EP0709864A2 - Giessharztransformator - Google Patents
Giessharztransformator Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0709864A2 EP0709864A2 EP95116433A EP95116433A EP0709864A2 EP 0709864 A2 EP0709864 A2 EP 0709864A2 EP 95116433 A EP95116433 A EP 95116433A EP 95116433 A EP95116433 A EP 95116433A EP 0709864 A2 EP0709864 A2 EP 0709864A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- bore
- connection
- cast resin
- wire
- transformer according
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 title claims description 16
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 title claims description 16
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 19
- 229910001369 Brass Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 239000010951 brass Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 238000005266 casting Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000032683 aging Effects 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005476 soldering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F5/00—Coils
- H01F5/04—Arrangements of electric connections to coils, e.g. leads
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F27/00—Details of transformers or inductances, in general
- H01F27/02—Casings
- H01F27/022—Encapsulation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F27/00—Details of transformers or inductances, in general
- H01F27/28—Coils; Windings; Conductive connections
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a cast resin transformer with at least one primary winding, at least one secondary winding and at least one with cast-in connection element, which is connected in an electrically conductive manner to the primary winding or the secondary winding via a connecting wire and to which, e.g. by means of a screw connection, a transformer-external connecting line can be connected, the connecting element having a hole for receiving the connecting wire and the connecting wire being inserted into the hole (DE-PS 29 04 746).
- connection elements in which in a casting compound together with the winding cast connection elements are mechanically fixed and electrically conductive via conductor rod to the winding in that these conductor rods have deformations in the manner of a knurling.
- the connecting wires are also connected to the conductor bars via solder joints.
- Similar transformers are also manufactured and sold, for example, by Trafo-Union GmbH under the name GEAFOL cast resin transformers.
- the object of the present invention is to establish a simple, reliable and inexpensive connection between the connecting wire and the connecting element.
- connection technology used allows one reliable operation of the transformer. There is no aging damage like a solder joint.
- the deformation is advantageously designed as a bulge.
- the bulge can be caused by upsetting, which is easy to manufacture.
- the bore can be designed as a blind bore or alternatively as a through bore.
- the connecting element can advantageously have a threaded bore for receiving a screw for connecting the connecting line, the bore being arranged radially or axially to the threaded bore. This allows the cast resin transformer to be connected to the network in a convenient manner.
- the threaded bore and / or the bore can advantageously be arranged eccentrically, so that a lateral connection is possible.
- the connecting element is preferably made of brass, the connecting wire preferably consisting of copper. This ensures good contact.
- a primary-side three-phase network with the phases R, S and T or a secondary-side three-phase network with the phases U, V and W can be connected to the connection elements 6 and 8 via transformer-external connecting lines 9, 10.
- the entire transformer including transformer core 4, windings 1, 2, connecting elements 6, 8 and connecting wires 5, 7 is cast in casting resin 11. So only the connection elements 6, 8 are accessible from the outside.
- the windings can also form individually cast structural units which are arranged on a common, non-cast core.
- connection elements 6, 8 are designed as hexagon cast nuts.
- the connection elements 6, 8 each have a threaded bore 12 into which a screw (not shown in FIG. 2) can be screwed.
- a screw not shown in FIG. 2
- the transformer-external connecting lines 9, 10 are connected to the transformer.
- the connection elements 6, 8 also each have a bore 13, which in the cast-in state of the connection elements 6, 8 is directed inwards and serves to accommodate the connection wires 5, 7.
- the connecting wire 5 inserted into the bore 13 has a bulge 14 in the area of the connecting element 6.
- the bulge 14 can e.g. to be caused by upsetting. Due to the bulge 14, the connecting wire 5 is mechanically fixed and electrically conductively connected to the connecting element 6.
- the connection is both gas and liquid tight. It can absorb tensile forces and acts as a protection against torsion.
- the bulge 14 can be designed differently depending on the configuration of the bore 13. If the bore 13 is a simple bore, the bulge 14 is at the entrance to the bore 13 arranged. If the bore is half open or has a puncture, the bulge 14 can alternatively or additionally also be arranged in the semi-open region of the bore 13 or in the puncture region of the bore 13.
- the bore 13 is arranged axially to the threaded bore 12, both the threaded bore 12 and the bore 13 being arranged outside the line of symmetry of the pouring nut 6, that is to say eccentrically. As a result, the pouring nut 6 can be kept compact.
- the bore 13 is designed as a blind bore in the present case.
- the bore 13 could also be designed as a through bore.
- FIG. 3 shows a further embodiment of the connection between connecting wire 7 and connecting element 8.
- the bore 13 is not arranged axially but radially to the threaded bore 12.
- the bore 13 is also formed as a through bore.
- it could also be designed as a blind bore.
- the invention described above is particularly advantageous when the connecting element 6, 8 is made of brass and the connecting wire 5, 7 is made of copper. With this combination in particular, flux is required for soldering, which can only be removed again with great effort. However, other working methods such as welding or squeezing are not possible for other technical reasons.
- the present invention therefore enables great cost savings, in particular in the combination "brass for casting nut and copper for connecting wire".
- other material combinations for example in connection with aluminum, are also possible.
- they are described above Features can be combined in any way within the scope of professional skill, without leaving the path of the present idea.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Coils Of Transformers For General Uses (AREA)
- Transformers For Measuring Instruments (AREA)
- Insulating Of Coils (AREA)
- Coils Or Transformers For Communication (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- Die vorliegende Erfindung betrifft einen Gießharztransformator mit mindestens einer Primärwicklung, mindestens einer Sekundärwicklung und mindestens einem mit eingegossenen Anschlußelement, das über einen Anschlußdraht mit der Primärwicklung oder der Sekundärwicklung elektrisch leitend verbunden ist und an das, z.B. mittels Schraubverbindung, eine transformatorexterne Anschlußleitung anschließbar ist, wobei das Anschlußelement eine Bohrung zur Aufnahme des Anschlußdrahtes aufweist und der Anschlußdraht in die Bohrung eingeführt ist (DE-PS 29 04 746).
- Aus der US-PS 38 38 372 ist eine Magnetspuleneinheit bekannt, bei der in einer Vergußmasse mitsamt der Wicklung eingegossene Anschlußelemente mechanisch fest und elektrisch leitend über Leiterstabe mit der Wicklung dadurch verbunden sind, daß diese Leiterstäbe Verformungen in der Art einer Rändelung aufweisen. Die Anschlußdrähte sind zusätzlich über Lötstellen mit den Leiterstäben verbunden.
- Ähnliche Transformatoren werden beispielsweise auch von der Trafo-Union GmbH unter der Bezeichnung GEAFOL-Gießharztransformatoren hergestellt und vertrieben.
- Die Aufgabe der vorliegenden Erfindung besteht darin, eine einfache, zuverlässige und kostengünstige Verbindung zwischen dem Anschlußdraht und dem Anschlußelement herzustellen.
- Diese Aufgabe wird bei einem Gießharztransformator der eingangs genannten Art erfindungsgemäß dadurch gelöst, daß daß der Anschlußdraht im Bereich des Anschlußelements eine Verformung aufweist, derart, daß der Anschlußdraht mechanisch fest und elektrisch leitend mit dem Anschlußelement verbunden ist. Die verwendete Verbindungstechnik erlaubt einen zuverlässigen Betrieb des Transformators. Alterungsschäden wie bei einer Lötstelle treten dabei nicht auf.
- Mit Vorteil ist die Verformung als Aufbauchung ausgebildet. Die Aufbauchung kann dabei durch Stauchen bewirkt sein, was der einfachen Herstellbarkeit entgegenkommt. Die Bohrung kann als Sackbohrung oder alternativ als Durchgangsbohrung ausgebildet sein.
- Das Anschlußelement kann vorteilhafterweise eine Gewindebohrung zur Aufnahme einer Schraube zum Anschließen der Anschlußleitung aufweisen wobei die Bohrung radial oder axial zur Gewindebohrung angeordnet ist. Damit kann der Gießharztransformator in zweckmäßiger Weise an das Netz angeschlossen werden.
- Die Gewindebohrung und/oder die Bohrung können mit Vorteil exzentrisch angeordnet sein, so daß eine seitliche Verbindung möglich ist. Das Anschlußelement besteht bevorzugt aus Messing, wobei der Anschlußdraht bevorzugt aus Kupfer besteht. Somit ist eine gute Kontaktierung gegeben.
- Weitere Vorteile und Einzelheiten ergeben sich aus der nachfolgenden Beschreibung eines Ausführungsbeispiels und der Zeichnung. Dabei zeigen:
- FIG 1
- einen Schnitt durch einen erfindungsgemäßen Drehstrom-Gießharztransformator und
- FIG 2 und 3
- jeweils die Verbindung eines Anschlußelements mit einem Anschlußdraht.
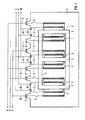
- FIG 1 zeigt einen Drehstromtransformator, der drei Primärwicklungen 1 und drei Sekundärwicklungen 2 aufweist, welche jeweils paarweise konzentrisch auf den drei Säulen 3 des Transformatorkerns 4 angeordnet sind. Die Primärwicklungen 1 sind über die Anschlußdrähte 5 mit den Anschlußelementen 6 verbunden. Die Sekundärwicklungen 2 sind über die Anschlußdrähte 7 mit den Anschlußelementen 8 verbunden. An die Anschlußelemente 6 bzw. 8 sind über transformatorexterne Anschlußleitungen 9, 10 ein primärseitiges Drehstromnetz mit den Phasen R, S und T bzw. ein sekundärseitiges Drehstromnetz mit den Phasen U, V und W anschließbar.
- Wie aus FIG 1 ersichtlich ist, ist der gesamte Transformator einschließlich Transformatorkern 4, Wicklungen 1, 2, Anschlußelementen 6, 8 und Anschlußdrähten 5, 7 in Gießharz 11 eingegossen. Von außen sind also nur die Anschlußelemente 6, 8 zugänglich. Die Wicklungen können alternativ auch jeweils für sich vergossene Baueinheiten bilden, die auf einem gemeinsamen, nicht vergossenen Kern angeordnet sind.
- Gemäß FIG 2 sind die Anschlußelemente 6, 8 als Sechskant-Eingießmuttern ausgebildet. Die Anschlußelemente 6, 8 weisen jeweils eine Gewindebohrung 12 auf, in welche eine in FIG 2 nicht näher dargestellte Schraube eindrehbar ist. Mittels einer derartigen Schraubverbindung werden die transformatorexternen Anschlußleitungen 9, 10 an den Transformator angeschlossen. Die Anschlußelemente 6, 8 weisen ferner jeweils eine Bohrung 13 auf, welche im eingegossenen Zustand der Anschlußelemente 6, 8 nach innen gerichtet ist und der Aufnahme der Anschlußdrähte 5, 7 dient.
- Wie aus FIG 2 ersichtlich ist, weist der in die Bohrung 13 eingeführte Anschlußdraht 5 im Bereich des Anschlußelements 6 eine Aufbauchung 14 auf. Die Aufbauchung 14 kann z.B. durch Stauchen bewirkt sein. Durch die Aufbauchung 14 ist der Anschlußdraht 5 mechanisch fest und elektrisch leitend mit den Anschlußelement 6 verbunden. Die Verbindung ist sowohl gas- als auch flüssigkeitsdicht. Sie kann Zugkräfte aufnehmen und wirkt als Verdrehungsschutz.
- Die Aufbauchung 14 kann je nach Ausgestaltung der Bohrung 13 verschieden ausgestaltet sein. Wenn die Bohrung 13 eine einfache Bohrung ist, ist die Aufbauchung 14 am Eingang der Bohrung 13 angeordnet. Wenn die Bohrung halb offen ist oder einen Einstich aufweist, kann die Aufbauchung 14 alternativ oder zusätzlich auch im halb offenen Bereich der Bohrung 13 bzw. im Einstichsbereich der Bohrung 13 angeordnet sein.
- Wie aus FIG 2 ersichtlich ist, ist die Bohrung 13 axial zur Gewindebohrung 12 angeordnet, wobei sowohl die Gewindebohrung 12 als auch die Bohrung 13 außerhalb der Symmetrielinie der Eingießmutter 6, also exzentrisch, angeordnet sind. Dadurch kann die Eingießmutter 6 kompakt gehalten werden. Wie ferner aus FIG 2 ersichtlich ist, ist die Bohrung 13 im vorliegenden Fall als Sackbohrung ausgebildet. Die Bohrung 13 könnte aber ebenso als Durchgangsbohrung ausgebildet sein.
- FIG 3 zeigt eine weitere Ausführungsform der Verbindung zwischen Anschlußdraht 7 und Anschlußelement 8. Der wesentliche Unterschied zur ersten Ausführungsform besteht darin, daß die Bohrung 13 nicht axial, sondern radial zur Gewindebohrung 12 angeordnet ist. Auch ist in diesem Ausführungsbeispiel die Bohrung 13 als Durchgangsbohrung ausgebildet. Sie könnte aber, so wie in FIG 2 dargestellt, auch als Sackbohrung ausgebildet sein.
- Obenstehend beschriebene Erfindung ist besonders vorteilhaft dann, wenn das Anschlußelement 6, 8 aus Messing besteht und der Anschlußdraht 5, 7 aus Kupfer. Insbesondere bei dieser Kombination ist nämlich bei Lötungen Flußmittel erforderlich, was sich nur unter großem Arbeitsaufwand wieder entfernen läßt. Andere Arbeitsverfahren wie beispielsweise Schweißen oder Quetschen sind dagegen aus anderen technischen Gründen nicht möglich.
- Insbesondere bei der Kombination "Messing für Eingießmutter und Kupfer für Anschlußdraht" ermöglicht die vorliegende Erfindung daher eine große Kostenersparnis. Es sind aber auch andere Materialkombinationen, z.B. in Verbindung mit Aluminium, möglich. Selbstverständlich sind die oben beschrieben Merkmale beliebig im Rahmen des fachmännischen Könnens kombinierbar, ohne daß der Weg der vorliegenden Idee verlassen wird.
Claims (9)
- Gießharztransformator mit mindestens einer Primärwicklung (1), mindestens einer Sekundärwicklung (2) und mindestens einem mit eingegossenen Anschlußelement (6,8), das über einen Anschlußdraht (5,7) mit der Primärwicklung (1) oder der Sekundärwicklung (2) leitend verbunden ist und an das, z.B. mittels Schraubverbindung, eine transformatorexterne Anschlußleitung (9,10) anschließbar ist, wobei das Anschlußelement (6,8) eine Bohrung (13) zur Aufnahme des Anschlußdrahtes (5,7) aufweist und der Anschlußdraht (5,7) in die Bohrung (13) eingeführt ist, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Anschlußdraht (5,7) im Bereich des Anschlußelements (6,8) eine Verformung (14) aufweist, derart, daß der Anschlußdraht (5,7) mechanisch fest und elektrisch leitend mit dem Anschlußelement (6,8) verbunden ist.
- Gießharztransformator nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Verformung (14) als Aufbauchung (14) ausgebildet ist.
- Gießharztransformator nach Anspruch 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Aufbauchung (14) durch Stauchen bewirkt ist.
- Gießharztransformator nach Anspruch 1, 2 oder 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Bohrung (13) als Sackbohrung (13) ausgebildet ist.
- Gießharztransformator nach Anspruch 1, 2 oder 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Bohrung (13) als Durchgangsbohrung (13) ausgebildet ist.
- Gießharztransformator nach einem der obigen Ansprüche dadurch gekennzeichnet,- daß das Anschlußelement (6,8) eine Gewindebohrung (12) zur Aufnahme einer Schraube zum Anschließen der Anschlußleitung (9,10) aufweist und- daß die Bohrung (13) radial zur Gewindebohrung (12) angeordnet ist.
- Gießharztransformator nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 5, dadurch gekennzeichnet,- daß das Anschlußelement (6,8) eine Gewindebohrung (12) zur Aufnahme einer Schraube zum Anschließen der Anschlußleitung (9,10) aufweist und- daß die Bohrung (13) axial zur Gewindebohrung (12) angeordnet ist.
- Gießharztransformator nach Anspruch 7, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Gewindebohrung (12) und/oder die Bohrung (13) exzentrisch angeordnet sind.
- Gießharztransformator nach einem der obigen Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Anschlußelement (6,8) aus Messing besteht und/oder der Anschlußdraht (5,7) aus Kupfer besteht.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE4438653A DE4438653C1 (de) | 1994-10-28 | 1994-10-28 | Gießharztransformator |
| DE4438653 | 1994-10-28 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0709864A2 true EP0709864A2 (de) | 1996-05-01 |
| EP0709864A3 EP0709864A3 (de) | 1996-06-05 |
| EP0709864B1 EP0709864B1 (de) | 1999-01-13 |
Family
ID=6531985
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP95116433A Expired - Lifetime EP0709864B1 (de) | 1994-10-28 | 1995-10-18 | Giessharztransformator |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0709864B1 (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE175806T1 (de) |
| DE (2) | DE4438653C1 (de) |
| ES (1) | ES2127451T3 (de) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012123341A3 (de) * | 2011-03-11 | 2012-12-20 | REO TRAIN TECHNOLOGIES GmbH | Elektrisches bauteil mit wenigstens einer in einer vergussmasse angeordneten elektrischen verlustleistungsquelle und einer kühleinrichtung |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3838372A (en) | 1971-10-29 | 1974-09-24 | Motorola Inc | Magnetic pickup assembly |
| DE2904746A1 (de) | 1979-02-08 | 1980-08-28 | Smit Transformatoren Bv | Wicklung fuer einen luftgekuehlten trockentransformator |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE406685C (de) * | 1923-09-13 | 1925-07-16 | Wolfgang Bauer | Klemme fuer elektrische Leitungen |
| DE3743222A1 (de) * | 1987-12-19 | 1989-06-29 | Asea Brown Boveri | Gekuehlte drosselspule fuer stromrichteranlagen |
| DE9114654U1 (de) * | 1991-11-25 | 1992-04-30 | Elektro-Kern GmbH & Co KG, 7990 Friedrichshafen | Magnetspule |
-
1994
- 1994-10-28 DE DE4438653A patent/DE4438653C1/de not_active Revoked
-
1995
- 1995-10-18 ES ES95116433T patent/ES2127451T3/es not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-10-18 DE DE59504800T patent/DE59504800D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1995-10-18 AT AT95116433T patent/ATE175806T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1995-10-18 EP EP95116433A patent/EP0709864B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3838372A (en) | 1971-10-29 | 1974-09-24 | Motorola Inc | Magnetic pickup assembly |
| DE2904746A1 (de) | 1979-02-08 | 1980-08-28 | Smit Transformatoren Bv | Wicklung fuer einen luftgekuehlten trockentransformator |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012123341A3 (de) * | 2011-03-11 | 2012-12-20 | REO TRAIN TECHNOLOGIES GmbH | Elektrisches bauteil mit wenigstens einer in einer vergussmasse angeordneten elektrischen verlustleistungsquelle und einer kühleinrichtung |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ATE175806T1 (de) | 1999-01-15 |
| ES2127451T3 (es) | 1999-04-16 |
| EP0709864A3 (de) | 1996-06-05 |
| EP0709864B1 (de) | 1999-01-13 |
| DE59504800D1 (de) | 1999-02-25 |
| DE4438653C1 (de) | 1996-06-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0232471A2 (de) | Hochspannungsstromwandler und Verfahren zur Herstellung eines derartigen Hochspannungsstromwandlers | |
| DE10130982A1 (de) | Temperaturfühler für die Statorwicklung von Elektromotoren | |
| DE2540605B2 (de) | Langgestreckte Einspannhülse aus verformbarem Metall | |
| EP0709864B1 (de) | Giessharztransformator | |
| EP1610350A2 (de) | Schweissstromwandler | |
| DE69705840T2 (de) | Verbesserung im stator kühlkompressormotoren | |
| CH660088A5 (de) | Scheibenisolator mit eingusselektrode und verfahren zu seiner herstellung. | |
| DE2244158A1 (de) | Drossel oder transformator, insbesondere als vorschaltgeraet fuer gasentladungslampen | |
| DE725978C (de) | Anordnung der aus Flachband bestehenden Primaerwicklung von Stromwandlern mit Schenkelkern | |
| DE10145570C2 (de) | Elektromotor | |
| EP3577665B1 (de) | Aktivteil für ein elektrisches hochspannungsgerät | |
| DE2418230C3 (de) | Kapazitiv gesteuerte Hochspannungswicklung aus Scheibenspulen für Transformatoren mit großen Leistungen | |
| DE202014006814U1 (de) | Wicklungsanordnung | |
| DE3239391C2 (de) | ||
| DE2509101C3 (de) | Elektrischer Rohrheizkörper mit flachovalem Querschnitt | |
| DE1915864C3 (de) | Drehstromöltransformator | |
| DE2425899A1 (de) | Wicklungsanordnung fuer transformatoren mit rechteckigem kernquerschnitt | |
| EP0102941B1 (de) | Drilleiterwicklung | |
| DE2513393C3 (de) | Hochspannungsstromwandler | |
| DE102017204930B4 (de) | Elektrisches Gerät zum Anschluss an ein Hochspannungsnetz | |
| DE2161635A1 (de) | Drossel oder transformator, insbesondere als vorschaltgeraet fuer gasentladungslampen | |
| EP0967690B1 (de) | Verfahren zum Verbinden eines dünnen Drahtes mit einem stromleitenden Kontaktelement und Produkte dieses Verfahrens | |
| DE19609260C2 (de) | Isolationsanordnung für rechteckige Wickeldrähte zur Herstellung von Wicklungen aus Scheibenspulen für Transformatoren und Drosseln | |
| DE19701295B4 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Verbinden zweier Leiter miteinander mit einer zweigeteilten Hülse | |
| DE754570C (de) | Topfstromwandler |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE ES FR GB IT LI NL PT SE |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE ES FR GB IT LI NL PT SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19960706 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19960821 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE ES FR GB IT LI NL PT SE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: THE PATENT HAS BEEN ANNULLED BY A DECISION OF A NATIONAL AUTHORITY Effective date: 19990113 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 175806 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19990115 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: SIEMENS SCHWEIZ AG Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59504800 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19990225 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2127451 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 19990524 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19991018 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19991019 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20000501 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 95116433.4 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 20000501 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20010430 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20001113 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20041020 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20051031 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: *SIEMENS A.G. Effective date: 20051031 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20080110 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20071214 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19991018 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PCAR Free format text: SIEMENS SCHWEIZ AG;INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY FREILAGERSTRASSE 40;8047 ZUERICH (CH) |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20081028 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20081017 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20081020 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090501 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20081031 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20081031 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20100630 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091102 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091018 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091018 |