WO2012043442A1 - アンテナ装置 - Google Patents
アンテナ装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2012043442A1 WO2012043442A1 PCT/JP2011/071824 JP2011071824W WO2012043442A1 WO 2012043442 A1 WO2012043442 A1 WO 2012043442A1 JP 2011071824 W JP2011071824 W JP 2011071824W WO 2012043442 A1 WO2012043442 A1 WO 2012043442A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- antenna
- wave
- receiving antenna
- receiving
- transmitting
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01Q—ANTENNAS, i.e. RADIO AERIALS
- H01Q1/00—Details of, or arrangements associated with, antennas
- H01Q1/52—Means for reducing coupling between antennas; Means for reducing coupling between an antenna and another structure
- H01Q1/521—Means for reducing coupling between antennas; Means for reducing coupling between an antenna and another structure reducing the coupling between adjacent antennas
- H01Q1/525—Means for reducing coupling between antennas; Means for reducing coupling between an antenna and another structure reducing the coupling between adjacent antennas between emitting and receiving antennas
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an antenna device such as a passive ID tag reader / writer.
- This application claims priority on the basis of Japanese Patent Application No. 2010-218634 filed in Japan on September 29, 2010, the contents of which are incorporated herein by reference.
- an antenna device such as a passive ID tag reader / writer transmits a radio wave to a responder such as an RF tag that exchanges information (transmits a main radio wave to an antenna different from the reception antenna), and a responder
- a receiving antenna for receiving radio waves transmitted from the receiver is provided adjacent to the receiving antenna, and the receiving antenna receives the received radio waves transmitted from the responding device while transmitting the radio wave (main radio wave) to the responding device with the transmitting antenna.
- the receiving antenna is configured to simultaneously transmit and receive radio waves.
- this type of antenna device if a part of the leaked radio wave leaking from the transmitting antenna is received by the receiving antenna directly or wrapping around, this leaked radio wave becomes a high level interference wave. As a result, the antenna pattern is distorted, and the receiving characteristics of the receiving antenna are deteriorated, so that the necessary gain and phase characteristics (isolation) cannot be secured. If a sufficient distance is provided between the transmission antenna and the reception antenna, it is possible to ensure isolation, but it is practically difficult to greatly separate the transmission antenna and the reception antenna as described above.
- the radio wave shield is provided between the transmission antenna and the reception antenna, there is a possibility that the leaked radio wave leaking from the transmission antenna may wrap around the radio wave shield and be received by the reception antenna. It was. Also, since the size of the radio wave shield is set according to the frequency of the radio wave (leakage radio wave) transmitted from the transmission antenna and the distance between the transmission antenna and the reception antenna, the frequency of the radio wave transmitted from the transmission antenna and the transmission antenna and reception A radio wave shield having a different size is required for each antenna device having a different antenna distance.
- the present invention enables leakage radio waves (interference waves) that reach the receiving antenna from the transmitting antenna easily and reliably even when the frequency of the radio wave (leakage radio wave) transmitted from the transmitting antenna and the distance between the transmitting antenna and the receiving antenna are different. It is an object of the present invention to provide an antenna device capable of securing isolation by attenuating the above.
- the present invention provides the following means.
- An antenna device includes a receiving antenna that receives radio waves, a transmitting antenna that is provided adjacent to the receiving antenna and transmits main radio waves to an antenna different from the receiving antenna, and the transmitting antenna. And a reflecting member that reflects a part of leaked radio waves leaking from the antenna toward the receiving antenna.
- the reflecting member is arranged so that the reflected wave reaching the receiving antenna is reflected from a part of the leaked radio wave and reaches the receiving antenna with a phase shift with respect to the direct wave of the leaking radio wave that reaches the receiving antenna. It is configured to attenuate the direct wave reaching the receiving antenna from the transmitting antenna by causing interference due to a phase shift between the direct wave and the reflected wave.
- the direct wave and the reflected wave can be made to interfere by reflecting a part of the leaked radio wave with a reflecting member so that it reaches the receiving antenna out of phase with respect to the direct wave of the leaked radio wave that reaches the receiving antenna directly from the transmitting antenna. It becomes possible. As a result, without providing a radio wave shield between the transmitting antenna and the receiving antenna as in the conventional antenna device, the reflecting member is disposed so that the phase of the reflected wave is shifted from the direct wave. It is possible to obtain an attenuation effect of interference waves (leakage radio waves and direct wave) that reach the receiving antenna from the antenna and deteriorate the reception characteristics of the receiving antenna.
- the transmission antenna is an antenna having directivity for transmitting radio waves toward a predetermined range and generating leaked radio waves outside the predetermined range. desirable.
- the transmission antenna is an antenna that emits radio waves (main radio waves) toward a predetermined range and leaks radio waves outside the predetermined range
- a reflective member is provided so that the leaked radio waves that reach the receiving antenna directly
- the direct wave and the reflected wave of the leaked radio wave reflected by the reflecting member are caused to interfere with each other, so that the interference wave that reliably reaches the receiving antenna from the transmitting antenna and degrades the receiving characteristics of the receiving antenna can be attenuated.
- the transmission antenna is an antenna that is formed in a rod shape, transmits radio waves from the end in the axial direction to the predetermined range, and radiates leaked radio waves in the center of the axis. There may be.
- the transmission antenna is an antenna that is formed in a rod shape such as a helical antenna and the leaked radio wave is radiated at the center of the axis
- the direct wave and the reflected wave of the leaked radio wave are caused to interfere with each other.
- the interference wave can be surely attenuated.
- the reflecting member converts the reflected wave that becomes the shortest propagation path among the reflected waves that reach the receiving antenna into a direct wave that becomes the shortest propagation path among the direct waves.
- the antenna is disposed so as to be shifted by a half wavelength at the position of the receiving antenna.
- the reflection member Since the reflection member is arranged so that the reflected wave of the leaked radio wave is shifted by a half wavelength at the receiving antenna position with respect to the direct wave, the direct wave and the reflected wave can be interfered with each other so as to cancel each other. Interference waves that reach the reception antenna and degrade the reception characteristics of the reception antenna can be eliminated.
- the transmitting antenna is an antenna such as a helical antenna
- a leaked radio wave is radiated at the center of the axis, but the reflected wave that is the shortest propagation path is half of the direct wave that is the shortest propagation path.
- the reflection member, the transmission antenna, and the transmission antenna according to the distance between the transmission antenna and the reception antenna and / or the frequency of the radio wave transmitted from the transmission antenna. It is desirable that the receiver antenna is configured to move relative to the receiver antenna.
- the transmission antenna depends on the distance between the transmission antenna and the reception antenna and / or the frequency of the radio wave transmitted from the transmission antenna.
- the relative position of the reflecting member with respect to the receiving antenna can be easily set so that the phases of the reflected wave and the direct wave are shifted.
- the reflection member is arranged so that the phase of the reflected wave is shifted with respect to the direct wave of the leaked radio wave without providing a radio wave shield between the transmitting antenna and the receiving antenna unlike the conventional antenna device.
- the present embodiment relates to an antenna device such as a reader / writer for a passive ID tag.
- the antenna device A of the present embodiment transmits radio waves to a responder such as an RF tag that exchanges information (transmits main radio waves to an antenna different from the receiving antenna 2).
- a transmission antenna 1 and a reception antenna 2 that receives radio waves transmitted from the responding device are provided adjacent to each other, and the transmission antenna 1 transmits radio waves (main radio waves and transmission radio waves) to the responding device.
- a radio wave is received by the receiving antenna 2, and the transmission antenna 1 and the receiving antenna 2 are configured to simultaneously transmit and receive the radio wave.
- the antenna device A of the present embodiment includes a reflection member 3 that transmits radio waves from the transmission antenna 1 and reflects part of the leaked radio waves leaking from the transmission antenna 1 toward the reception antenna 2. Has been.
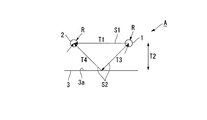
- the transmission antenna 1 and the reception antenna 2 are, for example, helical antennas, and the transmission antenna 1 and the reception antenna 2 have their axes O1 and O2 oriented in the same direction and at a predetermined interval T1.
- Side by side. That is, the transmission antenna 1 of the present embodiment is an antenna having directivity for transmitting radio waves toward a predetermined range and generating leaked radio waves outside the predetermined range. Further, it is an antenna that is formed in a rod shape and is generated by transmitting radio waves within a predetermined range from the end in the direction of the axis O1 and radiating leaked radio waves at the center of the axis O1.
- the reflecting member 3 is, for example, a reflecting mirror, a metal plate, a metal sheet, or the like.
- the reflecting member 3 is disposed with a predetermined interval T2 between the transmitting antenna 1 and the receiving antenna 2 with the reflecting surface 3a facing the transmitting antenna 1 and the receiving antenna 2 side. Further, at this time, the reflecting member 3 reflects the phase of the reflected wave S2 reflected from the reflecting member 3 and reaching the receiving antenna 2 with respect to the direct wave S1 radiated from the transmitting antenna 1 and reaching the receiving antenna 2 directly. It is disposed so as to reach the receiving antenna 2 with a shift.
- the reflecting member 3 is arranged so that the reflected wave S2 reaching the receiving antenna 2 is shifted by a half wavelength at the position of the receiving antenna with respect to the direct wave S1.
- the reflecting member 3 is not limited to being formed in a plate shape, and may be configured with, for example, a mesh structure or a grid structure as long as it can reflect radio waves.
- the antenna device A of the present embodiment configured as described above is used as a response device such as an RF tag for transmitting and receiving information, in which the transmitting antenna 1 and the receiving antenna 2 have directivity in the directions of the axes O1 and O2, respectively.
- Radio waves are transmitted from the transmission antenna 1.
- the transmitting antenna 1 generates leaked radio waves in the radiation direction centered on the axis O1.
- a leaked radio wave (direct wave S1, interference wave) radiated from the transmission antenna 1 is received by the reception antenna 2 adjacent to the transmission antenna 1 with a predetermined interval T1.
- the interference pattern becomes a large level and distortion occurs in the antenna pattern, so that the reception characteristic of the reception antenna 2 is deteriorated and the necessary gain and phase characteristic (isolation) cannot be secured.
- the antenna device A of the present embodiment includes the reflecting member 3, a part of the leaked radio wave radiated from the transmitting antenna 1 is reflected by the reflecting member 3 and reflected by the reflecting member 3.
- the reflected wave S2 reaches the receiving antenna 2.
- the reflecting member 3 has a half-wavelength at the position of the receiving antenna with respect to the direct wave S1 so that the reflected wave S2 reaches the receiving antenna 2 with a phase shifted from the direct wave S1. It arrange
- the difference (path difference) between the path T1 of the direct wave S1 directly reaching the receiving antenna 2 from the transmitting antenna 1 and the path (T3 + T4) of the reflected wave S2 reaching the receiving antenna 2 from the reflecting member 3 and the reflecting member 3 from the transmitting antenna 1. ) Is set so that the phases of the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2 reaching the receiving antenna 2 are shifted by a half wavelength.
- the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2 interfere with each other due to the phase difference between the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2 reaching the receiving antenna 2 (the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2 cancel each other), and the direct wave S1 is It is attenuated by the reflected wave S2.
- the interference wave is attenuated without providing a radio wave shield between the transmitting antenna 1 and the receiving antenna 2 as in the conventional antenna device.
- the interference wave is attenuated.
- the transmission antenna 1 and / or the reception antenna 2 is selected according to the distance T1 between the transmission antenna 1 and the reception antenna 2 and / or the frequency of the radio wave radiated from the transmission antenna 1. Isolation is ensured only by setting the relative position of the reflective member 3 to the direct wave S1 so that the reflected wave S2 interferes with the direct wave S1 and cancels each other.
- the reflecting member 3 and the transmitting antenna 1 and / or the receiving antenna 2 can be relatively moved in advance according to the distance T1 between the transmitting antenna 1 and the receiving antenna 2 and / or the frequency of the radio wave transmitted from the transmitting antenna 1. If the antenna device A is configured as described above, the path T1 of the direct wave S1 and the path (T3 + T4) of the reflected wave S2 even when the frequency of the radio wave and the distance T1 between the transmission antenna 1 and the reception antenna 2 are different.
- the relative positions of the transmitting antenna 1, the receiving antenna 2 and the reflecting member 3 can be easily and reliably set so that the difference is shifted by half a wavelength between the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2.
- FIG. 3 is a diagram showing the results of the demonstration experiment.
- the horizontal axis is the interval T2 between the transmitting antenna 1 and the receiving antenna 2
- the vertical axis is the isolation characteristic.
- the distance T1 between the two antennas 1 and 2 and the distance T2 between the transmitting antenna 1, the receiving antenna 2, and the reflecting member 3 are in a positional relationship in which interference between the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2 occurs. It was confirmed that a gain of about 8 to several tens dB can be gained. That is, the distance T1 between the antennas 1 and 2 and the distance T2 between the transmitting antenna 1 and the receiving antenna 2 and the reflecting member 3 are different from each other in the difference between the path T1 of the direct wave S1 and the path (T3 + T4) of the reflected wave S2. It has been proved that isolation can be ensured when the positional relationship of shifting the phase of the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2 reached (shifting the wavelength by half wavelength) is achieved.
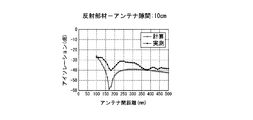
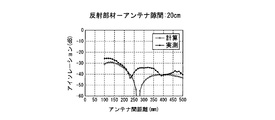
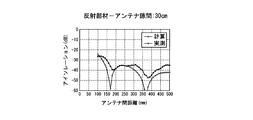
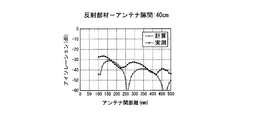
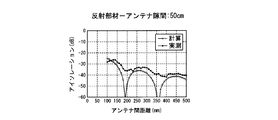
- FIGS. 4 to 9 the interval T2 between the transmitting antenna 1 and the receiving antenna 2 and the reflecting member 3 is changed stepwise to 6 cm, 10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, and 50 cm, and the transmitting antenna 1 in each case.
- the result of having confirmed the isolation characteristic by changing the distance T1 of the receiving antenna 2 is shown.
- FIGS. 4 to 9 show calculated values together with actual measured values.
- the calculation method of the calculated value will be described with reference to FIG. 2 showing the positional relationship between the transmitting antenna 1 and the receiving antenna 2 and the reflecting member 3.
- the propagation distance of the direct wave S1 is X
- the distance between the antennas is T1
- the radius of the transmission antenna 1 and the reception antenna 2 is R
- the propagation distance of the reflected wave S2 Z and the distance between the transmitting antenna 1 and the receiving antenna 2 and the reflecting member 3 is T2
- the amplitude value A 1 + cos (C Z ).
- the propagation loss of the direct wave S1 is V
- the antenna device A of the present embodiment a part of the leaked radio wave is reflected by the reflecting member so as to reach the reception antenna 2 with a phase shifted from the direct wave S1 of the leaky radio wave that reaches the reception antenna 2 directly from the transmission antenna 1.
- the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2 can be made to interfere with each other.
- the reflection member 3 is disposed so that the phase of the reflected wave S2 is shifted from the direct wave S1 without providing a radio wave shield between the transmitting antenna 1 and the receiving antenna 2 as in the conventional antenna device.
- the transmission antenna 1 and the reception antenna 2 In accordance with the distance T1 and / or the frequency of the radio wave transmitted from the transmission antenna 1, the relative position of the reflection member 3 with respect to the transmission antenna 1 and / or the reception antenna 2 is set so that the phases of the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2 are shifted. This makes it possible to ensure isolation easily and reliably.
- the transmission antenna 1 when the transmission antenna 1 has directivity for transmitting radio waves toward a predetermined range and leaks radio waves outside the predetermined range, the transmission antenna 1 When 1 is an antenna such as a helical antenna that is formed in a rod shape, transmits radio waves in a predetermined range from the end of the axis O1 direction, and leaks radio waves at the center of the axis O1, the reflection member 3 is provided. The direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2 of the leaked radio wave are caused to interfere with each other so that the interference wave can be surely attenuated.
- the reflecting member 3 is disposed so that the reflected wave S2 of the leaked radio wave is shifted by a half wavelength at the receiving antenna position with respect to the direct wave S1, the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2 are caused to interfere with each other so as to cancel each other. It is possible to eliminate an interference wave that reaches the reception antenna 2 from the transmission antenna 1 and degrades the reception characteristics of the reception antenna 2.
- the reflecting member 3 and the transmitting antenna 1 and / or the receiving antenna 2 are configured to move relative to each other, the frequency of the radio wave transmitted from the transmitting antenna 1 and the distance T1 between the transmitting antenna 1 and the receiving antenna 2 are different. Even so, depending on the distance T1 between the transmitting antenna 1 and the receiving antenna 2 and / or the frequency of the radio wave transmitted from the transmitting antenna 1, the relative position of the reflecting member 3 with respect to the transmitting antenna 1 and / or the receiving antenna 2 is It is possible to easily set the reflected wave S2 and the direct wave S1 to be out of phase.
- an antenna device A can be suitably employed in an automatic toll collection system such as ERP (Electronic Road Pricing) installed in a toll booth such as a highway.
- ERP Electronic Road Pricing
- the antenna device A of the present embodiment is provided on the roof portion of a police vehicle so that information can be exchanged with a responder mounted on another vehicle, and the contents of the license plate of the other vehicle are identified.
- the present invention can also be suitably employed for acquiring data while traveling.
- the roof portion of the vehicle may be used as the reflecting member 3.
- the present invention has been described assuming that the transmission antenna 1 and the reception antenna 2 are helical antennas, the transmission antenna and the reception antenna according to the present invention are not necessarily limited to helical antennas.
- the path T1 of the direct wave S1 that directly reaches the receiving antenna 2 from the transmitting antenna 1 and the path (T3 + T4) of the reflected wave S2 that reaches the receiving antenna 2 from the reflecting member 3 and the reflecting member 3 from the transmitting antenna 1.
- the difference is set so that the phases of the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2 are shifted by a half wavelength.
- the path difference is appropriately adjusted to shift the phases of the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2, so that the interference effect between the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2 can be sufficiently obtained.
- the path difference may be determined by the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2. If the setting is made so as to deviate by half a wavelength, the interference effect between the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2 may be reduced. Even in such a case, the direct wave S1 and the reflected wave S2 are adjusted by appropriately adjusting the path difference. It is possible to enhance the interference effect and effectively eliminate the interference wave that degrades the reception characteristics of the reception antenna 2.
- the antenna device of the present invention it is possible to obtain an interference wave attenuation effect that reaches the receiving antenna from the transmitting antenna and degrades the receiving characteristics of the receiving antenna.
Landscapes
- Details Of Aerials (AREA)
- Aerials With Secondary Devices (AREA)
- Radar Systems Or Details Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
このアンテナ装置は、受信アンテナ(2)と、送信アンテナ(1)と、主電波を送信するとともに送信アンテナ(1)から漏れ出した漏れ電波の一部を受信アンテナ(2)に向けて反射させる反射部材(3)とを備えてアンテナ装置(A)を構成する。また、反射部材(3)を、受信アンテナ(2)に直達する漏れ電波の直達波(S1)に対し、漏れ電波の一部を反射して受信アンテナ(2)に達する反射波(S2)が位相をずらして受信アンテナ(2)に達するように配設し、直達波(S1)と反射波(S2)の位相のずれによって干渉を生じさせて、送信アンテナ(1)から受信アンテナへの干渉波(直達波(S1))を減衰させるように構成する。
Description
本発明は、パッシブ型IDタグのリーダライタなどのアンテナ装置に関する。本願は、2010年9月29日に、日本国に出願された特願2010-218634号に基づき優先権を主張し、その内容をここに援用する。
例えばパッシブ型IDタグのリーダライタなどのアンテナ装置は、情報のやり取りを行うRFタグ等の応答機に電波を送信する(受信アンテナとは異なるアンテナに主電波を送信する)送信アンテナと、応答機から発信された電波を受信する受信アンテナを隣接して備え、送信アンテナで電波(主電波)を応答機に送信しつつ応答機から発信された受信電波を受信アンテナで受信し、これら送信アンテナと受信アンテナで同時に電波の送受信を行うように構成されている。
一方、この種のアンテナ装置においては、送信アンテナから漏れ出した漏れ電波の一部が直接的に、あるいは回り込んで受信アンテナで受信されてしまうと、この漏れ電波が大きなレベルの干渉波になってアンテナパターンに歪が生じ、受信アンテナの受信特性が劣化して必用利得や位相特性(アイソレーション)が確保できなくなる。そして、送信アンテナと受信アンテナの間に十分な距離を設ければ、アイソレーションを確保できるが、このように送信アンテナと受信アンテナを大きく離間させることが現実的に困難な場合が多い。
従来、送信アンテナと受信アンテナの間に電波シールドを設け、この電波シールドで漏れ電波を送信アンテナと受信アンテナ間で遮断してアイソレーションを確保することが提案、実用化されている(例えば、特許文献1、特許文献2参照)。
しかしながら、上記従来の送信アンテナと受信アンテナの間に電波シールドを設けてなるアンテナ装置においては、送信アンテナから漏れ出した漏れ電波が電波シールドを回り込んで受信アンテナに受信されてしまう可能性があった。また、送信アンテナから送信される電波(漏れ電波)の周波数や送信アンテナと受信アンテナの距離に応じて電波シールドの大きさを設定するため、送信アンテナから送信される電波の周波数や送信アンテナと受信アンテナの距離が異なるアンテナ装置毎に大きさの異なる電波シールドが必要になる。
本発明は、送信アンテナから送信される電波(漏れ電波)の周波数や送信アンテナと受信アンテナの距離が異なる場合であっても、容易に且つ確実に送信アンテナから受信アンテナに達する漏れ電波(干渉波)を減衰させてアイソレーションを確保することを可能にしたアンテナ装置を提供することを目的とする。
上記の目的を達するために、本発明は以下の手段を提供している。
本発明の第一の態様のアンテナ装置は、電波を受信する受信アンテナと、前記受信アンテナと隣接して設けられ、前記受信アンテナとは異なるアンテナに主電波を送信する送信アンテナと、前記送信アンテナから漏れ出した漏れ電波の一部を前記受信アンテナに向けて反射させる反射部材とを備える。前記反射部材は、前記受信アンテナに直達する前記漏れ電波の直達波に対し、前記漏れ電波の一部を反射して前記受信アンテナに達する反射波が位相をずらして前記受信アンテナに達するように配設され、前記直達波と前記反射波の位相のずれによって干渉を生じさせて、前記送信アンテナから前記受信アンテナに達する前記直達波を減衰させるように構成されている。
送信アンテナから受信アンテナに直達する漏れ電波の直達波に対し位相をずらして受信アンテナに達するように、漏れ電波の一部を反射部材で反射させることにより、直達波と反射波を干渉させることが可能になる。これにより、従来のアンテナ装置のように送信アンテナと受信アンテナの間に電波シールドを設けることなく、直達波に対して反射波の位相がずれるように反射部材を配設しておくことで、送信アンテナから受信アンテナに達して受信アンテナの受信特性を劣化させる干渉波(漏れ電波、直達波)の減衰効果を得ることが可能になる。
また、本発明の第二の態様のアンテナ装置は、前記送信アンテナが、所定の範囲に向けて電波を発信する指向性を有し、所定の範囲外に漏れ電波が発生するアンテナであることが望ましい。
送信アンテナが、所定の範囲に向けて電波(主電波)を発信するとともに所定の範囲外に漏れ電波が発生するアンテナである場合に、反射部材を設けることで、受信アンテナに直達する漏れ電波の直達波と反射部材で反射した漏れ電波の反射波を干渉させて、確実に送信アンテナから受信アンテナに達して受信アンテナの受信特性を劣化させる干渉波を減衰させることができる。
さらに、本発明の第三の態様のアンテナ装置において、前記送信アンテナは、棒状に形成され、軸線方向端部から前記所定の範囲に電波を送信し、軸線中心に漏れ電波が放射されるアンテナであってもよい。
送信アンテナが、例えばヘリカルアンテナなどの棒状に形成され、軸線中心に漏れ電波が放射されるアンテナである場合に、反射部材を設けることで、漏れ電波の直達波と反射波を干渉させて、より確実に干渉波を減衰させることができる。
また、本発明の第四の態様のアンテナ装置において、前記反射部材は、前記受信アンテナに達する前記反射波のうち最短伝搬行路となる反射波が前記直達波のうち最短伝搬行路となる直達波に対して前記受信アンテナ位置で半波長ずれるように配設されていることがより望ましい。
漏れ電波の反射波が直達波に対して受信アンテナ位置で半波長ずれるように反射部材が配設されているため、直達波と反射波を互いに打ち消し合うように干渉させることができ、送信アンテナから受信アンテナに達して受信アンテナの受信特性を劣化させる干渉波をなくすことが可能になる。また、このとき、送信アンテナがヘリカルアンテナなどのアンテナである場合には、軸線中心に漏れ電波が放射されるが、最短伝搬行路となる反射波が、最短伝搬行路となる直達波に対して半波長ずれるように反射部材を配設しておくことで、効果的に送信アンテナから受信アンテナに達して受信アンテナの受信特性を劣化させる干渉波をなくすことが可能になる。
さらに、本発明の第五の態様のアンテナ装置においては、前記送信アンテナと前記受信アンテナの距離及び/又は前記送信アンテナから送信される電波の周波数に応じて、前記反射部材と、前記送信アンテナ及び/又は前記受信アンテナとが相対移動するように構成されていることが望ましい。
送信アンテナから送信される電波の周波数や送信アンテナと受信アンテナの距離が異なる場合であっても、送信アンテナと受信アンテナの距離及び/又は送信アンテナから送信される電波の周波数に応じて、送信アンテナ及び/又は受信アンテナに対する反射部材の相対位置を、反射波と直達波の位相がずれるように容易に設定することが可能になる。
本発明のアンテナ装置においては、従来のアンテナ装置のように送信アンテナと受信アンテナの間に電波シールドを設けることなく、漏れ電波の直達波に対して反射波の位相がずれるように反射部材を配設しておくことにより、送信アンテナから受信アンテナに達して受信アンテナの受信特性を劣化させる干渉波の減衰効果を得ることが可能になる。
これにより、送信アンテナから送信される電波の周波数や送信アンテナと受信アンテナの距離が異なる場合であっても、送信アンテナと受信アンテナの距離及び/又は送信アンテナから送信される電波の周波数に応じて、送信アンテナ及び/又は受信アンテナに対する反射部材の相対位置を直達波と反射波の位相がずれるように設定するだけで、容易に且つ確実にアイソレーションを確保することが可能になる。
以下、図1から図9を参照し、本発明の一実施形態に係るアンテナ装置について説明する。本実施形態は、パッシブ型IDタグのリーダライタなどのアンテナ装置に関するものである。
本実施形態のアンテナ装置Aは、図1及び図2に示すように、情報のやり取りを行うRFタグ等の応答機に電波を送信する(受信アンテナ2とは異なるアンテナに主電波を送信する)送信アンテナ1と、応答機から発信された電波を受信する受信アンテナ2を隣接して備え、送信アンテナ1で電波(主電波、送信電波)を応答機に送信しつつ応答機から発信された受信電波を受信アンテナ2で受信し、これら送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2で同時に電波の送受信を行うように構成されている。また、本実施形態のアンテナ装置Aは、送信アンテナ1から電波を送信するとともに、この送信アンテナ1から漏れ出した漏れ電波の一部を受信アンテナ2に向けて反射させる反射部材3を備えて構成されている。
そして、本実施形態では、送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2が例えばヘリカルアンテナであり、これら送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2が互いの軸線O1、O2方向を同方向に向け、且つ所定の間隔T1をあけて並設されている。すなわち、本実施形態の送信アンテナ1は、所定の範囲に向けて電波を発信する指向性を有し、所定の範囲外に漏れ電波が発生するアンテナである。さらに、棒状に形成され、軸線O1方向端部から所定の範囲に電波を送信し、軸線O1中心に漏れ電波が放射されて発生するアンテナである。
また、反射部材3は、例えば反射鏡、金属板、金属シートなどである。反射部材3は、反射面3aを送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2側に向け、送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2の双方に対して所定の間隔T2をあけて配設されている。さらに、このとき、反射部材3は、送信アンテナ1から放射されて受信アンテナ2に直達する漏れ電波の直達波S1に対し、反射部材3で反射して受信アンテナ2に達する反射波S2が位相をずらして受信アンテナ2に達するように配設されている。
また、本実施形態において、反射部材3は、受信アンテナ2に達する反射波S2が直達波S1に対して受信アンテナ位置で半波長ずれるように配設されている。なお、この反射部材3は、板状に形成されていることに限定する必要はなく、電波を反射することが可能であれば、例えばメッシュ構造、グリッド構造などで構成されていてもよい。
そして、このように構成した本実施形態のアンテナ装置Aは、送信アンテナ1及び受信アンテナ2がそれぞれ、軸線O1、O2方向に指向性を有し、情報のやり取りを行うRFタグ等の応答機に送信アンテナ1から電波が送信される。また、このとき、送信アンテナ1は、軸線O1を中心とした放射方向に漏れ電波が発生する。このため、送信アンテナ1に対して所定の間隔T1をあけて隣接した受信アンテナ2に、送信アンテナ1から放射された漏れ電波(直達波S1、干渉波)が受信されてしまい、この漏れ電波が大きなレベルの干渉波になってアンテナパターンに歪が生じ、受信アンテナ2の受信特性が劣化して必用利得や位相特性(アイソレーション)が確保できなくなる可能性がある。
これに対し、本実施形態のアンテナ装置Aにおいては、反射部材3を備えているため、送信アンテナ1から放射された漏れ電波の一部が反射部材3によって反射され、この反射部材3で反射した反射波S2が受信アンテナ2に達する。また、このとき、反射部材3は、反射波S2が直達波S1に対して位相をずらして受信アンテナ2に達するように、さらに、反射波S2が直達波S1に対して受信アンテナ位置で半波長ずれるように配設されている。すなわち、送信アンテナ1から受信アンテナ2に直接達する直達波S1の行路T1と、送信アンテナ1から反射部材3、反射部材3から受信アンテナ2に達する反射波S2の行路(T3+T4)の差(行路差)が、受信アンテナ2に達する直達波S1と反射波S2の位相が半波長ずれるように設定されている。
このため、受信アンテナ2に達する直達波S1と反射波S2の位相のずれにより、直達波S1と反射波S2の干渉が起こり(直達波S1と反射波S2が互いに打ち消し合い)、直達波S1が反射波S2によって減衰される。これにより、従来のアンテナ装置のように、送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2の間に電波シールドを設けることなく、干渉波が減衰することになる。
このように受信アンテナ2に達する直達波S1と反射波S2の位相のずれにより、直達波S1と反射波S2の干渉が起こって干渉波が減衰されるため、送信電波の周波数や送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2の距離T2が異なる場合であっても、送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2の距離T1及び/又は送信アンテナ1から放射される電波の周波数に応じて、送信アンテナ1及び/又は受信アンテナ2に対する反射部材3の相対位置を、直達波S1に反射波S2が干渉して互いに打ち消し合うように設定しておくだけで、アイソレーションが確保されることになる。
そして、送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2の距離T1及び/又は送信アンテナ1から発信される電波の周波数に応じて、予め、反射部材3と、送信アンテナ1及び/又は受信アンテナ2とを相対移動できるようにアンテナ装置Aを構成しておくと、電波の周波数や送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2の距離T1が異なる場合であっても、直達波S1の行路T1と反射波S2の行路(T3+T4)の差が直達波S1と反射波S2の位相を半波長ずれるように、送信アンテナ1、受信アンテナ2、反射部材3の相対位置の設定が容易に且つ確実に行える。すなわち、送信電波の周波数や送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2の距離T1が異なる場合であっても、送信アンテナ1、受信アンテナ2、反射部材3の相対位置を可変にしておくと、容易に且つ確実にアイソレーションの確保が図れることになる。
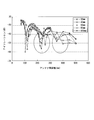
ここで、反射部材3を備えた本実施形態のアンテナ装置Aの優位性を確認した実証実験について説明する。図3は、実証実験の結果を示した図であり、送信アンテナ1及び受信アンテナ2と反射部材3との間隔T2を20mm、40mm、60mm、80mm、100mmで段階的に変化させたときのアイソレーション特性を示したものである。また、図3では、横軸を送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2の間隔T2とし、縦軸をアイソレーション特性としている。
そして、この図3から、両アンテナ1、2の間隔T1と、送信アンテナ1及び受信アンテナ2と反射部材3の間隔T2が、直達波S1と反射波S2の打ち消しの干渉が起こる位置関係になると、約8~10数dBの利得が稼げることが確認された。すなわち、両アンテナ1、2の間隔T1と、送信アンテナ1及び受信アンテナ2と反射部材3の間隔T2が、直達波S1の行路T1と反射波S2の行路(T3+T4)の差が受信アンテナ2に達した直達波S1と反射波S2の位相をずらす(波長を半波長ずらす)位置関係になると、アイソレーションを確保できることが実証された。
一方、図4~図9は、送信アンテナ1及び受信アンテナ2と反射部材3との間隔T2を6cm、10cm、20cm、30cm、40cm、50cmに段階的に変化させるとともに、各ケースで送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2の距離T1を変化させて、アイソレーション特性を確認した結果を示している。また、これら図4~図9には、実測値とともに計算値を示している。
ここで、計算値の算出方法について、送信アンテナ1及び受信アンテナ2と反射部材3の位置関係を示す図2を参照して説明する。まず、直達波S1の伝搬距離をX、アンテナ間距離をT1、送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2の半径をRとすると、直達波S1の伝搬距離Xは、X=T1-2Rとなる。さらに、反射波S2の伝搬距離をZ、送信アンテナ1及び受信アンテナ2と反射部材3の距離をT2とすると、反射波の伝達距離Zは、Z=2×(((T1/2)2+(T2+R)2)-1/2)-Rとなる。
さらに、直達波S1と反射波S2の行路差MはM=Z-Xとなり、送信アンテナ1から発信される送信電波の波長をFとして行路差Mから相対位相差Cを求めると、C=2×π×M/Fとなる。
そして、反射部材3で反射した際に位相が180度反転することから、受信側での相対位相差CZは、CZ=C+π(rad)となる。さらに、直達波S1に反射波S2が干渉した合成波の振幅値をAとすると、振幅値Aは、A=1+cos(CZ)となる。また、振幅値の対数値をBとすると、B=10×log(A)となり、さらに、直達波S1の伝搬ロスをVとすると、この伝搬ロスVは、V=20×log((4×π×(L-2R))/F)となる。
このように求めた伝搬ロスVと受信アンテナ2の横方向の指向性Pから、受信側でのアイソレーションの計算値Iは、I=B+V-Pによって求まる。
そして、このように求めた計算値と実測値を示した図4~図9からも、両アンテナ1、2の間隔T1と、送信アンテナ1及び受信アンテナ2と反射部材3の間隔T2が、直達波S1の行路T1と反射波S2の行路(T3+T4)の差が受信アンテナ2に達した直達波S1と反射波S2の位相をずらす(波長を半波長ずらす)位置関係になると、アイソレーションを確保できることが確認された。
したがって、本実施形態のアンテナ装置Aにおいては、送信アンテナ1から受信アンテナ2に直達する漏れ電波の直達波S1に対し位相をずらして受信アンテナ2に達するように、漏れ電波の一部を反射部材3で反射させることにより、直達波S1と反射波S2を干渉させることが可能になる。これにより、従来のアンテナ装置のように送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2の間に電波シールドを設けることなく、直達波S1に対して反射波S2の位相がずれるように反射部材3を配設しておくことで、送信アンテナ1から受信アンテナ2に達して受信アンテナ2の受信特性を劣化させる干渉波(漏れ電波)の減衰効果を得ることが可能になる。
よって、本実施形態のアンテナ装置Aによれば、送信アンテナ1から送信される電波の周波数や送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2の距離T1が異なる場合であっても、送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2の距離T1及び/又は送信アンテナ1から送信される電波の周波数に応じて、送信アンテナ1及び/又は受信アンテナ2に対する反射部材3の相対位置を直達波S1と反射波S2の位相がずれるように設定するだけで、容易に且つ確実にアイソレーションを確保することが可能になる。
また、本実施形態のように、送信アンテナ1が、所定の範囲に向けて電波を発信する指向性を有し、所定の範囲外に漏れ電波が発生するアンテナである場合に、さらに、送信アンテナ1が、棒状に形成され、軸線O1方向端部から所定の範囲に電波を送信し、軸線O1中心に漏れ電波が放射されるヘリカルアンテナなどのアンテナである場合に、反射部材3を設けることで、漏れ電波の直達波S1と反射波S2を干渉させて、確実に干渉波を減衰させることができる。
さらに、漏れ電波の反射波S2が直達波S1に対して受信アンテナ位置で半波長ずれるように反射部材3が配設されているため、直達波S1と反射波S2を互いに打ち消し合うように干渉させることができ、送信アンテナ1から受信アンテナ2に達して受信アンテナ2の受信特性を劣化させる干渉波をなくすことが可能になる。
また、反射部材3と、送信アンテナ1及び/又は受信アンテナ2とが相対移動するように構成すると、送信アンテナ1から送信される電波の周波数や送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2の距離T1が異なる場合であっても、送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2の距離T1及び/又は送信アンテナ1から送信される電波の周波数に応じて、送信アンテナ1及び/又は受信アンテナ2に対する反射部材3の相対位置を、反射波S2と直達波S1の位相がずれるように容易に設定することが可能になる。
そして、このようなアンテナ装置Aは、例えば高速道路等の料金所に設置されるERP(Electronic Road Pricing)などの自動料金収受システムにも好適に採用することが可能である。また、例えば警察車両のルーフ部上に本実施形態のアンテナ装置Aを設けておき、他の車両に搭載した応答機と情報のやり取りを行えるようにし、他の車両のナンバープレートの内容等の識別データを走行しながら取得することにも好適に採用することが可能である。さらに、この場合には、車両のルーフ部を反射部材3としてもよい。
以上、本発明に係るアンテナ装置の一実施形態について説明したが、本発明は上記の一実施形態に限定されるものではなく、その趣旨を逸脱しない範囲で適宜変更可能である。
例えば、本実施形態では、送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2がヘリカルアンテナであるものとして説明を行ったが、本発明に係る送信アンテナと受信アンテナは必ずしもヘリカルアンテナに限定しなくてもよい。
例えば、本実施形態では、送信アンテナ1と受信アンテナ2がヘリカルアンテナであるものとして説明を行ったが、本発明に係る送信アンテナと受信アンテナは必ずしもヘリカルアンテナに限定しなくてもよい。
また、本実施形態では、送信アンテナ1から受信アンテナ2に直接達する直達波S1の行路T1と、送信アンテナ1から反射部材3、反射部材3から受信アンテナ2に達する反射波S2の行路(T3+T4)の差(行路差)を、直達波S1と反射波S2の位相が半波長ずれるように設定するものとして説明を行った。これに対し、本発明においては、適宜前記行路差を調整して、直達波S1と反射波S2の位相をずらし、直達波S1と反射波S2の干渉効果が十分に得られるようにすればよく、必ずしも直達波S1と反射波S2の位相が半波長ずれるように前記行路差を設定することに限定しなくてもよい。特に図6、図8に示されるように反射部材3とアンテナ1、2の間隔T2、さらにアンテナ1、2の種類、形状などによっては、前記行路差を直達波S1と反射波S2の位相が半波長ずれるように設定すると、直達波S1と反射波S2の干渉効果が減少する場合もあり、このような場合においても、前記行路差を適宜調整することにより、直達波S1と反射波S2の干渉効果を高め、受信アンテナ2の受信特性を劣化させる干渉波を効果的に無くすることが可能である。
本発明のアンテナ装置によれば、送信アンテナから受信アンテナに達して受信アンテナの受信特性を劣化させる干渉波の減衰効果を得ることが可能になる。
1 送信アンテナ
2 受信アンテナ
3 反射部材
3a反射面
A アンテナ装置
O1送信アンテナの軸線
O2受信アンテナの軸線
R アンテナの半径
S1直達波
S2反射波
2 受信アンテナ
3 反射部材
3a反射面
A アンテナ装置
O1送信アンテナの軸線
O2受信アンテナの軸線
R アンテナの半径
S1直達波
S2反射波
Claims (5)
- 電波を受信する受信アンテナと、前記受信アンテナと隣接して設けられ、前記受信アンテナとは異なるアンテナに主電波を送信する送信アンテナと、前記送信アンテナから漏れ出した漏れ電波の一部を前記受信アンテナに向けて反射させる反射部材とを備え、
前記反射部材は、前記受信アンテナに直達する前記漏れ電波の直達波に対し、前記漏れ電波の一部を反射して前記受信アンテナに達する反射波が位相をずらして前記受信アンテナに達するように配設され、
前記直達波と前記反射波の位相のずれによって干渉を生じさせて、前記送信アンテナから前記受信アンテナに達する前記直達波を減衰させるように構成されているアンテナ装置。 - 前記送信アンテナが、所定の範囲に向けて電波を発信する指向性を有し、所定の範囲外に漏れ電波が発生するアンテナである請求項1記載のアンテナ装置。
- 前記送信アンテナは、棒状に形成され、軸線方向端部から前記所定の範囲に電波を送信し、軸線中心に漏れ電波が放射される請求項2記載のアンテナ装置。
- 前記反射部材は、前記受信アンテナに達する前記反射波のうち最短伝搬行路となる反射波が前記直達波のうち最短伝搬行路となる直達波に対して前記受信アンテナ位置で半波長ずれるように配設されている請求項1から請求項3のいずれかに記載のアンテナ装置。
- 前記送信アンテナと前記受信アンテナの距離及び/又は前記送信アンテナから送信される電波の周波数に応じて、前記反射部材と、前記送信アンテナ及び/又は前記受信アンテナとが相対移動するように構成されている請求項1から請求項4のいずれかに記載のアンテナ装置。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| SG2013022710A SG189121A1 (en) | 2010-09-29 | 2011-09-26 | Antenna device |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010218634A JP5619555B2 (ja) | 2010-09-29 | 2010-09-29 | アンテナ装置 |
| JP2010-218634 | 2010-09-29 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2012043442A1 true WO2012043442A1 (ja) | 2012-04-05 |
Family
ID=45892888
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2011/071824 WO2012043442A1 (ja) | 2010-09-29 | 2011-09-26 | アンテナ装置 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5619555B2 (ja) |
| SG (1) | SG189121A1 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2012043442A1 (ja) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2940907A4 (en) * | 2012-12-26 | 2016-01-06 | Huawei Tech Co Ltd | ANTENNA SYSTEM |
| CN107579351A (zh) * | 2016-07-05 | 2018-01-12 | 安普泰科电子韩国有限公司 | 天线组件 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006352871A (ja) * | 2005-06-13 | 2006-12-28 | Samsung Electronics Co Ltd | 隔離素子を含む平板型mimoアレーアンテナ |
| JP2007124235A (ja) * | 2005-10-27 | 2007-05-17 | Denso Corp | 放射ノイズの回り込み抑制方法 |
| JP2009124259A (ja) * | 2007-11-12 | 2009-06-04 | Japan Radio Co Ltd | アンテナ装置 |
| JP2010041291A (ja) * | 2008-08-04 | 2010-02-18 | Kddi Corp | 無線通信装置 |
-
2010
- 2010-09-29 JP JP2010218634A patent/JP5619555B2/ja active Active
-
2011
- 2011-09-26 SG SG2013022710A patent/SG189121A1/en unknown
- 2011-09-26 WO PCT/JP2011/071824 patent/WO2012043442A1/ja active Application Filing
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006352871A (ja) * | 2005-06-13 | 2006-12-28 | Samsung Electronics Co Ltd | 隔離素子を含む平板型mimoアレーアンテナ |
| JP2007124235A (ja) * | 2005-10-27 | 2007-05-17 | Denso Corp | 放射ノイズの回り込み抑制方法 |
| JP2009124259A (ja) * | 2007-11-12 | 2009-06-04 | Japan Radio Co Ltd | アンテナ装置 |
| JP2010041291A (ja) * | 2008-08-04 | 2010-02-18 | Kddi Corp | 無線通信装置 |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2940907A4 (en) * | 2012-12-26 | 2016-01-06 | Huawei Tech Co Ltd | ANTENNA SYSTEM |
| US9941585B2 (en) | 2012-12-26 | 2018-04-10 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Antenna system |
| CN107579351A (zh) * | 2016-07-05 | 2018-01-12 | 安普泰科电子韩国有限公司 | 天线组件 |
| TWI763682B (zh) * | 2016-07-05 | 2022-05-11 | 韓商太谷電子恩普(韓國)股份有限公司 | 天線組件 |
| CN107579351B (zh) * | 2016-07-05 | 2023-04-18 | 安普泰科电子韩国有限公司 | 天线组件 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5619555B2 (ja) | 2014-11-05 |
| JP2012073853A (ja) | 2012-04-12 |
| SG189121A1 (en) | 2013-05-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2017146163A1 (ja) | アンテナ装置 | |
| EP2522051B1 (en) | Antenna beam control elements, systems, architectures, and methods for radar, communications, and other applications | |
| JP5135317B2 (ja) | 車載レーダ装置、及びプログラム | |
| KR100441146B1 (ko) | 이동통신 서비스용 중계기의 노치형 안테나 | |
| CA2751283A1 (en) | Radio frequency positioning system for vehicles | |
| KR20190058072A (ko) | 차량용 레이더 장치 | |
| JP5574446B2 (ja) | アンテナ反射器 | |
| JP2007057483A (ja) | ミリ波レーダ装置 | |
| JP5619555B2 (ja) | アンテナ装置 | |
| JP2012215455A (ja) | 広覆域レーダ装置 | |
| CN102208717B (zh) | 平面双向辐射天线 | |
| JP6173242B2 (ja) | 探知妨害装置 | |
| JP3884772B2 (ja) | 偏平状のアンテナを自動車のウィンドウの内側に取り付けるためのアンテナ装置 | |
| JP2018121127A (ja) | 無線装置 | |
| JP4246051B2 (ja) | レーダ装置 | |
| JPH06294834A (ja) | 自動車アンテナの感度測定方法 | |
| US7365702B2 (en) | Antenna device | |
| JPH10108251A (ja) | 路車間通信システムにおける電波遮蔽回避方式 | |
| JP5249959B2 (ja) | マルチパス低減装置 | |
| US9543659B2 (en) | Reflector antenna device | |
| JP5893680B2 (ja) | 無線通信方法および無線通信システム | |
| JP2021148529A (ja) | レーダシステムの試験設備 | |
| KR200284309Y1 (ko) | 이동통신 서비스용 중계기의 노치형 안테나 | |
| JP3772191B2 (ja) | 電波反射体を用いた測定装置 | |
| JPH08105953A (ja) | レーダ装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 11828996 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 11828996 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |