EP0045342B1 - Kraftstoffzusammensetzung mit verbessertem Fliessvermögen bei tiefen Temperaturen - Google Patents
Kraftstoffzusammensetzung mit verbessertem Fliessvermögen bei tiefen Temperaturen Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0045342B1 EP0045342B1 EP80890087A EP80890087A EP0045342B1 EP 0045342 B1 EP0045342 B1 EP 0045342B1 EP 80890087 A EP80890087 A EP 80890087A EP 80890087 A EP80890087 A EP 80890087A EP 0045342 B1 EP0045342 B1 EP 0045342B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- fuel composition
- ethylene
- vinyl acetate
- weight
- copolymer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10L—FUELS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NATURAL GAS; SYNTHETIC NATURAL GAS OBTAINED BY PROCESSES NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C10G OR C10K; LIQUIFIED PETROLEUM GAS; USE OF ADDITIVES TO FUELS OR FIRES; FIRE-LIGHTERS
- C10L1/00—Liquid carbonaceous fuels
- C10L1/10—Liquid carbonaceous fuels containing additives
- C10L1/14—Organic compounds
- C10L1/18—Organic compounds containing oxygen
- C10L1/192—Macromolecular compounds
- C10L1/195—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- C10L1/197—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds derived from monomers containing a carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bond and an acyloxy group of a saturated carboxylic or carbonic acid
- C10L1/1973—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds derived from monomers containing a carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bond and an acyloxy group of a saturated carboxylic or carbonic acid mono-carboxylic
Definitions
- the present invention relates to heating or fuel mixtures, in particular middle distillates, with an addition of polymers which improves the fluidity of the mixture at low temperatures.
- paraffins contained in the middle distillates are suitable for installation and precipitate at low temperatures, gradually agglomerate into larger structures and ultimately reduce the flow and pumpability as well as the filterability, so that the Use of the oils is restricted.
- ethylene copolymers especially ethylene / vinyl acetate copolymers, as flow improvers for middle distillates in the concentration range 0.001 to 1 mass%, the average molecular mass from 500 to 50040 and the comonomer content from 1 to 60 mass% is generally known (DE-C No. 1147799, DE-A No. 1162630, DE-B No. 1645873, DE-A No. 2227786).
- the compounds used as inoculants have a molecular weight of 500 to 30,000 and preferably 500 to 10,000 and the compounds used as crystallization inhibitors have a molecular weight of 1200 to 20,000 and preferably 1200 to 6000.
- various copolymers of ethylene and vinyl acetate are used, the ratio between the concentration of the vinyl acetate and the molecular weight of the copolymer being particularly important.
- the object of the invention is to improve the low-temperature behavior of heating or fuel mixtures by adding special polymers, the presence of which improves the fluidity and pumpability at low temperatures.
- a fuel composition with improved fluidity at low temperatures consisting of heating or propellants with a boiling range above 453 K and of ethylene copolymers that the fuel composition has 0.001 to 0.5% by weight of an ethylene copolymer with a medium Molecular mass (number average) of 500 to 5000, preferably 1000 to 3500, and a comonomer content of 25 to 60 wt .-% contains, has 3 to 10 long chain branches per 10 4 carbon atoms.
- the long chain branches have a chain length of at least 100 carbon atoms and are sometimes considerably longer. This clearly distinguishes them from the short chain branches known from other flow improvers, which preferably consist of methyl groups.
- Ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers with an average molecular weight (number average) of 1000 to 3500, a vinyl acetate content of 35 to 50% by weight and 4 to 8 long-chain branches per 10 4 carbon atoms have proven to be particularly suitable. These copolymers show good dissolution behavior in most aromatic solvents, so that the additives can be added both in the form of a concentrate in an aromatic solvent or solvent mixture and directly in the fuel.
- copolymers show hardly any impairment of the action due to repeated cooling and heating, since they show good dissolution behavior.
- the ethylene / vinyl acetate copolymers used according to the invention have both the necessary polymethylene segments which are interrupted by the vinyl acetate units but can be incorporated into the lattice of the wax crystals at the defects, and also have voluminous groups due to the long chain branches, the further installation of the paraf contained in the middle distillates fine at the defects of the lattice and thus reduce further crystal growth.
- Photomicrographs of wax crystals deposited under extreme conditions of the untrimmed starting diesel fuel and of the diesel fuel mixed with the ethylene / vinyl acetate copolymers according to the invention showed that the addition of the ethylene / vinyl acetate copolymer significantly displaced the deposition of the waxes as a sponge-like mass or platelet-shaped crystals, so that the size of the wax crystals that form is reduced by 40 to 60%.
- the ethylene / vinyl acetate copolymer used can be provided with further large, space-filling substituents by esterification with 2-ethylhexyl acrylic, isobutyl acrylic, lauryl acrylic and phthalic acid.
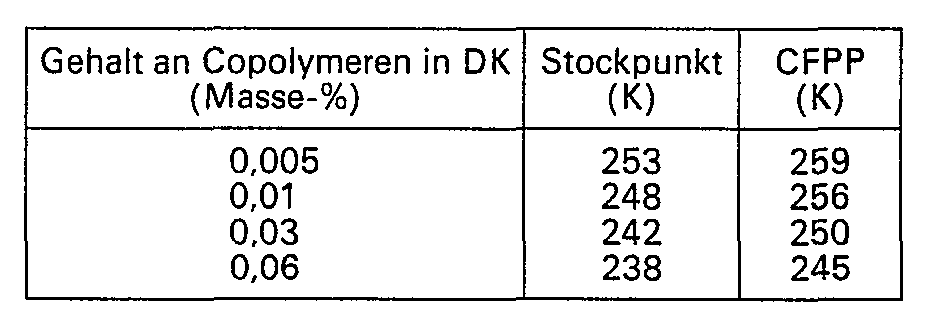
- a diesel fuel with a boiling range of 473 to 628 K, a pour point of 261 K and a CFPP of 266 K was used.
- an ethylene / vinyl acetate copolymer having a vinyl acetate content of 38 mass% of a number average molecular weight of 2650 and 5 long chain branches per 10 4 C atoms was added in the form of a solution. The following results were obtained:
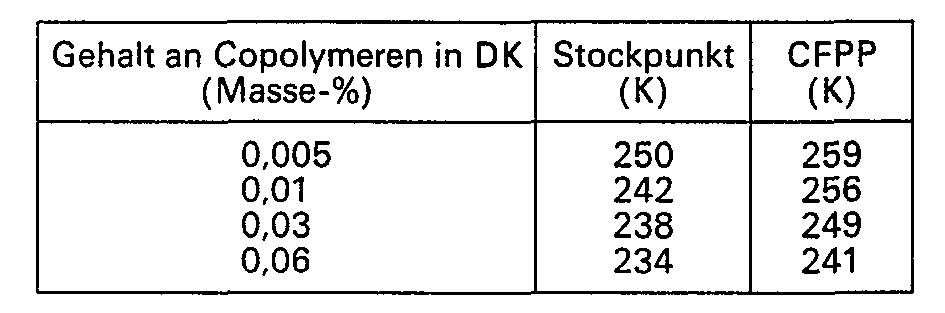
- a diesel fuel with a boiling range of 471 to 615 K, a pour point of 269 K and a CFPP of 267 K was used.
- An ethylene / vinyl acetate copolymer with a vinyl acetate content of 44% by mass, a number average molecular weight of 1870 and 8 long chain branches per 10 4 C atoms was added to this fuel in the form of a solution. The following results were obtained:
- a heating oil HE-D (according to TGL 3667) with a pour point of 286 K was added an ethylene / vinyl acetate copolymer with a vinyl acetate content of 44 mass%, a number average molecular mass of 1870 and 8 long chain branches per 10 4 C atoms. The following results were obtained:
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Emergency Medicine (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Liquid Carbonaceous Fuels (AREA)
- Solid Fuels And Fuel-Associated Substances (AREA)
- Addition Polymer Or Copolymer, Post-Treatments, Or Chemical Modifications (AREA)
Description
- Die vorliegende Erfindung bezieht sich auf Heiz-oder Treibstoffmischungen, insbesondere Mitteldestillate, mit einem Zusatz an Polymeren, der das Fliessvermögen der Mischung bei tiefen Temperaturen verbessert.
- Die in den Mitteldestillaten (Siedebereich 453-673 K bzw. 180 bis 400° C) enthaltenen Paraffine sind kirstallisationsfähig und fallen bei tiefen Temperaturen aus, agglomerieren allmählich zu grösseren Gebilden und setzen schliesslich die Fliess-und Pumpfähigkeit sowie die Filtrierbarkeit herab, so dass die Verwendung der Öle eingeschränkt wird.
- Es ist seit langem bekannt, dass eine Reihe von Polymeren, wie chlorierte Polyäthylene, Äthylen/ Propylen- Mischpolymere, Copolymere aus Äthylen mit Akrylestern oder Vinylestern, flüssige Kondensationsprodukte aus mehrfach ungesättigten Monoestern und aromatischen Kohlenwasserstoffen, Polyolefine, Polyestergemische, Polymethacrylate, Säureamide, akylierte Napthene allein oder im Gemisch, das Kälteverhalten von Mitteldestillaten und damit den Gebrauchswert erfiohen (H. Gondermann und H.H. Giere, "Chemiker Zeitung", 97 [1973] 9 S.462-469).
- Der Einsatz von Äthylencopolymeren, speziell Äthylen/Vinylacetat-Copolymeren, als Fliessverbesserer für Mitteldestillate in dem Konzentrationsbereich 0,001 bis 1 Masse-%, der mittleren Molekularmasse von 500 bis 50040 und dem Comonomerengehalt von 1 bis 60 Masse-% ist allgemein bekannt (DE-C Nr. 1147799, DE-A Nr. 1162630, DE-B Nr. 1645873, DE-A Nr.2227786).
- Es ist auch bekannt (DE-B Nr. 1914756), als Fliessverbesserer Copolymere zu benutzen, in denen bei der Herstellung durch die Begrenzung der Polymerisationstemperatur der Grad der Verzweigungen eingestellt wird. Bei diesen Ver-' zweigungen handelt es sich um sogenannte Kurzkettenverzweigungen oder Äthylenseitenketten. Diese bilden sich an dem Hauptkettenmolekül nach dem sogenannten backbiting- Mechanismus und enthalten 4 bis 6 C-Atome.
- Diese Art von Verzweigungen beeinträchtigt die Wirksamkeit von Fliessverbessern, da sie zum einen den Einbau des Polymeren in die Störstellen des Wachskristallgitters erschweren und zum anderen das weitere Anwachsen von Wachskristallen (Abschirmeffekt) nicht genügend verhindern.
- Es ist weiterhin bekannt, dass man Mitteldestillate mit verbessertem Tieftemperaturverhalten erhalten kann, wenn man sie mit einer Kombination von
- a) 1 bis 20 Gew.-Teilen einer als Kristallisationsverbesserer oder Impfkeime wirksamen polymeren Verbindung, und
- b) 1 bis 99 Gew.-Teilen einer als Wachskristallisationnhemmer wirksamen polymeren Verbindung
versetzt (DE-A Nr. 2206719). - Im allgemeinen weisen die als Impfkeime eingesetzten Verbindungen ein Molekulargewicht von 500 bis 30000 und vorzugsweise 500 bis 10000 und die als Kristallisationshemmer eingesetzten Verbindungen ein Molekulargewicht von 1200 bis 20000 und vorzugsweise 1200 bis 6000 auf. In den bevorzugten Ausführungsformen werden verschiedene Copolymere aus Äthylen und Vinylacetat eingesetzt, wobei das Verhältnis zwischen der Konzentration des Vinylacetates und dem Molekulargewicht des Copolymeren besonders wichtig ist.
- Aufgabe der Erfindung ist die Verbesserung des Kälteverhaltens von Heiz- oder Treibstoffmischungen durch Zusatz spezieller Polymerer, durch deren Gegenwart das Fliessvermögen und die Pumpfähigkeit bei tiefen Temperaturen verbessert werden.
- Zur Lösung der Aufgabe wird erfindungsgemäss bei einer Kraftstoffzusammensetzung mit verbessertem Fliessvermögen bei tiefen Temperaturen bestehend aus Heiz- oder Treibstoffen mit einem Siedebereich oberhalb von 453 K und aus Äthylencopolymeren vorgeschlagen, dass die Kraftstoffzusammensetzung 0,001 bis 0,5 Gew.-% eines Äthylencopolymeren mit einer mittleren Molekularmasse (Zahlenmittel) von 500 bis 5000, vorzugsweise 1000 bis 3500, und einem Comonomerengehalt von 25 bis 60 Gew.-% enthält, 3 bis 10 Langkettenverzweigungen pro 104 C-Atome besitzt.
- Die Langkettenverzweigungen besitzen eine Kettenlänge von mindestens 100 C-Atomen und sind teilweise beträchtlich länger. Damit unterscheiden sie sich deutlich von den Kurzkettenverzweigungen, die bei anderen Fliessverbesserern bekannt sind und vorzugsweise aus Methylgruppen bestehen. Es haben sich besonders ÄthylenVinylacetat-Copolymere mit einer mittleren Molekularmasse (Zahlenmittel) von 1000 bis 3500, einem Vinylacetatgehalt von 35 bis 50 Gew.-% und 4 bis 8 Langkettenverzweigungen pro 104 C-Atome als geeignet erwiesen. Diese Copolymeren zeigen ein gutes Lösungsverhalten in den meisten aromatischen Lösungsmitteln, so dass die Zusatzstoffe sowohl in Form eines Konzentrates in einem aromatischen Lösungsmittel bzw. Lösungsmittelgemisch als auch direkt in den Kraftstoff gegeben werden können.
- Besonders vorteilhaft ist, dass diese Copolymeren durch wiederholtes Abkühlen und Erwärmen kaum eine Beeinträchtigung der Wirkung zeigen, da sie ein gutes Lösungsverhalten zeigen.
- Aufgrund ihres Aufbaus und ihrer Zusammensetzung verfügen die erfindungsgemäss eingesetzten Äthylen/Vinylacetat-Copolymeren sowohl über die notwendigen Polymethylensegmente, die von den Vinylacetateinheiten unterbrochen werden, sich aber an den Störstellen in das Gitter der Wachskristalle einbauen können, als auch über voluminöse Gruppen aufgrund der Langkettenverzweigungen, die den weiteren Einbau der in den Mitteldestillaten enthaltenen Paraffine an den Störstellen der Gitter erschweren und damit das weitere Kristallwachstum vermindern.
- Mikrofotografien von unter extremen Bedingungen abgeschiedenen Wachskristallen des unbeschnittenen Ausgangsdieselkraftstoffes und des mit den erfindungsgemässen Äthylen/Vinylacetat-Copolymeren versetzten Dieselkraftstoffes zeigten, dass durch den Zusatz des Äthylen/Vinylacetat-Copolymeren die Abscheidung der Wachse als schwammartige Masse oder plättchenförmige Kristalle wesentlich verschoben wird, so dass die Grösse der sich bildenden Wachskristalle um 40 bis 60% verkleinert wird.
- Nach einer besonderen Ausführungsform der Erfindung kann das verwendete Äthylen/Vinylacetat-Copolymere durch Veresterung mit 2- Äthylhexylacryl-, Isobutylacryl-, Laurylacryl- und Phthalsäure, mit weiteren grossen, raumfüllenden Substituenten versehen sein.
- Es wurde ein Dieselkraftstoff mit einem Siedebereich von 473 bis 628 K, einem Stockpunkt von 261 K und einem CFPP von 266 K eingesetzt. Diesem Kraftstoff wurde ein Äthylen/Vinylacetat-Copolymeres mit einem Vinylacetatgehalt von 38 Masse-% einer zahlenmittleren Molekularmassevon 2650 und 5 Langkettenverzweigungen pro 104 C-Atomen in Form einer Lösung zugegeben. Dabei wurden folgende Ergebnisse erhalten:
- Es wurde ein Dieselkraftstoff mit einem Siedebereich von 471 bis 615 K, einem Stockpunkt von 269 K und einem CFPP von 267 K eingesetzt. Diesem Kraftstoff wurde ein Äthylen/Vinylacetat-Copolymeres mit einem Vinylacetatgehalt von 44 Masse-%, einer zahlenmittleren Molukularmasse von 1870 und 8 Langkettenverzweigungen pro 104 C-Atomen in Form einer Lösung zugegeben. Dabei wurden folgende Ergebnisse erhalten:
- Einem Heizöl HE-D (nach TGL 3667) mit einem Stockpunkt von 286 K wurde ein Äthylen/Vinylacetat-Copolymeres mit einem Vinylacetatgehalt von 44 Masse-%, einer zahlenmittleren Molekularmasse von 1870 und 8 Langkettenverzweigungen pro 104 C-Atomen zugesetzt. Es wurden dabei folgende Ergebnisse erhalten:
Claims (4)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT80890087T ATE5599T1 (de) | 1980-07-31 | 1980-07-31 | Kraftstoffzusammensetzung mit verbessertem fliessvermoegen bei tiefen temperaturen. |
| DE8080890087T DE3065883D1 (en) | 1980-07-31 | 1980-07-31 | Fuel composition with particular fluidity at low temperatures |
| EP80890087A EP0045342B1 (de) | 1980-07-31 | 1980-07-31 | Kraftstoffzusammensetzung mit verbessertem Fliessvermögen bei tiefen Temperaturen |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP80890087A EP0045342B1 (de) | 1980-07-31 | 1980-07-31 | Kraftstoffzusammensetzung mit verbessertem Fliessvermögen bei tiefen Temperaturen |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0045342A1 EP0045342A1 (de) | 1982-02-10 |
| EP0045342B1 true EP0045342B1 (de) | 1983-12-14 |
Family
ID=8187506
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP80890087A Expired EP0045342B1 (de) | 1980-07-31 | 1980-07-31 | Kraftstoffzusammensetzung mit verbessertem Fliessvermögen bei tiefen Temperaturen |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0045342B1 (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE5599T1 (de) |
| DE (1) | DE3065883D1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA1263663A (en) * | 1984-12-06 | 1989-12-05 | Joseph Fischer | Terpolymers of ethylene, vinyl acetate and isobutylene useful as pour point depressants in distillate oils |
| JPS6270488A (ja) * | 1985-09-24 | 1987-03-31 | Mitsubishi Petrochem Co Ltd | 燃料油添加剤および流動性の改善された燃料油 |
| GB9213870D0 (en) | 1992-06-30 | 1992-08-12 | Exxon Chemical Patents Inc | Oil additives and compositions |
| GB9213827D0 (en) * | 1992-06-30 | 1992-08-12 | Exxon Chemical Patents Inc | Oil additives and compositions |
| GB9213904D0 (en) * | 1992-06-30 | 1992-08-12 | Exxon Chemical Patents Inc | Oil additives and compositions |
| GB9213909D0 (en) * | 1992-06-30 | 1992-08-12 | Exxon Chemical Patents Inc | Oil additives and compositions |
| GB9417670D0 (en) * | 1994-09-02 | 1994-10-19 | Exxon Chemical Patents Inc | Oil additives, compositions and polymers for use therein |
| GB9417667D0 (en) * | 1994-09-02 | 1994-10-19 | Exxon Chemical Patents Inc | Oil additives, compositions and polymers for use therein |
| US5681359A (en) * | 1996-10-22 | 1997-10-28 | Quantum Chemical Corporation | Ethylene vinyl acetate and isobutylene terpolymer as a cold flow improver for distillate fuel compositions |
| US6495495B1 (en) | 1999-08-20 | 2002-12-17 | The Lubrizol Corporation | Filterability improver |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB968462A (en) * | 1961-12-21 | 1964-09-02 | Monsanto Chemicals | Reactive resins containing unsaturated groups |
| DE1914756C3 (de) * | 1968-04-01 | 1985-05-15 | Exxon Research and Engineering Co., Linden, N.J. | Verwendung von Ethylen-Vinylacetat- Mischpolymerisaten für Erdöl-Destillate |
| GB1314855A (en) * | 1970-06-17 | 1973-04-26 | Monsanto Chemicals | Lubricating oil compositions containing viscosity index improvers |
| US3887610A (en) * | 1971-12-09 | 1975-06-03 | Exxon Research Engineering Co | Emulsion polymerization of ethylene with chain transfer agents to form copolymers |
| EP0003489B1 (de) * | 1977-12-20 | 1983-01-12 | Imperial Chemical Industries Plc | Rohöl mit verbessertem Fliesspunktverhalten |
-
1980
- 1980-07-31 EP EP80890087A patent/EP0045342B1/de not_active Expired
- 1980-07-31 DE DE8080890087T patent/DE3065883D1/de not_active Expired
- 1980-07-31 AT AT80890087T patent/ATE5599T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| Brauer et al.:"Untersuchung zur Charakterisierung von Äthylen-Vinylazetat-Kopolymeren durch Gelchromatographie, Viskosimetrie und osmotisch Messungen", Plaste und Kautschuk 24, Seiten 630-635 (1977) * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0045342A1 (de) | 1982-02-10 |
| ATE5599T1 (de) | 1983-12-15 |
| DE3065883D1 (en) | 1984-01-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0398101B1 (de) | Neue Umsetzungsprodukte von Aminoalkylenpolycarbonsäuren mit sekundären Aminen und Erdölmitteldestillatzusammensetzungen, die diese enthalten | |
| EP0126363B1 (de) | Verwendung von Copolymeren aus Estern und Amiden der Acryl- und/oder Methacrylsäure als Stockpunkterniedriger für Paraffinlösungen | |
| EP0922716B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Ethylen-Terpolymeren und deren Verwendung als Zusatz zu Mineralöl und Mineralöldestillaten | |
| DE69308304T2 (de) | Ölzusätze und zusammensetzungen | |
| DE69507040T2 (de) | Ölzusätze, zusammensetzungen und polymeren zur hinein verwendung | |
| EP0254284B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Verbesserung der Fliessfähigkeit von Mineralölen und Mineralöldestillaten | |
| DE3137233A1 (de) | Zusammensetzungen zur verbesserung der kaltfiltirerbarkeit von mittleren erdoelschnitten | |
| EP0900836B2 (de) | Additiv zur Verbesserung der Fliessfähigkeit von Mineralölen und Mineralöldestillaten | |
| EP0045342B1 (de) | Kraftstoffzusammensetzung mit verbessertem Fliessvermögen bei tiefen Temperaturen | |
| EP0405270B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Verbesserung der Fliessfähigkeit von Mineralölen und Mineralöldestillaten | |
| DE69309926T2 (de) | Ölzusätze und zusammensetzungen | |
| DE69308303T2 (de) | Ölzusätze und zusammensetzungen | |
| DE69309928T3 (de) | Ölzusätze und zusammensetzungen | |
| DE3382624T3 (de) | Zwischendestillatzubereitungen mit verbessertem Fliessverhalten bei niedriger Temperatur. | |
| EP0721475B1 (de) | Copolymerisate auf ethylenbasis und ihre verwendung als fliessverbesserer in erdölmitteldestillaten | |
| DE69802198T3 (de) | Zusätze für ölzusammensetzungen | |
| DE2339175C2 (de) | ||
| DE2142111A1 (de) | Verfahren zum Transport paraffinischer Rohöle durch Leitungen | |
| EP0892012B2 (de) | Fliessverbesserer für Mineralöle | |
| DE4019623A1 (de) | Additive zur herabsetzung des stockpunktes und zur verhinderung des absetzens der unterhalb des bpa-punktes ausgeschiedenen paraffine | |
| EP0251002B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Verbesserung der Fliessfähigkeit von Mineralölen und Mineralöldestillaten | |
| DD154869A3 (de) | Kraftstoffzusammensetzung mit verbessertem fliessvermoegen bei tiefen temperaturen | |
| DE2620840C2 (de) | ||
| DD254956A1 (de) | Verfahren zur verbesserung des kaelteverhaltens von erdoelmitteldestillaten | |
| DE1913522A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines als Paraffinkristall-Modifiziermittel geeigneten AEthylen-Alkylacrylat-Mischpolymerisates |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19811028 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE DE FR NL SE |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE DE FR NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 5599 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19831215 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3065883 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19840119 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: BASF AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT Effective date: 19840718 |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: BAYER AG, LEVERKUSEN KONZERNVERWALTUNG RP PATENTAB Effective date: 19840827 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: RUHRCHEMIE AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT Effective date: 19840913 |
|
| PLBG | Opposition deemed not to have been filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009274 |
|
| 26D | Opposition deemed not to have been filed |
Opponent name: BAYER AG, LEVERKUSEN KONZERNVERWALTUNG RP PATENTAB Effective date: 19850529 |
|
| NLXE | Nl: other communications concerning ep-patents (part 3 heading xe) |
Free format text: IN PAT.BUL.03/85,PAGE 373 THE OPPOSITION NO.1 DEEMED NOT TO BE FILED |
|
| PLAB | Opposition data, opponent's data or that of the opponent's representative modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009299OPPO |
|
| PLBH | Opposition deemed not to have been filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009299OPPB |
|
| R26 | Opposition filed (corrected) |
Opponent name: BASF AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT, LUDWIGSHAFEN * 840913 HOE Effective date: 19840718 |
|
| R26D | Opposition deemed not to have been filed (corrected) |
Free format text: 850529 BAYER AG, LEVERKUSEN KONZERNVERWALTUNG RP PATENTABTEILUNG |
|
| NLXE | Nl: other communications concerning ep-patents (part 3 heading xe) |
Free format text: IN PAT.BUL.03/85,PAGE 373:CORR.:HOECHST AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19890621 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19890629 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19890630 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19890731 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19890803 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19890828 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| RDAG | Patent revoked |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009271 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT REVOKED |
|
| 27W | Patent revoked |
Effective date: 19900202 |
|
| NLR2 | Nl: decision of opposition | ||
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: VEB LEUNA-WERKE WALTER ULBRICHT Effective date: 19900731 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 80890087.2 Effective date: 19900523 |
|
| APAC | Appeal dossier modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS NOAPO |
|
| APAC | Appeal dossier modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS NOAPO |
|
| APAH | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNO |