JP5916526B2 - Power converter control device and multi-winding motor drive device - Google Patents
Power converter control device and multi-winding motor drive device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5916526B2 JP5916526B2 JP2012136690A JP2012136690A JP5916526B2 JP 5916526 B2 JP5916526 B2 JP 5916526B2 JP 2012136690 A JP2012136690 A JP 2012136690A JP 2012136690 A JP2012136690 A JP 2012136690A JP 5916526 B2 JP5916526 B2 JP 5916526B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- phase difference
- carrier
- power converter
- control device
- winding
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 title claims description 96
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 19
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 15
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 5
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000006698 induction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000001151 other effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000005069 ears Anatomy 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Control Of Ac Motors In General (AREA)
Description
この発明は、電機子巻線が複数の巻線群として多重化された多重巻線型電動機を駆動する複数の電力変換器を制御する電力変換器制御装置およびそれを備えた多重巻線型電動機駆動装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a power converter control device that controls a plurality of power converters that drive a multi-winding motor in which armature windings are multiplexed as a plurality of winding groups, and a multi-winding motor driving device including the same. It is about.
一般に、電動機をパルス幅変調(PWM)制御された電力変換器によって駆動するとき、電流高調波が発生して損失、騒音などの悪影響を与える。
多重巻線型電動機を駆動するための複数の電力変換器を制御する場合には、各々の電力変換器のスイッチングタイミングに一定の時間差を与えることにより電流高調波を低減する方法が知られている。スイッチングタイミングが同時に発生しないようにするため、キャリア比較するための各々のキャリア信号に所定の位相差を与えてPWM処理するようスイッチングタイミングを制御する装置が開示されている。
In general, when an electric motor is driven by a power converter that is controlled by pulse width modulation (PWM), current harmonics are generated, causing adverse effects such as loss and noise.
In the case of controlling a plurality of power converters for driving a multi-winding motor, a method of reducing current harmonics by giving a certain time difference to the switching timing of each power converter is known. In order to prevent the switching timing from occurring at the same time, an apparatus for controlling the switching timing so as to perform PWM processing by giving a predetermined phase difference to each carrier signal for carrier comparison is disclosed.
従来の多重巻線型電動機駆動装置(電力変換器制御装置)として、以下に示すPWM制御モータ装置がある。PWM制御モータ装置は、三角波発生回路により三角波信号を発生し、第1系統のコイルのU、V、W各相に対する電圧指令と三角波発生回路の出力とを第1のPWM変換回路に入力してPWM変換し、第1のPWM変換回路の出力に基づき第1系統のコイルへの電力供給を第1のインバータにより制御する。また、三角波発生回路の出力をずらし手段により所定位相だけずらし、第2系統のコイルのU、V、W各相に対する電圧指令とずらし手段の出力とを第2のPWM変換回路に入力してPWM変換し、第2のPWM変換回路の出力に基づき第2系統のコイルへの電力供給を第2のインバータにより制御する(例えば特許文献1)。 As a conventional multi-winding motor driving device (power converter control device), there is a PWM control motor device shown below. The PWM control motor device generates a triangular wave signal by a triangular wave generation circuit, and inputs a voltage command for the U, V, and W phases of the first system coil and an output of the triangular wave generation circuit to the first PWM conversion circuit. PWM conversion is performed, and power supply to the coils of the first system is controlled by the first inverter based on the output of the first PWM conversion circuit. Further, the output of the triangular wave generation circuit is shifted by a predetermined phase by the shift means, and the voltage command for the U, V, W phases of the second system coil and the output of the shift means are input to the second PWM conversion circuit and PWM is performed. Based on the output of the second PWM conversion circuit, power supply to the second system coil is controlled by the second inverter (for example, Patent Document 1).
また、従来の多重巻線型電動機駆動装置(電力変換器制御装置)の別例である負荷駆動装置では、第1の三相インバータの第1キャリア周波数と、第2の三相インバータの第2キャリア周波数とは互いに略等しく、第1の三相インバータのデューティ値と、第2の三相インバータのデューティ値とは互いに略等しく、第1の三相インバータと第2の三相インバータとは同じスイッチングパターンで動作し、第1キャリア信号と第2キャリア信号との位相差dが117.5度〜242.5度の範囲にある(例えば特許文献2)。 Further, in a load driving device which is another example of the conventional multi-winding motor driving device (power converter control device), the first carrier frequency of the first three-phase inverter and the second carrier of the second three-phase inverter. The frequency is substantially equal to each other, the duty value of the first three-phase inverter and the duty value of the second three-phase inverter are substantially equal to each other, and the first three-phase inverter and the second three-phase inverter have the same switching It operates in a pattern, and the phase difference d between the first carrier signal and the second carrier signal is in the range of 117.5 degrees to 242.5 degrees (for example, Patent Document 2).
上記特許文献1記載の装置では、複数のインバータのPWM制御に用いる三角波信号を所定位相だけずらし、各コイルに流れる電流によって生じる磁束の波形が合成することにより、合成磁束の波形のリップル幅を小さくして鉄損を低減する。これにより高調波損失を低減できるが、運転条件に拘わらず同じ位相差を与えるため騒音低減に対して十分な効果が得られないという問題点があった。
また、上記特許文献2記載の制御では、複数のキャリア信号間の位相差は可変であるが、操作者が位相差を主観的に変更するものであり、安定的な騒音低減効果は得られないものであった。
In the device described in
Further, in the control described in
この発明は、上記のような問題点を解決するためになされたものであり、複数の巻線群を備えた多重巻線型電動機を、電力変換器で発生するスイッチングに伴う騒音と損失を抑え、運転条件に応じて最適な環境で駆動可能な電力変換器制御装置および多重巻線型電動機駆動装置を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention was made to solve the above-described problems, and a multi-winding motor including a plurality of winding groups suppresses noise and loss associated with switching generated in a power converter, An object of the present invention is to provide a power converter control device and a multi-winding motor driving device that can be driven in an optimum environment according to operating conditions.
この発明の請求項1に係る電力変換器制御装置は、複数の巻線群を備えた多重巻線型電動機を駆動するために上記複数の巻線群にそれぞれ電力供給する複数の電力変換器をPWM制御するものであって、上記多重巻線型電動機の回転子の磁極位置を検出する位置検出手段と、与えられたトルク指令および上記位置検出器からの磁極位置信号に基づいて上記各電力変換器の三相電圧指令を生成する電圧指令演算部と、上記複数の電力変換器をそれぞれPWM制御するための複数のキャリア信号を等しい周波数で生成するキャリア生成部と、上記各電力変換器毎に上記三相電圧指令と上記キャリア信号とを比較してPWM処理されたスイッチングパルス信号を生成するキャリア比較部とを備える。そして、上記キャリア生成部は、上記磁極位置信号に基づく上記多重巻線型電動機の回転速度、上記トルク指令、あるいは上記回転速度と上記トルク指令とから演算される変調率のいずれか1つである位相差基準信号に基づいて決定される位相差を与えて上記複数のキャリア信号を生成し、上記位相差基準信号の値が低い領域では上記位相差を90度とし、上記位相差基準信号の値が高い領域では上記位相差を180度とするものである。 According to a first aspect of the present invention, there is provided a power converter control device for PWMing a plurality of power converters that respectively supply power to the plurality of winding groups in order to drive a multi-winding motor having a plurality of winding groups. A position detecting means for detecting the magnetic pole position of the rotor of the multi-winding motor, and the power converter based on a given torque command and a magnetic pole position signal from the position detector. A voltage command calculation unit that generates a three-phase voltage command, a carrier generation unit that generates a plurality of carrier signals for PWM control of each of the plurality of power converters at the same frequency, and the above three for each power converter. A carrier comparison unit that compares the phase voltage command with the carrier signal and generates a PWM-processed switching pulse signal; Then, the carrier generation unit is any one of the modulation factor is calculated from the rotational speed of the multi-wire wound motor based on the magnetic pole position signal, the torque command, or with the rotational speed and the torque command position A plurality of carrier signals are generated by giving a phase difference determined based on a phase difference reference signal. In a region where the value of the phase difference reference signal is low, the phase difference is 90 degrees, and the value of the phase difference reference signal is In the high region, the phase difference is 180 degrees .
この発明の請求項6に係る多重巻線型電動機駆動装置は、複数の巻線群を備えた多重巻線型電動機の上記複数の巻線群にそれぞれ電力供給する複数の電力変換器と、請求項1に係る上記電力変換器制御装置とを備え、該電力変換器制御装置が上記複数の電力変換器をPWM制御して上記多重巻線型電動機を駆動するものである。
According to a sixth aspect of the present invention, there is provided a multi-winding motor drive device comprising: a plurality of power converters each supplying power to the plurality of winding groups of a multi-winding motor having a plurality of winding groups; The power converter control device according to
この発明に係る電力変換器制御装置は上記キャリア生成部が、上記磁極位置信号に基づく上記多重巻線型電動機の回転速度、上記トルク指令、あるいは上記回転速度と上記トルク指令とから演算される変調率のいずれか1つである位相差基準信号に基づいて決定される位相差を与えて上記複数のキャリア信号を生成し、上記位相差基準信号の値が低い領域では上記位相差を90度とし、上記位相差基準信号の値が高い領域では上記位相差を180度とするため、複数の巻線群を備えた多重巻線型電動機を、電力変換器で発生するスイッチングに伴う騒音と損失を抑え、運転条件に応じて最適な環境で駆動できる。 In the power converter control device according to the present invention, the carrier generation unit has a modulation rate calculated from the rotational speed of the multi-winding motor, the torque command, or the rotational speed and the torque command based on the magnetic pole position signal. A plurality of carrier signals are generated by giving a phase difference determined based on a phase difference reference signal which is any one of the above, and the phase difference is set to 90 degrees in a region where the value of the phase difference reference signal is low, In the region where the value of the phase difference reference signal is high, the phase difference is set to 180 degrees, so that a multi-winding motor including a plurality of winding groups is suppressed in noise and loss associated with switching generated by the power converter, It can be driven in an optimal environment according to the operating conditions.
また、この発明に係る多重巻線型電動機駆動装置は、複数の巻線群を備えた多重巻線型電動機を、電力変換器で発生するスイッチングに伴う騒音と損失を抑え、運転条件に応じて最適な環境で駆動できる。 The multi-winding motor driving device according to the present invention is a multi-winding motor including a plurality of winding groups, which suppresses noise and loss associated with switching generated in the power converter, and is optimal according to operating conditions. Can be driven in the environment.
実施の形態1.
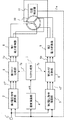
以下、この発明の実施の形態1による電力変換器制御装置および多重巻線型電動機駆動装置について、図1〜図6に基づいて以下に説明する。図1は、この発明の実施の形態1による電力変換器制御装置および多重巻線型電動機駆動装置の構成図である。図2は、電力変換器制御装置におけるキャリア信号のタイミングチャート図である。図3はキャリア信号の位相差によるスイッチングタイミングを示す第1の説明図、図4はキャリア信号の位相差によるスイッチングタイミングを示す第2の説明図である。図5はキャリア信号の位相差の制御特性の説明図であり、図6はキャリア生成部の詳細ブロック図である。
Hereinafter, a power converter control device and a multiple winding type motor drive device according to
図1は、例えば2つの巻線群を有する多重巻線型電動機10に対応する二重化した電力変換器制御装置を用いた多重巻線型電動機駆動装置の構成を示している。多重巻線型電動機10は、電動機を構成する巻線が2つの巻線群として多重化された多重巻線型電動機であり、多重巻線型電動機10を駆動するため、第1の巻線群に第1電力変換器8が接続され、第2の巻線群に第2電力変換器9が接続されている。多重巻線型電動機駆動装置は、複数の電力変換器(第1電力変換器8、第2電力変換器9)とこれらを制御する電力変換器制御装置にて構成され、電力変換器制御装置は、第1電力変換器8および第2電力変換器9を制御することにより、第1電力変換器8から第1の巻線群に電力供給し、第2電力変換器9から第2の巻線群に電力供給して多重巻線型電動機10を駆動する。
FIG. 1 shows a configuration of a multi-winding motor driving device using a dual power converter control device corresponding to a
図1に示すように、電力変換器制御装置は、第1電圧指令演算部2および第2電圧指令演算部3と、速度演算部4と、第1キャリア比較部5および第2キャリア比較部6と、キャリア生成部7とを備える。また電力変換器制御装置は、多重巻線型電動機10の回転子の磁極位置を検出するための位置検出器11、例えば、インクリメンタルエンコーダやレゾルバを備える。なお、多重巻線型電動機10が位置検出器11を備えても良く、その場合、電力変換器制御装置は、位置検出器11からの出力を得て回転子の磁極位置を検出する。また、位置検出手段として、位置検出器11の代わりに回転検出器を備えても良い。
As shown in FIG. 1, the power converter control device includes a first voltage
位置検出器11で検出された多重巻線型電動機10の回転子の磁極位置信号(電気角位置信号)θeは、速度演算部4に出力されるとともに、第1電圧指令演算部2および第2電圧指令演算部3にも出力される。
電力変換器制御装置の入力端子1に外部からトルク指令Nが入力され、第1電圧指令演算部2では、このトルク指令Nと、位置検出器11で検出された多重巻線型電動機10の回転子の磁極位置信号θeとに基づき、三相交流で表された第1の電圧指令v1*を生成し、第1キャリア比較部5に出力する。同様に第2電圧指令演算部3では、トルク指令Nが入力され、このトルク指令Nと、位置検出器11で検出された多重巻線型電動機10の回転子の磁極位置信号θeとに基づき、三相交流で表された第2の電圧指令v2*を生成し、第2キャリア比較部6に出力する。
なお、多重巻線型電動機10では、構造上、各巻線群間に一定の位相差が発生するため、この位相差を考慮した電圧指令v*(第1の電圧指令v1*、第2の電圧指令v2*)の演算を行う。
The magnetic pole position signal (electrical angle position signal) θe of the rotor of the multi-winding
A torque command N is input from the outside to the
In the
速度演算部4では、多重巻線型電動機10の回転子の磁極位置信号θeから、位相差基準信号となる多重巻線型電動機10の回転速度ωeを演算し、キャリア生成部7に出力する。キャリア生成部7は、速度演算部4からの回転速度ωeに基づいて位相差を決定し、この位相差を有する等しい周波数の2つのキャリア信号7a、7b(第1のキャリア信号7a、第2のキャリア信号7b)を出力する。なお、キャリア信号7a、7bには、三角波が用いられるのが一般的である。
第1キャリア比較部5では、第1電圧指令演算部2からの第1の電圧指令v1*と、キャリア生成部7が生成する第1のキャリア信号7aとを振幅比較することにより、PWM処理されたパルス信号である第1のスイッチングパルス5aを第1電力変換器8に出力する。第2キャリア比較部6では、第2電圧指令演算部3からの第2の電圧指令v2*と、キャリア生成部7が生成する第2のキャリア信号7bとを振幅比較することにより、PWM処理されたパルス信号である第2のスイッチングパルス5bを第2電力変換器9に出力する。
The
The first
次に、電力変換器制御装置の動作の詳細について説明する。
第1電圧指令演算部2、第2電圧指令演算部3では、上位の外部手段から入力されるトルク指令Nと位置検出器11からの磁極位置信号θeとから三相電圧指令v*(第1の電圧指令v1*、第2の電圧指令v2*)を演算して出力する。
三相電圧指令v*(vu*、vv*、vw*)の生成方法を以下に説明する。
なお、誘導電動機や同期電動機の制御を考える場合、三相交流座標系でなく直交二相座標系(回転座標系)であるdq座標で行われるのが一般的である。
Next, the detail of operation | movement of a power converter control apparatus is demonstrated.
In the first voltage
A method of generating the three-phase voltage command v * (vu * , vv * , vw * ) will be described below.
When control of induction motors and synchronous motors is considered, it is common to use dq coordinates that are orthogonal two-phase coordinate systems (rotating coordinate systems) instead of three-phase AC coordinate systems.
三相交流座標系からdq座標系への変換を行う行列式は、以下の式(1)で表される。式(1)において、idはd軸上で、iqはq軸上で表された電流値である。磁極位置信号θは、回転子の界磁磁束の方向をd軸としたときの、d軸の磁極位置を示している。この場合、θには電気角の磁極位置信号θeが用いられる。 A determinant that performs conversion from the three-phase AC coordinate system to the dq coordinate system is represented by the following expression (1). In Expression (1), id is a current value represented on the d-axis, and iq is a current value represented on the q-axis. The magnetic pole position signal θ indicates the d-axis magnetic pole position when the direction of the field magnetic flux of the rotor is the d-axis. In this case, an electrical angle magnetic pole position signal θe is used for θ.
式(1)より、id、iqは、以下の式(2)にて求められる。
まず、外部からのトルク指令Nに基づき、dq座標系で表された電流指令id*、iq*を生成する。多重化された複数の電力変換器(第1電力変換器8、第2電力変換器9)と多重巻線型電動機10との間に流れる電流iを電流センサを用いて検出し、電流制御ループを構成して電流(値)iを電流指令値i*どおりに流れるよう制御する。
即ち、電流センサで検出した相電流値i(iu、iv、iw)を、上記式(2)を用いてdq座標系で表された電流検出値id、iqに変換した後、電流指令id*、iq*との電流偏差をPI制御することにより電圧指令vd*、vq*を生成する。
さらに電圧指令vd*、vq*を、以下の式(3)を用いて座標変換することにより、三相電圧指令v*(vu*、vv*、vw*)に変換する。
First, based on an external torque command N, current commands id * and iq * expressed in the dq coordinate system are generated. The current i flowing between the multiple power converters (the
That is, after converting the phase current value i (iu, iv, iw) detected by the current sensor into the current detection values id, iq represented in the dq coordinate system using the above equation (2), the current command id * voltage command vd * by PI control the current deviation between iq *, generates a vq *.
Further, the voltage commands vd * and vq * are converted into a three-phase voltage command v * (vu * , vv * , vw * ) by performing coordinate conversion using the following equation (3).
一般に、dq座標系から三相交流座標系へ座標変換は以下の式(3)で表される。
以上のように、第1、第2電圧指令演算部2、3では、三相電圧指令v*(vu*、vv*、vw*)である第1の電圧指令v1*、第2の電圧指令v2*をそれぞれ生成して出力する。なお、必要に応じて各巻線群の機械的な位相差を磁極位置信号θeにおいて考慮し、第1の電圧指令v1*、第2の電圧指令v2*を生成する。
As described above, in the first and second voltage
速度演算部4は、位置検出器11からの回転子の磁極位置信号θeに基づき、以下の式(4)を用いて、回転速度ωeを演算する。
第1の電圧指令v1*、第2の電圧指令v2*は、第1キャリア比較部5、第2キャリア比較部6において、キャリア生成部7にて生成された第1のキャリア信号7a、第2のキャリア信号7bと振幅比較され、PWM処理された第1、第2のスイッチングパルス5a、5bが生成される。
図2に各巻線群の三角波のキャリア信号である第1のキャリア信号7aと第2のキャリア信号7bのタイミングの関係を示す。図2に示すように、実線で示した第1のキャリア信号7aと、点線で示した第2のキャリア信号7bとは、一定タイミングずらす処理がされている。この場合、キャリア信号7a、7bの位相差(以下、キャリア位相差と称す)は90度である。
The first voltage command v1 * and the second voltage command v2 * are generated by the
FIG. 2 shows a timing relationship between the
図3は、キャリア位相差が90度の場合の、第1、第2のスイッチングパルス5a、5bのスイッチングタイミングを示した図である。なお、キャリア位相差に比して第1の電圧指令v1*と第2の電圧指令v2*との位相差は僅かであるため、便宜上、第1の電圧指令v1*と第2の電圧指令v2*とは等しい電圧指令v*として表した。この例では、電圧指令v*の振幅が小さい場合であり、キャリア位相差が90度のときの各々のスイッチングパルス5a、5b、スイッチングタイミング、およびスイッチングノイズの関係を示している。
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing the switching timing of the first and
キャリア位相差が90度のときは、第1のスイッチングパルス5aと第2のスイッチングパルス5bの関係は、キャリア周期の1周期の1/4期間ずれた関係となる。また、第1のスイッチングタイミングと第2のスイッチングタイミングがちょうど1周期の1/4期間ごとに交互に来ることになり、多重巻線型電動機10の巻線群間の結合等に起因して発生するスイッチングノイズなどの騒音周波数はちょうど2倍となって発生する。
例えば、キャリア信号7a、7bが5KHzの周波数とすると、それぞれのスイッチングパルス5a、5bは10KHzの周波数で発生し、このときキャリア信号間に90度の位相差を設定すると、スイッチングパルス5a、5bによる騒音を20KHzの周波数に変化させることができ、人間の耳には聞こえにくい帯域に移動することができる。
When the carrier phase difference is 90 degrees, the relationship between the first switching pulse 5a and the
For example, if the carrier signals 7a and 7b have a frequency of 5 KHz, the switching
図4は、キャリア位相差が180度の場合の、第1、第2のスイッチングパルス5a、5bのスイッチングタイミングを示した図である。第1のスイッチングパルス5aと第2のスイッチングパルス5bの関係は1周期の1/2期間ずれた関係となる。この結果、第1のスイッチングタイミングと第2のスイッチングタイミングがほほ同じタイミングで発生することとなり、90度の場合のようなスイッチングパルスの周波数の変化は起こらない。従って、キャリア位相差を180度に設定したときには、騒音の低減効果は得られない。しかし、第1のスイッチングパルス5aと第2のスイッチングパルス5bの山谷の関係が反転しているため、各コイルに流れる電流によって生じる磁束の波形が合成された合成磁束の波形のリップル幅を小さくして鉄損を低減できるため、高調波損失を低減できる。
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the switching timing of the first and
上述したように、キャリア生成部7は、速度演算部4からの回転速度ωeに基づいてキャリア位相差を決定して、第1のキャリア信号7a、第2のキャリア信号7bを出力する。この際、回転速度ωeが低い条件では、キャリア位相差を90度に設定して低騒音効果を優先し、回転速度ωeが大きくなると、キャリア位相差を180度に設定して低損失効果を優先して制御する。
図5は、回転速度ωeとキャリア位相差の関係の一例を示したものである。回転速度ωeが所定値以下の時はキャリア位相差を90度に設定し、回転速度ωeが所定値を超えるとキャリア位相差を180度に切り換える。なお、この場合、キャリア位相差を90度から180度まで連続的に切り換えられているが、ステップ的に切り換えても良い。
As described above, the carrier generation unit 7 determines the carrier phase difference based on the rotation speed ωe from the
FIG. 5 shows an example of the relationship between the rotational speed ωe and the carrier phase difference. When the rotational speed ωe is less than or equal to a predetermined value, the carrier phase difference is set to 90 degrees, and when the rotational speed ωe exceeds a predetermined value, the carrier phase difference is switched to 180 degrees. In this case, the carrier phase difference is continuously switched from 90 degrees to 180 degrees, but may be switched stepwise.
キャリア位相差を決定して第1のキャリア信号7a、第2のキャリア信号7bを出力するキャリア生成部7の構成および詳細動作を、図6に基づき説明する。なお、キャリア位相差を有する複数のキャリア信号の生成方法は、これに限らず他の構成でも可能である。
図6に示すように、速度演算部4からの回転速度ωeが入力端子12に入力される。位相差演算部13は入力された回転速度ωeに応じて、第1のキャリア信号7aと第2のキャリア信号7bとの位相差を演算する。このとき、メモリマップを用いて出力を求めることや、回転速度を入力とする近似式から位相差の設定量を演算することも可能である。
The configuration and detailed operation of the carrier generation unit 7 that determines the carrier phase difference and outputs the
As shown in FIG. 6, the rotational speed ωe from the
比較回路14はキャリア比較用の一方のキャリア信号(第1のキャリア信号7a)を後述するアップ/ダウンカウンタ16により生成するときのアップ/ダウンカウンタ16の最大値と最小値の比較を行う。アップ/ダウンカウンタ16では、アップ/ダウンカウンタ16がアップカウント動作中に最大値まで進むと、ダウンカウント動作に切り換わり、ダウンカウント動作中に最小値まで進むとアップカウント動作に切り換わる。その結果、一定周期でアップカウント動作とダウンカウント動作を交互に繰り返されて三角波の形をした第1のキャリア信号7aを出力端子18から出力する。
The
位相差設定回路15は、アップ/ダウンカウンタ16の出力にキャリア位相差に相当する一定値の加算を行うことにより、第1のキャリア信号7aの出力と第2のキャリア信号7bの出力にタイミングの差を設定する。例えば、アップ/ダウンカウンタ16の出力が、ゼロ〜5000までのカウント値で動作する場合、2500の値を加算すると、1/4周期の位相差を与えることができる。
リミッタ回路17は、出力の振幅を所望の範囲に調整する。上記の例で、位相差設定回路15がカウント値に2500の値を加算すると、その結果は、2500〜7500の値を変化することになるので、5000を越えたカウント値については、5000を減算して0〜5000の値が出力されるようにリミッタ処理を行う。リミッタ処理された第2のキャリア信号7bは出力端子19から出力される。
The phase
The
以上のように、この実施の形態では、多重巻線型電動機10の回転速度ωeが低い条件では、キャリア位相差を90度に設定して低騒音効果を優先し、回転速度ωeが大きくなると、キャリア位相差を180度に設定して低損失効果を優先して制御する。一般的に電動機で発生する騒音は、電動機の低速運転時には大きく感じられ、高速運転時には小さく感じられる。この実施の形態では、騒音が大きく感じられる時に低騒音効果を優先し、それ以外の時は低損失効果を優先して制御することになり、電力変換器8、9で発生するスイッチングに伴う騒音と損失を抑え、運転条件に応じて最適な環境で多重巻線型電動機10を制御することができる。
またキャリア位相差を90度に設定する制御では、スイッチングに起因して発生するスイッチングノイズを高周波化できるので、多重巻線型電動機10の制御に及ぼす影響を低減することができる。
As described above, in this embodiment, when the rotational speed ωe of the
Further, in the control in which the carrier phase difference is set to 90 degrees, the switching noise generated due to switching can be increased in frequency, so that the influence on the control of the
また、多重化された複数の電力変換器を用いて多重巻線型電動機を駆動するときには、同じスイッチングタイミングでスイッチング素子を駆動すると高調波が増加することが知られている。この実施の形態では、各巻線群のU相同士など同じ相の電圧のスイッチングが同方向で同時に起こることがなく、低騒音効果を優先して制御している時も、高調波の増加が抑制できる。 In addition, when driving a multi-winding motor using a plurality of multiplexed power converters, it is known that harmonics increase when the switching element is driven at the same switching timing. In this embodiment, the switching of the voltage of the same phase such as the U phase of each winding group does not occur simultaneously in the same direction, and the increase in harmonics is suppressed even when the low noise effect is controlled with priority. it can.
なお、多重巻線型電動機の駆動の際に発生する騒音と損失は基本周波数に依存し、また周波数における電動機の動作は電動機の電気的特性に依存する。このため、キャリア位相差の切り換え方は電動機特性によって変更しても良い。また、キャリア位相差についても、電動機特性によっては、90度と180度で切り換えるのが必ずしも最良ではなく、この値に限定されるものではない。 Note that the noise and loss generated when driving the multi-winding motor depends on the fundamental frequency, and the operation of the motor at the frequency depends on the electrical characteristics of the motor. For this reason, the method of switching the carrier phase difference may be changed according to the motor characteristics. The carrier phase difference is not always best switched between 90 degrees and 180 degrees depending on the motor characteristics, and is not limited to this value.
また、この実施の形態では、多重巻線型電動機10として2つの巻線群を有する三相交流電動機を用いたが、特に相数や巻線群の数が限定されるものではない。また対象となる多重巻線型電動機は永久磁石型同期電動機でも誘導電動機でもいずれの電動機でもよい。
In this embodiment, a three-phase AC motor having two winding groups is used as the
実施の形態2.
次に、この発明の実施の形態2による電力変換器制御装置および多重巻線型電動機駆動装置について、図7、図8に基づいて以下に説明する。図7は、この発明の実施の形態2による電力変換器制御装置および多重巻線型電動機駆動装置の構成図である。図8は、電力変換器制御装置におけるキャリア信号の位相差の制御特性の説明図である。
図7において、図1と同一あるいは相当部分には、同一の符号を付している。図7は、実施の形態1と同様、例として2つの巻線群を有する多重巻線型電動機10に対応する二重化した電力変換器制御装置を用いた多重巻線型電動機駆動装置の構成を示している。
Next, a power converter control device and a multiple winding type motor drive device according to
In FIG. 7, the same or corresponding parts as those in FIG. FIG. 7 shows a configuration of a multi-winding motor driving device using a dual power converter control device corresponding to a
図7に示すように、キャリア生成部20は、入力された位相差基準信号としてのトルク指令Nに基づいてキャリア位相差を決定し、このキャリア位相差を有する等しい周波数の2つのキャリア信号20a、20b(第1のキャリア信号20a、第2のキャリア信号20b)を出力する。
この実施の形態2では、実施の形態1とは異なり、速度演算部がなく、回転速度でなくトルク指令Nに基づいてキャリア位相差を決定する。その他の構成は上記実施の形態1と同様である。
図8は、トルク指令Nとキャリア位相差の関係の一例を示したものである。トルク指令Nが所定値以下の時はキャリア位相差を90度に設定し、トルク指令Nが所定値を超えるとキャリア位相差を180度に切り換える。
As shown in FIG. 7, the
In the second embodiment, unlike the first embodiment, there is no speed calculation unit, and the carrier phase difference is determined based on the torque command N instead of the rotation speed. Other configurations are the same as those in the first embodiment.
FIG. 8 shows an example of the relationship between the torque command N and the carrier phase difference. When the torque command N is less than a predetermined value, the carrier phase difference is set to 90 degrees, and when the torque command N exceeds the predetermined value, the carrier phase difference is switched to 180 degrees.
このように、トルク指令Nが低い条件では、キャリア位相差を90度に設定して低騒音効果を優先し、トルク指令Nが大きくなると、キャリア位相差を180度に設定して低損失効果を優先して制御する。
一般的に電動機で発生する騒音は、電動機の低トルク運転時には大きくなり、高トルク運転時には小さくなる傾向がある。この実施の形態では、騒音が大きい時に低騒音効果を優先し、それ以外の時は低損失効果を優先して制御することになり、電力変換器8、9で発生するスイッチングに伴う騒音と損失を抑え、運転条件に応じて最適な環境で多重巻線型電動機10を制御することができる。実施の形態1に比較して、低トルクの際に騒音が大きく発生する傾向が大きい多重巻線型電動機10の場合に、特に有効である。その他の効果については上記実施の形態1と同様である。
Thus, under the condition where the torque command N is low, the carrier phase difference is set to 90 degrees to give priority to the low noise effect, and when the torque command N increases, the carrier phase difference is set to 180 degrees and the low loss effect is obtained. Give priority to control.
In general, the noise generated by an electric motor tends to increase during low-torque operation of the motor and decrease during high-torque operation. In this embodiment, the low noise effect is prioritized when the noise is loud, and the low loss effect is prioritized at other times, and the noise and loss associated with switching generated in the
実施の形態3.
次に、この発明の実施の形態3による電力変換器制御装置および多重巻線型電動機駆動装置について、図9、図10に基づいて以下に説明する。図9は、この発明の実施の形態3による電力変換器制御装置および多重巻線型電動機駆動装置の構成図である。図10は、電力変換器制御装置におけるキャリア信号の位相差の制御特性の説明図である。
図9において、図1と同一あるいは相当部分には、同一の符号を付している。図9は、実施の形態1と同様、例として2つの巻線群を有する多重巻線型電動機10に対応する二重化した電力変換器制御装置を用いた多重巻線型電動機駆動装置の構成を示している。
Next, a power converter control device and a multiple winding type motor drive device according to
In FIG. 9, the same or corresponding parts as those in FIG. FIG. 9 shows a configuration of a multi-winding motor driving device using a dual power converter control device corresponding to a
図9に示すように、変調率演算部21は、トルク指令Nと速度演算部4で求めた回転速度ωeとから位相差基準信号としての変調率pを演算する。
変調率演算部21では、まず、トルク指令Nからdq軸上の電流指令値id*、iq*を求め、さらに電流指令値id*、iq*と回転速度ωeから、dq軸上の電圧指令値vd*、vq*を以下の式(5)を用いて計算する。このとき、Rは抵抗値、Ld、Lqはdq座標系で表されたインダクタンス値、φは誘起電圧定数である。
As shown in FIG. 9, the
The modulation
さらに、電力変換器8、9に入力される直流母線電圧Vdcを用い、以下の式(6)から変調率pを求める。
キャリア生成部22は、入力された変調率pに基づいてキャリア位相差を決定し、このキャリア位相差を有する等しい周波数の2つのキャリア信号22a、22b(第1のキャリア信号22a、第2のキャリア信号22b)を出力する。
この実施の形態3では、回転速度ωeとトルク指令Nとを用いて演算された変調率pに基づいてキャリア位相差を決定する。その他の構成は上記実施の形態1と同様である。
図10は、変調率pとキャリア位相差の関係の一例を示したものである。変調率pが所定値以下の時はキャリア位相差を90度に設定し、変調率pが所定値を超えるとキャリア位相差を180度に切り換える。
The carrier generation unit 22 determines a carrier phase difference based on the input modulation rate p, and two
In the third embodiment, the carrier phase difference is determined based on the modulation factor p calculated using the rotational speed ωe and the torque command N. Other configurations are the same as those in the first embodiment.
FIG. 10 shows an example of the relationship between the modulation rate p and the carrier phase difference. When the modulation rate p is less than a predetermined value, the carrier phase difference is set to 90 degrees, and when the modulation rate p exceeds the predetermined value, the carrier phase difference is switched to 180 degrees.
このように、変調率pが低い条件では、キャリア位相差を90度に設定して低騒音効果を優先し、変調率pが大きくなると、キャリア位相差を180度に設定して低損失効果を優先して制御する。
一般的に電動機で発生する騒音は、電動機制御の変調率が低い時には大きくなり、変調率が高い時には小さくなる傾向がある。この実施の形態では、騒音が大きい時に低騒音効果を優先し、それ以外の時は低損失効果を優先して制御することになり、電力変換器8、9で発生するスイッチングに伴う騒音と損失を抑え、運転条件に応じて最適な環境で多重巻線型電動機10を制御することができる。実施の形態1、2に比較して、変調率が低い際に騒音が大きく発生する傾向が大きい多重巻線型電動機10の場合に、特に有効である。その他の効果については上記実施の形態1と同様である。
Thus, under the condition where the modulation rate p is low, the carrier phase difference is set to 90 degrees to give priority to the low noise effect, and when the modulation rate p increases, the carrier phase difference is set to 180 degrees and the low loss effect is obtained. Give priority to control.
In general, noise generated by an electric motor tends to increase when the modulation rate of motor control is low and to decrease when the modulation rate is high. In this embodiment, the low noise effect is prioritized when the noise is loud, and the low loss effect is prioritized at other times, and the noise and loss associated with switching generated in the
なお、この発明は、発明の範囲内において、各実施の形態を自由に組み合わせたり、各実施の形態を適宜、変形、省略することが可能である。 It should be noted that within the scope of the invention, the embodiments can be freely combined, or the embodiments can be appropriately modified or omitted.
2 第1電圧指令演算部、3 第2電圧指令演算部、4 速度演算部、
5 第1キャリア比較部、6 第2キャリア比較部、7 キャリア生成部、
7a 第1のキャリア信号、7b 第2のキャリア信号、8 第1電力変換器、
9 第2電力変換器、10 多重巻線型電動機、11 位置検出器、
15 位相差設定回路、20 キャリア生成部、20a 第1のキャリア信号、
20b 第2のキャリア信号、21 変調率演算部、22 キャリア生成部、
22a 第1のキャリア信号、22b 第2のキャリア信号。
2 1st voltage command calculating part, 3 2nd voltage command calculating part, 4 speed calculating part,
5 first carrier comparison unit, 6 second carrier comparison unit, 7 carrier generation unit,
7a first carrier signal, 7b second carrier signal, 8 first power converter,
9 Second power converter, 10 Multi-winding motor, 11 Position detector,
15 phase difference setting circuit, 20 carrier generation unit, 20a first carrier signal,
20b Second carrier signal, 21 Modulation rate calculator, 22 Carrier generator,
22a First carrier signal, 22b Second carrier signal.
Claims (6)
上記多重巻線型電動機の回転子の磁極位置を検出する位置検出器と、
与えられたトルク指令および上記位置検出器からの磁極位置信号に基づいて上記各電力変換器の三相電圧指令を生成する電圧指令演算部と、
上記複数の電力変換器をそれぞれPWM制御するための複数のキャリア信号を等しい周波数で生成するキャリア生成部と、
上記各電力変換器毎に上記三相電圧指令と上記キャリア信号とを比較してPWM処理されたスイッチングパルス信号を生成するキャリア比較部とを備え、
上記キャリア生成部は、上記磁極位置信号に基づく上記多重巻線型電動機の回転速度、上記トルク指令、あるいは上記回転速度と上記トルク指令とから演算される変調率のいずれか1つである位相差基準信号に基づいて決定される位相差を与えて上記複数のキャリア信号を生成し、上記位相差基準信号の値が低い領域では上記位相差を90度とし、上記位相差基準信号の値が高い領域では上記位相差を180度とすることを特徴とする電力変換器制御装置。 In a power converter control device that PWM-controls a plurality of power converters that respectively supply power to the plurality of winding groups in order to drive a multi-winding motor having a plurality of winding groups,
A position detector for detecting the magnetic pole position of the rotor of the multi-winding motor;
A voltage command calculation unit for generating a three-phase voltage command for each power converter based on a given torque command and a magnetic pole position signal from the position detector;
A carrier generation unit that generates a plurality of carrier signals for PWM control of the plurality of power converters at the same frequency;
A carrier comparison unit that generates a switching pulse signal subjected to PWM processing by comparing the three-phase voltage command and the carrier signal for each power converter,
The carrier generation unit is a phase difference reference that is one of a rotation speed of the multi-winding motor based on the magnetic pole position signal, the torque command, or a modulation rate calculated from the rotation speed and the torque command. A phase difference determined based on a signal is generated to generate the plurality of carrier signals. In a region where the value of the phase difference reference signal is low, the phase difference is 90 degrees, and a region where the value of the phase difference reference signal is high A power converter control device characterized in that the phase difference is 180 degrees .
上記キャリア生成部は、上記回転速度を上記位相差基準信号として、上記回転速度が所定値以下の時は上記位相差を90度とし、上記回転速度が上記所定値を超えると上記位相差を180度として上記複数のキャリア信号を生成することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の電力変換器制御装置。 A speed calculator that calculates the rotational speed of the multi-winding motor from the magnetic pole position signal from the position detector;
The carrier generator, the rotational speed of the phase difference reference signal, when the rotational speed is below a predetermined value the phase difference is 90 degrees, the phase difference when the rotation speed exceeds the predetermined value 180 The power converter control device according to claim 1, wherein the plurality of carrier signals are generated as a degree.
上記キャリア生成部は、上記変調率を上記位相差基準信号として、上記変調率が所定値以下の時は上記位相差を90度とし、上記変調率が上記所定値を超えると上記位相差を180度として上記複数のキャリア信号を生成することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の電力変換器制御装置。 A speed calculation unit that calculates the rotation speed of the multi-winding motor from the magnetic pole position signal from the position detector, and a modulation rate calculation unit that calculates the modulation rate from the rotation speed and the torque command,
The carrier generating unit, the modulation rate as the phase difference reference signal, when the modulation rate is less than the predetermined value the phase difference is 90 degrees, the phase difference when the modulation rate exceeds the predetermined value 180 The power converter control device according to claim 1, wherein the plurality of carrier signals are generated as a degree.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012136690A JP5916526B2 (en) | 2012-06-18 | 2012-06-18 | Power converter control device and multi-winding motor drive device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012136690A JP5916526B2 (en) | 2012-06-18 | 2012-06-18 | Power converter control device and multi-winding motor drive device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2014003783A JP2014003783A (en) | 2014-01-09 |
| JP2014003783A5 JP2014003783A5 (en) | 2014-11-27 |
| JP5916526B2 true JP5916526B2 (en) | 2016-05-11 |
Family
ID=50036418
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012136690A Active JP5916526B2 (en) | 2012-06-18 | 2012-06-18 | Power converter control device and multi-winding motor drive device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5916526B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107852125A (en) * | 2015-06-11 | 2018-03-27 | Ksr Ip控股有限责任公司 | The modulation design of polyphase machine |
| JP6611547B2 (en) * | 2015-10-09 | 2019-11-27 | キヤノンメディカルシステムズ株式会社 | Multi-stage inverter controller |
| JP2017131045A (en) * | 2016-01-21 | 2017-07-27 | 株式会社デンソー | Rotary electric machine control device |
| JP6776841B2 (en) * | 2016-11-21 | 2020-10-28 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | Rotating electric machine control system and its adjustment method |
| JP6328280B1 (en) * | 2017-01-25 | 2018-05-23 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Control device for double winding type rotating electrical machine |
| DE102017212574A1 (en) * | 2017-07-21 | 2019-01-24 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Electric machine |
| EP3460992B1 (en) * | 2017-09-22 | 2023-06-28 | Valeo eAutomotive Germany GmbH | Inverter for an electric machine, electric machine for a vehicle and method for operating an inverter |
| CN107732931B (en) * | 2017-11-10 | 2023-11-10 | 贵州电网有限责任公司电力科学研究院 | Hybrid power electronic transformer based on three-phase matrix transformation and modulation method thereof |
| CN107968442A (en) * | 2017-12-20 | 2018-04-27 | 云南电网有限责任公司电力科学研究院 | A kind of power forecasting method in the new energy region based on Rolling optimal strategy |
| KR102011831B1 (en) * | 2018-01-04 | 2019-10-14 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Motor driving apparatus and electric vehicle including the same |
| DE112018007148T5 (en) * | 2018-02-23 | 2020-11-05 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | CONTROL PROCESS FOR DYNAMOELECTRIC MACHINE, CONTROL DEVICE FOR DYNAMOELECTRIC MACHINE, AND DRIVE SYSTEM |
| CN111207866B (en) * | 2019-09-09 | 2021-09-10 | 浙江航驱汽车科技有限公司 | Automatic test system and method for external characteristics of power-assisted motor |
| CN115336168A (en) | 2020-04-06 | 2022-11-11 | 日立安斯泰莫株式会社 | Motor control device, electric vehicle, and motor control method |
| KR102459423B1 (en) * | 2020-09-10 | 2022-10-27 | 에스트라오토모티브시스템 주식회사 | Motor control method and system for reducing EMI in electric compressor of vehicle |
| JP7254198B2 (en) * | 2020-12-23 | 2023-04-07 | 東芝三菱電機産業システム株式会社 | Polyphase motor drive |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001197779A (en) * | 2000-01-12 | 2001-07-19 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | Motor drive apparatus |
| JP2002051566A (en) * | 2000-08-03 | 2002-02-15 | Toyota Central Res & Dev Lab Inc | Inverter control device and inverter control method |
| JP4727248B2 (en) * | 2004-07-15 | 2011-07-20 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Control device for inverter and converter |
| JP2008022671A (en) * | 2006-07-14 | 2008-01-31 | Toyota Motor Corp | Inverter control device, inverter control method, and vehicle |
| JP2008092739A (en) * | 2006-10-04 | 2008-04-17 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | Power conversion device and control method therefor |
| JP2008289322A (en) * | 2007-05-21 | 2008-11-27 | Toshiba Corp | Controller |
| US8115433B2 (en) * | 2008-09-23 | 2012-02-14 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | Electrical system for pulse-width modulated control of a power inverter using phase-shifted carrier signals and related operating methods |
-
2012
- 2012-06-18 JP JP2012136690A patent/JP5916526B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2014003783A (en) | 2014-01-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5916526B2 (en) | Power converter control device and multi-winding motor drive device | |
| KR101157732B1 (en) | Controller for electric motor | |
| JP5120669B2 (en) | Control device for motor drive device | |
| JP5862125B2 (en) | Control device for power converter | |
| JP5968010B2 (en) | Power converter control device | |
| WO2016059684A1 (en) | Drive and control mechanism for multiple-winding motor | |
| JP6369517B2 (en) | Control device for power converter | |
| WO2013046462A1 (en) | Power conversion control device, power conversion control method, electric motor and vehicle drive system | |
| WO2017141513A1 (en) | Power conversion apparatus | |
| WO2018043502A1 (en) | Inverter control device and electric motor driving system | |
| JP2014150655A (en) | Inverter device and control method therefor, and motor drive system | |
| JP7280170B2 (en) | Motor control device, motor control method, hybrid system, boost converter system, electric power steering system | |
| JP6351652B2 (en) | Power converter control device | |
| JP6742393B2 (en) | Electric power conversion device, generator motor control device, and electric power steering device | |
| JP6075161B2 (en) | Switched reluctance motor controller | |
| JP5135794B2 (en) | Motor control method | |
| JP5923215B2 (en) | Rotating machine and rotating machine drive system | |
| JP2014003746A (en) | Control device for drive system | |
| JP7042568B2 (en) | Motor control device and motor control method | |
| JP2013005604A (en) | Power converter control device | |
| JP6951945B2 (en) | Motor control device and motor control method | |
| JP7527485B2 (en) | Inverter control device and inverter control method | |
| JP6590457B2 (en) | Vehicle drive control device and vehicle drive control method | |
| JPWO2016056082A1 (en) | POWER CONVERTER AND ITS CONTROL METHOD, ELECTRIC POWER STEERING CONTROL DEVICE | |
| WO2024157363A1 (en) | Electric motor control device and electric motor control method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20141008 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20141008 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20150722 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150728 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150915 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20160308 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20160405 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5916526 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |