JP5387803B1 - Sintering machine ignition device and sintering machine - Google Patents
Sintering machine ignition device and sintering machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5387803B1 JP5387803B1 JP2013525071A JP2013525071A JP5387803B1 JP 5387803 B1 JP5387803 B1 JP 5387803B1 JP 2013525071 A JP2013525071 A JP 2013525071A JP 2013525071 A JP2013525071 A JP 2013525071A JP 5387803 B1 JP5387803 B1 JP 5387803B1
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- burner
- fuel gas
- sintering machine
- air
- ignition device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000005245 sintering Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 50
- 239000002737 fuel gas Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 49
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 26
- 229910001220 stainless steel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 239000010935 stainless steel Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 abstract description 17
- 239000003570 air Substances 0.000 description 35
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 14
- 229910001208 Crucible steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 10
- 230000008439 repair process Effects 0.000 description 10
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 description 8
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 8
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 7
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000000571 coke Substances 0.000 description 5
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000011295 pitch Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000004904 shortening Methods 0.000 description 3
- ATUOYWHBWRKTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propane Chemical compound CCC ATUOYWHBWRKTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005336 cracking Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008646 thermal stress Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910001209 Low-carbon steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000001154 acute effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012080 ambient air Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000567 combustion gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008602 contraction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000295 fuel oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003949 liquefied natural gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012856 packing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000001294 propane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035882 stress Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F27—FURNACES; KILNS; OVENS; RETORTS
- F27B—FURNACES, KILNS, OVENS, OR RETORTS IN GENERAL; OPEN SINTERING OR LIKE APPARATUS
- F27B21/00—Open or uncovered sintering apparatus; Other heat-treatment apparatus of like construction
- F27B21/06—Endless-strand sintering machines
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F27—FURNACES; KILNS; OVENS; RETORTS
- F27B—FURNACES, KILNS, OVENS, OR RETORTS IN GENERAL; OPEN SINTERING OR LIKE APPARATUS
- F27B21/00—Open or uncovered sintering apparatus; Other heat-treatment apparatus of like construction
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22B—PRODUCTION AND REFINING OF METALS; PRETREATMENT OF RAW MATERIALS
- C22B1/00—Preliminary treatment of ores or scrap
- C22B1/14—Agglomerating; Briquetting; Binding; Granulating
- C22B1/16—Sintering; Agglomerating
- C22B1/20—Sintering; Agglomerating in sintering machines with movable grates
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23D—BURNERS
- F23D14/00—Burners for combustion of a gas, e.g. of a gas stored under pressure as a liquid
- F23D14/20—Non-premix gas burners, i.e. in which gaseous fuel is mixed with combustion air on arrival at the combustion zone
- F23D14/22—Non-premix gas burners, i.e. in which gaseous fuel is mixed with combustion air on arrival at the combustion zone with separate air and gas feed ducts, e.g. with ducts running parallel or crossing each other
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F27—FURNACES; KILNS; OVENS; RETORTS
- F27D—DETAILS OR ACCESSORIES OF FURNACES, KILNS, OVENS, OR RETORTS, IN SO FAR AS THEY ARE OF KINDS OCCURRING IN MORE THAN ONE KIND OF FURNACE
- F27D99/00—Subject matter not provided for in other groups of this subclass
- F27D99/0001—Heating elements or systems
- F27D99/0033—Heating elements or systems using burners
- F27D2099/004—Heating elements or systems using burners directed upon the charge, e.g. vertically
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Manufacture And Refinement Of Metals (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Geochemistry & Mineralogy (AREA)
- Geology (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
Abstract
焼結機のパレットの幅方向にわたって延びる燃料ガス用通路と、該燃料ガス用通路を挟んでその両側に延在する空気用通路と、前記燃料ガス用通路からの燃料ガスの噴出流と前記空気用通路からの燃焼用空気の噴出流が交会する向きに開口させた多数対のノズル孔が、前記燃料ガス用通路および前記空気用通路の長さ方向に沿い離間して設けられたバーナーと、前記ノズル孔より下の燃焼雰囲気を覆うバーナーフードと、を有し、前記バーナーがステンレス製鋼板を溶接加工したバーナーである、焼結機の点火装置。
A fuel gas passage extending across the width direction of the pallet of the sintering machine, an air passage extending on both sides of the fuel gas passage, a jet flow of fuel gas from the fuel gas passage, and the air A burner provided with a plurality of nozzle holes opened in a direction in which the jet flow of combustion air from the gas passage meets each other along the length direction of the fuel gas passage and the air passage; And a burner hood for covering a combustion atmosphere below the nozzle hole, wherein the burner is a burner obtained by welding a stainless steel plate.
Description
本発明は、焼結鉱を製造するための焼結機に使用される点火装置、および該点火装置を設置した焼結機に関する。 The present invention relates to an ignition device used in a sintering machine for producing sintered ore, and a sintering machine provided with the ignition device.
一般に、焼結鉱を製造するための焼結機の点火装置は、パレット上に装入された焼結原料層上面に向けて、バーナーから、重油、コークス炉ガスあるいはコークス炉ガスと高炉ガスとの混合ガス等の燃料、および空気を噴射させて燃焼火炎を形成し、かかる燃焼火炎で焼結原料層を加熱して焼結原料層中のコークスを燃焼させるために用いられる。 In general, an ignition device of a sintering machine for producing sintered ore is composed of heavy oil, coke oven gas or coke oven gas and blast furnace gas from a burner toward the upper surface of a sintering raw material layer charged on a pallet. A combustion flame is formed by injecting a fuel such as a mixed gas and air and air, and the coke in the sintering raw material layer is burned by heating the sintering raw material layer with the combustion flame.
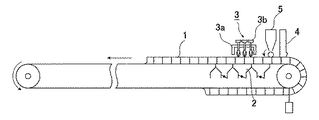
図6は、本発明に係わる点火装置を設置する焼結機を示す。図中、1はパレット(pallet)、2はウインドボックス、3は点火装置(ignition apparatus)であって、主として点火炉(ignition furnace)3aとバーナー3bとからなり、4は床敷(hearth layer)用ホッパー、5は原料ホッパーを示す。
FIG. 6 shows a sintering machine in which the ignition device according to the present invention is installed. In the figure, 1 is a pallet, 2 is a wind box, 3 is an ignition apparatus, and mainly comprises an
特開昭59−200183号公報(特許文献1)に開示されている点火装置は、焼結機のパレットの幅方向に延びる燃料ガス通路および燃焼用空気通路と、これらの通路から供給された燃料ガスおよび燃焼用空気の噴出流が互いに交会する向きに開口した多数対のノズル孔を、前記各通路の長さ方向に沿って離間して設けたバーナーと、を備えている。また、特許文献1には、燃料ガスと空気とを小径のノズル孔より交差するよう噴射させることで火炎を短くし、エネルギーロスを大幅に改善する技術が開示されている。しかしながら、特許文献1のように、燃焼室が小さくバーナー高さが低いと、炉体放散熱が少なく燃料使用量を抑制する長所がある一方で、焼結原料層を加熱した際に赤熱した焼結原料からバーナーへの輻射熱および火炎自体の熱により、バーナー本体を損傷する可能性がある。 An ignition device disclosed in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 59-200193 (Patent Document 1) includes a fuel gas passage and a combustion air passage extending in the width direction of a pallet of a sintering machine, and fuel supplied from these passages. A burner provided with a plurality of nozzle holes that are opened in a direction in which the flow of gas and combustion air ejected each other, separated from each other along the length direction of each of the passages. Patent Document 1 discloses a technique for shortening a flame and greatly improving energy loss by injecting fuel gas and air so as to intersect with a small diameter nozzle hole. However, as in Patent Document 1, when the combustion chamber is small and the burner height is low, there is an advantage in that the amount of heat dissipated in the furnace body is small and the amount of fuel used is suppressed. On the other hand, There is a possibility of damaging the burner body due to the radiant heat from the raw material to the burner and the heat of the flame itself.
これに対し、特開平4−28826号公報(特許文献2)には、耐熱鋳鋼製のバーナーチップの線膨張係数が軟鋼と比して大きいため操業時のバーナーチップの伸びが大きく、操業−休止を繰り返すうちにバーナーチップに割れが入り寿命を短くする課題に対して、バーナーチップをパレット幅方向に複数個に分割することで熱膨張吸収代を設け、膨張収縮に伴なう割れを防止する技術が開示されている。特許文献2には、燃料ガスと空気とを直角に交差するよう噴射させることでフレームが短炎になること、およびパレット両端郎の通気過多の部分に対して、ノズル孔径を中央部より端部を段階的に大きくして幅方向の均一着火を可能にすることが開示されている。
On the other hand, Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 4-28826 (Patent Document 2) discloses that since the coefficient of linear expansion of a burner tip made of heat-resistant cast steel is larger than that of mild steel, the elongation of the burner tip during operation is large, so In response to the problem of cracks entering the burner tip and shortening the service life, the thermal expansion absorption margin is provided by dividing the burner tip into multiple parts in the pallet width direction to prevent cracks associated with expansion and contraction. Technology is disclosed.
しかしながら、焼結機の突発停止等の要因により操業−休止を頻繁に繰り返す使用環境下では、依然としてバーナーノズルの熱変形、亀裂発生が起こり、バーナー寿命の短縮化に対する対策は不十分であった。 However, under the usage environment in which operation and stop are frequently repeated due to factors such as sudden stoppage of the sintering machine, thermal deformation and cracking of the burner nozzle still occur, and measures for shortening the burner life are insufficient.
本発明の目的は、操業−休止を頻繁に繰り返す使用環境下においても熱応力に耐性がある点火装置を提供すること、および、焼結機の点火装置の寿命を延ばし補修頻度を下げることである。 An object of the present invention is to provide an ignition device that is resistant to thermal stress even in a use environment in which operation and stop are frequently repeated, and to extend the life of the ignition device of the sintering machine and reduce the repair frequency. .
上記の課題を解決するための本発明の特徴は、以下の通りである。
[1]
焼結機のパレットの幅方向にわたって延びる燃料ガス用通路と、
該燃料ガス用通路を挟んでその両側に延在する空気用通路と、
前記燃料ガス用通路からの燃料ガスの噴出流と前記空気用通路からの燃焼用空気の噴出流が交会する向きに開口させた多数対のノズル孔が、前記燃料ガス用通路および前記空気用通路の長さ方向に沿い離間して設けられたバーナーと、
前記ノズル孔より下の燃焼雰囲気を覆うバーナーフードと、
を有し、
前記バーナーがステンレス製鋼板を溶接加工したバーナーである、
焼結機の点火装置。
[2]前記燃料ガスの噴出流と燃焼用空気の噴出流が30度以上60度以下の角度で交会する[1]に記載の焼結機の点火装置。
[3]前記バーナーはバーナー本体とバーナーチップとからなり、該バーナー本体と該バーナーチップが一体構造である[1]に記載の焼結機の点火装置。
[4]前記多数対のノズル孔が燃料ガスノズル孔と空気ノズル孔とからなり、
該燃料ガスノズル孔はバーナーの中心側に設けられ、外側を指向する向きに開口し、
該空気ノズル孔はバーナーの外側に内向きに開口している、
[1]に記載の焼結機の点火装置。The features of the present invention for solving the above-described problems are as follows.
[1]
A fuel gas passage extending across the width direction of the pallet of the sintering machine;
An air passage extending on both sides of the fuel gas passage;
The fuel gas passage and the air passage include a plurality of nozzle holes opened in a direction where the jet flow of the fuel gas from the fuel gas passage and the jet flow of the combustion air from the air passage meet each other. Burners provided apart along the length direction of
A burner hood that covers the combustion atmosphere below the nozzle hole;
Have
The burner is a burner obtained by welding a stainless steel plate.
Sintering machine ignition device.
[2] The ignition device for a sintering machine according to [1], wherein the jet flow of the fuel gas and the jet flow of the combustion air meet at an angle of 30 degrees to 60 degrees.
[3] The ignition device for a sintering machine according to [1], wherein the burner includes a burner body and a burner chip, and the burner body and the burner chip have an integral structure.
[4] The multiple pairs of nozzle holes include fuel gas nozzle holes and air nozzle holes,
The fuel gas nozzle hole is provided on the center side of the burner and opens in a direction facing the outside,
The air nozzle hole opens inwardly on the outside of the burner;
The ignition device for a sintering machine according to [1].
[5]焼結機のパレットの幅方向に、[1]乃至[4]の何れかに記載の焼結機の点火装置を、熱伸びを吸収する間隙を設けて複数並べ、点火炉内温度雰囲気において隣接するバーナーの端部が熱膨張により密接するように設けられた焼結機。 [5] A plurality of ignition devices for the sintering machine according to any one of [1] to [4] are arranged in the width direction of the pallet of the sintering machine with a gap for absorbing thermal elongation, and the temperature in the ignition furnace A sintering machine provided so that the ends of adjacent burners are in close contact with each other by thermal expansion in an atmosphere.
本発明により、焼結機パレット幅方向に均一な着火強度が得られ、燃料原単位が低い焼結機の点火装置であり、操業−休止を頻繁に繰り返す使用環境下においても熱応力に耐性がある点火装置を提供可能となった。 According to the present invention, a igniter for a sintering machine having a uniform ignition strength in the width direction of the pallet of the sintering machine and a low fuel consumption rate, which is resistant to thermal stress even in a use environment in which operation and stop are frequently repeated. An ignition device can be provided.
従来の耐熱鋳鋼製バーナーは、その材質や加工方法の制約から、バーナー本体とバーナーノズルに分割することが必要であり、バーナー本体とバーナーノズルを接続するフランジ面の繰り返し熱変形により、フランジ部の歪み、また、パッキンの劣化、切断による燃料ガス、燃焼空気漏れが生じることが問題であった。本発明者らが鋭意検討した結果、バーナーを耐熱鋳鋼製の分割式から、バーナー本体とバーナーノズルを一体構造としたステンレス製とすることにより操業−休止を頻繁に繰り返す使用環境下においても熱応力に耐性がある点火装置を提供可能であることを見出した。 Conventional heat-resistant cast steel burners need to be divided into a burner body and a burner nozzle due to restrictions on the material and processing method. The flange part is repeatedly deformed due to repeated thermal deformation of the flange surface connecting the burner body and the burner nozzle. Distortion, deterioration of packing, fuel gas due to cutting, and combustion air leakage occurred. As a result of intensive studies by the present inventors, it was found that the burner is made of stainless steel in which the burner main body and the burner nozzle are integrated from the split type made of heat-resistant cast steel. It has been found that it is possible to provide an ignition device that is resistant to.
表1は、材質変更の効果を比較した結果である。バーナーの材質を耐熱鋳鋼から、バーナー本体とバーナーノズルが一体構造のステンレス製に変更したので、フランジ部の歪みに起因した燃料漏れは無くなった。そして、バーナー、ノズルの肉厚を薄くすることで、残留応力およびバーナーの歪みを低減した。その結果、操業−休止を頻繁に繰り返す使用環境下においても長期間使用可能なバーナーとなった。 Table 1 shows the results of comparing the effects of changing the material. Since the material of the burner was changed from heat-resistant cast steel to stainless steel with a burner body and burner nozzle, the fuel leakage due to flange distortion was eliminated. The residual stress and burner distortion were reduced by reducing the thickness of the burner and nozzle. As a result, it became a burner that can be used for a long period of time even in a use environment in which operation and suspension are frequently repeated.
さらに、燃料ガスおよび燃焼用空気の噴出流が互いに交会する角度について検討した結果、その角度を60度以下とすることにより、ノズル部の温度を下げることが可能であり、ノズル部の亀裂発生防止効果があることを見出した。以下、表2と図4により説明する。 Furthermore, as a result of examining the angle at which the jets of fuel gas and combustion air meet each other, it is possible to reduce the temperature of the nozzle part by setting the angle to 60 degrees or less, and to prevent cracks in the nozzle part. I found it effective. Hereinafter, this will be described with reference to Table 2 and FIG.
表2は、実験用燃焼炉にバーナー幅500mmの実験バーナーを設置し、耐久性を評価した結果である。炉内のバーナーの対向面には鉄板を敷いてバーナーが下からの輻射熱を受ける構造とした。鉄板温度は、通常の焼結機操業と同等の1300℃の条件と、焼結機操業が変動した場合を想定した1350℃の条件で昇温、30分の指定温度キープ、降温を繰り返し、バーナーの損傷状況を観察した。 Table 2 shows the results of evaluating durability by installing an experimental burner having a burner width of 500 mm in an experimental combustion furnace. An iron plate is laid on the opposite surface of the burner in the furnace so that the burner receives radiant heat from below. The iron plate temperature is 1300 ° C equivalent to the normal sintering machine operation and 1350 ° C condition assuming the operation of the sintering machine fluctuating, repeating the specified temperature keep for 30 minutes and the temperature reduction, and the burner The damage situation of was observed.
バーナーを従来の耐熱鋳鋼製分割構造から比較的薄いステンレス鋼板の溶接一体構造とすることにより熱変形が無くなった。通常の焼結機操業では、焼結原料層表面温度(試験時炉内温度に相当)は1300℃であり、通常の操業範囲内ではバーナー材質をステンレス製とすることで亀裂発生を防止することが可能である。焼結機操業の変動により炉内温度が1350℃に上昇したとしても、燃料ガスおよび燃焼用空気の噴出流が互いに交会する角度を従来の90度から60度、40度と鋭角に交会させてノズル部温度を下げることにより、ノズル部の亀裂頻度を低下できることがわかった。表2に示すように、90度では試験回数3回で亀裂が発生したのに対して、60度では6回、40度では10回と耐久性が向上した。即ち、燃料ガスおよび燃焼用空気の噴出流が互いに交会する角度を60度以下とすることにより、ノズル部の温度を下げることができるので、ノズル部の亀裂発生防止効果があることを見出した。 By changing the burner from a conventional heat-resistant cast steel split structure to a relatively thin welded stainless steel plate, thermal deformation is eliminated. In normal operation of the sintering machine, the surface temperature of the sintering material layer (corresponding to the furnace temperature during the test) is 1300 ° C, and cracks are prevented by making the burner material stainless in the normal operating range. Is possible. Even if the furnace temperature rises to 1350 ° C due to fluctuations in the operation of the sintering machine, the angle at which the jets of fuel gas and combustion air meet each other is made to meet an acute angle of 90 degrees to 60 degrees and 40 degrees. It was found that the crack frequency of the nozzle part can be reduced by lowering the nozzle part temperature. As shown in Table 2, cracks occurred at 90 degrees with 3 tests, whereas durability at 6 degrees at 60 degrees and 10 times at 40 degrees. That is, it has been found that when the angle at which the jets of fuel gas and combustion air meet each other is set to 60 degrees or less, the temperature of the nozzle portion can be lowered, so that there is an effect of preventing cracks in the nozzle portion.
バーナーノズルからの距離と火炎温度の関係を図4に示した。燃料ガスおよび燃焼用空気の噴出流が互いに交会する角度を鋭角にするに従い、温度が1300℃以上である火炎部分は長くなり、バーナーと加熱面との距離を長くする必要が有る。噴出流が互いに交会する角度が30度から60度の範囲では、バーナーノズルから100mmまでの温度が大きく低下するのでノズル部温度を下げ、ノズル部の亀裂発生を防止するのに好適である。
噴出流の互いに交会する角度が30度未満ではバーナー火炎長さが850mm超えと長くなり、バーナーフードが大型化しエネルギーロスが増えるので好ましくない。The relationship between the distance from the burner nozzle and the flame temperature is shown in FIG. As the angle at which the jets of fuel gas and combustion air meet each other becomes sharper, the flame portion having a temperature of 1300 ° C. or higher becomes longer, and the distance between the burner and the heating surface needs to be increased. When the angle at which the ejected flows meet each other is in the range of 30 to 60 degrees, the temperature from the burner nozzle to 100 mm is greatly reduced, which is suitable for lowering the nozzle part temperature and preventing the occurrence of cracks in the nozzle part.
If the angle at which the jet flows meet each other is less than 30 degrees, the burner flame length becomes as long as more than 850 mm, which is not preferable because the burner hood becomes larger and energy loss increases.
本発明のステンレス製鋼板を溶接加工して製作したバーナーは、焼結機の幅方向に複数台並べて使用することが好ましい。幅方向に複数のバーナーを並べることにより、焼結機幅方向の燃焼条件を操業時の温度分布を見て個々に変更・調整可能となり、原料層厚の分布が変わるなどの操業条件が変化しても幅方向の温度分布の調整が可能となる。 It is preferable that a plurality of burners manufactured by welding the stainless steel plate of the present invention are used side by side in the width direction of the sintering machine. By arranging multiple burners in the width direction, the combustion conditions in the width direction of the sintering machine can be individually changed and adjusted by looking at the temperature distribution during operation, and the operation conditions such as the distribution of the raw material layer thickness change. However, the temperature distribution in the width direction can be adjusted.
本発明では複数のバーナー間に熱膨張吸収代を設けることが好ましい。熱膨張代の大きさは、操業中の点火炉内温度雰囲気において隣接するバーナーの端部が熱膨張により密接するように設ければ、操業中に、この膨張代から周囲の空気を吸引し点火フレームに乱れが生じることがない。 In the present invention, it is preferable to provide a thermal expansion absorption margin between a plurality of burners. If the temperature of the thermal expansion allowance is set so that the end of the adjacent burner is in close contact with the thermal expansion in the temperature atmosphere in the ignition furnace during operation, ambient air is sucked from the expansion allowance during operation and ignited. The frame is not disturbed.
また、バーナーにステンレス鋼板を用い薄肉化したことによりバーナーが軽量化された為、バーナー支持構造の簡素化が可能になると共に設置工事も容易となった。 In addition, since the burner has been reduced in weight by using a stainless steel plate for the burner, the burner support structure can be simplified and the installation work is facilitated.
以下、本発明の一実施形態を説明する。
図2に焼結機パレットと点火装置の一部を断面として示す。Bbはバーナー本体、Btはバーナーチップ、Fは火炎、Lはバーナー先端から焼結原料層表面までの距離を示している。燃料ガス供給管8および空気供給管9がパレットの幅全体に亘って設けられ、燃料ガス管6および燃焼用空気管7を備えた複数のバーナーが燃料ガス供給管8および空気供給管9とほぼ平行となるように熱膨張代分の間隙を設けて並べられている。ガス管6とガス供給管8とは短管10を介して、また空気管7と空気供給管9とは短管11を介して夫々個別に連通されている。燃料ガス供給管8と空気供給管9は、ガーダー26によって支持されている。Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described.
FIG. 2 shows a cross section of a part of the sintering machine pallet and the ignition device. Bb is a burner body, Bt is a burner tip, F is a flame, and L is the distance from the burner tip to the surface of the sintered raw material layer. A fuel gas supply pipe 8 and an air supply pipe 9 are provided over the entire width of the pallet, and a plurality of burners including the
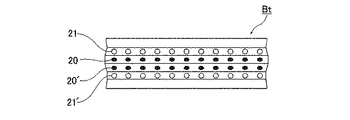
バーナー下部には、上記バーナーの燃料ガス供給管8および空気供給管9とにそれぞれ対応する多数のノズル孔20、20’、21、21’が図5に示すように小口径のノズル孔が管軸線方向に多数組列設されている。 In the lower part of the burner, a large number of nozzle holes 20, 20 ', 21, 21' respectively corresponding to the fuel gas supply pipe 8 and the air supply pipe 9 of the burner are shown in FIG. Many sets are arranged in the axial direction.
上記燃料ガスノズル孔20、20’は、両外側を指向する向きに、また上記空気ノズル孔21、21’の方は逆に内向きに開口させてあり、燃料ガスノズル21(21’)と空気ノズル20(20’)の噴射方向が互いに交会するように配置してフレームを短炎とすることが好ましい。 The fuel gas nozzle holes 20 and 20 ′ are opened in a direction facing both outer sides, and the air nozzle holes 21 and 21 ′ are opened inward, and the fuel gas nozzle 21 (21 ′) and the air nozzle are opened. It is preferable to arrange so that the injection directions of 20 (20 ′) intersect each other and to make the frame a short flame.
図1に本発明による点火装置の断面図を示す。上記のように、バーナー本体とバーナーチップを一体構造としている。なお、この図では燃料ガスとしてCOGを例示している。図中のθは、燃料ガスおよび燃焼用空気の噴出流が互いに交会する角度を示す。その際に、噴射方向が互いに交会する角度は大きい方がバーナー火炎長さが短くなり、パレット上焼結原料層上面とバーナーとの間隔を狭めることでエネルギーロスを小さくするのに有利である。一方、噴射方向が互いに交会する角度が小さいとバーナー火炎長さが長くなるが、ノズル部の温度が低くなり、ノズル部亀裂発生や熱変形の問題が生じ難い。以上により、噴射方向が互いに交会する角度は、30度以上60度以下が好ましい。さらに熱影響を小さくするために、ノズルが配列されるバーナー先端部以外のバーナー表面を、耐火断熱材で被覆することがより好ましい。 FIG. 1 shows a cross-sectional view of an ignition device according to the present invention. As described above, the burner body and the burner tip are integrated. In this figure, COG is illustrated as the fuel gas. In the figure, θ represents an angle at which the jets of fuel gas and combustion air meet each other. At this time, the larger the angle at which the injection directions intersect each other, the shorter the burner flame length, and it is advantageous to reduce the energy loss by narrowing the distance between the upper surface of the sintered raw material layer on the pallet and the burner. On the other hand, when the angle at which the jetting directions intersect with each other is small, the burner flame length becomes long, but the temperature of the nozzle portion becomes low, and the problem of nozzle portion cracking and thermal deformation hardly occurs. Accordingly, the angle at which the injection directions meet each other is preferably 30 degrees or more and 60 degrees or less. In order to further reduce the thermal influence, it is more preferable to cover the burner surface other than the burner tip where the nozzles are arranged with a refractory heat insulating material.
ノズル孔21、21’の両脇からは、前記ノズル孔より下の燃焼雰囲気を覆うバーナーフード24aが伸びている。バーナーフードを小型化し高温の範囲を囲うことで、エネルギーロスを低減し低い燃料原単位での操業が可能となる。
A
ノズル孔20、20’、21、21’の孔径およびピッチは、燃料ガスの種類、燃料ガスおよび空気の流量に応じて適宜調整されるべきものであるが、孔径は5〜30mm、ピッチは10〜40mmが好ましい。ピッチが広すぎる場合は火炎間に温度が低い部分が発生し焼結鉱に焼けむらができる問題が発生する。 The hole diameters and pitches of the nozzle holes 20, 20 ′, 21, and 21 ′ should be appropriately adjusted according to the type of fuel gas and the flow rates of the fuel gas and air, but the hole diameter is 5 to 30 mm and the pitch is 10 -40 mm is preferred. When the pitch is too wide, there is a problem that a portion having a low temperature is generated between the flames and the sintered ore can be burned unevenly.
燃料ガスは、2〜25kcal/Nm3の発熱量のガスを使用するのが好ましい。例えば、製鉄所で通常使用されるMガス(高炉ガスとコークス炉ガスの混合ガス)、Cガス(コークス炉ガス)、液化天然ガス、プロパンガス等が使用可能である。燃料ガスの発熱量が2kcal/Nm3未満では、燃料使用量が増加するので不経済である。燃焼用のガス・空気で内側から冷却させる自己冷却機能の点からは、発熱量が15kcal/Nm3以下の燃料ガスを使用するのがより好ましい。The fuel gas is preferably a gas having a calorific value of 2 to 25 kcal / Nm 3 . For example, it is possible to use M gas (mixed gas of blast furnace gas and coke oven gas), C gas (coke oven gas), liquefied natural gas, propane gas, etc. that are usually used in steelworks. If the calorific value of the fuel gas is less than 2 kcal / Nm 3 , the amount of fuel used increases, which is uneconomical. From the viewpoint of a self-cooling function of cooling from the inside with combustion gas / air, it is more preferable to use a fuel gas having a calorific value of 15 kcal / Nm 3 or less.
バーナーのノズル孔径、配置を最適化する際には、従来の耐熱鋳鋼製ではノズルチップを型から再製作が必要であったが、ステンレス製鋼板の溶接構造としたことによりノズル部分のみをドリルで再加工、溶接すればよく、調整が安価で短期間に可能となると共に、たとえ、バーナーに亀裂や割れが生じたとしても溶接で容易に補修が可能となった。また、熱変形が軽微であれば、薄肉のステンレス製鋼板を採用したことから、熱変形の矯正による短時間の補修で再使用可能となった。 When optimizing the nozzle hole diameter and arrangement of the burner, it was necessary to remanufacture the nozzle tip from the mold in the conventional heat-resistant cast steel, but by using a stainless steel plate welded structure, only the nozzle part can be drilled. It only has to be reworked and welded, making adjustments inexpensive and possible in a short period of time, and even if the burner is cracked or cracked, it can be easily repaired by welding. Also, if the thermal deformation was slight, a thin stainless steel plate was adopted, so that it could be reused with a short repair by correcting the thermal deformation.
焼結機ベッドの幅方向通過風量の分布に合わせて孔径を調整することも均一加熱の面で好ましいが、複数台並べたバーナー毎に燃料ガスおよび空気流量を調整すれば幅方向の均一着火を可能とできる。さらに、操業時の温度分布を見て、燃焼条件をバーナー毎に変更、調整できるようになり、原料層厚の分布が変わるなどの操業条件が変化したとしても、幅方向の温度分布が調整可能となる。 Adjusting the hole diameter according to the distribution of the passing airflow in the width direction of the sintering machine bed is also preferable in terms of uniform heating, but if the fuel gas and air flow rates are adjusted for each burner arranged in multiple units, uniform ignition in the width direction is possible. Possible. In addition, it is possible to change and adjust the combustion conditions for each burner by looking at the temperature distribution during operation, and the temperature distribution in the width direction can be adjusted even if the operating conditions such as the distribution of the raw material layer thickness change. It becomes.
また、各バーナーを上下角度変更可能に構成してもよい。各バーナーを昇降及び傾動することにより、焼結原料層表面とフレーム先端の接触面積を可変にできるから、均一着火の精度を高めることが可能となる。焼結原料層厚の変化、パレットスピードの変化、原料性状、原料中水分の変化などに応じて、バーナーを昇降及び傾動することで、焼結鉱の品質、歩留りの向上、燃料節減などの顕著な効果が得られる。 Moreover, you may comprise each burner so that an up-down angle change is possible. By raising and lowering and tilting each burner, the contact area between the surface of the sintering raw material layer and the frame tip can be made variable, so that the accuracy of uniform ignition can be improved. Changes in sintering material layer thickness, the pallet speed change, material properties, depending on the changes in the raw material moisture, by lifting and tilting the burner, the quality of sintered ore, improvement of the yield, such as fuel economy sensible A remarkable effect is obtained.
1日当り11000tの焼結鉱生産量の焼結工場において、耐熱鋳鋼製の点火バーナーからステンレス鋼板(SUS316)を溶接加工したバーナーに変更した。耐熱鋳鋼製のバーナーは焼結機幅3950mm全体にわたり一体成型されたバーナーであったが、ステンレス鋼板を溶接加工したバーナーは、800mm幅のバーナーを焼結機パレット横方向に5台並べて設置した。
燃料ガスおよび燃焼用空気の噴出流の角度は、耐熱鋳鋼製のバーナーでは90度であったが、ステンレス鋼板製のバーナーでは40度に変更した。
燃料ガスにはMガスを使用し、焼結原料層表面温度が1300℃となるように操業した。In a sinter factory with a sinter production volume of 11000t per day, the ignition burner made of heat-resistant cast steel was changed to a burner made by welding a stainless steel plate (SUS316). The burner made of heat-resistant cast steel was a burner integrally formed over the entire sintering machine width of 3950 mm. However, five burners welded with stainless steel plates were arranged side by side in the transverse direction of the sintering machine pallet.
The angle of the jet flow of fuel gas and combustion air was 90 degrees for the heat-resistant cast steel burner, but was changed to 40 degrees for the stainless steel burner.
M gas was used as the fuel gas, and the operation was performed so that the surface temperature of the sintering material layer was 1300 ° C.
上記の点火装置による操業の結果、耐熱鋳鋼製バーナー使用時は、6回/年の熱変形の矯正および亀裂の補修が必要で、補修時間は48時間/年であったが、ステンレス鋼板を溶接加工したバーナーに変更後は、1回/年の熱変形の矯正を実施したのみで、補修時間は40時間/年に短縮でき、補修頻度および補修時間を大幅に低下することができた。尚、補修時間はバーナー以外の焼結機設備の補修も含む補修時間である。 As a result of the operation by the above ignition device, when using a heat-resistant cast steel burner, 6 times / year of thermal deformation correction and crack repair are required, and the repair time was 48 hours / year. After changing to a burner that had been processed, the repair time could be shortened to 40 hours / year only by correcting the thermal deformation once per year, and the repair frequency and repair time could be greatly reduced. In addition, repair time is repair time also including repair of sintering machine facilities other than a burner.
Bb バーナー本体
Bt バーナーチップ
F 火炎
L バーナー先端から焼結原料層表面までの距離
1 パレット
2 ウインドボックス
3 点火装置
3a 点火炉
3b バーナー
4 床敷用ホッパー
5 原料ホッパー
6 燃料ガス管
7 燃焼用空気管
8 燃料ガス供給管
8a燃料ガス管内中心流路
9 空気供給管
9a空気管の管状流路
10、11 短管
17、17’ フランジ
20、20′、21、21′ ノズル孔
24(24a、24b) バーナーフード
26 ガーダー
Bb Burner body Bt Burner tip F Flame L Distance from burner tip to sintering raw material layer surface 1
10, 11 Short tube
17, 17 'flange
20, 20 ', 21, 21' Nozzle hole
24 (24a, 24b) Burner food
26 Girder
Claims (5)
該燃料ガス用通路を挟んでその両側に延在する空気用通路と、
前記燃料ガス用通路からの燃料ガスの噴出流と前記空気用通路からの燃焼用空気の噴出流が交会する向きに開口させた多数対のノズル孔が、前記燃料ガス用通路および前記空気用通路の長さ方向に沿い離間して設けられたバーナーと、
前記ノズル孔より下の燃焼雰囲気を覆うバーナーフードと、
を有し、
前記バーナーがステンレス製鋼板を溶接加工したバーナーである、
焼結機の点火装置。
A fuel gas passage extending across the width direction of the pallet of the sintering machine;
An air passage extending on both sides of the fuel gas passage;
The fuel gas passage and the air passage include a plurality of nozzle holes opened in a direction where the jet flow of the fuel gas from the fuel gas passage and the jet flow of the combustion air from the air passage meet each other. Burners provided apart along the length direction of
A burner hood that covers the combustion atmosphere below the nozzle hole;
Have
The burner is a burner obtained by welding a stainless steel plate.
Sintering machine ignition device.
2. The ignition device for a sintering machine according to claim 1, wherein the jet flow of the fuel gas and the jet flow of the combustion air meet at an angle of 30 degrees or more and 60 degrees or less.
2. The ignition device for a sintering machine according to claim 1, wherein the burner includes a burner body and a burner chip, and the burner body and the burner chip have an integral structure.
該燃料ガスノズル孔はバーナーの中心側に設けられ、外側を指向する向きに開口し、
該空気ノズル孔はバーナーの外側に内向きに開口している、
請求項1に記載の焼結機の点火装置。The multiple pairs of nozzle holes are composed of fuel gas nozzle holes and air nozzle holes,
The fuel gas nozzle hole is provided on the center side of the burner and opens in a direction facing the outside,
The air nozzle hole opens inwardly on the outside of the burner;
The ignition device for a sintering machine according to claim 1.
A plurality of ignition devices for the sintering machine according to any one of claims 1 to 4 are arranged in the width direction of the pallet of the sintering machine with a gap for absorbing thermal elongation, and are adjacent to each other in an ignition furnace temperature atmosphere. The sintering machine provided so that the end part of the burner to be brought into close contact by thermal expansion.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013525071A JP5387803B1 (en) | 2012-03-29 | 2013-01-25 | Sintering machine ignition device and sintering machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012076358 | 2012-03-29 | ||
| JP2012076358 | 2012-03-29 | ||
| PCT/JP2013/000371 WO2013145515A1 (en) | 2012-03-29 | 2013-01-25 | Sintering machine ignition apparatus and sintering machine |
| JP2013525071A JP5387803B1 (en) | 2012-03-29 | 2013-01-25 | Sintering machine ignition device and sintering machine |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP5387803B1 true JP5387803B1 (en) | 2014-01-15 |
| JPWO2013145515A1 JPWO2013145515A1 (en) | 2015-12-10 |
Family
ID=49258843
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013525071A Active JP5387803B1 (en) | 2012-03-29 | 2013-01-25 | Sintering machine ignition device and sintering machine |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5387803B1 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR101633210B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN104169668B (en) |
| IN (1) | IN2014KN01757A (en) |
| MY (1) | MY157876A (en) |
| PH (1) | PH12014501845B1 (en) |
| TW (1) | TWI528010B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2013145515A1 (en) |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS59133333A (en) * | 1983-01-20 | 1984-07-31 | Sumitomo Metal Ind Ltd | Combustion method of sintered ore |
| JPS59200183A (en) | 1983-04-28 | 1984-11-13 | 川崎製鉄株式会社 | Igniter for sintering machine |
| CN2041391U (en) * | 1988-09-03 | 1989-07-19 | 鞍山黑色冶金矿山设计研究院 | Banded sectional type porous burner |
| JPH0426724A (en) * | 1990-05-22 | 1992-01-29 | Kawasaki Steel Corp | Ignition device for sintering machine |
| JPH0428826A (en) | 1990-05-24 | 1992-01-31 | Kawasaki Steel Corp | Ignition device for sintering machine |
| JPH0816522B2 (en) * | 1991-04-04 | 1996-02-21 | 日本鋼管株式会社 | Burner for sintering material ignition |
| JPH0590296U (en) * | 1992-05-14 | 1993-12-10 | 川崎製鉄株式会社 | Ignition device of sintering machine |
| JPH06257956A (en) * | 1993-03-08 | 1994-09-16 | Kawasaki Steel Corp | Ignition equipment for sintering furnace |
| JP2001065824A (en) * | 1999-08-30 | 2001-03-16 | Kawasaki Steel Corp | Burner for ignition furnace of sintering machine |
| JP4735682B2 (en) * | 2008-08-21 | 2011-07-27 | Jfeスチール株式会社 | Method for producing sintered ore and sintering machine |
-
2013
- 2013-01-25 WO PCT/JP2013/000371 patent/WO2013145515A1/en active Application Filing
- 2013-01-25 MY MYPI2014702706A patent/MY157876A/en unknown
- 2013-01-25 CN CN201380013580.1A patent/CN104169668B/en active Active
- 2013-01-25 KR KR1020147027925A patent/KR101633210B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2013-01-25 JP JP2013525071A patent/JP5387803B1/en active Active
- 2013-01-25 IN IN1757KON2014 patent/IN2014KN01757A/en unknown
- 2013-01-28 TW TW102103174A patent/TWI528010B/en not_active IP Right Cessation
-
2014
- 2014-08-15 PH PH12014501845A patent/PH12014501845B1/en unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| PH12014501845A1 (en) | 2014-11-17 |
| KR101633210B1 (en) | 2016-06-23 |
| JPWO2013145515A1 (en) | 2015-12-10 |
| TW201341744A (en) | 2013-10-16 |
| WO2013145515A1 (en) | 2013-10-03 |
| TWI528010B (en) | 2016-04-01 |
| IN2014KN01757A (en) | 2015-10-23 |
| CN104169668B (en) | 2016-08-17 |
| PH12014501845B1 (en) | 2014-11-17 |
| MY157876A (en) | 2016-07-26 |
| CN104169668A (en) | 2014-11-26 |
| KR20140131392A (en) | 2014-11-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN107075379B (en) | Coke ovens with improved exhaust gas delivery in the secondary heating chamber | |
| KR880001688B1 (en) | Ignition device for sintering machine | |
| CN105316621A (en) | Carburization combined assembly structure for planet row transmission gears and heat treatment method | |
| JP4747599B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for producing sintered ore | |
| CN103438438A (en) | Method and device for preventing membrane water wall type boiler from high-temperature corrosion and coking | |
| KR100964904B1 (en) | Heater for annealing furnace | |
| JP6246455B2 (en) | Burner for sintering furnace ignition furnace | |
| JP5387803B1 (en) | Sintering machine ignition device and sintering machine | |
| CN202671582U (en) | Rotary retort-type heat treatment furnace | |
| CN102213417B (en) | Forced-draft flameless combustor | |
| JP2006132826A (en) | Igniting multi-burner and ignition system for sintering machine, and method of heating sintered raw material | |
| US20220074592A1 (en) | Assembly and method for injecting a gaseous combustion agent | |
| CN203549797U (en) | High-temperature corrosion prevention coking device for membrane wall type boiler | |
| JP2010107066A (en) | Sintering ignition furnace and method of manufacturing sintered ore | |
| US8087929B2 (en) | Equipment and method for heating gas in connection with sintering | |
| CN104155328A (en) | Oxygen-rich sintering test apparatus | |
| CN104833213A (en) | Furnace baking system for sintering ignition furnace | |
| KR102032755B1 (en) | The method for producing sintered ore by providing liquid fuel and apparatus thereof | |
| JP6421851B2 (en) | Burner for sintering furnace ignition furnace | |
| JP2015157896A (en) | Operation method of coke oven | |
| CA1161637A (en) | Installation and process for the production of hot air | |
| KR102142810B1 (en) | Burner apparatus and heating furnace having thereof | |
| KR101056226B1 (en) | Flow rate control method of blast furnace and wind hole | |
| JP2023079359A (en) | Chamber oven-type coke oven and method for producing coke | |
| JP2534419B2 (en) | Ignition device of sintering machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130910 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130923 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5387803 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |