RU79304U1 - WALL PROTECTION FOR BUILDINGS AND STRUCTURES (OPTIONS) - Google Patents
WALL PROTECTION FOR BUILDINGS AND STRUCTURES (OPTIONS) Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU79304U1 RU79304U1 RU2008119962/22U RU2008119962U RU79304U1 RU 79304 U1 RU79304 U1 RU 79304U1 RU 2008119962/22 U RU2008119962/22 U RU 2008119962/22U RU 2008119962 U RU2008119962 U RU 2008119962U RU 79304 U1 RU79304 U1 RU 79304U1
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- racks
- wall
- row
- formwork
- frame
- Prior art date
Links
Landscapes
- Building Environments (AREA)
Abstract
Полезная модель относится к строительству и может быть использована при сооружении монолитных стен различных зданий и сооружений. Стеновое ограждение (СО), включает наружный и внутренний слои в виде наружной и внутренней стенок (НС и ВС) несъемной опалубки (НО), закрепленных на каркасе (К) с размещенным между стенками слоем заполнителя. НС выполнена из плит, в виде фасадной защитной облицовки здания (ФЗО), а ВС выполнена из парогазопроницаемых панелей (ПП). К выполнен двухрядным, в виде наружного и внутреннего рядов стоек (НРС и ВРС), которые могут быть составными стойками (СС) с длиной, по высоте здания, установленных с горизонтальным технологическим шагом (ТШ) и связанных между собой монтажными связями (МС). Смежные стойки каждого ряда могут быть соединены поперечинами, расположенными с вертикальным ТШ по высоте каждого ряда стоек, при этом на НРС и ВРС смонтированы, соответственно, НС и ВС, в качестве заполнителя между которыми использован монолитный пенобетон (МП). В других вариантах конструкции СО (отличающихся в основном конструкцией К), двухрядный К с НРС и ВРС, установленных с ТШ и связанных между собой МС, стойки НРС состыкованы в держателях, закрепленных на перекрытиях, с образованием СС с длиной по высоте здания, при этом смежные стойки НРС при необходимости могут быть соединены поперечинами, расположенными с ТШ по высоте стоек, а ВРС установлен между перекрытиями, причем концы ВРС закреплены в верхних и нижних направляющих (ВН и НН), закрепленных на перекрытиях, при этом на НРС ВРС смонтированы, соответственно, ВН и ВС опалубки. Двухрядный К, может состоять из НРС и ВНР, связанных МС и размещенных с ТШ между перThe utility model relates to construction and can be used in the construction of monolithic walls of various buildings and structures. Wall fencing (CO), includes the outer and inner layers in the form of the outer and inner walls (HC and BC) of fixed formwork (BUT), mounted on the frame (K) with a filler layer placed between the walls. NS is made of slabs in the form of a facade protective cladding of a building (FZO), and aircraft is made of vapor-permeable panels (PP). K is made in two rows, in the form of the outer and inner rows of racks (LDCs and VRS), which can be composite racks (SS) with a length, building height, installed with a horizontal technological step (TS) and interconnected by mounting links (MS). Adjacent racks of each row can be connected by crossbars located along the vertical TS along the height of each row of racks, while on the LDC and VRS mounted, respectively, NS and VS, as a filler between which a monolithic foam concrete (MP) is used. In other versions of the construction of the SO (differing mainly in the construction of K), two-row K with LDCs and VRS installed with TS and interconnected MS, the struts of the LDCs are docked in holders mounted on the floors, with the formation of SS with a length along the height of the building, while if necessary, the adjacent racks of the LDCs can be connected by cross-members located along the TS along the height of the racks, and the HRV is installed between the ceilings, with the ends of the HRV fixed in the upper and lower rails (HV and LV) fixed to the floors, while the LDCs are mounted on ootvetstvenno, BH and BC molds. Double-row K, can consist of LDCs and VNR, connected by MS and placed with TS between lane
Description
Полезная модель относится к строительству и может быть использована при сооружении монолитных стен различных зданий и сооружений.The utility model relates to construction and can be used in the construction of monolithic walls of various buildings and structures.
Из уровня техники известны стены, содержащие размещенные между опалубками слои монолитного бетона и утеплителя (см. SU 1104218 А1, Е04В 2/30, 1983; SU 1749406 A1, E04В 2/84, 1992; DE 1708768 А, Е04В 2/26, 1971, DE 3601237 А, E04В 2/30, 1987).Walls are known from the prior art, containing layers of monolithic concrete and insulation placed between formwork (see SU 1104218 A1, ЕBВ 2/30, 1983; SU 1749406 A1, Е04В 2/84, 1992; DE 1708768 A, ЕBВ 2/26, 1971 , DE 3601237 A, E04B 2/30, 1987).
Основным недостатком аналогов является ненадежное соединение слоев между собой, что обуславливает необходимость введения усилительных элементов и стяжных болтов, усложняющих конструкцию.The main disadvantage of analogues is the unreliable connection of the layers between themselves, which necessitates the introduction of reinforcing elements and coupling bolts that complicate the design.
Известна также многослойная монолитная стена, содержащая несъемные щиты опалубки, которые соединены между собой гибкими связями и размещенный в пространстве между стенками опалубки, слой заполнителя, выполненного из полистиролбетона или подобного композитного материала (см. RU 0018282 U1, Е04В 2/26, 2001).Also known is a multilayer monolithic wall containing fixed formwork panels that are interconnected by flexible ties and placed in the space between the walls of the formwork, a filler layer made of polystyrene concrete or similar composite material (see RU 0018282 U1, ЕB 2/26, 2001).
При относительной простоте, данное решение, не обеспечивает необходимую устойчивость слоев стены, соответственно, не обеспечиваются высокие прочностные характеристики стены.With relative simplicity, this solution does not provide the necessary stability of the wall layers; accordingly, high strength characteristics of the wall are not provided.
Наиболее близким аналогом к заявленной полезной модели, является многослойная монолитная стена, содержащая наружную и внутреннюю стенки несъемной опалубки, между которыми размещен слой заполнителя из полистиролбетона, в слое которого с зазором относительно наружной стенки несъемной опалубки установлен каркас из металлических профилей, прикрепленный к внутренней стенке несъемной опалубки и соединенный гибкими связями с наружной стенкой несъемной опалубки.The closest analogue to the claimed utility model is a multilayer monolithic wall containing the outer and inner walls of fixed formwork, between which there is a filler layer made of polystyrene concrete, in the layer of which a frame of metal profiles is mounted with a gap relative to the outer wall of fixed formwork, attached to the inner wall of fixed formwork and connected by flexible connections to the outer wall of a fixed formwork.
При возведении этой стены монтируют каркас из тонкостенных металлических профилей, а также наружные и внутренние стенки несъемной опалубки. Внутреннюю стенку опалубки прикрепляют к каркасу (например, посредством анкеров) и соединяют его с наружной стенкой гибкими связями. При этом каркас устанавливают с зазором по отношению к наружной стенке опалубки, величина которого составляет 0,2-0,5 от толщины слоя заполнителя. Затем пространство между внутренней и наружной стенками (межопалубочное пространство) заполняют полистиролбетонным раствором. Наращивание опалубки и заполнение поли-стиролбетонным раствором межопалубочного пространства производят поярусно.When erecting this wall, a frame of thin-walled metal profiles is mounted, as well as the outer and inner walls of the fixed formwork. The inner wall of the formwork is attached to the frame (for example, by means of anchors) and connected to the outer wall by flexible ties. In this case, the frame is installed with a gap with respect to the outer wall of the formwork, the value of which is 0.2-0.5 of the thickness of the filler layer. Then, the space between the inner and outer walls (the interdeck space) is filled with polystyrene concrete solution. Formwork and filling with polystyrene-concrete solution of the inter-deck space are performed in tiers.
Недостатком этого аналога является невысокие прочностные характеристики многослойной монолитной стены, обусловленные наличием зазора между каркасом и наружной стенкой несъемной опалубки. Кроме того, значительно усложнен монтаж наружной стенки опалубки, поскольку гибкие связи не обеспечивают жесткость конструкции в процессе монтажа.The disadvantage of this analogue is the low strength characteristics of the multilayer monolithic wall, due to the presence of a gap between the frame and the outer wall of the fixed formwork. In addition, the installation of the outer wall of the formwork is much more complicated, since flexible connections do not provide structural rigidity during installation.
Полезная модель направлена на создание эстетичной, простой в изготовлении, быстровозводимой, прочной и устойчивой, монолитной теплозащитной стены.The utility model is aimed at creating an aesthetic, easy to manufacture, quickly erected, durable and stable, monolithic heat-shielding wall.
Решение поставленной задачи обеспечивается тем, что стеновое ограждение зданий и сооружений, включающее, наружный и внутренний слои в виде наружной и внутренней стенок несъемной опалубки, закрепленной на каркасе с размещенным между стенками слоем заполнителя, согласно полезной модели, наружная и внутренняя стенки несъемной опалубки выполнены, соответственно, из плитных или погонажных облицовочных материалов и из парогазопроницаемых панелей, при этом каркас выполнен двухрядным с наружным и внутренними рядами стоек, установленных в рядах с соответствующим каждому ряду шагом, при этом стойки выполнены составными с длиной по высоте здания и связанны между собой монтажными связями, причем на наружном и внутренних рядах стоек смонтированы, соответственно, внешние и внутренние стенки опалубки, в качестве заполнителя между которыми использован монолитный утеплитель, например, монолитный пенобетон. В вариантах выполнения, смежные стойки каждого ряда могут быть соединены поперечинами, расположенными с технологическим шагом по высоте каждого ряда стоек; при выполнении стенового ограждения в виде несущей стены, каркас дополнительно снабжен несущими стойками и балками перекрытий, при этом несущие стойки установлены с шагом между стойками внутреннего ряда.The solution to this problem is provided by the fact that the wall fencing of buildings and structures, including the outer and inner layers in the form of the outer and inner walls of the fixed formwork, mounted on the frame with a layer of aggregate placed between the walls, according to the utility model, the outer and inner walls of the fixed formwork are made, accordingly, from plate or molded facing materials and from gas-vapor-permeable panels, while the frame is double-row with the outer and inner rows of racks installed in a row ah with a step corresponding to each row, while the racks are made integral with the building height and connected by mounting ties, and the outer and inner rows of the racks are mounted, respectively, the outer and inner walls of the formwork, between which a monolithic insulation was used, for example, monolithic foam concrete. In embodiments, adjacent racks of each row can be connected by cross members located at a technological step along the height of each row of racks; when performing a wall fence in the form of a load-bearing wall, the frame is additionally equipped with load-bearing racks and floor beams, while the load-bearing racks are installed in increments between the racks of the inner row.
В другом варианте полезной модели, решение поставленной задачи обеспечивается тем, что стеновое ограждение здания, включающее, наружный и внутренний слои в виде наружной и внутренней стенок несъемной опалубки, закрепленной на каркасе с размещенным между стенками слоем заполнителя, согласно полезной модели, наружный слой выполнен из облицовочных плитных или погонажных материалов, внутренний слой выполнен из парогазопроницаемых панелей и размещен в проемах между перекрытиями и колоннами здания, при этом каркас выполнен двухрядным с наружным и внутренними рядами стоек, установленных в рядах с соответствующим каждому ряду шагом и связанных между собой монтажными связями, причем стойки наружного ряда выполнены с возможностью состыковки в держателях, закрепленных на перекрытиях, с образованием составных стоек с длиной по высоте здания, а стойки внутреннего ряда установлены между перекрытиями, причем концы этих стоек закреплены в верхних и нижних направляющих, In another embodiment of the utility model, the solution of the problem is provided by the fact that the wall of the building, including the outer and inner layers in the form of the outer and inner walls of the fixed formwork, mounted on the frame with a filler layer placed between the walls, according to the utility model, the outer layer is made of facing slab or molded materials, the inner layer is made of vapor-permeable panels and placed in the openings between the floors and columns of the building, while the frame is made of double-row with the inner and outer rows of racks installed in rows with a step corresponding to each row and interconnected by mounting ties, and the racks of the outer row are made with the possibility of joining in holders mounted on the floors, with the formation of composite racks with a length along the height of the building, and racks of the inner row installed between the floors, and the ends of these racks are fixed in the upper and lower rails,
закрепленных на поверхности перекрытий, при этом на наружном и внутренних рядах стоек смонтированы, соответственно, внешние и внутренние стенки опалубки, в качестве заполнителя между которыми использован монолитный утеплитель, например, монолитный пенобетон. В вариантах выполнения, держатели выполнены в виде фасонных накладок с боковыми щеками, снабженными удлиненными прорезями под болты резьбовых соединений; смежные стойки наружного ряда каркаса при необходимости могут быть соединены поперечинами, расположенными с шагом по высоте этих стоек, составляющим не более высоты облицовочных плит.fixed on the surface of the ceilings, while on the outer and inner rows of the racks are mounted, respectively, the outer and inner walls of the formwork, between which we used a monolithic insulation, for example, monolithic foam concrete. In embodiments, the holders are made in the form of shaped overlays with side cheeks provided with elongated slots for bolts of threaded joints; adjacent racks of the outer row of the frame, if necessary, can be connected by cross members located with a step along the height of these racks, which is no more than the height of the facing plates.
В следующем варианте выполнения, решение указанной задачи обеспечивается тем, что стеновое ограждение здания, включающее смонтированные на каркасе наружную и внутреннюю стенки в виде несъемной опалубки с размещенным между ними слоем заполнителя согласно полезной модели, наружный слой выполнен из облицовочных плитных или погонажных материалов, а внутренний слой выполнен из парогазопроницаемых панелей и размещен в проемах между перекрытиями и колоннами, при этом каркас выполнен двухрядным с наружным и внутренними рядами стоек, установленных в рядах с соответствующим каждому ряду шагом и связанных между собой монтажными связями, причем концы стоек обоих рядов закреплены в верхних и нижних направляющих, закрепленных на поверхности перекрытий, при этом на наружном ряде стоек закреплены составные балки, расположенные по длине стены здания и соединенные поперечинами (при необходимости), расположенными с шагом по длине балок, причем наружная и внутренняя стенки несъемной опалубки закреплены, соответственно, на балках и поперечинах и внутреннем ряде каркасных элементов, а в качестве заполнителя между стенками несъемной опалубки использован монолитный утеплитель, например, монолитный пенобетон. В вариантах выполнения, шаг установки поперечин и наружных балок составляет, соответственно, не более ширины плит облицовки и не более высоты плит облицовки.In the next embodiment, the solution to this problem is provided by the fact that the wall of the building, including the outer and inner walls mounted on the frame in the form of a fixed formwork with a filler layer placed between them, according to the utility model, the outer layer is made of facing slab or molded materials, and the inner the layer is made of vapor-permeable panels and is placed in the openings between the ceilings and columns, while the frame is made of two-row with the outer and inner rows of racks, installing connected in rows with each step corresponding to each row and interconnected by mounting ties, the ends of the racks of both rows being fixed in the upper and lower rails mounted on the surface of the floors, while on the outer row of racks are fixed beams located along the length of the wall of the building and connected by cross members (if necessary) located in increments of the length of the beams, the outer and inner walls of the fixed formwork being fixed, respectively, on the beams and crossbars and the inner row of frame elements, and monolithic insulation, for example, monolithic foam concrete, is used as a filler between the walls of fixed formwork. In embodiments, the installation step of the cross members and the outer beams is, respectively, no more than the width of the cladding plates and not more than the height of the cladding plates.
В еще одном варианте выполнения, решение поставленной задачи обеспечивается тем, что стеновое ограждение здания, включающее смонтированные на каркасе наружную и внутреннюю стенки в виде несъемной опалубки с размещенным между ними слоем заполнителя, согласно полезной модели, наружная и внутренняя стенки несъемной опалубки выполнены, соответственно, из облицовочных плитных или погонажных материалов и из парогазопроницаемых панелей, при этом каркас выполнен двухрядным с соединенными между собой монтажными связями наружным и внутренними рядами стоек, установленных в рядах с соответствующим каждому ряду шагом, причем наружный ряд стоек установлен со смещением от In another embodiment, the solution to this problem is provided by the fact that the wall of the building, including mounted on the frame of the outer and inner walls in the form of a fixed formwork with a filler layer placed between them, according to a utility model, the external and internal walls of the fixed formwork are made, respectively, from facing slabs or moldings and from gas-vapor-permeable panels, while the frame is made of two-row with external and internal connected by mounting links and rows of racks installed in rows with a step corresponding to each row, with the outer row of racks installed offset from
торцов перекрытий из условия размещения колонн в слое монолитного утеплителя со стороны внутреннего ряда стоек, концы стоек обоих рядов закреплены в верхних и нижних направляющих, установленных на поверхности перекрытий здания, а слой заполнителя выполнен в виде монолитного утеплителя, например, монолитного пенобетона. В вариантах выполнения, шаг установки наружного и внутреннего рядов стоек каркаса составляет, соответственно, не более ширины облицовочных плит и не более ширины панелей.the ends of the floors from the condition of placing the columns in the layer of monolithic insulation from the side of the inner row of racks, the ends of the racks of both rows are fixed in the upper and lower rails installed on the surface of the floors of the building, and the aggregate layer is made in the form of a monolithic insulation, for example, monolithic foam concrete. In embodiments, the installation step of the outer and inner rows of the struts of the frame is, respectively, not more than the width of the facing plates and not more than the width of the panels.
Во всех вышеуказанных вариантах выполнения, монтажные связи стоек каркаса выполнены в виде горизонтальных и наклонных, соответственно, термопрофилей и полос; в качестве направляющих и стоек использованы стальные фасонные оцинкованные профили; стойки, направляющие и монтажные связи скреплены между собой резьбовыми соединениями и/или заклепками; парогозопронецаемый слой выполнен из гипсоволокнистых или гипсокартонных панелей, в т.ч. во влагостойком исполнении; погонажные облицовочные материалы выполнены из досок или панелей, например, типа сайдинга с креплением досок и панелей к наружному ряду стоек за счет винтовых соединений, например, саморезов; плитные облицовочные материалы выполнены в виде фасадных плит с ровными или пазогребневыми кромками и закладными элементами в виде П-образных полосовых закладных элементов, с выступающими с тыльной стороны фасадных плит ножками в виде гибких монтажных полос; ножки закладных элементов фасадных плит загнуты вокруг стоек и зафиксированы за счет винтовых соединений, например, саморезов или заклепок; между стойками наружного ряда каркаса по всей высоте наружной стенки опалубки и с примыканием к ее внутренней поверхности сформированы вентиляционные каналы; вентиляционные каналы могут быть сформированы за счет размещения с внутренней стороны внешней опалубки, переставляемых элементов в виде вкладышей с прямоугольной или полукруглой формой поперечного сечения, изготовленных из материала с низкой адгезией, например, фторопласта; вентиляционные каналы могут быть сформированы за счет размещения с внутренней стороны внешней опалубки гибких съемных вкладышей, выполненных из материала с низкой адгезией; вентиляционные каналы могут быть сформированы за счет вставок в виде перфорированных трубчатых элементов, снабженных оболочкой из парогазопроницаемого материала, например, из крафт бумаги; вентиляционные каналы должны быть сообщены с вентиляционными отверстиями, выполненными в наружных стенках опалубки.In all the above embodiments, the mounting connections of the frame racks are made in the form of horizontal and inclined, respectively, thermal profiles and strips; as guides and racks steel shaped galvanized profiles are used; racks, guides and mounting connections are fastened together by threaded connections and / or rivets; the vapor-permeable layer is made of gypsum-fiber or gypsum-pasteboard panels, including in moisture resistant performance; molded cladding materials are made of boards or panels, for example, such as siding with fastening boards and panels to the outer row of racks due to screw connections, for example, screws; plate cladding materials are made in the form of facade plates with smooth or tongue-and-groove edges and embedded elements in the form of U-shaped strip embedded elements, with legs protruding from the rear of the facade plates in the form of flexible mounting strips; the legs of the embedded elements of the facade slabs are bent around the uprights and fixed by screw connections, for example, screws or rivets; between the racks of the outer row of the frame along the entire height of the outer wall of the formwork and adjacent to its inner surface, ventilation ducts are formed; ventilation channels can be formed by placing on the inner side of the outer formwork, rearranged elements in the form of inserts with a rectangular or semicircular cross-sectional shape made of a material with low adhesion, for example, fluoroplastic; ventilation channels can be formed by placing on the inner side of the outer formwork flexible removable liners made of material with low adhesion; ventilation ducts can be formed by inserts in the form of perforated tubular elements provided with a sheath of vapor-permeable material, for example, of kraft paper; ventilation ducts must be in communication with ventilation holes made in the outer walls of the formwork.
Наличие двухрядного металлического каркаса между наружной и внутренней стенками опалубки значительно повышает прочностные характеристики многослойной монолитной стены при технологической простоте изготовления. Кроме того, выполнение наружной стенки опалубки в виде фасадной отделки здания, The presence of a two-row metal frame between the outer and inner walls of the formwork significantly increases the strength characteristics of a multilayer monolithic wall with technological simplicity of manufacture. In addition, the implementation of the outer wall of the formwork in the form of a facade finish of the building,
наряду со значительным снижением стоимости строительства, позволяет обеспечить декоративное многообразие оформлений фасадов зданий.Along with a significant reduction in construction costs, it allows to provide a decorative variety of design of building facades.
Полезная модель иллюстрируется чертежами, где:The utility model is illustrated by drawings, where:
На фиг.1а и 1б показаны общие виды (продольный разрез) вариантов выполнения стенового ограждения; на фиг.2 показан каркас, вид спереди этих вариантов выполнения;On figa and 1b shows General views (longitudinal section) of embodiments of the wall fencing; figure 2 shows the frame, front view of these embodiments;
на фиг.3 показан общий вид (продольный разрез) другого варианта выполнения стенового ограждения; на фиг.4 показан каркас, вид спереди этого варианта выполнения;figure 3 shows a General view (longitudinal section) of another embodiment of a wall fence; figure 4 shows the frame, front view of this embodiment;
на фиг.5 показан общий вид (продольный разрез) следующего варианта выполнения стенового ограждения; на фиг.6 показан каркас, вид спереди этого варианта выполнения;figure 5 shows a General view (longitudinal section) of the next embodiment of the wall fencing; figure 6 shows the frame, front view of this embodiment;
на фиг.7 и 8 показаны общие виды (продольные разрезы) других вариантов выполнения стенового ограждения; на фиг.9 показан каркас, вид спереди этих вариантов выполнения;Figures 7 and 8 show general views (longitudinal sections) of other embodiments of wall fencing; figure 9 shows the frame, front view of these embodiments;
На фиг.10 показан фрагмент (аксонометрия) [-образного стального оцинкованного профиля, с просечкой для вентиляционного канала;Figure 10 shows a fragment (axonometry) of a [-shaped galvanized steel profile, with a notch for the ventilation duct;
на фиг 11 - вид спереди варианта выполнения фасадной плиты;Fig. 11 is a front view of an embodiment of a facade slab;
на фиг.12 - закладной П-образный элемент фасадной плиты;in Fig.12 - mortgage U-shaped element of the facade plate;
на фиг.13 - фрагмент внешней облицовки;Fig.13 is a fragment of the outer lining;
на фиг.14 - общий вид варианта (аксонометрия) держателя;on Fig - General view of a variant (axonometry) of the holder;
на фиг.15 - узел крепления профилей в держателях;on Fig - node mounting profiles in the holders;
на фиг.16 - вариант крепления поперечин к профилям;in Fig.16 is an option for mounting the cross members to the profiles;
на фиг.17 - вариант крепления плит облицовки к поперечинам;on Fig - option mounting plates of the cladding to the cross members;
на фиг.18 - общий вид (продольный разрез) фрагмента закладной вставки для формирования вентиляционных каналов;on Fig is a General view (longitudinal section) of a fragment of a mortgage insert for the formation of ventilation ducts;
на фиг.19 - увеличенный фрагмент фиг.1, 7, 8, с частью вентиляционного канала и вентиляционным отверстием в наружной стенке опалубки.in Fig.19 is an enlarged fragment of Fig.1, 7, 8, with part of the ventilation channel and the ventilation hole in the outer wall of the formwork.
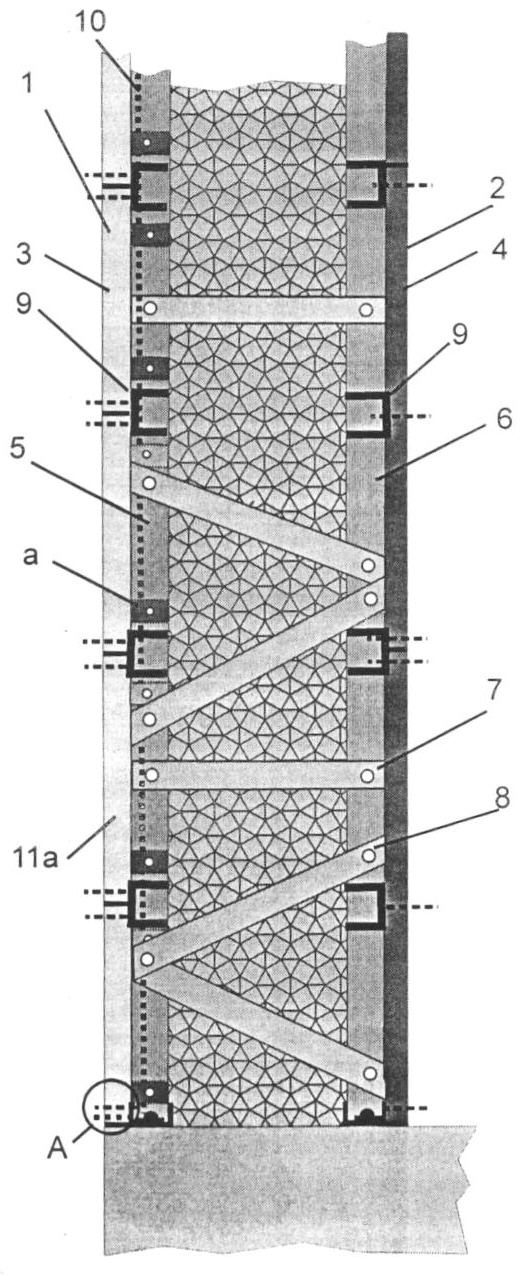
Стеновое ограждение, см. фиг.1, 2, содержит наружную и внутреннюю стенки 1 и 2 несъемной опалубки, выполненных, соответственно, из облицовочных плитных материалов в виде фасадных плит 3 и из парогазопроницаемых панелей 4, например, гипсоволокнистых или гипсокартонных (в т.ч. и влагостойких). Каркас выполнен в виде наружного и внутреннего рядов стоек 5 и 6 из оцинкованных металлических (стальных) профилей с фасонной, например, [-образной формой поперечного сечения (см. фиг.10). Стойки The wall fence, see figures 1, 2, contains the outer and inner walls 1 and 2 of the fixed formwork, made, respectively, of facing plate materials in the form of facade plates 3 and of vapor-vapor-permeable panels 4, for example, gypsum fiber or gypsum plasterboards (i.e. hours and moisture resistant). The frame is made in the form of the outer and inner rows of racks 5 and 6 of galvanized metal (steel) profiles with a shaped, for example, [-shaped cross-sectional shape (see Fig. 10). Racks
5 и 6 выполнены составными с длиной по высоте здания, которые установлены в наружном и внутренних рядах с соответствующим каждому ряду шагом. Стыковка составных стоек может быть выполнена любым известным способом, например, путем соединения концевых частей профилей с помощью накладок и саморезов. Оба ряда стоек 5 и 6 соединены между собой горизонтальными 7 и наклонными 8 монтажными связями. Смежные стойки каждого ряда могут быть соединены между собой поперечинами 9 из термопрофиля, например, из перфорированных оцинкованных металлических профилей с [-образной формой поперечного сечения, расположенных с шагом по высоте рядов составных стоек 5 и 6. Шаг установки поперечин 9 составляет не более высоты фасадных плит (наружный ряд и не более высоты панелей (внутренний ряд стоек). Наружная 1 и внутренняя 2 стенки опалубки прикреплены, соответственно к наружному и внутреннему рядам стоек 5 и 6. В качестве заполнителя между стенками 1 и 2 использован монолитный утеплитель, например, монолитный пенобетон. В слое монолитного утеплителя сформированы вентиляционные каналы 10, расположенные между стойками 5 по всей высоте наружной стенки опалубки с примыканием к внутренней стороне наружной стенки 1 опалубки. Фасадные плиты 3 могут быть выполнены как с ровными 11а, так и с пазогребневыми кромками 11б, см. фиг.1, 3, 11, 13. При сооружении несущей стены, например, при возведении одноэтажного здания, стойки выполнены из усиленного конструкционного профиля. При сооружении несущей стены малоэтажного здания, каркас может быть дополнительно снабжен несущими стойками 6а и балками «П» перекрытий, при этом несущие стойки 6а, выполнены из усиленного профиля и установлены с шагом между стойками 6 внутреннего рядя, которые в этом случае выполнены из обычного (не усиленного профиля). Этим обеспечивается необходимая прочность и теплоизоляция стенового ограждения.5 and 6 are made integral with a length along the height of the building, which are installed in the outer and inner rows with the corresponding step for each row. The joining of the composite racks can be performed in any known manner, for example, by connecting the ends of the profiles using plates and screws. Both rows of racks 5 and 6 are interconnected by horizontal 7 and inclined 8 mounting ties. Adjacent racks of each row can be interconnected by cross members 9 from a thermo-profile, for example, from perforated galvanized metal profiles with a [-shaped cross section, arranged with a step along the height of the rows of composite racks 5 and 6. The installation step of the cross-beams 9 is no more than the height of the front plates (outer row and not more than the height of the panels (inner row of racks). The outer 1 and inner 2 walls of the formwork are attached, respectively, to the outer and inner rows of racks 5 and 6. As a filler between walls 1 and 2 and monolithic insulation, for example, monolithic foam concrete, is used.In the layer of monolithic insulation, ventilation channels 10 are formed located between the posts 5 along the entire height of the outer wall of the formwork adjacent to the inner side of the outer wall of the formwork 1. Facade plates 3 can be made with even 11a or and with tongue-and-groove edges 11b, see FIGS. 1, 3, 11, 13. When constructing a load-bearing wall, for example, when erecting a one-story building, the racks are made of reinforced structural profile. When constructing the load-bearing wall of a low-rise building, the frame can be additionally equipped with load-bearing posts 6a and floor beams “P”, while the load-bearing posts 6a are made of reinforced profile and installed in increments between the posts 6 of the inner row, which in this case are made of ordinary ( not reinforced profile). This provides the necessary strength and thermal insulation of the wall fencing.
В вариантах выполнения, см. фиг.3-8, стеновые ограждения сооружаются на каркасах зданий в виде колонн с перекрытиями. В варианте, см., фиг.3-4, наружный ряд стоек 5 выполнен составным, при этом стойки состыкованы в держателях 12, закрепленных на перекрытиях 13 каркаса здания. Концы внутреннего ряда стоек 6 закреплены в верхних 14а и нижних 146 направляющих в виде профилей, закрепленных на поверхности перекрытий 13.In embodiments, see Figs. 3-8, wall fences are constructed on the frames of buildings in the form of columns with ceilings. In the embodiment, see FIGS. 3-4, the outer row of struts 5 is made integral, with the racks docked in holders 12 mounted on the ceilings 13 of the building frame. The ends of the inner row of uprights 6 are fixed in the upper 14a and lower 146 rails in the form of profiles fixed on the surface of the floors 13.
В варианте выполнения, см. фиг.5, 6, оба ряда стоек 5 и 6 закреплены между перекрытиями 13 посредством верхних и нижних направляющих, соответственно, 14а и 14б. В этом варианте, на наружном ряде стоек 5, по всей длине здания закреплены составные балки 15 установленные с шагом по высоте стоек 5. Смежные составные балки 15 могут быть соединены поперечинами 16 (см. фиг.16), установленными по In an embodiment, see FIGS. 5, 6, both rows of uprights 5 and 6 are secured between the ceilings 13 by means of the upper and lower guides, respectively, 14a and 14b. In this embodiment, on the outer row of racks 5, along the entire length of the building, composite beams 15 are mounted fixed in increments of the height of the racks 5. Adjacent composite beams 15 can be connected by cross members 16 (see Fig. 16) installed along
длине этих балок с шагом, составляющим не более ширины плит наружной облицовки. Наружная и внутренняя стенки несъемной опалубки закреплены, соответственно, на составных балках 15 с поперечинами 16 и внутреннем ряде стоек 6. Вентиляционные каналы в этом случае проходят сквозь составные балки 15, в которых выполнены сквозные просечки «п», см. фиг.10.the length of these beams in increments of no more than the width of the outer cladding plates. The outer and inner walls of the fixed formwork are fixed, respectively, on the composite beams 15 with the cross members 16 and the inner row of struts 6. The ventilation ducts in this case pass through the composite beams 15 in which the through-cuts “p” are made, see FIG. 10.
В варианте выполнения, см. фиг.7, так же как и в предыдущем варианте, оба ряда стоек 5 и 6 закреплены между перекрытиями посредством верхних и нижних направляющих, соответственно, 14а и 14б. Однако наружный и внутренний ряды стоек 5 и 6 установлены со смещением от торцов перекрытий с выполнением условия - размещения колонн 17 в слое заполнителя ближе к внутреннему ряду стоек 6, что обеспечивает теплоизоляцию. Наружная и внутренние стенки несъемной опалубки расположены между перекрытиями 13. Этот вариант выполнения предпочтителен при сооружении стеновых ограждения, примыкающим к лоджиям или балконам.In the embodiment, see Fig. 7, as in the previous embodiment, both rows of racks 5 and 6 are fixed between the ceilings by means of the upper and lower guides, respectively, 14a and 14b. However, the outer and inner rows of racks 5 and 6 are installed with an offset from the ends of the floors with the condition that the columns 17 are placed in the aggregate layer closer to the inner row of racks 6, which provides thermal insulation. The outer and inner walls of the fixed formwork are located between the floors 13. This embodiment is preferable for the construction of wall fencing adjacent to the loggias or balconies.
В варианте выполнения, см. фиг.8, наружная стенка несъемной опалубки примыкает к торцевым поверхностям перекрытий здания, при этом наружные ряды стоек 5 установлены с краю перекрытий, а вентиляционные каналы сформированы между перекрытиями.In the embodiment, see Fig. 8, the outer wall of the fixed formwork is adjacent to the end surfaces of the floors of the building, while the outer rows of racks 5 are installed with the edge of the floors, and ventilation ducts are formed between the floors.
Варианты по фиг.7, 8, менее материалоемки по сравнению с вариантом по фиг.5 (из-за отсутствия балок 15).The variants of Figs. 7, 8 are less material-intensive compared to the embodiment of Fig. 5 (due to the absence of beams 15).
Следует отметить, что в вариантах по фиг.3, 5, 7, 8, для снижения теплопотерь через торцы железобетонных перекрытий, стен и колонн предусмотрено (согласно Госту) устройство теплоизоляционных вставок «в».It should be noted that in the variants of FIGS. 3, 5, 7, 8, in order to reduce heat loss through the ends of reinforced concrete floors, walls and columns, a device for heat-insulating inserts “c” is provided (according to Gost).
В вариантах, показанных на фиг.1а, 1б, 3, 7 и 8, наружный и внутренний ряды стоек 5 и 6 установлены в рядах с соответствующим каждому ряду шагом. Целесообразно, чтобы шаг расположения стоек 5 в наружном ряду составлял не более ширины фасадных плит 3, а шаг установки стоек 6 внутреннего ряда составлял не более ширины панелей 4, что значительно упрощает и облегчает монтаж стенок 1 и 2 опалубки. Кроме того, во всех вариантах полезной модели, наружная стенка несъемной опалубки может быть выполнена из плитных или погонажных облицовочных материалов. При использовании погонажных облицовочных материалов, целесообразно использовать доски и/или панели, например, типа «сайдинга», которые могут быть прикреплены к наружному ряду стоек за счет винтовых соединений, например, саморезов. Общее требование к таким погонажныи облицовочным материалам - стойкость к внешним воздействиям, в т.ч. - влагостойкость.In the variants shown in figa, 1b, 3, 7 and 8, the outer and inner rows of the racks 5 and 6 are installed in rows with a step corresponding to each row. It is advisable that the step of arrangement of the uprights 5 in the outer row is no more than the width of the facade plates 3, and the installation step of the uprights 6 of the inner row is no more than the width of the panels 4, which greatly simplifies and facilitates the installation of the walls 1 and 2 of the formwork. In addition, in all variants of the utility model, the outer wall of the fixed formwork can be made of plate or molded facing materials. When using molded cladding materials, it is advisable to use boards and / or panels, for example, such as "siding", which can be attached to the outer row of racks due to screw connections, for example, screws. The general requirement for such molded cladding materials is resistance to external influences, incl. - moisture resistance.
При использовании плитных облицовочных материалов, эти материалы могут быть выполнены из фасадных плит как с ровными 11а кромками, так и с пазогребневыми 11б кромками и закладными элементами 18 в виде П-образных полосовых закладных элементов, с выступающими с тыльной стороны фасадных плит ножками «а» (см. фиг.12) в виде гибких монтажных полос. Фиксация ножек закладных элементов фасадных плит осуществлена как за счет их загибки вокруг стоек (или балок), так и за счет дополнительной фиксации на стойках (балках) посредством саморезов или заклепок. Парогозопронецаемый слой выполнен из панелей, например, гипсоволокнистых или гипсокартонных (в т.ч. во влагостойком исполнении), что облегчает монтаж внутренней стенки и снижает стоимость ограждения.When using plate cladding materials, these materials can be made of facade panels with even 11a edges, and with tongue-and-groove 11b edges and embedded elements 18 in the form of U-shaped strip embedded elements, with legs “a” protruding from the rear of the facade panels (see Fig. 12) in the form of flexible mounting strips. The fixing of the legs of the embedded elements of the facade slabs is carried out both due to their bending around the uprights (or beams), and due to the additional fixing on the uprights (beams) by means of self-tapping screws or rivets. The vapor-permeable layer is made of panels, for example, gypsum-fiber or gypsum plasterboards (including in a moisture-proof version), which facilitates the installation of the inner wall and reduces the cost of the fence.
Во всех вариантах полезной модели, предпочтительно, чтобы монтажные связи 7 и 8 были выполнены, соответственно, из термопрофилей и теромополос, т.е. из материалов, исключающих возникновение мостиков холода, например, из перфорированных оцинкованных металлических профилей и таких же полос. В качестве направляющих и стоек могут быть использованы стальные [-образные оцинкованные профили. Стойки, держатели, направляющие и монтажные связи могут быть скреплены между собой заклепками или резьбовыми соединениями, например, болтами или саморезами. Держатели 12 выполнены в виде фасонных накладок с боковыми щеками 19, снабженными удлиненными прорезями 20 под болты резьбовых соединений.In all variants of the utility model, it is preferable that the mounting connections 7 and 8 are, respectively, made of thermal profiles and thermal strips, i.e. from materials that exclude the occurrence of cold bridges, for example, from perforated galvanized metal profiles and the same strips. As guides and racks can be used steel [-shaped galvanized profiles. Racks, holders, guides and mounting links can be fastened together with rivets or threaded connections, for example, bolts or self-tapping screws. The holders 12 are made in the form of shaped overlays with side cheeks 19 provided with elongated slots 20 for bolts of threaded joints.
Сооружение вышеприведенных вариантов стеновых ограждений заключается в следующем.The construction of the above options for wall fencing is as follows.
На фундаменте здания (или в проемах между перекрытиями) монтируют двухрядный каркас, каркасные элементы которого (стойки, балки) связывают монтажными связями 7 и 8, которые выполняют, соответственно, из термопрофилей и термополос, т.е. из материалов, исключающих возникновение «мостиков холода», например, из перфорированных металлических оцинкованных профилей и полос. Наружный и внутренний ряды стоек 5 и 6 устанавливают в рядах с соответствующим каждому ряду шагом, причем шаг расположения стоек 5 в наружном ряду составляет не более ширины фасадных плит 3 (при использовании плитных облицовочных материалов), а шаг установки стоек 6 внутреннего ряда составляет не более ширины панелей 4, что позволяет значительно облегчить монтажные работы. На смонтированном каркасе закрепляют наружную 1 и внутреннюю 2 стенки несъемной опалубки, являющихся наружным и внутренним слоями стены (стенового ограждения). Затем, в пространство между стенками опалубки заливают утеплитель, в качестве которого используют, например, монолитный пенобетон. Для наружного слоя стен используют облицовочный материал в виде фасадных плит 3. Внутренний слой стен выполняют парогозопроницаемым, для чего используют, например, гипсокартонные или гипсоволокн истые панели 4, в т.ч. во влагостойком исполнении. Наращивание опалубки производят поярусно с поэтапным заполнением утеплителем A double-row frame is mounted on the foundation of the building (or in the openings between the floors), the frame elements of which (racks, beams) are connected by mounting ties 7 and 8, which are made, respectively, of thermal profiles and thermal strips, i.e. from materials that exclude the occurrence of "cold bridges", for example, from perforated galvanized metal profiles and strips. The outer and inner rows of racks 5 and 6 are installed in rows with a step corresponding to each row, and the step of arranging the racks 5 in the outer row is no more than the width of the facade panels 3 (when using plate facing materials), and the installation step of the racks 6 of the inner row is no more the width of the panels 4, which greatly facilitates installation work. On the mounted frame, the outer 1 and inner 2 walls of the fixed formwork are fixed, which are the outer and inner layers of the wall (wall fence). Then, a heater is poured into the space between the walls of the formwork, for example, monolithic foam concrete is used. For the outer layer of the walls, cladding material is used in the form of facade plates 3. The inner layer of the walls is vapor-permeable, for which purpose, for example, drywall or gypsum fiber panels 4 are used, including in moisture resistant performance. Formwork is produced in tiers with a gradual filling with insulation
пространство между стенками опалубки каждого яруса (по мере наращивания опалубки) с получением (в конечном итоге) в пространстве между стенками опалубки слоя монолитного пенобетона). В процессе поэтапной заливки утеплителя, в его слое формируют вентиляционные каналы, путем размещения с внутренней стороны внешней стенки 1 опалубки, переставляемых элементов (стоек) в виде вкладышей с прямоугольной или полукруглой формой поперечного сечения (условно не показаны), изготовленных из материала с низкой адгезией, например, фторопласта. Вкладыши устанавливают в пространстве между стенками опалубки с примыканием к внутренней поверхности стенки 1, перед заливкой порции утеплителя, а после заливки и набора начальной прочности уложенного слоя утеплителя, вкладыши приподнимают из этого слоя на высоту очередного укладываемого слоя с условием размещения нижних частей стоек-вкладышей в ранее затвердевшем слое. В некоторых случаях, например при размещении стенового ограждения в проемах между колоннами и перекрытиями, целесообразно, чтобы вкладыши были выполнены гибкими из материала с низкой адгезией к пенобетону. В этих случаях гибкие вкладыши оставляют в пространстве между стенками опалубки до полной заливки утеплителем всей высоты стенового ограждения, с последующим удалением вкладышей из затвердевшего слоя утеплителя, за счет выдергивания за верхний (или нижний) свободный конец. Вентиляционные каналы могут быть также сформированы за счет размещения с внутренней стороны внешней стенки опалубки 1 закладных вставок в виде перфорированных трубчатых элементов 21 (см. фиг.18), снабженных оболочкой 22 из любого парогазопроницаемого материала, например, из крафт бумаги. Закладные вставки оставляют в слое пенобетона, при этом за счет оболочки 22 исключается (в процессе заливки) попадание жидкого утеплителя внутрь вставок 21. Эти вставки выполняют или на всю высоту здания (составные вставки), или располагают между перекрытиями 13. При любом варианте выполнения, вентиляционные каналы 10 сообщают с вентиляционными отверстиями, которые выполняют в наружных стенках 1 опалубки, см. фиг.19.the space between the walls of the formwork of each tier (as the formwork increases) to obtain (ultimately) in the space between the walls of the formwork a layer of monolithic foam concrete). In the process of stage-by-stage filling of the insulation, ventilation ducts are formed in its layer by placing on the inner side of the outer wall 1 of the formwork, rearranged elements (racks) in the form of inserts with a rectangular or semicircular cross-sectional shape (not shown conditionally) made of a material with low adhesion , for example, fluoroplastic. The liners are installed in the space between the walls of the formwork adjacent to the inner surface of the wall 1, before pouring a portion of the insulation, and after pouring and setting the initial strength of the laid layer of insulation, the liners are lifted from this layer to the height of the next laying layer with the condition of placing the lower parts of the racks-inserts in previously hardened layer. In some cases, for example, when placing a wall fence in the openings between columns and ceilings, it is advisable that the liners be made of flexible material with low adhesion to foam concrete. In these cases, flexible liners are left in the space between the walls of the formwork until the heater completely fills the entire height of the wall fence, followed by removal of the liners from the hardened layer of insulation, by pulling out the upper (or lower) free end. Ventilation channels can also be formed by placing on the inner side of the outer wall of the formwork 1 embedded inserts in the form of perforated tubular elements 21 (see Fig. 18) provided with a shell 22 of any vapor-permeable material, for example, of kraft paper. Mortgage inserts are left in the foam concrete layer, and due to the shell 22, liquid insulation is prevented (during pouring) from entering the heat insulation inside the inserts 21. These inserts are either filled to the entire height of the building (composite inserts), or are placed between floors 13. In any embodiment, ventilation ducts 10 communicate with ventilation holes that are performed in the outer walls 1 of the formwork, see Fig. 19.
Наличие двух рядов каркасных элементов и выполнение слоя заполнителя из монолитного пенобетона повышает прочностные характеристики и теплоизоляционные свойства стенового ограждения, являющегося по существу многослойной монолитной стеной с жестким каркасом (который может быть выполнен из любых подходящих конструкционных материалов, в т.ч. металла, дерева или их сочетания), что позволяет использовать предложенную полезную модель не только для сооружения стеновых ограждений, но и для сооружения несущих стен малоэтажных зданий.The presence of two rows of frame elements and the implementation of a layer of aggregate of monolithic foam concrete increases the strength characteristics and thermal insulation properties of the wall fence, which is essentially a multilayer monolithic wall with a rigid frame (which can be made of any suitable structural materials, including metal, wood or their combinations), which makes it possible to use the proposed utility model not only for the construction of wall fences, but also for the construction of load-bearing walls of low-rise buildings.
Claims (58)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2008119962/22U RU79304U1 (en) | 2008-05-21 | 2008-05-21 | WALL PROTECTION FOR BUILDINGS AND STRUCTURES (OPTIONS) |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2008119962/22U RU79304U1 (en) | 2008-05-21 | 2008-05-21 | WALL PROTECTION FOR BUILDINGS AND STRUCTURES (OPTIONS) |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU79304U1 true RU79304U1 (en) | 2008-12-27 |
Family
ID=48229447
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2008119962/22U RU79304U1 (en) | 2008-05-21 | 2008-05-21 | WALL PROTECTION FOR BUILDINGS AND STRUCTURES (OPTIONS) |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU79304U1 (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015053654A1 (en) * | 2013-10-07 | 2015-04-16 | Алексей Игоревич ЦАПЛИН | Framing wall |
| RU188530U1 (en) * | 2018-06-14 | 2019-04-16 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью ООО "ОНЕКС" | The wall of the building is made of monolithic structural heat-insulating fiber-reinforced concrete with fixed formwork |
| RU2706288C1 (en) * | 2019-01-30 | 2019-11-15 | Сергей Михайлович Анпилов | Construction method |
| RU196310U1 (en) * | 2019-10-31 | 2020-02-25 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью "Национальная энергетическая компания" (ООО "НЭК") | Design with inner and outer lining on the LSTK frame with filling the inner cavity with foam concrete |
| RU213620U1 (en) * | 2022-04-14 | 2022-09-19 | Владимир Викторович Лозенко | WALL PANEL |
| WO2023200365A1 (en) * | 2022-04-14 | 2023-10-19 | Владимир Викторович ЛОЗЕНКО | Wall panel |
-
2008
- 2008-05-21 RU RU2008119962/22U patent/RU79304U1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015053654A1 (en) * | 2013-10-07 | 2015-04-16 | Алексей Игоревич ЦАПЛИН | Framing wall |
| RU188530U1 (en) * | 2018-06-14 | 2019-04-16 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью ООО "ОНЕКС" | The wall of the building is made of monolithic structural heat-insulating fiber-reinforced concrete with fixed formwork |
| RU2706288C1 (en) * | 2019-01-30 | 2019-11-15 | Сергей Михайлович Анпилов | Construction method |
| RU196310U1 (en) * | 2019-10-31 | 2020-02-25 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью "Национальная энергетическая компания" (ООО "НЭК") | Design with inner and outer lining on the LSTK frame with filling the inner cavity with foam concrete |
| RU213620U1 (en) * | 2022-04-14 | 2022-09-19 | Владимир Викторович Лозенко | WALL PANEL |
| WO2023200365A1 (en) * | 2022-04-14 | 2023-10-19 | Владимир Викторович ЛОЗЕНКО | Wall panel |
| RU2799676C1 (en) * | 2023-02-27 | 2023-07-10 | Федеральное государственное автономное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Северо-Восточный федеральный университет имени М.К.Аммосова" | Method of pairing a wall of light steel thin-walled structures with a basement over ventilated and cold undergrounds |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| RU2463413C2 (en) | Composite product for designed slabs | |
| CA2674833C (en) | Pre-cast rain screen wall panel | |
| US9856639B2 (en) | Wall assembly and a building structure including the wall assembly | |
| US20090113820A1 (en) | Prefabricated wall panel system | |
| US20100287865A1 (en) | Pre-cast rain screen wall panel | |
| US20150247317A1 (en) | Tension Reinforcement for Concrete | |
| US9399867B2 (en) | Concrete panel corner connection | |
| RU2376424C1 (en) | Ready-built and solid-cast building construction system | |
| RU79304U1 (en) | WALL PROTECTION FOR BUILDINGS AND STRUCTURES (OPTIONS) | |
| RU73889U1 (en) | BUILDING WALL (OPTIONS) | |
| RU2381334C1 (en) | Frame building | |
| RU2440472C1 (en) | Method to erect monolithic construction structure of building or facility "bliss house" | |
| RU2385998C1 (en) | Wall | |
| RU55804U1 (en) | RESIDENTIAL FRAME BUILDING, BUILDING FRAME AND BUILDING WALL | |
| EA012427B1 (en) | Insulating form for concrete walls | |
| RU76357U1 (en) | FRAME-PANEL BUILDING | |
| CA2566566C (en) | Multi-storey insulated concrete foam building and method of construction thereof | |
| RU2633602C1 (en) | Method of accelerated building erection using method of screwdriver assembly and building from facade panels with decorative external finishing and metal framework | |
| RU84033U1 (en) | WALL | |
| RU2422603C1 (en) | Block of slab retained form | |
| EP2063041B1 (en) | Prefabricated wall element with a skeleton for fastening boards | |
| RU94601U1 (en) | BLOCK FORMWORK | |
| RU213620U1 (en) | WALL PANEL | |
| US2212906A (en) | Building construction | |
| JP3627927B2 (en) | Reinforced concrete exterior insulation building |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM9K | Utility model has become invalid (non-payment of fees) |
Effective date: 20170522 |