WO2010032483A1 - 電化製品の種別を決定する情報処理装置、方法、サーバ - Google Patents
電化製品の種別を決定する情報処理装置、方法、サーバ Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2010032483A1 WO2010032483A1 PCT/JP2009/004750 JP2009004750W WO2010032483A1 WO 2010032483 A1 WO2010032483 A1 WO 2010032483A1 JP 2009004750 W JP2009004750 W JP 2009004750W WO 2010032483 A1 WO2010032483 A1 WO 2010032483A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- electrical appliance
- appliance
- definition file
- packet
- information processing
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L12/00—Data switching networks
- H04L12/28—Data switching networks characterised by path configuration, e.g. LAN [Local Area Networks] or WAN [Wide Area Networks]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L12/00—Data switching networks
- H04L12/28—Data switching networks characterised by path configuration, e.g. LAN [Local Area Networks] or WAN [Wide Area Networks]
- H04L12/2803—Home automation networks
- H04L12/2807—Exchanging configuration information on appliance services in a home automation network
- H04L12/2809—Exchanging configuration information on appliance services in a home automation network indicating that an appliance service is present in a home automation network
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L12/00—Data switching networks
- H04L12/28—Data switching networks characterised by path configuration, e.g. LAN [Local Area Networks] or WAN [Wide Area Networks]
- H04L12/2803—Home automation networks
- H04L12/2807—Exchanging configuration information on appliance services in a home automation network
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/34—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications involving the movement of software or configuration parameters
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L12/00—Data switching networks
- H04L12/28—Data switching networks characterised by path configuration, e.g. LAN [Local Area Networks] or WAN [Wide Area Networks]
- H04L12/2803—Home automation networks
- H04L2012/2847—Home automation networks characterised by the type of home appliance used
- H04L2012/2849—Audio/video appliances
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L12/00—Data switching networks
- H04L12/28—Data switching networks characterised by path configuration, e.g. LAN [Local Area Networks] or WAN [Wide Area Networks]
- H04L12/2803—Home automation networks
- H04L2012/2847—Home automation networks characterised by the type of home appliance used
- H04L2012/285—Generic home appliances, e.g. refrigerators
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an information processing apparatus, method, and server for determining the type of electrical appliance.
- Patent Document 1 a method of managing home appliances in the home by subscribing to a support service via the Internet is also disclosed (for example, Patent Document 1).
- Patent Document 1 it is necessary to subscribe to a support service via the Internet, and the user can easily obtain information about the appliance owned by the user without knowing it by others. It cannot be managed.
- An object of the present invention is to provide an information processing apparatus, method, and server that perform device identification of electrical appliances connected to a network.
- the present invention provides the following solutions.
- An information processing apparatus in which electrical appliances are communicably connected, Request packet transmitting means for transmitting a predetermined request packet to the electrical appliance; Response packet receiving means for receiving a response packet for determining the type of the electrical appliance from the electrical appliance that transmitted the request packet; Storage means for storing a definition file defined for each electrical appliance; Comparing the response packet and the definition file for each electrical appliance, and scoring means for scoring; A definition file having a high score of the scoring means, and electrical appliance type determination means for making electrical appliance information of the definition file electrical appliance information of the electrical appliance; An information processing apparatus comprising:
- the information processing apparatus transmits a predetermined request packet to the electrical appliance, and receives a response packet for determining the type of the electrical appliance from the electrical appliance that transmitted the request packet.
- the definition file stored in advance and the response packet are compared and scored (scoring). Then, a definition file with a high score is extracted, and the appliance type is determined using the appliance information of the definition file as the appliance information of the appliance.
- the request packet transmitting unit and the response packet receiving unit transmit and receive a plurality of packets between the electrical appliance and the information processing device,
- the information processing apparatus according to (1), wherein the electrical appliance type determination unit extracts a definition file having a high score at a total score of a plurality of packets.
- the type of appliance (electric appliance information) is specified at the total point of a plurality of packets. Can be raised. For example, even if the appliance name of the electrical appliance is unknown, it is possible to specify the electrical appliance information in stages so that the manufacturer name of the electrical appliance can be identified.
- scoring is performed based on the similarity between the response packet and the definition file. Therefore, even if the response packet and the definition file are not completely the same, the scoring is performed, and the device name of the electrical appliance, etc. Can be specified up to a certain range. For example, even if an appliance has no definition file due to a new product, it is possible to specify the appliance information from this similarity using the definition file of an existing product where the definition file exists.
- the request packet transmission means periodically detects the appliance connected to be communicable at a predetermined timing by transmitting a request packet to the appliance (1) to ( The information processing apparatus according to any one of 3).
- the information processing apparatus periodically transmits a request packet to the electrical appliance. Therefore, when the user connects a new electrical appliance, the information processing apparatus is newly connected.
- the received appliance receives the transmitted request packet and is automatically detected. For this reason, as long as the user is connected to the network, information on the electrical appliance (electric appliance information) can be obtained, and management becomes easy.
- a method comprising:
- the information processing apparatus transmits a predetermined request packet to the electrical appliance, and receives a response packet for determining the type of the electrical appliance from the electrical appliance that transmitted the request packet.
- the definition file stored in advance and the response packet are compared and scored (scoring). Then, a definition file with a high score is extracted, and the appliance type is determined using the appliance information of the definition file as the appliance information of the appliance.
- the request packet and the response packet are transmitted and received between the electrical appliance and the information processing apparatus, The method according to (5), wherein, in the step of setting the electrical appliance information, a definition file having a high score is extracted from a total score of a plurality of packets.
- the type of appliance (electric appliance information) is specified at the total point of a plurality of packets. Can be raised. For example, even if the appliance name of the electrical appliance is unknown, it is possible to specify the electrical appliance information in stages so that the manufacturer name of the electrical appliance can be identified.
- the response packet and the definition file for each appliance are compared, and the score is scored according to the similarity between the response packet and the definition file (5) or (6) Method.
- points are scored based on the similarity between the response packet and the definition file. Can be specified up to a certain range. For example, even if an appliance has no definition file due to a new product, it is possible to specify the appliance information from this similarity using the definition file of an existing product where the definition file exists.
- the appliance connected to be communicable is detected at a predetermined timing (5) To (7).
- the information processing apparatus periodically transmits a request packet to the electrical appliance. Therefore, when the user connects a new electrical appliance, the information processing apparatus is newly connected.
- the received appliance receives the transmitted request packet and is automatically detected. For this reason, as long as the user is connected to the network, information on the electrical appliance (electric appliance information) can be obtained, and management becomes easy.
- An electrical appliance type determination system including an information processing device to which an electrical appliance is communicably connected and a device recognition server connected to be communicable with the information processing device,
- the information processing apparatus includes: Packet receiving means for receiving a packet for determining the type of the electrical appliance from the electrical appliance; Type information requesting means for requesting information on the type of the electrical appliance by transmitting the packet to the device recognition server,
- the device recognition server is Storage means for storing a definition file defined for each electrical appliance; In response to a request from the information processing device, the packet and the definition file for each appliance are compared and scored, As a result of the scoring means, a definition file having a high score is extracted, and electrical appliance information of the definition file is transmitted to the information processing apparatus as electrical appliance information of the electrical appliance;
- An appliance type determination system comprising:
- the invention of (9) relates to the type of the electrical appliance by receiving a packet for determining the type of the electrical appliance from the electrical appliance and transmitting the received packet to the device recognition server.
- Request information In response to a request from the information processing apparatus, the device recognition server compares the packet and the definition file for each electrical appliance, scores, and extracts a definition file having a high score as a result of the scoring means, and the definition file
- the appliance information is determined as the appliance information of the appliance and is transmitted to the information processing apparatus.
- the invention of (9) it is possible to automatically specify the type of appliances connected so as to be communicable (such as a device name specifying the type of appliance) without involving the user.
- the device recognition server determines the appliance information, even if the definition file is newly updated, only the device recognition server database needs to be updated. There is no need to update the file. As a result, it is possible to centralize management of information for determining the type of electrical appliance. Since the definition file is updated each time the type of appliance is increased, the convenience is greatly enhanced by the unification.
- An appliance recognition server that is communicably connected to an information processing apparatus that is communicably connected to an electrical appliance, Receiving means for receiving a predetermined packet transmitted from the electrical appliance from the information processing apparatus; Storage means for storing a definition file defined for each electrical appliance; In response to a request from the information processing device, the predetermined packet and a definition file for each electrical appliance are compared and scored for scoring, As a result of the scoring means, a definition file with a high score is extracted, and electrical appliance information in the definition file is transmitted to the information processing apparatus as electrical appliance information of the electrical appliance.
- a device recognition server comprising:
- the invention of (10) it is possible to automatically specify the type of appliances connected so as to be communicable (such as a device name that specifies the type of appliance) without involving the user.
- the device recognition server determines the appliance information, even if the definition file is newly updated, only the device recognition server database needs to be updated. There is no need to update the file. As a result, it is possible to centralize management of information for determining the type of electrical appliance. Since the definition file is updated each time the type of appliance is increased, the convenience is greatly enhanced by the unification.
- the information processing apparatus is A response packet receiving step for receiving a packet for determining the type of the appliance from the appliance;
- the device recognition server is A storage step of storing a definition file defined for each electric appliance;
- the packet and the definition file for each electric appliance are compared and scored, As a result of the scoring step, a definition file having a high score is extracted, and electrical appliance information of the definition file is transmitted to the information processing apparatus as electrical appliance information of the electrical appliance. How to perform.
- the invention of (11) it is possible to automatically specify the type of electric appliances connected so as to be communicable (such as a device name specifying the type of electric appliance) without involving the user.
- the device recognition server determines the appliance information, even if the definition file is newly updated, only the device recognition server database needs to be updated. There is no need to update the file. As a result, it is possible to centralize management of information for determining the type of electrical appliance. Since the definition file is updated each time the type of appliance is increased, the convenience is greatly enhanced by the unification.
- An information processing apparatus in which electrical appliances are communicably connected, Packet receiving means for receiving from the appliance a broadcast packet or a multicast packet for determining a type of the appliance; Storage means for storing a definition file defined for each electrical appliance; A scoring means for comparing and scoring the definition file for each packet and the appliance; A definition file having a high score of the scoring means, and electrical appliance type determination means for making electrical appliance information of the definition file electrical appliance information of the electrical appliance;
- the information processing apparatus receives a broadcast packet or a multicast packet from an electrical appliance, compares the definition file stored in advance with the received packet, and scores ( Scoring). Then, a definition file with a high score is extracted, and the appliance type is determined using the appliance information of the definition file as the appliance information of the appliance.
- the information processing apparatus does not transmit a packet such as a request packet, but determines the type of electrical appliance by a broadcast packet or a multicast packet that is a passive packet. Is possible.
- a method executed by an information processing apparatus to which an electrical appliance is communicably connected Receiving from the appliance a broadcast packet or a multicast packet for determining the type of the appliance; Storing a definition file defined for each electrical appliance; Comparing the packet and the definition file for each appliance and scoring; Extracting a definition file having a high score in the step of scoring, and setting the appliance information of the definition file as appliance information of the appliance;
- a method comprising:
- the information processing apparatus receives a broadcast packet or a multicast packet from the electrical appliance, compares the definition file stored in advance with the received packet, and scores ( Scoring). Then, a definition file with a high score is extracted, and the appliance type is determined using the appliance information of the definition file as the appliance information of the appliance.
- the information processing apparatus does not transmit a packet such as a request packet, but determines the type of electrical appliance by a broadcast packet or a multicast packet that is a passive packet. Is possible.
- An appliance recognition server that is communicably connected to an information processing apparatus that is communicably connected to an electrical appliance, Receiving means for receiving from the information processing device a broadcast packet or multicast packet received from the electrical appliance for determining the type of the electrical appliance; Storage means for storing a definition file defined for each electrical appliance; In response to a request from the information processing device, the packet and the definition file for each appliance are compared and scored, An appliance that extracts a definition file having a high score as a result of the scoring means, and transmits the appliance information to the information processing apparatus as appliance information of the appliance as the appliance information of the appliance Type determination means;
- a device recognition server comprising:
- the invention of (14) it is possible to automatically specify the type of electric appliances connected so as to be communicable (such as a device name specifying the type of electric appliance) without involving the user.
- the device recognition server determines the appliance information, even if the definition file is newly updated, only the device recognition server database needs to be updated. There is no need to update the file. As a result, it is possible to centralize management of information for determining the type of electrical appliance. Since the definition file is updated each time the type of appliance is increased, the convenience is greatly enhanced by the unification.
- an information processing apparatus, method, and server for identifying a device connected to a network. Furthermore, it is possible to automatically detect an appliance connected so as to be communicable, and to specify information regarding the appliance device in a stepwise manner by scoring.
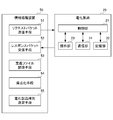
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing the overall configuration of the network system 1.
- FIG. 2 is a functional block diagram of the information processing apparatus 50 and the appliance 20.
- FIG. 3 is a flowchart of the type determination process.
- FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating an example of a MAC address.
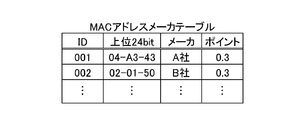
- FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating an example of the MAC address maker table.
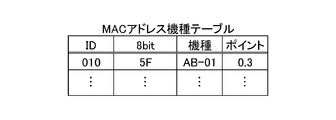
- FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating an example of the MAC address model table.
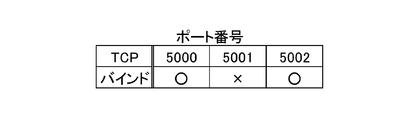
- FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating an example of a port number.
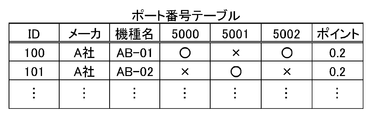
- FIG. 8 is a diagram illustrating an example of a port number table.
- FIG. 9 is a conceptual diagram illustrating an example of a scoring process and a process for specifying an electrical appliance.
- FIG. 9 is a conceptual diagram illustrating an example of a scoring process and a process for specifying an electrical appliance.
- FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating an example of a screen image displayed on the display device 360.
- FIG. 11 is a diagram illustrating an example of a hardware configuration of the information processing apparatus 50.
- FIG. 12 is a diagram illustrating an example of the electrical appliance type determination system 5 according to the second embodiment.
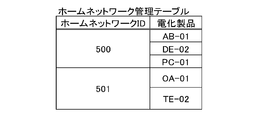
- FIG. 13 is a diagram illustrating an example of a home network management table according to the second embodiment.
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing the overall configuration of the network system 1.
- the network system 1 is a home network or office network system (local network), and includes an information processing apparatus 50, electrical appliances 20-a, 20-b, and 20-c, and a network 2.
- the information processing apparatus 50 is communicably connected to the appliances 20-a, 20-b, and 20-c via a network 2 such as a wired / wireless LAN.
- the electrical appliances 20-a, 20-b, and 20-c are electrical appliances having a network connection function.
- the recording media recording / reproducing device 20-a DVD, HD recording / reproducing device
- the telephone 20-b In addition to the computer 20-c, a refrigerator, an audio, a washing machine, a router, a television, a printer, and a multifunction machine are included.
- These electrical appliances 20-a, 20-b, and 20-c have a function of communicating with the information processing apparatus 50 through a network 1 using a protocol such as TCP / IP.
- FIG. 2 is a functional block diagram of the information processing apparatus 50 and the electrical appliance 20.
- the information processing apparatus 50 includes a request packet transmission unit 51, a response packet reception unit 52, a definition file storage unit 53, a scoring unit 54, and an electrical appliance type determination unit 55.
- the information processing apparatus 50 is an information device including the control unit 10 and the main memory 340, and may be a computer or a router. Each of the above means is implemented by a program that realizes this being read into the main memory 340 and executed by the control unit 10.
- the information processing apparatus 50 may be a dedicated information device provided with the above means, or may be an information device having other functions such as a personal computer.
- the request packet transmission unit 51 has a function of transmitting a request packet described later, and is realized by the communication I / F 330 and the control unit 10.
- the response packet receiving unit 52 has a function of receiving a response packet to be described later, and is realized by the communication I / F 330 and the control unit 10.
- the definition file storage unit 53 has a function of storing a definition file described later, and is realized by the hard disk 390, the main memory 340, and the like.
- the scoring means 54 has a function of scoring each definition file based on the definition file, and is realized by the control unit 10, the hard disk 390, the main memory 340, and the like.
- the appliance type determining means 55 has a function of finally determining the type of appliance, and is realized by the control unit 10, the hard disk 390, the main memory 340, and the like.
- the electrical appliance 20 includes at least a control unit 21 realized by a CPU, a communication unit 24 realized by a communication I / F, and a storage unit 22 realized by a hard disk and a main memory, and an input device such as a mouse.
- the operation unit 23 may be provided.
- FIG. 3 is a flowchart of the type determination process.
- the request packet transmission unit 51 of the information processing apparatus 50 transmits a request packet to the electrical appliance 20 (step S10).
- the request packet is packet data transmitted from the information processing apparatus 50 to the electrical appliance 20 in order to receive a response packet for determining the type of the electrical appliance 20.
- the request packet may be, for example, a command such as ARP (Address Resolution Protocol), ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), or SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), and uPnP (UniversalPlD). ) May be a compliant protocol.
- ARP Address Resolution Protocol
- ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol
- SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
- uPnP UniversalPlD
- the request packet transmission means 51 may be a mode in which a request packet is periodically transmitted to the electrical appliance 20. That is, the request packet transmission means 51 transmits the request packet every tens of seconds, every few minutes, or every several hours, thereby detecting the appliance 20 connected so as to be communicable at a predetermined timing.
- the information processing apparatus 50 when a new electrical appliance 20 is connected to the network system 1, the information processing apparatus 50 periodically transmits a request packet at a predetermined timing in order to detect the electrical appliance 20. According to this, since the information processing apparatus 50 can obtain information about the electrical appliance 20 when the user connects a new electrical appliance 20, the management of the electrical appliance 20 in the network system 1 is easy. It becomes.
- Electrical appliance information is information relating to electrical appliances, and is information including at least the type of electrical appliance (manufacturer name, device name, etc. for identifying the type of electrical appliance).
- the response packet receiving unit 52 of the information processing apparatus 50 receives a response packet from the predetermined electrical appliance 20 (step S11).
- the response packet is a packet data transmitted from the electrical appliance 20, and is packet data for determining the type of the electrical appliance 20 or as a clue for determining the type of the electrical appliance 20.
- the response packet is a response packet transmitted from the electrical appliance 20 that has received the request packet transmitted from the information processing apparatus 50.
- the third embodiment a case where the response packet is not a response packet of the request packet will be described.
- the information processing apparatus 50 performs definition file reference processing (step S12).
- the control unit 10 of the information processing apparatus 50 refers to and compares the definition file stored in the definition file storage unit 53 and performs the next scoring process (step S13).
- the definition file is data predetermined for each electrical appliance 20 and is necessary for specifying the type of the electrical appliance 20.
- the definition file (electrical appliance A definition file) is composed of one or more definition items (X5, Y2, Z3). 20 (electric appliance A in this case) is specified.
- the definition item is definition data for specifying the type of the electrical appliance 20 with one request packet and response packet.
- the scoring means 54 of the information processing apparatus 50 compares the definition file with the response packet to score (score) (step S13).
- the information processing apparatus 50 transmits one or more request packets (A1, B1, C1), and receives response packets (X5, Y8, Z9) corresponding thereto.
- the information processing apparatus 50 refers to the definition items stored in the definition file storage unit 53 for each electrical appliance definition file (electrical appliance A definition file, electrical appliance B definition file, electrical appliance C definition file), Compare with response packet.
- the MAC address is composed of a 48-bit code, the upper 24 bits are assigned as a vendor ID, a vendor-specific ID is given, and the next 8 bits is a model ID.
- the definition file storage means 53 may store a table for configuring a definition file for each electrical appliance.
- a table for configuring a definition file for each electrical appliance For example, as shown in FIG. 5, as the MAC address manufacturer table, the code of the upper 24 bits and the manufacturer name of the electrical appliance 20 (not necessarily the vendor name of the manufacturer but the entire electrical appliance 20 having the communication I / F). Vendor (manufacturer) name), points for scoring, and ID are associated with each other.
- FIG. 6 as the MAC address model table, the upper 24 bits code, the model name of the electrical appliance 20, the points for scoring, and the ID are associated with each other.
- the electrical appliance 20 Upon receiving the A1 packet transmitted as the request packet, the electrical appliance 20 transmits a response packet.
- the response packet (X5) is compared with the definition items in the definition file of the electrical appliance A. If they are the same, points are given with reference to each table.
- the response packet X5 is a packet including information on the target MAC address and the 48-bit code is “04-A3-43-5F-43-23” will be described. Since the upper 24 bits are the same as the definition item X5 (ID001), 0.3 points are given. Further, in the next 8 bits, since it is the same as the definition item (ID010), 0.3 points are given. Therefore, the electric appliance A definition file can obtain a total of 0.6 points.
- one request packet (A1) is scored for two definition items (ID001, ID010) by a response packet (X5).
- a plurality of definition items may be scored from the packet.
- the information processing apparatus 50 compares the response packet Y8 with Y2 of the appliance A definition file and compares the response packet Z9 with Z3 of the appliance A definition file to obtain each point (FIG. 9).
- the total score of the electrical appliance A definition file is the sum of all the points thus obtained. For this, an overall score is obtained for the definition file for each electrical appliance, such as the electrical appliance A definition file, the electrical appliance B definition file, the electrical appliance C definition file,.
- the information processing apparatus 50 receives a plurality of response packets from the electrical appliance 20 by transmitting a plurality of types of request packets.
- the electrical appliance type determining means 55 of the information processing apparatus 50 determines the type of the electrical appliance 20 (device) (step S14). That is, scoring as described above is performed on the definition files of all electrical appliances, and the types of electrical appliances 20 are determined by comparing the acquired scores and extracting a definition file with a high score.
- the overall score is obtained for the definition file for each electrical appliance, such as the electrical appliance A definition file, the electrical appliance B definition file, the electrical appliance C definition file, and the highest score.
- the definition file of the high electrical appliance is extracted to identify the electrical appliance 20.
- the appliance A definition file has 0.6.
- each definition item (X1, Y7, Z1) of the appliance B definition file is not the same as the response packet (X5, Y8, Z9).
- the electrical appliance C definition file (X5, Y8, Z8) and the response packet (X5, Y8, Z9) and the definition item Y8 are the same, 0.9 points were acquired in the electrical appliance A definition file. And In this case, among the definition files for the appliances A to C, the definition file for the appliance C is determined to be the highest overall point (0.9 points), and the definition file C is extracted. Is determined to be appliance C.
- the appliance A definition file is defined as a definition file up to the manufacturer name A
- the appliance B definition file is one of the types of devices in addition to the manufacturer name A (AB-01).
- the definition file can be specified up to.
- the electric appliance 20 is determined to be the electric appliance B (AB-01 of company A) that has a high overall score.
- the electrical appliance X has port numbers 5000 and 5002 in use and 5001 is not in use. For example, this status is detected by a NETSTAT command. Then, as shown in FIG. 8, the port number table stored in the definition file storage means 53 is referred to, and the port numbers in use (bind) are compared to determine the identity with the definition item of ID100. And give points. Port numbers 5000 and 5002 are in use, and if number 5001 is not used, 0.2 points are given.
- the NETSTAT command may transmit a packet to the partner electrical appliance 20 as a request packet.
- the information processing apparatus 50 is an electrical appliance. 20, broadcast or multicast packets may be received in advance, and NETSTAT command results may be obtained using these received packets.
- the scoring process may be performed on the basis of a packet for notifying the binding state of the above.
- points are assigned not only when the port numbers in the port number table and the binding status are completely the same, but also what percentage of existing ports are in use and what percentage is not in use.
- the points may be given according to the degree of use (the degree of use is not completely the same but is similar). For example, it is assumed that the usage degree of a port and points are stored in advance as a table. In this case, port numbers 5000 and 5002 are in use, and when port 5001 is not in use, 66% of the ports are in use. Therefore, when 66% of the ports are in use, the processing is such that a predetermined point is given with reference to the table.
- the OS (Operating System) version may be fixed and point grant may be executed.
- an nbns (Net BIOS Name Server) packet is received as a response packet transmitted in broadcast, OS version information is acquired, and the OS is identified based on this. Then, points may be given based on the identified version of the OS.
- FIG. 10 shows electrical appliance information (manufacturer name) of electrical appliances 20-b, 20-d, 20-e, and 20-f connected to the network system 1 when the information processing apparatus 50 includes the display device 360.
- Device name is displayed with an icon, but is a screen image diagram.
- the appliance information may be displayed on this screen in real time.
- the electrical appliance 20 when the electrical appliance 20 is specified, information on the corresponding electrical appliance 20 may be displayed. That is, as the electrical appliance information, in addition to the manufacturer name and the device name, the electrical appliance manufacturer homepage stored in advance associated with the information processing apparatus 50 may be displayed near the manufacturer name and the device name.
- FIG. 11 is a diagram illustrating a hardware configuration of the information processing apparatus 50.
- the server in which the present invention is implemented may be a standard server, and an example of the configuration is shown below.
- the information processing apparatus 50 includes a CPU 310 (a plurality of CPUs such as a CPU 320 may be added in a multiprocessor configuration), a bus line 490, a communication I / F (I / F: interface) 330, a main memory, and the like. 340, a basic input output system (BIOS) 350, a display device 360, an I / O controller 370, an input device 380 such as a keyboard and a mouse, a hard disk 390, an optical disk drive 400, and a semiconductor memory 420.
- the hard disk 390, the optical disk drive 400, and the semiconductor memory 420 are collectively referred to as the storage unit 120.
- the control unit 10 is a part that controls the information processing apparatus 50 in an integrated manner, and by reading and executing various programs stored in the hard disk 390 as appropriate, the control unit 10 cooperates with the hardware described above, and performs various types according to the present invention. The function is realized.
- the communication I / F 330 is a network adapter when the information processing apparatus 50 transmits / receives information and data to / from the electrical appliance 20 via the network 1 described above.
- the communication I / F 330 may include a modem, a cable modem, and an Ethernet (registered trademark) adapter.
- the BIOS 350 records a boot program executed by the CPU 310 when the information processing apparatus 50 is started up, a program depending on the hardware of the information processing apparatus 50, and the like.
- Display device 360 includes a display device such as a cathode ray tube display device (CRT) or a liquid crystal display device (LCD).
- CTR cathode ray tube display device
- LCD liquid crystal display device
- the storage unit 120 which is a storage device such as the hard disk 390, the optical disk drive 400, and the semiconductor memory 420 can be connected to the I / O controller 370.
- the input device 380 is for accepting input by the administrator of the information processing device 50.
- the hard disk 390 stores various programs for causing the hardware to function as the information processing apparatus 50, programs for executing the functions of the invention, and tables and records to be described later.
- the information processing apparatus 50 can also use a hard disk (not shown) separately provided as an external storage device.
- optical disk drive 400 for example, a DVD-ROM drive, a CD-ROM drive, a DVD-RAM drive, or a CD-RAM drive can be used.
- the optical disk 410 corresponding to each drive is used.
- a program or data may be read from the optical disk 410 by the optical disk drive 400 and provided to the main memory 340 or the hard disk 390 via the I / O controller 370.
- the computer in the present invention refers to an information processing device including a storage device, a control unit, and the like.
- the information processing device 50 includes an information processing device including the control unit 10, the storage unit 120, and the like.
- the information processing apparatus is included in the concept of the computer of the present invention.
- the information processing apparatus 50 has described an embodiment in which the type of the electrical appliance 20 is determined.
- the present invention is not limited to this, and the type of the electrical appliance 20 is recognized as a device connected via a public line.
- the mode determined by the server 500 will be described below as a second embodiment.
- the electrical appliance type determination system 5 includes an information processing device 20, an electrical appliance 20, and a device recognition server 500.
- the electrical appliance 20 and the information processing apparatus are communicably connected via a local network (home network), and the device recognition server 500 is communicably connected via a public line (such as the Internet). ing.
- the information processing apparatus 50 includes a request packet transmission unit 51, a response packet reception unit 52, an electrical appliance type information request unit 56, and an electrical appliance type information reception unit 57.
- the hardware configuration of the information processing apparatus 50 is the same as that of the first embodiment.
- the information processing apparatus 50 can be operated on, for example, a device on which a Java (registered trademark) VM (Java (registered trademark) Virtual Machine) and an OSGi (Open Services Gateway Initiative) framework operate.
- the request packet transmission unit 51 has a function of transmitting a request packet to the electrical appliance 20, and is realized by the communication I / F 330 (see FIG. 11) and the control unit 10.
- the response packet receiving unit 52 has a function of receiving a response packet from the electrical appliance 20 and is realized by the communication I / F 330 and the control unit 10.
- the appliance type information requesting unit 56 has a function of requesting information (electric appliance information) for specifying the appliance type from the device recognition server 500, and is realized by the communication I / F 330 and the control unit 10. . Specifically, a request packet transmitted from the information processing apparatus 50 to the electrical appliance 20 and a response packet responded by the electrical appliance 20 are transmitted to the device recognition server 500 to request electrical appliance information.
- the electrical appliance type information receiving unit 57 has a function of receiving information (electrical product information) specifying the electrical appliance type specified by the device recognition server 500, and is realized by the communication I / F 330 and the control unit 10.
- the device recognition server 500 includes a request receiving unit 501 that receives a request from the information processing apparatus 50, a scoring unit 502, a definition file database 503, and an appliance type determination unit 504.
- the device recognition server 500 is a computer, and the basic configuration of hardware may be the same as that of the information processing apparatus 50.
- the request reception unit 501 has a function of receiving a request for electrical appliance information from the information processing apparatus 50, and is realized by a control unit and a communication I / F. Specifically, a request packet transmitted from the information processing device 50 to the electrical appliance 20 and a response packet to which the electrical appliance 20 responds are received from the information processing device 50, and the scoring unit 502 is prompted to process. .
- the scoring unit 502 has a function of scoring each definition file based on the definition file, and is realized by a control unit and a hard disk. This function is the same as in the first embodiment.
- the definition file database (definition file storage means) 503 has a database function for storing a definition file to be described later, and is realized by a control unit and a hard disk. This function is the same as the definition file storage unit of the first embodiment. However, since the definition file database 503 is a dedicated server, the definition file can be handled rather than managed by the information processing apparatus 50. It is possible to increase the amount of data. Note that SQL may be used as the database language.
- the electrical appliance type determining means 55 has a function of finally determining the type of electrical appliance and transmitting it to the information processing apparatus 50, and is realized by a control unit and a hard disk. This function is the same as that of the first embodiment except for the function of transmitting appliance information, which is information about the finally determined type of appliance, to the information processing apparatus 50.
- the electrical appliance 20 has the same functional configuration as that of the first embodiment.
- the electrical appliance type determination system 5 including the information processing device 50 to which the electrical appliance 20 is communicably connected and the device recognition server 500 that is communicably connected to the information processing device 50 executes the following.
- the information processing apparatus 50 transmits a request packet transmission step for transmitting a predetermined request packet to the electrical appliance 20, and a response packet for determining the type of the electrical appliance 20 from the electrical appliance 20 that transmitted the request packet.
- the received response packet receiving step and the type information requesting step for requesting information on the type of the electrical appliance 20 by transmitting the response packet to the device recognition server 500 are executed.
- the device recognition server 500 stores the definition file determined for each electrical appliance 20 and the response packet and the definition file for each electrical appliance 20 in response to a request from the information processing apparatus 50.
- a scoring step for comparing and scoring a definition file with a high score by the scoring step is extracted, and the appliance information of the definition file is used as the appliance information of the appliance 20, and the appliance information is sent to the information processing device 50.
- the device recognition server 500 determines the appliance information, even if the definition file is newly updated, only the definition file database 503 of the device recognition server 500 needs to be updated. There is no need to update.
- the device recognition server 500 may store and manage the type of the electrical appliance 20 for each information processing apparatus 50.
- the device recognition server 500 stores a home network management table as shown in FIG. 13 in the database of the device recognition server 500, and stores and manages the appliance information acquired from the information processing apparatus 50 for each home network.
- the home network ID is one ID managed for each home network, and one corresponding home network ID may be given to one information processing apparatus 50.
- AB-01, DE-02, and PC-01 are detected as the electrical appliance 20, and are registered in the device recognition server 500.
- the appliances for each home network are stored in the device recognition server 500, so that the appliance recognition server 500 can manage the appliances 20 for each home network.
- the information processing apparatus 50 does not transmit the request packet to the electrical appliance 20 (the information processing apparatus 50 does not include the request packet transmission unit 51), and the type determination process (steps S11 to S14). It is embodiment which performs.
- the broadcast packet and the multicast packet (passive packet) transmitted from the electrical appliance 20 to the information processing apparatus 50 at a predetermined timing are processed as (response) packets.
- the information processing apparatus 50 When determining the type of the electrical appliance 20, the information processing apparatus 50 receives a broadcast or multicast packet from the electrical appliance 20 without transmitting a request packet to the electrical appliance 20, and based on these packets Then, the scoring process is performed with reference to the definition file to determine the type of the electrical appliance 20 (steps S12 to S14 of the type determination process in FIG. 3).
- Broadcast packets are data packets that are sent to all terminals on the network at the same time.
- a multicast packet is a data packet that is transmitted to a plurality of predetermined terminals on the network simultaneously, but not to all terminals, like a broadcast packet.
- an nbns packet that is a passive packet is received, OS version information is acquired, the OS is identified based on the OS version information, and points may be awarded based on the identified OS version.
- OS version information is acquired, the OS is identified based on the OS version information, and points may be awarded based on the identified OS version.
- points may be awarded based on the identified OS version.
- the definition file of the electrical appliance AB-01 it is assumed that “if the OS version is“ X type ”is used, 0.5 is added as a point” is registered as a definition item. At this time, if the OS version is specified as “X type” by the nbns packet, 0.5 is added to the point of the electrical appliance AB-01.
- the information processing apparatus 50 may identify the appliance 20 based on the total score obtained by receiving a plurality of types of broadcast or multicast packets and scoring them individually.
- the information processing device 50 transmits a request packet, receives a response packet to the request packet, and performs a scoring process, and a result of receiving a broadcast or multicast packet and performing a scoring process in combination
- the type of the electrical appliance 20 may be specified.
- the information processing apparatus 50 receives a broadcast or multicast packet from the electrical appliance 20 without transmitting a request packet to the electrical appliance 20. Based on these packets, the device recognition server 500 may perform scoring processing to determine the type of the appliance 20.
- the type of the electrical appliance 20 is determined by the information processing apparatus 50 or the device recognition server 500. However, the type is determined based on this data after receiving auxiliary data input from the user. May be. For example, when the user recognizes data related to the electrical appliance 20 (for example, a manufacturer name), the information processing apparatus 50 or the device recognition server 500 accepts the data related to the electrical appliance 20 and scores this data and the score. The type of electrical appliance is determined based on the result. That is, the information processing apparatus 50 or the device recognition server 500 determines, for example, the manufacturer name based on the input data from the user before scoring, refers only to the definition file related to the determined manufacturer name, and other manufacturers. Determine the type without referring to the definition file that contains the name.
- the manufacturer name for example, the manufacturer name
- the information processing apparatus 50 or the device recognition server 500 determines, for example, the manufacturer name based on the input data from the user before scoring, refers only to the definition file related to the determined manufacturer name, and other manufacturers. Determine the type without referring to the definition file that
- the input of the manufacturer name may be text input by the user to any of the electrical appliance 20, the information processing apparatus 50, or the device recognition server 500, or character recognition is performed from an image taken with a digital camera.
- the manufacturer name may be extracted from the data and the manufacturer name data may be used. That is, the information processing apparatus 50 or the device recognition server 500 receives an input of an image taken with a digital camera, performs character recognition on the image, and extracts information about the appliance 20 as text characters. The extracted text characters are used as input data.
- the model name of the electrical appliance 20 cannot be determined.
- the content of the question is not limited to the model name, and may ask the type of the electric appliance 20 (digital television, recording medium playback recorder, etc.), and the size, color, and shape of the assumed electric appliance 20 You may ask.
- the electrical appliance 20 is stored in advance in association with the size, color, shape, and the like, and a model name or the like can be identified by obtaining a response to these.
- a plurality of icons (images) of the electrical appliances 20 as candidates to be determined may be displayed and a selection of an icon may be received from the user.
- the input data is not limited to the manufacturer name described above, but may be a product name, a logo mark, a house mark, a model name, or the like.
- a product name, a logo mark, a house mark, a model name, and the like to be used constitute a definition item and are stored in advance as a definition file.
- data input from the user may be stored as definition items and used to update a database such as a definition file.
- the information processing apparatus 50 may acquire (capture) a request packet from the electrical appliance 20 to the external network and analyze the packet to determine the type of the electrical appliance 20. That is, when the electrical appliance 20 serving as the client terminal performs communication by transmitting an HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) request packet, all or a part of the packet from the first request packet to the end of communication is received. You may utilize for the determination of the classification of the electric appliance 20.
- HTTP Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
- the electrical appliance 20 when the electrical appliance 20 is a digital television, there may be a difference in contents that can be browsed and reproduced depending on the type of the digital television.
- the digital TV A has a Web page browsing function, a video playback function, and a rental video playback function
- the digital TV B has only a Web page browsing function. Therefore, when the electrical appliance 20 transmits a playback request packet of the video playback function and the information processing apparatus 50 captures the packet, the electrical appliance 20 determines that it is not the digital television B but the digital television A. .
- the type of the electrical appliance 20 may be determined according to the type of the requested packet according to the difference in the reproducible content.
- determining the type of the electrical appliance 20 it is also possible to determine the type of the electrical appliance 20 by classifying the types of DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) clients. It is also possible to use information as to whether or not the appliance 20 is compatible with IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6). Communication between the appliances 20 in the network may be established by using a manufacturer-specific protocol. For example, when a NAS (Network Attached Storage) and a personal computer are connected to a network (such as a LAN), the personal computer may detect the NAS and transmit a packet unique to the manufacturer. In this case, the information processing apparatus 50 may acquire a manufacturer-specific packet and determine the type.
- NAS Network Attached Storage
- a personal computer may detect the NAS and transmit a packet unique to the manufacturer.
- the information processing apparatus 50 may acquire a manufacturer-specific packet and determine the type.
- the type of the electrical appliance 20 may be determined based on the power consumption waveform formed as a time series graph of the power consumption of each electrical appliance 20. That is, since the waveform of power consumption differs depending on the type of the electrical appliance 20, the electrical power consumption waveform for each electrical appliance 20 is stored in advance, and the electrical appliance 20 is identified by comparing with the stored waveform. May be.
- the means and functions described above are realized by a computer (including a CPU, an information processing device, and various terminals) reading and executing a predetermined application program.
- the application program is provided in a form recorded on a computer-readable recording medium such as a flexible disk, CD (CD-ROM, etc.), DVD (DVD-ROM, DVD-RAM, etc.), for example.
- the computer reads the application program from the recording medium, transfers it to the internal storage device or the external storage device, stores it, and executes it.
- the program may be recorded in advance in a storage device (recording medium) such as a magnetic disk, an optical disk, or a magneto-optical disk, and provided from the storage device to a computer via a communication line.
- part or all of the application program may be provided from the server via the public line network, and the above-described method may be provided as a SaaS (Software as a Service) type service. That is, in this case, a part of the program for executing the above-described processing is transmitted from the server, executed on the terminal side, and implemented in cooperation with the server-side program.
- SaaS Software as a Service
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
- Selective Calling Equipment (AREA)
- Small-Scale Networks (AREA)
- Telephonic Communication Services (AREA)
Abstract
Description
前記電化製品に対して、所定のリクエストパケットを送信するリクエストパケット送信手段と、
前記リクエストパケットを送信した電化製品から、当該電化製品の種別を判別するためのレスポンスパケットを受信するレスポンスパケット受信手段と、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶する記憶手段と、
前記レスポンスパケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化する得点化手段と、
前記得点化手段の得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報とする電化製品種別決定手段と、
を備える情報処理装置。
前記電化製品種別決定手段が、複数のパケットの総合点で、得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出する、(1)に記載の情報処理装置。
前記電化製品に対して、所定のリクエストパケットを送信するステップと、
前記リクエストパケットを送信した電化製品から、当該電化製品の種別を判別するためのレスポンスパケットを受信するステップと、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶するステップと、
前記レスポンスパケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化するステップと、
前記得点化するステップの得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報とするステップと、
を備える方法。
前記電化製品情報とするステップでは、複数のパケットの総合点で、得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出する、(5)に記載の方法。
前記情報処理装置は、
前記電化製品から、当該電化製品の種別を判別するためのパケットを受信するパケット受信手段と、
前記パケットを前記機器認識サーバに送信することで、前記電化製品の種別に関する情報を要求する種別情報要求手段と、を備え、
前記機器認識サーバは、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶する記憶手段と、
前記情報処理装置からの要求に応じて、前記パケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化する得点化手段と、
前記得点化手段の結果として、得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報として、前記情報処理装置に送信する電化製品種別決定手段と、
を備える電化製品種別決定システム。
前記情報処理装置から、前記電化製品から送信された所定のパケットを受信する受信手段と、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶する記憶手段と、
前記情報処理装置からの要求に応じて、前記所定のパケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化する得点化手段と、
前記得点化手段の結果として、得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報として、前記情報処理装置に送信する電化製品種別決定手段と、
を備える機器認識サーバ。
前記情報処理装置が、
前記電化製品から、当該電化製品の種別を判別するためのパケットを受信するレスポンスパケット受信ステップと、
前記パケットを前記機器認識サーバに送信することで、前記電化製品の種別に関する情報を要求する種別情報要求ステップと、を実行し、
前記機器認識サーバが、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶する記憶ステップと、
前記情報処理装置からの要求に応じて、前記パケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化する得点化ステップと、
前記得点化ステップの結果として、得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報として、前記情報処理装置に送信する電化製品種別決定ステップと、を実行する方法。
前記電化製品から、ブロードキャストのパケット又はマルチキャストのパケットであって、当該電化製品の種別を判別するためのパケットを受信するパケット受信手段と、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶する記憶手段と、
前記パケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化する得点化手段と、
前記得点化手段の得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報とする電化製品種別決定手段と、
を備える情報処理装置。
前記電化製品から、ブロードキャストのパケット又はマルチキャストのパケットであって、当該電化製品の種別を判別するためのパケットを受信するステップと、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶するステップと、
前記パケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化するステップと、
前記得点化するステップでの得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報とするステップと、
を備える方法。
前記情報処理装置から、前記電化製品から受信したブロードキャストのパケット又はマルチキャストのパケットであって、当該電化製品の種別を判別するためのパケットを受信する受信手段と、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶する記憶手段と、
前記情報処理装置からの要求に応じて、前記パケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化する得点化手段と、
前記得点化手段の結果として、得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報として、前記情報処理装置に、前記電化製品情報を送信する電化製品種別決定手段と、
を備える機器認識サーバ。
図1は、ネットワークシステム1の全体構成を示す図である。
図2は、情報処理装置50と電化製品20の機能ブロック図である。
図3は、種別決定処理のフローチャートである。まず、情報処理装置50のリクエストパケット送信手段51は、電化製品20に対して、リクエストパケットを送信する(ステップS10)。
図10は、情報処理装置50が、表示装置360を有する場合に、ネットワークシステム1に接続された、電化製品20-b,20-d,20-e,20-fの電化製品情報(メーカ名、機器名)がアイコンとともに表示されたことを示すが画面イメージ図である。電化製品情報が特定されると、リアルタイムに、この画面に電化製品情報が表示されてよい。
図11は、情報処理装置50のハードウェア構成を示す図である。本発明が実施されるサーバは標準的なものでよく、以下に構成の一例を示す。
上記の第1実施形態では、情報処理装置50が電化製品20の種別を決定する実施態様について説明したが、これに限られず、電化製品20の種別を、公衆回線を介して接続された機器認識サーバ500が決定する態様を第2実施形態として、以下に説明する。
なお、電化製品20の種別が決定した後に、機器認識サーバ500が、情報処理装置50ごとに、電化製品20の種別を記憶し、管理してもよい。
第3実施形態では、情報処理装置50が、リクエストパケットを電化製品20に対して送信せずに(情報処理装置50がリクエストパケット送信手段51を備えない)、種別決定処理(ステップS11からS14)を実行する実施形態である。
上記実施形態によれば、情報処理装置50又は機器認識サーバ500により、電化製品20の種別が決定されるが、ユーザからの補助的なデータ入力を受付けて、このデータに基づいて、種別が決定されてもよい。例えば、ユーザが電化製品20に関するデータ(例えば、メーカ名)を認識している場合は、ユーザが電化製品20に関するデータを、情報処理装置50又は機器認識サーバ500が受付けて、このデータと得点化の結果に基づいて電化製品の種別を決定する。すなわち、情報処理装置50又は機器認識サーバ500は、得点化の前に、ユーザからの入力データにより、例えば、メーカ名を決定し、決定されたメーカ名に関する定義ファイルのみを参照し、他のメーカ名を含む定義ファイルの参照を行わないで、種別を決定する。
情報処理装置50がルータの場合は、電化製品20が公衆回線(インターネット)等の外部ネットワークに接続する際に、情報処理装置50を経由して、アクセスが行われる。したがって、情報処理装置50が、電化製品20から外部ネットワークへの要求パケットを取得(キャプチャ)し、このパケットを分析することで、電化製品20の種別を決定してもよい。すなわち、クライアント端末となる電化製品20が、HTTP(Hyper Text Transfer Protocol)要求パケットを送信して通信を行う際に、最初の要求パケットから通信が終了するまでのパケットのうちの全部又は一部を電化製品20の種別の決定に利用してもよい。
電化製品20の種別を決定するにあたって、DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)クライアントの種別を分類することで、電化製品20の種別を決定することも可能である。
IPv6(Internet Protocol Vertion 6)に対応した電化製品20であるか否かの情報を利用することも可能である。
メーカ独自のプロトコルを使用することで、ネットワーク内の電化製品20間の通信を確立する場合がある。例えば、NAS(Network Attached Strage)と、パソコンを(LAN等の)ネットワークに接続すると、パソコンが、NASを探知し、接続するためのメーカ独自のパケットを送信する場合がある。この場合に、情報処理装置50が、メーカ独自のパケットを取得して、種別を決定してもよい。
各電化製品20の消費電力を時系列でグラフとして形成した消費電力波形に基づいて、電化製品20の種別を決定してもよい。すなわち、消費電力の波形は、電化製品20の種別に応じて異なるため、予め電化製品20毎の消費電力の波形を記憶しておき、記憶された波形と比較することで、電化製品20を特定してもよい。
5 電化製品種別決定システム
20 電化製品
50 情報処理装置
51 リクエストパケット送信手段
52 レスポンスパケット受信手段
53 定義ファイル記憶手段
54 得点化手段
55 電化製品種別決定手段
500 機器認識サーバ
Claims (14)
- 電化製品が通信可能に接続された情報処理装置であって、
前記電化製品に対して、所定のリクエストパケットを送信するリクエストパケット送信手段と、
前記リクエストパケットを送信した電化製品から、当該電化製品の種別を判別するためのレスポンスパケットを受信するレスポンスパケット受信手段と、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶する記憶手段と、
前記レスポンスパケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化する得点化手段と、
前記得点化手段の得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報とする電化製品種別決定手段と、
を備える情報処理装置。 - 前記リクエストパケット送信手段と前記レスポンスパケット受信手段とは、前記電化製品と前記情報処理装置との間で、複数のパケットの送受信を行い、
前記電化製品種別決定手段が、複数のパケットの総合点で、得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出する、請求項1に記載の情報処理装置。 - 前記得点化手段は、前記レスポンスパケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、前記レスポンスパケットと前記定義ファイルとの類似度により得点化する請求項1または2に記載の情報処理装置。
- 前記リクエストパケット送信手段は、定期的に前記電化製品に対して、リクエストパケットを送信することで、前記通信可能に接続された電化製品を、所定のタイミングで検知する請求項1から3のいずれか一項に記載の情報処理装置。
- 電化製品が通信可能に接続された情報処理装置が実行する方法であって、
前記電化製品に対して、所定のリクエストパケットを送信するステップと、
前記リクエストパケットを送信した電化製品から、当該電化製品の種別を判別するためのレスポンスパケットを受信するステップと、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶するステップと、
前記レスポンスパケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化するステップと、
前記得点化するステップの得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報とするステップと、
を備える方法。 - 前記リクエストパケットと前記レスポンスパケットとは、前記電化製品と前記情報処理装置との間で、複数のパケットが送受信され、
前記電化製品情報とするステップでは、複数のパケットの総合点で、得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出する、請求項5に記載の方法。 - 前記得点化するステップでは、前記レスポンスパケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、前記レスポンスパケットと前記定義ファイルとの類似度により得点化する請求項5または6に記載の方法。
- 前記リクエストパケットを送信するステップでは、定期的に前記電化製品に対して、リクエストパケットを送信することで、前記通信可能に接続された電化製品を、所定のタイミングで検知する請求項5から7のいずれか一項に記載の方法。
- 電化製品が通信可能に接続された情報処理装置と、当該情報処理装置と通信可能に接続された機器認識サーバと、から構成される電化製品種別決定システムであって、
前記情報処理装置は、
前記電化製品から、当該電化製品の種別を判別するためのパケットを受信するパケット受信手段と、
前記パケットを前記機器認識サーバに送信することで、前記電化製品の種別に関する情報を要求する種別情報要求手段と、を備え、
前記機器認識サーバは、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶する記憶手段と、
前記情報処理装置からの要求に応じて、前記パケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化する得点化手段と、
前記得点化手段の結果として、得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報として、前記情報処理装置に送信する電化製品種別決定手段と、
を備える電化製品種別決定システム。 - 電化製品が通信可能に接続された情報処理装置と通信可能に接続された機器認識サーバであって、
前記情報処理装置から、前記電化製品から送信された所定のパケットを受信する受信手段と、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶する記憶手段と、
前記情報処理装置からの要求に応じて、前記所定のパケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化する得点化手段と、
前記得点化手段の結果として、得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報として、前記情報処理装置に送信する電化製品種別決定手段と、
を備える機器認識サーバ。 - 電化製品が通信可能に接続された情報処理装置と、当該情報処理装置と通信可能に接続された機器認識サーバと、から構成されるシステムが実行する方法であって、
前記情報処理装置が、
前記電化製品から、当該電化製品の種別を判別するためのパケットを受信するレスポンスパケット受信ステップと、
前記パケットを前記機器認識サーバに送信することで、前記電化製品の種別に関する情報を要求する種別情報要求ステップと、を実行し、
前記機器認識サーバが、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶する記憶ステップと、
前記情報処理装置からの要求に応じて、前記パケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化する得点化ステップと、
前記得点化ステップの結果として、得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報として、前記情報処理装置に送信する電化製品種別決定ステップと、を実行する方法。 - 電化製品が通信可能に接続された情報処理装置であって、
前記電化製品から、ブロードキャストのパケット又はマルチキャストのパケットであって、当該電化製品の種別を判別するためのパケットを受信するパケット受信手段と、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶する記憶手段と、
前記パケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化する得点化手段と、
前記得点化手段の得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報とする電化製品種別決定手段と、
を備える情報処理装置。 - 電化製品が通信可能に接続された情報処理装置が実行する方法であって、
前記電化製品から、ブロードキャストのパケット又はマルチキャストのパケットであって、当該電化製品の種別を判別するためのパケットを受信するステップと、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶するステップと、
前記パケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化するステップと、
前記得点化するステップでの得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報とするステップと、
を備える方法。 - 電化製品が通信可能に接続された情報処理装置と通信可能に接続された機器認識サーバであって、
前記情報処理装置から、前記電化製品から受信したブロードキャストのパケット又はマルチキャストのパケットであって、当該電化製品の種別を判別するためのパケットを受信する受信手段と、
前記電化製品ごとに定められた定義ファイルを記憶する記憶手段と、
前記情報処理装置からの要求に応じて、前記パケットと前記電化製品ごとの定義ファイルを比較し、得点化する得点化手段と、
前記得点化手段の結果として、得点が高い定義ファイルを抽出し、当該定義ファイルの電化製品情報を、前記電化製品の電化製品情報として、前記情報処理装置に、前記電化製品情報を送信する電化製品種別決定手段と、
を備える機器認識サーバ。
Priority Applications (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| ES09814328.2T ES2518419T3 (es) | 2008-09-22 | 2009-09-18 | Dispositivo de procesamiento de datos, procedimiento y servidor para determinar los tipos de aparatos eléctricos |
| KR1020117002122A KR101209014B1 (ko) | 2008-09-22 | 2009-09-18 | 전기제품의 종별을 결정하는 정보처리장치, 방법, 서버 |
| EP09814328.2A EP2330512B1 (en) | 2008-09-22 | 2009-09-18 | Data processing device, method, and server to determine types of electric appliances |
| CN200980136478.4A CN102160042B (zh) | 2008-09-22 | 2009-09-18 | 确定电器种类的信息处理装置、方法以及服务器 |
| US12/680,334 US8301625B2 (en) | 2008-09-22 | 2009-09-18 | Information processing device, method and server for determining type of electric appliance |
| US13/618,279 US8832090B2 (en) | 2008-09-22 | 2012-09-14 | Information processing device, method and server for determining type of electric appliance |
| US13/617,960 US8832089B2 (en) | 2008-09-22 | 2012-09-14 | Information processing device, method and server for determining type of electric appliance |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008243170 | 2008-09-22 | ||
| JP2008-243170 | 2008-09-22 |
Related Child Applications (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/680,334 A-371-Of-International US8301625B2 (en) | 2008-09-22 | 2009-09-18 | Information processing device, method and server for determining type of electric appliance |
| US13/618,279 Continuation US8832090B2 (en) | 2008-09-22 | 2012-09-14 | Information processing device, method and server for determining type of electric appliance |
| US13/617,960 Continuation US8832089B2 (en) | 2008-09-22 | 2012-09-14 | Information processing device, method and server for determining type of electric appliance |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2010032483A1 true WO2010032483A1 (ja) | 2010-03-25 |
Family
ID=42039330
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2009/004750 WO2010032483A1 (ja) | 2008-09-22 | 2009-09-18 | 電化製品の種別を決定する情報処理装置、方法、サーバ |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US8301625B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2330512B1 (ja) |
| JP (3) | JP4855499B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR101209014B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN102160042B (ja) |
| ES (1) | ES2518419T3 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2010032483A1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101917314A (zh) * | 2010-07-30 | 2010-12-15 | 中山大学 | 一种数字家庭信息处理方法及中间件系统 |
Families Citing this family (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4855499B2 (ja) * | 2008-09-22 | 2012-01-18 | 株式会社オプティム | 電化製品の種別を決定する情報処理装置、方法、サーバ |
| JP4898927B2 (ja) * | 2009-01-22 | 2012-03-21 | 株式会社オプティム | 電化製品の種別に応じてプログラム又はページを送信する情報処理装置、方法、プログラム |
| JP4892634B1 (ja) * | 2011-02-14 | 2012-03-07 | 株式会社オプティム | 電化製品の識別サーバ、識別方法、識別プログラム及び、識別システム |
| JP4769339B1 (ja) * | 2011-02-14 | 2011-09-07 | 和明 根布 | エネルギ消費監視システム、方法、及びコンピュータプログラム |
| US8656202B2 (en) * | 2011-05-20 | 2014-02-18 | Sharp Laboratories Of America, Inc. | Method and system for managing plug network based on appliance identification |
| KR101958902B1 (ko) * | 2011-09-30 | 2019-07-03 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 전자기기들의 그룹 제어 방법 및 그를 위한 전자기기 관리 시스템 |
| JP5647966B2 (ja) * | 2011-10-07 | 2015-01-07 | 株式会社オプティム | 端末修復方法、端末修復システム、及び、端末修復システム用プログラム |
| JP5714467B2 (ja) * | 2011-10-24 | 2015-05-07 | 株式会社オプティム | リモートサポートを受ける携帯型端末、リモートサポート方法、リモートサポート用プログラム、オペレータシステム、オペレータサーバ、及びオペレータ端末 |
| KR101334457B1 (ko) * | 2011-11-10 | 2013-11-29 | 한국전자통신연구원 | 센서 정보에 기초하여 센서 노드의 자동 접속을 설정하는 장치 및 방법 |
| JP5676499B2 (ja) * | 2012-01-25 | 2015-02-25 | 株式会社オプティム | 電化製品を制御する情報処理装置、プログラム実行方法及びプログラム |
| JP5702317B2 (ja) * | 2012-02-15 | 2015-04-15 | 株式会社オプティム | 営業販売促進サーバ、営業販売促進方法及び、営業販売促進プログラム |
| JP5600133B2 (ja) * | 2012-03-29 | 2014-10-01 | 株式会社富士通エフサス | 監視装置、監視方法および監視プログラム |
| JP5620434B2 (ja) | 2012-05-02 | 2014-11-05 | 株式会社オプティム | オペレータシステム、オペレータサーバ、リモートサポート方法、オペレータサーバ用プログラム、サポート対象電化製品、及び、サポート作業画面表示装置 |
| US8761757B2 (en) * | 2012-09-14 | 2014-06-24 | Tektronix, Inc. | Identification of communication devices in telecommunication networks |
| JP5501423B2 (ja) * | 2012-10-15 | 2014-05-21 | エヌ・ティ・ティ・コムウェア株式会社 | 機器同定装置、機器同定システム、機器同定方法、及び機器同定プログラム |
| JP5509292B2 (ja) * | 2012-10-15 | 2014-06-04 | エヌ・ティ・ティ・コムウェア株式会社 | 機器同定装置、機器同定方法、及び機器同定プログラム |
| JP5714620B2 (ja) | 2012-10-19 | 2015-05-07 | 株式会社オプティム | ユーザ端末、オペレータサーバ、リモートサポート方法、及びユーザ端末用プログラム |
| JP6041636B2 (ja) * | 2012-11-26 | 2016-12-14 | キヤノン株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理装置の制御方法、及びプログラム |
| JP5797674B2 (ja) * | 2013-01-09 | 2015-10-21 | 株式会社オプティム | オペレーション補佐端末、オペレータサーバ、オペレーション補佐方法、及び、オペレーション補佐プログラム |
| JP6194693B2 (ja) * | 2013-08-22 | 2017-09-13 | 富士通株式会社 | 通信装置、制御システム、通信プログラムおよび通信方法 |
| WO2015095170A1 (en) | 2013-12-19 | 2015-06-25 | Electrolux Home Products, Inc. | System, method, apparatus, and computer program product for configuring a network connected appliance to use online services |
| US20160112932A1 (en) * | 2014-10-20 | 2016-04-21 | Xiaomi Inc. | Methods and devices for displaying wireless device list |
| US9930060B2 (en) * | 2015-06-01 | 2018-03-27 | Duo Security, Inc. | Method for enforcing endpoint health standards |
| RU2742824C2 (ru) | 2016-03-31 | 2021-02-11 | БИТДЕФЕНДЕР АйПиАр МЕНЕДЖМЕНТ ЛТД | Системы и способы автоматической детекции устройств |
| TWI592774B (zh) * | 2016-08-08 | 2017-07-21 | 明基能源技術股份有限公司 | 電器設備的操作識別方法及應用其的操作識別系統 |
| GB2566010A (en) * | 2017-08-24 | 2019-03-06 | Connect Devices Ltd | Method and system for network devices |
| JP2019067474A (ja) * | 2017-10-05 | 2019-04-25 | 東芝メモリ株式会社 | 半導体記憶装置 |
| CN109639536A (zh) * | 2019-01-28 | 2019-04-16 | 中国信息通信研究院 | 一种智能无线设备参数提取的方法、系统、设备及介质 |
| KR102431518B1 (ko) * | 2020-11-30 | 2022-08-11 | 주식회사 쉬프트베리 | 네트워크 제어 서버 및 방법 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003259569A (ja) * | 2001-12-28 | 2003-09-12 | Atsushi Matsushita | 電気機器の遠隔検出方法及び遠隔制御方法並びに遠隔制御システムと、これに用いるコンセント |
| JP2004510254A (ja) * | 2000-09-26 | 2004-04-02 | ボランティス システムズ リミテッド | ネットワークサーバ |
| WO2006095593A1 (ja) * | 2005-03-09 | 2006-09-14 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | 制御装置、機器制御システム、機器制御プログラム、機器制御プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体及び設定確認データ作成方法 |
| JP2007305145A (ja) | 2007-06-20 | 2007-11-22 | Hitachi Ltd | 家電機器点検システム |
Family Cites Families (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6772420B1 (en) * | 1999-10-26 | 2004-08-03 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | System for obtaining appropriate device drivers by accessing table having list of manufacturers and link-layer addresses assigned to device drivers |
| US20030149757A1 (en) * | 2000-12-27 | 2003-08-07 | Reiko Ueno | Identification code management system for home network |
| US7069345B2 (en) * | 2001-05-09 | 2006-06-27 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | Device identification and control in network environment |
| KR100434270B1 (ko) * | 2001-05-30 | 2004-06-04 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 가전기기 네트워크 제어시스템 |
| JP2003101566A (ja) * | 2001-09-19 | 2003-04-04 | Hitachi Software Eng Co Ltd | ネットワーク機器の管理方法および装置 |
| JP2003153348A (ja) * | 2001-11-13 | 2003-05-23 | Toshiba Corp | 家電サーバ装置及び家電制御システム |
| KR20030075728A (ko) * | 2002-03-20 | 2003-09-26 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 홈 네트워크 시스템의 가전제품 연결상태 확인방법 |
| US7779026B2 (en) * | 2002-05-03 | 2010-08-17 | American Power Conversion Corporation | Method and apparatus for collecting and displaying network device information |
| US7580985B2 (en) * | 2002-05-13 | 2009-08-25 | Ricoh Co. Ltd. | Verification method of manufacturer and model for remote diagnostics, maintenance and control system over SNMP |
| US20040059817A1 (en) * | 2003-02-10 | 2004-03-25 | Matsushita Elec. Ind. Co., Ltd. | Identification code management system for home network |
| JP3800198B2 (ja) * | 2003-05-16 | 2006-07-26 | ソニー株式会社 | 情報処理装置、およびアクセス制御処理方法、並びにコンピュータ・プログラム |
| WO2005114926A1 (ja) * | 2004-05-20 | 2005-12-01 | Freebit Co., Ltd. | クライアント機器への接続をルーティングするためのサーバ |
| JP4526886B2 (ja) * | 2004-07-05 | 2010-08-18 | 株式会社日立製作所 | 無線装置、無線通信システムの制御方法、及び無線通信システム |
| US8510737B2 (en) * | 2005-01-07 | 2013-08-13 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method and system for prioritizing tasks made available by devices in a network |
| JP4434062B2 (ja) * | 2005-04-11 | 2010-03-17 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Webサーバ搭載機器への自動アクセス方法 |
| US7431831B2 (en) * | 2005-12-16 | 2008-10-07 | Chevron U.S.A. Inc. | Integrated in-line pretreatment and heavy oil upgrading process |
| JP2007199820A (ja) * | 2006-01-24 | 2007-08-09 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | ネットワーク接続装置 |
| KR20080011581A (ko) * | 2006-07-31 | 2008-02-05 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 원격제어를 위한 중계 장치 및 상기 장치를 이용한원격제어방법 |
| US20080243684A1 (en) * | 2007-03-19 | 2008-10-02 | Steven Ng | Method and apparatus for funding a transaction |
| US7769990B1 (en) * | 2007-03-23 | 2010-08-03 | Symantec Corporation | Using a monitoring process to update system configuration settings during restore operations |
| US8132186B1 (en) * | 2007-03-23 | 2012-03-06 | Symantec Corporation | Automatic detection of hardware and device drivers during restore operations |
| US7886185B1 (en) * | 2007-03-23 | 2011-02-08 | Symantec Corporation | Creation of a device database and synthesis of device driver information during dissimilar system restore |
| WO2009003310A1 (fr) * | 2007-06-29 | 2009-01-08 | China Mobile Communications Corporation | Système de stockage de données et procédé de traitement de données d'un appareil domestique informatique |
| JP4855499B2 (ja) * | 2008-09-22 | 2012-01-18 | 株式会社オプティム | 電化製品の種別を決定する情報処理装置、方法、サーバ |
| US9600824B2 (en) * | 2010-06-02 | 2017-03-21 | Universal Electronics Inc. | System and method for recommending home appliances to a consumer |
| WO2012011630A1 (en) * | 2010-07-20 | 2012-01-26 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Selective interaction between networked smart devices |
| US8645398B2 (en) * | 2012-01-24 | 2014-02-04 | Verizon Patent And Licensing Inc. | Cross-platform content popularity rankings |
| JP5676499B2 (ja) * | 2012-01-25 | 2015-02-25 | 株式会社オプティム | 電化製品を制御する情報処理装置、プログラム実行方法及びプログラム |
| US8533144B1 (en) * | 2012-11-12 | 2013-09-10 | State Farm Mutual Automobile Insurance Company | Automation and security application store suggestions based on usage data |
-
2009
- 2009-05-29 JP JP2009130552A patent/JP4855499B2/ja active Active
- 2009-09-18 US US12/680,334 patent/US8301625B2/en active Active
- 2009-09-18 EP EP09814328.2A patent/EP2330512B1/en not_active Not-in-force
- 2009-09-18 ES ES09814328.2T patent/ES2518419T3/es active Active
- 2009-09-18 CN CN200980136478.4A patent/CN102160042B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2009-09-18 WO PCT/JP2009/004750 patent/WO2010032483A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2009-09-18 KR KR1020117002122A patent/KR101209014B1/ko active IP Right Grant
-
2011
- 2011-04-04 JP JP2011083180A patent/JP4912503B2/ja active Active
- 2011-10-26 JP JP2011234536A patent/JP4882036B1/ja active Active
-
2012
- 2012-09-14 US US13/618,279 patent/US8832090B2/en active Active
- 2012-09-14 US US13/617,960 patent/US8832089B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004510254A (ja) * | 2000-09-26 | 2004-04-02 | ボランティス システムズ リミテッド | ネットワークサーバ |
| JP2003259569A (ja) * | 2001-12-28 | 2003-09-12 | Atsushi Matsushita | 電気機器の遠隔検出方法及び遠隔制御方法並びに遠隔制御システムと、これに用いるコンセント |
| WO2006095593A1 (ja) * | 2005-03-09 | 2006-09-14 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | 制御装置、機器制御システム、機器制御プログラム、機器制御プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体及び設定確認データ作成方法 |
| JP2007305145A (ja) | 2007-06-20 | 2007-11-22 | Hitachi Ltd | 家電機器点検システム |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP2330512A4 |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101917314A (zh) * | 2010-07-30 | 2010-12-15 | 中山大学 | 一种数字家庭信息处理方法及中间件系统 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2012080548A (ja) | 2012-04-19 |
| US20130013594A1 (en) | 2013-01-10 |
| US8832089B2 (en) | 2014-09-09 |
| EP2330512A4 (en) | 2012-11-21 |
| CN102160042B (zh) | 2014-11-26 |
| US20130013593A1 (en) | 2013-01-10 |
| JP2010097587A (ja) | 2010-04-30 |
| JP2011175657A (ja) | 2011-09-08 |
| JP4855499B2 (ja) | 2012-01-18 |
| EP2330512B1 (en) | 2014-09-03 |
| JP4912503B2 (ja) | 2012-04-11 |
| US20100257158A1 (en) | 2010-10-07 |
| US8301625B2 (en) | 2012-10-30 |
| ES2518419T3 (es) | 2014-11-05 |
| JP4882036B1 (ja) | 2012-02-22 |
| KR101209014B1 (ko) | 2012-12-07 |
| EP2330512A1 (en) | 2011-06-08 |
| KR20110065437A (ko) | 2011-06-15 |
| CN102160042A (zh) | 2011-08-17 |
| US8832090B2 (en) | 2014-09-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2010032483A1 (ja) | 電化製品の種別を決定する情報処理装置、方法、サーバ | |
| US8266248B2 (en) | Use of network composition descriptors for determining product compatibility | |
| JP4949534B2 (ja) | 電化製品の種別に応じてプログラム又はページを送信する情報処理装置、方法、プログラム | |
| JP5031864B2 (ja) | 所持品リストを表示するシステム、方法及びプログラム | |
| JP4846016B2 (ja) | 電化製品の種別に応じた消費電力量を表示する消費電力量管理装置、システム、方法、プログラム | |
| JP4793797B2 (ja) | 電化製品の種別に応じた情報を表示する情報処理装置、プログラム、システム、方法 | |
| JP5149919B2 (ja) | ユーザ登録を実行する情報処理装置、プログラム、システム、方法 | |
| JP4892638B2 (ja) | 電化製品の種別に応じた情報を表示する情報処理装置、プログラム、システム、方法 | |
| JP5411325B2 (ja) | 所持品リストを表示するシステム、方法及びプログラム | |
| JP4892634B1 (ja) | 電化製品の識別サーバ、識別方法、識別プログラム及び、識別システム | |
| JP5687258B2 (ja) | リモートサポートサーバ、ユーザ端末、リモートサポートシステム、リモートサポート方法、及びリモートサポートシステム用プログラム | |
| JP5107320B2 (ja) | 環境管理方法、環境管理システム、環境管理システム用プログラム | |
| JP5687253B2 (ja) | オペレータシステム及び、オペレータ方法 | |
| JP6313699B2 (ja) | ユーザ端末、リモートサーバ、リモート操作システム、リモート操作方法、及びリモート操作システム用プログラム | |
| WO2023183159A1 (en) | Method for providing upnp service, gateway device, storage medium and program product |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 200980136478.4 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 12680334 Country of ref document: US |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 09814328 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2009814328 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20117002122 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |