WO2014073405A1 - 光学表示パネルの連続製造方法および光学表示パネルの連続製造システム - Google Patents
光学表示パネルの連続製造方法および光学表示パネルの連続製造システム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2014073405A1 WO2014073405A1 PCT/JP2013/079097 JP2013079097W WO2014073405A1 WO 2014073405 A1 WO2014073405 A1 WO 2014073405A1 JP 2013079097 W JP2013079097 W JP 2013079097W WO 2014073405 A1 WO2014073405 A1 WO 2014073405A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- optical
- optical film
- film
- cell
- display panel
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/1303—Apparatus specially adapted to the manufacture of LCDs
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/1333—Constructional arrangements; Manufacturing methods
- G02F1/1335—Structural association of cells with optical devices, e.g. polarisers or reflectors
- G02F1/133528—Polarisers
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B5/00—Optical elements other than lenses
- G02B5/30—Polarising elements
- G02B5/3025—Polarisers, i.e. arrangements capable of producing a definite output polarisation state from an unpolarised input state
- G02B5/3033—Polarisers, i.e. arrangements capable of producing a definite output polarisation state from an unpolarised input state in the form of a thin sheet or foil, e.g. Polaroid
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an optical display panel continuous manufacturing method and an optical display panel continuous manufacturing system.
- the first polarizing film obtained by feeding out a strip-shaped first polarizing film having an absorption axis in the longitudinal direction from the first optical film roll and cutting the strip-shaped first polarizing film in the width direction is used as the liquid crystal cell.
- a continuous manufacturing method (so-called Roll to Panel (RTP) method) of a liquid crystal display panel in which a two-polarized film is bonded to a surface on the viewing side of the liquid crystal cell is disclosed (for example, see Patent Document 1). *
- the present invention has been made in view of the above problems, and an object of the present invention is to provide an optical display panel manufacturing method and a manufacturing system for manufacturing an optical display panel in which warpage is suppressed.
- the present invention is a method for continuously producing an optical display panel in which a first optical film is laminated on one side of an optical cell and a second optical film is laminated on the other side of the optical cell,
- the first optical film obtained by cutting the band-shaped first optical film in the width direction is supplied from the first optical film roll, and while transporting the optical cell, the first optical film is removed from the optical cell.
- the second optical film is taken out from and supplied from the housing portion in which the second optical film in a single wafer state is housed, and the second optical film is transported from the pair of sides facing the optical cell while transporting the optical cell.
- an optical film for example, a polarizing film
- an optical cell for example, a liquid crystal cell
- one surface is bonded by the RTP method and the other surface is an STP method.
- the sticking direction parallel (including the same).
- both the bonding direction and tension control can be secured, and the front and back of the optical cell (first and second surfaces) The tension can be easily canceled to make the stresses coincide (substantially coincide, substantially coincide), and the warpage of the optical display panel can be suppressed.
- the first bonding step and the second bonding step are performed on a series of conveyance units that convey the optical cell and the optical display panel.
- the thickness of the second optical film is larger than the thickness of the first polarizing film. That is, it is preferable to carry out an optical film having a larger thickness by a sheet to panel method (a method in which an optical film that has been in a single wafer state is bonded to an optical cell, hereinafter also referred to as an “STP method”).
- STP method since the optical film is bonded while adsorbing and releasing the optical film, the optical film is bonded without applying a large tension. It is not possible to apply a large tension to it).
- the RTP method is a continuous roll film, it is easy to apply tension, and conversely, if the film is bonded without applying tension (for example, free of tension), there is a problem of bubble generation and sticking displacement. Since it is likely to occur, bonding is performed while applying tension to the film. Therefore, a relatively thick (stress accumulation) optical film is bonded to one surface of the optical cell by the STP method, and a relatively thin (stress accumulation difficult) optical film is optically controlled by the RTP method while controlling the tension. By bonding to the other surface of the cell, warpage of the optical display panel can be further suppressed.
- the absorption axis of the first optical film bonded to one surface of the optical display panel and the absorption axis of the second optical film bonded to the other surface are orthogonal to each other,
- the absorption axis of the first optical film in a state wound around the first optical film roll is in the longitudinal direction
- the absorption axis of the strip-shaped second optical film used for manufacturing the single-wafer second optical film is in the longitudinal direction.
- This configuration makes it possible to manufacture a high-contrast optical display panel in which the occurrence of warpage is suppressed.
- the optical cell is a VA mode or IPS mode liquid crystal cell.
- the present invention is particularly suitable for producing a high-contrast VA mode or IPS mode liquid crystal display panel in which the occurrence of warpage is suppressed.
- Another aspect of the present invention is a system for continuously manufacturing an optical display panel in which a first optical film is laminated on one surface of an optical cell and a second optical film is laminated on the other surface of the optical cell.
- a series of transport units for transporting the optical cell and the optical display panel A first optical film supply unit for supplying the first optical film obtained by cutting the belt-shaped first optical film in the width direction from a first optical film roll; Supplying the first optical film from a pair of sides facing the optical cell while transporting the optical cell transported by the transport unit while feeding the first optical film supplied by the first optical film supply unit A first bonding portion to be bonded to one surface of the optical cell along the direction;
- a second optical film supply unit that takes out and supplies the second optical film from a storage unit in which the second optical film in a single wafer state is stored; While transporting the optical cell transported by the transport unit, the second optical film supplied by the second optical film supply unit is moved from the pair of sides facing the optical cell to the second optical film. And a second bonding part to be
- an optical film for example, a polarizing film
- an optical cell for example, a liquid crystal cell
- one surface is bonded by the RTP method and the other surface is an STP method.
- the sticking direction parallel (including the same).
- both the bonding direction and tension control can be secured, and the front and back of the optical cell (first and second surfaces) The tension can be easily canceled to make the stresses coincide (substantially coincide, substantially coincide), and the warpage of the optical display panel can be suppressed.
- either the process of a 1st bonding part and the process of a 2nd bonding part may be performed first, and the simultaneous or the bonding process period may partially overlap before and behind.
- the 1st pasting part and the 2nd pasting part are arranged in the conveyance part which conveys the optical cell and the optical display panel.
- the thickness of the second optical film is larger than the thickness of the first polarizing film.
- the absorption axis of the first optical film bonded to one surface of the optical display panel and the absorption axis of the second optical film bonded to the other surface are orthogonal to each other,
- the absorption axis of the first optical film in a state wound around the first optical film roll is in the longitudinal direction
- the absorption axis of the strip-shaped second optical film used for manufacturing the single-wafer second optical film is in the longitudinal direction.
- the optical cell is a VA mode or IPS mode liquid crystal cell.
- a method of supplying an optical film from an optical film roll for example, (1) a belt-like laminated optical film in which a belt-like optical film is laminated on a carrier film is fed out from the optical film roll.
- Examples of the method include a method of feeding a belt-shaped laminated optical film formed by laminating the formed belt-shaped optical film and supplying the optical film, and any of them can be used.
- the optical display panel continuous manufacturing system of this embodiment continuously manufactures an optical display panel in which a first optical film is laminated on one surface of an optical cell and a second optical film is laminated on the other surface of the optical cell.
- the first optical film obtained by cutting the belt-shaped first optical film in the width direction, and a series of transport units that transport the optical cell and the optical display panel.
- the first optical film supplied from the roll and the first optical film supplied by the first optical film supply unit are opposed to the optical cell while conveying the optical cell conveyed by the conveyance unit.
- a first bonding portion that is bonded to one surface of the optical cell along the supply direction of the first optical film from the side of the set and a second optical film in a single wafer state are accommodated.
- the second optical film supply unit that takes out and supplies the second optical film from the storage unit, and the second optical film supply unit that supplies the second optical film while conveying the optical cell conveyed by the conveyance unit.
- a second bonding portion that bonds the two optical films to the other surface of the optical cell along a supply direction of the second optical film from a pair of sides facing the optical cell.
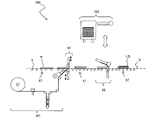
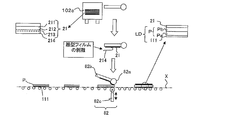
- FIGS. 1 to 3 are schematic views of a continuous manufacturing system for an optical display panel according to Embodiment 1.
- FIG. Hereinafter, a continuous manufacturing system of an optical display panel according to the present embodiment will be specifically described with reference to FIGS.
- a horizontally long liquid crystal cell is used as an optical cell
- a horizontally long liquid crystal display panel is used as an example of an optical display panel.
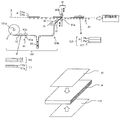
- the optical film roll those shown in FIGS. 1, 2, and 3 are used. That is, as the first optical film roll 1, a strip-shaped first polarizing film 11 (corresponding to the first optical film) having an absorption axis in the longitudinal direction is laminated on the first carrier film 12, and the liquid crystal cell P The belt-shaped first laminated optical film 10 having a width corresponding to the short side is wound.
- the second optical film 21 in a single wafer state is manufactured using a strip-shaped second polarizing film having an absorption axis in the longitudinal direction and a strip-shaped linearly polarized light separating film having a reflection axis in the width direction.
- a conventionally known method such as a method described in JP-A-2004-250213 can be used.
- each of the second polarizing film and the linearly polarized light separating film is laminated in a single sheet state in advance, or one of the second polarizing film and the linearly polarized light separating film is preliminarily formed into a single sheet state, and the other is used as a strip film.
- stacking the film of a state is mentioned.
- belt-shaped 1st polarizing film 11 has a strip
- the second optical film 21 in a single wafer state is formed by laminating a linearly polarized light separating film 211, a second polarizing film 212, and an adhesive 213, and a release film 214 is temporarily attached to protect the adhesive 213.
- the continuous manufacturing system 100 for a liquid crystal display panel includes a series of transport units X that transport the liquid crystal cells P and the liquid crystal display panel LD, a first optical film supply unit 101, 1 bonding part 81, the 2nd optical film supply part 102, and the 2nd bonding part 82 are included.
- the transport unit X transports the liquid crystal cell P and the liquid crystal display panel LD.
- the conveyance unit X includes a plurality of conveyance rollers X1, a suction plate, and the like.
- the first optical film supply unit 101 is obtained by cutting the strip-shaped first polarizing film 11 having a width corresponding to the short side of the liquid crystal cell P in the width direction with a length corresponding to the long side of the liquid crystal cell P.
- the first polarizing film 111 is supplied from the first optical film roll 1 to the first bonding unit 81. Therefore, in this embodiment, the 1st optical film supply part 101 is the 1st delivery part 101a, the 1st cutting part 41, the 1st tension adjustment part 51, the 1st peeling part 61, the 1st winding part 71, and several Transport roller portion 101b.
- the first feeding unit 101 a has a feeding shaft on which the first optical film roll 1 is installed, and feeds the strip-shaped first laminated optical film 10 from the first optical film roll 1.
- the first feeding unit 101a may be provided with two feeding shafts. Thereby, it is possible to quickly join the roll 1 to the roll film installed on the other feeding shaft without replacing the roll 1 with a new roll.
- the first cutting part 41 is configured to have cutting means 41a and suction means 41b, and half-cuts the strip-shaped first laminated optical film 10 in the width direction with a length corresponding to the long side of the liquid crystal cell P (first).
- the band-shaped first polarizing film 11 is cut in the width direction without cutting the carrier film 12).
- the first cutting unit 41 uses the cutting unit 41a to fix the band-shaped first laminated optical film 10 from the first carrier film 12 side by using the suction unit 41b, and fixes the band-shaped first polarized light.
- the film 11 (the film body 11 a and the adhesive 11 b) is cut in the width direction, and the first polarizing film 111 having a size corresponding to the liquid crystal cell P is formed on the first carrier film 12.
- the cutting means 41a includes a cutter, a laser device, a combination thereof, and the like.
- the first tension adjusting unit 51 has a function of maintaining the tension of the belt-shaped first laminated optical film 10.
- the first tension adjusting unit 51 is configured to include a dancer roll, but is not limited thereto.
- the first peeling unit 61 peels the first polarizing film 111 from the first carrier film 12 by folding the first laminated optical film 10 having the first carrier film 12 on the inside.
- Examples of the first peeling portion 61 include a wedge-shaped member and a roller.
- the first winding unit 71 winds up the first carrier film 12 from which the first polarizing film 111 has been peeled off.
- the first winding unit 71 has a winding shaft on which a roll for winding the first carrier film 12 is installed.
- the 1st bonding part 81 was supplied by the 1st optical film supply part 101, conveying the liquid crystal cell P conveyed by the conveyance part X, making the long side direction parallel to a conveyance direction (1st peeling part).
- a surface Pa on the viewing surface side of the liquid crystal cell P from the short side of the liquid crystal cell P along the supply direction of the first polarizing film 111 (long side direction of the liquid crystal cell P). Are bonded together via an adhesive 11b.
- the first bonding unit 81 includes a pair of bonding rollers 81a and 81b, and at least one of the bonding rollers 81a and 81b includes a driving roller.
- the 2nd optical film supply part 102 takes out the 2nd optical film 21 of a sheet
- the 2nd bonding part 82 is the 2nd optical film 21 supplied by the 2nd optical film supply part 102, conveying the liquid crystal cell P conveyed by the conveyance part X with the long side direction parallel to a conveyance direction. Is bonded to the surface Pb on the back side of the liquid crystal cell P from the short side of the liquid crystal cell P.
- the second bonding unit 82 includes a moving unit (not shown) that moves the sheet-shaped second optical film 21 from the housing unit 102c to the bonding position, and a sheet-fed release film 214 that has a sheet-fed state. 2
- the liquid crystal cell P is conveyed in contact with the surface of the liquid crystal cell P, a peeling portion (not shown) that peels from the optical film 21, a suction portion 82b that adsorbs the second optical film 21 in a single wafer state, a bonding roller 82a Drive roller 82c.
- the storage portion 102c is not limited to the form described in FIGS. 1 and 3 and may have other shapes, for example, a container having a mounting table for mounting the second optical film 21 in a single wafer state.
- the pedestal may be covered around it.
- the moving unit moves to the second optical film 21 in a single-wafer state placed in the accommodating unit 102c, and adsorbs the surface of the second optical film 21 at the adsorbing unit 82b and moves to the bonding position.
- the peeling portion peels the single-wafer release film 214 from the single-wafer second optical film 21.
- the peeling unit may peel the release film 214 by bonding the adhesive tape to the surface of the release film 214 using, for example, an adhesive tape and moving the adhesive tape.
- the second optical film 21 in a single wafer state adsorbed by the adsorbing part 82b is sent to the laminating roller 82a at the tip position, and the laminating roller 82a is rotated to be on the surface Pb on the back side of the liquid crystal cell P.
- the second optical film 21 is bonded from the short side.
- the driving roller 82c and the bonding roller 82a sandwich the liquid crystal cell P and the second optical film 21 and convey them downstream.
- the driving roller 82c and the bonding roller 82a may be driven together, or the driving roller 82c may be driven.
- the first optical film supply unit and the second optical film supply unit are arranged in the transport unit X of the liquid crystal cell so that the supply directions of the first polarizing film and the second optical film are parallel to each other. Therefore, the space occupied by the apparatus can be reduced. Moreover, in this embodiment, the bonding direction of the 1st polarizing film 111 in the 1st bonding part 81 with respect to liquid crystal cell P and the bonding direction of the 2nd optical film 21 in the 2nd bonding part 82 are parallel. Therefore, the warp of the liquid crystal display panel can be suitably suppressed.
- the first bonding unit bonds the first polarizing film from the lower side of the liquid crystal cell
- the second bonding unit bonds the second optical film from the upper side of the liquid crystal cell. It is not limited to.
- the first bonding unit may bond the first polarizing film from the upper side of the liquid crystal cell
- the second bonding unit may bond the second optical film from the lower side of the liquid crystal cell.
- the first polarizing film 111 is bonded to the surface Pa on the viewing side of the liquid crystal cell P along the supply direction of the first polarizing film 111 from the short side of the liquid crystal cell P, and the second optical film 21. Is bonded to the surface Pb on the back side of the liquid crystal cell P along the supply direction of the second optical film from the short side of the liquid crystal cell P. As long as it is bonded so that the absorption axis is orthogonal (crossed Nicols), it is not limited to this.
- the first polarizing film 111 may be bonded from the long side of the liquid crystal cell P, and the second optical film 21 may be bonded from the long side of the liquid crystal cell P.
- the width and cutting size of the second optical film are set according to whether the second optical film is bonded from the long side or the short side of the liquid crystal cell. Moreover, it bonds together so that the absorption axis of each polarizing film of the visual recognition side and back side of a liquid crystal cell may orthogonally cross (cross Nicol).
- the continuous manufacturing method of the optical display panel of Embodiment 1 continuously manufactures an optical display panel in which a first optical film is laminated on one surface of an optical cell and a second optical film is laminated on the other surface of the optical cell.
- the first optical film obtained by cutting the strip-shaped first optical film in the width direction is supplied from a first optical film roll, and the first optical film is conveyed while transporting the optical cell.
- the second optical film is taken out and supplied from the accommodated accommodating part, and the first optical film is conveyed along the supply direction of the second optical film from a pair of sides facing the optical cell while conveying the optical cell.
- the absorption axis of the first optical film bonded to one surface of the optical display panel and the absorption axis of the second optical film bonded to the other surface are orthogonal to each other and wound around the first optical film roll.
- the absorption axis of the first optical film in the formed state is in the longitudinal direction
- the absorption axis of the band-shaped second optical film used for manufacturing the second optical film in the sheet state is in the longitudinal direction.
- the second optical film is a laminated optical film in which a polarizing film and a linearly polarized light separating film are laminated, but is not limited thereto.
- the second optical film include a broadband retardation film and a laminated optical film in which a broadband retardation film and a polarizing film are laminated.
- the broadband retardation film is exemplified by a film in which a ⁇ / 4 retardation film and a ⁇ / 2 retardation film are laminated.
- Embodiment 1 As the optical film roll, a roll-shaped laminated optical film obtained by laminating a band-shaped optical film on a carrier film is used, but the configuration of the optical film roll is not limited to this. For example, by appropriately using a belt-shaped laminated optical film formed by laminating a band-shaped optical film in which a plurality of score lines are formed in the width direction on a carrier film (a cut optical film roll). Also good. In addition, a cutting part becomes unnecessary in the optical film supply part which supplies an optical film from the optical film roll with a notch.
- the cutting unit cuts the band-shaped optical film in the width direction and forms the optical film having a size corresponding to the optical cell on the carrier film.
- the band-shaped optical film is formed.
- the band-shaped optical film is cut in the width direction (skip cut) so as to avoid the defective part of the optical film of the optical film of the size corresponding to the optical cell on the carrier film (the non-defective optical that is bonded to the optical cell)
- an optical film including a defect portion may be formed in a size smaller than the optical cell (more preferably in a size as small as possible).
- each optical film roll a band-shaped optical film formed in the width direction so that a plurality of score lines avoid a defective portion is laminated on the carrier film, and corresponds to an optical cell on the carrier film.
- an optical film including a defective portion is formed in a size smaller than the optical cell (more preferably in a size as small as possible).
- the yield can be effectively improved by using a roll-shaped laminated optical film (an optical film roll having a cut).
- the optical film including the defective portion is peeled off from the carrier film and discharged, or wound around the winding portion together with the carrier film so as not to be bonded to the optical cell.
- a horizontally-long rectangular optical cell and an optical display panel have been described as examples.
- the shape of the optical cell and the optical display panel includes a pair of opposing sides and another pair of opposing sides. As long as it is a shape, it is not particularly limited.
- the film body of the polarizing film is, for example, a polarizer (thickness is generally about 1 to 80 ⁇ m) and a polarizer protective film (thickness is generally about 1 to 500 ⁇ m) attached to one or both sides of the polarizer. Formed without an agent or adhesive.
- a polarizer usually has an absorption axis in the stretching direction.
- a polarizing film including a long polarizer having an absorption axis in the longitudinal direction is also referred to as “MD polarizing film”, and a polarizing film including a long polarizer having an absorption axis in the width direction is also referred to as “TD polarizing film”. .
- films constituting the film body include, for example, retardation films such as ⁇ / 4 plates and ⁇ / 2 plates (thickness is generally 10 to 200 ⁇ m), viewing angle compensation films, brightness enhancement films, surface protection films, etc. Is mentioned.
- the thickness of the laminated optical film is, for example, in the range of 10 ⁇ m to 500 ⁇ m.
- the polarizer is obtained, for example, by dyeing, crosslinking, stretching, and drying a polyvinyl alcohol film.
- Each treatment of dyeing, crosslinking and stretching of the polyvinyl alcohol film need not be performed separately and may be performed simultaneously, and the order of the treatments may be arbitrary.
- a polyvinyl alcohol film is immersed in a solution containing iodine or a dichroic dye, dyed by adsorbing iodine or a dichroic dye, and stretched 3 times in a solution containing boric acid or borax. After uniaxial stretching at ⁇ 7 times, it is washed and dried.
- the pressure-sensitive adhesive is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include an acrylic pressure-sensitive adhesive, a silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive, and a urethane pressure-sensitive adhesive.
- the layer thickness of the pressure-sensitive adhesive is preferably in the range of 10 ⁇ m to 50 ⁇ m, for example.
- Examples of the peeling force between the pressure-sensitive adhesive and the carrier film include 0.15 (N / 50 mm width sample), but are not particularly limited thereto. The peeling force is measured according to JIS Z0237.
- carrier film for example, a conventionally known film such as a plastic film (for example, a polyethylene terephthalate film, a polyolefin film, or the like) can be used.
- a plastic film for example, a polyethylene terephthalate film, a polyolefin film, or the like
- an appropriate material according to the prior art such as a silicone-based, long-chain alkyl-based, fluorine-based or molybdenum sulfide-coated material may be used.
- the carrier film is generally called a release film (separator film).
- the release film 214 of Embodiment 1 the same film as the carrier film can be used.
- Examples of the film body of the linearly polarized light separation film include a reflective polarizing film having a multilayer structure having a reflection axis and a transmission axis.
- the reflective polarizing film can be obtained, for example, by alternately laminating and stretching a plurality of polymer films A and B of two different materials.
- the refractive index of only material A increases and changes in the stretching direction, birefringence is developed, and the stretching direction having a difference in refractive index at the interface of material AB becomes the reflection axis, and the direction in which no refractive index difference occurs (non-stretching direction). It becomes the transmission axis.
- This reflective polarizing film has a transmission axis in its longitudinal direction and a reflection axis in its short direction (width direction).
- a commercially available product may be used as it is, or a commercially available product may be used after secondary processing (for example, stretching).
- 3M company brand name DBEF and 3M company brand name APF are mentioned, for example.
- the liquid crystal cell has a structure in which a liquid crystal layer is sealed between a pair of substrates (a first substrate (viewing side surface) Pa and a second substrate (back surface) Pb) disposed to face each other.
- a liquid crystal layer is sealed between a pair of substrates (a first substrate (viewing side surface) Pa and a second substrate (back surface) Pb) disposed to face each other.
- VA vertical alignment
- IPS in-plane switching
- a liquid crystal display panel has a polarizing film bonded to one or both sides of a liquid crystal cell, and a drive circuit is incorporated as necessary.
- Organic EL cell (Organic EL cell, organic EL display panel)
- the organic EL cell has a configuration in which an electroluminescent layer is sandwiched between a pair of electrodes.
- an arbitrary type such as a top emission method, a bottom emission method, a double emission method, or the like can be used.
- the organic EL display panel has a polarizing film bonded to one or both sides of an organic EL cell, and a drive circuit is incorporated as necessary.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Nonlinear Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Liquid Crystal (AREA)
- Polarising Elements (AREA)
- Devices For Indicating Variable Information By Combining Individual Elements (AREA)
Abstract
帯状の第1光学フィルムを幅方向に切断することで得られた前記第1光学フィルムを第1光学フィルムロールから供給し、前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記第1光学フィルムを前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第1光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記光学セルの一方面に貼り合わせる第1貼合工程と、枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムが収容された収容部から前記第2光学フィルムを取り出して供給し、前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第2光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記第2光学フィルムを前記光学セルの他方面に貼り合わせる第2貼合工程とを含む、光学表示パネルの連続製造方法である。
Description
本発明は、光学表示パネルの連続製造方法および光学表示パネルの連続製造システムに関する。
第1光学フィルムロールから長手方向に吸収軸を有する帯状の第1偏光フィルムを繰り出し、前記帯状の第1偏光フィルムを幅方向に切断することで得られた前記第1偏光フィルムを前記液晶セルの背面側の面に貼り合わせ、第2光学フィルムロールから長手方向に吸収軸を有する帯状の第2偏光フィルムを繰り出し、前記帯状の第2偏光フィルムを幅方向に切断することで得られた前記第2偏光フィルムを前記液晶セルの視認側の面に貼り合わせる液晶表示パネルの連続製造方法(いわゆるRoll to Panel(RTP)方式)が開示されている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。
上記RTPシステムでは、光学フィルムを基板に貼り合わせる場合、表裏(基板の第1面、第2面)に貼り付けられたフィルムの貼合応力や収縮応力の違いにより液晶表示パネルに反りが発生する場合がある。近年、表裏非対称な偏光板が多くなっており、液晶表示パネルが益々反りやすい状況となっている(例えば、特許文献3,4参照。)。
上記液晶表示パネルの反りへの対応策としては、貼り付け時の張力をコントロールすることで反りの制御を実施することが考えられる。つまり、貼り付け時の反り状態が、貼り付けと逆面方向に反っている場合は張力過多で貼り付ける手法が考えられる。しかしながら、従来のように液晶セルの両面をRTP方式で貼付ける場合、互いに同一方向に吸収軸があるフィルムを使用することが通常であり、その場合、往々にして液晶セルに対して貼り付け方向が直交することになる。すなわち、貼り付け方向が平行にならないため、液晶セルの表裏で応力の相殺をすることができず、反りの矯正はし難くなる。
一方、液晶セルの両面共に枚葉状態の光学フィルム(光学シート)を貼り付ける方式(以下、Sheet to Panel(STP)方式ともいう)の場合は、RTP方式と異なり自由度は高く、貼り付け方向は自由に変更でき、表裏のフィルムの貼り付け方向を平行にすることができる。しかしながら、STP方式の場合は、吸着ステージにフィルムを吸着しながら貼りつけるため、大きな張力をかけられず、張力値も自由にコントロールできず成り行きの張力値とならざるを得ない。
つまり、液晶セルの両面ともRTP方式もしくは、STP方式で貼り付ける場合、反りに要する応力を相殺するための張力を施すには適さない構成であると推察される。
本発明は、上記の課題に鑑みてなされたものであり、反りの発生が抑制された光学表示パネルを製造するための光学表示パネルの製造方法および製造システムを提供することを目的とする。
本発明は、光学セルの一方面に第1光学フィルムが積層され、当該光学セルの他方面に第2光学フィルムが積層された光学表示パネルを連続的に製造する方法であって、
帯状の第1光学フィルムを幅方向に切断することで得られた前記第1光学フィルムを第1光学フィルムロールから供給し、前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記第1光学フィルムを前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第1光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記光学セルの一方面に貼り合わせる第1貼合工程と、
枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムが収容された収容部から前記第2光学フィルムを取り出して供給し、前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第2光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記第2光学フィルムを前記光学セルの他方面に貼り合わせる第2貼合工程とを含む。
帯状の第1光学フィルムを幅方向に切断することで得られた前記第1光学フィルムを第1光学フィルムロールから供給し、前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記第1光学フィルムを前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第1光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記光学セルの一方面に貼り合わせる第1貼合工程と、
枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムが収容された収容部から前記第2光学フィルムを取り出して供給し、前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第2光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記第2光学フィルムを前記光学セルの他方面に貼り合わせる第2貼合工程とを含む。
この構成によれば、光学セル(例えば液晶セル)に光学軸(例えば吸収軸)方向が同じ光学フィルム(例えば偏光フィルム)を貼り付ける際、その一方面をRTP方式で貼り、他方面をSTP方式で貼ることにより、貼り付け方向を平行(同一を含む)にすることが可能となる。さらに、片方をテンションフリーから張力過多まで自由に設定することができるRTP方式とすることで、貼合方向・張力制御共に自由度を確保でき、光学セルの表裏(第1面、第2面)の応力を一致(略一致、実質的に一致)させるための張力の相殺を容易に実現することができ、光学表示パネルに反りが発生するのを抑制できる。
上記発明において、第1貼合工程と第2貼合工程との順序はどちらが先に行われてもよく、同時あるいは貼付処理期間が前後で部分的に重複していてもよい。
上記発明の一実施形態として、前記第1貼合工程と前記第2貼合工程とが、前記光学セル及び前記光学表示パネルを搬送する一連の搬送部上で行なわれる。
上記発明の一実施形態として、第2光学フィルムの厚みが、第1偏光フィルムの厚みより大きいことが好ましい。すなわち、厚みがより大きい光学フィルムをSheet to Panel方式(予め枚葉状態にしておいた光学フィルムを光学セルに貼り合せる方式、以下「STP方式」ともいう。)で行うことが好ましい。STP方式は、光学フィルムの吸着とその解除を行ないながら、当該光学フィルムの貼り合せを行なうため、当該光学フィルムに対して大きな張力を掛けずに貼り合せを行なう(正確には、当該光学フィルムに対して大きな張力を掛けることができない)。一方、RTP方式は、連続ロール体フィルムであるため張力が掛けやすく、また逆に、フィルムに対して張力を掛けずに(例えば張力フリーで)貼り合せを行うと気泡発生や貼りズレの問題が生じやすいため、フィルムに対して張力を掛けながら貼り合せを行なう。よって、相対的に厚い(応力の溜まりやすい)光学フィルムをSTP方式で光学セルの一方面に貼り合せ、相対的に薄い(応力の溜まりにくい)光学フィルムを、張力をコントロールしながらRTP方式で光学セルの他方面に貼り合せることで、光学表示パネルの反りをより抑制することができる。
上記発明の一実施形態として、前記光学表示パネルの一方面に貼り合わされた第1光学フィルムの吸収軸と他方面に貼り合わされた第2光学フィルムの吸収軸とが互いに直交し、
前記第1光学フィルムロールに巻回された状態の前記第1光学フィルムの吸収軸が長手方向にあり、
前記枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムを製造するために用いられる帯状の第2光学フィルムの吸収軸が長手方向にある。
前記第1光学フィルムロールに巻回された状態の前記第1光学フィルムの吸収軸が長手方向にあり、
前記枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムを製造するために用いられる帯状の第2光学フィルムの吸収軸が長手方向にある。
この構成により、反りの発生が抑制された高いコントラストの光学表示パネルを製造することができる。
上記発明の一実施形態として、前記光学セルが、VAモードまたはIPSモードの液晶セルである。
本発明は、反りの発生が抑制された高コントラストのVAモードまたはIPSモードの液晶表示パネルを生産するのに特に好適である。
また、他の本発明は、光学セルの一方面に第1光学フィルムが積層され、当該光学セルの他方面に第2光学フィルムが積層された光学表示パネルを連続的に製造するシステムであって、
前記光学セル及び前記光学表示パネルを搬送する一連の搬送部と、
帯状の第1光学フィルムを幅方向に切断することで得られた前記第1光学フィルムを第1光学フィルムロールから供給する第1光学フィルム供給部と、
前記搬送部によって搬送された光学セルを搬送しながら、前記第1光学フィルム供給部によって供給された前記第1光学フィルムを前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第1光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記光学セルの一方面に貼り合わせる第1貼合部と、
枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムが収容された収容部から前記第2光学フィルムを取り出して供給する第2光学フィルム供給部と、
前記搬送部によって搬送された前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記第2光学フィルム供給部によって供給された前記第2光学フィルムを、前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第2光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記光学セルの他方面に貼り合わせる第2貼合部とを含む。
前記光学セル及び前記光学表示パネルを搬送する一連の搬送部と、
帯状の第1光学フィルムを幅方向に切断することで得られた前記第1光学フィルムを第1光学フィルムロールから供給する第1光学フィルム供給部と、
前記搬送部によって搬送された光学セルを搬送しながら、前記第1光学フィルム供給部によって供給された前記第1光学フィルムを前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第1光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記光学セルの一方面に貼り合わせる第1貼合部と、
枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムが収容された収容部から前記第2光学フィルムを取り出して供給する第2光学フィルム供給部と、
前記搬送部によって搬送された前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記第2光学フィルム供給部によって供給された前記第2光学フィルムを、前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第2光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記光学セルの他方面に貼り合わせる第2貼合部とを含む。
この構成によれば、光学セル(例えば液晶セル)に光学軸(例えば吸収軸)方向が同じ光学フィルム(例えば偏光フィルム)を貼り付ける際、その一方面をRTP方式で貼り、他方面をSTP方式で貼ることにより、貼り付け方向を平行(同一を含む)にすることが可能となる。さらに、片方をテンションフリーから張力過多まで自由に設定することができるRTP方式とすることで、貼合方向・張力制御共に自由度を確保でき、光学セルの表裏(第1面、第2面)の応力を一致(略一致、実質的に一致)させるための張力の相殺を容易に実現することができ、光学表示パネルに反りが発生するのを抑制できる。
上記発明において、第1貼合部の処理と第2貼合部の処理とは、どちらが先に行われもよく、同時あるいは貼付処理期間が前後で部分的に重複していてもよい。
上記発明の一実施形態として、前記第1貼合部と前記第2貼合部とが、前記光学セル及び前記光学表示パネルを搬送する前記搬送部に配置される。
上記発明の一実施形態として、第2光学フィルムの厚みが、第1偏光フィルムの厚みより大きいことが好ましい。
上記発明の一実施形態として、前記光学表示パネルの一方面に貼り合われた第1光学フィルムの吸収軸と他方面に貼り合わされた第2光学フィルムの吸収軸とが互いに直交し、
前記第1光学フィルムロールに巻回された状態の前記第1光学フィルムの吸収軸が長手方向にあり、
前記枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムを製造するために用いられる帯状の第2光学フィルムの吸収軸が長手方向にある。
前記第1光学フィルムロールに巻回された状態の前記第1光学フィルムの吸収軸が長手方向にあり、
前記枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムを製造するために用いられる帯状の第2光学フィルムの吸収軸が長手方向にある。
上記発明の一実施形態として、前記光学セルが、VAモードまたはIPSモードの液晶セルである。
本明細書において、光学フィルムロールから光学フィルムを供給する方法としては、例えば、(1)光学フィルムロールから、キャリアフィルム上に帯状の光学フィルムが積層されてなる帯状の積層光学フィルムを繰り出し、帯状の光学フィルムを幅方向に切断することで得られた光学フィルムを供給する方法、(2)光学フィルムロール(切り目入りの光学フィルムロール)から、キャリアフィルム上に幅方向に複数の切込線が形成された帯状の光学フィルムが積層されてなる帯状の積層光学フィルムを繰り出し、光学フィルムを供給する方法などが挙げられ、いずれも用いることができる。
本実施形態の光学表示パネルの連続製造システムは、光学セルの一方面に第1光学フィルムが積層され、当該光学セルの他方面に第2光学フィルムが積層された光学表示パネルを連続的に製造するシステムであって、前記光学セル及び前記光学表示パネルを搬送する一連の搬送部と、帯状の第1光学フィルムを幅方向に切断することで得られた前記第1光学フィルムを第1光学フィルムロールから供給する第1光学フィルム供給部と、前記搬送部によって搬送された光学セルを搬送しながら、前記第1光学フィルム供給部によって供給された前記第1光学フィルムを前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第1光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記光学セルの一方面に貼り合わせる第1貼合部と、枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムが収容された収容部から前記第2光学フィルムを取り出して供給する第2光学フィルム供給部と、前記搬送部によって搬送された前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記第2光学フィルム供給部によって供給された前記第2光学フィルムを、前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第2光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記光学セルの他方面に貼り合わせる第2貼合部とを含む。
<実施形態1>
図1~3は、実施形態1に係る光学表示パネルの連続製造システムの概略図である。以下、図1~3を参照しながら、本実施形態に係る光学表示パネルの連続製造システムを具体的に説明する。
図1~3は、実施形態1に係る光学表示パネルの連続製造システムの概略図である。以下、図1~3を参照しながら、本実施形態に係る光学表示パネルの連続製造システムを具体的に説明する。
なお、本実施形態では、光学セルとして横長長方形の液晶セル、光学表示パネルとして横長長方形の液晶表示パネルを例に挙げて説明する。光学フィルムロールとしては、図1、図2、図3に示すようなものを用いる。すなわち、第1光学フィルムロール1としては、第1キャリアフィルム12上に長手方向に吸収軸を有する帯状の第1偏光フィルム11(第1光学フィルムに相当する)が積層されてなり、液晶セルPの短辺に対応する幅を有する帯状の第1積層光学フィルム10が巻回されたものを用いる。
枚葉状態の第2光学フィルム21は、長手方向に吸収軸を有する帯状の第2偏光フィルムと、幅方向に反射軸を有する帯状の直線偏光分離フィルムを用いて製造される。具体的に、枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムを作製する方法としては、特開2004-250213号公報などに記載の方法等、従来公知の方法を用いることができる。例えば、第2偏光フィルムと直線偏光分離フィルムのそれぞれを予め枚葉状態にして積層する方法、あるいはいずれか一方を予め枚葉状態にして、他方を帯状のフィルムとして、当該帯状のフィルムに枚葉状態のフィルムを積層する方法が挙げられる。液晶セルに貼合せた時に、第1偏光フィルム111と第2偏光フィルム212の吸収軸同士が互いにクロスニコルの関係になる。
さらに、本実施形態では、帯状の第1偏光フィルム11は、図2に示すように、帯状のフィルム本体11aおよび粘着剤11bを有して構成される。図3に示すように、枚葉状態の第2光学フィルム21は、直線偏光分離フィルム211、第2偏光フィルム212、粘着剤213が積層され、粘着剤213の保護として離型フィルム214が仮着されている。
本実施形態に係る液晶表示パネルの連続製造システム100は、図1に示すように、液晶セルPおよび液晶表示パネルLDを搬送する一連の搬送部Xと、第1光学フィルム供給部101と、第1貼合部81と、第2光学フィルム供給部102と、第2貼合部82を含む。
(搬送部)
搬送部Xは、液晶セルPおよび液晶表示パネルLDを搬送する。搬送部Xは、複数の搬送ローラX1および吸着プレート等を有して構成される。
搬送部Xは、液晶セルPおよび液晶表示パネルLDを搬送する。搬送部Xは、複数の搬送ローラX1および吸着プレート等を有して構成される。
(第1光学フィルム供給部)
第1光学フィルム供給部101は、液晶セルPの短辺に対応する幅を有する帯状の第1偏光フィルム11を液晶セルPの長辺に対応する長さで幅方向に切断することで得られた第1偏光フィルム111を第1光学フィルムロール1から第1貼合部81に供給する。そのために本実施形態では、第1光学フィルム供給部101は、第1繰出部101a、第1切断部41、第1張力調整部51、第1剥離部61、第1巻取部71、および複数の搬送ローラ部101bを有する。
第1光学フィルム供給部101は、液晶セルPの短辺に対応する幅を有する帯状の第1偏光フィルム11を液晶セルPの長辺に対応する長さで幅方向に切断することで得られた第1偏光フィルム111を第1光学フィルムロール1から第1貼合部81に供給する。そのために本実施形態では、第1光学フィルム供給部101は、第1繰出部101a、第1切断部41、第1張力調整部51、第1剥離部61、第1巻取部71、および複数の搬送ローラ部101bを有する。
第1繰出部101aは、第1光学フィルムロール1が設置される繰出軸を有し、第1光学フィルムロール1から帯状の第1積層光学フィルム10を繰り出す。なお、第1繰出部101aには、2つの繰出軸が備えられていてもよい。これにより、ロール1を新たなロールに交換することなく、他方の繰出軸に設置されたロールのフィルムに速やかに継ぎ合わせることができる。
第1切断部41は、切断手段41aおよび吸着手段41bを有して構成され、帯状の第1積層光学フィルム10を液晶セルPの長辺に対応する長さで幅方向にハーフカットする(第1キャリアフィルム12を切断せずに帯状の第1偏光フィルム11を幅方向に切断する)。本実施形態では、第1切断部41は、吸着手段41bを用いて帯状の第1積層光学フィルム10を第1キャリアフィルム12側から吸着固定しながら、切断手段41aを用いて帯状の第1偏光フィルム11(フィルム本体11aおよび粘着剤11b)を幅方向に切断し、第1キャリアフィルム12上に液晶セルPに対応する大きさの第1偏光フィルム111を形成する。なお、切断手段41aとしては、カッター、レーザー装置、それらの組合せなどが挙げられる。
第1張力調整部51は、帯状の第1積層光学フィルム10の張力を保持する機能を有する。本実施形態では、第1張力調整部51は、ダンサーロールを有して構成されるが、これに限定されるものではない。
第1剥離部61は、第1キャリアフィルム12を内側にして帯状の第1積層光学フィルム10を折り返すことで、第1キャリアフィルム12から第1偏光フィルム111を剥離する。第1剥離部61としては、楔型部材、ローラなどが挙げられる。
第1巻取部71は、第1偏光フィルム111が剥離された第1キャリアフィルム12を巻き取る。第1巻取部71は、第1キャリアフィルム12を巻き取るためのロールが設置される巻取軸を有して構成される。
(第1貼合部)
第1貼合部81は、搬送部Xによって搬送された液晶セルPをその長辺方向を搬送方向に平行にして搬送しながら、第1光学フィルム供給部101によって供給された(第1剥離部61によって剥離された)第1偏光フィルム111を液晶セルPの短辺側から第1偏光フィルム111の供給方向(液晶セルPの長辺方向)に沿って液晶セルPの視認面側の面Paに粘着剤11bを介して貼り合わせる。なお、第1貼合部81は、一対の貼合ローラ81a、81bを有して構成され、貼合ローラ81a、81bの少なくとも一方が駆動ローラで構成される。
第1貼合部81は、搬送部Xによって搬送された液晶セルPをその長辺方向を搬送方向に平行にして搬送しながら、第1光学フィルム供給部101によって供給された(第1剥離部61によって剥離された)第1偏光フィルム111を液晶セルPの短辺側から第1偏光フィルム111の供給方向(液晶セルPの長辺方向)に沿って液晶セルPの視認面側の面Paに粘着剤11bを介して貼り合わせる。なお、第1貼合部81は、一対の貼合ローラ81a、81bを有して構成され、貼合ローラ81a、81bの少なくとも一方が駆動ローラで構成される。
(第2光学フィルム供給部)
第2光学フィルム供給部102は、枚葉状態の第2光学フィルム21が収容された容器102cから枚葉状態の第2光学フィルム21を取り出し、第2貼合部82の貼合位置へ供給する。本実施形態では、後述する第2貼合部82を用いて取り出し、供給を行う。
第2光学フィルム供給部102は、枚葉状態の第2光学フィルム21が収容された容器102cから枚葉状態の第2光学フィルム21を取り出し、第2貼合部82の貼合位置へ供給する。本実施形態では、後述する第2貼合部82を用いて取り出し、供給を行う。
(第2貼合部)
第2貼合部82は、搬送部Xによって搬送された液晶セルPをその長辺方向を搬送方向に平行にして搬送しながら、第2光学フィルム供給部102によって供給された第2光学フィルム21を液晶セルPの背面側の面Pbに、液晶セルPの短辺側から貼り合わせる。
第2貼合部82は、搬送部Xによって搬送された液晶セルPをその長辺方向を搬送方向に平行にして搬送しながら、第2光学フィルム供給部102によって供給された第2光学フィルム21を液晶セルPの背面側の面Pbに、液晶セルPの短辺側から貼り合わせる。
第2貼合部82は、収容部102cから貼合位置まで枚葉状態の第2光学フィルム21を移動する移動部(不図示)と、枚葉状態の離型フィルム214を枚葉状態の第2光学フィルム21から剥離する剥離部(不図示)と、枚葉状態の第2光学フィルム21を吸着する吸着部82bと貼合ローラ82aと、液晶セルP面と接して液晶セルPを搬送する駆動ローラ82cと、を有する。
収容部102cは、図1、3に記載された形態に限定されず、他の形状でもよく、例えば、枚葉状態の第2光学フィルム21を載せるための載置台を有する容器でもよく、この載置台がその周囲を覆われていてもよい。
移動部は、収容部102cに載置されている枚葉状態の第2光学フィルム21まで移動し、吸着部82bで、第2光学フィルム21の面を吸着し、貼合位置に移動する。
剥離部は、枚葉状態の離型フィルム214を枚葉状態の第2光学フィルム21から剥離する。剥離部は、例えば、粘着テープを用いて、粘着テープを離型フィルム214面に貼り合せ、粘着テープを移動させることで離型フィルム214を剥離してもよい。
吸着部82bに吸着している枚葉状態の第2光学フィルム21が先端位置の貼合ローラ82aに送られ、貼合ローラ82aを回転させて、液晶セルPの背面側の面Pbの上に第2光学フィルム21を短辺側から貼り合わせる。この際、駆動ローラ82cと貼合ローラ82aとで、液晶セルPおよび第2光学フィルム21とを挟み込んで下流側に搬送する。なお、駆動ローラ82cおよび貼合ローラ82aが共に駆動する機構でもよく、駆動ローラ82cが従動する機構でもよい。
本実施形態では、第1偏光フィルム、第2光学フィルムの供給方向が互いに平行になるように、第1光学フィルム供給部および第2光学フィルム供給部が、液晶セルの搬送部Xに配置されているため、装置の占有スペースを削減することができる。また、本実施形態では、液晶セルPに対する、第1貼合部81における第1偏光フィルム111の貼合方向と、第2貼合部82における第2光学フィルム21の貼合せ方向とが平行であるため、液晶表示パネルの反りを好適に抑制できる。
(実施形態1の別実施形態)
本実施形態では、搬送部Xによる液晶セルPの搬送方向に沿って、第1貼合部、第2貼合部がこの順に並んでいるが、これに制限されない。第1貼合部、第2貼合部の順序が逆でもよい。
本実施形態では、搬送部Xによる液晶セルPの搬送方向に沿って、第1貼合部、第2貼合部がこの順に並んでいるが、これに制限されない。第1貼合部、第2貼合部の順序が逆でもよい。
本実施形態では、第1貼合部は、第1偏光フィルムを液晶セルの下側から貼り合せ、第2貼合部は、第2光学フィルムを液晶セルの上側から貼り合わせているが、これに限定されない。第1貼合部は、第1偏光フィルムを液晶セルの上側から貼り合せ、第2貼合部は、第2光学フィルムを液晶セルの下側から貼り合わせてもよい。
また、本実施形態では、第1偏光フィルム111を液晶セルPの短辺側から第1偏光フィルム111の供給方向に沿って液晶セルPの視認側の面Paに貼り合わせ、第2光学フィルム21を液晶セルPの短辺側から第2光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って液晶セルPの背面側の面Pbに貼り合わせていたが、液晶セルの視認側と背面側とのそれぞれの偏光フィルムの吸収軸が直交(クロスニコル)するように貼り合せる限り、これに制限されない。第1偏光フィルム111を液晶セルPの長辺側から貼り合せ、第2光学フィルム21を液晶セルPの長辺側から貼り合せてもよい。ただし、第2光学フィルムを液晶セルの長辺側から貼り合わせるか短辺側から貼り合せるかに応じて、第2光学フィルムの幅及び切断サイズを設定する。また、液晶セルの視認側と背面側とのそれぞれの偏光フィルムの吸収軸が直交(クロスニコル)するように貼り合せる。
(光学表示パネルの連続製造方法)
実施形態1の光学表示パネルの連続製造方法は、光学セルの一方面に第1光学フィルムが積層され、当該光学セルの他方面に第2光学フィルムが積層された光学表示パネルを連続的に製造する方法であって、帯状の第1光学フィルムを幅方向に切断することで得られた前記第1光学フィルムを第1光学フィルムロールから供給し、前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記第1光学フィルムを前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第1光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記光学セルの一方面に貼り合わせる第1貼合工程と、枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムが収容された収容部から前記第2光学フィルムを取り出して供給し、前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第2光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記第2光学フィルムを前記光学セルの他方面に貼り合わせる第2貼合工程とを含む。
実施形態1の光学表示パネルの連続製造方法は、光学セルの一方面に第1光学フィルムが積層され、当該光学セルの他方面に第2光学フィルムが積層された光学表示パネルを連続的に製造する方法であって、帯状の第1光学フィルムを幅方向に切断することで得られた前記第1光学フィルムを第1光学フィルムロールから供給し、前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記第1光学フィルムを前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第1光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記光学セルの一方面に貼り合わせる第1貼合工程と、枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムが収容された収容部から前記第2光学フィルムを取り出して供給し、前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第2光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記第2光学フィルムを前記光学セルの他方面に貼り合わせる第2貼合工程とを含む。
また、前記光学表示パネルの一方面に貼り合われた第1光学フィルムの吸収軸と他方面に貼り合わされた第2光学フィルムの吸収軸とが互いに直交し、前記第1光学フィルムロールに巻回された状態の前記第1光学フィルムの吸収軸が長手方向にあり、前記枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムを製造するために用いられる帯状の第2光学フィルムの吸収軸が長手方向にある。
(第2光学フィルムの別例)
本実施形態では、第2光学フィルムが偏光フィルムと直線偏光分離フィルムとが積層された積層光学フィルムであったが、これに制限されない。第2光学フィルムとしては、広帯域位相差フィルム、広帯域位相差フィルムと偏光フィルムとが積層された積層光学フィルムなどが例示される。広帯域位相差フィルムは、λ/4位相差フィルムとλ/2位相差フィルムとを積層したフィルムが例示される。
本実施形態では、第2光学フィルムが偏光フィルムと直線偏光分離フィルムとが積層された積層光学フィルムであったが、これに制限されない。第2光学フィルムとしては、広帯域位相差フィルム、広帯域位相差フィルムと偏光フィルムとが積層された積層光学フィルムなどが例示される。広帯域位相差フィルムは、λ/4位相差フィルムとλ/2位相差フィルムとを積層したフィルムが例示される。
(実施形態1の変形例)
実施形態1では、光学フィルムロールとして、キャリアフィルム上に帯状の光学フィルムが積層されてなる帯状の積層光学フィルムが巻回されたものを用いるが、光学フィルムロールの構成はこれに限定されない。例えば、キャリアフィルム上に複数の切込線が幅方向に形成された帯状の光学フィルムが積層されてなる帯状の積層光学フィルムが巻回されたもの(切り目入りの光学フィルムロール)を適宜用いてもよい。なお、切り目入りの光学フィルムロールから光学フィルムを供給する光学フィルム供給部において、切断部は不要となる。
実施形態1では、光学フィルムロールとして、キャリアフィルム上に帯状の光学フィルムが積層されてなる帯状の積層光学フィルムが巻回されたものを用いるが、光学フィルムロールの構成はこれに限定されない。例えば、キャリアフィルム上に複数の切込線が幅方向に形成された帯状の光学フィルムが積層されてなる帯状の積層光学フィルムが巻回されたもの(切り目入りの光学フィルムロール)を適宜用いてもよい。なお、切り目入りの光学フィルムロールから光学フィルムを供給する光学フィルム供給部において、切断部は不要となる。
実施形態1では、切断部は、帯状の光学フィルムを幅方向に切断し、キャリアフィルム上に光学セルに対応する大きさの光学フィルムを形成していたが、歩留りを向上させる観点からは、帯状の光学フィルムの欠点部分を避けるように帯状の光学フィルムを幅方向に切断(スキップカット)して、キャリアフィルム上に光学セルに対応する大きさの光学フィルム(光学セルに貼り合わせられる良品の光学フィルム)を形成する他、欠点部分を含む光学フィルムを光学セルよりも小さいサイズで(より好ましくは、可能なかぎり小さいサイズで)形成してもよい。本発明においては、各々の光学フィルムロールとして、キャリアフィルム上に複数の切込線が欠点部分を避けるように幅方向に形成された帯状の光学フィルムが積層され、キャリアフィルム上に光学セルに対応する大きさの光学フィルム(光学セルに貼り合わせられる良品の光学フィルム)の他、欠点部分を含む光学フィルムを光学セルよりも小さいサイズで(より好ましくは、可能なかぎり小さいサイズで)形成されてなる帯状の積層光学フィルムが巻回されたもの(切り目入りの光学フィルムロール)を用いることによっても、同様に歩留りを効果的に向上させることができる。なお、欠点部分を含む光学フィルムは、キャリアフィルムから剥離して排出する、またはキャリアフィルムと共に巻取部に巻き取るなどして、光学セルに貼り合わされないようにすることが好ましい。切り目入りの光学フィルムロールを用いる場合や、帯状の積層光学フィルムを幅方向にフルカットを用いる場合についても、同様である。
実施形態1では、横長長方形の光学セルおよび光学表示パネルを例に挙げて説明したが、光学セルおよび光学表示パネルの形状は、対向する一組の辺と対向するもう一組の辺とを有する形状である限り、特に限定されない。
(光学フィルム)
偏光フィルムのフィルム本体は、例えば、偏光子(厚さは一般的に1~80μm程度)と、偏光子の片面または両面に偏光子保護フィルム(厚さは一般的に1~500μm程度)が接着剤または接着剤なしで形成される。偏光子は、通常、延伸方向が吸収軸となっている。長手方向に吸収軸を有する長尺の偏光子を含む偏光フィルムを「MD偏光フィルム」ともいい、幅方向に吸収軸を有する長尺の偏光子を含む偏光フィルムものを「TD偏光フィルム」ともいう。フィルム本体を構成する他のフィルムとして、例えば、λ/4板、λ/2板等の位相差フィルム(厚さは一般的に10~200μm)、視角補償フィルム、輝度向上フィルム、表面保護フィルム等が挙げられる。積層光学フィルムの厚みは、例えば、10μm~500μmの範囲が挙げられる。
偏光フィルムのフィルム本体は、例えば、偏光子(厚さは一般的に1~80μm程度)と、偏光子の片面または両面に偏光子保護フィルム(厚さは一般的に1~500μm程度)が接着剤または接着剤なしで形成される。偏光子は、通常、延伸方向が吸収軸となっている。長手方向に吸収軸を有する長尺の偏光子を含む偏光フィルムを「MD偏光フィルム」ともいい、幅方向に吸収軸を有する長尺の偏光子を含む偏光フィルムものを「TD偏光フィルム」ともいう。フィルム本体を構成する他のフィルムとして、例えば、λ/4板、λ/2板等の位相差フィルム(厚さは一般的に10~200μm)、視角補償フィルム、輝度向上フィルム、表面保護フィルム等が挙げられる。積層光学フィルムの厚みは、例えば、10μm~500μmの範囲が挙げられる。
偏光子は、例えば、ポリビニルアルコール系フィルムを染色、架橋、延伸、および乾燥処理して得られる。ポリビニルアルコール系フィルムの染色、架橋、延伸の各処理は、別々に行う必要はなく同時に行ってもよく、また、各処理の順番も任意でよい。なお、ポリビニルアルコール系フィルムとして、膨潤処理を施したポリビニルアルコール系フィルムを用いてもよい。一般には、ポリビニルアルコール系フィルムを、ヨウ素や二色性色素を含む溶液に浸漬し、ヨウ素や二色性色素を吸着させて染色し、ホウ酸やホウ砂等を含む溶液中で延伸倍率3倍~7倍で一軸延伸した後、洗浄して乾燥する。
粘着剤は、特に制限されず、例えば、アクリル系粘着剤、シリコーン系粘着剤、ウレタン系粘着剤等が挙げられる。粘着剤の層厚みは、例えば、10μm~50μmの範囲が好ましい。粘着剤とキャリアフィルムとの剥離力としては、例えば、0.15(N/50mm幅サンプル)が例示されるが、特にこれに限定されない。剥離力は、JIS Z0237に準じて測定される。
(キャリアフィルム)
キャリアフィルムは、例えばプラスチックフィルム(例えば、ポリエチレンテレフタレート系フィルム、ポリオレフィン系フィルム等)等の従来公知のフィルムを用いることができる。また、必要に応じシリコーン系や長鎖アルキル系、フッ素系や硫化モリブデン等の適宜な剥離剤でコート処理したものなどの、従来に準じた適宜なものを用いうる。なお、キャリアフィルムは、一般的に離型フィルム(セパレータフィルム)ともいわれる。実施形態1の離型フィルム214は、キャリアフィルムと同様のものを用いることができる。
キャリアフィルムは、例えばプラスチックフィルム(例えば、ポリエチレンテレフタレート系フィルム、ポリオレフィン系フィルム等)等の従来公知のフィルムを用いることができる。また、必要に応じシリコーン系や長鎖アルキル系、フッ素系や硫化モリブデン等の適宜な剥離剤でコート処理したものなどの、従来に準じた適宜なものを用いうる。なお、キャリアフィルムは、一般的に離型フィルム(セパレータフィルム)ともいわれる。実施形態1の離型フィルム214は、キャリアフィルムと同様のものを用いることができる。
直線偏光分離フィルムのフィルム本体は、例えば、反射軸と透過軸を有する多層構造の反射偏光フィルムが挙げられる。反射偏光フィルムは、例えば、2種類の異なる材料のポリマーフィルムA、Bを交互に複数枚積層して延伸することで得られる。延伸方向に材料Aのみの屈折率が増加変化し、複屈折性が発現され、材料AB界面の屈折率差がある延伸方向が反射軸となり、屈折率差の生じない方向(非延伸方向)が透過軸となる。この反射偏光フィルムは、その長手方向に透過軸を有し、その短手方向(幅方向)に反射軸を有している。反射偏光フィルムは、市販品をそのまま用いてもよく、市販品を2次加工(例えば、延伸)して用いてもよい。市販品としては、例えば、3M社製の商品名DBEF、3M社製の商品名APFが挙げられる。
(液晶セル、液晶表示パネル)
液晶セルは、対向配置される一対の基板(第1基板(視認側面)Pa、第2基板(背面)Pb)間に液晶層が封止された構成である。液晶セルは、任意のタイプのものを用いることができるが、高コントラストを実現するためには、垂直配向(VA)モード、面内スイッチング(IPS)モードの液晶セルを用いることが好ましい。液晶表示パネルは、液晶セルの片面または両面に偏光フィルムが貼り合わされたものであり、必要に応じて駆動回路が組込まれる。
液晶セルは、対向配置される一対の基板(第1基板(視認側面)Pa、第2基板(背面)Pb)間に液晶層が封止された構成である。液晶セルは、任意のタイプのものを用いることができるが、高コントラストを実現するためには、垂直配向(VA)モード、面内スイッチング(IPS)モードの液晶セルを用いることが好ましい。液晶表示パネルは、液晶セルの片面または両面に偏光フィルムが貼り合わされたものであり、必要に応じて駆動回路が組込まれる。
(有機ELセル、有機EL表示パネル)
有機ELセルは、一対の電極間に電界発光層が挟持された構成である。有機ELセルは、例えば、トップエミッション方式、ボトムエミッション方式、ダブルエミッション方式などの任意のタイプのものを用いることができる。有機EL表示パネルは、有機ELセルの片面または両面に偏光フィルムが貼り合わされたものであり、必要に応じて駆動回路が組込まれる。
有機ELセルは、一対の電極間に電界発光層が挟持された構成である。有機ELセルは、例えば、トップエミッション方式、ボトムエミッション方式、ダブルエミッション方式などの任意のタイプのものを用いることができる。有機EL表示パネルは、有機ELセルの片面または両面に偏光フィルムが貼り合わされたものであり、必要に応じて駆動回路が組込まれる。
1 光学フィルムロール
81、82 貼合部
P 液晶セル
LD 液晶表示パネル
81、82 貼合部
P 液晶セル
LD 液晶表示パネル
Claims (6)
- 光学セルの一方面に第1光学フィルムが積層され、当該光学セルの他方面に第2光学フィルムが積層された光学表示パネルを連続的に製造する方法であって、
帯状の第1光学フィルムを幅方向に切断することで得られた前記第1光学フィルムを第1光学フィルムロールから供給し、前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記第1光学フィルムを前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第1光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記光学セルの一方面に貼り合わせる第1貼合工程と、
枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムが収容された収容部から前記第2光学フィルムを取り出して供給し、前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第2光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記第2光学フィルムを前記光学セルの他方面に貼り合わせる第2貼合工程とを含む、光学表示パネルの連続製造方法。 - 前記光学表示パネルの一方面に貼り合わされた第1光学フィルムの吸収軸と他方面に貼り合わされた第2光学フィルムの吸収軸とが互いに直交し、
前記第1光学フィルムロールに巻回された状態の前記第1光学フィルムの吸収軸が長手方向にあり、
前記枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムを製造するために用いられる帯状の第2光学フィルムの吸収軸が長手方向にある、請求項1に記載の光学表示パネルの連続製造方法。 - 前記光学セルが、VAモードまたはIPSモードの液晶セルである、請求項1または2に記載の光学表示パネルの連続製造方法。
- 光学セルの一方面に第1光学フィルムが積層され、当該光学セルの他方面に第2光学フィルムが積層された光学表示パネルを連続的に製造するシステムであって、
前記光学セル及び前記光学表示パネルを搬送する一連の搬送部と、
帯状の第1光学フィルムを幅方向に切断することで得られた前記第1光学フィルムを第1光学フィルムロールから供給する第1光学フィルム供給部と、
前記搬送部によって搬送された光学セルを搬送しながら、前記第1光学フィルム供給部によって供給された前記第1光学フィルムを前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第1光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記光学セルの一方面に貼り合わせる第1貼合部と、
枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムが収容された収容部から前記第2光学フィルムを取り出して供給する第2光学フィルム供給部と、
前記搬送部によって搬送された前記光学セルを搬送しながら、前記第2光学フィルム供給部によって供給された前記第2光学フィルムを、前記光学セルの対向する一組の辺側から前記第2光学フィルムの供給方向に沿って前記光学セルの他方面に貼り合わせる第2貼合部とを含む、光学表示パネルの連続製造システム。 - 前記光学表示パネルの一方面に貼り合われた第1光学フィルムの吸収軸と他方面に貼り合わされた第2光学フィルムの吸収軸とが互いに直交し、
前記第1光学フィルムロールに巻回された状態の前記第1光学フィルムの吸収軸が長手方向にあり、
前記枚葉状態の第2光学フィルムを製造するために用いられる帯状の第2光学フィルムの吸収軸が長手方向にある、請求項4に記載の光学表示パネルの連続製造システム。 - 前記光学セルが、VAモードまたはIPSモードの液晶セルである、請求項4または5に記載の光学表示パネルの連続製造システム。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201380054082.1A CN104737065B (zh) | 2012-11-09 | 2013-10-28 | 光学显示面板的连续制造方法及光学显示面板的连续制造系统 |
| KR1020157015007A KR101646479B1 (ko) | 2012-11-09 | 2013-10-28 | 광학 표시 패널의 연속 제조 방법 및 광학 표시 패널의 연속 제조 시스템 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012247682A JP5782010B2 (ja) | 2012-11-09 | 2012-11-09 | 光学表示パネルの連続製造方法および光学表示パネルの連続製造システム |
| JP2012-247682 | 2012-11-09 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2014073405A1 true WO2014073405A1 (ja) | 2014-05-15 |
Family
ID=50684514
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/079097 WO2014073405A1 (ja) | 2012-11-09 | 2013-10-28 | 光学表示パネルの連続製造方法および光学表示パネルの連続製造システム |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5782010B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR101646479B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN104737065B (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI524985B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2014073405A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6095711B2 (ja) * | 2015-02-19 | 2017-03-15 | 住友化学株式会社 | 積層光学フィルムの製造方法 |
| KR101674354B1 (ko) * | 2016-05-30 | 2016-11-22 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | 광학 표시 소자의 제조 시스템 및 제조 방법 |
| KR101674352B1 (ko) * | 2016-05-30 | 2016-11-08 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | 광학 표시 소자의 제조 시스템 및 제조 방법 |
| JP6792367B2 (ja) * | 2016-07-22 | 2020-11-25 | 日東電工株式会社 | 枚葉状の光学フィルム |
| JP6654113B2 (ja) * | 2016-07-22 | 2020-02-26 | 日東電工株式会社 | 光学表示パネルの製造方法と光学表示パネルの製造システム |
| JP6732580B2 (ja) * | 2016-07-22 | 2020-07-29 | 日東電工株式会社 | 光学表示パネルの製造方法と光学表示パネルの製造システム |
| JP6792366B2 (ja) * | 2016-07-22 | 2020-11-25 | 日東電工株式会社 | 光学フィルムセット及びその製造方法 |
| KR102042053B1 (ko) | 2016-08-25 | 2019-11-07 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | 디스플레이 유닛의 제조 시스템 |
| TWI650142B (zh) | 2016-09-06 | 2019-02-11 | 日商澤井製藥股份有限公司 | 口腔内崩解錠添加用組成物 |
| JP6538014B2 (ja) * | 2016-09-06 | 2019-07-03 | 日東電工株式会社 | 光学的表示ユニットの連続製造装置及び連続製造方法 |
| JP6505877B1 (ja) * | 2018-01-04 | 2019-04-24 | 日東電工株式会社 | 切目を有する長尺の光学フィルムを搬送する搬送装置、並びに、光学表示パネルの連続製造システム |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010256757A (ja) * | 2009-04-28 | 2010-11-11 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | 光学表示パネルの製造方法 |
| JP2011197651A (ja) * | 2010-02-24 | 2011-10-06 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | 液晶表示装置の製造方法 |
| JP2012103594A (ja) * | 2010-11-12 | 2012-05-31 | Nitto Denko Corp | 液晶表示装置の製造方法 |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2823970B2 (ja) | 1991-04-05 | 1998-11-11 | 浜松ホトニクス株式会社 | 近接場走査光学顕微鏡 |
| CN101528445B (zh) | 2006-10-17 | 2016-08-17 | 日东电工株式会社 | 光学构件贴合方法以及使用该方法的装置 |
| JP5313002B2 (ja) | 2008-04-07 | 2013-10-09 | 日東電工株式会社 | 光学表示装置の製造方法 |
| JP4669070B2 (ja) * | 2009-05-21 | 2011-04-13 | 日東電工株式会社 | 光学表示装置の製造システム及び製造方法 |
| JP2012032559A (ja) | 2010-07-30 | 2012-02-16 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | ロール状偏光板のセット及びその製造方法並びに液晶パネルの製造方法 |
| JP2012053077A (ja) | 2010-08-31 | 2012-03-15 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | ロール状偏光板のセット及びその製造方法並びに液晶パネルの製造方法 |
| JP4921597B1 (ja) * | 2011-03-18 | 2012-04-25 | 日東電工株式会社 | 液晶表示パネルの連続製造システムおよび液晶表示パネルの連続製造方法、並びに、検査装置および検査方法 |
-
2012
- 2012-11-09 JP JP2012247682A patent/JP5782010B2/ja active Active
-
2013
- 2013-10-28 WO PCT/JP2013/079097 patent/WO2014073405A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2013-10-28 KR KR1020157015007A patent/KR101646479B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2013-10-28 CN CN201380054082.1A patent/CN104737065B/zh active Active
- 2013-11-08 TW TW102140736A patent/TWI524985B/zh active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010256757A (ja) * | 2009-04-28 | 2010-11-11 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | 光学表示パネルの製造方法 |
| JP2011197651A (ja) * | 2010-02-24 | 2011-10-06 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | 液晶表示装置の製造方法 |
| JP2012103594A (ja) * | 2010-11-12 | 2012-05-31 | Nitto Denko Corp | 液晶表示装置の製造方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN104737065B (zh) | 2016-09-07 |
| TWI524985B (zh) | 2016-03-11 |
| JP2014095833A (ja) | 2014-05-22 |
| KR20150082542A (ko) | 2015-07-15 |
| CN104737065A (zh) | 2015-06-24 |
| JP5782010B2 (ja) | 2015-09-24 |
| KR101646479B1 (ko) | 2016-08-05 |
| TW201422415A (zh) | 2014-06-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5782010B2 (ja) | 光学表示パネルの連続製造方法および光学表示パネルの連続製造システム | |
| JP5744819B2 (ja) | 光学表示パネルの連続製造方法および光学表示パネルの連続製造システム | |
| JP5945143B2 (ja) | 光学フィルムロールセットおよび光学フィルムロールセットの製造方法。 | |
| KR101853140B1 (ko) | 액정 표시 소자의 제조 방법 및 액정 표시 소자의 제조 시스템 | |
| JP6082140B2 (ja) | 光学表示パネルの連続製造方法および光学表示パネルの連続製造システム | |
| JP5905761B2 (ja) | 光学表示パネルの連続製造方法および光学表示パネルの連続製造システム | |
| US8894793B2 (en) | Method and system for manufacturing liquid crystal display device | |
| WO2013129160A1 (ja) | 光学表示パネルの製造方法および光学表示パネルの製造システム | |
| KR101862877B1 (ko) | 액정 표시 소자의 제조 방법 및 액정 표시 소자의 제조 시스템 | |
| JP5933066B2 (ja) | 光学表示パネルの連続製造方法および光学表示パネルの連続製造システム | |
| JP6148755B2 (ja) | 光学表示パネルの連続製造方法および光学表示パネルの連続製造システム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13852632 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20157015007 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 13852632 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |