JP5249024B2 - 電流を通す埋込み受動導体を使用するインプラント、システムおよび方法に対する改良 - Google Patents
電流を通す埋込み受動導体を使用するインプラント、システムおよび方法に対する改良 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5249024B2 JP5249024B2 JP2008519515A JP2008519515A JP5249024B2 JP 5249024 B2 JP5249024 B2 JP 5249024B2 JP 2008519515 A JP2008519515 A JP 2008519515A JP 2008519515 A JP2008519515 A JP 2008519515A JP 5249024 B2 JP5249024 B2 JP 5249024B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- electrode
- stimulation
- pickup
- electrodes
- conductive
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 title claims description 123
- 239000007943 implant Substances 0.000 title description 41
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title description 28
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 title description 5
- 230000000638 stimulation Effects 0.000 claims description 144
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 claims description 5
- 229920001296 polysiloxane Polymers 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000033001 locomotion Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000001902 propagating effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 210000001519 tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 105
- 210000005036 nerve Anatomy 0.000 description 42
- 206010033675 panniculitis Diseases 0.000 description 16
- 210000004304 subcutaneous tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 16
- 208000002193 Pain Diseases 0.000 description 13
- 230000036407 pain Effects 0.000 description 13
- 230000004936 stimulating effect Effects 0.000 description 13
- 210000003205 muscle Anatomy 0.000 description 11
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 10
- 238000002513 implantation Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000005611 electricity Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 description 7
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 description 7
- 229910001285 shape-memory alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000002646 transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229920004934 Dacron® Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 229920006309 Invista Polymers 0.000 description 4
- UELITFHSCLAHKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N acibenzolar-S-methyl Chemical compound CSC(=O)C1=CC=CC2=C1SN=N2 UELITFHSCLAHKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000005020 polyethylene terephthalate Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 241000282414 Homo sapiens Species 0.000 description 3
- 208000008238 Muscle Spasticity Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 230000036982 action potential Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 210000003050 axon Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000560 biocompatible material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000002537 cosmetic Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 3
- WABPQHHGFIMREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N lead(0) Chemical compound [Pb] WABPQHHGFIMREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 231100000252 nontoxic Toxicity 0.000 description 3
- 230000003000 nontoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 3
- 208000018198 spasticity Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 229910000838 Al alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 208000008035 Back Pain Diseases 0.000 description 2
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 206010028289 Muscle atrophy Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 229910000990 Ni alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000000746 body region Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 230000036760 body temperature Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000000133 brain stem Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 230000001276 controlling effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000035475 disorder Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000014509 gene expression Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001727 in vivo Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000007794 irritation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000020763 muscle atrophy Effects 0.000 description 2
- 201000000585 muscular atrophy Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 230000001537 neural effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 235000001968 nicotinic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 230000000399 orthopedic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008447 perception Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 2
- 210000002784 stomach Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 208000024891 symptom Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 206010002329 Aneurysm Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 101100011382 Aspergillus niger eglB gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010003694 Atrophy Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000012639 Balance disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000010392 Bone Fractures Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000024172 Cardiovascular disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010010904 Convulsion Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 101100285402 Danio rerio eng1a gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100285408 Danio rerio eng2a gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 208000014094 Dystonic disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 101150067694 ENG1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010017076 Fracture Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000018522 Gastrointestinal disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000016621 Hearing disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000282412 Homo Species 0.000 description 1
- 206010020852 Hypertonia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010021518 Impaired gastric emptying Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010021639 Incontinence Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000008930 Low Back Pain Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 1
- 208000019695 Migraine disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000016285 Movement disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000010428 Muscle Weakness Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000029578 Muscle disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000021642 Muscular disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010028372 Muscular weakness Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010052904 Musculoskeletal stiffness Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010028836 Neck pain Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000028389 Nerve injury Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000018737 Parkinson disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000004550 Postoperative Pain Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010037779 Radiculopathy Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 101100172294 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) ACF2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100172292 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) DSE4 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100172293 Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) eng2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010040880 Skin irritation Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229920000147 Styrene maleic anhydride Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910001069 Ti alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 206010044565 Tremor Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000000921 Urge Urinary Incontinence Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010046555 Urinary retention Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000013521 Visual disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000027418 Wounds and injury Diseases 0.000 description 1
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910001297 Zn alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000003187 abdominal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000036592 analgesia Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000037444 atrophy Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002567 autonomic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000033228 biological regulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000029162 bladder disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 210000000988 bone and bone Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000008468 bone growth Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000004556 brain Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000003169 central nervous system Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 206010008129 cerebral palsy Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000026106 cerebrovascular disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035606 childbirth Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003477 cochlea Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000010118 dystonia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 210000003027 ear inner Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000000245 forearm Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005021 gait Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002496 gastric effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035876 healing Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000002216 heart Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 208000014617 hemorrhoid Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000015181 infectious disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000004615 ingredient Substances 0.000 description 1
- 208000014674 injury Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000007918 intramuscular administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000003734 kidney Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000013150 knee replacement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 206010027599 migraine Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000037230 mobility Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007659 motor function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 201000006938 muscular dystrophy Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 210000004165 myocardium Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000002402 nanowire electron scattering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008764 nerve damage Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000000944 nerve tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000004007 neuromodulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002232 neuromuscular Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000001328 optic nerve Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 208000035824 paresthesia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000001575 pathological effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003836 peripheral circulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000000578 peripheral nerve Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000001428 peripheral nervous system Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000012805 post-processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007781 pre-processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000644 propagated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 206010061928 radiculitis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003019 respiratory muscle Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000002027 skeletal muscle Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000036556 skin irritation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 231100000475 skin irritation Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 201000002859 sleep apnea Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000019116 sleep disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000002269 spontaneous effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007920 subcutaneous administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009885 systemic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000017423 tissue regeneration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000037317 transdermal delivery Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009966 trimming Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000003708 urethra Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000003932 urinary bladder Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 208000029257 vision disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000029663 wound healing Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/02—Details
- A61N1/04—Electrodes
- A61N1/05—Electrodes for implantation or insertion into the body, e.g. heart electrode
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/18—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes
- A61N1/32—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents
- A61N1/36—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents for stimulation
- A61N1/36014—External stimulators, e.g. with patch electrodes
- A61N1/36021—External stimulators, e.g. with patch electrodes for treatment of pain
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/18—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes
- A61N1/32—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents
- A61N1/36—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents for stimulation
- A61N1/36014—External stimulators, e.g. with patch electrodes
- A61N1/36017—External stimulators, e.g. with patch electrodes with leads or electrodes penetrating the skin
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/18—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes
- A61N1/32—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents
- A61N1/36—Applying electric currents by contact electrodes alternating or intermittent currents for stimulation
- A61N1/3605—Implantable neurostimulators for stimulating central or peripheral nerve system
- A61N1/3606—Implantable neurostimulators for stimulating central or peripheral nerve system adapted for a particular treatment
- A61N1/36071—Pain
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/02—Details
- A61N1/04—Electrodes
- A61N1/0404—Electrodes for external use
- A61N1/0408—Use-related aspects
- A61N1/0456—Specially adapted for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation [TENS]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/02—Details
- A61N1/04—Electrodes
- A61N1/05—Electrodes for implantation or insertion into the body, e.g. heart electrode
- A61N1/0551—Spinal or peripheral nerve electrodes
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Pain & Pain Management (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Electrotherapy Devices (AREA)
Description
本発明は、外部デバイスかまたは埋込みデバイスのいずれかに、複数の標的体内組織に、そして選択的な標的体内組織に電流を通す受動導体(passive electrical conductor)を使用するインプラント、システムおよび方法に対する改良に関する。
体内組織および神経の電気刺激は、さまざまな指示のために広く使用されている。標的とされる体内部位または器官に電気刺激を送達するいくつかの手法が知られている。手法には、刺激の送達を集中させる必要のあるものもあり、それほど送達の的を絞る必要のないものもある。
本発明は、電流を外部電気デバイス又は埋込み電気デバイスのいずれかに、複数の標的体内組織に、そして選択的な標的体内組織に電流を流す受動導体を使用するインプラント、システムおよび方法に対する改良に関する。
a)対象の皮膚に電気を通すために表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極を提供するステップと、
b)対象の皮膚の上に間隔を空けた関係で配置される表面陰極電極と表面陽極電極との間を流れる電流の少なくとも一部のための導電経路としての役割を果たすインプラントを提供し、かつ電流の一部を標的体内組織まで伝達するステップであって、インプラントが、
埋め込まれると、表面陰極電極または表面陽極電極のいずれかまたは両方の下方に位置する皮下組織から標的体内組織まで延在するために十分な長さの受動導体を備え、
導体が、ピックアップ端および刺激端を有し、かつその端部の間にわたって絶縁され(being insulated between its ends)、ピックアップ端が複数の導電性ピックアップ電極を有し、刺激端が複数の導電性刺激電極を有し、導電性ピックアップ電極の各々が、1つまたは複数の対応する導電性刺激電極と電気的に接続され、それにより、表面陰極電極または表面陽極電極のいずれかまたは両方を導電性ピックアップ電極のうちの1つの上に配置することにより、電流の一部が、導電性ピックアップ電極のうちの1つに電気的に接続された1つまたは複数の対応する導電性刺激電極に伝達される、ステップと、
c)導電性ピックアップ電極を皮下組織に配置し、導電性刺激電極を標的体内組織の近傍に(in the vicinity of the target body tissue)配置し、対応する導電性刺激電極のうちの1つまたは複数を標的体内組織に近接して(proximate to the target body tissue)配置して、インプラントを対象の皮膚の下に完全に埋め込むステップと、
d)表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極を対象の皮膚の上に間隔を空けた関係で配置するステップであって、表面陰極電極または表面陽極電極のいずれかまたは両方を、標的体内組織に近接する1つまたは複数の対応する導電性刺激電極に電気的に接続される導電性ピックアップ電極の上に配置し、それにより、電流の一部が、標的体内組織を刺激するために導体を通って1つまたは複数の対応する導電性刺激電極まで伝達される、ステップと、
e)表面陰極電極と表面陽極電極との間に、直流電流、脈動電流または交流電流を印加して、電流の一部が、標的体内組織を刺激するために十分、インプラント内を流れるようにする、ステップと、
を含む、方法を提供する。
i)対象の皮膚に電気を通すための表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極であって、対象の皮膚の上に間隔を空けた関係で配置されると、表面陰極電極と表面陽極電極との下方かつ間に位置する皮下組織に電流を伝達する、表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極と、
ii)表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極に電気的に接続された、対象の体外の刺激装置であって、表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極に電流を供給する、刺激装置と、
iii)表面陰極電極と表面陽極電極との間を流れる電流の一部をピックアップし、かつ電流の一部を標的体内組織に伝達するインプラントであって、
埋め込まれると、表面陰極電極または表面陽極電極のいずれかまたは両方の下方に位置する皮下組織から標的体内組織まで延在するために十分な長さの受動導体を備え、
導体が、ピックアップ端および刺激端を有し、かつその端部の間にわたって絶縁され、ピックアップ端が複数の導電性ピックアップ電極を有し、刺激端が複数の導電性刺激電極を有し、導電性ピックアップ電極の各々が、1つまたは複数の対応する導電性刺激電極に電気的に接続され、それによって、表面陰極電極または表面陽極電極のいずれかまたは両方を導電性ピックアップ電極のうちの1つの上に配置することにより、電流の一部が、導電性ピックアップ電極のうちの1つに電気的に接続された1つまたは複数の対応する導電性刺激電極に伝達される、インプラントと、
を備えるシステムを提供する。
a)対象の皮膚に電気を通すために表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極を提供するステップと、
b)対象の皮膚の上に間隔を空けた関係で配置される表面陰極電極と表面陽極電極との間を流れる電流の少なくとも一部のための導電経路としての役割を果たすインプラントを提供し、かつ電流の一部を1つまたは複数の電気デバイスまで伝達するステップであって、インプラントが、
埋め込まれると、表面陰極電極または表面陽極電極のいずれかまたは両方の下方に位置する皮下組織から1つまたは複数の電気デバイスまで延在するために十分な長さの受動導体を備え、
導体が、ピックアップ端および送達端を有し、かつその端部の間にわたって絶縁され、ピックアップ端が、電流の十分な部分が導体を通って流れるのを可能にする十分な表面積を有する電気的終端を形成し、送達端が、電流の一部を1つまたは複数の電気デバイスに送達するための電気的終端を形成する、ステップと、
c)1つまたは複数の電気デバイスを提供するステップと、
d)ピックアップ端を表面陰極電極または表面陽極電極のいずれかまたは両方の下方に位置する皮下組織に配置して、インプラントを対象の皮膚の下に完全に埋め込むステップと、
e)1つまたは複数の電気デバイスを対象の皮膚の下に完全に埋め込むステップであって、1つまたは複数の電気デバイスが導体に沿って配置されるかまたはピックアップ端の電気的終端として形成され、1つまたは複数の電気デバイスが、導体に電気的に接続され、それにより電流が導体から1つまたは複数の電気デバイスに伝達される、ステップと、
f)表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極を対象の皮膚の上に間隔を空けた関係で配置するステップであって、表面陰極電極または表面陽極電極のいずれかまたは両方を導体のピックアップ端の上に配置し、そのため電流の一部が導体を通って1つまたは複数の電気デバイスに伝達され、かつ体内組織を通って表面陰極電極または表面陽極電極のいずれかまで戻る、ステップと、
g)表面陰極電極と表面陽極電極との間に、直流電流、脈動電流または交流電流を印加することにより、電流の一部が、1つまたは複数の電気デバイスに電流を送達するために十分、インプラントを流れるようにする、ステップと、
を含む、方法を提供する。
i)対象の皮膚に電気を通すための表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極であって、対象の皮膚の上に間隔を空けた関係で配置されると、表面陰極電極と表面陽極電極との下方にかつ間に位置する皮下組織に電流を伝達する、表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極と、
ii)表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極に電気的に接続された、対象の体外の刺激装置であって、表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極に電流を供給する、刺激装置と、
iii)表面陰極電極と表面陽極電極との間を流れる電流の一部をピックアップし、かつ電流のその部分を標的体内組織に伝達するインプラントであって、
埋め込まれると、表面陰極電極または表面陽極電極のいずれかまたは両方の下方に位置する皮下組織から1つまたは複数の電気デバイスまで延在するために十分な長さの受動導体を備え、
導体が、ピックアップ端および送達端を有し、かつその端部の間にわたって絶縁され、ピックアップ端が、表面陰極電極と表面陽極電極との間の体内組織内を流れる電流に優先して、印加されている電流の十分な部分が導体内を流れるのを可能にする、十分な表面積を有する電気的終端を形成し、それにより、1つまたは複数のデバイスに電流が供給され、送達端が、電流の一部を1つまたは複数のデバイスに送達するために1つまたは複数のデバイスとの電気的終端を形成する、インプラントと、
を備え、
iv)1つまたは複数の電気デバイスが、導体に電気的に接続され、それにより電流が導体から1つまたは複数の電気デバイスまで伝達される、
システムを提供する。
a)対象の皮膚に電気を通すために表面電極を提供するステップと、
b)標的体内組織からの電気信号のための導電経路としての役割を果たすインプラントを提供するステップであって、インプラントが、
埋め込まれると、対象の皮膚の上に配置された表面電極の下方に位置する皮下組織から標的体内組織まで延在するために十分な長さの受動導体を備え、
導体がピックアップ端および送達端を有し、かつその端部の間にわたって絶縁され、ピックアップ端が、標的体内組織からの電気信号が導体を通って流れるのを可能にする十分な表面積を有する電気的終端を形成し、送達端が、電気信号を1つまたは複数の電気デバイスに送達するための電気的終端を形成する、ステップと、
c)送達端を表面電極の下方に位置する皮下組織に配置し、ピックアップ端を標的体内組織に近接して配置して、インプラントを対象の皮膚の下に完全に埋め込むステップと、
d)表面電極を対象の皮膚の上に配置するステップであって、表面電極を導体の送達端の上に配置し、表面電極を1つまたは複数の外部デバイスに電気的に接続し、それにより標的体内組織からの電気信号が導体を通って1つまたは複数の外部デバイスまで伝達されるようにする、ステップと、
を含む、方法を提供する。
i)対象の皮膚に電気を通す少なくとも1つの表面電極と、
ii)標的体内組織からの電気信号をピックアップし、かつ電気信号を1つまたは複数の外部デバイスに伝送するインプラントであって、
埋め込まれると、少なくとも1つの表面陽極電極の下方に位置する皮下組織から標的体内組織まで延在するために十分な長さの受動導体を備え、
導体がピックアップ端および送達端を有し、かつその端部の間にわたって絶縁され、ピックアップ端が、標的体内組織からの信号が導体を通って流れるのを可能にする十分な表面積を有する電気的終端を形成し、送達端が、電気信号を1つまたは複数の電気デバイスに送達するための電気的終端を形成する、インプラントと、
を備える、システムを提供する。
a)対象の皮膚に電気を通すために1つまたは複数の表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極を提供するステップと、
b)1つまたは複数の外部刺激装置を提供するステップであって、1つまたは複数の外部刺激装置が、対象の体外にあり、1つまたは複数の表面陰極電極および1つまたは複数の表面陽極電極に電気的に接続され、1つまたは複数の表面陰極電極および1つまたは複数の表面陽極電極に電流を供給する、ステップと、
c)複数の標的体内組織を独立してまたは一致して電気的に刺激するために複数のインプラントであって、各インプラントが、対象の皮膚の上に間隔を空けた関係で配置される1つまたは複数の表面陰極電極と1つまたは複数の表面陽極電極との間を流れる電流の少なくとも一部のための導電経路としての役割を果たす、インプラントを提供し、かつ電流の一部を複数の標的体内組織に伝達するステップであって、各インプラントが、
埋め込まれると、1つまたは複数の表面陰極電極または1つまたは複数の表面陽極電極のいずれかの下方に位置する皮下組織から複数の標的体内組織複数の標的体内組織まで延在するために十分な長さの受動導体を備え、
各導体が、ピックアップ端および刺激端を有し、かつその端部の間にわたって絶縁され、ピックアップ端が、標的体内組織が刺激されるように電流の十分な部分が導体内を流れるのを可能にする十分な表面積を有する電気的終端を形成し、刺激端が、電流の一部を標的体内組織に送達するための電気的終端を形成する、ステップと、
d)導体のピックアップ端を、1つまたは複数の表面陰極電極または1つまたは複数の表面陽極電極のいずれかまたは両方の下方に位置する皮下組織に配置し、刺激端を複数の標的体内組織に近接して配置して、複数のインプラントを対象の皮膚の下に完全に埋め込むステップと、
e)表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極を対象の皮膚の上に間隔を空けた関係で配置するステップであって、表面陰極電極または表面陽極電極のいずれかまたは両方を導体のピックアップ端の上に配置し、それにより、電流の一部が導体を通って複数の標的体内組織に伝達され、それにより電流が複数の標的体内組織内を流れ、かつ体内組織を通って表面陰極電極または表面陽極電極のいずれかに戻る、ステップと、
f)1つまたは複数の表面陰極電極と1つまたは複数の表面陽極電極との間に、直流電流、脈動電流または交流電流を印加することにより、電流の一部が、複数の標的体内組織を刺激するために十分、複数のインプラントを流れるようにするステップと、
を含む、方法を提供する。
i)対象の皮膚に電気を通すための表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極であって、対象の皮膚の上に間隔を空けた関係で配置されると、複数の標的体内組織に電流を伝達する、表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極と、
ii)表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極に電気的に接続された、対象の体外の刺激装置であって、表面陰極電極および表面陽極電極に、直流電流、脈動電流または交流電流を印加する、刺激装置と、
iii)表面陰極電極と表面陽極電極との間を流れる電流の一部をピックアップし、かつ電流のその部分を複数の標的体内組織に伝達する複数のインプラントであって、その各々が、
埋め込まれると、表面陰極電極または表面陽極電極のいずれかの下方に位置する皮下組織から標的体内組織まで延在するために十分な長さの受動導体を備え、
導体が、ピックアップ端および刺激端を有し、かつその端部の間にわたって絶縁され、ピックアップ端が、表面陰極電極と表面陽極電極との間の体内組織内を流れる電流に優先して、印加される電流の十分な部分が導体内を流れるのを可能にする十分な表面積を有する電気的終端を形成し、それにより標的体内組織が刺激され、刺激端が、電流の一部を標的体内組織に伝達するための電気的終端を形成する、インプラントと、
を備える、システムを提供する。
本発明は、プロハースカ(Prochazka)による国際公開第2005/070494A1号パンフレット(2005年8月4日に公開、2004年1月22日に出願された米国仮特許出願第60/538,618号明細書に対する優先権を主張)と、ゴーント(Gaunto)およびプロハースカ(Prochazka)による2006年1月23日に出願された米国特許出願第11/337,824号明細書におい述べられているような「ルータシステム」の改良に関する。これら出願は、治療される症状に応じて神経インパルスを活性化するかまたは遮断する問題において神経等の標的体内組織を電気的に刺激するインプラントについて述べている。
本発明は、電気エネルギーを、電流によって電力が供給されるかまたは電気信号を処理する1つまたは複数の電気デバイスに送達するために使用することができるルータシステムを考慮する。かかる電気デバイスの非限定例には、たとえば、センサ(たとえばENGセンサ、温度センサ、圧力センサ、pHセンサ、インピーダンスセンサおよび当業者には既知である他のセンサ)、増幅器、フィルタ、高電圧/定電流発生器、スイッチ、電源、電池、電池充電回路、小型充電式電池、プロセッサ、周波数シフタ、過刺激保護回路、通信モジュール(有線または無線)および当業者に既知である他の適当なデバイスが含まれ得る。かかる電気デバイスは、体外にあってもよく、または体内に埋め込まれてもよい。
ルータシステムを、体内の標的組織からの電気信号(単極信号および双極信号)(電気信号グラフィック(electroneurographic)またはENG信号)を外部電気デバイスに送達するために使用することができる。一例として、ENGは、標的組織または器官の完全性を、標的組織または器官の自発的な電気的活動を記録することにより、または刺激に対する電気的に被刺激性の組織または器官の反応を評価することにより検査する、一般的な非侵襲性試験である。さらなる例として、聴性脳幹反応(Auditory Brainstem Response)(ABR)試験は、内耳および脳幹を含む上部聴覚系に関する目的情報(objective information)を提供する。標的組織は、通常、神経、たとえば末梢神経か、または器官、たとえば神経によって刺激される特定の筋肉である。
本発明は、ルータシステムを、電流を1つまたは複数の埋込み電気デバイス48に送達するために使用することも可能である、ということを考慮する。この目的のために、埋込み受動導体24は、ピックアップ端26と送達端28(刺激端28自体ではなく)とを有する。ピックアップ端26は、電流の十分な部分が導体24内を流れるのを可能にする。送達端28は、電流を1つまたは複数の電気デバイス48に送達する。
国際公開第2005/070494A1号パンフレットおよび米国特許出願第11/337,824号明細書は、2つ以上の標的体内組織を、神経インパルスを活性化することとは独立してまたはそれと一致して電気的に刺激するために複数のインプラントを含むものとして、ルータシステムの一実施形態について述べている。複数のインプラントが存在するためには、異なる標的体内組織を独立してまたは一致して刺激するために、複数の表面陰極電極と1つまたは複数の表面陽極電極とを、インプラントに対して適当に配置する必要がある。1つまたは複数の外部刺激装置が必要である。本発明は、後述するようないくつかの構成を考慮する。
この構成では、各表面陰極電極20a、20bを、異なる標的体内組織12a、12bまで延在する別個の埋込み受動導体24a、24bの上に配置する。各導体24a、24bは、そのピックアップ端26a、26bにおいて電気的終端30a、30bを形成し、複数の表面陰極電極20a、20bと1つの陽極電極22との間に流れる電流の少なくとも一部のための導電経路を提供する。各表面陰極電極20a、20bを、別個の刺激装置50a、50bに接続してもよく(すなわち、図8Aに示すように2つの別個のチャネルを形成する)、または単一の多チャネル刺激装置50に接続してもよい(たとえば、図8Bに示すように導電性材料65上に配置された単一パッチ、2チャネル表面電極)。表面陽極電極22を、別個の刺激装置50a、50bの各々に接続してもよく、または単一の多チャネル刺激装置50に接続してもよい。
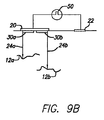
この構成では、表面陰極電極20を、2つ以上の別個の埋込み受動導体24a、24b、24cが任意の適当な手段、たとえば圧着接続67によるかまたは溶接によって接続される2つ以上の終端30の上に配置する(図9A)。代替構成では、表面陰極電極20を、2つ以上の導体24a、24bに電流を提供するために2つ以上の別個の終端30a、30bの上に配置してもよい(図9B)。
表面陰極電極20および刺激のあり得る位置ずれを補償するために、表面陰極電極20を切片に分割してもよく、各切片は、スイッチングマトリクスによって外部刺激装置50に個々に接続される。スイッチは、手動でまたはコントローラによって操作される。それにより、電気刺激は、導体24の終端30の上方に配置される表面陰極電極20の領域に主に送達される。当業者には、最適な刺激を送達するために、たとえばインピーダンスが最低である切片を選択することにより、適当なアルゴリズムを確定することができる、ということが理解されよう。この構成は、導体24との位置合せをより容易にし、電流を伝導する皮膚表面10をより小さくし、複数の導体24が存在する場合に刺激を平衡させる方法(a way of balancing stimulation)を提供する。
上述したように複数の標的体内組織を刺激するためにルータシステムを使用することができるが、特定の体内組織に対し他の体内組織より大きい刺激が必要である場合もある。たとえば、疼痛治療のための皮下刺激において、疼痛の領域全体を刺激することが必要である場合もある。本発明は、電流を選択的に送達するためにルータシステムを使用することができることをさらに考慮する。
Gan, L., Bornes, T., Denington, A. and Prochazka, A. (2005) The stimulus router: a novel means of directing current from surface electrodes to nerves. IFESS 2005 Conference Proceedings, pp. 21-23
Memberg W.D., Peckham P.H, Keith M.W. (June 1994) A surgically implanted intramuscular electrode for an implantable neuromuscular stimulation system
IEEE Transactions on Rehabilitation Engineering 2(2): 80-91
Prochazka, A. (2004) Neural Prosthesis Program Meeting, NIH Meeting, November 2004
Gaunt, R.A. and Prochazka, A. Method of routing electrical current to bodily tissues via implanted passive conductors. 米国特許出願第11/337,824号明細書、2006年1月23日出願
Prochazka, A., Wieler, M., Kenwell, Z.R., Gauthier, M.J.A. (1996) Garment for applying controlled electrical stimulation to restore motor function.米国特許第5,562,707号明細書、1996年10月8日出願
Prochazka, A. Method and apparatus for controlling a device or process with vibrations generated by tooth clicks.国際公開第2004/034937号パンフレット、2003年10月16日公開
Prochazka, A. Method of routing electrical current to bodily tissues via implanted passive conductors.国際公開第2005/070494A1号パンフレット、2005年8月4日公開
Prochazka, A. Method and apparatus for controlling a device or process with vibrations generated by tooth clicks.米国特許第6,961,623号明細書、2005年11月1日発行
Claims (18)
- 刺激電極を含む第1終端及びピックアップ電極を含む第2終端を有する受動導体であって、前記刺激電極が標的組織に隣接し、前記ピックアップ電極が完全に皮膚の表面下に位置するよう、体内に配置されるための受動導体と、
前記受動導体の前記第2終端に接続された絶縁裏材であって、前記ピックアップ電極の効力を向上させるための絶縁裏材と、
を備える装置。 - 前記絶縁裏材が、シリコーン又はポリエステルからなる、請求項1に記載の装置。
- 前記絶縁裏材の少なくとも一部が、前記ピックアップ電極の周辺に配置される、請求項1に記載の装置。
- 前記ピックアップ電極の少なくとも一部がコイル状である、請求項1の装置。
- 前記刺激電極が複数の刺激電極のうちの一つの刺激電極である、請求項1の装置。
- 前記刺激電極の表面積が、約50平方ミリメートル以下である、請求項1の装置。
- 前記刺激電極の表面積が、約10平方ミリメートル以上約50平方ミリメートル以下である、請求項1の装置。
- 前記ピックアップ電極が複数のピックアップ電極のうちの一つのピックアップ電極であり、
前記刺激電極が複数の刺激電極のうちの一つの刺激電極であり、
前記複数の刺激電極の各々の刺激電極が、前記複数のピックアップ電極のうちの対応するピックアップ電極に電気的に接続されている、
請求項1の装置。 - 前記受動導体の前記第1終端に接続されたアンカを更に備え、
前記受動導体が体内に配置されたときに、前記アンカが、前記標的組織に対する前記刺激電極の動きを制限する、
請求項1の装置。 - 身体の外に配置されるための電気デバイスであり、電気信号を少なくとも送受信するための電気デバイスと、
前記電気デバイスに電気的に接続される電極であって、前記身体の皮膚の表面に接続されるための電極と、
ピックアップ電極を含む近位端部が前記電極の下方に位置するよう、完全に体内に配置されるための受動導体であり、前記近位端部及び刺激電極を含む遠位端部の間で前記電気信号の少なくとも一部を伝搬するための受動導体であり、前記刺激電極が標的組織に隣接し、前記近位端部が前記ピックアップ電極の効力を向上させるための絶縁裏材を含む受動導体と、
を備えるシステム。 - 前記電気デバイスが、刺激装置、信号発生器、増幅器、及びスイッチのいずれか一つを含む、請求項10のシステム。
- 前記受動導体の遠位端部が複数の刺激電極を含む、請求項10のシステム。
- 前記受動導体の前記近位端部がコイル状の前記ピックアップ電極を含み、
前記受動導体の前記遠位端部が複数の刺激電極を含む、
請求項10のシステム。 - 前記絶縁裏材がシリコーン又はポリエステルからなる、請求項10のシステム。
- 第1の電気的終端を含む第1終端及び第2の電気的終端を含む第2終端を有する受動導体であって、前記第1の電気的終端が標的組織に隣接して配置され、前記第2の電気的終端が皮膚の表面下に配置されるよう、体内に配置されるための受動導体と、
前記受動導体の第2終端に接続された絶縁裏材であって、前記皮膚の表面に接続された電極によって生じた経皮電流の一部を前記第2の電気的終端に向ける絶縁裏材と、
を備える装置。 - 前記絶縁裏材がシリコーン又はポリエステルからなる、請求項15の装置。
- 前記第1の電気的終端が約50平方ミリメートル以下の表面積を有する刺激電極であり、
前記第2の電気的終端がコイル状のピックアップ電極である、
請求項15の装置。 - 前記受動導体の第1終端に接続されたアンカを更に備え、前記受動導体が体内に配置されたときに、前記アンカが前記標的に対する前記第1の電気的終端の動きを制限する、請求項15の装置。
Applications Claiming Priority (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US69482205P | 2005-06-28 | 2005-06-28 | |
| US60/694,822 | 2005-06-28 | ||
| US70311705P | 2005-07-27 | 2005-07-27 | |
| US60/703,117 | 2005-07-27 | ||
| US78471306P | 2006-03-21 | 2006-03-21 | |
| US60/784,713 | 2006-03-21 | ||
| PCT/US2006/025146 WO2007002741A1 (en) | 2005-06-28 | 2006-06-28 | Improvements to an implant, system and method using implanted passive conductors for routing electrical current |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011281270A Division JP2012075933A (ja) | 2005-06-28 | 2011-12-22 | 電流を通す埋込み受動導体を使用するインプラント、システムおよび方法に対する改良 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008544813A JP2008544813A (ja) | 2008-12-11 |
| JP2008544813A5 JP2008544813A5 (ja) | 2009-07-16 |
| JP5249024B2 true JP5249024B2 (ja) | 2013-07-31 |
Family
ID=37149409
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008519515A Expired - Fee Related JP5249024B2 (ja) | 2005-06-28 | 2006-06-28 | 電流を通す埋込み受動導体を使用するインプラント、システムおよび方法に対する改良 |
| JP2011281270A Ceased JP2012075933A (ja) | 2005-06-28 | 2011-12-22 | 電流を通す埋込み受動導体を使用するインプラント、システムおよび方法に対する改良 |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011281270A Ceased JP2012075933A (ja) | 2005-06-28 | 2011-12-22 | 電流を通す埋込み受動導体を使用するインプラント、システムおよび方法に対する改良 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US8332029B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP1899002A1 (ja) |
| JP (2) | JP5249024B2 (ja) |
| AU (1) | AU2006261666B2 (ja) |
| CA (1) | CA2608397A1 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2007002741A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (90)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8626302B2 (en) * | 1998-06-03 | 2014-01-07 | Spr Therapeutics, Llc | Systems and methods to place one or more leads in muscle for providing electrical stimulation to treat pain |
| EP1706178B1 (en) | 2004-01-22 | 2013-04-24 | Rehabtronics Inc. | System for routing electrical current to bodily tissues via implanted passive conductors |
| US20100016929A1 (en) * | 2004-01-22 | 2010-01-21 | Arthur Prochazka | Method and system for controlled nerve ablation |
| US8099168B2 (en) | 2008-10-22 | 2012-01-17 | Martin William Roche | Post-operative pain inhibitor for joint replacement and method thereof |
| CA2608397A1 (en) | 2005-06-28 | 2007-01-04 | Bioness Development, Llc | Improvements to an implant, system and method using implanted passive conductors for routing electrical current |
| EP1981589B1 (en) * | 2006-01-23 | 2016-04-13 | Rehabtronics Inc. | System for routing electrical current to bodily tissues via implanted passive conductors |
| US8483820B2 (en) * | 2006-10-05 | 2013-07-09 | Bioness Inc. | System and method for percutaneous delivery of electrical stimulation to a target body tissue |
| US8738137B2 (en) | 2007-08-23 | 2014-05-27 | Bioness Inc. | System for transmitting electrical current to a bodily tissue |
| CA2697381A1 (en) * | 2007-08-23 | 2009-02-26 | Bioness, Inc. | System for transmitting electrical current to a bodily tissue |
| US9757554B2 (en) | 2007-08-23 | 2017-09-12 | Bioness Inc. | System for transmitting electrical current to a bodily tissue |
| CA2703867C (en) * | 2007-10-29 | 2017-06-20 | Case Western Reserve University | Onset-mitigating high-frequency nerve block |
| US7890182B2 (en) | 2008-05-15 | 2011-02-15 | Boston Scientific Neuromodulation Corporation | Current steering for an implantable stimulator device involving fractionalized stimulation pulses |
| US20090326602A1 (en) * | 2008-06-27 | 2009-12-31 | Arkady Glukhovsky | Treatment of indications using electrical stimulation |
| US8255057B2 (en) | 2009-01-29 | 2012-08-28 | Nevro Corporation | Systems and methods for producing asynchronous neural responses to treat pain and/or other patient conditions |
| EP2243510B1 (en) | 2009-04-22 | 2014-04-09 | Nevro Corporation | Sytems for selective high frequency spinal cord modulation for inhibiting pain with reduced side effects |
| WO2010124128A1 (en) | 2009-04-22 | 2010-10-28 | Nevro Corporation | Spinal cord modulation for inducing paresthetic and anesthetic effects, and associated systems and methods |
| US8788045B2 (en) | 2010-06-08 | 2014-07-22 | Bluewind Medical Ltd. | Tibial nerve stimulation |
| US8788048B2 (en) | 2010-11-11 | 2014-07-22 | Spr Therapeutics, Llc | Systems and methods for the treatment of pain through neural fiber stimulation |
| US8788047B2 (en) | 2010-11-11 | 2014-07-22 | Spr Therapeutics, Llc | Systems and methods for the treatment of pain through neural fiber stimulation |
| US8788046B2 (en) | 2010-11-11 | 2014-07-22 | Spr Therapeutics, Llc | Systems and methods for the treatment of pain through neural fiber stimulation |
| US9457186B2 (en) | 2010-11-15 | 2016-10-04 | Bluewind Medical Ltd. | Bilateral feedback |
| US9186504B2 (en) | 2010-11-15 | 2015-11-17 | Rainbow Medical Ltd | Sleep apnea treatment |
| AU2012204526B2 (en) | 2011-01-03 | 2016-05-19 | California Institute Of Technology | High density epidural stimulation for facilitation of locomotion, posture, voluntary movement, and recovery of autonomic, sexual, vasomotor, and cognitive function after neurological injury |
| CN103608067A (zh) | 2011-01-21 | 2014-02-26 | 加利福尼亚理工学院 | 脊髓刺激法的聚对二甲苯基微电极阵列植入 |
| US9409023B2 (en) | 2011-03-24 | 2016-08-09 | California Institute Of Technology | Spinal stimulator systems for restoration of function |
| JP5816461B2 (ja) * | 2011-05-18 | 2015-11-18 | 仁彦 多田 | 電極パッド及びこれを備えた気道確保装置 |
| WO2013036880A1 (en) | 2011-09-08 | 2013-03-14 | Thacker James R | Selective high frequency spinal cord modulation for inhibiting pain, including cephalic and/or total body pain with reduced side effects, and associated systems and methods |
| WO2013067538A1 (en) | 2011-11-04 | 2013-05-10 | Nevro Corporation | Medical device communication and charding assemblies for use with implantable signal generators |
| USD736383S1 (en) | 2012-11-05 | 2015-08-11 | Nevro Corporation | Implantable signal generator |
| ES2728143T3 (es) | 2011-11-11 | 2019-10-22 | Univ California | Estimulación transcutánea de la médula espinal: herramienta no invasiva para la activación del circuito locomotor |
| US9393409B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2016-07-19 | Neuroenabling Technologies, Inc. | Non invasive neuromodulation device for enabling recovery of motor, sensory, autonomic, sexual, vasomotor and cognitive function |
| US10092750B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2018-10-09 | Neuroenabling Technologies, Inc. | Transcutaneous neuromodulation system and methods of using same |
| US20150018728A1 (en) | 2012-01-26 | 2015-01-15 | Bluewind Medical Ltd. | Wireless neurostimulators |
| EP2822641B1 (en) | 2012-03-08 | 2019-06-19 | SPR Therapeutics, Inc. | System for treatment of pain related to limb joint replacement surgery |
| WO2014076698A1 (en) | 2012-11-13 | 2014-05-22 | Elminda Ltd. | Neurophysiological data analysis using spatiotemporal parcellation |
| US9861812B2 (en) | 2012-12-06 | 2018-01-09 | Blue Wind Medical Ltd. | Delivery of implantable neurostimulators |
| EP3878507A1 (en) * | 2013-03-15 | 2021-09-15 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Multi-site transcutaneous electrical stimulation of the spinal cord for facilitation of locomotion |
| US9895539B1 (en) | 2013-06-10 | 2018-02-20 | Nevro Corp. | Methods and systems for disease treatment using electrical stimulation |
| EP3049148B1 (en) | 2013-09-27 | 2020-05-20 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Engaging the cervical spinal cord circuitry to re-enable volitional control of hand function in tetraplegic subjects |
| US9333345B2 (en) | 2013-10-03 | 2016-05-10 | Ensilver Canada | Electrical stimulation for a functional electrical stimulation system |
| CA2866025A1 (en) | 2013-10-03 | 2015-04-03 | Quiang Song | Sensor unit for a functional electrical stimulation (fes) orthotic system |
| US9375569B2 (en) | 2013-10-03 | 2016-06-28 | Ensilver Canada | Controller unit for a functional electrical stimulation (FES) orthotic system |
| WO2015071901A2 (en) * | 2013-11-13 | 2015-05-21 | Elminda Ltd. | Method and system for managing pain |
| US20160263376A1 (en) | 2013-11-27 | 2016-09-15 | The Governing Council Of The University Of Toronto | Systems and methods for improved treatment of overactive bladder |
| US11633593B2 (en) | 2013-11-27 | 2023-04-25 | Ebt Medical, Inc. | Treatment of pelvic floor disorders using targeted lower limb nerve stimulation |
| US10556107B2 (en) | 2013-11-27 | 2020-02-11 | Ebt Medical, Inc. | Systems, methods and kits for peripheral nerve stimulation |
| CA3190484A1 (en) | 2013-11-27 | 2015-06-04 | Ebt Medical, Inc. | Systems and methods of enhancing electrical activation of nervous tissue |
| WO2015106286A1 (en) | 2014-01-13 | 2015-07-16 | California Institute Of Technology | Neuromodulation systems and methods of using same |
| EP3183028A4 (en) | 2014-08-21 | 2018-05-02 | The Regents of the University of California | Regulation of autonomic control of bladder voiding after a complete spinal cord injury |
| AU2015308779B2 (en) | 2014-08-27 | 2020-06-25 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Multi-electrode array for spinal cord epidural stimulation |
| KR20170078640A (ko) * | 2014-10-31 | 2017-07-07 | 아벤트, 인크. | 비침습적 신경 자극 시스템 |
| US9364657B2 (en) | 2014-10-31 | 2016-06-14 | Ensilver Canada | Cuff unit for a functional electrical stimulation system |
| WO2016092611A1 (ja) * | 2014-12-08 | 2016-06-16 | オリンパス株式会社 | 神経刺激装置 |
| US9764146B2 (en) | 2015-01-21 | 2017-09-19 | Bluewind Medical Ltd. | Extracorporeal implant controllers |
| US9597521B2 (en) | 2015-01-21 | 2017-03-21 | Bluewind Medical Ltd. | Transmitting coils for neurostimulation |
| US10004896B2 (en) | 2015-01-21 | 2018-06-26 | Bluewind Medical Ltd. | Anchors and implant devices |
| AU2016265904B2 (en) | 2015-05-21 | 2021-04-08 | Ebt Medical, Inc. | Systems and methods for treatment of urinary dysfunction |
| US9782589B2 (en) | 2015-06-10 | 2017-10-10 | Bluewind Medical Ltd. | Implantable electrostimulator for improving blood flow |
| US11291847B2 (en) | 2015-06-16 | 2022-04-05 | The Regents Of The University Of Colorado, A Body Corporate | Systems and methods for preventing, diagnosing, and/or treating one or more medical conditions via neuromodulation |
| WO2017035512A1 (en) | 2015-08-26 | 2017-03-02 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Concerted use of noninvasive neuromodulation device with exoskeleton to enable voluntary movement and greater muscle activation when stepping in a chronically paralyzed subject |
| US11097122B2 (en) | 2015-11-04 | 2021-08-24 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Magnetic stimulation of the spinal cord to restore control of bladder and/or bowel |
| US10105540B2 (en) | 2015-11-09 | 2018-10-23 | Bluewind Medical Ltd. | Optimization of application of current |
| US9713707B2 (en) | 2015-11-12 | 2017-07-25 | Bluewind Medical Ltd. | Inhibition of implant migration |
| US10420939B2 (en) | 2016-03-31 | 2019-09-24 | The Cleveland Clinic Foundation | Nerve stimulation to promote neuroregeneration |
| EP3463550B1 (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2024-03-27 | Lab Schöpfergeist AG | Nerve stimulation apparatus and method |
| AU2017315473B2 (en) * | 2016-08-26 | 2022-09-29 | Spr Therapeutics, Inc. | Devices and methods for delivery of electrical current for pain relief |
| US11540973B2 (en) | 2016-10-21 | 2023-01-03 | Spr Therapeutics, Llc | Method and system of mechanical nerve stimulation for pain relief |
| US10124178B2 (en) | 2016-11-23 | 2018-11-13 | Bluewind Medical Ltd. | Implant and delivery tool therefor |
| WO2018204492A1 (en) | 2017-05-04 | 2018-11-08 | University Of Pittsburgh - Of The Commonwealth System Of Higher Education | Peripheral neuromodulation to treat bladder and bowel dysfunction |
| US20180353764A1 (en) | 2017-06-13 | 2018-12-13 | Bluewind Medical Ltd. | Antenna configuration |
| EP3974021B1 (en) | 2017-06-30 | 2023-06-14 | ONWARD Medical N.V. | A system for neuromodulation |
| US11338135B2 (en) | 2017-10-23 | 2022-05-24 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Medical devices for cancer therapy with electric field shaping elements |
| US20190117970A1 (en) * | 2017-10-23 | 2019-04-25 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Electric field shaping leads for treatment of cancer |
| US11992684B2 (en) | 2017-12-05 | 2024-05-28 | Ecole Polytechnique Federale De Lausanne (Epfl) | System for planning and/or providing neuromodulation |
| EP3653256B1 (en) | 2018-11-13 | 2022-03-30 | ONWARD Medical N.V. | Control system for movement reconstruction and/or restoration for a patient |
| EP3653260A1 (en) | 2018-11-13 | 2020-05-20 | GTX medical B.V. | Sensor in clothing of limbs or footwear |
| EP3695878B1 (en) | 2019-02-12 | 2023-04-19 | ONWARD Medical N.V. | A system for neuromodulation |
| US11420049B2 (en) | 2019-04-22 | 2022-08-23 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Systems for administering electrical stimulation to treat cancer |
| US11691006B2 (en) | 2019-04-22 | 2023-07-04 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Electrical stimulation devices for cancer treatment |
| CN113766948A (zh) | 2019-04-22 | 2021-12-07 | 波士顿科学国际有限公司 | 对癌症的电与化学组合治疗 |
| WO2020219521A1 (en) | 2019-04-23 | 2020-10-29 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Electrical stimulation with thermal treatment or thermal monitoring |
| EP3958956B1 (en) | 2019-04-23 | 2024-02-28 | Boston Scientific Scimed Inc. | Electrodes for electrical stimulation to treat cancer |
| US11607542B2 (en) | 2019-04-23 | 2023-03-21 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Electrical stimulation for cancer treatment with internal and external electrodes |
| US11065461B2 (en) | 2019-07-08 | 2021-07-20 | Bioness Inc. | Implantable power adapter |
| DE19211698T1 (de) | 2019-11-27 | 2021-09-02 | Onward Medical B.V. | Neuromodulation system |
| EP4110455B1 (en) | 2020-02-24 | 2024-05-22 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Systems for treatment of pancreatic cancer |
| JP7562109B2 (ja) | 2020-04-13 | 2024-10-07 | 国立大学法人東海国立大学機構 | 神経刺激システムおよび神経刺激方法 |
| US11400299B1 (en) | 2021-09-14 | 2022-08-02 | Rainbow Medical Ltd. | Flexible antenna for stimulator |
| IL314010A (en) * | 2022-01-02 | 2024-08-01 | Exact Neuro LLC | Device and method for transmitting current through the skin |
| WO2024130043A2 (en) * | 2022-12-15 | 2024-06-20 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Fine wire muscle interfaces |
Family Cites Families (120)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3204637A (en) * | 1963-02-07 | 1965-09-07 | Erich J Frank | Stimulating apparatus |
| US3426748A (en) | 1965-11-23 | 1969-02-11 | Gen Electric | Stimulator analyzer and locater |
| US3835864A (en) | 1970-09-21 | 1974-09-17 | Rasor Ass Inc | Intra-cardiac stimulator |
| US3774618A (en) | 1972-07-03 | 1973-11-27 | Avery Labor Inc | Implantable nerve stimulation electrode |
| US3964470A (en) | 1974-07-25 | 1976-06-22 | Medtronic, Inc. | Percutaneous intradermal electrical connection system and implant device |
| US3995644A (en) | 1975-09-16 | 1976-12-07 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Administrator Of The National Aeronautics And Space Administration | Percutaneous connector device |
| US4102344A (en) | 1976-11-15 | 1978-07-25 | Mentor Corporation | Stimulator apparatus for internal body organ |
| JPS56122245A (en) | 1980-02-29 | 1981-09-25 | Pilot Pen Co Ltd:The | Automatic control system for transmission or recording and transmission and reception |
| US4793353A (en) | 1981-06-30 | 1988-12-27 | Borkan William N | Non-invasive multiprogrammable tissue stimulator and method |
| US4419995A (en) | 1981-09-18 | 1983-12-13 | Hochmair Ingeborg | Single channel auditory stimulation system |
| US4417888A (en) | 1982-03-15 | 1983-11-29 | Renal Systems, Inc. | Percutaneous implant |
| JPH0661366B2 (ja) * | 1986-06-03 | 1994-08-17 | ザ・リ−ジエンツ・オブ・ザ・ユニバ−シテイ・オブ・カリフオルニア | 解剖学的系における器官の協調及び同期機能制御装置 |
| US4922927A (en) | 1987-12-30 | 1990-05-08 | Intermedics, Inc. | Transvenous defibrillating and pacing lead |
| SE465910B (sv) | 1988-01-28 | 1991-11-18 | Jan Axel Svensson | Anordning foer sammankoppling av katetrar i en hudgenomgaang |
| US5080099A (en) | 1988-08-26 | 1992-01-14 | Cardiotronics, Inc. | Multi-pad, multi-function electrode |
| US4987897A (en) | 1989-09-18 | 1991-01-29 | Medtronic, Inc. | Body bus medical device communication system |
| US5056518A (en) | 1990-07-02 | 1991-10-15 | Electro-Biology, Inc. | Optimization of bone formation at cathodes |
| IL97701A (en) | 1991-03-28 | 1995-06-29 | Univ Ben Gurion | Device for desecrating the hand |
| US5443065A (en) | 1991-09-24 | 1995-08-22 | Angeion Corporation | Connector for medical device |
| US5565005A (en) | 1992-02-20 | 1996-10-15 | Amei Technologies Inc. | Implantable growth tissue stimulator and method operation |
| DE69228531T2 (de) | 1992-02-20 | 1999-07-29 | Neomedics, Inc., Budd Lake, N.J. | Implantierbarer Knochenwachstumsstimulator |
| US5356428A (en) | 1992-03-31 | 1994-10-18 | Cardiotronics, Inc. | Non-invasive, radiolucent electrode |
| US5441518A (en) | 1993-07-22 | 1995-08-15 | Angeion Corporation | Implantable cardioverter defibrillator system having independently controllable electrode discharge pathway |
| JPH06292733A (ja) * | 1992-12-14 | 1994-10-21 | Masaharu Saito | パルス発振装置 |
| US5325870A (en) | 1992-12-16 | 1994-07-05 | Angeion Corporation | Multiplexed defibrillation electrode apparatus |
| US5397338A (en) * | 1993-03-29 | 1995-03-14 | Maven Labs, Inc. | Electrotherapy device |
| US5465715A (en) | 1993-08-13 | 1995-11-14 | Ludlow Corporation | Positive locking biomedical electrode and connector system |
| GB9321086D0 (en) | 1993-10-13 | 1993-12-01 | Univ Alberta | Hand stimulator |
| JPH07308392A (ja) * | 1994-03-25 | 1995-11-28 | Japan Steel Works Ltd:The | 電気刺激による耳鳴り治療器 |
| US5545191A (en) | 1994-05-06 | 1996-08-13 | Alfred E. Mann Foundation For Scientific Research | Method for optimally positioning and securing the external unit of a transcutaneous transducer of the skin of a living body |
| US5571148A (en) | 1994-08-10 | 1996-11-05 | Loeb; Gerald E. | Implantable multichannel stimulator |
| US5604976A (en) | 1994-10-18 | 1997-02-25 | Pi Medical Corporation | Method of making percutaneous connector for multi-conductor electrical cables |
| US5591217A (en) | 1995-01-04 | 1997-01-07 | Plexus, Inc. | Implantable stimulator with replenishable, high value capacitive power source and method therefor |
| KR100395863B1 (ko) | 1995-05-08 | 2003-11-14 | 매사츄세츠 인스티튜트 오브 테크놀러지 | 신호송신매질로서인체를사용한비접촉센싱및신호송신용시스템 |
| US6076016A (en) | 1995-10-19 | 2000-06-13 | Feierbach; Gary F. | Galvanic transdermal conduction communication system and method |
| WO1997029802A2 (en) | 1996-02-20 | 1997-08-21 | Advanced Bionics Corporation | Improved implantable microstimulator and systems employing the same |
| US5776178A (en) | 1996-02-21 | 1998-07-07 | Medtronic, Inc. | Medical electrical lead with surface treatment for enhanced fixation |
| CA2171067A1 (en) | 1996-03-05 | 1997-09-06 | Brian J. Andrews | Neural prosthesis |
| US5983141A (en) | 1996-06-27 | 1999-11-09 | Radionics, Inc. | Method and apparatus for altering neural tissue function |
| US6726684B1 (en) | 1996-07-16 | 2004-04-27 | Arthrocare Corporation | Methods for electrosurgical spine surgery |
| US5674253A (en) * | 1996-09-06 | 1997-10-07 | Incontrol, Inc. | Cardioversion system with cardioverting energy attenuator |
| US5843132A (en) * | 1996-10-07 | 1998-12-01 | Ilvento; Joseph P. | Self-contained, self-powered temporary intravenous pacing catheter assembly |
| US5796827A (en) | 1996-11-14 | 1998-08-18 | International Business Machines Corporation | System and method for near-field human-body coupling for encrypted communication with identification cards |
| US5957965A (en) | 1997-03-03 | 1999-09-28 | Medtronic, Inc. | Sacral medical electrical lead |
| US6006122A (en) | 1997-09-25 | 1999-12-21 | Medtronic, Inc. | Medical electrical lead |
| US6212434B1 (en) | 1998-07-22 | 2001-04-03 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Single pass lead system |
| SE513670C2 (sv) | 1997-12-18 | 2000-10-16 | Grogrunden Ab Nr 444 | Percutan benförankrad genomföringsanordning |
| US5945762A (en) * | 1998-02-10 | 1999-08-31 | Light Sciences Limited Partnership | Movable magnet transmitter for inducing electrical current in an implanted coil |
| US5916244A (en) | 1998-02-20 | 1999-06-29 | Katecho, Inc. | External heart stimulation electrode having reduced edge effect |
| US8489200B2 (en) | 1998-07-06 | 2013-07-16 | Abiomed, Inc. | Transcutaneous energy transfer module with integrated conversion circuitry |
| US6735474B1 (en) | 1998-07-06 | 2004-05-11 | Advanced Bionics Corporation | Implantable stimulator system and method for treatment of incontinence and pain |
| US6941171B2 (en) | 1998-07-06 | 2005-09-06 | Advanced Bionics Corporation | Implantable stimulator methods for treatment of incontinence and pain |
| US5948006A (en) | 1998-10-14 | 1999-09-07 | Advanced Bionics Corporation | Transcutaneous transmission patch |
| US6668191B1 (en) | 1998-10-26 | 2003-12-23 | Birinder R. Boveja | Apparatus and method for electrical stimulation adjunct (add-on) therapy of atrial fibrillation, inappropriate sinus tachycardia, and refractory hypertension with an external stimulator |
| US6564102B1 (en) | 1998-10-26 | 2003-05-13 | Birinder R. Boveja | Apparatus and method for adjunct (add-on) treatment of coma and traumatic brain injury with neuromodulation using an external stimulator |
| US6366814B1 (en) | 1998-10-26 | 2002-04-02 | Birinder R. Boveja | External stimulator for adjunct (add-on) treatment for neurological, neuropsychiatric, and urological disorders |
| US20030212440A1 (en) | 2002-05-09 | 2003-11-13 | Boveja Birinder R. | Method and system for modulating the vagus nerve (10th cranial nerve) using modulated electrical pulses with an inductively coupled stimulation system |
| US6505074B2 (en) | 1998-10-26 | 2003-01-07 | Birinder R. Boveja | Method and apparatus for electrical stimulation adjunct (add-on) treatment of urinary incontinence and urological disorders using an external stimulator |
| US6351674B2 (en) | 1998-11-23 | 2002-02-26 | Synaptic Corporation | Method for inducing electroanesthesia using high frequency, high intensity transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation |
| AU2492000A (en) | 1999-01-06 | 2000-07-24 | Ball Semiconductor Inc. | Implantable neuro-stimulator |
| US6292699B1 (en) | 1999-01-29 | 2001-09-18 | Electro-Biology, Inc. | Direct current stimulation of spinal interbody fixation device |
| WO2000057950A1 (en) | 1999-03-30 | 2000-10-05 | Uab Research Foundation | Method and apparatus for passive cardiac stimulation |
| US6266567B1 (en) | 1999-06-01 | 2001-07-24 | Ball Semiconductor, Inc. | Implantable epicardial electrode |
| EP1194094B1 (en) | 1999-06-11 | 2007-03-14 | Cochlear Limited | Stimulus output monitor and control circuit for electrical tissue stimulator |
| US6233488B1 (en) | 1999-06-25 | 2001-05-15 | Carl A. Hess | Spinal cord stimulation as a treatment for addiction to nicotine and other chemical substances |
| US6445955B1 (en) | 1999-07-08 | 2002-09-03 | Stephen A. Michelson | Miniature wireless transcutaneous electrical neuro or muscular-stimulation unit |
| US6438428B1 (en) | 1999-10-27 | 2002-08-20 | Axelgaard Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | Electrical stimulation compress |
| US6377853B1 (en) | 1999-12-09 | 2002-04-23 | Urosurge, Inc. | Implantable electro-acupuncture device |
| US7013179B2 (en) | 2000-01-07 | 2006-03-14 | Biowave Corporation | Percutaneous electrode array |
| US20030028232A1 (en) | 2000-01-20 | 2003-02-06 | Medtronic, Inc. | Method of lmplanting a medical electrical lead |
| US6393323B1 (en) | 2000-01-31 | 2002-05-21 | Mcgill University | Electronic stimulator implant for modulating and synchronizing bladder and sphincter function |
| JP4916635B2 (ja) | 2000-02-03 | 2012-04-18 | ベイラー・カレツジ・オブ・メデイシン | 骨内神経剥離の方法及び器具 |
| US7146210B2 (en) | 2000-02-17 | 2006-12-05 | Standen Ltd. | Apparatus and method for optimizing tumor treatment efficiency by electric fields |
| US6754472B1 (en) | 2000-04-27 | 2004-06-22 | Microsoft Corporation | Method and apparatus for transmitting power and data using the human body |
| US6725096B2 (en) | 2000-05-05 | 2004-04-20 | Advanced Bionics Corporation | Multiple in-line contact connector |
| JP3525889B2 (ja) | 2000-11-28 | 2004-05-10 | 日本電気株式会社 | 周囲の他者に知覚されずに操作する通報方法及び処理システム |
| WO2002053225A2 (en) | 2000-12-29 | 2002-07-11 | Medtronic, Inc. | Electrode system for stimulating the left heart chamber |
| US20060064140A1 (en) | 2001-01-30 | 2006-03-23 | Whitehurst Todd K | Methods and systems for stimulating a trigeminal nerve to treat a psychiatric disorder |
| US6735475B1 (en) | 2001-01-30 | 2004-05-11 | Advanced Bionics Corporation | Fully implantable miniature neurostimulator for stimulation as a therapy for headache and/or facial pain |
| WO2002065896A2 (en) | 2001-02-20 | 2002-08-29 | Case Western Reserve University | Systems and methods for reversibly blocking nerve activity |
| US6892098B2 (en) | 2001-04-26 | 2005-05-10 | Biocontrol Medical Ltd. | Nerve stimulation for treating spasticity, tremor, muscle weakness, and other motor disorders |
| US6928320B2 (en) | 2001-05-17 | 2005-08-09 | Medtronic, Inc. | Apparatus for blocking activation of tissue or conduction of action potentials while other tissue is being therapeutically activated |
| US6796828B2 (en) | 2001-06-01 | 2004-09-28 | Sherwood Services Ag | Return pad cable connector |
| JP2005501617A (ja) | 2001-08-28 | 2005-01-20 | メドトロニック・インコーポレーテッド | 電気刺激により心臓のメカニカル機能不全を治療するシステム |
| DK1444004T3 (da) | 2001-10-18 | 2012-03-12 | Uroplasty Inc | Elektrisk nervestimulationssystem og fremgangsmåder |
| US6829508B2 (en) | 2001-10-19 | 2004-12-07 | Alfred E. Mann Foundation For Scientific Research | Electrically sensing and stimulating system for placement of a nerve stimulator or sensor |
| CN1620324A (zh) | 2001-12-20 | 2005-05-25 | 阿尔扎公司 | 有一整体模制的槽座架的电输送装置 |
| US6999821B2 (en) | 2002-01-18 | 2006-02-14 | Pacesetter, Inc. | Body implantable lead including one or more conductive polymer electrodes and methods for fabricating same |
| US6896675B2 (en) | 2002-03-05 | 2005-05-24 | Baylis Medical Company Inc. | Intradiscal lesioning device |
| US7162303B2 (en) | 2002-04-08 | 2007-01-09 | Ardian, Inc. | Renal nerve stimulation method and apparatus for treatment of patients |
| US20050038474A1 (en) | 2002-04-30 | 2005-02-17 | Wool Thomas J. | Implantable automatic defibrillator with subcutaneous electrodes |
| US6847844B2 (en) | 2002-06-06 | 2005-01-25 | University Of Pittsburgh Of The Commonwealth System Of Higher Education | Method of data communication with implanted device and associated apparatus |
| US7203548B2 (en) | 2002-06-20 | 2007-04-10 | Advanced Bionics Corporation | Cavernous nerve stimulation via unidirectional propagation of action potentials |
| WO2004034937A1 (en) | 2002-10-17 | 2004-04-29 | Arthur Prochazka | Method and apparatus for controlling a device or process with vibrations generated by tooth clicks |
| TR200202651A2 (tr) | 2002-12-12 | 2004-07-21 | Met�N�Tulgar | VücutÁdışındanÁdirekÁtedaviÁsinyaliÁtransferliÁÁbeyinÁpili |
| US7047071B2 (en) * | 2003-04-11 | 2006-05-16 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Patient stratification for implantable subcutaneous cardiac monitoring and therapy |
| WO2005007120A2 (en) | 2003-07-18 | 2005-01-27 | The Johns Hopkins University | System and method for treating nausea and vomiting by vagus nerve stimulation |
| AU2003904032A0 (en) | 2003-08-04 | 2003-08-14 | Ventracor Limited | Improved Transcutaneous Power and Data Transceiver System |
| US20050070970A1 (en) | 2003-09-29 | 2005-03-31 | Knudson Mark B. | Movement disorder stimulation with neural block |
| US8428717B2 (en) | 2003-10-14 | 2013-04-23 | Medtronic, Inc. | Method and apparatus for monitoring tissue fluid content for use in an implantable cardiac device |
| EP1711222A4 (en) | 2003-12-19 | 2011-02-09 | Savacor Inc | DIGITAL ELECTRODE FOR HEART RTHYTHMUS MANAGEMENT |
| EP1706178B1 (en) | 2004-01-22 | 2013-04-24 | Rehabtronics Inc. | System for routing electrical current to bodily tissues via implanted passive conductors |
| US20100016929A1 (en) | 2004-01-22 | 2010-01-21 | Arthur Prochazka | Method and system for controlled nerve ablation |
| US20060206165A1 (en) | 2005-03-14 | 2006-09-14 | Jaax Kristen N | Occipital nerve stimulation to treat headaches and other conditions |
| US20080306571A1 (en) | 2005-03-16 | 2008-12-11 | Borgens Richard B | Devices For Treatment of Central Nervous System Injuries |
| US8473049B2 (en) | 2005-05-25 | 2013-06-25 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Implantable neural stimulator with mode switching |
| MX2007013000A (es) | 2005-04-18 | 2008-03-18 | Bioness Dev Llc | Sistema y metodo relacionado para determinar una medicion entre ubicaciones en un cuerpo. |
| US8958883B2 (en) | 2005-04-19 | 2015-02-17 | Pierre-Yves Mueller | Electrical stimulation device and method for therapeutic treatment and pain management |
| CA2608397A1 (en) | 2005-06-28 | 2007-01-04 | Bioness Development, Llc | Improvements to an implant, system and method using implanted passive conductors for routing electrical current |
| US7415309B2 (en) | 2005-07-11 | 2008-08-19 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Percutaneous access for neuromodulation procedures |
| EP1981589B1 (en) | 2006-01-23 | 2016-04-13 | Rehabtronics Inc. | System for routing electrical current to bodily tissues via implanted passive conductors |
| US8116875B2 (en) | 2006-06-16 | 2012-02-14 | Neuropoint Medical, Inc. | Implantable neurostimulation systems |
| JP5250549B2 (ja) | 2006-06-19 | 2013-07-31 | ハイランド インストゥルメンツ, インコーポレイテッド | 生体組織の刺激のための器具および方法 |
| US8483820B2 (en) | 2006-10-05 | 2013-07-09 | Bioness Inc. | System and method for percutaneous delivery of electrical stimulation to a target body tissue |
| KR100911240B1 (ko) | 2007-05-14 | 2009-08-06 | 가천의과학대학교 산학협력단 | 무선 전력 전송 방식 심부 뇌자극 장치 |
| US8738137B2 (en) | 2007-08-23 | 2014-05-27 | Bioness Inc. | System for transmitting electrical current to a bodily tissue |
| CA2697381A1 (en) | 2007-08-23 | 2009-02-26 | Bioness, Inc. | System for transmitting electrical current to a bodily tissue |
| CA2703867C (en) | 2007-10-29 | 2017-06-20 | Case Western Reserve University | Onset-mitigating high-frequency nerve block |
| US9452288B2 (en) | 2007-12-06 | 2016-09-27 | Boston Scientific Neuromodulation Corporation | Multimodal neurostimulation systems and methods |
| US20090326602A1 (en) | 2008-06-27 | 2009-12-31 | Arkady Glukhovsky | Treatment of indications using electrical stimulation |
-
2006
- 2006-06-28 CA CA002608397A patent/CA2608397A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2006-06-28 JP JP2008519515A patent/JP5249024B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2006-06-28 WO PCT/US2006/025146 patent/WO2007002741A1/en active Application Filing
- 2006-06-28 US US11/993,393 patent/US8332029B2/en active Active
- 2006-06-28 AU AU2006261666A patent/AU2006261666B2/en not_active Ceased
- 2006-06-28 EP EP06785730A patent/EP1899002A1/en not_active Withdrawn
-
2011
- 2011-12-22 JP JP2011281270A patent/JP2012075933A/ja not_active Ceased
-
2012
- 2012-09-14 US US13/618,739 patent/US8538517B2/en active Active
-
2013
- 2013-09-16 US US14/027,930 patent/US8862225B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US8862225B2 (en) | 2014-10-14 |
| WO2007002741A1 (en) | 2007-01-04 |
| EP1899002A1 (en) | 2008-03-19 |
| AU2006261666A1 (en) | 2007-01-04 |
| AU2006261666B2 (en) | 2011-05-26 |
| US20130013041A1 (en) | 2013-01-10 |
| CA2608397A1 (en) | 2007-01-04 |
| JP2008544813A (ja) | 2008-12-11 |
| AU2006261666A2 (en) | 2009-07-09 |
| US20140172053A1 (en) | 2014-06-19 |
| US8332029B2 (en) | 2012-12-11 |
| US20100198298A1 (en) | 2010-08-05 |
| JP2012075933A (ja) | 2012-04-19 |
| US8538517B2 (en) | 2013-09-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5249024B2 (ja) | 電流を通す埋込み受動導体を使用するインプラント、システムおよび方法に対する改良 | |
| US11478648B2 (en) | Antenna and methods of use for an implantable nerve stimulator | |
| EP1706178B1 (en) | System for routing electrical current to bodily tissues via implanted passive conductors | |
| JP5308339B2 (ja) | 電気刺激を標的体組織へ経皮送達するためのシステムおよび方法 | |
| JP2009529352A (ja) | 埋め込まれた受動導体を介して電流を体組織へルーティングする方法 | |
| CN108697886A (zh) | 用于频率调整以优化可植入神经刺激器的充电的方法和系统 | |
| AU2011213849B2 (en) | Improvements to an implant, system and method using implanted passive conductors for routing electrical current | |
| KR20080101931A (ko) | 이식된 수동 전도체를 통해 신체 조직으로 전류를 전달하는방법 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20090109 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20090326 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090528 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110922 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20111222 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20120509 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120907 |
|
| A911 | Transfer to examiner for re-examination before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20120918 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20121010 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20130109 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20130117 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20130208 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20130218 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130307 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130405 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130411 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20160419 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |