing thickness of the insulation elements.
- the side surfaces of the insulation elements also increase in thickness and the friction forces that can be transmitted over these surfaces.
- the insulation elements remain stable in relation to each other Position.
- the irregular arrangement of the insulation holder only to be observed in the finished work when certain influences occur.
- the consequences of an irregular not according to the instructions
- the arrangement of the insulation holders can no longer be corrected at this point, without large dismantling measures associated with high costs become.
- the insulation plate at partial damp plaster layers on the finished surface of the thermal insulation composite system sign off.
- the material thickness and the color of the plaster layer affects then the degree of impairment. So much for such impairments are unavoidable, there should at least be a regular grid that leads to the visual result for the viewer, the mark the insulation plate is deliberately wanted.
- FR 2 694 319 A1 is an insulating element made of polystyrene known in which in the area of holes for receiving screws x-shaped stiffening elements are inserted. Due to the rigid design of polystyrene plates it is possible to use such stiffening elements during of the foaming of the polystyrene and encased in the insulation element to integrate. However, this method of production is very expensive and does not lead to a high committee if the procedure is imprecise usable insulation elements. In addition, such insulation elements with inserted stiffening elements, or only to a very limited extent adaptable to the installation conditions. Cutting the insulation elements in the area of the stiffening elements is almost impossible. Furthermore is the number of holes that can be inserted through the stiffening elements limited to accommodate the screws.
- the object of the invention is to further develop an insulating element in such a way that the processing in the facade insulation is considerably simplified.
- the solution to this problem provides for a generic insulation element that the insulation element consists of mineral fibers bonded with binders and has markings for the arrangement of the insulation holder at least on a large surface, with a number of markings corresponding to the number of insulation holders required being provided are spaced from the edges.
- An insulation element designed according to the invention thus has markings which corresponds in number to the number of insulation holders to be placed.
- the processing person is thus an insulation element Provided both the number and the location of the insulation holder if processed correctly.
- the ones described above Disadvantages with arbitrary setting of the insulation holder are therefore in substantially avoided.
- the insulation element consists of mineral fibers, those for thermal insulation especially in the facade area are suitable and easy to work with, especially given the circumstances of the building to be insulated.
- the markings are preferably designed as a paint application, since these Markings without great technical effort during the production of such Have insulation elements applied.
- the markings are burned into the surface by local heating are. At least one is used during the manufacture of the insulation elements Surface heated locally, which means that the contained in the insulation elements Binder reacts to the extent that there is a color difference between the heated Spot and the rest of the surface.
- the insulating element consists of rock wool fibers bound with binders.
- the markings are particularly regular, preferably point or axially symmetrical.
- the markings depending on the size and location as well as other geometric properties, in particular the thickness of the insulating element are arranged.
- the design of the insulation element according to the invention becomes the required one or intended arrangement of the holding plates according to size and location, below Under certain circumstances, depending on the thickness of the insulation board from the outset fixed. If the number and arrangement of the insulation holder depends on changes from the height of the building to be insulated sees the invention Design of an insulation element a correspondingly differentiated Design of height-dependent insulation element batches in front.
- the markings can be point-shaped and / or cross-shaped in order to to enable precise placement of the insulation holder.
- the markings have a size that corresponds to the surface area of the insulation holder, especially the insulation plate matches.
- the markings are designed as optically effective symbols, which are made with the help of colors or by baking.
- the markings for example in the form of points or crosses information about the type and shape of the insulation holder can be applied.
- the required size of the insulation plate can be designed accordingly the marking can be specified so that after mounting the Insulation elements a quick and easy visual inspection of the properly insulation holder used is possible.
- the markings connected to one another by line-shaped and / or grid-line-shaped elements are.
- the markings in depressions to be arranged in the insulation element and / or the markings as depressions to train.
- the thickness of the insulation plate reduces that on the plaster base applied plaster layer, which tends to become thinner Base and finishing layers result in a reinforcing fabric only is still incompletely embedded.
- Thermal insulation composite system more susceptible to damage. It therefore makes sense to Insert the insulation plate sunk into the surface of the insulation elements.
- the depressions are preferably worked out mechanically or at thermoplastic insulation materials by local heating with the associatedshrinking and compaction processes. The wells can also be highlighted.
- hygrothermal properties in the depressions thin layers of base plaster, construction adhesive or similar hygrothermal properties having arranged materials. These materials have in essentially the same hygrothermal properties as the one to be applied Basic plaster.
- those arranged in the recesses can be used Materials have aggregates, especially plastics that store moisture Have properties.
- the shape and the diameter and the desired recess depth of the insulation plate areas close to the surface are made from the insulation element with the help of for example, core drills.
- the now having a recess Areas of the insulation element have a higher compressibility on, since the supporting effect of the edge areas is eliminated.
- the insulation holder is therefore when tightening his core screw or when driving in its firing pin is pulled or pressed deeper into the insulation element.
- the area be elasticized in and around the depressions. You can do this in this area for example exposed to one or more pressure loads the composite of mineral fibers given by the binder dissolve. Due to a higher elasticity in the recesses, the Insulation holder with greater countersink depth can be installed.
- the markings are made from the outset with a large compared to the material thickness of the insulation element Depth worked out of the insulation element.
- the closure bodies can be made of mineral fibers or another compressible Insulation material should be formed.
- the pull-out force of the closure body is determined by the frictional forces that can be achieved achieved between the closure body and the insulating element. she can significantly increased by gluing the closure body in the recess or to the level of the transverse tensile strength of the neighboring insulation areas to be brought.
- the inventive design of an insulating element made of mineral fibers with recesses also provides very economical thermal insulation because the depth of the recesses means the length of the insulation holder regardless of the material thickness of the insulation element can.
- the wells are at least in depth but also in terms of their shape to which the shape and length of the usually used insulation holder of a certain design and Length turned off. This also stresses the shaft of the Insulation holder less or the shaft needs more insulation not to be made thicker. This can save material costs and thermal bridges can be reduced.
- the materials at least Once hardened form a stiff layer to create an even layer To ensure power transmission to the insulation element. Furthermore, due to this design, the volume of basic plaster reduced by the insulation plate compensated and the optical effects caused by the insulation holder Impairment of the cleaned outer surface (finishing plaster) in the damp Condition significantly reduced or canceled.
- the Insulation element has a lamination, in particular in the form of a glass fleece, the markings being arranged on the lamination.
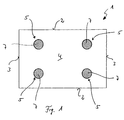
- An insulation element 1 shown in FIG. 1 is a cuboid insulation plate trained and consists of fiber material, namely rock wool.
- the insulation element 1 is produced in a manner known per se and has two parallel to one another extending side surfaces 2 and two perpendicular to the side surfaces 2 arranged narrow sides 3. Furthermore, the insulation element 1 has two large surfaces 4, of which only one can be seen in FIG. 1 and which both are aligned parallel to each other.
- the insulation element 1 has four markings 5, which on the one hand are formed as depressions in the large surface 4 are and on the other hand form a template that the arrangement of Specify insulation holders 6 ( Figure 3).
- construction adhesive there is a thin layer of construction adhesive in the recessed markings arranged.
- a thin layer of basic plaster can also be provided be, the base plaster or the construction adhesive completely or partially can fill out. If necessary, the construction adhesive or the base plaster Supplements or plastics that have increased moisture retention serve.
- FIG. 3 shows the arrangement of several insulation elements 1 on a facade 8 shown.
- the insulation elements 1 are in association with butt joints arranged.
- the insulation elements 1 with the Connect facade 8 having structure, the insulation 1 glued to the facade 8 by means of an adhesive layer 9.
- the insulation holder 6, which have insulation plate 10, in the as Wells formed markings 5, previously corresponding Bores are drilled in which the insulation holder 6 is anchored become.
- the plaster layer 11 is applied to the insulation elements 1.
- the plaster layer 11 usually consists of a base plaster and a Finishing plaster.
- the adhesive layer 9 is shown over the entire surface.
- the insulation elements 1 with at least about 60% of their area on the Glue facade 8.
- These are insulation elements 1 which are used for Picking up a plaster layer 11 are suitable and thus rigid.
- Mineral wool insulation boards with a high bulk density and sufficient shear rigidity is used.
- the number of insulation holders 6 depends on the type of insulation material of the insulation elements 1 and / or depending on the height of the building with the expected one Wind suction load and the design of the insulation holder 6 with regard Diameter and arrangement.
- the second embodiment of the insulating element shown in Figures 4 to 6 1 essentially corresponds to the embodiment according to FIGS. 1 through 3. It will therefore be used below for matching construction elements the reference numerals used in Figures 1 to 3 used.
- closure body 12 are used.
- These closure bodies consist of mineral fibers and can be increased compared to the bulk density of the insulation element Show bulk density.
- the closure body 12 are attached in the wells, so that the plaster layer 11 is even in the area of the closure body 12 Forms layer and does not lead to the closure body 12 falling out.
- closure bodies 12 are also in the region of their Shell surface via an additional adhesive layer 13 with the walls of the Glued wells. Furthermore, the closure body 12, for example be elasticized by flexing.
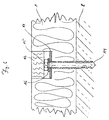
- FIG. 6 shows in detail the fastening of the insulation board 1 by means of the insulation holder 6 on the facade 8.
- Each insulation holder 6 consists of a die Insulation board 1 through dowels 14 and one through the dowels 14 Screw 15.
- the dowel 14 has its arranged in the recess End a collar 16, which rests on a pressure plate 17.
- the pressure plate 17 has an outer contour that matches the inner contour of the depression matches.
- the pressure plate 17 is used for uniform pressure introduction in the insulation plate 1.
- the diameter of the pressure plate 17 is particularly dependent on the strength of the insulation board 1.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Architecture (AREA)
- Acoustics & Sound (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Civil Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Building Environments (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Material From Animals Or Micro-Organisms (AREA)
- Thermotherapy And Cooling Therapy Devices (AREA)
- Floor Finish (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19946395A DE19946395C2 (de) | 1999-09-28 | 1999-09-28 | Fassadendämmelement |
| DE19946395 | 1999-09-28 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1088945A2 true EP1088945A2 (fr) | 2001-04-04 |
| EP1088945A3 EP1088945A3 (fr) | 2003-01-15 |
| EP1088945B1 EP1088945B1 (fr) | 2005-01-26 |
Family
ID=7923545
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP00118845A Expired - Lifetime EP1088945B1 (fr) | 1999-09-28 | 2000-08-31 | Elément d'isolation d'une façade |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1088945B1 (fr) |
| AT (1) | ATE287997T1 (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE19946395C2 (fr) |
Cited By (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1318250A2 (fr) | 2001-12-05 | 2003-06-11 | EJOT Kunststofftechnik GmbH & Co. KG | Cheville et méthode de montage de panneaux isolants |
| WO2003076735A1 (fr) | 2002-03-11 | 2003-09-18 | Deutsche Rockwool Mineralwoll Gmbh & Co. Ohg | Systeme d'isolation thermique et/ou acoustique et element isolant |
| DE10241231A1 (de) * | 2002-03-11 | 2003-10-02 | Rockwool Mineralwolle | Wärme- und/oder Schalldämmsystem sowie Dämmelement |
| DE10213490A1 (de) * | 2002-03-26 | 2003-11-13 | Ejot Kunststofftech Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Montage von Dämmstoffplatten |
| EP1505218A2 (fr) | 2003-08-08 | 2005-02-09 | Saint-Gobain Isover G+H Ag | Système composite d'isolation thermique |
| EP1624131A2 (fr) * | 2004-08-02 | 2006-02-08 | Hasit Trockenmörtel GmbH | Plaque support isolant pour bandes de briques recuites, façade en briques recuites et procédé pour fixer de telles briques sur une paroi |
| DE102007018774A1 (de) | 2007-04-20 | 2008-10-23 | Saint-Gobain Isover G+H Ag | Fassadendämmplatte für die Dämmung von Außenfassaden von Gebäuden, Wärmedamm-Verbundsystem mit derartigen Fassadendämmplatten sowie Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Fassadendämmplatte |
| WO2008140510A2 (fr) * | 2006-05-02 | 2008-11-20 | Huber Engineered Woods Llc | Procédé et système pour l'installation de divers composants de revêtement d'immeubles |
| US8250823B2 (en) | 2003-08-26 | 2012-08-28 | Ejot Gmbh & Co. Kg | Dowels and methods for the assembly of insulating panels |
| FR2977265A1 (fr) * | 2011-07-01 | 2013-01-04 | Isobox Technologies | Panneau composite pour l'isolation thermique de facade de batiments |
| EP2759650A1 (fr) * | 2013-01-25 | 2014-07-30 | Unger-Diffutherm GmbH | Plaque isolante et procédé et dispositif pour fabrication de celle-ci |
| EP2770130A1 (fr) * | 2013-02-26 | 2014-08-27 | Ibercal Morteros, S.L. | Ensemble d'isolation pour l'habillage extérieur de bâtiments |
| EP3933134A1 (fr) * | 2020-06-29 | 2022-01-05 | Ergazakis, Ioannis | Feuille d'isolation thermique externe |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10219504B4 (de) * | 2001-05-02 | 2017-07-06 | Josef Mang Gmbh & Co. Kg | Dämmstoffplatte |
| DE102007053690A1 (de) | 2007-11-10 | 2009-05-14 | Construction Research & Technology Gmbh | Plattenförmiges Dämmelement |
| DE102011005458B4 (de) * | 2011-03-11 | 2016-08-04 | Prototec Gesellschaft für individuelle Industrieplanungen mbH | Gerüstbefestigungsbausatz und Verwendung desselben |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2694319A1 (fr) | 1992-07-30 | 1994-02-04 | Sicof Ste Indle Cale Facade | Panneau pour habillage isolant des parois de bâtiments. |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2358521A2 (fr) * | 1976-07-12 | 1978-02-10 | Miplacol | Procede d'isolation thermique et phonique de batiments |
| SE430706B (sv) * | 1980-09-16 | 1983-12-05 | Byggutveckling Ab | Forfarande att bekleda hus samt fasadbeklednadselement for utforande av forfarandet |
| US4653246A (en) * | 1984-01-05 | 1987-03-31 | Hepler Jacque P | Insulation board for attachment to walls |
| DE4319340C1 (de) * | 1993-06-11 | 1995-03-09 | Rockwool Mineralwolle | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Mineralfaser-Dämmstoffplatten und Vorrichtung zur Durchführung des Verfahrens |
| DE19542403A1 (de) * | 1995-11-14 | 1997-05-15 | Gruenzweig & Hartmann | Mineralwolleprodukte mit Kennzeichnung |
| DE29622196U1 (de) * | 1996-12-20 | 1997-02-20 | SAINT-GOBAIN ISOVER G+H AG, 67059 Ludwigshafen | Formteile aus Mineralwolle-Nadelfilz |
| DE29705691U1 (de) * | 1997-03-27 | 1997-09-04 | Deutsche Rockwool Mineralwoll-Gmbh, 45966 Gladbeck | Mineralwolleprodukt |
| DE29822362U1 (de) * | 1998-12-15 | 1999-04-08 | Pfleiderer Dämmstofftechnik International GmbH & Co., 92318 Neumarkt | Dämmstoffbahn |
-
1999
- 1999-09-28 DE DE19946395A patent/DE19946395C2/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2000
- 2000-08-31 AT AT00118845T patent/ATE287997T1/de active
- 2000-08-31 EP EP00118845A patent/EP1088945B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-08-31 DE DE50009338T patent/DE50009338D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2694319A1 (fr) | 1992-07-30 | 1994-02-04 | Sicof Ste Indle Cale Facade | Panneau pour habillage isolant des parois de bâtiments. |
Cited By (26)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2840201A1 (fr) | 2001-12-05 | 2015-02-25 | EJOT GmbH & Co. KG | Dispositif d'enfoncement d'un élément expansible dans une cheville. |
| EP1318250A2 (fr) | 2001-12-05 | 2003-06-11 | EJOT Kunststofftechnik GmbH & Co. KG | Cheville et méthode de montage de panneaux isolants |
| EP1318250A3 (fr) * | 2001-12-05 | 2003-10-01 | EJOT Kunststofftechnik GmbH & Co. KG | Cheville et méthode de montage de panneaux isolants |
| EP2295672A2 (fr) | 2001-12-05 | 2011-03-16 | EJOT GmbH & Co. KG | Cheville et procédé de montage de plaques de matériau isolant |
| EP1870533A1 (fr) | 2001-12-05 | 2007-12-26 | EJOT GmbH & Co. KG | Cheville et procédé de montage de plaques de matériau isolant |
| EP2295672A3 (fr) * | 2001-12-05 | 2012-12-26 | EJOT GmbH & Co. KG | Cheville et procédé de montage de plaques de matériau isolant |
| EP2752533A1 (fr) | 2001-12-05 | 2014-07-09 | EJOT GmbH & Co. KG | Dispositif d'enfoncement d'un élément expansible dans une cheville |
| DE10241231A1 (de) * | 2002-03-11 | 2003-10-02 | Rockwool Mineralwolle | Wärme- und/oder Schalldämmsystem sowie Dämmelement |
| DE10241231B4 (de) * | 2002-03-11 | 2006-02-09 | Deutsche Rockwool Mineralwoll Gmbh + Co Ohg | Wärme- und/oder Schalldämmsystem sowie Dämmelement |
| WO2003076735A1 (fr) | 2002-03-11 | 2003-09-18 | Deutsche Rockwool Mineralwoll Gmbh & Co. Ohg | Systeme d'isolation thermique et/ou acoustique et element isolant |
| DE10213490B4 (de) * | 2002-03-26 | 2005-02-03 | Ejot Kunststofftechnik Gmbh & Co. Kg | Verfahren zur Montage von Dämmstoffplatten |
| DE10213490A1 (de) * | 2002-03-26 | 2003-11-13 | Ejot Kunststofftech Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Montage von Dämmstoffplatten |
| EP1505218A3 (fr) * | 2003-08-08 | 2005-12-14 | Saint-Gobain Isover G+H Ag | Système composite d'isolation thermique |
| DE10336795A1 (de) * | 2003-08-08 | 2005-03-10 | Saint Gobain Isover G & H Ag | Wärmedämmverbundsystem |
| EP1505218A2 (fr) | 2003-08-08 | 2005-02-09 | Saint-Gobain Isover G+H Ag | Système composite d'isolation thermique |
| US8250823B2 (en) | 2003-08-26 | 2012-08-28 | Ejot Gmbh & Co. Kg | Dowels and methods for the assembly of insulating panels |
| EP1624131A3 (fr) * | 2004-08-02 | 2006-11-29 | Hasit Trockenmörtel GmbH | Plaque support isolant pour bandes de briques recuites, façade en briques recuites et procédé pour fixer de telles briques sur une paroi |
| DE102004037384A1 (de) * | 2004-08-02 | 2006-03-30 | HASIT Trockenmörtel-GmbH | Klinkerriemchenträgerdämmplatte, Klinkerfassade und Verfahren zum Befestigen von Klinkerriemchen an einer Wand |
| EP1624131A2 (fr) * | 2004-08-02 | 2006-02-08 | Hasit Trockenmörtel GmbH | Plaque support isolant pour bandes de briques recuites, façade en briques recuites et procédé pour fixer de telles briques sur une paroi |
| WO2008140510A3 (fr) * | 2006-05-02 | 2009-04-30 | Huber Engineered Woods Llc | Procédé et système pour l'installation de divers composants de revêtement d'immeubles |
| WO2008140510A2 (fr) * | 2006-05-02 | 2008-11-20 | Huber Engineered Woods Llc | Procédé et système pour l'installation de divers composants de revêtement d'immeubles |
| DE102007018774A1 (de) | 2007-04-20 | 2008-10-23 | Saint-Gobain Isover G+H Ag | Fassadendämmplatte für die Dämmung von Außenfassaden von Gebäuden, Wärmedamm-Verbundsystem mit derartigen Fassadendämmplatten sowie Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Fassadendämmplatte |
| FR2977265A1 (fr) * | 2011-07-01 | 2013-01-04 | Isobox Technologies | Panneau composite pour l'isolation thermique de facade de batiments |
| EP2759650A1 (fr) * | 2013-01-25 | 2014-07-30 | Unger-Diffutherm GmbH | Plaque isolante et procédé et dispositif pour fabrication de celle-ci |
| EP2770130A1 (fr) * | 2013-02-26 | 2014-08-27 | Ibercal Morteros, S.L. | Ensemble d'isolation pour l'habillage extérieur de bâtiments |
| EP3933134A1 (fr) * | 2020-06-29 | 2022-01-05 | Ergazakis, Ioannis | Feuille d'isolation thermique externe |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE19946395A1 (de) | 2001-04-26 |
| EP1088945A3 (fr) | 2003-01-15 |
| ATE287997T1 (de) | 2005-02-15 |
| DE19946395C2 (de) | 2002-11-28 |
| DE50009338D1 (de) | 2005-03-03 |
| EP1088945B1 (fr) | 2005-01-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1088945A2 (fr) | Elément d'isolation d'une façade | |
| EP1337725B1 (fr) | Procede pour fixer des plaques d'isolation thermique et douille necessaire a cet effet | |
| DE102014002154A1 (de) | Gebäudeplatte, insbesondere zur Verwendung als Boden-, Wand- oder Deckenplatte | |
| EP1469992A1 (fr) | Revetement pour murs et sols | |
| DE19951105C2 (de) | Wärme- und/oder Schalldämmelement | |
| DE3519752A1 (de) | Mineralfaserprodukt als daemmplatte oder daemmbahn | |
| EP1799926B1 (fr) | Toit de batiment, structure a couche d'isolation et element d'isolation a fibres minerales destine a un toit de batiment | |
| EP1559844B1 (fr) | Element d' isolation et système composite d' isolation thermique | |
| EP2067905A2 (fr) | Elément d'habillage pour un mur extérieur dans la zone d'un intrados de fenêtre ou de porte | |
| EP3414406B1 (fr) | Système composite d'isolation thermique apte au démantèlement, et procédé de pose et d'enlèvement | |
| EP0964110A2 (fr) | Isolation thermique et/ou acoustique pour bâtiment | |
| EP1081301A2 (fr) | Elément d'isolation pour l'isolation thermique et/ou acoustique de murs de bâtiments | |
| EP1203847A1 (fr) | Elément isolant | |
| DE4238134C2 (de) | Verfahren zur wärmedämmenden Verkleidung eines Gebäudes mit steinernen Platten und nach diesem Verfahren hergestellte Verkleidung | |
| EP0278584A1 (fr) | Plaque céramique pour former une couverture de sol | |
| DE10066165B4 (de) | Wärmedämmverbundsystem sowie bandförmiges Element für die Befestigung von Dämmstoffelementen | |
| DE19860993C2 (de) | Dämmstoffelement | |
| DE19806454C2 (de) | Dämmstoffelement | |
| EP1295998B1 (fr) | Isolation acoustique et thermique; Elément d'isolation et lamelle de fibres minérales | |
| DE20018907U1 (de) | Dämmstoffelement und Wärmedämmverbundsystem für die Dämmung von Gebäudefassaden | |
| DE102014119132B4 (de) | Fliese und Verfahren zur Verlegung mehrerer derartiger Fliesen | |
| DE4101133C2 (de) | Verfahren zur Befestigung von Bahnen an Holzwolle-Leichtbauplatten | |
| DE102004035011A1 (de) | Verbundelement | |
| WO2003076735A1 (fr) | Systeme d'isolation thermique et/ou acoustique et element isolant | |
| DE10241231A1 (de) | Wärme- und/oder Schalldämmsystem sowie Dämmelement |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: DEUTSCHE ROCKWOOL MINERALWOLL GMBH & CO. OHG |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20030708 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT DE |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20031007 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: GERMAN |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 50009338 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20050303 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20051027 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20100812 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 287997 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20110831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110831 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 50009338 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: STENGER WATZKE RING INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY, DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R081 Ref document number: 50009338 Country of ref document: DE Owner name: ROCKWOOL INTERNATIONAL A/S, DK Free format text: FORMER OWNER: DEUTSCHE ROCKWOOL MINERALWOLL GMBH + CO OHG, 45966 GLADBECK, DE Effective date: 20140801 Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 50009338 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: STENGER WATZKE RING INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY, DE Effective date: 20140801 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20150825 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 50009338 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170301 |