EP0214837B1 - Procédé pour changer des bobines sur un banc à broches et dispositif pour effectuer ce procédé - Google Patents
Procédé pour changer des bobines sur un banc à broches et dispositif pour effectuer ce procédé Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0214837B1 EP0214837B1 EP19860306818 EP86306818A EP0214837B1 EP 0214837 B1 EP0214837 B1 EP 0214837B1 EP 19860306818 EP19860306818 EP 19860306818 EP 86306818 A EP86306818 A EP 86306818A EP 0214837 B1 EP0214837 B1 EP 0214837B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- bobbin
- bobbins
- bar
- peg
- peg bar
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01H—SPINNING OR TWISTING
- D01H9/00—Arrangements for replacing or removing bobbins, cores, receptacles, or completed packages at paying-out or take-up stations ; Combination of spinning-winding machine
- D01H9/02—Arrangements for replacing or removing bobbins, cores, receptacles, or completed packages at paying-out or take-up stations ; Combination of spinning-winding machine for removing completed take-up packages and replacing by bobbins, cores, or receptacles at take-up stations; Transferring material between adjacent full and empty take-up elements
- D01H9/04—Doffing arrangements integral with spinning or twisting machines
- D01H9/046—Doffing arrangements integral with spinning or twisting machines for flyer type machines
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a bobbin changing method in a roving frame and an apparatus for carrying out this bobbin changing method. More particularly, the present invention relates to a bobbin changing method in a roving frame in which full bobbins held on a bobbin wheel of a roving frame, having a top-support-type flyer, are exchanged with empty bobbins suspended by the respective bobbin supporting members which are arranged in advance in upper corresponding positions above the roving frame, and an apparatus for carrying out this bobbin changing method.
- a bobbin changing apparatus in which an operation of exchanging bobbins is carried out by a bobbin changer capable of running along a machine frame of a roving frame, is disclosed in Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication No. 50-89642.
- the exchange of bobbins is carried out for each bobbin held by the respective bobbin wheels of the roving frame by one bobbin changing arm moving forward and backward and in the vertical direction.
- each of two empty bobbins suspended by the respective bobbin supporting members of a transporting apparatus is held and taken out by the bobbin changing arm and placed on the corresponding peg of a bobbin reserving mechanism, and the bobbin reserving mechanism is swung to retreat the empty bobbins to the position where the taking-out of each full bobbins is not disturbed.
- the full bobbins are then taken out from bobbin wheels by the bobbin changing arm and mounted on the corresponding bobbin supporting members supported by the transporting apparatus, and the bobbin reserving mechanism is returned to the original position and the full bobbins are held by the corresponding bobbin changing arms and fed onto the corresponding bobbin wheels of the roving frame.
- the bobbin changing arm transfers full bobbins on the respective bobbin wheels of front and rear rows to the bobbin supporting members while maintaining the distance between the front and rear full bobbins as it is, the same distance as that between the full bobbins on the respective bobbin wheels of front and rear rows must be maintained between the bobbin supporting members of the transporting apparatus. If full bobbins suspended by the bobbin supporting members of the transporting apparatus are arranged in a zigzag manner, the automation of a roving bobbin exchange in a spinning frame becomes very difficult.
- two bobbin changing arms working separately for the front and rear rows of bobbin wheels, are used for full bobbins and empty bobbins, respectively, and independent moving mechanisms are used to cause the respective bobbin changing arms to make forward-backward movements and vertical movements between the respective bobbin wheels of the roving frame and the corresponding bobbin supporting members of a bobbin delivery means. Accordingly, the construction becomes complicated and it is impossible to design the bobbin changing apparatus in a compact form.
- the basic technical idea for attaining this object is that the unitary cycle of bobbin changing work, consisting of the bobbin changing operation of displacing and exchanging full bobbins and empty bobbins between the respective bobbin wheels of a roving frame and the corresponding bobbin supporting members which are arranged in advance in upper corresponding positions above the roving frame concerned is divided into the step of vertically moving each one of the full bobbins and the corresponding one of the empty bobbins between a bobbin transfer position, which is common for each one of the full bobbins and the corresponding one of the empty bobbins, at the level of the bobbin wheels of the roving frame and a bobbin holding and releasing position of the bobbin supporting member, which is common for the each one of the full bobbins and the respective one of the corresponding empty bobbins, along the same course, except for a part thereof, and the step of transferring the bobbins between the respective bobbin wheels of the roving frame
- the construction of the bobbin changing apparatus for carrying out this bobbin changing method is greatly simplified and the apparatus can be made compact, and the bobbin changing operation can be performed assuredly and promptly. Furthermore, since in the displacing courses for full bobbins and empty bobbins, the bobbin transferring position and the bobbin holding releasing position of each one of the bobbin supporting members are common to the corresponding full bobbin and empty bobbin, in order to avoid interference in the vertical movements of the full bobbins and empty bobbins, a stand-by position for each empty bobbin is formed in the displacing course for each one of the empty bobbins at a position deviated from a linear course connecting the above-mentioned holding and releasing position and the bobbin transferring position.
- the bobbins are moved in the state where the upper flange portion of each bobbin is suspended; and where the full bobbins are elevated from their transfer positions to the respective corresponding bobbin holding and releasing positions of the bobbin supporting members and are held by the respective corresponding bobbin supporting members, and where the empty bobbins are received from the bobbin supporting members and are brought down to the above-mentioned respective transfer positions, the bobbins are displaced in the state where each bobbin is held at the bottom thereof.
- the manner of holding bobbins to be displaced is changed at the above-mentioned respective common bobbin transfer position. Accordingly, in the bobbin changing apparatus of a roving frame according to the present invention, the apparatus height can be effectively reduced, and thus the method according to the present invention contributes greatly to the compactness of the bobbin changing apparatus.
- the bobbin changing method in a roving frame based on the above-mentioned basic technical concept, according to the present invention, is a bobbin changing method in which the bobbin changing operation of a group of bobbins is carried out by using a bobbin changing apparatus for empty bobbins prepared and arranged in advance at an upper position of the roving frame and full bobbins held on bobbin wheels of the flyer frame.
- the bobbin changing apparatus After completion of the above-mentioned unit operation for a group of bobbins, the bobbin changing apparatus is displaced along bobbin rails and is located at a position corresponding to bobbin wheels for the subsequent unit operation, and this unit operation is repeated, until the above-mentioned bobbin changing operation is completed for all bobbin wheels of a roving frame.
- This method is characterized by the following constitutional elements of the invention, that is, the bobbin changing operation is carried out by displacing full bobbins and empty bobbins along the respective bobbin moving courses formed between the positions of bobbin wheels of the roving frame and the corresponding positions for holding bobbins by the respective bobbin supporting members and releasing these bobbins therefrom above the roving frame; a common lower bobbin transfer position is formed in each of the above-mentioned bobbin displacing courses, to which position a full bobbin taken out from a bobbin wheel of the roving frame is carried before this bobbin is displaced to the above-mentioned position for holding by the corresponding bobbin supporting member and empty bobbin previously received from the corresponding supporting member is displaced before this empty bobbin is carried to a such position for mounting the corresponding bobbin wheel of the roving frame, at substantially the same height level as the height of the bobbin wheels within the bobbin changing apparatus; the
- a bobbin transporting apparatus comprising a plurality of transporting members, each having a plurality of bobbin supporting members for suspending a bobbin is travelled along transporting rail means laid out in the longitudinal direction of the roving frame in the upper portion of the roving frame and is stopped at predetermined positions for carrying out the bobbin changing operation.
- the pitches of bobbin supporting members are made to correspond with the pitches of bobbin hangers of the creel of a spinning frame. Accordingly, when the operation is carried out in a roving frame in which front and rear rows (two rows) of bobbin wheels are arranged, this two-row arrangement is not in agreement with the one-row arrangement of the bobbin supporting members and the operation is disturbed by this disagreement.
- a peg bar for full bobbins and a peg bar for empty bobbins are used for moving full bobbins and empty bobbins between the above-mentioned common lower transfer positions and the common upper transfer positions for the respective bobbin supporting members, these two peg bars are moved between the position coinciding to the common lower and upper bobbin transfer positions along the above-mentioned respective displacing courses except an intermediate stand-by position for each peg bar for empty bobbins, a carrying mechanism is used to carry full bobbins and empty bobbins between the respective bobbin wheels of the roving frame and the respective corresponding common lower bobbin transfer positions, the full bobbins received from the respective bobbin wheels of the roving frame are transferred to the respective corresponding peg bar for full
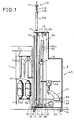
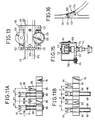
- a bobbin changing machine AD is positioned at a predetermined position in front of a roving frame 1.
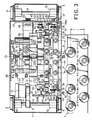
- top support type front and rear flyers 3 are disposed in a zigzag manner on a top rail 2 of the roving frame 1 and one group of four top support type flyers 3 are arranged in one staff so that a pitch P1 (Fig. 3) is maintained between adjacent flyers 3 and a pitch P2 is maintained between adjacent flyers 3 of adjacent groups, in the longitudinal direction of the top rail 2.
- a distance L is set between the front and rear rows of the flyers 3.
- the flyers 3 are rotated at a high speed through driving shafts and gears (not shown) arranged within the top rail 2.
- a bobbin rail 4 is vertically movably arranged, and bobbin wheels 5a and 5b concentric with the flyers 3 are arranged on the bobbin rail 4 and are rotated at a high speed through driving shafts and gears (not shown).
- This automatic bobbin changing system comprises the bobbin changing apparatus AD of the present invention and a roving bobbin transporting apparatus CR located above a roving frame 1.
- the bobbin changing apparatus AD is first described.
- running wheels 9 secured to wheel shafts 8 are rotatably supported on a bottom plate 7 of a body 6 of the bobbin changing apparatus AD through a pair of bearings 10 at front and rear parts thereof, in the running direction.
- a driven pulley 11 is secured to one wheel 8 (the left wheel in Fig. 3) and a timing belt 14 is mounted between this pulley 11 and a driving pulley 13 of a driving motor 12 located on the bottom plate 7.
- the running wheels 9 are mounted on running rails 15 laid out on the front floor surface of the roving frame 1 along the entire length of the roving frame 1, so as to be able to run in the longitudinal direction thereof.
- Approach members 16 are arranged at respective staff centers (bobbin changing centers CL1, CL2, ..., of the roving frame 1) between bobbin wheels 5a and 5b on the floor surface along the longitudinal direction of the machine frame.
- a proximity switch 17 capable of detecting the approach member 16 is secured to the bottom plate 7 of the machine body 6 of the bobbin changing apparatus AD at a position conforming to the center of the pitch of bobbin changing arms for the respective second and third front and rear rows of a bobbin changing bar (described below as bobbin changing center CL of the bobbin changing apparatus AD).
- bobbin changing center CL of the bobbin changing apparatus AD The construction of the bobbin changing bar and bobbin changing arms will be explained in detail later.
- the bobbin changing apparatus AD When the driving motor 12 is driven, the bobbin changing apparatus AD is displaced on the running rails 15 along the front face of the roving frame 1, and when the approach member 16 confronts the proximity switch 17, the bobbin changing apparatus AD is atopped at a predetermined bobbin changing position.
- Pegs 20 for one staff are arranged on the top face of the full bobbin peg bar 18 so that the distance between two adjacent pegs 20 is equal to the bobbin pitch P of a spinning creel.
- Each peg 20 is vertically slidable on the upper face of the full bobbin peg bar 18 and is urged upward by a spring 21, and the top end of the peg 20 is positioned by a fall- preventing screw 22.
- Guide blocks 23 are secured to both the left and right ends of the full bobbin peg bar 18, and these guide blocks 23 are slidably mounted on the corresponding respective guide bars 27 mounted perpendicularly to the corresponding respective slide blocks 26, which are slidably mounted on the corresponding respective guide bars 25 extended from the left and right end portions of the bottom plate 7 of the machine body 6 to the top plate 24 thereof.
- One end of each of first and second links 28 and 29 is connected by a pin to the front faces of the left and right guide blocks 23 and the front faces of the left and right slide blocks 26, respectively.
- both ends of the full bobbin peg bar 18 can be extended to create a pair of end portions having the same function as the above-mentioned guide block 23.
- a pin 31 on the side of each slide block 26 is located vertically below a pin 30 on the side of the corresponding guide block 23.
- the other ends of the first and second links 28 and 29 are turnably connected by a pin to supporting shafts of a corresponding cam follower 32.
- Cam plates 34 confronting the corresponding cam followers 32 and having a inwardly inclined face 34a are attached to left and right outer side plates 33 of the full bobbin guide bars 25 of the body 8, in the vertical direction of the machine body 6 substantially along the entire length thereof (the cam plates 34 are omitted in Figs. 1 and 2).
- the intervening space between the two inclined faces 34a is narrowed upward as shown in Fig. 5.
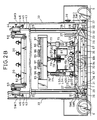
- a driving shaft 35 is rotatably supported on the bottom plate 7 over the distance between the side plates 33 along the running direction of the bobbin changing apparatus AD.
- Driving sprockets 36 are secured to the both end portions of the driving shaft 35 between the full bobbin guide bars 25 and the side plates 33 in both sides, and a sprocket 37 is secured to one end of the driving shaft 35 which projects toward the running wheel beyond the side plate 33 as shown in Fig. 2B.
- a chain 40 is mounted between this sprocket 37 and a sprocket 39 of the rotation shaft of a driving motor 38.
- Driven sprockets 41 are rotatably supported on a respective bracket attached to the top plate 24 vertically above the corresponding driving sprockets 36, and lifting chains 42 are mounted between left and right corresponding driving and driven sprockets 36 and 41, respectively (Fig. 1).
- a cam lever 46 having a cam follower 45 is connected by a key to one end of a shaft 47 rotatably mounted on the lift block 44 on the side of the corresponding side plate 33 and is swung in the front-rear direction (left-right direction in Fig. 6), and a fan-shaped sector gear 48 is connected by a key to the other end of the shaft 47.
- This sector gear 48 is engaged with a gear 51 of a swinging arm 50 supported by a supporting shaft 49 and swingably movable in the vertical direction.
- the shaft 49 is secured to each lift block 44.
- Each swinging arm 50 clips a stationary shaft 52 with the top end thereof and a pair of timing belt pulleys 53 integrally secured to both the left and right sides of the empty bobbin peg bar 19 are rotatably fitted to the corresponding swinging arm 50.
- a timing pulley 54 is connected by a key to the top end of each supporting shaft 49 so that the pulley 54 does not turn relative to the corresponding lift block 44.
- Timing belts 56 is mounted between the above-mentioned each pair of timing pulleys 54 and 53 through a respective tension pulley 55, so that even if the swinging arms 50 swing, the empty bobbin peg bar 19 is always kept at the horizontal posture.
- Driving sprockets 57 secured to a driving shaft 58 are rotatably supported at the bottom plate 7 of the machine body 6 of the bobbin changing apparatus in the rear of the empty bobbin guide bars 43, and a driven sprocket 59 is secured to one end of the driving shaft 58 and a driving chain 62 is mounted between this sprocket 59 and a sprocket 61 of a driving motor 60 (see Figs. 1 and 3).
- Driven sprockets 63 corresponding to the driving sprockets 57 are pivoted in the vicinity of the top plate 24 vertically above the driving sprockets 57.
- a pair of lift chains 64 are mounted between each pair of these driving and driven sprockets 57 and 63, and an intermediate part of each chain 64 is connected to the rear face of the corresponding lift block 44 (see Fig. 6).
- Grooved cam plates 64 having a cam groove 65a, in which the cam followers 45 are fitted and guided, are secured to the inner sides of the left and right side plates 33.
- Each cam groove 65a is formed to have a cam groove shape such that with the vertical movement of each lift blocks 44, the empty bobbin peg bar 19 can be displaced along a locus T shown in Fig.
- each peg 20 is located in the rear of the empty bobbin guide bar 43 so that the pegs 20 do not interfere with the vertical movement of the full bobbin peg bar 19 carrying full bobbins FB thereon.
- the upper receiving position S8 of the empty bobbin peg bar 19 and the common upper transfer position S6 and completion position (fall end) S5 of the common lower transfer position of the empty bobbin peg bar 19 are in agreement with the respective positions S4, S2, and S1 of the full bobbin peg bar 19.
- the lift device for the empty bobbin peg bar 19 is thus constructed with a mechanism for forward-backward movement.
- brackets 67 are arranged on the left and right sides at positions equidistant with respect to the bobbin changing center CL.
- Horizontal guide bars 68 are laterally arranged between the brackets 67 and rear plates 66.
- a supporting block 69c is secured on the axial line of the bobbin changing center CL and a feed bar 69a parallel to the horizontal bars 68 is rotatably supported between the supporting block 69c and the rear plate 66.
- a sprocket 69b is secured to the end of the feed bar 69a on the side of the rear plate 66, and a chain 71 b is mounted between this sprocket 69b and a sprocket 85 of a motor 70.
- a feed screw 72 is formed on the feed bar 69a substantially along the entire length thereof.
- Legs of a gate-like slide base 73 are fitted in the horizontal guide bars 68 movably in the front-rear direction, and a plate 74 is secured to the lower faces of the legs.
- a feed bracket 75 having a female screw engaged with the feed screw 72 of the feed bar 69 is secured to this plate 74.
- Lift bars 77 arranged vertically on the left and right lower parts of a bobbin changing bar 76 are vertically movably fitted on the upper portions of the legs of the slide base 73 respectively.
- a lift screw lever 78 is vertically mounted at an intermediate part between the lift bars 77 of the bobbin changing bar 76, and a female screw 80 of a driving sprocket 79 rotatably supported on the slide base 73 is screwed to the screw lever 78.
- a chain 83 is mounted between the driving sprocket 79 and a sprocket 82 of a driving motor 81 secured to the slide base 73.
- the bobbin changing bar 76 can make a forward-backward movement on the front side of the roving frame and a vertical movement.
- the upper face of the bobbin changing bar 76 is opened to form sliding faces 84, and sliders 85 and 86 for the front and rear rows, which have bobbin changing arms (bobbin changing arms for the front and rear rows) described below, are alternately arranged on the sliding faces 84 in the order of the slider for the front row and the slider for the rear row from the left side, when seen from the back face of the machine body 6 of the bobbin changing apparatus AD, as shown in Fig. 9.
- the sliders 85 and 86 are movable only in the left-right direction (Fig.
- a groove cam 93 having cylindrical cam grooves 93A and 93B formed on both sides with a distance corresponding to the distance between the sliders 85 and 86 for the front and rear rows, is slidably spline-fitted to the spline shaft 89.
- Cam followers 95 are arranged on the lower faces of the sliders 85 and 86 for the respective front and rear rows at positions corresponding to the cam grooves 93A and 93B. These cam followers 95 are engaged with the corresponding cam grooves.
- the sliders 85 and 86 for the respective front and rear rows slide in two adjacent groove cams, except those located on both the ends, and when these groove cams 93A and 93B are turned by a predetermined angle e (between points A and B shown in Fig. 10), the slider pitch is changed from P1 to P (or vice versa) (Fig.
- Each slider 85 for the front row has, integrated therewith, each bobbin changing arm 96 for the front row, which can confront the row of bobbin wheels 5a of the roving frame 1, and the bifurcate top end of the slider 85 supports a flange B1 of the upper portion of the bobbin from below.
- Each one of sliders 86 for two bobbins of the rear row is provided with a bobbin changing arm 97 for the corresponding one of two bobbins of rear row, which can confront the row of bobbin wheels 5b, and each bobbin changing arm 97 for the bobbins of rear row has bifrucated fork portion connecting the tip ends of left and right guide levers 98.
- the guide levers 98 are inserted in slide apertures 99 of the respective sliders 86 for the two bobbins of the rear row so that the bobbin changing arms 97 for the two bobbins of the rear row can slide in the front-rear direction.
- Racks 100 are formed on the lower sides of each guide lever 98.
- a pinion 101 rotatably supported on each slider 86 for the rear row is engaged with the rack 100.
- the pinion 101 is spline-fitted to the spline shaft 90 and each slider 85 for the bobbin of front row is freely fitted to the corresponding spline shaft 90.
- the device for changing the front-rear distance between the bobbin changing arms 96 and 96 for the respective front and rear rows is thus constructed.
- the tooth numbers of respective gears of the gear row 91 are set so that when the spline shaft 89 is turned by e, each bobbin changing arm 97 for the rear row is displaced by L, and the operation of changing the zigzag arrangement of bobbins of one staff in the roving frame 1 to the arrangement in agreement with the bobbin arrangement of the spinning creel (or reverse change), as shown in Fig. 11, can be synchronously performed by one driving motor 92.
- proximity switches SW1 through SW8 are arranged at predetermined positions in the vertical direction.
- the proximity switches SW1 through SW4 are for detecting approach members 102 (Fig. 2) mounted on the slide blocks 26 of the full bobbin peg bar 18, and these proximity switches SW1 through SW4 confirm, in the order form below, the preparation position (lower end) S1 of the position for lower transfer operation of the full bobbin peg bar 18, the slightly elevated receiving position S2 of the above-mentioned position for the lower transfer operation, and the intermediate stop position S3 and the position for upper transfer operation S4, respectively, to stop the driving motor 38 (Fig. 3) and stop the full bobbin peg bar 18 at the respective positions.
- the proximity switches SW5 through SW8 are for detecting approach members 103 (Fig. 3) projected from the rear faces of the slide blocks 44 of the empty bobbin peg bar 19, and these proximity switches SW5 through SW8 confirm, in the order from below, the completion position (lower end) S5 of the position for lower transfer operation of the empty bobbin peg bar 19, the slightly elevated receiving position S6 of the position for the lower transfer operation, the stand-by position S7 shown in Fig. 8, and the position for upper transfer operation S8, respectively, to stop the driving motor 60 (Fig. 3) and stop the empty bobbin peg bar 19 at the respective positions.
- Limit switches LS1 through LS3 are for confirming the retreat end of the slide base 73, the transfer position (the position where the forks of the bobbin changing arms 96 and 97 for the bobbins of front and rear rows are arranged in one line vertically above the line of the pegs of the full bobbin peg bar 18), and the front ends of the forks of zigzag bobbin changing arms for the respective bobbins of front and rear rows on zigzag bobbin wheels, and the limit switches LS1 through LS3 are energized by a dog 104 attached to the leg of the slide base 73 to stop the slide base 73 at the respective positions. Furthermore, as shown in Fig.
- a dog 105 is attached to one slide bar 77 on the lower face of the slide base 77 and upper and lower limit switches LS4 and LS5 are arranged on the slide based through brackets to confirm the rise end and drop end of the bobbin changing bar 76 and stop the bobbin changing bar 76 at the respective positions.
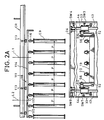
- a roving bobbin transporting unit CR used in combination with the bobbin changing apparatus AD of the present invention will now be described with reference to Fig. 2 and Figs. 12 through 17.
- a main transporting rail connecting the roving frame 1 to the creel of the spinning frame (not shown) is laid out above the end side of the machine frame.
- a branched transporting rail 111 on the side of the roving frame is connected to the main transporting rail 110 through a changeover switch device 112.
- the branched transporting rail 111 is disposed vertically above the full bobbin peg bar 18 of the bobbin changing apparatus AD at the time of bobbin changing along the bobbin wheels 5a and 5b of the roving frame 1 and is laid out at the rear of the machine frame while bypassing the outer end side of the machine frame.
- Each of the transporting rails 110 and 111 has a rectangular cross-section having the lower side opened, and wheels 113 roll within the transporting rails 110 and 111 to displace bobbin transporting members 114 for the transportation of roving bobbins along the transporting rails 110 and 111.
- a plurality (6 in the present embodiment) of bobbin supporting members 116 are suspended from the lower side of a base plate 116 of the bobbin transporting member 114 while keeping the bobbin pitch P of the spinning creel in the longitudinal direction between two adjacent bobbin supporting members 116.
- the bobbin transporting members 114 are connected to each other through a connecting lever 117, These bobbin transporting member 114 are connected so that roving bobbins of one roving frame can be held, whereby a large bobbin transporting unit 118 is constructed.
- the bobbin changing centers are set at points L1, L2, Vietnamese, that is, these centers are set at the center between the second and third bobbin supporting member 116 members counted from the bobbin supporting member 116 located on the right end in Fig. 2A and the positions apart from this center by 4.P and multiples thereof.
- a driving device 119 which is provided with a mechanism for displacing the transporting unit 118, is mounted on the transporting rail 110 in a condition wherein it is capable of running on the branched transporting rail.
- a plurality of driving devices 119 are arranged at intervals shorter than the entire length of the transporting unit 118. In this driving device 119 (Figs.
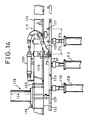
- swinging arms 122 are supported swingably in the horizontal direction with a vertical shaft 121 on both sides of a base 120 secured across the transporting rails 110 and 111, a rotary disk 123 is rotatably supported on one swinging arm 122, and a rotary disk 125 attached to a driving motor 124 is rotatably supported on the other swinging arm 122, so that the rotary disk 125 confronts the rotary disk 123.
- the base plate 115 of the bobbin transporting member 114 is clipped from both sides by the force of a spring 126 and the rotary disk 125 is positively driven to move the bobbin transporting unit 118.
- a proximity switch PX for detecting the positioning split cotter pin 127 is attached to the transporting rail 111 through a bracket 128 (see Fig. 15). On the side opposite to the proximity switch PX, a catcher 129 is swung by the operation of a cylinder 130 mounted on the rail 111. (see Fig. 14).
- the transporting unit 118 is at the first bobbin changing position L1
- the first positioning split cotter pin 127 confronts the proximity switch PX and the catcher 129 is capable of engaging to the split cotter pin 127, and after the completion of the bobbin change operation for the first bobbin transporting member 114, the catcher 129 is capable of disengaging from this positioning split cotter pin 127.
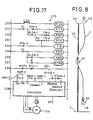
- the driving motor 124 and cylinder 130 make a one-pitch (P4) feeding of the bobbin transporting unit 118, and after completion of the bobbin changing operation, displace the bobbin transporting unit 118 to the spinning process to feed full roving bobbins to the spinning frames, and displace the bobbin transporting unit having empty bobbins EB to the roving frames which must carry out the bobbin changing operation by a control circuit 210 shown in Fig. 17.
- a controller SPC is disposed to control the driving motor 124, and turning-ON and turning-OFF of the motor and changing of the rotation speed or rotation direction are controlled by opening and closing contacts RMH-1 and the like.
- the changeover switch device 112 (see Fig. 16) comprises a supporting bracket 131 secured to the transporting rail 110 and a solenoid 133 turnably mounted to the bracket 131, a swing arm 134 turnably pivoted on a free end portion of a piston of the solenoid 133, a delivery course changeover plate 32, one end portion of which is connected by a pin to the other end of the swing arm 134 in a condition such that the plate 132 is capable of taking two guide positions for guiding the transporting unit 118 along the transporting rail 110 or to the branched transporting rail 111.
- the bobbin changing operation by the above-mentioned preferable embodiment will be hereinafter described in detail.
- the transporting unit 118 having empty bobbins EB is displaced to the branched transporting rail 111 along the front face of the roving frame 1 from the main transporting rail 110.
- the driving device 119 closes a contact Hi of a high speed switch of the circuit 205 shown in Fig.
- a contact RTHR-1 connected to the controller SPC of the circuit 209 is closed and the forward end of the cylinder 130 turns ON the forward end limit switch LSA (circuit 200) to turn ON a relay RLSA, whereby a contact RLSA-2 of the contact 206 is closed to turn ON a relay RMH and close contacts RMH-1 and RMH-2 of the circuit 209, and the driving motor 124 (Fig. 14) of the driving device 119 is reversed at a high speed to displace the transporting unit 118 at a high speed by the rotary disk 125.
- the proximity switch 135 As shown in Fig.
- the contact Hi of the circuit 205 is opened and the solenoid SOL is changed over to retreat the cylinder 130 and engage the catcher 129 with the first positioning split cotter pin 127, whereby the bobbin changing center L1 of the transporting unit 118 is made to correspond with the bobbin changing center CL1 of the roving frame 1 and the transporting unit 118 is stopped at the bobbin changing position.
- the bobbin changing bar 76 is located at the position of the lower end or retreat end (stand-by position), the full bobbin peg bar 18 is located at the preparation position (lower end position) S1 of the common lower transfer position and the empty bobbin peg bar 19 is located at the stand-by position S7 (Fig. 18A).
- the one-line arrangement of the bobbin changing arms 96 and 97 for the respective front and rear rows of the bobbin wheels (hereinafter refers only to the respective front and rear rows) is changed to the zigzag arrangement, and simultaneously, by rotating the feed bar 69a, bobbin changing bar 76 is advanced toward the full bobbins FB on the respective bobbin wheels 5a, 5b and is stopped at the forward end.
- the forks of the bobbin changing arms 96 and 97 for the respective front and rear rows are inserted below the upper flanges BT of the corresponding full bobbins FB and the lift screw lever 78 is turned to raise the bobbin changing bar 76 to the rise end and suspend the full bobbins FB on the respective bobbin changing arms 96 and 7 for the respective front and rear rows.
- the empty bobbin peg bar 9 is moved forward from the standby position S7 by driving the lift chains 64, and raised to the upper transfer position S8, and four empty bobbins EB of the transporting unit 118 at the bobbin changing position are loaded on the pegs 20 of the empty bobbin peg bar 9 (Fig. 18B).
- the empty bobbin peg bar 19 having the empty bobbins EB loaded thereon is displaced downward, and retreated and stopped at the stand-by position S7.
- the bobbin changing bar 76 is being retreated, the bobbin changing arms 96 and 97 for the respective front and rear rows, which have the full bobbins FB suspended therefrom, are re-arranged from the zigzag arrangement into a one-line arrangement, and the bobbin changing arms 96 and 97 for the respective front and rear rows are stopped at the transfer position where the respective full bobbins FB taken out are located vertically above the respective pegs 20 of the full bobbin peg bar 18.
- the full bobbin peg bar 18 is slightly elevated, and the full bobbins FB are placed on the respective pegs 20 at the receiving position S2 (see Fig. 18C). Then, the bobbin changing bar 76 is retreated to the retreat end and the lift chain 42 are driven to elevate the full bobbin peg bar 18 upward in the vertical direction and attach the full bobbins FB to the bobbin supporting member 116.
- the empty bobbin peg bar 19 located at the stand-by position S7 is displaced downward to the lower transfering position S6 where the bobbin changing arms 96 and 97 of the bobbin changing bar 76 for the respective front and rear rows, located at the elevated end and retreat end in the one-line arrangement, are at a height allowing insertion of their furcate free end portions into the upper flanges BT of the corresponding empty bobbins EB (Fig. 18D).
- the full bobbin peg bar 18 is displaced downward and stopped at the intermediate stop position S3, and the bobbin changing arms 96 and 97 for the respective front and rear rows, which are located at the rise end and retreat end in the one-line arrangement, are advanced and stopped at the above-mentioned transfer position and the furcate free end portions of the bobbin changing arms 96 and 97 are inserted below the respective upper flanges BT of the corresponding empty bobbins EB.
- the empty bobbin peg bar 19 is then slightly displaced downward and located at the completion position (lower end position) S5 of the common lower transfer position which coincides with the above mentioned position S6, and the empty bobbins EB are suspended in a one-line arrangement of the bobbin changing arms 96 and 97 for the respective front and rear rows (Fig. 18E). Then, while the one-line arrangement of the bobbin changing arms 96 and 97 for the respective front and rear rows is changed to the zigzag arrangement, the bobbin changing bar 76 is located on the advance end and the bobbin changing bar 76 is displaced downward, and the empty bobbins EB are attached to the corresponding empty bobbin wheels 5a and 5b of the roving frame 1 (Fig. 18F).
- the bobbin changing bar 76 is retreated to the retreat end, and the zigzag arrangement of the bobbin changing arms 96 and 97 for the front and rear rows is changed to the one-line arrangement (Fig. 18G). Then, the empty bobbin peg bar 19 located at the completion position S5 of the common lower transfer position is displaced upward to the stand- by position S7 and the full bobbin peg bar 8 located at the intermediate stop position S3 is displaced downward to the preparation position S1 of the common lower tranfer position, see Fig. 18.H.
- the bobbin changing apparatus AD When one cycle of the bobbin changing operation is thus completed, the bobbin changing apparatus AD is displaced to the position for the next bobbin changing operation. At this point, a contact Pi (for issuing a one-pitch feed signal) of the circuit 201 shown in Fig. 17 is closed to turn ON a relay RTP. Thereupon, a contact TRP-1 of the circuit 208 is turned OFF to effect changeover of the solenoid SOL of the solenoid valve of the cylinder 130, and the cylinder 130 is advanced to swing the catcher 129 upward and release the engagement with the first positioning split cotter pin 127.
- a contact Pi for issuing a one-pitch feed signal
- a contact TRP-1 of the circuit 208 is turned OFF to effect changeover of the solenoid SOL of the solenoid valve of the cylinder 130, and the cylinder 130 is advanced to swing the catcher 129 upward and release the engagement with the first positioning split cotter pin 127.
- the cylinder 130 turns ON the limit switch LSA to turn ON a relay RLSA, and a contact RLSA-1 of the circuit 202 is turned ON and a relay RMP is turned ON. Accordingly, contacts RMP-1 and RMP-2 of the controller SPC of the circuit 209 are turned ON to rotate the driving motor 124 at a low speed in the normal direction and move the transportation unit 118 in the direction of arrow B in Fig. 19.
- the proximity switch contact PX of the circuit 203 and relay RPX are turned ON (at this point, the contact PI is turned OFF), and the contact RPX-1 of the circuit 201 is turned OFF, the relay RTP is turned OFF, RPX-2 of the circuit 204 is turned ON and a timer TR is turned ON.
- the contact TRP-1 of the circuit 208 is turned ON to effect changeover of the solenoid SOL, and the timer TR turns the driving motor 124 in the normal direction excessively for a predetermined time so that the cylinder 130 is retreated, the catcher 129 is brought down, the transportation unit 118 is displaced at a low speed, the second positioning split cotter pin 127 which has been moved is caught by the catcher 129, and the second positioning split cotter pin 127 is firmly pressed to the front end portion of the catcher 129.
- the timer TR runs out, the timer contacts TR-1 and TR-2 are turned OFF, the relays RMP and RPX are turned OFF, the timer TR is reset, and the driving motor 124 is stopped.
- the transporting unit 18 is displaced by one pitch P4, and as shown in Fig. 19B, the bobbin changing center C1 of the bobbin changing apparatus AD is made to correspond with the second bobbin changing centers CL1 and L2 of the roving frame 1 and the transporting unit 118, and the second bobbin changing operation is started.
- the contact Hi is closed at the circuit 205 to turn ON the relay RTH and turn OFF the contact RTH-1 and to effect changeover of the solenoid SOL, whereby the cylinder 130 for the catcher 129 is advanced to elevate the catcher 129 and the limit switch LSH at the advance end is turned ON to turn ON the relay RLSA and turn ON the relay RMH.
- the contacts RMH-1 and RMH-2 connected to the controller of the circuit 209 are closed, and at this point, since the contact RTHR-2 is closed, the driving motor 124 is rotated at a high speed in the normal direction and the transporting unit 118 suspending full bobbins for one spinning frame is transported to the position adjacent to the creel of the spinning frame.
- a sufficient vertical space is formed between the lower ends of the bobbins suspended from the transporting unit 118 and the top end of the bobbin changing apparatus AD. Accordingly, as shown in Fig. 12, in the portion CP where the transporting rails 110 and 111 cross the running rail of the bobbin changing apparatus AD in one plane, even if the transporting unit 118 having bobbins suspended therefrom is superposed on the bobbin changing apparatus AD in a plane, since the transporting unit 118 is not superposed on the bobbin changing apparatus AD in the vertical direction, layout of the transporting rail and the running rail of the bobbin changing apparatus AD or a running rail 136 (Fig. 12) for a truck for loading and moving the bobbin changing apparatus along the side face of the roving frame can be facilitated.
- the post treatment at the time of transporting doffed full bobbins to the spinning frame can be simplified.
- the rising slide block or lift block is further moved upward by utilizing this movement of raising the peg bars, and therefore, the actual rise end of the slide block or lift block is at a position lower than the upper transfer position of each peg bar and the height of the machine body of the bobbin changing apparatus can be effectively reduced.
- the position for controlling the bobbin changing bar can be set at three points (front end, rear end, and intermediate position), and the control of the bobbin changing bar is facilitated and the space necessary for the movement of the bobbin changing bar in the forward-backward direction is reduced.
- the full bobbin peg bar is raised to the receiving position from the preparation position and full bobbins are loaded on the full bobbin peg bar, but there may be adopted a modification in which the full bobbin peg bar is stopped at the receiving positon of the common lower transfer position and the bobbin changing bar is vertically moved to transfer full bobbins onto the full bobbin peg bar.
- a known battery car or the like may be used as the driving device of the transporting unit.
- bobbin changing bars for the respective front and rear rows of the bobbin wheels of a roving frame are not limited to those used in the present embodiment, but means using a screw feed mechanism or a cylinder, as disclosed in EP-A 0 148 129, may be used.
- the lift devices for full and empty bobbins utilize chains and chain sprockets, but lift devices utilizing a belt driving mechanism or other type of known lifting devices may be used.
- four bobbins are subjected to the bobbin changing operation at a time, but an appropriate number of bobbins may be treated at a time according to the arrangement of bobbin wheels in the roving frame.
- the same upper transfer position is used for the full bobbin peg bar and empty bobbin peg bar in the above-mentioned embodiment as the common upper transfer position, but there may be adopted a modification in which the forward-backward movement mechanism of the lift device for the empty bobbin peg bar is omitted, a vertical lift device similar to that for the full bobbin peg bar is used, and two rails for the full bobbin peg bar and the empty bobbin peg bar are arranged above the full bobbin peg bar and the empty bobbin peg bar, respectively.
- full bobbins are taken out on the full bobbin peg bar and attached to the bobbin supporting members of the full bobbin transporting rail located vertically above, and then the empty bobbin peg bar is raised to receive empty bobbins from the empty bobbin transporting rail, and after the empty bobbin peg bar is brought down, the bobbin changing arm is advanced and empty bobbins are fed to the roving frame.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Spinning Or Twisting Of Yarns (AREA)
Claims (12)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP198175/85 | 1985-09-06 | ||
| JP19817585A JPH0663150B2 (ja) | 1985-09-06 | 1985-09-06 | 粗紡機の管替装置 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0214837A2 EP0214837A2 (fr) | 1987-03-18 |
| EP0214837A3 EP0214837A3 (en) | 1987-12-02 |
| EP0214837B1 true EP0214837B1 (fr) | 1989-12-20 |
Family
ID=16386720
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19860306818 Expired EP0214837B1 (fr) | 1985-09-06 | 1986-09-03 | Procédé pour changer des bobines sur un banc à broches et dispositif pour effectuer ce procédé |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0214837B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JPH0663150B2 (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE3667672D1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0638119Y2 (ja) * | 1987-08-21 | 1994-10-05 | 豊和工業株式会社 | 粗紡機の管換装置における安全装置 |
| IT1222819B (it) * | 1987-10-02 | 1990-09-12 | Marzoli & C Spa | Apparecchiatura per banchi a fusi,atta ad effettuare,in modo automatico.il prelievo delle spole e la loro sostituzione con tubi vuoti,sui quali avvolgere lo stoppino |
| FR2665187B1 (fr) * | 1990-07-30 | 1992-11-20 | Schlumberger Cie N | Dispositif de levee automatique de bobines sur un banc a broches pour fibres longues et fibres courtes et procede mettant en óoeuvre ce dispositif. |
| JPH08113834A (ja) * | 1994-10-14 | 1996-05-07 | Toyota Autom Loom Works Ltd | 粗紡機における管替方法及び管替装置 |
| JP2993869B2 (ja) * | 1995-06-30 | 1999-12-27 | 株式会社山本製作所 | 穀槽における竪のオーガーの支持機枠の組付装置 |
| DE19631445A1 (de) * | 1996-08-03 | 1998-02-05 | Zinser Textilmaschinen Gmbh | Vorspinnmaschine mit Spulenwechselvorrichtung |
| EP1666650B1 (fr) * | 2004-12-01 | 2008-04-02 | Rovira Trias, Juan | Banc à broches pour former et pour délivrer des bobines |
| DE102006024553B4 (de) * | 2006-05-23 | 2008-05-08 | Oerlikon Textile Gmbh & Co. Kg | Vorspinnmaschine mit selbstständiger Spulenwechselvorrichtung |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5089642A (fr) * | 1973-12-13 | 1975-07-18 | ||
| DE3066048D1 (en) * | 1979-07-10 | 1984-02-09 | Rieter Ag Maschf | Apparatus for the automatic doffing of full bobin packages from and for the donning of empty bobin tubes onto the spindles of a preparatory spinning machine |
| EP0148129B1 (fr) * | 1983-12-28 | 1989-05-31 | Howa Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Procédé et appareil pour changer des bobines sur un banc à broches |
-
1985
- 1985-09-06 JP JP19817585A patent/JPH0663150B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1986
- 1986-09-03 EP EP19860306818 patent/EP0214837B1/fr not_active Expired
- 1986-09-03 DE DE8686306818T patent/DE3667672D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPH0663150B2 (ja) | 1994-08-17 |
| EP0214837A3 (en) | 1987-12-02 |
| DE3667672D1 (de) | 1990-01-25 |
| EP0214837A2 (fr) | 1987-03-18 |
| JPS6257944A (ja) | 1987-03-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US4473997A (en) | Method and apparatus for switching roving bobbins in a spinning frame | |
| EP0258188B1 (fr) | Procédé pour rattacher des mèches et pour échanger des bobines de mèche dans un métier à filer à anneau et machine pour la mise en oeuvre de ce procédé | |
| US4721262A (en) | Textile machine for producing cross-wound bobbins | |
| EP0214837B1 (fr) | Procédé pour changer des bobines sur un banc à broches et dispositif pour effectuer ce procédé | |
| US5715669A (en) | Bobbin transporting system for roving and spinning machines with apparatus to exchange bobbins of differing pitches | |
| EP0259267A2 (fr) | Procédé pour échanger des bobines de mèche et dispositif pour sa mise en oeuvre | |
| US4690342A (en) | Textile machine for producing cross-wound bobbins | |
| JPH06305640A (ja) | 綾巻ボビンを製造する機械から綾巻ボビンを取出しかつ当該機械に空の巻管を供給するための装置 | |
| EP0124662B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour interchanger les bobines d'alimentation en mèche sur une machine de filature | |
| KR0132621B1 (ko) | 로우빙 보빈 이송 장치를 갖는 정방 | |
| US5522210A (en) | Flyer frame | |
| JPH0518924B2 (fr) | ||
| EP0434630B1 (fr) | Procédé pour échanger des bobines de mèche dans des métiers à filer à anneaux | |
| JPS6257945A (ja) | 粗紡機の管替方法 | |
| US5996327A (en) | Method of and apparatus for transporting full bobbins and empty bobbin cores | |
| US5272865A (en) | Method and apparatus for exchanging roving bobbins in a ring spinning frame | |
| JPS61119730A (ja) | 粗紡機における管替方法及びその装置 | |
| JPS6257946A (ja) | 粗紡機の管替機 | |
| JPH1121020A (ja) | 粗糸ボビン搬送方法及び粗糸ボビン搬送システム | |
| JPH0377291B2 (fr) | ||
| JPS61174432A (ja) | 粗紡機の管替機 | |
| JP2684777B2 (ja) | 粗糸端位置整列装置 | |
| JPH0640208Y2 (ja) | パッケージ交換ロボット | |
| JP2897560B2 (ja) | 台車へのパッケージ移載装置 | |
| JPH0325525B2 (fr) |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19860924 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19880427 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed |
Owner name: JACOBACCI & PERANI S.P.A. |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3667672 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19900125 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19930730 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| ITTA | It: last paid annual fee | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19940903 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19940923 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19940928 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19940930 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19940903 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Effective date: 19950930 Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19950930 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Effective date: 19960531 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19960601 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20050903 |