JP2010040771A - Method of manufacturing semiconductor device - Google Patents
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010040771A JP2010040771A JP2008202138A JP2008202138A JP2010040771A JP 2010040771 A JP2010040771 A JP 2010040771A JP 2008202138 A JP2008202138 A JP 2008202138A JP 2008202138 A JP2008202138 A JP 2008202138A JP 2010040771 A JP2010040771 A JP 2010040771A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- film
- metal film
- groove
- wiring
- forming
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/0001—Technical content checked by a classifier
- H01L2924/0002—Not covered by any one of groups H01L24/00, H01L24/00 and H01L2224/00
Landscapes
- Internal Circuitry In Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、Cu(銅)を主成分とする金属材料からなるCu配線を有する半導体装置の製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device having a Cu wiring made of a metal material mainly composed of Cu (copper).
高集積化された半導体装置において、配線の材料として、Al(アルミニウム)よりも導電性の高いCuを採用したものがある。Cuからなる配線は、Cuがドライエッチングによる微細なパターニングが困難であることから、ダマシン法により、半導体基板上の絶縁膜(層間絶縁膜)に形成された微細な溝に埋設される。
絶縁膜の材料としては、通常、SiO2が採用される。ところが、Cuは、SiO2への拡散性が高い。そのため、SiO2からなる絶縁膜に形成された溝の内面とCuからなる配線とが直に接すると、Cuが絶縁膜中に拡散し、これにより絶縁膜の絶縁耐圧が低下する。したがって、絶縁膜とCuからなる配線との間には、Cuの絶縁膜への拡散を防止するためのバリア膜が必要となる。
Some highly integrated semiconductor devices employ Cu, which has higher conductivity than Al (aluminum), as a wiring material. A wiring made of Cu is buried in a fine groove formed in an insulating film (interlayer insulating film) on a semiconductor substrate by a damascene method because fine patterning of Cu by dry etching is difficult.
As a material for the insulating film, SiO 2 is usually employed. However, Cu has high diffusibility to SiO 2 . Therefore, when the inner surface of the groove formed in the insulating film made of SiO 2 and the wiring made of Cu are in direct contact with each other, Cu diffuses into the insulating film, thereby reducing the withstand voltage of the insulating film. Therefore, a barrier film for preventing diffusion of Cu into the insulating film is necessary between the insulating film and the wiring made of Cu.
バリア膜を形成する手法として、CuとMn(マンガン)との合金(CuMn合金)を用いた自己形成プロセスが知られている(たとえば、特許文献1参照)。この自己形成プロセスでは、配線の形成に先立ち、スパッタ法により、溝の内面を含む絶縁膜の表面上に、CuMn合金からなる合金膜が形成される。次いで、めっき法により、合金膜上に、Cuからなるめっき層が形成される。その後、熱処理が行われることにより、合金膜中のMnが絶縁膜中のSi(シリコン)およびO(酸素)と結合し、溝の内面上にMnxSiyOz(x,y,z:零よりも大きい数。以下、単に「MnSiO」と記載する。)からなるバリア膜が形成される。
バリア膜の形成に寄与しない余分なMnは、Cuからなるめっき層中に拡散する。Mnのめっき層中への拡散量が多いと、そのめっき層を平坦化して形成されるCu配線中にMnが残留し、配線の抵抗が増大する。そのため、CuMn合金からなる合金膜は、バリア膜の形成に必要十分な厚さに形成されることが好ましい。
しかし、スパッタ法では、溝の底面と比べてその側面にCuMn合金が付着しにくいため、溝の底面上における合金膜の厚さがバリア膜の形成に必要十分な厚さとなるように、合金膜が全体的に薄く形成されると、合金膜における溝の側面上に形成される部分が薄くなりすぎる。その結果、合金膜と溝の側面との密着性が低下し、溝の側面上で合金膜の膜剥がれが生じるおそれがある。膜剥がれが生じると、その部分に、MnSiOからなるバリア膜が良好に形成されない。
Excess Mn that does not contribute to the formation of the barrier film diffuses into the plating layer made of Cu. If the diffusion amount of Mn into the plating layer is large, Mn remains in the Cu wiring formed by planarizing the plating layer, and the resistance of the wiring increases. For this reason, the alloy film made of a CuMn alloy is preferably formed to a thickness necessary and sufficient for forming the barrier film.
However, in the sputtering method, the CuMn alloy is less likely to adhere to the side surface than the bottom surface of the groove, so that the alloy film on the bottom surface of the groove is thick enough to form the barrier film. When the film is formed to be thin as a whole, the portion formed on the side surface of the groove in the alloy film becomes too thin. As a result, the adhesion between the alloy film and the side surface of the groove is lowered, and the alloy film may be peeled off on the side surface of the groove. When film peeling occurs, a barrier film made of MnSiO is not satisfactorily formed at that portion.
そこで、本発明の目的は、バリア膜を良好に形成することができながら、Cu配線中のMnの残留量を低減することができる、半導体装置の製造方法を提供することである。 Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to provide a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device, which can reduce the amount of Mn remaining in a Cu wiring while being able to satisfactorily form a barrier film.
前記の目的を達成するための請求項1記載の発明は、SiおよびOを含む絶縁性材料からなる絶縁層を形成する絶縁層形成工程と、前記絶縁層に溝を形成する溝形成工程と、スパッタ法により、前記溝の内面にMnOx(x:零よりも大きい数)からなる金属膜を被着させる金属膜被着工程と、前記金属膜上にCuを主成分とする金属材料からなるCu配線を形成する配線形成工程とを含む、半導体装置の製造方法である。
The invention according to
この方法によれば、まず、SiおよびOを含む絶縁性材料からなる絶縁層に、溝が形成される。次に、スパッタ法により、溝の内面(溝が凹状に形成される場合、その溝の側面および底面)に、MnOx(x:零よりも大きい数、以下、単に「MnO」と記載する。)からなる金属膜が被着される。このとき、溝の内面、つまり絶縁層における溝に臨む部分には、スパッタリングのエネルギーによって、金属膜中のMnOが入り込む。これにより、絶縁層中のSiおよびOと金属膜中のMnOとが結合して、溝の内面に、MnSiOからなるバリア膜が形成される。その後、金属膜(バリア膜)上に、Cuを主成分とするCu配線が形成される。 According to this method, first, a groove is formed in an insulating layer made of an insulating material containing Si and O. Next, MnO x (x: a number larger than zero, hereinafter simply referred to as “MnO”) is written on the inner surface of the groove (when the groove is formed in a concave shape, the side and bottom surfaces of the groove) by sputtering. ) Is deposited. At this time, MnO in the metal film enters the inner surface of the groove, that is, the portion of the insulating layer facing the groove by the energy of sputtering. As a result, Si and O in the insulating layer and MnO in the metal film are combined to form a barrier film made of MnSiO on the inner surface of the groove. Thereafter, a Cu wiring containing Cu as a main component is formed on the metal film (barrier film).
MnOは、CuMn合金と比較して、SiおよびOを含む絶縁材料に対する密着性が高い。そのため、MnOからなる金属膜は、所望する厚さのバリア膜の形成に必要十分な程度の小さい厚さに形成されても、溝の側面からの膜剥がれを生じにくい。したがって、溝の内面上にバリア膜を良好に形成することができる。また、溝の内面に金属膜を被着させる際に、スパッタリングのエネルギーによってMnSiOからなるバリア膜を形成することができるので、バリア膜を形成するための熱処理を行う必要がない。 MnO has higher adhesion to an insulating material containing Si and O than a CuMn alloy. Therefore, even if the metal film made of MnO is formed to a thickness as small as necessary and sufficient for forming a barrier film having a desired thickness, film peeling from the side surface of the groove hardly occurs. Therefore, a barrier film can be satisfactorily formed on the inner surface of the groove. In addition, when depositing a metal film on the inner surface of the groove, a barrier film made of MnSiO can be formed by sputtering energy, so that it is not necessary to perform a heat treatment for forming the barrier film.
そして、金属膜をそのような小さい厚さ(所望する厚さのバリア膜の形成に必要十分な厚さ)に形成することにより、バリア膜の形成に寄与しない余分なMnの量を低減することができる。これにより、バリア膜上に形成されるCu配線中のMnの残留量を低減することができる。
よって、溝の内面上にバリア膜を良好に形成することができながら、Cu配線中のMnの残留量を低減することができる。
Then, by forming the metal film to such a small thickness (thickness necessary and sufficient for forming a barrier film having a desired thickness), the amount of excess Mn that does not contribute to the formation of the barrier film is reduced. Can do. Thereby, the residual amount of Mn in the Cu wiring formed on the barrier film can be reduced.
Therefore, the residual amount of Mn in the Cu wiring can be reduced while the barrier film can be satisfactorily formed on the inner surface of the groove.
また、請求項2に記載のように、前記絶縁層の下層に、前記Cu配線と電気的に接続される下配線が形成されていてもよい。この場合、前記溝形成工程後であって前記金属膜被着工程の前に、前記溝から前記下配線に向けて延び、前記絶縁層を厚さ方向に貫通するビアホールを形成するビアホール形成工程が行われ、前記金属膜被着工程後に、前記ビアホールにCuを主成分とするビアを形成するビア形成工程が行われることにより、下配線とCu配線との電気的な接続を達成することができる。また、前記金属膜被着工程では、前記溝の内面に加えて、前記ビアホールの側面および前記下配線の表面における前記ビアホールに臨む部分に前記金属膜が被着されることにより、ビアホールの側面に、MnSiOからなるバリア膜を形成することができる。
Moreover, the lower wiring electrically connected with the said Cu wiring may be formed in the lower layer of the said insulating layer like
金属膜の材料であるMnOは、Cuと比較して電気抵抗が高い。そのため、下配線の表面におけるビアホールに臨む部分上にMnOからなる金属膜が存在していると、ビアと下配線との間の電気抵抗が高くなる。
そこで、請求項3に記載のように、前記ビア形成工程に先立ち、水素還元処理により、前記金属膜における前記下配線の表面に接する部分からOを除去する工程を含むことが好ましい。Oが除去されることにより、MnOがMnに還元される。そして、Mnがビアなどに拡散することにより、下配線上から金属膜が消失する。
MnO, which is a material for the metal film, has a higher electrical resistance than Cu. For this reason, if a metal film made of MnO is present on a portion of the surface of the lower wiring facing the via hole, the electrical resistance between the via and the lower wiring is increased.
Therefore, it is preferable to include a step of removing O from a portion of the metal film in contact with the surface of the lower wiring by a hydrogen reduction process prior to the via formation step. By removing O, MnO is reduced to Mn. Then, when Mn diffuses into the vias, the metal film disappears from the lower wiring.
また、その工程に代えて、請求項4に記載のように、前記ビア形成工程に先立ち、逆スパッタ法により、前記金属膜における前記下配線の表面に接する部分を選択的に除去する工程が行われてもよい。逆スパッタ法は、スパッタ法と同一のスパッタリング装置で実施することができる。そのため、金属膜における下配線の表面に接する部分を除去する工程で逆スパッタ法が用いられることにより、同一のスパッタリング装置において、金属膜被着工程に連続して、その金属膜の部分的な除去の工程を行うことができる。さらに、Cu配線がめっき法により形成される場合には、スパッタ法により、金属膜上にシード膜が形成される。この場合、金属膜被着工程およびその金属膜の部分的な除去の工程に加えて、そのシード膜を形成する工程を同一のスパッタリング装置で連続して行うことができる。そのため、半導体製造装置の構成を簡素化することができ、また、それらの工程間での半導体ウエハ(前記絶縁層が形成されたウエハ状態の半導体基板)の搬送が不要であるので、半導体装置の製造に要する時間を短縮することができる。 Further, instead of the step, the step of selectively removing a portion of the metal film in contact with the surface of the lower wiring by reverse sputtering is performed prior to the via forming step. It may be broken. The reverse sputtering method can be performed with the same sputtering apparatus as the sputtering method. Therefore, the reverse sputtering method is used in the process of removing the portion of the metal film that contacts the surface of the lower wiring, and in the same sputtering apparatus, the metal film is partially removed continuously after the metal film deposition process. These steps can be performed. Furthermore, when the Cu wiring is formed by plating, a seed film is formed on the metal film by sputtering. In this case, in addition to the metal film deposition step and the partial removal step of the metal film, the step of forming the seed film can be continuously performed with the same sputtering apparatus. Therefore, the configuration of the semiconductor manufacturing apparatus can be simplified, and since it is not necessary to transport the semiconductor wafer (the semiconductor substrate in the wafer state on which the insulating layer is formed) between these processes, The time required for manufacturing can be shortened.
請求項5に記載のように、前記配線形成工程は、スパッタ法により、前記金属膜上にCuを主成分とする金属材料からなるシード膜を形成する工程と、めっき法により、前記シード膜上にCuからなるめっき層を形成する工程とが含まれていてもよい。
ただし、めっき層は、めっき成長したままの状態では、その結晶構造が均一でなく、比抵抗が高い。そこで、めっき法により第2配線およびビアが形成される場合には、請求項
6に記載のように、前記配線形成工程後、熱処理により、前記めっき層を結晶化させる結晶化工程を含むことが好ましい。これにより、めっき層の結晶構造が均一化(結晶化)されるので、そのめっき層からなるCu配線およびビアの比抵抗を低減することができる。
According to a fifth aspect of the present invention, the wiring forming step includes a step of forming a seed film made of a metal material mainly composed of Cu on the metal film by a sputtering method, and a step of forming a seed film on the seed film by a plating method. And a step of forming a plating layer made of Cu.
However, the plating layer has a non-uniform crystal structure and a high specific resistance in a state where the plating is grown. Therefore, when the second wiring and the via are formed by a plating method, as described in
以下では、本発明の実施の形態を、添付図面を参照して詳細に説明する。
図1は、本発明の一実施形態に係る半導体装置の構造を示す模式的な断面図である。
半導体装置1は、半導体基板(図示せず)上に、Cuを配線材料として用いた多層配線構造を有している。
半導体基板は、たとえば、Si(シリコン)基板からなる。半導体基板の表層部には、MOSFET(Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor)などの機能素子が作り込まれている。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
FIG. 1 is a schematic cross-sectional view showing the structure of a semiconductor device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
The
The semiconductor substrate is made of, for example, a Si (silicon) substrate. A functional element such as a MOSFET (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) is formed in the surface layer portion of the semiconductor substrate.
半導体基板上には、SiO2(酸化シリコン)からなる第1絶縁層2が積層されている。
第1絶縁層2の表層部には、所定の配線パターンに対応した微細な第1溝3が形成されている。第1溝3の内面(側面および底面)には、MnSiOからなる第1バリア膜4が形成されている。そして、第1溝3内には、第1バリア膜4を介して、Cuを主成分とする金属材料からなる第1配線5が埋設されている。
A first insulating
A fine
第1絶縁層2上には、第2絶縁層6が積層されている。第2絶縁層6は、拡散防止膜7、第1層間絶縁膜8、エッチングストッパ膜9および第2層間絶縁膜10を、第1絶縁層2側からこの順に積層した構造を有している。
拡散防止膜7は、たとえば、SiC(炭化シリコン)およびSiCN(炭窒化シリコン)を積層した構造を有している。第1層間絶縁膜8および第2層間絶縁膜10は、たとえば、SiO2からなる。エッチングストッパ膜9は、たとえば、SiCからなる。
A second insulating
The diffusion prevention film 7 has a structure in which, for example, SiC (silicon carbide) and SiCN (silicon carbonitride) are laminated. The first
第2絶縁層6の表層部には、所定の配線パターンに対応した第2溝11が形成されている。また、第2絶縁層6には、第1配線5と第2溝11とが対向する部分に、ビアホール12が貫通して形成されている。
第2溝11およびビアホール12の内面には、MnSiOからなる第2バリア膜13が形成されている。そして、第2溝11およびビアホール12内には、第2バリア膜13を介して、それぞれCuを主成分とする金属材料からなる第2配線14およびビア15が埋設されている。第2配線14およびビア15は、一体をなしている。
A
A
図2A〜2Gは、本発明の第1の実施形態に係る半導体装置の製造工程を順に示す模式的な断面図である。
図2Aに示すように、第1バリア膜4および第1配線5が埋設された第1絶縁層2上に、CVD(Chemical Vapor Deposition:化学的気相成長)法により、拡散防止膜7、第1層間絶縁膜8、エッチングストッパ膜9および第2層間絶縁膜10がこの順に積層される。これにより、第1絶縁層2上に、第2絶縁層6が形成される。
2A to 2G are schematic cross-sectional views sequentially showing manufacturing steps of the semiconductor device according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
As shown in FIG. 2A, on the first insulating
その後、図2Bに示すように、第2絶縁層6に、第2溝11およびビアホール12が形成される。具体的には、まず、第2絶縁層6上に、ビアホール12が形成されるべき部分を選択的に露出させる開口を有するマスク(図示せず)が形成される。そして、そのマスクを介して、第2層間絶縁膜10、エッチングストッパ膜9および第1層間絶縁膜8がドライエッチングされる。このとき、適当なタイミングで反応ガス(エッチャント)を切り換えることにより、第2層間絶縁膜10、エッチングストッパ膜9および第1層間絶縁膜8が連続的にエッチングされる。次に、第2絶縁層6上からマスクが除去された後、第2絶縁層6上に、第2溝11が形成されるべき部分を選択的に露出させる開口を有する新たなマスク(図示せず)が形成される。そして、そのマスクを介して、第2層間絶縁膜10がドライエッチングされる。その後、拡散防止膜7およびエッチングストッパ膜9の露出した部分が除去されることにより、第2溝11およびビアホール12が形成される。
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 2B, the
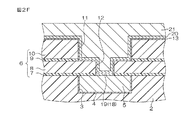
次いで、図2Cに示すように、スパッタ法により、第2溝11およびビアホール12の内面を含む第2絶縁層6の表面全域、ならびに第1配線5の表面におけるビアホール12に臨む部分に、MnOからなる金属膜18が被着される。金属膜18は、第2バリア膜13の形成に必要かつ十分な程度の厚さ(たとえば、1〜10nm)に形成される。このとき、金属膜18における第2絶縁層6に接する部分(第2溝11およびビアホール12の内面を含む第2絶縁層6の表面全域)には、スパッタリングのエネルギーによって、金属膜18中のMnOが入り込む。これにより、第2絶縁層6中のSiおよびOと金属膜18中のMnOとが結合して、第2溝11およびビアホール18の内面を含む第2絶縁層6の表面全域に、MnSiOからなるバリア膜13が形成される。金属膜18における第2絶縁層6に接する部分は、第2バリア膜13の形成に伴って消失し、第1配線5上にのみ金属膜18が残る。
Next, as shown in FIG. 2C, by sputtering, the entire surface of the second insulating
その後、水素還元処理が行われる。この水素還元処理により、図2Dに示すように、第1配線5上に残された金属膜18が還元されて、その金属膜18がMnからなるMn膜19に変質する。水素還元処理は、たとえば、水素雰囲気中での熱処理であってもよいし、水素プラズマ処理であってもよい。
次いで、図2Eに示すように、スパッタ法により、第2バリア膜13の表面全域およびMn膜19の表面を被覆するように、Cuを主成分とする金属材料からなるシード膜20が形成される。
Thereafter, a hydrogen reduction process is performed. By this hydrogen reduction treatment, as shown in FIG. 2D, the
Next, as shown in FIG. 2E, a
その後、図2Fに示すように、めっき法により、シード膜20上にCuからなるめっき層21が形成される。めっき層21は、ビアホール12および第2溝11を埋め尽くす厚さに形成される。
めっき層21は、めっき成長したままの状態では、その結晶構造が均一でなく、比抵抗が高い。そこで、めっき成長後には、めっき層21を結晶化(結晶構造の均一化)するための熱処理が行われる。このとき、図2Gに示すように、Mn膜19中のMnは、めっき層21中を移動し、めっき層21の表面に析出する。したがって、Mn膜19は、この結晶化のための熱処理時に消失する。
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 2F, a
The plated
次いで、CMP(Chemical Mechanical Polishing:化学的機械的研磨)法により、めっき層21および第2バリア膜13が研磨される。この研磨は、めっき層21および第2バリア膜13における第2溝11外に形成されている不要部分がすべて除去されて、第2絶縁層6(第2層間絶縁膜10)が露出し、その第2絶縁層6の露出した表面と第2溝11内のめっき層21の表面とが面一になるまで続けられる。これにより、図1に示す半導体装置1が得られる。
Next, the
MnOからなる金属膜18は、SiO2からなる第2層間絶縁膜10に対する密着性が比較的高い。そのため、金属膜18が所望する厚さの第2バリア膜13の形成に必要かつ十分な程度の小さい厚さに形成されても、第2溝11の側面からの(第2層間絶縁膜10に対する)金属膜18の膜剥がれを生じにくい。したがって、第2溝11の内面上に第2バリア膜13を良好に形成することができる。また、第2溝11の内面に金属膜18を被着させる際に、スパッタリングのエネルギーによって第2バリア膜13を形成することができるので、第2バリア膜13を形成するための熱処理を行う必要がない。
The
また、水素還元処理により、金属膜18における第1配線5の表面に接する部分からOが除去されて、その部分がMnからなるMn膜19に還元される。このMn膜19は、ビア15などに拡散することによって消失する。Mnは、Cuよりも電気抵抗が高いので、こうして第1配線5上から金属膜18(Mn膜19)が除去されることにより、第1配線5とビアとの間にMnOからなる金属膜18が残された構成と比較して、第1配線5と第2配線14との間の電気抵抗を低減することができる。
Moreover, O is removed from the part in contact with the surface of the
また、めっき成長により形成されるめっき層21は、めっき成長したままの状態では、その結晶構造が均一でなく、比抵抗が高い。めっき層21の形成後に、めっき層21の結晶化のための熱処理が行われることにより、めっき層21の結晶構造が均一化(結晶化)されるので、そのめっき層21からなる第2配線14およびビア15の比抵抗を低減することができる。
In addition, the
図3A〜3Gは、本発明の第2の実施形態に係る半導体装置の製造工程を順に示す模式的な断面図である。
図3Aに示すように、第1バリア膜4および第1配線5が埋設された第1絶縁層2上に、CVD(Chemical Vapor Deposition:化学的気相成長)法により、拡散防止膜7、第1層間絶縁膜8、エッチングストッパ膜9および第2層間絶縁膜10がこの順に積層される。これにより、第1絶縁層2上に、第2絶縁層6が形成される。
3A to 3G are schematic cross-sectional views sequentially showing manufacturing steps of the semiconductor device according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
As shown in FIG. 3A, on the first insulating
その後、図3Bに示すように、第2絶縁層6に、第2溝11およびビアホール12が形成される。具体的には、まず、第2絶縁層6上に、ビアホール12が形成されるべき部分を選択的に露出させる開口を有するマスク(図示せず)が形成される。そして、そのマスクを介して、第2層間絶縁膜10、エッチングストッパ膜9および第1層間絶縁膜8がドライエッチングされる。このとき、適当なタイミングで反応ガス(エッチャント)を切り換えることにより、第2層間絶縁膜10、エッチングストッパ膜9および第1層間絶縁膜8が連続的にエッチングされる。次に、第2絶縁層6上からマスクが除去された後、第2絶縁層6上に、第2溝11が形成されるべき部分を選択的に露出させる開口を有する新たなマスク(図示せず)が形成される。そして、そのマスクを介して、第2層間絶縁膜10がドライエッチングされる。その後、拡散防止膜7およびエッチングストッパ膜9の露出した部分が除去されることにより、第2溝11およびビアホール12が形成される。
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 3B, the
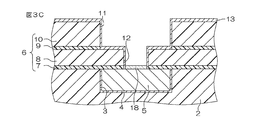
次いで、図3Cに示すように、スパッタ法により、第2溝11およびビアホール12の内面を含む第2絶縁層6の表面全域、ならびに第1配線5の表面におけるビアホール12に臨む部分に、MnOからなる金属膜18が被着される。金属膜18は、第2バリア膜13の形成に必要かつ十分な程度の厚さ(たとえば、1〜10nm)に形成される。このとき、金属膜18における第2絶縁層6に接する部分(第2溝11およびビアホール12の内面を含む第2絶縁層6の表面全域)には、スパッタリングのエネルギーによって、金属膜18中のMnOが入り込む。これにより、第2絶縁層6中のSiおよびOと金属膜18中のMnOとが結合して、第2溝11およびビアホール18の内面を含む第2絶縁層6の表面全域に、MnSiOからなるバリア膜13が形成される。金属膜18における第2絶縁層6に接する部分は、第2バリア膜13の形成に伴って消失し、第1配線5上にのみ金属膜18が残る。
Next, as shown in FIG. 3C, by sputtering, the entire surface of the second insulating
その後、図3Dに示すように、逆スパッタ法により、第1配線5上に残された金属膜18が除去される。具体的には、金属膜18に対して、ほぼ鉛直方向(第2絶縁層6の積層方向に沿う方向)からガス粒子(たとえば、アルゴンガス粒子)を衝突させることにより、第1配線5上に形成された部分が除去される。第2バリア膜13は、第2絶縁層6と強く結合しているため、この逆スパッタ法によって除去されない。
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 3D, the
次いで、図3Eに示すように、スパッタ法により、第2バリア膜13の表面全域および第1配線5におけるビアホール12を介して露出する部分を被覆するように、Cuを主成分とする金属材料からなるシード膜20が形成される。
その後、図3Fに示すように、めっき法により、シード膜20上にCuからなるめっき層21が形成される。めっき層21は、ビアホール12および第2溝11を埋め尽くす厚さに形成される。
Next, as shown in FIG. 3E, by sputtering, a metal material mainly composed of Cu is used to cover the entire surface of the
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 3F, a
次に、めっき層21を結晶化(結晶構造の均一化)するための熱処理が行われる。
そして、CMP(Chemical Mechanical Polishing:化学的機械的研磨)法により、めっき層21および第2バリア膜13が研磨される。この研磨は、めっき層21および第2バリア膜13における第2溝11外に形成されている不要部分がすべて除去されて、第2絶縁層6(第2層間絶縁膜10)が露出し、その第2絶縁層6の露出した表面と第2溝11内のめっき層21の表面とが面一になるまで続けられる。これにより、図1に示す半導体装置1が得られる。
Next, heat treatment is performed to crystallize the plating layer 21 (uniform crystal structure).
Then, the
この実施形態に係る製造方法によっても、第1の実施形態に係る製造方法(図2A〜図2G)と同様の効果を奏することができる。また、この実施形態では、逆スパッタ法によって、第2バリア膜13の形成後に、第1配線5上に残された金属膜が除去される。これにより、第1配線5と第2配線14との間の電気抵抗を低減することができる。
また、スパッタ法および逆スパッタ法は、同一のスパッタリング装置で実施することができるので、金属膜18におけるビアホール12の底面上に形成された部分を除去するために逆スパッタ法が用いられることにより、同一のスパッタリング装置において、金属膜18を形成する工程に連続して、その金属膜18の部分的な除去の工程を行うことができる。さらに、金属膜18の除去の工程に連続して、シード膜20を形成する工程を行うことができる。したがって、半導体製造装置の構成を簡素化することができ、また、それらの工程間での半導体ウエハ(前記絶縁層が形成されたウエハ状態の半導体基板)の搬送が不要であるので、半導体装置1の製造に要する時間を短縮することができる。
Also by the manufacturing method according to this embodiment, the same effects as those of the manufacturing method according to the first embodiment (FIGS. 2A to 2G) can be obtained. In this embodiment, the metal film remaining on the
In addition, since the sputtering method and the reverse sputtering method can be performed with the same sputtering apparatus, the reverse sputtering method is used to remove the portion formed on the bottom surface of the via
なお、第1バリア膜4および第1配線5の形成手法については、その説明を省略したが、第1バリア膜4および第1配線5は、第2バリア膜13および第2配線14の形成手法と同様な手法で形成することができる。すなわち、フォトリソグラフィおよびエッチングにより、第1絶縁層2にその表面から掘り下がった形状の第1溝3が形成された後、スパッタ法により、MnOからなる金属膜が第1溝3の側面および底面に被着される。このとき、スパッタリングのエネルギーによって第1絶縁層2中のSiおよびOと、金属膜中のMnOとが結合し、第1溝3の側面および底面上に、MnSiOからなる第1バリア膜4が形成される。その後、第1バリア膜4上に、めっき法により、Cuを主成分とする金属材料からなるシード膜およびCuからなるめっき層が順に形成される。そして、CMP法により、そのめっき層の不要部分(第1溝3外の部分)が除去される。これにより、第1溝3内に、第1バリア膜4および第1配線5が得られる。
The description of the method for forming the
以上、本発明の2つの実施形態を説明したが、本発明は、さらに他の形態で実施することもできる。
たとえば、拡散防止膜7は、SiCおよびSiCNを積層した構造を有しているとした。しかし、拡散防止膜7は、Cuの拡散に対するバリア性を有していればよく、たとえば、SiCのみからなる構造であってもよい。
As mentioned above, although two embodiment of this invention was described, this invention can also be implemented with another form.
For example, the diffusion prevention film 7 has a structure in which SiC and SiCN are laminated. However, the diffusion preventing film 7 only needs to have a barrier property against the diffusion of Cu, and for example, may have a structure made of only SiC.
また、第1層間絶縁膜8および第2層間絶縁膜10は、SiO2からなるとした。しかし、第1層間絶縁膜8および第2層間絶縁膜10の材料は、SiおよびOを含む絶縁性材料であればよく、その材料として、SiO2以外に、たとえば、SiOC(炭素が添加された酸化シリコン)、またはSiOF(フッ素が添加された酸化シリコン)などを例示することができる。
The first
その他、特許請求の範囲に記載された事項の範囲で種々の設計変更を施すことが可能である。 In addition, various design changes can be made within the scope of matters described in the claims.
1 半導体装置
6 第2絶縁層(絶縁層)
11 第2溝(溝)
12 ビアホール
13 第2バリア膜(バリア膜)
14 第2配線(Cu配線)
15 ビア
18 金属膜
19 Mn膜
20 シード膜
21 めっき層
11 Second groove (groove)
12 via
14 Second wiring (Cu wiring)
15 Via 18
Claims (6)
前記絶縁層に溝を形成する溝形成工程と、
スパッタ法により、前記溝の内面にMnOx(x:零よりも大きい数)からなる金属膜を被着させる金属膜被着工程と、
前記金属膜上にCuを主成分とする金属材料からなるCu配線を形成する配線形成工程とを含む、半導体装置の製造方法。 An insulating layer forming step of forming an insulating layer made of an insulating material containing Si and O;
A groove forming step of forming a groove in the insulating layer;
A metal film deposition step of depositing a metal film made of MnO x (x: a number greater than zero) on the inner surface of the groove by sputtering;
And a wiring forming step of forming a Cu wiring made of a metal material containing Cu as a main component on the metal film.
前記溝形成工程後であって前記金属膜被着工程の前に、前記溝から前記下配線に向けて延び、前期絶縁層を厚さ方向に貫通するビアホールを形成するビアホール形成工程と、
前記金属膜被着工程後に、前記ビアホールにCuを主成分とするビアを形成するビア形成工程とを含み、
前記金属膜被着工程では、前記溝の内面に加えて、前記ビアホールの側面および前記下配線の表面における前記ビアホールに臨む部分に前記金属膜が被着される、請求項1に記載の半導体装置の製造方法。 A lower wiring electrically connected to the Cu wiring is formed under the insulating layer,
A via hole forming step for forming a via hole extending from the groove toward the lower wiring and penetrating the insulating layer in the thickness direction after the groove forming step and before the metal film deposition step;
A via formation step of forming a via mainly comprising Cu in the via hole after the metal film deposition step;
2. The semiconductor device according to claim 1, wherein, in the metal film deposition step, in addition to the inner surface of the groove, the metal film is deposited on a side surface of the via hole and a portion facing the via hole on the surface of the lower wiring. Manufacturing method.
スパッタ法により、前記金属膜上にCuを主成分とする金属材料からなるシード膜を形成する工程と、
めっき法により、前記シード膜上にCuからなるめっき層を形成する工程とを含む、請求項1〜4のいずれか一項に記載の半導体装置の製造方法。 The wiring formation step includes
Forming a seed film made of a metal material mainly composed of Cu on the metal film by sputtering;
The manufacturing method of the semiconductor device as described in any one of Claims 1-4 including the process of forming the plating layer which consists of Cu on the said seed film | membrane by the plating method.
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008202138A JP2010040771A (en) | 2008-08-05 | 2008-08-05 | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
| US12/536,472 US8110504B2 (en) | 2008-08-05 | 2009-08-05 | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
| US13/345,046 US8647984B2 (en) | 2008-08-05 | 2012-01-06 | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008202138A JP2010040771A (en) | 2008-08-05 | 2008-08-05 | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010040771A true JP2010040771A (en) | 2010-02-18 |
| JP2010040771A5 JP2010040771A5 (en) | 2011-09-22 |
Family
ID=42013006
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008202138A Pending JP2010040771A (en) | 2008-08-05 | 2008-08-05 | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2010040771A (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012173067A1 (en) * | 2011-06-16 | 2012-12-20 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Semiconductor device manufacturing method, semiconductor device, semiconductor device manufacturing apparatus, and storage medium |
| WO2013153777A1 (en) * | 2012-04-11 | 2013-10-17 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device, semiconductor device, and apparatus for producing semiconductor |
| WO2014013941A1 (en) * | 2012-07-18 | 2014-01-23 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device |
| CN113088902A (en) * | 2021-04-12 | 2021-07-09 | 贵州大学 | Process method for preparing single-phase high manganese silicon film under raw material oxidation condition |
Citations (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS63121640A (en) * | 1986-11-11 | 1988-05-25 | Sumitomo Metal Ind Ltd | Case hardening steel |
| JPH11152528A (en) * | 1997-11-18 | 1999-06-08 | Japan Energy Corp | Production of high purity mn material, and high purity mn material for thin film formation |
| JP2001284678A (en) * | 2000-03-17 | 2001-10-12 | Read Rite Corp | Spin-valve magnetoresistive effect element |
| JP2001345325A (en) * | 2000-06-02 | 2001-12-14 | Nec Kyushu Ltd | Wiring formation method of semiconductor device |
| JP2004052036A (en) * | 2002-07-19 | 2004-02-19 | Kubota Corp | Member for heating furnace having excellent carburization resistance |
| JP2004319834A (en) * | 2003-04-17 | 2004-11-11 | Renesas Technology Corp | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP2006135363A (en) * | 2006-02-14 | 2006-05-25 | Renesas Technology Corp | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the semiconductor device |
| JP2007059660A (en) * | 2005-08-25 | 2007-03-08 | Sony Corp | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP2007173511A (en) * | 2005-12-22 | 2007-07-05 | Sony Corp | Method for fabricating a semiconductor device |
| JP2007208170A (en) * | 2006-02-06 | 2007-08-16 | Toshiba Corp | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP2007221103A (en) * | 2006-01-20 | 2007-08-30 | Fujitsu Ltd | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device |
| WO2008027214A2 (en) * | 2006-08-30 | 2008-03-06 | Lam Research Corporation | Methods and apparatus for barrier interface preparation of copper interconnect |
| JP2008066428A (en) * | 2006-09-06 | 2008-03-21 | Sony Corp | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| WO2008049019A2 (en) * | 2006-10-17 | 2008-04-24 | Enthone Inc. | Copper deposition for filling features in manufacture of microelectronic devices |
| JP2008124275A (en) * | 2006-11-13 | 2008-05-29 | Fujitsu Ltd | Manufacturing method for semiconductor device |
| JP2008153472A (en) * | 2006-12-18 | 2008-07-03 | Toshiba Corp | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
| JP2008192684A (en) * | 2007-02-01 | 2008-08-21 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
-
2008
- 2008-08-05 JP JP2008202138A patent/JP2010040771A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS63121640A (en) * | 1986-11-11 | 1988-05-25 | Sumitomo Metal Ind Ltd | Case hardening steel |
| JPH11152528A (en) * | 1997-11-18 | 1999-06-08 | Japan Energy Corp | Production of high purity mn material, and high purity mn material for thin film formation |
| JP2001284678A (en) * | 2000-03-17 | 2001-10-12 | Read Rite Corp | Spin-valve magnetoresistive effect element |
| JP2001345325A (en) * | 2000-06-02 | 2001-12-14 | Nec Kyushu Ltd | Wiring formation method of semiconductor device |
| JP2004052036A (en) * | 2002-07-19 | 2004-02-19 | Kubota Corp | Member for heating furnace having excellent carburization resistance |
| JP2004319834A (en) * | 2003-04-17 | 2004-11-11 | Renesas Technology Corp | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP2007059660A (en) * | 2005-08-25 | 2007-03-08 | Sony Corp | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP2007173511A (en) * | 2005-12-22 | 2007-07-05 | Sony Corp | Method for fabricating a semiconductor device |
| JP2007221103A (en) * | 2006-01-20 | 2007-08-30 | Fujitsu Ltd | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device |
| JP2007208170A (en) * | 2006-02-06 | 2007-08-16 | Toshiba Corp | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP2006135363A (en) * | 2006-02-14 | 2006-05-25 | Renesas Technology Corp | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the semiconductor device |
| WO2008027214A2 (en) * | 2006-08-30 | 2008-03-06 | Lam Research Corporation | Methods and apparatus for barrier interface preparation of copper interconnect |
| JP2010503204A (en) * | 2006-08-30 | 2010-01-28 | ラム リサーチ コーポレーション | Method and apparatus for adjusting the barrier interface of copper wiring |
| JP2008066428A (en) * | 2006-09-06 | 2008-03-21 | Sony Corp | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| WO2008049019A2 (en) * | 2006-10-17 | 2008-04-24 | Enthone Inc. | Copper deposition for filling features in manufacture of microelectronic devices |
| JP2010507263A (en) * | 2006-10-17 | 2010-03-04 | エントン インコーポレイテッド | Copper deposition to embed features in the fabrication of microelectronic devices |
| JP2008124275A (en) * | 2006-11-13 | 2008-05-29 | Fujitsu Ltd | Manufacturing method for semiconductor device |
| JP2008153472A (en) * | 2006-12-18 | 2008-07-03 | Toshiba Corp | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
| JP2008192684A (en) * | 2007-02-01 | 2008-08-21 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012173067A1 (en) * | 2011-06-16 | 2012-12-20 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Semiconductor device manufacturing method, semiconductor device, semiconductor device manufacturing apparatus, and storage medium |
| KR20140041745A (en) * | 2011-06-16 | 2014-04-04 | 도쿄엘렉트론가부시키가이샤 | Semiconductor device manufacturing method, semiconductor device, semiconductor device manufacturing apparatus, and storage medium |
| TWI470679B (en) * | 2011-06-16 | 2015-01-21 | Tokyo Electron Ltd | Semiconductor device manufacturing method |
| JPWO2012173067A1 (en) * | 2011-06-16 | 2015-02-23 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Semiconductor device manufacturing method, semiconductor device, semiconductor device manufacturing apparatus, and storage medium |
| KR101659469B1 (en) | 2011-06-16 | 2016-09-23 | 도쿄엘렉트론가부시키가이샤 | Semiconductor device manufacturing method, semiconductor device, semiconductor device manufacturing apparatus, and storage medium |
| WO2013153777A1 (en) * | 2012-04-11 | 2013-10-17 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device, semiconductor device, and apparatus for producing semiconductor |
| JPWO2013153777A1 (en) * | 2012-04-11 | 2015-12-17 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Semiconductor device manufacturing method, semiconductor device, and semiconductor manufacturing apparatus |
| WO2014013941A1 (en) * | 2012-07-18 | 2014-01-23 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device |
| JPWO2014013941A1 (en) * | 2012-07-18 | 2016-06-30 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
| CN113088902A (en) * | 2021-04-12 | 2021-07-09 | 贵州大学 | Process method for preparing single-phase high manganese silicon film under raw material oxidation condition |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI269404B (en) | Interconnect structure for semiconductor devices | |
| US7507659B2 (en) | Fabrication process of a semiconductor device | |
| JP2008187072A (en) | Semiconductor device manufacturing method and semiconductor device | |
| US8647984B2 (en) | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| JP2002252281A (en) | Semiconductor device and its fabrication method | |
| JP2008047719A (en) | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| US8039390B2 (en) | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| JP2006324414A (en) | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same | |
| US20070200237A1 (en) | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP2007287816A (en) | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| JP2006324584A (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2010040771A (en) | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| TW201227826A (en) | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| JP2006135363A (en) | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the semiconductor device | |
| JP2006245240A (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2004119698A (en) | Semiconductor device and its manufacturing method | |
| JP2009004633A (en) | Multilayer interconnection structure and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP2010080607A (en) | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| JP2010040772A (en) | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| JP2006245268A (en) | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| US20100244265A1 (en) | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same | |
| US20090166882A1 (en) | Method for forming metal line in semiconductor device | |
| JP2010080606A (en) | Method of manufacturing semiconductor apparatus | |
| JPH11111842A (en) | Multilayered wiring structure and its manufacture | |
| JP5720381B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20100630 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110805 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110805 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20131114 |