JP6229456B2 - Vibrating piece, vibrator, oscillator, electronic device and moving object - Google Patents
Vibrating piece, vibrator, oscillator, electronic device and moving object Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6229456B2 JP6229456B2 JP2013242636A JP2013242636A JP6229456B2 JP 6229456 B2 JP6229456 B2 JP 6229456B2 JP 2013242636 A JP2013242636 A JP 2013242636A JP 2013242636 A JP2013242636 A JP 2013242636A JP 6229456 B2 JP6229456 B2 JP 6229456B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- resonator element
- axis direction
- axis
- vibration
- vibrating
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Oscillators With Electromechanical Resonators (AREA)
- Piezo-Electric Or Mechanical Vibrators, Or Delay Or Filter Circuits (AREA)
Description
本発明は、振動片、この振動片を備えている振動子、発振器、電子機器及び移動体に関する。 The present invention relates to a resonator element, a vibrator including the resonator element, an oscillator, an electronic device, and a moving object.
従来、振動片として、厚みすべり振動する振動部、振動部の外縁のうち、少なくとも厚みすべり振動の変位方向と交差する外縁に沿って一体化され、振動部より厚さの薄い周辺部、及び周辺部に設けられている凸部、を含む素板と、振動部に設けられている励振電極とを含み、凸部の長さを振動部の短辺寸法に合わせた構成の振動片が知られている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。
上記振動片は、生産性に優れ、振動部と周辺部との段差(メサ部の堀量)を大きくしても、CI値の劣化を生じさせないとされている。
Conventionally, as a vibrating piece, a vibrating part that vibrates in thickness shear, and an outer edge of the vibrating part that is integrated along at least the outer edge that intersects with the displacement direction of the thickness sliding vibration, and is thinner and thinner around the vibrating part There is known a resonator element that includes a base plate including a convex portion provided on a portion, and an excitation electrode provided on the vibration portion, and the length of the convex portion is adjusted to the short side dimension of the vibration portion. (For example, refer to Patent Document 1).
The vibrator element is excellent in productivity, and it is said that the CI value does not deteriorate even if the step between the vibrating part and the peripheral part (the amount of excavation of the mesa part) is increased.
上記振動片は、周辺部に設けられている凸部の長さを振動部の短辺寸法に合わせた構成としていることから、凸部の剛性などによりスプリアス(不要振動)である屈曲振動成分の抑制には効果があるものの、主振動である厚みすべり振動の、周辺部における減衰作用が、長い凸部によって阻害される虞がある。
これにより、上記振動片は、厚みすべり振動の振動エネルギーの閉じ込めが不十分となる虞がある。
このことから、上記振動片は、厚みすべり振動の振動エネルギーの外部への漏洩により、CI値が増加(劣化)し、振動特性が劣化する虞がある。
Since the vibration piece has a configuration in which the length of the convex portion provided in the peripheral portion is matched to the short side dimension of the vibration portion, the bending vibration component that is spurious (unnecessary vibration) due to the rigidity of the convex portion or the like. Although effective in suppression, there is a possibility that the damping action in the peripheral portion of the thickness shear vibration which is the main vibration is hindered by the long convex portion.
As a result, the vibration piece may be insufficiently confined in vibration energy of the thickness shear vibration.
For this reason, there is a possibility that the CI value increases (deteriorates) and the vibration characteristics deteriorate due to leakage of the vibration energy of the thickness shear vibration to the outside.
本発明は、上記課題の少なくとも一部を解決するためになされたものであり、以下の形態または適用例として実現することが可能である。 SUMMARY An advantage of some aspects of the invention is to solve at least a part of the problems described above, and the invention can be implemented as the following forms or application examples.
[適用例1]本適用例にかかる振動片は、厚みすべり振動する振動部、前記振動部より厚み寸法が薄い周辺部、を含む素板と、少なくとも前記振動部に設けられている励振電極と、を備え、前記厚みすべり振動の振動方向を第1方向とし、前記第1方向と交差する方向を第2方向とした場合、前記素板は、前記第1方向において、前記周辺部と前記振動部との間に第1段差部を有し、前記第2方向において、前記周辺部と前記振動部との間に第2段差部を有し、前記第1方向に沿って、前記周辺部の第1領域と第2領域とは、前記振動部を挟むように配置されており、前記第1領域及び前記第2領域の少なくともいずれか一方に、前記周辺部の厚み方向に突出し前記第2方向に沿って延びる凸部を有し、前記凸部の前記第2方向に沿った長さは、前記振動部の前記第2方向に沿った長さより短く、かつ前記第1方向からみて前記振動部の幅の範囲内にあることを特徴とする。 [Application Example 1] A resonator element according to this application example includes a vibrating plate that vibrates in thickness and slide, a base plate that includes a peripheral portion having a thickness smaller than that of the vibrating portion, and an excitation electrode provided at least in the vibrating portion. When the vibration direction of the thickness-shear vibration is the first direction and the direction intersecting the first direction is the second direction, the base plate and the vibration in the first direction A first step portion between the peripheral portion and the vibration portion in the second direction, and a second step portion between the peripheral portion and the vibration portion in the second direction. The first region and the second region are arranged so as to sandwich the vibrating portion, and project in the thickness direction of the peripheral portion in at least one of the first region and the second region, and then in the second direction. A length extending along the second direction of the convex portion Characterized in that the shorter than the length along the second direction of the vibration part, and viewed from the first direction is in the range of width of the vibrating portion.
これによれば、振動片は、素板が第1方向において、周辺部と振動部との間に第1段差部、第2方向において、周辺部と振動部との間に第2段差部、を有し、周辺部の第1領域及び第2領域の少なくともいずれか一方に、周辺部の厚み方向に突出し第2方向に沿って延びる凸部を有し、凸部の第2方向に沿った長さが、振動部の第2方向に沿った長さより短く、かつ第1方向からみて振動部の幅の範囲内にある。
この結果、振動片は、従来(例えば、特許文献1の構成)より短い凸部、及び第2段差部によって、屈曲振動成分を抑制しつつ、周辺部における厚みすべり振動を減衰させ、厚みすべり振動の振動エネルギーの閉じ込めを効率よく行うことができる。
これにより、振動片は、CI値が低下し(良好となり)、振動特性を向上させることができる。
According to this, the resonator element has the first step portion between the peripheral portion and the vibrating portion in the first direction, the second step portion between the peripheral portion and the vibrating portion in the second direction, And at least one of the first region and the second region of the peripheral portion has a convex portion protruding in the thickness direction of the peripheral portion and extending along the second direction, and along the second direction of the convex portion. The length is shorter than the length along the second direction of the vibration part, and is within the range of the width of the vibration part when viewed from the first direction.
As a result, the vibration piece attenuates the thickness shear vibration in the peripheral portion while suppressing the flexural vibration component by the convex portion and the second step portion shorter than the conventional one (for example, the configuration of Patent Document 1), and the thickness shear vibration. The vibration energy can be confined efficiently.
As a result, the CI value of the resonator element decreases (becomes better), and the vibration characteristics can be improved.
[適用例2]上記適用例にかかる振動片において、前記振動部の前記第1方向に沿った長さをMx、前記第2段差部の前記第1方向に沿った長さをNx、前記励振電極の前記第1方向に沿った長さをEx、前記凸部の前記第1方向に沿った長さをDx、前記第2段差部と前記凸部との前記第1方向に沿った間隔をSx、前記素板に生じる屈曲振動の波長をλとしたときに、Mx=(v+1/2)×λ±0.1λ(但し、vは正の整数)、Nx=λ/2×p±0.1λ(但し、pは正の整数)、Ex=(w+1/2)×λ±0.1λ(但し、wは正の整数)、Dx=λ/2×m±0.1λ(但し、mは正の整数)、Sx=λ/2×n±0.1λ(但し、nは正の整数)、の関係を満たすことが好ましい。 Application Example 2 In the resonator element according to the application example described above, the length of the vibrating portion along the first direction is Mx, the length of the second step portion along the first direction is Nx, and the excitation is performed. The length of the electrode along the first direction is Ex, the length of the convex portion along the first direction is Dx, and the distance between the second stepped portion and the convex portion along the first direction is defined as Dx. Sx where Mx = (v + 1/2) × λ ± 0.1λ (where v is a positive integer), Nx = λ / 2 × p ± 0, where λ is the wavelength of the bending vibration generated in the base plate .1λ (where p is a positive integer), Ex = (w + 1/2) × λ ± 0.1λ (where w is a positive integer), Dx = λ / 2 × m ± 0.1λ (where m Is a positive integer), and preferably satisfies the relationship of Sx = λ / 2 × n ± 0.1λ (where n is a positive integer).
これによれば、振動片は、Mx=(v+1/2)×λ±0.1λ、Nx=λ/2×p±0.1λ、Ex=(w+1/2)×λ±0.1λ、Dx=λ/2×m±0.1λ、Sx=λ/2×n±0.1λ、の関係を満たすことから、屈曲振動成分をより抑制しつつ、周辺部における厚みすべり振動をより減衰させ、厚みすべり振動の振動エネルギーの閉じ込めをより効率よく行うことができる。 According to this, the vibration piece is Mx = (v + 1/2) × λ ± 0.1λ, Nx = λ / 2 × p ± 0.1λ, Ex = (w + 1/2) × λ ± 0.1λ, Dx = Λ / 2 × m ± 0.1λ, Sx = λ / 2 × n ± 0.1λ, satisfying the relationship, further suppressing the bending vibration component and further damping the thickness shear vibration in the peripheral part, It is possible to more efficiently confine the vibration energy of the thickness shear vibration.
[適用例3]上記適用例にかかる振動片において、前記素板の前記第1方向に沿った長さをLx、前記振動部の厚みをtとしたときに、10≦Lx/t≦40、の関係を満たすことが好ましい。 Application Example 3 In the resonator element according to the application example, when the length of the base plate along the first direction is Lx and the thickness of the vibration part is t, 10 ≦ Lx / t ≦ 40, It is preferable to satisfy the relationship.
これによれば、振動片は、10≦Lx/t≦40、の関係を満たすことから、屈曲振動成分を抑制しつつ、周辺部における厚みすべり振動を減衰させ、厚みすべり振動の振動エネルギーの閉じ込めをより顕著に行うことができる。 According to this, since the resonator element satisfies the relationship of 10 ≦ Lx / t ≦ 40, the thickness shear vibration in the peripheral portion is attenuated while suppressing the flexural vibration component, and the vibration energy of the thickness shear vibration is confined. Can be performed more remarkably.
[適用例4]上記適用例にかかる振動片において、前記凸部の前記第2方向に沿った長さをDz、前記振動部の前記第2方向に沿った長さをMzとしたときに、0<Dz/Mz≦0.7、の関係を満たすことが好ましい。 Application Example 4 In the resonator element according to the application example described above, when the length of the convex portion along the second direction is Dz and the length of the vibration portion along the second direction is Mz, It is preferable to satisfy the relationship of 0 <Dz / Mz ≦ 0.7.
これによれば、振動片は、0<Dz/Mz≦0.7、の関係を満たすことから、屈曲振動成分を更に抑制しつつ、周辺部における厚みすべり振動を更に減衰させ、厚みすべり振動の振動エネルギーの閉じ込めを更に効率よく行うことができる。 According to this, since the resonator element satisfies the relationship of 0 <Dz / Mz ≦ 0.7, the thickness shear vibration in the peripheral portion is further attenuated while further suppressing the flexural vibration component, and the thickness shear vibration is reduced. The vibration energy can be confined more efficiently.
[適用例5]上記適用例にかかる振動片において、前記凸部の前記周辺部からの高さをDy、前記振動部の前記周辺部からの高さをMyとしたときに、0<Dy/My≦1、の関係を満たすことが好ましい。 Application Example 5 In the resonator element according to the application example, when the height of the convex portion from the peripheral portion is Dy and the height of the vibration portion from the peripheral portion is My, 0 <Dy / It is preferable to satisfy the relationship of My ≦ 1.
これによれば、振動片は、0<Dy/My≦1、の関係を満たすことから、凸部の周辺部からの高さDyを、振動部の周辺部からの高さMy以下にすることにより、屈曲振動成分を抑制しつつ、周辺部における厚みすべり振動を減衰させ、厚みすべり振動の振動エネルギーの閉じ込めを更に効率よく行うことができる。 According to this, since the resonator element satisfies the relationship of 0 <Dy / My ≦ 1, the height Dy from the peripheral portion of the convex portion is set to be equal to or lower than the height My from the peripheral portion of the vibrating portion. Thus, while suppressing the bending vibration component, the thickness shear vibration in the peripheral portion can be attenuated, and the vibration energy of the thickness shear vibration can be more efficiently confined.
[適用例6]上記適用例にかかる振動片において、前記凸部の前記周辺部からの高さが、前記第1段差部及び前記第2段差部の段差のうち、いずれか1つの前記段差の前記周辺部からの高さと同じであることが好ましい。 Application Example 6 In the resonator element according to the application example described above, the height of the convex portion from the peripheral portion is any one of the steps of the first step portion and the second step portion. The height from the peripheral portion is preferably the same.
これによれば、振動片は、凸部の周辺部からの高さが、第1段差部及び第2段差部の段差のうち、いずれか1つの段差の周辺部からの高さと同じであることから、例えば、エッチングによって凸部と、第1段差部及び第2段差部の1つの段差とを、一括して形成することができる。
この結果、振動片は、生産性を向上させることができる。
According to this, the vibration piece has the same height from the periphery of the convex portion as the height from the periphery of any one of the steps of the first step portion and the second step portion. Thus, for example, the convex portion and one step of the first step portion and the second step portion can be collectively formed by etching.
As a result, the resonator element can improve productivity.
[適用例7]上記適用例にかかる振動片において、前記第2段差部及び前記凸部における前記第2方向に沿って延びる各壁面が傾斜面であり、前記傾斜面は、前記素板に生じる屈曲振動の最大振幅となる領域を含んでいることが好ましい。 Application Example 7 In the resonator element according to the application example, each wall surface extending along the second direction in the second step portion and the convex portion is an inclined surface, and the inclined surface is generated in the base plate. It is preferable to include a region having the maximum amplitude of bending vibration.
これによれば、振動片は、第2段差部及び凸部における第2方向に沿って延びる各壁面が傾斜面であり、この傾斜面が素板に生じる屈曲振動の最大振幅となる領域を含んでいることから、この傾斜面によって屈曲振動成分を更に抑制することができる。 According to this, in the resonator element, each wall surface extending along the second direction in the second step portion and the convex portion is an inclined surface, and the inclined surface includes a region having the maximum amplitude of the bending vibration generated in the base plate. Therefore, the bending vibration component can be further suppressed by this inclined surface.
[適用例8]本適用例にかかる振動子は、上記適用例のいずれか一例に記載の振動片と、前記振動片が収容されている容器と、を備えていることを特徴とする。 Application Example 8 A vibrator according to this application example includes the resonator element according to any one of the application examples described above and a container in which the resonator element is accommodated.
これによれば、本構成の振動子は、上記適用例のいずれか一例に記載の振動片と、振動片が収容されている容器と、を備えていることから、上記適用例のいずれか一例に記載の効果を奏する振動子を提供することができる。 According to this, since the vibrator of this configuration includes the resonator element according to any one of the above application examples and the container in which the resonator element is accommodated, any one example of the above application examples. It is possible to provide a vibrator having the effects described in (1).
[適用例9]本適用例にかかる発振器は、上記適用例のいずれか一例に記載の振動片と、前記振動片を駆動する回路と、を備えていることを特徴とする。 Application Example 9 An oscillator according to this application example includes the resonator element according to any one of the application examples described above and a circuit that drives the resonator element.
これによれば、本構成の発振器は、上記適用例のいずれか一例に記載の振動片と、振動片を駆動する回路と、を備えていることから、上記適用例のいずれか一例に記載の効果を奏する発振器を提供することができる。 According to this, since the oscillator of this configuration includes the resonator element described in any one of the application examples described above and a circuit that drives the resonator element, the oscillator described in any one of the application examples described above. An oscillator having an effect can be provided.
[適用例10]本適用例にかかる電子機器は、上記適用例のいずれか一例に記載の振動片を備えていることを特徴とする。 Application Example 10 An electronic apparatus according to this application example includes the resonator element according to any one of the application examples described above.
これによれば、本構成の電子機器は、上記適用例のいずれか一例に記載の振動片を備えていることから、上記適用例のいずれか一例に記載の効果を奏する電子機器を提供することができる。 According to this, since the electronic device of this configuration includes the resonator element according to any one of the application examples, the electronic device having the effects described in any one of the application examples is provided. Can do.
[適用例11]本適用例にかかる移動体は、上記適用例のいずれか一例に記載の振動片を備えていることを特徴とする。 Application Example 11 A moving body according to this application example includes the resonator element according to any one of the application examples described above.
これによれば、本構成の移動体は、上記適用例のいずれか一例に記載の振動片を備えていることから、上記適用例のいずれか一例に記載の効果を奏する移動体を提供することができる。 According to this, since the movable body of this structure is provided with the vibration piece as described in any one example of the said application example, providing the movable body which has an effect as described in any one example of the said application example is provided. Can do.
以下、本発明を具体化した実施形態について図面を参照して説明する。 DESCRIPTION OF EXEMPLARY EMBODIMENTS Hereinafter, embodiments of the invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
(第1実施形態)
最初に、振動片の一例としての水晶振動片について説明する。
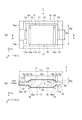
図1は、第1実施形態の水晶振動片の概略構成を示す模式斜視図である。図2は、図1の水晶振動片の模式平断面図であり、図2(a)は、Y’軸方向から見た平面図、図2(b)は、図2(a)のA−A線での断面図である。なお、分かり易くするために、各構成要素の寸法比率は実際と異なる。
(First embodiment)
First, a quartz crystal resonator element as an example of a resonator element will be described.
FIG. 1 is a schematic perspective view illustrating a schematic configuration of the quartz crystal resonator element according to the first embodiment. 2 is a schematic plan sectional view of the quartz crystal vibrating piece of FIG. 1, FIG. 2 (a) is a plan view seen from the Y′-axis direction, and FIG. 2 (b) is an A- It is sectional drawing in A line. In addition, in order to make it intelligible, the dimension ratio of each component differs from actual.
図1、図2に示すように、水晶振動片1は、水晶の結晶軸である、電気軸としてのX軸、機械軸としてのY軸、及び光学軸としてのZ軸のうち、X軸を回転軸として、Z軸の+(プラス)側をY軸の−(マイナス)方向へ回転させた軸をZ’軸とし、Y軸の+側をZ軸の+方向へ回転させた軸をY’軸とし、X軸及びZ’軸に平行な面を主面11,12とし、Y’軸に沿った方向(Y’軸方向)を厚み方向とする、水晶の原石(ランバード)などから切り出された素板としての水晶基板10を備えている。
水晶基板10は、厚みすべり振動する略矩形状の振動部13と、平面視で(Y’軸方向から見て)振動部13を囲み、振動部13より厚み寸法(Y’軸方向の寸法)が薄い周辺部14と、を含んでいる。
振動部13は、周辺部14の+Y’側及び−Y’側の両方に突出している。
As shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, the quartz
The
The vibrating
水晶振動片1は、水晶基板10と、少なくとも振動部13に設けられている(ここでは、振動部13から周辺部14の一部にまで設けられている)励振電極15,16と、を備えている。
水晶基板10は、第1方向としてのX軸方向において、周辺部14と振動部13との間に1つの段差が設けられた第1段差部17を有し、X軸方向と交差(ここでは直交)する第2方向としてのZ’軸方向において、周辺部14と振動部13との間に2つの段差が設けられた第2段差部を有している。
第1段差部17及び第2段差部18は、振動部13(周辺部14)の+Y’側及び−Y’側の両方に設けられている。
The quartz
The
The
そして、水晶基板10は、X軸方向に沿って、周辺部14の第1領域(ここでは−X側の領域)と第2領域(ここでは+X側の領域)とが、振動部13を挟むように配置されており、第1領域及び第2領域の少なくともいずれか一方(ここでは両方)に、周辺部14の厚み方向としてのY’軸方向に突出し、Z’軸方向に沿って延びる凸部19を有している。凸部19は、周辺部14の+Y’側及び−Y’側の両方に突出している。
ここで、凸部19のZ’軸方向に沿った長さは、振動部13のZ’軸方向に沿った長さより短く、かつX軸方向からみて振動部13の幅の範囲内(振動部13が形成されている範囲内)にある。(詳細後述)。
In the
Here, the length of the
水晶基板10の周辺部14の第1領域及び第2領域のいずれか一方の領域(ここでは第1領域)は、励振電極15,16のそれぞれから引き出されたマウント電極15a,16aが設けられた固定端となっており、他方の領域(ここでは第2領域)は自由端となっている。
One of the first region and the second region (here, the first region) of the
マウント電極15aは、振動部13の主面11を覆い、且つ周辺部14の主面11aの一部を覆うように設けられた励振電極15から、X軸方向に沿って周辺部14の−X側の端部に引き出され、端部の側面に沿って周辺部14の主面12aに回り込み、励振電極16の近傍まで延在している。
マウント電極16aは、振動部13の主面12を覆い、且つ周辺部14の主面12aの一部を覆うように設けられた励振電極16から、X軸方向に沿って周辺部14の−X側の端部に引き出され、端部の側面に沿って周辺部14の主面11aに回り込み、励振電極15の近傍まで延在している。
励振電極15,16及びマウント電極15a,16aは、例えば、Cr(クロム)を下地層とし、その上にAu(金)が積層された構成の金属被膜となっている。
The
The
The
図2に示すように、水晶振動片1は、振動部13のX軸方向に沿った長さをMx、第2段差部18のX軸方向に沿った長さをNx、励振電極15,16のX軸方向に沿った長さをEx、凸部19のX軸方向に沿った長さをDx、第2段差部18と凸部19とのX軸方向に沿った間隔をSx、水晶基板10に生じる屈曲振動の波長をλとしたときに、
Mx=(v+1/2)×λ±0.1λ(但し、vは正の整数)、
Nx=λ/2×p±0.1λ(但し、pは正の整数)、
Ex=(w+1/2)×λ±0.1λ(但し、wは正の整数)、
Dx=λ/2×m±0.1λ(但し、mは正の整数)、
Sx=λ/2×n±0.1λ(但し、nは正の整数)、
の関係を満たしていることが好ましい。なお、ここで寸法のバラツキである±0.1λは、この程度の製造バラツキ範囲であれば、水晶振動片1の特性への影響は小さいことを示している。
As shown in FIG. 2, the quartz
Mx = (v + 1/2) × λ ± 0.1λ (where v is a positive integer),
Nx = λ / 2 × p ± 0.1λ (where p is a positive integer),
Ex = (w + 1/2) × λ ± 0.1λ (where w is a positive integer),
Dx = λ / 2 × m ± 0.1λ (where m is a positive integer),
Sx = λ / 2 × n ± 0.1λ (where n is a positive integer),
It is preferable that the relationship is satisfied. Here, ± 0.1λ, which is a variation in dimensions, indicates that the influence on the characteristics of the quartz
これにより、水晶振動片1は、図3の水晶振動片の模式要部断面図に示すように、第2段差部18及び凸部19におけるZ’軸方向に沿って延びる各壁面(側面)及び励振電極15,16の端面が、水晶基板10に生じるスプリアス(不要振動)である屈曲振動の最大振幅の位置と略一致するように設けられることが可能となる。
具体的には、上記各壁面(例えば、壁面19aなど)及び端面は、図3の2点鎖線で示した想定される屈曲振動の波形Bの頂点(最大振幅点)Pを通りY’軸と平行な仮想直線Cと、略一致するように設けられることが可能となる。
ここで、屈曲振動の波長λは、水晶振動片1の共振周波数fから、例えば、λ/2=(1.332/f)−0.0024、などの数式によって求めることができる。
なお、図3では説明の便宜上、ハッチングを省略してある。
Thereby, as shown in the schematic cross-sectional view of the main part of the quartz crystal vibrating piece in FIG. 3, the quartz
Specifically, each of the wall surfaces (for example, the
Here, the wavelength λ of the bending vibration can be obtained from the resonance frequency f of the quartz
In FIG. 3, hatching is omitted for convenience of explanation.
図2に戻って、水晶振動片1は、水晶基板10のX軸方向に沿った長さをLx、振動部13の厚みをtとしたときに、
10≦Lx/t≦40、
の関係を満たしていることが好ましい。
Returning to FIG. 2, when the
10 ≦ Lx / t ≦ 40,
It is preferable that the relationship is satisfied.
また、水晶振動片1は、凸部19のZ’軸方向に沿った長さをDz、振動部13のZ’軸方向に沿った長さをMzとしたときに、
0<Dz/Mz≦0.7、
の関係を満たしていることが好ましい。
Further, when the
0 <Dz / Mz ≦ 0.7,
It is preferable that the relationship is satisfied.
また、水晶振動片1は、凸部19の周辺部14からの高さをDy、振動部13の周辺部14からの高さをMyとしたときに、
0<Dy/My≦1、
の関係を満たしていることが好ましい。
The quartz
0 <Dy / My ≦ 1,
It is preferable that the relationship is satisfied.
また、水晶振動片1は、凸部19の周辺部14からの高さDyが、第1段差部17及び第2段差部18の段差のうち、いずれか1つの段差(ここでは、第2段差部18の段差18aとする)の周辺部14からの高さNyと同じ(Dy=Ny)であることが好ましい。
Further, in the quartz
なお、水晶振動片1は、一例として、水晶基板10のX軸方向に沿った長さLxが1.0mm程度、Z’軸方向に沿った長さが0.6mm程度のものが想定されている。
なお、上記の各数式は、発明者らの実験及びシミュレーション解析などにより得られた知見に基づいている。
As an example, the
In addition, each said numerical formula is based on the knowledge obtained by experiment, simulation analysis, etc. of inventors.
上述したように、本実施形態の水晶振動片1は、水晶基板10がX軸方向において、周辺部14と振動部13との間に第1段差部17、Z’軸方向において、周辺部14と振動部13との間に第2段差部18、を有し、周辺部14の第1領域及び第2領域の少なくともいずれか一方に、周辺部14の厚み方向(Y’軸方向)に突出しZ’軸方向に沿って延びる凸部19を有し、凸部19のZ’軸方向に沿った長さが、振動部13のZ’軸方向に沿った長さより短く、かつX軸方向からみて振動部13の幅の範囲内にある。
この結果、水晶振動片1は、従来(例えば、特許文献1の構成)より短い凸部19、及び第2段差部18によって、屈曲振動成分を抑制しつつ、周辺部14における厚みすべり振動を減衰させ、厚みすべり振動の振動エネルギーの閉じ込めを効率よく行うことができる。
これにより、水晶振動片1は、CI値が低下し(良好となり)、振動特性を向上させることができる。
As described above, in the quartz
As a result, the quartz
As a result, the
また、水晶振動片1は、Mx=(v+1/2)×λ±0.1λ、Nx=λ/2×p±0.1λ、Ex=(w+1/2)×λ±0.1λ、Dx=λ/2×m±0.1λ、Sx=λ/2×n±0.1λ、の関係を満たすことから、第2段差部18及び凸部19におけるZ’軸方向に沿って延びる各壁面(側面)及び励振電極15,16の端面が、水晶基板10に生じるスプリアス(不要振動)である屈曲振動の最大振幅の位置と略一致するように設けられることが可能となる。
この結果、水晶振動片1は、屈曲振動成分をより抑制しつつ、周辺部14における厚みすべり振動をより減衰させ、厚みすべり振動の振動エネルギーの閉じ込めをより効率よく行うことができる。
The quartz
As a result, the quartz
また、水晶振動片1は、10≦Lx/t≦40、の関係を満たすことから、屈曲振動成分を抑制しつつ、周辺部14における厚みすべり振動を減衰させ、厚みすべり振動の振動エネルギーの閉じ込めをより顕著に行うことができる。
Further, since the
また、水晶振動片1は、0<Dz/Mz≦0.7、の関係を満たすことから、屈曲振動成分を更に抑制しつつ、周辺部14における厚みすべり振動を更に減衰させ、厚みすべり振動の振動エネルギーの閉じ込めを更に効率よく行うことができる。
ここで、上記について図を用いて詳述する。
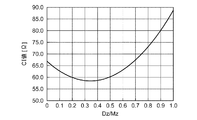
図4は、凸部のZ’軸方向に沿った長さDzと、振動部のZ’軸方向に沿った長さMzとの比(Dz/Mz)と、CI値との関係を示すグラフである。図4の横軸はDz/Mzを表し、縦軸はCI値(Ω)を表す。
なお、図4は、発明者らによる本実施形態のサンプル品(水晶基板10のLxが約1.0mm、Z’軸方向に沿った長さが約0.6mm、共振周波数が約26MHz)を用いた実験結果をグラフ化したものである。
Further, since the quartz
Here, the above will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 4 is a graph showing the relationship between the ratio (Dz / Mz) between the length Dz along the Z′-axis direction of the convex portion and the length Mz along the Z′-axis direction of the vibration portion, and the CI value. It is. The horizontal axis in FIG. 4 represents Dz / Mz, and the vertical axis represents the CI value (Ω).
FIG. 4 shows the sample product of the present embodiment by the inventors (Lx of the
図4に示すように、水晶振動片1は、0<Dz/Mz≦0.7、の関係を満たすことにより、CI値が70Ω未満に抑制されていることが分かる。また、水晶振動片1は、0.1≦Dz/Mz≦0.6、の関係を満たすことにより、CI値が更に低い65Ω未満に抑制されていることが分かる。
さらに、水晶振動片1は、0.2≦Dz/Mz≦0.5、の関係を満たすことにより、CI値がより低い60Ω以下に抑制されていることが分かる。加えて、水晶振動片1は、0.3≦Dz/Mz≦0.4、の関係を満たすことにより、CI値が最も抑制されていることが分かる。
図4から、水晶振動片1は、0<Dz/Mz≦0.7、の関係を満たすことによって、屈曲振動成分を更に抑制しつつ、周辺部14における厚みすべり振動を更に減衰させ、厚みすべり振動の振動エネルギーの閉じ込めを更に効率よく行えることが裏付けられたといえる。
As shown in FIG. 4, the
Furthermore, it can be seen that the
From FIG. 4, the quartz
また、水晶振動片1は、0<Dy/My≦1、の関係を満たすことから、凸部19の周辺部14からの高さDyを、振動部13の周辺部14からの高さMy以下にすることにより、屈曲振動成分を抑制しつつ、周辺部14における厚みすべり振動を減衰させ、厚みすべり振動の振動エネルギーの閉じ込めを更に効率よく行うことができる。
Further, since the quartz
また、水晶振動片1は、凸部19の周辺部14からの高さDyが、第2段差部18の段差18aの周辺部14からの高さNyと同じ(Dy=Ny)であることから、例えば、エッチングによって凸部19と、第2段差部18の段差18aとを、一括して形成することができる。
この結果、水晶振動片1は、生産性を向上させることができる。
Further, in the
As a result, the
なお、水晶振動片1は、第1段差部17の段差が2つ以上でもよく、第2段差部18の段差が3つ以上でもよい。これによれば、水晶振動片1は、段差が増えることによって、厚みすべり振動の振動エネルギーの閉じ込めを更に顕著に行うことができる。
また、水晶振動片1は、第2段差部18の段差を1つとしてもよい。これによれば、水晶振動片1は、段差を形成するための加工回数が減ることにより、第2段差部18の形状を精度よく形成することができる。なお、この場合には、Nxは0となる。
In the
Further, the
また、水晶振動片1は、凸部19が周辺部14の−X側の第1領域または+X側の第2領域のいずれか一方のみに設けられていてもよい。この場合でも、水晶振動片1は、屈曲振動成分を抑制しつつ、周辺部14における厚みすべり振動を減衰させ、厚みすべり振動の振動エネルギーの閉じ込め効果を得ることができる。
また、水晶振動片1は、励振電極15,16が振動部13の主面11,12の範囲内に設けられていてもよい。これによれば、水晶振動片1は、励振電極15,16が第1段差部17及び第2段差部18に跨らないことから、励振電極15,16を均一に形成することができる。なお、励振電極15,16は、駆動効率の観点からいえば面積が大きい方が好ましい。
In the
In the quartz
(変形例)
次に、第1実施形態の変形例について説明する。
図5は、第1実施形態の変形例の水晶振動片の概略構成を示す模式要部断面図である。なお、図5では説明の便宜上、電極類、ハッチングを省略してある。また、第1実施形態との共通部分には、同一符号を付して詳細な説明を省略し、第1実施形態と異なる部分を中心に説明する。
(Modification)
Next, a modification of the first embodiment will be described.
FIG. 5 is a schematic cross-sectional view of an essential part showing a schematic configuration of a quartz crystal resonator element according to a modification of the first embodiment. In FIG. 5, for convenience of explanation, electrodes and hatching are omitted. Also, common parts with the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals, detailed description thereof will be omitted, and description will be made centering on parts different from the first embodiment.
図5に示すように、変形例の水晶振動片2は、例えば、ウエットエッチング法を用いて形成されている。このことから、水晶振動片2は、水晶のエッチング異方性によって第2段差部18及び凸部19におけるZ’軸方向に沿って延びる各壁面(側面)が傾斜面となっている。
ここで、上記各傾斜面(壁面)は、水晶基板10に生じるスプリアス(不要振動)である屈曲振動の最大振幅となる領域を含んでいる。具体的には、各傾斜面(例えば、壁面19aなど)は、図5の2点鎖線で示した想定される屈曲振動の波形Bの頂点(最大振幅点)Pを通りY’軸と平行な仮想直線Cと、交差するように設けられている。
As shown in FIG. 5, the quartz
Here, each of the inclined surfaces (wall surfaces) includes a region having the maximum amplitude of bending vibration that is spurious (unnecessary vibration) generated in the
これによれば、水晶振動片2は、第2段差部18及び凸部19におけるZ’軸方向に沿って延びる各壁面が傾斜面であり、この傾斜面が水晶基板10に生じる屈曲振動の最大振幅となる領域を含んでいることから、この傾斜面によって屈曲振動成分を更に抑制することができる。
この結果、水晶振動片2は、CI値が低下し、振動特性を向上させることができる。
なお、水晶振動片2において、Mx、Nx、Sx及びDxの起点及び終点は、各傾斜面上にあるものとする。
According to this, in the
As a result, the
In the
(第2実施形態)
次に、上述した振動片と、振動片が収容されている容器と、を備えている振動子の一例としての水晶振動子について説明する。
(Second Embodiment)
Next, a crystal resonator as an example of a resonator including the above-described resonator element and a container that stores the resonator element will be described.
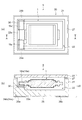
図6は、第2実施形態の水晶振動子の概略構成を示す模式図である。図6(a)は、リッド(蓋体)側から見た平面図であり、図6(b)は、図6(a)のA−A線での断面図である。なお、平面図では、リッドを省略してある。また、上記第1実施形態との共通部分には、同一符号を付して詳細な説明を省略し、上記第1実施形態と異なる部分を中心に説明する。 FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram illustrating a schematic configuration of the crystal resonator according to the second embodiment. 6A is a plan view seen from the lid (lid) side, and FIG. 6B is a cross-sectional view taken along line AA of FIG. 6A. In the plan view, the lid is omitted. Also, common parts with the first embodiment will be denoted by the same reference numerals, detailed description thereof will be omitted, and different parts from the first embodiment will be mainly described.
図6に示すように、水晶振動子5は、上記第1実施形態の水晶振動片1または変形例の水晶振動片2のいずれか(ここでは、水晶振動片1とする)と、水晶振動片1が収容されている容器としてのパッケージ20と、を備えている。
パッケージ20は、平面形状が略矩形で凹部22が設けられたパッケージベース21と、パッケージベース21の凹部22を覆う平板状のリッド23と、を備え、略直方体形状に形成されている。
As shown in FIG. 6, the
The
パッケージベース21には、セラミックグリーンシートを成形して積層し焼成した酸化アルミニウム質焼結体、ムライト質焼結体、窒化アルミニウム質焼結体、炭化珪素質焼結体、ガラスセラミックス焼結体などのセラミックス系の絶縁性材料、水晶、ガラス、シリコン(高抵抗シリコン)などが用いられている。
リッド23には、パッケージベース21と同材料、または、コバール、42アロイなどの金属が用いられている。
The
The
パッケージベース21の凹部22内の段差部22aには、水晶振動片1のマウント電極15a,16aに対向する位置に、内部端子24a,24bが設けられている。
水晶振動片1は、マウント電極15a,16aが、金属フィラーなどの導電性物質が混合された、エポキシ系、シリコーン系、ポリイミド系などの導電性接着剤30を介して内部端子24a,24bに接合されている。
In the quartz
パッケージベース21の凹部22とは反対側の外底面25(外側の底面)には、矩形状の電極端子26a,26bが設けられている。
電極端子26a,26bは、図示しない内部配線により内部端子24a,24bと電気的に接続されている。詳述すると、電極端子26aは、内部端子24aと電気的に接続され、電極端子26bは、内部端子24bと電気的に接続されている。
なお、内部端子24a,24b、電極端子26a,26bは、例えば、W(タングステン)、Mo(モリブデン)などのメタライズ層にNi(ニッケル)、Au(金)などの各被膜をメッキなどにより積層した金属被膜からなる。
The
The
水晶振動子5は、水晶振動片1がパッケージベース21の内部端子24a,24bに接合された状態で、パッケージベース21の凹部22がリッド23により覆われ、パッケージベース21とリッド23とがシームリング、低融点ガラス、接着剤などの接合部材27で接合されることにより、パッケージベース21の凹部22が気密に封止されている。
なお、パッケージベース21の気密に封止された凹部22内は、減圧された真空状態(真空度の高い状態)または窒素、ヘリウム、アルゴンなどの不活性ガスが充填された状態となっている。
In the
Note that the hermetically sealed
なお、パッケージ20は、平板状のパッケージベース21と凹部を有するリッド23などから構成されていてもよい。また、パッケージ20は、パッケージベース21及びリッド23の両方に凹部を有していてもよい。
The
水晶振動子5は、例えば、電子機器のICチップ内に集積化された発振回路から、電極端子26a,26bを経由して印加される駆動信号によって、水晶振動片1が厚みすべり振動を励振されて所定の周波数で共振(発振)し、電極端子26a,26bから共振信号(発振信号)を出力する。
In the
上述したように、第2実施形態の水晶振動子5は、水晶振動片1と、水晶振動片1が収容されているパッケージ20と、を備えていることから、第1実施形態に記載の効果が奏された水晶振動子を提供することができる。具体的には、CI値が低く振動特性に優れた水晶振動子を提供することができる。
なお、水晶振動子5は、水晶振動片1に代えて、変形例の水晶振動片2を用いても、上記と同様の効果、及び変形例の水晶振動片2特有の効果が奏された水晶振動子を提供することができる。
なお、水晶振動子5は、マウント電極15a,16aと内部端子24a,24bとの電気的接続が、導電性接着剤30に代えて、金属ワイヤーを用いたワイヤーボンディングや、バンプによって行われてもよい。
As described above, the
In addition, even if the
In the
(第3実施形態)
次に、上述した振動片と、振動片を駆動する回路と、を備えている発振器の一例としての水晶発振器について説明する。
(Third embodiment)
Next, a crystal oscillator as an example of an oscillator including the above-described resonator element and a circuit that drives the resonator element will be described.
図7は、第3実施形態の水晶発振器の概略構成を示す模式図である。図7(a)は、リッド側から見た平面図であり、図7(b)は、図7(a)のA−A線での断面図である。なお、平面図では、リッドを省略してある。また、上記第1実施形態及び第2実施形態との共通部分には、同一符号を付して詳細な説明を省略し、上記第1実施形態及び第2実施形態と異なる部分を中心に説明する。 FIG. 7 is a schematic diagram showing a schematic configuration of the crystal oscillator of the third embodiment. FIG. 7A is a plan view seen from the lid side, and FIG. 7B is a cross-sectional view taken along the line AA of FIG. 7A. In the plan view, the lid is omitted. In addition, common portions with the first embodiment and the second embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals, detailed description thereof is omitted, and description will be made focusing on portions different from the first embodiment and the second embodiment. .
図7に示すように、水晶発振器6は、上記第1実施形態の水晶振動片1または変形例の水晶振動片2のいずれか(ここでは、水晶振動片1とする)と、水晶振動片1を駆動する(発振させる)回路としてのICチップ40と、水晶振動片1及びICチップ40が収容されているパッケージ20と、を備えている。
As shown in FIG. 7, the
発振回路を内蔵するICチップ40は、パッケージベース21の凹部22の底面22bに、図示しない接着剤などを用いて固定されている。
ICチップ40は、図示しない接続パッドが、Au(金)、Al(アルミニウム)などの金属ワイヤー41により、凹部22の底面22bに設けられている内部接続端子22cと電気的に接続されている。
The
In the
内部接続端子22cは、W(タングステン)、Mo(モリブデン)などのメタライズ層にNi(ニッケル)、Au(金)などの各被膜をメッキなどにより積層した金属被膜からなり、図示しない内部配線を経由して、パッケージ20の外底面25の四隅に設けられた電極端子26a,26b,26c,26d、内部端子24a,24bなどと電気的に接続されている。
なお、ICチップ40の接続パッドと内部接続端子22cとの接続には、金属ワイヤー41を用いたワイヤーボンディングによる接続方法以外に、ICチップ40を反転させてのフリップチップ実装による接続方法などを用いてもよい。
The
The connection between the connection pad of the
水晶発振器6は、ICチップ40から内部接続端子22c、内部端子24a,24b、などを経由して印加される駆動信号によって、水晶振動片1が厚みすべり振動を励振されて所定の周波数で共振(発振)する。
そして、水晶発振器6は、この発振に伴って生じる発振信号をICチップ40、電極端子26a,26d(26c,26b)などを経由して外部に出力する。
The
Then, the
上述したように、第3実施形態の水晶発振器6は、水晶振動片1と、水晶振動片1を駆動するICチップ40と、水晶振動片1及びICチップ40が収容されているパッケージ20と、を備えていることから、第1実施形態に記載の効果が奏された水晶発振器を提供することができる。具体的には、CI値が低く振動特性に優れた水晶発振器を提供することができる。
なお、水晶発振器6は、水晶振動片1に代えて、変形例の水晶振動片2を用いても、上記と同様の効果、及び変形例の水晶振動片2特有の効果が奏された水晶発振器を提供することができる。
なお、水晶発振器6は、ICチップ40をパッケージ20に内蔵ではなく、外付けした構成のモジュール構造(例えば、1つの基板上に水晶振動子5及びICチップ40が個別に搭載されている構造)としてもよい。
As described above, the
Note that the
The
(第4実施形態)
次に、上述した振動片を備えている電子機器として、携帯電話機を一例に挙げて説明する。
図8は、第4実施形態の携帯電話機を示す模式斜視図である。
携帯電話機700は、上記第1実施形態の水晶振動片1または変形例の水晶振動片2を備えている携帯電話機である。
図8に示す携帯電話機700は、上述した水晶振動片(1または2)を、例えば、基準クロック発振源などのタイミングデバイスとして用い、更に液晶表示装置701、複数の操作ボタン702、受話口703、及び送話口704を備えて構成されている。
これによれば、携帯電話機700は、水晶振動片(1または2)を備えていることから、上記第1実施形態及び変形例で説明した効果が奏され、優れた性能を発揮することができる。
なお、携帯電話機700の形態は、図示のタイプに限定されるものではなく、いわゆるスマートフォンタイプでもよい。
(Fourth embodiment)
Next, a mobile phone will be described as an example of an electronic device including the above-described resonator element.
FIG. 8 is a schematic perspective view showing the mobile phone according to the fourth embodiment.
A
A
According to this, since the
Note that the form of the
上述した振動片は、上記携帯電話機700のような携帯電話機に限らず、電子ブック、パーソナルコンピューター、テレビ、デジタルスチールカメラ、ビデオカメラ、ビデオレコーダー、ナビゲーション装置、ページャー、電子手帳、電卓、ワードプロセッサー、ワークステーション、テレビ電話、POS端末、電子ゲーム機器、タッチパネルを備えた機器などのタイミングデバイスとして好適に用いることができ、いずれの場合にも上記第1実施形態及び変形例で説明した効果が奏され、優れた性能を発揮する電子機器を提供することができる。
The above-mentioned vibrating piece is not limited to the mobile phone such as the
(第5実施形態)
次に、上述した振動片を備えている移動体として、自動車を一例に挙げて説明する。
図9は、第5実施形態の自動車を示す模式斜視図である。
自動車800は、上記第1実施形態の水晶振動片1または変形例の水晶振動片2を備えている自動車である。
自動車800は、上述した水晶振動片(1または2)を、例えば、搭載されている各種電子制御式装置(例えば、電子制御式燃料噴射装置、電子制御式ABS装置、電子制御式一定速度走行装置など)の基準クロックを発生するタイミングデバイスとして用いている。
これによれば、自動車800は、水晶振動片(1または2)を備えていることから、上記第1実施形態及び変形例で説明した効果が奏され、優れた性能を発揮することができる。
(Fifth embodiment)
Next, an automobile will be described as an example of the moving body including the above-described vibrating piece.
FIG. 9 is a schematic perspective view showing the automobile of the fifth embodiment.
The
The
According to this, since the
上述した振動片は、上記自動車800に限らず、自走式ロボット、自走式搬送機器、列車、船舶、飛行機、人工衛星などを含む移動体のタイミングデバイスとして好適に用いることができ、いずれの場合にも上記第1実施形態及び変形例で説明した効果が奏され、優れた性能を発揮する移動体を提供することができる。
The above-described vibrating element can be suitably used as a timing device for a mobile body including not only the
1,2…振動片としての水晶振動片、5…振動子としての水晶振動子、6…発振器としての水晶発振器、10…素板としての水晶基板、11,12,11a,12a…主面、13…振動部、14…周辺部、15,16…励振電極、15a,16a…マウント電極、17…第1段差部、18…第2段差部、18a…段差、19…凸部、19a…壁面、20…容器としてのパッケージ、21…パッケージベース、22…凹部、22a…段差部、22b…底面、22c…内部接続端子、23…リッド(蓋体)、24a,24b…内部端子、25…外底面、26a,26b,26c,26d…電極端子、27…接合部材、30…導電性接着剤、40…回路としてのICチップ、41…金属ワイヤー、700…電子機器としての携帯電話機、701…液晶表示装置、702…操作ボタン、703…受話口、704…送話口、800…移動体としての自動車、B…屈曲振動の波形、C…仮想直線、P…頂点(最大振幅点)。
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (13)
前記水晶基板は、
厚みすべり振動する振動部と、
前記振動部より厚さが薄い周辺部と、
を含み、
前記周辺部は、
前記振動部の前記X軸方向の一方側に配置されている第1領域と、
前記振動部の前記X軸方向の他方側に配置されている第2領域と、
を含み、
前記第1領域及び前記第2領域の少なくともいずれか一方に、前記周辺部よりも前記Y’軸方向に突出しており、前記Z’軸方向に沿った長さが、前記振動部の前記Z’軸方向に沿った長さより短く、且つ、前記X軸方向からみて前記振動部の前記Z’軸方向に沿った幅の範囲内にある凸部を有していることを特徴とする振動片。 Of the crystal axes of quartz, among the X, Y, and Z axes, the X axis is the rotation axis, the axis that is rotated on the positive side of the Z axis in the negative direction of the Y axis is the Z ′ axis, and the Y axis A crystal in which the + side of the axis is rotated in the + direction of the Z axis is the Y ′ axis, the plane parallel to the X and Z ′ axes is the main surface, and the direction along the Y ′ axis is the thickness direction Equipped with a substrate,
The quartz substrate is
A vibrating part that vibrates in thickness,
And the peripheral portion is thinner than the vibration portion,
Only including,
Before Symbol periphery,
A first region disposed on one side of the vibrating portion in the X-axis direction ;
A second region disposed on the other side in the X-axis direction of the vibrating portion ;
Including
At least one of the first region and the second region protrudes in the Y′- axis direction from the peripheral portion , and the length along the Z′-axis direction is the Z ′ of the vibration unit. shorter than the length along the axial direction, and the vibration piece, characterized in that it has a convex portion which is within the range of the Z 'width along the axial direction of the vibration part as viewed from the X-axis direction.
前記振動部と前記凸部との間に、段差部を備えていることを特徴とする振動片。A vibrating piece comprising a step portion between the vibrating portion and the convex portion.
前記段差部は、前記周辺部からの前記Y’軸方向の高さが前記凸部と同じであることを特徴とする振動片。 The stepped portion has a height in the Y′-axis direction from the peripheral portion that is the same as that of the convex portion.
前記段差部は、前記振動部よりも厚さが薄いことを特徴とする振動片。The resonator element according to claim 1, wherein the stepped portion is thinner than the vibrating portion.
少なくとも前記振動部に設けられている励振電極を備え、
前記振動部の前記X軸方向に沿った長さをMx、前記段差部の前記X軸方向に沿った長さをNx、前記励振電極の前記X軸方向に沿った長さをEx、前記凸部の前記X軸方向に沿った長さをDx、前記段差部と前記凸部との前記X軸方向に沿った間隔をSx、前記水晶基板に生じる屈曲振動の波長をλとしたときに、
Mx=(v+1/2)×λ±0.1λ(但し、vは正の整数)、
Nx=λ/2×p±0.1λ(但し、pは正の整数)、
Ex=(w+1/2)×λ±0.1λ(但し、wは正の整数)、
Dx=λ/2×m±0.1λ(但し、mは正の整数)、
Sx=λ/2×n±0.1λ(但し、nは正の整数)、
の関係を満たすことを特徴とする振動片。 In the resonator element according to any one of claims 2 to 4 ,
Comprising an excitation electrode provided at least in the vibration part;
Mx a length along the X-axis direction of the vibrating portion, wherein the X-axis direction to the length along Nx before Kidan difference portion, the length along the X-axis direction of the excitation electrodes Ex, and Dx the X-axis direction to the length along the protrusion, Sx the spacing along the X-axis direction of the convex portion and the front Kidan difference portion, the wavelength of bending vibration generated in the quartz substrate λ When
Mx = (v + 1/2) × λ ± 0.1λ (where v is a positive integer),
Nx = λ / 2 × p ± 0.1λ (where p is a positive integer),
Ex = (w + 1/2) × λ ± 0.1λ (where w is a positive integer),
Dx = λ / 2 × m ± 0.1λ (where m is a positive integer),
Sx = λ / 2 × n ± 0.1λ (where n is a positive integer),
A vibrating piece characterized by satisfying the relationship
前記水晶基板の前記X軸方向に沿った長さをLx、前記振動部の厚さをtとしたときに、
10≦Lx/t≦40、
の関係を満たすことを特徴とする振動片。 The resonator element according to claim 5 ,
A length along the X-axis direction of the quartz substrate Lx, the thickness of the vibrating section when the t,
10 ≦ Lx / t ≦ 40,
A vibrating piece characterized by satisfying the relationship
前記凸部の前記Z’軸方向に沿った長さをDz、前記振動部の前記Z’軸方向に沿った長さをMzとしたときに、
0<Dz/Mz≦0.7、
の関係を満たすことを特徴とする振動片。 In the resonator element according to any one of claims 1 to 6 ,
'The length along the axial direction Dz, the Z of the vibration unit' the Z of the convex portion length along the axial direction is taken as Mz,
0 <Dz / Mz ≦ 0.7,
A vibrating piece characterized by satisfying the relationship
前記凸部の前記周辺部からの前記Y’軸方向の高さをDy、前記振動部の前記周辺部からの前記Y’軸方向の高さをMyと
したときに、
0<Dy/My≦1、
の関係を満たすことを特徴とする振動片。 In the resonator element according to any one of claims 1 to 7 ,
When the height in the Y′- axis direction from the peripheral portion of the convex portion is Dy, and the height in the Y′- axis direction from the peripheral portion of the vibrating portion is My,
0 <Dy / My ≦ 1,
A vibrating piece characterized by satisfying the relationship
前記段差部の主面と前記周辺部の主面とを繋いでおり前記Z’軸方向に沿って延びている第1壁面、及び前記凸部の主面と前記周辺部の主面とを繋いでおり前記Z’軸方向に沿って延びている第2面、が傾斜面であり、
前記傾斜面は、前記水晶基板に生じる屈曲振動の最大振幅となる領域を含んでいることを特徴とする振動片。 In the resonator element according to any one of claims 1 to 6,
The first wall surface that extends along the front Symbol Z 'axis direction and connects the main surface of the main surface and the peripheral portion of the front Kidan difference unit, and the main principal surface and the peripheral portion of the convex portion a second surface that extends along the front Symbol Z 'axis direction and connects the surface, an inclined surface,
The inclined surface includes a region having a maximum amplitude of bending vibration generated in the quartz substrate .
前記振動片が収容されている容器と、を備えていることを特徴とする振動子。 A resonator element according to any one of claims 1 to 9 ,
And a container in which the vibrating piece is accommodated.
前記振動片を駆動する回路と、を備えていることを特徴とする発振器。 A resonator element according to any one of claims 1 to 9 ,
And a circuit for driving the resonator element.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013242636A JP6229456B2 (en) | 2013-11-25 | 2013-11-25 | Vibrating piece, vibrator, oscillator, electronic device and moving object |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013242636A JP6229456B2 (en) | 2013-11-25 | 2013-11-25 | Vibrating piece, vibrator, oscillator, electronic device and moving object |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015103936A JP2015103936A (en) | 2015-06-04 |
| JP2015103936A5 JP2015103936A5 (en) | 2016-12-15 |
| JP6229456B2 true JP6229456B2 (en) | 2017-11-15 |
Family
ID=53379325
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013242636A Active JP6229456B2 (en) | 2013-11-25 | 2013-11-25 | Vibrating piece, vibrator, oscillator, electronic device and moving object |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6229456B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6560035B2 (en) * | 2015-06-29 | 2019-08-14 | 京セラ株式会社 | Thickness sliding crystal element |
| JP2017028486A (en) * | 2015-07-22 | 2017-02-02 | 京セラクリスタルデバイス株式会社 | Piezoelectric device for high temperature use |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5471303B2 (en) * | 2009-10-27 | 2014-04-16 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Vibrating piece and vibrator |
| JP5589167B2 (en) * | 2010-11-19 | 2014-09-17 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Piezoelectric vibrating piece and piezoelectric vibrator |
| JP2013093654A (en) * | 2011-10-24 | 2013-05-16 | Nippon Dempa Kogyo Co Ltd | Crystal vibration piece and crystal device |
| JP5991464B2 (en) * | 2012-03-19 | 2016-09-14 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Vibrating piece and manufacturing method thereof, vibrating element, vibrator, electronic device, and electronic apparatus |
-
2013
- 2013-11-25 JP JP2013242636A patent/JP6229456B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2015103936A (en) | 2015-06-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5943187B2 (en) | Vibration element, vibrator, electronic device, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP5982898B2 (en) | Vibration element, vibrator, electronic device, oscillator, and electronic device | |
| JP5943186B2 (en) | Vibrating piece, vibrator, electronic device, and electronic equipment | |
| JP5991464B2 (en) | Vibrating piece and manufacturing method thereof, vibrating element, vibrator, electronic device, and electronic apparatus | |
| US10181836B2 (en) | Resonator element, resonator, oscillator, electronic device, and moving object | |
| JP5967354B2 (en) | Vibrating piece and manufacturing method thereof, vibrating element, vibrator, electronic device, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP6252209B2 (en) | Piezoelectric vibrating piece and piezoelectric device using the piezoelectric vibrating piece | |
| JP2014090290A (en) | Vibration piece, vibration device, electronic apparatus and mobile | |
| JP2014068098A (en) | Vibration piece, vibration device, electronic apparatus and moving body | |
| JP2020136999A (en) | Crystal element, crystal device, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP2013239947A (en) | Vibration device, vibration device module, electronic apparatus, and movable body | |
| JP6229456B2 (en) | Vibrating piece, vibrator, oscillator, electronic device and moving object | |
| JP6256036B2 (en) | Vibrator, oscillator, electronic device, and moving object | |
| US8525606B2 (en) | Vibrator element, vibrator, oscillator, and electronic device | |
| JP2014165910A (en) | Vibration piece, vibrator, oscillator, electronic apparatus and mobile | |
| JP5434712B2 (en) | Piezoelectric vibrating piece and piezoelectric device | |
| JP2014050067A (en) | Vibration device, electronic equipment, and mobile device | |
| JP3975927B2 (en) | Piezoelectric vibrating piece, piezoelectric device using the piezoelectric vibrating piece, mobile phone device using the piezoelectric device, and electronic equipment using the piezoelectric device | |
| JP6327327B2 (en) | Vibrator, electronic device, mobile object, and oscillator | |
| JP2012090083A (en) | Vibration device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP2017017569A (en) | Vibration piece, vibration device, electronic apparatus and movable body | |
| JP2013197801A (en) | Vibration piece, oscillator, electronic device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP7293037B2 (en) | Crystal elements, crystal devices and electronic equipment | |
| JP2015046807A (en) | Vibration piece, vibrator, oscillator, electronic apparatus and moving body | |
| JP4020031B2 (en) | Piezoelectric vibrating piece, piezoelectric device using the piezoelectric vibrating piece, mobile phone device using the piezoelectric device, and electronic equipment using the piezoelectric device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20160617 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20160627 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20161028 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20161028 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20170822 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20170919 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20171002 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6229456 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |