EP0798062A2 - Elément en mousse métallique - Google Patents
Elément en mousse métallique Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0798062A2 EP0798062A2 EP97105225A EP97105225A EP0798062A2 EP 0798062 A2 EP0798062 A2 EP 0798062A2 EP 97105225 A EP97105225 A EP 97105225A EP 97105225 A EP97105225 A EP 97105225A EP 0798062 A2 EP0798062 A2 EP 0798062A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- component
- semi
- finished product
- foamed
- contour
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B22—CASTING; POWDER METALLURGY
- B22F—WORKING METALLIC POWDER; MANUFACTURE OF ARTICLES FROM METALLIC POWDER; MAKING METALLIC POWDER; APPARATUS OR DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR METALLIC POWDER
- B22F3/00—Manufacture of workpieces or articles from metallic powder characterised by the manner of compacting or sintering; Apparatus specially adapted therefor ; Presses and furnaces
- B22F3/10—Sintering only
- B22F3/11—Making porous workpieces or articles
- B22F3/1121—Making porous workpieces or articles by using decomposable, meltable or sublimatable fillers
- B22F3/1125—Making porous workpieces or articles by using decomposable, meltable or sublimatable fillers involving a foaming process
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B22—CASTING; POWDER METALLURGY
- B22F—WORKING METALLIC POWDER; MANUFACTURE OF ARTICLES FROM METALLIC POWDER; MAKING METALLIC POWDER; APPARATUS OR DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR METALLIC POWDER
- B22F3/00—Manufacture of workpieces or articles from metallic powder characterised by the manner of compacting or sintering; Apparatus specially adapted therefor ; Presses and furnaces
- B22F3/10—Sintering only
- B22F3/11—Making porous workpieces or articles
- B22F3/1103—Making porous workpieces or articles with particular physical characteristics
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B22—CASTING; POWDER METALLURGY
- B22F—WORKING METALLIC POWDER; MANUFACTURE OF ARTICLES FROM METALLIC POWDER; MAKING METALLIC POWDER; APPARATUS OR DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR METALLIC POWDER
- B22F7/00—Manufacture of composite layers, workpieces, or articles, comprising metallic powder, by sintering the powder, with or without compacting wherein at least one part is obtained by sintering or compression
- B22F7/002—Manufacture of composite layers, workpieces, or articles, comprising metallic powder, by sintering the powder, with or without compacting wherein at least one part is obtained by sintering or compression of porous nature
- B22F7/004—Manufacture of composite layers, workpieces, or articles, comprising metallic powder, by sintering the powder, with or without compacting wherein at least one part is obtained by sintering or compression of porous nature comprising at least one non-porous part
- B22F7/006—Manufacture of composite layers, workpieces, or articles, comprising metallic powder, by sintering the powder, with or without compacting wherein at least one part is obtained by sintering or compression of porous nature comprising at least one non-porous part the porous part being obtained by foaming
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B22—CASTING; POWDER METALLURGY
- B22F—WORKING METALLIC POWDER; MANUFACTURE OF ARTICLES FROM METALLIC POWDER; MAKING METALLIC POWDER; APPARATUS OR DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR METALLIC POWDER
- B22F2998/00—Supplementary information concerning processes or compositions relating to powder metallurgy
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T29/00—Metal working
- Y10T29/49—Method of mechanical manufacture
- Y10T29/49826—Assembling or joining
- Y10T29/49904—Assembling a subassembly, then assembling with a second subassembly
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/12—All metal or with adjacent metals
- Y10T428/12382—Defined configuration of both thickness and nonthickness surface or angle therebetween [e.g., rounded corners, etc.]
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/12—All metal or with adjacent metals
- Y10T428/1241—Nonplanar uniform thickness or nonlinear uniform diameter [e.g., L-shape]
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/12—All metal or with adjacent metals
- Y10T428/12479—Porous [e.g., foamed, spongy, cracked, etc.]
Definitions
- the invention relates to a component made of a metallic foam material according to the preamble of claim 1 or claim 2.
- the invention further relates to a method for the final shaping of a component formed from a substantially flat metallic foam material according to the preamble of claim 6 and devices for carrying out the method .
- Metallic foam materials that either contain only a foamable layer comprising metal powder and blowing agents or that contain a layer comprising foamable metal powder and blowing agents that is provided with at least one solid metal sheet as a cover layer, whereby there are metallic bonds between the solid metal sheet and the foamable layer known per se.
- DE 41 01 630 A1 shows how a foam material is formed from a metallic powder and the addition of a gas-releasing blowing agent powder, preferably a metal hydride, which is subjected to a high pressure and high temperature after mixing, which can be done, for example, by a warm Rolling process can be achieved, and then cooled, so that a foamable semi-finished product is formed.
- a gas-releasing blowing agent powder preferably a metal hydride
- DE 44 26 627 A1 describes the production of a material with a foamable layer consisting of metal powder and blowing agent, which is at least delimited by a solid metallic cover layer.
- a connection of the different layers by roll cladding is proposed, whereby a flat layer material is formed which is to be foamed after its final shaping.
- the invention has for its object to provide metallic lightweight components for a constant dimensional production, Especially in vehicle construction, to create flat foam materials of the type mentioned.
- the invention provides components with the features of claims 1 or 2 and a manufacturing method according to claim 6 for various starting materials.
- the component according to the invention solves all the essential geometric requirements that are placed on flat metallic components in body and vehicle construction.
- the formation of the transition angle between 100 ° and less than 180 ° ensures that the structure of the foamed layer in the area of the transitions is not interrupted, drawn in or thinned, so that the mechanical stability and dimensional accuracy of the component is retained over its entire area.
- a component according to the invention has a very low mass, at the same time providing high rigidity, in particular in the case of multi-layer composites, so that such components can be used both in the load-bearing area of the body and for cladding and shielding purposes.
- Integral foam can be used in particular as crash elements, the cellular structure of the foamed material giving it very good energy absorption capacity when the component is deformed. Due to the inventive design of the component, it is possible to deform it so far before it is foamed that it can be used, for example, as the inner layer of a bumper made of z. B. plastic can be used.
- Components that comprise a foamed metallic layer that is provided on one side with a solid metallic cover layer are suitable for forming very light and highly rigid components, for example a vehicle roof that does not require a stiffening substructure.
- Materials that have a foamed layer and cladding on both sides with a solid metal sheet are suitable for producing components that have a smooth-walled surface that absorbs tensile and compressive forces on both sides, for example for the rear transverse wall of a vehicle.
- the foamed layer takes on the function of the spacer and the transmission of the thrust forces.
- Such a component also has high rigidity and low mass, is suitable for absorbing high energies, for example in the event of an accident, and is also good soundproofing.
- the foamed layer usually consists of an aluminum-based metal powder with added parts - for example silicon.
- the mechanical properties of the component can be adjusted by a suitable choice of the alloy elements and proportions.
- the use of light metal alloys is also suitable for solid metal sheets.
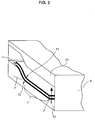
- a component 1 according to the invention has a foamed layer 2 which comprises a metal powder and a blowing agent which have been homogeneously mixed with one another by a mixing process and then compressed under the action of pressure, for example by axial pressing or by extrusion, to form a compact, foamable semi-finished product 2 '' and has been solidified.
- the foamed layer 2 is provided on the top and bottom sides with a solid metal sheet 3, 4, which is not mandatory, however, and in particular when a component 1 according to the invention is formed as a crash element. It is also possible to connect a foamed layer 2 with only one solid metal cover layer 3 or 4 or to produce composites from several different foamed layers, possibly separated by solid metal layers, for example to create impact elements in which, depending on the impact speed and thus -energy a different number of foamed layers takes part in the deformation due to the impact.
- the connection between the layer 2 foamed at the end of the method and the solid metal sheets 3 and 4 has come about under the action of pressure in such a way that a metallic bond between the individual layers 2 ', 3 ', 4' has been reached before the forming and foaming.
- This flat composite material 6 is first cut into pieces of a suitable size, for example using a saw.
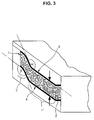
- the shape 8 used to form the composite material 6 to form the semi-finished product 7 has angles ⁇ transverse to the contact surface of the composite material 6 in a size between approximately 100 ° and 260 °, the edges being rounded, so that the composite material 6 is bent directly to avoid. As a result, the bond is retained even in the angular ranges, and the mechanical strength of the semi-finished product 7 achieved by the shaping has no specific weak points.
- the shaping can be carried out by known customary shaping measures, for example by deep drawing with and without hold-down devices, as is known in body construction, or by a one-sided shaping method, such as the fluid cell method.
- a semi-finished product 7 which contains either plane-flat or curved surface areas 7 ′′ and possibly contours 7 ′ formed therefrom and which comprises a foamable layer 2 ′ for further processing.
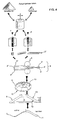
- the semifinished product 7 is inserted into a foaming mold 9, one wall 12 of which supports a side 10 of the semifinished product 7 substantially so that this side 10 must already have its final contour, since further contouring by foaming the semifinished product 7 into a component 1 no longer causes deformation of this side 10.
- the walls 12, 13 of the foaming mold 9 can be made of steel or ceramic, for example. In any case, it is important that the component 1 does not make any connection with the walls 12, 13 of the foaming mold 9, despite its internal pressure prevailing during foaming. In order to prevent any sticking together here, these walls 12, 13 can be coated.
- the thickness of the component 1 can be preselected - and thus also its density and its mechanical strength. It is thereby achieved that the same starting material can be used for components 1 with completely different properties.
- Its rigidity can also be adjusted in this way. For example, the different stiffness requirements of a short car roof or a long roof of a station wagon can be met via the degree of foaming.
- the upper wall 13 of the foaming mold can be omitted if only small demands are made on the dimensional accuracy of the foaming semi-finished product 7, such as in the formation of crash elements.
- the two opposite walls 12 and 13 of the foaming mold 9 have essentially parallel surface structures, since it is not possible to emboss further structures, for example, only into one surface 11 of the semi-finished product 7, for example through recesses in the delimiting wall 13 of the foaming mold 10th
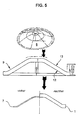
- components 1 are obtained as lightweight series products, which can be used, for example, as body panels, as bulkheads or partition walls opposite the engine or trunk or for crash-protecting and stiffening functions within the body.
- Such components can be curved overall, for example for use as door outer panels, or comprise pronounced contours 1 'worked out from plane or curved areas 1'', which in the area of the transitions with respect to the curved or plane surface area have angles ⁇ of the order of magnitude between 100 ° and less have than 180 °, so that hereby the most diverse requirements for body panels or body panels can be fulfilled - with very light and torsion-resistant components 1.
- angles ⁇ of the same order of magnitude can occur within the pronounced contours 1 ', so that here too there is maximum flexibility and adaptability to the requirements of the body builder.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Composite Materials (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
- Powder Metallurgy (AREA)
- Body Structure For Vehicles (AREA)
- Vehicle Interior And Exterior Ornaments, Soundproofing, And Insulation (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19612781A DE19612781C1 (de) | 1996-03-29 | 1996-03-29 | Bauteil aus metallischem Schaumwerkstoff, Verfahren zum Endformen dieses Bauteils und Vorrichtung zur Ausführung des Verfahrens |
| DE19612781 | 1996-03-29 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0798062A2 true EP0798062A2 (fr) | 1997-10-01 |
| EP0798062A3 EP0798062A3 (fr) | 1998-10-07 |
| EP0798062B1 EP0798062B1 (fr) | 2001-12-19 |
Family
ID=7790011
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP97105225A Expired - Lifetime EP0798062B1 (fr) | 1996-03-29 | 1997-03-27 | Elément en mousse métallique |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US6090232A (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP0798062B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JPH1058575A (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE19612781C1 (fr) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0915007A2 (fr) * | 1997-11-07 | 1999-05-12 | DaimlerChrysler AG | Structure de carosserie comportant au moins une cloison transversale |
| DE19905124C1 (de) * | 1998-12-23 | 2000-08-03 | Mannesmann Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung eines Profilteils |
| DE19941199A1 (de) * | 1999-08-30 | 2001-03-01 | Arved Huebler | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Verbundkörper-Bauteiles sowie Verbundkörper-Bauteil |
| US6573309B1 (en) | 1999-03-03 | 2003-06-03 | Henkel Teroson Gmbh | Heat-curable, thermally expandable moulded park |
| WO2003054069A1 (fr) | 2001-12-21 | 2003-07-03 | Henkel Teroson Gmbh | Systemes expansibles a base de resine epoxyde modifies avec des polymeres thermoplastiques |
| US8288447B2 (en) | 2006-06-07 | 2012-10-16 | Henkel Ag & Co. Kgaa | Foamable compositions based on epoxy resins and polyesters |
Families Citing this family (62)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19648164C2 (de) * | 1996-11-21 | 2000-01-27 | Karmann Gmbh W | Karosserieteil, insbesondere Profilrahmenträger |
| US6103341A (en) | 1997-12-08 | 2000-08-15 | L&L Products | Self-sealing partition |
| DE19847273B4 (de) * | 1998-01-02 | 2004-06-17 | Wilhelm Karmann Gmbh | Verfahren zum Endformen eines aus einem im wesentlichen flächigen Halbzeug gebildeten Bauteils |
| DE29800005U1 (de) * | 1998-01-02 | 1999-05-06 | Wilhelm Karmann GmbH, 49084 Osnabrück | Bauteil, insbesondere Karosseriebauteil für Kraftfahrzeuge |
| NO981119L (no) * | 1998-01-14 | 1999-07-15 | Norsk Hydro As | Bilkarosseri |
| DE19813554A1 (de) * | 1998-03-27 | 1999-09-30 | Vaw Ver Aluminium Werke Ag | Verbundblech oder -band in Sandwichstruktur sowie Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung |
| AT408317B (de) * | 1998-04-09 | 2001-10-25 | Mepura Metallpulver | Verfahren zur herstellung von schaummetall-formkörpern |
| DE19849600C1 (de) * | 1998-10-28 | 2001-02-22 | Schunk Sintermetalltechnik Gmb | Verfahren zur Herstellung von einem metallischen Verbundwerkstoff |
| DE19852277C2 (de) * | 1998-11-13 | 2000-12-14 | Schunk Sintermetalltechnik Gmb | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines metallischen Verbundwerkstoffes sowie Halbzeug für einen solchen |
| DE19854173C2 (de) * | 1998-11-24 | 2000-11-23 | Fritz Michael Streuber | Metallschaumformkörper |
| DE19854175C1 (de) * | 1998-11-24 | 2000-03-23 | Fritz Michael Streuber | Metallschaumfügeverfahren |
| DE19908867A1 (de) * | 1999-03-01 | 2000-09-07 | Arved Huebler | Verbundkörper sowie Verfahren zum Herstellen eines Verbundkörpers |
| DE19911213C1 (de) * | 1999-03-12 | 2000-11-09 | Zf Lemfoerder Metallwaren Ag | Verbundbauteil und Verfahren zur Herstellung des Verbundbauteiles |
| DE19954755A1 (de) * | 1999-11-15 | 2001-05-17 | Schunk Sintermetalltechnik Gmb | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Aufschäumen eines metallischen Werkstoffes |
| US6131897A (en) | 1999-03-16 | 2000-10-17 | L & L Products, Inc. | Structural reinforcements |
| DE19932883C1 (de) * | 1999-07-16 | 2000-10-12 | Schunk Sintermetalltechnik Gmb | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Aufschäumen eines metallischen Schaumwerkstoffs |
| DE19933870C1 (de) * | 1999-07-23 | 2001-02-22 | Schunk Sintermetalltechnik Gmb | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines metallischen Verbundwerkstoffkörpers sowie Verbundwerkstoffkörper |
| US6358584B1 (en) | 1999-10-27 | 2002-03-19 | L&L Products | Tube reinforcement with deflecting wings and structural foam |
| US6481911B1 (en) | 1999-11-24 | 2002-11-19 | Fritz Michael Streuber | Jointing method for joining preformed bodies |
| US6668457B1 (en) * | 1999-12-10 | 2003-12-30 | L&L Products, Inc. | Heat-activated structural foam reinforced hydroform |
| NL1014116C2 (nl) * | 2000-01-19 | 2001-07-20 | Corus Aluminium Walzprod Gmbh | Werkwijze en inrichting voor het vormen van een laminaat van gecomprimeerd metaalpoeder met een schuimmiddel tussen twee metaallagen, en daarmee gevormd produkt. |
| WO2001058741A1 (fr) * | 2000-02-11 | 2001-08-16 | L & L Products, Inc. | Systeme de renfort structurel pour vehicules automobiles |
| US6467834B1 (en) | 2000-02-11 | 2002-10-22 | L&L Products | Structural reinforcement system for automotive vehicles |
| NO311708B1 (no) * | 2000-02-25 | 2002-01-14 | Cymat Corp | Fremgangsmåte og utstyr for tildannelse av stöpte produkter |
| US6296298B1 (en) | 2000-03-14 | 2001-10-02 | L&L Products, Inc. | Structural reinforcement member for wheel well |
| US6482486B1 (en) | 2000-03-14 | 2002-11-19 | L&L Products | Heat activated reinforcing sleeve |
| US6422575B1 (en) | 2000-03-14 | 2002-07-23 | L&L Products, Inc. | Expandable pre-formed plug |
| US6321793B1 (en) | 2000-06-12 | 2001-11-27 | L&L Products | Bladder system for reinforcing a portion of a longitudinal structure |
| US6820923B1 (en) | 2000-08-03 | 2004-11-23 | L&L Products | Sound absorption system for automotive vehicles |
| US6561571B1 (en) | 2000-09-29 | 2003-05-13 | L&L Products, Inc. | Structurally enhanced attachment of a reinforcing member |
| US6471285B1 (en) | 2000-09-29 | 2002-10-29 | L&L Products, Inc. | Hydroform structural reinforcement system |
| CA2344088A1 (fr) * | 2001-01-16 | 2002-07-16 | Unknown | Methode et appareil pour la production d'une mousse metallique |
| US6706239B2 (en) | 2001-02-05 | 2004-03-16 | Porvair Plc | Method of co-forming metal foam articles and the articles formed by the method thereof |
| US6852272B2 (en) * | 2001-03-07 | 2005-02-08 | Advanced Ceramics Research, Inc. | Method for preparation of metallic and ceramic foam products and products made |
| US6660224B2 (en) * | 2001-08-16 | 2003-12-09 | National Research Council Of Canada | Method of making open cell material |
| ATE320872T1 (de) * | 2001-08-17 | 2006-04-15 | Cymat Corp | Verfahren zum niederdruckgiessen von metallschaum |
| ATE307218T1 (de) * | 2002-02-01 | 2005-11-15 | Cymat Corp | Verfahren zur herstellung von metallschaum und eine vorrichtung zu deren durchführung |
| CA2477121C (fr) * | 2002-03-04 | 2011-03-01 | Cymat Corp. | Turbine etanche pour la production de mousse metallique, systeme et procede a cet effet |
| US20040018353A1 (en) * | 2002-07-25 | 2004-01-29 | L&L Products, Inc. | Composite metal foam damping/reinforcement structure |
| DE10260419B4 (de) * | 2002-12-21 | 2009-06-18 | Wilhelm Karmann Gmbh | Bauteile und Halbzeuge mit metallischer Schaumlage |
| DE10260418A1 (de) * | 2002-12-21 | 2004-07-15 | Wilhelm Karmann Gmbh | Bauteile und Halbzeuge mit metallischer Schaumlage |
| DE10302298A1 (de) * | 2003-01-22 | 2004-08-05 | Henkel Kgaa | Hitzehärtbare, thermisch expandierbare Zusammensetzung mit hohem Expansionsgrad |
| DE10304078A1 (de) | 2003-01-31 | 2004-08-26 | Wilhelm Karmann Gmbh | Bauteile mit metallischer Schaumlage |
| EP1468765A1 (fr) * | 2003-04-16 | 2004-10-20 | Corus Technology BV | Préforme pour feuille moussée et produit moussé fabriqué à partir de ladite feuille |
| AT412876B (de) * | 2003-08-05 | 2005-08-25 | Arc Leichtmetallkompetenzzentrum Ranshofen Gmbh | Schäumbares halbzeug und verfahren zur herstellung von metallteilen mit innerer porosität |
| US7516529B2 (en) * | 2003-12-17 | 2009-04-14 | General Motors Corporation | Method for producing in situ metallic foam components |
| US7328831B1 (en) | 2004-06-25 | 2008-02-12 | Porvair Plc | Method of making a brazed metal article and the article formed thereby |
| JP4051052B2 (ja) * | 2004-07-09 | 2008-02-20 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 車両のボンネットフード構造 |
| DE102004036873B4 (de) * | 2004-07-29 | 2007-06-28 | Wilhelm Karmann Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Bauteilherstellung |
| DE102004038932A1 (de) * | 2004-08-11 | 2006-02-23 | Mtu Aero Engines Gmbh | Verfahren zum Verbinden von Bauteilen |
| DE102004040888A1 (de) * | 2004-08-24 | 2006-04-13 | Wilhelm Karmann Gmbh | Herstellung von Bauteilen mit zumindest einer metallischen Schaumlage |
| DE102004054961A1 (de) * | 2004-11-13 | 2006-05-18 | Wilhelm Karmann Gmbh | Vorrichtung zum Aufschäumen von metallischen Halbzeugen mit zumindest einer aufschäumbaren Lage |
| DE102005005041A1 (de) * | 2005-02-03 | 2006-08-10 | Märkisches Werk GmbH | Ventil zur Steuerung des Gasaustauschs, insbesondere bei Verbrennungsmotoren |
| DE202005006240U1 (de) * | 2005-04-18 | 2005-10-20 | Seeliger, Hans-Wolfgang | Metallschaum-Sandwichs |
| DE102005032098B4 (de) * | 2005-07-08 | 2012-09-06 | Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung e.V. | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von Metallschaum-Verbundkörpern und Metallschaum-Verbundhohlkörper |
| US20070154731A1 (en) * | 2005-12-29 | 2007-07-05 | Serguei Vatchiants | Aluminum-based composite materials and methods of preparation thereof |
| DE102006020860B4 (de) * | 2006-05-04 | 2008-02-07 | Alulight International Gmbh | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Verbundkörpern sowie danach hergestellte Verbundkörper |
| US9403213B2 (en) * | 2006-11-13 | 2016-08-02 | Howmedica Osteonics Corp. | Preparation of formed orthopedic articles |
| US10539041B2 (en) | 2013-10-22 | 2020-01-21 | General Electric Company | Cooled article and method of forming a cooled article |
| CN103831979B (zh) * | 2014-03-11 | 2016-02-10 | 哈尔滨理工大学 | 一种陶瓷基波纹夹芯结构复合材料的制备模具 |
| CN104177110B (zh) * | 2014-08-28 | 2016-01-20 | 哈尔滨理工大学 | 波纹构型陶瓷基复合材料平板的制备方法 |
| FR3067270B1 (fr) * | 2017-06-13 | 2021-12-24 | Safran | Procede de realisation d'une piece metallique par deliantage et frittage |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0189674A2 (fr) * | 1985-01-26 | 1986-08-06 | Imi Titanium Limited | Formation de corps poreux |
| DE4018360C1 (en) * | 1990-06-08 | 1991-05-29 | Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft Zur Foerderung Der Angewandten Forschung Ev, 8000 Muenchen, De | Porous metal body prodn. - involves compaction at low temp. followed by heating to near melting point of metal |
| DE4424157A1 (de) * | 1993-07-29 | 1995-02-02 | Fraunhofer Ges Forschung | Poröser metallischer Werkstoff mit anisotropen Eigenschaften |
| DE4426627A1 (de) * | 1993-07-29 | 1995-02-02 | Fraunhofer Ges Forschung | Metallischer Verbundwerkstoff und Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung |
Family Cites Families (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2974034A (en) * | 1957-12-12 | 1961-03-07 | Lor Corp | Method of foaming granulated metal |
| US2983597A (en) * | 1959-06-11 | 1961-05-09 | Lor Corp | Metal foam and method for making |
| US3087807A (en) * | 1959-12-04 | 1963-04-30 | United Aircraft Corp | Method of making foamed metal |
| US3214265A (en) * | 1963-03-11 | 1965-10-26 | Lor Corp | Method of making metal foam bodies |
| US3981720A (en) * | 1970-04-22 | 1976-09-21 | Swiss Aluminum Limited | Foaming of metal by the catalyzed and controlled decomposition of zirconium hydride and titanium hydride |
| US3873392A (en) * | 1971-06-14 | 1975-03-25 | Ethyl Corp | Pressure contouring and bonding of metal foams |
| US3839080A (en) * | 1971-06-21 | 1974-10-01 | Ethyl Corp | Plastic coated metallic foams |
| US3719223A (en) * | 1971-12-09 | 1973-03-06 | Ethyl Corp | Method for quietly casting foamed metal |
| JPS4915877A (fr) * | 1972-06-09 | 1974-02-12 | ||
| US3929425A (en) * | 1973-02-26 | 1975-12-30 | Ethyl Corp | Foamed metal bodies |
| US4411679A (en) * | 1980-03-10 | 1983-10-25 | Pelton Robert S | Method of producing foamed construction materials |
| DE3600480A1 (de) * | 1986-01-10 | 1987-07-16 | Licentia Gmbh | Verfahren zum herstellen eines poroesen presslings |
| DE3728918A1 (de) * | 1987-08-29 | 1989-03-09 | Monforts Eisengiesserei | Gusskoerpermodell und verfahren zum herstellen eines hohlen gusskoerpers |
| DE4101630A1 (de) * | 1990-06-08 | 1991-12-12 | Fraunhofer Ges Forschung | Verfahren zur herstellung aufschaeumbarer metallkoerper und verwendung derselben |
| DE4206303C1 (fr) * | 1992-02-28 | 1993-06-17 | Mepura Metallpulver Ges.M.B.H., Ranshofen, At | |
| US5281251A (en) * | 1992-11-04 | 1994-01-25 | Alcan International Limited | Process for shape casting of particle stabilized metal foam |
| US5744254A (en) * | 1995-05-24 | 1998-04-28 | Virginia Tech Intellectual Properties, Inc. | Composite materials including metallic matrix composite reinforcements |
| US5890268A (en) * | 1995-09-07 | 1999-04-06 | Case Western Reserve University | Method of forming closed cell metal composites |
-
1996
- 1996-03-29 DE DE19612781A patent/DE19612781C1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
1997
- 1997-03-27 US US08/828,789 patent/US6090232A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1997-03-27 DE DE59705836T patent/DE59705836D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-03-27 JP JP9074867A patent/JPH1058575A/ja active Pending
- 1997-03-27 EP EP97105225A patent/EP0798062B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1999
- 1999-08-16 US US09/374,809 patent/US6094798A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1999-11-17 US US09/441,579 patent/US20010023027A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0189674A2 (fr) * | 1985-01-26 | 1986-08-06 | Imi Titanium Limited | Formation de corps poreux |
| DE4018360C1 (en) * | 1990-06-08 | 1991-05-29 | Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft Zur Foerderung Der Angewandten Forschung Ev, 8000 Muenchen, De | Porous metal body prodn. - involves compaction at low temp. followed by heating to near melting point of metal |
| DE4424157A1 (de) * | 1993-07-29 | 1995-02-02 | Fraunhofer Ges Forschung | Poröser metallischer Werkstoff mit anisotropen Eigenschaften |
| DE4426627A1 (de) * | 1993-07-29 | 1995-02-02 | Fraunhofer Ges Forschung | Metallischer Verbundwerkstoff und Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0915007A2 (fr) * | 1997-11-07 | 1999-05-12 | DaimlerChrysler AG | Structure de carosserie comportant au moins une cloison transversale |
| EP0915007A3 (fr) * | 1997-11-07 | 2000-09-13 | DaimlerChrysler AG | Structure de carosserie comportant au moins une cloison transversale |
| US6286896B1 (en) | 1997-11-07 | 2001-09-11 | Daimlerchrysler Ag | Body structure with at least one transverse connection and method of making same |
| DE19905124C1 (de) * | 1998-12-23 | 2000-08-03 | Mannesmann Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung eines Profilteils |
| US6573309B1 (en) | 1999-03-03 | 2003-06-03 | Henkel Teroson Gmbh | Heat-curable, thermally expandable moulded park |
| DE19941199A1 (de) * | 1999-08-30 | 2001-03-01 | Arved Huebler | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Verbundkörper-Bauteiles sowie Verbundkörper-Bauteil |
| WO2003054069A1 (fr) | 2001-12-21 | 2003-07-03 | Henkel Teroson Gmbh | Systemes expansibles a base de resine epoxyde modifies avec des polymeres thermoplastiques |
| US8288447B2 (en) | 2006-06-07 | 2012-10-16 | Henkel Ag & Co. Kgaa | Foamable compositions based on epoxy resins and polyesters |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US6090232A (en) | 2000-07-18 |
| EP0798062B1 (fr) | 2001-12-19 |
| JPH1058575A (ja) | 1998-03-03 |
| DE19612781C1 (de) | 1997-08-21 |
| US6094798A (en) | 2000-08-01 |
| US20010023027A1 (en) | 2001-09-20 |
| EP0798062A3 (fr) | 1998-10-07 |
| DE59705836D1 (de) | 2002-01-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0798062B1 (fr) | Elément en mousse métallique | |
| DE3215616C2 (de) | Verfahren zum Herstellen von Verbundbauteilen in Sandwichbauweise, insbesondere für Kraftfahrzeuge | |
| DE60128624T2 (de) | Formteil, das aus einem Stahlblech hergestellt ist, und Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung | |
| DE4426627A1 (de) | Metallischer Verbundwerkstoff und Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung | |
| DE19635734A1 (de) | Verstärktes Formteil, Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung und seine Verwendung | |
| DE102006049014B4 (de) | Verbundblech mit hohem Energieabsorptionsvermögen, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und Bauteil | |
| EP3446848B1 (fr) | Élément isolant ainsi que son procédé de fabrication | |
| DE10024004C2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Bauteils aus Verbundwerkstoff | |
| DE19729566C2 (de) | Metallverbundplatte | |
| EP1459881B1 (fr) | Procédé pour la fabrication d'une pièce de carosserie de véhicule | |
| DE2709644A1 (de) | Mehrschichtplatte | |
| DE19723034A1 (de) | Karosserierahmenbauteil für die Karosserie eines Kraftfahrzeuges und Verfahren für dessen Herstellung | |
| DE1923161B2 (de) | Matte zum Verkleiden von Wänden von Kraftfahrzeugkarosserien und Verfahren zur Herstellung der Matte | |
| DE19911213C1 (de) | Verbundbauteil und Verfahren zur Herstellung des Verbundbauteiles | |
| DE102013022247A1 (de) | Fahrzeug-Karosserieelement | |
| DE102015205829B4 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von geschäumten Sandwichelementen | |
| DE102014208835A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Kunststoffbauteils | |
| DE102018208244A1 (de) | Verbundbauteil für ein Fahrzeug und Verfahren zum Herstellen eines Verbundbauteils | |
| DE19800008C1 (de) | Verfahren zum Endformen eines Bauteils mit einer Schicht aus metallischem Schaumwerkstoff | |
| DE10339068A1 (de) | Wölbstrukturiertes Karosseriebauteil und Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung | |
| EP0927589B9 (fr) | Elément de construction comprenant une couche de mousse métallique pour carrosseries de véhicules à moteur | |
| EP0927590A2 (fr) | Elément de construction comprenant une couche de mousse métallique pour carrosseries à moteur | |
| DE102004036873B4 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Bauteilherstellung | |
| DE10212450A1 (de) | Verkleidungsteil sowie Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von mehrlagigen Verkleidungsteilen, insbesondere von Innenverkleidungsteilen für Kraftfahrzeuge | |
| DE102011007680B4 (de) | Energieabsorptionselement zur Absorption von Aufprallenergie sowie Verfahren zur Herstellung |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): DE FR GB IT SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): DE FR GB IT SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19981204 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19991217 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE FR GB IT SE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59705836 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20020131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20020319 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20020327 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20110607 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20110518 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20110530 Year of fee payment: 15 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20110518 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20120327 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20121130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120327 Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120402 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 59705836 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20121002 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120327 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20121002 |