JP2010002427A - Inertial sensor, inertial sensor device and its manufacturing method - Google Patents
Inertial sensor, inertial sensor device and its manufacturing method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010002427A JP2010002427A JP2009224160A JP2009224160A JP2010002427A JP 2010002427 A JP2010002427 A JP 2010002427A JP 2009224160 A JP2009224160 A JP 2009224160A JP 2009224160 A JP2009224160 A JP 2009224160A JP 2010002427 A JP2010002427 A JP 2010002427A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- axis
- gyro sensor
- sensor device
- mold
- inertial sensor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 29
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 92
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 26
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 57
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims description 57
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 26
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 claims description 23
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- 230000002542 deteriorative effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 2
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 30
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 12
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 11
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 description 11
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 9
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 9
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 6
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000012856 packing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001154 acute effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000006071 cream Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920006332 epoxy adhesive Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000010453 quartz Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000004904 shortening Methods 0.000 description 2
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon dioxide Inorganic materials O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005284 excitation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012778 molding material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002441 reversible effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001721 transfer moulding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Gyroscopes (AREA)
- Pressure Sensors (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、加速度センサやジャイロセンサ等の慣性センサ、及びその製造方法に関わり、特に車載用のナビゲーション装置等に好適なものである。 The present invention relates to an inertial sensor such as an acceleration sensor and a gyro sensor, and a manufacturing method thereof, and is particularly suitable for an in-vehicle navigation device.
カーナビゲーション装置が広く普及している。このようなカーナビゲーション装置において、自動車等の車両の現在位置を検出する際には、所謂GPS(Global Positioning System)を用いて測位する方法と、車両の移動方向、及び移動距離を自立的に測位する方法とが併用されている。このため、カーナビゲーション装置においては、車両の移動方向、及び移動距離を自立的に測位するために車両に加わる加速度や角速度等を検出するジャイロセンサ(角速度センサ)や加速度センサ等の慣性センサが搭載されている。
このような慣性センサにより角速度や加速度等を検出する場合は、検出すべき方向に検出軸を向ける必要があり、例えば、ジャイロセンサであれば検出軸が鉛直上方を向くように設置する必要があった。
Car navigation devices are widely used. In such a car navigation device, when detecting the current position of a vehicle such as an automobile, a method of positioning using a so-called GPS (Global Positioning System), and the vehicle moving direction and moving distance are independently determined. The method to do is used together. For this reason, in a car navigation apparatus, an inertial sensor such as a gyro sensor (angular velocity sensor) or an acceleration sensor for detecting acceleration or angular velocity applied to the vehicle in order to independently determine the moving direction and moving distance of the vehicle is mounted. Has been.
When detecting an angular velocity, acceleration, or the like with such an inertial sensor, the detection axis needs to be directed in the direction to be detected. For example, in the case of a gyro sensor, the detection axis needs to be installed vertically upward. It was.
ところで、近年、カーナビゲーション装置は、小型化が進み、従来、座席の下やトランクルーム内等に配置されていた装置本体(以下、「ナビゲーション本体」と称する)を運転席と助手席との間に位置するセンターコンソールに設置するタイプのものが開発されている。
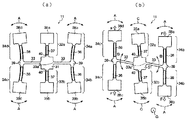
図15は、センターコンソールに設置されたナビゲーション本体を示した図であり、(a)はその全体斜視図、(b)はカーナビゲーション本体に実装されているジャイロセンサを示した図である。
図15(a)に示すように、センターコンソール102にナビゲーション本体100を設置する場合、ナビゲーション本体100に取り付けられている表示装置101の視認性や、図示しない操作パネルの操作性の観点から表示装置101、及び操作パネルの盤面を運転者の目線方向に向けることが好ましい。つまり、ナビゲーション本体100を水平方向から斜め上方に傾斜させてセンターコンソール102内に設置することが好ましい。しかしながら、ナビゲーション本体100を斜め上方に傾斜させてセンターコンソール102に設置した場合は、図15(b)に示すようにナビゲーション本体100内のプリント基板103上に実装されているジャイロセンサ104の検出軸Gが、本来向けられるべき方向である鉛直方向Vからナビゲーション本体100の取り付け角度(傾き角)θだけ傾いてしまうため、ジャイロセンサ104において検出される角速度に誤差が生じる。
By the way, in recent years, the size of car navigation devices has been reduced, and a device main body (hereinafter referred to as “navigation main body”) that has been conventionally arranged under a seat or in a trunk room is interposed between a driver seat and a passenger seat. A type to be installed on the center console located has been developed.
FIGS. 15A and 15B are diagrams showing a navigation main body installed on the center console. FIG. 15A is an overall perspective view, and FIG. 15B is a diagram showing a gyro sensor mounted on the car navigation main body.
As shown in FIG. 15A, when the navigation
通常のカーナビゲーション装置では、ナビゲーション本体100の取り付け角度により発生するジャイロセンサ104等の検出誤差を補正するため、ソフトウェアの演算処理により検出結果の補正が行われているが、このようなソフトウェアによる補正処理には限界があり、例えば、ナビゲーション本体100の傾き角θが、30°以上になるとソフトウェアの演算処理では補正しきれないのが現状であった。
このため、カーナビゲーション装置では、斜めに傾けて搭載した場合でも正確に検出を行なうことができる慣性センサが求められ、そのようなセンサが各種提案されている。
In a normal car navigation apparatus, in order to correct a detection error of the
For this reason, in car navigation devices, an inertial sensor that can detect accurately even when mounted obliquely, various types of such sensors have been proposed.
例えば、特許文献1には、センサ内部の角速度検出素子を保持部材により傾けることで、センサの形状やセンサの実装方法を変えずに検出軸を傾けるようにした角速度センサが開示されている。
また特許文献2には、一定の方向性を有する物理量の当該方向、及び大きさを検出する検出素子と、検出素子を固定支持する取付部とを備えるセンサ装置において、検出素子が方向、及び大きさを検出する基準である検出軸の方向と当該検出する際に実際に検出素子に加わる物理量の方向との差として予測される角度差を減少させる減少方向に予め設定された減少角度だけ傾斜して取付部に固定するようにしたセンサ装置が開示されている。
また特許文献3には、振動子を支持基板に接続する脚部、及びその支持基板とパッケージ用基板とを接続する接着剤によって、パッケージ内の振動子の角度を設定し、振動子の検出軸を所望方向に配向させるようにした振動子の支持構造が開示されている。
For example,
Further, in
In
しかしながら、上記特許文献1、2に開示されているセンサでは、検出素子である水晶振動子を取付部に直接固定しているため、取付部が水晶振動子からの振動漏れや不要振動モード等の発生原因となり、検出性能を悪化させる虞があった。
また上記特許文献1、2に開示されているセンサでは、検出素子自体を傾けて取り付ける必要があるため、取り付け角度ごとに専用の冶具が必要になり、製造コストの上昇を招いていた。このように専用の冶具が必要になるのは、特許文献1、2に開示されているセンサでは、検出素子を取付部に取り付けた後、検出素子にレーザを照射してセンサの調整を行っているため、検出素子の取り付け角度を変えた場合は取り付け角度ごとレーザの焦点が異なり、冶具を共有化することができないからである。
また上記特許文献2では、検出素子を傾けて取り付けるために、検出素子自体にスリットを形成するようにしている。このため、検出素子の加工コストが高くなり、この点からも製造コストの上昇を招いていた。
さらにまた、上記特許文献1、2では、センサの内部で検出素子を傾けるようにしているため、センサを実装基板に実装する際に、検出軸の角度を任意の角度に変更することができないという問題点があった。
However, in the sensors disclosed in
Further, in the sensors disclosed in
In
Furthermore, in
また特許文献3では、振動片(振動子)を支持基板に接続する脚部(ボンディングワイヤ)は、振動片からの振動漏れや、不要振動モードの発生に関連が深く、センサの検出性能を悪くする場合がある。また、接着剤によって角度を変えることは、製造上のばらつきが大きく、設定する角度の精度が悪い。
また、特許文献1、2における取付部は素子を直接固定するものであり、取付部が振動子からの振動漏れや、不要振動モードなどの発生原因になり、物理量の検出性能を悪くする場合がある。
そこで、発明者は、従来の接合方法によりセンサ素子を固定したセンサデバイスを、リードフレームに接合してモールドする方法に着目した。この方法によれば、センサ素子は従来の接合方法にて固定されるので振動漏れや不要振動モードの発生が抑えられ、センサが動作に応答する検出軸に応じた設置角度をリードフレームの形状によって制御することができるうえに、モールドすることにより機械的な強度を確保することができる。
しかしながら、この方法では、センサを収容したセンサデバイスは、リードフレームの形状を制御することにより、センサが動作に応答する検出軸に応じて実装面に対して傾けられる。このため、センサデバイスの外形に沿ってモールドする従来のモールド方法を用いてセンサ装置を形成すると、センサ装置の外形が実装面に対して平行でなくなる。このため、実装工程での作業性が悪くなる虞があった。
In
In addition, the attachment part in
In view of this, the inventor has focused on a method in which a sensor device having a sensor element fixed by a conventional bonding method is bonded to a lead frame and molded. According to this method, since the sensor element is fixed by a conventional joining method, the occurrence of vibration leakage and unnecessary vibration modes can be suppressed, and the installation angle corresponding to the detection axis to which the sensor responds to operation depends on the shape of the lead frame. In addition to being controllable, mechanical strength can be secured by molding.
However, in this method, the sensor device containing the sensor is tilted with respect to the mounting surface according to the detection axis in which the sensor responds to the operation by controlling the shape of the lead frame. For this reason, when the sensor device is formed using a conventional molding method in which molding is performed along the outer shape of the sensor device, the outer shape of the sensor device is not parallel to the mounting surface. For this reason, there exists a possibility that the workability | operativity in a mounting process may worsen.
本発明は上記した点を鑑みてなされたものであり、検出素子の検出性能を悪化させることなく、検出軸を所定角度に設定できる慣性センサと、その製造方法を提供することを目的とする。
また、本発明は所定の傾斜を有する実装面に取り付けてもセンサの検出軸を精度良く設定でき、センサの検出軸とモールドの底面および上面とを所望の角度に設定することが可能で作業性が良好な慣性センサ装置の製造方法を提供することを目的とする。
The present invention has been made in view of the above points, and an object thereof is to provide an inertial sensor capable of setting a detection axis at a predetermined angle without deteriorating the detection performance of the detection element, and a method for manufacturing the same.
In addition, the present invention can set the detection axis of the sensor with high accuracy even when it is mounted on a mounting surface having a predetermined inclination, and can set the detection axis of the sensor and the bottom and top surfaces of the mold at desired angles. It is an object of the present invention to provide a method for manufacturing an inertial sensor device having a good quality.
上記目的を達成するため、本発明の慣性センサは、検出軸方向の物理量の大きさを検出する検出素子と、検出素子の略中央を支持する可撓性を有する複数の支持部材と、検出素子を収納するパッケージ用基板と、を備え、複数の支持部材の延長方向をX軸、検出素子の平面内において直交する軸をY軸、X軸とY軸とに直交する軸をZ軸としたときに、支持部材に加わる検出素子のY軸方向の荷重成分が複数の支持部材において略同一であり、且つ、Z軸方向の荷重成分が複数の支持部材間において略同一であることを特徴とする。
このように構成すれば、複数の支持部材には加速度により等しい作用が働くため、加速度に伴う力の変化に対して支持部材の機械的共振周波数の設定条件を乱れ難くすることができる。即ち、支持部材の共振周波数が予期せぬ値に乱れ、更に、例えば、温度変化に伴い慣性センサの駆動周波数が変化する過程で、当該共振周波数が慣性センサの駆動振動付近に移動してしまうと、慣性センサの駆動周波数が支持部材の共振周波数に結合してしまい(誘引されてしまい)慣性センサの出力信号がジャンプするという不具合を防止することができる。
In order to achieve the above object, an inertial sensor of the present invention includes a detection element that detects the magnitude of a physical quantity in the detection axis direction, a plurality of flexible support members that support substantially the center of the detection element, and a detection element A plurality of support members extending in the direction of the X axis, the axis perpendicular to the plane of the detection element as the Y axis, and the axis perpendicular to the X axis and the Y axis as the Z axis. Sometimes the load component in the Y-axis direction of the detection element applied to the support member is substantially the same in the plurality of support members, and the load component in the Z-axis direction is substantially the same among the plurality of support members. To do.
If comprised in this way, since an equal effect | action acts on a some support member by acceleration, it can make it difficult to disturb the setting conditions of the mechanical resonance frequency of a support member with respect to the change of the force accompanying acceleration. That is, if the resonance frequency of the support member is disturbed to an unexpected value, and further, for example, the resonance frequency moves to the vicinity of the drive vibration of the inertial sensor in the process of changing the drive frequency of the inertial sensor with a temperature change. Thus, it is possible to prevent a problem that the inertial sensor output frequency jumps due to the drive frequency of the inertial sensor being coupled to the resonance frequency of the support member.
また本発明の慣性センサは、検出素子は、角速度を検出する検出軸がZ軸方向で、且つ、Z軸と鉛直方向との成す角がθであり、Y軸方向の荷重成分とZ軸方向の荷重成分とを合成した荷重成分が少なくとも重力加速度に基づく荷重成分であることを特徴とする。
このように慣性センサを構成すると、慣性センサを傾斜させて配置した場合も複数の支持部材に加速度により等しい作用が働くため、加速度に伴う力の変化に対して支持部材の機械的共振周波数の設定条件を乱れ難くすることができる。即ち、支持部材の共振周波数が予期せぬ値に乱れ、更に、例えば、温度変化に伴い慣性センサの駆動周波数が変化する過程で、当該共振周波数が慣性センサの駆動振動付近に移動してしまうと、慣性センサの駆動周波数が支持部材の共振周波数に結合してしまい(誘引されてしまい)慣性センサの出力信号がジャンプするという不具合を防止することができる。
また、慣性センサを傾斜させた状態で慣性センサの駆動周波数を検査することが可能になり検査工程を簡略化することができる。
さらに、この場合は重力加速度とZ軸方向とは一致するので、Y軸方向は移動体の進行方向と一致することになるので、移動体の移動時の加速度に対しても支持部材の共振周波数が乱れ難いという利点がある。
In the inertial sensor of the present invention, the detection element has a detection axis for detecting the angular velocity in the Z-axis direction, and an angle between the Z-axis and the vertical direction is θ, and the load component in the Y-axis direction and the Z-axis direction The load component obtained by combining the load components is a load component based on at least gravitational acceleration.
When the inertial sensor is configured in this way, even when the inertial sensor is tilted, an equal action is exerted on the plurality of support members due to the acceleration. Therefore, the mechanical resonance frequency of the support member is set with respect to a force change caused by the acceleration. Conditions can be made difficult to disturb. That is, if the resonance frequency of the support member is disturbed to an unexpected value, and further, for example, the resonance frequency moves to the vicinity of the drive vibration of the inertial sensor in the process of changing the drive frequency of the inertial sensor with a temperature change. Thus, it is possible to prevent a problem that the inertial sensor output frequency jumps due to the drive frequency of the inertial sensor being coupled to the resonance frequency of the support member.
In addition, the driving frequency of the inertial sensor can be inspected with the inertial sensor tilted, and the inspection process can be simplified.
Further, in this case, since the gravitational acceleration and the Z-axis direction coincide with each other, the Y-axis direction coincides with the traveling direction of the moving body. There is an advantage that it is difficult to disturb.
また本発明の慣性センサは、当該慣性センサの短手方向を傾斜させることによりZ軸と鉛直方向とのなす角がθとなるように構成されていることを特徴とする。
このように構成すると、当該慣性センサを組み込んで傾斜構造の慣性センサ装置を構成したときに装置の低背化を実現することができる。
The inertial sensor of the present invention is characterized in that the angle formed by the Z axis and the vertical direction is θ by inclining the short direction of the inertial sensor.
If comprised in this way, when the said inertial sensor is integrated and the inertial sensor apparatus of an inclination structure is comprised, the shortening of an apparatus is realizable.
本発明の慣性センサと、慣性センサと電気的に接続される複数リード端子と、慣性センサを収納するモールドパッケージと、を備えた慣性センサ装置を特徴とする。
このように慣性センサ装置を構成すれば、複数の支持部材には加速度により等しい作用が働くため、加速度に伴う力の変化に対して支持部材の機械的共振周波数の設定条件を乱れ難くすることができる。即ち、支持部材の共振周波数が予期せぬ値に乱れ、更に、例えば、温度変化に伴い慣性センサの駆動周波数が変化する過程で、当該共振周波数が慣性センサの駆動振動付近に移動してしまうと、慣性センサの駆動周波数が支持部材の共振周波数に結合してしまい(誘引されてしまい)慣性センサの出力信号がジャンプするという不具合を防止することができる。
また本発明の慣性センサは、前記モールドパッケージが、該モールドパッケージの一部分から前記モールドパッケージの底面方向に向かって伸びるリード端子と、前記一部分と対向する前記モールドパッケージの一部分から前記リード端子より長いリード端子を前記モールドパッケージの底面方向に向かって伸びる構成を有し、前記長いリード端子は前記モールドパッケージ側に向けて複数の屈折部を有するように構成されていることを特徴とする。
このように構成すると、当該慣性センサを搭載基板に搭載したときの半田上がりによる慣性センサの浮きを防止することができる。
The present invention is characterized by an inertial sensor device including the inertial sensor of the present invention, a plurality of lead terminals electrically connected to the inertial sensor, and a mold package for housing the inertial sensor.
If the inertial sensor device is configured in this manner, the plurality of support members have the same effect due to the acceleration, so that it is difficult to disturb the setting condition of the mechanical resonance frequency of the support member with respect to a change in force accompanying the acceleration. it can. That is, if the resonance frequency of the support member is disturbed to an unexpected value, and further, for example, the resonance frequency moves to the vicinity of the drive vibration of the inertial sensor in the process of changing the drive frequency of the inertial sensor with a temperature change. Thus, it is possible to prevent a problem that the inertial sensor output frequency jumps due to the drive frequency of the inertial sensor being coupled to the resonance frequency of the support member.
In the inertial sensor of the present invention, the mold package has a lead terminal extending from a part of the mold package toward the bottom surface of the mold package, and a lead longer than the lead terminal from a part of the mold package facing the part. The terminal is configured to extend toward the bottom surface of the mold package, and the long lead terminal is configured to have a plurality of refracting portions toward the mold package.
With this configuration, it is possible to prevent the inertial sensor from being lifted due to solder rise when the inertial sensor is mounted on the mounting board.
また本発明は、実装基板との電気的接続をする複数のリード端子を有し、複数のリード端子によって構成されるリードフレームと、リードフレームの形状に基づいて設置角度が決まり、且つ検出軸に対する動作に応答するセンサを含むセンサデバイスと、をモールド方法により樹脂でモールドした慣性センサ装置の製造方法であって、リードフレームにセンサデバイスを接合した後に、凹部がそれぞれ形成された下金型および上金型を、凹部形成面どうしを、リードフレームを挟んで重ねることにより画定されるキャビティ内にセンサデバイスを収容し、キャビティに樹脂を充填して成形するモールド方法において、リードフレームと対面するキャビティの上下面が、リードフレームの両主面に対してそれぞれ傾けて形成され、且つ、上下面が平行になるように凹部が形成された下金型および上金型からなるモールド金型を用いることを特徴とする。
この構成によれば、動作に応答する検出軸に応じたセンサデバイスの実装面に対する設置角度が調整されたセンサデバイスを、実装面に対して平行な外形にてモールドすることができる。これにより、実装するときの作業性が良好な慣性センサ装置を製造することができる。
In addition, the present invention has a plurality of lead terminals that are electrically connected to the mounting substrate, the installation angle is determined based on the lead frame constituted by the plurality of lead terminals, and the shape of the lead frame, and with respect to the detection axis. A method of manufacturing an inertial sensor device in which a sensor device including a sensor that responds to an operation is molded with a resin by a molding method, and a lower mold and an upper mold each having a recess formed after the sensor device is joined to a lead frame In a molding method in which a sensor device is accommodated in a cavity defined by stacking recess-forming surfaces with a lead frame sandwiched between molds, and the cavity is filled with a resin, the cavity is opposed to the lead frame. Upper and lower surfaces are formed to be inclined with respect to both main surfaces of the lead frame, and upper and lower surfaces Characterized by using a mold die consisting of lower die and upper die which recesses are formed in parallel.
According to this configuration, the sensor device whose installation angle with respect to the mounting surface of the sensor device corresponding to the detection axis that responds to the operation is adjusted can be molded with an outer shape parallel to the mounting surface. Thereby, an inertial sensor device with good workability when mounting can be manufactured.
また本発明は、慣性センサ装置の製造方法において、キャビティのリードフレームと対面する上下面が、リードフレームの両主面に対してセンサデバイスの設置角度と同じ角度で傾けて形成されたモールド金型を用いることを特徴とする。
この構成によれば、上記した構成のモールド金型を用いることで、センサデバイスの底面と慣性センサ装置の底面とが角度をもって斜めに配置されるようにモールドを成形でき、慣性センサ装置の底面の法線と検出軸とが所定の角を成して形成される。
従って、慣性センサ装置が実装される傾斜した実装基板の基板面と鉛直方向との成す角と同じ角度に慣性センサ装置の底面の法線と検出軸とが成す角を設定することで、傾斜した面に本発明の慣性センサ装置を取り付けてもセンサの検出軸を精度良く設定することができる慣性センサ装置を製造することができる。
According to the present invention, in the method of manufacturing an inertial sensor device, a mold mold in which the upper and lower surfaces facing the lead frame of the cavity are inclined with respect to both main surfaces of the lead frame at the same angle as the installation angle of the sensor device. It is characterized by using.
According to this configuration, the mold can be formed such that the bottom surface of the sensor device and the bottom surface of the inertial sensor device are obliquely arranged at an angle by using the mold mold having the above configuration. The normal line and the detection axis are formed at a predetermined angle.
Therefore, by setting the angle formed by the normal line of the bottom surface of the inertial sensor device and the detection axis to the same angle as the angle formed by the substrate surface of the inclined mounting substrate on which the inertial sensor device is mounted and the vertical direction, the inclination is set. Even if the inertial sensor device of the present invention is attached to the surface, it is possible to manufacture an inertial sensor device that can accurately set the detection axis of the sensor.
以下、本発明の実施形態について説明する。
なお、本実施形態では本発明の慣性センサの一例としてジャイロセンサを例に挙げて説明する。
図1は、本実施形態のジャイロセンサ装置の構成を示した図であり、(a)はその上面図、(b)は側面図である。
この図1に示すジャイロセンサ装置1は、その内部にジャイロセンサ10の角速度検出軸G(検出軸G)が当該ジャイロセンサ装置1の上面の垂線Vに対して角度θだけ傾いた状態で、例えば樹脂などのモールド材からなる樹脂部2により封止されている。樹脂部2の長手方向両側からは、それぞれ複数本のリード端子3が外部に引き出されている。
尚、ジャイロセンサ装置1の上面とジャイロセンサ装置1の搭載側の面とは平行である。リード端子3は、樹脂部2内においてジャイロセンサ10と電気的に接続されている。この場合、樹脂部2の底面側に近い位置から露出しているリード端子3は、樹脂部2の底面に電極端子8を形成するためにリード端子3を屈折部4a、4bで内側に折り曲げるようにしている。一方、樹脂部2の底面側より離れた位置から露出しているリード端子3も、樹脂部2の底面に電極端子8を形成するためにリード端子3を折り曲げるようにしているが、樹脂部2から露出しているリード端子3のリード部分が長くなるため、屈折部4c、4d、4eで内側に折り曲げるようにしている。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described.
In this embodiment, a gyro sensor will be described as an example of the inertial sensor of the present invention.
1A and 1B are diagrams showing the configuration of the gyro sensor device of the present embodiment, in which FIG. 1A is a top view and FIG. 1B is a side view.
The
The upper surface of the
図2は、上記した本実施形態のジャイロセンサ装置の実装例を示した図である。この図2(a)に示すように本実施形態のジャイロセンサ装置1のリード端子3を実装基板51上のパターン電極52に半田53により接続すれば、その検出軸Gを実装基板51の搭載面の垂線(鉛直方向V)に対して角度θだけ傾けた状態で実装することができる。
また、本実施形態のジャイロセンサ装置1において、底面より離れた位置から露出しているリード端子3に屈折部4c、4d、4eを設けたのは以下の理由による。
例えば、図2(b)に示すように、リード部分が長いリード端子3の屈折部4c、4dの間に屈折部4eを設けない場合、リード部分が短いリード端子3に比べて大量の半田53が付着する。そのため、半田53の表面張力のバランス差が左右で大きくなり、リード部分が短いリード端子3が実装面51から浮いてしまうおそれがある。つまり、ジャイロセンサ装置1が傾斜して取り付けられてしまうので傾斜角度に狂いが生じるおそれがある。
そこで、本実施形態のジャイロセンサ装置1では、リード部分が長いリード端子3の半田上がり量を制限するために、このリード端子3の3カ所に屈折部4c、4d、4eを形成した。このように構成すれば、リード部分が長いリード端子3の半田上がり量を制限できるので、実装基板51に取り付けられるジャイロセンサ装置1の傾斜角度に狂いが生じるのを防止することができる。
特に、リード部分が長いリード端子3の高さとリード端子3の屈折部4aの高さ位置が等しくなるように構成すると、左右のリード端子3の半田上がり量を等しくできるのでより好ましいものとなる。
更に、例え、長いリード端子3の屈折部4dより上側に半田上がりが起きたとしても、この部分のリード端子3の面とパターン電極52とは全く対面していないので、この場合は、ジャイロセンサ装置1を傾かせるような表面張力は発生しない。
尚、ジャイロセンサ装置1は、その上面とジャイロセンサ装置1の搭載側の面とが平行であるので、部品搭載装置を使ってジャイロセンサ装置1の上面を吸着した後、実装基板51に対して垂直方向にジャイロセンサ装置1を移動させて搭載することができる。
これによれば、ジャイロセンサ装置1は、実装基板51への搭載時に複数のリード端子3に等しい力をかけた状態、又は樹脂部2の底面に均等な力をかけた状態で実装基板51に押さえつけられる。従って、実装基板51の搭載面とジャイロセンサ装置1の上面との平行度は高く保もたれる。即ち、実装基板51に取り付けられるジャイロセンサ装置1は、その検出軸Gと実装基板51の搭載面の垂線との角度θに狂いが生じることなく実装基板51に搭載される。
また、本実施形態のジャイロセンサ10は、ジャイロセンサ10の短手方向を傾斜させることによりZ軸と鉛直方向とのなす角がθとなるように構成している。このように構成すると、ジャイロセンサ10を組み込んでジャイロセンサ装置1を構成したときに装置の低背化を実現することができる。
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing an implementation example of the gyro sensor device of the present embodiment described above. As shown in FIG. 2A, if the
In the
For example, as shown in FIG. 2B, when the refracting portion 4 e is not provided between the refracting
Therefore, in the
In particular, it is more preferable to configure the
Furthermore, even if the solder rises above the refracting
Since the upper surface of the
According to this, the
Further, the
次に、本実施形態のジャイロセンサ装置におけるリード端子とジャイロセンサとの接合方法について説明する。
図3(a)は、本実施形態のジャイロセンサ装置1において使用するリード端子ユニットの構造を示した図、図3(b)はリード端子ユニットにジャイロセンサを接合した状態を示した上面図、図3(c)はリード端子ユニットにジャイロセンサを接合した状態を示した裏面図、図3(d)はリード端子にジャイロセンサを接合する際の不具合を示した図である。
この図3(a)に示すように、本実施形態のジャイロセンサ装置1において使用するリード端子ユニット61は、複数本のリード端子3と共にダイパッド5を備えている。そして、本実施形態では、ジャイロセンサ10とリード端子3とを接続する際に、リード端子が撓むのを防止するために、リード端子3間、及び縁部63との間を吊りリード62により接続するようにしている。
リード端子ユニット61の上面にあるダイパッド5とジャイロセンサ10とは、例えば接着剤を介して機械的に接続されている。なお、接着剤として導電性接着剤を用いて、さらに電気的に接続しても良い。またリード端子ユニット61の各リード端子3は、ジャイロセンサ10の底面にある電極端子8とボンディングワイヤ、或いは導電性接着剤により電気的に接続されている。
Next, a method for joining the lead terminal and the gyro sensor in the gyro sensor device of the present embodiment will be described.
3A is a view showing the structure of a lead terminal unit used in the
As shown in FIG. 3A, the lead
The
ここで、例えばリード端子3の吊りリード62が無い場合、図3(d)に示すように、リード端子ユニット61にジャイロセンサ10を搭載したときに、リード端子3が撓んでダイパッド5を軸にして回転してしまうことがある。その結果、高い精度でジャイロセンサ10をリード端子3に搭載することができず、ジャイロセンサ10の傾斜角度に狂いが生じるおそれがある。これに対して、本実施形態のジャイロセンサ装置1では、リード端子3を吊りリード62により固定したことで、リード端子3の撓みが抑制され、ジャイロセンサ10の回転を抑制することができる。
これにより、本実施形態のジャイロセンサ装置1の傾斜角度の精度を高めることができる。なお、図3(a)に示すリード端子ユニット61にはリード端子3の先端側を固定した3本の吊りリード62が存在するが、リード端子3の先端側を固定する為の吊りリード62は、ダイパッド5を境にして対角位置に少なくとも2カ所設けるようにすれば良い。そうすれば、ジャイロセンサ10の対角方向の回転も抑えることができる。なお、吊りリード62は樹脂部2の形成後に切断される。
Here, for example, when there is no
Thereby, the precision of the inclination angle of the
次に、第1の実施形態にかかるジャイロセンサ装置の製造方法について説明する。
図4は、ジャイロセンサ装置の製造工程を説明するフローチャート図である。
まず、ステップS1において、リード端子3を構成するダイパッド5またはジャイロセンサ10に接着剤(非導電性接着剤、エポキシ系接着剤)を塗布した後、ダイパッド5にジャイロセンサ10を載せて接着する。
次に、ステップS2において、ワイヤボンディング法によって、リード端子3とジャイロセンサ10の底面にある電極端子8との間にワイヤを形成してボンディング配線を行なう。
次に、ステップS3では、ジャイロセンサ10を樹脂によってモールドするモールド形成を行なう。モールド形成は、キャビティが形成された上金型および下金型に、キャビティ内にジャイロセンサ10が収容されるようにリード端子3を挟み込み、キャビティ内に樹脂を充填してモールドする所謂トランスファモールド法により行なう。この時、モールドの外に出ているリードは、伸びた状態である。また、リード端子3は、複数のジャイロセンサ10を搭載できるようにパターンが複数形成されている。
この工程では、まず、上金型および下金型を樹脂の特性に合せた所定温度に加熱して保持してから、下金型の位置決めピンを位置基準にするなどの方法により、下金型上にジャイロセンサ10がボンディングされたリード端子3を位置決めして載せる。次に、樹脂タブレットを下金型のプランジャポットに入れ、リード端子3を下金型との間に挟み込むように上金型を重ね、所定の圧力を掛けて均一に型締めする。このとき、上金型および下金型の各キャビティ内にジャイロセンサ10が収容された状態となる。
次に、プランジャポット内の樹脂タブレットを所定温度にプレヒートして樹脂を溶融させ、プランジャを所定の位相・速度・温度にて稼動させて溶融樹脂を上金型および下金型のゲートからキャビティ内に注入する。キャビティ内に樹脂が充填された後、一定時間保持して樹脂を成形する。樹脂成形後、型締めを開放して上金型を外してから、キャビティ周辺に樹脂がはみ出すことによって生じる樹脂の残カルの除去を行ない、下金型からモールド樹脂成形されたリード端子3を取り出し、所定温度のオーブン内にて所定時間乾燥させる。
Next, a method for manufacturing the gyro sensor device according to the first embodiment will be described.
FIG. 4 is a flowchart for explaining the manufacturing process of the gyro sensor device.
First, in step S <b> 1, an adhesive (non-conductive adhesive, epoxy adhesive) is applied to the
Next, in step S2, a wire is formed between the
Next, in step S3, mold formation for molding the
In this process, first, the upper die and the lower die are heated and held at a predetermined temperature that matches the characteristics of the resin, and then the lower die is positioned by using the positioning pin of the lower die as a position reference. The
Next, the resin tablet in the plunger pot is preheated to a predetermined temperature to melt the resin, and the plunger is operated at a predetermined phase / speed / temperature to move the molten resin from the gates of the upper mold and the lower mold into the cavity. Inject. After the cavity is filled with the resin, the resin is molded by holding for a certain period of time. After the resin molding, the mold clamping is released and the upper mold is removed, and then the residual resin generated by the resin protruding around the cavity is removed, and the
次に、ステップS4において、プレスなどにより、リード端子3のリード端子の端および各リード間の吊りリードを切断して個片にする。次に、ステップS5において、モールドから露出しているリード端子に、Sn(錫)や半田などの接合金属をめっきする端子めっきを行なう。そして、屈折部4a、4cより樹脂部2との間を固定して、屈折部4a、4cを所定の形状に折り曲げる。次に、屈折部4b、4dと樹脂部2との間を固定して、屈折部4b、4dを折り曲げ、ジャイロセンサ装置1を得る(ステップS6)。
なお、端子めっきは、リード切断する前に行なってもよく、また、リード切断した後にリード曲げした後に行なってもよい。
最後に、特性検査や外観検査などの必要な検査を実施し(ステップS7)、本実施形態のジャイロセンサ装置1の製造工程を終了する。
このように構成すれば、ジャイロセンサ10の検出軸と樹脂部2の上面とを所望の角度に設定した本実施形態のジャイロセンサ装置1を高い生産性で製造する製造方法を提供することができる。
Next, in step S4, the ends of the lead terminals of the
The terminal plating may be performed before cutting the lead, or may be performed after bending the lead after cutting the lead.
Finally, necessary inspections such as characteristic inspection and appearance inspection are performed (step S7), and the manufacturing process of the
If comprised in this way, the manufacturing method which manufactures the
次に、上記したジャイロセンサ装置1の製造方法において、モールド形成に用いるモールド金型について図面に沿って説明する。
図13は、モールド金型を構成する上金型と下金型のうちの下金型110Aを説明する平面図であり、図14は、モールド金型110の全体構成を説明するための、下金型110Aにリードフレーム3をはさんで上金型110Bを取り付けた状態での図13のa−a線断面図である。
モールド金型110は、上金型110Bと下金型110Aとで構成されている。ここでは、まず、モールド金型110の樹脂注入経路等の構成をわかりやすく説明するために、図13に従って下金型110Aの構成を説明する。
下金型110Aは、金属等による下金型本体120に複数の凹部(キャビティ)が形成され、それら複数の凹部が、同じく凹部である連結通路(ゲートなど)によりそれぞれ連通して直列に接続された構成を有している。
Next, in the manufacturing method of the
FIG. 13 is a plan view for explaining a
The
In the
下金型110Aには、下金型本体120に形成された円筒形の凹部内に図示しないプランジャが設置されたプランジャポット115が設けられている。プランジャポット115の側壁の一部は開放されており、そこから連絡通路として延びる溝状のランナ116Aが、直方立方形の凹部である一つめのキャビティ111Aと接続されている。一つめのキャビティ111Aのプランジャポット115との接続部分の反対側には、二つめのキャビティ112が配設され、両者の間は溝状のゲート113Aで連通して接続されている。さらに、二つめのキャビティ112の一つめのキャビティ111Aとの接続部分の反対側にはゲート114が延びており、このゲート114が同様にして次のキャビティと連通して接続されるが図示を省略している。以上述べたように、プランジャポット115と各キャビティ111A、112および必要数の次のキャビティが、それぞれランナ116Aとゲート113A、114および必要数の次のゲートを介して直列に連通して接続されている。
なお、図中に二点鎖線で示す直方形の領域は、樹脂封止する際のリードフレーム載置位置3aを示している。
一方、上金型110Bには、上記した下金型110Aと重ねられる面の同じ位置に同一形状の開口部を有したプランジャポットと複数のキャビティ、およびこれらを連通するランナと複数のゲートとが形成されている。この上金型110Bと下金型110Aと重ね合わせて固定することにより、容器状の空間であるプランジャポット115及び複数のキャビティと、それらを連通させて直列に結んで樹脂の連絡路となるランナ及び複数のゲートとが、それぞれ形成されるようになっている。
The
In addition, the rectangular area shown with a dashed-two dotted line in the figure has shown the lead frame mounting position 3a at the time of resin sealing.
On the other hand, the
次に、図13に従って、センサデバイスとしてジャイロセンサ10が搭載されたリードフレーム3をモールドするときの状態における、上金型110Bと下金型110Aにより形成されるモールド金型110について、特にキャビティの断面形状を中心に詳細に説明する。
図6に示すように、下金型110Aの下金型本体120に形成された凹部であるキャビティ111Aの凹底部分161Aは、下金型110Aにリードフレーム3を搭載したときのリードフレーム3との平行線170に対して角度θだけ傾けて形成されている。この凹底部分161Aにより、ジャイロセンサ装置1の底面が形成される。したがって、この下金型110Aによってモールド形成して得られるジャイロセンサ装置1の法線と、ジャイロセンサ10の検出軸Gとの関係が所望の角度θに設定されたジャイロセンサ装置1を形成されるようになっている。
同様に、図14に示す上金型110Bの上金型本体130に形成された凹部であるキャビティ111Bの凹底部分161Bは、リードフレーム3が搭載された下金型110A上に重ねて固定したときのリードフレーム3との平行線270に対して角度θだけ傾けて形成されている。この凹底部分161Bにより、ジャイロセンサ装置1の上面が形成される。したがって、この下金型110Aによってモールド形成して得られるジャイロセンサ装置1の上面の法線と、ジャイロセンサ10の検出軸Gとの関係が所望の角度θに設定されたジャイロセンサ装置1を形成されるようになっている。
Next, referring to FIG. 13, the
As shown in FIG. 6, the
Similarly, the
ジャイロセンサ10が搭載されたリードフレーム3を、下金型110Aと上金型110Bとに挟んで固定(型締め)したとき、下金型110Aのキャビティ111Aと上金型110Bのキャビティ111Bとにより、センサデバイス10をモールドするためのひとつのキャビティが形成される。
また、下金型110Aのランナ116Aと上金型110Bのランナ116Bにより、図示しないプランジャポットから前記のひとつのキャビティに溶融樹脂を充填するときの樹脂の注入路となるひとつのランナが構成される。
さらに、下金型110Aのゲート113Aと上金型110Bのゲート113Bにより形成されるひとつのゲートが、前記のひとつのキャビティから次のキャビティに向けての樹脂の注入路となる。
When the
Further, the
Further, one gate formed by the
なお、本実施形態では、上金型110Bのランナ116Bとゲート113Bが、下金型110Aのランナ116Aとゲート113Aよりも厚み方向に大きく形成されている。これにより、各キャビティに溶融樹脂を充填するときに、上金型110B側の方が樹脂の流れが強めとなる。これは、溶融樹脂注入時に、ボンディングワイヤおよび金ボールによるジャイロセンサ10のボンディング部に樹脂が強く当たるのを回避するためである。これに限らず、ランナおよびゲートを、ジャイロセンサ10のボンディング部を避けて上金型110B側だけに設ける構成としてもよい。
なお、各キャビティ111A、111Bの側壁部分は、リードフレーム3との接触面に対して垂直もしくは垂直よりも鋭角となる角度に傾けて形成されている。
In the present embodiment, the
The side walls of the cavities 111 </ b> A and 111 </ b> B are formed so as to be inclined with respect to the contact surface with the
このように本実施形態のジャイロセンサ装置の1の製造方法においては、下金型110Aの下金型本体120には、下金型110Aにリードフレーム3を搭載したときのリードフレーム3との平行線170に対して角度θだけ傾けて形成された凹底部分161Aを有する凹部であるキャビティ111Aを形成した。また、上金型110Bの上金型本体130には、リードフレーム3が搭載された下金型110A上に重ねて固定したときのリードフレーム3との平行線270に対して角度θだけ傾けて形成された凹部であるキャビティ111Bを形成した。そして、下金型110Aと上金型110Bの各キャビティ111A、111Bにジャイロセンサ10を収容させるようにリードフレーム3を挟んで固定し、溶融させたモールド用の樹脂をキャビティ111A、111Bに充填して成形することにより、ジャイロセンサ装置1を形成する構成とした。
Thus, in the manufacturing method of the
この構成によれば、下金型110Aの凹底部分161Aにより形成される底面と、上金型110Bの凹底部分161Bにより形成される上面とを有するモールドパッケージ91を製造することができる。これにより、所定の検出軸Gに対する動作に応答するセンサと、このセンサを収容したジャイロセンサ10と、このジャイロセンサ10の端子と実装基板との導通をするリードと、ジャイロセンサ10を固定するモールドとを有し、センサの検出軸Gとジャイロセンサ装置の底面とを所望の角度に設定するジャイロセンサ装置を提供することができる。
また、ジャイロセンサの検出軸Gとジャイロセンサ装置の底面および上面とを所望の角度に設定するジャイロセンサ装置の底面と上面を平行にして製造することができる。これにより、ジャイロセンサ装置を実装基板などに実装するときに、例えばマウンタにより通常のチップ型電子部品と同様にピックアップできる。また、ジャイロセンサ装置を梱包するためのトレイやフープ状梱包材(テーピング)を特殊な形状にする必要がなく、従来の部品トレイやフープ状梱包材を用いることができる。したがって、高い生産性で実装することが可能なジャイロセンサ装置を製造することができる。
According to this configuration, it is possible to manufacture a mold package 91 having a bottom surface formed by the
Further, it is possible to manufacture the gyro sensor device in which the detection axis G of the gyro sensor and the bottom surface and top surface of the gyro sensor device are set at desired angles so that the bottom surface and top surface of the gyro sensor device are parallel to each other. Thus, when the gyro sensor device is mounted on a mounting board or the like, it can be picked up by a mounter in the same manner as a normal chip type electronic component. Moreover, it is not necessary to make a tray or a hoop-shaped packing material (taping) for packing the gyro sensor device into a special shape, and a conventional component tray or a hoop-shaped packing material can be used. Therefore, a gyro sensor device that can be mounted with high productivity can be manufactured.
また本実施形態では、上金型110Bのランナ116Bとゲート113Bを、下金型110Aのランナ116Aとゲート113Aよりも厚み方向に大きく形成した。
この構成によれば、各キャビティに溶融樹脂を充填するときに、上金型110B側の方が樹脂の流れが強めとなるので、下金型110A側に配置されるジャイロセンサ10のボンディングワイヤおよび金ボールによるボンディング部への樹脂によるストレスを軽減することができる。これにより、ボンディングワイヤの切断やボンディング部のオープン不良の発生を抑えることができる。
In this embodiment, the
According to this configuration, since the resin flow is stronger on the
さらに本実施形態では、下金型110Aおよび上金型110Bの各キャビティ111A、111Bの側壁部分を、リードフレーム3との接触面に対して垂直もしくは垂直よりも鋭角となる角度に傾けて形成する構成とした。これにより、モールド形成後に下金型110Aおよび上金型110Bを取り外すときの抜け性がよくなり、作業性を向上することができる。
Furthermore, in the present embodiment, the side walls of the
図5は、第2の実施形態に係るジャイロセンサ装置の構成を示した図である。
この図5に示すジャイロセンサ装置20も、その内部にジャイロセンサ10の検出軸Gが当該ジャイロセンサ装置を搭載する搭載面の鉛直方向Vに対して角度θだけ傾いた状態で樹脂部2により封止されている。
この場合も樹脂部2の長手方向両側からそれぞれ複数本のリード端子3が外部に引き出されているが、このリード端子3は樹脂部2内の屈折部6eと屈折部6fと屈折部6gで折り曲げられることで、ジャイロセンサ10が当該ジャイロセンサ装置1の上面に対して角度θだけ傾斜されている。このように構成した場合は、屈折部6aと屈折部6bの間の長さは、屈折部6cと屈折部6dの間の長さとほぼ等しくできる。よって、実装基板51に取り付けたときにジャイロセンサ装置1の傾斜角度に狂いが生じるのを防止することができる。
FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of the gyro sensor device according to the second embodiment.
The
In this case as well, a plurality of
次に、第2の実施形態に係るジャイロセンサ装置の製造方法を簡単に説明しておく。
この場合は、先ず、リード端子3の屈折部6e及び6gが凸に、屈折部6fが凹になるようプレスする。次に、リード端子3のダイパッド5またはジャイロセンサ10に接着材53(非導電性接着剤、エポキシ系接着剤)を塗布した後、ダイパッド5にジャイロセンサ10を載せて接着する。
次に、ワイヤボンディング法によって、例えば、リード端子3に金ボール9bを載せ、金ボール9bを始点とし、ジャイロセンサ10の底面にある電極端子8を終点としたワイヤ9aを形成する。なお、電極端子8に金ボール9bを載せて始点と終点とを入れ替えても良い。ワイヤボンディングに際しては、図6に示される治具80を用いる。治具80は、リード端子3に対応するように、複数の各ジャイロセンサ10の上面をはめ込める形状を有する。ここで、治具の底面81とリード端子3の全体とは角度θを成す。そのため、ジャイロセンサ10をはめた場合、ジャイロセンサ10の底面と治具底面81とが平行になる。ワイヤボンディングの際、治具底面81を下向きに略水平に置くことで、ジャイロセンサ10の底面が略水平になり、ワイヤボンディングが正確に行われる。
次に、ジャイロセンサ10を樹脂によってモールドする。この時、モールドの外に出ているリードは、伸びた状態である。次に、リード端子3の端6h、6iおよび各リード端子3間の吊りリードを切断する。次に、リード屈折部6b、6dより樹脂部2側の箇所を固定して、リード屈折部6b、6dを折り曲げる。次に、リード屈折部6a、6cと樹脂部2との間を固定して、リード屈折部6a、6cを折り曲げる。
このように構成すれば、ジャイロセンサの検出軸Gと樹脂部2の上面とを所望の角度(ジャイロセンサ装置を搭載する搭載面の鉛直方向Vとの角度θ)に設定したジャイロセンサ装置20を高い生産性で製造する製造方法を提供することができる。尚、ジャイロセンサ装置20の上面とジャイロセンサ装置20が搭載される面とは平行である。
Next, a method for manufacturing the gyro sensor device according to the second embodiment will be briefly described.
In this case, first, the
Next, by a wire bonding method, for example, a
Next, the
If comprised in this way, the
図7は、第3の実施形態に係るジャイロセンサ装置の構成を示した図である。
この図7に示すジャイロセンサ装置30も、その内部にジャイロセンサ10が当該ジャイロセンサ装置30を搭載する搭載面の鉛直方向Vに対して角度θだけ傾いた状態で樹脂部2により封止されている。
この場合も樹脂部2の長手方向両側からそれぞれ複数本のリード端子3が外部に引き出されているが、このリード端子3は樹脂部2内の屈折部7e〜7lにより長手方向両側のリード端子3が階段状に折り曲げられることで、ジャイロセンサ10が当該ジャイロセンサ装置30の上面に対して角度θだけ傾斜するように配置されている。このように構成した場合は、屈折部7aと屈折部7bの間の長さは、屈折部7cと屈折部7dの間の長さとほぼ等しくできる。よって、実装基板51に取り付けたときにジャイロセンサ装置1の傾斜角度に狂いが生じるのを防止することができる。
また、ジャイロセンサ10をリード端子3の上段側の段部上に並行に配置することで、ジャイロセンサ10当該ジャイロセンサ装置30の上面に対して平行に配置することができる。つまり、ジャイロセンサ10を配置する段部位置を変更するだけでジャイロセンサ10の検出軸Gが鉛直方向Vのものと検出軸Gから所望の角度θだけ傾斜したものを作製することができる。
FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating the configuration of the gyro sensor device according to the third embodiment.
The
Also in this case, a plurality of
Further, by arranging the
次に、第3の実施形態に係るジャイロセンサの製造方法について述べる。
この場合、リード端子3の屈折部7e、7g、7j、7lを凸に、屈折部7f、7h、7i、7kを凹にするようにプレスする。なお、リード端子3は図示しないが、上下左右の方向に複数連結されており、複数のジャイロセンサ10の底をはめ込める形状を有する。
ジャイロセンサ10の底面にある電極端子8またはリード端子の屈折部7g近傍、47i近傍に半田クリームを塗布し、その半田クリームを融点以上の温度に加熱した後、常温に戻すことで、電極端子8とリードとを機械的および電気的に接続する。
次に、ジャイロセンサ10を樹脂によってモールドする。この時、モールドの外に出ているリードは伸びた状態である。次に、リード端子3の先端部および各吊りリード間を切断する。この後、屈折部7b、7dより樹脂部2側の箇所を固定して、屈折部7b、7dを折り曲げる。この後、屈折部7a、7cと樹脂部2との間を固定して屈折部7a、7cを折り曲げる。このように構成すれば、上記したようなジャイロセンサ装置30を高い生産性で製造する製造方法を提供することができる。
Next, a gyro sensor manufacturing method according to the third embodiment will be described.
In this case, pressing is performed so that the refracting portions 7e, 7g, 7j, and 7l of the
Solder cream is applied to the
Next, the
次に、本実施形態のジャイロセンサ装置に搭載されるジャイロセンサ10について説明する。
図8はジャイロセンサ10の内部構成を示した断面図、図9はジャイロセンサ10に設けられている支持基板の構成を示した図である。
この図8に示すように、ジャイロセンサ10は、角速度を検出する検出素子として水晶振動素子11を有する。水晶振動素子11は、図9(a)(b)に示すように、可撓性を有する支持部材であるワイヤ13によって支持基板12に機械的、電気的に接続されている。支持基板12は、接着剤14によってセラミックパッケージ17の内部底面に接続されている。また支持基板12の中央には開口部12aが形成されており、この開口部12aを介して支持基板12の裏面側から上面側にワイヤ13が配置されている。またセラミックパッケージ17の上面には、金属からなる蓋体16が低融点金属等の封止部材19によって接合されている。これにより、セラミックパッケージ17の内部を真空封止するようにしている。なお、蓋体16としてガラス蓋を用いることも可能であり、この場合は封止部材19として低融点ガラス等が用いられる。セラミックパッケージ17の外部底面から側面にかけて電極端子8が形成されている。電極端子8は、セラミックパッケージ17に形成されている図示しない内部導体を介して水晶振動素子11に接続されている。
尚、図8に示す6本のワイヤ13のうち水晶振動素子11を主に支える支持部材としてのワイヤ13は少なくともそれぞれ中央に並ぶ2本のワイヤ13である。
Next, the
FIG. 8 is a cross-sectional view showing the internal configuration of the
As shown in FIG. 8, the
Of the six
図10(a)は、本実施形態の水晶振動素子11を概略的に示す平面図、図10(b)は、水晶振動素子11の検出振動モードの振動を示す平面図である。
この図10に示す水晶振動素子11は、基部31と、基部31から突出する一対の検出振動片32a、32b、基部31から突出する一対の接続部33と、各接続部33の先端に設けられている各駆動振動片34a、34b、34c、34dとを備えている。各駆動振動片34a、34b、34c、34dの各主面には、それぞれ細長い溝が形成されており、各駆動振動片34a、34b、34c、34dの横断面形状は略H字形状となっている。また、溝内に励振電極(駆動電極、以下同じ)36が形成されている。各駆動振動片34a、34b、34c、34dの各先端にはそれぞれ幅広部または重量部38a、38b、38c、38dが設けられている。各検出振動片32a、32bの各主面には、それぞれ細長い溝が形成されており、各検出振動片32a、32bの横断面形状は略H字形状となっている。また、溝内に検出電極37が形成されている。各検出振動片32a、32bの各先端にはそれぞれ幅広部または重量部35a、35bが設けられている。
図10(a)は駆動モードの振動を示す。駆動時には、各駆動振動片34a、34b、34c、34dが、それぞれ、接続部33への付け根39を中心として矢印Aのように屈曲振動する。この状態で水晶振動素子11を、水晶振動素子11に略垂直な回転軸Gの周りに角速度ωで回転させる。すると、図10(b)に示すように、重量部38a、38b、38c、38dに、屈曲振動の方向Aおよび回転軸Gの両方に垂直な方向である方向にコリオリ力Fが加わる。その結果、接続部33が基部31への付け根33aを中心として、矢印Bのように屈曲振動する。各検出振動片32a、32bが、それぞれ、その反作用によって、基部31の付け根40を中心として、矢印Cのように屈曲振動する。矢印Cの屈曲振動によって圧電現象が生じ、検出電極37の電位が変化する。この電位の変化を図示しない検出回路によって検出することで、検出軸(回転軸)G回りの角速度ωを求める。ここで、水晶振動素子11の+X軸/−X軸の結晶軸方向を矢印Aの方向となるようにし、水晶振動素子11のZ軸の結晶軸方向を回転軸Gと揃えると検出効率が高い。
また、このような構成の水晶振動素子11からなる検出素子は、回転軸Gの方向が水晶振動素子11の厚み方向であるので、回転軸が検出振動片の延長方向と一致する音叉振動子と比較してジャイロセンサ10を低背に構成することができる。
FIG. 10A is a plan view schematically showing the
The
FIG. 10A shows vibration in the drive mode. At the time of driving, each of the
In addition, since the direction of the rotation axis G is the thickness direction of the
ここで、図8に示すように、ジャイロセンサ10に搭載される支持部材であるワイヤ13の延長方向をX軸、このX軸に対して水晶振動素子11の搭載面内において直交する軸をY軸、X軸とY軸とに直交する軸をZ軸とし、図11(a)(b)に示すように、ジャイロセンサ10の傾斜方向をX軸方向と一致させたとする。この場合、図11(a)(b)に示すワイヤ13aの共振周波数とワイヤ13bの共振周波数との間に周波数差が発生し、ジャイロセンサ10の動作状態が不安定になるおそれがあった。
即ち、図11(b)に示すようにワイヤ13a側を高く、ワイヤ13b側を低くして検出軸Gに角度θの傾斜を持たせた場合は重力加速度のX軸成分の方向に対するワイヤ13aの延長方向と、ワイヤ13bの延長方向とが逆向きの関係になる。その為、ワイヤ13a、13bが受ける加速度の影響(慣性力の方向)が異なる。例えば、図11(c)に示すように水晶振動素子11の共振周波数をfref、水晶振動素子11の水平時におけるワイヤ13a、13bの共振周波数をf0とした場合、傾斜状態では重力加速度のX軸成分の影響によりワイヤ13aには伸張力が発生し、一方、ワイヤ13bには圧縮力が発生するのでワイヤ13aの共振周波数faは高くなり、ワイヤ13bの共振周波数fbは低くなる。従って、ワイヤ13aと13bの共振周波数が大きく異なる場合がある。ワイヤ13a、13bの共振周波数が大きく異なる場合は、水晶振動素子11の共振周波数に近づき、共振エネルギーの結合が起きる可能性があると共に、水晶振動素子11の搭載状態も不安定となり易い。
そこで、本実施の形態では、図12(a)(b)に示すようにジャイロセンサ10(水晶振動素子11)の傾斜方向がY軸方向となる向きでジャイロセンサ10をジャイロセンサ装置1に搭載するようにした。即ち、ワイヤ13aとワイヤ13bとを傾斜方向を中心軸として対称的に配置した構成すると、Y軸方向に加速度が加わった場合でも、ワイヤ13a、13bに対しては、同じように加速度が影響するので、図12(c)に示すようにワイヤ13a、13bの共振周波数に周波数差が発生しにくくなる。よって、例えば、周波数調整等の管理がし易いという利点がある。また、ワイヤ13a、13bの延長方向と加速度方向(Y軸方向)が一致しないので、ワイヤ13が受ける加速度の影響が小さい。従って、図12(c)に示すようにワイヤ13a、13bの共振周波数の変動量が小さくでき、共振エネルギーの結合が起き難いという利点がある。
さらに、図12(a)に示すようにワイヤ13aとワイヤ13bとを傾斜方向を中心軸として対称的に配置し、且つ、ワイヤ13aの延長方向とワイヤ13bの延長方向とが傾斜方向に対して直交した構成の場合、水平時はY軸方向の加速度の向きが逆向き(G)であっても、ワイヤ13a、13bの共振周波数の変化特性はほぼ同じになるので、例えば本実施形態のジャイロセンサを水平状態で搭載することも可能になる。
尚、このような構成のジャイロセンサ10を備えたジャイロセンサ装置では、車両にY軸方向と車両の加速度方向とが一致するように組み込まれるので、車両の進行方向の加速度に対してもワイヤ13aと13bの共振周波数の変化特性が与えるジャイロセンサ装置への悪影響を抑えることができる。
また、支持部材13は水晶振動素子11の基部31と一体化した水晶からなるリード状のものであっても良い。
Here, as shown in FIG. 8, the extending direction of the
That is, as shown in FIG. 11B, when the
Therefore, in this embodiment, as shown in FIGS. 12A and 12B, the
Further, as shown in FIG. 12 (a), the
In the gyro sensor device including the
The
1、20、30…ジャイロセンサ装置、2…樹脂部、3…リードフレーム(リード端子)、5…ダイパッド、10…ジャイロセンサ(センサデバイス)、11…水晶振動素子、12…支持基板、13a、13b…ワイヤ、14…接着剤、16…蓋体、17…セラミックパッケージ。
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (7)
前記検出素子の略中央を支持する可撓性を有する複数の支持部材と、
前記検出素子を収納するパッケージ用基板と、を備え、
前記複数の支持部材の延長方向をX軸、前記検出素子の平面内において直交する軸をY軸、前記X軸と前記Y軸とに直交する軸をZ軸としたときに、
前記支持部材に加わる前記検出素子のY軸方向の荷重成分が前記複数の支持部材において略同一であり、且つ、前記Z軸方向の荷重成分が前記複数の支持部材間において略同一であることを特徴とする慣性センサ。 A detection element for detecting the magnitude of the physical quantity in the detection axis direction;
A plurality of flexible support members that support substantially the center of the detection element;
A package substrate for housing the detection element,
When the extending direction of the plurality of support members is the X axis, the axis orthogonal to the plane of the detection element is the Y axis, and the axis orthogonal to the X axis and the Y axis is the Z axis,
The load component in the Y-axis direction of the detection element applied to the support member is substantially the same in the plurality of support members, and the load component in the Z-axis direction is substantially the same between the plurality of support members. Features inertial sensors.
前記Y軸方向の荷重成分と前記Z軸方向の荷重成分とを合成した荷重成分が少なくとも重力加速度に基づく荷重成分であることを特徴とする請求項1に記載の慣性センサ。 The detection element has a detection axis for detecting an angular velocity in the Z-axis direction, and an angle between the Z-axis and the vertical direction is θ,
The inertial sensor according to claim 1, wherein a load component obtained by combining the load component in the Y-axis direction and the load component in the Z-axis direction is a load component based on at least gravitational acceleration.
該慣性センサと電気的に接続される複数リード端子と、
前記慣性センサを収納するモールドパッケージと、を備えたことを特徴とする慣性センサ装置。 An inertial sensor according to claims 1 to 3,
A plurality of lead terminals electrically connected to the inertial sensor;
An inertial sensor device comprising: a mold package for housing the inertial sensor.
前記リードフレームに前記センサデバイスを接合した後に、凹部がそれぞれ形成された下金型および上金型を、前記凹部形成面どうしを前記リードフレームを挟んで重ねることにより画定されるキャビティ内に前記センサデバイスを収容し、前記キャビティに樹脂を充填して成形するモールド方法において、前記リードフレームと対面する前記キャビティの上下面が、前記リードフレームの両主面に対してそれぞれ傾けて形成され、且つ該上下面が平行になるように前記凹部が形成された前記下金型および前記上金型からなるモールド金型を用いることを特徴とする慣性センサ装置の製造方法。 It has a plurality of lead terminals that are electrically connected to the mounting board, the installation angle is determined based on the lead frame constituted by the plurality of lead terminals, and the shape of the lead frame, and responds to the operation with respect to the detection axis A method of manufacturing an inertial sensor device in which a sensor device including a sensor is molded with resin by a molding method,
After the sensor device is joined to the lead frame, the sensor is placed in a cavity defined by stacking the lower mold and the upper mold each having a recess formed between the recess forming surfaces with the lead frame interposed therebetween. In the molding method of housing a device and filling the cavity with a resin, the upper and lower surfaces of the cavity facing the lead frame are formed to be inclined with respect to both main surfaces of the lead frame, and A method of manufacturing an inertial sensor device, comprising using the lower mold in which the recesses are formed so that the upper and lower surfaces are parallel to each other and the mold mold including the upper mold.
前記キャビティの前記リードフレームと対面する上下面が、前記リードフレームの両主面に対して前記センサデバイスの前記設置角度と同じ角度で傾けて形成された前記モールド金型を用いることを特徴とする慣性センサ装置の製造方法。 In the manufacturing method of the inertial sensor device according to claim 6,
The upper and lower surfaces of the cavity facing the lead frame are tilted at the same angle as the installation angle of the sensor device with respect to both main surfaces of the lead frame. Manufacturing method of inertial sensor device.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009224160A JP2010002427A (en) | 2006-08-09 | 2009-09-29 | Inertial sensor, inertial sensor device and its manufacturing method |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006216505 | 2006-08-09 | ||
| JP2006249404 | 2006-09-14 | ||
| JP2009224160A JP2010002427A (en) | 2006-08-09 | 2009-09-29 | Inertial sensor, inertial sensor device and its manufacturing method |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007119281A Division JP5622347B2 (en) | 2006-08-09 | 2007-04-27 | Inertial sensor device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010002427A true JP2010002427A (en) | 2010-01-07 |
| JP2010002427A5 JP2010002427A5 (en) | 2010-06-17 |
Family
ID=41584253
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009224160A Pending JP2010002427A (en) | 2006-08-09 | 2009-09-29 | Inertial sensor, inertial sensor device and its manufacturing method |
| JP2013096955A Expired - Fee Related JP5686153B2 (en) | 2006-08-09 | 2013-05-02 | Inertial sensor device |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013096955A Expired - Fee Related JP5686153B2 (en) | 2006-08-09 | 2013-05-02 | Inertial sensor device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (2) | JP2010002427A (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008096420A (en) * | 2006-08-09 | 2008-04-24 | Epson Toyocom Corp | Inertial sensor, inertial sensor device, and production method thereof |
| JP2013210375A (en) * | 2006-08-09 | 2013-10-10 | Seiko Epson Corp | Inertial sensor device |
| CN111121762A (en) * | 2018-10-29 | 2020-05-08 | 精工爱普生株式会社 | Sensor unit, electronic apparatus, and moving object |
Citations (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0574999A (en) * | 1991-09-12 | 1993-03-26 | Fujitsu Miyagi Electron:Kk | Semiconductor device and its manufacture |
| JPH09166445A (en) * | 1995-12-15 | 1997-06-24 | Miyota Kk | Angular velocity sensor |
| JPH09236616A (en) * | 1995-11-30 | 1997-09-09 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | Acceleration sensor and its manufacture |
| JPH11317326A (en) * | 1998-03-06 | 1999-11-16 | Rohm Co Ltd | Electronic component |
| JPH11325915A (en) * | 1998-05-18 | 1999-11-26 | Murata Mfg Co Ltd | Angular velocity sensor |
| JP2000337884A (en) * | 1999-03-25 | 2000-12-08 | Murata Mfg Co Ltd | Angular velocity sensor |
| JP2001500611A (en) * | 1996-09-12 | 2001-01-16 | テミツク テレフンケン マイクロエレクトロニツク ゲゼルシヤフト ミツト ベシユレンクテル ハフツング | Acceleration measuring device |
| JP2002280616A (en) * | 2001-03-16 | 2002-09-27 | Nichia Chem Ind Ltd | Package mold and light emitting device using the same |
| JP2003185439A (en) * | 2001-12-20 | 2003-07-03 | Nec Tokin Corp | Piezoelectric vibrating gyro |
| JP2004354169A (en) * | 2003-05-28 | 2004-12-16 | Seiko Epson Corp | Support mechanism of oscillator and oscillator unit |
| JP2004361175A (en) * | 2003-06-03 | 2004-12-24 | Seiko Epson Corp | Element-mounted package |
| JP2006064539A (en) * | 2004-08-26 | 2006-03-09 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | Gyroscope sensor and method for detecting angular speed |
| JP2006105963A (en) * | 2004-09-10 | 2006-04-20 | Ngk Insulators Ltd | Support structure for oscillator, and instrument for measuring physical quantity |
| JP2006284373A (en) * | 2005-03-31 | 2006-10-19 | Seiko Epson Corp | Piezo-electric device |
| JP2008096420A (en) * | 2006-08-09 | 2008-04-24 | Epson Toyocom Corp | Inertial sensor, inertial sensor device, and production method thereof |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR860700076A (en) * | 1984-03-22 | 1986-01-31 | 로버트 씨·워커 | Impedance Matched Leads |
| JPS61160956A (en) * | 1985-01-08 | 1986-07-21 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Semiconductor device |
| JPH0225273Y2 (en) * | 1986-04-30 | 1990-07-11 | ||
| JPH0497558A (en) * | 1990-08-15 | 1992-03-30 | Nec Corp | Semiconductor integrated circuit and its manufacture |
| JPH07320800A (en) * | 1994-05-18 | 1995-12-08 | Star Micronics Co Ltd | Terminal and its manufacture |
| JPH0832007A (en) * | 1994-07-08 | 1996-02-02 | Sumitomo Electric Ind Ltd | Semiconductor device and semiconductor device assembly |
| JPH10253652A (en) * | 1997-03-14 | 1998-09-25 | Denso Corp | Sensor device and its manufacture as well as lead frame used for manufacture of the same |
| JPH10288625A (en) * | 1997-04-15 | 1998-10-27 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Semiconductor acceleration sensor |
| JP2002090384A (en) * | 2000-09-13 | 2002-03-27 | Microstone Corp | Structure of motion sensor and internal connecting method |
| JP2003227844A (en) * | 2002-02-04 | 2003-08-15 | Pioneer Electronic Corp | Sensor device and electronic apparatus for mobile body |
| CN100510631C (en) * | 2002-05-28 | 2009-07-08 | 多摩川精机株式会社 | Angular velocity sensor |
| JP2005249428A (en) * | 2004-03-01 | 2005-09-15 | Ngk Insulators Ltd | Support structure for oscillator, method for manufacturing the same, and package for oscillator |
| JP2010002427A (en) * | 2006-08-09 | 2010-01-07 | Epson Toyocom Corp | Inertial sensor, inertial sensor device and its manufacturing method |
-
2009
- 2009-09-29 JP JP2009224160A patent/JP2010002427A/en active Pending
-
2013
- 2013-05-02 JP JP2013096955A patent/JP5686153B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0574999A (en) * | 1991-09-12 | 1993-03-26 | Fujitsu Miyagi Electron:Kk | Semiconductor device and its manufacture |
| JPH09236616A (en) * | 1995-11-30 | 1997-09-09 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | Acceleration sensor and its manufacture |
| JPH09166445A (en) * | 1995-12-15 | 1997-06-24 | Miyota Kk | Angular velocity sensor |
| JP2001500611A (en) * | 1996-09-12 | 2001-01-16 | テミツク テレフンケン マイクロエレクトロニツク ゲゼルシヤフト ミツト ベシユレンクテル ハフツング | Acceleration measuring device |
| JPH11317326A (en) * | 1998-03-06 | 1999-11-16 | Rohm Co Ltd | Electronic component |
| JPH11325915A (en) * | 1998-05-18 | 1999-11-26 | Murata Mfg Co Ltd | Angular velocity sensor |
| JP2000337884A (en) * | 1999-03-25 | 2000-12-08 | Murata Mfg Co Ltd | Angular velocity sensor |
| JP2002280616A (en) * | 2001-03-16 | 2002-09-27 | Nichia Chem Ind Ltd | Package mold and light emitting device using the same |
| JP2003185439A (en) * | 2001-12-20 | 2003-07-03 | Nec Tokin Corp | Piezoelectric vibrating gyro |
| JP2004354169A (en) * | 2003-05-28 | 2004-12-16 | Seiko Epson Corp | Support mechanism of oscillator and oscillator unit |
| JP2004361175A (en) * | 2003-06-03 | 2004-12-24 | Seiko Epson Corp | Element-mounted package |
| JP2006064539A (en) * | 2004-08-26 | 2006-03-09 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | Gyroscope sensor and method for detecting angular speed |
| JP2006105963A (en) * | 2004-09-10 | 2006-04-20 | Ngk Insulators Ltd | Support structure for oscillator, and instrument for measuring physical quantity |
| JP2006284373A (en) * | 2005-03-31 | 2006-10-19 | Seiko Epson Corp | Piezo-electric device |
| JP2008096420A (en) * | 2006-08-09 | 2008-04-24 | Epson Toyocom Corp | Inertial sensor, inertial sensor device, and production method thereof |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008096420A (en) * | 2006-08-09 | 2008-04-24 | Epson Toyocom Corp | Inertial sensor, inertial sensor device, and production method thereof |
| JP2013210375A (en) * | 2006-08-09 | 2013-10-10 | Seiko Epson Corp | Inertial sensor device |
| CN111121762A (en) * | 2018-10-29 | 2020-05-08 | 精工爱普生株式会社 | Sensor unit, electronic apparatus, and moving object |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5686153B2 (en) | 2015-03-18 |
| JP2013210375A (en) | 2013-10-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5622347B2 (en) | Inertial sensor device | |
| JP5164015B2 (en) | Multi-axis gyro sensor | |
| JP5686153B2 (en) | Inertial sensor device | |
| CN115144613A (en) | Inertial sensor and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP2009041962A (en) | External force detection device and method of manufacturing | |
| JP2006214898A (en) | Piezo-electric device and electronic equipment | |
| JP2014119412A (en) | Multi-axis physical quantity detection apparatus, manufacturing method of multi-axis physical quantity detection apparatus, electronic apparatus and moving body | |
| JP2010151580A (en) | Sensor device | |
| JP2006234462A (en) | Inertial sensor | |
| JP2022046922A (en) | Electronic device | |
| JP2022046920A (en) | Electronic device | |
| JP2007281377A (en) | Lid for electronic component and electronic component | |
| JP2008051629A (en) | Sensor module | |
| JP2007071672A (en) | Angular velocity sensor | |
| JP2006234462A5 (en) | ||
| JP2008058145A (en) | Inertial sensor and manufacturing method of inertial sensor | |
| JP2014098565A (en) | Electronic device, method of manufacturing electronic device, electronic apparatus, and moving body | |
| JP2008058144A (en) | Inertial sensor and manufacturing method of inertial sensor | |
| JP2020136324A (en) | Method for manufacturing electronic device | |
| JP2011149789A (en) | Manufacturing method of motion sensor and motion sensor | |
| US12123891B2 (en) | Physical quantity sensor, physical quantity sensor device, and method for manufacturing physical quantity sensor device | |
| JP2008058143A (en) | Inertial sensor, manufacturing method of inertial sensor, and mounting structure of inertial sensor body | |
| JP5757174B2 (en) | Sensor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2024003931A (en) | Inertial sensor, inertial sensor manufacturing method, and inertial measurement unit | |
| JP5757352B2 (en) | Sensor device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100426 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100426 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20110729 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20110729 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110819 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120221 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120417 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20130205 |