WO2021024588A1 - モビリティ制御システム、方法、および、プログラム - Google Patents
モビリティ制御システム、方法、および、プログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2021024588A1 WO2021024588A1 PCT/JP2020/021376 JP2020021376W WO2021024588A1 WO 2021024588 A1 WO2021024588 A1 WO 2021024588A1 JP 2020021376 W JP2020021376 W JP 2020021376W WO 2021024588 A1 WO2021024588 A1 WO 2021024588A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- communication
- mobility
- control
- status
- situation
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W60/00—Drive control systems specially adapted for autonomous road vehicles
- B60W60/001—Planning or execution of driving tasks
- B60W60/0015—Planning or execution of driving tasks specially adapted for safety
- B60W60/0018—Planning or execution of driving tasks specially adapted for safety by employing degraded modes, e.g. reducing speed, in response to suboptimal conditions
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R16/00—Electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for; Arrangement of elements of electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for
- B60R16/02—Electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for; Arrangement of elements of electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for electric constitutive elements
- B60R16/023—Electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for; Arrangement of elements of electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for electric constitutive elements for transmission of signals between vehicle parts or subsystems
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W50/00—Details of control systems for road vehicle drive control not related to the control of a particular sub-unit, e.g. process diagnostic or vehicle driver interfaces
- B60W50/04—Monitoring the functioning of the control system
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G05—CONTROLLING; REGULATING
- G05D—SYSTEMS FOR CONTROLLING OR REGULATING NON-ELECTRIC VARIABLES
- G05D1/00—Control of position, course, altitude or attitude of land, water, air or space vehicles, e.g. using automatic pilots
- G05D1/02—Control of position or course in two dimensions
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/09—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/30—Services specially adapted for particular environments, situations or purposes
- H04W4/40—Services specially adapted for particular environments, situations or purposes for vehicles, e.g. vehicle-to-pedestrians [V2P]
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W2556/00—Input parameters relating to data
- B60W2556/45—External transmission of data to or from the vehicle
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W24/00—Supervisory, monitoring or testing arrangements
- H04W24/08—Testing, supervising or monitoring using real traffic
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a mobility control system, a mobility control method, and a mobility control program that perform control according to the communication status of mobility equipped with a communication function.
- mobility is defined as meaning means of transportation (for example, a vehicle such as a vehicle).
- Patent Document 1 describes a system that takes measures when an abnormality occurs in communication data in an in-vehicle system.
- the system described in Patent Document 1 collects information for determining the state from each information processing device in the in-vehicle system when an abnormality of communication data occurs in the in-vehicle system, and causes a security abnormality and a safety abnormality. Identify the presence or absence of occurrence for each. Then, the system determines the action to be taken for the abnormality and notifies each information processing apparatus.
- Patent Document 2 describes a system for diagnosing abnormalities in a vehicle in real time by transmitting diagnostic target data to a center device.
- the diagnostic target data detected by the diagnostic vehicle device is transmitted to the center device, it is determined whether or not the center device is a rare event, and whether or not the diagnostic vehicle is abnormal based on the determination result. And send the diagnosis result to the diagnostic vehicle device.
- Patent Document 1 and Patent Document 2 are premised on proper communication with the outside. That is, no consideration is given to the case where some abnormality or malfunction occurs in the communication itself with the outside. Therefore, when mobility is controlled on the premise of connecting to the outside, even if some trouble or abnormality occurs in the communication itself with the outside, appropriate measures should be taken according to the communication situation. It is hoped that it will be done.
- an object of the present invention is to provide a mobility control system, a mobility control method, and a mobility control program that can perform appropriate control according to the communication status of mobility on the premise of communication with the outside. ..
- the mobility control system is a mobility control system that is mounted on the mobility to be controlled and controls according to the state of the mobility, and is a communication state detection unit that detects a communication state with an external device and a communication state. Based on the above, a control unit that controls to limit the operation function of mobility is provided, the communication status detection unit detects the communication availability or the communication speed status as the communication status, and the control unit is based on the communication status. It is characterized by determining the function to be restricted.
- the mobility control method according to the present invention is a mobility control method that performs control according to a target mobility state, and detects whether communication is possible or a communication speed status as a communication state with an external device, and sets the communication state. Based on this, it is characterized by performing control that limits the operating function of mobility.
- the mobility control program according to the present invention is a mobility control program applied to a computer mounted on the mobility to be controlled and performing control according to the state of the mobility, and the computer detects the communication state with an external device.
- the communication status detection process and the control process that controls to limit the operation function of the mobility based on the communication status are executed, and the communication status detection process detects the availability of communication or the status of the communication speed as the communication status.
- the control process is characterized in that the function to be restricted is determined based on the communication state.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of an embodiment of the mobility control system according to the present invention.
- the mobility control system 100 of the present embodiment includes a communication device 10, a unit 20, a communication state detection unit 30, a control unit 40, and an input / output device 50.
- the mobility control system 100 is a system that is mounted on the mobility 300 to be controlled and takes measures according to the state of the mobility 300.
- a specific example of the mobility 300 is a connected car.
- various functions of an autonomous driving vehicle using GPS (Global Positioning System), road installation equipment, the Internet, etc. will be described as specific examples.
- the mobility 300 is not limited to a vehicle, and may be, for example, a train or an aircraft.
- the mobility control system 100 communicates with the security center server 210 in the external security center 200 via the communication device 10.
- the security center server 210 transmits various information necessary for controlling mobility to the mobility control system 100.
- the communication device 10 is a device that communicates with the security center server 210 or an arbitrary external server (not shown).
- the mode of the communication device 10 is arbitrary, and is realized by, for example, a communication device equipped with a module dedicated to the vehicle.
- the communication device 10 may notify the communication status detection unit 30, which will be described later, of the communication status, or may notify the detected abnormality or malfunction.
- the unit 20 is a unit that detects and controls various states of mobility, and is realized by, for example, various electronic control units (ECU: Electronic Control Unit). Although only one unit 20 is shown in FIG. 1, the number of units 20 is not limited to one, and may be two or more.
- the mobility control system 100 includes a plurality of units 20 according to the control target.
- control targets include an engine, a brake, a meter, a car navigation system, and an airbag.
- the communication state detection unit 30 detects the communication state with the external device. Specifically, the communication state detection unit 30 detects the communication state of the communication device 10 with the security center server 210 and the external server. The communication state detection unit 30 may detect the communication state by periodically inquiring the communication device 10 about the state, or may detect the communication state based on the communication status notified from the communication device 10. .. Further, the communication state detection unit 30 may detect an invalid packet (value, replay, etc.) in the CAN (Controller Area Network).
- CAN Controller Area Network
- the communication status detection unit 30 detects at least one of communication availability, communication speed status, and unauthorized communication as the communication status. At that time, the communication state detection unit 30 may collect various status information of the mobility 300 and identify a place where an abnormality or a defect has occurred.
- situations where communication is not possible include situations where communication is disconnected, authentication with the outside is in progress, communication equipment is out of order, and a communication error has occurred. Further, as an example of a situation in which the communication speed is low (a situation in which communication is limited), there are situations such as congestion and low-speed communication mode.
- examples of situations where unauthorized communication is being performed include being under a DoS (Denial of Service attack) attack, performing abnormal communication from within mobility, and performing unusual processing.
- DoS Delivery of Service attack
- unusual processing for example, an unusual process is occurring, a specific process is accessing an unusual file, or an unusual IP address or port is being accessed. , Accessing with an invalid ID or password, etc.
- the control unit 40 controls to limit the operating function of the mobility 300 based on the communication state detected by the communication state detection unit 30. Specifically, the control unit 40 determines a function to be restricted based on the communication state, and performs various controls on the determined function. For example, in the case of a connected car in which mobility automatically operates, the control unit 40 controls automatic driving that can be realized with limited functions.
- the control unit 40 controls to limit the functions installed in the mobility 300 to those that do not communicate. For example, in the case of automatic operation, the control unit 40 controls automatic operation that can be realized by a function that does not perform communication.
- Functions related to autonomous driving that do not communicate include functions that use short-range sensors and some vehicle operation functions, such as inter-vehicle distance measurement and maintenance function, lane departure correction function, collision avoidance function, parking support function, and device detection function. Can be mentioned.
- the control unit 40 controls to limit the functions installed in the mobility 300 in which the expected communication amount exceeds a predetermined standard. For example, in the case of automatic operation, the control unit 40 limits the functions so that automatic operation and services that require large-capacity communication are not performed, and can be realized with functions that the expected communication amount does not exceed a predetermined standard. Controls automatic driving. Examples of functions that require large-capacity communication include dynamic maps, video data transmission (remote control function, etc.), and upload / download functions for detailed vehicle data and logs.
- a function that the expected communication volume does not exceed a predetermined standard a function that can be realized with a small amount of communication
- a vehicle position information notification function GPS
- a vehicle data distribution function of about status running, stopped, (During a failure, etc.)
- an emergency call function that asks the cloud side for SOS from the driver
- an abnormality detection alert function that notifies the presence or absence of an abnormality, and so on.
- the control unit 40 controls to enable the functions that can be realized with a small amount of communication as described above and to disable the functions that require large-capacity communication. You may. In that case, a function that can be selected according to the limited communication amount may be defined, and the control unit 40 may select a function to be operated according to the communication speed. Further, the priority of the function to be operated may be determined in advance, and the control unit 40 may determine the function according to the priority within the range of the allowable communication amount.
- control unit 40 may determine that appropriate control cannot be performed and perform control to limit the function for automatically determining the situation. For example, in the case of automatic operation, the control unit 40 may perform control to stop the automatic operation itself.
- control unit 40 may block a specific address or a specific port, block the entire network, stop or restart a process, delete or update a file, or restart or update a communication unit.
- control unit 40 may collect information at the time of abnormality occurrence from the network in mobility and analyze the cause of the abnormality. Then, depending on the cause of the abnormality, the control unit 40 may take measures against the cause, implement OTA (Over the Air), recover the reduced function by immediate action, maintain the degenerate operation, and the like. Further, the control unit 40 may notify the security center server 210 (for example, SOC: security operation center), the mobile terminal of the driver, and the input / output device 50 described later of the communication status.
- security center server 210 for example, SOC: security operation center
- the input / output device 50 is a device that performs input / output processing between the operator of the mobility 300 and the mobility control system 100.
- the input / output device 50 is realized by, for example, IVI (in-vehicle infotainment).
- IVI in-vehicle infotainment
- the input / output device 50 may display on the IVI screen that an abnormality has occurred in response to an instruction from the control unit 40.
- the communication state detection unit 30 and the control unit 40 are realized by a computer processor (for example, a CPU (Central Processing Unit) or a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)) that operates according to a program (mobility control program).
- a computer processor for example, a CPU (Central Processing Unit) or a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)
- a program mobility control program
- the program may be stored in a storage unit (not shown) included in the mobility control system 100, and the processor may read the program and operate as the communication state detection unit 30 and the control unit 40 according to the program.
- the function of the mobility control system 100 may be provided in the SaaS (Software as a Service) format.
- the communication state detection unit 30 and the control unit 40 may be realized by dedicated hardware, respectively. Further, a part or all of each component of each device may be realized by a general-purpose or dedicated circuit (circuitry), a processor, or a combination thereof. These may be composed of a single chip or may be composed of a plurality of chips connected via a bus. A part or all of each component of each device may be realized by a combination of the above-mentioned circuit or the like and a program.
- the plurality of information processing devices and circuits may be centrally arranged. It may be distributed.
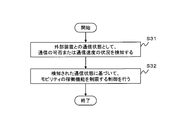
- FIG. 2 is a flowchart showing an operation example of the mobility control system 100 of the present embodiment.
- the communication state detection unit 30 detects whether or not communication is possible or the state of communication speed as the communication state with the external device (step S11).
- the control unit 40 controls to limit the operation function of the mobility based on the detected communication state (step S12).
- the communication state detection unit 30 detects the availability of communication or the communication speed status as the communication state with the external device, and the control unit 40 determines the mobility based on the communication state. Controls to limit operating functions. Therefore, appropriate control can be performed according to the communication status of mobility on the premise of communication with the outside.
- a response to a cyber attack can be considered as a first utilization example. This is because if a car is connected to the Internet, it may become a target of cyber attacks and the car may be manipulated illegally from the outside.
- the control unit 40 may cut off the connection with the Internet or notify the driver or the call center. Good. This makes it possible to prevent car hacking and accidents caused by cyber attacks.
- the control unit 40 prompts the driver to stop the vehicle or notifies the driver or the call center. You may do it. This makes it possible to prevent unexpected behavior based on an abnormal state and accidents due to the generated behavior.
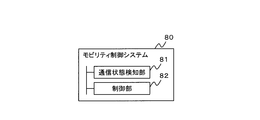
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing an outline of the mobility control system according to the present invention.
- the mobility control system 80 is a mobility control system (for example, mobility control system 100) that is mounted on a controlled mobility (for example, mobility 300) and performs control according to the state of the mobility, and is an external device.
- a communication state detection unit 81 (for example, a communication state detection unit 30) that detects a communication state with (for example, a security center server 210 or an external server) and a control that limits the operation function of mobility are performed based on the communication state.
- the communication state detection unit 81 detects whether communication is possible or the communication speed status as the communication state, and the control unit 82 determines a function to limit based on the communication state.
- the communication state detection unit 81 detects a situation in which communication with an external device cannot be performed as a communication state, and the control unit 82 detects a situation in which communication is not possible, and when the communication state detection unit 81 detects a situation in which communication is not possible, a function mounted on the mobility. Of these, control may be performed to limit the functions that do not communicate.
- Mobility may be a connected car that performs autonomous driving.
- the control unit 82 may control the automatic operation that can be realized by a function that does not perform communication.
- the communication state detection unit 81 detects a situation in which the communication speed is decreasing as a communication state
- the control unit 82 assumes that the communication state detection unit 81 detects a situation in which the communication speed is decreasing.
- Control may be performed to limit the functions (for example, dynamic map, etc.) in which the amount of communication to be performed exceeds a predetermined standard.
- control unit 82 performs automatic driving that can be realized by the functions installed in the mobility that the expected communication volume does not exceed a predetermined standard. Control may be performed.
- the mobility control system 80 may consider unauthorized communication as the communication state, in addition to the communication availability and the communication speed status. That is, the communication state detection unit 81 detects at least one of communication availability, communication speed status, and unauthorized communication as the communication state, and the control unit 82 determines a function to limit based on the communication state. You may.
- the communication state detection unit 81 is receiving a DoS attack, abnormal communication is being performed from within the mobility, or a process different from the process assumed in advance is being performed as the communication state.
- the control unit 82 may perform control that limits the function of detecting the situation and making an automatic determination.
- the processes different from the normal are the processes that generate a process different from the process assumed in advance, the process that the specific process is accessing a file different from the file assumed in advance, and the process assumed in advance. It may be at least one of the processes of accessing with an IP address or port different from the IP address or port of the user, and the process of accessing with an invalid ID or password.
- control unit 82 may perform control to stop the automatic driving itself.
- a mobility control system mounted on the mobility to be controlled and performing control according to the state of the mobility, based on a communication state detection unit that detects the communication state with an external device and the communication state.
- the communication state detection unit detects whether or not communication is possible or the communication speed status as a communication state, and the control unit sets the communication state to the control unit that controls the operation function of the mobility.
- a mobility control system characterized by determining the functions to be restricted based on.
- the communication state detection unit detects a situation in which communication with an external device cannot be performed as a communication state, and the control unit detects a situation in which communication is not possible, and when the communication state detection unit detects a situation in which communication is not possible, the function installed in the mobility Of these, the mobility control system according to Appendix 1, which controls the functions that do not communicate.
- Appendix 3 The mobility control system according to Appendix 2, wherein the mobility is a connected car that performs automatic driving, and the control unit controls automatic driving that can be realized by a function that does not perform communication.
- the communication state detection unit detects a situation in which the communication speed is decreasing as a communication state, and the control unit is assumed when the communication state detection unit detects a situation in which the communication speed is decreasing.
- the mobility control system according to Appendix 1, which controls to limit functions in which the amount of communication exceeds a predetermined standard.
- Mobility is a connected car that performs automatic driving, and the control unit is a function that can be realized by the functions installed in mobility that the expected communication volume does not exceed a predetermined standard.
- a mobility control program that is installed in the mobility to be controlled and is applied to a computer that controls according to the state of the mobility, and is a communication state detection that detects the communication state of the computer with an external device. Based on the processing and the communication state, a control process for controlling the operation function of the mobility is executed, and the communication state detection process detects whether communication is possible or the communication speed status as the communication state. , A mobility control program for determining a function to be restricted based on the communication state in the control process.
- Communication equipment 10
- Communication status detection unit 40
- Control unit 50
- Input / output device 100
- Mobility control system 200
- Security center 210
- Security center server 300 Mobility
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Transportation (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Aviation & Aerospace Engineering (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
- Control Of Driving Devices And Active Controlling Of Vehicle (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021537592A JP7447905B2 (ja) | 2019-08-02 | 2020-05-29 | モビリティ制御システム、方法、および、プログラム |
| US17/630,622 US20220250655A1 (en) | 2019-08-02 | 2020-05-29 | Mobility control system, method, and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019142901 | 2019-08-02 | ||
| JP2019-142901 | 2019-08-02 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2021024588A1 true WO2021024588A1 (ja) | 2021-02-11 |
Family
ID=74502609
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2020/021376 Ceased WO2021024588A1 (ja) | 2019-08-02 | 2020-05-29 | モビリティ制御システム、方法、および、プログラム |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20220250655A1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP7447905B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2021024588A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPWO2022219753A1 (enExample) * | 2021-04-14 | 2022-10-20 | ||
| US20230234606A1 (en) * | 2022-01-21 | 2023-07-27 | Hyundai Mobis Co., Ltd. | System for controlling vehicle based on state of controller and system for controlling vehicle based on communication state |
| US20240101161A1 (en) * | 2022-02-07 | 2024-03-28 | Nuro, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for state-based attack detection |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20220170151A (ko) * | 2021-06-22 | 2022-12-29 | 현대자동차주식회사 | 차량 내부 네트워크에 대한 침입 대응 방법 및 장치 |
| US20240129301A1 (en) * | 2022-10-13 | 2024-04-18 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Vehicle network security |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018025865A (ja) * | 2016-08-08 | 2018-02-15 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 送信要否判定装置及び進路計画システム |
| JP2018132985A (ja) * | 2017-02-16 | 2018-08-23 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 車両通信システム |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102015208053A1 (de) * | 2015-04-30 | 2016-11-03 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Verringern einer Gefährdung für ein und/oder durch ein sich auf einem Parkplatz befindendes Fahrzeug |
| US10516683B2 (en) * | 2017-02-15 | 2019-12-24 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Systems and methods for security breach detection in vehicle communication systems |
| JP6938177B2 (ja) | 2017-03-14 | 2021-09-22 | パイオニア株式会社 | 制御装置、制御方法、及び、プログラム |
| US11873005B2 (en) * | 2017-05-18 | 2024-01-16 | Driveu Tech Ltd. | Device, system, and method of wireless multiple-link vehicular communication |
-
2020
- 2020-05-29 US US17/630,622 patent/US20220250655A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2020-05-29 WO PCT/JP2020/021376 patent/WO2021024588A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2020-05-29 JP JP2021537592A patent/JP7447905B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018025865A (ja) * | 2016-08-08 | 2018-02-15 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 送信要否判定装置及び進路計画システム |
| JP2018132985A (ja) * | 2017-02-16 | 2018-08-23 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 車両通信システム |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPWO2022219753A1 (enExample) * | 2021-04-14 | 2022-10-20 | ||
| WO2022219753A1 (ja) * | 2021-04-14 | 2022-10-20 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | 制御システム、制御方法、及びプログラム |
| JP2025028118A (ja) * | 2021-04-14 | 2025-02-28 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | 制御システム、制御方法、及びプログラム |
| US20230234606A1 (en) * | 2022-01-21 | 2023-07-27 | Hyundai Mobis Co., Ltd. | System for controlling vehicle based on state of controller and system for controlling vehicle based on communication state |
| US20240101161A1 (en) * | 2022-02-07 | 2024-03-28 | Nuro, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for state-based attack detection |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2021024588A1 (enExample) | 2021-02-11 |
| US20220250655A1 (en) | 2022-08-11 |
| JP7447905B2 (ja) | 2024-03-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11469921B2 (en) | Security device, network system, and fraud detection method | |
| JP7447905B2 (ja) | モビリティ制御システム、方法、および、プログラム | |
| JP7231559B2 (ja) | 異常検知電子制御ユニット、車載ネットワークシステム及び異常検知方法 | |
| JP7113337B2 (ja) | サーバ装置、車両装置、車両用システム及び情報処理方法 | |
| JP6578224B2 (ja) | 車載システム、プログラムおよびコントローラ | |
| US20200059383A1 (en) | In-vehicle gateway device and communication restriction method | |
| KR101936891B1 (ko) | 운전 행위 안내 정보의 생성 방법 및 장치 | |
| CN112537318B (zh) | 用于远程控制机动车的方法 | |
| JP2019008618A (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及びプログラム | |
| WO2021111681A1 (ja) | 情報処理装置、制御方法及びプログラム | |
| JP7605251B2 (ja) | モビリティ制御システム、方法、および、プログラム | |
| CN111386218A (zh) | 用于在网络故障期间辅助驾驶车辆的方法及相关系统 | |
| JP7409247B2 (ja) | 不正侵入防止装置、不正侵入防止方法、及び不正侵入防止用プログラム | |
| JP6417984B2 (ja) | 車載通信システム | |
| WO2020044638A1 (ja) | 車載通信システム、データ取得装置、管理装置および監視方法 | |
| CN115811732B (zh) | 控制装置、车辆、控制系统、控制方法以及记录介质 | |
| US20250178617A1 (en) | In-vehicle electronic device | |
| US20220286473A1 (en) | Anomaly detection system and anomaly detection method | |
| CN119271466A (zh) | 图形处理单元gpu的故障检测方法、装置及电子设备 | |
| JP2021124500A (ja) | 整合性レベルを有する位置決めデータを提供するテレマティクス制御エンティティ | |
| US20250150470A1 (en) | Security method and security device | |
| US20250055910A1 (en) | Monitoring device, monitoring method, and recording medium | |
| US20240017732A1 (en) | Notification apparatus, notification method, and non-transitory computer-readable storage medium | |
| US20210089044A1 (en) | Method for controlling a motor vehicle remotely | |
| JP2025187576A (ja) | 情報処理システム、情報処理装置、情報処理方法およびプログラム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 20849245 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2021537592 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 20849245 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |