JP2009131026A - Electric motor and refrigerant compressor loading the same - Google Patents
Electric motor and refrigerant compressor loading the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2009131026A JP2009131026A JP2007302799A JP2007302799A JP2009131026A JP 2009131026 A JP2009131026 A JP 2009131026A JP 2007302799 A JP2007302799 A JP 2007302799A JP 2007302799 A JP2007302799 A JP 2007302799A JP 2009131026 A JP2009131026 A JP 2009131026A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- electric motor
- balancer
- permanent magnet
- end plate
- iron core
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Manufacture Of Motors, Generators (AREA)
- Permanent Field Magnets Of Synchronous Machinery (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、空気調和装置や冷凍装置等の各種産業機械に用いられる電動機及びそれを搭載した冷媒圧縮機に関し、特に低コスト化及び信頼性の向上を可能にした電動機及びそれを搭載した冷媒圧縮機に関するものである。 TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention relates to an electric motor used in various industrial machines such as an air conditioner and a refrigeration apparatus, and a refrigerant compressor equipped with the electric motor, and particularly, an electric motor capable of reducing cost and improving reliability and refrigerant compression equipped with the electric motor. Related to the machine.
近年、各種の電動機には、省エネルギーや環境保全等の観点から高効率化や省資源化(小型、軽量化)が求められている。その実現方法のひとつとして、「外周近傍に複数の磁石挿入用開口部を設けた鉄心抜板を多数枚積層して鉄心積層体を形成し、前記磁石挿入用開口部に永久磁石を挿着するとともに、前記鉄心積層体の両端面に端板を設け、前記鉄心積層体と両端板とに形成した複数のリベット挿通穴にリベットを挿通してかしめ固定してなる永久磁石式回転子において、前記リベットのかしめ時のリベットの径方向の膨らみに対応して前記磁石挿入用開口部の内周壁面の一部を変形させるよう前記リベット挿通穴を前記磁石挿入用開口部の近傍に設けた」永久磁石式回転子が存在する(たとえば、特許文献1参照)。 In recent years, various types of electric motors are required to be highly efficient and resource-saving (smaller and lighter) from the viewpoints of energy saving and environmental protection. As one of the realization methods, “a number of iron core punches having a plurality of magnet insertion openings in the vicinity of the outer periphery are laminated to form an iron core laminate, and a permanent magnet is inserted into the magnet insertion opening. In addition, in the permanent magnet rotor in which end plates are provided on both end faces of the core laminate, and rivets are inserted and fixed by caulking through a plurality of rivet insertion holes formed in the core laminate and both end plates, The rivet insertion hole is provided in the vicinity of the magnet insertion opening so as to deform a part of the inner peripheral wall surface of the magnet insertion opening corresponding to the radial bulge of the rivet during caulking of the rivet. There is a magnetic rotor (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
特許文献1記載の永久磁石式回転子は、永久磁石の軸方向の上部に端板やバランサを配置する構成となっている。このため、端版やバランサを磁性体で構成すると磁石から発生する磁束のうち軸方向への磁束が短絡し、所定の磁力が半径方向に出ず、外側に装着される固定子との有効差交磁束が減ってしまう。そうすると、この永久磁石式回転子を備えた電動機に要求される所定の性能を発揮することができないことになる。そこで、永久磁石式回転子では、端版やバランサを非磁性体で構成することが一般的となっている。 The permanent magnet type rotor described in Patent Document 1 has a configuration in which an end plate and a balancer are arranged in the upper part of the permanent magnet in the axial direction. For this reason, when the end plate or balancer is made of a magnetic material, the magnetic flux in the axial direction of the magnetic flux generated from the magnet is short-circuited, and the predetermined magnetic force does not come out in the radial direction. The magnetic flux will decrease. If it does so, the predetermined performance requested | required of the electric motor provided with this permanent magnet type rotor cannot be exhibited. Therefore, in the permanent magnet type rotor, it is common to form the end plate and the balancer with a non-magnetic material.
また、バランサには、回転子が回転することにより遠心力が加わるため、機械的強度が要求される。そのため、材質として金属(たとえば、黄銅やSUS等)が選択されることが多い。このような非磁性金属は一般に高価であり、永久磁石式回転子を製造するために多くのコストを要することになってしまう。さらに、バランサと端板との材質を異なるものとした場合、バランサと端板との間のイオン化傾向の違いで電食が起こり、機械的強度の劣化や潤滑油等の劣化、スラッジ(固体粒子と液体(水など)との混合物)等が発生し、電動機の信頼性を低下させてしまう可能性があり、電動機が搭載される圧縮機等の信頼性も低下してしまうことになる。 Further, the balancer is required to have mechanical strength because centrifugal force is applied as the rotor rotates. For this reason, a metal (for example, brass or SUS) is often selected as the material. Such non-magnetic metals are generally expensive and require a lot of cost to manufacture a permanent magnet rotor. Furthermore, if the balancer and the end plate are made of different materials, electrolytic corrosion occurs due to the difference in ionization tendency between the balancer and the end plate, resulting in deterioration of mechanical strength, deterioration of lubricating oil, sludge (solid particles And a liquid (a mixture of water and the like) and the like may occur, which may reduce the reliability of the electric motor, and also reduce the reliability of the compressor and the like on which the electric motor is mounted.
本発明は、以上のような課題を解決するためになされたもので、安価で信頼性の高い電動機及びそれを搭載した冷媒圧縮機を提供するものである。 The present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems, and provides an inexpensive and highly reliable electric motor and a refrigerant compressor equipped with the electric motor.
本発明に係る電動機は、永久磁石を挿入するための磁石挿入用開口部が形成された円板状の鉄心抜板を複数枚積層させて構成された鉄心積層体と、前記磁石挿入用開口部から挿入され、前記鉄心積層体に挿着された永久磁石と、前記鉄心積層体の軸方向の両端部に設けられた端板と、前記鉄心積層体に設けられた少なくとも一方の端板に設けられ、回転軸の回転を安定化するバランサとを備え、前記バランサを非磁性体の板材及び磁性体の板材を重ねて構成するとともに、前記永久磁石に近い方に前記非磁性体の板材を配置したことを特徴とする。 An electric motor according to the present invention includes an iron core laminate formed by laminating a plurality of disk-shaped iron core punches formed with magnet insertion openings for inserting permanent magnets, and the magnet insertion openings. A permanent magnet inserted into the core stack, end plates provided at both axial ends of the core stack, and at least one end plate provided in the core stack. And a balancer for stabilizing the rotation of the rotating shaft. The balancer is configured by stacking a nonmagnetic plate and a magnetic plate, and the nonmagnetic plate is disposed closer to the permanent magnet. It is characterized by that.
本発明に係る電動機は、永久磁石を挿入するための磁石挿入用開口部が形成された円板状の鉄心抜板を複数枚積層させて構成された鉄心積層体と、前記磁石挿入用開口部から挿入され、前記鉄心積層体に挿着された永久磁石と、前記鉄心積層体の軸方向の両端部に設けられた端板と、前記鉄心積層体に設けられた少なくとも一方の端板に設けられ、回転軸の回転を安定化するバランサとを備え、前記永久磁石と前記端板との間に非磁性体からなるスペーサ部材を設けたことを特徴とする。 An electric motor according to the present invention includes an iron core laminate formed by laminating a plurality of disk-shaped iron core punches formed with magnet insertion openings for inserting permanent magnets, and the magnet insertion openings. A permanent magnet inserted into the core stack, end plates provided at both axial ends of the core stack, and at least one end plate provided in the core stack. And a balancer that stabilizes the rotation of the rotating shaft, and a spacer member made of a non-magnetic material is provided between the permanent magnet and the end plate.
本発明に係る電動機は、永久磁石を挿入するための磁石挿入用開口部が形成された円板状の鉄心抜板を複数枚積層させて構成された鉄心積層体と、前記磁石挿入用開口部から挿入され、前記鉄心積層体に挿着された永久磁石と、前記鉄心積層体の軸方向の両端部に設けられた端板と、前記鉄心積層体に設けられた少なくとも一方の端板に設けられ、回転軸の回転を安定化するバランサとを備え、前記永久磁石の軸方向の長さを前記端板間の長さより短くすることで前記永久磁石と前記端板との間にエアギャップを形成したことを特徴とする。 An electric motor according to the present invention includes an iron core laminate formed by laminating a plurality of disk-shaped iron core punches formed with magnet insertion openings for inserting permanent magnets, and the magnet insertion openings. A permanent magnet inserted into the core stack, end plates provided at both axial ends of the core stack, and at least one end plate provided in the core stack. And a balancer for stabilizing the rotation of the rotating shaft, and by making the axial length of the permanent magnet shorter than the length between the end plates, an air gap is formed between the permanent magnet and the end plate. It is formed.
本発明に係る冷媒圧縮機は、上述の電動機を搭載したことを特徴とする。 A refrigerant compressor according to the present invention includes the above-described electric motor.
本発明に係る電動機によれば、永久磁石から発生する磁束のうち軸方向の磁束が短絡することがない。また、複雑な構造とすることなく、永久磁石から発生する磁束のうち軸方向の磁束の短絡を防止できる。したがって、安価で信頼性の高い電動機を提供することが可能になる。また、本発明に係る冷媒圧縮機によれば、上述の電動機を搭載しているので、電動機の有する効果を全部有することになる。 According to the electric motor according to the present invention, the magnetic flux in the axial direction of the magnetic flux generated from the permanent magnet is not short-circuited. Moreover, short-circuiting of the magnetic flux in the axial direction among magnetic fluxes generated from the permanent magnet can be prevented without using a complicated structure. Therefore, it is possible to provide an inexpensive and highly reliable electric motor. Moreover, according to the refrigerant compressor which concerns on this invention, since the above-mentioned electric motor is mounted, it has all the effects which an electric motor has.
以下、本発明の実施の形態を図面に基づいて説明する。
実施の形態1.
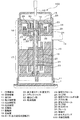
図1は、本発明の実施の形態1に係る冷媒圧縮機100の断面構成の一例を示す縦断面図である。図1に基づいて、冷媒圧縮機100の構成及び動作について説明する。この冷媒圧縮機100は、スクロール式圧縮機である場合を例に示しており、たとえば冷蔵庫や冷凍庫、自動販売機、空気調和器、冷凍装置、給湯器等の冷凍サイクル(ヒートポンプサイクル)の構成要素となるものである。なお、図1を含め、以下の図面では各構成部材の大きさの関係が実際のものとは異なる場合がある。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
Embodiment 1 FIG.
FIG. 1 is a longitudinal sectional view showing an example of a sectional configuration of a
この冷媒圧縮機100は、冷凍サイクルを循環する冷媒を吸入し、圧縮して高温高圧の状態として吐出させるものである。そして、冷媒圧縮機100は、圧縮部16と駆動部17とに分類できる。この圧縮部16及び駆動部17は、密閉容器(シェル)10内に収納されている。この密閉容器10は、圧力容器となっている。図1に示すように、圧縮部16が密閉容器10の上側に配置され、駆動部17が密閉容器10の下側に配置されている。この密閉容器10の底部は、冷凍機油1を貯留する油だめ11となっている。また、密閉容器10には、冷媒ガスを吸入するための吸入側配管12と、冷媒ガスを吐出するための吐出側配管13とが連接されている。
The
圧縮部16は、吸入側配管12から吸入した冷媒ガスを圧縮して密閉容器10内の吐出空間15に排出する機能を有している。この吐出空間15に排出された冷媒ガスは、吐出側配管13から冷媒圧縮機100の外部に吐出されるようになっている。駆動部17は、圧縮部16で冷媒ガスを圧縮するために、圧縮部16を構成する旋回スクロール24を駆動する機能を果たすようになっている。つまり、駆動部17がクランクシャフト21を介して旋回スクロール24を駆動することによって、圧縮部16で冷媒ガスを圧縮するようになっているのである。
The
圧縮部16は、旋回スクロール24と、固定スクロール28と、フレーム31とで概略構成されている。図1に示すように、旋回スクロール24は下側に、固定スクロール28は上側に配置されるようになっている。固定スクロール28には、一方の面に立設された渦巻状突起であるラップ部29が形成されている。また、旋回スクロール24にも、一方の面に立設され、ラップ部29と実質的に同一形状の渦巻状突起であるラップ部25が形成されている。旋回スクロール24及び固定スクロール28は、ラップ部25とラップ部29とを互いに噛み合わせ、密閉容器10内に装着されている。そして、ラップ部25とラップ部29との間には、相対的に容積が変化する圧縮室18が形成される。
The
固定スクロール28は、フレーム31に図示省略のボルト等によって固定されている。固定スクロール28の中央部には、圧縮され、高圧となった冷媒ガスを吐出する吐出ポート30が形成されている。そして、圧縮され、高圧となった冷媒ガスは、固定スクロール28の上部に設けられている吐出空間15に排出されるようになっている。旋回スクロール24は、固定スクロール28に対して自転運動することなく公転旋回運動を行うようになっている。また、旋回スクロール24のラップ部25形成面とは反対側の面(以下、スラスト面と称する)の略中心部には、中空円筒形状の旋回スクロールボス部26が形成されている。この旋回スクロールボス部26には、後述するクランクシャフト21の上端に設けられた偏心ピン部22が嵌入(係合)されているのである。
The
フレーム31は、密閉容器10の内周面に固着され、中心部にクランクシャフト21を貫通させるため貫通孔が形成されている。また、フレーム31には、旋回スクロール24のスラスト面27側から軸方向下側に貫通する排油穴32が形成されており、スラスト面27を潤滑した冷凍機油1を油だめ11に戻すようになっている。図1では、排油穴32が1つだけ形成されている場合を例に示しているが、これに限定するものではない。たとえば、排油穴32を2つ以上形成してもよい。なお、フレーム31は、その外周面を焼き嵌めや溶接等によって密閉容器10の内周面に固定するとよい。
The
駆動部17は、クランクシャフト21に固定されたロータ(永久磁石式回転子)19と、密閉容器10に収容され、固着保持された固定子20と、回転軸であるクランクシャフト21とで構成されている。ロータ19は、クランクシャフト21に固定され、固定子20への通電が開始することにより回転駆動し、クランクシャフト21を回転させるようになっている。また、固定子20の外周面は焼き嵌め等により密閉容器10に固着支持されている。すなわち、ロータ19及び固定子20でモータ(電動機)を構成しているのである。なお、電動機については、以下で詳細に説明するものとする。
The
クランクシャフト21は、ロータ19の回転に伴って回転し、旋回スクロール24を旋回させるようになっている。このクランクシャフト21の上端部は、旋回スクロール24の旋回スクロールボス部26と回転自在に嵌合する偏心ピン部22が形成されている。また、クランクシャフト21の内部には、上端面まで連通している給油流路23が形成されている。この給油流路23は、油だめ11に貯留してある冷凍機油1の流路となるものである。油だめ11に溜まっている冷凍機油1は、クランクシャフト21の回転に伴い、冷凍機油1を吸い上げて給油流路23を流れて圧縮部16に給油されるようになっている。
The
旋回スクロール24と固定スクロール28との間には、旋回スクロール24の偏心旋回運動中における自転運動を阻止するためのオルダムリング33が配設されている。このオルダムリング33は、旋回スクロール24と固定スクロール28との間に配設され、旋回スクロール24の自転運動を阻止するとともに、公転旋回運動を可能とする機能を果たすようになっている。つまり、オルダムリング33は、旋回スクロール24の自転防止機構として機能している。
An
ここで、冷媒圧縮機100の動作について簡単に説明する。
モータを構成するロータ19は、固定子20が発生する回転磁界からの回転力を受けて回転する。それに伴って、ロータ19に固定されたクランクシャフト21が回転駆動する。旋回スクロール24は、クランクシャフト21の偏心ピン部22に係合されており、旋回スクロール24の自転回転運動がオルダムリング33の自転防止機構によって公転旋回運動に変換される。このクランクシャフト21の回転駆動によって、密閉容器10内の冷媒ガスが固定スクロール28のラップ部29と旋回スクロール24のラップ部25とにより形成される圧縮室18内へ流れ、吸入過程が開始する。
Here, the operation of the
The
圧縮室18内に冷媒ガスが吸入されると、偏心させられた旋回スクロール24の公転旋回運動で、圧縮室18の容積を減少させる圧縮過程へと移行する。つまり、圧縮部16では、旋回スクロール24が公転旋回運動すると、冷媒ガスが吸入口となる旋回スクロール24のラップ部25及び固定スクロール28のラップ部29の最外周開口部から取り込まれて、旋回スクロール24の回転とともに徐々に圧縮されながら中心部に向かうようになっている。なお、冷凍サイクルを循環してきた低圧状態の冷媒は、吸入側配管12から密閉容器10内に流入するようになっている。
When the refrigerant gas is sucked into the
そして、圧縮室18で圧縮された冷媒ガスは、吐出過程に移行する。つまり、冷媒ガスは、固定スクロール28の吐出ポート30を通過し、吐出空間15を経由してから冷媒圧縮機100の外部へと吐出されるのである。冷媒圧縮機100の吐出側配管13から吐出された冷媒は、高温高圧の状態となって、まず冷凍サイクルを構成する凝縮器に流入するようになっており、その後冷凍サイクルを構成する各機器を循環して、再度冷媒圧縮機100に吸入される。それから、固定子20への通電を停止すると冷媒圧縮機100は停止する。
Then, the refrigerant gas compressed in the
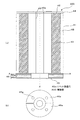
図2は、実施の形態1に係る電動機200の断面構成を示す縦断面図である。図2に基づいて、電動機200について詳細に説明する。電動機200は、上述した冷媒圧縮機10の駆動部17として搭載され、クランクシャフト21を回転駆動する機能を有している。この電動機200は、駆動部17を構成し、クランクシャフト21に固定されたロータ19と、密閉容器10内に固着保持された固定子20と、駆動軸であるクランクシャフト21とを主な構成部品としている。また、電動機200は、永久磁石3を利用した永久磁石式回転子を採用したことを特徴としている。
FIG. 2 is a longitudinal sectional view showing a sectional configuration of the
この電動機200は、複数枚の円板状の鉄心抜板48を積層して構成された鉄心積層体41と、石挿入用開口部2から挿入され、鉄心積層体41に挿着された永久磁石43と、鉄心積層体41の軸方向の両端部に設けられ、磁石挿入用開口部42及び永久磁石43の軸方向両端部を覆うように円板状の鉄板で形成されている端板44と、鉄心積層体41と端板44とをかしめ固定するリベット45と、一方の端板44(図面下側の端板44)の鉄心積層体41側とは反対側に設けられ、リベット45で併せて固定されるバランサ46とで構成されている。
The
鉄心積層体41には、外周近傍に複数の磁石挿入用開口部42が、磁石挿入用開口部42の近傍にリベット挿通穴45a(図2(b)参照)が、中心部に回転軸挿着穴49がそれぞれ形成されている。つまり、鉄心積層体41は、磁石挿入用開口部42、リベット挿通穴45a及び回転軸挿着穴49が形成されている複数枚の鉄心抜板48が積層されて構成されている。磁石挿入用開口部42は、永久磁石43が挿入できる形状であればよく、形状を特に限定するものではない。また、端板44は、非磁性体の鉄板で構成されており、リベット挿通穴45a及び回転軸挿着穴49aが形成されている。この端板44は、回転軸挿着穴49aの中心が鉄心積層体41の回転軸挿着穴49の中心と同一線上(図で示す線X)となるように配置されている。
The
リベット45は、鉄心積層体41及び端板44に形成された複数のリベット挿通穴45aに挿通され、鉄心積層体41と端板44とをかしめ固定するとともに、バランサ46をも固定するようになっている。バランサ46は、回転軸の回転を安定化するためのものであり、隣り合う複数のリベット45により一方の端板44(図面下側の端板44)と一緒に固定されるようになっている。バランサ46は、図2に示すように、複数枚の板材(バランサ46a及びバランサ45b)を積層させて構成されている。また、各板材は、1枚の板材を重ねて構成してもよく、複数枚の略半円状の板材(図2(b)参照)で構成してもよい。たとえば、略半円状の板材を2枚一組として組み合わせ、それらを何層かに積層させてバランサ46を構成してもよい。
The
このバランサ46は、非磁性体のバランサ46aと、磁性体のバランサ46bとで構成されている。バランサ46aは、バランサ46bと端板44とに挟まれるように配置されている。つまり、バランサ46aが図面上側に、バランサ46bが図面下側に配置されており、バランサ46b、バランサ46a、端板44の順に配置されているのである。これは、磁性体からなるバランサ46bを永久磁石43から所定の距離を置くようにするためである。なお、バランサ46aの軸方向の厚さは、端板44の厚さと併せて永久磁石43の半径方向の厚さ以上の厚さを最低限度とする。
The
このように構成された電動機200では、永久磁石43の軸方向の両端部に非磁性体からなる端板44を、永久磁石43の軸方向の一方の端部(図面下側)に非磁性体からなる所定量のバランサ46aを配置するため、永久磁石43から発生する磁束のうち軸方向への磁束が短絡することがない。また、磁性体からなるバランサ46bは、永久磁石43から所定の距離を置くように離されているために、永久磁石43からの磁気抵抗が高く、磁束の短絡が発生することがない。つまり、永久磁石43から発生した磁束が半径方向のみに向かうのである(有効磁束(図で示す矢印))。
In the
以上のように、電動機200は、非磁性体のバランサ46aと磁性体のバランサ46bとでバランサ46が構成されているため、安価なSPHC材(熱間圧延鋼板)等の板金を採用してバランサ46bを構成することができる。したがって、電動機200は、製造に要するコストを抑制するとともに、信頼性の高いものとすることができる。また、積層構造のバランサ46を採用することで、枚数を変化させることができ、バランス量を調整することが可能となる。したがって、電動機200のバランス量が違う場合であっても、新たな厚みのバランサが不要であり、生産効率が向上する。
As described above, in the
この実施の形態1では、電動機200の底部側にバランサ46を配置した場合を例に説明したが、これに限定するものではなく、電動機200の上部や底部及び上部の双方にバランサ46を配置するようにしてもよい。また、実施の形態1では、バランサ46a及びバランサ46bを複数枚の板材を積層して構成した場合を例に示しているが、これに限定するものではなく、バランサ46a及びバランサ46bを1枚の板材で構成するようにしてもよい。特に、バランサ46aは、その軸方向の厚さを、端板44の厚さと併せて永久磁石43の半径方向の厚さ以上の厚さとできればよいのである。さらに、バランサ64aとバランサ64bとをイオン化傾向のあまり違わない素材で構成すれば、イオン化傾向の違いで発生する電食を防ぐことができる。なお、電食の防止については、実施の形態6で詳しく説明する。
In the first embodiment, the case where the
実施の形態2.
図3は、本発明の実施の形態2に係る電動機300の構成を説明するための説明図である。図3に基づいて、電動機300について詳細に説明する。図3(a)が電動機300の断面構成を示す縦断面図を、図3(b)が電動機300のA−A断面を示す平面図である。この電動機300は、電動機200と同様に実施の形態1で説明した冷媒圧縮機100に搭載され、クランクシャフト21を回転駆動する機能を有している。また、電動機300は、永久磁石3を利用した永久磁石式回転子を採用したことを特徴としている。なお、実施の形態2では実施の形態1との相違点を中心に説明し、実施の形態1と同一部分には、同一符号を付して説明を省略するものとする。
Embodiment 2.
FIG. 3 is an explanatory diagram for explaining a configuration of an
この実施の形態2に係る電動機300は、一方の端板44(図面下側)の一部をバランサ46で代用している点で実施の形態1に係る電動機200と相違している。図3(b)に示すように、非磁性体からなる2枚一組のバランサ46aの一部で一方の端板44の代わりをしている。つまり、非磁性体からなる2枚一組のバランサ46aの一部が一方の端板44を兼用しているのである。このバランサ46を構成する略半円状の2枚のバランサ46aの一部(図面最上段のバランサ46a)で磁石挿入用開口部42及び永久磁石43の軸方向一方の端部(図面下側)を覆うようになっているのである。
The
このような場合においても、バランサ46aの軸方向の厚さは、永久磁石43の半径方向の厚さ以上の厚さを最低限度とすることが望ましい。つまり、実施の形態1で説明したよりも端板4の厚み分だけ、バランサ46aの厚みが要求されることになる。この場合も、端板44の代用となるバランサ46aの回転軸挿着穴49aの中心が、鉄心積層体41の回転軸挿着穴49の中心と同一線上(図で示す線X)となるように、略半円状の2枚のバランサ46aを円状に組み合わせて配置する。
Even in such a case, it is desirable that the thickness of the
以上のように、電動機300は、バランサ46の一部で一方の端板44の代わりをするので、端板44を構成する新たな部品が不要になり、部品の種類を低減することができるとともに、永久磁石43の軸方向の一方の端部(図面下側)に非磁性体からなる所定量のバランサ46aを配置するため、永久磁石43から発生する磁束のうち軸方向への磁束が短絡することがない。また、磁性体からなるバランサ46bは、永久磁石43から所定の距離を置くように離されているために、永久磁石43からの磁気抵抗が高く、磁束の短絡が発生することがない。つまり、永久磁石43から発生した磁束が半径方向のみに向かうのである。
As described above, since the
この実施の形態2では、電動機300の底部側にバランサ46を配置した場合を例に説明したが、これに限定するものではなく、電動機300の上部や底部及び上部の双方にバランサ46を配置するようにしてもよい。また、実施の形態2では、バランサ46a及びバランサ46bを複数枚の板材を積層して構成した場合を例に示しているが、これに限定するものではなく、バランサ46a及びバランサ46bを1枚の板材で構成するようにしてもよい。特に、バランサ46aは、その軸方向の厚さを、永久磁石43の半径方向の厚さ以上の厚さとできればよいのである。さらに、バランサ64aとバランサ64bとをイオン化傾向のあまり違わない素材で構成すれば、イオン化傾向の違いで発生する電食を防ぐことができる。
In the second embodiment, the case where the
実施の形態3.
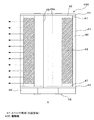
図4は、本発明の実施の形態3に係る電動機400の断面構成を示す縦断面図である。図4に基づいて、電動機400の構成について説明する。この電動機400は、電動機200及び電動機300と同様に実施の形態1で説明した冷媒圧縮機100に搭載され、クランクシャフト21を回転駆動する機能を有している。また、電動機400は、永久磁石3を利用した永久磁石式回転子を採用したことを特徴としている。なお、実施の形態3では実施の形態1及び実施の形態2との相違点を中心に説明し、実施の形態1及び実施の形態2と同一部分には、同一符号を付して説明を省略するものとする。
Embodiment 3.
FIG. 4 is a longitudinal sectional view showing a sectional configuration of an
この実施の形態3に係る電動機400は、永久磁石43の軸方向両端部に非磁性体からなるスペーサ部材47を挿入している点で実施の形態1に係る電動機200及び実施の形態2に係る電動機300と相違している。つまり、電動機400は、永久磁石43と端板44との間にスペーサ部材47を設け、永久磁石43の軸方向両端部に所定の距離を形成しているのである。このスペーサ部材47の軸方向の厚さは、永久磁石43の半径方向の厚さ以上の厚さを最低限度とすることが望ましい。こうすることで、端板44及びバランサ46を磁性体で構成することもできる。
The
以上のように、電動機400は、永久磁石43の軸方向両端部に非磁性体からなるスペーサ部材47を設けたので、永久磁石43から発生する磁束のうち軸方向への磁束が短絡せず、磁束が固定子側(変形方向)に向かう(有効磁束(図で示す矢印))。したがって、電動機400は、実施の形態1に係る電動機200及び実施の形態2に係る電動機300の有する効果に加え、性能低下を更に防止することができる。また、電動機400では、端板44及びバランサ46を磁性体、たとえばSPHC材等の板金で構成すれば、製造に要するコストを抑制することが可能である。
As described above, since the
この実施の形態3では、電動機400の底部側にバランサ46を配置した場合を例に説明したが、これに限定するものではなく、電動機400の上部や底部及び上部の双方にバランサ46を配置するようにしてもよい。また、スペーサ部材47は、非磁性体の材質であればよく、特に材質を限定するものではない。さらに、実施の形態3では、永久磁石43の軸方向両端部に端板44を配置した場合を例に示しているが、実施の形態2に係る電動機300のように、バランサ46の一部で一方の端板44を兼用してもよい。
In the third embodiment, the case where the
実施の形態4.
図5は、本発明の実施の形態4に係る電動機500の断面構成を示す縦断面図である。図5に基づいて、電動機500の構成について説明する。この電動機500は、電動機200、電動機300及び電動機400と同様に実施の形態1で説明した冷媒圧縮機100に搭載され、クランクシャフト21を回転駆動する機能を有している。また、電動機500は、永久磁石3を利用した永久磁石式回転子を採用したことを特徴としている。なお、実施の形態4では実施の形態1〜実施の形態3との相違点を中心に説明し、実施の形態1〜実施の形態3と同一部分には、同一符号を付して説明を省略するものとする。
Embodiment 4.
FIG. 5 is a longitudinal sectional view showing a sectional configuration of an
この実施の形態4に係る電動機500は、鉄心積層体41の内壁面(永久磁石43との接触面)に複数のストッパ41aを形成し、永久磁石43の軸方向両端部にエアギャップ(空隙)50を形成している点で実施の形態1に係る電動機200、実施の形態2に係る電動機300及び実施の形態3に係る電動機400と相違している。つまり、電動機500では、ストッパ41aで永久磁石43の軸方向の長さ範囲を規制し、軸方向に所定の長さとなるエアギャップ50を形成しているのである。このエアギャップ50軸方向の距離は、永久磁石43の半径方向の厚さ以上の距離を最低限度とすることが望ましい。こうすることで、端板44及びバランサ46を磁性体で構成することもできる。
In the
以上のように、電動機500は、永久磁石43の軸方向両端部にエアギャップ50を形成したので、永久磁石43から発生する磁束のうち軸方向への磁束が短絡せず、磁束が固定子側に向かう(有効磁束(図で示す矢印))。したがって、電動機500は、実施の形態1に係る電動機200、実施の形態2に係る電動機300及び実施の形態3に係る電動機400の有する効果に加え、性能低下を更に防止することができる。また、端板44及びバランサ46を磁性体、たとえばSPHC材等の板金で構成すれば、製造に要するコストを更に抑制することができる。
As described above, since the
この実施の形態4では、電動機500の底部側にバランサ46を配置した場合を例に説明したが、これに限定するものではなく、電動機500の上部や底部及び上部の双方にバランサ46を配置するようにしてもよい。また、実施の形態4では、永久磁石43の軸方向両端部に端板44を配置した場合を例に示しているが、実施の形態2に係る電動機300のように、バランサ46の一部で一方の端板44を兼用してもよい。さらに、ストッパ41aは、エアギャップ50を確保できるものであればよく、特に形状や大きさを限定するものではない。
In the fourth embodiment, the case where the
実施の形態5.
図6は、本発明の実施の形態5に係る電動機600の断面構成を示す縦断面図である。図6に基づいて、電動機600の構成について説明する。この電動機600は、電動機200、電動機300、電動機400及び電動機500と同様に実施の形態1で説明した冷媒圧縮機100に搭載され、クランクシャフト21を回転駆動する機能を有している。また、電動機600は、永久磁石3を利用した永久磁石式回転子を採用したことを特徴としている。なお、実施の形態5では実施の形態1〜実施の形態4との相違点を中心に説明し、実施の形態1〜実施の形態4と同一部分には、同一符号を付して説明を省略するものとする。
Embodiment 5.
FIG. 6 is a longitudinal sectional view showing a sectional configuration of an
この実施の形態5に係る電動機600は、端板44及びバランサ46を同一の材質で構成していることを特徴としている。端板44とバランサ46とが異なる材質であると、イオン化傾向の違いによって、接合部分で電食が発生する。この電食は、機械的強度の劣化や潤滑油等の劣化、スラッジの発生を誘発することになる。また、電動機600が搭載される冷媒圧縮機100の密閉容器10内部温度は、電動機600の発熱や吸入冷媒の温度によって種々変化するため、電食が発生する可能性が高い。そこで、電動機600は、端板44及びバランサ46を同一の材質で構成し、電食の発生を効果的に防ぐことができるのである。ただし、この場合にも、永久磁石43から発生する磁束のうち軸方向の磁束を短絡させないようにすることが要求される。
The
すなわち、電動機600の特徴事項を、実施の形態3に係る電動機400及び実施の形態4に係る電動機500の特徴事項と組み合わせて適用することが好ましい。たとえば、スペーサ部材47やエアギャップ50を設けた状態においては、端板44及びバランサ46の材質は、非磁性体であっても、磁性体であってもよいために、非磁性体又は磁性体の同一材質で端板44及びバランサ46を構成することができる。こうすれば、端板44及びバランサ46のイオン化傾向が同じになるため、端板44とバランサ46との接合部分での電食を防止できる。
That is, it is preferable to apply the feature matter of the
以上のように、電動機600は、端板44及びバランサ46を同一の材質で構成しているので、バランサ46と端板44との間におけるイオン化傾向の違いで発生する電食の可能性がなく、機械的強度の劣化や潤滑油等の劣化、スラッジの発生を防止し、信頼性を低下させることがない。また、電動機600の特徴を、実施の形態3に係る電動機400及び実施の形態4に係る電動機500の特徴事項と組み合わせれば、永久磁石43の軸方向両端部に非磁性体からなるスペーサ部材47やエアギャップ50のため、永久磁石43から発生する磁束のうち軸方向への磁束を短絡させないこともできる(図で示す矢印)。
As described above, in the
この実施の形態5では、電動機600の底部側にバランサ46を配置した場合を例に説明したが、これに限定するものではなく、電動機600の上部や底部及び上部の双方にバランサ46を配置するようにしてもよい。また、端板44及びバランサ46を構成する材質は、同一のものであればよく、特に材質を限定するものではない。さらに、実施の形態3及び実施の形態4と組み合わせる場合においては、端板44及びバランサ46を構成する材質は、非磁性体であっても、磁性体であってもよい。
In the fifth embodiment, the case where the
実施の形態6.
端板44及びバランサ46のイオン化傾向について詳細に説明する。端板44及びバランサ46を異なる金属で構成すると、両者の標準電極電位が異なるため、電位差が生じ、金属のイオン化が起こり、電食が発生することになる。一般的に、冷媒圧縮機では、端板44がSUS304(標準電極電位:0.80)で、バランサ46が黄銅(標準電極電位:−0.04)で構成されることが多い。そうすると、両者の標準電極電位の差は、0.8程度となる。ボルタの電池では、亜鉛(Zn)と銅(Cu)とで電位差1.0程度でイオン化(電腐)が行なわれており、これ以上の電位差では電解質(たとえば、水)があると電腐が容易に発生する。
Embodiment 6 FIG.
The ionization tendency of the
よって、冷媒圧縮機の実績からみても電位差0.8以下であれば電食の発生を防止することができると考えられる。たとえば、端板44がSUS304で、バランサ46が亜鉛(標準電極電位:−0.76)で構成すると、電位差が1.0を越えてしまい、電食が発生し易くなる。したがって、実施の形態1〜実施の形態5に係る冷媒圧縮機100では、端板44及びバランサ46を同一材質で構成する、あるいは、イオン化傾向の近い材質で構成することを特徴としているため、温度や水分量を問わず、電食の発生を防止することができるようになっている。
Therefore, it is considered that the occurrence of electrolytic corrosion can be prevented if the potential difference is 0.8 or less from the viewpoint of the performance of the refrigerant compressor. For example, if the
1 冷凍機油、10 密閉容器、11 油だめ、12 吸入側配管、13 吐出側配管、15 吐出空間、16 圧縮部、17 駆動部、18 圧縮室、19 ロータ(永久磁石式回転子)、20 固定子、21 クランクシャフト、22 偏心ピン部、23 給油流路、24 旋回スクロール、25 ラップ部、26 旋回スクロールボス部、27 スラスト面、28 固定スクロール、29 ラップ部、30 吐出ポート、31 フレーム、32 排油穴、33 オルダムリング、41 鉄心積層体、41a ストッパ、42 磁石挿入用開口部、43 永久磁石、44 端板、45 リベット、45a リベット挿通穴、46 バランサ、46a バランサ、46b バランサ、47 スペーサ部材、48 鉄心抜板、49 回転軸挿着穴、49a 回転軸挿着穴、50 エアギャップ、100 冷媒圧縮機、200 電動機、300 電動機、400 電動機、500 電動機、600 電動機。 DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1 Refrigerating machine oil, 10 airtight container, 11 sump, 12 suction side piping, 13 discharge side piping, 15 discharge space, 16 compression part, 17 drive part, 18 compression chamber, 19 rotor (permanent magnet type rotor), 20 fixation Child, 21 Crankshaft, 22 Eccentric pin part, 23 Oil supply flow path, 24 Orbiting scroll, 25 Wrap part, 26 Orbiting scroll boss part, 27 Thrust surface, 28 Fixed scroll, 29 Wrap part, 30 Discharge port, 31 Frame, 32 Oil drain hole, 33 Oldham ring, 41 Iron core laminate, 41a Stopper, 42 Magnet insertion opening, 43 Permanent magnet, 44 End plate, 45 Rivet, 45a Rivet insertion hole, 46 balancer, 46a balancer, 46b Balancer, 47 spacer Member, 48 Iron core punch, 49 Rotating shaft insertion hole, 49a Rotating shaft insertion hole , 50 air gap, 100 refrigerant compressor, 200 electric motor, 300 electric motor, 400 electric motor, 500 electric motor, 600 electric motor.
Claims (13)
前記磁石挿入用開口部から挿入され、前記鉄心積層体に挿着された永久磁石と、
前記鉄心積層体の軸方向の両端部に設けられた端板と、
前記鉄心積層体に設けられた少なくとも一方の端板に設けられ、回転軸の回転を安定化するバランサとを備え、
前記バランサを非磁性体の板材及び磁性体の板材を重ねて構成するとともに、前記永久磁石に近い方に前記非磁性体の板材を配置した
ことを特徴とする電動機。 An iron core laminate formed by laminating a plurality of disk-shaped iron core punches having magnet insertion openings for inserting permanent magnets; and
A permanent magnet inserted from the magnet insertion opening and inserted into the core laminate;
End plates provided at both ends in the axial direction of the core laminate,
A balancer that is provided on at least one end plate provided in the iron core laminate and stabilizes rotation of the rotary shaft;
The balancer is configured by stacking a nonmagnetic plate and a magnetic plate, and the nonmagnetic plate is disposed closer to the permanent magnet.
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の電動機。 2. The electric motor according to claim 1, wherein a thickness of the non-magnetic material plate in an axial direction is equal to or greater than a thickness of the permanent magnet in a radial direction.
前記磁石挿入用開口部から挿入され、前記鉄心積層体に挿着された永久磁石と、
前記鉄心積層体の軸方向の両端部に設けられた端板と、
前記鉄心積層体に設けられた少なくとも一方の端板に設けられ、回転軸の回転を安定化するバランサとを備え、
前記永久磁石と前記端板との間に非磁性体からなるスペーサ部材を設けた
ことを特徴とする電動機。 An iron core laminate formed by laminating a plurality of disk-shaped iron core punches having magnet insertion openings for inserting permanent magnets; and
A permanent magnet inserted from the magnet insertion opening and inserted into the core laminate;
End plates provided at both ends in the axial direction of the core laminate,
A balancer that is provided on at least one end plate provided in the iron core laminate and stabilizes rotation of the rotary shaft;
An electric motor comprising a spacer member made of a non-magnetic material between the permanent magnet and the end plate.
ことを特徴とする請求項3に記載の電動機。 The electric motor according to claim 3, wherein the thickness of the spacer member in the axial direction is equal to or greater than the thickness of the permanent magnet in the radial direction.
前記磁石挿入用開口部から挿入され、前記鉄心積層体に挿着された永久磁石と、
前記鉄心積層体の軸方向の両端部に設けられた端板と、
前記鉄心積層体に設けられた少なくとも一方の端板に設けられ、回転軸の回転を安定化するバランサとを備え、
前記永久磁石の軸方向の長さを前記端板間の長さより短くすることで前記永久磁石と前記端板との間にエアギャップを形成した
ことを特徴とする電動機。 An iron core laminate formed by laminating a plurality of disk-shaped iron core punches having magnet insertion openings for inserting permanent magnets; and
A permanent magnet inserted from the magnet insertion opening and inserted into the core laminate;
End plates provided at both ends in the axial direction of the core laminate,
A balancer that is provided on at least one end plate provided in the iron core laminate and stabilizes rotation of the rotary shaft;
An electric motor in which an air gap is formed between the permanent magnet and the end plate by making an axial length of the permanent magnet shorter than a length between the end plates.
ことを特徴とする請求項5に記載の電動機。 The electric motor according to claim 5, wherein a distance in an axial direction of the air gap is equal to or greater than a thickness in a radial direction of the permanent magnet.
ことを特徴とする請求項5又は6に記載の電動機。 The electric motor according to claim 5 or 6, wherein a stopper that makes the length of the permanent magnet in the axial direction shorter than the length between the end plates is provided on the inner wall surface of the iron core laminate.
ことを特徴とする請求項1〜7のいずれかに記載の電動機。 The electric motor according to claim 1, wherein the balancer also serves as the end plate.
ことを特徴とする請求項3〜7のいずれかに記載の電動機。 The electric motor according to any one of claims 3 to 7, wherein the end plate and the balancer are made of a magnetic material.
ことを特徴とする請求項3〜7のいずれかに記載の電動機。 The electric motor according to any one of claims 3 to 7, wherein the end plate and the balancer are made of the same magnetic or non-magnetic material.
ことを特徴とする請求項1〜10のいずれかに記載の電動機。 The electric motor according to claim 1, wherein the balancer is composed of a plurality of plate members.
ことを特徴とする請求項1〜11のいずれかに記載の電動機。 The electric motor according to claim 1, wherein the balancer is configured by combining substantially semicircular plate members.
ことを特徴とする冷媒圧縮機。 A refrigerant compressor comprising the electric motor according to any one of claims 1 to 12.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007302799A JP2009131026A (en) | 2007-11-22 | 2007-11-22 | Electric motor and refrigerant compressor loading the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007302799A JP2009131026A (en) | 2007-11-22 | 2007-11-22 | Electric motor and refrigerant compressor loading the same |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009131026A true JP2009131026A (en) | 2009-06-11 |
| JP2009131026A5 JP2009131026A5 (en) | 2011-08-18 |
Family
ID=40821409
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007302799A Pending JP2009131026A (en) | 2007-11-22 | 2007-11-22 | Electric motor and refrigerant compressor loading the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2009131026A (en) |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011030286A (en) * | 2009-07-21 | 2011-02-10 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Electric motor |
| JP2014165971A (en) * | 2013-02-22 | 2014-09-08 | Meidensha Corp | Rotor structure of permanent magnet motor |
| JP2015226368A (en) * | 2014-05-27 | 2015-12-14 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Rotor for rotary electric machine |
| JP2016092966A (en) * | 2014-11-05 | 2016-05-23 | 日本電産テクノモータ株式会社 | Rotor and motor |
| JP2018074868A (en) * | 2016-11-04 | 2018-05-10 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Magnet embedded rotary electric machine and manufacturing method thereof |
| CN109681427A (en) * | 2017-10-19 | 2019-04-26 | 日立江森自控空调有限公司 | Sealed electrical compressor |
| JP2020088988A (en) * | 2018-11-20 | 2020-06-04 | 日本電産株式会社 | Rotor and motor |
| JP2021055878A (en) * | 2019-09-27 | 2021-04-08 | 株式会社富士通ゼネラル | Refrigeration cycle device |
| WO2022144967A1 (en) * | 2020-12-28 | 2022-07-07 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Rotor, electric motor, compressor, and refrigeration cycle device |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH08251848A (en) * | 1995-01-11 | 1996-09-27 | Yaskawa Electric Corp | Rotor of permanent magnet type synchronous rotary machine |
| JP2000037061A (en) * | 1998-07-15 | 2000-02-02 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Rotor for motor and its manufacture |
| JP2000078786A (en) * | 1998-08-28 | 2000-03-14 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Rotor |
| JP2000125491A (en) * | 1998-10-12 | 2000-04-28 | Toshiba Corp | Permanent magnet motor for compressor |
| JP2001037119A (en) * | 1999-07-16 | 2001-02-09 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Permanent magnet type synchronous motor |
| JP2005143299A (en) * | 2001-03-30 | 2005-06-02 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Synchronous induction motor |
-
2007
- 2007-11-22 JP JP2007302799A patent/JP2009131026A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH08251848A (en) * | 1995-01-11 | 1996-09-27 | Yaskawa Electric Corp | Rotor of permanent magnet type synchronous rotary machine |
| JP2000037061A (en) * | 1998-07-15 | 2000-02-02 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Rotor for motor and its manufacture |
| JP2000078786A (en) * | 1998-08-28 | 2000-03-14 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Rotor |
| JP2000125491A (en) * | 1998-10-12 | 2000-04-28 | Toshiba Corp | Permanent magnet motor for compressor |
| JP2001037119A (en) * | 1999-07-16 | 2001-02-09 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Permanent magnet type synchronous motor |
| JP2005143299A (en) * | 2001-03-30 | 2005-06-02 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Synchronous induction motor |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011030286A (en) * | 2009-07-21 | 2011-02-10 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Electric motor |
| JP2014165971A (en) * | 2013-02-22 | 2014-09-08 | Meidensha Corp | Rotor structure of permanent magnet motor |
| JP2015226368A (en) * | 2014-05-27 | 2015-12-14 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Rotor for rotary electric machine |
| JP2016092966A (en) * | 2014-11-05 | 2016-05-23 | 日本電産テクノモータ株式会社 | Rotor and motor |
| JP2018074868A (en) * | 2016-11-04 | 2018-05-10 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Magnet embedded rotary electric machine and manufacturing method thereof |
| CN109681427A (en) * | 2017-10-19 | 2019-04-26 | 日立江森自控空调有限公司 | Sealed electrical compressor |
| JP2019074067A (en) * | 2017-10-19 | 2019-05-16 | 日立ジョンソンコントロールズ空調株式会社 | Hermetic electric compressor |
| JP2020088988A (en) * | 2018-11-20 | 2020-06-04 | 日本電産株式会社 | Rotor and motor |
| JP7192431B2 (en) | 2018-11-20 | 2022-12-20 | 日本電産株式会社 | rotor and motor |
| JP2021055878A (en) * | 2019-09-27 | 2021-04-08 | 株式会社富士通ゼネラル | Refrigeration cycle device |
| WO2022144967A1 (en) * | 2020-12-28 | 2022-07-07 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Rotor, electric motor, compressor, and refrigeration cycle device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2009131026A (en) | Electric motor and refrigerant compressor loading the same | |
| JP4841536B2 (en) | Motor and refrigerant compressor provided with the same | |
| US8992188B2 (en) | Revolution type compressor | |
| CN110603716A (en) | Rotor, motor, compressor, and air conditioner | |
| US10954944B2 (en) | Compressor having counterweight assembly | |
| WO2015125254A1 (en) | Rotor, permanent magnet electric motor equipped with said rotor, fluid machine equipped with permanent magnet electric motor, and rotor manufacturing method | |
| JP2010226830A (en) | Electric motor, and compressor mounted with the same | |
| JP5114709B2 (en) | Hermetic scroll compressor and its assembly method | |
| JP5839913B2 (en) | Fluid machine and method of manufacturing fluid machine | |
| JP5506219B2 (en) | Refrigerant compressor and fluid compressor | |
| JP2011111969A (en) | Scroll compressor | |
| JP5334555B2 (en) | Electric motor and refrigerant compressor equipped with the same | |
| EP3163083B1 (en) | Electric compressor | |
| JP2014070585A (en) | Rotary compressor | |
| JP2010144528A (en) | Compressor | |
| JP5660772B2 (en) | Rotor, magnet-embedded electric motor, and electric compressor | |
| JP2005184873A (en) | Motor compressor | |
| JP7042455B2 (en) | Compressor | |
| JP2004274995A (en) | Permanent magnet rotating electric machine and compressor using the same | |
| JP2011072100A (en) | Self-starting permanent-magnet synchronous motor, and compressor and air conditioner using the same | |
| JP6320575B2 (en) | Electric compressor | |
| JP2000287424A (en) | Rotor of rotary compressor and manufacture thereof | |
| JP5559839B2 (en) | Hermetic scroll compressor | |
| JP2020007928A (en) | Scroll compressor | |
| WO2024176546A1 (en) | Electric motor, compressor, and device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100712 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20110524 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110701 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110726 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110920 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120327 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20120724 |