JP3981478B2 - Electronic component mounting device - Google Patents
Electronic component mounting device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3981478B2 JP3981478B2 JP27697698A JP27697698A JP3981478B2 JP 3981478 B2 JP3981478 B2 JP 3981478B2 JP 27697698 A JP27697698 A JP 27697698A JP 27697698 A JP27697698 A JP 27697698A JP 3981478 B2 JP3981478 B2 JP 3981478B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- electronic component
- mounting
- mounting head
- movable body
- detection means
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Automatic Assembly (AREA)
- Supply And Installment Of Electrical Components (AREA)
- Control Of Position Or Direction (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【産業上の利用分野】
本発明は、電子部品の組立や装着を行なう業界等において用いる電子部品装着装置及びその方法に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
プリント基板等への電子部品の装着は、図18(a)に示すように、XY方向へ任意に移動する電子部品装着装置80における装着ヘッド81によって、電子部品82の供給部83と装着部84とを往復して昇降し、その吸着と離脱とを繰り返すことで所定の装着が行われる。
【0003】
従来の電子部品装着装置80にあって、図18(b)に示すように、装着ヘッド81は、XY方向へ移動する可動体85へ複数個(例えば4個や6個)が所定間隔で固着されている。
【0004】
そして、これら複数個の装着ヘッド81,81,81…に吸着保持された電子部品82,82,82…は、この電子部品82の下側を走行するCCDカメラ等のセンサ86によって、この装着ヘッド81における吸着ノズル87に吸着されたときの保持状態が検出され、あらかじめ定められたデータ以外の検出情報を得たときは、プリント基板88への装着前までに電子部品82の姿勢や位置等が補正される。
【0005】
しかしながら、前記した複数個を並べ設けた装着ヘッド81は、そのそれぞれの取付ピッチが一定(不変)となる固定状態に設けられているため、例えば、電子部品82の供給部83にあって、載置されている多数の電子部品82の間隔(ピッチ)が装着ヘッド81,81,81…の取付間隔(ピッチ)と一致していないと同時吸着ができない。
【0006】
そのため、個々の装着ヘッド81に対して、複数個の装着ヘッド81,81,81…を支承している可動体85の全体を移動させて、装着ヘッド81の一個ずつをその供給部83の電子部品82の吸着位置に対応させなくてはならず、全ての装着ヘッド81に対する電子部品82の吸着保持の作業時間に手間取り、電子部品装着業界が大きな課題としているそのタクト時間の短縮化に対して大きな障害となっている。
【0007】
このことは、装着部84においての電子部品82の装着においても同様の現象が生ずるものであって、プリント基板88へ装着すべき多数の電子部品82の装着間隔(ピッチ)が、電子部品82が吸着保持されている装着ヘッド81,81,81…の取付間隔(ピッチ)と一致していないと同時装着ができない(一般的にはほとんど一致していない)。
【0008】
そのため、個々の装着ヘッド81に対して、複数個の装着ヘッド81,81,81…を支承している可動体85の全体を移動させて、装着ヘッド81の一個ずつをその装着部84のプリント基板88への電子部品82の載置位置に対応させなくてはならず、全ての装着ヘッド81による電子部品82の装着作業に手間取り、タクト時間の短縮化が図れない。
【0009】
また、これら電子部品82の同時吸着および同時装着以外にあっても、装着ヘッド81の取付間隔(ピッチ)が不変式の場合は、個々の装着ヘッド81の左右方向への移動調整を行うことができないので、前記した同様の操作により、個々の装着ヘッド81に対して、複数個の装着ヘッド81,81,81…を支承している可動体85の全体を移動させて吸着位置および装着位置を調整しなければならない。
【0010】
更に、各装着ヘッド81に吸着保持させた電子部品82の吸着保持状態の検出を行なうセンサ86および装着ヘッド81は、その構成が、移動カメラ軸機構やZ軸サーボモータ,ボールネジ,スプラインシャフト等のようにその部品点数が多くなり、装置全体のコストの上昇につながる。等の様々な問題点を有するものであった。
【0011】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
本発明は前記した問題点を解決するためになされたもので、複数個の装着ヘッドが個別に可変制御され、それぞれが任意に広がって電子部品を吸着し、吸着された電子部品は、その保持状態を該電子部品の下方に位置する検出手段によって検出され、あらかじめ決められたプリント基板上の所定位置へ装着されることにより、各電子部品の一連の装着作業にあって、可動する装置全体の移動量が最も少なくなるように各部材が制御されて、装着作動時間を可及的に短縮させてタクトタイムの短縮化が図れ、かつ、装着ヘッドや検出手段の構成を簡略化させることができる電子部品装着装置およびその方法を提供することを目的としている。
【0012】
前記した目的を達成するための本発明の手段は、機体に設けられて前後方向へ移動する進退体と、前記進退体の一側に設けられて左右方向へ移動する可動体と、前記可動体の垂直面上を個々に左右方向若しくは左右方向・上下方向へ移動し、かつ電子部品の供給部と装着部とを前記可動体とともに移動する複数個の装着ヘッドと、前記装着ヘッドに設けられて上下方向へ移動し、かつ縦軸方向を中心に回転する電子部品吸着部材と、前記電子部品吸着部材に吸着された電子部品を検出する検出手段と、前記検出手段の検出信号を受け、あらかじめ定められたデータに基づいて演算する制御手段とを備えた電子部品装着装置の構成にある。
【0013】
そして、前記検出手段は、前記装着ヘッドの下方を移動する電子部品装着装置の構成にある。
【0016】
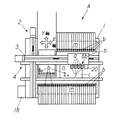
図1〜図4においてAは、チップ部品やIC部品等の電子部品bを、その供給部mより受け取って装着部nへ移送し、プリント基板c上の所定の個所へ装着する電子部品装着装置である。
【0017】
なお、前記した電子部品装着装置Aには、機体1においてその一側若しくは両側にパーツフィーダ等により順次搬送されて待機する電子部品bの供給部mが、また、機体1内において移送部材(図示せず)によりプリント基板cが搬入出される電子部品bの装着部nが設けられている。
【0018】
そして、その構成は、図1および図2,図4に示すように、機体1へ取り付けて、第一駆動手段2により前後方向(Y軸方向)へ任意に移動する進退体3と、この進退体3に取り付けて第二駆動手段4により左右方向(X軸方向)へ任意に移動する可動体5とが設けられている。
【0019】
この可動体5には、複数個(単個でも構わない)の装着ヘッド7が、後記する第五駆動手段6bにより上下方向(昇降方向)若しくは上下・左右方向(昇降方向およびX軸方向)へ進退自在に係合させてある。
【0020】
なお、この複数個の装着ヘッド7の下端部には、電子部品bの上面を吸着する吸着パット式や、その外周を把持するチャック式等の電子部品吸着部材である吸着ノズル9が取り付けられているもので、本実施例においては吸着パット式について示すものであり、この吸着ノズル9は回転手段8aにより縦軸方向(Z軸方向)を中心として回転自在としてあり、該吸着ノズル9が第三駆動手段8bにより装着ヘッド7に対して昇降自在となっている。
【0021】
また、これら第一駆動手段2および第二駆動手段4,第三駆動手段8b,回転手段8aは、例えば、慣用のモータと螺軸等からなる手段が用いられるもので、モータは数値制御可能なサーボモータ等を用いて高精度で作動される。
【0022】
更に、この第一駆動手段2にあっては、図5に示すように、機体1側に設けた固定部材11と、進退体3側に設けた可動部材12とからなる慣用のリニアモータ手段を用いることができる。
【0023】
また、前記した第二駆動手段4は、図6に示すように、進退体3側に設けた固定部材11と、可動体5側に設けた可動部材12とからなる慣用のリニアモータ手段を用いることができる。
【0024】
更にまた、前記した第三駆動手段8bは、図4に示すように、螺軸とモータによる昇降構成はもちろんのこと、図6に示すように、装着ヘッド7側に設けた固定部材11と、吸着ノズル9側に設けた可動部材12とからなる慣用のリニアモータ手段を用いることができる。
【0025】
そして、これら各リニアモータ手段における固定部材11は、図2に示すように、平坦化された平板状の磁性材料からなるもので、この表面に、所定幅の溝13を所定ピッチで縦横マトリックス状の二次元配列で形成することで、これらの溝13に囲まれる突起部として多数の歯14が形成される。
【0026】
また、これら溝13内には、例えば、合成樹脂等の非磁性材が充填され、固定部材11の表面全域が平坦な平滑面として加工される。
【0027】
一方、前記した可動部材12は、例えば、複数対の電磁石15を内蔵し、各電磁石15の磁極16を固定部材11の歯14に対峙させてある。
【0028】
これら各磁極16は、固定部材11の歯14に対応したピッチの歯17を有していて、各電磁石15は、その歯17が固定部材11の歯14に対して所定のずれを持つように配置される。
【0029】
そして、対をなす電磁石15は、例えば、sin電流とcos電流とにより所定の位相差をもって通電制御されて励磁され、歯14,17を介して固定部材11との間に磁気ループを形成しながら、固定部材11の表面において上下方向および左右方向への推力を発生させる。
【0030】
この推力によって可動部材12が、すなわち、装着ヘッド7が固定部材11の表面上で前記した各方向へそれぞれ移動駆動される。
【0031】
なお、可動部材12の移動量は、電磁石15の通電電流をパルス的に与え、そのパルス数を制御手段18等を介してカウントすることで所定に制御することができる。
【0032】
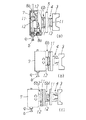
更に、前記した装着ヘッド7,7,7…は、図2および図3に示すように、可動体5の垂直平面上を上下方向若しくは上下・左右方向へ第五駆動手段6bにより進退自在に取り付けられている。
【0033】
この第五駆動手段6bは、可動体5側に設けた固定部材11と、装着ヘッド7側に設けた可動部材12とからなるリニアモータ手段が用いられる。
【0034】
このリニアモータ手段は、その一つの手段として、前記した第一,第二および第三駆動手段2,4,8bに採用した構成と同様のものが用いられる。
【0035】
なお、この第五駆動手段6bを用いた装着ヘッド7の移動にあって、図6(a)および図17に示すように、左右方向のみの移動の場合や、図6(b)に示すように、上下方向のみの移動の場合があるもので、リニアモータ手段以外にも、他の手段として、図示してないが慣用の螺軸とモータとからなる手段が用いられる。
【0036】
更に、図6(c)に示すように、この第五駆動手段6bの構成を、左右方向のみの移動の第五駆動手段6b1と、上下方向のみの移動の第五駆動手段6b2とを適宜組み合わせて構成することもできる。
【0037】
また、該吸着ノズル9に吸着保持された電子部品bは、その吸着状態を検出手段20より認識される。
【0038】
この検出手段20は、取付体24を介して可動体5若しくは進退体3に取り付けられていて、装着ヘッド7に保持された電子部品bの保持状態を検出するものであり、CCD等のカメラセンサーやレーザ発信器等の慣用な手段が用いられるものであるが、本実施例にあっては、図7〜図10等において示されるように、視覚センサ21と、光像入射手段22と、光源23とにより構成される。
【0039】
このうち、視覚センサ21は、略水平の取付体24の一側に取り付けられ、装着ヘッド7に保持された電子部品bに対して側方に配設されるもので、慣用のCCDカメラを用いるものであって、電子部分bの画像を認識して取り込み、この検出信号を後記する制御手段18へ送信する。
【0040】
なお、前記した画像認識にあっては、吸着保持された電子部品bの全体のサイズや全体の前後左右方向の位置,リードピッチ,リード曲がり,リード本数等の各チェックを行なうもので、位置補正の結果、後記する制御手段18により電子部品bが定められた正しい位置に合致するようにする。
【0041】
前記光像入射手段22は、視覚センサ21に対応して取付体24の他側において装着ヘッド7の電子部品bの真下において、該取付体24の移動軌跡上に取り付けられているもので、その光射面が45°をなすプリズムやミラーを用いるものであって、該光射面は、視覚センサ21と装着ヘッド7の電子部品b面へそれぞれ対応している。
【0042】
前記した光源23は、光像入射手段22を介して装着ヘッド7の電子部品bおよび視覚センサ21へ照明光を送り、視覚センサ21による計測の安定化を図るもので、該視覚センサ21と同一光軸を有する同軸落射式等を用いてこの視覚センサ21の前側に配設される。
【0043】
なお、この検出手段20において、該光源23の発光位置と発光時間とを規制する位置検出部材25が設けられているものであって、光電管や近接スイッチ等が用いられるもので、可動体5あるいは進退体3へ、各装着ヘッド7に対応させて、光源23の射光開始と射光停止との検出子26,27を取り付け、これら検出子26,27に対応する検出体28を取付体24に設けてある。
【0044】
そして、この検出手段20は、機体1の適所に固定的に設けてもよいが、装着ヘッド7と共に連動移動するように構成すれば、吸着保持された電子部品bの移動の間に該電子部品bの吸着状態が検出される。
【0045】
その検出手段20の取付構成は、例えば、図3および図4に示すように、該検出手段20を支持させた取付体24を、可動体5に対して、数値制御可能なサーボモータ等により移動制御される第四駆動手段6aによって、該装着ヘッド7の下方を左右方向へ進退運動するように取り付けられる。
【0046】
なお、この検出手段20の取り付けにあっては、図7に示すように、進退体3へ取付部材31を介して設けてもよく、この場合、第二駆動手段4により可動体5が、すなわち、装着ヘッド7が横移動することで検出手段20により電子部品bの吸着保持状態が検出できる。
【0047】
更に、図8に示すように、検出手段20を、進退体3へ第四駆動手段6aを介して取付部材31および取付体24により設けてもよいもので、検出手段20の移動は第四駆動手段6aにより行われるものであり、その検出工程は、検出手段20の往路または復路を一検出工程としたり、検出手段20が往復することで一検出工程とするものである。
【0048】
また、この検出手段20は、図9および図10に示すように、可動体5の垂直面へ、あるいは、図11に示すように、進退体3の所定面へ第四駆動手段6aにより左右方向へ進退自在に取り付けることもできる。
【0049】
そして、この第四駆動手段6aは、前記した第一,第二,第三および第五駆動手段2,4,8bおよび6bと同様のリニアモータ手段の構成からなるものが用いられるもので、可動体5側に設けた固定部材11と、検出手段20側に設けた可動部材12とよりなり、該リニアモータ手段の詳細な構成は、前記した第一,第二,第三および第五駆動手段2,4,8bおよび6bの説明を援用する。
【0050】
更に、使用する検出手段20は、図9および図10に示すように、電子部品bの下面を、直接、光源23を備えたCCD等の視覚センサ21に対応させる構成とする。
【0051】
前記した制御手段18は、検出手段20に連係させてこの検出信号を受けて、あらかじめ定められたデータに基づいて演算し、前記各手段2,4,6a,6b,あるいは8a,8b,吸着ノズル9の吸着手段(図示せず)を個別に任意に制御するもので、慣用のコンピュータが用いられる。
【0052】
この検出手段20からの画像情報等の信号は、コンピュータからなる制御手段18に送られ所定の演算等がなされて、プリント基板cへの電子部品bの装着に際して、該電子部品bが定められた正しい位置に装着されるように制御手段18が前記した各手段2,4,6a,6b,8aおよび8bを制御する。
【0053】
したがって、本発明に係る電子部品装着装置Aおよび方法の一実施例の作用は以下の通りである。
【0054】
基板c上には、電子部品bがそれぞれ所定適所に装着されるもので、この作業にあっては、これら設定値や動作順序等のデータがあらかじめ、制御手段18に記憶されている。
【0055】
そして、その電子部品bの装着は、制御手段18による各制御によって、第一駆動手段2,第二駆動手段4,第四駆動手段6a,第五駆動手段6b,回転手段8aおよび第三駆動手段8bを操作して、電子部品bの供給部mへ装着ヘッド7を移動させて該電子部品bを受け取る。
【0056】
このとき、装着ヘッド7のリニアモータ手段からなる第五駆動手段6bは、図12(a)および図13(a)に示す状態から、図12(b)および図13(b)に示すように、前記したプログラムに沿って個々の装着ヘッド7が独立して移動されるように作動するもので、可動体5の垂直面に設けられた固定部材11面を個々の装着ヘッド7に設けられた可動部材12が上下方向および左右方向へ移動する。
【0057】
なお、図12に示す検出手段20のタイプは、可動体5(進退体3でも可)に設けた螺軸とモータとからなる第四駆動手段6aにより検出手段20の左右方向への往復動作を行なうものであり、図13に示す検出手段20のタイプは、可動体5に設けたリニアモータ手段からなる第四駆動手段6aにより検出手段20の左右方向への往復動作を行なうものである。
【0058】
すると、この個々の装着ヘッド7は、供給部mにおいて吸着準備がされた電子部品bの待機位置(所定ピッチ)に合わせる調整が行なわれて、該電子部品bの同時吸着あるいは連続した吸着が行なわれるものである。
【0059】
この調整動作は、可動体5に取り付けられた装着ヘッド7が供給部mへ移動する間に全て完了する。
【0060】
電子部品bを吸着保持した各装着ヘッド7は、再び、リニアモータ手段からなる第五駆動手段6bの作動により、図12(c)および図13(c)に示すように、上下方向および左右方向へ移動して各装着ヘッド7の間隔(ピッチ)が最小に縮まった調整がなされる。
【0061】
この状態で、可動体5に付設した検出手段20が、各装着ヘッド7における最外側の位置から、図12(c)および図13(c)に示すように、各装着ヘッド7に吸着保持された電子部品bを撮像し、その吸着保持状態を検出するもので、間隔が縮まった各装着ヘッド7の保持する電子部品bの検出は、検出手段20の移動量が短縮されるため、短時間で行なわれる。
【0062】
検出された電子部品bの画像情報は、制御手段18に送信されて所定の画像処理がなされて、あらかじめ定められたデータと比較演算して、その値が該データと異なるときは、制御手段18において正規の値となるような補正がなされるもので、第一駆動手段2や第二駆動手段4,回転手段8aに対して所定の移動信号が与えられるものである。
【0063】
特に、本実施例においては、リニアモータ手段からなる第五駆動手段6bに、プリント基板cへの装着情報に基づいたデータ(座標値)や、前記した補正された値が送信され、図12(d)および図13(d)に示すように、電子部品bの装着位置に合わせる調整が行なわれて、装着部nにおいて、該電子部品bの同時装着あるいは連続した装着が行なわれるものである。
【0064】
この検出手段20によって得られた情報に基づいた前記した補正は、装着ヘッド7の装着部nにおけるプリント基板cへの移動の間に全て完了する。
【0065】
これにより、電子部品bの供給部mにおける該電子部品bの吸着保持と、装着部nにおける該電子部品bの装着とに要する時間が、従来装置と比べて大幅に短縮され、これに相応してそのタクトタイムの大きな短縮化が図れる。
【0066】
特に、第一駆動手段2と第二駆動手段4とによる装着ヘッド7の移動に際して、各装着ヘッド7の第五駆動手段6bにより、該各装着ヘッド7の各電子部品bは個々に単独に移動して、そのX軸方向(左右方向)に対する座標値の補正は既に行なわれているため、Y軸方向(前後方向)のみに対して座標値の補正を行なえばよいので、一層、電子部品bのタクトタイムの短縮が望める。
【0067】
なお、装着ヘッド7は、図14に示すように、進退体3または可動体5に対して両側に配設することもあるもので、各装着ヘッド7は可動体5へ第五駆動手段6bにより左右方向若しくは左右・上下方向へ進退自在となるように取り付けられている。
【0068】
また、これに伴って、検出手段20も、第四駆動手段6aにより可動体5において左右方向へ移動自在となるように配されるものであり、この取り付けは、例えば、図11に示すように、進退体3に対して行なってもよい。
【0069】
なお、複数個の装着ヘッド7を、可動体5に対してその取付ピッチが可変制御される前記した実施例にあって、第五駆動手段6bはリニアモータ手段以外の構成も採用し得るもので、例えば、図15(a)に示すように、可動体5の左右ガイド40へ進退自在に係合させた複数個の装着ヘッド7は、それぞれ個々に連係させた螺軸41とモータ42とからなるものや、図15(b)に示すように、それぞれ個々に連係させたベルト43とモータ44とからなるもの等の第五駆動手段6bを用いることができる。
【0070】
図16は、本実施例にあって進退体3を複数に、例えば、2個に設けた例を示すもので、2個の進退体3へそれぞれ可動体5,5が個々の第二駆動手段4,4により左右方向に移動される。
【0071】
また、可動体5へ第五駆動手段6bにより移動自在に取り付けられた装着ヘッド7は、図16(a)に示す場合は、進退体3に対してそれぞれ相対的に外側へ向いており、図16(b)に示す場合は、進退体3に対してそれぞれ相対的に内側へ向いている。
【0072】
装着ヘッド7の内側へ向いた構成のものは、図16(c)に示すように、該装着ヘッド7を全て一直線状に並設することができて、図1に示すような、機体1の両側に電子部品bの供給部mが配された場合、この進退体3,3に取り付けられた可動体5,5の装着ヘッド7,7は、そのそれぞれの装着ヘッド7,7が一側の供給部mと他側の供給部mとを自由に行き来することができて、吸着ノズル9による電子部品bの吸着が効率よく行なえる。
【0073】
【発明の効果】
前述したように本発明の電子部品装着装置は、複数個の装着ヘッドを個別に可変することができ、これにより、複数個の装着ヘッドにおける電子部品の同時吸着と同時装着の両工程若しくはどちらか一方の工程を行なうことができるため、従来装置と比べて、電子部品の装着に際して、その全体に要するそれぞれの時間を短縮することができ、電子部品装着処理の大幅な効率向上が図れる。
【0074】
第一,第二,第三,第四および第五駆動手段の各駆動手段のうち、少なくとも1つ以上の駆動手段にリニアモータ手段を用いることによって、その駆動手段の構成が簡略化され、装置全体の製作コストを削減することができる。等の格別な効果を奏するものである。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 本発明に関する電子部品装着方法を採用した電子部品装着装置の一実施例の概略を示す平面図である。
【図2】 図1における装着ヘッドの第五駆動手段の概要部を示す拡大側面図である。
【図3】 図1における装置の装着ヘッドの要部を示す斜視図である。
【図4】 図3における装置の側面図である。
【図5】 図1における装置の第一駆動手段の他の例を示す説明図である。
【図6】 図1における装置の第二駆動手段の他の例を示す説明図である。
【図7】 図1における装置の検出手段の他の取り付け例を示す側面図である。
【図8】 図1における装置の検出手段の取り付け変形例を示す側面図である。
【図9】 図1における装置の検出手段の他の取り付け例を示す斜視図である。
【図10】 図9における装置の側面図である。
【図11】 図1における装置の検出手段の他の取り付け例を示す側面図である。
【図12】 図1における装置の電子部品の装着動作を示す説明図である。
【図13】 図1における装置の他の例の検出手段による電子部品の装着動作を示す説明図である。
【図14】 図1における装置の装着ヘッドの他の配設例を示す側面図である。
【図15】 図1における装置の第五駆動手段の他の例をそれぞれ示す説明図である。
【図16】 図1における装置の装着ヘッドの更に他の配設例を示す説明図である。
【図17】 図6(a)における装置の第五駆動手段を示す斜視図である。
【図18】 従来の電子部品装着装置を示すもので、(a)はその概略の平面図を、(b)は要部の斜視図をそれぞれ示す。
【符号の説明】
A 電子部品装着装置
b 電子部品
1 機体
2 第一駆動手段
3 進退体
4 第二駆動手段
5 可動体
6a 第四駆動手段
6b 第五駆動手段
7 装着ヘッド
8a 回転手段
8b 第三駆動手段
9 電子部品吸着部材(吸着ノズル)
11 固定部材
12 可動部材
18 制御手段
20 検出手段
21 視覚センサ
22 光像入射手段
23 光源[0001]
[Industrial application fields]
The present invention relates to an electronic component mounting apparatus and method used in the industry for assembling and mounting electronic components.
[0002]
[Prior art]
As shown in FIG. 18A, the
[0003]
In the conventional electronic
[0004]
The
[0005]
However, the
[0006]
Therefore, the entire
[0007]
This also occurs in the mounting of the
[0008]
Therefore, the entire
[0009]
Even if the
[0010]
Further, the
[0011]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
The present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems, and a plurality of mounting heads are individually variably controlled, and each of them is arbitrarily spread and sucks an electronic component, and the sucked electronic component is retained. The state is detected by the detection means located below the electronic component, and is mounted at a predetermined position on the printed circuit board determined in advance. Each member is controlled so that the amount of movement is minimized, the mounting operation time can be shortened as much as possible, the tact time can be shortened, and the configuration of the mounting head and the detection means can be simplified. An object of the present invention is to provide an electronic component mounting apparatus and method.
[0012]
Means of the present invention for achieving the above-mentioned object includes an advancing / retracting body that is provided in an airframe and moves in the front-rear direction, a movable body that is provided on one side of the advancing / retreating body and moves in the left-right direction, and the movable body of the upper vertical plane to move individually to the left and right direction or the left-right direction and the vertical direction, and a plurality of mounting heads which move the mounting portion and the supply portion of the electronic component together with the movable member, provided in said mounting head An electronic component suction member that moves in the vertical direction and rotates about the vertical axis direction, a detection means that detects the electronic component sucked by the electronic component suction member, and a detection signal from the detection means, is determined in advance. The electronic component mounting apparatus includes control means for calculating based on the obtained data.
[0013]
And the said detection means exists in the structure of the electronic component mounting apparatus which moves below the said mounting head .
[0016]
1 to 4, A is an electronic component mounting apparatus that receives an electronic component b such as a chip component or an IC component from its supply unit m, transfers it to the mounting unit n, and mounts it on a predetermined location on the printed circuit board c. It is.
[0017]
In the electronic component mounting apparatus A described above, the supply part m of the electronic component b which is sequentially transported by a parts feeder or the like to the one side or both sides in the body 1 and waits is also provided in the body 1 as a transfer member (see FIG. (Not shown) is provided with a mounting portion n for the electronic component b into which the printed circuit board c is carried in and out.
[0018]
As shown in FIGS. 1, 2, and 4, the structure includes an advancing / retracting
[0019]
In this
[0020]
A
[0021]
The first driving means 2, the second driving means 4, the third driving means 8b, and the
[0022]
Further, in the first drive means 2, as shown in FIG. 5, conventional linear motor means comprising a fixed member 11 provided on the machine body 1 side and a
[0023]
Further, as shown in FIG. 6, the second driving means 4 uses a conventional linear motor means comprising a fixed member 11 provided on the advancing / retracting
[0024]
Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 4, the third driving means 8b described above has a fixing member 11 provided on the mounting
[0025]
As shown in FIG. 2, the fixing member 11 in each of the linear motor means is made of a flattened flat magnetic material, and grooves 13 having a predetermined width are formed on the surface in a vertical and horizontal matrix form at a predetermined pitch. By forming the two-dimensional array, a large number of
[0026]
Further, these grooves 13 are filled with, for example, a nonmagnetic material such as synthetic resin, and the entire surface of the fixing member 11 is processed as a flat smooth surface.
[0027]
On the other hand, the
[0028]
Each of these
[0029]
The paired
[0030]
With this thrust, the
[0031]
Note that the amount of movement of the
[0032]
Further, as shown in FIGS. 2 and 3, the mounting
[0033]
As the fifth drive means 6b, linear motor means comprising a fixed member 11 provided on the
[0034]
As this linear motor means, the same structure as that employed in the first, second and third driving means 2, 4 and 8b is used.
[0035]
In the movement of the mounting
[0036]
Further, as shown in FIG. 6 (c), the configuration of the fifth driving means 6b is appropriately combined with the fifth driving means 6b1 that moves only in the horizontal direction and the fifth driving means 6b2 that moves only in the vertical direction. It can also be configured.
[0037]
In addition, the electronic component b sucked and held by the
[0038]
The detection means 20 is attached to the
[0039]
Among these, the
[0040]
In the image recognition described above, the overall size of the electronic component b held by suction, the overall position in the front-rear and left-right directions, the lead pitch, the lead bend, the number of leads, etc. are checked. As a result, the electronic device b is matched with the determined correct position by the control means 18 described later.
[0041]
The light image incident means 22 is mounted on the movement locus of the mounting
[0042]
The
[0043]
The detection means 20 is provided with a
[0044]
The detection means 20 may be fixedly provided at an appropriate position of the machine body 1, but if it is configured to move together with the mounting
[0045]
For example, as shown in FIGS. 3 and 4, the attachment structure of the detection means 20 is moved with respect to the
[0046]
As shown in FIG. 7, the detection means 20 may be attached to the advance /
[0047]
Further, as shown in FIG. 8, the detection means 20 may be provided to the advance /
[0048]
Further, the detection means 20 is moved in the left-right direction by the fourth drive means 6a to the vertical surface of the
[0049]
The fourth driving means 6a is composed of a linear motor means similar to the first, second, third and fifth driving means 2, 4, 8b and 6b described above, and is movable. It comprises a fixed member 11 provided on the
[0050]
Further, as shown in FIGS. 9 and 10, the detection means 20 to be used is configured such that the lower surface of the electronic component b directly corresponds to the
[0051]
The control means 18 is linked to the detection means 20, receives this detection signal, calculates based on predetermined data, and each of the
[0052]
A signal such as image information from the detection means 20 is sent to the control means 18 formed of a computer and subjected to predetermined calculations and the like, and the electronic component b is determined when the electronic component b is mounted on the printed circuit board c. The control means 18 controls each of the above-mentioned
[0053]
Therefore, the operation of one embodiment of the electronic component mounting apparatus A and method according to the present invention is as follows.
[0054]
On the board c, electronic components b are respectively mounted at predetermined positions. In this work, data such as setting values and operation order are stored in the control means 18 in advance.
[0055]
The electronic component b is mounted by first control means 2, second drive means 4, fourth drive means 6 a, fifth drive means 6 b, rotation means 8 a and third drive means by each control by the control means 18. By operating 8b, the mounting
[0056]
At this time, the fifth drive means 6b comprising the linear motor means of the mounting
[0057]
The type of the detection means 20 shown in FIG. 12 is such that the detection means 20 is reciprocated in the left-right direction by a fourth drive means 6a comprising a screw shaft and a motor provided on the movable body 5 (or the advance / retreat body 3). The type of the detection means 20 shown in FIG. 13 is one in which the detection means 20 is reciprocated in the left-right direction by a fourth drive means 6 a comprising linear motor means provided on the
[0058]
Then, the individual mounting heads 7 are adjusted in accordance with the standby position (predetermined pitch) of the electronic component b prepared for suction in the supply unit m, and the electronic component b is simultaneously sucked or continuously sucked. It is what
[0059]
This adjustment operation is all completed while the mounting
[0060]
As shown in FIGS. 12 (c) and 13 (c), the mounting
[0061]
In this state, the detection means 20 attached to the
[0062]
The detected image information of the electronic component b is transmitted to the control means 18, subjected to predetermined image processing, compared with predetermined data, and when the value is different from the data, the control means 18. Is corrected so as to be a normal value, and a predetermined movement signal is given to the first driving means 2, the second driving means 4, and the
[0063]
In particular, in the present embodiment, data (coordinate values) based on the mounting information on the printed circuit board c and the corrected values are transmitted to the fifth driving means 6b comprising linear motor means, as shown in FIG. As shown in d) and FIG. 13 (d), an adjustment is made to match the mounting position of the electronic component b, and the electronic component b is mounted simultaneously or continuously in the mounting portion n.
[0064]
The above correction based on the information obtained by the detection means 20 is all completed during the movement of the mounting
[0065]
As a result, the time required for sucking and holding the electronic component b in the supply part m of the electronic component b and the mounting of the electronic component b in the mounting part n is significantly shortened compared to the conventional apparatus. The tact time can be greatly shortened.
[0066]
In particular, when the mounting
[0067]
As shown in FIG. 14, the mounting
[0068]
Accordingly, the detection means 20 is also arranged so as to be movable in the left-right direction on the
[0069]
In the above-described embodiment in which the mounting pitch of the plurality of mounting
[0070]
FIG. 16 shows an example in which a plurality of, for example, two advance /
[0071]
In addition, in the case shown in FIG. 16A, the mounting
[0072]
As shown in FIG. 16 (c), the configuration of the mounting
[0073]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, the electronic component mounting apparatus according to the present invention can individually change a plurality of mounting heads, whereby both or both of the steps of simultaneous adsorption and simultaneous mounting of electronic components by the plurality of mounting heads are performed. Since one process can be performed, the time required for the entire electronic component can be reduced when mounting the electronic component compared to the conventional apparatus, and the efficiency of the electronic component mounting process can be greatly improved.
[0074]
By using linear motor means for at least one of the drive means of the first, second, third, fourth and fifth drive means, the structure of the drive means is simplified, and the device The overall production cost can be reduced. It has a special effect such as.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a plan view showing an outline of an embodiment of an electronic component mounting apparatus employing an electronic component mounting method according to the present invention.
FIG. 2 is an enlarged side view showing a schematic part of fifth drive means of the mounting head in FIG. 1;
3 is a perspective view showing a main part of a mounting head of the apparatus in FIG. 1. FIG.
4 is a side view of the device in FIG. 3. FIG.
FIG. 5 is an explanatory diagram showing another example of the first driving means of the apparatus in FIG. 1;
6 is an explanatory view showing another example of the second driving means of the apparatus in FIG. 1. FIG.
7 is a side view showing another example of attachment of the detection means of the apparatus in FIG. 1. FIG.
8 is a side view showing a modified example of attachment of the detection means of the apparatus in FIG. 1. FIG.
9 is a perspective view showing another example of attachment of the detection means of the apparatus in FIG. 1. FIG.
10 is a side view of the device in FIG. 9. FIG.
11 is a side view showing another example of attachment of the detection means of the apparatus in FIG. 1. FIG.
12 is an explanatory view showing an operation of mounting an electronic component of the apparatus in FIG. 1. FIG.
13 is an explanatory diagram showing an electronic component mounting operation by a detection unit of another example of the apparatus in FIG. 1. FIG.
14 is a side view showing another example of arrangement of the mounting head of the apparatus in FIG. 1. FIG.
FIG. 15 is an explanatory view showing another example of the fifth drive means of the apparatus in FIG. 1;
16 is an explanatory view showing still another arrangement example of the mounting head of the apparatus in FIG. 1. FIG.
FIG. 17 is a perspective view showing fifth drive means of the apparatus in FIG.
18A and 18B show a conventional electronic component mounting apparatus, in which FIG. 18A is a schematic plan view and FIG. 18B is a perspective view of a main part.
[Explanation of symbols]
A Electronic component mounting apparatus b Electronic component 1
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 11
Claims (2)
前記進退体の一側に設けられて左右方向へ移動する可動体と、
前記可動体の垂直面上を個々に左右方向若しくは左右方向・上下方向へ移動し、かつ電子部品の供給部と装着部とを前記可動体とともに移動する複数個の装着ヘッドと、
前記装着ヘッドに設けられて上下方向へ移動し、かつ縦軸方向を中心に回転する電子部品吸着部材と、
前記電子部品吸着部材に吸着された電子部品を検出する検出手段と、
前記検出手段の検出信号を受け、あらかじめ定められたデータに基づいて演算する制御手段とを備えたことを特徴とする電子部品装着装置。Advancing and retreating body that is provided in the aircraft and moves in the front-rear direction,
A movable body provided on one side of the advancing and retracting body and moving in the left-right direction;
A plurality of mounting heads that individually move in the left-right direction or the left-right direction / up-down direction on the vertical surface of the movable body, and that move the electronic component supply unit and the mounting unit together with the movable body;
An electronic component suction member that is provided in the mounting head and moves in the vertical direction and rotates around the vertical axis direction;
Detection means for detecting an electronic component adsorbed on the electronic component adsorption member;
An electronic component mounting apparatus comprising: control means for receiving a detection signal from the detection means and calculating based on predetermined data.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP27697698A JP3981478B2 (en) | 1998-09-30 | 1998-09-30 | Electronic component mounting device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP27697698A JP3981478B2 (en) | 1998-09-30 | 1998-09-30 | Electronic component mounting device |
Related Child Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004338402A Division JP3981685B2 (en) | 2004-11-24 | 2004-11-24 | Electronic component mounting device |
| JP2005070821A Division JP3981689B2 (en) | 2005-03-14 | 2005-03-14 | Electronic component mounting device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2000114787A JP2000114787A (en) | 2000-04-21 |
| JP2000114787A5 JP2000114787A5 (en) | 2005-07-14 |
| JP3981478B2 true JP3981478B2 (en) | 2007-09-26 |
Family
ID=17577044
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP27697698A Expired - Fee Related JP3981478B2 (en) | 1998-09-30 | 1998-09-30 | Electronic component mounting device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3981478B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4516663B2 (en) * | 2000-04-26 | 2010-08-04 | Juki株式会社 | Linear motion device, XY movement device, and electronic component mounting device |
| WO2002026011A2 (en) * | 2000-09-19 | 2002-03-28 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Component suction device, component mounting apparatus and component mounting method |
| JP4514321B2 (en) * | 2000-12-08 | 2010-07-28 | パナソニック株式会社 | Component mounting equipment |
| JP4610125B2 (en) * | 2001-06-14 | 2011-01-12 | Juki株式会社 | Electronic component mounting device |
| JP2003025267A (en) * | 2001-07-23 | 2003-01-29 | Yamaha Motor Co Ltd | Part storage device |
| CN101267728B (en) * | 2002-11-21 | 2011-09-21 | 富士机械制造株式会社 | Element mounting device |
| DE102005027901A1 (en) * | 2005-06-16 | 2006-12-28 | Siemens Ag | Placement head for a placement machine for equipping substrates with electrical components |
| JP4728181B2 (en) * | 2006-06-30 | 2011-07-20 | パナソニック株式会社 | Component mounting equipment |
| JP4809799B2 (en) * | 2007-03-30 | 2011-11-09 | ヤマハ発動機株式会社 | Mounting machine, mounting method thereof, and moving method of board imaging means in mounting machine |
| JP5075106B2 (en) * | 2008-12-25 | 2012-11-14 | ヤマハ発動機株式会社 | IC handler |
| JP5654745B2 (en) * | 2009-11-30 | 2015-01-14 | 京セラクリスタルデバイス株式会社 | Piezoelectric vibration element mounting device |
| CN102151875B (en) * | 2011-03-15 | 2013-04-24 | 长沙一派数控机床有限公司 | Linear servo integrated PCB (Printed Circuit Board) drilling device |
| JP5357201B2 (en) * | 2011-03-16 | 2013-12-04 | リンテック株式会社 | Labeling device |
| JP5999946B2 (en) * | 2012-03-23 | 2016-09-28 | 富士機械製造株式会社 | Electronic component mounting equipment |
| JP6230604B2 (en) * | 2013-07-23 | 2017-11-15 | 富士機械製造株式会社 | Working machine |
| CN110383431B (en) * | 2017-02-17 | 2023-08-22 | 株式会社国际电气 | Substrate processing apparatus, method for manufacturing semiconductor device, and storage medium |
| CN107605895A (en) * | 2017-08-14 | 2018-01-19 | 罗博特科智能科技股份有限公司 | A kind of Tie Tou mechanisms for being used to mount |
| JP7318941B2 (en) * | 2020-10-27 | 2023-08-01 | 株式会社フジキカイ | labeling machine |
-
1998
- 1998-09-30 JP JP27697698A patent/JP3981478B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2000114787A (en) | 2000-04-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3981478B2 (en) | Electronic component mounting device | |
| JP2000114787A5 (en) | ||
| JPH07193396A (en) | Part mounting device | |
| JP2002368494A (en) | Electric component mounting system and positional error detecting method in the same system | |
| JP2863731B2 (en) | Electronic component mounting apparatus and method | |
| JP7466500B2 (en) | Method for automatically placing electronic components on a component carrier - Patents.com | |
| JP3955206B2 (en) | Component mounting method and component mounting apparatus | |
| JP3981689B2 (en) | Electronic component mounting device | |
| JP4050396B2 (en) | Electronic component mounting apparatus and mounting head mounting method for electronic component mounting apparatus | |
| JP4227833B2 (en) | Component mounting equipment | |
| JP3790020B2 (en) | Surface mount machine | |
| JP3981685B2 (en) | Electronic component mounting device | |
| JP3109963B2 (en) | Surface mounting machine | |
| JP7312812B2 (en) | Parts mounting machine | |
| JP4077553B2 (en) | Electronic component mounting method and electronic component mounting apparatus | |
| JP4296029B2 (en) | Electronic component mounting equipment | |
| JPH0661693A (en) | Component mounting machine | |
| JP2008166547A (en) | Surface mounting equipment, and control method of surface mounting equipment | |
| JP4077826B2 (en) | Electronic component mounting method and electronic component mounting apparatus | |
| JP4011810B2 (en) | Surface mount component mounting machine | |
| JP3523637B2 (en) | Electronic component mounting device | |
| JP2000312100A (en) | Component recognition unit of surface-mounting machine | |
| JP4353602B2 (en) | Component mounting equipment | |
| JP2002185198A (en) | Method for detecting displacement of electrical component caused by absorption nozzle and method for mounting electrical component | |
| JP4298080B2 (en) | Component recognition method and apparatus for surface mounter |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20040329 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20041124 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20041124 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20061212 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070202 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20070306 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070418 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A132 Effective date: 20070522 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20070626 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20070702 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100706 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110706 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110706 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120706 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120706 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130706 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |