EP0056099A2 - Supervisory apparatus for remote-control systems - Google Patents
Supervisory apparatus for remote-control systems Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0056099A2 EP0056099A2 EP81109263A EP81109263A EP0056099A2 EP 0056099 A2 EP0056099 A2 EP 0056099A2 EP 81109263 A EP81109263 A EP 81109263A EP 81109263 A EP81109263 A EP 81109263A EP 0056099 A2 EP0056099 A2 EP 0056099A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- central station
- monitoring device
- criterion
- telegram
- address
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000012806 monitoring device Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 37
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 19
- 230000004069 differentiation Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 19
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 16
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000001208 nuclear magnetic resonance pulse sequence Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 abstract description 4
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 abstract 3
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000007257 malfunction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000015654 memory Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000013589 supplement Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08C—TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS FOR MEASURED VALUES, CONTROL OR SIMILAR SIGNALS
- G08C25/00—Arrangements for preventing or correcting errors; Monitoring arrangements
Definitions
- the invention relates to a monitoring device for telecontrol devices with at least one central station and with substations, the stations using a common transmission path by means of pulse telegrams that follow one another in time.
- exchange and the impulse telegrams contain an address part, an information part and a differentiation criterion which, depending on whether the impulse telegram in question originates from a central station or substation, is a central station criterion or substation criterion, and the query telegram and the associated response telegram have the same address.
- the pulse telegrams can be used in addition to the address part, information part and differentiation criterion e.g. have a synchronous character, a fuse attachment and / or the like.
- a telecontrol device as is required for such a monitoring device, is already known (Siemens-Zeitschrift, 48th year (1974), Supplement to news transmission technology, pages 292 to 294).
- the contents from the corresponding counters or memories of the telecontrol center can be displayed. If the head office is disturbed, the meaningfulness of these displays is very low or the displays themselves are even disturbed. Such a display is therefore not suitable for monitoring the telecontrol center itself.
- the object of the invention is to design a monitoring device of the type specified above in such a way that the function of at least one central station is monitored with particularly great reliability.
- One finding within the scope of the invention is that this is expediently carried out in connection with an observation of the telecontrol telegrams transmitted on the transmission link.
- the monitoring device is designed to solve this problem in such a way that the monitoring device which can be connected to the transmission link contains an evaluation device for evaluating the pulse telegrams transmitted on the transmission link with regard to the address and the differentiation criterion and display means for displaying the address and the differentiation criterion and that of distinguishing criteria determined by the evaluation device can be monitored by means of a monitoring arrangement in such a way that interruptions in the occurrence of central station criteria which exceed a predetermined time period trigger an alarm signal.
- the monitoring device can be connected to the transmission link via its own modem or a modem of the central station or a substation.
- a certain bit of the telecontrol telegram can serve as the distinguishing criterion, the logical "1" being the central station criterion and the logical "0" being the substation criterion.
- the monitoring device is preferably located at the location of the telecontrol center or - if there are several telecontrol centers - at least at the location of one of the telecontrol centers. However, it can also be arranged as a test device at another point on the transmission link.
- the measures mentioned have the advantage that the telecontrol device can be monitored particularly reliably to determine whether there are central telegrams at regular intervals on the transmission link formed, in particular, by a line common to all stations. If this is not the case, a failure alarm is issued.
- the monitoring device is particularly advantageous for telecontrol devices with several central stations, in which an initially active central station is replaced in the event of a fault by a further central station, which changes from the passive to the active state as soon as it no longer receives central telegrams after a certain waiting time. If a monitoring device located at one of such central stations detects that no more central telegrams are being transmitted, it is namely certain that the central station in question itself has failed.
- the monitoring device can be further perfected by the fact that the monitoring device is spatially adjacent to a central station and that, in addition to the central station criteria, test pulse sequences formed in the central station can also be monitored by means of the monitoring arrangement in such a way that interruptions in the occurrence exceeding a predetermined time period trigger an alarm signal from test pulses.
- the monitoring devices of a central station are arranged spatially adjacent and a criterion obtained from the alarm signal is fed to the start input of a device for sequence control contained in the central station as a start signal.
- An automatic start that tries to restart a microcomputer system of the central can be switched on as soon as the central station no longer sends telecontrol telegrams or is recognized as faulty.
- such starting attempts consist in resetting a device for sequence control to a zero position, from which it automatically starts again.
- the differentiation criterion can be displayed by means of a separate light-emitting diode, which is arranged adjacent to the device for address display.
- the monitoring device is expediently designed such that the display means for displaying the telegram address and the differentiation criterion contain a numerical display element with additional characters, in particular a decimal point, and that a control signal derived from the differentiation criterion is fed to the input of the numerical display element which is assigned to the decimal point.
- Central telegrams and station telegrams can be clearly distinguished from one another in the optical display using particularly simple means, although the query telegram from the telecontrol center and the subsequent response telegram from a substation each have the same telegram address.
- the additional optical character used to distinguish query and response telegram addresses advantageously does not require any special effort. E.g. additional characters such as +, - ,: or the like can be used.
- the check as to whether central telegrams are on the line at regular intervals is expediently carried out in that the monitoring arrangement for evaluating the distinguishing criterion contains a counter, the clock input of which is connected to a clock generator of the monitoring device, the reset input of which can be acted upon with control signals derived from the central station criteria and whose advancement can be blocked when a predetermined counter reading is reached.
- the monitoring of test pulse sequences formed in the central station is expediently achieved in that the monitoring arrangement contains at least one counter, the clock input of which is connected to a clock generator and the reset input of which is connected to the output of a test device contained in the central station, which, at undisturbed operation, provides test pulses at regular intervals delivers.
- the monitoring device is designed such that the monitoring arrangement contains a counter, the clock input of which is connected to a clock generator and the reset input of which can be acted upon by the clock pulses of a clock generator contained in the central station.
- the further counter advantageously makes it possible to reliably monitor the correspondence between the clock of the remote control center and the clock used in the monitoring.
- the additional character of the numerical display element can be controlled by the control signal in such a way that it is activated when the substation criterion is present, the result of the sequence of telecontrol telegrams running over the transmission link is particularly easy to recognize.
- the clock frequency can be set to the bit repetition frequencies that can be selected in the telecontrol device with regard to its clock frequency.
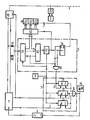
- the figure shows a monitoring device which is connected to a central station.
- the central station 1 is connected to the transmission line 3 via the modem 10.
- the transmission line 3 connects the central station 1 to the substations and possibly to further central stations, of which only the substation 2 is shown with its modem 20.
- the telecontrol telegrams transmitted from the central station 1 to the modem 10 or from the modem 10 to the central station 1 are fed to the monitoring device 5 via the decoupling diodes 61, 62.
- the monitoring device 5 evaluates the data stream.
- the arrangement 51 contained therein which essentially consists of a shift register which can be controlled by the clock generator 6, receives the pulse telegrams and, after a serial-parallel conversion, forwards them on its output bus byte by byte to the device 52 for synchronous character evaluation. If the device 52 recognizes a synchronous character, it releases the control device 53.
- the control device 53 which is connected to the clock generator 6, starts counting the clock pulses from the time of the release and, when a predetermined number of clock pulses is reached, outputs a strobe pulse as a logic “1” to the control circuit 42.
- the drive circuit 42 the is connected to the arrangement 51 via a seven bit wide address bus, is caused by the strobe to adopt the binary coded address.
- the control circuit 42 is used to control the device 41 for numerical display. It contains an address memory and one or more encoders, with the aid of which the control signals required for controlling the device 41 for numerical display are obtained from the binary-coded address information. In an intermediate stage, the address is preferably first converted into the BCD code and then subsequently into the control signals customary for controlling 7-segment display elements.
- the device 41 for numerical display contains a display element which serves to display a decimal point. This display element is controlled separately via the D flip-flop 54.
- This D flip-flop 54 is connected to the output of the control device 53 with its clock input and to a connection of the output of the arrangement 51 with its D input.
- the telecontrol telegrams on which the exemplary embodiment is based are composed of several bytes each with 8 bits.
- the telecontrol telegram begins with a synchronous byte.
- Another byte serves as an address byte and consists of a so-called Z-bit, which serves as a differentiation criterion, and seven address bits.
- the D flip-flop 54 is caused by the strobe pulse of the control device 53 to take over the Z bit and appears at the output of the D flip-flop as a control signal for the additional character of the device 41 a stored central station criterion Z 'as a logical "1".
- the monitoring device 5, the clock generator 6 and the drive circuit 42 may be of a small microcomputer system are constructed in particular with the aid.
- the monitoring arrangement 7 contains the counters 71, 72 and 73, which are each connected to the clock generator 6 with a clock input. The advancement by the clock is blocked when the counter end position is reached in that the output of the counter is connected to an enable input E.
- the outputs of the counters 71, 72 and 73 are also routed to the inputs of the triple-OR element 74, the output of which is routed both to the display device 75 and via the automatic start device 9 to the reset input R of the central station 1.
- the alarm signals of the counters 71, 72, 73 can be displayed individually or only in part, or can be fed to the automatic start.
- the counters 71, 72 and 73 designed as binary counters are reset in different ways.
- the counter 71 is connected with its reset input R to the output of the AND gate 55, which has one input together with the D input of the D flip-flop 54 at a connection of the output of the arrangement 51 and with the other input on Output of the control device 53 is.
- the AND gate 55 queries the Z bit supplied by the arrangement 51 with the aid of the strobe signal emitted by the device 53.
- the counter 71 is therefore reset with each central station telegram. If central station telegrams are missing during a predetermined period of time, the counter 71 reaches its end position and emits an alarm signal to the OR element 74.
- the reset inputs of counters 72 and 73 are dynamic inputs that only respond to positive clock edges.
- the reset input R of the counter 72 is connected to a clock output of the central station 1, which is also connected to a clock input of the modem 10.
- the counter 72 therefore monitors the clock pulse sequence of the central station 1.
- the reset input of the counter 73 is connected to a test pulse output S of the central station 1.
- the device for sequence control of the central station 1 sends monitoring pulses to the test pulse output at regular intervals, even when another central station sends query telegrams to the transmission link and the central station under consideration must therefore remain passive.
- control signal Z ' it controls an optical display for identifying the substation telegrams, which is formed by the decimal point of the device 41 for the numerical display. If the Z bit is missing during a certain period of time, the LED 74 of the display device 75 is activated via the OR gate 74 to emit a central alarm. In addition, this alarm causes the automatic start 9 to restart a microprocessor which is used to control the sequence of the control center 1.
- This automatic start 9 is formed by a clock pulse generator, which emits start pulses at regular time intervals when it is released by an alarm signal via its enable input E.
- the device 41 for digit display makes the addresses of the telegrams running via the telecontrol network and thus the cycle sequence and the telegram exchange visible.
- the telegram addresses of the telecontrol telegrams are displayed on the device 41 for numerical display.
- the decimal point is used to display substation telegrams. The display remains until a new telegram arrives.
- the monitoring device has its own clock supply which is independent of the sequence control of the central station 1 and therefore also recognizes malfunctions of the sequence control which are caused by a faulty clock.
- the own clock supply also makes it possible to use the monitoring device as a service and / or test module in the entire telecontrol network to control the exchange of telegrams.
- the clock generator 6, the device 5 for telegram evaluation and the device 41 with the control circuit 42 are used.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Selective Calling Equipment (AREA)
- Remote Monitoring And Control Of Power-Distribution Networks (AREA)
- Ultra Sonic Daignosis Equipment (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Die Erfindung bezieht sich auf eine Uberwachungseinrichtung für Fernwirkeinrichtungen mit wenigstens einer Zentralstation und mit Unterstationen, wobei die Stationen über eine gemeinsame Übertragungsstrecke mittels zeitlich aufeinanderfolgender Impulstelegramme Informationen . austauschen und die Impulstelegramme einen Adressenteil, einen Informationsteil und ein Unterscheidungskriterium enthalten, das je nachdem, ob das betreffende Impulstelegramm von einer Zentralstation oder Unterstation stammt, ein Zentralstationskriterium oder Unterstationskriterium ist und wobei jeweils das Abfragetelegramm und das zugehörige Antworttelegramm die gleiche Adresse haben. Dabei können die Impulstelegramme zusätzlich zum Adressenteil, Informationsteil und Unterscheidungskriterium z.B. ein Synchronzeichen, einen Sicherungsanhang und/oder dgl. aufweisen.The invention relates to a monitoring device for telecontrol devices with at least one central station and with substations, the stations using a common transmission path by means of pulse telegrams that follow one another in time. exchange and the impulse telegrams contain an address part, an information part and a differentiation criterion which, depending on whether the impulse telegram in question originates from a central station or substation, is a central station criterion or substation criterion, and the query telegram and the associated response telegram have the same address. The pulse telegrams can be used in addition to the address part, information part and differentiation criterion e.g. have a synchronous character, a fuse attachment and / or the like.
Eine Fernwirkeinrichtung, wie sie bei einer derartigen Überwachungseinrichtung vorausgesetzt wird, ist bereits bekannt (Siemens-Zeitschrift, 48. Jahrgang (1974), Beiheft Nachrichten-Übertragungstechnik, Seite 292 bis 294).A telecontrol device, as is required for such a monitoring device, is already known (Siemens-Zeitschrift, 48th year (1974), Supplement to news transmission technology, pages 292 to 294).
Man kann für die Anzeige der Adressen von ausgesendeten oder empfangenen Fernwirktelegrammen die Inhalte aus den entsprechenden Zählern bzw. Speichern der Fernwirkzentrale anzeigen. Ist die Zentrale gestört, so ist der Aussagewert dieser Anzeigen jedoch sehr gering oder die Anzeigen sind sogar selbst gestört. Für eine eigene Überwachung der Fernwirkzentrale ist eine derartige Anzeige somit nicht ohne weiteres geeignet.For the display of the addresses of transmitted or received telecontrol telegrams, the contents from the corresponding counters or memories of the telecontrol center can be displayed. If the head office is disturbed, the meaningfulness of these displays is very low or the displays themselves are even disturbed. Such a display is therefore not suitable for monitoring the telecontrol center itself.
Aufgabe der Erfindung ist es, eine Überwachungseinrichtung der vorstehend näher bezeichneten Art derart auszubilden, daß die Funktion wenigstens einer Zentralstation mit besonders großer Zuverlässigkeit überwacht wird. Eine Erkenntnis im Rahmen der Erfindung besteht darin, daß dies zweckmäßigerweise in Verbindung mit einer Beobachtung der auf der Übertragungsstrecke übertragenen Fernwirktelegramme geschieht.The object of the invention is to design a monitoring device of the type specified above in such a way that the function of at least one central station is monitored with particularly great reliability. One finding within the scope of the invention is that this is expediently carried out in connection with an observation of the telecontrol telegrams transmitted on the transmission link.
Gemäß der Erfindung wird die Überwachungseinrichtung zur Lösung dieser Aufgabe derart ausgebildet, daß die an die Übertragungsstrecke anschließbare Überwachungseinrichtung eine Auswerteeinrichtung zur Auswertung der auf der Übertragungsstrecke übertragenen Impulstelegramme hinsichtlich der Adresse und des Unterscheidungskriteriums und Anzeigemittel zur Anzeige der Adresse und des Unterscheidungskriteriums enthält und daß die von der Auswerteeinrichtung ermittelten Unterscheidungskriterien mittels einer Überwachungsanordnung derart überwachbar sind, daß eine vorgegebene Zeitspanne überschreitende Unterbrechungen im Auftreten von Zentralstationskriterien ein Alarmsignal auslösen. Die Überwachungseinrichtung kann dabei über ein eigenes Modem oder ein Modem der Zentralstation oder einer Unterstation an die Übertragungstrecke angeschlossen werden. Als Unterscheidungskriterium kann insbesondere ein bestimmtes Bit des Fernwirktelegrammes dienen, wobei die logische "1" das Zentralstationskriterium und die logische "0" das Unterstationskriterium ist. Vorzugsweise befindet sich die Überwachungseinrichtung am Ort der Fernwirkzentrale oder - falls mehrere Fernwirkzentralen vorhanden sind - wenigstens am Orte einer der Fernwirkzentralen. Sie kann jedoch auch als Prüfeinrichtung an einer anderen Stelle der Übertragungsstrecke angeordnet sein.According to the invention, the monitoring device is designed to solve this problem in such a way that the monitoring device which can be connected to the transmission link contains an evaluation device for evaluating the pulse telegrams transmitted on the transmission link with regard to the address and the differentiation criterion and display means for displaying the address and the differentiation criterion and that of distinguishing criteria determined by the evaluation device can be monitored by means of a monitoring arrangement in such a way that interruptions in the occurrence of central station criteria which exceed a predetermined time period trigger an alarm signal. The monitoring device can be connected to the transmission link via its own modem or a modem of the central station or a substation. In particular, a certain bit of the telecontrol telegram can serve as the distinguishing criterion, the logical "1" being the central station criterion and the logical "0" being the substation criterion. The monitoring device is preferably located at the location of the telecontrol center or - if there are several telecontrol centers - at least at the location of one of the telecontrol centers. However, it can also be arranged as a test device at another point on the transmission link.
Durch die genannten Maßnahmen ergibt sich der Vorteil, daß-sich die Fernwirkeinrichtung besonders zuverlässig daraufhin überwachen läßt, ob auf der, insbesondere durch eine allen Stationen gemeinsamen Leitung gebildeten Übertragungsstrecke in regelmäßigen Abständen Zentraltelegramme sind. Ist dies nicht der Fall, wird ein Ausfallalarm abgegeben.The measures mentioned have the advantage that the telecontrol device can be monitored particularly reliably to determine whether there are central telegrams at regular intervals on the transmission link formed, in particular, by a line common to all stations. If this is not the case, a failure alarm is issued.
Von besonderem Vorteil ist die Überwachungseinrichtung bei Fernwirkeinrichtungen mit mehreren Zentralstationen, bei denen eine zunächst aktive Zentralstation im Störungsfall durch eine weitere Zentralstation abgelöst wird, die vom passiven in den aktiven Zustand übergeht, sobald sie nach einer bestimmten Wartezeit keine Zentralentelegramme mehr empfängt. Stellt eine Überwachungseinrichtung, die sich bei einer von solchen Zentralstationen befindet, fest, daß keine Zentralentelegramme mehr übertragen werden, so ist nämlich sicher, daß die betreffende Zentralstation selbst ausgefallen ist.The monitoring device is particularly advantageous for telecontrol devices with several central stations, in which an initially active central station is replaced in the event of a fault by a further central station, which changes from the passive to the active state as soon as it no longer receives central telegrams after a certain waiting time. If a monitoring device located at one of such central stations detects that no more central telegrams are being transmitted, it is namely certain that the central station in question itself has failed.
In Weiterbildung der Erfindung läßt sich die Überwachungseinrichtung dadurch noch weiter vervollkommnen, daß die Überwachungseinrichtung einer Zentralstation räumlich benachbart'angeordnet ist und daß mittels der Überwachungsanordnung zusätzlich zu den Zentralstationskriterien auch in der Zentralstation gebildete Prüfimpulsfolgen derart überwachbar sind, daß eine vorgegebene Zeitspanne überschreitende Unterbrechungen im Auftreten von Prüfimpulsen ein Alarmsignal auslösen. Diese Maßnahmen ermöglichen es in vorteilhafter Weise, in Fernwirkeinrichtungen mit mehreren Zentralstationen Funktionsstörungen einer Zentralstation auch dann festzustellen, wenn eine andere Zentralstation die Abfragetelegramme aussendet.In a further development of the invention, the monitoring device can be further perfected by the fact that the monitoring device is spatially adjacent to a central station and that, in addition to the central station criteria, test pulse sequences formed in the central station can also be monitored by means of the monitoring arrangement in such a way that interruptions in the occurrence exceeding a predetermined time period trigger an alarm signal from test pulses. These measures advantageously make it possible to determine malfunctions in a central station in telecontrol devices with a plurality of central stations even when another central station is sending the query telegrams.
In weiterer Ausgestaltung der Erfindung werden die Überwachungseinrichtungen einer Zentralstation räumlich benachbart angeordnet und ein aus dem Alarmsignal gewonnenes Kriterium dem Starteingang einer in der Zentralstation enthaltenen Einrichtung zur Ablaufsteuerung als Startsignal zugeführt. Dabei kann eine Startautomatik, die ein Mikrocomputersystem der Zentrale neu zu starten versucht, eingeschaltet werden, sobald die Zentralstation keine Fernwirktelegramme mehr aussendet oder als gestört erkannt wird. Insbesondere bestehen solche Startversuche im Rücksetzen einer Einrichtung zur Ablaufsteuenng auf eine Nullstellung, von der sie selbsttätig neu startet.In a further embodiment of the invention, the monitoring devices of a central station are arranged spatially adjacent and a criterion obtained from the alarm signal is fed to the start input of a device for sequence control contained in the central station as a start signal. An automatic start that tries to restart a microcomputer system of the central can be switched on as soon as the central station no longer sends telecontrol telegrams or is recognized as faulty. In particular, such starting attempts consist in resetting a device for sequence control to a zero position, from which it automatically starts again.
Das Unterscheidungskriterium kann mittels einer eigenen Leuchtdiode angezeigt werden, die der Vorrichtung zur Adressenanzeige benachbart angeordnet ist.The differentiation criterion can be displayed by means of a separate light-emitting diode, which is arranged adjacent to the device for address display.
Zweckmäßigerweise wird die Überwachungseinrichtung derart ausgebildet, daß die Anzeigemittel zur Anzeige der Telegrammadresse und des Unterscheidungskriteriums ein Ziffernanzeigeelement mit Zusatzzeichen, insbesondere Dezimalpunkt enthalten und daß ein aus dem Unterscheidungskriterium abgeleitetes Steuersignal dem Eingang des Ziffernanzeigeelementes zugeführt ist, der dem Dezimalpunkt zugeordnet ist. Dabei lassen sich Zentralentelegramme und Stationstelegramme bei der optischen Anzeige mit besonders einfachen Mitteln besonders übersichtlich voneinander unterscheiden, obwohl das Abfragetelegramm der Fernwirkzentrale und das folgende Antworttelegramm einer Unterstation jeweils die gleiche Telegrammadresse haben. Das zur Unterscheidung von Abfrage- und Antworttelegramm-Adressen dienende zusätzliche optische Zeichen erfordert in vorteilhafter Weise keinen besonderen Aufwand. Z.B. können Zusatzzeichen wie +,-,: oder dgl. Verwendung finden.The monitoring device is expediently designed such that the display means for displaying the telegram address and the differentiation criterion contain a numerical display element with additional characters, in particular a decimal point, and that a control signal derived from the differentiation criterion is fed to the input of the numerical display element which is assigned to the decimal point. Central telegrams and station telegrams can be clearly distinguished from one another in the optical display using particularly simple means, although the query telegram from the telecontrol center and the subsequent response telegram from a substation each have the same telegram address. The additional optical character used to distinguish query and response telegram addresses advantageously does not require any special effort. E.g. additional characters such as +, - ,: or the like can be used.
Die Prüfung, ob in regelmäßigen Abständen Zentralentelegra mme auf der Leitung sind, wird zweckmäßigerweise dadurch vorgenommen, daß die Überwachungsanordnung zur Auswertung des Unterscheidungskriteriums.einen Zähler enthält, dessen Takteingang an einen Taktgeber der Überwachungseinrichtung angeschlossen, dessen Rücksetzeingang mit aus den Zentralstationskriterien abgeleiteten Steuersignalen beaufschlagbar und dessen Weiterschaltung bei Erreichen eines vorgegebenen Zählerstandes blockierbar ist.The check as to whether central telegrams are on the line at regular intervals is expediently carried out in that the monitoring arrangement for evaluating the distinguishing criterion contains a counter, the clock input of which is connected to a clock generator of the monitoring device, the reset input of which can be acted upon with control signals derived from the central station criteria and whose advancement can be blocked when a predetermined counter reading is reached.
Die Überwachung von in der Zentralstation gebildeten Prüfimpulsfolgen wird zweckmäßigerweise dadurch erreicht, daß die Überwachungsanordnung wenigstens einen Zähler enthält, dessen Takteingang an einen Taktgeber angeschlossen und dessen Rücksetzeingang mit dem Ausgang einer in der Zentralstation enthaltenen Prüfeinrichtung verbunden ist, die bei ungestörtem Betrieb in regelmäßigen Abständen Früfimpulse abgibt.The monitoring of test pulse sequences formed in the central station is expediently achieved in that the monitoring arrangement contains at least one counter, the clock input of which is connected to a clock generator and the reset input of which is connected to the output of a test device contained in the central station, which, at undisturbed operation, provides test pulses at regular intervals delivers.
In weiterer Ausgestaltung der.Erfindung wird die Überwachungseinrihtung derart ausgebildet, daß die Überwachungsanordnung einen Zähler enthält, dessen Takteingang mit einem Taktgeber verbunden und dessen Rücksetzeingang mit den Taktimpulsen eines in der Zentralstation enthaltenen Taktgebers beaufschlagbar ist. Dabei ermöglicht es der weitere Zähler in vorteilhafter Weise, die Übereinstimmung des Taktes der Fernwirkzentrale mit dem bei der Überwachung verwendeten Takt seinerseits sicher zu überwachen.In a further embodiment of the invention, the monitoring device is designed such that the monitoring arrangement contains a counter, the clock input of which is connected to a clock generator and the reset input of which can be acted upon by the clock pulses of a clock generator contained in the central station. The further counter advantageously makes it possible to reliably monitor the correspondence between the clock of the remote control center and the clock used in the monitoring.
Ist das Zusatzzeichen des Ziffernanzeigeelementes durch das Steuersignal derart steuerbar, daß es bei vorhandenem Unterstationskriterium aktiviert ist, so ergibt sich eine besonders leicht erkennbare Anzeige der Folge der über die Übertragungsstrecke laufenden Fernwirktelegramme.If the additional character of the numerical display element can be controlled by the control signal in such a way that it is activated when the substation criterion is present, the result of the sequence of telecontrol telegrams running over the transmission link is particularly easy to recognize.
Insbesondere ist der Taktgeber hinsichtlich seiner Taktfrequenz auf die bei der Fernwirkeinrichtung wählbaren Bitfolgefrequenzen einstellbar.In particular, the clock frequency can be set to the bit repetition frequencies that can be selected in the telecontrol device with regard to its clock frequency.
Die Erfindung wird anhand des in der Figur dargestellten Ausführungsbeispieles näher erläutert.The invention is explained in more detail with reference to the embodiment shown in the figure.
Die Fig. zeigt eine Überwachungseinrichtung, die an eine Zentralstation angeschlossen ist.The figure shows a monitoring device which is connected to a central station.
Bei der in der Fig. gezeigten Überwachungseinrichtung ist die Zentralstation 1 über das Modem 10 an die Übertragungsleitung 3 angeschlossen. Die Übertragungsleitung 3 verbindet die Zentralstation 1 mit den Unterstationen und ggf. mit weiteren Zentralstationen,von denen lediglich die Unterstation 2 mit ihrem Modem 20 dargestellt ist.In the monitoring device shown in the figure, the
Die von der Zentralstation 1 zum Modem 10 bzw. vom Modem 10 zur Zentralstation 1 übermittelten Fernwirktelegramme werden über die Entkopplungsdioden 61,62 der Überwachungseinrichtung 5 zugeführt. Die Überwachungseinrichtung 5 wertet den Datenstrom aus. Die darin enthaltene Anordnung 51, die im wesentlichen aus einem durch den Taktgenerator 6 steuerbaren Schieberegister besteht, empfängt die Impulstelegramme und gibt sie nach einer Seriell-Parallel-Umsetzung an ihrem Ausgangsbus-byteweise an die Einrichtung 52 zur Synchronzeichenauswertung weiter. Erkennt die Einrichtung 52 ein Synchronzeichen, so gibt sie die Steuervorrichtung 53 frei. Die Steuervorrichtung 53, die an den Taktgenerator 6 angeschlossen ist, beginnt vom Zeitpunkt der Freigabe ab mit dem Zählen der Taktimpulse und gibt bei Erreichen einer vorgegebenen Zahl von Taktimpulsen einen Strobe-Impuls als logische "1" an die Ansteuerschaltung 42 ab. Die Ansteuerschaltung 42, die über einen sieben Bit breiten Adressenbus mit der Anordnung 51 verbunden ist, wird durch den Strobe-Impuls zur Übernahme der binär codierten Adresse veranlaßt.The telecontrol telegrams transmitted from the
Die Ansteuerschaltung 42 dient zur Steuerung der Vorrichtung 41 zur Ziffernanzeige. Sie enthält einen Adressenspeicher und einen oder mehrere Codierer, mit deren Hilfe die zur Ansteuerung der Vorrichtung 41 zur Ziffernanzeige erforderlichen Steuersignale aus der binär codierten Adresseninformation gewonnen werden. Vorzugsweise wird die Adresse in einer Zwischenstufe zunächst in den BCD-Code und daran anschließend in die zur Ansteuerung von 7-Segment-Anzeigeelementen üblichen Steuersignale überführt.The
Die Vorrichtung 41 zur Ziffernanzeige enthält ein Anzeigeelement, das zur Anzeige eines Dezimalpunktes dient. Dieses Anzeigeelement wird über das D-Flip-Flop 54 gesondert angesteuert. Dieses D-Flip-Flop 54 liegt mit seinem Takteingang am Ausgang der Steuervorrichtung 53 und mit seinem D-Eingang an einem Anschluß des Ausganges der Anordnung 51.The device 41 for numerical display contains a display element which serves to display a decimal point. This display element is controlled separately via the D flip-
Die dem Ausführungsbeispiel zugrundeliegenden Fernwirktelegramme sind aus mehreren Bytes mit je 8 Bit zusammengesetzt. Das Fernwirktelegramm beginnt mit einem Synchronbyte. Ein weiteres Byte dient als Adressbyte und besteht aus einem als Unterscheidungskriterium dienenden sogenannten Z-Bit und sieben Adressenbits.The telecontrol telegrams on which the exemplary embodiment is based are composed of several bytes each with 8 bits. The telecontrol telegram begins with a synchronous byte. Another byte serves as an address byte and consists of a so-called Z-bit, which serves as a differentiation criterion, and seven address bits.
Liegt das Adressenbyte am Ausgang der Anordnung 51..an, so wird das D-Flip-Flop 54 durch den Strobe-Impuls der Steuervorrichtung 53 veranlaßt, das Z-Bit zu übernehmen und am Ausgang des D-Flip-Flops erscheint als Steuersignal für das Zusatzzeichen der Vorrichtung 41 ein gespeichertes Zentralstationskriterium Z' als logische "1".If the address byte is at the output of the
' Die Überwachungseinrichtung 5, der Taktgenerator 6 und die Ansteuerschaltung 42 können insbesondere mit Hilfe eines kleinen Mikrocomputersystems aufgebaut werden. 'The monitoring device 5, the
Die Überwachungsanordnung 7 enthält die Zähler 71, 72 und 73, die jeweils mit einem Takteingang an den Taktgenerator 6 angeschlossen sind. Die Fortschaltung durch den Takt wird bei Erreichen der Zählerendstellung dadurch blockiert, daß der Ausgang des Zählers mit einem Enable-Eingang E verbunden ist. Die Ausgänge der Zähler 71,72 und 73 sind ferner an die Eingänge des Dreifach-Oder-Gliedes 74 geführt, dessen Ausgang sowohl an die Anzeigevorrichtung 75 als auch über die Startautomatik 9 an den Rücksetzeingang R der Zentralstation 1 geführt ist. In Abwandlung des gezeigten Ausführungsbeispieles können die Alarmsignale der Zähler 71,72,73 andererseits einzeln oder nur zum Teil zusammengefaßt angezeigt bzw. der Startautomatik zugeführt werden.The monitoring arrangement 7 contains the
Die als Binärzähler ausgebildeten Zähler 71,72 und 73 werden auf unterschiedliche Art zurückgesetzt.The
Der Zähler 71 ist mit seinem Rücksetzeingang R an den Ausgang des Und-Gliedes 55 angeschlossen, das mit dem einen Eingang zusammen mit dem D-Eingang des D-Flip-Flops 54 an einem Anschluß des Ausganges der Anordnung 51 und mit dem anderen Eingang am Ausgang der Steuervorrichtung 53 liegt. Das Und-Glied 55 fragt mit Hilfe des von der Vorrichtung 53 abgegebenen Strobe-Signals das von der Anordnung 51 gelieferte Z-Bit ab. Der Zähler 71 wird daher bei jedem Zentralstationstelegramm zurückgesetzt. Fehlen Zentralstationstelegramme während einer vorgegebenen Zeitspanne, so erreicht der Zähler 71 seine Endstellung-und gibt-ein Alarmsignal an das Oder-Glied 74 ab.The
Die Rücksetzeingänge der Zähler 72 und 73 sind dynamische Eingänge, die nur auf positive Taktflanken ansprechen.The reset inputs of
Der Rücksetzeingang R des Zählers 72 ist an einen Taktausgang der Zentralstation 1 angeschlossen, der auch an einen Takteingang des Modems 10 geführt ist. Der Zähler 72 überwacht daher die Taktimpulsfolge der Zentralstation 1.The reset input R of the
Der Rücksetzeingang des Zählers 73 ist an einen Prüfimpulsausgang S der Zentralstation 1 angeschlossen. Die Einrichtung zur Ablaufsteuerung der Zentralstation 1 gibt an den Prüfimpulsausgang in regelmäßigen Abständen Überwachungsimpulse ab und zwar auch dann, wenn eine andere Zentralstation Abfragetelegramme an die Übertragungsstrecke abgibt und die betrachtete Zentralstation daher passiv bleiben muß.The reset input of the
Aus den Adressenbytes der Fernwirktelegramme wird als Unterscheidungskriterium das sogenannte Z-Bit ausgewertet und zur Steuerung von drei verschiedenen Funktionen verwendet: Als Steuersignal Z' steuert es eine optische Anzeige zur Kennzeichnung der Unterstationstelegramme, die durch den Dezimalpunkt der Vorrichtung 41 zur Ziffernanzeige gebildet ist. Fehlt das Z-Bit während eines bestimmten Zeitraumes, so wird über das Oder-Glied 74 die Leuchtdiode_der Anzeigevorrichtung 75 zur Abgabe eines Zentralen-Alarms aktiviert. Außerdem veranlaßt dieser Alarm über die Startautomatik 9 den Neustart eines Mikroprozessors, der zur Ablaufsteuerung der Zentrale 1 dient. Diese Startautomatik 9 wird durch einen Taktimpulsgeber gebildet, der in regelmäßigen Zeitabständen Startimpulse abgibt, wenn er durch ein Alarmsignal über seinen Enable-Eingang E freigegeben wird.From the address bytes of the telecontrol telegrams, the so-called Z-bit is evaluated as a differentiating criterion and used to control three different functions: As control signal Z ', it controls an optical display for identifying the substation telegrams, which is formed by the decimal point of the device 41 for the numerical display. If the Z bit is missing during a certain period of time, the LED 74 of the
Die Vorrichtung 41 zur Ziffernanzeige macht die Adressen der über das Fernwirknetz laufenden Telegramme und damit den Zyklusablauf und den Telegrammaustausch sichtbar. An der Vorrichtung 41 zur Ziffernanzeige werden die Telegrammadressen der Fernwirktelegramme angezeigt. Der Dezimalpunkt dient der Anzeige von Unterstationstelegrammen. Die Anzeige bleibt solange stehen, bis ein neues Telegramm eintrifft.The device 41 for digit display makes the addresses of the telegrams running via the telecontrol network and thus the cycle sequence and the telegram exchange visible. The telegram addresses of the telecontrol telegrams are displayed on the device 41 for numerical display. The decimal point is used to display substation telegrams. The display remains until a new telegram arrives.
Die Überwachungseinrichtung besitzt eine eigene, von der Ablaufsteuerung der Zentralstation 1 unabhängige Taktversorgung und erkennt daher auch Fehlfunktionen der Ablaufsteuerung, welche durch einen gestörten Takt verursacht werden.The monitoring device has its own clock supply which is independent of the sequence control of the
Die eigene Taktversorgung ermöglicht es ferner, die Überwachungseinrichtung als Service- und/oder Prüf-Baugruppe im gesamten Fernwirknetz zur Kontrolle des Telegrammaustausches zu verwenden. In diesem Fall werden nur der Taktgenerator 6, die Einrichtung 5 zur Telegrammauswertung und die Vorrichtung 41 mit der Ansteuerschaltung 42 benützt.The own clock supply also makes it possible to use the monitoring device as a service and / or test module in the entire telecontrol network to control the exchange of telegrams. In this case, only the
Claims (9)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT81109263T ATE17895T1 (en) | 1981-01-12 | 1981-10-29 | MONITORING DEVICE FOR TELECONTROL DEVICES. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19813100683 DE3100683A1 (en) | 1981-01-12 | 1981-01-12 | MONITORING DEVICE FOR REMOTE CONTROL DEVICE |
| DE3100683 | 1981-01-12 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0056099A2 true EP0056099A2 (en) | 1982-07-21 |
| EP0056099A3 EP0056099A3 (en) | 1983-07-27 |
| EP0056099B1 EP0056099B1 (en) | 1986-02-05 |
Family
ID=6122468
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP81109263A Expired EP0056099B1 (en) | 1981-01-12 | 1981-10-29 | Supervisory apparatus for remote-control systems |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0056099B1 (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE17895T1 (en) |
| DE (2) | DE3100683A1 (en) |
| DK (1) | DK8482A (en) |
| NO (1) | NO155869C (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0113478A1 (en) * | 1982-12-24 | 1984-07-18 | Hitachi, Ltd. | FAil safe system for information transmission systems |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1566782B1 (en) * | 1967-04-13 | 1970-10-08 | Siemens Ag | Procedure for testing pulse-operated circuits and circuit arrangements for its implementation |
| DE2516681A1 (en) * | 1975-04-16 | 1976-10-21 | Siemens Ag | Remote control system with central and further stations - can have additional station evaluating signal exchange between central and further stations |
| DE2928492A1 (en) * | 1979-07-14 | 1981-01-15 | Licentia Gmbh | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR MONITORING CABLES CONNECTING SEVERAL STATIONS, ESPECIALLY IN TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORKS |
| DE2929597A1 (en) * | 1979-07-21 | 1981-02-05 | Licentia Gmbh | Alarm indication signal recognition circuit - connects digital signal from transmitter to first input of NOR-circuit, whose output goes to counter input |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2806677C2 (en) * | 1978-02-16 | 1983-08-25 | Dieter Dipl.-Phys. Dr. 8031 Eichenau Philipp | Selective remote-controlled switching system |
-
1981
- 1981-01-12 DE DE19813100683 patent/DE3100683A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 1981-10-29 EP EP81109263A patent/EP0056099B1/en not_active Expired
- 1981-10-29 AT AT81109263T patent/ATE17895T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1981-10-29 DE DE8181109263T patent/DE3173740D1/en not_active Expired
-
1982
- 1982-01-08 NO NO820050A patent/NO155869C/en unknown
- 1982-01-11 DK DK8482A patent/DK8482A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1566782B1 (en) * | 1967-04-13 | 1970-10-08 | Siemens Ag | Procedure for testing pulse-operated circuits and circuit arrangements for its implementation |
| DE2516681A1 (en) * | 1975-04-16 | 1976-10-21 | Siemens Ag | Remote control system with central and further stations - can have additional station evaluating signal exchange between central and further stations |
| DE2928492A1 (en) * | 1979-07-14 | 1981-01-15 | Licentia Gmbh | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR MONITORING CABLES CONNECTING SEVERAL STATIONS, ESPECIALLY IN TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORKS |
| DE2929597A1 (en) * | 1979-07-21 | 1981-02-05 | Licentia Gmbh | Alarm indication signal recognition circuit - connects digital signal from transmitter to first input of NOR-circuit, whose output goes to counter input |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| SIEMENS-ZEITSCHRIFT, Band 48, 1974 Beiheft "Nachrichten-Ubertragungstechnik" * |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0113478A1 (en) * | 1982-12-24 | 1984-07-18 | Hitachi, Ltd. | FAil safe system for information transmission systems |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DK8482A (en) | 1982-07-13 |
| DE3100683A1 (en) | 1982-08-12 |
| DE3173740D1 (en) | 1986-03-20 |
| EP0056099A3 (en) | 1983-07-27 |
| NO820050L (en) | 1982-07-13 |
| EP0056099B1 (en) | 1986-02-05 |
| NO155869C (en) | 1987-06-10 |
| ATE17895T1 (en) | 1986-02-15 |
| NO155869B (en) | 1987-03-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE4036639C2 (en) | ||
| DE3431171C2 (en) | Track vacancy detection device with axle counting | |
| DE2817089A1 (en) | HAZARD WARNING SYSTEM | |
| DE2539977B2 (en) | Circuit arrangement for the detection of faulty states of peripheral units in a data processing system | |
| EP0067339A2 (en) | Method and arrangement for disturbance detection in hazard signalling systems, especially fire signalling systems | |
| EP0177019A2 (en) | Data transmission arrangement comprising a tree-structured data network | |
| EP0004909B1 (en) | Annunciator of danger | |
| EP0322698A1 (en) | Methode for the transmission of information | |
| DE3418084A1 (en) | REMOTE MONITORING DEVICE FOR DATA TRANSFER | |
| DE1812505C3 (en) | Telecontrol system with multiple use of a transmission channel | |
| EP0056099B1 (en) | Supervisory apparatus for remote-control systems | |
| DE3150313C2 (en) | Arrangement for determining and reporting the position of a number of switches and for monitoring the connection line | |
| EP0106985B1 (en) | Operation monitoring of digital transmission links | |
| EP0060339B1 (en) | Station for a remote control device | |
| DE3032619C2 (en) | Telecontrol device with at least one central station and with further stations | |
| DE2337290B2 (en) | Monitoring device for a thyristor valve | |
| DE19921247A1 (en) | Software application monitoring procedure e.g. for personal computers (PCs) | |
| EP0048939B1 (en) | Signal transmission arrangements having stations that can be optionally equipped with input units | |
| DE4203276A1 (en) | Monitoring of information displayed by light-emitting diodes - registering data and control signals by groups of diodes through which current is assessed | |
| DE3202025C2 (en) | Device for the operational control of thyristors of a high voltage valve | |
| EP0193835A1 (en) | Apparatus for collecting monitoring information in transmission systems | |
| DE10347196B4 (en) | Device for checking an interface | |
| DE2853147C2 (en) | Data input and output arrangement | |
| DE3141220C2 (en) | ||
| DE2908629C2 (en) | Call procedure for telecontrol systems in joint traffic |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19811029 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| RHK1 | Main classification (correction) |
Ipc: G08C 25/00 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI SE |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI SE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19860205 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19860205 Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19860205 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 17895 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19860215 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19860228 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3173740 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19860320 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19861029 Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19861029 |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: STANDARD ELEKTRIK LORENZ AG Effective date: 19861104 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19891219 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19901022 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| ITTA | It: last paid annual fee | ||
| RDAG | Patent revoked |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009271 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT REVOKED |
|
| 27W | Patent revoked |
Effective date: 19901105 |
|
| GBPR | Gb: patent revoked under art. 102 of the ep convention designating the uk as contracting state | ||
| APAH | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNO |