JP6740422B2 - Optical glass and optical element - Google Patents
Optical glass and optical element Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6740422B2 JP6740422B2 JP2019087337A JP2019087337A JP6740422B2 JP 6740422 B2 JP6740422 B2 JP 6740422B2 JP 2019087337 A JP2019087337 A JP 2019087337A JP 2019087337 A JP2019087337 A JP 2019087337A JP 6740422 B2 JP6740422 B2 JP 6740422B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- component
- glass
- optical
- less
- content
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000005304 optical glass Substances 0.000 title claims description 93
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 title claims description 41
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 20
- 229910021193 La 2 O 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 16
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- 229910010413 TiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052688 Gadolinium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052769 Ytterbium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052746 lanthanum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052727 yttrium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000004615 ingredient Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 128
- 238000004031 devitrification Methods 0.000 description 42
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 32
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 23
- 238000002834 transmittance Methods 0.000 description 20
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 17
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 16
- 230000001965 increasing effect Effects 0.000 description 16
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N platinum Chemical compound [Pt] BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- 238000004040 coloring Methods 0.000 description 11
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 11
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 11
- 229910018068 Li 2 O Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 229910006404 SnO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 239000006060 molten glass Substances 0.000 description 8
- 229910018072 Al 2 O 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 229910015902 Bi 2 O 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 229910005191 Ga 2 O 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 229910005793 GeO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 7
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000009477 glass transition Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229910052761 rare earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000003595 spectral effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 206010040925 Skin striae Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000013585 weight reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004075 alteration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052788 barium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052792 caesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000004679 hydroxides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910052744 lithium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000007517 polishing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052712 strontium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910018626 Al(OH) Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910016569 AlF 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910016036 BaF 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910004261 CaF 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910005690 GdF 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910013553 LiNO Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052765 Lutetium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- UEZVMMHDMIWARA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Metaphosphoric acid Chemical class OP(=O)=O UEZVMMHDMIWARA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910008449 SnF 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052776 Thorium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005275 alloying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002518 antifoaming agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001495 arsenic compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052790 beryllium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052793 cadmium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004649 carbonic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000005266 casting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052804 chromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007812 deficiency Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003292 diminished effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000006025 fining agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004673 fluoride salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000007496 glass forming Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005816 glass manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940093920 gynecological arsenic compound Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000002611 lead compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052748 manganese Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910001512 metal fluoride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052758 niobium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000002823 nitrates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910000510 noble metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052762 osmium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000704 physical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003303 reheating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052711 selenium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000010583 slow cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052716 thallium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- QHGNHLZPVBIIPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N tin(II) oxide Inorganic materials [Sn]=O QHGNHLZPVBIIPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052723 transition metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000003624 transition metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052720 vanadium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052726 zirconium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Landscapes
- Glass Compositions (AREA)
Description
本発明は、光学ガラス及び光学素子に関する。 The present invention relates to an optical glass and an optical element.
近年、光学系を使用する機器のデジタル化や高精細化が急速に進んでおり、デジタルカメラやビデオカメラ等の撮影機器や、プロジェクタやプロジェクションテレビ等の画像再生(投影)機器等の各種光学機器の分野では、光学系で用いられるレンズやプリズム等の光学素子の枚数を削減し、光学系全体を軽量化及び小型化する要求が強まっている。 In recent years, digitalization and high definition of devices using an optical system have been rapidly advanced, and various optical devices such as photographing devices such as digital cameras and video cameras and image reproducing (projection) devices such as projectors and projection televisions. In the field, there is an increasing demand for reducing the number of optical elements such as lenses and prisms used in the optical system and reducing the weight and size of the entire optical system.
光学素子を作製する光学ガラスの中でも特に、光学系全体の軽量化及び小型化を図ることが可能な、1.75以上の屈折率(nd)を有し、23以上50以下のアッベ数(νd)を有する高屈折率低分散ガラスの需要が非常に高まっている。このような高屈折率低分散ガラスとしては、特許文献1及び2に代表されるようなガラス組成物が知られている。 Among optical glasses for producing optical elements, in particular, the optical system has a refractive index ( nd ) of 1.75 or more and can reduce the weight and size of the entire optical system, and has an Abbe number of 23 or more and 50 or less ( The demand for high-refractive-index, low-dispersion glasses with ν d ) is very high. As such a high refractive index and low dispersion glass, glass compositions represented by Patent Documents 1 and 2 are known.
光学ガラスから光学素子を作製する方法としては、例えば、光学ガラスから形成されたゴブ又はガラスブロックに対して研削及び研磨を行って光学素子の形状を得る方法、光学ガラスから形成されたゴブ又はガラスブロックを再加熱して成形(リヒートプレス成形)して得られたガラス成形体を研削及び研磨する方法、及び、ゴブ又はガラスブロックから得られたプリフォーム材を超精密加工された金型で成形(精密モールドプレス成形)して光学素子の形状を得る方法が知られている。いずれの方法であっても、熔融したガラス原料からゴブ又はガラスブロックを形成する際に、安定なガラスが得られることが求められる。 As a method for producing an optical element from optical glass, for example, a method for obtaining a shape of an optical element by grinding and polishing a gob or a glass block formed from the optical glass, a gob or glass formed from the optical glass. A method of grinding and polishing a glass molded body obtained by reheating a block and molding (reheat press molding), and molding a preform material obtained from a gob or a glass block with an ultra-precision machined mold A method of obtaining the shape of an optical element by (precision mold press molding) is known. Whichever method is used, it is required to obtain stable glass when forming a gob or a glass block from a molten glass raw material .
ここで、得られるゴブ又はガラスブロックを構成するガラスの失透に対する安定性(耐失透性)が低下してガラスの内部に結晶が発生した場合、もはや光学素子として好適なガラスを得ることができない。Here, when the stability of the glass constituting the gob or the glass block to be obtained against devitrification (devitrification resistance) is lowered and crystals are generated inside the glass, it is no longer possible to obtain a glass suitable as an optical element. Can not.
また、光学ガラスの材料コストを低減するために、光学ガラスを構成する諸成分の原料費は、なるべく安価であることが望まれる。ところが、特許文献1及び2に記載されたガラスは、このような要求に十分応えるものとは言い難い。Further, in order to reduce the material cost of the optical glass, it is desired that the raw material costs of the components constituting the optical glass be as low as possible. However, it is difficult to say that the glasses described in Patent Documents 1 and 2 sufficiently meet such requirements.
本発明は、上記問題点に鑑みてなされたものであって、その目的とするところは、屈折率及びアッベ数が所望の範囲内にある安定なガラスを、より安価に得ることにある。 The present invention has been made in view of the above problems, and an object of the present invention is to obtain a stable glass having a refractive index and an Abbe number within desired ranges at a lower cost.
本発明者らは、上記課題を解決するために、鋭意試験研究を重ねた結果、B2O3成分及びLa2O3成分を必須成分として含有するガラスにおいて、Y2O3成分の含有量を所定の範囲内におくことにより、所望の高屈折率及び高アッベ数を有する安定なガラスが得られながらも、ガラスの材料コストが低減されることを見出し、本発明を完成するに至った。具体的には、本発明は以下のようなものを提供する。 In order to solve the above-mentioned problems, the inventors of the present invention have conducted extensive studies to find that the content of the Y 2 O 3 component in the glass containing the B 2 O 3 component and the La 2 O 3 component as essential components. by placing the within a predetermined range, stable glass having a desired high refractive index and high Abbe number while obtained, found that the material cost of the glass is reduced, thereby completing the present invention .. Specifically, the present invention provides the following.
(1) 質量%でB2O3成分を1.0〜30.0%及びLa2O3成分を10.0〜60.0%含有し、Y2O3成分の含有量が30.0%以下である光学ガラス。 (1) the B 2 O 3 component in weight% containing 10.0 to 60.0% of 1.0 to 30.0% and La 2 O 3 component, the content of Y 2 O 3 component 30.0 % Or less optical glass.
(2) 質量%で
Gd2O3成分 0〜40.0%
Yb2O3成分 0〜20.0%
である(1)に記載の光学ガラス。
(2) Gd 2 O 3 component 0 to 40.0% by mass%
Yb 2 O 3 component 0 to 20.0%
The optical glass according to (1).
(3) Ln2O3成分(式中、LnはLa、Gd、Y、Ybからなる群より選択される1種以上)の質量和が30.0%以上70.0%以下である(1)又は(2)に記載の光学ガラス。 (3) The sum of Ln 2 O 3 components (wherein Ln is at least one selected from the group consisting of La, Gd, Y, and Yb) is 30.0% or more and 70.0% or less (1 ) Or the optical glass as described in (2).
(4) 質量比(Gd2O3+Yb2O3)/(La2O3+Y2O3)が0.50以下である(1)から(3)のいずれかに記載の光学ガラス。 (4) The optical glass as described in any one of (1) to (3), wherein the mass ratio (Gd 2 O 3 +Yb 2 O 3 )/(La 2 O 3 +Y 2 O 3 ) is 0.50 or less.
(5) 質量%で、Ta2O5成分の含有量が15.0%以下である(1)から(4)のいずれかに記載の光学ガラス。 (5) The optical glass according to any one of (1) to (4), wherein the content of the Ta 2 O 5 component is 15.0% or less in mass%.
(6) Gd2O3成分、Yb2O3成分及びTa2O5成分の含有量の和が20.0%以下である(1)から(5)のいずれかに記載の光学ガラス。 (6) The optical glass as described in any one of (1) to (5), wherein the sum of the contents of the Gd 2 O 3 component, the Yb 2 O 3 component and the Ta 2 O 5 component is 20.0% or less.
(7) 質量%で
WO3成分 0〜25.0%
Nb2O5成分 0〜20.0%
TiO2成分 0〜20.0%
である(1)から(6)のいずれかに記載の光学ガラス。
(7) WO 3 component 0 to 25.0% by mass%
Nb 2 O 5 component 0 to 20.0%
TiO 2 component 0 to 20.0%
The optical glass according to any one of (1) to (6).
(8) Nb2O5成分及びWO3成分の含有量の和が1.0%以上30.0%以下である(1)から(7)のいずれかに記載の光学ガラス。 (8) The optical glass according to any one of (1) to (7), wherein the sum of the contents of the Nb 2 O 5 component and the WO 3 component is 1.0% or more and 30.0% or less.
(9) 質量%で、SiO2成分の含有量が20.0%以下である(1)から(8)のいずれかに記載の光学ガラス。 (9) The optical glass as described in any one of (1) to (8), wherein the content of the SiO 2 component is 20.0% or less in mass %.
(10) B2O3成分及びSiO2成分の含有量の和が1.0%以上30.0%以下である(1)から(9)のいずれかに記載の光学ガラス。 (10) The optical glass according to any one of (1) to (9), wherein the sum of the contents of the B 2 O 3 component and the SiO 2 component is 1.0% or more and 30.0% or less.
(11) 質量比(Nb2O5+WO3)/(B2O3+SiO2)が0.15以上2.00以下である(1)から(10)のいずれかに記載の光学ガラス。 (11) The optical glass according to any one of (1) to (10), wherein the mass ratio (Nb 2 O 5 +WO 3 )/(B 2 O 3 +SiO 2 ) is 0.15 or more and 2.00 or less.
(12) 質量%で
MgO成分 0〜20.0%
CaO成分 0〜20.0%
SrO成分 0〜20.0%
BaO成分 0〜25.0%
である(1)から(11)のいずれかに記載の光学ガラス。
(12) 0 to 20.0% by weight of MgO component
CaO component 0-20.0%
SrO component 0-20.0%
BaO component 0 to 25.0%
The optical glass according to any one of (1) to (11).
(13) RO成分(式中、RはMg、Ca、Sr、Baからなる群より選択される1種以上)の質量和が25.0%以下である(1)から(12)のいずれかに記載の光学ガラス。 (13) Any one of (1) to (12) in which the mass sum of the RO component (wherein R is at least one selected from the group consisting of Mg, Ca, Sr, and Ba) is 25.0% or less. Optical glass according to.
(14) 質量%で
Li2O成分 0〜10.0%
Na2O成分 0〜10.0%
K2O成分 0〜10.0%
Cs2O成分 0〜10.0%
である(1)から(13)のいずれかに記載の光学ガラス。
(14)% by weight Li 2 O component from 0 to 10.0%
Na 2 O component 0 to 10.0%
K 2 O component 0 to 10.0%
Cs 2 O component 0 to 10.0%
The optical glass according to any one of (1) to (13).
(15) Rn2O成分(式中、RnはLi、Na、K、Csからなる群より選択される1種以上)の質量和が15.0%以下である(1)から(14)のいずれかに記載の光学ガラス。 (15) The sum of masses of the Rn 2 O components (in the formula, Rn is at least one selected from the group consisting of Li, Na, K, and Cs) is 15.0% or less, and (1) to (14) The optical glass according to any of the above.
(16) 質量%で
P2O5成分 0〜10.0%
GeO2成分 0〜10.0%
ZrO2成分 0〜15.0%
ZnO成分 0〜15.0%
Al2O3成分 0〜10.0%
Ga2O3成分 0〜10.0%
Bi2O3成分 0〜10.0%
TeO2成分 0〜20.0%
SnO2成分 0〜1.0%
Sb2O3成分 0〜1.0%
である(1)から(15)のいずれか記載の光学ガラス。
(16)% by weight P 2 O 5 component from 0 to 10.0%
GeO 2 component 0 to 10.0%
ZrO 2 component 0 to 15.0%
ZnO component 0 to 15.0%
Al 2 O 3 component 0 to 10.0%
Ga 2 O 3 component 0 to 10.0%
Bi 2 O 3 component 0 to 10.0%
TeO 2 component 0 to 20.0%
SnO 2 component 0-1.0%
Sb 2 O 3 component 0-1.0%
The optical glass according to any one of (1) to (15).
(17) 1.75以上の屈折率(nd)を有し、23以上50以下のアッベ数(νd)を有する(1)から(16)のいずれか記載の光学ガラス。 (17) has 1.75 or more of refractive index (n d), 23 to 50. Abbe number ([nu d) any description of the optical glass (1) to (16) having a.
(18) 1300℃以下の液相温度を有する(1)から(17)のいずれか記載の光学ガラス。 (18) The optical glass according to any one of (1) to (17), which has a liquidus temperature of 1300° C. or lower.
(19) (1)から(18)のいずれか記載の光学ガラスを母材とする光学素子。 (19) An optical element using the optical glass according to any one of (1) to (18) as a base material.
(20) (19)記載の光学素子を備える光学機器。 (20) An optical device including the optical element according to (19).
本発明によれば、屈折率及びアッベ数が所望の範囲内にあり、且つ光学機器の軽量化に寄与しうる安定なガラスを、より安価に得ることができる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, the stable glass which has a refractive index and an Abbe number in a desired range and can contribute to weight reduction of an optical device can be obtained more cheaply.
本発明の光学ガラスは、酸化物換算組成のガラス全質量に対する質量%で、B2O3成分を1.0〜30.0%及びLa2O3成分を10.0〜60.0%含有し、Y2O3成分の含有量が30.0%以下である。La2O3成分を必須成分として含有し、且つY2O3成分の含有量を所定の範囲内にすることで、高価であり且つガラスの比重を増加することの多い希土類元素、特にGd2O3やYb2O3を低減しても、高い屈折率及びアッベ数が得られ、且つ液相温度の上昇が抑えられる。そのため、1.75以上の屈折率及び23以上50以下のアッベ数を有しながらも、比重が小さく光学機器の軽量化に寄与しうる、耐失透性の高い光学ガラスを、より安価に得ることができる。 The optical glass of the present invention contains the B 2 O 3 component in an amount of 1.0 to 30.0% and the La 2 O 3 component in an amount of 1.0 to 60.0% by mass% based on the total mass of the glass in terms of oxide composition. However, the content of the Y 2 O 3 component is 30.0% or less. By containing the La 2 O 3 component as an essential component and setting the content of the Y 2 O 3 component within a predetermined range, a rare earth element which is expensive and often increases the specific gravity of glass, particularly Gd 2 Even if O 3 and Yb 2 O 3 are reduced, a high refractive index and Abbe number can be obtained, and an increase in liquidus temperature can be suppressed. Therefore, an optical glass having a high devitrification resistance, which has a refractive index of 1.75 or more and an Abbe's number of 23 or more and 50 or less and which has a small specific gravity and can contribute to weight reduction of optical equipment, can be obtained at a lower cost. be able to.
以下、本発明の光学ガラスの実施形態について詳細に説明するが、本発明は、以下の実施形態に何ら限定されるものではなく、本発明の目的の範囲内において、適宜変更を加えて実施することができる。なお、説明が重複する箇所については、適宜説明を省略する場合があるが、発明の趣旨を限定するものではない。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the optical glass of the present invention will be described in detail, but the present invention is not limited to the following embodiments, and is appropriately modified and implemented within the scope of the object of the present invention. be able to. It should be noted that although the description may be omitted as appropriate for the overlapping description, it does not limit the gist of the invention.
[ガラス成分]
本発明の光学ガラスを構成する各成分の組成範囲を以下に述べる。本明細書中で特に断りがない場合、各成分の含有量は、全て酸化物換算組成のガラス全質量に対する質量%で表示されるものとする。ここで、「酸化物換算組成」とは、本発明のガラス構成成分の原料として使用される酸化物、複合塩、金属弗化物等が熔融時に全て分解され酸化物へ変化すると仮定した場合に、当該生成酸化物の総質量を100質量%として、ガラス中に含有される各成分を表記した組成である。
[Glass component]
The composition range of each component constituting the optical glass of the present invention will be described below. In the present specification, unless otherwise specified, the content of each component is represented by% by mass based on the total mass of the glass having an oxide-converted composition. Here, the "oxide equivalent composition" means that when the oxide used as a raw material of the glass constituent of the present invention, a complex salt, a metal fluoride and the like are all decomposed during melting and converted into an oxide, It is a composition in which each component contained in the glass is expressed with the total mass of the produced oxide as 100 mass %.
<必須成分、任意成分について>
B2O3成分は、ガラス形成酸化物として欠かすことの出来ない必須成分である。
特に、B2O3成分を1.0%以上含有することで、ガラスの耐失透性を高められ、且つガラスの分散を小さくできる。従って、B2O3成分の含有量は、好ましくは1.0%、より好ましくは5.0%、さらに好ましくは8.5%、さらに好ましくは10.5%を下限とする。
一方、B2O3成分の含有量を30.0%以下にすることで、より大きな屈折率を得易くでき、化学的耐久性の悪化を抑えられる。従って、B2O3成分の含有量は、好ましくは30.0%、より好ましくは25.0%、さらに好ましくは20.0%を上限とする。
B2O3成分は、原料としてH3BO3、Na2B4O7、Na2B4O7・10H2O、BPO4等を用いることができる。
<About essential and optional components>
The B 2 O 3 component is an essential component that is indispensable as a glass-forming oxide.
In particular, by containing the B 2 O 3 component in an amount of 1.0% or more, the devitrification resistance of the glass can be increased and the dispersion of the glass can be reduced. Therefore, the lower limit of the content of the B 2 O 3 component is preferably 1.0%, more preferably 5.0%, further preferably 8.5%, and further preferably 10.5%.
On the other hand, by setting the content of the B 2 O 3 component to 30.0% or less, it is possible to easily obtain a larger refractive index and suppress deterioration of chemical durability. Therefore, the upper limit of the content of the B 2 O 3 component is preferably 30.0%, more preferably 25.0%, and further preferably 20.0%.
As the B 2 O 3 component, H 3 BO 3 , Na 2 B 4 O 7 , Na 2 B 4 O 7 ·10H 2 O, BPO 4 or the like can be used as a raw material.
La2O3成分は、ガラスの屈折率を高め、分散を小さく(アッベ数を大きく)する成分である。特に、La2O3成分を10.0%以上含有することで、所望の高屈折率を得ることができる。従って、La2O3成分の含有量は、好ましくは10.0%、より好ましくは20.0%、さらに好ましくは26.0%、さらに好ましくは34.0%、さらに好ましくは39.0%を下限とする。
一方、La2O3成分の含有量を60.0%以下にすることで、ガラスの耐失透性を高められる。従って、La2O3成分の含有量は、好ましくは60.0%、より好ましくは58.0%、さらに好ましくは56.0%を上限とする。
La2O3成分は、原料としてLa2O3、La(NO3)3・XH2O(Xは任意の整数)等を用いることができる。
The La 2 O 3 component is a component that increases the refractive index of glass and reduces dispersion (enlarges Abbe number). In particular, by containing the La 2 O 3 component in an amount of 10.0% or more, a desired high refractive index can be obtained. Therefore, the content of the La 2 O 3 component is preferably 10.0%, more preferably 20.0%, further preferably 26.0%, further preferably 34.0%, further preferably 39.0%. Is the lower limit.
On the other hand, when the content of the La 2 O 3 component is 60.0% or less, the devitrification resistance of the glass can be improved. Therefore, the upper limit of the content of the La 2 O 3 component is preferably 60.0%, more preferably 58.0%, further preferably 56.0%.
As the La 2 O 3 component, La 2 O 3 , La(NO 3 ) 3 .XH 2 O (X is an arbitrary integer) or the like can be used as a raw material.
Y2O3成分は、0%超含有する場合に、高屈折率及び高アッベ数を維持しながらも、ガラスの材料コストを抑えられ、且つ比重を低減できる任意成分である。このY2O3成分は、希土類元素の中でも材料コストが安く、他の希土類元素に比べて比重を低減し易いため、本発明の光学ガラスにとって有用である。従って、Y2O3成分の含有量は、好ましくは0%超、より好ましくは0.5%超、さらに好ましくは1.0%超としてもよい。
一方で、Y2O3成分の含有量を30.0%以下にすることで、ガラスの屈折率の低下を抑えられ、且つガラスの耐失透性を高められる。従って、Y2O3成分の含有量は、好ましくは30.0%、より好ましくは25.0%、さらに好ましくは20.0%を上限とする。
Y2O3成分は、原料としてY2O3、YF3等を用いることができる。
The Y 2 O 3 component is an optional component capable of suppressing the material cost of glass and reducing the specific gravity while maintaining a high refractive index and a high Abbe number when the content exceeds 0%. The Y 2 O 3 component is low in material cost among rare earth elements and easily reduces specific gravity as compared with other rare earth elements, and thus is useful for the optical glass of the present invention. Therefore, the content of the Y 2 O 3 component may be preferably more than 0%, more preferably more than 0.5%, still more preferably more than 1.0%.
On the other hand, by setting the content of the Y 2 O 3 component to 30.0% or less, it is possible to suppress the decrease in the refractive index of the glass and to enhance the devitrification resistance of the glass. Therefore, the upper limit of the content of the Y 2 O 3 component is preferably 30.0%, more preferably 25.0%, and further preferably 20.0%.
As the Y 2 O 3 component, Y 2 O 3 , YF 3 or the like can be used as a raw material.
Gd2O3成分は、0%超含有する場合に、ガラスの屈折率を高め、且つアッベ数を高められる任意成分である。
一方で、希土類元素の中でも特に高価なGd2O3成分を40.0%以下に低減することで、ガラスの材料コストが低減されるため、より安価な光学ガラスを作製できる。また、これによりガラスのアッベ数の必要以上の上昇を抑えられる。従って、Gd2O3成分の含有量は、それぞれ好ましくは40.0%、より好ましくは30.0%、さらに好ましくは20.0%、さらに好ましくは15.0%を上限とし、さらに好ましくは10.0%未満とする。
Gd2O3成分は、原料としてGd2O3、GdF3等を用いることができる。
The Gd 2 O 3 component is an optional component capable of increasing the refractive index of glass and increasing the Abbe number when the content exceeds 0%.
On the other hand, by reducing the Gd 2 O 3 component, which is particularly expensive among rare earth elements, to 40.0% or less, the material cost of the glass is reduced, and thus a cheaper optical glass can be manufactured. In addition, this can prevent the Abbe number of the glass from increasing more than necessary. Therefore, the content of the Gd 2 O 3 component is preferably 40.0%, more preferably 30.0%, further preferably 20.0%, further preferably 15.0% as the upper limit, and further preferably It is less than 10.0%.
For the Gd 2 O 3 component, Gd 2 O 3 , GdF 3 or the like can be used as a raw material.
Yb2O3成分は、0%超含有する場合に、ガラスの屈折率を高め、且つ分散を小さくできる任意成分である。
一方で、Yb2O3成分の含有量を20.0%以下にすることで、ガラスの耐失透性を高められる。従って、Yb2O3成分の含有量は、好ましくは20.0%、より好ましくは10.0%、さらに好ましくは5.0%を上限とする。
Yb2O3成分は、原料としてYb2O3等を用いることができる。
The Yb 2 O 3 component is an optional component that can increase the refractive index of the glass and reduce the dispersion when the content exceeds 0%.
On the other hand, by setting the content of the Yb 2 O 3 component to 20.0% or less, the devitrification resistance of the glass can be enhanced. Therefore, the upper limit of the content of the Yb 2 O 3 component is preferably 20.0%, more preferably 10.0%, and further preferably 5.0%.
As the Yb 2 O 3 component, Yb 2 O 3 or the like can be used as a raw material.
Ln2O3成分(式中、LnはLa、Gd、Y、Ybからなる群より選択される1種以上)の含有量の和(質量和)は、30.0%以上75.0%以下が好ましい。
特に、この和を30.0%以上にすることで、ガラスの分散を小さくできる。従って、Ln2O3成分の質量和は、好ましくは30.0%、より好ましくは40.0%、さらに好ましくは45.0%、さらに好ましくは54.0%を下限とする。
一方で、この和を70.0%以下にすることで、ガラスの液相温度が低くなるため、耐失透性を高められる。従って、Ln2O3成分の質量和は、好ましくは70.0%、より好ましくは68.0%、さらに好ましくは65.0%を上限とする。
The sum of the contents of the Ln 2 O 3 component (wherein Ln is at least one selected from the group consisting of La, Gd, Y, and Yb) (sum by mass) is 30.0% or more and 75.0% or less. Is preferred.
In particular, by setting this sum to 30.0% or more, the dispersion of glass can be reduced. Therefore, the lower limit of the mass sum of the Ln 2 O 3 component is preferably 30.0%, more preferably 40.0%, further preferably 45.0%, and further preferably 54.0%.
On the other hand, by setting this sum to 70.0% or less, the liquidus temperature of the glass becomes low, so that the devitrification resistance can be enhanced. Therefore, the upper limit of the mass sum of the Ln 2 O 3 component is preferably 70.0%, more preferably 68.0%, and further preferably 65.0%.
ここで、La2O3成分及びY2O3成分の含有量の和に対する、Gd2O3成分及びYb2O3成分の含有量の和の比率(質量比)は、0.50以下が好ましい。これにより、高いアッベ数と高い透過率を維持しながらも、高価なGd2O3成分やYb2O3成分の使用が低減されるため、ガラスの材料コストを抑えられる。従って、質量比(Gd2O3+Yb2O3)/(La2O3+Y2O3)は、好ましくは0.50、より好ましくは0.30、さらに好ましくは0.22、さらに好ましくは0.20を上限とする。 Here, the ratio (mass ratio) of the sum of the contents of the Gd 2 O 3 component and the Yb 2 O 3 component to the sum of the contents of the La 2 O 3 component and the Y 2 O 3 component is 0.50 or less. preferable. As a result, the use of expensive Gd 2 O 3 component and Yb 2 O 3 component is reduced while maintaining a high Abbe number and high transmittance, so that the material cost of glass can be suppressed. Therefore, the mass ratio (Gd 2 O 3 +Yb 2 O 3 )/(La 2 O 3 +Y 2 O 3 ) is preferably 0.50, more preferably 0.30, even more preferably 0.22, and even more preferably The upper limit is 0.20.
Ta2O5成分は、0%超含有する場合に、ガラスの屈折率を高め、且つ耐失透性を高められる任意成分である。
一方で、高価なTa2O5成分を15.0%以下に低減することで、ガラスの材料コストが低減されるため、より安価な光学ガラスを作製できる。また、Ta2O5成分の含有量を15.0%以下にすることで、原料の熔解温度が低くなり、原料の熔解に要するエネルギーが低減されるため、光学ガラスの製造コストをも低減できる。従って、Ta2O5成分の含有量は、好ましくは15.0%、より好ましくは13.0%、さらに好ましくは8.0%を上限とする。特に、より安価な光学ガラスを作製する観点では、Ta2O5成分の含有量は、好ましくは5.0%、より好ましくは4.0%を上限とし、さらに好ましくは1.0%未満とする。
Ta2O5成分は、原料としてTa2O5等を用いることができる。
The Ta 2 O 5 component is an optional component that can increase the refractive index of the glass and the devitrification resistance when the content exceeds 0%.
On the other hand, by reducing the expensive Ta 2 O 5 component to 15.0% or less, the material cost of the glass is reduced, so that a cheaper optical glass can be manufactured. Further, by setting the content of the Ta 2 O 5 component to be 15.0% or less, the melting temperature of the raw material is lowered and the energy required for melting the raw material is reduced, so that the manufacturing cost of the optical glass can also be reduced. .. Therefore, the upper limit of the content of the Ta 2 O 5 component is preferably 15.0%, more preferably 13.0%, and further preferably 8.0%. Particularly, from the viewpoint of producing a cheaper optical glass, the content of the Ta 2 O 5 component is preferably 5.0%, more preferably 4.0% as the upper limit, and further preferably less than 1.0%. To do.
As the Ta 2 O 5 component, Ta 2 O 5 or the like can be used as a raw material.
また、本発明の光学ガラスでは、Gd2O3成分、Yb2O3成分及びTa2O5成分の含有量の和(質量和)は、20.0%以下が好ましい。これにより、これら高価な成分の含有量が低減されるため、ガラスの材料コストを抑えられる。従って、質量和(Gd2O3+Yb2O3+Ta2O5)は、好ましくは20.0%、より好ましくは15.0%、さらに好ましくは13.0%、さらに好ましくは10.0%を上限とする。 Moreover, in the optical glass of the present invention, the sum (mass sum) of the contents of the Gd 2 O 3 component, the Yb 2 O 3 component and the Ta 2 O 5 component is preferably 20.0% or less. As a result, the contents of these expensive components are reduced, so that the material cost of glass can be suppressed. Therefore, the mass sum (Gd 2 O 3 +Yb 2 O 3 +Ta 2 O 5 ) is preferably 20.0%, more preferably 15.0%, further preferably 13.0%, further preferably 10.0%. Is the upper limit.
WO3成分は、0%超含有する場合に、他の高屈折率成分によるガラスの着色を低減しながら屈折率を高め、且つガラスの耐失透性を高められる任意成分である。また、WO3成分は、ガラス転移点を低くできる成分でもある。そのため、WO3成分の含有量は、好ましくは0%超、より好ましくは0.1%、さらに好ましくは0.5%、さらに好ましくは0.6%を下限としてもよい。
一方で、WO3成分の含有量を25.0%以下にすることで、WO3成分によるガラスの着色を低減して可視光透過率を高めることができる。従って、WO3成分の含有量は、好ましくは25.0%、より好ましくは20.0%、さらに好ましくは15.0%を上限とする。
WO3成分は、原料としてWO3等を用いることができる。
The WO 3 component is an optional component capable of increasing the refractive index while reducing the coloring of the glass due to other high refractive index components and increasing the devitrification resistance of the glass when the content thereof exceeds 0%. The WO 3 component is also a component that can lower the glass transition point. Therefore, the lower limit of the content of the WO 3 component may preferably be more than 0%, more preferably 0.1%, even more preferably 0.5%, and even more preferably 0.6%.
On the other hand, when the content of the WO 3 component is 25.0% or less, coloring of the glass due to the WO 3 component can be reduced and the visible light transmittance can be increased. Therefore, the upper limit of the content of the WO 3 component is preferably 25.0%, more preferably 20.0%, further preferably 15.0%.
As the WO 3 component, WO 3 or the like can be used as a raw material.
Nb2O5成分は、0%超含有する場合に、ガラスの屈折率を高められ、且つ耐失透性を高められる任意成分である。そのため、Nb2O5成分の含有量は、好ましくは0%超、より好ましくは1.0%超、さらに好ましくは1.5%超、さらに好ましくは2.0%超、さらに好ましくは4.0%超にしてもよい。
一方で、Nb2O5成分の含有量を20.0%以下にすることで、Nb2O5成分の過剰な含有によるガラスの耐失透性の低下や、可視光の透過率の低下を抑えることができる。従って、Nb2O5成分の含有量は、好ましくは20.0%、より好ましくは15.0%、さらに好ましくは13.0%を上限とする。
Nb2O5成分は、原料としてNb2O5等を用いることができる。
The Nb 2 O 5 component is an optional component that can increase the refractive index of the glass and the devitrification resistance when the content is more than 0%. Therefore, the content of the Nb 2 O 5 component is preferably more than 0%, more preferably more than 1.0%, further preferably more than 1.5%, further preferably more than 2.0%, further preferably 4. It may be more than 0%.
On the other hand, by setting the content of the Nb 2 O 5 component to 20.0% or less, the devitrification resistance of the glass is lowered and the transmittance of visible light is lowered by the excessive content of the Nb 2 O 5 component. Can be suppressed. Therefore, the upper limit of the content of the Nb 2 O 5 component is preferably 20.0%, more preferably 15.0%, and further preferably 13.0%.
As the Nb 2 O 5 component, Nb 2 O 5 or the like can be used as a raw material.
TiO2成分は、0%超含有する場合に、ガラスの屈折率を高め、アッベ数を低く調整し、且つ耐失透性を高められる任意成分である。そのため、TiO2成分の含有量は、好ましくは0%超、より好ましくは0.5%、さらに好ましくは1.0%を下限としてもよい。
一方で、TiO2の含有量を20.0%以下にすることで、ガラスの着色を低減して可視光透過率を高め、ガラスのアッベ数の必要以上の低下を抑えられる。また、TiO2成分の過剰な含有による失透を抑えられる。従って、TiO2成分の含有量は、好ましくは20.0%、より好ましくは18.0%、さらに好ましくは15.0%を上限とし、さらに好ましくは10.0%未満とする。
TiO2成分は、原料としてTiO2等を用いることができる。
The TiO 2 component is an optional component that can increase the refractive index of the glass, adjust the Abbe number to be low, and enhance the devitrification resistance when the content exceeds 0%. Therefore, the lower limit of the content of the TiO 2 component is preferably more than 0%, more preferably 0.5%, and further preferably 1.0%.
On the other hand, by setting the content of TiO 2 to 20.0% or less, coloring of the glass is reduced, visible light transmittance is increased, and unnecessary reduction of the Abbe number of the glass can be suppressed. Further, devitrification due to excessive inclusion of the TiO 2 component can be suppressed. Therefore, the content of the TiO 2 component is preferably 20.0%, more preferably 18.0%, further preferably 15.0% as the upper limit, and further preferably less than 10.0%.
As the TiO 2 component, TiO 2 or the like can be used as a raw material.
ここで、Nb2O5成分及びWO3成分の含有量の和(質量和)は、1.0%以上30.0%以下が好ましい。
特に、この和を1.0%以上にすることで、ガラスの材料コストを低減するためにTa2O5成分や希土類元素を低減しても、ガラスの屈折率を高められ、着色を低減でき、且つ耐失透性を高められる。従って、質量和(Nb2O5+WO3)は、好ましくは1.0%を下限とし、より好ましくは2.0%超、さらに好ましくは4.0%超、さらに好ましくは7.0%超、さらに好ましくは8.0%超とする。
一方、この和を30.0%以下にすることで、これら成分の過剰な含有による着色やを低減でき、耐失透性を高められる。従って、質量和(Nb2O5+WO3)は、好ましくは30.0%、より好ましくは25.0%、さらに好ましくは20.0%を上限とする。
Here, the sum (mass sum) of the contents of the Nb 2 O 5 component and the WO 3 component is preferably 1.0% or more and 30.0% or less.
In particular, by setting this sum to 1.0% or more, the refractive index of the glass can be increased and the coloring can be reduced even if the Ta 2 O 5 component or the rare earth element is reduced in order to reduce the material cost of the glass. And, the devitrification resistance can be enhanced. Therefore, the total mass (Nb 2 O 5 +WO 3 ) preferably has a lower limit of 1.0%, more preferably more than 2.0%, further preferably more than 4.0%, further preferably more than 7.0%. And more preferably more than 8.0%.
On the other hand, by setting this sum to 30.0% or less, coloring and the like due to excessive inclusion of these components can be reduced, and devitrification resistance can be enhanced. Therefore, the upper limit of the mass sum (Nb 2 O 5 +WO 3 ) is preferably 30.0%, more preferably 25.0%, and further preferably 20.0%.
本発明の光学ガラスでは、上述のようにB2O3成分を30.0%以下に低減しながらも、Ta2O5成分の含有量を15.0%以下にし、且つNb2O5成分及びWO3成分の含有量の和を1.0%以上にすることが好ましい。これにより、屈折率を下げるB2O3成分が低減される一方で、屈折率を高めるNb2O5成分及びWO3成分が所定以上含有されることで、ガラスの屈折率が高められる。それとともに、屈折率と耐失透性を高める成分の中でも高価なTa2O5成分が低減される一方で、より安価なNb2O5成分及びWO3成分が含有されることで、より耐失透性の高い光学ガラスが得られる。従って、屈折率が高く耐失透性の高い光学ガラスの材料コストを抑えられる。より好ましくは、B2O3成分を16.4%以下にし、Ta2O5成分の含有量を5.0%以下にし、且つNb2O5成分及びWO3成分の含有量の和を7.0%以上にしてもよい。 In the optical glass of the present invention, the content of the Ta 2 O 5 component is reduced to 15.0% or less and the Nb 2 O 5 component is reduced while reducing the B 2 O 3 component to 30.0% or less as described above. It is preferable that the sum of the contents of WO 3 and WO 3 components is 1.0% or more. As a result, the B 2 O 3 component that lowers the refractive index is reduced, while the Nb 2 O 5 component and the WO 3 component that raise the refractive index are contained in a predetermined amount or more, so that the refractive index of the glass is increased. At the same time, the expensive Ta 2 O 5 component is reduced among the components that enhance the refractive index and the devitrification resistance, while the cheaper Nb 2 O 5 component and WO 3 component are contained, so that it is more resistant. An optical glass with high devitrification can be obtained. Therefore, the material cost of the optical glass having a high refractive index and a high devitrification resistance can be suppressed. More preferably, the B 2 O 3 component is 16.4% or less, the Ta 2 O 5 component content is 5.0% or less, and the sum of the Nb 2 O 5 component content and the WO 3 component content is 7%. You may make it 0.0% or more.
SiO2成分は、0%超含有する場合に、熔融ガラスの粘度を高め、ガラスの着色を低減でき、且つ耐失透性を高められる任意成分である。従って、SiO2成分の含有量は、好ましくは0%超、より好ましくは1.0%、さらに好ましくは3.0%を下限としてもよい。
一方で、SiO2成分の含有量を20.0%以下にすることで、ガラス転移点の上昇を抑え、且つ屈折率の低下を抑えることができる。従って、SiO2成分の含有量は、好ましくは20.0%、より好ましくは15.0%、さらに好ましくは10.0%、さらに好ましくは8.0%を上限とする。
SiO2成分は、原料としてSiO2、K2SiF6、Na2SiF6等を用いることができる。
The SiO 2 component is an optional component that can increase the viscosity of the molten glass, reduce the coloring of the glass, and enhance the devitrification resistance when the content exceeds 0%. Therefore, the lower limit of the content of the SiO 2 component is preferably more than 0%, more preferably 1.0%, and further preferably 3.0%.
On the other hand, by setting the content of the SiO 2 component to 20.0% or less, it is possible to suppress an increase in the glass transition point and a decrease in the refractive index. Therefore, the upper limit of the content of the SiO 2 component is preferably 20.0%, more preferably 15.0%, further preferably 10.0%, and further preferably 8.0%.
For the SiO 2 component, SiO 2 , K 2 SiF 6 , Na 2 SiF 6 or the like can be used as a raw material.
ここで、B2O3成分及びSiO2成分の含有量の和(質量和)は、1.0%以上30.0%以下が好ましい。
特に、この和を1.0%以上にすることで、B2O3成分やSiO2成分の欠乏による耐失透性の低下を抑えられる。従って、質量和(B2O3+SiO2)は、好ましくは1.0%、より好ましくは5.0%、さらに好ましくは10.0%を下限とする。
一方で、この和を30.0%以下にすることで、これらの成分の過剰な含有による屈折率の低下が抑えられるので、所望の高屈折率を得易くできる。従って、質量和(B2O3+SiO2)は、好ましくは30.0%、より好ましくは25.0%、さらに好ましくは21.0%を上限とする。
Here, the sum (mass sum) of the contents of the B 2 O 3 component and the SiO 2 component is preferably 1.0% or more and 30.0% or less.
In particular, by setting this sum to 1.0% or more, it is possible to suppress the deterioration of the devitrification resistance due to the deficiency of the B 2 O 3 component and the SiO 2 component. Therefore, the lower limit of the mass sum (B 2 O 3 +SiO 2 ) is preferably 1.0%, more preferably 5.0%, and further preferably 10.0%.
On the other hand, by setting this sum to 30.0% or less, the decrease in the refractive index due to the excessive inclusion of these components can be suppressed, so that the desired high refractive index can be easily obtained. Therefore, the upper limit of the mass sum (B 2 O 3 +SiO 2 ) is preferably 30.0%, more preferably 25.0%, and further preferably 21.0%.
また、B2O3成分及びSiO2成分の含有量の和に対する、Nb2O5成分及びWO3成分の含有量の和の比率(質量比)は、0.15以上2.00以下が好ましい。
特に、この比率を0.15以上にすることで、高い耐失透性を維持しながらも屈折率を高められる。従って、質量比(Nb2O5+WO3)/(B2O3+SiO2)は、好ましくは0.15、より好ましくは0.25、さらに好ましくは0.30、さらに好ましくは0.35、さらに好ましくは0.40を下限とする。
一方で、この比率を2.00以下にすることで、Nb2O5成分やWO3成分の過剰な含有や、B2O3成分やSiO2成分の欠乏による耐失透性の低下を抑えられる。従って、質量比(Nb2O5+WO3)/(B2O3+SiO2)は、好ましくは2.00、より好ましくは1.50、さらに好ましくは1.20を上限とする。
The ratio (mass ratio) of the sum of the contents of the Nb 2 O 5 component and the WO 3 component to the sum of the contents of the B 2 O 3 component and the SiO 2 component is preferably 0.15 or more and 2.00 or less. ..
In particular, by setting this ratio to 0.15 or more, the refractive index can be increased while maintaining high devitrification resistance. Therefore, the mass ratio (Nb 2 O 5 +WO 3 )/(B 2 O 3 +SiO 2 ) is preferably 0.15, more preferably 0.25, still more preferably 0.30, still more preferably 0.35. More preferably, the lower limit is 0.40.
On the other hand, by the ratio 2.00, suppressing excessive content or Nb 2 O 5 component and WO 3 components, a reduction in the devitrification resistance due to absence of the B 2 O 3 component and the SiO 2 component To be Therefore, the upper limit of the mass ratio (Nb 2 O 5 +WO 3 )/(B 2 O 3 +SiO 2 ) is preferably 2.00, more preferably 1.50, and further preferably 1.20.
MgO成分、CaO成分、SrO成分及びBaO成分は、0%超含有する場合に、ガラス原料の熔融性やガラスの耐失透性を高められる任意成分である。
一方で、MgO成分、CaO成分及びSrO成分の各々の含有量を20.0%以下にすること、及び/又は、BaO成分の含有量を25.0%以下にすることで、これらの成分の過剰な含有による、屈折率の低下や耐失透性の低下を抑えられる。従って、MgO成分、CaO成分及びSrO成分の各々の含有量は、好ましくは20.0%、より好ましくは10.0%、さらに好ましくは5.0%を上限とする。また、BaO成分の含有量は、好ましくは25.0%、より好ましくは15.0%、さらに好ましくは10.0%、さらに好ましくは8.0%を上限とする。
MgO成分、CaO成分、SrO成分及びBaO成分は、原料としてMgCO3、MgF2、CaCO3、CaF2、Sr(NO3)2、SrF2、BaCO3、Ba(NO3)2、BaF2等を用いることができる。
The MgO component, the CaO component, the SrO component and the BaO component are optional components capable of enhancing the meltability of the glass raw material and the devitrification resistance of the glass when the content thereof exceeds 0%.
On the other hand, by making the content of each of the MgO component, CaO component and SrO component 20.0% or less, and/or the content of BaO component 25.0% or less, A decrease in refractive index and a decrease in devitrification resistance due to excessive content can be suppressed. Therefore, the upper limit of the content of each of the MgO component, CaO component, and SrO component is preferably 20.0%, more preferably 10.0%, and further preferably 5.0%. Moreover, the upper limit of the content of the BaO component is preferably 25.0%, more preferably 15.0%, further preferably 10.0%, and further preferably 8.0%.
The MgO component, the CaO component, the SrO component and the BaO component are MgCO 3 , MgF 2 , CaCO 3 , CaF 2 , Sr(NO 3 ) 2 , SrF 2 , BaCO 3 , Ba(NO 3 ) 2 and BaF 2 as raw materials. Can be used.
RO成分(式中、RはMg、Ca、Sr、Baからなる群より選択される1種以上)の含有量の合計(質量和)は、25.0%以下が好ましい。これにより、RO成分の過剰な含有による、ガラスの屈折率の低下や耐失透性の低下を抑えられる。従って、RO成分の質量和は、好ましくは25.0%、より好ましくは15.0%、さらに好ましくは10.0%、さらに好ましくは5.0%を上限とする。 The total content (sum) of the RO components (wherein R is at least one selected from the group consisting of Mg, Ca, Sr, and Ba) is preferably 25.0% or less. As a result, it is possible to prevent a decrease in the refractive index and the devitrification resistance of the glass due to the excessive inclusion of the RO component. Therefore, the upper limit of the sum of masses of the RO components is preferably 25.0%, more preferably 15.0%, further preferably 10.0%, and further preferably 5.0%.
Li2O成分、Na2O成分、K2O成分及びCs2O成分は、0%超含有する場合に、ガラスの熔融性を改善し、且つガラス転移点を低くできる任意成分である。このうちNa2O成分、K2O成分及びCs2O成分は、ガラスの耐失透性を高められる成分でもある。ここで、Li2O成分、Na2O成分、K2O成分及びCs2O成分の各々の含有量を10.0%以下にすることで、ガラスの屈折率を低下し難くし、且つ、耐失透性を高められる。従って、Li2O成分、Na2O成分、K2O成分及びCs2O成分の各々の含有量は、好ましくは10.0%、より好ましくは8.0%、さらに好ましくは5.0%を上限とする。
特に、Li2O成分の含有量を3.0%以下にすることで、ガラスの粘性が高くなるため、ガラスの脈理を低減できる。従って、ガラスの脈理を低減する観点では、Li2O成分の含有量は、好ましくは3.0%、より好ましくは1.0%、さらに好ましくは0.3%を上限としてもよい。
Li2O成分、Na2O成分、K2O成分及びCs2O成分は、原料としてLi2CO3、LiNO3、Li2CO3、NaNO3、NaF、Na2SiF6、K2CO3、KNO3、KF、KHF2、K2SiF6、Cs2CO3、CsNO3等を用いることができる。
The Li 2 O component, the Na 2 O component, the K 2 O component and the Cs 2 O component are optional components that can improve the glass meltability and lower the glass transition point when the content exceeds 0%. Of these, the Na 2 O component, the K 2 O component, and the Cs 2 O component are also components that can enhance the devitrification resistance of the glass. Here, by setting the content of each of the Li 2 O component, the Na 2 O component, the K 2 O component, and the Cs 2 O component to 10.0% or less, it becomes difficult to lower the refractive index of the glass, and Can improve devitrification resistance. Therefore, the content of each of the Li 2 O component, Na 2 O component, K 2 O component, and Cs 2 O component is preferably 10.0%, more preferably 8.0%, and further preferably 5.0%. Is the upper limit.
In particular, by setting the content of the Li 2 O component to 3.0% or less, the viscosity of the glass becomes high, so that the striae of the glass can be reduced. Therefore, from the viewpoint of reducing the striae of the glass, the upper limit of the content of the Li 2 O component is preferably 3.0%, more preferably 1.0%, and further preferably 0.3%.
The Li 2 O component, Na 2 O component, K 2 O component and Cs 2 O component are Li 2 CO 3 , LiNO 3 , Li 2 CO 3 , NaNO 3 , NaF, Na 2 SiF 6 , K 2 CO 3 as raw materials. , KNO 3 , KF, KHF 2 , K 2 SiF 6 , Cs 2 CO 3 , CsNO 3 and the like can be used.
Rn2O成分(式中、RnはLi、Na、K、Csからなる群より選択される1種以上)の合計量は、15.0%以下が好ましい。これにより、ガラスの屈折率の低下を抑え、且つ耐失透性を高められる。従って、Rn2O成分の質量和は、好ましくは15.0%、より好ましくは10.0%、さらに好ましくは5.0%を上限とする。 The total amount of Rn 2 O components (wherein Rn is at least one selected from the group consisting of Li, Na, K, and Cs) is preferably 15.0% or less. This makes it possible to suppress the decrease in the refractive index of the glass and enhance the devitrification resistance. Therefore, the upper limit of the mass sum of the Rn 2 O component is preferably 15.0%, more preferably 10.0%, and further preferably 5.0%.
P2O5成分は、0%超含有する場合に、ガラスの耐失透性を高められる任意成分である。特に、P2O5成分の含有量を10.0%以下にすることで、ガラスの化学的耐久性、特に耐水性の低下を抑えられる。従って、P2O5成分の含有量は、好ましくは10.0%、より好ましくは5.0%、さらに好ましくは3.0%を上限とする。
P2O5成分は、原料としてAl(PO3)3、Ca(PO3)2、Ba(PO3)2、BPO4、H3PO4等を用いることができる。
The P 2 O 5 component is an optional component that can enhance the devitrification resistance of the glass when the content exceeds 0%. In particular, by setting the content of the P 2 O 5 component to 10.0% or less, it is possible to suppress the decrease in the chemical durability of the glass, particularly the water resistance. Therefore, the upper limit of the content of the P 2 O 5 component is preferably 10.0%, more preferably 5.0%, and further preferably 3.0%.
As the P 2 O 5 component, Al(PO 3 ) 3 , Ca(PO 3 ) 2 , Ba(PO 3 ) 2 , BPO 4 , H 3 PO 4 or the like can be used as a raw material.
GeO2成分は、0%超含有する場合に、ガラスの屈折率を高め、且つ耐失透性を向上できる任意成分である。しかしながら、GeO2は原料価格が高いため、その量が多いと材料コストが高くなることで、Gd2O3成分やTa2O5成分を低減することによるコスト低減の効果が減殺される。従って、GeO2成分の含有量は、好ましくは10.0%、より好ましくは5.0%、さらに好ましくは1.0%を上限とし、最も好ましくは含有しない。
GeO2成分は、原料としてGeO2等を用いることができる。
The GeO 2 component is an optional component capable of increasing the refractive index of glass and improving the devitrification resistance when the content exceeds 0%. However, since the raw material price of GeO 2 is high, the material cost increases when the amount thereof is large, and the effect of cost reduction by reducing the Gd 2 O 3 component and Ta 2 O 5 component is diminished. Therefore, the content of the GeO 2 component is preferably 10.0%, more preferably 5.0%, further preferably 1.0%, and the most preferably not included.
For the GeO 2 component, GeO 2 or the like can be used as a raw material.
ZrO2成分は、0%超含有する場合に、ガラスの高屈折率化及び低分散化に寄与でき、且つガラスの耐失透性を高められる。そのため、ZrO2成分の含有量は、好ましくは0%超、より好ましくは1.0%、さらに好ましくは3.0%を下限としてもよい。
一方で、ZrO2成分を15.0%以下にすることで、ZrO2成分の過剰な含有によるガラスの耐失透性の低下を抑えられる。従って、ZrO2成分の含有量は、好ましくは15.0%、より好ましくは10.0%、さらに好ましくは8.0%を上限とする。
ZrO2成分は、原料としてZrO2、ZrF4等を用いることができる。
When the ZrO 2 component is contained in an amount of more than 0%, it can contribute to the high refractive index and low dispersion of the glass and can enhance the devitrification resistance of the glass. Therefore, the lower limit of the ZrO 2 component content is preferably more than 0%, more preferably 1.0%, and further preferably 3.0%.
On the other hand, by setting the ZrO 2 component to 15.0% or less, it is possible to prevent the devitrification resistance of the glass from being lowered due to the excessive inclusion of the ZrO 2 component. Therefore, the upper limit of the ZrO 2 component content is preferably 15.0%, more preferably 10.0%, and even more preferably 8.0%.
As the ZrO 2 component, ZrO 2 , ZrF 4 or the like can be used as a raw material.
ZnO成分は、0%超含有する場合に、ガラス転移点を低くし、且つ化学的耐久性を高められる任意成分である。
一方で、ZnO成分の含有量を15.0%以下にすることで、ガラスの屈折率の低下や、耐失透性の低下を抑えられる。また、これにより熔融ガラスの粘性が高められるため、ガラスへの脈理の発生を低減できる。従って、ZnO成分の含有量は、好ましくは15.0%、より好ましくは10.0%、さらに好ましくは5.0%未満、さらに好ましくは1.1%を上限とする。
ZnO成分は、原料としてZnO、ZnF2等を用いることができる。
The ZnO component is an optional component that can lower the glass transition point and enhance the chemical durability when the content exceeds 0%.
On the other hand, by setting the content of the ZnO component to be 15.0% or less, it is possible to suppress a decrease in the refractive index of the glass and a decrease in the devitrification resistance. Further, this increases the viscosity of the molten glass, so that the occurrence of striae in the glass can be reduced. Therefore, the upper limit of the ZnO component content is preferably 15.0%, more preferably 10.0%, even more preferably less than 5.0%, and further preferably 1.1%.
For the ZnO component, ZnO, ZnF 2 or the like can be used as a raw material.
Al2O3成分及びGa2O3成分は、0%超含有する場合に、ガラスの化学的耐久性を高め、且つガラスの耐失透性を高められる任意成分である。
一方で、Al2O3成分及びGa2O3成分の各々の含有量を10.0%以下にすることで、これらの過剰な含有によるガラスの耐失透性の低下を抑えられる。従って、Al2O3成分及びGa2O3成分の各々の含有量は、好ましくは10.0%、より好ましくは5.0%、さらに好ましくは3.0%を上限とする。
Al2O3成分及びGa2O3成分は、原料としてAl2O3、Al(OH)3、AlF3、Ga2O3、Ga(OH)3等を用いることができる。
The Al 2 O 3 component and the Ga 2 O 3 component are optional components capable of enhancing the chemical durability of the glass and enhancing the devitrification resistance of the glass when the content thereof exceeds 0%.
On the other hand, by setting the content of each of the Al 2 O 3 component and the Ga 2 O 3 component to 10.0% or less, it is possible to suppress the deterioration of the devitrification resistance of the glass due to the excessive content thereof. Therefore, the upper limit of the content of each of the Al 2 O 3 component and the Ga 2 O 3 component is preferably 10.0%, more preferably 5.0%, and further preferably 3.0%.
As the Al 2 O 3 component and the Ga 2 O 3 component, Al 2 O 3 , Al(OH) 3 , AlF 3 , Ga 2 O 3 , Ga(OH) 3 or the like can be used as a raw material.
Bi2O3成分は、0%超含有する場合に、屈折率を高め、且つガラス転移点を下げられる任意成分である。
一方で、Bi2O3成分の含有量を10.0%以下にすることで、ガラスの耐失透性を高められ、且つ、ガラスの着色を低減して可視光透過率を高められる。従って、Bi2O3成分の含有量は、好ましくは10.0%、より好ましくは5.0%、さらに好ましくは3.0%を上限とする。
Bi2O3成分は、原料としてBi2O3等を用いることができる。
The Bi 2 O 3 component is an optional component capable of increasing the refractive index and decreasing the glass transition point when the content exceeds 0%.
On the other hand, by setting the content of the Bi 2 O 3 component to 10.0% or less, the devitrification resistance of the glass can be increased, and the coloring of the glass can be reduced to increase the visible light transmittance. Therefore, the upper limit of the content of the Bi 2 O 3 component is preferably 10.0%, more preferably 5.0%, and further preferably 3.0%.
For the Bi 2 O 3 component, Bi 2 O 3 or the like can be used as a raw material.
TeO2成分は、0%超含有する場合に、屈折率を高め、且つガラス転移点を下げられる任意成分である。
しかしながら、TeO2は白金製の坩堝や、溶融ガラスと接する部分が白金で形成されている溶融槽でガラス原料を熔融する際、白金と合金化しうる問題がある。従って、TeO2成分の含有量は、好ましくは20.0%、より好ましくは10.0%、さらに好ましくは5.0%を上限とし、さらに好ましくは含有しない。
TeO2成分は、原料としてTeO2等を用いることができる。
The TeO 2 component is an optional component capable of increasing the refractive index and decreasing the glass transition point when the content exceeds 0%.
However, TeO 2 has a problem that it can be alloyed with platinum when the glass raw material is melted in a platinum crucible or a melting tank in which a portion in contact with the molten glass is formed of platinum. Therefore, the content of the TeO 2 component is preferably 20.0%, more preferably 10.0%, further preferably 5.0% as the upper limit, and further preferably no content.
As the TeO 2 component, TeO 2 or the like can be used as a raw material.
SnO2成分は、0%超含有する場合に、熔融ガラスの酸化を低減して清澄し、且つガラスの可視光透過率を高められる任意成分である。
一方で、SnO2成分の含有量を1.0%以下にすることで、熔融ガラスの還元によるガラスの着色や、ガラスの失透を低減できる。また、SnO2成分と熔解設備(特にPt等の貴金属)の合金化が低減されるため、熔解設備の長寿命化を図れる。従って、SnO2成分の含有量は、好ましくは1.0%、より好ましくは0.7%、さらに好ましくは0.5%を上限とする。
SnO2成分は、原料としてSnO、SnO2、SnF2、SnF4等を用いることができる。
The SnO 2 component is an optional component which, when contained in an amount of more than 0%, can reduce the oxidization of the molten glass to clarify it and increase the visible light transmittance of the glass.
On the other hand, by setting the content of the SnO 2 component to 1.0% or less, coloring of the glass due to reduction of the molten glass and devitrification of the glass can be reduced. Further, alloying of the SnO 2 component and the melting equipment (particularly noble metal such as Pt) is reduced, so that the life of the melting equipment can be extended. Therefore, the upper limit of the content of the SnO 2 component is preferably 1.0%, more preferably 0.7%, and even more preferably 0.5%.
For the SnO 2 component, SnO, SnO 2 , SnF 2 , SnF 4 or the like can be used as a raw material.
Sb2O3成分は、0%超含有する場合に、熔融ガラスを脱泡できる任意成分である。
一方で、Sb2O3量が多すぎると、可視光領域の短波長領域における透過率が悪くなる。従って、Sb2O3成分の含有量は、好ましくは1.0%、より好ましくは0.7%、さらに好ましくは0.5%を上限とする。
Sb2O3成分は、原料としてSb2O3、Sb2O5、Na2H2Sb2O7・5H2O等を用いることができる。
The Sb 2 O 3 component is an optional component that can degas the molten glass when it is contained in an amount of more than 0%.
On the other hand, if the amount of Sb 2 O 3 is too large, the transmittance in the short wavelength region of the visible light region becomes poor. Therefore, the upper limit of the Sb 2 O 3 component content is preferably 1.0%, more preferably 0.7%, and even more preferably 0.5%.
Sb 2 O 3 component can be used Sb 2 O 3, Sb 2 O 5, Na 2 H 2 Sb 2 O 7 · 5H 2 O and the like as raw materials.
なお、ガラスを清澄し脱泡する成分は、上記のSb2O3成分に限定されるものではなく、ガラス製造の分野における公知の清澄剤、脱泡剤或いはそれらの組み合わせを用いることができる。 The component for clarifying and defoaming the glass is not limited to the above Sb 2 O 3 component, and a known fining agent, defoaming agent or a combination thereof in the field of glass production can be used.
<含有すべきでない成分について>
次に、本発明の光学ガラスに含有すべきでない成分、及び含有することが好ましくない成分について説明する。
<Ingredients that should not be contained>
Next, components that should not be contained in the optical glass of the present invention and components that are not preferable to be contained will be described.
他の成分を本願発明のガラスの特性を損なわない範囲で必要に応じ、添加することができる。ただし、Ti、Zr、Nb、W、La、Gd、Y、Yb、Luを除く、V、Cr、Mn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cu、Ag及びMo等の各遷移金属成分は、それぞれを単独又は複合して少量含有した場合でもガラスが着色し、可視域の特定の波長に吸収を生じる性質があるため、特に可視領域の波長を使用する光学ガラスにおいては、実質的に含まないことが好ましい。 Other components can be added, if necessary, within a range that does not impair the characteristics of the glass of the present invention. However, each transition metal component such as V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Ag, and Mo, except Ti, Zr, Nb, W, La, Gd, Y, Yb, and Lu, is used alone. Alternatively, even if a small amount is included in the composite, the glass is colored and has a property of causing absorption at a specific wavelength in the visible region. Therefore, in an optical glass using a wavelength in the visible region, it is preferable not to include substantially. ..
また、PbO等の鉛化合物及びAs2O3等の砒素化合物は、環境負荷が高い成分であるため、実質的に含有しないこと、すなわち、不可避な混入を除いて一切含有しないことが望ましい。 Further, since lead compounds such as PbO and arsenic compounds such as As 2 O 3 are components having a high environmental load, it is desirable that they are not substantially contained, that is, they are not contained at all except inevitable mixing.
さらに、Th、Cd、Tl、Os、Be、及びSeの各成分は、近年有害な化学物資として使用を控える傾向にあり、ガラスの製造工程のみならず、加工工程、及び製品化後の処分に至るまで環境対策上の措置が必要とされる。従って、環境上の影響を重視する場合には、これらを実質的に含有しないことが好ましい。 Furthermore, in recent years, Th, Cd, Tl, Os, Be, and Se components have tended to be refrained from being used as harmful chemical substances, and are not only used in the glass manufacturing process but also in the processing process and post-commercial disposal. Environmental measures need to be taken. Therefore, when importance is attached to the influence on the environment, it is preferable that they are not substantially contained.
本発明のガラス組成物は、その組成が酸化物換算組成のガラス全質量に対する質量%で表されているため直接的にモル%の記載に表せるものではないが、本発明において要求される諸特性を満たすガラス組成物中に存在する各成分のモル%表示による組成は、酸化物換算組成で概ね以下の値をとる。
B2O3成分 2.0〜55.0モル%、及び
La2O3成分 5.0〜30.0モル%、
並びに
Y2O3成分 0〜20.0モル%、
Gd2O3成分 0〜20.0モル%、
Yb2O3成分 0〜10.0モル%、
Ta2O5成分 0〜5.0モル%、
WO3成分 0〜20.0モル%、
Nb2O5成分 0〜15.0モル%、
TiO2成分 0〜40.0モル%、
SiO2成分 0〜50.0モル%、
MgO成分 0〜50.0モル%、
CaO成分 0〜40.0モル%、
SrO成分 0〜30.0モル%、
BaO成分 0〜35.0モル%、
Li2O成分 0〜30.0モル%、
Na2O成分 0〜25.0モル%、
K2O成分 0〜20.0モル%、
Cs2O成分 0〜10.0モル%、
P2O5成分 0〜15.0モル%、
GeO2成分 0〜10.0モル%、
ZrO2成分 0〜20.0モル%、
ZnO成分 0〜50.0モル%、
Al2O3成分 0〜20.0モル%、
Ga2O3成分 0〜5.0モル%、
Bi2O3成分 0〜5.0モル%、
TeO2成分 0〜20.0モル%、
SnO2成分 0〜0.3モル%、又は
Sb2O3成分 0〜0.5モル%
The glass composition of the present invention cannot be directly represented in the description of mol% because the composition is represented by mass% based on the total mass of the glass in terms of oxide composition, but various characteristics required in the present invention The composition represented by mol% of each component present in the glass composition satisfying the above conditions takes approximately the following values in terms of oxide.
B 2 O 3 component from 2.0 to 55.0 mol%, and La 2 O 3 component from 5.0 to 30.0 mol%,
And Y 2 O 3 component 0 to 20.0 mol %,
Gd 2 O 3 component 0 to 20.0 mol%,
Yb 2 O 3 component 0 to 10.0 mol%,
Ta 2 O 5 component 0-5.0 mol%,
WO 3 component 0 to 20.0 mol%,
Nb 2 O 5 component 0 to 15.0 mol%,
TiO 2 component 0 to 40.0 mol%,
SiO 2 component 0 to 50.0 mol %,
MgO component 0-50.0 mol%,
CaO component 0-40.0 mol%,
SrO component 0 to 30.0 mol%,
BaO component 0 to 35.0 mol%,
Li 2 O component 0 to 30.0 mol%,
Na 2 O component 0 to 25.0 mol%,
K 2 O component 0 to 20.0 mol%,
Cs 2 O component 0 to 10.0 mol%,
P 2 O 5 component 0 to 15.0 mol%,
GeO 2 component 0 to 10.0 mol%,
ZrO 2 component 0 to 20.0 mol%,
ZnO component 0-50.0 mol%,
Al 2 O 3 component 0 to 20.0 mol%,
Ga 2 O 3 component 0-5.0 mol%,
Bi 2 O 3 component 0-5.0 mol%,
TeO 2 component 0 to 20.0 mol%,
SnO 2 component 0 to 0.3 mol% or Sb 2 O 3 component 0 to 0.5 mol%
[製造方法]
本発明の光学ガラスは、例えば以下のように作製される。すなわち、上記原料を各成分が所定の含有量の範囲内になるように均一に混合し、作製した混合物を白金坩堝に投入し、ガラス組成の熔融難易度に応じて電気炉で1100〜1500℃の温度範囲で2〜5時間熔融し、攪拌均質化した後、適当な温度に下げてから金型に鋳込み、徐冷することにより作製される。
[Production method]
The optical glass of the present invention is produced, for example, as follows. That is, the above raw materials were uniformly mixed so that each component was within a predetermined content range, the prepared mixture was put into a platinum crucible, and the temperature was set to 1100 to 1500° C. in an electric furnace depending on the difficulty of melting the glass composition. It is prepared by melting in the temperature range of 2 to 5 hours, stirring and homogenizing, lowering to an appropriate temperature, casting in a mold, and then slowly cooling.
[物性]
本発明の光学ガラスは、高屈折率及び高アッベ数(低分散)を有することが好ましい。特に、本発明の光学ガラスの屈折率(nd)は、好ましくは1.75、より好ましくは1.80、さらに好ましくは1.85を下限とする。この屈折率の上限は、好ましくは2.20、より好ましくは2.15、さらに好ましくは2.10であってもよい。また、本発明の光学ガラスのアッベ数(νd)は、好ましくは23、より好ましくは25、さらに好ましくは28、さらに好ましくは30、さらに好ましくは31、さらに好ましくは32を下限とし、好ましくは50、より好ましくは45を上限とし、さらに好ましくは39未満とする。
このような高屈折率を有することで、光学素子の薄型化を図っても大きな光の屈折量を得ることができる。また、このような低分散を有することで、単レンズであっても光の波長による焦点のずれ(色収差)が小さくなる。加えて、このような低分散を有することで、例えば高分散(低いアッベ数)を有する光学素子と組み合わせた場合に、高い結像特性等を図ることができる。
従って、本発明の光学ガラスは、光学設計上有用であり、特に高い結像特性等を図りながらも、光学系の小型化を図ることができ、光学設計の自由度を広げることができる。
[Physical properties]
The optical glass of the present invention preferably has a high refractive index and a high Abbe number (low dispersion). In particular, the lower limit of the refractive index ( nd ) of the optical glass of the present invention is preferably 1.75, more preferably 1.80, and further preferably 1.85. The upper limit of this refractive index may be preferably 2.20, more preferably 2.15, and further preferably 2.10. In addition, the Abbe number (ν d ) of the optical glass of the present invention is preferably 23, more preferably 25, further preferably 28, further preferably 30, further preferably 31, and further preferably 32, and the lower limit is preferably The upper limit is 50, more preferably 45, and further preferably less than 39.
By having such a high refractive index, a large amount of refraction of light can be obtained even when the optical element is made thin. Further, by having such low dispersion, even with a single lens, the shift of the focus (chromatic aberration) due to the wavelength of light is reduced. In addition, by having such a low dispersion, it is possible to achieve high imaging characteristics and the like when combined with an optical element having a high dispersion (low Abbe number), for example.
Therefore, the optical glass of the present invention is useful for optical design, and while achieving particularly high imaging characteristics, the optical system can be downsized and the degree of freedom in optical design can be expanded.
また、本発明の光学ガラスは、比重が小さいことが好ましい。より具体的には、本発明の光学ガラスの比重は5.50[g/cm3]以下である。これにより、光学素子やそれを用いた光学機器の質量が低減されるため、光学機器の軽量化に寄与することができる。従って、本発明の光学ガラスの比重は、好ましくは5.50、より好ましくは5.40、好ましくは5.30を上限とする。なお、本発明の光学ガラスの比重は、概ね3.00以上、より詳細には3.50以上、さらに詳細には4.00以上であることが多い。
本発明の光学ガラスの比重は、日本光学硝子工業会規格JOGIS05−1975「光学ガラスの比重の測定方法」に基づいて測定する。
Further, the optical glass of the present invention preferably has a low specific gravity. More specifically, the specific gravity of the optical glass of the present invention is 5.50 [g/cm 3 ] or less. This reduces the mass of the optical element and the optical device using the optical element, which can contribute to the weight reduction of the optical device. Therefore, the upper limit of the specific gravity of the optical glass of the present invention is preferably 5.50, more preferably 5.40, and preferably 5.30. The specific gravity of the optical glass of the present invention is generally 3.00 or more, more specifically 3.50 or more, and more specifically 4.00 or more.
The specific gravity of the optical glass of the present invention is measured based on the Japan Optical Glass Industry Association Standard JOGIS05-1975 "Method for measuring specific gravity of optical glass".
本発明の光学ガラスは、耐失透性が高いこと、より具体的には、低い液相温度を有することが好ましい。すなわち、本発明の光学ガラスの液相温度は、好ましくは1300℃、より好ましくは1290℃、さらに好ましくは1280℃を上限とする。これにより、より低い温度で熔融ガラスを流出しても、作製されたガラスの結晶化が低減されるため、特に熔融状態からガラスを形成したときの失透を低減でき、ガラスを用いた光学素子の光学特性への影響を低減できる。また、ガラスの熔解温度を低くしてもガラスを成形できるため、ガラスの成形時に消費するエネルギーを抑えることで、ガラスの製造コストを低減できる。一方、本発明の光学ガラスの液相温度の下限は特に限定しないが、本発明によって得られるガラスの液相温度は、好ましくは500℃、より好ましくは600℃、さらに好ましくは700℃を下限としてもよい。なお、本明細書中における「液相温度」は、50mlの容量の白金製坩堝に30ccのカレット状のガラス試料を白金坩堝に入れて1350℃で完全に熔融状態にし、所定の温度まで降温して12時間保持し、炉外に取り出して冷却した後直ちにガラス表面及びガラス中の結晶の有無を観察し、結晶が認められない一番低い温度を表す。ここで降温する際の所定の温度は、1300℃までの10℃刻みの温度である。 The optical glass of the present invention preferably has high devitrification resistance, and more specifically has a low liquidus temperature. That is, the upper limit of the liquidus temperature of the optical glass of the present invention is preferably 1300°C, more preferably 1290°C, and further preferably 1280°C. As a result, even if the molten glass flows out at a lower temperature, the crystallization of the produced glass is reduced, so that devitrification particularly when the glass is formed from the molten state can be reduced, and the optical element using the glass can be reduced. Can reduce the influence on the optical characteristics. Further, since the glass can be molded even if the melting temperature of the glass is lowered, it is possible to reduce the manufacturing cost of the glass by suppressing the energy consumed during the molding of the glass. On the other hand, the lower limit of the liquidus temperature of the optical glass of the present invention is not particularly limited, but the liquidus temperature of the glass obtained by the present invention is preferably 500° C., more preferably 600° C., further preferably 700° C. as the lower limit. Good. In addition, the "liquidus temperature" in this specification means that a 30 cc cullet-shaped glass sample is put into a platinum crucible having a capacity of 50 ml and completely melted at 1350° C., and the temperature is lowered to a predetermined temperature. The glass surface and the presence/absence of crystals in the glass are observed immediately after cooling for 12 hours and taken out of the furnace to show the lowest temperature at which no crystals are observed. The predetermined temperature when the temperature is lowered here is a temperature in steps of 10° C. up to 1300° C.
本発明の光学ガラスは、可視光透過率、特に可視光のうち短波長側の光の透過率が高く、それにより着色が少ないことが好ましい。
特に、本発明の光学ガラスは、ガラスの透過率で表すと、厚み10mmのサンプルで分光透過率70%を示す波長(λ70)は、好ましくは550nm、より好ましくは520nm、さらに好ましくは500nm、さらに好ましくは480nmを上限とする。
また、本発明の光学ガラスにおける、厚み10mmのサンプルで分光透過率5%を示す最も短い波長(λ5)は、好ましくは440nm、より好ましくは420nm、さらに好ましくは400nm、さらに好ましくは380nmを上限とする。
これらにより、ガラスの吸収端が紫外領域の近傍になり、可視光に対するガラスの透明性が高められるため、この光学ガラスを、レンズ等の光を透過させる光学素子に好ましく用いることができる。
It is preferable that the optical glass of the present invention has a high visible light transmittance, in particular, a light transmittance on the short wavelength side of the visible light, and thus the coloring is small.
In particular, the optical glass of the present invention has a wavelength (λ 70 ) at which a sample having a thickness of 10 mm and a spectral transmittance of 70% is represented by a glass transmittance, preferably 550 nm, more preferably 520 nm, further preferably 500 nm. More preferably, the upper limit is 480 nm.
In the optical glass of the present invention, the shortest wavelength (λ 5 ) showing a spectral transmittance of 5% in a sample having a thickness of 10 mm is preferably 440 nm, more preferably 420 nm, further preferably 400 nm, and further preferably 380 nm is the upper limit. And
These make the absorption edge of the glass close to the ultraviolet region and enhance the transparency of the glass with respect to visible light. Therefore, this optical glass can be preferably used for an optical element such as a lens that transmits light.
本発明の光学ガラスは、低い部分分散比(θg,F)を有することが好ましい。より具体的には、本発明の光学ガラスの部分分散比(θg,F)は、アッベ数(νd)との間で、(−2.50×10−3×νd+0.6571)≦(θg,F)≦(−2.50×10−3×νd+0.6971)の関係を満たすことが好ましい。これにより、部分分散比(θg,F)の小さい光学ガラスが得られるため、光学ガラスを光学素子の色収差の低減等に役立てられる。
従って、本発明の光学ガラスの部分分散比(θg,F)は、好ましくは(−2.50×10−3×νd+0.6571)、より好ましくは(−2.50×10−3×νd+0.6591)、さらに好ましくは(−2.50×10−3×νd+0.6611)を下限とする。
一方で、本発明の光学ガラスの部分分散比(θg,F)は、好ましくは(−2.50×10−3×νd+0.6971)、より好ましくは(−2.50×10−3×νd+0.6921)、さらに好ましくは(−2.50×10−3×νd+0.6871)を上限とする。
The optical glass of the present invention preferably has a low partial dispersion ratio (θg, F). More specifically, the partial dispersion ratio (θg, F) of the optical glass of the present invention is (−2.50×10 −3 ×ν d +0.6571)≦ with the Abbe number (ν d ). It is preferable that the relationship of (θg, F)≦(−2.50×10 −3 ×ν d +0.6971) is satisfied. As a result, an optical glass having a small partial dispersion ratio (θg, F) can be obtained, and thus the optical glass can be used to reduce chromatic aberration of the optical element.
Therefore, the partial dispersion ratio (θg, F) of the optical glass of the present invention is preferably (−2.50×10 −3 ×ν d +0.6571), and more preferably (−2.50×10 −3 ×). ν d +0.6591), and more preferably (−2.50×10 −3 ×ν d +0.6611).
On the other hand, the partial dispersion ratio (θg, F) of the optical glass of the present invention is preferably (−2.50×10 −3 ×ν d +0.6971), more preferably (−2.50×10 −3). Xν d +0.6921), and more preferably (−2.50×10 −3 ×ν d +0.6871).
[ガラス成形体及び光学素子]
作製された光学ガラスから、例えば研磨加工の手段、又は、リヒートプレス成形や精密プレス成形等のモールドプレス成形の手段を用いて、ガラス成形体を作製することができる。すなわち、光学ガラスに対して研削及び研磨等の機械加工を行ってガラス成形体を作製したり、光学ガラスから作製したプリフォームに対してリヒートプレス成形を行った後で研磨加工を行ってガラス成形体を作製したり、研磨加工を行って作製したプリフォームや、公知の浮上成形等により成形されたプリフォームに対して精密プレス成形を行ってガラス成形体を作製したりすることができる。なお、ガラス成形体を作製する手段は、これらの手段に限定されない。
[Glass molded article and optical element]
A glass molded product can be produced from the produced optical glass by using, for example, a polishing process means or a mold press molding means such as reheat press molding or precision press molding. That is, optical glass is subjected to mechanical processing such as grinding and polishing to produce a glass molded body, or preform made from optical glass is subjected to reheat press molding and then polishing processing is performed to perform glass molding. A glass molded body can be manufactured by producing a body or performing precision press molding on a preform produced by performing a polishing process or a preform formed by a known float forming. The means for producing the glass molded body is not limited to these means.
このように、本発明の光学ガラスから形成したガラス成形体は、様々な光学素子及び光学設計に有用であるが、その中でも特に、レンズやプリズム等の光学素子に用いることが好ましい。これにより、径の大きなガラス成形体の形成が可能になるため、光学素子の大型化を図りながらも、カメラやプロジェクタ等の光学機器に用いたときに高精細で高精度な結像特性及び投影特性を実現できる。 As described above, the glass molded body formed from the optical glass of the present invention is useful for various optical elements and optical designs, and among them, it is particularly preferably used for optical elements such as lenses and prisms. As a result, it becomes possible to form a glass molded body with a large diameter. Therefore, while enlarging the optical element, high-definition and high-precision imaging characteristics and projection characteristics can be achieved when used in optical equipment such as cameras and projectors. The characteristics can be realized.
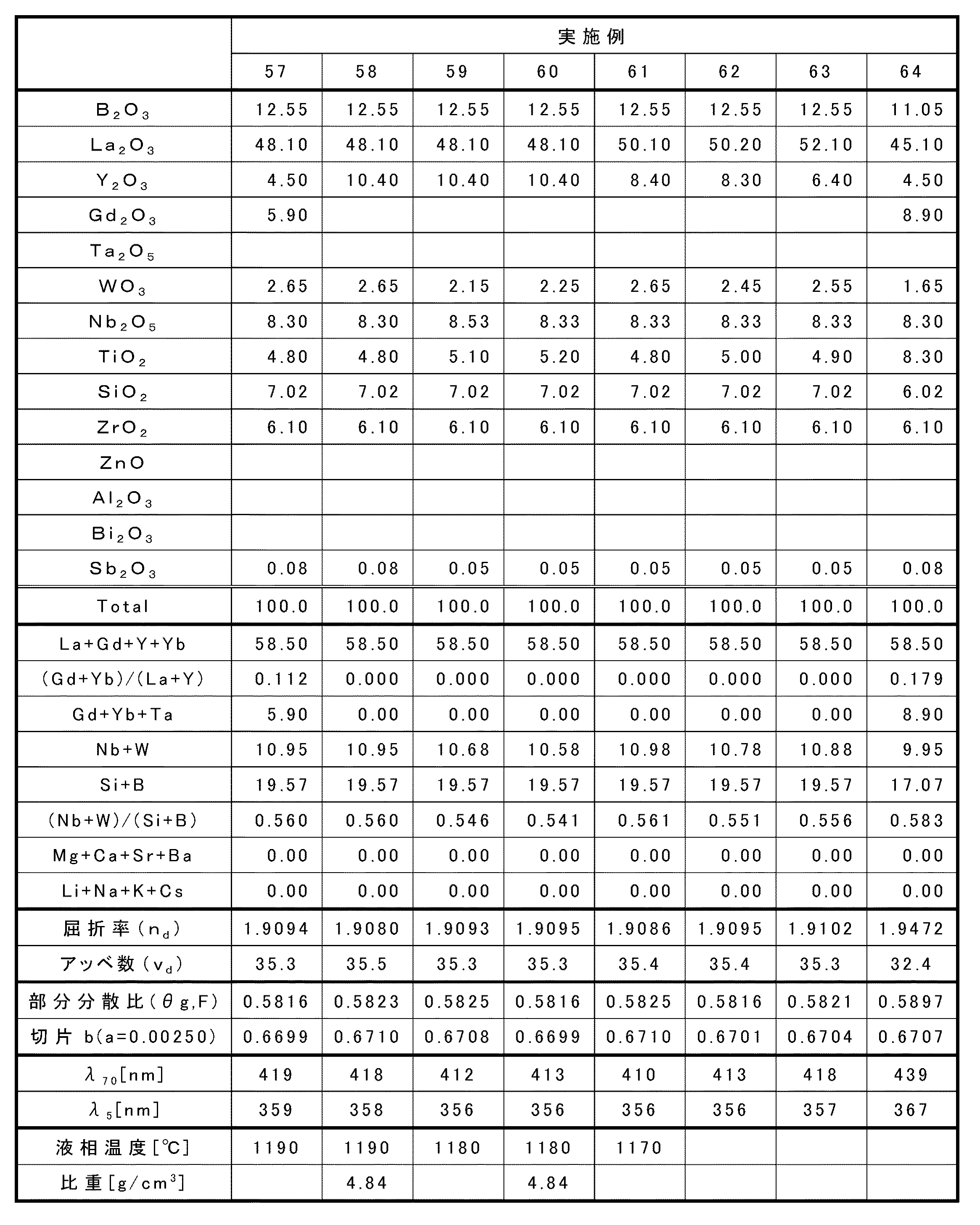
本発明の実施例(No.1〜No.132)及び比較例(No.A)の組成、並びに、これらのガラスの屈折率(nd)、アッベ数(νd)、部分分散比(θg,F)、液相温度、分光透過率が5%及び70%を示す波長(λ5及びλ70)並びに比重の結果を表1〜表19に示す。なお、以下の実施例はあくまで例示の目的であり、これらの実施例のみ限定されるものではない。 The composition of the embodiment of the present invention (No.1~No.132) and Comparative Example (No. A), and the refractive index of these glasses (n d), Abbe number ([nu d), the partial dispersion ratio ([theta] g , F), liquidus temperature, wavelengths (λ 5 and λ 70 ) at which spectral transmittances are 5% and 70%, and specific gravity are shown in Tables 1 to 19. It should be noted that the following embodiments are merely for the purpose of illustration, and the embodiments are not limited thereto.
本発明の実施例及び比較例のガラスは、いずれも各成分の原料として各々相当する酸化物、水酸化物、炭酸塩、硝酸塩、弗化物、水酸化物、メタ燐酸化合物等の通常の光学ガラスに使用される高純度原料を選定し、表に示した各実施例の組成の割合になるように秤量して均一に混合した後、白金坩堝に投入し、ガラス組成の熔融難易度に応じて電気炉で1100〜1500℃の温度範囲で2〜5時間熔融した後、攪拌均質化してから金型等に鋳込み、徐冷してガラスを作製した。 The glasses of Examples and Comparative Examples of the present invention are ordinary optical glasses such as oxides, hydroxides, carbonates, nitrates, fluorides, hydroxides, metaphosphoric acid compounds, etc., each of which corresponds to the raw material of each component. The high-purity raw material used for was selected, weighed and uniformly mixed so as to have the composition ratio of each example shown in the table, and then charged into a platinum crucible, depending on the melting difficulty of the glass composition. After melting in an electric furnace in a temperature range of 1100 to 1500° C. for 2 to 5 hours, the mixture was stirred and homogenized, then cast into a mold or the like, and slowly cooled to produce glass.
ここで、実施例及び比較例のガラスの屈折率、アッベ数、及び部分分散比(θg,F)は、日本光学硝子工業会規格JOGIS01―2003に基づいて測定した。そして、求められたアッベ数及び部分分散比の値について、関係式(θg,F)=−a×νd+bにおける、傾きaが0.0025のときの切片bを求めた。ここで、屈折率、アッベ数、及び部分分散比は、徐冷降温速度を−25℃/hrにして得られたガラスについて測定を行うことで求めた。 Here, the refractive index, the Abbe number, and the partial dispersion ratio (θg, F) of the glass of Examples and Comparative Examples were measured based on Japan Optical Glass Industry Association Standard JOGIS01-2003. Then, for the values of the obtained Abbe number and the partial dispersion ratio, the intercept b when the slope a was 0.0025 in the relational expression (θg, F)=−a×ν d +b was obtained. Here, the refractive index, the Abbe's number, and the partial dispersion ratio were determined by measuring the glass obtained at a slow cooling rate of -25°C/hr.
また、実施例及び比較例のガラスの透過率は、日本光学硝子工業会規格JOGIS02に準じて測定した。なお、本発明においては、ガラスの透過率を測定することで、ガラスの着色の有無と程度を求めた。具体的には、厚さ10±0.1mmの対面平行研磨品をJISZ8722に準じ、200〜800nmの分光透過率を測定し、λ5(透過率5%時の波長)及びλ70(透過率70%時の波長)を求めた。 Further, the transmittances of the glasses of Examples and Comparative Examples were measured according to Japan Optical Glass Industry Association Standard JOGIS02. In the present invention, the presence or absence and the degree of coloring of the glass were determined by measuring the transmittance of the glass. Specifically, a face-to-face parallel polished product having a thickness of 10±0.1 mm was measured for spectral transmittance at 200 to 800 nm according to JIS Z8722, and λ 5 (wavelength at 5% transmittance) and λ 70 (transmittance) were measured. The wavelength at 70%) was determined.
また、実施例及び比較例のガラスの液相温度は、50mlの容量の白金製坩堝に30ccのカレット状のガラス試料を白金坩堝に入れて1350℃で完全に熔融状態にし、1300℃〜1160℃まで10℃刻みで設定したいずれかの温度まで降温して12時間保持し、炉外に取り出して冷却した後直ちにガラス表面及びガラス中の結晶の有無を観察し、結晶が認められない一番低い温度を求めた。 Further, the liquidus temperature of the glass of Examples and Comparative Examples is 1300° C. to 1160° C., in which a 30 cc cullet-shaped glass sample was put into a platinum crucible with a capacity of 50 ml and completely melted at 1350° C. The temperature is lowered to any of the temperatures set in steps of 10°C and kept for 12 hours, taken out of the furnace and immediately cooled, and then the presence or absence of crystals on the glass surface and the glass is observed. The temperature was determined.
また、実施例及び比較例のガラスの比重は、日本光学硝子工業会規格JOGIS05−1975「光学ガラスの比重の測定方法」に基づいて測定した。 The specific gravities of the glass of Examples and Comparative Examples were measured based on Japan Optical Glass Industry Association Standard JOGIS05-1975 "Method of measuring specific gravity of optical glass".
本発明の実施例の光学ガラスは、いずれも比重が5.50以下、より詳細には5.20以下であった。そのため、本発明の実施例の光学ガラスは、比重が小さいことが明らかになった。 The optical glasses of the examples of the present invention each had a specific gravity of 5.50 or less, more specifically 5.20 or less. Therefore, it was revealed that the optical glass of the example of the present invention has a small specific gravity.
また、本発明の実施例の光学ガラスは、いずれも液相温度が1300℃以下、より詳細には1220℃以下であり、所望の範囲内であった。このため、本発明の実施例の光学ガラスは、液相温度が低く、耐失透性が高いことが明らかになった。 Further, the optical glass of each of the examples of the present invention had a liquidus temperature of 1300° C. or lower, more specifically 1220° C. or lower, which was within the desired range. Therefore, it was revealed that the optical glass of the example of the present invention has a low liquidus temperature and high devitrification resistance.
また、本発明の実施例の光学ガラスは、λ70(透過率70%時の波長)がいずれも550nm以下、より詳細には505nm以下であった。また、本発明の実施例の光学ガラスは、λ5(透過率5%時の波長)がいずれも440nm以下、より詳細には379nm以下であった。 Further, the optical glasses of the examples of the present invention each had a λ 70 (wavelength at a transmittance of 70%) of 550 nm or less, more specifically 505 nm or less. Further, the optical glasses of the examples of the present invention each had a λ 5 (wavelength at a transmittance of 5%) of 440 nm or less, more specifically 379 nm or less.
また、本発明の実施例の光学ガラスは、いずれも屈折率(nd)が1.75以上、より詳細には1.87以上であるとともに、この屈折率は2.20以下、より詳細には2.01以下であり、所望の範囲内であった。 The optical glasses of Examples of the present invention are both refractive index (n d) of 1.75 or more, with more detail is 1.87 or more, the refractive index is 2.20 or less, more detail Was 2.01 or less, which was within the desired range.
また、本発明の実施例の光学ガラスは、いずれもアッベ数(νd)が23以上、より詳細には28以上であるとともに、このアッベ数は50以下、より詳細には39以下であり、所望の範囲内であった。 Further, in each of the optical glasses of Examples of the present invention, the Abbe number (ν d ) is 23 or more, more specifically 28 or more, and the Abbe number is 50 or less, more specifically 39 or less, It was within the desired range.
また、本発明の実施例の光学ガラスは、いずれも部分分散比(θg,F)が(−2.50×10−3×νd+0.6571)以上、より詳細には(−2.50×10−3×νd+0.6683)以上であった。その反面で、本発明の実施例の光学ガラスの部分分散比(−2.50×10−3×νd+0.6971)以下、より詳細には(−2.50×10−3×νd+0.6750)以下であった。そのため、これらの部分分散比(θg,F)が所望の範囲内にあることがわかった。 Further, the optical glasses of the examples of the present invention each have a partial dispersion ratio (θg, F) of (−2.50×10 −3 ×ν d +0.6571) or more, more specifically (−2.50). ×10 −3 ×ν d +0.6683) or more. On the other hand, the partial dispersion ratio (−2.50×10 −3 ×ν d +0.6971) of the optical glass of the example of the present invention or less, more specifically (−2.50×10 −3 ×ν d ). +0.6750) or less. Therefore, it was found that these partial dispersion ratios (θg, F) were within the desired range.
従って、本発明の実施例の光学ガラスは、屈折率及びアッベ数が所望の範囲内にありながらも安価に作製でき、耐失透性が高く、着色が少なく、且つ比重が小さいことが明らかになった。 Therefore, it is apparent that the optical glass of the examples of the present invention can be manufactured at low cost while the refractive index and the Abbe number are within the desired ranges, the devitrification resistance is high, the coloring is small, and the specific gravity is small. became.
さらに、本発明の実施例の光学ガラスを用いて、ガラスブロックを形成し、このガラスブロックに対して研削及び研磨を行い、レンズ及びプリズムの形状に加工した。その結果、安定に様々なレンズ及びプリズムの形状に加工することができた。 Further, a glass block was formed using the optical glass of the example of the present invention, and the glass block was ground and polished to be processed into the shape of a lens and a prism. As a result, various lens and prism shapes could be stably processed.
以上、本発明を例示の目的で詳細に説明したが、本実施例はあくまで例示の目的のみであって、本発明の思想及び範囲を逸脱することなく多くの改変を当業者により成し得ることが理解されよう。 Although the present invention has been described in detail above for the purpose of illustration, the present embodiment is merely for the purpose of illustration, and many modifications can be made by those skilled in the art without departing from the idea and scope of the present invention. Will be understood.
Claims (6)
B2O3成分を1.0〜13.90%、
La2O3成分を39.0〜56.0%
Y 2 O 3 成分を1.80〜20.0%、
Nb 2 O 5 成分を1.0%超15.0%以下、
TiO 2 成分を9.20%以上20.0%以下、及び
WO 3 成分を0.5%以上15.0%以下
含有し、
Gd 2 O 3 成分の含有量が2.80%以下、
Yb 2 O 3 成分の含有量が2.80%以下、
SiO 2 成分の含有量が15.0%以下、
Ta 2 O 5 成分の含有量が1.0%未満
であり、
Gd 2 O 3 成分、Yb 2 O 3 成分及びTa 2 O 5 成分の含有量の和が2.80%以下であり、
Ln 2 O 3 成分(式中、LnはLa、Gd、Y、Ybからなる群より選択される1種以上)の質量和が45.0%以上65.0%以下であり、
1.75以上の屈折率(n d )を有し、23以上50以下のアッベ数(ν d )を有する光学ガラス。 % By mass B 2 O 3 ingredient 1.0 to 13.90%,
La 2 O 3 component 39.0 to 56.0 %
Y 2 O 3 ingredient from 1.80 to 20.0%,
Nb 2 O 5 component is more than 1.0% and not more than 15.0%,
9.20% or more and 20.0% or less of TiO 2 component, and
Containing WO 3 component in an amount of 0.5% or more and 15.0% or less ,
The content of Gd 2 O 3 component is 2.80% or less,
The content of the Yb 2 O 3 component is 2.80% or less,
The content of SiO 2 component is 15.0% or less,
Ta 2 O 5 Ri is 1.0% less than <br/> der content of the component,
The sum of the contents of the Gd 2 O 3 component, the Yb 2 O 3 component and the Ta 2 O 5 component is 2.80% or less,
Ln 2 O 3 component (wherein Ln is at least one selected from the group consisting of La, Gd, Y, and Yb) has a mass sum of 45.0% or more and 65.0% or less,
An optical glass having a refractive index ( nd ) of 1.75 or more and an Abbe number (ν d ) of 23 or more and 50 or less .
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011289956 | 2011-12-28 | ||
| JP2011289956 | 2011-12-28 | ||
| JP2012190082 | 2012-08-30 | ||
| JP2012190082 | 2012-08-30 |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016194368A Division JP6560650B2 (en) | 2011-12-28 | 2016-09-30 | Optical glass and optical element |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2019131465A JP2019131465A (en) | 2019-08-08 |
| JP6740422B2 true JP6740422B2 (en) | 2020-08-12 |
Family
ID=50617630
Family Applications (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012278571A Active JP6096501B2 (en) | 2011-12-28 | 2012-12-20 | Optical glass and optical element |
| JP2016194368A Active JP6560650B2 (en) | 2011-12-28 | 2016-09-30 | Optical glass and optical element |
| JP2019087337A Active JP6740422B2 (en) | 2011-12-28 | 2019-05-07 | Optical glass and optical element |
Family Applications Before (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012278571A Active JP6096501B2 (en) | 2011-12-28 | 2012-12-20 | Optical glass and optical element |
| JP2016194368A Active JP6560650B2 (en) | 2011-12-28 | 2016-09-30 | Optical glass and optical element |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (3) | JP6096501B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102081464B1 (en) * | 2012-03-26 | 2020-02-25 | 호야 가부시키가이샤 | Optical glass and use thereof |
| JP6501054B2 (en) * | 2014-06-30 | 2019-04-17 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Optical glass |
| JP6587286B2 (en) * | 2014-11-07 | 2019-10-09 | Hoya株式会社 | Glass, glass material for press molding, optical element blank, and optical element |
| JP6738243B2 (en) * | 2016-08-31 | 2020-08-12 | Hoya株式会社 | Glass, glass material for press molding, optical element blank and optical element |
| JP7048348B2 (en) * | 2018-02-28 | 2022-04-05 | 株式会社オハラ | Optical glass, preforms and optical elements |
| JP7512893B2 (en) * | 2018-08-31 | 2024-07-09 | Agc株式会社 | Optical Glass and Optical Components |
| JP7394523B2 (en) * | 2018-10-11 | 2023-12-08 | Hoya株式会社 | Optical glass, glass materials for press molding, optical element blanks and optical elements |
| JP6699809B1 (en) * | 2019-08-26 | 2020-05-27 | Agc株式会社 | Optical glass |
| CN112028473B (en) * | 2020-09-07 | 2022-02-11 | 成都光明光电股份有限公司 | Optical glass for precision mould pressing |
| JP2021046354A (en) * | 2020-12-03 | 2021-03-25 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Production method of glass material, and glass material |
| CN115504666A (en) * | 2022-08-26 | 2022-12-23 | 成都光明光电股份有限公司 | Optical glass and optical element |
| CN115304269A (en) * | 2022-08-26 | 2022-11-08 | 成都光明光电股份有限公司 | Optical glass |
| CN115286237A (en) * | 2022-08-26 | 2022-11-04 | 成都光明光电股份有限公司 | Optical glass and optical element |
| CN115231819A (en) * | 2022-08-26 | 2022-10-25 | 成都光明光电股份有限公司 | High refractive index optical glass |
| CN115286238A (en) * | 2022-08-26 | 2022-11-04 | 成都光明光电股份有限公司 | Optical glass |
| CN115321815A (en) * | 2022-08-26 | 2022-11-11 | 成都光明光电股份有限公司 | High-refraction high-dispersion optical glass |
| CN115304274A (en) * | 2022-08-26 | 2022-11-08 | 成都光明光电股份有限公司 | High-refraction high-dispersion optical glass |
| CN115321814A (en) * | 2022-08-26 | 2022-11-11 | 成都光明光电股份有限公司 | Optical glass |
Family Cites Families (43)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5416527B1 (en) * | 1970-04-17 | 1979-06-22 | ||
| JPS4980115A (en) * | 1972-12-07 | 1974-08-02 | ||
| JPS52129716A (en) * | 1976-04-26 | 1977-10-31 | Hoya Glass Works Ltd | Optical glass |
| JPS52155614A (en) * | 1976-06-22 | 1977-12-24 | Obara Optical Glass | Optical glass of high difraction index and low dispersion |
| JPS54161619A (en) * | 1978-06-07 | 1979-12-21 | Jenaer Glaswerk Schott & Gen | Light weight* high refractive index glass for glass lense |
| JPS55121925A (en) * | 1979-03-14 | 1980-09-19 | Ohara Inc | Optical glass |
| JPS565345A (en) * | 1979-06-28 | 1981-01-20 | Nippon Kogaku Kk <Nikon> | Optical glass |
| JPS5678447A (en) * | 1979-11-29 | 1981-06-27 | Minolta Camera Co Ltd | Optical glass |
| JPS5734044A (en) * | 1980-08-07 | 1982-02-24 | Nippon Kogaku Kk <Nikon> | Optical glass |
| DE3130039C2 (en) * | 1981-07-30 | 1984-07-12 | Schott Glaswerke, 6500 Mainz | CdO-ThO? 2? -Free, high refractive index optical glass with the optical position nd = 1.85 - 2.05 and vd 25-43 |
| DE3201346C2 (en) * | 1982-01-18 | 1986-03-13 | Schott Glaswerke, 6500 Mainz | Highly refractive optical glasses with refractive indices of 1.84 - 1.87 and Abbe numbers of 30 - 33 in the system SiO 2 -B 2 O 3 -Alkalioxid-Erdalkalioxid / ZnO-PbO-La 2 O 3 ; -ZrO 2 -TiO 2 -Nb 2 O 5 |
| DE3201344C2 (en) * | 1982-01-18 | 1984-02-16 | Schott Glaswerke, 6500 Mainz | High refractive index optical glasses in the system SiO 2 -B 2 O 3 -Alkalioxid-Erdalkaloxid-La 2 O 3 -ZrO 2 -TiO 5 2-2 -Nb with refractive indices of 1.79 - 1.82, Abbezahlen? 32 and densities ≦ 4.0 |
| JPS59195553A (en) * | 1983-04-19 | 1984-11-06 | Ohara Inc | Optical glass |
| JPS6042245A (en) * | 1983-08-10 | 1985-03-06 | Nippon Kogaku Kk <Nikon> | Directly moldable optical glass |
| JPS6046948A (en) * | 1983-08-25 | 1985-03-14 | Nippon Kogaku Kk <Nikon> | Glass having high refractive index and low despersion |
| DE3343418A1 (en) * | 1983-12-01 | 1985-06-20 | Schott Glaswerke, 6500 Mainz | OPTICAL GLASS WITH REFRACTION VALUES> = 1.90, PAYBACK> = 25 AND WITH HIGH CHEMICAL RESISTANCE |
| JPS61163138A (en) * | 1985-01-12 | 1986-07-23 | Nippon Kogaku Kk <Nikon> | Optical glass having high refractive index and low dispersion |
| JP3238740B2 (en) * | 1992-03-17 | 2001-12-17 | 株式会社オハラ | Optical glass |
| JPH08217484A (en) * | 1995-02-13 | 1996-08-27 | Ohara Inc | Optical glass |
| JP3396450B2 (en) * | 1998-10-02 | 2003-04-14 | 株式会社オハラ | Glasses for glasses and optics |
| JP4127949B2 (en) * | 2000-06-27 | 2008-07-30 | Hoya株式会社 | Optical glass and optical product using the same |
| JP4093524B2 (en) * | 2001-02-20 | 2008-06-04 | Hoya株式会社 | Optical glass, press-molding preform and optical parts |
| JP4017832B2 (en) * | 2001-03-27 | 2007-12-05 | Hoya株式会社 | Optical glass and optical components |
| JP4286652B2 (en) * | 2002-12-27 | 2009-07-01 | Hoya株式会社 | Optical glass, glass gob for press molding, and optical element |
| JP2006111482A (en) * | 2004-10-14 | 2006-04-27 | Konica Minolta Opto Inc | Optical glass and optical element |
| JP4361004B2 (en) * | 2004-11-15 | 2009-11-11 | Hoya株式会社 | Optical glass, precision press-molding preform and manufacturing method thereof, and optical element and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP4508987B2 (en) * | 2005-08-31 | 2010-07-21 | Hoya株式会社 | Optical glass, precision press-molding preform and manufacturing method thereof, and optical element and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP5160042B2 (en) * | 2006-03-31 | 2013-03-13 | Hoya株式会社 | Manufacturing method of glass optical element |
| JP2008137877A (en) * | 2006-12-05 | 2008-06-19 | Hoya Corp | Optical glass and optical element |
| JP5358888B2 (en) * | 2007-02-22 | 2013-12-04 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Optical glass and optical element |
| JP5594807B2 (en) * | 2007-09-25 | 2014-09-24 | 株式会社オハラ | Optical glass |
| WO2009072335A1 (en) * | 2007-12-06 | 2009-06-11 | Asahi Glass Co., Ltd. | Optical glass and preforms for precision press molding and optical elements made by using the glass |
| JP5138401B2 (en) * | 2008-01-30 | 2013-02-06 | Hoya株式会社 | Optical glass, glass gob for press molding, optical element, manufacturing method thereof, and manufacturing method of optical element blank |
| JP4948569B2 (en) * | 2008-06-27 | 2012-06-06 | Hoya株式会社 | Optical glass |
| JP5180758B2 (en) * | 2008-09-30 | 2013-04-10 | Hoya株式会社 | Optical glass, glass gob for press molding, optical element, manufacturing method thereof, and manufacturing method of optical element blank |
| JP2010083702A (en) * | 2008-09-30 | 2010-04-15 | Hoya Corp | Optical glass, glass gob for press forming and optical element |
| JP5427460B2 (en) * | 2009-04-14 | 2014-02-26 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Optical glass |
| JP5678477B2 (en) * | 2009-05-28 | 2015-03-04 | 旭硝子株式会社 | Optical glass |
| US8835336B2 (en) * | 2009-11-26 | 2014-09-16 | Konica Minolta Advanced Layers, Inc. | Optical glass and optical element |
| JP2011153048A (en) * | 2010-01-28 | 2011-08-11 | Konica Minolta Opto Inc | Optical glass |
| JP5987364B2 (en) * | 2011-03-09 | 2016-09-07 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Optical glass |
| JP5761603B2 (en) * | 2011-07-01 | 2015-08-12 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Optical glass |
| JP5880919B2 (en) * | 2011-08-01 | 2016-03-09 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Optical glass |
-
2012
- 2012-12-20 JP JP2012278571A patent/JP6096501B2/en active Active
-
2016
- 2016-09-30 JP JP2016194368A patent/JP6560650B2/en active Active
-
2019
- 2019-05-07 JP JP2019087337A patent/JP6740422B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6096501B2 (en) | 2017-03-15 |
| JP2019131465A (en) | 2019-08-08 |
| JP2017039640A (en) | 2017-02-23 |
| JP6560650B2 (en) | 2019-08-14 |
| JP2014062024A (en) | 2014-04-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6740422B2 (en) | Optical glass and optical element | |
| JP6409039B2 (en) | Optical glass and optical element | |
| JP6033486B2 (en) | Optical glass, preform material and optical element | |
| JP5979723B2 (en) | Optical glass and optical element | |
| TWI616415B (en) | Optical glass and optical components | |
| JP5827067B2 (en) | Optical glass and optical element | |
| JP6560651B2 (en) | Optical glass and optical element | |
| JP2012229148A (en) | Optical glass and optical element | |
| JP6188553B2 (en) | Optical glass, preform material and optical element | |
| JP6363141B2 (en) | Optical glass, preform material and optical element | |
| JP5875572B2 (en) | Optical glass, preform material and optical element | |
| JPWO2019031095A1 (en) | Optical glass, optical element and optical equipment | |
| JP2017171578A (en) | Optical glass and optical element | |
| JP6091251B2 (en) | Optical glass and optical element | |
| JP6049591B2 (en) | Optical glass, preform material and optical element | |
| JP2013209232A (en) | Optical glass and optical element | |
| JP6689057B2 (en) | Optical glass, preforms and optical elements | |
| JP6033487B2 (en) | Optical glass and optical element | |
| JP6165281B2 (en) | Optical glass and optical element | |
| JP2017057121A (en) | Optical glass, preform and optical element | |
| JP6611410B2 (en) | Optical glass, preform material and optical element | |
| JP2013209233A (en) | Optical glass and optical element | |
| JP2019031441A (en) | Optical glass and optical element | |
| JP2014162708A (en) | Optical glass and optical element |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190606 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20190606 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20200110 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20200721 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20200722 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6740422 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |