EP0132013B1 - Bilge shore for shoring a ship in a dock - Google Patents
Bilge shore for shoring a ship in a dock Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0132013B1 EP0132013B1 EP84201052A EP84201052A EP0132013B1 EP 0132013 B1 EP0132013 B1 EP 0132013B1 EP 84201052 A EP84201052 A EP 84201052A EP 84201052 A EP84201052 A EP 84201052A EP 0132013 B1 EP0132013 B1 EP 0132013B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- ship
- bilge
- superstructure
- substructure
- shore
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000000284 resting effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000036316 preload Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000003032 molecular docking Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005096 rolling process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000006096 absorbing agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005086 pumping Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000035939 shock Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000004075 alteration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013016 damping Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007667 floating Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B63—SHIPS OR OTHER WATERBORNE VESSELS; RELATED EQUIPMENT
- B63C—LAUNCHING, HAULING-OUT, OR DRY-DOCKING OF VESSELS; LIFE-SAVING IN WATER; EQUIPMENT FOR DWELLING OR WORKING UNDER WATER; MEANS FOR SALVAGING OR SEARCHING FOR UNDERWATER OBJECTS
- B63C5/00—Equipment usable both on slipways and in dry docks
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B63—SHIPS OR OTHER WATERBORNE VESSELS; RELATED EQUIPMENT
- B63C—LAUNCHING, HAULING-OUT, OR DRY-DOCKING OF VESSELS; LIFE-SAVING IN WATER; EQUIPMENT FOR DWELLING OR WORKING UNDER WATER; MEANS FOR SALVAGING OR SEARCHING FOR UNDERWATER OBJECTS
- B63C5/00—Equipment usable both on slipways and in dry docks
- B63C5/02—Stagings; Scaffolding; Shores or struts
- B63C5/04—Bilge or keel blocks
Definitions
- the invention relates to a bilge shore for supporting a ship against tilting motion when resting on keel blocks in a dock, comprising a substructure placeable on a dock floor, a superstructure spaced from the substructure and moveable relative to the substructure both in a vertical direction and in a direction at an angle thereto, and at least one elastomeric member mounted between the substructure and the superstructure for pressing the superstructure upwards against the underside of the ship in a supporting manner, in which the elastomeric member produces a spring force suitable for supporting the ship and keeping it in a balanced position even when the ship tilts through an angle relative to the vertical.
- Such a bilge shore is known from British patent 838,073.
- the substructure of the prior bilge shore is divided into two parts which can be displaced relative to each other by means of a wedge.
- the height of the substructure is adjusted by inserting the wedge to a greater or lesser extent therein.
- a drawback inherent in this prior bilge shore is that, prior to the docking of the ship, first the height of the superstructure relative to the dock floor has to be adjusted by means of the wedge in connection with the bilge rise of the ship.
- the elastomeric members are provided merely to permit alignment of a top plate of the superstructure with the ship's bottom.
- U.S. Patent 2,390,300 discloses a shock absorber for merely absorbing and damping the rolling movement of a ship to be docked in open sea prior to this ship being made to rest on keel blocks. This shock absorber is fully unsuitable for supporting the docked ship as it is not capable of exerting any supporting power.
- the bilge shore according to the invention is provided with a biasing device connecting the movable superstructure with the substructure so as to preload the elastomeric member, there being provided no further means for adjusting the height of the superstructure.
- the ship to be docked during the pumping out or during the lifting of the dock will first touch the bilge shores and subsequently bed down on the keel blocks. During this procedure first the resilient bilge shores are compressed until the weight of the ship is taken up by the keel blocks.
- the bilge shores are compressed in order to provide a certain amount of spring pressure at a given compression of the elastomeric members, in order to maintain the equilibrium of the ship after it rests on the keel blocks relatively to its longitudinal axis.
- This feature fixes the minimum height of compressed bilge shores, so that also the maximum height of the bilge shores with unloaded elastomeric members is fixed, i.e. is considerably higher than the height of the keel blocks.
- the ship When during docking, e.g. by pumping over ballast from starboard to port, the weight distribution of the ship is changed, the ship will further compress the resilient bilge shores placed on port side due to the larger weight on port side. This compression causes on port side a larger and on starboard side a smaller counter-pressure of the resilient bilge shores, so that a new equilibrium condition is produced.
- a stop element for the superstructure the compression is blocked at a maximum permissible magnitude, so as to prevent the ship from heeling over in an unacceptable manner in case a change in weight takes place that is larger than the maximum spring pressure.
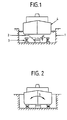
- Fig. 1 shows a diagrammatic arrangement of a dock 1 on the bottom of which there are arranged keel blocks 2 with on either side thereof compressible bilge shores 3.
- the bilge shores are designed in such a manner that they project above the keel blocks in initial position along e.g. a distance d.
- the compressible bilge shores 3 are designed in such a manner that, after having being compressed along the distance d, they provide a sufficient spring pressure for maintaining the ship in equilibrium relative to the keel blocks. This spring pressure is normally so large that the bilge shores are capable of also resisting within certain limits a rolling S (Fig. 2) of the ship relatively to its longitudinal axis, as a result of e.g. a displacement of a weight from starboard to port and vice versa.
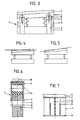
- a bilge shore 3 comprising a substructure 5 to be placed on a dock bottom, a movable superstructure 6 in the form of e.g. a beam which is adapted to rest against the underside of a ship, and a resilient construction 7 in the form of elastomeric members connecting the superstructure to the substructure in order to move the superstructure up and down substantially in the vertical plane relatively to the substructure.
- a movable superstructure 6 in the form of e.g. a beam which is adapted to rest against the underside of a ship
- a resilient construction 7 in the form of elastomeric members connecting the superstructure to the substructure in order to move the superstructure up and down substantially in the vertical plane relatively to the substructure.
- a biasing device comprising a plurality of vertical supporting beams 8 the one ends of which are attached to the substructure 5, while the other ends thereof are provided with a vertical guide slot 9 extending in axial direction of the supporting beam, through which slot extends the one end of a horizontally positioned cam 10 which is attached with its other end to the upper beam 6.
- the top end of the guide slot 9 defines the extent of the bias in the elastomeric members 7.
- the bias can be made adjustable by e.g. mounting the vertical supporting beams 8 slidable in vertical direction on the substructure 5.
- the top of the beam 6 is provided with a layer of flexible material 11, e.g. rubber.
- This beam 6 can also be placed at an angle relative to the horizontal in order to support flat ships and ships having a rise of floor, as diagrammatically shown in Fig. 4 and Fig. 5, respectively.
- the resilient construction is capable of resisting rollings S within certain limits.
- the bilge shore is provided with a stop 12 on which the top beam 6 comes to rest after the maximum permissible compression has been reached. It is clear that the length of the guide slot 9 is such that this extends to beyond the stop 12.
- Fig. 6 show a second embodiment of a bilge shore 3, provided with a substructure 13 in the form of a block, e.g. a block of concrete, a box-shaped superstructure 14 which is telescopically slidable relatively to the block 13, and a resilient construction 15 in the form of an elastomeric fender which is mounted in the box-shaped superstructure and rests on the block 13.
- a substructure 13 in the form of a block, e.g. a block of concrete
- a box-shaped superstructure 14 which is telescopically slidable relatively to the block 13
- a resilient construction 15 in the form of an elastomeric fender which is mounted in the box-shaped superstructure and rests on the block 13.
- the block 13 For adjusting a bias in the fender 15, the block 13 comprises a slotted hole 16 through which extends a pin 17 coupled to the box-shaped structure 14. The place of the slotted hole is decisive for the bias in the fender 15.
- the compression can be limited to a maximum permissible compression value.
- the bilge shore shown in Fig. 7 is substantially identical to the embodiment shown in Fig. 3, on the understanding that this employs as biasing device a chain 22 coupled between the substructure 20 and the superstructure 21 for biasing the elastomeric members 23. Furthermore, a stop 24 is present for limiting the compression of the superstructure 21. Likewise for preventing damage to the underside of a ship to be docked, a layer of flexible material 25 is applied to the superstructure 21.
- the elastomeric members in such a manner that the spring graph, at a given compression, obtains rather suddenly a higher value.
- the stops 12, 18 and 24 are not necessary.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Ocean & Marine Engineering (AREA)
- Vibration Prevention Devices (AREA)
- Bridges Or Land Bridges (AREA)
- Filling Or Discharging Of Gas Storage Vessels (AREA)
- Load-Engaging Elements For Cranes (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| NL8302535 | 1983-07-14 | ||
| NL8302535 | 1983-07-14 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0132013A1 EP0132013A1 (en) | 1985-01-23 |
| EP0132013B1 true EP0132013B1 (en) | 1986-11-26 |
Family
ID=19842166
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP84201052A Expired EP0132013B1 (en) | 1983-07-14 | 1984-07-12 | Bilge shore for shoring a ship in a dock |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0132013B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JPS6038281A (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR940009264B1 (enExample) |
| DE (1) | DE3461443D1 (enExample) |
| IN (1) | IN161244B (enExample) |
| SG (1) | SG77887G (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH03293492A (ja) * | 1990-04-10 | 1991-12-25 | Kajima Corp | 地下式トランクルーム |
| GB2335167B (en) * | 1998-01-13 | 2001-06-06 | Babtie Group Ltd | Docking system for marine vessels |
| KR100722546B1 (ko) * | 2005-10-26 | 2007-05-28 | 조영식 | 선박 건조용 드라이도크 구조물 |
| CN115158605A (zh) * | 2022-08-18 | 2022-10-11 | 上海外高桥造船有限公司 | 坞墩组件和斜底船的支撑结构 |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE472896C (de) * | 1929-03-07 | Paul Matthiessen | Elastisches Auflager fuer Wasserflugzeuge | |
| US2390300A (en) * | 1943-05-20 | 1945-12-04 | Frederic R Harris | Shock-absorbing floating dry dock |
| GB838073A (en) * | 1956-07-24 | 1960-06-22 | John Blain Hunt | Improvements in or relating to apparatus for the dry docking of ships |
| US3721096A (en) * | 1970-08-26 | 1973-03-20 | Ass Ideas Int Inc | Soft support system for hulls and the like |
| JPS49129299U (enExample) * | 1973-03-06 | 1974-11-06 | ||
| JPS49133400U (enExample) * | 1973-03-15 | 1974-11-15 | ||
| FR2350246A1 (fr) * | 1976-05-05 | 1977-12-02 | Amco | Dispositif pour le soutenement des navires |
-
1984
- 1984-07-10 IN IN497/CAL/83A patent/IN161244B/en unknown
- 1984-07-12 EP EP84201052A patent/EP0132013B1/en not_active Expired
- 1984-07-12 DE DE8484201052T patent/DE3461443D1/de not_active Expired
- 1984-07-13 KR KR1019840004107A patent/KR940009264B1/ko not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1984-07-14 JP JP59146703A patent/JPS6038281A/ja active Granted
-
1987
- 1987-09-23 SG SG778/87A patent/SG77887G/en unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPS6038281A (ja) | 1985-02-27 |
| DE3461443D1 (en) | 1987-01-15 |
| KR940009264B1 (ko) | 1994-10-06 |
| IN161244B (enExample) | 1987-10-31 |
| SG77887G (en) | 1988-04-15 |
| JPH0358956B2 (enExample) | 1991-09-09 |
| KR850001095A (ko) | 1985-03-14 |
| EP0132013A1 (en) | 1985-01-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US5140923A (en) | Raising and lowering device | |
| KR102048296B1 (ko) | 외력흡수형 부잔교 | |
| CN104890830A (zh) | 深水动力定位半潜式平台调谐垂荡板减摇减荡控制系统 | |
| GB2165188A (en) | Installation and removal vessel | |
| EP0132013B1 (en) | Bilge shore for shoring a ship in a dock | |
| US4364323A (en) | Vertical stressed mooring tether in a floating oil platform | |
| KR101763817B1 (ko) | 갱웨이 장치 | |
| GB2252081A (en) | Offshore platform | |
| KR102138940B1 (ko) | 쐐기를 이용한 탄성 마찰댐퍼 및 이를 이용한 댐핑구조물 | |
| US5359746A (en) | Ramp junction | |
| KR20170119057A (ko) | 능동형 레그 장착 유니트 및 이를 가지는 해양 플랫폼 | |
| US3677017A (en) | Dock fender structure | |
| KR101293331B1 (ko) | 탄성기구 및 이를 이용한 탄성체의 분력을 이용한 수평변위 조절기구와 교좌장치 | |
| US4483621A (en) | Vibration table | |
| KR102001365B1 (ko) | 가동형 정박장치 | |
| JP3989314B2 (ja) | 浮体式橋梁の係留システム | |
| JP3889914B2 (ja) | 橋梁用支承 | |
| KR20020095271A (ko) | 교량의 탄성 슬라이드 받침장치 | |
| EP2228490B1 (en) | Device for sitting on the seabed for self-raising sea vessels | |
| SU1255510A1 (ru) | Плавучий док | |
| JP3222574B2 (ja) | 可動橋の支承装置およびこれを用いた支承構造 | |
| GB2335167A (en) | Docking system for marine vessels | |
| KR200228272Y1 (ko) | 충격완화용 일방향 교좌장치 | |
| JPH10252040A (ja) | 大型浮遊物の係留装置 | |
| JP2512820B2 (ja) | 免振装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): DE FR GB NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19841221 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE FR GB NL SE |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3461443 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19870115 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19940616 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19940711 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19940720 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19940731 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| EAL | Se: european patent in force in sweden |
Ref document number: 84201052.2 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19950712 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19950713 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19950929 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19950712 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19960402 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 84201052.2 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Effective date: 19960430 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19970201 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 19970201 |