JP5368478B2 - レーザ生成プラズマ源の斜入射集光光学系 - Google Patents
レーザ生成プラズマ源の斜入射集光光学系 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5368478B2 JP5368478B2 JP2010543446A JP2010543446A JP5368478B2 JP 5368478 B2 JP5368478 B2 JP 5368478B2 JP 2010543446 A JP2010543446 A JP 2010543446A JP 2010543446 A JP2010543446 A JP 2010543446A JP 5368478 B2 JP5368478 B2 JP 5368478B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- axis
- mirror
- optical system
- along
- source
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 claims description 77
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 claims description 40
- 238000009304 pastoral farming Methods 0.000 claims description 31
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 claims description 24
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 claims description 20
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 claims description 20
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 18
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000001459 lithography Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 claims 2
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 51
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 12
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 12
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 12
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 11
- 230000000116 mitigating effect Effects 0.000 description 10
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 10
- 238000005323 electroforming Methods 0.000 description 9
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 9
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 8
- 229910052707 ruthenium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 6
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 229910052741 iridium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 229910052703 rhodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 230000003746 surface roughness Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229910003460 diamond Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000010432 diamond Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000001900 extreme ultraviolet lithography Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229910017709 Ni Co Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910003267 Ni-Co Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910003262 Ni‐Co Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000005291 magnetic effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000001902 propagating effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000002114 nanocomposite Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000002086 nanomaterial Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000011241 protective layer Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910003266 NiCo Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000009713 electroplating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003302 ferromagnetic material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000000873 masking effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052758 niobium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000002310 reflectometry Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052726 zirconium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000001154 acute effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003518 caustics Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910010293 ceramic material Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009833 condensation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005494 condensation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000356 contaminant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011109 contamination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005137 deposition process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008020 evaporation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012467 final product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 1
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000004678 hydrides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000010849 ion bombardment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000670 limiting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000696 magnetic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000005459 micromachining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002159 nanocrystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000036961 partial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000704 physical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011253 protective coating Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005546 reactive sputtering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035939 shock Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052718 tin Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/70—Microphotolithographic exposure; Apparatus therefor
- G03F7/708—Construction of apparatus, e.g. environment aspects, hygiene aspects or materials
- G03F7/70908—Hygiene, e.g. preventing apparatus pollution, mitigating effect of pollution or removing pollutants from apparatus
- G03F7/70916—Pollution mitigation, i.e. mitigating effect of contamination or debris, e.g. foil traps
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B82—NANOTECHNOLOGY
- B82Y—SPECIFIC USES OR APPLICATIONS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MEASUREMENT OR ANALYSIS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT OF NANOSTRUCTURES
- B82Y10/00—Nanotechnology for information processing, storage or transmission, e.g. quantum computing or single electron logic
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/70—Microphotolithographic exposure; Apparatus therefor
- G03F7/70008—Production of exposure light, i.e. light sources
- G03F7/70033—Production of exposure light, i.e. light sources by plasma extreme ultraviolet [EUV] sources
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/70—Microphotolithographic exposure; Apparatus therefor
- G03F7/70058—Mask illumination systems
- G03F7/7015—Details of optical elements
- G03F7/70166—Capillary or channel elements, e.g. nested extreme ultraviolet [EUV] mirrors or shells, optical fibers or light guides
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G21—NUCLEAR PHYSICS; NUCLEAR ENGINEERING
- G21K—TECHNIQUES FOR HANDLING PARTICLES OR IONISING RADIATION NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; IRRADIATION DEVICES; GAMMA RAY OR X-RAY MICROSCOPES
- G21K1/00—Arrangements for handling particles or ionising radiation, e.g. focusing or moderating
- G21K1/06—Arrangements for handling particles or ionising radiation, e.g. focusing or moderating using diffraction, refraction or reflection, e.g. monochromators
- G21K1/062—Devices having a multilayer structure
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G21—NUCLEAR PHYSICS; NUCLEAR ENGINEERING
- G21K—TECHNIQUES FOR HANDLING PARTICLES OR IONISING RADIATION NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; IRRADIATION DEVICES; GAMMA RAY OR X-RAY MICROSCOPES
- G21K1/00—Arrangements for handling particles or ionising radiation, e.g. focusing or moderating
- G21K1/06—Arrangements for handling particles or ionising radiation, e.g. focusing or moderating using diffraction, refraction or reflection, e.g. monochromators
- G21K1/067—Arrangements for handling particles or ionising radiation, e.g. focusing or moderating using diffraction, refraction or reflection, e.g. monochromators using surface reflection, e.g. grazing incidence mirrors, gratings
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05G—X-RAY TECHNIQUE
- H05G2/00—Apparatus or processes specially adapted for producing X-rays, not involving X-ray tubes, e.g. involving generation of a plasma
- H05G2/001—Production of X-ray radiation generated from plasma
- H05G2/003—Production of X-ray radiation generated from plasma the plasma being generated from a material in a liquid or gas state
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G21—NUCLEAR PHYSICS; NUCLEAR ENGINEERING
- G21K—TECHNIQUES FOR HANDLING PARTICLES OR IONISING RADIATION NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; IRRADIATION DEVICES; GAMMA RAY OR X-RAY MICROSCOPES
- G21K2201/00—Arrangements for handling radiation or particles
- G21K2201/06—Arrangements for handling radiation or particles using diffractive, refractive or reflecting elements
- G21K2201/061—Arrangements for handling radiation or particles using diffractive, refractive or reflecting elements characterised by a multilayer structure
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G21—NUCLEAR PHYSICS; NUCLEAR ENGINEERING
- G21K—TECHNIQUES FOR HANDLING PARTICLES OR IONISING RADIATION NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; IRRADIATION DEVICES; GAMMA RAY OR X-RAY MICROSCOPES
- G21K2201/00—Arrangements for handling radiation or particles
- G21K2201/06—Arrangements for handling radiation or particles using diffractive, refractive or reflecting elements
- G21K2201/064—Arrangements for handling radiation or particles using diffractive, refractive or reflecting elements having a curved surface
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G21—NUCLEAR PHYSICS; NUCLEAR ENGINEERING
- G21K—TECHNIQUES FOR HANDLING PARTICLES OR IONISING RADIATION NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; IRRADIATION DEVICES; GAMMA RAY OR X-RAY MICROSCOPES
- G21K2201/00—Arrangements for handling radiation or particles
- G21K2201/06—Arrangements for handling radiation or particles using diffractive, refractive or reflecting elements
- G21K2201/065—Arrangements for handling radiation or particles using diffractive, refractive or reflecting elements provided with cooling means
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G21—NUCLEAR PHYSICS; NUCLEAR ENGINEERING
- G21K—TECHNIQUES FOR HANDLING PARTICLES OR IONISING RADIATION NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; IRRADIATION DEVICES; GAMMA RAY OR X-RAY MICROSCOPES
- G21K2201/00—Arrangements for handling radiation or particles
- G21K2201/06—Arrangements for handling radiation or particles using diffractive, refractive or reflecting elements
- G21K2201/067—Construction details
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Spectroscopy & Molecular Physics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- High Energy & Nuclear Physics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Atmospheric Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Plasma & Fusion (AREA)
- Nanotechnology (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Exposure Of Semiconductors, Excluding Electron Or Ion Beam Exposure (AREA)
- Exposure And Positioning Against Photoresist Photosensitive Materials (AREA)
- Optical Elements Other Than Lenses (AREA)
- X-Ray Techniques (AREA)
Description
2)NIMの表面領域は比較的小さいため、結果的に熱負荷密度が非常に高い。これにより、NIMの熱制御は困難となる。
3)プラズマ源のほとんどの出力は約10nmから120nmの間であるが、マルチレイヤコーティングが13.5nm付近の極めて狭い帯域幅でしか反射しない非常に狭い通過帯域として作用するため、熱負荷の総量はNIMでは高くなる。これにより更にNIMの熱制御が複雑となる。
4)図2の構成は、DPP源では一般的に使用されるデブリ軽減ツール(DMT)が使用できなくなる。このタイプのDMTは、光源からの高速の粒子の速度を弱めるため、光源付近に放射状に配されガス(Ar、N2等)が充填された多数のラメラからなる。しかし、このタイプのDMTは図2の構成における放射を完全に遮ってしまう。
5)光源からの高エネルギーのイオンや粒子による反射層の腐食を解消し、ミラーの寿命を延ばすためには、反射層の厚みを増やす必要がある。しかし、NIMにおいては、これはマルチレイヤコーティングの層の数を増やすことになると共に、製造工程を複雑にし、製造コストを増加させる。
6)(一単位領域毎の)イオンや粒子の流れは、NIMにおいては小さな領域のわりには比較的高い。よって、腐食及び/又は堆積はNIMにおいては比較的高い。
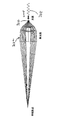
同心のミラー構成において、図3に示すWolter設計のように、ミラー306の厚みは、集光効率に直接的な影響を及ぼす。これは、光源304から発光されたEUV光の一部がミラーの厚みによってブロックされるからである。集光効率を可能な限り最大限にするため、ミラー306の厚みはできるだけ小さくしなければならない。従って、ミラー306の製造には金属が適宜使用される。これにより、ミラーの厚みを小さくすることができ、自重によりミラーが変形することを防ぐための十分なメカニカル且つ構造的な剛性を付与する。
1.薄い金属のシェルの製造
2.マスタの形状の再現、特に2反射ミラーでは、モノシリック構造の二つの反射面の再現が可能であり、しかもその二面間において他の光学的な整合を必要とすることがない
3.典型的には1−2nm rms未満で研磨されるマスタの粗さの再現(1mmから10nmの空間波長範囲において十分に高い反射率を確実にするため)であり、ミラーの内側面よりもはるかに簡単に研磨できる
電鋳工程によってマスタの形状が再現されるため、マスタは最終製品のミラーの光学的性能を確実に満たすのに十分な表面精度を有する必要がある。良好な性能を実現するため、マスタはダイアモンド旋盤によって製造されてもよい。
1.異なる分離層、例えばミラーの面に固着しない窒化物層、炭化物層、炭窒化物層等、不活性セラミック材料を選択できる
2.適切な障壁材料を用いてミラー基材と反射層との間にAuを遮蔽することができる
また、集光器302は、シェル(ミラー306)の温度を略一定且つ均一に保ち、プラズマ源304からの大きな熱負荷によって引き起こされる過度の変形を防ぐことができる。熱制御システム(図示せず)は、ミラー306の裏面の光源304からの光の光路をブロックしない領域に一体的に設けられる。統合熱管理システム(図示せず)は、(a)適切な流体によって冷却されるパイプ、(b)ペルチェセル、(c)位相遷移流体によって冷却されるパイプ、(d)ミラーの裏面を微細加工すること或いは電鋳工程の際にミラーの裏面を適宜マスキングすることによって得られるマイクロチャンネル等の冷却素子を含む。統合熱管理システム(図示せず)は、代わりに又は追加として、ジュール効果によって加熱された適当な流体やワイヤによって加熱されたパイプ等の加熱素子を含む。統合熱管理システム(図示せず)は、代わりに又は追加として、温度センサや熱制御のハードウエアやソフトウエアを有する。
2.ミラー入口縁312の前方に流体冷却パイプライン(図示せず)を取り付ける
ミラーシェル306が取り付けられる集光器302の支持構造(図示せず)はまた、例えば、周囲のボディ(図示せず)からの熱放射や真空空間(図示せず)における不純なプラズマ等による熱負荷の影響を削減又は排除するため、冷却される。
再び図1及び図3を参照すると、集光器302の最大出口開口数(NA)は、通常照射器106の入口NAによって制限される。この制限は、光源304とIF間の距離の実際の制限と共に、ミラー306の長さの制限も決める。この制限により、各ミラー306は、光源304からの光の角度のついた部分のみを集光する場合がある。集光効率を最大化するために、光源204からの集光器302で捕らえられる最も大きい角度も最大化されなければならない。その結果、複数のミラー306は、典型的には最大集光角度が約40度から約85度の範囲となるように光源304からの所望の角度範囲をカバーするため同心に配されなければならない。本発明の第一実施形態(図3)では、6つの同心のミラー306が採用されている。しかし、好適な実施形態では、集光器302の同心ミラー306の数は5から16である。
13.5nmの代表的な動作波長で十分な反射を実現するため、ミラー306の光学面は、好適には(限定されるわけではないが)Pd、Ir、Pt、Mo、Rh、更に好ましくはRuからなる適切な材料(ここでは「反射層」と称する)によってコーティングされる。
Claims (20)
- 極紫外線及びX線放射用の光源−集光光学系であって、軸に沿って、
燃料ターゲットを有し、前記燃料ターゲットがレーザ光により照射されるとき放射を行うレーザ生成プラズマ(LPP)源と、
前記軸に沿って前記LPP源に相対的に配され、前記放射の一部を集光し、前記軸上の中間焦点に向ける、斜入射集光器と、
前記LPP源と前記中間焦点との間に前記軸に沿って配され、前記軸に沿って前記燃料ターゲットに対しレーザ光を反射させるミラーと、
を備え、
レーザ光は前記軸に沿って前記ミラーに入射し、
前記ミラーに反射したレーザ光は前記軸に沿って前記燃料ターゲットに戻って向けられる、
光源−集光光学系。 - 前記燃料ターゲットは、Li、Sn、又はXeを含む、
請求項1に記載の光源−集光光学系。 - 前記燃料ターゲットは、燃料液滴ジェネレータから出される燃料液滴を含む、
請求項2に記載の光源−集光光学系。 - 更に、前記燃料ターゲット上にレーザ光を合焦させるレンズを備える、
請求項1に記載の光源−集光光学系。 - 前記斜入射集光器は、斜入射集光器の温度分布を管理する熱管理システムを有する、
請求項1に記載の光源−集光光学系。 - 前記斜入射集光器は、同心に配され又は入れ子状の斜入射ミラーを備える、
請求項1に記載の光源−集光光学系。 - 前記斜入射ミラーは、電鋳金属から形成されてなる、
請求項6に記載の光源−集光光学系。 - 前記斜入射ミラーは、反射コーティングがなされた光学面をそれぞれ有する、
請求項7に記載の光源−集光光学系。 - 請求項1に記載の集光光学系と、
前記集光光学系に相対的に配され同光学系からの放射を受光する光学集光レンズと、
前記光学集光レンズからの放射を受光する反射マスクと、
を備える、リソグラフィシステム。 - 極紫外線及びX線放射用の光源−集光光学系であって、軸に沿って、
燃料ターゲットを有するレーザ生成プラズマ(LPP)源と、
前記燃料ターゲットに向けられ放射されるレーザ光を生成するレーザと、
前記軸に沿って前記LPP源に相対的に配され、前記放射の一部を集光し、中間焦点に向ける、入れ子状の電鋳ミラーを有する斜入射集光器と、
前記LPP源と前記中間焦点との間に前記軸に沿って配され、前記軸に沿って前記燃料ターゲットに対しレーザ光を反射させるミラーと、
を備え、
レーザ光は前記軸に沿って前記ミラーに入射し、
前記ミラーに反射したレーザ光は前記軸に沿って前記燃料ターゲットに戻って向けられる、
光源−集光光学系。 - 極紫外線及びX線放射用の光源−集光光学系であって、軸に沿って、
燃料ターゲットを有するレーザ生成プラズマ(LPP)源と、
前記燃料ターゲットに向けられ放射されるレーザ光を生成するレーザと、
前記軸に沿って前記LPP源に相対的に配され、前記放射の一部を集光し、中間焦点に向ける、入れ子状の電鋳ミラーを有する斜入射集光器と、
前記斜入射集光器に隣接して前記LPP源の反対側に軸に沿って配され、前記軸に沿って前記斜入射集光器を通ってレーザ光を反射するミラーと、
を備える、光源−集光光学系。 - 前記燃料ターゲットは、燃料液滴ジェネレータより出されるSnの液滴である、
請求項10又は11に記載の光源−集光光学系。 - 各電鋳ミラーは、反射コーティングされた光学面を有する、
請求項10又は11に記載の光源−集光光学系。 - 前記電鋳ミラーは、同心に配されている、
請求項10又は11に記載の光源−集光光学系。 - 請求項10又は11に記載の集光光学系と、
前記集光光学系に相対的に配され同光学系からの放射を受光する光学集光レンズと、
前記光学集光レンズからの放射を受光する反射マスクと、
を備える、リソグラフィシステム。 - 極紫外線又はX線放射を集光する方法であって、
集光器軸を有する斜入射集光器を設け、
前記集光器軸上であって前記斜入射集光器との相対位置に燃料ターゲットを配し、
レーザ光により前記燃料ターゲットを照射して、前記放射を行うレーザ生成プラズマ(LPP)源を形成し、
前記斜入射集光器で前記放射の一部を集光し、集光された放射を中間焦点に向け、
前記LPP源と前記中間焦点との間に前記軸に沿って配されたミラーにより、前記軸に沿って前記燃料ターゲットに対しレーザ光を反射させる方法であって、
レーザ光は前記軸に沿って前記ミラーに入射し、
前記ミラーに反射したレーザ光は前記軸に沿って前記燃料ターゲットに戻って向けられる、
方法。 - 前記燃料ターゲットを、燃料液滴ジェネレータより出されるSnの液滴とする、
請求項16に記載の方法。 - 極紫外線又はX線放射を集光する方法であって、
集光器軸を有する斜入射集光器を設け、
前記集光器軸上であって前記斜入射集光器との相対位置に燃料ターゲットを配し、
レーザ光により前記燃料ターゲットを照射して、前記放射を行うレーザ生成プラズマ(LPP)源を形成し、
レーザ光が前記斜入射集光器を通り前記軸に沿って反射するように、ミラーを前記斜入射集光器に隣接して前記LPP源の反対側に前記軸に沿って配し、
前記斜入射集光器で前記放射の一部を集光し、集光された放射を中間焦点に向けること、
を含む、方法。 - 前記斜入射集光器を同心に配された電鋳ミラーにより形成することを含む、
請求項16に記載の方法。 - 極紫外線及びX線放射用の光源−集光光学系であって、軸に沿って、
燃料ターゲットを有し、前記燃料ターゲットがレーザ光により照射されるとき放射を行うレーザ生成プラズマ(LPP)源と、
前記軸に沿って前記LPP源に相対的に配され、前記放射の一部を集光し、前記軸上の中間焦点に向ける、斜入射集光器と、
前記斜入射集光器に隣接して前記LPP源の反対側に軸に沿って配され、前記軸に沿って前記斜入射集光器を通ってレーザ光を反射するミラーと、
を備える、光源−集光光学系。
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP08001536.5A EP2083328B1 (en) | 2008-01-28 | 2008-01-28 | Grazing incidence collector for laser produced plasma sources |
| EP08001536.5 | 2008-01-28 | ||
| PCT/EP2009/000539 WO2009095220A2 (en) | 2008-01-28 | 2009-01-28 | Grazing incidence collector for laser produced plasma sources |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011512647A JP2011512647A (ja) | 2011-04-21 |
| JP2011512647A5 JP2011512647A5 (ja) | 2012-03-15 |
| JP5368478B2 true JP5368478B2 (ja) | 2013-12-18 |
Family
ID=39766873
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010543446A Active JP5368478B2 (ja) | 2008-01-28 | 2009-01-28 | レーザ生成プラズマ源の斜入射集光光学系 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8411815B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2083328B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5368478B2 (ja) |
| DE (1) | DE112009000120T5 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2009095220A2 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (26)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI457715B (zh) * | 2008-12-27 | 2014-10-21 | Ushio Electric Inc | Light source device |
| DE102009047712A1 (de) * | 2009-12-09 | 2011-06-16 | Carl Zeiss Smt Gmbh | EUV-Lichtquelle für eine Beleuchtungseinrichtung einer mikrolithographischen Projektionsbelichtungsanlage |
| US8330131B2 (en) * | 2010-01-11 | 2012-12-11 | Media Lario, S.R.L. | Source-collector module with GIC mirror and LPP EUV light source |
| JP5093267B2 (ja) | 2010-03-11 | 2012-12-12 | ウシオ電機株式会社 | 集光鏡アッセンブリおよびこの集光鏡アッセンブリを用いた極端紫外光光源装置 |
| JP5670174B2 (ja) * | 2010-03-18 | 2015-02-18 | ギガフォトン株式会社 | チャンバ装置および極端紫外光生成装置 |
| US8587768B2 (en) | 2010-04-05 | 2013-11-19 | Media Lario S.R.L. | EUV collector system with enhanced EUV radiation collection |
| US8810775B2 (en) * | 2010-04-16 | 2014-08-19 | Media Lario S.R.L. | EUV mirror module with a nickel electroformed curved mirror |
| DE102010028655A1 (de) * | 2010-05-06 | 2011-11-10 | Carl Zeiss Smt Gmbh | EUV-Kollektor |
| US9057962B2 (en) * | 2010-06-18 | 2015-06-16 | Media Lario S.R.L. | Source-collector module with GIC mirror and LPP EUV light source |
| US8686381B2 (en) * | 2010-06-28 | 2014-04-01 | Media Lario S.R.L. | Source-collector module with GIC mirror and tin vapor LPP target system |
| US20120050707A1 (en) * | 2010-08-30 | 2012-03-01 | Media Lario S.R.L | Source-collector module with GIC mirror and tin wire EUV LPP target system |
| US20120050706A1 (en) * | 2010-08-30 | 2012-03-01 | Media Lario S.R.L | Source-collector module with GIC mirror and xenon ice EUV LPP target system |
| US8344339B2 (en) * | 2010-08-30 | 2013-01-01 | Media Lario S.R.L. | Source-collector module with GIC mirror and tin rod EUV LPP target system |
| US8258485B2 (en) * | 2010-08-30 | 2012-09-04 | Media Lario Srl | Source-collector module with GIC mirror and xenon liquid EUV LPP target system |
| DE102010039965B4 (de) | 2010-08-31 | 2019-04-25 | Carl Zeiss Smt Gmbh | EUV-Kollektor |
| CN102621815B (zh) * | 2011-01-26 | 2016-12-21 | Asml荷兰有限公司 | 用于光刻设备的反射光学部件及器件制造方法 |
| US9632419B2 (en) | 2011-09-22 | 2017-04-25 | Asml Netherlands B.V. | Radiation source |
| NL2010274C2 (en) * | 2012-02-11 | 2015-02-26 | Media Lario Srl | Source-collector modules for euv lithography employing a gic mirror and a lpp source. |
| JP2013211517A (ja) * | 2012-03-01 | 2013-10-10 | Gigaphoton Inc | Euv光集光装置 |
| DE102012220465A1 (de) | 2012-11-09 | 2014-05-15 | Carl Zeiss Smt Gmbh | EUV-Kollektor |
| EP2746850B1 (en) | 2012-12-20 | 2015-03-18 | USHIO Denki Kabushiki Kaisha | Method of manufacturing mirror shells of a nested shells grazing incidence mirror |
| US8872143B2 (en) * | 2013-03-14 | 2014-10-28 | Asml Netherlands B.V. | Target for laser produced plasma extreme ultraviolet light source |
| DE102014006265B4 (de) | 2013-05-03 | 2017-08-24 | Media Lario S.R.L. | Sn-dampf-euv-llp-quellsystem für die euv-lithographie |
| US9585236B2 (en) | 2013-05-03 | 2017-02-28 | Media Lario Srl | Sn vapor EUV LLP source system for EUV lithography |
| DE102013107192A1 (de) | 2013-07-08 | 2015-01-08 | Carl Zeiss Laser Optics Gmbh | Reflektives optisches Element für streifenden Einfall im EUV-Wellenlängenbereich |
| IT202000017086A1 (it) * | 2020-07-14 | 2022-01-14 | Istituto Naz Di Astrofisica | Procedimento per la realizzazione di elementi ottici per ottiche di telescopi utilizzabili in missioni spaziali |
Family Cites Families (34)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6566668B2 (en) * | 1997-05-12 | 2003-05-20 | Cymer, Inc. | Plasma focus light source with tandem ellipsoidal mirror units |
| US6586757B2 (en) | 1997-05-12 | 2003-07-01 | Cymer, Inc. | Plasma focus light source with active and buffer gas control |
| US6278764B1 (en) | 1999-07-22 | 2001-08-21 | The Regents Of The Unviersity Of California | High efficiency replicated x-ray optics and fabrication method |
| US6831963B2 (en) * | 2000-10-20 | 2004-12-14 | University Of Central Florida | EUV, XUV, and X-Ray wavelength sources created from laser plasma produced from liquid metal solutions |
| EP1152555A1 (en) | 2000-05-03 | 2001-11-07 | Media Lario S.r.L. | Telescope mirror for high bandwidth free space optical data transmission |
| US7180081B2 (en) * | 2000-06-09 | 2007-02-20 | Cymer, Inc. | Discharge produced plasma EUV light source |
| US7410265B2 (en) * | 2000-09-13 | 2008-08-12 | Carl Zeiss Smt Ag | Focusing-device for the radiation from a light source |
| US7916388B2 (en) * | 2007-12-20 | 2011-03-29 | Cymer, Inc. | Drive laser for EUV light source |
| US6633048B2 (en) | 2001-05-03 | 2003-10-14 | Northrop Grumman Corporation | High output extreme ultraviolet source |
| DE10158216A1 (de) | 2001-11-28 | 2003-06-18 | Carlos Alberto Valenzuela | Spiegel, optisches Abbildungssystem und deren Verwendung |
| DE10214259A1 (de) * | 2002-03-28 | 2003-10-23 | Zeiss Carl Semiconductor Mfg | Kollektoreinheit für Beleuchtungssysteme mit einer Wellenlänge <193 nm |
| TWI242690B (en) * | 2002-08-15 | 2005-11-01 | Asml Netherlands Bv | Reflector assembly, lithographic projection apparatus, radiation system with the reflector assembly, and method of manufacturing an integrated structure by a lithographic process |
| DE60319735T2 (de) * | 2002-12-19 | 2009-04-16 | Carl Zeiss Smt Ag | Beleuchtungssytem mit einer effizienteren kollektoroptik |
| US7217940B2 (en) * | 2003-04-08 | 2007-05-15 | Cymer, Inc. | Collector for EUV light source |
| US7075713B2 (en) * | 2003-05-05 | 2006-07-11 | University Of Central Florida Research Foundation | High efficiency collector for laser plasma EUV source |
| US6841322B1 (en) | 2003-06-30 | 2005-01-11 | Intel Corporation | Detecting erosion in collector optics with plasma sources in extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography systems |
| US7230258B2 (en) | 2003-07-24 | 2007-06-12 | Intel Corporation | Plasma-based debris mitigation for extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light source |
| FR2860385B1 (fr) * | 2003-09-26 | 2007-06-01 | Cit Alcatel | Source euv |
| JP4584261B2 (ja) | 2003-11-25 | 2010-11-17 | メディア ラリオ ソシエタ ア レスポンサビリタ リミタータ | 電鋳による冷却および熱交換システムの製造 |
| US7423275B2 (en) | 2004-01-15 | 2008-09-09 | Intel Corporation | Erosion mitigation for collector optics using electric and magnetic fields |
| US7196342B2 (en) * | 2004-03-10 | 2007-03-27 | Cymer, Inc. | Systems and methods for reducing the influence of plasma-generated debris on the internal components of an EUV light source |
| US7164144B2 (en) * | 2004-03-10 | 2007-01-16 | Cymer Inc. | EUV light source |
| US7483223B2 (en) * | 2004-05-06 | 2009-01-27 | Carl Zeiss Smt Ag | Optical component having an improved transient thermal behavior and method for improving the transient thermal behavior of an optical component |
| FR2871622B1 (fr) * | 2004-06-14 | 2008-09-12 | Commissariat Energie Atomique | Dispositif de generation de lumiere dans l'extreme ultraviolet et application a une source de lithographie par rayonnement dans l'extreme ultraviolet |
| US7868304B2 (en) * | 2005-02-07 | 2011-01-11 | Asml Netherlands B.V. | Method for removal of deposition on an optical element, lithographic apparatus, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby |
| DE102005014433B3 (de) * | 2005-03-24 | 2006-10-05 | Xtreme Technologies Gmbh | Verfahren und Anordnung zur effizienten Erzeugung von kurzwelliger Strahlung auf Basis eines lasererzeugten Plasmas |
| DE102005052257B4 (de) | 2005-11-02 | 2013-11-14 | Symrise Ag | Verfahren zur Herstellung von C1-C8-Alkancarbonsäure-C1-C4-alkylestern |
| DE102005053415A1 (de) * | 2005-11-04 | 2007-05-10 | Carl Zeiss Laser Optics Gmbh | Optisches Bauelement mit verbessertem thermischen Verhalten |
| US7372049B2 (en) | 2005-12-02 | 2008-05-13 | Asml Netherlands B.V. | Lithographic apparatus including a cleaning device and method for cleaning an optical element |
| DE102006027856B3 (de) | 2006-06-13 | 2007-11-22 | Xtreme Technologies Gmbh | Anordnung zur Erzeugung von extrem ultravioletter Strahlung mittels elektrischer Entladung an regenerierbaren Elektroden |
| ATE528692T1 (de) * | 2006-07-28 | 2011-10-15 | Media Lario Srl | Optische multireflexionssysteme und ihre herstellung |
| TW200808134A (en) * | 2006-07-28 | 2008-02-01 | Ushio Electric Inc | Light source device for producing extreme ultraviolet radiation and method of generating extreme ultraviolet radiation |
| ATE528693T1 (de) * | 2006-09-15 | 2011-10-15 | Media Lario Srl | Optisches kollektorsystem |
| EP2076801A1 (en) * | 2006-10-13 | 2009-07-08 | Media Lario S.r.L. | Coated mirrors and their fabication |
-
2008
- 2008-01-28 EP EP08001536.5A patent/EP2083328B1/en active Active
-
2009
- 2009-01-28 US US12/734,829 patent/US8411815B2/en active Active
- 2009-01-28 JP JP2010543446A patent/JP5368478B2/ja active Active
- 2009-01-28 DE DE112009000120T patent/DE112009000120T5/de not_active Ceased
- 2009-01-28 WO PCT/EP2009/000539 patent/WO2009095220A2/en active Application Filing
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2011512647A (ja) | 2011-04-21 |
| EP2083328A1 (en) | 2009-07-29 |
| US8411815B2 (en) | 2013-04-02 |
| EP2083328B1 (en) | 2013-06-19 |
| WO2009095220A3 (en) | 2009-11-26 |
| DE112009000120T5 (de) | 2011-03-17 |
| US20100303199A1 (en) | 2010-12-02 |
| WO2009095220A2 (en) | 2009-08-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5368478B2 (ja) | レーザ生成プラズマ源の斜入射集光光学系 | |
| US7843632B2 (en) | EUV optics | |
| NL2014254B1 (en) | Source-Collector modules for EUV lithography employing a GIC mirror and a LPP source. | |
| JP4799620B2 (ja) | 放射システムおよびリソグラフィ装置 | |
| JP5856382B2 (ja) | Euvの集光を強化したeuv集光器システム | |
| US6278764B1 (en) | High efficiency replicated x-ray optics and fabrication method | |
| EP1946331B1 (en) | Mirror for high power euv lamp system | |
| EP1730763A2 (en) | Euv light source | |
| WO2008012111A1 (en) | Multi-reflection optical systems and their fabrication | |
| US7211810B2 (en) | Method for the protection of an optical element, lithographic apparatus, and device manufacturing method | |
| JP2010506224A (ja) | コーティングされたミラー及びその製造 | |
| JP6731541B2 (ja) | 極端紫外光生成装置 | |
| JP2005294087A (ja) | 光源ユニット、照明光学装置、露光装置および露光方法 | |
| JP4725814B2 (ja) | 光源ユニット、照明光学装置、露光装置および露光方法 | |
| US12028958B2 (en) | High-brightness laser produced plasma source and method of generation and collection radiation | |
| WO2023079042A1 (en) | High-brightness laser produced plasma source and method of generating and collecting radiation | |
| JP2005099571A (ja) | 多層膜反射鏡、反射多層膜の成膜方法、成膜装置及び露光装置 | |
| US20080073592A1 (en) | Reflective optical illumination collector | |
| JP6926227B2 (ja) | 極端紫外光生成装置及び電子デバイスの製造方法 | |
| Kubiak et al. | High‐power laser plasma sources: Soft x‐ray projection lithography and other applications |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120124 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20120124 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20121227 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130129 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130412 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130514 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130719 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130903 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130912 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5368478 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |