WO2022014273A1 - 撮像支援制御装置、撮像支援制御方法、撮像支援システム - Google Patents
撮像支援制御装置、撮像支援制御方法、撮像支援システム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2022014273A1 WO2022014273A1 PCT/JP2021/023607 JP2021023607W WO2022014273A1 WO 2022014273 A1 WO2022014273 A1 WO 2022014273A1 JP 2021023607 W JP2021023607 W JP 2021023607W WO 2022014273 A1 WO2022014273 A1 WO 2022014273A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- target
- composition
- subject
- user
- guide
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/60—Control of cameras or camera modules
- H04N23/63—Control of cameras or camera modules by using electronic viewfinders
- H04N23/631—Graphical user interfaces [GUI] specially adapted for controlling image capture or setting capture parameters
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/60—Control of cameras or camera modules
- H04N23/64—Computer-aided capture of images, e.g. transfer from script file into camera, check of taken image quality, advice or proposal for image composition or decision on when to take image
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/01—Input arrangements or combined input and output arrangements for interaction between user and computer
- G06F3/016—Input arrangements with force or tactile feedback as computer generated output to the user
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/16—Sound input; Sound output
- G06F3/167—Audio in a user interface, e.g. using voice commands for navigating, audio feedback
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/60—Control of cameras or camera modules
- H04N23/61—Control of cameras or camera modules based on recognised objects
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/60—Control of cameras or camera modules
- H04N23/63—Control of cameras or camera modules by using electronic viewfinders
- H04N23/631—Graphical user interfaces [GUI] specially adapted for controlling image capture or setting capture parameters
- H04N23/632—Graphical user interfaces [GUI] specially adapted for controlling image capture or setting capture parameters for displaying or modifying preview images prior to image capturing, e.g. variety of image resolutions or capturing parameters
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/60—Control of cameras or camera modules
- H04N23/63—Control of cameras or camera modules by using electronic viewfinders
- H04N23/633—Control of cameras or camera modules by using electronic viewfinders for displaying additional information relating to control or operation of the camera
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/60—Control of cameras or camera modules
- H04N23/69—Control of means for changing angle of the field of view, e.g. optical zoom objectives or electronic zooming
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03B—APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR TAKING PHOTOGRAPHS OR FOR PROJECTING OR VIEWING THEM; APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS EMPLOYING ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ACCESSORIES THEREFOR
- G03B17/00—Details of cameras or camera bodies; Accessories therefor
- G03B17/18—Signals indicating condition of a camera member or suitability of light
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03B—APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR TAKING PHOTOGRAPHS OR FOR PROJECTING OR VIEWING THEM; APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS EMPLOYING ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ACCESSORIES THEREFOR
- G03B17/00—Details of cameras or camera bodies; Accessories therefor
- G03B17/38—Releasing-devices separate from shutter
Definitions
- This technology relates to an image pickup support control device and a method thereof for controlling so that a guide for a composition change operation by a user is performed, and a technical field of an image pickup support system equipped with an image pickup support control device.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a technique for performing voice guidance on a composition change operation by a user so as not to cause an inappropriate composition.
- voice guidance may not be suitable depending on the situation in which imaging is performed. For example, in a noisy situation outdoors or in a noisy situation such as imaging a child running around even indoors, the user may not be able to hear the voice guide.
- voice guidance is not suitable even in situations where quietness is required, such as in situations where wild animals such as wild birds are imaged.
- This technology was made in view of the above circumstances, and the purpose is to improve the imaging support performance by providing appropriate imaging support even when the display or sound guide is unsuitable. do.
- the image pickup support control device is provided with a control unit that controls so that the guide for the composition change operation by the user is performed by tactile presentation to the user based on the difference between the target composition and the actual composition. Is.
- a control unit that controls so that the guide for the composition change operation by the user is performed by tactile presentation to the user based on the difference between the target composition and the actual composition. Is.
- control unit may be configured to change the mode of tactile presentation for the guide based on the size of the difference between the target composition and the actual composition. Conceivable. This makes it possible for the user to grasp whether the difference between the target composition and the actual composition is small or large by the difference in the mode of tactile presentation for the guide.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is arranged at a position determined by the user operation in the image frame, and the image frame of the target subject.
- the operation related to the setting of the arrangement position in the inside is performed as a drawing operation on the screen for displaying the through image of the captured image, and the control unit determines which operation type the drawing operation belongs to among the plurality of operation types. Therefore, it is conceivable that the setting conditions other than the arrangement position among the setting conditions of the target composition are determined.
- the operation type of the drawing operation is a type of operation that can be performed as a drawing operation, and examples thereof include an operation of drawing a point, an operation of drawing a circle, and an operation of drawing an ellipse.
- the setting condition of the target composition means a condition for determining what kind of composition the target composition should be, for example, the arrangement position of the target subject in the image frame and a single target subject. Conditions such as whether to use or to have a plurality of items can be mentioned. According to the above configuration, the user can specify the placement position of the target subject and the setting conditions other than the placement position among the setting conditions of the target composition by one operation as a drawing operation on the screen. It becomes.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is arranged at a position determined by the user operation in the image frame, and the control unit is the target. It is conceivable to have a configuration in which the designation of the subject is accepted by voice input from the user. This eliminates the need for the user to operate an operator such as a button or a touch panel when designating the target subject.
- the control unit accepts a drawing operation on the screen for displaying the through image of the captured image, determines the situation of the camera that obtains the captured image, and specifies the situation.
- a specific mark is drawn by the drawing operation, a composition satisfying the composition condition associated with the situation and the drawn mark is set as the target composition.
- a specific mark for example, a mark imitating a famous character in the theme park is drawn.
- it is possible to set a composition that satisfies the composition conditions associated with the situation and the mark as the target composition such as a composition in which the character is placed at a position in the image frame corresponding to the drawn mark. be.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is arranged at a position determined by the user operation in the image frame, and the image frame of the target subject.
- the operation of designating the arrangement range within is performed as a drawing operation on the screen for displaying the through image of the captured image, and the control unit determines which of the plurality of operation types the drawing operation belongs to.
- the configuration is such that the number of the target subjects to be arranged within the arrangement range is determined.
- the user can specify the arrangement range of the target subject and the number of target subjects to be arranged within the arrangement range by one operation as a drawing operation on the screen.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is placed at the target position in the image frame, and the control unit determines the movement of the target subject. It is conceivable to have a configuration in which the guide for arranging the target subject at the target position is controlled based on the detected movement of the target subject. This makes it possible to perform a guide in consideration of the movement of the target subject as a guide for realizing the composition of arranging the target subject at the target position in the image frame.
- the control unit performs the guide based on the relationship between the predicted position of the target subject after a predetermined time and the position of the target. ..
- the guide is performed based on the difference between the current position of the target subject and the target position, and the position of the target subject is set to the target position. There may be situations where it is difficult to match. Therefore, as described above, the guide is performed based on the position after a predetermined time predicted from the movement of the target subject.
- control unit is configured to set the target composition based on the determination result of the image pickup target scene. This makes it possible to automatically set a target composition according to the scene to be imaged, such as a scene in which a train is imaged at a station or a scene in which a sunset is imaged, based on a scene determination result.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is placed at the target position in the image frame, and the control unit is such that the target subject captures the image. It is conceivable to predict the position of the target state according to the target scene and control the guide so that the predicted position matches the target position.
- the target state according to the scene to be imaged is determined according to the scene, for example, the state in which the train is stopped in the scene where the train is imaged at the station, or the state in which the sun is set in the scene at sunset. It means a target state of the target subject, specifically, a state of being a shutter chance, for example. According to the above configuration, it is possible to appropriately support the user so that the target subject in the target state is imaged by the target composition.
- the control unit enables the function of the guide when it is estimated that the user is not viewing the screen displaying the through image of the captured image. It is conceivable to configure it. As a result, the guide according to the present technology is automatically performed in the situation where the user performs imaging without looking at the screen.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is arranged at the target position in the image frame according to the target size, and the control unit is the target. It is conceivable to configure the zoom control so that the size of the subject becomes the target size. This makes it possible to eliminate the need for a zoom operation by the user in order to realize imaging with a target composition.
- the image pickup support control device In the image pickup support control device according to the present technology described above, is the situation in which the user can move when the control unit determines that the size of the target subject cannot be set to the target size by the zoom control? It is conceivable that the guide is performed to change the positional relationship between the user and the target subject when it is determined whether or not the user can move. As a result, it is possible to prevent inconveniences such as the user being inconvenienced by the guide being performed even though the user cannot move due to the image pickup in a crowded person or the like.
- the information processing apparatus controls the image pickup so that the guide for the composition change operation by the user is performed by the tactile presentation to the user based on the difference between the target composition and the actual composition. It is a support control method. Even with such an image pickup support control method, the same operation as that of the image pickup support control device according to the present technology can be obtained.
- the imaging support system provides a guide on the composition change operation by the user based on the difference between the target composition and the actual composition, and the tactile presentation device having the tactile presentation unit for presenting the tactile sensation to the user. It is provided with an image pickup support control device having a control unit that controls the tactile presentation to be performed by the tactile presentation. Even with such an image pickup support system, the same operation as that of the image pickup support control device according to the present technology can be obtained.
- FIG. 1 It is a block diagram which showed the internal structure example of the information processing apparatus as one Embodiment of the image pickup support control apparatus which concerns on this technique. It is a figure for demonstrating a specific example of the image pickup support method as an embodiment. It is a flowchart which showed the example of the specific processing procedure for realizing the image pickup support method explained with FIG. It is explanatory drawing of the process according to the type of a drawing operation. It is explanatory drawing of the example which displays the name information of a subject type on a screen. It is explanatory drawing of the example which sets the subject within the range drawn on the screen as a target subject. It is explanatory drawing about the setting example of the target composition when a specific mark is drawn in a specific situation.
- Configuration of image pickup support control device as an embodiment> ⁇ 2.
- An example of imaging support method> ⁇ 3.
- Processing procedure> ⁇ 4.
- About the method of specifying the setting conditions of the target composition> ⁇ 5.
- About the method of specifying the subject> ⁇ 6.
- Method of specifying target composition according to the situation> ⁇ 7.
- Correspondence when there are multiple target subjects> ⁇ 8.
- Control according to the movement of the target subject> ⁇ 9.
- Variations on tactile presentation> ⁇ 10.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an example of an internal configuration of an information processing device 1 as an embodiment of an image pickup support control device according to the present technology.
- the information processing apparatus 1 includes an image pickup unit 2, a display unit 3, an operation unit 4, a communication unit 5, a sensor unit 6, a control unit 7, a memory unit 8, a sound output unit 9, and a tactile presentation unit 10.
- a bus 11 for connecting each of these parts to each other so as to be capable of data communication is provided.
- the information processing device 1 is configured as an information processing device having a camera function, such as a smartphone or a tablet terminal.
- the image pickup unit 2 is configured as a camera unit including an image pickup optical system and an image sensor such as a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) sensor or a CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) sensor, and obtains an image captured by digital data.
- the image pickup optical system is provided with a zoom lens, and it is possible to perform optical zoom by driving the zoom lens.
- the image pickup unit 2 includes a camera unit that captures an image in a direction opposite to the direction in which the screen 3a of the display unit 3 described later is directed as a so-called out-camera, and a direction in which the screen 3a is directed as a so-called in-camera. It is also possible to have a configuration including both camera units that capture images in the same direction.
- the display unit 3 is configured to have a display device capable of displaying an image such as an LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) or an organic EL (Electro Luminescence) display, and displays various information on the screen 3a of the display device. ..
- a display device capable of displaying an image such as an LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) or an organic EL (Electro Luminescence) display, and displays various information on the screen 3a of the display device. ..
- the operation unit 4 comprehensively represents operators such as buttons, keys, and a touch panel provided in the information processing device 1.
- the touch panel is formed to detect an operation involving contact with the screen 3a.
- the communication unit 5 performs wireless or wired data communication with the external device of the information processing device 1.
- a communication network such as LAN (Local Area Network) or the Internet
- short-range wireless communication such as Bluetooth (Bluetooth: registered trademark), etc. may be mentioned. can.
- the sensor unit 6 comprehensively represents various sensors included in the information processing apparatus 1.
- the sensor in the sensor unit 6 include a microphone, a G sensor (accelerometer), a gyro sensor (angle velocity sensor), a temperature sensor, a position sensor for detecting the position of the information processing device 1, a proximity sensor, an illuminance sensor, and the like.
- the position sensor include a GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) sensor, a geomagnetic sensor for geomagnetic positioning, and the like.
- Wi-Fi positioning using the radio wave strength of Wi-Fi Wi-Fi positioning using the radio wave strength of Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity: registered trademark) can also be performed.
- the control unit 7 is configured to include, for example, a microcomputer having a CPU (Central Processing Unit), a ROM (Read Only Memory), and a RAM (Random Access Memory). By executing the corresponding processing, control for realizing various operations and various operations of the information processing unit 1 is performed. For example, the control unit 7 performs various controls on the image pickup unit 2. As an example, for example, an instruction to start or end an imaging operation, an optical zoom control described above, an electronic zoom control, and the like are performed. Further, the control unit 7 controls the output information of the display unit 3, the sound output unit 9, and the information output unit as the tactile presentation unit 10.
- a microcomputer having a CPU (Central Processing Unit), a ROM (Read Only Memory), and a RAM (Random Access Memory).
- control is performed so that the image captured by the image pickup unit 2 is displayed as a through image on the display unit 3 in response to the establishment of a predetermined condition such as activation of a camera application. Further, the display control of the image related to the GUI (Graphical User Interface) is performed in response to the operation input or the like via the operation unit 4.
- GUI Graphic User Interface
- control unit 7 has a function as an image recognition processing unit 7a and a function as a guide control unit 7b as shown in the figure.
- the image recognition processing unit 7a performs image recognition processing on the image captured by the image pickup unit 2.
- the image recognition processing unit 7a includes subject detection processing for detecting an image area having a specific image feature such as face detection or pupil detection as the subject, and the type of the detected subject (the detected subject type 7a). For example, a subject recognition process for recognizing a person, a dog, a cat, a bird, a table, a flower, a bicycle, a car, a ship, a mountain, etc.) and a tracking process for tracking the position of the detected subject are performed.
- the control unit 7 performs a process of displaying information indicating the result of the above image recognition process on the display unit 3 while displaying the through image. For example, information indicating the range of the subject detected by the subject detection process described above (for example, frame information) is displayed on the display unit 3. In addition, information indicating the type of the subject recognized by the subject recognition process can be displayed on the display unit 3.
- the guide control unit 7b controls the image captured by the image pickup unit 2 so that the user guides the composition change operation based on the difference between the target composition and the actual composition. The specific processing performed by the control unit 7 as the guide control unit 7b will be described again.
- the memory unit 8 is composed of, for example, a semiconductor storage device such as a flash memory or a non-volatile storage device such as an HDD (Hard Disk Drive), and various data used for processing by the control unit 7 are stored.
- the memory unit 8 is used as a memory for storing the image captured by the image pickup unit 2.
- the control unit 7 stores one frame image captured at the timing instructed by the shutter operation by the user in the memory unit 8.
- the image data of the moving image obtained by the imaging unit 2 is stored in the memory unit 8 according to the recording start operation.
- the sound output unit 9 is provided with a speaker and outputs various sounds in response to an instruction from the control unit 7.
- the tactile presentation unit 10 includes a tactile presentation device that presents a tactile sensation to a user.
- the tactile presentation unit 10 includes a vibration device as a tactile presentation device, and is capable of presenting a tactile sensation to a user by vibration.
- the guide for the composition change operation by the user is performed by the tactile presentation (vibration in this example) by the tactile presentation unit 10.
- the composition change operation means an operation for changing the composition, such as changing the direction of the camera, changing the positional relationship between the camera and the subject, and zooming.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is arranged at the target position in the image frame according to the target size.
- the target composition is set based on the user's operation input. Further, in this example, it is assumed that the user specifies the target subject.
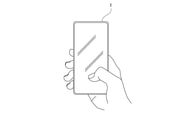
- FIG. 2A is a diagram for explaining an example of a method for designating a target subject.
- a mark indicating the range of the detected subject is displayed as shown by the broken line mark in the figure. Will be done.
- the guide control unit 7b in the control unit 7 accepts an operation (for example, a touch operation) for designating a mark indicating the range of the detected subject displayed in this way as a designation operation for the target subject.
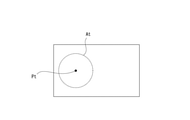
- FIG. 2B and 2C are diagrams for explaining an example of a target area At designation operation as an area where the target subject should be accommodated.
- the operation of designating the target area At is an operation of drawing a circle on the screen 3a as shown in FIG. 2B.
- the guide control unit 7b sets the range designated by such a drawing operation as the target area At (see FIG. 2C).
- the center position of the target area At is set as the target position Pt
- the position Ps of the target subject matches the target position Pt
- the size of the target subject is designated as the target area At.
- a composition that satisfies the condition that the target size is based on the size is set as the target composition.
- the target size of the target subject is assumed to be the same as the size specified as the target area At. It is not essential that the size of the target subject exactly matches the size specified as the target area At, for example, the target is within ⁇ 10% of the size specified as the target area At. It can also be set as a size and subject to this target size.
- the guide control unit 7b makes it possible to perform a guide for realizing the target composition according to the setting of the target area At according to the user operation.
- the size of the target subject is adjusted by the guide control unit 7b performing the zoom control of the image pickup unit 2. That is, in this example, since the size adjustment of the target subject is automatically performed on the information processing apparatus 1 side, the guide related to the size of the target subject is not performed.
- the position Ps of the target subject is sequentially grasped (for example, for each frame) by the tracking process by the image recognition processing unit 7a, and the guide control unit 7b is the position regarding the target position Pt and the position Ps of the target subject. Recognize the relationship.
- the guide control unit 7b guides the change of the direction of the information processing apparatus 1 (camera) from the positional relationship that is sequentially recognized in this way.
- the guide at this time is performed by changing the mode of tactile presentation based on the size of the difference between the target composition and the actual composition.
- the mode of vibration is changed according to the distance between the position Ps of the target subject and the target position Pt. For example, as the distance between the position Ps of the target subject and the target position Pt decreases, the vibration cycle is shortened.
- a first threshold value and a second threshold value are set for the separation distance between the position Ps of the target subject and the target position Pt, and the separation distance is the first threshold value.
- the number of vibrations per unit time is once when the distance exceeds the first threshold value, and the number of vibrations per unit time is twice when the separation distance is equal to or less than the first threshold value and exceeds the second threshold value.
- an example may be given in which the number of vibrations per unit time is set to 3 times.
- the user By performing the vibration control as described above, the user approaches the target composition in the process of changing the direction of the information processing apparatus 1 even in the situation where the image is taken without gazing at the screen 3a. It becomes possible to easily grasp whether or not the person is moving away, and it becomes easier to match the target composition.
- FIG. 2D illustrates the state of the screen 3a when the target composition is achieved. That is, in this example, it is a state when the position Ps of the target subject coincides with the target position Pt.
- the achievement condition of the target composition is that the distance between the position Ps of the target subject and the target position Pt is equal to or less than a predetermined threshold value other than 0, or the position Ps of the target subject and the target position Pt match per unit time.
- Other conditions can be set, such as setting the achievement condition of the target composition that the number of times reaches a predetermined number of times.
- the guide control unit 7b causes the tactile presentation unit 10 to execute a notification to that effect.
- the notification when the target composition is achieved is made to be different from the tactile presentation for the guide when the target composition is not achieved.
- the user performs the shutter operation upon receiving the notification of the achievement of the target composition as described above. This makes it possible to capture a still image with the target composition.
- FIG. 3 The process shown in FIG. 3 is executed by the control unit 7 (CPU) based on a program stored in a predetermined storage device such as a built-in ROM.
- the control unit 7 starts the process shown in FIG. 3, for example, in response to the activation of the camera application.
- control unit 7 determines in step S101 whether or not it is in the guide mode. That is, it is determined whether or not the mode enables the guide function for the composition change operation described above. If it is not the guide mode, the control unit 7 shifts to the normal mode processing. That is, the process shifts to the process for imaging without a guide.
- control unit 7 starts the image recognition process in step S102. That is, the processing as the image recognition processing unit 7a described above is started, and the subject detection processing, the subject recognition processing, and the subject tracking processing are performed.
- step S103 following step S102 the control unit 7 performs a designation acceptance process for the target subject. That is, the operation of designating the mark indicating the range of the detected subject displayed on the screen 3a in the subject detection process is accepted.
- the control unit 7 When the designation operation of the object subject is detected, the control unit 7 performs the designation acceptance process of the target area At in step S104. That is, in this example, the drawing operation of the circle on the screen 3a as illustrated in FIG. 2B is accepted.
- the control unit 7 sets the target position Pt (in this example, it is set at the center position of the target area At).
- step S105 the control unit 7 executes the zoom adjustment process. That is, zoom control is performed on the image pickup unit 2 so that the size of the target subject in the captured image matches the size of the target area At.
- step S106 the control unit 7 starts the guide process. That is, based on the positional relationship between the target position Pt and the position Ps of the target subject, which are sequentially recognized based on the tracking process of the target subject, the guide of the composition change operation is controlled so as to be performed by the vibration presentation of the tactile presentation unit 10. Specifically, in this example, guidance is performed by changing the mode of vibration according to the separation distance between the position Ps of the target subject and the target position Pt. For example, as illustrated above, it is conceivable to perform control to shorten the vibration cycle as the distance between the position Ps of the target subject and the target position Pt becomes smaller.
- the tactile presentation unit 10 Notification to that effect will be given by the vibration presentation by.
- step S107 the control unit 7 waits until the shutter operation is detected, and when the shutter operation is detected, the guide process is terminated in step S108 and the process proceeds to step S109.
- step S109 the control unit 7 determines whether or not the imaging is completed. That is, it is determined whether or not a predetermined condition predetermined as an imaging end condition such as detection of an end operation of the camera application is satisfied. For example, if the end operation of the camera application is not detected and it is determined that the imaging is not completed, the control unit 7 returns to step S103. As a result, for the next still image imaging, designation acceptance of the target subject and the target area At, zoom adjustment processing and guide processing based on the designated target subject and the target area At are performed.
- step S109 if it is determined in step S109 that the imaging is completed, the control unit 7 ends the image recognition process in step S110 and ends the series of processes shown in FIG.
- the guide function as an embodiment can be suitably applied to when capturing a moving image.
- the guide for the composition change operation for adjusting the size of the target subject and the target area At is not performed, but for such size adjustment.
- both the alignment of the target subject and the target area At and the guide of the size are performed, it is conceivable to perform vibration for the guide in a time-division manner. For example, it is conceivable to assign the first half period within the unit period to the guide for alignment and the second half period to the guide for size adjustment.
- both guides can be performed by a method other than time division, such as expressing the alignment guide by the vibration intensity and the size alignment guide by the number of vibrations per unit time.
- the direction guide may be performed in four directions of up, down, left, and right, or may be performed only in two directions of vertical and horizontal.
- the operation of designating the target area At that is, the operation related to the setting of the arrangement position in the image frame of the target subject is the operation of drawing a circle on the screen 3a. It is also possible to determine the type of drawing operation for the target composition, and to determine the setting condition excluding the arrangement position of the target subject among the setting conditions of the target composition according to the type of such drawing operation.
- the setting condition of the target composition means a condition for determining what kind of composition the target composition should be, for example, the arrangement position of the target subject in the image frame and the target subject. The conditions of singular or plural can be mentioned.
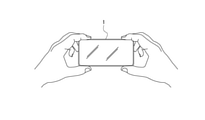
- Examples of the type of drawing operation include drawing a quadrangle as shown in FIGS. 4A to 4D, drawing a point, drawing an ellipse, drawing a circle by multi-touch by two-finger touch, and the like.
- the setting conditions excluding the placement position of the target subject among the setting conditions of the target composition are defined.
- the guide control unit 7b sets a target composition setting condition (arrangement of the target subject) corresponding to the type of the drawing operation performed by the user according to which of the plurality of predetermined types belongs. (Excluding the position setting conditions) is determined.
- the condition that the whole body of the subject is included in the quadrangle is determined as a setting condition of the target composition.
- the target composition is not based on the size of the target subject, but on the condition that the position of the point is set as the target position Pt and the target subject is placed at the target position Pt. Determined as the setting condition of.
- the ellipse is drawn as shown in FIG. 4C, the condition that a plurality of target subjects are arranged in the ellipse is determined as the setting condition of the target composition.
- the circle is drawn by multi-tap as shown in FIG.
- the condition that the target subject is arranged in the circle is determined as the setting condition of the target composition without the condition of the size of the target subject. ..
- the size of the target subject is matched with the size of the circle, and the target subject is set at the target position Pt determined from the drawing area of the circle. It can be said that this is an example of determining the condition of placement as the setting condition of the target composition.
- the user can specify the placement position of the target subject and set the setting conditions excluding the placement position among the setting conditions of the target composition.
- the designation can be performed by one operation as a drawing operation for the screen 3a. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the user operation burden.
- the control unit 7 is configured so that the type name of the subject that can be recognized by the subject recognition process described above can be identified by voice, and the pronunciation of the type name of the subject that can be recognized by the subject recognition process is recognized. Then, the subject belonging to the type is determined as the target subject.
- the process of determining the target subject based on the input voice can be performed at a stage where the subject has not yet been detected in the captured image.
- the user when it is desired to target a dog or a child as a target subject, the user can detect the presence of the dog or a child nearby from surrounding sounds or the like, so that the target subject is detected in the image (in the image frame). Regardless of whether or not it is, it is effective to accept the target subject designation by voice.
- the target subject before detection is specified, the subject is set as the target subject according to the fact that the subject of the corresponding type is detected in the image.
- the designation acceptance of the target subject can be performed by displaying the name information of the type of the candidate subject and the mark indicating the range thereof, as illustrated in FIG. 5, for example.
- the guide control unit 7b displays on the screen 3a a mark indicating the range and name information of the type of the detected subject whose type can be recognized.
- the designation acceptance of the target subject as illustrated in FIG. 6, it is also possible to accept the drawing operation of the range with respect to the screen 3a.
- the subject within the drawn range is set as the target subject.
- Such an acceptance method is a suitable method when the object that the user wants to be the target subject cannot be detected by the subject detection process.
- the method illustrated in FIG. 6 may be inferior in tracking robustness, improvement can be expected by using background subtraction and optical flow methods.
- the target subject is specified by the range drawing operation as shown in FIG. 6, in order to make the user identify whether the target area At is specified in the acceptance state or the target subject is in the acceptance state. It is conceivable to give a notification of.
- the information indicating the subject type that can be recognized by the subject recognition process can be displayed in a list on the screen 3a and accepted as the designation from among them.
- an error notification may be performed. This notification is made, for example, by vibration presentation by the tactile presentation unit 10.
- the setting of the target composition according to the user's operation is not limited to the specific examples exemplified so far.
- the situation of the information processing apparatus 1 functioning as a camera is determined, the situation is a specific situation, and a specific mark is drawn by a drawing operation on the screen 3a, the situation and the drawn mark are used. It is also possible to set a composition that satisfies the composition conditions associated with the target composition as a target composition.
- FIG. 7 when the information processing apparatus 1 is located in a specific theme park and a mark imitating a specific character in the theme park is drawn on the screen 3a, the character is drawn.
- This is an example of setting a composition that is placed at a position within the image frame corresponding to the mark as a target composition.
- a star mark is drawn on the screen 3a in a situation where the information processing device 1 is directed to the sky outdoors, the brightest star is within the range of the star mark.
- the composition in which is arranged is set as the target composition.
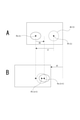
- the subject identification information I1 as illustrated in FIG. 8 is stored in the storage device that can be read by the control unit 7 such as the memory unit 8. Will be done.
- the guide control unit 7b determines whether or not the situation of the information processing apparatus 1 is a predetermined specific situation. For example, in the case of FIG. 7, it is determined whether or not the situation is located in a specific theme park. This determination can be made, for example, based on the detection signal of the position sensor in the sensor unit 6. Further, in the above-mentioned star example, it is determined whether or not the information processing apparatus 1 is directed to the sky outdoors.
- This determination can be made based on, for example, the detection signal of the position sensor or the microphone in the sensor unit 6 and the detection signal of the G sensor or the gyro sensor. By making such a determination, the guide control unit 7b recognizes the type of the situation in which the information processing apparatus 1 is placed.
- the guide control unit 7b determines whether or not the drawn mark is a specific mark when a drawing operation is performed on the screen 3a. For example, in the example of FIG. 7, it is determined whether or not the mark imitates a specific character, and in the above-mentioned star example, it is determined whether or not the mark is a star-shaped mark. By making such a determination, the guide control unit 7b recognizes the type of the drawn mark.
- the subject identification information I1 is associated with information indicating the type of the target subject for each combination of the situation type and the mark type, and the guide control unit 7b is associated with the situation type and the mark type as described above.
- the guide control unit 7b sets the subject specified from the subject type information obtained by referring to the information processing apparatus 1 as the target subject, and the target subject is within the range of the mark drawn on the screen 3a.
- the composition that satisfies the condition that is placed is set as the target composition.
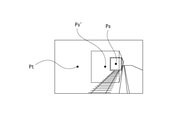
- FIG. 9 illustrates a situation in which a plurality of target subjects as “dogs” are detected in the image frame of the captured image.
- a drawing operation for specifying a range is performed so as to have two bulging portions on the screen 3a as shown in FIG. 10A
- two target subjects out of a plurality of detected target subjects are within the specified range.
- the drawing operation for specifying the range is performed so as to have a predetermined number or more (for example, at least 3 or more) of bulges as shown in FIG. 10B
- all of the detected plurality of target subjects are specified as the specified range.
- the guide control unit 7b determines which operation type the drawing operation belongs to among the plurality of operation types. Accordingly, the number of target subjects to be arranged within the arrangement range can be determined.
- the user can specify the placement range of the target subject and place the target subject within the placement range. It is possible to specify the number of target subjects by one operation as a drawing operation for the screen 3a. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the user operation burden.
- the user can estimate whether or not there are a plurality of objects as target subjects in the surroundings from the surrounding conditions (visual sense, sound, etc.). For example, it is possible to estimate whether there are a plurality of dogs from the bark of a dog and the voice of a child. From this point, regarding the acceptance of the designation of the placement range of the target subject and the determination of the number of placements of the target subject according to the type of drawing operation for specifying the placement range, the target subject is not detected in the captured image. You can also do it.
- the target subject While executing the guide for arranging a plurality of target subjects in the specified arrangement range, if there is a target subject that is partly away from other target subjects, the target is close to the arrangement range. Only the subject may be tracked.
- the size of the arrangement range specified by the user it may be dynamically determined which subject among the plurality of target subjects is to be the tracking target for the guide. For example, in the case of two target subjects, if the image size of the specified arrangement range is smaller than a predetermined size such as 100 pixels ⁇ 100 pixels, one target subject is used for guiding, otherwise two target subjects are used for guiding. It may be a tracking target.
- the subject closest to the arrangement range among the plurality of target subjects detected in the image is selected. It is conceivable to set it as a tracking target for the guide.
- the characteristics of the plurality of target subjects for example, coat color, size, etc. in the case of a dog
- Control according to the movement of the target subject Various controls can be considered as controls according to the movement of the target subject. For example, it is conceivable to estimate the moving direction of the target subject from the image analysis of the captured image and guide how to hold the information processing device 1 (camera) according to the direction. Specifically, for example, in the case of a scene in which a monkey climbs a tree as shown in FIG. 11, a guide instructing the user to hold the monkey vertically as shown in FIG. 12 is performed. Further, in the case of a scene in which a crab moves as shown in FIG. 13A or a scene in which a child walks around as shown in FIG. 13B, a guide instructing the user to hold the crab as illustrated in FIG. 14 is performed.
- the direction in which the target subject moves can be estimated from, for example, the direction and amount of the background flowing in the captured image.
- guide control for detecting the movement of the target subject and arranging the target subject at the target position Pt based on the detected movement of the target subject is performed. You can also do it.
- FIG. 15A illustrates the relationship between the position Ps (t) of the target subject, the target area At (t), and the target position Pt (t) at a certain time (t).
- the separation distance between the position Ps (t) of the target subject and the target position Pt (t) is defined as “d”.
- the amount of movement of the target subject during the predetermined period is set to "do" as shown in the figure at the time point (t + 1) after the elapse of the predetermined period from the time (t), the user faces the camera according to the guide at the time point (t).
- the image frame side is moved by "di" as shown in FIG. 15B, the target subject also moves by "do", so the position Ps (t + 1) of the target subject is placed at the target position Pt (t + 1). Will be difficult.
- the movement amount "de” of the target subject between each frame is calculated over the past plurality of frames of the captured image, and the guide is performed based on the movement amount de. It is not a simple average, but a constant velocity, acceleration, and deceleration are calculated in an identifiable manner.
- the movement amount de is a vector quantity having a distance and a direction.
- the guide control unit 7b sets "d-de” as the target value of the movement amount on the image frame side when the target subject is moving in the direction approaching the target position Pt, and moves the camera too much to the user. Control to be guided to request no.
- the guide control unit 7b sets "d + de” as the target value of the movement amount on the image frame side, and guides the user to move the camera more. Control to be done.
- the guide control unit 7b obtains the movement amount of the target subject based on, for example, captured images for a plurality of past frames, and predicts the position of the target subject after a predetermined time from the movement amount. Then, the guide is performed based on the relationship between the position predicted in this way and the target position Pt. Specifically, for example, it is conceivable to perform a guide that changes the mode of vibration according to the magnitude of the separation distance between the predicted position and the target position Pt.
- the target composition is set by the guide control unit 7b based on the determination result of the scene to be imaged.
- the optimum composition is predetermined for the scene to be imaged in which the train as illustrated in FIG. 16 exists on the platform of the station.
- a composition in which the target subject is a train and the target area At (target position Pt) is set as shown in FIG. 17 is defined as the target composition.
- a plurality of combinations of the imaging target scene and the optimum composition are defined.
- the guide control unit 7b determines the current image capture target scene by image analysis processing or the like of the image captured by the image pickup unit 2.
- the method for determining the scene to be imaged is not particularly limited.
- a method using AI (artificial intelligence) learned to classify scenes from images can be mentioned.
- the guide control unit 7b sets the optimum composition determined for the determined imaging target scene as the target composition.
- the guide control unit 7b performs a process for guiding.
- the guide is not performed based on the current position of the target subject, but is performed based on the position where the target subject is in the target state, which is determined according to the scene to be imaged.
- the target state here means the target state of the target subject determined according to the scene to be imaged. Specifically, it means, for example, a state in which a shutter chance occurs.
- the state in which the train as the target subject is stopped is defined as the target state.
- the guide control unit 7b predicts the position Ps'in which the subject as a train is in the target state, that is, the stopped state from the current captured image, and the predicted position Ps'
- the tactile presentation unit 10 is controlled so that a guide for being arranged at the target position Pt is performed.
- the position (Ps') at which the train is stopped at the platform of the station can be estimated from the position of the stop line of the train, for example, by detecting the image of the stop line of the train at the platform.
- the speed of the train may be calculated from the captured image, and the position where the train is stopped may be estimated based on the speed. In estimating the stop position based on such speed, the information on the distance to the train is used, but the information on the distance may be calculated by using the time difference of the captured image, or the distance measuring sensor may be used. It may be obtained by using it separately.
- the shutter may be automatically released (the captured image of the still image is stored in the memory unit 8) on condition that the target subject is within the target area At.
- the size of the target area At may be set to a size based on the size of the train when the train reaches the stop position.
- a scene related to a train is illustrated as an example of a scene to be imaged, but a guide can be performed by the same method for a sunset scene as illustrated in FIG. 19A, for example.
- a composition in which the target subject is the sun and the target area At (target position Pt) is set as shown in FIG. 19B is defined as the target composition.
- a state in which the sun sets is defined as a target state of the target subject.
- the current time information can also be used to determine whether or not the scene is a scene to be imaged at sunset.
- the guide control unit 7b predicts the position Ps'where the target subject is in the target state, that is, the position where the sun sets, from the current captured image as illustrated in FIG. 19A.
- the position where the sun sets can be predicted by obtaining the movement trajectory of the sun from the captured image within a certain period in the past and based on the movement trajectory.
- the guide control unit 7b in this case is tactile so that a guide is performed so that the predicted position Ps'is placed at the target position Pt.
- the presentation unit 10 is controlled.
- the target composition for each scene to be imaged may be determined based on the result of analyzing the composition of a large number of captured images uploaded on the Internet, such as the captured image posted on the SNS (Social Networking Service) site. can.
- the user's favorite composition can be learned and determined based on the result of analyzing the composition of the past captured image by the user.
- vibration for the guide not only the vibration for the guide but also other information can be notified by vibration at the same time.
- the distance between the position Ps of the target subject and the target position Pt by vibration it is conceivable to notify the intensity of the movement of the subject by vibration.
- the distance from the target position Pt is expressed by the difference in vibration frequency, and the amount of movement between the frames of the subject is expressed by the intensity of vibration.
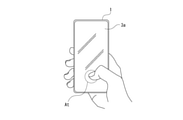
- the vibration for the guide can be performed in the form of screen vibration as illustrated in FIG.
- the target position Pt is specified by touching the screen 3a and then the finger is kept touching the screen 3a, and after the target position Pt is specified, guidance is performed by screen vibration.
- the vibration intensity for example, the vibration becomes stronger as it gets closer.
- a piezo element may be used as the vibration device in this case.
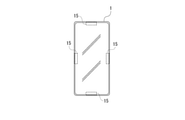
- vibration devices 15 arranged on the upper, lower, left and right sides of the information processing apparatus 1.
- the user can be notified in which direction the information processing apparatus 1 should be moved, depending on which position the vibrating device is vibrated.
- the guide function for the composition change operation can be enabled or disabled based on the user operation. For example, on a smartphone, it is conceivable to enable the guide function when an operation of setting the "visually impaired mode" is performed in the accessibility item in the "setting" menu.
- the hand may be raised high to take an image, and in such a case, the image is taken without looking at the screen 3a. Therefore, it is assumed that the estimation of whether or not the user raises his / her hand to perform imaging is performed as the estimation of whether or not the user is not looking at the screen 3a, and the user raises his / her hand to perform imaging. Enable the guide function when estimated.
- the user raises his / her hand it is possible to estimate whether or not the user raises his / her hand to perform imaging, for example, based on the captured image of the in-camera and the detection signal by the G sensor or the gyro sensor in the sensor unit 6. Alternatively, it can be performed by using the detection signal by the height sensor.
- the estimation of whether or not the user is not looking at the screen 3a can be performed, for example, as the estimation of whether or not the user's line of sight is directed to the screen 3a. Whether or not the user's line of sight is directed to the screen 3a can be estimated based on, for example, an image captured by the in-camera.
- the guide function it is also conceivable to enable the guide function according to the recognition of a specific type of subject from the captured image. Alternatively, it is conceivable to enable the guide function according to the determination that the movement of the subject is large. Further, the activation condition of the guide function may be these AND conditions. For example, if the "child" is recognized as the subject and the movement of the subject is large, the guide function is enabled.
- the target composition requires that the size of the target subject be adjusted to the target size, the size of the target subject is too large or too small for the target size, and the size adjustment by zooming is the target. There may be cases where the size cannot be adjusted. When the zoom cannot be further performed or when it is predicted that the target size cannot be adjusted by the size adjustment by the zoom, it is conceivable to notify the user by the tactile presentation of the tactile presentation unit 10.
- step S105 when the user determines that the size of the target subject cannot be set to the target size by the zoom control, the user An example of determining whether or not the situation can be moved and notifying the error when it is determined that the situation cannot be moved will be described.
- a guide for changing the positional relationship between the user and the target subject is performed.
- FIG. 22 shows an excerpt of a part of the processing to be executed after step S103 in the processing shown in FIG.
- the control unit 7 sets the size of the target subject to the size of the target area At in step S201.
- This zoom value is obtained as a value within the zoomable range (for example, 35 mm to 100 mm, etc.).
- step S202 following step S201 the control unit 7 determines whether or not it is within the zoomable range. Specifically, it is determined whether or not the zoom value Td described above is within the range of the minimum zoom value TR or more and the maximum zoom value TE or less described below.
- the minimum zoom value TR is the minimum value in the zoomable range
- the maximum zoom value TE is the maximum value in the zoomable range.
- the maximum zoom value TE is set to the maximum value in the zoomable range by the optical zoom.
- the maximum zoom value TE may be determined in consideration of image quality deterioration due to digital zoom. The condition that the image quality becomes coarse due to the digital zoom and it becomes impossible to recognize what kind of object is different depending on the brightness, environment, type of subject, and user's visual acuity, so the maximum zoom value TE is adaptively according to those conditions, for example. It may be determined.
- step S202 If it is determined in step S202 that the range is within the zoomable range, the control unit 7 proceeds to step S105 to execute the zoom adjustment process. In this case, the processes after step S105 shown in FIG. 3 are executed to guide the position Ps of the target subject to the target position Pt.
- step S202 determines that the range is not within the zoomable range
- the control unit 7 performs the zoom adjustment process in step S203.
- the zoom adjustment process is performed to adjust to the minimum zoom value TR (when it is large with respect to the target size) or the maximum zoom value TE (when it is small with respect to the target size).
- step S204 the control unit 7 determines whether or not the user can move. That is, it is determined whether or not the situation is such that the user cannot move forward or backward by taking an image in a crowded place, for example. Whether or not the user can move is determined based on, for example, analysis of the captured image by the imaging unit 2, detection sound by the microphone in the sensor unit 6, (environmental sound around the information processing device 1), and the like. Can be done.
- step S204 If it is determined in step S204 that the user can move, the control unit 7 proceeds to step S205 to start the guide process for the size. That is, the guide for adjusting the size of the target subject to the target size is controlled so as to be performed by the tactile presentation of the tactile presentation unit 10. As this guide, the user decides whether to move the information processing apparatus 1 forward (in the direction closer to the target subject) or backward, at least depending on whether the size of the target subject is smaller or larger than the target size. Make sure it is done in a recognizable form. After starting the guide processing for the size in step S205, the control unit 7 may proceed to the processing in step S107 shown in FIG.
- step S204 If it is determined in step S204 that the user is not in a movable situation, the control unit 7 executes error notification processing in step S206. That is, the user is notified that the size of the target subject cannot be adjusted to the target size. It is conceivable that this notification is executed by the tactile presentation of the tactile presentation unit 10. In the error notification process in step S206, a notification urging the user to change the size of the target area At may be given.
- the control unit 7 determines whether or not the user can move when it is determined that the size of the target subject cannot be set to the target size by the zoom control.
- a guide is provided to change the positional relationship between the user and the target subject.
- finger fogging means a state in which at least a part of the finger of the user holding the camera touches the lens or the like to block at least a part of the imaging field of view.
- the presence or absence of finger fogging can be determined, for example, from a captured image.
- whether or not the camera shake is large can be determined from the detection signal by the G sensor or the gyro sensor in the sensor unit 6 or the captured image (for example, the difference between frames).
- the presence or absence of out-of-focus can be determined as to whether or not AF (autofocus) is performed on the specified target subject.
- the tactile presentation unit 10 When the control unit 7 determines that such a situation of finger fogging, out-of-focus, or large camera shake has occurred, the tactile presentation unit 10 performs a predetermined notification as an error notification by the tactile presentation.
- out-of-focus it is conceivable to issue different notifications according to the type of cause. For example, different error notifications are given depending on whether the problem is solved by the user moving the position or the target subject needs to be redesignated. In this case, the action to be taken by the user can be notified by tactile presentation, sound, or the like.
- the error notification it is also possible to notify that a specific object (for example, a dangerous object: a bicycle, a car, etc.) is detected in the captured image during the guide (for example, a tactile presentation is performed).
- a specific object for example, a dangerous object: a bicycle, a car, etc.
- the embodiment is not limited to the specific example described above, and can be configured as an embodiment modification.
- the in-camera recognizes the type of user and switches various settings of the information processing apparatus 1.
- the user is an elderly person, it is conceivable to set the shutter speed to be increased in order to prevent camera shake.
- the user is an elderly person, it is conceivable to set the vibration intensity at the time of guiding to be increased.
- the UI User Interface
- the English version may be changed to the English version.
- the vibration device for the guide and the camera for obtaining the captured image are mounted on an integrated device as the information processing device 1
- the vibration device for the guide is described. It is not limited to being mounted on a device integrated with a camera that obtains an captured image.
- the tactile presentation device 20 that presents vibration for a guide is separated.
- FIG. 23 the same reference numerals are given to the parts that are the same as the parts that have been explained so far, and the description thereof will be omitted.
- the image pickup support system 100 includes an information processing device 1A and a tactile presentation device 20.
- the tactile presentation device 20 includes a tactile presentation unit 10, a control unit 21, and a communication unit 22.
- the information processing apparatus 1A is different from the information processing apparatus 1 shown in FIG. 1 in that the control unit 7A is provided in place of the control unit 7.
- the communication unit 5 is configured to be capable of performing data communication with the communication unit 22 in the tactile presentation device 20.
- the control unit 7A is different from the control unit 7 in that it has a guide control unit 7bA instead of the guide control unit 7b.
- the guide control unit 7bA controls so that the guide for the composition change operation is performed by the tactile presentation by the tactile presentation unit 10 in the tactile presentation device 20.
- a tactile presentation instruction for a guide is given to the control unit 21 via the communication unit 5, and the control unit 21 causes the tactile presentation unit 10 in the tactile presentation device 20 to execute the tactile presentation according to the instruction. ..
- the device form of the tactile presentation device 20 for example, a device form worn by the user, such as a smart watch or a glasses-type information processing device capable of communicating with the information processing device 1A such as a smartphone or a tablet terminal.
- a device form such as a stand device such as a tripod that supports the information processing device 1A that functions as a camera can be considered.
- the information processing device 1A has the tactile presentation unit 10.
- vibration has been exemplified as an example of tactile presentation for a guide, but as tactile presentation, for example, presentation other than vibration such as blowing air can be performed.
- the guide for the composition change operation by the user is performed by tactile presentation to the user based on the difference between the target composition and the actual composition. It is provided with a control unit (guide control units 7b, 7bA) for controlling the information processing.
- guide control units 7b, 7bA for controlling the information processing.
- the control unit changes the mode of tactile presentation for the guide based on the size of the difference between the target composition and the actual composition. This makes it possible for the user to grasp whether the difference between the target composition and the actual composition is small or large by the difference in the mode of tactile presentation for the guide. Therefore, even in a situation where the user cannot or is difficult to see the screen, it is possible to increase the ease of adjusting to the target composition and improve the imaging support performance.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is arranged at a position determined by the user operation in the image frame, and the target composition is arranged in the image frame of the target subject.
- the operation related to the position setting is performed as a drawing operation on the screen (3a) for displaying the through image of the captured image, and the control unit determines which of the plurality of operation types the drawing operation belongs to. Therefore, the setting conditions excluding the placement position among the setting conditions of the target composition are determined.
- the operation type of the drawing operation is a type of operation that can be performed as a drawing operation, and examples thereof include an operation of drawing a point, an operation of drawing a circle, and an operation of drawing an ellipse.
- the setting condition of the target composition means a condition for determining what kind of composition the target composition should be, for example, the arrangement position of the target subject in the image frame and a single target subject. Conditions such as whether to use or to have a plurality of items can be mentioned. According to the above configuration, the user can specify the placement position of the target subject and the setting conditions other than the placement position among the setting conditions of the target composition by one operation as a drawing operation on the screen. It becomes. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the user operation burden.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is arranged at a position determined by the user operation in the image frame, and the control unit is the target subject.
- the designation is accepted by voice input from the user. This eliminates the need for the user to operate an operator such as a button or a touch panel when designating the target subject. Therefore, when designating the target subject, it is not necessary for the user to search for the target subject on the screen or to search for the operator for designation, which is suitable for taking an image without gazing at the screen. In particular, a user interface suitable for the visually impaired can be realized.
- the control unit accepts a drawing operation on the screen for displaying the through image of the captured image, determines the situation of the camera that obtains the captured image, and the situation is a specific situation. And when a specific mark is drawn by the drawing operation, a composition satisfying the composition condition associated with the situation and the drawn mark is set as the target composition.
- a specific mark for example, a mark imitating a famous character in the theme park is drawn.
- compositions that satisfies the composition conditions associated with the situation and the mark as the target composition, such as a composition in which the character is placed at a position in the image frame corresponding to the drawn mark. be. Therefore, it is possible to perform a plurality of composition setting conditions by one operation of drawing a mark, and it is possible to reduce the burden on the user operation.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is arranged at a position determined by the user operation in the image frame, and the target composition is arranged in the image frame of the target subject.
- the range designation operation is performed as a drawing operation on the screen for displaying the through image of the captured image, and the control unit is within the arrangement range according to which of the plurality of operation types the drawing operation belongs to.
- the number of target subjects to be placed is determined. As a result, the user can specify the arrangement range of the target subject and the number of target subjects to be arranged within the arrangement range by one operation as a drawing operation on the screen. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the user operation burden.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is placed at the target position in the image frame, and the control unit detects the movement of the target subject.
- the guide for arranging the target subject at the target position is controlled based on the detected movement of the target subject. This makes it possible to perform a guide in consideration of the movement of the target subject as a guide for realizing the composition of arranging the target subject at the target position in the image frame. Therefore, it is possible to improve the accuracy of the guide in response to the case where the target subject is a moving subject.
- the control unit guides the target subject based on the relationship between the predicted position and the target position after a predetermined time.
- the guide is performed based on the difference between the current position of the target subject and the target position, and the position of the target subject is set to the target position.
- the guide is performed based on the position after a predetermined time predicted from the movement of the target subject. Therefore, it is possible to improve the accuracy of the guide in response to the case where the target subject is a moving subject.
- the control unit sets the target composition based on the determination result of the image pickup target scene. This makes it possible to automatically set a target composition according to the scene to be imaged, such as a scene in which a train is imaged at a station or a scene in which a sunset is imaged, based on a scene determination result. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the operational burden on the user when performing imaging with an appropriate target composition according to the scene to be imaged.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is placed at the target position in the image frame.
- the control unit The position where the target subject is in the target state according to the image capture target scene is predicted, and the guide is controlled so that the predicted position matches the target position. This makes it possible to appropriately support the user so that the target subject in the target state is captured by the target composition. Therefore, it is possible to improve the user support performance related to the composition change at the time of imaging.
- the control unit enables the guide function when it is estimated that the user is not looking at the screen displaying the through image of the captured image.
- the guide according to the present embodiment is automatically performed in a situation where the user performs imaging without looking at the screen. Therefore, it is possible to appropriately support the user. Further, it is possible to prevent the guide function from being enabled even when the guide is unnecessary, such as when the user performs an image while looking at the screen, and the convenience can be improved.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is arranged at the target position in the image frame according to the target size
- the control unit is the size of the target subject.
- the zoom is controlled so that is the target size. This makes it possible to eliminate the need for a zoom operation by the user in order to realize imaging with a target composition. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the user operation burden.
- the control unit determines whether or not the user can move when it is determined that the size of the target subject cannot be set to the target size by the zoom control.
- a guide is provided to change the positional relationship between the user and the target subject.
- the information processing apparatus controls so that the guide for the composition change operation by the user is performed by tactile presentation to the user based on the difference between the target composition and the actual composition.
- This is an imaging support control method. Even with such an image pickup support control method, the same operations and effects as those of the image pickup support control device as the above-described embodiment can be obtained.
- the imaging support system (100) as an embodiment is based on a tactile presentation device (20) having a tactile presentation unit (10) that presents a tactile sensation to a user, and a difference between a target composition and an actual composition. It is provided with an image pickup support control device (information processing device 1A) having a control unit (guide control unit 7bA) that controls the guide for the composition change operation by the user so as to be performed by the tactile presentation of the tactile presentation unit. ..
- an image pickup support control device information processing device 1A
- guide control unit 7bA control unit that controls the guide for the composition change operation by the user so as to be performed by the tactile presentation of the tactile presentation unit.
- An image pickup support control device provided with a control unit that controls so that a guide for a composition change operation by a user is performed by tactile presentation to the user based on the difference between a target composition and an actual composition.
- the control unit The imaging support control device according to (1) above, which changes the mode of tactile presentation for the guide based on the magnitude of the difference between the target composition and the actual composition.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is placed at a position determined according to the user operation in the image frame.
- the operation related to the setting of the arrangement position of the target subject in the image frame is performed as a drawing operation on the screen for displaying the through image of the captured image.
- the control unit Described in (1) or (2) above, the setting conditions excluding the arrangement position among the setting conditions of the target composition are determined according to which operation type the drawing operation belongs to among the plurality of operation types.
- Imaging support control device (4)
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is placed at a position determined according to the user operation in the image frame.
- the control unit The imaging support control device according to any one of (1) to (3) above, which accepts the designation of the target subject by voice input from the user.
- the control unit While accepting drawing operations on the screen that displays the through image of the captured image, When the situation of the camera that obtains the captured image is determined and the situation is a specific situation and the specific mark is drawn by the drawing operation, the situation is associated with the drawn mark.
- the image pickup support control device according to any one of (1) to (6) above, wherein a composition satisfying the composition condition is set as the target composition.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is placed at a position determined according to the user operation in the image frame.
- the operation of designating the arrangement range of the target subject in the image frame is performed as a drawing operation on the screen for displaying the through image of the captured image.
- the control unit The description according to any one of (1) to (5) above, wherein the number of the target subjects to be arranged within the arrangement range is determined according to which operation type the drawing operation belongs to among the plurality of operation types. Imaging support control device.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is placed at the target position in the image frame.
- the control unit The description according to any one of (1) to (6) above, wherein the movement of the target subject is detected, and the guide for arranging the target subject at the target position is controlled based on the detected movement of the target subject.
- Imaging support control device The control unit The imaging support control device according to (7), wherein the guide is performed based on the relationship between the predicted position of the target subject after a predetermined time and the target position.
- the control unit The image pickup support control device according to (1) or (2) above, wherein the target composition is set based on the determination result of the image pickup target scene.
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is placed at the target position in the image frame.
- the control unit The imaging support control according to (9) above, wherein the target subject predicts a position where the target state becomes a target state according to the imaging target scene, and the guide is controlled so that the predicted position matches the target position.
- Device. (11) The control unit The imaging support control device according to any one of (1) to (10) above, which enables the function of the guide when it is estimated that the user is not viewing the screen displaying the through image of the captured image. .. (12)
- the target composition is a composition that satisfies the condition that the target subject is arranged at the target position in the image frame according to the target size.
- the control unit The imaging support control device according to any one of (1) to (11), wherein zoom control is performed so that the size of the target subject becomes the target size. (13) The control unit When it is determined by the zoom control that the size of the target subject cannot be set to the target size, it is determined whether or not the user can move, and when it is determined that the user can move, the situation is determined.
- the image pickup support control device according to (12) above, wherein the guide for changing the positional relationship between the user and the target subject is performed.
- Information processing equipment An imaging support control method that controls a user to guide a composition change operation by presenting a tactile sensation to the user based on the difference between the target composition and the actual composition.
- a tactile presentation device having a tactile presentation unit that presents tactile sensations to the user
- An image pickup support control device having a control unit for controlling so that a guide for a composition change operation by the user is performed by the tactile presentation of the tactile presentation unit based on the difference between the target composition and the actual composition is provided.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Audiology, Speech & Language Pathology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202180048263.8A CN115777201A (zh) | 2020-07-14 | 2021-06-22 | 成像辅助控制装置、成像辅助控制方法和成像辅助系统 |
| US18/009,538 US20230224571A1 (en) | 2020-07-14 | 2021-06-22 | Imaging assistance control apparatus, imaging assistance control method, and imaging assistance system |
| JP2022536203A JPWO2022014273A1 (enExample) | 2020-07-14 | 2021-06-22 | |
| DE112021003749.8T DE112021003749T5 (de) | 2020-07-14 | 2021-06-22 | Bildgebungsassistenz-steuervorrichtung, bildgebungsassistenz-steuerverfahren und bildgebungsassistenzsystem |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020-120697 | 2020-07-14 | ||
| JP2020120697 | 2020-07-14 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2022014273A1 true WO2022014273A1 (ja) | 2022-01-20 |
Family
ID=79555268
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2021/023607 Ceased WO2022014273A1 (ja) | 2020-07-14 | 2021-06-22 | 撮像支援制御装置、撮像支援制御方法、撮像支援システム |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20230224571A1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JPWO2022014273A1 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN115777201A (enExample) |
| DE (1) | DE112021003749T5 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2022014273A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023104706A (ja) * | 2022-01-18 | 2023-07-28 | キヤノン株式会社 | 振動装置、撮像装置、振動装置の制御方法、およびプログラム |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011193125A (ja) * | 2010-03-12 | 2011-09-29 | Sony Corp | 画像処理装置および方法、プログラム、並びに撮像装置 |
| JP2013157953A (ja) * | 2012-01-31 | 2013-08-15 | Nikon Corp | 撮像装置および撮像装置の制御プログラム |
| JP2013229900A (ja) * | 2013-06-11 | 2013-11-07 | Casio Comput Co Ltd | 撮像装置、画像生成方法、およびプログラム |
| JP2014164172A (ja) * | 2013-02-26 | 2014-09-08 | Nikon Corp | 撮像装置およびプログラム |
| JP2019179049A (ja) * | 2018-03-30 | 2019-10-17 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置 |
Family Cites Families (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4654974B2 (ja) * | 2006-05-23 | 2011-03-23 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 撮影装置および撮影方法 |
| JP2008244804A (ja) * | 2007-03-27 | 2008-10-09 | Fujifilm Corp | 撮像装置及び撮像方法並びに制御プログラム |
| JP5040760B2 (ja) * | 2008-03-24 | 2012-10-03 | ソニー株式会社 | 画像処理装置、撮像装置、表示制御方法およびプログラム |
| TW201023633A (en) * | 2008-12-05 | 2010-06-16 | Altek Corp | An image capturing device for automatically position indicating and the automatic position indicating method thereof |
| US20100225773A1 (en) * | 2009-03-09 | 2010-09-09 | Apple Inc. | Systems and methods for centering a photograph without viewing a preview of the photograph |
| US20110080489A1 (en) * | 2009-10-02 | 2011-04-07 | Sony Ericsson Mobile Communications Ab | Portrait photo assistant |
| US8605165B2 (en) * | 2010-10-06 | 2013-12-10 | Ai Cure Technologies Llc | Apparatus and method for assisting monitoring of medication adherence |
| JP2011146821A (ja) * | 2010-01-12 | 2011-07-28 | Canon Inc | 触覚情報提示装置、触覚情報提示方法、及びプログラム |
| JP5640466B2 (ja) * | 2010-05-31 | 2014-12-17 | 株式会社ニコン | デジタルカメラ |
| CN103621056A (zh) * | 2011-06-23 | 2014-03-05 | 株式会社尼康 | 拍摄装置 |
| KR101832959B1 (ko) * | 2011-08-10 | 2018-02-28 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 휴대 전자기기 및 이의 제어방법 |
| CN114584705A (zh) * | 2014-12-24 | 2022-06-03 | 佳能株式会社 | 变焦控制装置、变焦控制装置的控制方法和记录介质 |
| JP2016140030A (ja) * | 2015-01-29 | 2016-08-04 | 株式会社リコー | 画像処理装置、撮像装置、及び画像処理プログラム |
| EP3465684A1 (en) * | 2016-05-27 | 2019-04-10 | IMINT Image Intelligence AB | System and method for a zoom function |
| JP6882016B2 (ja) * | 2017-03-06 | 2021-06-02 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置、撮像システム、撮像装置の制御方法、および、プログラム |
| WO2019188035A1 (ja) * | 2018-03-28 | 2019-10-03 | ソニー株式会社 | 撮像装置及び撮像装置における通知制御方法、並びに情報処理装置 |
| JP7451122B2 (ja) * | 2019-09-27 | 2024-03-18 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像制御装置、撮像装置、及び撮像制御方法 |
| JP7383438B2 (ja) * | 2019-09-27 | 2023-11-20 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像制御装置、撮像装置、及び撮像制御方法 |
| JP2023104706A (ja) * | 2022-01-18 | 2023-07-28 | キヤノン株式会社 | 振動装置、撮像装置、振動装置の制御方法、およびプログラム |
-
2021
- 2021-06-22 US US18/009,538 patent/US20230224571A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2021-06-22 WO PCT/JP2021/023607 patent/WO2022014273A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2021-06-22 JP JP2022536203A patent/JPWO2022014273A1/ja not_active Abandoned
- 2021-06-22 DE DE112021003749.8T patent/DE112021003749T5/de active Pending
- 2021-06-22 CN CN202180048263.8A patent/CN115777201A/zh active Pending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011193125A (ja) * | 2010-03-12 | 2011-09-29 | Sony Corp | 画像処理装置および方法、プログラム、並びに撮像装置 |
| JP2013157953A (ja) * | 2012-01-31 | 2013-08-15 | Nikon Corp | 撮像装置および撮像装置の制御プログラム |
| JP2014164172A (ja) * | 2013-02-26 | 2014-09-08 | Nikon Corp | 撮像装置およびプログラム |
| JP2013229900A (ja) * | 2013-06-11 | 2013-11-07 | Casio Comput Co Ltd | 撮像装置、画像生成方法、およびプログラム |
| JP2019179049A (ja) * | 2018-03-30 | 2019-10-17 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置 |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023104706A (ja) * | 2022-01-18 | 2023-07-28 | キヤノン株式会社 | 振動装置、撮像装置、振動装置の制御方法、およびプログラム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE112021003749T5 (de) | 2023-04-27 |
| JPWO2022014273A1 (enExample) | 2022-01-20 |
| CN115777201A (zh) | 2023-03-10 |
| US20230224571A1 (en) | 2023-07-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11860511B2 (en) | Image pickup device and method of tracking subject thereof | |
| RU2679199C1 (ru) | Способ и устройство для управления фотосъемкой беспилотного воздушного транспортного средства | |
| JP6766086B2 (ja) | 撮像装置およびその制御方法 | |
| JP6481866B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、撮像装置、情報処理方法、及び、プログラム | |
| EP3125529B1 (en) | Method and device for image photographing | |
| CN107430856B (zh) | 信息处理系统和信息处理方法 | |
| US12236618B2 (en) | Photographing method and electronic device | |
| JP6091669B2 (ja) | 撮像装置、撮像アシスト方法及び撮像アシストプログラムを記録した記録媒体 | |
| US20210152750A1 (en) | Information processing apparatus and method for controlling the same | |
| EP3113071B1 (en) | Method and device for acquiring iris image | |
| EP3968626A1 (en) | Photography method, photography apparatus, electronic device, and storage medium | |
| EP3770849A1 (en) | Image capturing method and device, computer readable storage medium | |
| EP3989118A1 (en) | Target tracking method and system, readable storage medium and moving platform | |
| US10771707B2 (en) | Information processing device and information processing method | |
| US11729488B2 (en) | Image capturing apparatus, method for controlling the same, and storage medium | |
| US11818457B2 (en) | Image capturing apparatus, control method therefor, and storage medium | |
| WO2015154359A1 (zh) | 拍摄的实现方法及装置 | |
| WO2022228259A1 (zh) | 一种目标追踪方法及相关装置 | |
| CN111147744B (zh) | 拍摄方法、数据处理方法、装置、电子设备及存储介质 | |
| JP7199808B2 (ja) | 撮像装置およびその制御方法 | |
| WO2022014273A1 (ja) | 撮像支援制御装置、撮像支援制御方法、撮像支援システム | |
| JP2023133348A (ja) | 撮影プログラム、情報処理装置、および方法 | |
| JP2025509199A (ja) | ウェアラブルマルチメディアデバイスを使用して画像を表示すること | |
| JP2016082356A (ja) | 電子機器およびプログラム | |
| CN117041728A (zh) | 对焦方法及装置、电子设备、可读存储介质 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 21843129 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2022536203 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 21843129 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |