JP2009277726A - Laminated circuit board, motor controller and steering device for vehicle - Google Patents
Laminated circuit board, motor controller and steering device for vehicle Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2009277726A JP2009277726A JP2008125118A JP2008125118A JP2009277726A JP 2009277726 A JP2009277726 A JP 2009277726A JP 2008125118 A JP2008125118 A JP 2008125118A JP 2008125118 A JP2008125118 A JP 2008125118A JP 2009277726 A JP2009277726 A JP 2009277726A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- housing
- substrate body
- layer
- shaft
- circuit board
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/0001—Technical content checked by a classifier
- H01L2924/0002—Not covered by any one of groups H01L24/00, H01L24/00 and H01L2224/00
Abstract
Description
本発明は、積層回路基板、モータ制御装置および車両用操舵装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a laminated circuit board, a motor control device, and a vehicle steering device.
通常、積層回路基板は、導体層と絶縁層とを積層して形成されている(例えば、特許文献1〜4参照)。
積層回路基板は、導体層と絶縁層とが積層された製造中間体を打ち抜き加工することにより形成される。絶縁層は、例えばセラミック等を含有する合成樹脂を用いて形成されている。このため、打ち抜きによって切断された切断面に、セラミック粉等の粉塵(異物)が発生するおそれがある。このような粉塵は、積層回路基板に電子部品を接合する際の接合不良の原因となる可能性がある。特に、電動パワーステアリング装置の電動モータを制御する制御基板において、このような粉塵は、モータ軸受等に侵入して軸受の摩耗を促進する原因となるおそれがある。 The laminated circuit board is formed by punching a manufacturing intermediate in which a conductor layer and an insulating layer are laminated. The insulating layer is formed using, for example, a synthetic resin containing ceramic or the like. For this reason, there is a possibility that dust (foreign matter) such as ceramic powder may be generated on the cut surface cut by punching. Such dust may cause bonding failure when bonding electronic components to the laminated circuit board. In particular, in a control board that controls an electric motor of an electric power steering apparatus, such dust may enter a motor bearing or the like and promote wear of the bearing.
本発明は、かかる背景のもとでなされたもので、積層回路基板から異物が生じることを防止できる積層回路基板、モータ制御装置および車両用操舵装置を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made under such a background, and an object of the present invention is to provide a laminated circuit board, a motor control device, and a vehicle steering device that can prevent foreign matters from being produced from the laminated circuit board.
上記目的を達成するため、本発明は、導体(312a,312c,314a,316a,316b,316d)を含む層(312,314,316)と絶縁層(311,313,315,317)とを積層してなる基板本体(301)と、被覆部材(304)とを備え、上記基板本体は、積層方向(D)に対向する表面(301a)および裏面(301b)と、側面(301c)とを含み、上記側面は、上記被覆部材によって被覆されていることを特徴とする積層回路基板(78)である(請求項1)。 In order to achieve the above object, the present invention comprises a layer (312, 314, 316) including conductors (312a, 312c, 314a, 316a, 316b, 316d) and an insulating layer (311, 313, 315, 317). The substrate body includes a front surface (301a) and a back surface (301b) facing the stacking direction (D), and a side surface (301c). The side surface is a laminated circuit board (78) covered with the covering member (claim 1).
例えば、積層回路基板は、導体を含む層と絶縁層とが積層された製造中間体を打ち抜き加工することにより、形成される。絶縁層は、例えばセラミック等を含有する合成樹脂を用いて形成されている。また、積層回路基板の側面は、導体を含む層と絶縁層とが打ち抜き加工によって露出している。
本発明によれば、基板本体の側面が被覆部材で覆われていることにより、例えば、この側面から、絶縁層を構成する材料が粉塵(異物)として飛散することを防止できる。これにより、基板本体の表面等に異物が付着してしまうことを防止でき、積層回路基板に電子部品を接合する際の接合不良を確実に防止できる。
For example, a laminated circuit board is formed by stamping a manufacturing intermediate in which a layer including a conductor and an insulating layer are laminated. The insulating layer is formed using, for example, a synthetic resin containing ceramic or the like. Moreover, the layer including the conductor and the insulating layer are exposed on the side surface of the multilayer circuit board by punching.
According to the present invention, since the side surface of the substrate main body is covered with the covering member, for example, the material constituting the insulating layer can be prevented from being scattered as dust (foreign matter) from this side surface. Thereby, it can prevent that a foreign material adheres to the surface etc. of a board | substrate body, and can prevent the joining defect at the time of joining an electronic component to a laminated circuit board reliably.
また、本発明において、上記絶縁層は、基材と、この基材よりも熱伝導率が高い熱伝導材とを含む場合がある(請求項2)。この場合、絶縁層の熱伝導性を高くすることができ、基板本体の放熱性をより高くすることができる。
また、本発明において、上記基板本体にはビアホール(308)が設けられ、上記基板本体の表面は、ワイヤボンディングによる接合のための接合部(326)を含み、上記接合部は、上記積層方向に関して、上記ビアホールを避けて配置されている場合がある(請求項3)。この場合、基板本体のうちビアホールが形成されている部分は、ビアホールの形成作業に伴って基板本体表面に凹凸が生じることとなる。その一方で、ビアホールが形成されていない部分は、ビアホールを形成する作業が行われないので、基板本体の表面に凹凸が生じることが無い。このように、基板本体の表面のうち凹凸が生じていない平滑な部分に接合部が設けられるので、接合部と、この接合部にボンディングされたボンディングワイヤとの接合を確実に行うことができ、両者の接合強度を十分に確保することができる。しかも、ボンディングパッドのような別部品を用いて接合部を形成する必要がないので、コスト安価である。
Moreover, in this invention, the said insulating layer may contain a base material and a heat conductive material whose heat conductivity is higher than this base material (Claim 2). In this case, the thermal conductivity of the insulating layer can be increased, and the heat dissipation of the substrate body can be further increased.
In the present invention, the substrate body is provided with a via hole (308), and the surface of the substrate body includes a bonding portion (326) for bonding by wire bonding, and the bonding portion is related to the stacking direction. In some cases, the via holes are disposed away from the via holes. In this case, the portion of the substrate body where the via hole is formed has irregularities on the surface of the substrate body as the via hole is formed. On the other hand, since the operation for forming the via hole is not performed in the portion where the via hole is not formed, the surface of the substrate body is not uneven. Thus, since the joint portion is provided in the smooth portion of the surface of the substrate body where the irregularities are not generated, the joint portion and the bonding wire bonded to the joint portion can be reliably bonded, It is possible to sufficiently secure the bonding strength between the two. In addition, since it is not necessary to form a joint using another component such as a bonding pad, the cost is low.
また、本発明において、上記積層回路基板は、基板本体の裏面に接合される金属ベース(302)と、この金属ベースに形成される位置決め孔(321a,321b)とを備え、上記位置決め孔に、上記金属ベースが設置される基板設置部材(77a)に形成された位置決め部材(318,319)を嵌合可能である場合がある(請求項4)。この場合、基板設置部材に対する積層回路基板の位置決めの精度をより高くすることができる。 In the present invention, the multilayer circuit board includes a metal base (302) bonded to the back surface of the substrate body and positioning holes (321a, 321b) formed in the metal base. In some cases, positioning members (318, 319) formed on the board installation member (77a) on which the metal base is installed can be fitted (claim 4). In this case, the positioning accuracy of the laminated circuit board with respect to the board installation member can be further increased.
また、本発明において、上記の積層回路基板と、上記積層回路基板の基板本体に実装されたモータ駆動用素子(83)を含むモータ駆動回路(82)とを含む場合がある(請求項5)。この場合、積層回路基板から粉塵(異物)が発生することが防止されているので、このような異物がモータの軸受等に侵入してモータの軸受の摩耗が促進されることを防止できる。 Further, the present invention may include the above-described multilayer circuit board and a motor drive circuit (82) including a motor drive element (83) mounted on the board body of the multilayer circuit board (Claim 5). . In this case, since dust (foreign matter) is prevented from being generated from the laminated circuit board, it is possible to prevent such foreign matter from entering the motor bearing or the like and promoting wear of the motor bearing.
また、本発明において、モータ制御装置(78)と、上記モータ制御装置によって駆動され、操舵機構(4)に操舵力を付与する電動モータ(18)とを備える場合がある(請求項6)。この場合、積層回路基板に実装される電子部品の接合不良が確実に防止されているとともに、モータの軸受等の摩耗が抑制された車両用操舵装置を実現することができる。 In the present invention, there may be provided a motor control device (78) and an electric motor (18) that is driven by the motor control device and applies a steering force to the steering mechanism (4). In this case, it is possible to realize a vehicle steering apparatus in which the bonding failure of the electronic components mounted on the multilayer circuit board is reliably prevented and the wear of the motor bearings and the like is suppressed.
なお、上記において、括弧内の数字等は、後述する実施の形態における対応構成要素の参照符号を表すものであるが、これらの参照符号により特許請求の範囲を限定する趣旨ではない。 In the above description, numbers in parentheses represent reference numerals of corresponding components in the embodiments described later, but the scope of the claims is not limited by these reference numerals.
以下には、図面を参照して、本発明の実施形態について具体的に説明する。
図1は、本発明の一実施形態に係る車両用操舵装置としての電動パワーステアリング装置1の概略構成を示す模式図である。
図1を参照して、電動パワーステアリング装置1は、操舵部材としてのステアリングホイール2と、ステアリングホイール2の回転に連動して転舵輪3を転舵する操舵機構4と、運転者の操舵を補助するための操舵補助機構5とを備えている。ステアリングホイール2と操舵機構4とは、ステアリングシャフト6および中間軸7を介して機械的に連結されている。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be specifically described with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing a schematic configuration of an electric
Referring to FIG. 1, an electric
本実施の形態では、操舵補助機構5がステアリングシャフト6にアシスト力(操舵補助力)を与える例に則して説明するが、本発明を、操舵補助機構5が後述するピニオン軸にアシスト力を与える構造や、操舵補助機構5が後述するラック軸にアシスト力を与える構造に適用することが可能である。
ステアリングシャフト6は、直線状に延びている。また、ステアリングシャフト6は、ステアリングホイール2に連結された入力軸8と、中間軸7に連結された出力軸9とを含む。入力軸8と出力軸9とは、トーションバー10を介して同一軸線上で相対回転可能に連結されている。すなわち、ステアリングホイール2に一定値以上の操舵トルクが入力されると、入力軸8および出力軸9は、互いに相対回転しつつ同一方向に回転するようになっている。
In the present embodiment, the steering assist mechanism 5 will be described based on an example in which an assist force (steering assist force) is applied to the
The
ステアリングシャフト6の周囲に配置されたトルクセンサ11は、入力軸8および出力軸9の相対回転変位量に基づいて、ステアリングホイール2に入力された操舵トルクを検出する。トルクセンサ11のトルク検出結果は、制御装置としてのECU12(Electronic Control Unit :電子制御ユニット)に入力される。また、車速センサ90からの車速検出結果がECU12に入力される。中間軸7は、ステアリングシャフト6と操舵機構4とを連結している。
A
操舵機構4は、ピニオン軸13と、転舵軸としてのラック軸14とを含むラックアンドピニオン機構からなる。ラック軸14の各端部には、タイロッド15およびナックルアーム(図示せず)を介して転舵輪3が連結されている。
ピニオン軸13は、中間軸7に連結されている。ピニオン軸13は、ステアリングホイール2の操舵に連動して回転するようになっている。ピニオン軸13の先端(図1では下端)には、ピニオン16が連結されている。
The steering mechanism 4 includes a rack and pinion mechanism including a
The
ラック軸14は、自動車の左右方向に沿って直線状に延びている。ラック軸14の軸方向の途中部には、上記ピニオン16に噛み合うラック17が形成されている。このピニオン16およびラック17によって、ピニオン軸13の回転がラック軸14の軸方向移動に変換される。ラック軸14を軸方向に移動させることで、転舵輪3を転舵することができる。
The
ステアリングホイール2が操舵(回転)されると、この回転が、ステアリングシャフト6および中間軸7を介して、ピニオン軸13に伝達される。そして、ピニオン軸13の回転は、ピニオン16およびラック17によって、ラック軸14の軸方向移動に変換される。これにより、転舵輪3が転舵される。
操舵補助機構5は、操舵補助用の電動モータ18と、電動モータ18の出力トルクを操舵機構4に伝達するための伝達機構としての減速機構19とを含む。減速機構19としては、例えばウォームギヤ機構などの食い違い軸歯車機構や、平行軸歯車機構などを用いることができる。本実施形態では、減速機構19として、ウォームギヤ機構が用いられている。すなわち、減速機構19は、駆動ギヤ(伝達機構の駆動側部材)としてのウォーム軸20と、このウォーム軸20と噛み合う従動ギヤ(伝達機構の従動側部材)としてのウォームホイール21とを含む。減速機構19は、伝達ハウジングとしてのギヤハウジング22内に収容されている。
When the
The steering assist mechanism 5 includes a steering assist
ウォーム軸20は、図示しない継手を介して電動モータ18の回転軸(図示せず)に連結されている。ウォーム軸20は、電動モータ18によって回転駆動される。また、ウォームホイール21は、ステアリングシャフト6とは同行回転可能に連結されている。ウォームホイール21は、ウォーム軸20によって回転駆動される。
電動モータ18がウォーム軸20を回転駆動すると、ウォーム軸20によってウォームホイール21が回転駆動され、ウォームホイール21およびステアリングシャフト6が同行回転する。そして、ステアリングシャフト6の回転は、中間軸7を介してピニオン軸13に伝達される。ピニオン軸13の回転は、ラック軸14の軸方向移動に変換される。これにより、転舵輪3が転舵される。すなわち、電動モータ18によってウォーム軸20を回転駆動することで、転舵輪3が転舵されるようになっている。
The
When the
電動モータ18は、ECU12によって制御される。ECU12は、トルクセンサ11からのトルク検出結果、車速センサ90からの車速検出結果等に基づいて電動モータ18を制御する。具体的には、ECU12では、トルクと目標アシスト量との関係を車速毎に記憶したマップを用いて目標アシスト量を決定し、電動モータ18の発生するアシスト力を目標アシスト量に近づけるように制御する。
The
図2および図3は、それぞれ操舵補助機構5の概略斜視図であり、互いに別角度から操舵補助機構5を見た図である。本実施の形態の主に特徴とするところは、上記の制御装置としてのECU12を収容するためのハウジングHを、図2および図3に示すように、互いに接触する(例えば互いの端面を突き合わせた状態、或いは互いの端部を嵌合させた状態である)第1のハウジング23および第2のハウジング24によって構成した点にある。
2 and 3 are schematic perspective views of the steering assist mechanism 5, respectively, and are views of the steering assist mechanism 5 viewed from different angles. The main feature of the present embodiment is that the housing H for housing the
すなわち、ECU12を収容するためのハウジングHを構成する第1のハウジング23および第2のハウジング24は互いに接触しており(直接に係合しており)、両ハウジング23,24の間に、別のハウジングが介在していない。これにより、格段の小型化が図られている。
第1のハウジング23および第2のハウジング24は、一端が開放した概ね四角箱形に形成されている。第1および第2のハウジング23,24の互いの端部は、突き合わされ固定ねじ91により互いに締結されている。
In other words, the
The
一方、電動モータのモータハウジング25は、筒状のモータハウジング本体26と、上記の第1のハウジング23とにより構成されている。具体的には、ECU12を収容するためのハウジングHの一部である第1のハウジング23が、電動モータ12のモータハウジング25の少なくとも一部とは単一の材料で一体に形成されている。換言すると、モータハウジング25の少なくとも一部と、ECU12を収容するためのハウジングHの一部とが兼用されている。
On the other hand, the
また、ギヤハウジング22は、ウォーム軸20が収容された筒状の駆動ギヤ収容ハウジング27と、ウォームホイール21が収容された筒状の従動ギヤ収容ハウジング28と、上記の第2のハウジング24とにより構成されている。具体的には、ECU12を収容するためのハウジングHの一部である第2のハウジング24が、ギヤハウジング22の駆動ギヤ収容ハウジング27および従動ギヤ収容ハウジング28とは単一の材料で一体に形成されている。換言すると、ギヤハウジング22の一部と、ECU12を収容するためのハウジングHの一部とが兼用されている。
The
第1のハウジング23の側壁としての外周壁92の外周92aには、筒状突起93が突出形成されており、その筒状突起93内には、第1のハウジング23の外部に臨む電気コネクタ94が配置されている。図示していないが、電気コネクタ94には、バッテリーからECU12に電源供給するための端子や、外部からの信号の入、出力用の端子が設けられている。
A
電動パワーステアリング装置の要部の断面図である図4を参照して、減速機構19(伝達機構)の従動側部材としてのウォームホイール21、および電気コネクタ94は、減速機構19(伝達機構)の駆動側部材としてのウォーム軸20の中心軸線C3を含み且つウォームホイール21の中心軸線21aとは平行な平面Q1に対して、同側に配置されている。
Referring to FIG. 4 which is a cross-sectional view of the main part of the electric power steering apparatus, the
この場合、電動モータ18の回転軸37の軸方向X1に沿って見たときに、突出部となる電気コネクタ94および従動ギヤ収容ハウジング28が同側に突出することになる。その結果、実質的な小型化および省スペース化を図ることができ、車両への搭載性が向上する。
また、図3を参照して、電動モータ18の後述する回転軸37の軸方向X1に沿って見たときに、電気コネクタ94および従動ギヤ収容ハウジング28の互いの少なくとも一部が互いに重なり合うレイアウトとされている。これにより、実質的な小型化および省スペース化を図ることができ、車両への搭載性が向上する。
In this case, when viewed along the axial direction X1 of the
Further, with reference to FIG. 3, when viewed along an axial direction X1 of a rotating shaft 37 (to be described later) of the
また、回転軸37の軸方向X1に沿って見たときに、電気コネクタ94およびセンサハウジング35の互いの少なくとも一部が互いに重なり合うレイアウトとされている。これにより、実質的な小型化および省スペース化を図ることができ、車両への搭載性が向上する。
モータハウジング25の第1のハウジング23は、例えばアルミニウム合金(例えば鋳造品、冷間鍛造品)により形成され、操舵補助機構5の軽量化が図られている。また、駆動ギヤ収容ハウジング27、従動ギヤ収容ハウジング28および第2のハウジング24で構成されるギヤハウジング22は、例えばアルミニウム合金(例えば鋳造品、冷間鍛造品)により形成され、操舵補助機構5の軽量化が図られている。また、モータハウジング25のモータハウジング本体26には、例えば非磁性の板金が用いられている。
Further, when viewed along the axial direction X1 of the
The
モータハウジング本体26は、円筒状の周壁29と、周壁29の一端を閉塞する底壁30と、周壁29の他端からその径方向外方に張り出した環状のフランジ31とを含む。
環状のフランジ31の周方向の一部から径方向外方に張り出したブラケット32が設けられている。そのブラケット32のねじ挿通孔33に挿通された固定ねじ34が、第1のハウジング23のねじ孔にねじ込まれることにより、モータハウジング本体26と第1のハウジング23とが一体に固定されている。上記のねじ挿通孔33は、モータハウジング本体26の周方向に延びる長孔に形成されているので、第1のハウジング23に対して、モータハウジング本体26の周方向位置を調整可能となっている。
The
A
また、ECU12を収容するためのハウジングHを構成する第1のハウジング23および第2のハウジング24は、固定ねじ91を用いて互いに固定されている。
ギヤハウジング22の従動ギヤ収容ハウジング28には、トルクセンサ11が収容された筒状のセンサハウジング35が連結されており、従動ギヤ収容ハウジング28およびセンサハウジング35は、固定ねじ36を用いて互いに固定されている。ステアリングシャフト6が、筒状の従動ギヤ収容ハウジング28およびセンサハウジング35内に挿通されている。
Further, the
A
図4を参照して、電動モータ18のモータハウジング25である第1のハウジング23とこの第1のハウジング23に接触する第2のハウジング24とによって、制御装置としてのECU12を収容する収容室100が形成されている。第1のハウジング23および第2のハウジング24の互いの端面が突き合わされており、両端面間が環状のシール部材95によって封止されている。
Referring to FIG. 4, a
シール部材95は、図6に示すように、第1および第2のハウジング23,24の何れか一方、例えば第2のハウジング24の端面98に形成された環状溝99に収容され、他方の、例えば第1のハウジング23の端面(フランジ88の端面88aに相当)に接触している。シール部材95としては、例えばOリングを用いることができる。
再び図4を参照して、第1のハウジング23は、収容室100の一部を区画する第1の内壁面101を含み、第2のハウジング24は収容室100の一部を区画する第2の内壁面102を含み、これら第1の内壁面101および第2の内壁面102は、電動モータ18の回転軸37の軸方向X1に対向している。
As shown in FIG. 6, the
Referring again to FIG. 4, the
また、第2のハウジング24の第2の内壁面102は、環状平面により構成されており、その環状平面は、電動モータ18の回転軸37の中心軸線C1または上記中心軸線C1の延長線C2(通例、ウォーム軸20の中心軸線C3に一致)とは直交し且つ上記中心軸線C1または上記延長線C2の回りを取り囲んでいる。
第2の内壁面102のなす環状平面の延長面P1が、ステアリングシャフト6を取り囲む筒状部としての従動ギヤ収容ハウジング28の外周面28aの主要部のなす円筒面P2と図4のように交差するか、または接する状態にある。具体的には、従動ギヤ収容ハウジング28は、ステアリングシャフト6が嵌合するウォームホイール21を取り囲んでいる。
In addition, the second
The extended surface P1 of the annular plane formed by the second
また、制御装置としてのECU12は、回転軸37の中心軸線C1または延長線C2の回りに配置されている。
電動モータ18の回転軸37およびウォーム軸20が同軸上に並べて配置されており、回転軸37およびウォーム軸20は、互いの間に介在する継手38を介して同軸的に動力伝達可能に連結されている。継手38は、電動モータ18の回転軸37と同行回転する環状の入力部材39と、ウォーム軸20と同行回転する環状の出力部材40と、入力部材39および出力部材40の間に介在し入力部材39および出力部材40を動力伝達可能に連結する環状の弾性部材41とを有している。
Further, the
A rotating
ウォーム軸20は、ギヤハウジング22の駆動ギヤ収容ハウジング27の駆動ギヤ収容孔42に収容されている。ウォーム軸20は第1の端部20aおよび第2の端部20bを有しており、ウォーム軸20の軸方向の中間部にウォーム20cが形成されている。
ウォーム軸20の第1の端部20aは、駆動ギヤ収容孔42の一端(電動モータ18側の端部)の内周の軸受保持部44に保持された第1の軸受45によって、回転可能に支持されている。ウォーム軸20の第2の端部20bは、駆動ギヤ収容孔42の他端の内周の軸受保持部46に保持された第2の軸受47によって、回転可能に支持されている。
The
The
第1の軸受45は、内輪48と、外輪49と、内輪48および外輪49の間に介在する複数の転動体50とを有する転がり軸受からなる。内輪48は、ウォーム軸20の第1の端部20aに同行回転可能に保持されている。内輪48の一方の端面は、ウォーム軸20の外周に設けられた位置決め段部に当接している。ウォーム軸20の第1の端部20aには、小径の突軸51が延設されており、その突軸51には、継手38の出力部材40が同行回転可能に且つ軸方向移動不能に嵌合されている。出力部材40は内輪48の他方の端面に当接しており、ウォーム軸20の上記位置決め段部と出力部材40の間に、内輪48が挟持されている。これにより、ウォーム軸20に対する内輪45の軸方向移動が規制されている。
The
外輪49の一方の端面が、駆動ギヤ収容孔42の軸受保持部44の一側に隣接する段部に、所定の隙間を隔てて対向している。また、駆動ギヤ収容孔42の軸受保持部44の他側に隣接するねじ部に、環状の固定部材52がねじ込まれており、固定部材52が外輪49の他方の端面を押圧している。これにより、外輪49の軸方向移動が規制されている。 固定部材52は、外周にねじが形成された筒状の本体52aと、本体52aの一端から径方向内方に延びる内方フランジ52bと、本体52aの他端から径方向外方に延びる外方フランジ52cとを有している。内方フランジ52bが、外輪49の他方の端面を押圧している。また、外方フランジ52cは、ECU12の収容室を区画する第2のハウジング24の第2の内壁面102に押圧されており、これにより、固定部材52の緩み止めが達成されている。
One end surface of the
固定部材52の筒状の本体52a内には、継手38の一部が収容されている。これにより、回転軸37の軸方向X1に関しての、電動パワーステアリング装置1の小型化が達成されている。
第2の軸受47は、内輪53と、外輪54と、内輪53および外輪54の間に介在する複数の転動体55とを有する転がり軸受からなる。内輪53は、ウォーム軸20の第2の端部20bに同行回転可能に保持されている。内輪53の一方の端面は、ウォーム軸20の外周に設けられた位置決め段部に当接している。これにより、ウォーム軸20に対する内輪53の軸方向移動(第1の軸受45側への移動)が規制されている。
A part of the joint 38 is accommodated in the cylindrical
The
駆動ギヤ収容孔42の軸受保持部46に隣接する、駆動ギヤ収容孔42の入口部に、ねじ部56が形成されており、そのねじ部56に、第1および第2の軸受45,47に一括して予圧を付与するための予圧付与部材57がねじ込まれている。予圧付与部材57は、円板状の本体58を有しており、本体58の外周には、上記ねじ部56に螺合するねじ部59が形成されている。また、本体58の一方の端面に、第2の軸受47の外輪54の一方の端面を押圧する環状凸部60が形成されている。
A
本体58の他方の端面には、当該予圧付与部材57を回動操作するための工具を係合する、例えば断面多角形形状の工具係合孔61が形成されている。また、本体58のねじ部59に螺合されたロックナット62によって、予圧付与部材57が止定されるようになっている。
ウォーム軸20の第1および第2の端部20a,20bを支持する第1および第2の軸受45,47は、何れも公知のシール軸受により構成されている。具体的には、転動体の軸方向X1の両側において、内輪と外輪の間を密封するシール部材62を備えており、そのシール部材62は、内輪または外輪の何れか一方に固定される。また、シール部材62は他方に摺接するリップを有している。
A
The first and
ウォーム軸20の両端を支持する第1および第2の軸受45,47がシール軸受により構成されているので、ギヤハウジング22内のグリース等の潤滑剤が、ECU12を収容する収容室100側へ漏れ出ることがない。ただし、収容室100内の密封性を高めるために、例えば、固定部材52の本体52aの外周のねじ部とこれに螺合するねじ部との間に、液体パッキンを介在させてもよい。
Since the first and
本実施形態では、電動モータ18としてブラシレスモータが用いられている。電動モータ18は、上記モータハウジング25と、このモータハウジング25内に収容されたロータ64およびステータ65を含む。
ロータ64は、回転軸37の外周に同行回転可能に取り付けられた環状のロータコア66と、ロータコア66の外周に同行回転可能に取り付けられた例えば環状の永久磁石からなるロータマグネット67とを有している。ロータマグネット67には、複数の磁極が周方向に並べて配置されている。これらの磁極は、ロータ64の周方向に関して、N極およびS極が交互に入れ替わるようにされている。
In the present embodiment, a brushless motor is used as the
The
ステータ65は、モータハウジング25のモータハウジング本体26の内周に固定されている。ステータ65は、モータハウジング本体26の内周に固定されたステータコア68と、複数のコイル69とを含む。ステータコア68は、環状のヨークと、このヨークの内周から径方向内方へ突出する複数のティースとを含む。各コイル69は対応するティースに巻回されている。
The
また、モータハウジング25のモータハウジング本体26と第1のハウジング23とにより区画されるモータ室70内には、環状またはC形形状をなすバスバー71が収容されている。各ティースに巻回されたコイル69は、バスバー71と接続されている。バスバー71は、各コイル69と電流印加線との接続部に用いられる導電接続材であり、バスバー71は、各コイル69に、図示しない電力供給源からの電力を配電するための配電部材として機能する。
A
また、モータハウジング25のモータハウジング本体26と第1のハウジング23とにより区画されるモータ室70内には、ロータ64の回転位置を検出するための回転位置検出装置72が収容されている。回転位置検出装置72は、第1のハウジング23に固定されたステータ73と、回転軸37とは同行回転可能に取り付けられたロータ74とを有している。回転位置検出装置72としては、例えばレゾルバを用いることができる。また、ホール素子を用いることもできる。
A rotation
回転位置検出装置72は、電動モータ18の回転軸37の軸方向X1に関して電動モータ18のロータ64のロータコア66と、第2のハウジング24との間に配置されていればよい。したがって、本実施の形態のように、モータ室70内に配置されていてもよいし、ECU12の収容室100を区画する第1のハウジング23の中央に設けられた後述する筒状部89内に配置されていてもよい。
The rotational
また、図4を参照して、回転軸37は、モータハウジング25の一部とECU12を収容するハウジングの一部とを兼用する第1のハウジング23によって保持された第3の軸受75および第4の軸受76によって、回転可能に支持されている。第3および第4の軸受75,76は、第1および第2の軸受45,47と同じ構成のシール軸受により構成されている。
Referring to FIG. 4, the
ECU12の収容室100を区画するハウジングHの一部である第1のハウジング23は、収容室100とモータ室70とを仕切る仕切り壁77を底壁として含んでいる。この仕切り壁77に、上記第1の内壁面101が設けられている。仕切り壁77の外周の近傍からモータハウジング本体26側に向かって筒状突起104が延びており、その筒状突起104の外周に、モータハウジング本体26の一端が嵌合されている。
The
また、仕切り壁77は、上記の第3の軸受75の外輪を保持するための保持孔105を有している。仕切り壁77からモータハウジング本体26側に向けて延びる筒状突起106が形成されている。筒状突起106は上記保持孔105とは同軸的に形成されている。筒状突起106は、モータハウジング本体26に係合する上記の筒状突起104よりも小径に形成されている。この筒状突起106の内周には、回転位置検出装置72のステータ73が固定されている。
The partition wall 77 has a holding
また、仕切り壁77から第2のハウジング24側に向けて延びる筒状部89が形成されている。筒状部89は上記の保持孔105とは同軸的に形成されている。筒状部89内の内周には、上記の第4の軸受76の外輪が保持されている。筒状部89の一端には、径方向内方に延びる環状フランジ107が延設されており、第4の軸受76の外輪の一端が環状フランジ107に当接することにより、筒状部89に対する第4の軸受76の外輪の軸方向移動が規制されている。
Further, a
一方、第4の軸受76の内輪は、回転軸37の外周に形成された環状の位置決め段部と、継手38の入力部材39の端面との間に挟持されており、これにより、回転軸37に対する第4の軸受76の内輪の軸方向移動が規制されている。
収容室100には、ECU12の一部を構成するパワー基板78および制御基板79が収容され保持されている。パワー基板78には、電動モータ18を駆動するためのパワー回路の少なくとも一部(例えばFETなどのスイッチング素子)が実装されている。上記の各コイル69と接続されたバスバー71は、第1のハウジング23の上記仕切り壁77を挿通して収容室100内に進入するバスバー端子80を介して、パワー基板78に接続されている。
On the other hand, the inner ring of the
In the
また、回転位置検出装置72が、第1のハウジング23の仕切り壁77を挿通して収容室100内に進入するバスバー端子81を介して、制御基板79に接続されている。
収容室100内において、パワー回路が実装されたパワー基板78は、第1の内壁面101および第2の内壁面102のうち第1の内壁面101に相対的に近接して配置されている。すなわち、上記の仕切り壁77は、電動モータ18の回転軸37の軸方向X1に関しての厚みt1が相対的に厚い厚肉部77aと相対的に薄い薄肉部77bとを含んでいる。厚肉部77aは、収容室100内に突出するように設けられている。
In addition, the rotational
In the
上記のパワー基板78は、厚肉部77aにおける第1の内壁面101に近接して或いは本実施の形態のように接触して配置されている。具体的には、第1の内壁面101において、厚肉部77aの部分が、パワー基板78を受ける座部103となっている。
本実施の形態では、パワー基板78は厚肉部77aにおける第1の内壁面101に対して熱伝導可能に接触しており、上記の厚肉部77aは、パワー基板78の熱を逃がすためのヒートシンクとして機能している。
The
In the present embodiment, the
継手38の入力部材39は、電動モータ18の回転軸37の端部に同行回転可能に嵌合する筒状部39aを有しており、制御基板79は、入力部材39の筒状部39aの周囲に配置されている。具体的には、制御基板79の中央の挿通孔79aに、筒状部39aが挿通されている。
制御基板79は、電動モータ18の回転軸37の軸方向X1に関して、第2のハウジング24の第2の内壁面102とパワー基板78との間に配置されている。パワー基板78および制御基板79は、電動モータ18の回転軸37の軸方向X1に関して所定の間隔を隔てて配置されている。また、電動モータ18の回転軸37の中心軸線C1に沿う方向に関して、制御基板79および継手38の互いの少なくとも一部が重なるようにレイアウトされている。
The
The
収容室100内において、第1のハウジング23の仕切り壁77の薄肉部77bと制御基板79との間に形成される収容空間S1は、電動モータ18の回転軸37の軸方向X1に関して、十分な高さを有している。図4では図示していないが、この収容空間S1には、後述する図5に示す複数のコンデンサ85やリレー86等の比較的大型で背の高い部品が収容されるようになっており、収容室100内の空間の有効利用が図られている。
In the
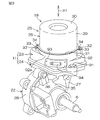
次いで、分解斜視図である図5を参照して、上記のパワー基板78には、電動モータ18を駆動するためのモータ駆動回路としてのパワー回路82が実装されている。図5および図7を参照して、パワー基板78に実装されるパワー回路82には、スイッチング素子としての複数のFET83(電解効果型トランジスタ)と、FET83によるスイッチングノイズを低減するための複数のスナバ回路200とが含まれている。パワー基板78は、片面に回路が実装されたモータ制御装置である積層回路基板を構成している。パワー基板78は、基板本体301と、ヒートシンクとしての厚肉部77aに対して面接触する例えばアルミニウム板からなる高熱伝導板としての金属ベース302とを含んでいる。
Next, referring to FIG. 5, which is an exploded perspective view, a
また、上記の制御基板79には、電動モータ18を駆動するパワー回路82を制御するための制御回路84が実装されている。制御基板79に実装された制御回路84は、電動モータ18の回転軸37の中心軸線C1(または中心軸線C1の延長線C2)の回りに配置されている。制御回路84には、パワー回路82の各FET83を制御するドライバと、このドライバを制御するCPUとが含まれている。
A
また、ECU12は、上述した複数のコンデンサ85や、必要に応じて電動モータ18に流れる電流を遮断するためのリレー86、その他の非発熱要素を有している。コンデンサ85は、電動モータ18への電力ラインに配置され、電動モータ18に流れる電流のリップルを除去する平滑用の電解コンデンサである。通例、この種のコンデンサ85は、大容量であり大型である。非発熱要素としてのコンデンサ85およびリレー86等は、環状の合成樹脂製のホルダ120によって支持されたサブアセンブリSAを構成しており、第1のハウジング23に対して一括して取り付け操作が行えるようになっている。
Further, the
各コンデンサ85は、ホルダ120に設けられた例えばアングル状の保持部121に、横倒し状態で保持されている。すなわち、大型のコンデンサ85の長手方向を上記中心軸線C1に平行な方向に対して直交する方向に向けて配置することにより、上記中心軸線C1に沿う方向に関しての、収容室100の小型化が図られている。
第1のハウジング23は、一端が開放した概ね四角箱型の部材である。具体的には、第1のハウジング23は、一端が開放した概ね四角箱型の本体87を備えている。本体87は、概ね四角環状をなす外周壁92と、外周壁92の一端から径方向外方に向けて張り出した四角環状のフランジ88と、底壁としての上記仕切り壁77とを有している。
Each
The
収容室100内において、仕切り壁77の中央部には、本体87の開放側(第2のハウジング24側)に向かって延びる筒状部89が形成されている。外周壁92は、仕切り壁77の外周縁から延設されており、筒状部89を取り囲んでいる。本体87および筒状部89は、単一の部材で一体に形成されている。
フランジ88の端面88a(図5では、上面)は、平面にされている。この端面88aに上記のシール部材95が接触することになる。また、フランジ88は、径方向外方に向かって突出する複数(本実施の形態では一対)のブラケット状の取付部96を有している。各取付部96には、当該取付部96をその厚み方向に貫通するねじ挿通孔97が形成されている。各ねじ挿通孔97には、第1および第2のハウジング23,24を締結するための上記の固定ねじ91が挿通される。
In the
An
四角環状をなす外周壁92は、4つの側壁111〜114を有しており、対向する一対の側壁112,114の端部に、上記取付部96が延設されている。また、上記ヒートシンクとして機能する、仕切り壁77の厚肉部77aは、上記取付部96が延設された1つの側壁112の内面に連続して形成されている。
第1の内壁面101のうち、厚肉部77aにおける部分が、パワー基板78を受ける座部103を構成している。座部103は、発熱要素としてのFET83を有するパワー基板78に、熱伝導可能に接触している。発熱要素の熱は、パワー基板78から、ヒートシンクを構成する厚肉部77aおよび取付部96を介して、第2のハウジング24とは一体のギヤハウジング22側へ逃がされる。
The outer
Of the first
固定ねじ91による締結に用いられる取付部96では、フランジ88の他の部分と比較して、第2のハウジング24に対する接触面積が広くなっている。その取付部96が設けられた側壁112に連続して、熱容量の大きいヒートシンクとなる厚肉部77aを設けてある。
パワー基板78が、座部103に取り付けられた後、コンデンサ85、リレー86およびホルダ120を含むサブアセンブリSAが取り付けられる。このとき、環状のホルダ120の中央部が大きく開放されているので、パワー基板78の表面の大部分は、ホルダ120により覆われることなく、開放する状態になる。これにより、パワー基板78の表面に隣接する十分な放熱スペースが確保されるようにしてある。
In the
After the
図8は、パワー基板78が第1のハウジング23の厚肉部77aに固定された状態を示す要部の断面図である。図8を参照して、厚肉部77aは、基板設置部材として設けられている。この厚肉部77aの一側面303は、軸線C1とは直交して平坦に延びている。この一側面303に、パワー基板78が設置されている。
パワー基板78は、基板本体301および金属ベース302と、被覆部材304とを備えている。
FIG. 8 is a cross-sectional view of the main part showing a state in which the
The
基板本体301は、絶縁体からなる絶縁層と、導電体を含む層とを積層してなる。具体的には、基板本体301は、基板本体301の表面層としての第1の層311と、第2の層312と、第3の層313と、第4の層314と、第5の層315と、第6の層316と、基板本体301の裏面層としての第7の層317と、を含んでいる。各上記第1〜第7の層311〜317が、軸線C1に沿う積層方向Dに沿ってこの順に配置されている。
The
奇数番目の層としての第1、第3、第5、および第7の層311,313,315,317は、絶縁体からなる絶縁層を構成している。この絶縁体として、基材としての合成樹脂材料に、セラミックの粉末やガラス繊維等の、合成樹脂材料よりも熱伝導率が高い熱伝導材を添加したものを例示することができる。これにより、基板本体301の熱伝導性を高めており、熱抵抗が小さくされている。
The first, third, fifth, and
偶数番目の層としての第2、第4および第6の層312,314,316は、それぞれ、導体を含む層を構成している。
第2の層312は、導体としての導電部312aと、絶縁体としての絶縁部312bとを含んでいる。導電部312aは、銅等の金属を用いて形成されている。絶縁部312bは、上記第1の層311と同様の材料を用いて形成されており、導電部312aを取り囲んでいる。
The second, fourth, and
The
第4の層314は、導体としての導電部314aと、絶縁体としての絶縁部314bとを含んでいる。導電部314aは、導電部312aと同様の材料を用いて形成されている。絶縁部314bは、上記第1の層311と同様の材料を用いて形成されており、導電部314aを取り囲んでいる。
第6の層316は、導体としての導電部316a,316bと、絶縁体としての絶縁部316cとを含んでいる。各導電部316a,316bは、第2の層312の導電部312aと同様の材料を用いて形成されている。絶縁部316cは、上記第1の層311と同様の材料を用いて形成されている。絶縁部316cは、導電部316a,316bが互いに直接接触しないように、これらの導電部316a,316bをそれぞれ取り囲んでいる。
The
The
第2の層312の導電部312aの一部と、第6の層316の導電部316aの一部とは、積層方向Dに対向している。また、第4の層314の導電部314aの一部と、第6の層316の導電部316bの一部とは、積層方向Dに対向している。
第1の層311の表面、すなわち、基板本体301の表面301aには、導電部305a,305b,305cがそれぞれ設けられている。各導電部305a,305b,305cは、第2の層312の導電部312aと同様の材料を用いて形成されている。
A part of the
導電部305aと、第2の層312の導電部312aと、第6の層316の導電部316aのそれぞれの一部は、積層方向Dに互いに対向している。
導電部305bと、第2の層312の導電部312aのそれぞれの一部は、積層方向Dに互いに対向している。
導電部305cと、第4の層314の導電部314aと、第6の層316の導電部316bのそれぞれの一部は、積層方向Dに互いに対向している。
Each of the
A part of each of the
Each of the
導電部305aの表面には、めっき層306が形成されている。めっき層306は、例えば、ニッケル金めっき(Ni+Auめっき)である。めっき層306の表面には、半田307を用いて、モータ駆動用素子としてのFET83が接合されている。これにより、FET83は、導電部305aに接合されている。すなわち、FET83は、基板本体301にベアチップ実装されている。
A
基板本体301には、基板本体301の放熱性を増すためのビアホール308a〜308gが形成されている。なお、基板本体301のビアホールを総称していうときは、単にビアホール308という。
各ビアホール308a〜308gは、基板本体301のうち、裏面層としての第7の層307以外の層、すなわち、第1〜第6の層311〜316を貫く層間接続孔である。ビアホール308a〜308dは、FET83が実装されている導電部305aに対応して形成されている。ビアホール308eは、導電部305bに対応して形成されている。ビアホール308f,308gは、導電部305cに対応して形成されている。
Via
Each of the via
ビアホール308a〜308dは、それぞれ、導電部305a、第1の層311、第2の層312の導電部312a、第3の層313、第4の層314の絶縁部314b、第5の層315および第6の層316の導電部316aを貫いている。
ビアホール308eは、導電部305b、第1の層311、第2の層312の導電部312a、第3の層313、第4の層314の絶縁部314b、第5の層315、および第6の層316の絶縁部316cを貫いている。
The via
The via
ビアホール308f,308gは、第1の層311、第2の層312の絶縁部312b、第3の層313、第4の層314の導電部314a、第5の層315、および第6の層316の導電部316bを貫いている。
ビアホール308a〜308dには、それぞれ、銅等の金属製のピン部材309が圧入固定されている。これにより、導電部305a,第2の層312の導電部312aおよび第6の層316の導電部316aは、ピン部材309を介して電気的に接続されている。
The via holes 308 f and 308 g include the
A
ビアホール308eにも同様に、ピン部材309が圧入固定されている。これにより、導電部305b、および第2の層312の導電部312aが電気的に接続されている。
ビアホール308f,308gにも同様に、ピン部材309が圧入固定されている。これにより、導電部305c、第4の層314の導電部314aおよび第6の導電部316bが電気的に接続されている。
Similarly, a
Similarly, a
上記の構成により、各導電部305a,305b,305cからの熱は、対応するピン部材309を介して、第7の層317に伝わり、さらに金属ベース302から第1のハウジング23の厚肉部77aに伝わる。
FET83は、スイッチング素子として機能することから発熱量が多い。このため、FET83が実装される導電部305aに対応して複数のピン部材309が設けられている。これにより、FET83からの熱をより多く厚肉部77aに伝えることができる。
With the above configuration, the heat from each of the
Since the
また、各ピン部材309が第7の層317を貫通していないことから、各ピン部材309が金属ベース302に接触することを防止でき、両者が電気的に接続されることを防止できる。
基板本体301において、第1の層311がこの基板本体301の表面301aを形成しており、第7の層317がこの基板本体301の裏面301bを形成している。これらの表面301aおよび裏面301bは、積層方向Dに相対向している。また、基板本体301において、第1〜第7の層311〜317が協働して、基板本体301の外側面301cを構成している。外側面301cは、全体として環状をなしている。
In addition, since each
In the
基板本体301は、後述するように、絶縁体と導体を含む層とを圧接して形成された板状の製造中間体を打ち抜いて形成したものである。したがって、基板本体301の外側面301cに、基板本体301を構成する樹脂やガラス繊維やセラミック等が粉塵(異物)として付着している場合がある。
本実施の形態の特徴の1つは、この外側面301cの全部を被覆部材304で覆うことで、基板本体301の外側面301cからの異物が飛散することを防止している点にある。
As will be described later, the
One of the features of this embodiment is that the
被覆部材304は、基板本体301の外側面301cに所定の材料をコーティングすることにより薄膜状に形成されている。この被覆部材304を構成する材料として、ポリイミド樹脂(PI)、エポキシ樹脂(EP)およびシリコン樹脂(SI)を例示することができる。被覆部材304の外側面304aは、基板本体301の外側面301cと平行な平滑な面に形成されている。
The covering
金属ベース302は、ヒートシンクとして設けられており、積層方向Dに沿って見たとき、基板本体301と合致する形状に形成されている。金属ベース302は、前述したように、アルミニウム合金等の熱伝導性に優れた材料を用いて形成されている。この金属ベース302は、積層方向Dに対向する表面302aおよび裏面302bを含んでいる。これらの表面302aおよび裏面302bは、互いに平行である。金属ベース302の表面302aは、基板本体301の裏面301bに接着剤等を用いて固定されており、両者が全面的に面接触している。
The
金属ベース302の裏面302bは、その全部が、厚肉部77aの一側面303に面接触している。これにより、基板本体301から金属ベース302に伝わった熱を、厚肉部77aに十分に逃がすことができる。
金属ベース302に関連して、位置決め部材318,319が設けられている。各位置決め部材318,319は、パワー基板78を第1のハウジング23の厚肉部77aに対して精度良く位置決めするためのものであり、絶縁体を用いて形成されている。
The
In relation to the
各位置決め部材318,319は、積層方向Dに沿って延びる棒状に形成されており、一端部および他端部の双方が、先細りテーパ状に形成されている。
一方の位置決め部材318の一端部は、金属ベース302の裏面302bに形成された第1の位置決め孔321aに嵌合されており、他端部は、厚肉部77aの一側面303に形成された第2の位置決め孔322aに嵌合されている。各第1および第2の位置決め孔321a,322aは、位置決め部材318の対応する一端部および他端部の形状に合致する形状に形成されている。なお、一方の位置決め部材318を、第1のハウジング23と同一の材料で一体成形してもよい。
Each positioning
One
他方の位置決め部材319は、第1の位置決め孔321bおよび第2の位置決め孔322bの双方に嵌合されている。第1の位置決め孔321bは、基板本体301および金属ベース302の双方を貫通している。他方の位置決め部材319の中間部は、基板本体301、金属ベース302および厚肉部77aのそれぞれを挿通している。第1の位置決め孔321bのうち、基板本体301側の一部は、他方の位置決め部材319の外径形状に合致するテーパ状に形成されており、他方の位置決め部材319の一端部が嵌合している。
The
第2の位置決め孔322bは、厚肉部77aの一側面303に形成されている。他方の位置決め部材319の他端部は、第2の位置決め孔322bに嵌合されている。第2の位置決め孔322bは、他方の位置決め部材319の対応する他端部の形状に合致する形状に形成されている。なお、他方の位置決め部材319を、第1のハウジング23と同一の材料で一体成形してもよい。
The
一方の位置決め部材318と、他方の位置決め部材319とは、互いに離隔して配置されており、パワー基板78が何れかの位置決め部材318,319の周りに回転してしまうことを位置決め部材318,319が協働して防止している。
パワー基板78は、ねじ部材325を用いて厚肉部77aに固定されている。具体的には、パワー基板78にねじ挿通孔323が貫通形成されている。厚肉部77aには、このねじ挿通孔323に対応する箇所にねじ孔324が形成されている。これらのねじ挿通孔323およびねじ孔324を挿通するねじ部材325によって、パワー基板78が厚肉部77aに固定されている。なお、図示していないが、ねじ部材325を用いたねじ締結構造がパワー基板78のうちの別の部分にも設けられており、パワー基板78が厚肉部77aに堅固に固定されている。
One
The
図9は、図7のIX−IX線に沿う要部の断面図である。図9を参照して、基板本体301の表面301aには、導電部305dおよび導電部305eが設けられている。導電部305eの表面には、ニッケル金めっき層306が形成されている。このニッケル金めっき層306には、半田307を用いてFET83がベアチップ実装されている。
導電部305dとFET83とは、ワイヤボンディングを用いて電気的に接続されている。具体的には、導電部305dの表面にボンディングワイヤ310の一端が接合されており、FET83の表面にボンディングワイヤ310の他端が接合されている。
FIG. 9 is a cross-sectional view of a main part taken along line IX-IX in FIG. Referring to FIG. 9,
The
導電部305dには、ワイヤボンディングによる接合のための接合部326と、接合部326を避けて配置された非接合部327とが設けられている。接合部326は、導電部305dのうちFET83寄りに位置する一部分に設けられており、平滑な面に形成されている。この接合部326に上記ボンディングワイヤ310の一端が接合されている。すなわち、ボンディングワイヤ310の一端は、ボンディングパッドを用いることなく、導電部305dに接合されている。導電部305dとFET83とを、伸縮性のあるボンディングワイヤによって電気的に接続することにより、両者に生じる熱応力を緩和することができる。
The
非接合部327は、接合部326と比べてFET83から遠い位置に配置されており、接合部326とは積層方向Dに重なっていない。パワー基板78には、非接合部327および第1〜第6の層311〜316を貫通するビアホール308hが形成されている。接合部326は、積層方向Dに関してビアホール308hを避けて配置されている。
基板本体301の表面301aのうち、ビアホール308hが形成されている部分(非接合部327)は、後述するように、基板本体301を打ち抜いてビアホール308hを形成することに起因する凹凸が生じている。なお、この凹凸は微小であるため、図9では図示していない。この凹凸は、ボンディングワイヤ310の一端を十分に圧接して十分な接合強度を確保するためには好ましく無い。このような凹凸が生じていない接合部326にボンディングワイヤ310の一端を接合することにより、ボンディングワイヤ310の一端を導電部305dに十分な強度で接合することができる。
The
Of the
ビアホール308hは、前述のビアホール308a〜308gと同様の層間接続孔であり、例えば、非接合部327、第1の層311、第2の層312の導電部312c、第3の層313、第4の層314の絶縁部314b、第5の層315および第6の層316の絶縁部316cを貫通している。
このビアホール308hには、ピン部材309が圧入されており、導電部305dと第2の層312の導電部312cとを電気的に接続している。
The via
A
導電部305eにも、ビアホール308hと同様のビアホール308i〜308lが形成されている。各ビアホール308i〜308lには、それぞれ、ピン部材309が圧入されており、例えば、導電部305eと、第6の層316の導電部316dとを電気的に接続している。
図7を参照して、基板本体301の一側縁には、導電部305f,305g,305hが設けられている。各導電部305f,305g,305hは、導電部305dと同様に接合部326および非接合部327を含んでいる。各導電部305f,305g,305hの各接合部326には、ボンディングワイヤ310の一端がそれぞれ接合されている。各ボンディングワイヤ310の他端は、バスバー端子80にそれぞれ接合されている。各非接合部327には、それぞれ、ピン部材309が配置されている。
Via
Referring to FIG. 7,
以上の概略構成を有するパワー基板78は、例えば、以下のようにして製造される。図10(A)を参照して、まず、導電部305a,305b,305cおよび第1〜第7の層311〜317のそれぞれが横並びに複数設けられることで形成された製造中間体331を、プレス部材338で打ち抜く。これにより、図10(B)に示すように、導電部305a,305b,305cおよび第1〜第7の層311〜317を含む製造中間体332が形成される。
The
次に、この製造中間体332の外側面の全面にコーティングを施す。これにより、図10(C)に示すように、被覆部材304が形成される。これにより、第1〜第7の層311〜317の材料としての合成樹脂やガラス繊維やセラミックの粉末が飛散することが防止されている。
次いで、製造中間体332に孔を形成する。具体的には、パンチ部材339を用いて第1の位置決め孔321bを形成する。また、パンチ部材340を用いてビアホール308a〜308g等の各ビアホール308を形成する。また、パンチ部材341を用いてねじ挿通孔323を形成する。これにより、製造中間体333が形成される。
Next, a coating is applied to the entire outer surface of the
Next, holes are formed in the
次に、図11(A)に示すように、ビアホール308a〜308g等の各ビアホール308にピン部材309を圧入固定する。なお、ビアホール308a〜308g等の各ビアホール308にピン部材309を圧入固定する前に、これらのビアホール308の内周面に銅めっき層を形成しておいてもよい。また、ピン部材309を、圧入固定ではなく、すきま嵌めによって対応するビアホール308にそれぞれ挿入し、導電性の接着剤を用いてピン部材309を対応するビアホール308に固定してもよい。
Next, as shown in FIG. 11A, the
次に、図11(B)に示すように、FETやボンディングワイヤ等の部材が接合される導電部(導電部305a等)に、めっき層306を形成する。これにより、基板本体301が形成される。
次いで、図12(A)に示すように、基板本体301の裏面301bに、金属ベース302の表面302aを接着剤等を用いて固定することにより、パワー基板78が形成される。その後、図12(B)に示すように、パワー基板78の基板本体301の表面301aを酸素プラズマの雰囲気下におくことで、めっき層306の表面の洗浄処理を施す。
Next, as shown in FIG. 11B, a
Next, as shown in FIG. 12A, the
具体的には、密閉状の空間を構成する処理室343にパワー基板78を収容する。処理室343内は、プラズマ発生装置344を通過した酸素プラズマで満たされている。処理室343内の温度は、例えば基板本体301の表面301aの温度が100℃以下となるように設定される。また、処理室343には真空ポンプ345が接続されており、処理室343内が真空状態に保たれている。
Specifically, the
基板本体301を酸素プラズマの雰囲気下においた後は、図12(C)に示すように、基板本体301を水素プラズマの雰囲気下におく。図12(C)に示す工程において、図12(B)に示す工程と異なっているのは、酸素プラズマに代えて水素プラズマを用いている点である。
上記のように、真空状態(負圧状態)で、酸素プラズマの次に水素プラズマを基板本体301の表面301aに当てることで、基板本体301の表面301a上にあるめっき層306に形成された炭素化合物および酸化物を、還元反応によって除去することができる。
After the
As described above, the carbon formed on the
その結果、後述する半田リフロー時に、半田307にボイドが発生することを防止でき、半田307を用いた部材の接合強度や、FETの動作時の発熱を抑制することができる。さらには、半田307のフィレット形状を安定化することができ、半田307を用いた接合強度をより向上できる。
なお、酸素プラズマを基板本体301の表面301aに当てる工程の前後に、アルゴンプラズマを基板本体301の表面301aに当てる工程を実施してもよい。
As a result, it is possible to prevent voids from being generated in the
Note that the step of applying argon plasma to the
次に、図13(A)に示すように、パワー基板78の導電部305a等にFET83を実装し、図13(B)に示すように、このパワー基板78をリフロー炉346内に送る。その後、パワー基板78をリフロー炉346から取り出す。これにより、半田307がFET83およびめっき層306に固着し、FET83が導電部305aに接合される。
以上説明したように、本実施の形態によれば、基板本体301の外側面301cが被覆部材304で覆われていることにより、この外側面301cから、絶縁層を構成する材料等が粉塵(異物)として飛散することを防止できる。
Next, as shown in FIG. 13A, the
As described above, according to the present embodiment, since the
これにより、基板本体301の表面301a等に異物が付着してしまうことを防止でき、基板本体301にFET83等の電子部品を接合する際の接合不良を確実に防止できる。
また、絶縁層としての第1、第3、第5および第7の層311,313,315,317は、基材としての合成樹脂よりも熱伝導率が高い熱伝導材としてのセラミック粉末等を含んでいる。これにより、第1、第3、第5および第7の層311,313,315,317の熱伝導性を高くすることができ、基板本体301の放熱性をより高くすることができる。
Thereby, it can prevent that a foreign material adheres to the
The first, third, fifth, and
さらに、ワイヤボンディングによる接合のための接合部326を、積層方向Dに関して、ビアホール308を避けて配置している。基板本体301のうちビアホール308が形成されている部分は、ビアホール308のパンチを用いた形成作業に伴って凹凸が生じることとなる。その一方で、ビアホール308が形成されていない部分は、ビアホール308を形成する作業が行われないので、基板本体301の表面301aに凹凸が生じることが無い。
Further, the
このように、基板本体301の表面301aのうち凹凸が生じていない平滑な部分に接合部326が設けられるので、接合部326と、この接合部326にボンディングされたボンディングワイヤ310との接合を確実に行うことができ、両者の接合強度を十分に確保することができる。しかも、ボンディングパッドのような別部品を用いて接合部326を形成する必要がないので、コスト安価である。
As described above, since the
また、位置決め部材318,319を用いることにより、第1のハウジング23の厚肉部77aに対するパワー基板78の位置決めの精度をより高くすることができる。
さらに、基板本体301から粉塵(異物)が発生することが防止されているので、このような異物が電動モータ18の各軸受75,76等に侵入してこれらの軸受75,76の摩耗が促進されることを防止できる。
Further, by using the
Further, since dust (foreign matter) is prevented from being generated from the
また、多数のビアホール308を備えていることで十分な放熱性が確保されていることから、放熱のためのスペースが少なくて済み、パワー基板78のさらなる小型化を達成することができる。
以上より、基板本体301に実装される各種電子部品の接合不良が確実に防止されているとともに、電動モータ18の軸受75,76等の摩耗が抑制された電動パワーステアリング装置1を実現することができる。
Moreover, since sufficient heat dissipation is ensured by providing a large number of via holes 308, a space for heat dissipation can be reduced, and further miniaturization of the
As described above, it is possible to realize the electric
また、電動モータ18のロータ64の回転位置を検出する回転位置検出装置72を、電動モータ18の回転軸37の軸方向X1に関して、電動モータ18のロータ64と第2のハウジング24との間に配置したので、回転位置検出装置72をECU12に近づけて配置することができる。その結果、回転位置検出装置72およびECU12を、経路長の短い内部配線としてのバスバー端子81によって容易に接続することができる。したがって、経路長の長い外部配線が用いられる従来の場合と比較して、電波ノイズの影響を受け難くなる。また、外部配線のための配線部材を削減することができる。
Further, a rotational
また、収容室100の一部を区画する第2のハウジング24の第2の内壁面102が、電動モータ18の回転軸37の中心軸線C1(またはその延長線C2)とは直交し且つ中心軸線C1(またはその延長線C2)の回りを取り囲む環状平面を含んでいる。すなわち、電動モータ18の回転軸37の軸方向X1に関して、収容室100内へ不必要な出っ張りがない。したがって、収容室100が上記軸方向X1に関して小型であっても、収容室100として十分な内容積を確保することができ、可及的に電動パワーステアリング装置1を小型化することができる。
In addition, the second
また、上記第2のハウジング24が、電動モータ18の動力を操舵機構4に伝達する伝達機構としての減速機構19が収容されたギヤハウジング22であるので下記の利点がある。すなわち、ECU12は、通例、本実施の形態のようにパワー基板78に実装されたスイッチング素子(FET83)等の発熱要素を含んでいる。一方、減速機構19は殆ど発熱しない。このような減速機構19を収容したギヤハウジング22を介して、上記の発熱要素からの熱を収容室100の外部へ効果的に放出することができる。
Further, since the
また、電動モータ18の回転軸37の中心軸線C1に沿う方向に関して、制御基板79および継手38の互いの少なくとも一部が重なるように配置されているので、電動パワーステアリング装置1をより小型にすることができる。
第2の内壁面102のなす環状平面の延長面P1が、操舵力を伝達するための軸(本実施の形態ではステアリングシャフト6に相当)を取り囲む筒状部としての従動ギヤ収容ハウジング28の外周面28aの主要部のなす円筒面P2と図4のように交差するか、または接する状態にある。したがって、電動モータ18の回転軸37の軸方向X1に関して、収容室100を、ステアリングシャフト6側に十分に近づけて配置することになり、回転軸37の軸方向X1に関して、電動パワーステアリング装置1をより小型にすることができる。
Further, since the
An outer peripheral surface of the driven
なお、操舵力を伝達するための軸としては、上記のステアリングシャフト6に限らず、操舵機構4としてのラックアンドピニオン機構のピニオン軸13であってもよいし、また、ラック軸14であってもよい。前者の場合、ピニオン軸13を取り囲む筒状のピニオンハウジング(図示せず)の外周面の主要部のなす円筒面と、上記延長面P1とが交差または接することになる。また、後者の場合、ラック軸14を取り囲む筒状のラックハウジング(図示せず)の外周面の主要部のなす円筒面と、上記延長面P1とが交差または接することになる。
The shaft for transmitting the steering force is not limited to the
また、制御装置としてのECU12を、電動モータ18の回転軸37の中心軸線C1または上記中心軸線C1の延長線C2の回りに配置したので、収容室100の内部のスペースをECU12の配置に有効に利用することができ、ひいては、回転軸37の軸方向X1に関して、電動パワーステアリング装置1をより小型にすることができる。
また、上記第1のハウジング23は、収容室100とモータ室70とを仕切る仕切り壁77を含み、パワー基板78が仕切り壁77の第1の内壁面101に相対的に近接して設けられている。特に、パワー基板78が、仕切り壁77の厚肉部77aにおける、第1の内壁面101に対して熱伝導可能に接触している。したがって、第1のハウジング23の仕切り壁77の厚肉部77aをヒートシンクとして利用して、FET83等の発熱要素を有するパワー基板78の熱を第1のハウジング23からこれに接触する第2のハウジング24側へ効果的に逃がすことができる。
Further, since the
The
収容室100内において、第1のハウジング23の仕切り壁77の薄肉部77bに対向する収容空間S1は、電動モータ18の回転軸37の軸方向X1に関して、十分な高さを有しているので、この収容空間S1には、図5に示すコンデンサ85やリレー86等の背の高い部品を収容することにより、収容室100内の空間の有効利用が図られている。
また、図示していないが、ステアリングホイール2の操舵角を検出する操舵状態検出センサとしての操舵角センサを収容したハウジングと上記の第2のハウジングとが兼用された構成であってもよい。
In the
Further, although not shown, a structure in which a housing that houses a steering angle sensor as a steering state detection sensor that detects a steering angle of the
本発明は、以上の実施形態の内容に限定されるものではなく、請求項記載の範囲内において種々の変更が可能である。例えば、ピン部材309は、樹脂が埋設された銅部材であってもよい。また、位置決め部材318,319の何れかを廃止してもよい。パワー基板78は、第1のハウジング23の第1の壁101に沿わされていることから、1本の位置決め部材でも、パワー基板78の位置決めを精度良く行うことができる。また、断面多角形形状の位置決め部材を用いれば、1本の位置決め部材でも、パワー基板78が位置決め部材の周りを回動してしまうことを防止できる。
The present invention is not limited to the contents of the above embodiments, and various modifications can be made within the scope of the claims. For example, the
上述の実施形態では、いわゆるコラムアシスト式の電動パワーステアリング装置に本発明が適用された例について説明したが、これに限らず、いわゆるピニオンアシスト式の電動パワーステアリング装置や、いわゆるラックアシスト式の電動パワーステアリング装置に、本発明を適用してもよい。
また、上述の実施形態では、本発明が、電動モータの出力を操舵補助力として出力する電動パワーステアリング装置に適用された例について説明したが、これに限らない。例えば、操舵部材の操舵角に対する転舵輪の転舵角の比を変更可能な伝達比可変機構を備え、伝達比可変機構を駆動するために電動モータの出力を用いる伝達比可変式の車両用操舵装置や、操舵部材と転舵輪との機械的な連結が解除され、転舵輪を電動モータの出力で操向するステア・バイ・ワイヤ式の車両用操舵装置等に、本発明を適用してもよい。
In the above-described embodiment, an example in which the present invention is applied to a so-called column assist type electric power steering apparatus has been described. The present invention may be applied to a power steering device.
In the above-described embodiment, the example in which the present invention is applied to the electric power steering apparatus that outputs the output of the electric motor as the steering assist force has been described, but the present invention is not limited thereto. For example, a transmission ratio variable mechanism that includes a transmission ratio variable mechanism capable of changing a ratio of a steered wheel turning angle to a steering angle of a steering member, and that uses an output of an electric motor to drive the transmission ratio variable mechanism, is used for vehicle steering. Even if the present invention is applied to a device, a steer-by-wire type vehicle steering device in which the mechanical connection between the steering member and the steered wheel is released and the steered wheel is steered by the output of the electric motor, etc. Good.
また、ECU12のパワー基板78および制御基板79の少なくとも一部を樹脂でモールドするようにしてもよい。
また、上述の実施形態では、電動モータ18として、ブラシレスモータを用いる例について説明したが、これに限らず、ブラシレスモータ以外のモータを、電動モータ18として用いてもよい。
Further, at least a part of the
In the above-described embodiment, an example in which a brushless motor is used as the
1…電動パワーステアリング装置(車両用操舵装置)、4…操舵機構、18…電動モータ、77a…厚肉部(基板設置部材)、78…パワー基板(積層回路基板、モータ制御装置)、82…モータ駆動回路、83…FET(モータ駆動用素子)、301…基板本体、301a…(基板本体の)表面、301b…(基板本体の)裏面、301c…(基板本体の)外側面、302…金属ベース、304…被覆部材、308…ビアホール、311,313,315,317…絶縁層、312,314,316…導体を含む層、312a,312c,314a,316a,316b,316d…導電部(導体)、318,319…位置決め部材、321a,321b…第1の位置決め孔、326…接合部、D…積層方向。
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (6)
被覆部材とを備え、
上記基板本体は、積層方向に対向する表面および裏面と、側面とを含み、
上記側面は、上記被覆部材によって被覆されていることを特徴とする積層回路基板。 A substrate body formed by laminating a layer including a conductor and an insulating layer;
A covering member,
The substrate body includes a front surface and a back surface facing the stacking direction, and a side surface,
The laminated circuit board, wherein the side surface is covered with the covering member.
上記基板本体の表面は、ワイヤボンディングによる接合のための接合部を含み、
上記接合部は、上記積層方向に関して、上記ビアホールを避けて配置されている積層回路基板。 In Claim 1 or 2, the substrate body is provided with a via hole,
The surface of the substrate body includes a bonding portion for bonding by wire bonding,
The laminated circuit board is arranged such that the joining portion avoids the via hole in the lamination direction.
上記位置決め孔に、上記金属ベースが設置される基板設置部材に形成された位置決め部材を嵌合可能である積層回路基板。 In any one of Claims 1-3, the said laminated circuit board is equipped with the metal base joined to the back surface of a board | substrate body, and the positioning hole formed in this metal base,
A laminated circuit board capable of fitting a positioning member formed on a board installation member on which the metal base is installed into the positioning hole.
上記積層回路基板の基板本体に実装されたモータ駆動用素子を含むモータ駆動回路とを含むモータ制御装置。 The laminated circuit board according to any one of claims 1 to 4,
A motor control device comprising: a motor drive circuit including a motor drive element mounted on the board body of the multilayer circuit board.
上記モータ制御装置によって駆動され、操舵機構に操舵力を付与する電動モータとを備える車両用操舵装置。 A motor control device according to claim 5;
A vehicle steering apparatus comprising: an electric motor that is driven by the motor control apparatus and applies a steering force to a steering mechanism.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008125118A JP2009277726A (en) | 2008-05-12 | 2008-05-12 | Laminated circuit board, motor controller and steering device for vehicle |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008125118A JP2009277726A (en) | 2008-05-12 | 2008-05-12 | Laminated circuit board, motor controller and steering device for vehicle |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009277726A true JP2009277726A (en) | 2009-11-26 |
| JP2009277726A5 JP2009277726A5 (en) | 2011-10-27 |
Family
ID=41442914
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008125118A Pending JP2009277726A (en) | 2008-05-12 | 2008-05-12 | Laminated circuit board, motor controller and steering device for vehicle |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2009277726A (en) |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010195219A (en) * | 2009-02-25 | 2010-09-09 | Nsk Ltd | Electric power steering device |
| JP2012009609A (en) * | 2010-06-24 | 2012-01-12 | Jtekt Corp | Multi-layer circuit board |
| JP2012009608A (en) * | 2010-06-24 | 2012-01-12 | Jtekt Corp | Element mounting circuit and method for mounting semiconductor element to circuit board |
| WO2012153402A1 (en) * | 2011-05-11 | 2012-11-15 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Electric power steering device |
| EP2635096A1 (en) | 2012-02-28 | 2013-09-04 | Jtekt Corporation | Control unit for electric motor and vehicle steering system including the same |
| JP2014090030A (en) * | 2012-10-29 | 2014-05-15 | Jtekt Corp | Control device and vehicle steering gear including the same |
| EP2779811A1 (en) | 2013-03-11 | 2014-09-17 | Jtekt Corporation | Drive circuit device |
| US9686854B2 (en) | 2012-09-25 | 2017-06-20 | Denso Corporation | Electronic device |
| JP2018039497A (en) * | 2016-07-29 | 2018-03-15 | ジョンソン エレクトリック ソシエテ アノニム | Electronic control unit (ecu), control box, and cooling fan module (cfm) having them |
| JP2018098397A (en) * | 2016-12-14 | 2018-06-21 | 株式会社デンソー | Circuit board |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS57170579U (en) * | 1981-04-22 | 1982-10-27 | ||
| JPH0626297U (en) * | 1992-08-28 | 1994-04-08 | 株式会社安川電機 | Circuit board storage device |
| JPH06132670A (en) * | 1992-10-16 | 1994-05-13 | Nippondenso Co Ltd | Metal base multi layer interconnection substrate |
| JP2000253537A (en) * | 1999-02-26 | 2000-09-14 | Sumitomo Wiring Syst Ltd | Electric junction box |
| JP2002120739A (en) * | 2000-10-18 | 2002-04-23 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Electric power steering device |
| JP2007329371A (en) * | 2006-06-09 | 2007-12-20 | Shin Kobe Electric Mach Co Ltd | Laminate circuit board |
-
2008
- 2008-05-12 JP JP2008125118A patent/JP2009277726A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS57170579U (en) * | 1981-04-22 | 1982-10-27 | ||
| JPH0626297U (en) * | 1992-08-28 | 1994-04-08 | 株式会社安川電機 | Circuit board storage device |
| JPH06132670A (en) * | 1992-10-16 | 1994-05-13 | Nippondenso Co Ltd | Metal base multi layer interconnection substrate |
| JP2000253537A (en) * | 1999-02-26 | 2000-09-14 | Sumitomo Wiring Syst Ltd | Electric junction box |
| JP2002120739A (en) * | 2000-10-18 | 2002-04-23 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Electric power steering device |
| JP2007329371A (en) * | 2006-06-09 | 2007-12-20 | Shin Kobe Electric Mach Co Ltd | Laminate circuit board |
Cited By (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010195219A (en) * | 2009-02-25 | 2010-09-09 | Nsk Ltd | Electric power steering device |
| JP2012009609A (en) * | 2010-06-24 | 2012-01-12 | Jtekt Corp | Multi-layer circuit board |
| JP2012009608A (en) * | 2010-06-24 | 2012-01-12 | Jtekt Corp | Element mounting circuit and method for mounting semiconductor element to circuit board |
| WO2012153402A1 (en) * | 2011-05-11 | 2012-11-15 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Electric power steering device |
| CN103502081B (en) * | 2011-05-11 | 2016-02-10 | 三菱电机株式会社 | Driven steering device |
| US9099901B2 (en) | 2011-05-11 | 2015-08-04 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Electric power steering apparatus |
| JP5619279B2 (en) * | 2011-05-11 | 2014-11-05 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Electric power steering device |
| CN103502081A (en) * | 2011-05-11 | 2014-01-08 | 三菱电机株式会社 | Electric power steering device |
| CN103287483A (en) * | 2012-02-28 | 2013-09-11 | 株式会社捷太格特 | Control unit for electric motor and vehicle steering system including the same |
| CN103287483B (en) * | 2012-02-28 | 2016-12-07 | 株式会社捷太格特 | The controlling device and possess its vehicle steering operation device of electro-motor |
| JP2013179762A (en) * | 2012-02-28 | 2013-09-09 | Jtekt Corp | Control device for electric motor and vehicle steering device including the same |
| US9178402B2 (en) | 2012-02-28 | 2015-11-03 | Jtekt Corporation | Control unit for electric motor and vehicle steering system including the same |
| EP2635096A1 (en) | 2012-02-28 | 2013-09-04 | Jtekt Corporation | Control unit for electric motor and vehicle steering system including the same |
| US9686854B2 (en) | 2012-09-25 | 2017-06-20 | Denso Corporation | Electronic device |
| JP2014090030A (en) * | 2012-10-29 | 2014-05-15 | Jtekt Corp | Control device and vehicle steering gear including the same |
| JP2014176225A (en) * | 2013-03-11 | 2014-09-22 | Jtekt Corp | Drive circuit device |
| US9373560B2 (en) | 2013-03-11 | 2016-06-21 | Jtekt Corporation | Drive circuit device |
| EP2779811A1 (en) | 2013-03-11 | 2014-09-17 | Jtekt Corporation | Drive circuit device |
| JP2018039497A (en) * | 2016-07-29 | 2018-03-15 | ジョンソン エレクトリック ソシエテ アノニム | Electronic control unit (ecu), control box, and cooling fan module (cfm) having them |
| JP2018098397A (en) * | 2016-12-14 | 2018-06-21 | 株式会社デンソー | Circuit board |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2009277726A (en) | Laminated circuit board, motor controller and steering device for vehicle | |
| JP5316839B2 (en) | Motor and vehicle steering apparatus including the same | |
| JP5397658B2 (en) | Vehicle steering apparatus and subassembly transfer method | |
| JP5063722B2 (en) | Electric drive device and electric power steering device equipped with the same | |
| US10424991B2 (en) | Drive device | |
| JP4246212B2 (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP5634610B2 (en) | Electric drive | |
| WO2014188803A1 (en) | Power conversion apparatus | |
| WO2009101788A1 (en) | Vehicle steering device | |
| JP5397652B2 (en) | Vehicle steering system | |
| US20120014070A1 (en) | Control device | |
| WO2007007880A1 (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP5071728B2 (en) | Motor control device and vehicle steering apparatus provided with the same | |
| JP2016119794A (en) | Drive device | |
| JP2016146702A (en) | Electric driving device and electric power steering device | |
| JP6040602B2 (en) | Motor unit | |
| JP5397654B2 (en) | Vehicle steering system | |
| JP2010273494A (en) | Motor drive device | |
| JP5234331B2 (en) | Vehicle steering system | |
| JP2014008796A (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| US8576573B2 (en) | Controller, electric power steering provided with the same, method of manufacturing bus bar, and method of manufacturing controller | |
| WO2019159406A1 (en) | Electronic control device and electric drive device | |
| JP5196237B2 (en) | Vehicle steering system | |
| JP2009190477A (en) | Steering device for vehicle | |
| JP5397659B2 (en) | Vehicle steering system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110218 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110901 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110905 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120517 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120607 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120803 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20130221 |