WO2018163490A1 - 視認支援装置、方法およびプログラム - Google Patents
視認支援装置、方法およびプログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2018163490A1 WO2018163490A1 PCT/JP2017/036703 JP2017036703W WO2018163490A1 WO 2018163490 A1 WO2018163490 A1 WO 2018163490A1 JP 2017036703 W JP2017036703 W JP 2017036703W WO 2018163490 A1 WO2018163490 A1 WO 2018163490A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- driver
- information
- target
- visual
- vehicle
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W40/00—Estimation or calculation of non-directly measurable driving parameters for road vehicle drive control systems not related to the control of a particular sub unit, e.g. by using mathematical models
- B60W40/08—Estimation or calculation of non-directly measurable driving parameters for road vehicle drive control systems not related to the control of a particular sub unit, e.g. by using mathematical models related to drivers or passengers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W50/00—Details of control systems for road vehicle drive control not related to the control of a particular sub-unit, e.g. process diagnostic or vehicle driver interfaces
- B60W50/08—Interaction between the driver and the control system
- B60W50/14—Means for informing the driver, warning the driver or prompting a driver intervention
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/16—Anti-collision systems
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N7/00—Television systems
- H04N7/18—Closed-circuit television [CCTV] systems, i.e. systems in which the video signal is not broadcast
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B21/00—Alarms responsive to a single specified undesired or abnormal condition and not otherwise provided for
- G08B21/02—Alarms for ensuring the safety of persons
- G08B21/06—Alarms for ensuring the safety of persons indicating a condition of sleep, e.g. anti-dozing alarms
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a visual assistance device, method, and program for assisting visual recognition by a driver.
- the driver's line of sight and an object such as an obstacle existing in front of the vehicle are detected, and based on the detection information, the driver's visual recognition is determined, and if necessary, a warning is issued. And devices that perform corrective braking are known.
- Japanese Unexamined Patent Application Publication No. 2014-137604 discloses one such device.
- This device reduces the processing load, places the target position in a check table that manages the driver's field of view information as a two-dimensional plane, and associates the driver's line of sight movement position with the check table. Whether or not the object is visually recognized is determined based on whether or not the line-of-sight movement position overlaps with the object.
- the objects detected by such an apparatus are various, such as a person, an animal, a vehicle, a fallen object, and a fixed object. These various objects do not necessarily have the same properties, characteristics, and characteristics, and may vary greatly depending on the type.
- the conventional devices handle the detected objects uniformly and perform processing for necessary functions regardless of the types of the objects.
- This invention provides a novel visual assistance device that appropriately supports visual recognition by a driver according to the type of target.
- a first aspect of the present invention is a visual assistance device that assists visual recognition by a driver of a vehicle including a driver monitoring sensor, a vehicle monitoring sensor, and a warning output device.
- the visual assistance device includes a driver state information acquisition unit that acquires state information related to the driver based on driver monitoring information of the driver monitoring sensor, and the vehicle based on vehicle monitoring information of the vehicle monitoring sensor.
- An object detection unit that detects an object existing around the vehicle, a visual determination unit that determines whether or not the driver's visual observation is appropriate, and the visual determination unit that determines that the driver's visual inspection is inappropriate
- a warning information output unit for outputting warning information for generating a warning in the warning output device.
- the visual determination unit specifies which of the plurality of groups classified in advance the object belongs to.
- the visual determination unit determines whether the visual observation of the driver is appropriate based on the state information and group information of a group to which the target belongs.
- a wake-up support device relates to the wake-up support device according to the first aspect, wherein the state information includes line-of-sight direction information indicating the direction of the driver's line of sight and the stay of the driver's line of sight.
- Line-of-sight dwell time information representing time
- the group information includes threshold information representing a threshold of the accumulated dwell time of the driver's line-of-sight set individually in advance for each group.
- the visual determination unit based on the position information representing the position of the object, the line-of-sight direction information, and the line-of-sight dwell time information, represents a cumulative accumulated gaze that represents the accumulated dwell time of the driver's line of sight directed to the object. Time information is calculated and the calculated gaze accumulated dwell time information is compared with the threshold information. If the gaze accumulated dwell time information is equal to or greater than the threshold information, it is determined that the driver's visual observation is appropriate.
- a wake-up support apparatus relates to the wake-up support apparatus according to the second aspect, wherein the plurality of groups can at least predict a motion with the first group including a target whose motion cannot be predicted.
- the first aspect of the present invention it is specified which of the plurality of groups classified in advance the object detected by the object detection unit, the state information regarding the driver's state, and the group to which the object belongs Whether or not the driver's visual observation is appropriate is determined based on the individually set group information. For this reason, whether or not the driver's visual observation is appropriate is not determined uniformly, but is determined according to the type of the object. Thereby, the suitable determination result corresponding to a kind to object is obtained. Accordingly, an appropriate warning is output according to the type of the target. That is, the output of an erroneous alarm is reduced. Thereby, unnecessary processing is reduced. Also, it is possible to avoid bothering and frustrating the driver due to a false alarm.
- whether or not the driver's visual observation is appropriate is determined based on the accumulated dwell time of the driver's line of sight toward the subject. This determination is performed by comparing the accumulated dwell time of the driver's line of sight with a threshold of accumulated dwell time set individually in advance for each group. For example, when the driver first turns his gaze to the first target, then moves his gaze to the second target and then returns his gaze to the first target again, driving directed to the first target This is done by comparing the sum of the first residence time and the second residence time of the person's line of sight with the threshold of the accumulated residence time. For this reason, it finally becomes possible to know whether the driver has visually observed the target over an appropriate time according to the type of the target. Accordingly, an appropriate warning is output according to the type of the target. That is, the output of an erroneous alarm is reduced. Thereby, unnecessary processing is reduced. Also, it is possible to avoid bothering and frustrating the driver due to a false alarm.
- the target detected by the target detection unit is a motion that cannot be predicted, a motion that can be predicted, or a motion that has substantially no motion.
- the driver is required to look at the object for a subject whose motion can be predicted longer than a subject that does not substantially move.
- the driver is required to look at the object longer than the object whose movement can be predicted for the object whose movement cannot be predicted. Accordingly, an appropriate warning is output according to the type of the target. That is, the output of an erroneous alarm is reduced. Thereby, unnecessary processing is reduced. Also, it is possible to avoid bothering and frustrating the driver due to a false alarm.
- each aspect of the present invention it is possible to provide a novel visual assistance device, method, and program for appropriately assisting visual recognition by a driver according to the type of target.
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an overall configuration of an automatic driving control system including a driving assistance device including a visual assistance device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of the visual assistance device according to the embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing the procedure of visual assistance by the visual assistance device shown in FIG.
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an overall configuration of an automatic driving control system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- This automatic driving control system is mounted on a vehicle 1 such as a passenger car.
- the vehicle 1 includes, as basic equipment, a power unit 2 including a power source and a transmission, and a steering device 3 equipped with a steering wheel 3a.
- a power unit 2 including a power source and a transmission
- a steering device 3 equipped with a steering wheel 3a.
- An engine and / or a motor is used as the power source.
- the vehicle 1 is configured to be able to travel in either the manual operation mode or the automatic operation mode.
- the manual driving mode is a mode in which the vehicle 1 is driven mainly by a driver's manual driving operation, for example.
- the manual operation mode includes, for example, an operation mode for driving the vehicle based only on the driver's driving operation, and an operation mode for performing driving operation support control for supporting the driving operation of the driver while mainly driving the driver's driving operation. Is included.
- the driving operation support control assists the steering torque so that the driver's steering becomes an appropriate steering amount based on the curvature of the curve when the vehicle 1 is traveling on the curve, for example.
- the driving operation support control includes control for assisting a driver's accelerator operation (for example, operation of an accelerator pedal) or brake operation (for example, operation of a brake pedal), manual steering (manual operation of steering), and manual speed adjustment (speed). Adjustment manual operation) is also included.
- a driver's accelerator operation for example, operation of an accelerator pedal
- brake operation for example, operation of a brake pedal
- manual steering manual operation of steering
- speed manual speed adjustment
- Adjustment manual operation is also included.
- manual steering the vehicle 1 is steered mainly by the driver's operation of the steering wheel 3a.
- the manual speed adjustment the speed of the vehicle is adjusted mainly by the driver's accelerator operation or brake operation.
- the driving operation support control does not include control for forcibly intervening in the driving operation of the driver and automatically driving the vehicle.
- the driving operation of the driver is reflected in the driving of the vehicle within a preset allowable range, but forcibly intervenes in the driving of the vehicle under certain conditions (for example, deviation from the lane of the vehicle). Control to do is not included.
- the automatic operation mode is a mode that realizes an operation state in which the vehicle automatically travels along the road on which the vehicle travels, for example.
- the automatic driving mode includes, for example, a driving state in which the vehicle automatically travels toward a preset destination without driving by the driver.
- the automatic driving mode it is not always necessary to automatically control all of the vehicle, and the driving state in which the driving operation of the driver is reflected in the driving of the vehicle within the preset allowable range is also included in the automatic driving mode. That is, the automatic driving mode includes control for forcibly intervening in driving of the vehicle under certain conditions, while reflecting the driving operation of the driver in driving of the vehicle within a preset allowable range.
- the vehicle 1 is also provided with an automatic driving control device 5 for executing driving control in the automatic driving mode.
- the automatic driving control device 5 acquires sensing information from the steering sensor 11, the accelerator pedal sensor 12, the brake pedal sensor 13, the GPS receiver 14, the gyro sensor 15, and the vehicle speed sensor 16, respectively.
- the automatic driving control device 5 is a peripheral monitoring system that monitors these sensing information, route information generated by a navigation system (not shown), traffic information acquired by road-to-vehicle communication, and positions and movements of surrounding people and vehicles.
- the vehicle 1 is automatically controlled based on the information obtained by the above.
- Automatic control includes, for example, automatic steering (automatic steering operation) and automatic speed adjustment (automatic driving of speed).
- Automatic steering is an operating state in which the steering device 3 is automatically controlled.
- Automatic steering includes LKA (Lane Keeping Assist).
- LKA Li Keeping Assist
- the LKA automatically controls the steering device 3 so that the vehicle 1 does not deviate from the traveling lane even when the driver does not perform the steering operation.
- the driver's steering operation may be reflected in the steering of the vehicle in a range where the vehicle 1 does not deviate from the travel lane (allowable range).
- automatic steering is not limited to LKA.
- Automatic speed adjustment is an operating state in which the speed of the vehicle 1 is automatically controlled.
- Automatic speed adjustment includes ACC (Adaptive Cruise Control). For example, when there is no preceding vehicle ahead of the vehicle 1, ACC performs constant speed control that causes the vehicle 1 to travel at a constant speed at a preset speed, and when the preceding vehicle exists ahead of the vehicle 1. Is a follow-up control that adjusts the vehicle speed of the vehicle 1 in accordance with the inter-vehicle distance from the preceding vehicle.
- the automatic operation control device 5 decelerates the vehicle 1 according to the driver's brake operation (for example, operation of the brake pedal) even when ACC is being executed.
- the automatic operation control device 5 can perform the driver's accelerator operation (for example, accelerator) up to a preset maximum allowable speed (for example, the maximum speed legally determined on the traveling road) even during execution of ACC.
- the vehicle can be accelerated according to the pedal operation.
- the automatic speed adjustment is not limited to ACC but also includes CC (Cruise Control).
- the vehicle 1 is also provided with a driving support device 6.
- the driving support device 6 may have various functions.
- the driving support device 6 operates in cooperation with a driver monitoring function and a notification device that constitutes a driver monitoring system that monitors the driver and grasps the state of the driver in cooperation with the driver monitoring sensor.
- a warning output function that constitutes a warning output system that issues a warning according to the state of the driver
- a driving mode switching control function that constitutes a driving mode switching control system that controls switching of the driving mode according to the driver's state, an outside sensor, and According to the driver's state in cooperation with the visual assistance function, the biological information sensor, and the stimulus output device that constitute the visual assistance system that cooperates with the notification device to assist the visual recognition by the driver based on the state of the driver. It may have a wake-up support function that constitutes a wake-up support system that promotes driver wake-up.
- the driver's condition is, for example, whether the driver is concentrating on driving, whether the driver is looking aside, whether the driver is drowsy, Whether the driver is in a panic, whether the driver is asleep, and if the driver is in automatic driving, is the driver ready to return to manual driving? And so on.
- the driver's state also includes changes in the driver's state that appear within a short period of time, in other words, the driver's movement. That is, the state of the driver may be, for example, the movement of the driver's line of sight. The movement of the driver's line of sight can be grasped by, for example, the direction of the driver's line of sight and the residence time of the driver's line of sight in that direction.
- driver monitoring information for example, monitoring video information of a driver is acquired by a driver monitoring sensor.
- driver's eye opening degree, blinking frequency, eye movement, and the like are analyzed.
- the direction of the driver's line of sight and the staying time, the driver's arousal level, and the like are recognized based on the analysis result.
- the state of the driver is specified by comparing the direction of the driver's line of sight and the staying time, the driver's arousal level, and the like with a preset threshold value.
- the driving support device 6 includes at least a driver monitoring unit 6a that performs the driver monitoring function and a visual support unit 6b that performs the visual support function.
- the driver monitoring unit 6a constitutes a driver monitoring system 8 in cooperation with a driver camera 7 as a driver monitoring sensor.
- the visual recognition support unit 6b constitutes the vehicle exterior visual recognition system 10 in cooperation with the vehicle exterior camera 9A serving as a vehicle exterior monitoring sensor.
- the vehicle outside visual recognition system 10 has a warning output device 9B, and cooperates with the driver monitoring system 8 to point out a driver's oversight, in other words, visual assistance that supports visual recognition by the driver.
- the system is configured.
- the driver monitoring unit 6a and the visual assistance unit 6b constitute a visual assistance device 6A.
- the driving support device 6 includes the visual recognition support device 6A.
- the driver's state grasped by the driver monitoring unit 6a includes at least the movement of the driver's line of sight, that is, the direction of the driver's line of sight and the dwell time of the driver's line of sight in that direction. That is, the driver monitoring unit 6a acquires information related to the direction of the driver's line of sight and the residence time.
- the driver camera 7 is installed at a position in front of the driver, such as on the dashboard, for example, and images the driver who drives the vehicle 1 to visually recognize driver monitoring information, for example, video information of the driver. Output to 6A.
- the vehicle outside camera 9A images a predetermined range around the vehicle 1, for example, in front of the vehicle 1, and outputs vehicle outside monitoring information, for example, video information outside the vehicle, to the visual recognition support device 6A.
- the warning output device 9B has, for example, a speaker as an output function, and outputs the warning information output from the visual recognition support device 6A from the speaker.
- the warning output device 9B may further include a display for displaying warning information.
- the warning output device 9B may be configured using a voice output function or an image display function of the navigation system.
- the visual assistance device 6A is a device that cooperates with the outside camera 9A and the warning output device 9B to assist the driver to visually recognize the surroundings of the vehicle 1, and is configured as follows.
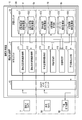
- FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing the functional configuration.
- the visual recognition support device 6A includes a control unit 61, an input / output interface unit 62, and a storage unit 63.
- the input / output interface unit 62 converts the input analog signal into digital data and outputs the digital data to the control unit 61, and converts the digital data output from the control unit 61 into an analog signal and outputs the analog signal. Specifically, the input / output interface unit 62 converts a driver monitoring signal input from the driver camera 7 into driver monitoring data and outputs the driver monitoring data to the control unit 61. The input / output interface unit 62 also converts the vehicle outside monitoring signal input from the vehicle outside camera 9 ⁇ / b> A into vehicle outside monitoring data and outputs the vehicle outside monitoring data to the control unit 61. The input / output interface unit 62 further converts the warning data output from the control unit 61 into a warning signal and outputs the warning signal to the warning output device 9B.
- the storage unit 63 uses, as a storage medium, a non-volatile memory that can be written and read at any time, such as an SSD (Solid State Drive) or an HDD (Hard Disk Drive).
- the storage unit 63 includes a driver monitoring information storage unit 631, a driver state information storage unit 632, an out-of-vehicle monitoring information storage unit 633, and a target information storage unit 634 as storage areas used for carrying out this embodiment. And a group information storage unit 635 and a determination result information storage unit 636.
- the storage unit 63 is not limited to a nonvolatile memory, and may be a volatile memory such as a RAM.
- the group information storage unit 635 stores in advance group information related to a plurality of groups classified according to the types of objects that may be detected by the visual recognition support device 6A.
- the group information includes, for example, classification information representing the relationship between the target type and the group, and threshold information that is a criterion for determining the viewing time by the driver.
- the threshold information is, for example, information representing a threshold of the accumulated residence time of the driver's line of sight directed toward the target.
- the control unit 61 has a CPU (Central Processing Unit) and a program memory constituting the computer.
- the control unit 61 includes a driver monitoring information acquisition unit 611, a driver state information acquisition unit 612, an out-of-vehicle monitoring information acquisition unit 613, and a target detection unit 614 as control functions necessary for carrying out this embodiment.
- a visual determination unit 615 and a warning information output unit 616 are provided. All of these control functions are realized by causing the CPU to execute a program stored in the program memory.
- the driver monitoring information acquisition unit 611 takes in the driver monitoring information output from the driver camera 7 via the input / output interface unit 62, and stores the acquired driver monitoring information in the driver monitoring information storage unit 63. Store in the unit 631.
- the driver state information acquisition unit 612 reads driver monitoring information, for example, monitoring video information of the driver at a preset time interval from the driver monitoring information storage unit 631, and each time driving based on the driver monitoring information is performed. Status information about the status of the person.
- the state information is not limited to this, but in this embodiment, the state information includes at least line-of-sight direction information indicating the direction of the driver's line of sight and line-of-sight dwell time information indicating the dwell time of the driver's line of sight.
- the driver state information acquisition unit 612 stores the acquired state information in the driver state information storage unit 632 of the storage unit 63.
- the out-of-vehicle monitoring information acquisition unit 613 captures out-of-vehicle monitoring information output from the out-of-vehicle camera 9A, for example, monitoring video information outside the vehicle via the input / output interface unit 62, and captures the captured out-of-vehicle monitoring information in the storage unit 63.
- the data is stored in the storage unit 633.
- the target detection unit 614 reads out-of-vehicle monitoring information from the out-of-vehicle monitoring information storage unit 633 at a preset time interval, and detects the target based on the out-of-vehicle monitoring information each time.
- the object means an existence that can be an obstacle to the traveling of the vehicle 1 and an existence that should be avoided in the traveling direction of the vehicle 1.
- the detection of the target includes determination as to whether or not the target exists within the shooting range of the outside camera 9A.
- the target detection unit 614 identifies the target based on the outside monitoring information.
- Object identification includes detecting the position of the object and identifying the type of object. Object detection and identification can be performed using image processing technology or pattern recognition technology.
- the target detection unit 614 stores target information related to the target, for example, target information including target position information and type information, in the target information storage unit 634 of the storage unit 63.
- the target position information may be information indicating the direction of the target with respect to the driver, for example.
- the visual determination unit 615 reads the state information, the target information, and the group information from the driver state information storage unit 632, the target information storage unit 634, and the group information storage unit 635, respectively, at predetermined time intervals. Based on the information, the target information, and the group information, it is determined whether or not the driver's visual observation is appropriate. Specifically, the visual determination unit 615 determines whether the driver has viewed the target based on the target position information and the driver's gaze direction information. In addition, the visual determination unit 615 is based on the target position information, the driver's gaze direction information, and the driver's gaze dwell time information. Calculate time information.
- the visual determination unit 615 determines whether or not the driver has viewed the target with sufficient time based on the target type information, the threshold information of the visual time, and the driver's gaze accumulated dwell time information. To do.
- the visual determination unit 615 stores the determination result information in the determination result information storage unit 636 of the storage unit 63.
- the warning information output unit 616 reads the determination result information from the determination result information storage unit 636 at a preset time interval, and when the determination result information indicates that the driver's visual observation is inappropriate, the warning output device Warning information for generating a warning is output to 9B.
- the warning information includes visual awakening information that prompts the driver to visually observe the object, and attention-aware information that prompts the driver to visually observe the target for a longer time.
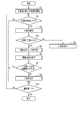
- FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing the overall control procedure and control contents.
- driver monitoring system 8 starts monitoring the driver in step S1. Driver monitoring continues, for example, throughout driving.
- the driver camera 7 When driving is started, the driver camera 7 is activated, and continuously captures a predetermined range including the driver's face, and outputs driver monitoring information that is video information thereof.
- the visual assistance device 6 ⁇ / b> A takes in the driver monitoring information output from the driver camera 7 under the control of the driver monitoring information acquisition unit 611, and stores the acquired driver monitoring information in the driver of the storage unit 63. The information is stored in the monitoring information storage unit 631.
- the visual recognition support device 6A When the acquisition of the driver monitoring information is started, the visual recognition support device 6A performs a grasping process for grasping the state of the driver every time a predetermined time elapses under the control of the driver state information obtaining unit 612. Do.
- the time interval of the grasping process may be set to a short time so that the driver's state can be grasped substantially continuously.
- the driver state information acquisition unit 612 reads the driver monitoring information from the driver monitoring information storage unit 631 at a preset time interval. Next, every time the driver monitoring information is read, the driver status information acquisition unit 612 acquires status information related to the driver status based on the driver monitoring information.
- the state information includes at least line-of-sight direction information representing the direction of the driver's line of sight and line-of-sight residence time information representing the residence time of the driver's line of sight in that direction.
- the driver state information acquisition unit 612 stores state information including line-of-sight direction information and line-of-sight dwell time information in the driver state information storage unit 632 of the storage unit 63.
- the monitoring system 10 outside the vehicle starts monitoring outside the vehicle in step S1 in parallel with monitoring the driver by the driver monitoring system 8.
- the monitoring outside the vehicle is continued throughout the driving, for example, like the monitoring of the driver.
- the outside camera 9A When the operation is started, the outside camera 9A is activated, and continuously captures a predetermined range around the vehicle 1 and outputs the outside monitoring information as the video information.
- the visual assistance device 6A takes in from the outside monitoring information output from the outside camera 9A under the control of the outside monitoring information acquisition unit 613, and stores the taken outside monitoring information in the outside monitoring information storage unit 633 of the storage unit 63. .
- the visual assistance device 6A stores the vehicle outside monitoring information every time a certain time elapses in step S2 under the control of the object detection unit 614.
- the vehicle outside monitoring information is read from the unit 633, and processing for detecting objects existing around the vehicle 1 is performed. This process can be performed using an image processing technique or a pattern recognition technique. If the target is not detected by the target detection unit 614, the process proceeds to step S9 for determining the end of driving. On the other hand, if the target is detected by the target detection unit 614, the process proceeds to step S3 for identifying the target.
- the object detection unit 614 further performs a process of identifying the object in step S3.
- the process for identifying the target includes, for example, a process for detecting the position of the target and a process for identifying the type of the target. This process can be performed using an image processing technique or a pattern recognition technique.
- the target detection unit 614 stores target information including target position information and type information in the target information storage unit 634 of the storage unit 63.
- the target position information may be target direction information representing the direction of the target with respect to the vehicle 1, for example, the direction in which the target exists with respect to the position of the driver of the vehicle 1.
- the target means an existence that can be an obstacle to the traveling of the vehicle 1 and an existence that should be avoided in the traveling direction of the vehicle 1.
- the target is not limited to this, but is, for example, a person, an animal, a vehicle, a ball, a sign, a guardrail, a curb, a falling object, or the like.
- the process for identifying the type of object is not limited to this, but for example, the object is an adult, the object is a child, the object is a vehicle, the object is a ball, or the object is a sign Alternatively, it may be a process of specifying whether the target is a fallen object. Therefore, the target type information may be information indicating what the target is.
- the visual assistance device 6A determines whether or not the driver has visually observed the target in step S4 under the control of the visual determination unit 615. For this reason, the visual determination unit 615 reads the state information related to the driver's state from the driver state information storage unit 632 and the target information related to the target from the target information storage unit 634 every time a predetermined time elapses.
- the driver state information includes line-of-sight direction information indicating the direction of the driver's line of sight and line-of-sight dwell time information indicating the dwell time of the driver's line of sight.
- the object information regarding the object includes position information and type information of the object.
- the target position information includes target direction information indicating a direction with respect to the driver of the vehicle 1.
- the visual determination unit 615 determines whether or not the driver has visually observed the target based on the driver state information and the target information regarding the target. For this reason, the visual determination unit 615 compares the target direction information and the line-of-sight direction information. If the two match, the visual determination unit 615 determines that the driver has viewed the target. If the two do not match, the driver determines It is determined that the subject was not visually observed. The visual determination unit 615 causes the determination result information storage unit 636 of the storage unit 63 to store determination result information indicating whether or not the driver has viewed the target.
- step S5 for specifying the target group.
- step S8 a warning is output.
- step S5 Identification of target group If the result of comparison between the target direction information and the line-of-sight direction information is the same, then the visual assistance device 6A is detected in step S5 under the control of the visual determination unit 615. Identify the group to which the target belongs.
- the group information storage unit 635 stores in advance information about a plurality of groups classified according to the type of target that may be detected by the visual recognition support device 6A.
- the group information includes classification information representing the relationship between the target type and the group.
- the group information storage unit 635 stores the classification information as a table, for example.
- Examples of target types include adults, children, vehicles, balls, animals, signs, guardrails, and falling objects.
- the plurality of groups as a whole include all types of objects that may be detected by the visual assistance device 6A. That is, the type of object included in one group is not included in another group. Therefore, the detected object belongs to any one of a plurality of groups.
- the plurality of groups include, for example, a first group that includes a target whose motion is unpredictable, a second group that includes a target whose motion can be predicted, and a third group that includes a target that is substantially free of motion. Composed.
- the first group may include, for example, a child, a ball, and an animal as a target whose movement is unpredictable, but is not limited thereto.
- the second group is not limited to an object whose motion can be predicted, but may include, for example, an adult and a vehicle.
- the third group may include, for example, but not limited to, a sign, a guardrail, and a fallen object as a substantially stationary object, for example, a fixed object.
- the visual determination unit 615 sequentially reads information on the types of objects that may be detected by the visual assistance device 6A from the group information storage unit 635, and detects each time. Compare with the type information of the target. This comparison process continues until the detected target type information matches the target type information read from the group information storage unit 635.
- the visual determination unit 615 is a group including the target to which the detected target belongs. Is determined. In this way, the group to which the detected object belongs is specified.
- the visual assistance device 6A acquires threshold information preset in a group to which the target belongs in step S6 under the control of the visual determination unit 615.
- the group information storage unit 635 stores in advance threshold information, which is a criterion for determining the visual time by the driver, in addition to the classification information indicating the relationship between the target type and the group.
- the threshold information is, for example, information representing a threshold of the accumulated residence time of the driver's line of sight directed toward the target.
- the threshold information is set individually for each group. Therefore, the threshold information set for one group is different from the threshold information set for another group.
- the plurality of groups includes a first group including a target whose motion is unpredictable, a second group including a target whose motion is predictable, and a target including substantially no motion.
- the threshold information of the first group is set larger than the threshold information of the second group
- the threshold information of the second group is set larger than the threshold information of the third group.
- the threshold information of the first group may be set to 3 seconds
- the threshold information of the second group may be set to 1.5 seconds
- the threshold information of the third group may be set to 0.5 seconds. .
- the threshold information of the group including the object whose motion can be predicted is set to be larger than the threshold information of the group including the object whose motion can be predicted, and the threshold information including the target whose motion can be predicted It is set to be larger than the threshold information of the group including the target that is not in
- the visual assistance device 6A under the control of the visual judgment unit 615, in step S7, did the driver visually observe the target over a sufficient time according to the detected target? No, that is, whether sufficient time has been spent for visual inspection. Whether or not the driver has viewed the object for a sufficient time is considered to be related to whether or not the driver has carefully recognized the object by carefully viewing the object.
- the visual determination unit 615 reads from the driver state information storage unit 632, the gaze direction information indicating the driver's gaze direction, the gaze dwell time information indicating the dwell time of the driver's gaze, and the driver Based on the target position information indicating the direction of the target with respect to the driver, read from the state information storage unit 632, gaze accumulated dwell time information representing the accumulated dwell time of the driver's gaze directed to the target is calculated. Subsequently, the visual determination unit 615 compares the calculated line-of-sight accumulated dwell time information with threshold information set in advance for the detected target group read from the group information storage unit 635.
- the cumulative dwell time of the driver's line of sight directed at the object is simply the total time that the driver viewed the object. For example, when the driver first turns his gaze to the first target, then moves his gaze to the second target and then returns his gaze to the first target again, the accumulated gaze dwell time for the first target Is the sum of the first residence time and the second residence time of the driver's line of sight directed to the first object.
- the visual determination unit 615 visually observes the target with sufficient time corresponding to the type, that is, the driver's visual observation is appropriate. On the other hand, if the driver's gaze accumulated dwell time information is less than the threshold information, the driver did not take sufficient time corresponding to the type of the subject's visual observation, that is, the driver's visual observation Is determined to be inappropriate.
- the visual determination unit 615 stores the determination result information in the determination result information storage unit 636 of the storage unit 63.
- the visual assistance device 6A outputs warning information for generating a warning to the warning output device 9B as necessary in steps S8 and S9 under the control of the warning information output unit 616.
- the warning information output unit 616 determines whether or not the driver in step S4 visually observes the target and whether or not the driver's visual observation in step S7 is appropriate every time a predetermined time elapses.
- the determination result information on the information is read from the determination result information storage unit 636.
- the warning information output unit 616 When the determination result information indicates that the driver did not view the target, the warning information output unit 616 outputs warning information that causes the warning output device 9B to output a message that prompts the driver to view the target. . When the determination result information indicates that the driver's visual observation is inappropriate, the warning information output unit 616 causes the warning output device 9B to output a message that prompts the driver to look at the target again for a long time. Output warning information.
- the warning output device 9B outputs a warning message as sound, for example, according to the warning information.
- step S10 Driving Completion Determination Subsequently, the visual assistance device 6A determines whether or not driving has ended in step S10. When it determines with driving
- state information relating to the state of the driver is acquired based on the driver monitoring information of the driver camera 7 which is a driver monitoring sensor for monitoring the driver.
- the vehicle outside monitoring information of the vehicle outside camera 9A that is a vehicle outside monitoring sensor that monitors the periphery of the vehicle 1, a target existing around the vehicle 1 is detected, and target information related to the detected target is acquired.
- Whether or not the driver has viewed the target is determined based on the line-of-sight direction information included in the state information and the target direction information included in the target information. Further, based on the line-of-sight direction information included in the state information and the target direction information included in the target information, based on the line-of-sight dwell time information included in the state information, accumulation of the driver's line of sight toward the target Line-of-sight accumulated residence time information representing the residence time is calculated. Further, based on the type information included in the target information, a group to which the detected target belongs is specified, and based on threshold information that is group information set in the group and calculated line-of-sight accumulated dwell time information It is determined whether or not the driver's visual observation is appropriate.
- a warning is output unnecessarily for visual observation of a fixed object that does not need to be observed for a long time, and conversely, prediction such as a child or a ball that needs to be viewed for a long time is unnecessary. It is conceivable that a warning that would otherwise need to be output may not be output for visual inspection of the object.
- the threshold for a target that can predict movement is set to be longer than the threshold for a target that does not substantially move.
- the threshold value for a target whose motion cannot be predicted is set longer than the threshold value for a target whose motion can be predicted.
- the driver monitoring sensor is configured by the driver camera 7 and the state of the driver is determined based on the driver monitoring information that is video information including the driver's face obtained by the driver camera 7.
- the driver monitoring sensor is not limited to the driver camera 7, and is configured by a motion sensor that acquires the driver's motion information, and acquires the driver's state information based on the motion information obtained by the motion sensor. It may be.
- the plurality of groups is configured by the three groups of the first group, the second group, and the third group.
- the plurality of groups is not limited to this, and more You may comprise from a group.
- the vehicle type, the function of the automatic driving control device, the control function and control procedure of the visual assistance device, and the control content can be variously modified and implemented without departing from the gist of the present invention.
- the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment as it is, and can be embodied by modifying the constituent elements without departing from the scope of the invention in the implementation stage.
- various inventions can be formed by appropriately combining a plurality of constituent elements disclosed in the embodiment. For example, some components may be deleted from all the components shown in the embodiment. Furthermore, you may combine suitably the component covering different embodiment.
- a visual assistance device for assisting visual recognition by a driver of a vehicle provided with a driver monitoring sensor, a vehicle external monitoring sensor, and a warning output device, comprising a hardware processor and a memory
- the hardware processor is Based on the driver monitoring information of the driver monitoring sensor, obtain state information about the driver, store the obtained state information in the memory, Based on the vehicle outside monitoring information of the vehicle outside monitoring sensor, a target existing around the vehicle is detected, and detection information related to the detected target is stored in the memory, The group information previously set for each group stored in advance in the memory and the detection information are read from the memory.
- the target is Identifying which of the plurality of classified groups belongs, and determining whether or not the driver's visual observation is appropriate based on the state information and the group information of the group to which the target belongs, and the determination result Storing information in the memory; Visual assistance that reads the determination result information from the memory and outputs warning information for generating a warning to the warning output device when the determination result information indicates that the driver's visual observation is inappropriate apparatus.
- a visual assistance method for assisting visual recognition by a driver of a vehicle including a driver monitoring sensor, an outside monitoring sensor, and a warning output device, Using the hardware processor, based on the driver monitoring information of the driver monitoring sensor, to acquire the state information about the driver, to store the acquired state information in a memory, Using the hardware processor, based on out-of-vehicle monitoring information of the out-of-vehicle monitoring sensor, detects a target existing around the vehicle, and stores detection information related to the detected target in the memory, Using the hardware processor, group information set individually in advance for each group stored in advance in the memory and the detection information are read from the memory, and the read detection information and group information are read.
- the operation of the object detected by the object detection step is specified to which of a plurality of previously classified groups It is determined whether or not the person's visual observation is appropriate, and the determination result information is stored in the memory,
- the warning output device is configured to generate a warning.
- a visual assistance method that outputs warning information.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Transportation (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
- Emergency Alarm Devices (AREA)
- Control Of Driving Devices And Active Controlling Of Vehicle (AREA)
- Closed-Circuit Television Systems (AREA)
Abstract
運転者監視センサと車外監視センサと警告出力装置とを備えた車両の運転者による視認を支援する視認支援装置を提供する。 視認支援装置は、運転者監視センサの運転者監視情報に基づいて、前記運転者に関する状態情報を取得する運転者状態情報取得部と、車外監視センサの車外監視情報に基づいて、前記車両の周辺に存在する対象を検知する対象検知部と、前記対象が、予め分類された複数のグループのいずれに属するかを特定し、前記状態情報と前記対象が属するグループのグループ情報とに基づいて、前記運転者の目視が適切であったか否かを判定する目視判定部と、前記目視判定部により前記運転者の目視が不適切であると判定された場合に、前記警告出力装置に警告を発生させるための警告情報を出力する警告情報出力部とを備える。
Description
この発明は、運転者による視認を支援する視認支援装置、方法およびプログラムに関する。
従来、運転者の視線と車両の例えば前方に存在する障害物等の対象とを検知し、それらの検知情報に基づいて、対象に対する運転者による視認を判定して、必要に応じて、注意喚起や矯正制動などを行う装置が知られている。
例えば特開2014-137604号公報は、このような装置のひとつを開示している。この装置は、処理負荷の軽減を図って、運転者の視界の情報を二次元平面として管理するチェックテーブルに対象の位置を配置し、また、運転者の視線の移動位置をチェックテーブルに対応付け、視線の移動位置と対象との重なりの有無に基づいて対象が視認されたか否かを判定している。
このような装置において検知される対象は、人であったり、動物であったり、車両であったり、落下物であったり、固定物であったりなど、さまざまなである。これらさまざまな対象は、その性質や特性、特質などは必ずしも同じではなく、種類によっては大きく異なっていることがある。
しかしながら、これまでの装置は、対象の種類に関係なく、検知した対象を画一的に扱って、必要な機能のための処理を行っている。
この発明は、運転者による視認を対象の種類に応じて適切に支援する新規な視認支援装置を提供するものである。
上記課題を解決するため、この発明の第1の態様は、運転者監視センサと車外監視センサと警告出力装置とを備えた車両の運転者による視認を支援する視認支援装置である。視認支援装置は、前記運転者監視センサの運転者監視情報に基づいて、前記運転者に関する状態情報を取得する運転者状態情報取得部と、前記車外監視センサの車外監視情報に基づいて、前記車両の周辺に存在する対象を検知する対象検知部と、前記運転者の目視が適切であったか否かを判定する目視判定部と、前記目視判定部により前記運転者の目視が不適切であると判定された場合に、前記警告出力装置に警告を発生させるための警告情報を出力する警告情報出力部とを備える。前記目視判定部は、前記対象が、予め分類された複数のグループのいずれに属するかを特定する。前記目視判定部は、前記状態情報と前記対象が属するグループのグループ情報とに基づいて、前記運転者の目視が適切であったか否かを判定する。
この発明の第2の態様による覚醒支援装置は、第1の態様による覚醒支援装置に係り、前記状態情報は、前記運転者の視線の方向を表す視線方向情報と、前記運転者の視線の滞留時間を表す視線滞留時間情報とを含み、前記グループ情報は、グループ毎に予め個別に設定された前記運転者の視線の累積滞留時間の閾値を表す閾値情報を含んでいる。前記目視判定部は、前記対象の位置を表す位置情報と前記視線方向情報と前記視線滞留時間情報とに基づいて、前記対象に向けられた前記運転者の視線の累積滞留時間を表す視線累積滞留時間情報を算出し、算出した前記視線累積滞留時間情報を前記閾値情報と比較し、前記視線累積滞留時間情報が前記閾値情報以上である場合、前記運転者の目視が適切であると判定する。
この発明の第3の態様による覚醒支援装置は、第2の態様による覚醒支援装置に係り、前記複数のグループは、少なくとも、動きが予測不能な対象を含む第1のグループと、動きが予測可能な対象を含む第2のグループと、動きが実質的にない対象を含む第3のグループとを含み、前記第1のグループの前記閾値情報は前記第2のグループの前記閾値情報よりも大きく、前記第2のグループの前記閾値情報は前記第3のグループの前記閾値情報よりも大きい。
この発明の第1の態様によれば、対象検知部により検知された対象が、予め分類された複数のグループのいずれに属するかが特定され、運転者の状態に関する状態情報と、対象が属するグループの個別に設定されたグループ情報とに基づいて、運転者の目視が適切であったか否かが判定される。このため、運転者の目視が適切であったか否かは、画一的に判定されるのではなく、対象の種類に応じて判定される。これにより、対象に種類に対応した好適な判定結果が得られる。従って、対象に種類に対応して、適切な警告が出力されるようになる。すなわち、誤った警報が出力されることが低減される。これにより、不要な処理が低減される。また、誤った警報により、運転者をわずらわせたり、いらだたせたりすることが避けられる。
この発明の第2の態様によれば、運転者の目視が適切であったか否かは、対象に向けられた運転者の視線の累積滞留時間に基づいて判定される。この判定は、運転者の視線の累積滞留時間を、グループ毎に予め個別に設定された累積滞留時間の閾値と比較することにより行われる。例えば、運転者が、まず第1の対象に視線を向け、次に第2の対象に視線を移した後、再び第1の対象に視線を戻した場合、第1の対象に向けられた運転者の視線の1度目の滞留時間と2度目の滞留時間との合計を、累積滞留時間の閾値と比較することにより行われる。このため、最終的に運転者が、対象の種類に応じた適切な時間をかけて、対象を目視したかがわかるようになる。従って、対象に種類に対応して、適切な警告が出力されるようになる。すなわち、誤った警報が出力されることが低減される。これにより、不要な処理が低減される。また、誤った警報により、運転者をわずらわせたり、いらだたせたりすることが避けられる。
この発明の第3の態様によれば、対象検知部により検知された対象が、動きが予測不能なものか、動きが予測可能なものか、動きが実質的にないものかのいずれであるかが特定される。運転者は、動きが予測可能な対象に対しては、動きが実質的にない対象よりも、対象を長く目視することが求められる。また、運転者は、動きが予測不能な対象に対しては、動きが予測可能な対象よりも、対象を長く目視することが求められる。従って、対象に種類に対応して、適切な警告が出力されるようになる。すなわち、誤った警報が出力されることが低減される。これにより、不要な処理が低減される。また、誤った警報により、運転者をわずらわせたり、いらだたせたりすることが避けられる。
すなわち、この発明の各態様によれば、運転者による視認を対象の種類に応じて適切に支援する新規な視認支援装置、方法およびプログラムを提供することができる。
以下、図面を参照してこの発明に係わる実施形態を説明する。
[一実施形態]
(構成)
図1は、この発明の一実施形態に係る自動運転制御システムの全体構成を示す図である。この自動運転制御システムは、乗用車等の車両1に搭載される。
[一実施形態]
(構成)
図1は、この発明の一実施形態に係る自動運転制御システムの全体構成を示す図である。この自動運転制御システムは、乗用車等の車両1に搭載される。
車両1は、基本設備として、動力源および変速装置を含むパワーユニット2と、ステアリングホイール3aが装備された操舵装置3とを備えている。動力源としては、エンジンまたはモータ、あるいはその両方が用いられる。
車両1は、手動運転モードまたは自動運転モードのいずれかの運転モードで走行可能に構成されている。
手動運転モードは、例えば、運転者の手動による運転操作を主体として車両1を走行させるモードである。手動運転モードには、例えば、運転者の運転操作のみに基づいて車両を走行させる動作モードと、運転者の運転操作を主体としながら運転者の運転操作を支援する運転操作支援制御を行う動作モードが含まれる。
運転操作支援制御は、例えば、車両1のカーブ走行時にカーブの曲率に基づいて運転者の操舵が適切な操舵量となるように操舵トルクをアシストする。また運転操作支援制御には、運転者のアクセル操作(例えばアクセルペダルの操作)またはブレーキ操作(例えばブレーキペダルの操作)を支援する制御と、手動操舵(操舵の手動運転)および手動速度調整(速度調整の手動運転)も含まれる。手動操舵は、運転者のステアリングホイール3aの操作を主体として車両1の操舵を行う。手動速度調整は、運転者のアクセル操作又はブレーキ操作を主体として車両の速度調整を行う。
なお、運転操作支援制御には、運転者の運転操作に強制的に介入して、車両を自動走行させる制御は含まれない。すなわち、手動運転モードには、予め設定された許容範囲において運転者の運転操作を車両の走行に反映させるが、一定条件(例えば車両の車線逸脱等)の下で車両の走行に強制的に介入する制御は含まれない。
一方、自動運転モードは、例えば、車両の走行する道路に沿って自動で車両を走行させる運転状態を実現するモードである。自動運転モードには、例えば、運転者が運転操作をすることなく、予め設定された目的地に向かって自動的に車両を走行させる運転状態が含まれる。自動運転モードは、必ずしも車両の全ての制御を自動で行う必要はなく、予め設定された許容範囲において運転者の運転操作を車両の走行に反映する運転状態も自動運転モードに含まれる。すなわち、自動運転モードには、予め設定された許容範囲において運転者の運転操作を車両の走行に反映させるが、一定条件の下で車両の走行に強制的に介入する制御が含まれる。
図1において、車両1はまた、自動運転モードによる運転制御を実行するための自動運転制御装置5を備えている。自動運転制御装置5は、ステアリングセンサ11、アクセルペダルセンサ12、ブレーキペダルセンサ13、GPS受信機14、ジャイロセンサ15、および車速センサ16からそれぞれセンシング情報を取得する。自動運転制御装置5は、これらのセンシング情報と、図示しないナビゲーションシステムで生成される経路情報や、路車間通信により取得される交通情報、周辺の人や車両の位置と動きを監視する周辺監視システムにより得られる情報をもとに、車両1の走行を自動制御する。
自動制御には、例えば、自動操舵(操舵の自動運転)と自動速度調整(速度の自動運転)がある。自動操舵は、操舵装置3を自動で制御する運転状態である。自動操舵にはLKA(Lane Keeping Assist)が含まれる。LKAは、例えば、運転者がステアリング操作をしない場合であっても、車両1が走行車線から逸脱しないように自動で操舵装置3を制御する。なお、LKAの実行中であっても、車両1が走行車線を逸脱しない範囲(許容範囲)において運転者のステアリング操作を車両の操舵に反映してもよい。なお、自動操舵はLKAに限らない。
自動速度調整は、車両1の速度を自動で制御する運転状態である。自動速度調整にはACC(Adaptive Cruise Control)が含まれる。ACCとは、例えば、車両1の前方に先行車が存在しない場合は予め設定された設定速度で車両1を定速走行させる定速制御を行い、車両1の前方に先行車が存在する場合には先行車との車間距離に応じて車両1の車速を調整する追従制御を行うものである。自動運転制御装置5は、ACCを実行中であっても、運転者のブレーキ操作(例えばブレーキペダルの操作)に応じて車両1を減速させる。また自動運転制御装置5は、ACCを実行中であっても、予め設定された最大許容速度(例えば走行中の道路において法的に定められた最高速度)まで、運転者のアクセル操作(例えばアクセルペダルの操作)に応じて車両を加速させることもできる。なお、自動速度調整は、ACCに限らず、CC(Cruise Control:定速制御)等も含まれる。
図1において、車両1はまた、運転支援装置6を備えている。運転支援装置6は、さまざまな機能を有していてよい。例えば、運転支援装置6は、運転者監視センサと共働して運転者を監視して運転者の状態を把握する運転者監視システムを構成する運転者監視機能、報知装置と共働して運転者の状態に応じて警告を発する警告出力システムを構成する警告出力機能、運転者の状態に応じて運転モードの切り替えを制御する運転モード切替制御システムを構成する運転モード切替制御機能、車外センサおよび報知装置と共働して運転者の状態に基づいて運転者による視認を支援する視認支援システムを構成する視認支援機能、生体情報センサおよび刺激出力装置と共働して運転者の状態に応じて運転者の覚醒を促す覚醒支援システムを構成する覚醒支援機能などを有していてよい。
運転者の状態は、例えば、運転者が運転に集中しているか否か、運転者が脇見をしているか否か、運転者が眠気を催しているか否か、運転者が運転以外の作業をしているか否か、運転者がパニックを起こしているか否か、運転者が居眠りをしているか否か、また自動運転中であれば、運転者が手動運転に復帰可能な状態であるか否かなど、さまざまであってよい。
運転者の状態はまた、短時間の内に現れた運転者の状態の変化、言い換えれば、運転者の動きも含んでいる。つまり、運転者の状態は、例えば、運転者の視線の動きであってもよい。運転者の視線の動きは、例えば、運転者の視線の方向と、その方向における運転者の視線の滞留時間で把握され得る。
運転者の状態の把握は、例えば、次のようにして行う。まず、運転者監視センサにより運転者監視情報たとえば運転者の監視映像情報を取得する。次に、取得した監視映像情報に基づいて、運転者の眼の開き具合、瞬きの頻度、眼球運動等を分析する。続いて、分析結果に基づいて、運転者の視線の方向と滞留時間、運転者の覚醒度等を認識する。さらに、運転者の視線の方向と滞留時間、運転者の覚醒度等を、予め設定された閾値と比較することにより、運転者の状態を特定する。
この実施形態では、運転支援装置6は、少なくとも、運転者監視機能を実施する運転者監視部6aと、視認支援機能を実施する視認支援部6bとを有している。運転者監視部6aは、運転者監視センサとしての運転者カメラ7と共働して運転者監視システム8を構成している。また、視認支援部6bは、車外監視センサとしての車外カメラ9Aと共働して車外視認システム10を構成している。さらに、車外視認システム10は、警告出力装置9Bを有しており、運転者監視システム8と共働して、運転者の見落とし等を指摘する、言い換えれば、運転者による視認を支援する視認支援システムを構成している。また、運転者監視部6aと視認支援部6bは視認支援装置6Aを構成している。言い換えれば、運転支援装置6は、視認支援装置6Aを内包している。
運転者監視部6aにおいて把握される運転者の状態は、少なくとも、運転者の視線の動き、すなわち、運転者の視線の方向と、その方向における運転者の視線の滞留時間を含んでいる。すなわち、運転者監視部6aは、運転者の視線の方向と滞留時間に関する情報を取得する。
運転者カメラ7は、例えばダッシュボード上のような運転者の正面となる位置に設置され、車両1を運転する運転者を撮像して、運転者監視情報たとえば運転者の映像情報を視認支援装置6Aへ出力する。
車外カメラ9Aは、車両1の周辺たとえば前方の所定の範囲を撮像して、車外監視情報たとえば車外の映像情報を視認支援装置6Aへ出力する。
警告出力装置9Bは、例えば、出力機能としてスピーカを有し、視認支援装置6Aから出力された警告情報をスピーカから出力する。警告出力装置9Bはさらに、警告情報を表示する表示器を有していてもよい。警告出力装置9Bは、ナビゲーションシステムの音声出力機能や画像表示機能を利用して構成されてもよい。
視認支援装置6Aは、車外カメラ9Aおよび警告出力装置9Bと共働して、車両1の周辺に対する運転者による視認を支援する装置であり、以下のように構成されている。図2は、その機能構成を示すブロック図である。
視認支援装置6Aは、制御ユニット61と、入出力インタフェースユニット62と、記憶ユニット63とを備えている。
入出力インタフェースユニット62は、入力されたアナログ信号をデジタルデータに変換して制御ユニット61へ出力し、また、制御ユニット61から出力されたデジタルデータをアナログ信号に変換して出力する。具体的には、入出力インタフェースユニット62は、運転者カメラ7から入力された運転者監視信号を運転者監視データに変換して制御ユニット61へ出力する。入出力インタフェースユニット62はまた、車外カメラ9Aから入力された車外監視信号を車外監視データに変換して制御ユニット61へ出力する。入出力インタフェースユニット62はさらに、制御ユニット61から出力された警告データを警告信号に変換して警告出力装置9Bへ出力する。
記憶ユニット63は、記憶媒体として、例えばSSD(Solid State Drive)やHDD(Hard Disk Drive)等の随時書き込みおよび読み出しが可能な不揮発性メモリを使用したものである。記憶ユニット63は、本実施形態を実施するために使用する記憶領域として、運転者監視情報記憶部631と、運転者状態情報記憶部632と、車外監視情報記憶部633と、対象情報記憶部634と、グループ情報記憶部635と、判定結果情報記憶部636とを備えている。記憶ユニット63は、不揮発性メモリに限らず、RAMのような揮発性メモリで構成されてもよい。
グループ情報記憶部635は、視認支援装置6Aにより検知される可能性のある対象の種類に従って分類された複数のグループに関するグループ情報を予め記憶している。グループ情報は、例えば、対象の種類とグループの関係を表す分類情報と、運転者による目視時間の判定基準である閾値情報とを含んでいる。閾値情報は、例えば、対象に向けられた運転者の視線の累積滞留時間の閾値を表す情報である。
制御ユニット61は、コンピュータを構成するCPU(Central Processing Unit)およびプログラムメモリを有している。制御ユニット61は、本実施形態を実施するために必要な制御機能として、運転者監視情報取得部611と、運転者状態情報取得部612と、車外監視情報取得部613と、対象検知部614と、目視判定部615と、警告情報出力部616とを備えている。なお、これらの制御機能はいずれもプログラムメモリに格納されたプログラムをCPUに実行させることにより実現される。
運転者監視情報取得部611は、運転者カメラ7から出力された運転者監視情報を、入出力インタフェースユニット62を介して取り込み、この取り込んだ運転者監視情報を記憶ユニット63の運転者監視情報記憶部631に記憶させる。
運転者状態情報取得部612は、運転者監視情報記憶部631から予め設定された時間間隔で運転者監視情報たとえば運転者の監視映像情報を読み込み、その都度、運転者監視情報に基づいて、運転者の状態に関する状態情報を取得する。状態情報は、これに限らないが、この実施形態では、少なくとも、運転者の視線の方向を表す視線方向情報と、運転者の視線の滞留時間を表す視線滞留時間情報とを含んでいる。運転者状態情報取得部612は、取得した状態情報を、記憶ユニット63の運転者状態情報記憶部632に記憶させる。
車外監視情報取得部613は、車外カメラ9Aから出力された車外監視情報たとえば車外の監視映像情報を、入出力インタフェースユニット62を介して取り込み、この取り込んだ車外監視情報を記憶ユニット63の車外監視情報記憶部633に記憶させる。
対象検知部614は、車外監視情報記憶部633から予め設定された時間間隔で車外監視情報を読み込み、その都度、車外監視情報に基づいて、対象の検知を行う。ここにおいて、対象とは、車両1の走行にとって障害になり得る存在や、車両1の進行方向上に位置する避けるべき存在を意味している。対象の検知は、車外カメラ9Aの撮影範囲内に対象が存在するか否かの判定を含んでいる。対象検知部614はまた、対象を検知した場合、車外監視情報に基づいて、対象の識別を行う。対象の識別は、対象を位置の検出と、対象の種類の認定を含んでいる。対象の検知と識別は、画像処理技術やパターン認識技術を利用して実施可能である。対象検知部614は、対象に関する対象情報、例えば、対象の位置情報と種類情報を含む対象情報を、記憶ユニット63の対象情報記憶部634に記憶させる。対象の位置情報は、例えば、運転者に対する対象の方向を表す情報であってよい。
目視判定部615は、予め設定された時間間隔で、運転者状態情報記憶部632と対象情報記憶部634とグループ情報記憶部635から状態情報と対象情報とグループ情報をそれぞれ読み込み、その都度、状態情報と対象情報とグループ情報に基づいて、運転者の目視が適切であったか否かを判定する。詳しくは、目視判定部615は、対象の位置情報と運転者の視線方向情報とに基づいて、運転者が対象を目視したか否かを判定する。また、目視判定部615は、対象の位置情報と運転者の視線方向情報と運転者の視線滞留時間情報とに基づいて、対象に向けられた運転者の視線の累積滞留時間を表す視線累積滞留時間情報を算出する。さらに、目視判定部615は、対象の種類情報と目視時間の閾値情報と運転者の視線累積滞留時間情報とに基づいて、運転者が対象を十分な時間をかけて目視したか否かを判定する。目視判定部615は、判定結果情報を、記憶ユニット63の判定結果情報記憶部636に記憶させる。
警告情報出力部616は、予め設定された時間間隔で、判定結果情報記憶部636から判定結果情報を読み込み、判定結果情報が、運転者の目視が不適切であることを示す場合、警告出力装置9Bに警告を発生させる警告情報を出力する。警告情報は、運転者に対象の目視を促す目視喚起情報と、運転者に対象をもっと長く注意深く目視することを促す注視喚起情報とを含んでいる。
(動作例)
次に、前述したように構成された警告装置の動作例を説明する。図3はその全体の制御手順と制御内容を示すフローチャートである。
次に、前述したように構成された警告装置の動作例を説明する。図3はその全体の制御手順と制御内容を示すフローチャートである。
(1A)運転者の監視と状態把握
運転が開始されると、運転者監視システム8は、ステップS1において、運転者の監視を開始する。運転者の監視は、例えば、運転の間中、継続される。
運転が開始されると、運転者監視システム8は、ステップS1において、運転者の監視を開始する。運転者の監視は、例えば、運転の間中、継続される。
運転が開始されると、運転者カメラ7が起動し、運転者の顔を含む所定の範囲を連続的に撮像してその映像情報である運転者監視情報を出力する。この状態で視認支援装置6Aは、運転者監視情報取得部611の制御の下、運転者カメラ7から出力された運転者監視情報を取り込み、この取り込んだ運転者監視情報を記憶ユニット63の運転者監視情報記憶部631に記憶させる。
運転者監視情報の取得が開始されると、視認支援装置6Aは、次に運転者状態情報取得部612の制御の下、一定時間が経過する毎に、運転者の状態を把握する把握処理を行う。この把握処理の時間間隔は、例えば運転者の状態把握を実質的に連続的に行えるような短時間に設定されるとよい。
運転者状態情報取得部612は、運転者監視情報記憶部631から予め設定された時間間隔で運転者監視情報を読み込む。次に、運転者状態情報取得部612は、運転者監視情報を読み込む毎に、運転者監視情報に基づいて、運転者の状態に関する状態情報を取得する。この実施形態では、状態情報は、少なくとも、運転者の視線の方向を表す視線方向情報と、その方向における運転者の視線の滞留時間を表す視線滞留時間情報とを含んでいる。運転者状態情報取得部612は、視線方向情報と視線滞留時間情報を含む状態情報を、記憶ユニット63の運転者状態情報記憶部632に記憶させる。
(1B)車外の監視
また、運転が開始されると、車外監視システム10は、運転者監視システム8による運転者の監視に並行して、ステップS1において、車外の監視を開始する。車外の監視は、例えば、運転者の監視と同様、運転の間中、継続される。
また、運転が開始されると、車外監視システム10は、運転者監視システム8による運転者の監視に並行して、ステップS1において、車外の監視を開始する。車外の監視は、例えば、運転者の監視と同様、運転の間中、継続される。
運転が開始されると、車外カメラ9Aが起動し、車両1の周辺の所定の範囲を連続的に撮影してその映像情報である車外監視情報を出力する。視認支援装置6Aは、車外監視情報取得部613の制御の下、車外カメラ9Aから出力された車外監視情報から取り込み、この取り込んだ車外監視情報を記憶ユニット63の車外監視情報記憶部633に記憶させる。
(2)対象の検知
車外監視情報の取得が開始されると、視認支援装置6Aは、次に対象検知部614の制御の下、ステップS2において、一定時間が経過する毎に、車外監視情報記憶部633から車外監視情報を読み込み、車両1の周辺に存在する対象を検知する処理を行う。この処理は、画像処理技術やパターン認識技術を利用して実施可能である。対象検知部614により、対象が検知されない場合は、運転終了を判定するステップS9の処理へ進む。反対に、対象検知部614により、対象が検知された場合は、対象を識別するステップS3の処理へ進む。
車外監視情報の取得が開始されると、視認支援装置6Aは、次に対象検知部614の制御の下、ステップS2において、一定時間が経過する毎に、車外監視情報記憶部633から車外監視情報を読み込み、車両1の周辺に存在する対象を検知する処理を行う。この処理は、画像処理技術やパターン認識技術を利用して実施可能である。対象検知部614により、対象が検知されない場合は、運転終了を判定するステップS9の処理へ進む。反対に、対象検知部614により、対象が検知された場合は、対象を識別するステップS3の処理へ進む。
(3)対象の識別
対象を検知するステップS2の処理において、対象が検知された場合、対象検知部614はさらに、ステップS3において、対象を識別する処理を行う。ここで、対象を識別する処理は、例えば、対象の位置を検出する処理と、対象の種類を認定する処理を含んでいる。この処理は、画像処理技術やパターン認識技術を利用して実施可能である。対象検知部614は、対象の位置情報と種類情報を含む対象情報を記憶ユニット63の対象情報記憶部634に記憶させる。ここにおいて、対象の位置情報は、車両1に対する対象の方向、例えば、車両1の運転者の位置に対して対象が存在する方向を表す対象方向情報であってよい。
対象を検知するステップS2の処理において、対象が検知された場合、対象検知部614はさらに、ステップS3において、対象を識別する処理を行う。ここで、対象を識別する処理は、例えば、対象の位置を検出する処理と、対象の種類を認定する処理を含んでいる。この処理は、画像処理技術やパターン認識技術を利用して実施可能である。対象検知部614は、対象の位置情報と種類情報を含む対象情報を記憶ユニット63の対象情報記憶部634に記憶させる。ここにおいて、対象の位置情報は、車両1に対する対象の方向、例えば、車両1の運転者の位置に対して対象が存在する方向を表す対象方向情報であってよい。
前述したように、対象とは、車両1の走行にとって障害になり得る存在や、車両1の進行方向上に位置する避けるべき存在を意味している。対象は、これに限らないが、例えば、人、動物、車両、ボール、標識、ガードレール、縁石、落下物などである。対象の種類を認定する処理は、これに限らないが、例えば、対象が大人であるか、対象が子供であるか、対象が車両であるか、対象がボールであるか、対象が標識であるか、対象が落下物であるか等を特定する処理であってよい。従って、対象の種類情報は、対象が何であるかを表す情報であってよい。
(4)目視の判定
次に、視認支援装置6Aは、目視判定部615の制御の下、ステップS4において、運転者が対象を目視したか否かの判定を行う。このため、目視判定部615は、一定時間が経過する毎に、運転者の状態に関する状態情報を運転者状態情報記憶部632から読み込むとともに、対象に関する対象情報を対象情報記憶部634から読み込む。
次に、視認支援装置6Aは、目視判定部615の制御の下、ステップS4において、運転者が対象を目視したか否かの判定を行う。このため、目視判定部615は、一定時間が経過する毎に、運転者の状態に関する状態情報を運転者状態情報記憶部632から読み込むとともに、対象に関する対象情報を対象情報記憶部634から読み込む。
運転者の状態情報は、運転者の視線の方向を表す視線方向情報と、運転者の視線の滞留時間を表す視線滞留時間情報とを含んでいる。対象に関する対象情報は、対象の位置情報と種類情報を含んでいる。対象の位置情報は、車両1の運転者に対する方向を表す対象方向情報を含んでいる。
次に目視判定部615は、運転者の状態情報と対象に関する対象情報とに基づいて、運転者が対象を目視したか否かを判定する。このため、目視判定部615は、対象方向情報と視線方向情報を比較し、両者が合致した場合は、運転者が対象を目視したと判定し、両者が合致しなかった場合は、運転者が対象を目視しなかったと判定する。目視判定部615は、運転者が対象を目視したか否かを表す判定結果情報を、記憶ユニット63の判定結果情報記憶部636に記憶させる。
目視判定部615により、運転者が対象を目視したと判定された場合は、対象のグループを特定するステップS5の処理へ進む。反対に、目視判定部615により、運転者が対象を目視しなかったと判定された場合は、警告を出力するステップS8の処理へ進む。
(5)対象のグループの特定
対象方向情報と視線方向情報の比較の結果、両者が合致した場合、次に、視認支援装置6Aは、目視判定部615の制御の下、ステップS5において、検知された対象が属するグループを特定する。
対象方向情報と視線方向情報の比較の結果、両者が合致した場合、次に、視認支援装置6Aは、目視判定部615の制御の下、ステップS5において、検知された対象が属するグループを特定する。
グループ情報記憶部635は、視認支援装置6Aにより検知される可能性のある対象の種類に従って分類された複数のグループに関する情報を予め記憶している。グループ情報は、対象の種類とグループの関係を表す分類情報を含んでいる。グループ情報記憶部635は、分類情報を例えばテーブルとして記憶している。
対象の種類は、例えば、大人、子供、車両、ボール、動物、標識、ガードレール、落下物などである。複数のグループは、全体として、視認支援装置6Aにより検知される可能性のある対象の種類をすべて網羅的に含んでいる。つまり、1つのグループに含まれている対象の種類は、別のグループには含まれていない。従って、検知された対象は、複数のグループのうちのいずれか1つのグループに属する。
複数のグループは、例えば、動きが予測不能な対象を含む第1のグループと、動きが予測可能な対象を含む第2のグループと、動きが実質的にない対象を含む第3のグループとから構成される。第1のグループは、動きが予測不能な対象として、これに限らないが、例えば、子供、ボール、動物を含んでいてよい。第2のグループは、動きが予測可能な対象として、これに限らないが、例えば、大人、車両を含んでいてよい。第3のグループは、実質的に動きのない対象、例えば固定物として、これに限らないが、例えば、標識、ガードレール、落下物を含んでいてよい。
検知された対象が属するグループを特定するため、目視判定部615は、視認支援装置6Aにより検出される可能性のある対象の種類の情報をグループ情報記憶部635から順番に読み込み、その都度、検知された対象の種類情報と比較する。この比較の処理は、検知された対象の種類情報が、グループ情報記憶部635から読み込んだ対象の種類の情報と合致するまで続ける。検知された対象の種類情報が、グループ情報記憶部635から読み込んだ対象の種類の情報と合致した場合に、目視判定部615は、その対象を含むグループを、検知された対象が属するグループであると判定する。こうにして、検知された対象が属するグループが特定される。
(6)閾値情報の取得
続いて、視認支援装置6Aは、目視判定部615の制御の下、ステップS6において、対象が属するグループに予め設定された閾値情報を取得する。
続いて、視認支援装置6Aは、目視判定部615の制御の下、ステップS6において、対象が属するグループに予め設定された閾値情報を取得する。
グループ情報記憶部635は、対象の種類とグループの関係を表す分類情報に加えて、運転者による目視時間の判定基準である閾値情報を予め記憶している。閾値情報は、例えば、対象に向けられた運転者の視線の累積滞留時間の閾値を表す情報である。閾値情報は、グループ毎に個別に設定されている。従って、1つのグループに設定された閾値情報は、別のグループに設定された閾値情報とは相違している。
例えば、前述したように、複数のグループが、動きが予測不能な対象を含む第1のグループと、動きが予測可能な対象を含む第2のグループと、動きが実質的にない対象を含む第3のグループとから構成される場合、第1のグループの閾値情報は第2のグループの閾値情報よりも大きく、第2のグループの閾値情報は第3のグループの閾値情報よりも大きく設定されている。例えば、これに限らないが、第1のグループの閾値情報は3秒、第2のグループの閾値情報は1.5秒、第3のグループの閾値情報は0.5秒に設定されていてよい。
動きが実質的にない対象、例えば標識やガードレールなどの固定物に対しては、対象を目視している時間、すなわち、対象に向けられた視線の滞留時間は非常に短くても、運転に必要な情報を収集するには、十分であると考えられる。これに対して、動きが予測可能な対象、例えば大人や車両に対しては、運転に必要な情報を収集するため、動きが実質的にない対象に対してよりも長く目視している必要があると考えられる。さらに、動きが予測可能な対象、例えば子供やボールや動物に対しては、運転に必要な情報を収集するため、動きが予測可能な対象に対してよりもさらに長く目視している必要があると考えられる。
従って、動きが予測可能な対象を含むグループの閾値情報は、動きが予測可能な対象を含むグループの閾値情報よりも大きく設定され、動きが予測可能な対象を含む閾値情報は、動きが実質的にない対象を含むグループの閾値情報よりも大きく設定されている。
(7)目視時間の判定
次に、視認支援装置6Aは、目視判定部615の制御の下、ステップS7において、検知された対象に応じた十分な時間をかけて運転者が対象を目視したか否か、つまり、目視に十分な時間をかけたか否かを判定する。運転者が対象を十分な時間をかけて目視したか否かは、運転者が対象を注意深く目視して対象を正確に認識したか否かに関連していると考えられる。
次に、視認支援装置6Aは、目視判定部615の制御の下、ステップS7において、検知された対象に応じた十分な時間をかけて運転者が対象を目視したか否か、つまり、目視に十分な時間をかけたか否かを判定する。運転者が対象を十分な時間をかけて目視したか否かは、運転者が対象を注意深く目視して対象を正確に認識したか否かに関連していると考えられる。
このため、目視判定部615は、運転者状態情報記憶部632から読み込んだ、運転者の視線の方向を表す視線方向情報と、運転者の視線の滞留時間を表す視線滞留時間情報と、運転者状態情報記憶部632から読み込んだ、運転者に対する対象の方向を表す対象の位置情報とに基づいて、対象に向けられた運転者の視線の累積滞留時間を表す視線累積滞留時間情報を算出する。続いて、目視判定部615は、算出した視線累積滞留時間情報を、グループ情報記憶部635から読み込んだ、検知された対象のグループに予め設定された閾値情報と比較する。
対象に向けられた運転者の視線の累積滞留時間は、簡単に言えば、運転者が対象を目視した時間の合計である。例えば、運転者が、まず第1の対象に視線を向け、次に第2の対象に視線を移した後、再び第1の対象に視線を戻した場合、第1の対象に対する視線累積滞留時間は、第1の対象に向けられた運転者の視線の1度目の滞留時間と2度目の滞留時間との合計である。
目視判定部615は、運転者の視線累積滞留時間情報が閾値情報以上である場合、運転者は対象をその種類に対応した十分な時間をかけて目視した、すなわち、運転者の目視は適切であったと判定し、反対に、運転者の視線累積滞留時間情報が閾値情報未満である場合、運転者は対象の目視にその種類に対応した十分な時間をかけなかった、すなわち、運転者の目視は不適切であったと判定する。目視判定部615は、判定結果情報を、記憶ユニット63の判定結果情報記憶部636に記憶させる。
(8)警告の出力
視認支援装置6Aは、警告情報出力部616の制御の下、ステップS8およびステップS9において、必要に応じて、警告出力装置9Bに警告を発生させるための警告情報を出力する処理を行う。このため、警告情報出力部616は、一定時間が経過する毎に、ステップS4における運転者が対象を目視したか否かの判定と、ステップS7における運転者の目視が適切であったか否かの判定に関する判定結果情報を判定結果情報記憶部636から読み込む。
視認支援装置6Aは、警告情報出力部616の制御の下、ステップS8およびステップS9において、必要に応じて、警告出力装置9Bに警告を発生させるための警告情報を出力する処理を行う。このため、警告情報出力部616は、一定時間が経過する毎に、ステップS4における運転者が対象を目視したか否かの判定と、ステップS7における運転者の目視が適切であったか否かの判定に関する判定結果情報を判定結果情報記憶部636から読み込む。
判定結果情報が、運転者が対象を目視しなかったことを示す場合、警告情報出力部616は、対象を目視することを運転者に促すメッセージを警告出力装置9Bに出力させる警告情報を出力する。また、判定結果情報が、運転者の目視が不適切であったことを示す場合、警告情報出力部616は、再び対象を長く目視することを運転者に促すメッセージを警告出力装置9Bに出力させる警告情報を出力する。
警告出力装置9Bは、警告情報に従って、警告のメッセージを、例えば音声として出力する。
(9)運転終了判定
続いて、視認支援装置6Aは、ステップS10において、運転が終了したか否かを判定する。運転が終了していないと判定した場合は、車両1の周辺の対象を検知するステップS2の処理に戻る。反対に、運転が終了したと判定した場合は、視認支援の制御を終了する。
続いて、視認支援装置6Aは、ステップS10において、運転が終了したか否かを判定する。運転が終了していないと判定した場合は、車両1の周辺の対象を検知するステップS2の処理に戻る。反対に、運転が終了したと判定した場合は、視認支援の制御を終了する。
(効果)
以上詳述したように、この発明の実施形態では、運転者を監視する運転者監視センサである運転者カメラ7の運転者監視情報に基づいて、運転者の状態に関する状態情報が取得されるとともに、車両1の周辺を監視する車外監視センサである車外カメラ9Aの車外監視情報に基づいて、車両1の周辺に存在する対象が検知されるとともに、検知された対象に関する対象情報が取得される。
以上詳述したように、この発明の実施形態では、運転者を監視する運転者監視センサである運転者カメラ7の運転者監視情報に基づいて、運転者の状態に関する状態情報が取得されるとともに、車両1の周辺を監視する車外監視センサである車外カメラ9Aの車外監視情報に基づいて、車両1の周辺に存在する対象が検知されるとともに、検知された対象に関する対象情報が取得される。
状態情報に含まれる視線方向情報と、対象情報に含まれる対象方向情報とに基づいて、運転者が対象を目視したか否かが判定される。また、状態情報に含まれる視線方向情報と、対象情報に含まれる対象方向情報とに基づいて、状態情報に含まれる視線滞留時間情報とに基づいて、対象に向けられた運転者の視線の累積滞留時間を表す視線累積滞留時間情報が算出される。さらに、対象情報に含まれる種類情報に基づいて、検知された対象が属するグループが特定され、そのグループに設定されたグループ情報である閾値情報と、算出された視線累積滞留時間情報とに基づいて、運転者の目視が適切であったか否かが判定される。
このため、運転者の目視が適切であったか否かは、画一的に判定されるのではなく、対象の種類に応じて判定される。これにより、対象に種類に対応した好適な判定結果が得られる。従って、対象に種類に対応した適切な警告が出力されるようになる。
例えば、画一的な判定においては、長く目視する必要のない固定物の目視に対して、不必要に警告が出力されたり、反対に、長く目視する必要のある子供やボールなどの予測不要な対象の目視に対して、本来ならば出力される必要のある警告が出力されなかったりすることが考えられる。
これに対して、この実施形態では、対象の種類に応じた閾値情報に基づいて、運転者の目視が適切であったか否かが判定される。このため、不必要な警告が出力されたり、本来ならば必要な警告が出力されなかったりすることが避けられる。
すなわち、誤った警報が出力されることが低減される。これにより、不要な処理が低減される。また、誤った警報により、運転者をわずらわせたり、いらだたせたりすることが避けられる。
動きが予測可能な対象に対する閾値は、動きが実質的にない対象に対する閾値よりも長く設定されている。また、動きが予測不能な対象に対する閾値は、動きが予測可能な対象に対する閾値よりも長く設定されている。これにより、運転者は、動きが予測可能な対象に対しては、動きが実質的にない対象よりも、対象を長く目視することが求められる。また、運転者は、動きが予測不能な対象に対しては、動きが予測可能な対象よりも、対象を長く目視することが求められる。
[他の実施形態]
実施形態では、運転者監視センサが運転者カメラ7で構成され、運転者カメラ7により得られる運転者の顔を含む映像情報である運転者監視情報に基づいて運転者の状態を判定する場合を例にとって説明した。しかし、運転者監視センサは、運転者カメラ7に限らず、運転者の動き情報を取得する動きセンサで構成し、動きセンサにより得られる動き情報に基づいて、運転者の状態情報を取得するようにしてもよい。
実施形態では、運転者監視センサが運転者カメラ7で構成され、運転者カメラ7により得られる運転者の顔を含む映像情報である運転者監視情報に基づいて運転者の状態を判定する場合を例にとって説明した。しかし、運転者監視センサは、運転者カメラ7に限らず、運転者の動き情報を取得する動きセンサで構成し、動きセンサにより得られる動き情報に基づいて、運転者の状態情報を取得するようにしてもよい。
実施形態では、複数のグループが第1のグループと第2のグループと第3のグループとの3つのグループから構成された例を示したが、複数のグループは、これに限らず、さらに多くのグループから構成されてもよい。
その他、車両の種類、自動運転制御装置の機能、視認支援装置の制御機能と制御手順および制御内容等についても、この発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲で種々変形して実施可能である。
要するにこの発明は、上記実施形態そのままに限定されるものではなく、実施段階ではその要旨を逸脱しない範囲で構成要素を変形して具体化できる。また、上記実施形態に開示されている複数の構成要素の適宜な組み合せにより種々の発明を形成できる。例えば、実施形態に示される全構成要素から幾つかの構成要素を削除してもよい。さらに、異なる実施形態に亘る構成要素を適宜組み合せてもよい。
上記の実施形態の一部又は全部は、以下の付記のようにも記載されうるが、以下には限られるものではない。
(付記1)
運転者監視センサと車外監視センサと警告出力装置とを備えた車両の運転者による視認を支援する視認支援装置であって、ハードウェアプロセッサとメモリとを有し、
前記ハードウェアプロセッサが、
前記運転者監視センサの運転者監視情報に基づいて、前記運転者に関する状態情報を取得し、取得した前記状態情報を前記メモリに記憶させ、
前記車外監視センサの車外監視情報に基づいて、前記車両の周辺に存在する対象を検知し、検知した前記対象に関する検知情報を前記メモリに記憶させ、
前記メモリに予め記憶されているグループ毎に予め個別に設定されたグループ情報と、前記検知情報とを前記メモリから読み込み、読み込んだ前記検知情報と前記グループ情報とに基づいて、前記対象が、予め分類された複数のグループのいずれに属するかを特定し、前記状態情報と前記対象が属するグループのグループ情報とに基づいて、前記運転者の目視が適切であったか否かを判定し、その判定結果情報を前記メモリに記憶させ、
前記メモリから前記判定結果情報を読み込み、前記判定結果情報が、前記運転者の目視が不適切であることを示す場合、前記警告出力装置に警告を発生させるための警告情報を出力する、視認支援装置。
(付記2)
運転者監視センサと車外監視センサと警告出力装置とを備えた車両の運転者による視認を支援する視認支援方法であって、
ハードウェアプロセッサを用いて、前記運転者監視センサの運転者監視情報に基づいて、前記運転者に関する状態情報を取得し、取得した前記状態情報をメモリに記憶させ、
前記ハードウェアプロセッサを用いて、前記車外監視センサの車外監視情報に基づいて、前記車両の周辺に存在する対象を検知し、検知した前記対象に関する検知情報を前記メモリに記憶させ、
前記ハードウェアプロセッサを用いて、前記メモリに予め記憶されているグループ毎に予め個別に設定されたグループ情報と、前記検知情報とを前記メモリから読み込み、読み込んだ前記検知情報と前記グループ情報とに基づいて、前記対象検知ステップにより検知された前記対象が、予め分類された複数のグループのいずれに属するかを特定し、前記状態情報と前記対象が属するグループのグループ情報とに基づいて、前記運転者の目視が適切であったか否かを判定し、その判定結果情報を前記メモリに記憶させ、
前記ハードウェアプロセッサを用いて、前記メモリから前記判定結果情報を読み込み、前記判定結果情報が、前記運転者の目視が不適切であることを示す場合、前記警告出力装置に警告を発生させるための警告情報を出力する、視認支援方法。
(付記1)
運転者監視センサと車外監視センサと警告出力装置とを備えた車両の運転者による視認を支援する視認支援装置であって、ハードウェアプロセッサとメモリとを有し、
前記ハードウェアプロセッサが、
前記運転者監視センサの運転者監視情報に基づいて、前記運転者に関する状態情報を取得し、取得した前記状態情報を前記メモリに記憶させ、
前記車外監視センサの車外監視情報に基づいて、前記車両の周辺に存在する対象を検知し、検知した前記対象に関する検知情報を前記メモリに記憶させ、
前記メモリに予め記憶されているグループ毎に予め個別に設定されたグループ情報と、前記検知情報とを前記メモリから読み込み、読み込んだ前記検知情報と前記グループ情報とに基づいて、前記対象が、予め分類された複数のグループのいずれに属するかを特定し、前記状態情報と前記対象が属するグループのグループ情報とに基づいて、前記運転者の目視が適切であったか否かを判定し、その判定結果情報を前記メモリに記憶させ、
前記メモリから前記判定結果情報を読み込み、前記判定結果情報が、前記運転者の目視が不適切であることを示す場合、前記警告出力装置に警告を発生させるための警告情報を出力する、視認支援装置。
(付記2)
運転者監視センサと車外監視センサと警告出力装置とを備えた車両の運転者による視認を支援する視認支援方法であって、
ハードウェアプロセッサを用いて、前記運転者監視センサの運転者監視情報に基づいて、前記運転者に関する状態情報を取得し、取得した前記状態情報をメモリに記憶させ、
前記ハードウェアプロセッサを用いて、前記車外監視センサの車外監視情報に基づいて、前記車両の周辺に存在する対象を検知し、検知した前記対象に関する検知情報を前記メモリに記憶させ、
前記ハードウェアプロセッサを用いて、前記メモリに予め記憶されているグループ毎に予め個別に設定されたグループ情報と、前記検知情報とを前記メモリから読み込み、読み込んだ前記検知情報と前記グループ情報とに基づいて、前記対象検知ステップにより検知された前記対象が、予め分類された複数のグループのいずれに属するかを特定し、前記状態情報と前記対象が属するグループのグループ情報とに基づいて、前記運転者の目視が適切であったか否かを判定し、その判定結果情報を前記メモリに記憶させ、
前記ハードウェアプロセッサを用いて、前記メモリから前記判定結果情報を読み込み、前記判定結果情報が、前記運転者の目視が不適切であることを示す場合、前記警告出力装置に警告を発生させるための警告情報を出力する、視認支援方法。
Claims (5)
- 運転者監視センサと車外監視センサと警告出力装置とを備えた車両の運転者による視認を支援する視認支援装置であって、
前記運転者監視センサの運転者監視情報に基づいて、前記運転者に関する状態情報を取得する運転者状態情報取得部と、
前記車外監視センサの車外監視情報に基づいて、前記車両の周辺に存在する対象を検知する対象検知部と、
前記対象が、予め分類された複数のグループのいずれに属するかを特定し、前記状態情報と前記対象が属するグループのグループ情報とに基づいて、前記運転者の目視が適切であったか否かを判定する目視判定部と、
前記目視判定部により前記運転者の目視が不適切であると判定された場合に、前記警告出力装置に警告を発生させるための警告情報を出力する警告情報出力部とを備える、視認支援装置。 - 前記状態情報は、前記運転者の視線の方向を表す視線方向情報と、前記運転者の視線の滞留時間を表す視線滞留時間情報とを含み、前記グループ情報は、グループ毎に予め個別に設定された前記運転者の視線の累積滞留時間の閾値を表す閾値情報を含み、前記目視判定部は、前記対象の位置を表す位置情報と前記視線方向情報と前記視線滞留時間情報とに基づいて、前記対象に向けられた前記運転者の視線の累積滞留時間を表す視線累積滞留時間情報を算出し、算出した前記視線累積滞留時間情報を前記閾値情報と比較し、前記視線累積滞留時間情報が前記閾値情報以上である場合、前記運転者の目視が適切であると判定する、請求項1に記載の視認支援装置。
- 前記複数のグループは、少なくとも、動きが予測不能な対象を含む第1のグループと、動きが予測可能な対象を含む第2のグループと、動きが実質的にない対象を含む第3のグループとを含み、前記第1のグループの前記閾値情報は前記第2のグループの前記閾値情報よりも大きく、前記第2のグループの前記閾値情報は前記第3のグループの前記閾値情報よりも大きい、請求項2に記載の視認支援装置。
- 運転者監視センサと車外監視センサと警告出力装置とを備えた車両の運転者による視認を支援する視認支援方法であって、
前記運転者監視センサの運転者監視情報に基づいて、前記運転者に関する状態情報を取得する運転者状態取得ステップと、
前記車外監視センサの車外監視情報に基づいて、前記車両の周辺に存在する対象を検知する対象検知ステップと、
前記対象検知ステップにより検知された前記対象が、予め分類された複数のグループのいずれに属するかを特定し、前記状態情報と前記対象が属するグループのグループ情報とに基づいて、前記運転者の目視が適切であったか否かを判定する目視判定部と、
前記目視判定部により前記運転者の目視が不適切であると判定された場合に、前記警告出力装置に警告を発生させるための警告情報を出力する警告情報出力ステップとを有している、視認支援方法。 - 請求項1ないし請求項3のいずれかひとつに記載の視認支援装置が備える各部の機能または請求項4に記載の覚醒支援方法の各ステップの処理をコンピュータに実行させるプログラム。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017-046345 | 2017-03-10 | ||
| JP2017046345A JP6468306B2 (ja) | 2017-03-10 | 2017-03-10 | 視認支援装置、方法およびプログラム |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2018163490A1 true WO2018163490A1 (ja) | 2018-09-13 |
Family
ID=63447413
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/036703 WO2018163490A1 (ja) | 2017-03-10 | 2017-10-10 | 視認支援装置、方法およびプログラム |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6468306B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2018163490A1 (ja) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022119571A (ja) * | 2021-02-04 | 2022-08-17 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 車両用シートベルト装置 |
| CN115220441A (zh) * | 2022-03-24 | 2022-10-21 | 华东师范大学 | 一种基于生物视觉感知的无人小车集群任务协同方法 |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2020230312A1 (ja) | 2019-05-15 | 2020-11-19 | 日産自動車株式会社 | 運転支援方法及び運転支援システム |
| CN110246305A (zh) * | 2019-08-01 | 2019-09-17 | 肇庆学院 | 一种基于机器视觉的疲劳驾驶检测预警系统及方法 |
| DE102020003018A1 (de) | 2020-05-19 | 2021-11-25 | Daimler Ag | Verfahren zur Ermittlung einer Reaktionsfähigkeit |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007072632A (ja) * | 2005-09-05 | 2007-03-22 | Toyota Motor Corp | 車載警報装置 |
| JP2013092992A (ja) * | 2011-10-27 | 2013-05-16 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | 車両周辺監視装置 |
| JP2016066231A (ja) * | 2014-09-24 | 2016-04-28 | パイオニア株式会社 | 衝突防止装置、衝突防止方法、衝突防止プログラムおよび記録媒体 |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008254710A (ja) * | 2007-04-09 | 2008-10-23 | Fujitsu Ten Ltd | 障害物検知装置 |
-
2017
- 2017-03-10 JP JP2017046345A patent/JP6468306B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2017-10-10 WO PCT/JP2017/036703 patent/WO2018163490A1/ja active Application Filing
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007072632A (ja) * | 2005-09-05 | 2007-03-22 | Toyota Motor Corp | 車載警報装置 |
| JP2013092992A (ja) * | 2011-10-27 | 2013-05-16 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | 車両周辺監視装置 |
| JP2016066231A (ja) * | 2014-09-24 | 2016-04-28 | パイオニア株式会社 | 衝突防止装置、衝突防止方法、衝突防止プログラムおよび記録媒体 |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022119571A (ja) * | 2021-02-04 | 2022-08-17 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 車両用シートベルト装置 |
| JP7229283B2 (ja) | 2021-02-04 | 2023-02-27 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 車両用シートベルト装置 |
| CN115220441A (zh) * | 2022-03-24 | 2022-10-21 | 华东师范大学 | 一种基于生物视觉感知的无人小车集群任务协同方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6468306B2 (ja) | 2019-02-13 |
| JP2018151765A (ja) | 2018-09-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2018163490A1 (ja) | 視認支援装置、方法およびプログラム | |
| JP7080598B2 (ja) | 車両制御装置および車両制御方法 | |
| US9786192B2 (en) | Assessing driver readiness for transition between operational modes of an autonomous vehicle | |
| WO2018186127A1 (ja) | 走行支援装置 | |
| US11001271B2 (en) | Drive assistance device | |
| CN110192084B (zh) | 自动驾驶辅助装置、方法及程序 | |
| JP6611085B2 (ja) | 車両制御装置 | |
| JP6447647B2 (ja) | 運転モード切替制御装置、方法およびプログラム | |
| JP6937335B2 (ja) | 車両制御システム | |
| KR101999079B1 (ko) | 표시 장치의 제어 방법 및 표시 장치 | |
| US11414099B2 (en) | Dynamic stop time threshold selection for hands-free driving | |
| JP2008186416A (ja) | 物体検出装置、通信システム、および車車間通信装置 | |
| US20240000354A1 (en) | Driving characteristic determination device, driving characteristic determination method, and recording medium | |
| JP6631569B2 (ja) | 運転状態判定装置、運転状態判定方法及び運転状態判定のためのプログラム | |
| WO2018168049A1 (ja) | 集中度判定装置、集中度判定方法及び集中度判定のためのプログラム | |
| US11685311B2 (en) | System and method for warning a driver of a vehicle of an object in a proximity of the vehicle | |
| JP5013175B2 (ja) | 走行制御装置および方法、プログラム、並びに記録媒体 | |
| JP6631564B2 (ja) | 自動運転車両監視装置、方法およびプログラム | |
| JP2018149822A (ja) | 運転モード切替制御装置、方法及びプログラム | |
| WO2018168050A1 (ja) | 集中度判定装置、集中度判定方法及び集中度判定のためのプログラム | |
| WO2018168046A1 (ja) | 集中度判定装置、集中度判定方法及び集中度判定のためのプログラム | |
| WO2018163536A1 (ja) | 運転者身体コンディション回復支援装置、方法およびプログラム | |
| WO2023112212A1 (ja) | 運転支援装置及びコンピュータプログラム並びにコンピュータプログラムを記録した記録媒体 | |
| JP7129147B2 (ja) | 車両用装置、安全運転支援システム、及び、安全運転支援方法 | |
| WO2018168047A1 (ja) | 集中度判定装置、集中度判定方法及び集中度判定のためのプログラム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 17899744 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 17899744 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |