EP0064595B2 - Renvoi d'angle pour la liaison entre tiges de verrouillage et de commande aux fenêtres, portes ou analogues - Google Patents
Renvoi d'angle pour la liaison entre tiges de verrouillage et de commande aux fenêtres, portes ou analogues Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0064595B2 EP0064595B2 EP82102658A EP82102658A EP0064595B2 EP 0064595 B2 EP0064595 B2 EP 0064595B2 EP 82102658 A EP82102658 A EP 82102658A EP 82102658 A EP82102658 A EP 82102658A EP 0064595 B2 EP0064595 B2 EP 0064595B2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- band
- guide channel
- plastic
- angular deflection
- guide
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 47
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 47
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 210000002105 tongue Anatomy 0.000 claims description 55
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 241000761557 Lamina Species 0.000 claims 3
- 230000003014 reinforcing effect Effects 0.000 claims 2
- 230000004308 accommodation Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 abstract description 10
- 230000008719 thickening Effects 0.000 description 11
- 230000002787 reinforcement Effects 0.000 description 7
- 241000446313 Lamella Species 0.000 description 5
- 238000001746 injection moulding Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910001369 Brass Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000004026 adhesive bonding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011324 bead Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000010951 brass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008094 contradictory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005489 elastic deformation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005755 formation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007257 malfunction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003351 stiffener Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004753 textile Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E05—LOCKS; KEYS; WINDOW OR DOOR FITTINGS; SAFES
- E05F—DEVICES FOR MOVING WINGS INTO OPEN OR CLOSED POSITION; CHECKS FOR WINGS; WING FITTINGS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR, CONCERNED WITH THE FUNCTIONING OF THE WING
- E05F7/00—Accessories for wings not provided for in other groups of this subclass
- E05F7/08—Means for transmitting movements between vertical and horizontal sliding bars, rods, or cables
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E05—LOCKS; KEYS; WINDOW OR DOOR FITTINGS; SAFES
- E05Y—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASSES E05D AND E05F, RELATING TO CONSTRUCTION ELEMENTS, ELECTRIC CONTROL, POWER SUPPLY, POWER SIGNAL OR TRANSMISSION, USER INTERFACES, MOUNTING OR COUPLING, DETAILS, ACCESSORIES, AUXILIARY OPERATIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR, APPLICATION THEREOF
- E05Y2900/00—Application of doors, windows, wings or fittings thereof
- E05Y2900/10—Application of doors, windows, wings or fittings thereof for buildings or parts thereof
- E05Y2900/13—Type of wing
- E05Y2900/132—Doors
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E05—LOCKS; KEYS; WINDOW OR DOOR FITTINGS; SAFES
- E05Y—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASSES E05D AND E05F, RELATING TO CONSTRUCTION ELEMENTS, ELECTRIC CONTROL, POWER SUPPLY, POWER SIGNAL OR TRANSMISSION, USER INTERFACES, MOUNTING OR COUPLING, DETAILS, ACCESSORIES, AUXILIARY OPERATIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR, APPLICATION THEREOF
- E05Y2900/00—Application of doors, windows, wings or fittings thereof
- E05Y2900/10—Application of doors, windows, wings or fittings thereof for buildings or parts thereof
- E05Y2900/13—Type of wing
- E05Y2900/148—Windows
Definitions
- the invention relates to corner deflections of the type mentioned in the preamble of claim 1.
- corner deflections consist of an angular guide channel which is attached in the corner region of a window or door leaf and has an arch transition in the region of its angle apex.
- the guide channel which can have a C-shaped profile cross section, receives a flexible band, which is connected at both ends to the drive rods of the rods to be coupled, which is why holes are generally provided for an attachment to rivets.
- riveting requires expensive riveting machines, which must be available in the guide channel before the tape is installed.
- the metal strips peel open in relation to the filler material in between, making assembly work more difficult.
- These numerous layers in the belt are required to fill the clear height in the profile of the guide channel, because otherwise, when the pressure forces are transmitted, wave-like deformations of the leaf springs occur, which cause malfunctions and reduce the lifespan of the corner drive.
- a reduction in the number of metal strips is not possible for manufacturing reasons, because the clear height of the guide channel cannot be made as thin as desired, because during the bending process of the guide channel, the channel profile in the area of the bending apex would be reduced too much, and thereby the longitudinal displaceability of the band on it Hinder place.
- the flexible band has to withstand numerous load changes in practice and experience shows that the life of the band decreases considerably if the thickness of the metal strips used is increased.
- the invention has for its object to develop a smooth, reliable corner deflection of the type mentioned in the preamble of claim 1, which on the one hand meets the apparently contradicting demands for inexpensive manufacture and long life of the corner deflection. This is achieved according to the invention by the measures specified in the characterizing part of claim 1, which have the following special significance.
- the guide channel does not have to be made of expensive brass in order to establish good sliding properties in the case of the invention, but rather is already provided by the plastic tongues.
- the guide channel can therefore be produced from steel or brass-clad steel at a significantly lower cost.
- the further processing of the guide channel is also simplified because it can be welded better to a cover bracket that completes the corner deflection.
- the metallic inner lamellae and the plastic tongues are advantageously connected to the structural unit according to the invention by the formations mentioned in claim 2, which can be joined together according to claim 3 by gluing or welding.
- the material for the welded joints are stored in the thickened ends.
- the projections penetrating through the openings in the inner lamellae not only fix the longitudinal and transverse position of the components to one another, but also determine the desired pre-curvature of the band. It is in fact possible to give the plastic tongue lying on the convex side of the band a greater length and, in the assembled state, a greater curvature than the other plastic tongue coming to lie on the concave side via the projections. This simplifies the threading work when assembling the band in the guide channel.
- the projections on the plastic tongues are formed as male and female locking elements.
- a combination of the components to the named unit is then possible manually, without tools.
- the end-side thickening also allows the plastic masses to be conducted well during the injection molding process, in order to be able to form the moldings or the male and female locking elements in the mold without any problems.
- the measures of claim 5 provide a special reinforcement for the later rivet attachment point of the drive rod, without this affecting the assembly process of the tape.
- the reinforcement plate can be inserted into the guide rail after threading the tape and inserted into the pocket. Another point of attachment results from the later rivet for the guide rod, which is not only attached to the tape, but also to the plate.
- the arrow shape according to claim 6 also facilitates the insertion of the reinforcement plate into the pocket.
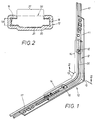
- the corner deflection 10 comprises an angular cover rail 11, which has to cover the groove in the corner region of a window or door leaf, in each of which a locking or control linkage is arranged.
- the linkage redirects movement from a handle from one side of the wing to the other.
- a flexible band 50 which is received in a longitudinally displaceable manner in an angularly curved guide channel 12, is used to transmit this movement.
- the cross-sectional profile of the guide channel 12 is shown enlarged in FIG. 2 and the outline of the band 50 to be inserted therein is indicated.
- the guide channel 12 While the cover rail 11 passes through with its two angle legs up to the angle corner 15. the guide channel 12 has in its center piece an arch transition 13 with a given radius of curvature. In this area, the guide channel 12 stands out from the angle legs of the cover rail 11. The legs 14 of the guide channel 12 adjoining this arc piece 13 on both sides are stretched and firmly connected to the angle legs of the cover rail 11 by spot welding or the like.
- rivets 16 for connecting rod end pieces are fastened in the end regions of the band later mounted in the guide channel, which are then part of the final corner deflection 10 and to which known coupling pieces for the connecting rods are not shown, which are not shown in detail .
- the drive rods themselves can be connected to the belt 50 instead of the drive rod end piece.
- the guide channel 12 has the C-profile shown in FIG. 2 and determines the two U-shaped longitudinal edges 18 which generate a predetermined clear U-height 19.
- the U longitudinal edges 18 are connected to one another via a channel base 30 which is provided with a longitudinal dent 31.
- This longitudinal dent 31 serves to stiffen the C-profile and to accommodate outstanding ones Ends of a head in the rivet 16.
- the clear U-height 19 in the guide channel 12 cannot be made arbitrarily small.
- the inserted flexible band 20 has an adapted cross-sectional profile, as can be seen from the chain line in FIG. 2. One long side of the band 50 is exposed through the C opening 37 of the guide channel 12.
- a flexible band 50 which, for assembly, forms a structural unit consisting of four layers, which, as shown in FIG. 4, consists of two prefabricated plastic tongues 51, 52 and an intermediate pair of inner plates 45, 46 made of metal .
- the lamellae 45, 46 have a first hole 26 for a later rivet 16, which is indicated in its position in FIG. 3 and which is initially missing in the structural unit 50 prior to its assembly.
- the plastic tongues 51, 52 have corresponding, albeit enlarged holes 53.
- the slats 45, 46 also have a second opening 27 in the end region.
- the longitudinal spacing of the two openings 27 from one another is different in the two lamellae 45, 46 by a few tenths of a millimeter in order to produce the pre-curvature of the band 50 which can be seen in FIG.
- This curvature also encompasses the two plastic tongues 51, 52 and is brought about by the fact that these have correspondingly length-coordinated male or female locking elements 54, 55 which are in engagement with one another in the finished structural unit.
- the male-shaped closure element 54 comprises a cylindrical shaft 56 which is threaded through the openings 27 of the inner lamellae 45, 46 and fixes them in position relative to one another. At the end of the shaft there is a closing head 57 which, with elastic deformation, engages in a closing opening 58 in the matrix-shaped closure elements 55 of the plastic tongue 51 lying on the other surface side of the band 50. In addition to the closing opening 58, there is also an enlarged receptacle 59 which, in the event of a coupling, receives the closing head 57 of the male-shaped closure element 54.
- the plastic tongues 51, 52 are provided with thickened end regions 22, which take on a stiffening function.
- the thickened end regions 22 are limited to a central zone 41, the thinner edge regions 42, which are set apart, remain on both sides. As can be seen from FIG. 2, this thickened central zone 41 can extend into the C-profile opening 37 of the guide channel 12 on the one hand or the longitudinal dent 31 on the bottom and therefore does not interfere.
- the thickening 22 in the tongue 51 lying on the inside of the angle has a greater thickness 32 ′ than the thickness 33 ′ of the other plastic tongue 52 corresponds.
- the plastic tongues 51, 52 have a continuous longitudinal strip 47 on their respectively outwardly facing surfaces, which allows the already mentioned longitudinal edge areas 42 to run over the entire tongue length.
- the width of the longitudinal strips 47 is limited to the width of the aforementioned central zone 41 of the thickening 22. This results in the heel height 69 shown in FIG. 7 between the longitudinal strips 47 and the edge areas 42.
- FIGS. 9 to 12 show a second exemplary embodiment of a flexible band 50 'according to the invention, which in many respects has the same structure and mode of operation as the previously described exemplary embodiment of the band 50 from FIGS. 3 to 8. In this respect, the previous one applies Description.
- the same reference numerals are therefore used to designate corresponding components. The only differences are in the following respects:
- One end 48 of the plastic tongue 51 'arranged on the inside of the angle is set back relative to the band end 49, which is why the lamella surface 63, according to FIG. 9, is exposed in this section.
- a reinforcement plate 60 is placed on this section 63, which is provided with a hole 62, which coincides with the holes 26 of the pair of plates 45, 46 already mentioned several times, which also here by the engaged locking elements 54, 55 form a structural unit with the plastic tongues 51 ', 52.
- the reinforcement plate 60 stabilizes the area intended for connecting the drive rods and is provided with an arrow-shaped plug end 61, which is inserted into a pocket 64 at the tongue end 48 and is thereby further secured in position on the structural unit 50 '.
- This pocket 64 comes about through a top wall 66 in a U-profile that is created at this point.
- the plug end 61 couples behind the top wall 66.
- the one hole 53 of the plastic tongue 51 ', where the associated drive rod is to be connected, is provided with a bead 67 to support the rivet there.
- tongues 51, 51', 52 are made in an injection mold from castable plastics.
- several tongues are produced side by side in a molding tool and are initially connected to one another by sprue bars.
- the sprue bars are later cut off when the tongues are separated.
- the sprue bars are located at the attachment points designated 68 in the figure. So that there are no protruding edges when cutting off the sprue bars, the edge recesses recognizable from the figures are formed at the attachment points 68.
- the feeds of the plastic are in the area of the end side thickenings 21, which is why here relatively large mold spaces are available in the injection mold, which ensure good conduction of the pourable plastic in all other areas of the tongue.
- the same takes place in a corresponding manner in the longitudinal strips 47 of the tongues 51, 51 ', 52 which run through the middle. Only the edge regions 42 mentioned above are made thinner by the paragraph 69 shown in FIG 2. Fill in the clear internal height 19 of the guide channel 12.
- the thickness of the tongues 51, 51 ', 52 can also be designed differently in the remaining sections of the band and the concave tongue facing the inside of the angle can also be made thicker than the opposite convex tongue.
- the application of these measures depends on the operating case. Because of the favorable friction properties of the plastic tongues with respect to the guide channel, the guide fit can be very narrow and can be precisely adjusted by the injection molding of the tongues. A stroke loss when actuating the handle can then no longer be ascertained, which was previously noticeable in that a stroke movement at the output-side end of the corner deflection occurred only after a certain stroke distance of the drive-side end of the corner deflection. Good freedom of play has been achieved.
Landscapes
- Connection Of Plates (AREA)
- Flexible Shafts (AREA)
- Joining Of Corner Units Of Frames Or Wings (AREA)
- Operating, Guiding And Securing Of Roll- Type Closing Members (AREA)
Claims (11)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT82102658T ATE9376T1 (de) | 1981-05-09 | 1982-03-30 | Eckumlenkung zum kuppeln von verschluss- und steuergestaengen an fenstern, tueren od. dgl. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE3118435 | 1981-05-09 | ||
| DE3118435A DE3118435A1 (de) | 1981-05-09 | 1981-05-09 | Eckumlenkung zum kuppeln von verschluss- und steuergestaengen an fenstern, tueren o.dgl. |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0064595A1 EP0064595A1 (fr) | 1982-11-17 |
| EP0064595B1 EP0064595B1 (fr) | 1984-09-12 |
| EP0064595B2 true EP0064595B2 (fr) | 1988-05-25 |
Family
ID=6131881
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP82102658A Expired EP0064595B2 (fr) | 1981-05-09 | 1982-03-30 | Renvoi d'angle pour la liaison entre tiges de verrouillage et de commande aux fenêtres, portes ou analogues |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0064595B2 (fr) |
| AT (1) | ATE9376T1 (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE3118435A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT386040B (de) * | 1983-08-13 | 1988-06-27 | Rsb Holding & Management Ag | Einhand-drehkipp-beschlag fuer ein fenster |
| FR2556400B1 (fr) * | 1983-12-09 | 1986-07-18 | Ferco Int Usine Ferrures | Renvoi d'angle pour tringle de manoeuvre d'une ferrure de fenetre, porte ou analogue |
| EP0173236B1 (fr) * | 1984-08-22 | 1990-04-04 | Josef Oster | Ferrure pour fenêtres ou portes |
| DE3545860A1 (de) * | 1985-12-23 | 1987-07-02 | Schuermann & Co Heinz | Eckumlenkeinrichtung eines riegelstangenbeschlages eines fensters oder einer tuer |
| DE9203338U1 (de) * | 1992-03-12 | 1993-07-08 | Siegenia-Frank Kg, 5900 Siegen | Treibstange für Fenster- und Türbeschläge, insbesondere Treibstangen-Kupplungsstück für Beschlags-Bauteile sowie mit einem solchen Treibstangen-Kupplungsstück ausgestattetes Beschlags-Bauteil |
| IT1393807B1 (it) * | 2008-10-30 | 2012-05-11 | Gsg Int Spa | Dispositivo di chiusura per infissi. |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1134295B (de) * | 1957-11-09 | 1962-08-02 | Zuendapp Werke G M B H | Kabelzug zur UEbertragung von Zug- und/oder Druckkraeften, insbesondere fuer Kraftfahrzeuge |
| DE2240345A1 (de) * | 1972-08-17 | 1974-02-28 | Frank Gmbh Wilh | Zugelement fuer fenster, tueren od.dgl. |
| DE2941631C2 (de) * | 1979-10-13 | 1985-06-20 | Siegenia-Frank Kg, 5900 Siegen | Eckumlenkung für Treibstangenbeschläge |
-
1981
- 1981-05-09 DE DE3118435A patent/DE3118435A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1982
- 1982-03-30 DE DE8282102658T patent/DE3260697D1/de not_active Expired
- 1982-03-30 EP EP82102658A patent/EP0064595B2/fr not_active Expired
- 1982-03-30 AT AT82102658T patent/ATE9376T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE3260697D1 (en) | 1984-10-18 |
| ATE9376T1 (de) | 1984-09-15 |
| DE3118435A1 (de) | 1982-12-02 |
| EP0064595A1 (fr) | 1982-11-17 |
| EP0064595B1 (fr) | 1984-09-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0336084B1 (fr) | Fermeture d'une ouverture, telle qu'une porte ou portail | |
| DE3020621C2 (de) | Gliederbandabdeckung | |
| EP1757838B1 (fr) | Chaîne rigide d'entraînement | |
| DE19547846A1 (de) | Rollenkettenbolzen mit minimalem Überstand | |
| EP3404290A1 (fr) | Chaîne de poussée rigide au glissement actionnable par un entraînement à chaîne | |
| EP0064595B2 (fr) | Renvoi d'angle pour la liaison entre tiges de verrouillage et de commande aux fenêtres, portes ou analogues | |
| DE2935158C3 (de) | Stranggepreßtes Bauelement zum Aufbau von Wänden, insbesondere von Kraftfahrzeugen | |
| EP0128391B1 (fr) | Porte à coulisses mobile sur un arc | |
| EP2960545B1 (fr) | Chaîne de poussée autoportante | |
| DE102016111542A1 (de) | Schubkette mit standardisiertem Endstück | |
| DE102020200266B4 (de) | Mit einem Kettenantrieb betätigbare schiebesteife Schubkette | |
| DE2635446A1 (de) | Laengenverstellbare gestaengekupplung fuer treibstangenbeschlaege an fenstern, tueren o.dgl. | |
| EP0030385A1 (fr) | Elément pour portes, portails ou analogues et procédé pour sa fabrication | |
| EP3489450B1 (fr) | Porte | |
| AT409025B (de) | Eckumlenkung von treibstangen-beschlägen für fenster, türen od.dgl. | |
| DE8324586U1 (de) | Längsverstellbare Gestängekupplung an Treibstangenbeschlägen für Fenster, Türen oder dgl. | |
| EP3258132B1 (fr) | Dispositif de renvoi de chaîne de poussée et chaîne de poussée | |
| DE3323265C2 (fr) | ||
| DE3439545C2 (fr) | ||
| DE3123128A1 (de) | Eckumlenkung fuer treibstangenbeschlaege | |
| EP1223273B1 (fr) | Barre d'accouplement | |
| DE2836683A1 (de) | Kupplungsvorrichtung fuer auf mass ablaengbare schienen, insbesondere deck- oder stulpschienen bei treibstangenbeschlaegen von fenstern, tueren o.dgl. | |
| DE2159244C3 (de) | Eckumlenkung für Treibstangenbeschläge | |
| DE8208893U1 (de) | Eckumlenkung zum kuppeln von verschluss- und steuergestaengen an fenstern, tueren od. dgl. | |
| EP0384142B1 (fr) | Tige de commande avec moyens d'accouplement intégraux |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE DE FR GB |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19821019 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE DE FR GB |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: THE PATENT HAS BEEN ANNULLED BY A DECISION OF A NATIONAL AUTHORITY Effective date: 19840912 Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19840912 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 9376 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19840915 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3260697 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19841018 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19850330 |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: SIEGENIA-FRANK KG Effective date: 19850511 |
|
| EN | Fr: translation not filed | ||
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee | ||
| PUAH | Patent maintained in amended form |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009272 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT MAINTAINED AS AMENDED |
|
| 27A | Patent maintained in amended form |
Effective date: 19880525 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B2 Designated state(s): AT BE DE FR GB |
|
| EN3 | Fr: translation not filed ** decision concerning opposition | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19881121 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19920728 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19931201 |