JP4479018B2 - Game machine - Google Patents
Game machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4479018B2 JP4479018B2 JP23756999A JP23756999A JP4479018B2 JP 4479018 B2 JP4479018 B2 JP 4479018B2 JP 23756999 A JP23756999 A JP 23756999A JP 23756999 A JP23756999 A JP 23756999A JP 4479018 B2 JP4479018 B2 JP 4479018B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- symbol
- reach
- identification information
- value
- random number
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Pinball Game Machines (AREA)
- Display Devices Of Pinball Game Machines (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、パチンコ機等の遊技機に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来、遊技機の一種として、複数種類の図柄等を、予め定められた配列で変動表示するための表示装置を備えたパチンコ機が知られている。
【0003】
この種のパチンコ機では、表示装置での変動表示停止時の表示図柄(停止図柄)に応じて、リーチ状態を経た後に遊技者に有利な特別遊技状態となる「当たりリーチ状態」、リーチ状態を経た後に特別遊技状態とはならない「外れリーチ状態」、又は、リーチ状態を経ず、かつ、特別遊技状態ともならない「外れ状態」が発生させられる。停止図柄には、当たり図柄、外れリーチ図柄、及び、外れ図柄がある。
【0004】
前記のようなパチンコ機では、遊技者の操作に応じて変化する遊技状況が、所定の条件を満たすこと(例えば、遊技球が作動口に入賞すること等)によって、表示装置において、図柄の変動表示が開始される。また、上記当たり図柄、外れリーチ図柄、及び、外れ図柄の中から、停止図柄が選択され、その選択された停止図柄で前記変動表示が停止させられる。そして、当たり図柄で停止した場合には、特別変動入賞装置が遊技者にとって有利な状態となるように切換えられる。
【0005】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
本発明は、上記例示した遊技機等において、興趣の向上を好適に図ることのできる遊技機を提供することを目的とするものである。
【0006】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記の課題を解決するために、本発明においては、
複数の図柄表示領域において複数の図柄を変動表示可能な表示手段と、
所定の遊技状況を検出する遊技状況検出手段と、
前記遊技状況検出手段による検出結果に基づき、遊技者に有利な特別遊技状態を発生させるか否かの抽選を行うとともに、前記表示手段の各図柄表示領域にて複数の図柄の変動表示を開始させ、所定時間後に停止表示させ、
前記抽選の結果が当たりである場合には、前記複数の図柄表示領域において図柄を特定の当たり組み合わせパターンにて停止表示させ、前記特別遊技状態を発生させ、
前記抽選の結果が当たりでない場合には、前記特別遊技状態を発生させることなく前記複数の図柄表示領域において少なくとも1つの第1の外れ組み合わせパターンを含む複数の外れ組み合わせパターンのうち所定の外れ組み合わせパターンにて図柄を停止表示させる制御手段とを備える遊技機であって、
所定の第1条件が成立しているか否かを判別可能な判別手段と、
該判別手段により第1条件が成立していないと判別されたことに基づき、前記少なくとも1つの第1の外れ組み合わせパターンを含む複数の外れ組み合わせパターンのうちいずれかの外れ組み合わせパターンで図柄の停止表示を行う第1停止表示手段と、
前記判別手段により第1条件が成立していると判別されたことに基づき、前記少なくとも1つの第1の外れ組み合わせパターンで図柄の停止表示を行う第2停止表示手段とを有し、
前記制御手段は、
遊技機の制御を司る第1制御手段と、
該第1制御手段とは別に設けられ、前記表示手段における前記図柄の変動表示を制御する第2制御手段とを有して構成され、
前記第1制御手段は、
前記第2制御手段に特定信号を出力可能に構成され、
前記第2制御手段は、
前記特定信号の入力に基づいて前記図柄の変動表示を制御可能に構成されるとともに、
前記第1停止表示手段と、
前記第2停止表示手段と、
前記第1停止表示手段が停止表示する外れ組み合わせパターンを、前記少なくとも1つの第1の外れ組み合わせパターンを含む複数の外れ組み合わせパターンのうちいずれの外れ組み合わせパターンとするかを、前記特定信号の入力に基づき決定する決定手段とを有していることを特徴とする。
また、前記少なくとも1つの第1の外れ組み合わせパターンを含む複数の外れ組み合わせパターンは、リーチを行うが外れとなるリーチ外れ組み合わせパターンと、リーチを行わず外れとなる非リーチ外れ組み合わせパターンとを含み、前記少なくとも1つの第1の外れ組み合わせパターンは、リーチを行わず外れとなる非リーチ外れ組み合わせパターンであることとしてもよい。
また、前記少なくとも1つの第1の外れ組み合わせパターンを含む複数の外れ組み合わせパターンは、リーチを行うが外れとなるリーチ外れ組み合わせパターンと、リーチを行わず外れとなる非リーチ外れ組み合わせパターンとを含み、前記少なくとも1つの第1の外れ組み合わせパターンは、リーチを行うが外れとなるリーチ外れ組み合わせパターンであることとしてもよい。
また、前記少なくとも1つの第1の外れ組み合わせパターンは、複数であることとしてもよい。
また、前記遊技機はパチンコ機であることとしてもよい。
【0007】
【発明の実施の形態】
手段1.遊技者の操作に応じて変化する遊技状況を検出する遊技状況検出手段と、前記遊技状況検出手段による検出結果に基づき、複数の識別情報を変動表示しうる可変表示装置と、前記識別情報が特定の識別情報となって最終的に停止表示されることを必要条件に、遊技者に有利な特別遊技状態を発生させる特別遊技状態発生手段とを備えた遊技機であって、前記特定の識別情報は、複数パターンからなり、かつ、そのうちの少なくとも1つの特定の識別情報の実際の出現率を、表面上の出現率と異ならせるようにしたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0008】
上記手段によれば、遊技者の操作に応じて変化する遊技状況が遊技状況検出手段により検出され、前記遊技状況検出手段による検出結果に基づき、可変表示手段において、複数の識別情報が変動表示されうる。そして、識別情報が特定の識別情報となって最終的に停止表示されることを必要条件に、特別遊技状態発生手段では、遊技者に有利な特別遊技状態が発生させられる。さて、上記手段では、特定の識別情報が複数パターンからなり、特別遊技状態が発生させられるに際しては、識別情報が、前記複数パターンあるうちの1種類の特定の識別情報となって最終的に停止表示される。ここで、少なくとも1つの特定の識別情報の実際の出現率が、表面上の出現率と異なる。このため、少なくとも1つの特定の識別情報の停止表示される確率を独立した選定において設定することができ、表面上の出現率に拘束されることなく実際の出現率を設定することが可能となり、設計上の自由度が増す。また、少なくとも1つの特定の識別情報の実際の出現率が、表面上の出現率と異なるため、遊技者にとって面白味が増すとともに、出現率の相異に付随する様々な演出等を行うことも可能となる。
【0009】
手段2.手段1において、実際の出現率が表面上の出現率と異ならされた前記特定の識別情報は、毎回の識別情報の変動に際し、必ず出現表示される可能性を有するよう構成したことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0010】
手段3.手段1において、実際の出現率が表面上の出現率と異ならされた前記特定の識別情報のうち少なくとも1つは、所定の遊技モード中において出現表示されないよう構成したことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0011】
手段4.遊技者の操作に応じて変化する遊技状況を検出する遊技状況検出手段と、前記遊技状況検出手段による検出結果に基づき、複数の識別情報を変動表示しうる可変表示装置と、前記識別情報が特定の識別情報となって最終的に停止表示されることを必要条件に、遊技者に有利な特別遊技状態を発生させる特別遊技状態発生手段とを備えた遊技機であって、前記特定の識別情報は、複数パターンからなり、実際に最終的に停止表示される特定の識別情報に偏りを持たせたことを特徴とする遊技機。上記手段においても、基本的には上記手段1と同様の作用が奏される。
【0012】
手段5.手段1〜4のいずれかにおいて、前記識別情報が前記特定の識別情報とは異なる外れ識別情報となって最終的に停止表示された場合、前記特別遊技状態を発生させないようにするとともに、前記外れ識別情報は、複数パターンからなり、かつ、そのうちの少なくとも1つの外れ識別情報の実際の出現率を、表面上の出現率と異ならせるようにしたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0013】
手段6.手段5において、実際の出現率が表面上の出現率と異ならされた前記外れ識別情報は、毎回の識別情報の変動に際し、必ず出現表示される可能性を有するよう構成したことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0014】
手段7.手段5において、実際の出現率が表面上の出現率と異ならされた前記外れ識別情報のうち少なくとも1つは、所定の遊技モード中において出現表示されないよう構成したことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0015】
手段8.手段1〜5のいずれかにおいて、前記識別情報が前記特定の識別情報とは異なる外れ識別情報となって最終的に停止表示された場合、前記特別遊技状態を発生させないようにするとともに、前記外れ識別情報は、複数パターンからなるうちの1つのパターンが内部的に決定されるものであり、かつ、そのうちの少なくとも1つの外れ識別情報のパターンが決定される内部確率を、該外れ識別情報が表面上停止表示される確率よりも高くしたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0016】
手段9.手段8において、前記可変表示装置は、複数の表示領域において複数の識別情報を変動表示しうるよう構成されているとともに、前記複数パターンからなる外れ識別情報は、複数の各表示領域において停止表示される識別情報の組み合わせによって構成され、前記外れ識別情報のパターンとして、所定の識別情報の組み合わせが他の組み合わせよりも決定されやすくしたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0017】
手段10.手段9において、前記外れ識別情報のパターンは、各識別情報の停止表示前において所定条件が成立した場合に前記組み合わせの中から1つが選択されることにより決定されるものであることを特徴とする遊技機。
【0018】
手段11.手段8において、前記可変表示装置は、複数の表示領域において複数の識別情報を変動表示しうるよう構成されているとともに、前記複数パターンからなる外れ識別情報は、複数の各表示領域において停止表示される識別情報の組み合わせによって構成され、前記外れ識別情報のパターンは、前記各表示領域毎に識別情報が個々に決定されることに基づいて定められることを特徴とする遊技機。
【0019】
手段12.手段11において、前記各表示領域毎に、所定の識別情報が決定される内部確率を、該識別情報が表面上停止表示される確率よりも高くし、結果として、少なくとも1つの外れ識別情報のパターンが決定される内部確率を、該外れ識別情報が表面上停止表示される確率よりも高くしたことを特徴とする遊技機。ここで、「所定の識別情報」とあるのは、外れ識別情報となる組み合わせであれば、所定の識別情報が各表示領域毎に相異していても、一部同一であってもよい。
【0020】
手段13.手段11において、少なくとも1の表示領域について、所定の識別情報が決定される内部確率を、該識別情報が表面上停止表示される確率よりも高くしたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0021】
手段14.手段1〜4のいずれかにおいて、前記識別情報が前記特定の識別情報とは異なる外れ識別情報となって最終的に停止表示された場合、前記特別遊技状態を発生させないようにするとともに、前記外れ識別情報は、複数パターンからなり、かつ、実際に最終的に停止表示される外れ識別情報に偏りを持たせたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0022】
手段15.手段1〜4のいずれかにおいて、前記識別情報が前記特定の識別情報とは異なる外れ識別情報となって最終的に停止表示された場合、前記特別遊技状態を発生させないようにするとともに、前記外れ識別情報は、複数パターンからなり、かつ、全ての各外れ識別情報の実際の出現率を、表面上の出現率と等しくするようにしたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0023】
手段16.手段1〜15のいずれかにおいて、少なくとも前記識別情報が特定の識別情報となって最終的に停止表示される前段階に、リーチ識別情報(結果的に特定の識別情報となるもの及び結果的に特定の識別情報とならないものの双方を含む)を停止表示させてリーチ遊技状態を演出表示しうるよう構成するとともに、前記リーチ識別情報は、複数パターンからなり、かつ、そのうちの少なくとも1つのリーチ識別情報の実際の出現率を、表面上の出現率と異ならせるようにしたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0024】
手段17.手段16において、実際の出現率が表面上の出現率と異ならされた前記リーチ識別情報は、毎回の識別情報の変動に際し、必ず出現表示される可能性を有するよう構成したことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0025】
手段18.手段16において、実際の出現率が表面上の出現率と異ならされた前記リーチ識別情報のうち少なくとも1つは、所定の遊技モード中において出現表示されないよう構成したことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0026】
手段19.手段1〜15のいずれかにおいて、少なくとも前記識別情報が特定の識別情報となって最終的に停止表示される前段階に、リーチ識別情報(結果的に特定の識別情報となるもの及び結果的に特定の識別情報とならないものの双方を含む)を停止表示させてリーチ遊技状態を演出表示しうるよう構成するとともに、前記リーチ識別情報は、複数パターンからなり、かつ、実際に停止表示されるリーチ識別情報に偏りを持たせたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0027】
手段20.手段1〜15のいずれかにおいて、少なくとも前記識別情報が特定の識別情報となって最終的に停止表示される前段階に、リーチ識別情報(結果的に特定の識別情報となるもの及び結果的に特定の識別情報とならないものの双方を含む)を停止表示させてリーチ遊技状態を演出表示しうるよう構成するとともに、前記リーチ識別情報は、複数パターンからなり、かつ、全ての各リーチ識別情報の実際の出現率を、表面上の出現率と等しくするようにしたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0028】
手段21.手段1〜20のいずれかにおいて、前記識別情報が一旦特定の識別情報となって停止表示された後、再度の変動表示を行い、前記一旦停止表示された特定の識別情報と同一の又は異なる特定の識別情報となって最終的に停止表示されるよう構成するとともに、前記一旦停止表示される特定の識別情報は、複数パターンからなり、かつ、そのうちの少なくとも1つの一旦停止表示される特定の識別情報の実際の出現率を、表面上の出現率と異ならせるようにしたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0029】
手段22.手段21において、実際の出現率が表面上の出現率と異ならされた前記一旦停止表示される特定の識別情報は、毎回の識別情報の変動に際し、必ず出現表示される可能性を有するよう構成したことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0030】
手段23.手段21において、実際の出現率が表面上の出現率と異ならされた前記一旦停止表示される特定の識別情報のうち少なくとも1つは、所定の遊技モード中において出現表示されないよう構成したことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0031】
手段24.手段1〜20のいずれかにおいて、前記識別情報が一旦特定の識別情報となって停止表示された後、再度の変動表示を行い、前記一旦停止表示された特定の識別情報と同一の又は異なる特定の識別情報となって最終的に停止表示されるよう構成するとともに、前記一旦停止表示される特定の識別情報は、複数パターンからなり、かつ、実際に一旦停止表示される特定の識別情報に偏りを持たせたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0032】
手段25.手段1〜20のいずれかにおいて、前記識別情報が一旦特定の識別情報となって停止表示された後、再度の変動表示を行い、前記一旦停止表示された特定の識別情報と同一の又は異なる特定の識別情報となって最終的に停止表示されるよう構成するとともに、前記一旦停止表示される特定の識別情報は、複数パターンからなり、かつ、全ての各一旦停止表示される特定の識別情報の実際の出現率を、表面上の出現率と等しくするようにしたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0033】
手段26.手段1〜25のいずれかにおいて、前記特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つに関するカウント値を計数するカウント値計数手段と、前記カウント値計数手段によって計数されたカウント値に基づいて前記特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つのパターンを決定するパターン決定手段とを設け、かつ、前記カウント値と前記特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つのパターンとの間の対応関係に偏りを持たせ(、少なくとも1つの特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つの実際の出現率を、表面上の出現率と異ならせ)るようにしたことを特徴とする遊技機。なお、(1)特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報に関するカウント値としては、それぞれ同じものを用いてもよいし、相互に異なるものを用いてもよい。(2)カウント値に基づいてパターンが決定される対象は、特定の識別情報のみ、外れ識別情報のみ、リーチ識別情報のみ、一旦停止表示される識別情報のみでもよいし、これらの任意の組み合わせ、例えば、特定の識別情報と外れ識別情報、特定の識別情報とリーチ識別情報、特定の識別情報と一旦停止表示される識別情報、外れ識別情報とリーチ識別情報、外れ識別情報と一旦停止表示される識別情報、リーチ識別情報と一旦停止表示される識別情報、特定の識別情報と外れ識別情報とリーチ識別情報、特定の識別情報と外れ識別情報と一旦停止表示される識別情報、外れ識別情報とリーチ識別情報と一旦停止表示される識別情報、特定の識別情報と外れ識別情報とリーチ識別情報と一旦停止表示される識別情報でもよい。
【0034】
手段27.手段26において、前記カウント値と前記特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つのパターンとの間の対応関係が、カウント値(個々のカウント値及びカウント値の範囲の少なくとも一方)に応じて相異しうるようにしたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0035】
手段28.手段26又は27において、前記カウント値が第1の所定条件を満たした場合に、前記特定の識別情報の第1の所定のパターン、外れ識別情報の第1の所定のパターン、リーチ識別情報の第1の所定のパターン、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の第1の所定のパターンのうち少なくとも1つのパターンが決定され、前記カウント値が第2の所定条件を満たした場合に、前記特定の識別情報の第2の所定のパターン、外れ識別情報の第2の所定のパターン、リーチ識別情報の第2の所定のパターン、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の第2の所定のパターンのうち少なくとも1つのパターンが決定されるよう構成するとともに、前記カウント値が、前記第2の所定条件よりも前記第1の所定条件の方を満たしやすくなるようにしたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0036】
手段29.手段1〜28のいずれかにおいて、前記特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つに関するカウント値を計数するカウント値計数手段と、前記カウント値計数手段によって計数されたカウント値に基づいてパターン決定テーブルを参酌することにより前記特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つのパターンを決定するパターン決定手段とを設け、かつ、前記パターン決定テーブルにおいて前記カウント値と前記特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つのパターンとの間の対応関係に偏りを持たせ(、少なくとも1つの特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つの実際の出現率を、表面上の出現率と異ならせ)るようにしたことを特徴とする遊技機。但し、上記手段26の「なお書き(1)(2)は、本手段についても同様のことがいえる。
【0037】
手段30.手段29において、前記パターン決定テーブルには、前記カウント値と前記特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つのパターンとの間の対応関係が、カウント値(個々のカウント値及びカウント値の範囲の少なくとも一方)に応じて相異しうる設定がなされていることを特徴とする遊技機。
【0038】
手段31.手段29又は30において、前記パターン決定テーブルには、前記カウント値が第1の所定条件を満たした場合に、前記特定の識別情報の第1の所定のパターン、外れ識別情報の第1の所定のパターン、リーチ識別情報の第1の所定のパターン、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の第1の所定のパターンのうち少なくとも1つのパターンが決定され、前記カウント値が第2の所定条件を満たした場合に、前記特定の識別情報の第2の所定のパターン、外れ識別情報の第2の所定のパターン、リーチ識別情報の第2の所定のパターン、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の第2の所定のパターンのうち少なくとも1つのパターンが決定され、かつ、前記カウント値が、前記第2の所定条件よりも前記第1の所定条件の方を満たしやすくなるよう設定がなされていることを特徴とする遊技機。
【0039】
手段32.手段29〜31のいずれかにおいて、前記パターン決定テーブルには、前記カウント値と前記特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つのパターンとの間の対応関係が予め組み込まれていることを特徴とする遊技機。
【0040】
手段33.手段29〜32のいずれかにおいて、前記パターン決定テーブルには、前記カウント値と前記特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つのパターンとの間の基本的な対応関係が予め組み込まれているとともに、前記パターン決定テーブルに対し、、さらなる前記カウント値と前記特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つのパターンとの間の別途の対応関係を追加可能となっていることを特徴とする遊技機。
【0041】
手段34.手段33において、前記基本的な対応関係は、特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つの実際の出現率が、表面上の出現率と等しくなるような関係であり、前記別途の対応関係は、特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つの実際の出現率が、表面上の出現率と異なるような関係であることを特徴とする遊技機。
【0042】
手段35.手段33又は34において、前記パターン決定テーブルに対し、所定のデータを追加補充又は削除することで、前記別途の対応関係を調整可能としたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0043】
手段36.手段29〜35のいずれかにおいて、前記パターン決定テーブルには、前記カウント値と前記特定の識別情報、外れ識別情報、リーチ識別情報、及び、一旦停止表示される識別情報の少なくとも1つのパターンとの間の対応関係に偏りを持たせるべく、各識別情報のパターンが決定される比率が予め定められていることを特徴とする遊技機。
【0044】
手段37.手段36において、前記比率は、百分率又はそれに準ずる率で定められていることを特徴とする遊技機。
【0045】
手段38.手段36又は37において、前記比率は、適宜変更可能となっていることを特徴とする遊技機。
【0046】
手段39.手段36〜38のいずれかにおいて、前記パターン決定手段は、前記カウント値が前記比率との関係において、所定条件を満たすか否かを判定し、前記所定条件を満たす場合に、前記比率に対応するパターンを今回のパターンとして決定するものであることを特徴とする遊技機。
【0047】
手段40.手段1〜39のいずれかにおいて、最終的に停止表示される特定の識別情報に応じて、遊技モードを、通常モードと該通常モードよりも遊技者にとって望ましい特別モードとの間で切換可能としたことを特徴とする遊技機。
【0048】
(第1の実施の形態)
以下に、パチンコ遊技機(以下、単に「パチンコ機」という)を具体化した一実施の形態を、図面に基づいて詳細に説明する。
【0049】
なお、周知のように、パチンコ機1は、外枠と、該外枠の前部に設けられ外枠の一側部にて開閉可能に設けられた前面枠とを備えている。また、その前面枠の前面側にはガラス扉枠が開閉自在に設けられている。前面枠の後側(ガラス扉枠の奥、外枠の内側)には、遊技盤2が着脱可能に装着されている。この遊技盤2は内レール、外レール等を備え、これらのレールは、遊技球発射装置によって発射された遊技球5を、遊技盤2の上部に案内する。また、ガラス扉枠の下側において、前面枠には前飾枠が開閉可能に設けられ、前飾枠には、上受皿が設けられている。一方、前面枠の下部には、前記上受皿よりも下方位置にて下受皿が設けられているとともに、遊技球発射装置を構成するハンドルが設けられている。
【0050】
図1に示すように、パチンコ機1の遊技盤2には、作動口3及び大入賞口4が設けられている。作動口3は、遊技球5の通路を備えており、その通路入口には羽根6が開閉可能に支持されている。大入賞口4の奥には、シーソー7が設けられており、その右側にはVゾーン8が、左側には入賞通路9が設けられている(左右逆でもよい)。そして、大入賞口4に入賞した遊技球5は、シーソー7上を転がって、Vゾーン8又は入賞通路9のいずれか一方を通って図示しない入賞球処理装置の方へと導かれる。また、大入賞口4の前には、シャッタ11が設けられている。このシャッタ11は、大入賞口4の側部に設けられた大入賞口用ソレノイド12により作動させられ、大入賞口4を開閉する。詳しくは、当該ソレノイド12が励磁状態となることにより、シャッタ11が略水平に傾き、これにより大入賞口4が開かれる。また、ソレノイド12が非励磁状態となることにより、シャッタ11が略垂直状態となり、これにより大入賞口4は閉鎖される。
【0051】
前記大入賞口4の一側部には、シーソー用ソレノイド10が設けられている。シーソー用ソレノイド10は通常、非励磁状態となっており、この状態においては、遊技球5がVゾーン8を通過するようにシーソー7を傾けている。また、シーソー用ソレノイド10が励磁状態となることにより、シーソー7は、遊技球5が入賞通路9を通過するように傾動させられる。本実施の形態では、シャッタ11が開状態において、遊技球5が1つでもVゾーン8を通過した場合には、シーソー用ソレノイド10が励磁される。そして、シャッタ11が閉じられることにより、シーソー用ソレノイド10が非励磁状態となる。
【0052】
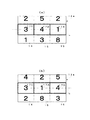
遊技盤2の中央部分には、可変表示装置としての特別図柄表示装置13が組込まれている。この特別図柄表示装置13は、液晶ディスプレイ(LCD)よりなる表示部13aを備えており、ここに複数の図柄列が表示される。図2に示すように、本実施の形態では、これらの図柄列(識別情報列)として左図柄列14、中図柄列15及び右図柄列16の3つの図柄列が表示されるが、それ以外の数の図柄列が表示されてもよい。
【0053】
図2に示すように、各図柄列14〜16は、それぞれ複数個の識別情報としての図柄17A〜17Hによって構成されている。各図柄17A〜17Hは、それぞれ「1」〜「8」の数字によって構成され、これらの数字は昇順にそれぞれ1つずつ均等に配列されている。なお、図柄17A〜17Hの数は上記例に何ら限定されるものではなく、また、図柄の種類も数字図柄に限定されることなく、文字図柄や、絵図柄により構成されていてもよい。これらの図柄17A〜17Hは、特別遊技図柄としての大当たり図柄、外れリーチ図柄及び外れ図柄のいずれかになり得る。もちろん、これらの間に外れ図柄にのみなりうる図柄を配置してもよい。
【0054】
通常変動に際しては、各図柄列14〜16においては、各図柄17A〜17Hがスクロールすることにより変動表示される。より詳しくは、各図柄17A〜17Hは上から下へとスクロール表示される。
【0055】
本実施の形態では、図2(b)に示すように、中央の1本の横ラインによって大当たりラインLが構成されている(1ラインと称される)。つまり、各図柄列14〜16に1つずつ設けられた有効枠(該有効枠が大当たりラインLを構成するともいえる)に図柄17A〜17Hが表示される態様となっている。なお、本実施の形態では、各図柄列14〜16の各有効枠の上下には、有効枠に表示される図柄の次の図柄及び1つ前の図柄も併せて表示されるようになっている。但し、上記1ラインに限定されることなく、2ライン、3ライン、或いは5ライン以上の大当たりラインを有していても何ら差し支えない。
【0056】
また、図1に示すように、特別図柄表示装置13の上部には普通図柄表示装置51が併設されている。普通図柄表示装置51は、発光ダイオード(LED)よりなる4つの保留ランプ52と、普通図柄表示部たるLEDよりなる7セグ表示部53とを有している。
【0057】
さらに、前記特別図柄表示装置13の左右両側方には一対の通過ゲート54が配設されている。同通過ゲート54を遊技球5が通過すると前記普通図柄表示装置51が作動する。本実施の形態では、普通図柄表示装置51は、「0」から「9」までの数字を可変表示して7セグ表示部53にセグメント表示させ、その数字が所定値(本実施の形態では「7」)で停止した場合に、作動口3の羽根6を所定秒数開放させる。この開放により、作動口3への入賞が比較的容易なものとなる。普通図柄表示装置51は、遊技球5の通過ゲート54の通過回数を4回まで記憶することができ、保留ランプ52でその保留数を表示する。従って、4つの保留ランプ52が点灯している状態で遊技球5が通過ゲート54を通過しても保留球としてカウントされず、保留ランプ52が点灯している限り、遊技球5が通過ゲート54を通過しなくとも保留数に応じた回数だけ普通図柄表示装置51は作動するようになっている。
【0058】
図2(a)に示すように、特別図柄表示装置13の表示部13aでは、各図柄列14〜16の図柄変動(回転変動)が、遊技球5の作動口3への入賞に基づいて開始させられる。また、大当たり図柄、外れリーチ図柄、外れ図柄の中から1つが選択され、これが停止図柄として設定される。停止図柄とは、各図柄列14〜16が図柄変動を停止したときに有効枠に表示される図柄である。本実施の形態では、図柄変動は、左図柄列14、右図柄列16、中図柄列15の順に停止させられるが、これはあくまでも1例にすぎず、別の順序で停止させられるようにしてもよい。
【0059】
大当たり図柄は、リーチ状態を経た後、遊技者に有利な特別遊技状態としての大当たり状態を発生させるための図柄である。詳しくは、図2(b)に示すように、全ての図柄列14〜16の変動が停止させられたとき、表示されている図柄17A〜17Hの組合せが、予め定められた大当たりの組合せとなる場合がある。すなわち、同一種類の図柄17A〜17Hが大当たりラインLに沿って並んだときに、同一図柄17A〜17Hの組合せ(例えば、図2(b)では「3」、「3」、「3」の図柄17C)となる場合がある。この組合せを構成する図柄が「大当たり図柄」である。大当たりの組合せが成立することを必要条件に、特別電動役物が作動し(大入賞口4が開かれ)、遊技者にとって有利な大当たり状態が発生させられる。すなわち、より多くの景品球を獲得することが可能となる。
【0060】
また、例えば図2(c)に示すように、リーチ状態とは、大当たり直前の状態をいう。リーチ状態には、右図柄列16の図柄変動が、大当たりラインL上において左図柄列14の停止図柄と同一種類の図柄で停止する状態が含まれる。図2(c)に示す例では、大当たりラインL上で停止している左・右両図柄列14,16の図柄17A〜17Hが共に「3」の図柄17Cとなっている。
【0061】
上記のリーチ状態には、中図柄列15の図柄変動が、最終的に左・右両図柄列14,16の停止図柄と同一種類の図柄(大当たり図柄)で停止して大当たり状態になるもの以外にも、異なる種類の図柄(これを「外れリーチ図柄」という)で停止して、大当たり状態とならないもの(以下、「外れリーチ状態」という)が含まれる。さらには、中図柄列15の図柄変動が一旦停止した後(一旦停止しなくてもよい)、同一種類の図柄17A〜17Hが大当たりラインLに沿って並んだ状態で、再度全図柄列14〜16が変動し、その後全図柄列14〜16の図柄17A〜17Hが揃って同時に停止するような場合(再変動リーチ、全回転リーチとも称される)も含まれる。
【0062】
上記リーチ状態においては、種々のリーチパターンが設定されている。リーチパターンとしては、「ノーマルリーチ」、「フラッシュリーチ」、「拡大リーチ」、「コマ送りリーチ」等の種々のリーチパターンが設定されている。これらリーチパターンのうち、「ノーマルリーチ」以外のリーチは、いわゆる「スーパーリーチ」と称されるものである。「スーパーリーチ」の動作が開始された場合には、一般に「ノーマルリーチ」の場合に比べて、大当たり状態が発生する期待値(大当たり期待値)が高くなるようになっている。
【0063】
遊技球5の作動口3への入賞に基づいて各図柄列14〜16の図柄変動が開始させられることはすでに説明したが、この変動表示中にさらに遊技球5が作動口3に入賞した場合には、通過ゲート54を通過した場合と同様、その分の変動表示は、現在行われている変動表示の終了後に行われる。つまり、変動表示が待機(保留)される。この保留される変動表示の最大回数は、パチンコ機の機種毎に決められている。本実施の形態では保留最大回数が4回に設定されているが、これに限られるものではない。
【0064】
図1に示すように、特別図柄表示装置13において、表示部13aの上方には、発光ダイオード(LED)からなる保留ランプ18a,18b,18c,18dが組み込まれている。当該保留ランプ18a〜18dの数は、前述した保留最大回数と同じ(この場合4個)である。保留ランプ18a〜18dは、変動表示の保留毎に点灯させられ、その保留に対応した変動表示の実行に伴い消灯させられる。
【0065】
なお、このほかにも、パチンコ機1の複数箇所には、遊技効果を高めるための他の各種ランプや電飾部材が取付けられている。これらの電飾部材等は、遊技の進行に応じて点灯状態(消灯、点灯、点滅等)が変えられる。さらに、パチンコ機1には、遊技の進行に応じて効果音を発生する図示しないスピーカが設けられている。
【0066】
遊技者の操作に応じて変化するパチンコ機1の遊技状態を検出するべく、本実施の形態では、遊技盤2には、スルースイッチ20、作動口用スイッチ21、Vゾーン用スイッチ22及びカウントスイッチ23等がそれぞれ取付けられている。スルースイッチ20は、遊技球の通過ゲート54の通過を検出し、作動口用スイッチ21は、遊技球5の作動口3への入賞を検出する。また、Vゾーン用スイッチ22は遊技球5の大入賞口4のうちのVゾーン8への入賞を検出し、カウントスイッチ23は、遊技球5の大入賞口4への入賞を検出する。
【0067】
本実施の形態では、各スイッチ20〜23の検出結果に基づきソレノイド10,12、特別図柄表示装置13、各保留ランプ18a〜18d、普通図柄表示装置51(7セグ表示部53及び保留ランプ52)、羽根6等をそれぞれ駆動制御するために制御装置24が設けられている。制御装置24は、読み出し専用メモリ(ROM)、中央処理装置(CPU)、ランダムアクセスメモリ(RAM)等を備えている。ROMは所定の制御プログラムや初期データを予め記憶しており、CPUはROMの制御プログラム等に従って各種演算処理を実行する。RAMは、CPUによる演算結果を、図3に示す図柄乱数バッファ31〜36、図4に示す図柄乱数エリア41(i)〜45(i)、図5に示す停止図柄エリア46〜48等に一時的に記憶する。
【0068】
図3に示すように、図柄乱数バッファは、左・中・右の3つの外れ図柄乱数バッファ31,32,33と、左・中・右の3つの外れリーチ図柄乱数バッファ34,35,36とによって構成されている。図4に示すように、図柄乱数エリアは、5つの内部乱数エリア41(i)と、5つの外れリーチ乱数エリア42(i)と、5つの左外れ図柄乱数エリア43(i)と、5つの中外れ図柄乱数エリア44(i)と、5つの右外れ図柄乱数エリア45(i)とによって構成されている。iは、5つずつ存在する各図柄乱数エリアを区別するためのものであり、「0」、「1」、「2」、「3」、「4」の値をとる。iの各値は、保留されている変動表示の回数に対応している。また、図5に示すように、停止図柄エリアは、左・中・右の各停止図柄乱数エリア46,47,48によって構成されている。
【0069】
また、本実施の形態においては、CPU(制御装置24)による制御の1つとして、遊技モードを切り換えるためのモード切換制御がある。本実施の形態においては、2つのモードが用意されている。すなわち、例えば300分の1程度の比較的低確率で大当たり遊技状態を発生させる通常モードと、その約5倍である60分の1程度の高確率で大当たり遊技状態を発生させる確率変動(確変)モードとがある。
【0070】
なお、一般的に、確変モードの概念としては、(1)7セグ表示部53に「7」が表示される確率を通常時に比べて高め、作動口3の羽根6を開放させる機会を増やすこと、(2)7セグ表示部53における数字の変動時間を短くすること、(3)羽根6の開放時間を長くすること(及び/又は入賞個数を多くすること)、(4)特別図柄表示装置13の表示部13aの図柄17A〜17Hの変動時間を短くすること、(5)大当たり期待値が通常モードに比べて高くなること等が挙げられるが、本実施の形態における確変モードにおいては、これら(1)〜(5)のうち、(5)のみ、すなわち、大当たり期待値が単に高められることのみが実行される。
【0071】
本実施の形態では、パチンコ機1の電源投入時においては、通常モードに設定される。また、その後は、大当たり遊技状態となった際に、確変モード又は通常モードのいずれかが選択されて、次回の大当たり遊技状態が発生するまでの間、当該選択されたモードが実行される。換言すれば、本実施の形態では、大当たり遊技状態となったときの図柄17A〜17H(大当たり図柄)が奇数(「1」、「3」、「5」、「7」)の場合に確変モードが実行され、大当たり遊技状態となったときの図柄17A〜17H(大当たり図柄)が偶数(「2」、「4」、「6」、「8」)の場合に、通常モードが実行される。
【0072】
また、本実施の形態では、いわゆるリーチ目表示が実行されるようになっている。すなわち、今回の図柄変動に際しては大当たり状態は発生しないものの、図柄変動の保留分の中で大当たり状態が発生するものがある場合(保留分の中の内部乱数カウンタCIの値が大当たり値である場合)には、近い将来大当たり状態が発生することを予告(報知)するべく特定の出目(本実施の形態では「3」「4」「1」の図柄(左、中、右図柄列の順):これをリーチ目と称する)で停止表示されるようになっている(図14(a)参照)。
【0073】
さらに、本実施の形態では、大当たり状態の発生とは無関係に、上記リーチ目と同様の出目(「3」「4」「1」の図柄)が停止表示されやすくなっている。これにより、「3」「4」「1」の図柄が停止表示された場合、遊技者は、大当たり発生の前兆たるリーチ目なのか、はたまたいわゆるガセのリーチ目なのか、わくわくしながら今後の図柄変動を見守ることとなる。
【0074】
併せて、本実施の形態では、大当たり状態の発生とは無関係に、上記リーチ目に似通った出目(「3」「1」「4」の図柄)が停止表示されやすくなっている(図14(b)参照)。これにより、「3」「1」「4」の図柄が停止表示された場合、遊技者は、上記リーチ目と何らかの関連があるのではないかと推測する場合が生じうるように構成されている。
【0075】
次に、前記のように構成されたパチンコ機1の作用及び効果について説明する。図7から図13のフローチャートは、制御装置24によって実行される各種ルーチンを示している。これらのルーチンの処理は、カウンタ群及び入賞判定フラグFE等に基づいて実行される。カウンタ群は、ラウンドカウンタCR、保留カウンタCH、入賞カウンタCE、内部乱数カウンタCI、外れリーチ乱数カウンタCO、大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCB、左・中・右の各図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDR、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCC、リーチ種別決定カウンタCV等よりなっている。
【0076】
なお、ラウンドカウンタCRは、ラウンド回数をカウントするためのものであり、入賞カウンタCEは大入賞口4への遊技球5の入賞個数をカウントするためのものである。また、保留カウンタCHは変動表示の保留回数をカウントするためのものであり、「0」,「1」,「2」,「3」,「4」の値を順にとる。これらの値は、前述した図柄乱数エリア41(i)〜45(i)の「(i)」に対応している。従って、CH=0は、保留されていない状態を意味する。
【0077】
図6(a)に示すように、内部乱数カウンタCIは、特別図柄表示装置13での大当たり状態を決定するためのものである。また、外れリーチ乱数カウンタCOは外れリーチ状態時の表示を行うか否かを決定するためのものである。さらに、大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBは、大当たり図柄を決定するためのものである。併せて、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCは、「3」「4」「1」(左中右図柄列14〜16に対応)又は「3」「1」「4」の図柄を停止表示させるか否かを決定するためのものである。これらのカウンタCI,CO,CB,CCはそれぞれ所定時間(例えば「2ms」)毎に値を所定範囲内で更新する。各値は、所定の条件に従って乱数として読み出される。また、各カウンタCI,CO,CB,CCは、各値がそれぞれ特定の値になった場合に、初期値に戻すようになっている。例えば、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCは、「0」〜「99」までの値をとり、大当たり時以外において、その時々に参酌された値が、「7」〜「17」の範囲内にあるときに、「3」「4」「1」の図柄が停止表示されるようになっている。また、大当たり時以外において、その時々に参酌された特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCの値が、「57」〜「67」の範囲内にあるときに、「3」「1」「4」の図柄が停止表示されるようになっている。
【0078】
左・中・右の各図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRは、大当たり時又はリーチ目停止表示時以外で、かつ、前記特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCの値が「7」〜「17」或いは「57」〜「67」の範囲外にある場合において、外れリーチ時又は外れ時における停止図柄等を決定するためのものである。左図柄乱数カウンタCDLは、所定時間(例えば「2ms」)毎に値を所定範囲内で更新し、特定の値になると初期値に戻す。中図柄乱数カウンタCDCは、左図柄乱数カウンタCDLが一巡する毎に値を所定範囲内で更新し、特定の値になると初期値に戻す。右図柄乱数カウンタCDRは、中図柄乱数カウンタCDCが一巡する毎に値を所定範囲内で更新し、特定の値になると初期値に戻す。従って、左・中・右の各図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRのカウント値は、外れリーチ時において、ランダム性をもって停止図柄を決定するために用いられる値である。
【0079】
また、図6(b)に示すリーチ種別決定カウンタCVは、リーチ状態発生時において上述した複数種類のリーチパターンのうちの1つを選択するために用いられるものであり、例えば左図柄乱数カウンタCDLが一巡する毎に値(乱数値)を更新し、特定の値になると初期値に戻す。ただし、各リーチパターンには重み付けがなされており、各リーチパターンの選択される確率は個々に異なったものとなっている。
【0080】
さらに、これらのカウンタ群は、通常モード用と確変モード用とでそれぞれ用意されている。つまり、これらの各カウンタ群は、通常モード用カウンタテーブルと確変モード用カウンタテーブルとにおいてそれぞれ用意されている。そして、通常モード時においては通常モード用カウンタテーブルのカウンタ群の更新、振り分け等が適宜行われ、確変モード時においては確変モード用カウンタテーブルのカウンタ群の更新、振り分け等が適宜行われる。もちろん、上記のように別々に用意する必要はなく(共通のカウンタ群を用いてもよく)、例えば確変モード時においては、内部乱数カウンタCIの大当たり値を単に増大させることとしてもよい。
【0081】
なお、入賞判定フラグFEは、Vゾーンへの入賞の有無を判定するために用いられるものである。同フラグFEは、入賞なしの場合に「0」に設定され、入賞ありの場合に「1」に設定される。
【0082】
さて、図7のフローチャートは、上述した各カウンタCI,CO,CB,CDL,CDC,CDR,CV,CCの更新後に、図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRの値(乱数)の組合せを分別し(振分け)、その振分けられた値を対応する図柄乱数バッファ31〜36に格納するための「乱数振分けルーチン」を示している。このルーチンは、パチンコ機1の電源投入後、所定時間(2ms)毎に実行される。このルーチンが開始されると、制御装置24はまずステップS1において、内部乱数カウンタCI、外れリーチ乱数カウンタCO、大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCB、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCにそれぞれ「1」を加算する(更新する)。
【0083】
また、ステップS2において、左図柄乱数カウンタCDLに「1」を加算する。中・右図柄乱数カウンタCDC,CDRに関しては、それぞれ左・中図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDCの値に応じて更新処理を行う。詳しくは、左図柄乱数カウンタCDLが初期値に戻されるタイミングであれば中図柄乱数カウンタCDCに「1」を加算し、それ以外のタイミングであれば同カウンタCDCの値を維持する。また、中図柄乱数カウンタCDCが初期値に戻されるタイミングであれば右図柄乱数カウンタCDRに「1」を加算し、それ以外のタイミングであれば同カウンタCDRの値を維持する。さらに、ステップS3において、制御装置24は、リーチ種別決定カウンタCVを更新する。
【0084】
次に、ステップS4において、図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRの値の組合せが、予め定められた「外れ図柄の組合せ」であるか否かを判断する。そして、この条件が満たされていると、ステップS5において各図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRの値を、対応する外れ図柄乱数バッファ31,32,33に格納する。ここで、対応する外れ図柄乱数バッファ31〜33とは、具体的には左図柄乱数カウンタCDLに関しては左外れ図柄乱数バッファ31を指し、中図柄乱数カウンタCDCに関しては中外れ図柄乱数バッファ32を指し、右図柄乱数カウンタCDRに関しては右外れ図柄乱数バッファ33を指すものとする(後述するステップS7に関しても同様)。そして、制御装置24は、ステップS5の処理を実行した後、その後の処理を一旦終了する。
【0085】
一方、前記ステップS4の条件が満たされていない場合には、ステップS6において、図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRの値の組合せが、予め定められた「外れリーチ図柄の組合せ」であるか否かを判断する。そして、この条件が満たされていると、ステップS7において、各図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRの値を、対応する外れリーチ図柄乱数バッファ34,35,36に格納し、その後の処理を一旦終了する。
【0086】
なお、ステップS6の条件が満たされていない場合には、前記ステップS5,7のいずれの処理をも行うことなく、「乱数振分けルーチン」を終了する。この場合とは、各図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRの値の組合せが、外れ図柄、外れリーチ図柄のいずれの組合せでもない場合、すなわち、大当たり図柄の組合せの場合である。
【0087】
このように、「乱数振分けルーチン」では、所定時間毎に3つの図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRの値の組合せがチェックされる。そして、外れ図柄の組合せの場合には、外れ図柄乱数バッファ31〜33に乱数が格納され、前後2コマ以上ずれた外れリーチ図柄の場合には、外れリーチ図柄乱数バッファ34〜36に乱数が格納される。また、大当たり図柄の組合せの場合には、乱数はどの図柄乱数バッファ31〜36にも格納されない。
【0088】
次に、図8のフローチャートに示す「格納処理ルーチン」について説明する。このルーチンの主な機能は、遊技球5が作動口3に入賞する毎に、乱数カウンタCI,CO,CDL,CDC,CDRの値を図柄乱数エリア41(i)〜45(i)に格納することである。
【0089】
当該「格納処理ルーチン」が開始されると、制御装置24は、ステップS10において、作動口用スイッチ21の検出結果に基づき、遊技球5が作動口3に入賞したか否かを判定する。そして、この判定条件が満たされていない場合には、その後の処理を一旦終了し、満たされている場合には、ステップS11において、保留カウンタCHの値が最大保留回数(この場合「4」)よりも小さいか否かを判定する。
【0090】
保留カウンタCHの値が最大保留回数よりも小さい場合には、ステップS12において、保留カウンタCHに「1」を加算する。また、続くステップS13において、制御装置24は対応する保留ランプ(18aから18dのうちの1つ)を点灯させ、ステップS14へ移行する。一方、前記ステップS11の判定条件が満たされていない場合には、前述したステップS12以降の処理を行うことなくその後の処理を一旦終了する。従って、図柄変動表示は、4回までしか保留されず、それ以上の入賞があっても保留は記憶されない。
【0091】
ステップS14において、制御装置24は、内部乱数カウンタCIの値を内部乱数エリア41(i)に格納する。また、次のステップS15において、外れリーチ乱数カウンタCOの値を、外れリーチ乱数エリア42(i)に格納する。さらに、ステップS16において、制御装置24は、左・中・右の各外れ図柄乱数バッファ31〜33の値(CDL,CDC,CDR)を、対応する左・中・右の各外れ図柄乱数エリア43(i)〜45(i)に格納し、その後の処理を一旦終了する。
【0092】
このように、「格納処理ルーチン」においては、乱数カウンタCI,CO,CDL,CDC,CDRの値が各図柄乱数エリア41(i)〜45(i)に格納される。なお、ステップS14〜ステップS16では、例えばステップS12での更新後の保留カウンタCHの値が「3」であれば、内部乱数エリア41(i=3)、外れリーチ乱数エリア42(i=3)、左外れ図柄乱数エリア43(i=3)、中外れ図柄乱数エリア44(i=3)、右外れ図柄乱数エリア45(i=3)が、今回制御周期での格納場所となる。
【0093】
次に、図9、図10のフローチャートに示す「特別電動役物制御ルーチン」について説明する。このルーチンは、前述した「乱数振分けルーチン」、「格納処理ルーチン」等の演算結果を用いて特別電動役物や、特別図柄表示装置13等を制御するためのものであり、パチンコ機1の電源投入後、所定時間毎に実行される。
【0094】
この「特別電動役物制御ルーチン」が開始されると、制御装置24はまずステップS20において、保留カウンタCHの値が「0」でないか否かを判定する。そして、否定判定された場合、つまり、保留カウンタCHの値が「0」の場合には、その後の処理を一旦終了する。これに対し、前記判定条件が満たされている(CH=1,2,3,4)場合には、ステップS30において、「i」を「0」に設定し、次のステップS40において保留カウンタCHが「i」と同一でないか否かを判定する。
【0095】
そして、この判定条件が満たされている場合(CH≠i)には、ステップS50において、内部乱数エリア41(i+1)、外れリーチ乱数エリア42(i+1)、外れ図柄乱数エリア43(i+1)〜45(i+1)の各データを、1つ前のエリア41(i)〜45(i)にそれぞれシフトする。次いで、ステップS60において、制御装置24は、「i」に「1」を加算し、ステップS40へ戻る。
【0096】
一方、ステップS40の判定条件が満たされない場合(CH=i)には、ステップS70へ移行し、保留ランプ18a〜18dのうち前記保留カウンタCHに対応するものを消灯させる。また、次のステップS80において保留カウンタCHから「1」を減算する。
【0097】
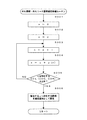
次に、制御装置24は、ステップS90において、図柄の変動開始処理を実行する。詳しくは、図11の「変動開始処理ルーチン」に示すように、ステップS901において、内部乱数カウンタCIの値が大当たり値であるか否かを判定する。そして、内部乱数カウンタCIの値が大当たり値の場合には、ステップS902において、大当たり値に対応する(大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値に基づく)大当たり図柄を確定図柄としてメモリに記憶し、ステップS907へ移行する。
【0098】
一方、ステップS901における判定条件が満たされていないと、ステップS903において、リーチ目図柄記憶処理を実行する。すなわち、図12の「リーチ目図柄記憶処理ルーチン」に示すように、ステップS9031において制御装置24は、現在保留分として格納されている内部乱数カウンタCIの値の中に、大当たり値が存在しているか否かを判定する。そして、否定判定された場合には、何らの処理をも行うことなくその後の処理を一旦終了する。これに対し、ステップS9031で肯定判定された場合には、極めて近い将来大当たり状態が発生しうるものとして、それを遊技者にリーチ目でもって予告(報知)するべく、ステップS9032において、強制的に「3」「4」「1」の図柄(図14(a)参照)を確定図柄として記憶し、その後の処理を一旦終了する。従って、今回は大当たり状態は発生しないが、近い将来大当たり状態が発生することが明らかな場合には、いわゆるリーチ目として、「3」「4」「1」の図柄が最終的に停止表示されることとなる。また、その時点で、保留分が複数あるような場合には、大当たり状態の発生まで「3」「4」「1」のリーチ目が連続的に停止表示されうることとなる。
【0099】
このように、リーチ目図柄記憶処理を実行した後、制御装置24は、次のステップS904において、特別外れ図柄記憶処理を実行する。すなわち、図13の「特別外れ図柄記憶処理ルーチン」に示すように、ステップS9041において制御装置24は、今回の特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCの値が予め定められた第1の所定範囲内(7以上17以下)にあるか否かを判定する。そして、肯定判定された場合には、ステップS9042において、いわゆるガセのリーチ目を表示するべく、上記リーチ目と同じ「3」「4」「1」の図柄(図14(a)参照)を確定図柄として記憶し、その後の処理を一旦終了する。また、前記ステップS9041で否定判定された場合には、ステップS9043において、今回の特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCの値が予め定められた第2の所定範囲内(57以上67以下)にあるか否かを判定する。そして、肯定判定された場合には、ステップS9044において、前記リーチ目に類似した出目を表示するべく、「3」「1」「4」の図柄(図14(b)参照)を確定図柄として記憶し、その後の処理を一旦終了する。一方、ステップS9043で否定判定された場合には、何らの処理をも行うことなくその後の処理を一旦終了する。
【0100】
従って、今回の特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCの値が第1の所定範囲内にある場合にも、大当たり状態の発生とは無関係に前記リーチ目と同じ「3」「4」「1」の図柄が最終的に停止表示されることとなる。また、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCの値が第2の所定範囲内にある場合には、前記リーチ目と似通った「3」「1」「4」の図柄が最終的に停止表示されることとなる。
【0101】
さて、上記のように特別外れ図柄記憶処理を実行した後、制御装置24は、ステップS905において、外れリーチ乱数カウンタCOの値が予め定められた外れリーチ値と同じであるか否かを判定する。そして、外れリーチ乱数カウンタCOの値が外れリーチ値と同一である場合には、ステップS906において、外れリーチ値に対応する図柄(外れリーチ図柄)を確定図柄としてメモリに記憶し、ステップS907へ移行する。
【0102】
さらに、ステップS905の判定条件が満たされていない場合には、ステップS908において、ステップS16での外れ図柄を停止図柄としてメモリに記憶し、ステップS909へ移行する。
【0103】
さて、ステップS902又はステップS906から移行して、ステップS907においては、前記リーチ種別決定カウンタCVに基づいてリーチパターンを取得する。すなわち、上述した「ノーマルリーチ」、「フラッシュリーチ」、「拡大リーチ」、「コマ送りリーチ」等の種々のリーチパターンのうちのいずれかを決定する。
【0104】
そして、ステップS907又はステップS908から移行して、ステップS909においては、特別図柄表示装置13の図柄変動を開始させ、「変動開始処理ルーチン」を終了する。
【0105】
さて、上記のように、ステップS90(「変動開始処理ルーチン」)の処理を実行した後、制御装置24は、図9のステップS110において、左右両図柄列14,16(中図柄列15以外)における図柄17A〜17Hを、前記ステップS902,S906,S908のいずれかの処理で記憶した停止図柄(確定図柄)に差替える。また、差替え後の図柄17A〜17Lが左右両図柄列14,16にて表示されるよう図柄変動を停止させる。
【0106】
次に、ステップS120において、制御装置24は、リーチ動作処理を行う。詳しくは、ステップS907で取得したリーチパターンが、「ノーマルリーチ」の場合には、ノーマルリーチ動作処理(通常時と同様の変動態様で、遊技者が図柄視認できる程度のゆっくりとした変動処理)を行い、リーチパターンが「フラッシュリーチ」の場合には、フラッシュリーチ動作(図柄17A〜17Hをフラッシュさせながら変動表示させる)処理を行い、リーチパターンが「拡大リーチ」の場合には、拡大リーチ動作(図柄17A〜17Hを拡大させながら変動表示させる)処理を行う。また、リーチパターンが「コマ送りリーチ」の場合には、コマ送りリーチ動作(図柄17A〜17Hを1コマずつ一旦停止させながら変動表示させる。)処理を行う。これらのリーチ演出に際しては、遊技者に一層のどきどき感を持たせるべく音声、光等の演出をも併せて行ったり、図柄17A〜17H、背景の色彩等をそれまでとは異ならせることとしてもよい。そして、その後の処理を一旦終了する。一方、リーチパターンが取得されていない場合には、いずれのリーチ動作処理をも行うことなく、当該「リーチ動作処理ルーチン」を一旦終了する。
【0107】
上記のように、ステップS120(「リーチ動作処理ルーチン」)の処理を実行した後、制御装置24は、ステップS130において、中図柄列15での図柄変動を停止させる。なお、中図柄列15での変動停止に際し、ステップS135に示すような再抽選処理を実行してもよい。詳しくは、再抽選処理を実行する条件が成立している場合(例えば通常モードの付与される大当たり図柄が一旦停止表示された場合等)には、全図柄列14〜16の図柄17A〜17Hを同時に再変動させる。そして、所定条件が成立した後、全図柄列14〜16の図柄17A〜17Hを揃った状態で停止させる。一方、再抽選処理を実行する条件が成立していない場合には、何らの処理をも実行しない。
【0108】
さて、制御装置24は、次に、ステップS140において、図柄17A〜17Hの組合せが大当たりの組合せであるか否かを判定する。なお、この際には、停止図柄の差替えが正しく行われたか否かの確認も行われる。そして、この判定条件が満たされていない場合には、「特別電動役物制御ルーチン」を終了する。また、図柄17A〜17Hの組合せが大当たりの組合せである場合には、ステップS150において、ラウンドカウンタCRを「0」にクリヤする。なお、このとき、制御装置24によって大当たり報知表示がなされるとともに、モード判定処理が実行される。より詳しくは、今回の大当たり状態における大当たり図柄が奇数の場合には、大当たり終了後次回の遊技において確変モードとするべく遊技モードフラグが「1」に設定され、大当たり図柄が偶数の場合には、大当たり終了後次回の遊技において通常モードとするべく遊技モードフラグが「0」に設定される等の処理が行われる。もちろん、大当たり図柄とは無関係に、通常モード又は確変モードを選択することとしてもよい。
【0109】
さて、次に、制御装置24は、ステップS160(図10参照)において、入賞カウンタCEを「0」にクリヤするとともに、入賞判定フラグFEを「0」に設定する。また、続くステップS170においては、ラウンドカウンタCRを「1」ずつインクリメントする。
【0110】
さらに、ステップS180において、制御装置24は、大入賞口用ソレノイド12を励磁させる。すると、シャッタ11が倒れて略水平状態となり、大入賞口4が開放される。この開放により、遊技球5のVゾーン8及び入賞通路9への入賞が可能となる。
【0111】
次に、ステップS190において、制御装置24は、入賞カウンタCEの値が予め定められた所定値CEmaxよりも小さいか否かを判定する。そして、この判定条件が満たされている場合には、ステップS200において、未だ大入賞口4の閉鎖予定時期が到来していないか否かを判定する。この閉鎖予定時期が到来していない場合には、処理をステップS190へ戻す。その結果、大入賞口4の開放開始後に所定値CEmax個よりも多くの遊技球5が入賞するか、閉鎖予定時期が到来するかしない限りは、大入賞口4が開放され続ける。これに対し、ステップS190又はステップS200のいずれか一方が満たされていないと、ステップS210において、制御装置24は、大入賞口用ソレノイド12を消磁する。すると、シャッタ11が起こされて略垂直状態となり、大入賞口4が閉鎖される。
【0112】
続いて、ステップS220において、制御装置24は、ラウンドカウンタCRの値が予め定められた所定値CRmaxよりも小さいか否かを判定する。そして、ラウンドカウンタCRの値が所定値CRmax未満の場合には、続くステップS230において入賞判定フラグFEが「1」であるか否かを判定する。入賞判定フラグFEが「1」の場合には、処理をステップS160へと戻す。従って、一旦大当たり遊技状態が発生すると、遊技球5がVゾーン8に入賞することによる継続条件が、所定値CRmax回数満たされるまでは、大入賞口4が開閉のサイクルを繰り返す。例えば所定値CEmaxが「10」に設定され、大入賞口4の開放時間が「約29.5秒」に設定され、所定値CRmaxが「16」に設定されている場合には、大入賞口4の開放後、(1)遊技球5が大入賞口4へ10個入賞すること、(2)約29.5秒が経過すること、のいずれか一方の条件が満たされた時点で大入賞口4が閉鎖される。この大入賞口4の開閉のサイクルが遊技球5のVゾーン8への入賞を条件に最大で16回(16ラウンド)繰り返されることとなる。
【0113】
そして、ステップS220又はステップS230の判定条件のいずれか一方が満たされていない場合には、大当たり状態が終了したものとして、その旨を表示部13aに表示するとともに、次回の遊技モードを前記遊技モードフラグに基づいて報知する処理を実行し、本ルーチンを終了する。
【0114】
以上詳述したように、本実施の形態によれば、(1)いわゆるリーチ目表示が実行され、また、(2)大当たり状態の発生とは無関係に、上記リーチ目と同様の出目(「3」「4」「1」の図柄)でもってガセのリーチ目表示が実行される。このため、見た目では各図柄列14〜16の図柄17A〜17Hはそれぞれ均等の割合で存在するのであるが、本実施の形態では実際には「3」「4」「1」の図柄が停止表示されやすくなっている。このため、遊技者は見た目の図柄17A〜17Hと実際の図柄17A〜17Hとの停止表示頻度の違いに驚きを覚えるとともに、特殊な遊技性を堪能することができる。その結果、興趣の飛躍的な向上を図ることができる。
【0115】
また、本実施の形態では、大当たり状態の発生に密接に関連するリーチ目の表示以外にも、ガセのリーチ目を表示することとした。従って、「3」「4」「1」の図柄が停止表示された場合、遊技者は、大当たり発生の前兆たるリーチ目なのか、はたまたいわゆるガセのリーチ目なのか、わくわくしながら今後の図柄変動を見守ることとなる。そのため、さらなる興趣の向上が図られる。
【0116】
さらに、大当たり状態の発生とは無関係に、上記リーチ目に似通った出目(「3」「1」「4」の図柄)が停止表示されやすくなっている。このため、「3」「1」「4」の図柄が停止表示された場合、遊技者は、上記リーチ目と何らかの関連があるのではないかと推測する場合が生じ、遊技内容にさらに厚みが増すこととなる。
【0117】
併せて、本実施の形態では、上記特別な図柄(「3」「4」「1」又は「3」「1」「4」の図柄)が停止表示されやすくするために、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCなるものを別途設け、その値が所定範囲内にあるか否かに応じて、「3」「4」「1」又は「3」「1」「4」の図柄を停止表示することとした。従って、所定範囲を適宜変更することで、「3」「4」「1」等の出目の出現率(前記特定の図柄が最終的に停止表示される確率)を適宜調整することができる。
【0118】
尚、上記実施の形態の記載内容に限定されず、例えば次のように実施してもよい。
【0119】
(1a)上記実施の形態では、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCの値が第1の所定範囲内(例えば7以上17以下)にある場合には、いわゆるガセのリーチ目を表示するべく、リーチ目と同じ「3」「4」「1」の図柄を最終的に停止させ、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCの値が第2の所定範囲内(例えば57以上67以下)にある場合には、「3」「1」「4」の図柄を最終的に停止させることとした。これに対し、リーチ目に似通った図柄の停止表示を行わない構成としてもよい。
【0120】
(1b)また、所定範囲ではなく、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCの値が所定値(例えば7、或いは7,17等:所定値は単数でも複数でも可)の場合にリーチ目と同じ「3」「4」「1」の図柄を最終的に停止させることとしてもよい。
【0121】
(1c)さらに、(第1の)所定範囲を複数の値、範囲群から構成してもよい。例えば特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCの値が7、17〜27、87〜97の場合に「3」「4」「1」の図柄を最終的に停止させることとしてもよい。
【0122】
(1d)併せて、上記実施の形態では特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCの値が前記所定範囲内にない場合には、ステップS906(外れリーチ図柄を別途決定)又はステップS908(外れ図柄を別途決定)の処理を経ることとした。これに対し、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCの値に対応させて大当たり時以外の確定図柄を設定することとしてもよい。例えば、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCの値が0〜39の場合には「4」「3」「1」が、40〜79の場合には「3」「1」「4」が、80〜92の場合には「3」「4」「1」が、93〜99の場合には「1」「2」「1」、「2」「3」「2」等の外れリーチ図柄が最終的に停止表示される図柄となるようにしてもよい。このような構成とした場合、左・中・右の各図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRは不必要となる。
【0123】
(1e)上記実施の形態では、別途特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCを設け、その値に応じて、最終的に停止される図柄を設定可能としたが、当該カウンタCCを用いずに、例えば内部乱数カウンタCIの値に対応させて、最終的に停止される図柄を決定することとしてもよい。この場合、別途カウンタCCを設ける必要がないというメリットがある。
【0124】
(1f)上記実施の形態では、いわゆるリーチ目に関連させて、リーチ目と同様の図柄の出現率を見た目よりも増大させることとした。これに対し、リーチ目とは無関係の特定の外れ図柄(又は外れリーチ図柄)の出現率を、見た目と異ならせるようにしてもよい。例えば、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCの値が所定範囲内にある場合には、「1」「2」「3」が最終的に停止表示されるような構成としてもよい。この場合、そのような特定の外れ図柄に全く意味を持たせないようにしてもよいし、何らかの意味合いを持たせるようにしてもよい。意味合いを持たせる場合の具体例としては、例えば特定の外れ図柄で最終的に停止表示された場合に、(1)遊技モードが通常モードから確変モードに切換えられることとしたり、(2)確変モードから通常モードに切り換えられることとしたり、(1)と(2)とを組み合わせたりすることが例として挙げられる。さらに、この場合、現在の遊技モード(確変モード中であるか否か等)に応じて、特定の外れ図柄の出現率を可変とすることとしてもよい。
【0125】
上記のような構成とすることで、前記特定の外れ図柄の出現頻度が、見た目よりも増えたり減ったりすることとなり、面白味が増す。もちろん、このような上記リーチ目と同様の図柄と、前記特定の外れ図柄との双方の出現頻度が、見た目と異なるようにしてもよい。なお、上記各事項は、後述する実施の形態(特に第2の実施の形態)についても同様のことがいえる。
【0126】
(第2の実施の形態)
次に、第2の実施の形態について説明する。但し、本実施の形態において、上記第1の実施の形態と重複する部分等については、その説明を省略することとし、以下には、相違点を中心として説明することとする。
【0127】
上記第1の実施の形態では、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCなるものを別途設け、そのカウンタCCの値が第1の所定範囲内にある場合に、いわゆるガセのリーチ目を表示するべく、リーチ目と同じ「3」「4」「1」の図柄を最終的に停止させることとした。これに対し、本実施の形態では、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCを用いず、左・中・右の各図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDR及び図15(a)〜(c)に示すテーブルを用いているという点で特徴を有している。
【0128】
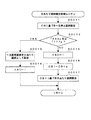
本実施の形態では、ステップS904において特別外れ図柄記憶処理を実行していた第1の実施の形態とは異なり、図16の「変動開始処理ルーチン」に示すように、ステップS903で、リーチ目図柄記憶処理を実行した後、制御装置24は、直接ステップS905へ移行し、外れリーチ乱数カウンタCOの値が予め定められた外れリーチ値と同じであるか否かを判定する。そして、その判定結果に応じてステップS906又はステップS908で外れリーチ図柄又は外れ図柄を確定図柄として記憶するようにしている。
【0129】
図17は、ステップS906又はステップS908の処理に際し行われる「外れ図柄・外れリーチ図柄確定処理ルーチン」を示すフローチャートである。同図に示すように、処理がこのルーチンに移行すると、制御装置24は、ステップS001において、まず、しきい値xを初期化するべく「0」に設定する。また、これとともに、ステップS002において加算回数nを「0」に設定する。
【0130】
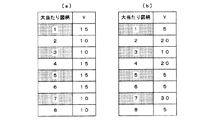
そして、次のステップS003において、制御装置24は、加算回数nを「1」ずつインクリメントする。また、続くステップS004において、制御装置24は、現在のしきい値xに対し、n回目の加算値y(n)を加算し、その値を新たなしきい値xとして設定する。ここで、n回目の加算値y(n)というのは、図15のテーブルに示すように、例えば左図柄列14については、1回目の加算値y(n=1)が「10」、2回目の加算値y(n=2)が「10」、3回目の加算値y(n=3)が「30」、4回目の加算値y(n=4)が「10」、・・・、8回目の加算値y(n=8)が「10」といった具合に、図柄数(本実施の形態では「1」〜「8」までの8つ)に応じて、予め設定されているものである。
【0131】
さらに、次のステップS005において、制御装置24は、現在設定されているしきい値xが対応する各左・中・右の各図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRの値(但し、カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRは、いずれも「0」〜「99」までの値をとるとする)以上であるか否かを判定する。そして、現在設定されているしきい値xが対応する各左・中・右の各図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRの値以上の場合には、ステップS006において、該当する加算値y(n)に対応する図柄を確定図柄として設定し、その後の処理を一旦終了する。
【0132】
一方、ステップS005で否定判定された場合には、ステップS003へ処理を戻し、ステップS005で肯定判定されるまでステップS003〜005の処理を繰り返す。
【0133】
例えば、今回、対応する左図柄乱数カウンタCDLの値が「45」であったとする。この場合、n=1の場合にはx=10となって、ステップS005で否定判定され、n=2の場合にはx=20となって、ステップS005で否定判定される。そして、n=3の場合には、x=50となって、ステップS005で肯定判定されることとなる。従って、この場合、該当する加算値yに対応する図柄は図15(a)のテーブルより「3」となる。つまり、今回、対応する左図柄乱数カウンタCDLの値が「45」であった場合には、左図柄列14において、確定図柄として設定され記憶されるのは「3」ということになる。
【0134】
また、例えば今回、対応する中図柄乱数カウンタCDCの値が「55」であったとする。この場合、n=1〜3の場合にはいずれもステップS005で否定判定され、n=4の場合にx=60となって、ステップS005で肯定判定されることとなる。従って、この場合、該当する加算値yに対応する図柄は図15(b)のテーブルより「4」となる。つまり、今回、対応する中図柄乱数カウンタCDCの値が「55」であった場合には、中図柄列15において、確定図柄として設定され記憶されるのは「4」ということになる。
【0135】
さらに、例えば今回、対応する右図柄乱数カウンタCDRの値が「25」であったとする。この場合、n=1の場合にx=30となって、ステップS005でいきなり肯定判定されることとなる。従って、この場合、該当する加算値yに対応する図柄は図15(c)のテーブルより「1」となる。つまり、今回、対応する右図柄乱数カウンタCDRの値が「25」であった場合には、右図柄列16において、確定図柄として設定され記憶されるのは「1」ということになる。
【0136】
本実施の形態では図15の各テーブルの各加算値yの合計値は「100」となるよう設定されており、このことから、加算値yは、各図柄が確定図柄として設定される確率(パーセンテージ)をも表しているのである。従って、各テーブルの加算値yの値からも明らかなように、本実施の形態では、左図柄列14においては「3」の図柄17Cが、中図柄列15においては「4」の図柄17Dが、右図柄列16においては「1」の図柄17Aが、それぞれ他の図柄よりも最終的に停止表示される確率(出現率、出現頻度)が見た目よりも高くなっているのである。
【0137】
以上詳述したように、本実施の形態によれば、上記第1の実施の形態で説明した作用効果に加えて、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCを別途設ける必要がないので、データ容量の削減、制御内容の簡素化等を図ることができる。
【0138】
また、本実施の形態では、各図柄列14〜16の最終的に停止表示される図柄を設定する際に用いる各テーブルの各加算値yの合計値が「100」となるようにしたため、加算値yは、各図柄が確定図柄として設定される確率をも表すこととなる。このため、各図柄が停止表示される確率を適宜調整しようとした場合に、その出現させたい比率をそのままパーセンテージとして加算値yを設定すれば済むこととなる。このため、各図柄の出現率の設定が非常に容易なものとなり、出現率を設定するに際し複雑かつ難解な演算等を行わなくても済む。
【0139】
さらに、図柄の出現率を変更しようとした場合には、各テーブルの加算値yの値を適宜パーセンテージとして設定し直すだけでよい。その結果、出現率の変更の要請があった場合には、極めて容易に出現率の変更再設定を行うことができる。
【0140】
尚、上記実施の形態の記載内容に限定されず、例えば次のように実施してもよい。
【0141】
(2a)上記第2の実施の形態では、加算値yに基づいてしきい値xを求め、このしきい値xと対応する各左・中・右の各図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRの値とを比較し、その比較結果に基づいて最終的に停止表示される図柄を設定するようにしていた。これに対し、単純に左・中・右の各図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRの値に応じて、左・中・右の各図柄列14〜16における最終的に停止される図柄を設定することとしてもよい。
【0142】
(2b)例えば、図18(a),(b),(c)に示すように、各図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRが「0」〜「9」の値をとることとして、各カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRの値と、図柄とを一義的に対応させて設定することとしてもよい。図18(a)を例にとって説明すると、今回対応する左図柄乱数カウンタCDLの値が「0」の場合には、今回左図柄列14において最終的に設定される図柄は「1」の図柄17Aとなり、CDLの値が「1」の場合には、今回左図柄列14において最終的に設定される図柄は「2」の図柄17Bとなり、カウンタCDLの値が「2」、「3」又は「4」の場合には、今回左図柄列14において最終的に設定される図柄は「3」の図柄17Cとなり、カウンタCDLの値が「5」の場合には、今回左図柄列14において最終的に設定される図柄は「4」の図柄17Dとなり、・・・、左図柄乱数カウンタCDLの値が「9」の場合には、今回左図柄列14において最終的に設定される図柄は「8」の図柄17Hとなる。従って、この場合、左図柄列14においては、「3」の図柄17Cが他の図柄に比べて3倍の出現率で出現表示されることとなる。また、同様に、図18(b),(c)に示すように、中・右図柄列15,16においては、それぞれ「4」の図柄17D、「1」の図柄17Aが他の図柄に比べて3倍の出現率で出現表示される。このように、左・中・右の各図柄乱数カウンタCDL,CDC,CDRの値に基づいて、一義的に左・中・右の各図柄列14〜16における最終的に停止される図柄を設定することとしてもよい。
【0143】
(2c)また、例えば図19に示すように、図柄乱数カウンタ(例えば左図柄乱数カウンタCDL)が「0」〜「9」の値をとることとして、今回対応する左図柄乱数カウンタCDLの値が「0」の場合には、今回左図柄列14において最終的に設定される図柄は「1」の図柄17Aとなり、CDLの値が「1」の場合には、今回左図柄列14において最終的に設定される図柄は「2」の図柄17Bとなり、カウンタCDLの値が「2」の場合には、今回左図柄列14において最終的に設定される図柄は「3」の図柄17Cとなり、カウンタCDLの値が「3」の場合には、今回左図柄列14において最終的に設定される図柄は「4」の図柄17Dとなり、・・・、左図柄乱数カウンタCDLの値が「7」の場合には、今回左図柄列14において最終的に設定される図柄は「8」の図柄17Hとなるよう基本データを設定しておく。そして、例えば「3」の図柄17Cの出現率を高めようとした場合には、追加データとして、カウンタCDLの値が「8」又は「9」の場合には、今回左図柄列14において最終的に設定される図柄が「3」の図柄17Cとなるよう設定することとしてもよい。このような構成とすることで、基本データを変更することなく、追加データを適宜切り換えることで、任意に所定の図柄の出現率の調整を行うことができる。
【0144】
(2d)上記実施の形態(特に第1の実施の形態)では、「3」「4」「1」といった具合に、左、中、右の全図柄列14〜16についての停止図柄をセットにして出現頻度を見た目と異ならせるようにしたが、上記各実施の形態を応用することで、左図柄列14のみ、中図柄列15のみ、右図柄列16のみといった具合に1つの図柄列の図柄に関してだけ、出現頻度を見た目と異ならせることとしてもよい。また、もちろん、左図柄列14と中図柄列15、左図柄列14と右図柄列16、中図柄列15と右図柄列16といった具合に2つの図柄列の図柄に関してだけ、出現頻度を見た目と異ならせることとしてもよい。
【0145】
(2e)上記各実施の形態では、「3」「4」「1」といった外れ図柄の出現頻度を見た目と異ならせることとしたが、各実施の形態を応用することにより、外れリーチ図柄の出現頻度を見た目と異ならせることもできる。
【0146】
例えば、上記第1の実施の形態において、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCCの値が所定範囲内にある場合には、「1」「2」「1」等の外れリーチ図柄を確定図柄として記憶することとしてもよい。この場合、外れリーチ乱数カウンタCOにかかわらず、リーチパターンが取得され、リーチ遊技状態が演出されることとなる(また、リーチ演出を行わないこととしてもよい)。
【0147】
また、例えば上記第2の実施の形態において、テーブルの加算値yの値を適宜調整することで、外れリーチ図柄(例えば「3」「4」「3」等)が最終的に停止表示される確率を高めたり低くしたりすることも可能となる。
【0148】
(第3の実施の形態)
次に、第3の実施の形態について説明する。但し、本実施の形態において、上記第1、第2の実施の形態と重複する部分等については、その説明を省略することとし、以下には、相違点を中心として説明することとする。
【0149】
上記第1及び第2の実施の形態では、リーチ目と同じ「3」「4」「1」の図柄、ひいては、外れ図柄の出現率を見た目と異ならせることとした。また、上記別例(2e)では外れリーチ図柄の出現率を見た目と異ならせることができることにも言及した。これに対し、本実施の形態では、「3」「3」「3」、「4」「4」「4」といった大当たり図柄(大当たり出目)の出現率を見た目と異ならせるようにしたという点で特徴を有している。
【0150】
本実施の形態では、ステップS902の大当たり図柄の決定処理において、図20に示すような処理が実行される。すなわち、図20は、制御装置24により実行される「大当たり図柄確定処理ルーチン」を示すフローチャートである。処理がこのルーチンに移行すると、制御装置24はまずステップS0001において、しきい値xを初期化するべく「0」に設定する。また、これとともに、ステップS0002において加算回数nを「0」に設定する。
【0151】
そして、次のステップS0003において、制御装置24は、加算回数nを「1」ずつインクリメントする。また、続くステップS0004において、制御装置24は、現在のしきい値xに対し、n回目の加算値Y(n)を加算し、その値を新たなしきい値xとして設定する。ここで、n回目の加算値Y(n)というのは、図21のテーブルに示すように、大当たり図柄について、1回目の加算値Y(n=1)が「15」、2回目の加算値Y(n=2)が「10」、3回目の加算値Y(n=3)が「15」、4回目の加算値Y(n=4)が「10」、・・・、8回目の加算値Y(n=8)が「10」といった具合に、大当たり図柄数(本実施の形態では「1」〜「8」までの8つ)に応じて、予め設定されているものである。
【0152】
さらに、次のステップS0005において、制御装置24は、現在設定されているしきい値xが対応する大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値(但し、カウンタCBは、「0」〜「99」までの値をとるとする)以上であるか否かを判定する。そして、現在設定されているしきい値xが対応する大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値以上の場合には、ステップS0006において、該当する加算値Y(n)に対応する図柄を大当たり図柄として設定し、その後の処理を一旦終了する。
【0153】
一方、ステップS0005で否定判定された場合には、ステップS0003へ処理を戻し、ステップS0005で肯定判定されるまでステップS0003〜0005の処理を繰り返す。
【0154】
例えば、今回、対応する大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値が「37」であったとする。この場合、n=1の場合にはx=15となって、ステップS0005で否定判定され、n=2の場合にはx=25(15+10)となって、ステップS0005で否定判定される。そして、n=3の場合には、x=40(15+10+15)となって、ステップS0005で肯定判定されることとなる。従って、この場合、該当する加算値Yに対応する大当たり図柄は図21のテーブルより「3」となる。つまり、今回、対応する大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値が「37」であった場合には、大当たり図柄として「3」「3」「3」が設定され記憶されることになる。
【0155】
本実施の形態では図21のテーブルの各加算値Yの合計値は第2の実施の形態の場合と同様「100」となるよう設定されており、このことから、加算値Yは、各大当たり図柄が確定図柄として設定される確率(パーセンテージ)をも表しているのである。従って、テーブルの加算値Yの値からも明らかなように、本実施の形態では、「1」、「3」、「5」、「7」といった奇数の大当たり図柄17A,17C,17E,17Gが、偶数の大当たり図柄よりも最終的に停止表示される確率(出現率、出現頻度)が見た目よりも高くなっているのである。換言すれば、見た目では、大当たり状態終了後に確変モードが付与される確率は、通常モードと同様50%であるのに対し、実際に確変モードが付与される確率は、15×4=60%となっているのである。
【0156】
以上詳述したように、本実施の形態によれば、上記第1、第2の実施の形態で説明した作用効果の外に、大当たり図柄の出現率を見た目と実際とで異ならせることとした。このため、遊技者は見た目の大当たり図柄の出現率と実際の大当たり図柄の出現率の違いに驚きを覚えるとともに、特殊な遊技性を堪能することができる。その結果、興趣の飛躍的な向上を図ることができる。
【0157】
特に、本実施の形態では、大当たり図柄の種類によって、大当たり終了後の遊技において確変モードが付与されるか否かが決定される。従って、本実施の形態のようなテーブルの加算値Yの調整を適宜行うことで、確変モードの付与される確率を見た目と異ならせることができる。その結果、興趣の向上に拍車がかけられることとなる。
【0158】
また、上述したように、大当たり図柄を設定する際に用いるテーブルの各加算値Yの合計値が「100」となるようにしたため、加算値Yは、各大当たり図柄が確定図柄として設定される確率をも表すこととなる。このため、各大当たり図柄が停止表示される確率を適宜調整しようとした場合に、その出現させたい比率をそのままパーセンテージとして加算値Yを設定すれば済むこととなる。このため、大当たり図柄の出現率の設定が非常に容易なものとなり、出現率を設定するに際し複雑かつ難解な演算等を行わなくても済む。
【0159】
さらに、大当たり図柄の出現率を変更しようとした場合には、各テーブルの加算値Yの値を適宜パーセンテージとして設定し直すだけでよい。その結果、出現率の変更の要請があった場合には、極めて容易に出現率の変更再設定を行うことができる。
【0160】
尚、上記実施の形態の記載内容に限定されず、例えば次のように実施してもよい。
【0161】
(3a)上記第3の実施の形態では、実際に確変モードの付与される確率を見た目と異ならせることとした(見た目は50%であるのに対し、実際には60%の確率で確変モードが付与される)。これに対し、実際に確変モードの付与される確率を見た目と同じにして、個々の大当たり図柄の出現率を見た目と異ならせることとしてもよい。例えば、大当たり図柄の決定に際し、図22(a),(b)に示すようなテーブルを用いて大当たり図柄を決定することとしてもよい。
【0162】
(3b)例えば、図22(a)のようなテーブルを用いた場合には、同じ確変モードの付与される図柄であっても、「3」、「7」の大当たり図柄は、「1」、「5」の大当たり図柄よりも実際の出現率が低く設定されている。このような設定を行うことにより、遊技場の営業に関し、「3」、「7」の図柄で大当たり状態が発生した場合には、景品球を交換することなく継続遊技を行うことのできるような営業形態を採用している場合には、「3」、「7」の出現率を低くできることから、継続遊技が比較的行われにくいものとなる。また、逆に、同図のテーブルでは、同じ通常モードの付与される図柄であっても、「4」、「6」の大当たり図柄は、「2」、「8」の大当たり図柄よりも実際の出現率が高く設定されている。このような設定を行うことにより、遊技場の営業に関し、「4」、「6」の図柄で大当たり状態が発生した場合には、景品球を全て交換しなければならないといった営業形態を採用している場合には、「4」、「6」の出現率を高くできることから、継続遊技がさらに行われにくいものとなる。もちろん、上記の関係に拘泥されることなく、「3」、「7」の出現率を高く設定したり、「4」、「6」の出現率低く設定したりもできる。
【0163】
(3c)また、例えば、図22(b)のようなテーブルを用いた場合には、「7」の大当たり図柄が極端に出現しやすくなっている。このような構成とすることで、「7」の図柄17Gでリーチ状態が発生した場合、遊技者にとってのわくわく感は極端に高められることとなる。この場合、例えば図23に示すように、大当たりラインとして上中下の3本及び斜めの2本のクロスラインよりなる5ラインタイプ(大当たりラインが5つ用意されているタイプ)の表示部13aを有することとすると、例えば、同図に示すように「6」、「7」のクロスラインでリーチ状態が発生すると、大当たり状態が発生する場合には、5:30の割合で「7」の大当たり図柄が停止表示されうることから、遊技者は「7」の図柄17Gでの大当たりに熱い期待感を寄せることとなる。かかる意味で、一層の興趣の向上を図ることも可能となる。
【0164】
(3d)上記第3の実施の形態では、加算値Yに基づいてしきい値xを求め、このしきい値xと対応する大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値とを比較し、その比較結果に基づいて大当たり図柄を設定するようにしていた。これに対し、単純に大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値に応じて、大当たり図柄を設定することとしてもよい。
【0165】
(3e)例えば、図24(a)に示すように、大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBが「0」〜「99」の値をとることとして、該カウンタCBの値と、大当たり図柄とを一義的に対応させて設定することとしてもよい。同図に基づいて説明すると、今回対応する大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値が「0」〜「14」の場合には、大当たり図柄は「1」の図柄17Aとなり、CBの値が「15」〜「24」の場合には、大当たり図柄は「2」の図柄17Bとなり、・・・・、大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値が「90」〜「99」の場合には、大当たり図柄は「8」の図柄17Hとなる。従って、この場合、上記第3の実施の形態と同様の出現率で大当たり図柄が停止表示されることとなる。
【0166】
また、例えば図24(b)に示すように、大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBが「0」〜「9」の値をとることとして、今回対応する大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値が「0」の場合には、大当たり図柄は「1」の図柄17Aとなり、CBの値が「1」の場合には、大当たり図柄は「2」の図柄17Bとなり、・・・、大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値が「6」〜「8」の場合には、大当たり図柄は「7」の図柄17Gとなり、大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値が「9」の場合には、大当たり図柄は「8」の図柄17Hとなるようにしてもよい。この場合、「7」の図柄で大当たりになる確率は、他の個々の図柄に比べて3倍高く設定されることとなる。もちろん、上記第2の実施の形態の別例(2c)で説明したような基本データ及び追加データの概念を適用することとしてもよい。
【0167】
(3f)さらに、左・中・右の各図柄列14〜16の少なくとも1つに、オールマイティ図柄「A」(全図柄に相当するもの:従って、上記実施の形態に対応させると、「A」「3」「3」、「4」「4」「A」等で最終的に停止表示された場合にも大当たり状態が発生することとなる)が表示されることとして、当該オールマイティ図柄の調整によって、実際の図柄(実際の大当たり図柄)の出現率を見た目と異ならせることとしてもよい。
【0168】
(3g)例えば、図25に示すように、1つの図柄列(図では左図柄列14)にオールマイティ図柄「A」が出現表示されうることとして、オールマイティ図柄「A」に関連して大当たり状態となった場合(例えば「A」「2」「2」が最終的に停止表示された場合)、又は奇数のゾロ目で最終的に停止表示された場合に、確変モードが付与されることとする。この場合、見た目上は、図26に示すように確変モードが付与される大当たり図柄の方が、通常モードが付与される大当たり図柄(「2」「2」「2」、「4」「4」「4」、「6」「6」「6」、「8」「8」「8」)よりも多くなる。これに対し、実際の出現率を、確変モードが付与される大当たり図柄と、通常モードが付与される大当たり図柄とで対等となるようにしてもよい。図26では、上記第3の実施の形態で説明したのと同様の態様で大当たり図柄が設定されることとした場合のテーブルの一例が示されている。同図に示すように、確変モードが付与される個々の大当たり図柄の出現率(加算値Y)の値を、通常モードが付与される個々の大当たり図柄の出現率(加算値Y)の値よりも小さく設定することで、実際の出現率が、確変モードが付与される大当たり図柄と、通常モードが付与される大当たり図柄とで対等となりうる。もちろん、確変モードが付与される大当たり図柄の実際の出現率を、通常モードが付与される大当たり図柄の実際の出現率よりも低くなるようにしてもよい。
【0169】
さらに、オールマイティ図柄「A」に関連して大当たり状態となった場合には通常モードが付与され、いかなる図柄でもゾロ目で最終的に停止表示された場合に、確変モードが付与されるような場合、或いは、その逆の場合においても、上記例を適用することができる。
【0170】
併せて、複数(例えば2つ、或いは3つ以上)の図柄列にオールマイティ図柄「A」が出現表示されうることとして(この場合、見た目上、オールマイティ図柄「A」に関連して大当たり状態が発生する確率がさらに高められる)、上記例を適用することとしてもよい。
【0171】
(3h)また、オールマイティ図柄を設定することなく、見た目上確変モードの付与される大当たり図柄が、通常モードの付与される図柄よりも多く(又は少なく)設定されているような場合でも上記例を適用しうる。例えば、(1)偶数図柄で大当たり状態が発生すると、通常モードが付与され、奇数図柄で大当たり状態が発生すると、確変モードが付与されるような場合、単純に見た目上奇数図柄(或いは偶数図柄)の数を、偶数図柄(或いは奇数図柄)の数よりも多く設定しておいて、実際の出現率を見た目と異ならせることとしてもよい。(2)また、別途絵図柄を用意しておき、偶数図柄で大当たり状態が発生すると通常モードが付与され、奇数図柄又は絵図柄で大当たり状態が発生すると、確変モードが付与されるような場合、見た目上、確変モードの付与される図柄の数を、通常モードの付与される偶数図柄の数よりも多く設定でき、かかる設定下で、実際の出現率を見た目と異ならせることとしてもよい。
【0172】
(3i)そのときどきの遊技モードに応じて、大当たり図柄決定に際し使用するテーブル(又はテーブルの加算値等)やカウンタを変更することとしてもよい。例えば、通常モード中においては、実際に確変モードが付与される確率を見た目よりも低く(或いは高く)設定しておいて、確変モード中においては、実際に確変モードが付与される確率を見た目よりも高く(或いは低く)設定しておくこととしてもよい。
【0173】
(第4の実施の形態)
次に、第4の実施の形態について説明する。但し、本実施の形態において、上記第1〜第3の実施の形態と重複する部分等については、その説明を省略することとし、以下には、相違点を中心として説明することとする。
【0174】
上記第3の実施の形態では、テーブル等を用いることにより、実際の各大当たり図柄の出現率を見た目と異ならせることとした。これに対し、本実施の形態では、再抽選処理によって、実際の大当たり図柄の出現率を、見た目の大当たり図柄の出現率と異ならせるようにしたという点で特徴を有している。
【0175】
なお、本実施の形態においては、各図柄列14〜16の図柄として「1」〜「8」の図柄17A〜17Hが用意され、「3」「3」「3」又は「7」「7」「7」の図柄17C又は17Gで大当たりとなった場合に限って確変モードが付与され、その他の図柄で大当たりとなった場合には通常モードが付与されるものとする。従って、本実施の形態において、確変モードの付与される図柄で大当たり状態が発生する確率は、見た目上、8分の2となっている。但し、実際に、「3」「3」「3」又は「7」「7」「7」の図柄17C又は17Gで大当たりとなる確率は16分の7に設定されている。
【0176】
本実施の形態では、ステップS902の大当たり図柄の決定処理において、図27に示すような処理が実行される。すなわち、図27は、制御装置24により実行される「大当たり図柄確定処理ルーチン」を示すフローチャートである。処理がこのルーチンに移行すると、制御装置24はまず、ステップS0011において、大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値に基づいて、一旦停止図柄を設定する。ここで、一旦停止図柄は、大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値に基づいて、各図柄毎に均等に設定される。例えば、大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値が「0」〜「7」の値をとるものとして、CB=0の場合には一旦停止図柄が「1」「1」「1」に設定され、CB=1の場合には一旦停止図柄が「2」「2」「2」に設定され、CB=2の場合には一旦停止図柄が「3」「3」「3」に設定され、・・・、CB=7の場合には一旦停止図柄が「8」「8」「8」に設定されるものとする。従って、この場合、一旦停止図柄として、「3」「3」「3」又は「7」「7」「7」といった確変モードの付与される図柄が設定される確率は、見た目上と同様4分の1である。
【0177】
また、制御装置24は続くステップS0012において、ステップS0011で設定された一旦停止図柄が、「3」「3」「3」又は「7」「7」「7」といった確変モードの付与される図柄であるか否かを判定する。そして、肯定判定された場合には、ステップS0013において、当該「3」「3」「3」又は「7」「7」「7」といった一旦停止図柄を最終的な大当たり図柄として設定する。さらに、続くステップS0014において、制御装置24は再抽選実行フラグXSCを「0」に設定し、その後の処理を一旦終了する。従って、この場合には、全図柄列14〜16の図柄が一旦停止表示された段階で、大当たり図柄が確定され、再抽選処理は実行されない(もちろん見せかけの再抽選を行ってもよい)。
【0178】
一方、前記ステップS0012で否定判定された場合には、ステップS0015へ移行する。ステップS0015において、制御装置24は、再抽選処理を実行するべく、再抽選実行フラグXSCを「1」に設定する。
【0179】
また、次のステップS0016においては、前記大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値に所定値αを加算した値を再抽選用大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCB1として設定する。但し、再抽選用大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCB1も「0」〜「7」の値をとることとし、「7」の次には「0」に値を戻す。従って、例えば大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBの値が「7」(この場合、一旦停止図柄は「8」「8」「8」となる)で、所定値αの値が「3」の場合には、再抽選用大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCB1の値は「2」となる。なお、この所定値αの値は固定値としてもよいが、遊技者に再抽選後の大当たり図柄が察知されないよう、そのときどきによって変動しうる可変値であることが望ましい。もちろん、所定値αを減算等することによって、再抽選用大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCB1の値を求めることとしてもよい。
【0180】
そして、ステップS0017において、制御装置24は、再抽選用大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCB1の値に基づいて、最終的な大当たり図柄を設定する。ここで、大当たり図柄も、上記一旦停止図柄と同様、再抽選用大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCB1の値に基づいて、各図柄毎に均等に設定される。従って、上記例において、再抽選用大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCB1の値が「2」となっている場合には、最終的な大当たり図柄として「3」「3」「3」の図柄17Cが設定されることとなる。
【0181】
また、図28は、ステップS135の処理に際し実行される「再抽選処理ルーチン」を示すフローチャートである。同図に示すように、処理がこのルーチンに移行すると、制御装置24はまずステップS1351において、現在再抽選実行フラグXCSが「1」に設定されているか否かを判定する。そして、否定判定された場合には、何らの処理をも行うことなくその後の処理を一旦終了する。
【0182】
これに対し、再抽選実行フラグXCSが「1」に設定されている場合には、ステップS1352において、全図柄列14〜16の図柄を、当該図柄が揃った状態で再度変動させる。そして、次のステップS1353において、ステップS0017で設定した再抽選用大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCB1の値に基づく大当たり図柄を最終的に停止表示させる。また、最後にステップS1354において、再抽選実行フラグXCSを「0」に設定し、その後の処理を一旦終了する。
【0183】
このように、本実施の形態によれば、確変モードの付与される図柄で大当たり状態が発生する確率は、見た目上、8分の2となっているのに対し、実際に、確変モードの付与される図柄で大当たりとなる確率は16分の7となる。このため、上記第3の実施の形態と同様、遊技者は見た目の大当たり図柄の出現率と実際の大当たり図柄の出現率の違いに驚きを覚えるとともに、特殊な遊技性を堪能することができる。その結果、興趣の飛躍的な向上を図ることができる。
【0184】
また、本実施の形態では、再抽選処理によって、実際の大当たり図柄の出現率を、見た目の大当たり図柄の出現率と異ならせるようにした。このため、上記のようなテーブル等の設定を行わずとも済む。特に、本実施の形態では、大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCB、再抽選用大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCB1の値に基づいて、一旦停止図柄、最終的な大当たり図柄を各図柄毎に均等に設定すればよい。そのため、設定に手間を要することがなく、設計を容易に行うことができる。
【0185】
尚、上記実施の形態の記載内容に限定されず、例えば次のように実施してもよい。
【0186】
(4a)上記実施の形態では、一旦停止図柄が所定の図柄(確変モードの付与される図柄)でない場合、再度1回のみ最終的な大当たり図柄の内部的な抽選を行うこととした。これに対し、3段階以上の抽選を行ってもよい。このように再抽選回数と、大当たり図柄数とを適宜組み合わせることで、必要に応じた出現率設定を行うことが可能となる。例えば上記例において、CB1に基づいて設定される大当たり図柄が「3」「3」「3」又は「7」「7」「7」ではない場合には、再度再抽選用大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCB2を設定して、最終的な大当たり図柄を設定することとしてもよい。この場合、実際に確変モードの付与される図柄が最終的に停止される確率は、2/8+6/8*2/8+、6/8*6/8*2/8=37/64となりうる。
【0187】
(4b)上記実施の形態では、大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCB、再抽選用大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCB1の値に基づいて、一旦停止図柄、最終的な大当たり図柄を各図柄毎に均等に設定することとした。これに対し、カウンタCB,CB1と大当たり図柄の対応関係を必ずしも均等にしなくてもよい。このように、対応関係を適宜調整することで、最終的な大当たり図柄の出現率の調整をさらにきめ細やかに行うことができる。また、実際に確変モードの付与される大当たり図柄が最終的に停止される確率の調整も比較的容易に行うことができる。
【0188】
(4c)上記実施の形態では、一旦停止表示後、再抽選処理を演出表示することとしたが、このような再抽選処理を遊技者に見せないこととしてもよい。すなわち、再抽選処理をあくまでも内部的に実施して(内部的に複数段階の抽選を行うこととして)、結果的に最終決定された大当たり図柄のみを停止表示することとしてもよい。
【0189】
(4d)上記実施の形態では、「3」「3」「3」又は「7」「7」「7」の2種類の大当たり図柄を確変モードの付与される大当たり図柄とした。これに対し、確変モードの付与される大当たり図柄を、例えば「7」「7」「7」1種類だけとしてもよい。この場合、「7」「7」「7」の図柄で大当たり状態が発生する確率が非常に多くなり、遊技者にとっての驚きは一層増幅されることとなる。
【0190】
(4e)上記第4の実施の形態では、大当たり図柄の再抽選を行うこととしたが、上記実施の形態を応用して、リーチ図柄の再抽選を行うこととしてもよい。例えば左右の図柄列14,16が共に「4」、「4」の図柄17Dで一旦停止したとする。再抽選処理が行われない限りは、遊技者は、通常モードしか付与されない「4」での大当たりを期待するしかないが、この時点で、左右両図柄列14,16を再変動させることで(リーチ図柄の再抽選)、「3」、「3」等で停止表示される場合が生じ、この場合確変モードの付与される図柄での大当たり状態の発生を期待することができる。
【0191】
また、別途実施しうる事項について、以下に記す。
【0192】
(A)上記実施の形態では、確変モードの概念として、(1)7セグ表示部53に「7」が表示される確率を通常時に比べて高め、作動口3の羽根6を開放させる機会を増やすこと、(2)7セグ表示部53における数字の変動時間を短くすること、(3)羽根6の開放時間を長くすること(及び/又は入賞個数を多くすること)、(4)特別図柄表示装置13の表示部13aの図柄17A〜17Hの変動時間を短くすること、(5)大当たり期待値が通常モードに比べて高くなることのうち、(5)のみ、すなわち、大当たり期待値が単に高められることのみが実行されることとした。これに対し、(5)を含む(1)〜(4)のうちの少なくとも1つを満たすことを、確変モードとしてとらえてもよい。すなわち、(1)〜(4)の任意の組合せ(例えば(1)と(2)、(1)と(3)、(1)と(4)、(2)と(3)、(2)と(4)、(3)と(4)、(1)と(2)と(3)、(1)と(2)と(4)、(1)と(3)と(4)、(2)と(3)と(4)、(1)と(2)と(3)と(4))と(5)を組み合わせたものを確変モードとしてとらえてもよい。
【0193】
また、確変モードに代えて、或いは、加えて、時間短縮(時短)モード(上記(1)〜(4)の任意の組み合わせ)を実行しうるパチンコ機にも適用してもよい。
【0194】
さらに、確変モードを実行しないパチンコ機にも具体化できる。
【0195】
(B)時短モード、確変モードとしては、次回の大当たり時まで継続されるようにしてもよいし、図柄17A〜17Hの予め定められた所定回転変動回数だけ継続され、その後通常モードに切り替えられるようにしてもよい。また、時短モード、確変モードが選択された場合には、大当たり状態が2回又はそれ以上発生するまで、当該特別モードが継続されるようにしてもよい。併せて、結果的に、大当たり図柄に応じて、確変モードや時短モードの継続回数(大当たり状態の継続発生回数)を可変とするようにしてもよい。例えば「1」、「5」で大当たりの場合には、次回の大当たりまで確変モードが継続され、「3」、「7」で大当たりの場合には、次々回の大当たりまで確変モードが継続されるようにしてもよい。
【0196】
(C)上記実施の形態では、再変動処理を行うこととしたが、かかる処理を省略してもよい。
【0197】
(D)表示装置13としては、上述した液晶ディスプレイ以外にも、CRT、ドットマトリックス、LED、エレクトロルミネセンス(EL)、蛍光表示菅等を用いてもよい。
【0198】
(E)上記実施の形態では、普通図柄表示装置51は、「0」から「9」までの数字を可変表示して7セグ表示部53にセグメント表示させ、その数字が所定値(本実施の形態では「7」)で停止した場合に、作動口3の羽根6を所定秒数開放させることとした。これに対し、7セグ表示以外の他の表示方法(例えばランプの点灯等)を用いて表示するようにしてもよい。また、羽根6を開放させる以外にも別の作動口を設けておいてシャッタを開放するようにしてもよい。
【0199】
(F)上記実施の形態とは異なるタイプのパチンコ機等として実施してもよい。例えば、一度大当たりすると、それを含めて複数回(例えば2回、3回)大当たり状態が発生するまで、大当たり期待値が高められるようなパチンコ機(通称、2回権利物、3回権利物と称される)として実施してもよい。また、大当り図柄が表示された後に所定の領域に遊技球を入賞させることを必要条件として特別遊技状態となるパチンコ機として実施してもよい。また、パチンコ機以外にも、アレパチ、雀球、スロットマシン等の各種遊技機として実施することも可能である。なお、スロットマシンは、例えばコインを投入して図柄有効ラインを決定させた状態で操作レバーを操作することにより図柄が変動され、ストップボタンを操作することにより図柄が停止されて確定される周知のものである。従って、スロットマシンの基本概念としては、「複数の図柄からなる図柄列を変動表示した後に確定図柄を表示する図柄表示手段を備え、始動用操作手段(例えば操作レバー)の操作に起因して図柄変動が開始され、停止用操作手段(例えばストップボタン)の操作に起因して或いは所定時間経過することにより図柄変動が停止され、その停止時の確定図柄が特定図柄であることを必要条件として遊技者に有利な特別遊技状態を発生させる特別遊技状態発生手段とを備えたスロットマシン」となる。
【0200】
(G)上記実施の形態では、大当たり状態の終了時に遊技モードの表示を行うようにしたが(ステップS240)、このような表示を行わなくてもよい。また、大当たり時や、大当たり中に表示するようにしてもよい。さらには、大当たり後、次回の大当たり時まで継続的に表示するようにしてもよい。また、表示部に表示する以外にもランプや音でモードを報知するようにしてもよい。
【0201】
(H)上記実施の形態における見た目の図柄の表示確率と、実際の図柄の表示確率、或いは、見た目の確変モードの付与される確率と、実際の確変モードの付与される確率等に関する各数値はあくまでも一例に過ぎない。すなわち、前記各確率は任意であって、適宜変更可能である。
【0202】
(I)各種表示、音声等の報知態様を、遊技モード(例えば、通常モードと確変モード)の相違や大当たり期待値の相違に応じて適宜切換制御して実施することとしてもよい。例えば、大当り期待値が大きくする場合等に、図柄を緑色から赤色に切り換えるように制御したり、音声を変更することなどが挙げられる。このような色の切換や音の変更等は、遊技状態が通常とは異なる状態であることを遊技者に明確にする、大当り期待値が大きくなったことを遊技者に明示する等の効果をもたらす。ここから導き出される技術思想としては、「図柄表示色等の報知態様を遊技状態に応じて切換表示すること。」、「図柄表示色等の報知態様を遊技モードに応じて切換表示すること。」、「図柄表示色等の報知態様を大当たり期待値の相違に応じて切換表示すること。」などがある。
【0203】
(J)可変表示装置としての表示装置13を制御する表示制御装置を、遊技機全体の制御を司る主制御装置(制御装置24)とは別に設け、主制御装置が表示制御装置へ図柄自体の指令を出力するのではなくモード信号を出力し、モード信号に応じて表示制御装置が当該モードに対応した確定図柄を選定して表示するように構成してもよい。この場合、大当たり図柄乱数カウンタCBや、特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタCC等の各種カウンタやテーブル等を表示制御装置に記憶させておけばよくなり、主制御装置側では図柄や表示装置13の種類を意識せずに確率設定などのプログラム設計を容易に行うことができる。
【0204】
(K)通常モードと確変モード等の遊技モードとの選定として、可変表示装置としての表示装置13(表示部13a)における図柄の種類(奇数・偶数)により報知するタイプのものとは別に、いずれのモードが選定されたかを所謂第4図柄と称される図柄を変動させた後に確定表示させるモード報知手段を設けてもよい。そして、当該第4図柄の出現率を見た目と実際とで異ならせることとしてもよい。
【0205】
(L)上記第1〜第4の実施の形態(各種別例も含む)を適宜組み合わせることとしてもよい。例えば、(1)外れ図柄の出現率を見た目と実際とで異ならせること、(2)外れリーチ図柄の出現率を見た目と実際とで異ならせること、(3)大当たり図柄の出現率を見た目と実際とで異ならせること、(4)上記(3)を再抽選を行うことによって実行することのうち、(1)(2)の組み合わせ、(1)(3)の組み合わせ、(1)(4)の組み合わせ、(2)(3)の組み合わせ、(2)(4)の組み合わせ、(3)(4)の組み合わせ、(1)(2)(3)の組み合わせ、(1)(2)(4)の組み合わせ、(1)(3)(4)の組み合わせ、(2)(3)(4)の組み合わせ、(1)(2)(3)(4)の組み合わせを適宜実施しうる。
【0206】
(M)各テーブル、カウンタの数値は、上記実施の形態における数値に何ら限定されるものではない。また、そのときどきの遊技状況に応じて乱数幅を可変としてもよい。
【0207】
(N)上記(L)の(1)〜(4)及びこれらの組み合わせに関し、いわゆるシリーズ機(兄弟機)間で統一性(関連性)を持たせることとしてもよい。なお、シリーズ機とは、スペックが相異する(例えば大当たり確率が相異したり、登場するキャラクタが相異したり、確変モード付与率が相異したり、通常モード以外に付与される遊技モードが確変モードと時短モードとの間で相異したり、遊技球の購入方法が相異したり(いわゆる現金機及びCR機間の相異)、リーチの種類が相異したりする等)が、同等又は類似の可変表示装置、或いは、セル板等を具備している複数種類の遊技機をいう。
【0208】
(O)上記各実施の形態では、予め設定されているあらゆる図柄が実際に停止表示されるようになっていた。これに対し、所定の条件が満たされている場合(例えば所定の遊技モード時)には最終的に停止表示されないような図柄を設けることとしてもよい。例えば、確変モード時には中図柄列15に「4」の図柄17Dが停止表示されないこととすると、左右両図柄列14,16において「4」の図柄17Dが停止表示され、リーチ状態が発生したとしても、中図柄列15に「4」は停止表示されないことから、「4」の図柄で大当たり状態が発生することはない。そのため、「4」の図柄で大当たり状態が発生することで確変モードが終了してしまうという遊技者にとっての懸念が払拭されることとなり、さらに面白味が増すケースが起こりうる。
【0209】
(P)上記各実施の形態では、左・中・右の3つの図柄列14〜16によって表示部13aが構成されていたが、上中下の図柄列によって構成されていてもよい。また、図柄列の数は、1つであっても、2つであっても、或いは4つ以上であってもよい。
【0210】
例えば、左右2つの図柄列によって表示部が構成されているとした場合、次のような制御を行うこともできる。すなわち、図29に示すように、左右図柄列とも「0」〜「5」の図柄によって構成されており、奇数のゾロ目で大当たり状態が発生した場合に確変モードが付与され、偶数のゾロ目で大当たり状態が発生した場合に通常モードが付与されるとする。この場合、最初に停止する方の図柄列(例えば左図柄列)に関し、「0」〜「2」の図柄は実際に停止表示されやすく、「3」〜「5」の図柄が停止表示されにくいものとし、かつ、「3」〜「5」の図柄が一旦停止表示された場合に大当たり状態が発生しやすいものとする。このような構成とすることで、遊技者は最初に停止される図柄列において「3」〜「5」の図柄が一旦停止表示されることを望むとともに、一旦「3」又は「5」の図柄が停止表示された場合には、確変モードが付与されることを願って、わくわく感が最高潮に達しうる。また特に、「3」〜「5」の間では、確変モードが付与される確率が、通常モードが付与される確率よりも高くなるため、かかる意味でも興趣のさらなる向上が図られることとなる。
【0211】
【発明の効果】
本発明によれば、興趣の向上を好適に図ることができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】第1の実施の形態におけるパチンコ機を示す正面図である。
【図2】(a)は表示部の表示状態(変動時)の例を示す模式図であり、(b)は大当たり状態の1態様を示す模式図であり、(c)はリーチ状態の1態様を示す模式図である。
【図3】図柄乱数バッファの概念を説明する図表である。
【図4】図柄乱数エリアの概念を説明する図表である。
【図5】停止図柄エリアの概念を説明する図表である。
【図6】(a)は乱数カウンタの概念を説明する図表であり、(b)はリーチ種別決定カウンタ等の概念を説明する図表であり、(c)は特別外れ図柄乱数カウンタの概念を説明する図表である。
【図7】制御装置により実行される「乱数振分けルーチン」を示すフローチャートである。
【図8】「格納処理ルーチン」を示すフローチャートである。
【図9】「特別電動役物制御ルーチン」の一部を示すフローチャートである。
【図10】「特別電動役物制御ルーチン」の一部であって、図9の続きを示すフローチャートである。
【図11】「変動開始処理ルーチン」を示すフローチャートである。
【図12】「リーチ目図柄記憶処理ルーチン」を示すフローチャートである。
【図13】「特別外れ図柄記憶処理ルーチン」を示すフローチャートである。
【図14】(a)は表示部のリーチ目等の例を示す模式図であり、(b)は前記リーチ目に似通った表示態様を示す模式図である。
【図15】(a)〜(c)は第2の実施の形態において、それぞれ左中右の図柄と、加算値(出現率)との対応関係を示すテーブルである。
【図16】制御装置によって実行される「変動開始処理ルーチン」を示すフローチャートである。
【図17】「外れ図柄・外れリーチ図柄確定処理ルーチン」を示すフローチャートである。
【図18】(a)〜(c)は別の実施の形態において、それぞれ左中右の外れ図柄乱数カウンタと、外れ図柄との対応関係を示すテーブルである。
【図19】別の実施の形態において、例えば左外れ図柄乱数カウンタと、左外れ図柄との対応関係を示すテーブルである。
【図20】第3の実施の形態において、制御装置によって実行される「大当たり図柄確定処理ルーチン」を示すフローチャートである。
【図21】大当たり図柄と加算値(出現率)との対応関係を示すテーブルである。
【図22】(a),(b)は、それぞれ別の実施の形態における大当たり図柄と加算値(出現率)との対応関係を示すテーブルである。
【図23】別の実施の形態における表示部の表示状態(ダブルリーチ時)の例を示す模式図である。
【図24】(a),(b)は、それぞれ別の実施の形態における大当たり図柄カウンタと大当たり図柄との対応関係を示すテーブルである。
【図25】別の実施の形態において左中右の(大当たり)図柄の例を示す図表である。
【図26】別の実施の形態における大当たり図柄と加算値(出現率)との対応関係を示すテーブルである。
【図27】第4の実施の形態において、制御装置によって実行される「大当たり図柄確定処理ルーチン」を示すフローチャートである。
【図28】制御装置によって実行される「再抽選処理ルーチン」を示すフローチャートである。
【図29】別の実施の形態において最初に停止表示される図柄の特性を示す図表である。
【符号の説明】
1…パチンコ機、2…遊技盤、3…作動口、4…大入賞口、5…遊技球、13…特別図柄表示装置、13a…表示部、14…左図柄列、15…中図柄列、16…右図柄列、17A〜17H…図柄、24…制御装置。[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a gaming machine such as a pachinko machine.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Conventionally, as a type of gaming machine, for variably displaying multiple types of symbols etc. in a predetermined arrangementtablePachinko machines equipped with an indicating device are known.
[0003]
This kind of pachinko machine is advantageous to the player after reaching the reach state according to the display design (stop design) when the variable display is stopped on the display device.Special gamesBecome a state ``Hit reachThe “exit reach state” that does not become the special game state after passing the “state”, the reach state, or the “release state” that does not pass the reach state and does not become the special game state is generated. For the stop symbol,ThisRitual design, OutsideReach design, andOutsideThere is a design.
[0004]
In the pachinko machine as described above, the game situation that changes according to the player's operation satisfies a predetermined condition (for example, a game ball wins an operating slot, etc.)tableIn the display device, the symbol variation display is started. Also, aboveThisFrom among the design, outreach reach, and outage design,stopA stop symbol is selected, and the variable display is stopped at the selected stop symbol. AndThisIn the case of stopping at a symbol, the special variable winning device is advantageous for the playerWhenIt is switched to become.
[0005]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
An object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine that can suitably improve interest in the above-exemplified gaming machines and the like.
[0006]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
To solve the above problemsIn the present invention,
Display means capable of variably displaying a plurality of symbols in a plurality of symbol display areas;
Game situation detecting means for detecting a predetermined game situation;
Based on the detection result by the gaming status detection means, a lottery is performed as to whether or not a special gaming state advantageous to the player is generated, and a plurality of symbols are displayed in a variable manner in each symbol display area of the display means. , Stop display after a predetermined time,
If the result of the lottery is a win, the symbols are stopped and displayed in a specific winning combination pattern in the plurality of symbol display areas, and the special gaming state is generated.
If the result of the lottery is not successful, a predetermined outlier combination pattern out of a plurality of outlier combination patterns including at least one first outlier combination pattern in the plurality of symbol display areas without generating the special gaming state And a control means for stopping and displaying the design at
Discriminating means capable of discriminating whether or not a predetermined first condition is satisfied;
Based on the fact that the first condition is determined not to be established by the determining means, the symbol is stopped and displayed by one of the outlier combination patterns including the at least one first outlier combination pattern. First stop display means for performing
Based on the fact that the first condition is determined to be established by the determining means, and having a second stop display means for displaying a stop of the symbol with the at least one first outlier combination pattern,
The control means includes
First control means for controlling the gaming machine;
Provided separately from the first control means, and having a second control means for controlling the display of fluctuations of the symbol in the display means,
The first control means includes
The second control means is configured to output a specific signal,
The second control means includes
Based on the input of the specific signal, it is configured to be able to control the variation display of the symbol,
Said first stop display means;
Said second stop display means;
Which one of the plurality of outlier combination patterns including the at least one first outcombination pattern is used as the outlier combination pattern that the first stop display means stops and displays is input to the specific signal. And determining means for determining based on.
Further, the plurality of outlier combination patterns including the at least one first outlier combination pattern include a reach outlier combination pattern that performs a reach but is out of reach, and a non-reach outlier combination pattern that is out of the reach without performing a reach, The at least one first outlier combination pattern may be a non-reach outlier combination pattern that is out of reach without performing reach.
Further, the plurality of outlier combination patterns including the at least one first outlier combination pattern include a reach outlier combination pattern that performs a reach but is out of reach, and a non-reach outlier combination pattern that is out of the reach without performing a reach, The at least one first out-of-combination pattern may be a out-of-reach combination pattern that performs reach but is out.
The at least one first outlier combination pattern may be plural.
The gaming machine may be a pachinko machine.
[0007]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
[0008]
According to the above means, a gaming situation that changes according to the player's operation is detected by the gaming situation detection means, and a plurality of identification information is variably displayed on the variable display means based on the detection result by the gaming situation detection means. sell. The special game state generating means generates a special game state advantageous to the player on the condition that the identification information becomes specific identification information and is finally stopped and displayed. In the above means, when the specific identification information consists of a plurality of patterns and a special gaming state is generated, the identification information becomes one type of specific identification information among the plurality of patterns and finally stops. Is displayed. Here, the actual appearance rate of at least one specific identification information is different from the appearance rate on the surface. For this reason, it is possible to set the probability that at least one specific identification information is stopped and displayed in independent selection, and it is possible to set the actual appearance rate without being restricted by the appearance rate on the surface, Increase design freedom. In addition, since the actual appearance rate of at least one specific identification information is different from the appearance rate on the surface, it is more interesting for the player, and various effects accompanying the difference in the appearance rate can be performed. It becomes.
[0009]
Mean 2. In the
[0010]
Means 3. A gaming machine according to
[0011]
[0012]
[0013]
[0014]
Mean 7 The gaming machine according to
[0015]
[0016]
[0017]
[0018]
Means 11. In the
[0019]
Means 12. In the means 11, the internal probability that predetermined identification information is determined for each display area is made higher than the probability that the identification information is stopped and displayed on the surface, and as a result, at least one pattern of outlier identification information is obtained. The gaming machine is characterized in that the internal probability for determining is set higher than the probability that the off-identification information is stopped and displayed on the surface. Here, as long as “predetermined identification information” is a combination that becomes out-of-line identification information, the predetermined identification information may be different for each display area or may be partially the same.
[0020]
[0021]
[0022]
[0023]
[0024]
[0025]
Means 18. The gaming machine according to
[0026]
Means 19. In any one of the
[0027]
[0028]
Means 21. In any one of the
[0029]
[0030]
[0031]
[0032]
[0033]
Means 26. In any one of the
[0034]
Means 27. In the means 26, a correspondence relationship between the count value and the specific identification information, outlier identification information, reach identification information, and at least one pattern of the identification information that is temporarily stopped is expressed as a count value (individual count information). A gaming machine characterized by being able to differ depending on at least one of a range of a value and a count value).
[0035]
Means 28. In the means 26 or 27, when the count value satisfies the first predetermined condition, the first predetermined pattern of the specific identification information, the first predetermined pattern of the outlier identification information, the first of the reach identification information One predetermined pattern and at least one pattern of the first predetermined pattern of identification information that is temporarily stopped and displayed are determined, and when the count value satisfies a second predetermined condition, Among the second predetermined pattern of identification information, the second predetermined pattern of out-of-bound identification information, the second predetermined pattern of reach identification information, and the second predetermined pattern of identification information that is temporarily stopped The configuration is such that at least one pattern is determined, and the count value is more likely to satisfy the first predetermined condition than the second predetermined condition. Gaming machine and butterflies.
[0036]
Means 29. In any one of the
[0037]
[0038]
Means 31. In the
[0039]
[0040]
[0041]
Means 34. In the
[0042]
Means 35. A gaming machine according to claim 33 or 34, wherein the additional correspondence can be adjusted by adding or replenishing predetermined data to or from the pattern determination table.
[0043]
Means 36. In any one of the means 29 to 35, the pattern determination table includes the count value and at least one pattern of the specific identification information, outlier identification information, reach identification information, and identification information temporarily stopped and displayed. A gaming machine, wherein a ratio for determining a pattern of each identification information is determined in advance so that the correspondence relationship between them is biased.
[0044]
Means 37. In the means 36, the ratio is determined as a percentage or a rate equivalent thereto.
[0045]
Means 38. In the means 36 or 37, the ratio can be changed as appropriate.
[0046]
[0047]
[0048]
(First embodiment)
Hereinafter, an embodiment in which a pachinko gaming machine (hereinafter simply referred to as “pachinko machine”) is embodied will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
[0049]
As is well known, the
[0050]
As shown in FIG. 1, the
[0051]
A
[0052]
A special
[0053]
As shown in FIG. 2, each symbol row 14-16 is comprised by the symbol 17A-17H as a some identification information, respectively. Each of the symbols 17A to 17H is configured by numbers “1” to “8”, and these numbers are equally arranged one by one in ascending order. Note that the number of symbols 17A to 17H is not limited to the above example, and the type of symbol is not limited to a numeric symbol, and may be composed of a character symbol or a picture symbol. These symbols 17A to 17H can be any of a jackpot symbol, a miss reach symbol, and a miss symbol as special game symbols. Of course, you may arrange | position the symbol which can become only a deviating symbol between these.
[0054]
In the normal variation, the symbols 17A to 17H are variably displayed in the
[0055]
In the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 2 (b), a jackpot line L is constituted by one horizontal line at the center (referred to as one line). In other words, the symbols 17A to 17H are displayed in the effective frames provided for each of the
[0056]
Further, as shown in FIG. 1, a normal symbol display device 51 is provided at the upper part of the special
[0057]
Further, a pair of passage gates 54 are disposed on the left and right sides of the special
[0058]
As shown in FIG. 2A, in the display unit 13 a of the special
[0059]
The jackpot symbol is a symbol for generating a jackpot state as a special gaming state advantageous to the player after the reach state. Specifically, as shown in FIG. 2B, when the variation of all the
[0060]
For example, as shown in FIG. 2C, the reach state refers to a state immediately before the big hit. The reach state includes a state in which the symbol variation of the
[0061]
In the above reach state, the symbol variation of the
[0062]
In the reach state, various reach patterns are set. As the reach pattern, various reach patterns such as “normal reach”, “flash reach”, “enlarged reach”, and “frame advance reach” are set. Among these reach patterns, the reach other than “normal reach” is referred to as so-called “super reach”. When the operation of “super reach” is started, generally, the expected value at which a big hit state occurs (expected value for big hit) is higher than in the case of “normal reach”.
[0063]
Although it has already been described that the symbol variation of each
[0064]
As shown in FIG. 1, in the special
[0065]
In addition to this, various other lamps and electrical decoration members for enhancing the gaming effect are attached to a plurality of locations of the
[0066]
In the present embodiment, the
[0067]
In the present embodiment, the
[0068]
As shown in FIG. 3, the design random number buffer includes three left, middle, and right out symbol random number buffers 31, 32, and 33, and three left, middle, and right out reach symbol random number buffers 34, 35, and 36. It is constituted by. As shown in FIG. 4, the design random number area includes five internal random number areas 41 (i), five outreach reach random number areas 42 (i), five left left design random number areas 43 (i), and five It is composed of an out-of-line design random number area 44 (i) and five out-of-right design random number areas 45 (i). i is for distinguishing each of the five design random number areas, and takes values of “0”, “1”, “2”, “3”, and “4”. Each value of i corresponds to the number of variable displays held. Further, as shown in FIG. 5, the stop symbol area is composed of left, middle and right stop symbol
[0069]
In the present embodiment, as one of the controls by the CPU (control device 24), there is mode switching control for switching the game mode. In the present embodiment, two modes are prepared. That is, for example, a normal mode in which a jackpot gaming state is generated with a relatively low probability of about 1/300, and a probability variation (probability change) in which a jackpot gaming state is generated with a high probability of about 1/60, which is about five times that There is a mode.
[0070]
In general, the concept of the probability variation mode is as follows: (1) The probability that “7” is displayed on the 7-segment display unit 53 is increased compared to the normal time, and the opportunity to open the
[0071]
In the present embodiment, the normal mode is set when the
[0072]
In the present embodiment, so-called reach-eye display is executed. In other words, although the jackpot state does not occur at the time of the symbol variation this time, there is a case where a jackpot state occurs among the reserved portions of the symbol variation (when the value of the internal random number counter CI in the reserved portion is a jackpot value) ) Includes a specific event (in this embodiment, “3”, “4”, “1” symbols (in order of left, middle, right symbol sequence) to notify (inform) that a jackpot state will occur in the near future. ): This is called a reach eye), and is stopped (see FIG. 14A).
[0073]
Furthermore, in the present embodiment, regardless of the occurrence of the big hit state, the same outcome as the reach eyes (designs “3”, “4”, “1”) is easily stopped and displayed. As a result, if the symbols “3”, “4”, and “1” are stopped and displayed, the player will be excited to see if he is a reach that is a precursor to the occurrence of a jackpot or a so-called “gase” reach. I will watch the changes in the design.
[0074]
In addition, in the present embodiment, regardless of the occurrence of the big hit state, the appearance similar to the reach (the symbols “3”, “1”, “4”) is easily stopped and displayed (FIG. 14). (See (b)). As a result, when the symbols “3”, “1”, and “4” are stopped and displayed, the player may assume that there is some relation to the reach.
[0075]
Next, the operation and effect of the
[0076]
The round counter CR is for counting the number of rounds, and the winning counter CE is for counting the number of winning
[0077]
As shown in FIG. 6A, the internal random number counter CI is for determining the jackpot state in the special
[0078]
The left, middle, and right symbol random number counters CDL, CDC, and CDR are other than the jackpot or reach eye stop display, and the value of the special outlier symbol random number counter CC is “7” to “17” or “57”. In the case of being out of the range of “67” to “67”, the stop symbol at the time of outreach or at the time of outage is determined. The left symbol random number counter CDL updates the value within a predetermined range every predetermined time (for example, “2 ms”), and returns it to the initial value when it reaches a specific value. The middle symbol random number counter CDC updates the value within a predetermined range every time the left symbol random number counter CDL makes a round, and returns it to the initial value when it reaches a specific value. The right symbol random number counter CDR updates the value within a predetermined range every time the middle symbol random number counter CDC makes a round, and returns it to the initial value when it reaches a specific value. Therefore, the count values of the left, middle, and right symbol random number counters CDL, CDC, and CDR are values used to determine a stop symbol with randomness at the time of outlier reach.
[0079]
Further, the reach type determination counter CV shown in FIG. 6B is used to select one of the above-described plurality of types of reach patterns when the reach state occurs. For example, the left symbol random number counter CDL The value (random value) is updated each time one completes, and when it reaches a specific value, it is returned to the initial value. However, each reach pattern is weighted, and the probability that each reach pattern is selected is individually different.
[0080]
Further, these counter groups are prepared for the normal mode and the probability variation mode, respectively. That is, each of these counter groups is prepared in the normal mode counter table and the probability variation mode counter table. In the normal mode, the counter group of the normal mode counter table is updated and distributed as appropriate, and in the probability change mode, the counter group of the probability change mode counter table is updated and distributed as appropriate. Of course, it is not necessary to prepare them separately as described above (a common counter group may be used). For example, in the probability variation mode, the jackpot value of the internal random number counter CI may be simply increased.
[0081]
The winning determination flag FE is used to determine whether or not there is a winning in the V zone. The flag FE is set to “0” when there is no winning, and is set to “1” when there is a winning.
[0082]
The flowchart of FIG. 7 discriminates combinations of the values (random numbers) of the design random number counters CDL, CDC, CDR after updating the counters CI, CO, CB, CDL, CDC, CDR, CV, CC described above ( The “random number distribution routine” for storing the distributed values in the corresponding symbol random number buffers 31 to 36 is shown. This routine is executed every predetermined time (2 ms) after the
[0083]
In step S2, “1” is added to the left symbol random number counter CDL. The middle / right symbol random number counters CDC and CDR are updated according to the values of the left and middle symbol random number counters CDL and CDC, respectively. Specifically, “1” is added to the middle symbol random number counter CDC at the timing when the left symbol random number counter CDL is returned to the initial value, and the value of the counter CDC is maintained at other timings. Further, if the middle symbol random number counter CDC is returned to the initial value, “1” is added to the right symbol random number counter CDR, and if not, the value of the counter CDR is maintained. Further, in step S3, the
[0084]
Next, in step S4, it is determined whether or not the combination of the values of the symbol random number counters CDL, CDC, CDR is a predetermined “combination symbol combination”. If this condition is satisfied, the values of the symbol random number counters CDL, CDC, CDR are stored in the corresponding off symbol random number buffers 31, 32, 33 in step S5. Here, the corresponding out symbol random number buffers 31 to 33 specifically refer to the left symbol random number buffer 31 for the left symbol random number counter CDL, and the symbol symbol
[0085]
On the other hand, if the condition of step S4 is not satisfied, whether or not the combination of the values of the design random number counters CDL, CDC, CDR is a predetermined “combination of outreach symbols” in step S6. Judging. If this condition is satisfied, the values of the symbol random number counters CDL, CDC, CDR are stored in the corresponding outreach symbol random number buffers 34, 35, 36 in step S7, and the subsequent processing is temporarily terminated. To do.
[0086]
If the condition in step S6 is not satisfied, the “random number distribution routine” is terminated without performing any of the processes in steps S5 and S7. In this case, the combination of the values of the respective symbol random number counters CDL, CDC, CDR is not a combination of an outlier symbol or an outlier reach symbol, that is, a combination of jackpot symbols.
[0087]
Thus, in the “random number distribution routine”, combinations of the values of the three symbol random number counters CDL, CDC, and CDR are checked every predetermined time. In the case of a combination of detachment symbols, random numbers are stored in the detachment symbol random number buffers 31-33, and in the case of a detachment symbol shifted by two or more frames, random numbers are stored in the detachment symbol random number buffers 34-36. Is done. In the case of a jackpot symbol combination, random numbers are not stored in any symbol random number buffers 31-36.
[0088]
Next, the “storage processing routine” shown in the flowchart of FIG. 8 will be described. The main function of this routine is to store the values of the random number counters CI, CO, CDL, CDC, CDR in the symbol random number areas 41 (i) to 45 (i) every time the
[0089]
When the “storage process routine” is started, the
[0090]
If the value of the hold counter CH is smaller than the maximum hold count, “1” is added to the hold counter CH in step S12. In the following step S13, the
[0091]
In step S14, the
[0092]
As described above, in the “storage processing routine”, the values of the random number counters CI, CO, CDL, CDC, CDR are stored in the symbol random number areas 41 (i) to 45 (i). In steps S14 to S16, for example, if the value of the hold counter CH after the update in step S12 is “3”, the internal random number area 41 (i = 3) and the outreach random number area 42 (i = 3). , The left off symbol random number area 43 (i = 3), the off center symbol random number area 44 (i = 3), and the right off symbol random number area 45 (i = 3) serve as storage locations in the current control cycle.
[0093]
Next, the “special electric accessory control routine” shown in the flowcharts of FIGS. 9 and 10 will be described. This routine is for controlling the special electric accessory, the special
[0094]
When this “special electric accessory control routine” is started, the
[0095]
When this determination condition is satisfied (CH ≠ i), in step S50, the internal random number area 41 (i + 1), the outreach random number area 42 (i + 1), and the out symbol random number areas 43 (i + 1) to 45 Each data of (i + 1) is shifted to the previous area 41 (i) to 45 (i), respectively. Next, in step S60, the
[0096]
On the other hand, when the determination condition of step S40 is not satisfied (CH = i), the process proceeds to step S70, and the lamps 18a to 18d corresponding to the hold counter CH are turned off. In the next step S80, “1” is subtracted from the hold counter CH.
[0097]
Next, in step S90, the
[0098]
On the other hand, if the determination condition in step S901 is not satisfied, the reach symbol storing process is executed in step S903. That is, as shown in the “reach eye symbol storage processing routine” in FIG. 12, in step S9031, the
[0099]
In this way, after executing the reach eye symbol storing process, the
[0100]
Therefore, even when the value of the special out-of-line design random number counter CC in this time is within the first predetermined range, the same “3”, “4”, “1” symbols as in the reach are obtained regardless of the occurrence of the jackpot state. Eventually it will be stopped. In addition, when the value of the special outlier design random number counter CC is within the second predetermined range, symbols “3”, “1”, and “4” similar to the reach eyes are finally stopped and displayed. Become.
[0101]
Now, after executing the special out symbol storing process as described above, the
[0102]
Further, if the determination condition in step S905 is not satisfied, in step S908, the off symbol in step S16 is stored in the memory as a stop symbol, and the process proceeds to step S909.
[0103]
Now, the process proceeds from step S902 or step S906, and in step S907, a reach pattern is acquired based on the reach type determination counter CV. That is, any one of various reach patterns such as “normal reach”, “flash reach”, “enlarged reach”, and “frame advance reach” described above is determined.
[0104]
And it transfers from step S907 or step S908, and in step S909, the symbol fluctuation | variation of the special
[0105]
Now, as described above, after executing the processing of step S90 ("variation start processing routine"), the
[0106]
Next, in step S120, the
[0107]
As described above, after executing the processing of step S120 (“reach operation processing routine”), the
[0108]
Now, in step S140, the
[0109]
Next, in step S160 (see FIG. 10), the
[0110]
Furthermore, in step S180, the
[0111]
Next, in step S190, the
[0112]
Subsequently, in step S220, the
[0113]
Then, when either one of the determination conditions of step S220 or step S230 is not satisfied, it is determined that the jackpot state has ended, and that fact is displayed on the display unit 13a, and the next game mode is set to the game mode. A process of notifying based on the flag is executed, and this routine is terminated.
[0114]
As detailed above, according to the present embodiment,(1)The so-called reach eye display is executed,(2)Regardless of the occurrence of the big hit state, the reach display of the gusset is executed with the same appearance as the reach eyes (designs “3”, “4” and “1”). For this reason, the symbols 17A to 17H of the
[0115]
Further, in the present embodiment, in addition to the display of reach eyes that are closely related to the occurrence of the jackpot state, the reach eyes of gasses are displayed. Therefore, if the symbols “3”, “4”, and “1” are stopped and displayed, the player will be excited to see if he is a reach that is a sign of a big hit or a so-called “gase” reach. I will watch over the fluctuation of the design. Therefore, further improvement of interest is achieved.
[0116]
In addition, regardless of the occurrence of the big hit state, the appearance similar to the reach (the symbols “3”, “1”, “4”) is easily stopped and displayed. For this reason, when the symbols “3”, “1”, and “4” are stopped and displayed, there is a case where the player guesses that there is some relation with the reach eye, and the game content is further increased in thickness. It will be.
[0117]
In addition, in this embodiment, the special symbol random number counter is used in order to make it easy to stop and display the special symbols (“3”, “4”, “1” or “3”, “1”, “4”). CC is provided separately, and the symbols “3”, “4”, “1” or “3”, “1”, “4” are stopped and displayed depending on whether the value is within the predetermined range. . Accordingly, by appropriately changing the predetermined range, it is possible to appropriately adjust the appearance rate (probability that the specific symbol is finally stopped and displayed) such as “3”, “4”, and “1”.
[0118]
In addition, it is not limited to the description content of the said embodiment, For example, you may implement as follows.
[0119]
(1a) In the above embodiment, when the value of the special outlier symbol random number counter CC is within a first predetermined range (for example, 7 or more and 17 or less), a reach eye is displayed to display a so-called gusset reach eye. When the symbols “3”, “4”, and “1” are finally stopped and the value of the special out-of-band design random number counter CC is within the second predetermined range (for example, 57 to 67), “3” The symbols “1” and “4” were finally stopped. On the other hand, it is good also as a structure which does not perform the stop display of the symbol similar to reach eyes.
[0120]
(1b) Further, when the value of the special out-of-band design random number counter CC is not a predetermined range but is a predetermined value (for example, 7, or 7, 17 etc .: the predetermined value may be singular or plural), “3”, which is the same as the reach The symbols “4” and “1” may be finally stopped.
[0121]
(1c) Furthermore, the (first) predetermined range may be composed of a plurality of values and range groups. For example, the symbols “3”, “4”, and “1” may be finally stopped when the value of the special outlier design random number counter CC is 7, 17 to 27, 87 to 97.
[0122]
(1d) In addition, in the above embodiment, if the value of the special out symbol random number counter CC is not within the predetermined range, step S906 (determining the outreach symbol separately) or step S908 (determining the out symbol separately) It was decided to go through the process. On the other hand, a definite symbol other than the big hit time may be set in correspondence with the value of the special loss symbol random number counter CC. For example, “4”, “3”, and “1” are “4”, “3”, and “1” when the value of the special outlier design random number counter CC is 0 to 39, and “3”, “1”, and “4” are 80 to 92 when the value is 40 to 79. In the case of “3”, “4”, “1”, and in the case of 93-99, “1” “2” “1”, “2” “3” “2” etc. You may make it become the symbol by which a stop display is carried out. In such a configuration, the left, middle, and right symbol random number counters CDL, CDC, CDR are unnecessary.
[0123]
(1e) In the above embodiment, a special out-of-design symbol random number counter CC is separately provided, and a symbol to be finally stopped can be set according to the value. However, without using the counter CC, for example, an internal random number counter The symbol to be finally stopped may be determined in accordance with the value of the counter CI. In this case, there is an advantage that it is not necessary to provide a separate counter CC.
[0124]
(1f) In the above-described embodiment, the appearance rate of the same symbols as the reach eyes is increased from the appearance in relation to the so-called reach eyes. On the other hand, the appearance rate of a specific out symbol (or out of reach symbol) unrelated to the reach eye may be made different from the appearance. For example, when the value of the special outlier design random number counter CC is within a predetermined range, “1”, “2”, and “3” may be finally stopped and displayed. In this case, such a specific off symbol may be given no meaning or may have some meaning. As a specific example of giving meaning, for example, when it is finally stopped and displayed with a specific out-of-design,(1)The game mode can be switched from the normal mode to the probability change mode,(2)You can switch from probability variation mode to normal mode,(1)When(2)As an example, it may be combined. Furthermore, in this case, the appearance rate of a specific outlier symbol may be made variable according to the current game mode (whether or not the probability variation mode is being executed).
[0125]
By setting it as the above structures, the appearance frequency of the said specific off symbol will increase or decrease rather than it looks, and an interestingness will increase. Of course, the appearance frequency of both the symbols similar to the above reach eyes and the specific outlier symbols may be different from the appearance. Note that the same can be said for each of the above-described embodiments (particularly the second embodiment).
[0126]
(Second Embodiment)
Next, a second embodiment will be described. However, in the present embodiment, the description of the same part as the first embodiment will be omitted, and the difference will be mainly described below.
[0127]
In the first embodiment, a special outlier symbol random number counter CC is separately provided, and when the value of the counter CC is within the first predetermined range, the reach of the so-called gusset reach is displayed. The symbols “3”, “4”, and “1” that are the same as those in FIG. On the other hand, in the present embodiment, the special outlier symbol random number counter CC is not used, but the left, middle, and right symbol random number counters CDL, CDC, CDR and the tables shown in FIGS. 15A to 15C are used. It has the feature that it is.
[0128]
In the present embodiment, unlike the first embodiment in which the special out symbol storing process is executed in step S904, as shown in the “variation start processing routine” in FIG. After executing the storage process, the
[0129]
FIG. 17 is a flowchart showing the “outgoing symbol / outgoing reach design determination processing routine” performed in the process of step S906 or step S908. As shown in the figure, when the process proceeds to this routine, the
[0130]
In the next step S003, the
[0131]
Further, in the next step S005, the
[0132]
On the other hand, if a negative determination is made in step S005, the process returns to step S003, and the processes in steps S003 to 005 are repeated until an affirmative determination is made in step S005.
[0133]
For example, it is assumed that the value of the corresponding left symbol random number counter CDL is “45” this time. In this case, if n = 1, x = 10, and a negative determination is made in step S005. If n = 2, x = 20, and a negative determination is made in step S005. When n = 3, x = 50, and an affirmative determination is made in step S005. Therefore, in this case, the symbol corresponding to the corresponding added value y is “3” from the table of FIG. In other words, if the value of the corresponding left symbol random number counter CDL is “45” this time, in the
[0134]
Also, for example, assume that the value of the corresponding medium symbol random number counter CDC is “55” this time. In this case, a negative determination is made in step S005 when n = 1 to 3, and x = 60 when n = 4, and an affirmative determination is made in step S005. Therefore, in this case, the symbol corresponding to the corresponding added value y is “4” from the table of FIG. In other words, when the value of the corresponding middle symbol random number counter CDC is “55” this time, it is “4” that is set and stored as a confirmed symbol in the
[0135]
Further, for example, assume that the value of the corresponding right symbol random number counter CDR is “25” this time. In this case, when n = 1, x = 30, and an affirmative determination is suddenly made in step S005. Therefore, in this case, the symbol corresponding to the corresponding added value y is “1” from the table of FIG. That is, this time, when the value of the corresponding right symbol random number counter CDR is “25”, in the
[0136]
In the present embodiment, the total value of each added value y in each table in FIG. 15 is set to “100”. From this, the added value y is the probability that each symbol is set as a confirmed symbol ( (Percentage). Therefore, as is apparent from the value of the addition value y in each table, in the present embodiment, the symbol 17C of “3” is present in the
[0137]
As described above in detail, according to the present embodiment, in addition to the function and effect described in the first embodiment, it is not necessary to separately provide a special outlier random number counter CC. The control content can be simplified.
[0138]
In the present embodiment, since the total value of each added value y of each table used when setting the symbols to be finally stopped and displayed in each of the
[0139]
Further, when the appearance rate of the symbol is to be changed, it is only necessary to reset the value of the addition value y in each table as a percentage as appropriate. As a result, when there is a request for changing the appearance rate, it is possible to change and reset the appearance rate very easily.
[0140]
In addition, it is not limited to the description content of the said embodiment, For example, you may implement as follows.
[0141]
(2a) In the second embodiment, the threshold value x is obtained based on the added value y, and the left, middle, and right symbol random number counters CDL, CDC, CDR corresponding to the threshold value x are calculated. The symbols that are finally stopped and displayed are set based on the comparison result. On the other hand, the symbols to be finally stopped in the left, middle, and
[0142]
(2b) For example, as shown in FIGS. 18 (a), 18 (b), and 18 (c), each symbol random number counter CDL, CDC, CDR takes a value of “0” to “9”, and each counter CDL , CDC, CDR values and symbols may be set so as to uniquely correspond to each other. Referring to FIG. 18A as an example, when the value of the left symbol random number counter CDL corresponding to the current time is “0”, the symbol 17A whose symbol is finally set in the
[0143]
(2c) For example, as shown in FIG. 19, assuming that the symbol random number counter (for example, the left symbol random number counter CDL) takes a value of “0” to “9”, the value of the corresponding left symbol random number counter CDL is In the case of “0”, the symbol that is finally set in the
[0144]
(2d) In the above-described embodiment (particularly the first embodiment), the stop symbols for all the left, middle, and
[0145]
(2e) In each of the above embodiments, the appearance frequency of “3”, “4”, and “1” is different from the appearance frequency, but by applying each embodiment, the appearance of the outreach symbol The frequency can be different from the appearance.
[0146]
For example, in the first embodiment, when the value of the special out symbol random number counter CC is within a predetermined range, out of reach symbols such as “1”, “2”, “1”, etc. are stored as final symbols. It is good. In this case, a reach pattern is acquired and a reach gaming state is produced regardless of the outlier reach random number counter CO (or the reach effect may not be performed).
[0147]
Also, for example, in the second embodiment described above, by appropriately adjusting the value of the addition value y in the table, the outlier reach symbol (for example, “3” “4” “3” etc.) is finally stopped and displayed. It is also possible to increase or decrease the probability.
[0148]
(Third embodiment)
Next, a third embodiment will be described. However, in this embodiment, the description of the same parts as those in the first and second embodiments will be omitted, and the difference will be mainly described below.
[0149]
In the first and second embodiments, the symbols “3”, “4”, and “1”, which are the same as the reach eyes, and thus the appearance rate of the dismissed symbols are made different from the appearance. In addition, it is also mentioned that in the above-mentioned another example (2e), the appearance rate of the detachable reach can be made different from the appearance. On the other hand, in the present embodiment, the appearance rate of jackpot symbols (jackpots) such as “3”, “3”, “3”, “4”, “4”, and “4” is made different from the appearance. It has the characteristics.
[0150]
In the present embodiment, the process shown in FIG. 20 is executed in the jackpot symbol determination process in step S902. That is, FIG. 20 is a flowchart showing a “hit symbol determination processing routine” executed by the
[0151]
In the next step S0003, the
[0152]
Further, in the next step S0005, the
[0153]
On the other hand, if a negative determination is made in step S0005, the process returns to step S0003, and the processes in steps S0003 to 0005 are repeated until an affirmative determination is made in step S0005.
[0154]
For example, it is assumed that the value of the corresponding jackpot symbol random number counter CB is “37” this time. In this case, when n = 1, x = 15, and a negative determination is made in step S0005. When n = 2, x = 25 (15 + 10), and a negative determination is made in step S0005. When n = 3, x = 40 (15 + 10 + 15), and an affirmative determination is made in step S0005. Therefore, in this case, the jackpot symbol corresponding to the corresponding added value Y is “3” from the table of FIG. That is, when the value of the corresponding jackpot symbol random number counter CB is “37” this time, “3”, “3”, and “3” are set and stored as the jackpot symbol.
[0155]
In the present embodiment, the total value of each added value Y in the table of FIG. 21 is set to “100” as in the second embodiment. It also represents the probability (percentage) that the symbol is set as the final symbol. Therefore, as is apparent from the value of the added value Y in the table, in this embodiment,
[0156]
As described above in detail, according to the present embodiment, in addition to the effects described in the first and second embodiments, the appearance rate of the jackpot symbol is made to be different from the actual appearance. . For this reason, the player can be surprised at the difference between the appearance rate of the appearance jackpot symbol and the actual appearance rate of the jackpot symbol, and can enjoy special game characteristics. As a result, it is possible to dramatically improve the interest.
[0157]
In particular, in the present embodiment, whether or not the probability variation mode is given in the game after the jackpot is determined is determined according to the type of jackpot symbol. Therefore, by appropriately adjusting the addition value Y of the table as in the present embodiment, the probability that the probability variation mode is given can be made different from the appearance. As a result, the improvement of interest will be spurred.
[0158]
Further, as described above, since the total value of each added value Y of the table used when setting the jackpot symbol is set to “100”, the added value Y is the probability that each jackpot symbol is set as a confirmed symbol. Will also be expressed. For this reason, when the probability of each jackpot symbol being stopped and displayed is appropriately adjusted, the added value Y can be set with the ratio to appear as it is as a percentage. For this reason, it is very easy to set the appearance rate of the jackpot symbol, and it is not necessary to perform complicated and difficult operations when setting the appearance rate.
[0159]
Furthermore, when the appearance rate of the jackpot symbol is to be changed, it is only necessary to reset the value of the added value Y of each table as a percentage as appropriate. As a result, when there is a request for changing the appearance rate, it is possible to change and reset the appearance rate very easily.
[0160]
In addition, it is not limited to the description content of the said embodiment, For example, you may implement as follows.
[0161]
(3a) In the third embodiment, the probability that the probability variation mode is actually given is made different from the appearance (the appearance is 50%, but the probability variation mode is actually 60% probability). Is granted). On the other hand, it is also possible to make the appearance rate of each jackpot symbol different from the appearance by making the probability that the probability variation mode is actually given the same. For example, when determining the jackpot symbol, the jackpot symbol may be determined using a table as shown in FIGS. 22 (a) and 22 (b).
[0162]
(3b) For example, when a table as shown in FIG. 22 (a) is used, even if a symbol to which the same probability variation mode is given, the jackpot symbol of “3” and “7” is “1”, The actual appearance rate is set lower than the jackpot symbol of “5”. By making such a setting, if a big hit state occurs with the symbols “3” and “7” in relation to the business of the game hall, it is possible to continue the game without exchanging the prize balls. When the sales form is adopted, since the appearance rate of “3” and “7” can be lowered, the continuous game is relatively difficult to be performed. On the other hand, in the table shown in the figure, the jackpot symbols of “4” and “6” are more actual than the jackpot symbols of “2” and “8” even if the same normal mode is given. Appearance rate is set high. By making such a setting, when a big hit state occurs with the symbols "4" and "6" for the game hall sales, a business form is adopted in which all prize balls must be exchanged. If it is, the appearance rate of “4” and “6” can be increased, so that it is more difficult to continue the game. Of course, the appearance rate of “3” and “7” can be set high or the appearance rate of “4” and “6” can be set low without being bound by the above relationship.
[0163]
(3c) For example, when a table as shown in FIG. 22B is used, the jackpot symbol “7” is extremely likely to appear. With such a configuration, when a reach state occurs with the
[0164]
(3d) In the third embodiment, the threshold value x is obtained based on the added value Y, the threshold value x is compared with the value of the corresponding jackpot symbol random number counter CB, and based on the comparison result. The jackpot symbol was set. On the other hand, a jackpot symbol may be set simply according to the value of the jackpot symbol random number counter CB.
[0165]
(3e) For example, as shown in FIG. 24A, assuming that the jackpot symbol random number counter CB takes a value of “0” to “99”, the value of the counter CB and the jackpot symbol are uniquely associated. It is good also as setting it. When the value of the jackpot symbol random number counter CB corresponding to this time is “0” to “14”, the jackpot symbol is “1” symbol 17A and the value of CB is “15” to “14”. In the case of “24”, the jackpot symbol becomes the symbol 17B of “2”,..., When the value of the jackpot symbol random number counter CB is “90” to “99”, the jackpot symbol is “8”. It becomes the pattern 17H. Therefore, in this case, the jackpot symbol is stopped and displayed at the same appearance rate as in the third embodiment.
[0166]
Further, for example, as shown in FIG. 24B, assuming that the jackpot symbol random number counter CB takes a value of “0” to “9”, the value of the jackpot symbol random number counter CB corresponding to this time is “0”. The jackpot symbol is a symbol 17A of “1”, and when the value of CB is “1”, the jackpot symbol is a symbol 17B of “2”,..., The value of the jackpot symbol random number counter CB is “6” ”To“ 8 ”, the jackpot symbol is a
[0167]
(3f) Furthermore, at least one of each of the left, middle, and
[0168]
(3g) For example, as shown in FIG. 25, the almighty symbol “A” can appear and be displayed in one symbol row (left
[0169]
Furthermore, a normal mode is given when a big hit state is associated with the almighty symbol “A”, and a probability change mode is given when any symbol is finally stopped and displayed with a doublet. The above example can be applied to the case or vice versa.
[0170]
In addition, it is assumed that an almighty symbol “A” may appear and be displayed in a plurality of (for example, two, three or more) symbol columns (in this case, a jackpot state in relation to the almighty symbol “A” in appearance) The above example may be applied).
[0171]
(3h) In addition, even when the jackpot symbol to which the apparent probability change mode is given is set more (or less) than the symbol to which the normal mode is given without setting the almighty symbol, the above example Can be applied. For example,(1)When a jackpot state occurs with an even number of symbols, the normal mode is assigned. When a jackpot state occurs with an odd number of symbols, the probability variation mode is assigned. If the odd number symbol (or even number of symbols) is simply apparent, It is also possible to set more than the number of symbols (or odd symbols) and make the actual appearance rate different from the appearance.(2)In addition, when a symbol pattern is prepared separately and a jackpot state occurs with an even number of symbols, a normal mode is given, and when a jackpot state occurs with an odd number of symbols or a picture symbol, a probability variation mode is given, The number of symbols to which the probability variation mode is assigned can be set larger than the number of even symbols to which the normal mode is assigned, and the actual appearance rate may be made different from the appearance under such setting.
[0172]
(3i) Depending on the game mode at that time, the table (or the added value of the table, etc.) and the counter used for determining the jackpot symbol may be changed. For example, in the normal mode, the probability that the probability variation mode is actually given is set lower (or higher) than the actual probability that the probability variation mode is given. May be set higher (or lower).
[0173]
(Fourth embodiment)
Next, a fourth embodiment will be described. However, in this embodiment, the description of the same parts as those in the first to third embodiments will be omitted, and the following description will focus on the differences.
[0174]
In the third embodiment, the actual appearance rate of each jackpot symbol is made different from the appearance by using a table or the like. On the other hand, the present embodiment is characterized in that the appearance rate of the actual jackpot symbol is made different from the appearance rate of the apparent jackpot symbol by the re-lottery process.
[0175]
In this embodiment, symbols 17A to 17H of “1” to “8” are prepared as symbols of the
[0176]
In the present embodiment, the process shown in FIG. 27 is executed in the jackpot symbol determination process in step S902. That is, FIG. 27 is a flowchart showing a “hit symbol determination processing routine” executed by the
[0177]
In the following step S0012, the
[0178]
On the other hand, if a negative determination is made in step S0012, the process proceeds to step S0015. In step S0015, the
[0179]
In the next step S0016, a value obtained by adding a predetermined value α to the value of the jackpot symbol random number counter CB is set as a re-lottery jackpot symbol random number counter CB1. However, the re-lottery jackpot symbol random number counter CB1 also takes a value of “0” to “7”, and the value is returned to “0” after “7”. Therefore, for example, when the value of the jackpot symbol random number counter CB is “7” (in this case, the temporarily stopped symbols are “8”, “8”, “8”) and the predetermined value α is “3”, The value of the re-lottery jackpot symbol random number counter CB1 is “2”. The predetermined value α may be a fixed value, but it is desirable that the predetermined value α is a variable value that can be changed from time to time so that the player does not detect the jackpot symbol after the re-lottery. Of course, the value of the re-lottery jackpot symbol random number counter CB1 may be obtained by subtracting the predetermined value α.
[0180]
In step S0017, the
[0181]
FIG. 28 is a flowchart showing a “re-lottery process routine” executed in the process of step S135. As shown in the figure, when the process proceeds to this routine, the
[0182]
On the other hand, when the re-lottery execution flag XCS is set to “1”, in step S1352, the symbols of all
[0183]
Thus, according to the present embodiment, the probability that a jackpot state occurs in a symbol to which a probability variation mode is imparted is apparently two-eighth, whereas the probability variation mode is actually imparted. The probability of winning a jackpot with a symbol to be played is 7/16. For this reason, as in the third embodiment, the player can be surprised at the difference between the appearance rate of the appearance jackpot symbol and the appearance rate of the actual jackpot symbol, and can enjoy special game characteristics. As a result, it is possible to dramatically improve the interest.
[0184]
In the present embodiment, the actual jackpot symbol appearance rate is made different from the appearance jackpot symbol appearance rate by the re-lottery process. For this reason, it is not necessary to set the table as described above. In particular, in the present embodiment, the stop symbol and the final jackpot symbol may be set equally for each symbol based on the values of the jackpot symbol random number counter CB and the re-lottery jackpot symbol random number counter CB1. Therefore, the design can be easily performed without requiring time and effort for setting.
[0185]
In addition, it is not limited to the description content of the said embodiment, For example, you may implement as follows.
[0186]
(4a) In the above embodiment, when the stop symbol is not a predetermined symbol (a symbol to which the probability variation mode is given), the final jackpot symbol is subjected to internal lottery only once again. On the other hand, a lottery of three or more stages may be performed. In this way, by appropriately combining the number of re-lotteries and the number of jackpot symbols, the appearance rate can be set as necessary. For example, in the above example, if the jackpot symbol set based on CB1 is not “3” “3” “3” or “7” “7” “7”, the lottery symbol random number counter CB2 for re-lottery is set again. It is good also as setting and setting a final jackpot symbol. In this case, the probability that the symbol to which the probability variation mode is assigned is finally stopped can be 2/8 + 6/8 * 2/8 +, 6/8 * 6/8 * 2/8 = 37/64.
[0187]
(4b) In the above embodiment, based on the values of the jackpot symbol random number counter CB and the re-lottery jackpot symbol random number counter CB1, the stop symbol and the final jackpot symbol are set evenly for each symbol. . On the other hand, the correspondence between the counters CB and CB1 and the jackpot symbol does not necessarily have to be equalized. Thus, by adjusting the correspondences as appropriate, the final jackpot symbol appearance rate can be adjusted more finely. In addition, it is possible to relatively easily adjust the probability that the jackpot symbol to which the probability variation mode is actually applied will be finally stopped.
[0188]
(4c) In the above embodiment, after the stop display, the re-lottery process is effect-displayed. However, such a re-lottery process may not be shown to the player. That is, the re-lottery process may be performed internally (assuming that multiple stages of lottery are performed internally), and only the jackpot symbol that is finally determined may be stopped and displayed as a result.
[0189]
(4d) In the above embodiment, the two types of jackpot symbols “3”, “3”, “3”, “7”, “7”, and “7” are the jackpot symbols to which the probability variation mode is given. On the other hand, the jackpot symbol to which the probability variation mode is given may be only one type, for example, “7” “7” “7”. In this case, the probability of a jackpot state occurring in the symbols “7”, “7”, and “7” is extremely increased, and the surprise for the player is further amplified.
[0190]
(4e) In the fourth embodiment, the jackpot symbol is re-drawn, but the above embodiment may be applied to re-draw the reach symbol. For example, it is assumed that the left and
[0191]
In addition, items that can be implemented separately are described below.
[0192]
(A) In the above embodiment, as a concept of the probability variation mode, (1) the probability that “7” is displayed on the 7-segment display unit 53 is increased as compared with the normal time, and the opportunity to open the
[0193]
Further, instead of or in addition to the probability variation mode, the present invention may also be applied to a pachinko machine that can execute a time reduction (time reduction) mode (any combination of the above (1) to (4)).
[0194]
Furthermore, it can be embodied in a pachinko machine that does not execute the probability variation mode.
[0195]
(B) The time reduction mode and the probability change mode may be continued until the next big hit time, or may be continued for a predetermined number of rotation fluctuations of the symbols 17A to 17H, and then switched to the normal mode. It may be. Further, when the time reduction mode or the probability variation mode is selected, the special mode may be continued until the big hit state occurs twice or more. In addition, as a result, the number of continuations of the probability variation mode and the time reduction mode (the number of continuation occurrences of the jackpot state) may be made variable in accordance with the jackpot symbol. For example, if the jackpot is “1” or “5”, the probability variation mode is continued until the next jackpot, and if the jackpot is “3” or “7”, the probability variation mode is continued until the next jackpot. It may be.
[0196]
(C) In the above embodiment, the re-variation process is performed, but such a process may be omitted.
[0197]
(D) As the
[0198]
(E) In the above embodiment, the normal symbol display device 51 variably displays the numbers from “0” to “9” and causes the 7-segment display unit 53 to display the segments. In the embodiment, when stopping at “7”), the
[0199]
(F) You may implement as a pachinko machine etc. of a different type from the said embodiment. For example, once a big hit, a pachinko machine that raises the expected value of the big hit until a big hit state occurs (for example, two times or three times) including that (for example, a two-time right item, a three-time right item) May also be implemented. Further, it may be implemented as a pachinko machine that enters a special gaming state on the condition that a game ball is awarded in a predetermined area after the big hit symbol is displayed. In addition to pachinko machines, the present invention can be implemented as various gaming machines such as alepatchi, sparrow balls, and slot machines. In the slot machine, for example, a symbol is changed by operating a control lever in a state where a symbol effective line is determined by inserting coins, and a symbol is stopped and confirmed by operating a stop button. Is. Accordingly, the basic concept of the slot machine is that it is provided with a symbol display means for displaying a fixed symbol after a symbol string consisting of a plurality of symbols is variably displayed, and is caused by the operation of a starting operation means (for example, an operating lever). The game starts on the condition that the symbol variation is stopped due to the operation of the stop operating means (for example, the stop button) or when a predetermined time elapses and the confirmed symbol at the time of the stop is a specific symbol. Slot machine having special gaming state generating means for generating a special gaming state advantageous to the user.
[0200]
(G) In the above embodiment, the game mode is displayed at the end of the jackpot state (step S240), but such display may not be performed. Further, it may be displayed at the time of jackpot or during jackpot. Further, after the jackpot, the display may be continued until the next jackpot. Moreover, you may make it alert | report a mode with a lamp | ramp or a sound besides displaying on a display part.
[0201]
(H) Each numerical value regarding the display probability of the appearance symbol in the above embodiment, the display probability of the actual symbol, the probability of giving the appearance probability change mode, the probability of giving the actual probability change mode, etc. It is just an example. That is, the probabilities are arbitrary and can be changed as appropriate.
[0202]
(I) Notification modes such as various displays and voices may be appropriately switched and executed according to differences in game modes (for example, normal mode and probability change mode) and jackpot expectation values. For example, when the big hit expectation value is increased, control is performed so that the symbol is switched from green to red, or the sound is changed. Such color switching or sound change has the effect of clarifying to the player that the gaming state is different from the normal state, and clearly indicating to the player that the expected value of the big hit has increased. Bring. The technical idea derived from this is “to switch and display the notification mode such as the symbol display color according to the game state”, “to switch and display the notification mode such as the symbol display color according to the game mode.” , “Switch the display mode of the symbol display color or the like according to the difference in the expected value of jackpot”.
[0203]
(J) A display control device that controls the
[0204]
(K) As a selection between the normal mode and the game mode such as the probability change mode, in addition to the type that is notified by the type of symbol (odd number / even number) in the display device 13 (display unit 13a) as a variable display device, Mode notification means may be provided for confirming whether or not the mode is selected after the symbol called the fourth symbol is changed. And it is good also as making the appearance rate of the said 4th symbol differ by the appearance and the actual.
[0205]
(L) The first to fourth embodiments (including various examples) may be appropriately combined. For example,(1)Make the appearance rate of outliers different from the actual appearance,(2)Make the appearance rate of outreach reach different from the actual appearance,(3)Make the appearance rate of jackpot symbols different from the actual appearance,(4)the above(3)Out of performing by re-drawing(1) (2)A combination of(1) (3)A combination of(1) (4)A combination of(2) (3)A combination of(2) (4)A combination of(3) (4)A combination of(1) (2) (3)A combination of(1) (2) (4)A combination of(1) (3) (4)A combination of(2) (3) (4)A combination of(1) (2) (3) (4)These combinations can be implemented as appropriate.
[0206]
(M) The numerical values of the tables and counters are not limited to the numerical values in the above embodiment. Further, the random number width may be variable according to the game situation at that time.
[0207]
(N) Above (L)(1)~(4)And regarding these combinations, it is good also as giving unity (relevance) between what is called a series machine (brother machine). Note that the specs differ from the series machines (for example, the jackpot probability is different, the characters that appear are different, the probability variation mode grant rate is different, or the game mode that is granted other than the normal mode Is different between the probability change mode and the short-time mode, the purchase method of game balls is different (so-called cash machine and CR machine), the type of reach is different, etc.) , An equivalent or similar variable display device or a plurality of types of gaming machines equipped with cell boards and the like.
[0208]
(O) In each of the above embodiments, all preset symbols are actually stopped and displayed. On the other hand, when a predetermined condition is satisfied (for example, in a predetermined game mode), it is possible to provide a symbol that is not finally stopped and displayed. For example, if the symbol 17D of “4” is not stopped and displayed in the
[0209]
(P) In each of the above embodiments, the display unit 13a is configured by the three
[0210]
For example, when the display unit is composed of two left and right symbol rows, the following control can be performed. That is, as shown in FIG. 29, both the left and right symbol rows are composed of symbols “0” to “5”, and a probability variation mode is given when a big hit state is generated with an odd number of double eyes, and an even number of double eyes Assume that the normal mode is given when a big hit state occurs. In this case, regarding the symbol sequence that stops first (for example, the left symbol sequence), the symbols “0” to “2” are actually easy to stop and display, and the symbols “3” to “5” are not easily displayed to stop. It is assumed that a big hit state is likely to occur when the symbols “3” to “5” are once stopped and displayed. With such a configuration, the player desires that the symbols “3” to “5” are temporarily stopped in the symbol sequence to be stopped first, and once the symbols “3” or “5” are displayed. When is displayed in a stopped state, the excitement can reach its climax in the hope that the probability variation mode will be given. In particular, between “3” and “5”, the probability that the probability variation mode is given is higher than the probability that the normal mode is given. Therefore, even in this sense, the interest is further improved.
[0211]
【The invention's effect】
According to the present invention, it is possible to suitably improve the interest.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a front view showing a pachinko machine according to a first embodiment.
2A is a schematic diagram showing an example of a display state (at the time of change) of a display unit, FIG. 2B is a schematic diagram showing one mode of a jackpot state, and FIG. 2C is a diagram in a reach state. It is a schematic diagram which shows an aspect.
FIG. 3 is a chart for explaining the concept of a design random number buffer.
FIG. 4 is a chart for explaining the concept of a symbol random number area.
FIG. 5 is a chart for explaining the concept of a stop symbol area.
6A is a chart for explaining the concept of a random number counter, FIG. 6B is a chart for explaining the concept of a reach type determination counter and the like, and FIG. 6C is a chart for explaining the concept of a special outlier design random number counter; It is a chart to do.
FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing a “random number distribution routine” executed by the control device.
FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing a “storage processing routine”;
FIG. 9 is a flowchart showing a part of a “special electric accessory control routine”;
10 is a flowchart showing a continuation of FIG. 9, which is a part of the “special electric accessory control routine”.
FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing a “variation start processing routine”;
FIG. 12 is a flowchart showing a “reach eye symbol storage processing routine”.
FIG. 13 is a flowchart showing a “special loss symbol storage processing routine”.
14A is a schematic diagram illustrating an example of reach eyes of the display unit, and FIG. 14B is a schematic diagram illustrating a display mode similar to the reach eyes.
FIGS. 15A to 15C are tables showing correspondences between left middle and right symbols and added values (appearance rates), respectively, in the second embodiment;
FIG. 16 is a flowchart showing a “variation start processing routine” executed by the control device;
FIG. 17 is a flowchart showing a “deletion symbol / decoupling reach determination process routine”.
FIGS. 18A to 18C are tables showing the correspondence between left and right out symbol random number counters and out symbols in another embodiment.
FIG. 19 is a table showing a correspondence relationship between, for example, an off-left symbol random number counter and an off-left symbol in another embodiment;
FIG. 20 is a flowchart showing a “hit symbol determination process routine” executed by the control device in the third embodiment;
FIG. 21 is a table showing a correspondence relationship between jackpot symbols and added values (appearance rate).
FIGS. 22A and 22B are tables showing correspondence relationships between jackpot symbols and added values (appearance rates) in different embodiments, respectively.
FIG. 23 is a schematic diagram illustrating an example of a display state (during double reach) of a display unit in another embodiment.
FIGS. 24A and 24B are tables showing correspondence relationships between jackpot symbol counters and jackpot symbols in different embodiments, respectively.
FIG. 25 is a chart showing an example of a left middle right (big hit) symbol in another embodiment;
FIG. 26 is a table showing a correspondence relationship between jackpot symbols and added values (appearance rate) in another embodiment;
FIG. 27 is a flowchart showing a “hit symbol determination process routine” executed by the control device in the fourth embodiment;
FIG. 28 is a flowchart showing a “re-lottery processing routine” executed by the control device.
FIG. 29 is a chart showing characteristics of symbols that are first stopped and displayed in another embodiment;
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (5)
所定の遊技状況を検出する遊技状況検出手段と、
前記遊技状況検出手段による検出結果に基づき、遊技者に有利な特別遊技状態を発生させるか否かの抽選を行うとともに、前記表示手段の各図柄表示領域にて複数の図柄の変動表示を開始させ、所定時間後に停止表示させ、
前記抽選の結果が当たりである場合には、前記複数の図柄表示領域において図柄を特定の当たり組み合わせパターンにて停止表示させ、前記特別遊技状態を発生させ、
前記抽選の結果が当たりでない場合には、前記特別遊技状態を発生させることなく前記複数の図柄表示領域において少なくとも1つの第1の外れ組み合わせパターンを含む複数の外れ組み合わせパターンのうち所定の外れ組み合わせパターンにて図柄を停止表示させる制御手段とを備える遊技機であって、
所定の第1条件が成立しているか否かを判別可能な判別手段と、
該判別手段により第1条件が成立していないと判別されたことに基づき、前記少なくとも1つの第1の外れ組み合わせパターンを含む複数の外れ組み合わせパターンのうちいずれかの外れ組み合わせパターンで図柄の停止表示を行う第1停止表示手段と、
前記判別手段により第1条件が成立していると判別されたことに基づき、前記少なくとも1つの第1の外れ組み合わせパターンで図柄の停止表示を行う第2停止表示手段とを有し、
前記制御手段は、
遊技機の制御を司る第1制御手段と、
該第1制御手段とは別に設けられ、前記表示手段における前記図柄の変動表示を制御する第2制御手段とを有して構成され、
前記第1制御手段は、
前記第2制御手段に特定信号を出力可能に構成され、
前記第2制御手段は、
前記特定信号の入力に基づいて前記図柄の変動表示を制御可能に構成されるとともに、
前記第1停止表示手段と、
前記第2停止表示手段と、
前記第1停止表示手段が停止表示する外れ組み合わせパターンを、前記少なくとも1つの第1の外れ組み合わせパターンを含む複数の外れ組み合わせパターンのうちいずれの外れ組み合わせパターンとするかを、前記特定信号の入力に基づき決定する決定手段とを有していることを特徴とする遊技機。 Display means capable of variably displaying a plurality of symbols in a plurality of symbol display areas;
Game situation detecting means for detecting a predetermined game situation;
Based on the detection result by the gaming status detection means, a lottery is performed to determine whether or not a special gaming state advantageous to the player is generated, and a plurality of symbols are displayed in a variable manner in each symbol display area of the display means. , Stop display after a predetermined time,
If the result of the lottery is a win, the symbols are stopped and displayed in a specific winning combination pattern in the plurality of symbol display areas, and the special gaming state is generated.
If the result of the lottery is not successful, a predetermined outlier combination pattern among a plurality of outlier combination patterns including at least one first outlier combination pattern in the plurality of symbol display areas without generating the special gaming state And a control means for stopping and displaying the design at
Discriminating means capable of discriminating whether or not a predetermined first condition is satisfied;
Based on the fact that the first condition is determined not to be established by the determining means, the symbol is stopped and displayed by one of the outlier combination patterns including the at least one first outlier combination pattern. First stop display means for performing
Based on the fact that the first condition is determined to be established by the determining means, and having a second stop display means for displaying a stop of the symbol with the at least one first outlier combination pattern,
The control means includes
First control means for controlling the gaming machine;
Provided separately from the first control means, and having a second control means for controlling the display of fluctuations of the symbol in the display means,
The first control means includes
The second control means is configured to output a specific signal,
The second control means includes
Based on the input of the specific signal, it is configured to be able to control the variation display of the symbol,
Said first stop display means;
Said second stop display means;
Which one of the plurality of outlier combination patterns including the at least one first outcombination pattern is set as the outlier combination pattern that the first stop display means stops displaying is input to the specific signal. A gaming machine comprising: a determining means for determining based on the game machine.
リーチを行うが外れとなるリーチ外れ組み合わせパターンと、 Reach out-of-reach combination pattern that performs reach but out of reach,
リーチを行わず外れとなる非リーチ外れ組み合わせパターンとを含み、 Including non-reach out-of-reach combination patterns that are out of reach without being reached,
前記少なくとも1つの第1の外れ組み合わせパターンは、 The at least one first outlier combination pattern is:
リーチを行わず外れとなる非リーチ外れ組み合わせパターンであることを特徴とする請求項1記載の遊技機。 2. The gaming machine according to claim 1, wherein the gaming machine is a non-reach out-of-reach combination pattern that is out of reach without performing reach.
リーチを行うが外れとなるリーチ外れ組み合わせパターンと、 Reach out-of-reach combination pattern that performs reach but out of reach,
リーチを行わず外れとなる非リーチ外れ組み合わせパターンとを含み、 Including non-reach out-of-reach combination patterns that are out of reach without being reached,
前記少なくとも1つの第1の外れ組み合わせパターンは、 The at least one first outlier combination pattern is:
リーチを行うが外れとなるリーチ外れ組み合わせパターンであることを特徴とする請求項1記載の遊技機。 The gaming machine according to claim 1, wherein the game machine is a reach-removal combination pattern that performs reach but is disengaged.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP23756999A JP4479018B2 (en) | 1999-08-24 | 1999-08-24 | Game machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP23756999A JP4479018B2 (en) | 1999-08-24 | 1999-08-24 | Game machine |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009203210A Division JP4661975B2 (en) | 2009-09-03 | 2009-09-03 | Game machine |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2001062096A JP2001062096A (en) | 2001-03-13 |
| JP2001062096A5 JP2001062096A5 (en) | 2006-11-09 |
| JP4479018B2 true JP4479018B2 (en) | 2010-06-09 |
Family
ID=17017268
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP23756999A Expired - Lifetime JP4479018B2 (en) | 1999-08-24 | 1999-08-24 | Game machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4479018B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002153656A (en) * | 2000-11-22 | 2002-05-28 | Heiwa Corp | Game machine |
| JP4586376B2 (en) * | 2003-03-05 | 2010-11-24 | 株式会社竹屋 | Game machine |
| JP2004344402A (en) * | 2003-05-22 | 2004-12-09 | Maruhon Ind Co Ltd | Game machine, computer program and recording medium |
| JP3988164B2 (en) * | 2003-12-24 | 2007-10-10 | タイヨーエレック株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP4189590B2 (en) * | 2004-03-15 | 2008-12-03 | 奥村遊機株式會社 | Pachinko machine |
| JP2006288540A (en) * | 2005-04-07 | 2006-10-26 | Okumura Yu-Ki Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP5023341B2 (en) * | 2005-11-08 | 2012-09-12 | 株式会社大一商会 | Game machine |
| JP2008161397A (en) * | 2006-12-28 | 2008-07-17 | Net Kk | Game machine |
| JP4777272B2 (en) * | 2007-02-15 | 2011-09-21 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP4777271B2 (en) * | 2007-02-15 | 2011-09-21 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP2007136227A (en) * | 2007-02-26 | 2007-06-07 | Kyoraku Sangyo Kk | Pachinko game machine |
| JP5228859B2 (en) * | 2008-09-26 | 2013-07-03 | 株式会社三洋物産 | Game machine |
| JP4478817B2 (en) * | 2009-03-13 | 2010-06-09 | タイヨーエレック株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP5417216B2 (en) * | 2010-02-19 | 2014-02-12 | 株式会社平和 | Game machine |
| JP5085706B2 (en) * | 2010-09-28 | 2012-11-28 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP5356441B2 (en) * | 2011-03-11 | 2013-12-04 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP5497090B2 (en) * | 2012-03-26 | 2014-05-21 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
-
1999
- 1999-08-24 JP JP23756999A patent/JP4479018B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2001062096A (en) | 2001-03-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4479018B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4427835B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2001000685A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4501172B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP3823526B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5929789B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4816782B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4661975B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5252040B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5310800B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4474692B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4670999B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5846115B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2010279787A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2007229518A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4631106B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4670981B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5796660B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4692670B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5637202B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5617882B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4591536B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6079694B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4154915B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP4337295B2 (en) | Game machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20060802 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20060921 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090707 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090903 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20091110 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20100223 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20100308 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130326 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number: 4479018 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130326 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20160326 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |