EP0288564B1 - Detecteur de vehicules sur une piste - Google Patents
Detecteur de vehicules sur une piste Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0288564B1 EP0288564B1 EP86905931A EP86905931A EP0288564B1 EP 0288564 B1 EP0288564 B1 EP 0288564B1 EP 86905931 A EP86905931 A EP 86905931A EP 86905931 A EP86905931 A EP 86905931A EP 0288564 B1 EP0288564 B1 EP 0288564B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- signal
- circuit
- level
- output
- phase
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000001131 transforming effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 11
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 10
- 230000010355 oscillation Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000005281 excited state Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003321 amplification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008033 biological extinction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008094 contradictory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000977 initiatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003199 nucleic acid amplification method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000011664 signaling Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B61—RAILWAYS
- B61L—GUIDING RAILWAY TRAFFIC; ENSURING THE SAFETY OF RAILWAY TRAFFIC
- B61L1/00—Devices along the route controlled by interaction with the vehicle or train
- B61L1/18—Railway track circuits
- B61L1/181—Details
- B61L1/187—Use of alternating current
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a vehicle detecting apparatus for detecting whether or not a vehicle is present on a railroad or on rails in a marshaling yard.
- a railway relay in which rails are used as parts of a circuit, a short circuit is formed between two rails through wheels and a wheel shaft when a train is present on a track and the change of the voltage by the formation of the short circuit is read to actuate the relay and detect the presence or absence of the vehicle. More specifically, a predetermined length of the track is divided into sections, and rails of the specific section are utilized as parts of an electric circuit. If a short circuit is formed between the rails by a train present on the track, the presence of the vehicle in this section is detected by an electromagnetic track relay. Various safety devices of the railway signal system are controlled by this detection signal. As one of the railway relay of this type, there is known an alternating current railway relay which is actuated by an alternating current flowing in rails.
- an alternating current railway relay disclosed in a pamphlet published by LM ERICSSON Signalling Systems Department, Sweden is driven and controlled by utilizing a semiconductor switch.
- this alternating railway relay comprises an electric circuit including a first transformer for the input of an alternating current local signal applied as a reference signal to rails of the specific section, a second transformer for the input of a track signal, which is connected to rails on which a train runs, a third transformer for putting out a train detection judgement signal, a plurality of thyristors, a plurality of diodes and an output relay to be actuated based on the detection signal of the third transformer.
- the phase of the track signal for the specific closed section is made different by ⁇ from that for the adjacent precedent section.
- the phase of the track signal of the specific section becomes in agreement with the phase of the local signal and the voltage level of the track signal is maintained at a level above a predetermined value because of formation of no short circuit between the rails, that is, only when these two conditions are satisfied, an alternating current output is generated on the secondary side of the third transformer, and a signal of the absence of a train is put out to excite the railway relay.
- the phase of the track signal is made different in respective track sections, and the presence of a vehicle is informed based on the result of the judgement of the voltage level and phase of the track signal.
- the phase of the local signal and track signal it is most advantageous to detect the zero level at which the polarity of the signal is changed.
- the threshold level for receipt of signals is elevated to broaden the noise-insensitive region.
- the judgement of the phase is precise when the alternating current signals, that is, the track signal and local signals, are close to the zero points, because the judgement is hardly influenced by changes of amplitudes of the signals.
- the output relay is operated by the on-off operation of the local signal by the thyristor through the first and third transformers, and the conventional apparatus cannot be integrated as a detection apparatus having so-called intelligent functions necessary for a train detection sensor, such as the function of a precise level judgement and the filter function.
- the level judgement of the track signal becomes impossible and even if a train is present and the track signal is at the low level, the circuit is constructed and an output is generated in the third transformer, with the result that no fail-safe effect is attained. This is a defect which is essentially caused because the voltage exciting the output relay depends on the frequency of the input signal, that is, the third transformer directly treats the frequency of the input signal.
- the track circuits are a kind of coded track circuits wherein one of rate codes is modulated by a local signal, the modulated code signal is delivered from a code transmitter through a typical track section and received by a receiver, the received signal which is applied as a track signal is demodulated to attain the code signal, a level judgement and a phase judgement of the demodulated code signal are performed and then existence or nonexistence of a vehicle on the track section is detected based on the both judgements.
- DE-A-2047147 describes an apparatus which includes the features of the pre-characterising part of claim 1.
- Another object of the present invention is to provide a vehicle detecting apparatus having a fail-safe effect.
- an apparatus for detecting a vehicle on a track which comprises a track circuit in which a local signal which is an alternating current voltage signal of a specific frequency is applied to a specific closed section of a pair of rails, and a track signal whose voltage varies according to the presence or absence of a vehicle on the rails, is produced, phase judgement means for judging whether the phase of the local signal and the track signal are the same, and level judgement means for judging whether a voltage level of the track signal is higher than a predetermined value and which produces a signal indicative of the absence of a vehicle on the pair of rails in the specific closed section only when both the local signal and the track signal are of the same phase and the level of the track signal is higher than the predetermined value, characterised in that the apparatus comprises:
- the first and second logical product circuits may be constructed by a single logical product computing oscillating circuit.
- the judgement of the phases can be performed at a low level to reduce the influences of variations of the amplitude and the level judgement can be performed at a high level to improve the noise resistance.
- the local input signal can be subjected to integration processing.
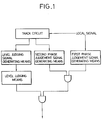
- a vehicle 1 runs on two rails 2 and 3 in the direction indicated by the arrow.
- the rails 2 and 3 are divided into a plurality of sections such as a specific section 4 and a section 5 rear with respect to the direction of advance of the vehicle.
- a transmission signal which is an alternating current reference voltage Vl (this signal is simultaneously fed to the reception side and acts as a local signal Sl ) is applied to the rails of each of the block sections 4 and 5.
- the rails 2 and 3 are utilized as parts of the circuit and the voltage Vt between the rails 2 and 3 is put out as a track signal St for reception.
- This circuit is known as the alternating current track circuit.
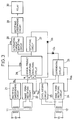
- the transmission signal of the track is a sine wave alternating current signal shown in Fig. 7-A and is put in a rectifying smoothening circuit 21 and a wave form rectifying circuit 22 through a transformer 11.
- the rectifying smoothening circuit 21 is a known circuit for rectifying and smoothening an alternating current signal arid forming a direct current output power source Vs.
- the wave form rectifying circuit 22 acts as the first phase judgement signal generating means and is a known circuit, for example, a Schmitt circuit for rectifying a sine wave local signal to a rectangular wave as shown in Fig. 7-C. By these circuits, a rectangular wave phase judgement signal vibrating with the reference voltage level being as the center is obtained.
- the track signal St is put in a level judging signal 23 and a wave form rectifying circuit 24 through a second transformer 12.
- the level judging circuit 23 is a circuit for detecting whether or not a voltage obtained by transforming the track signal St by the transformer 12 acting as the level judgement signal generating means, that is , a level judging signal, is higher than a predetermined value.
- this circuit comprises a level detecting circuit such as a Schmitt circuit and a known voltage doubling half-wave rectifying circuit for rectifying the output of this detecting circuit, which includes, for example, capacitors C1 and C2 and diodes D1 and D2, as shown in Fig. 4.
- a relatively high threshold level is set in the Schmitt circuit.
- the voltage doubling half-wave rectifying circuit rectifies and smoothens the alternating current voltage put out from the Schmitt circuit by the diode D2 and the capacitor C2 through the coupling capacitor C1 and the clamp diode D1 and a rectified output is obtained from an output terminal D.
- the voltage doubling half-wave rectifying circuit has such a fail-safe structure that at the time of a trouble such as disconnection, no rectified output is obtained (a known four-terminal capacitor which generates no output at the time of disconnection of a terminal is shown as the capacitor C2).
- the direct current voltage Vs of the rectifying smoothening circuit 21 is put in the rectifying circuit.
- the diode D1 is constructed so that a computing oscillator of the subsequent stage is oscillated by the output of the rectifying circuit by clamping the input signal from the capacitor C1 to this input power source Vs.
- the wave form rectifying circuit 24 has a threshold level sufficiently lower than the track signal St put in the circuit 24. Accordingly, a wave-rectified output which changes substantially at the zero point of the track signal St can be produced.
- a differential circuit 25 comprises, for example, a capacitor C3 and a resistor R1, as shown in Fig. 5, and has such a known structure that the reference voltage level is set at the above-mentioned level Vs. Thus, the phase of the track signal is generated substantially at the zero point (reference voltage level).
- the phase signal of the track signal only a positive signal is put into an input terminal c of a three-input logical product circuit 26 through a diode D4.
- a structure capable of performing a desired operation may be formed even by omitting the diode D4.
- the logical product circuit 26 has three input terminals a, b and c, and this circuit receives the output of the wave form rectifying circuit 22 at the input terminal a and the output of the level detecting circuit 23 at the input terminal b.
- the logical product circuit 26 is a logical product computing oscillating circuit shown in Fig.
- the logical product computing oscillating circuit generates an oscillating output when all of the inputs at the input terminals a, b and c are higher than the power source voltage Vs and has a fail-safe structure in which when a constituent element of the circuit gets out of order, oscillation is impossible and therefore, no output is generated at the time of a trouble,
- the type of the transistor is changed to NPN from PNP and the direction of the diode is reversed.
- Transistors Tr1 and Tr2 are connected to each other through an attenuation resistor R6, and the collector of the transistor Tr2 is connected to the base of a transistor Tr3 through a level shifting Zener diode ZD1 and the connecting point between a Zener diode ZD2 connected to the collector of the transistor Tr3 and a resistor R4 is connected to the base of the transistor Tr1 through a resistor R5.
- R2 and R3 represent collector resistors
- R7 represents a resistor on the leak current side, that is, a resistor for flowing of a leak current of the base of the transistor Tr3
- Vs represents an input power source
- C represents an output terminal.
- the operation of the transistors Tr1 through Tr3 is not reversed and the oscillation is stopped. Also when a trouble such as disconnection is caused in the circuit, the oscillation is stopped and no oscillating output is generated at the output terminal C.
- the Zener voltages VZD2 and VZD2 of the Zener diodes ZD1 and ZD2 be selected to satisfy the condition of VZD2 ⁇ Vs ⁇ VZD1.
- a computing oscillator of a high output can be constructed by connecting a known amplifier to the input terminal.
- the level judging circuit 23 and the rectifying circuit 27 described hereinafter may comprise, for example, the voltage doubling half-wave rectifying circuit, and this voltage doubling half-wave rectifying circuit and the logical product computing oscillator shown in Fig. 6 may be a known fail-safe logical product circuit in which no output is produced unless input signals are applied to all of the input terminals a, b and c, disclosed in, for example, Japanese Utility Model Application Laid-Open Specification No. 4764/82 or Japanese patent Publication No. 38211/76.
- the rectified output of the rectifying circuit 27 for rectifying the output of the logical product computing oscillating circuit 26 is fed back to the input terminal c, in which the output of the differential circuit 25 is put, through the diode D3.
- An alternating current amplifying circuit 28 amplifies the oscillating output of the logical product computing oscillating circuit 26, and the amplified output is rectified by a rectifying smoothening circuit 29 to drive a trade relay 30, as in the conventional apparatus.
- the above-mentioned transformer 12, wave form rectifying circuit 24, differential circuit 25, rectifying circuit 27 and diodes D3 and D4 constitute the second phase judgement signal generating means, and the wave rectifying circuit 24 and differential circuit 25 constitute the means for detecting the zero point of the track signal.
- the alternating current local signal shown in Fig. 7-A is put in the rectifying smoothening circuit 21 and wave form rectifying circuit 22 through the first transformer 11.
- the rectifying smoothening circuit 21 there is generated the direct current output Vs to be used as the power for driving the level detecting circuit 23, wave form rectifying circuits 22 and 24, amplifying circuit 28, logical product computing oscillating circuit 26 and track relay 30.
- a rectangular wave shown in Fig. 7-C is generated as the phase judging signal. This phase judging signal oscillates with the reference voltage level (corresponding to the zero point of the track signal) being as the center.
- the track signal St put in the second transformer 12 from the rails 2 and 3 has a shape of a sine save as shown in Fig. 7-B.
- the track signal St is put in the level judging circuit 23 and wave form rectifying circuit 24, and a rectified direct current output VL1 for detecting a level higher than a predetermined value, as shown in Fig. 7-D, is produced from the former circuit.
- a rectangular wave as shown in Fig. 7-E is put out from the latter circuit and a differential pulse as shown in Fig. 7-F is put out from the differential circuit 25.
- each of the outputs of the wave form rectifying circuits 22 and 24, level judging circuit 23 and differential circuit 25 is put out in the state where the direct current output Vs of the rectifying smoothening circuit 21 is over-lapped.
- each of positive pulses of the wave rectifying circuit 22, level judging circuit 23 and differential circuit 25 to be put into the input terminals a, b and c of the logical product computing oscillating circuit 26, respectively, has an input level higher than the power source voltage Vs at which initiation of the oscillation is possible,
- the phase judgement condition (the local signal and the track signal are of the same phase) is established (first logical product)
- the logical product (second logical product) of this established condition and the already established level judgement condition (the voltage level of the track signal is higher than a predetermined value) is established and oscillation is initiated in the logical product computing oscillating circuit 26.
- the oscillating output of the computing oscillating circuit 26 is put in the alternating current amplifying circuit 28 and is simultaneously rectified by the rectifying circuit 27 and fed back to the input terminal c through the diode D3 to self-retain the output of the computing oscillator 26 until the phase signal on the local signal side (Fig. 7-C) falls, whereby amplification of the pulse width is effected (see Fig. 7-G).
- the diode D3 prevents extinction of the differential pulse at the capacitor C2 of the rectifying circuit 27.
- the pulse width-amplified output, shown in Fig. 7-G, of the computing oscillating circuit 26 is amplified by the alternating amplifying circuit 28, rectified by the rectifying smoothening circuit 29 and supplied to the relay 30 to retain the relay 30 in the excited state. Namely, the absence of a train in the track circuit is informed.
- the track signal St put out from the wave rectifying circuit 24 is differentiated and the positive differential pulse is put in the computing oscillating circuit 26, whereby the oscillating output is self-retained and maintained.
- the phase to be judged is simultaneously determined.
- the judged value of the phase is changed with this change of the voltage level. This change becomes great as the set value for the judgement of the level is large.
- the conventional apparatus is disadvantageous in that if increase of the precision of the level judgement is intended, the precision of the phase judgement is reduced and if maintenance of a high precision of the phase judgement is intended, the precision of the level judgement is reduced.
- the set value for the level judgement can be increased, and the phase judgement can always be done at the point where the phase judging signal crosses the reference voltage, that is, at the point (zero point) where the track signal is changed to the positive value from the negative value. Accordingly, the detection precision can be elevated and the reliability can be improved.
- known fail-safe logical product computing oscillating circuit 26, level judging circuit 23, rectifying circuit 27, alternating current amplifying circuit 28 and differential circuit 25 are used, a fail-safe structure is realized in the detecting apparatus.
- the computing oscillating circuit 26 is not self-retained if the diode D3 is opened, a power sufficient to excite the relay 30 is not obtained, and since the differential pulse is absorbed in the capacitor C2 and no signal is put in the input terminal c of the computing oscillating circuit 26 if a short circuit is formed, a fail-safe effect is attained.
- the logical product of the level judgement and the phase judgement is made by one logical product circuit, but the present invention is not limited to this structure. Namely, there may be adopeted a structure in which the phase judgement is carried out by using a fail-safe logical product circuit, the relay 30 is driven by this judgement signal and the contact output of the relay driven by the output of the level judging circuit 23 is connected in series to the contact output of the relay 30.
- the rectifying circuit is used as the level judging circuit 23, it is obvious that the output may be rectified by using a known level detector of the alternating current input type.
- the input level of the track signal is stable, it is obvious that an alternating current output from the level detecting circuit of the level judging circuit 23, as indicated by a dot line in Fig. 3, can be utilized instead of the wave rectifying circuit 24. Furthermore, if the input detection level of the logical product circuit is made equal to the judgement level of the track signal, the logical product circuit can be utilized as the level judging circuit 23. In this case, it is sufficient if the level judging circuit 23 is replaced by a rectifying circuit.
- the capacity of the smoothening capacitor C2 of the interposed rectifying circuit can be increased, whereby an erroneous operation by a noise of the track signal or the like can be moderated.
- the local input signal is rectified to obtain a direct current power and precise and various level detections can be performed by this direct current power, and the logical computation is carried out as the logical processing of the output of such level detection and such processing can be integrated, whereby the size of the apparatus can be reduced. Moreover, when the apparatus gets out of order, the output is inevitably reduced to zero and the relay falls to the safe side, and a fail-safe effect can be assuredly attained.
- phase judgement can be made at a voltage level close to the reference level while the level judgement can be made at a voltage level higher than a predetermined value, and precise phase judgement and level judgement become possible.
- the apparatus for detecting a vehicle on a track is most effectively utilized for detecting a train on a rails in a signal system of a railroad line or in an unmanned operation system in a factory, a dockyard or an assorting or marshaling yard.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Train Traffic Observation, Control, And Security (AREA)
Claims (9)
- Appareil de détection d'un véhicule (1) sur une voie (2, 3), comprenant un circuit de voie dans lequel un signal local, qui est un signal de tension alternative d'une fréquence spécifique, est appliqué à une section spécifique fermée d'une paire de rails (2, 3), et un signal de voie dont la tension varie en fonction de la présence ou de l'absence d'un véhicule sur les rails, est produit, un moyen (22, 24, 25) d'évaluation de phase pour évaluer si les phases du signal local et du signal de voie sont les mêmes, et un moyen (23) d'évaluation de niveau pour évaluer si un niveau de tension du signal de voie est supérieur à une valeur prédéterminée et qui produit un signal indiquant l'absence d'un véhicule sur la paire de rails dans la section fermée spécifique uniquement lorsque le signal local et le signal de voie ont tous deux la même phase et le niveau du signal de voie est supérieur à la valeur prédéterminée,
caractérisé en ce que l'appareil comprend:un premier moyen (22) de génération d'un signal d'évaluation de phase qui reçoit le signal local sinusoïdal et le met sous la forme d'une onde rectangulaire dont le niveau de tension de référence est le niveau zéro du signal local, afin de produire un premier signal d'évaluation de phase pour évaluer la phase du signal local, ledit premier signal d'évaluation de phase étant une forme d'onde rectangulaire vibratoire centrée autour dudit niveau de tension de référence,un deuxième moyen (24, 25) de génération d'un signal d'évaluation de phase qui reçoit le signal de voie sinusoïdal et le met sous la forme d'une onde rectangulaire dont le niveau de tension de référence est le niveau zéro du signal de voie et produit un deuxième signal d'évaluation de phase pour évaluer la phase du signal de voie, ledit deuxième signal d'évaluation de phase étant une forme d'onde rectangulaire vibratoire centrée autour du niveau de tension de référence défini en dernier,un moyen (12) de génération de signal d'évaluation de niveau pour fournir un signal d'évaluation de niveau en vue d'évaluer un niveau du signal de voie, ledit signal d'évaluation de niveau étant une forme d'onde vibratoire qui est centrée autour d'un niveau de tension de référence dérivé du signal de voie,un premier circuit de produit logique (26) qui comprend une source d'énergie (Vs) et un circuit à semi-conducteur et est conçu pour recevoir le premier signal d'évaluation de phase fourni par ledit premier moyen (22) de génération d'un signal d'évaluation de phase et ledit deuxième signal d'évaluation de phase fourni par ledit deuxième moyen (24, 25) de génération d'un signal d'évaluation de phase, et pour produire un signal indiquant que les signaux d'évaluation de phase ont tous deux la même phase lorsque les deux signaux d'évaluation de phase ont la même phase et sont supérieurs à la tension (Vs) de la source d'énergie, mais qui ne génère aucun signal en cas de défaillance du premier circuit de produit logique due, par exemple, à un court-circuit ou à une coupure;un circuit d'évaluation de niveau (23) qui produit un signal lorsque le niveau de tension du signal d'évaluation de niveau est supérieur à une valeur prédéterminée qui est supérieure au niveau zéro du signal de voie, mais qui ne fournit aucun signal lors d'une défaillance du circuit d'évaluation de niveau due, par exemple, à un court-circuit ou à une coupure,un deuxième circuit de produit logique (26) qui produit un signal indiquant l'absence d'un véhicule uniquement lorsque le premier circuit de produit logique (26) et le circuit d'évaluation de niveau (23) produisent tous deux simultanément des signaux, mais qui ne produit aucun signal en cas de défaillance du deuxième circuit de produit logique due, par exemple, à un court-circuit ou à une coupure, etdans lequel le deuxième moyen (24, 25) de génération de signal d'évaluation de phase comprend un circuit différentiel (25) pour différentier le signal de sortie du circuit d'évaluation de niveau (23) et un moyen de retenue automatique pour réinjecter la sortie du premier circuit de produit logique (26) à l'entrée du premier circuit de produit logique à travers une diode (D3) et retenir automatiquement la sortie du premier circuit de produit logique. - Appareil de détection de véhicule selon la revendication 1, dans lequel le deuxième moyen de génération de signal d'évaluation de phase comprend un transformateur (12) pour transformer la tension du signal de voie, et un premier circuit redresseur de forme d'onde (24) pour redresser le signal de sortie du transformateur (12) en un signal rectangulaire centré autour de la tension de référence, ledit circuit différentiel (25) différentiant la sortie du premier circuit redresseur de forme d'onde (24).
- Appareil de détection de véhicule selon la revendication 1, dans lequel le circuit d'évaluation de niveau (23) comprend un circuit à seuil pour produire uniquement une tension supérieure à une valeur prédéterminée du signal d'évaluation de niveau produit par le moyen (12) de génération de signal d'évaluation de niveau et un circuit redresseur à une alternance, doubleur de tension (C1, C2, D1, D2) pour traiter le signal de sortie du circuit à seuil.
- Appareil de détection de véhicule selon la revendication 1, dans lequel le premier circuit de produit logique et le deuxième circuit de produit logique constituent un moyen oscillant (26) de calcul de produit logique possédant une borne d'entrée (a) pour recevoir la sortie du premier moyen (22) de génération d'un signal d'évaluation de phase, une borne d'entrée (b) pour recevoir la sortie du circuit d'évaluation de niveau (23), une borne d'entrée (c) pour recevoir la sortie du deuxième moyen (24, 25) de génération d'un signal d'évaluation de phase et une borne d'entrée d'une tension de référence pour recevoir un signal d'une tension continue Vs, et qui est construit de façon à ce qu'une sortie oscillante soit générée lorsque des tensions excédant la plage de la tension continue Vs sont appliquées simultanément aux trois bornes d'entrée (a), (b) et (c).
- Appareil de détection de véhicule selon la revendication 4, dans lequel le premier moyen (22) de génération d'un signal d'évaluation de phase comprend un deuxième circuit redresseur de forme d'onde pour redresser le signal local en un signal rectangulaire et pour fournir le signal rectangulaire à la borne d'entrée (a), et le deuxième moyen (24, 25) de génération d'un signal d'évaluation de phase comprend un premier circuit redresseur de forme d'onde pour redresser un signal de voie en un signal rectangulaire, un circuit différentiel (25) pour différentier la sortie du premier circuit redresseur de forme d'onde (24) et pour fournir la sortie différentiée à la borne d'entrée (c), un circuit redresseur (27) pour redresser la sortie oscillante du circuit oscillant (26) de calcul de produit logique et un moyen de retenue automatique comportant une diode (D3) pour injecter la sortie du circuit redresseur (27) à la borne (c).
- Appareil de détection de véhicule selon la revendication 4, dans lequel le moyen oscillant de calcul de produit logique comprend un premier transistor (Tr1) branché, par le biais d'une première résistance (R2) du collecteur, entre la borne d'entrée (a) et la borne d'entrée de la tension de référence, la tension du collecteur dudit premier transistor (Tr1) étant appliquée à la base par le biais d'une résistance d'atténuation, un deuxième transistor (Tr2) branché, par le biais d'une deuxième résistance (R3) du collecteur, entre la borne d'entrée (b) et la borne d'entrée de la tension de référence, la tension du collecteur du deuxième transistor étant appliquée à la base par le biais d'une première diode Zener (ZD1), une résistance de fuite (R7) interposée entre la base et la terre, et un troisième transistor (Tr3) branché, par le biais d'une troisième résistance (R4) du collecteur et une deuxième diode Zener (ZD2) étant appliquée à la base du premier transistor (Tr1) et une borne de sortie étant branchée entre la deuxième diode Zener (ZD2) et le collecteur du troisième transistor (Tr3).
- Appareil de détection de véhicule selon la revendication 6, dans lequel le premier moyen (22) de génération d'un signal d'évaluation de phase comprend un deuxième circuit redresseur de forme d'onde (22) pour redresser le signal local en un signal rectangulaire et pour produire un signal rectangulaire qui est injecté à la borne d'entrée (a), et le deuxième moyen de génération d'un signal d'évaluation de phase comprend un premier circuit redresseur de forme d'onde (24) pour redresser le signal de voie en un signal rectangulaire, un circuit différentiel (25) pour différentier la sortie du premier circuit redresseur de forme d'onde et pour produire un signal différentié qui est injecté à la borne d'entrée (c), un circuit redresseur (27) pour redresser la sortie oscillante du circuit oscillant (26) de calcul de produit logique et une diode (D3) pour injecter la sortie du circuit redresseur à la borne (c).
- Appareil de détection de véhicule selon la revendication 7, dans lequel le moyen (23) d'évaluation de niveau comprend un circuit à seuil pour produire une tension supérieure à une valeur prédéterminée du signal d'évaluation de niveau produit par le moyen (12) de génération de signal d'évaluation de niveau et un circuit redresseur à une alternance, doubleur de tension (C1, C2, D1, D2) pour traiter le signal de sortie du circuit à seuil.
- Appareil de détection de véhicule selon la revendication 1, dans lequel le premier moyen (22) de génération d'un signal d'évaluation de phase, le deuxième moyen (24, 25) de génération d'un signal d'évaluation de phase, le moyen (12) de génération d'un signal d'évaluation de niveau, le circuit (23) d'évaluation de niveau, le premier circuit (26) de produit logique et le deuxième circuit (26) de produit logique utilisent comme source d'énergie une sortie continue obtenue par redressement du signal local.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP1986/000508 WO1988002326A1 (fr) | 1986-10-03 | 1986-10-03 | Detecteur de vehicules sur une piste |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0288564A1 EP0288564A1 (fr) | 1988-11-02 |
| EP0288564A4 EP0288564A4 (fr) | 1989-06-21 |
| EP0288564B1 true EP0288564B1 (fr) | 1999-01-20 |
Family
ID=13874550
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP86905931A Expired - Lifetime EP0288564B1 (fr) | 1986-10-03 | 1986-10-03 | Detecteur de vehicules sur une piste |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0288564B1 (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE3650708T2 (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO1988002326A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE465458B (sv) * | 1990-01-25 | 1991-09-16 | Eb Signal Ab | Spaarledningssystem |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR1258776A (fr) * | 1960-06-08 | 1961-04-14 | Siemens Ag | Installation pour l'exploitation de tensions alternatives par comparaison à une tension de référence en particulier pour le service de sécurité des chemins de fer |
| DE2047147A1 (de) * | 1970-09-24 | 1972-03-30 | Sel | Einrichtung zum Überwachen von Gleisabschnitten für Eisenbahnverkehrs anlagen |
| FR2214620B1 (fr) * | 1973-01-19 | 1975-04-04 | Jeumont Schneider | |
| US4065081A (en) * | 1976-12-09 | 1977-12-27 | General Signal Corporation | Alternating current track circuits |
| US4417229A (en) * | 1980-10-15 | 1983-11-22 | Safetran Systems Corporation | Means for use on a railroad to distinguish between traction current and signal current |
| IT1150556B (it) * | 1981-06-26 | 1986-12-17 | Sasib Spa | Rele statico di binario in corrente alternata |
-
1986
- 1986-10-03 EP EP86905931A patent/EP0288564B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1986-10-03 WO PCT/JP1986/000508 patent/WO1988002326A1/fr not_active Ceased
- 1986-10-03 DE DE3650708T patent/DE3650708T2/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE3650708T2 (de) | 1999-07-01 |
| DE3650708D1 (de) | 1999-03-04 |
| WO1988002326A1 (fr) | 1988-04-07 |
| EP0288564A1 (fr) | 1988-11-02 |
| EP0288564A4 (fr) | 1989-06-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US6603306B1 (en) | Proximity switch, a target, a system of such proximity switches and targets, and a method of determining the presence of a target by a proximity switch | |
| US4525699A (en) | Electronic monitoring system with malfunction indicator | |
| US3696243A (en) | Broken rail detector | |
| JP2720107B2 (ja) | 鉄道信号システム | |
| US6504485B2 (en) | Monitoring apparatus and control apparatus for traffic signal lights | |
| CA1154831A (fr) | Recepteur a alimentation commandee par le signal | |
| EP0288564B1 (fr) | Detecteur de vehicules sur une piste | |
| US3553488A (en) | Fail-safe circuit arrangement | |
| US9882559B2 (en) | Wireless proximity sensor with a target device comprising an inverter | |
| US3752426A (en) | Train detector | |
| US3252141A (en) | Fail-safe control system | |
| KR830001844B1 (ko) | 차량의 기계 동작을 감지하는 장치 | |
| JPS6329457B2 (fr) | ||
| JP2934085B2 (ja) | 列車検知装置 | |
| JPH0678062B2 (ja) | 列車検知装置 | |
| US5074499A (en) | System for transmitting initialization information between fixed installations and trains | |
| US20030112062A1 (en) | Demodulation circuit and demodulation method | |
| US4056739A (en) | Fail-safe electronic polarized relay | |
| JPS6260032B2 (fr) | ||
| JP3588707B2 (ja) | 波形整形回路 | |
| KR940005035B1 (ko) | 무인차의 충돌방지 제어방법 및 그 장치 | |
| KR950003946Y1 (ko) | 열차감지회로 | |
| JPH0948348A (ja) | 自動列車停止装置 | |
| JPH0526708B2 (fr) | ||
| JP3586366B2 (ja) | 保守用車割出防止装置の地上装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19870413 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): DE GB |
|
| A4 | Supplementary search report drawn up and despatched |
Effective date: 19890621 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19910513 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE GB |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3650708 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19990304 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 19990421 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20020926 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20021028 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20031003 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20031003 |