EP3134344B2 - Method and apparatus for operating a mobile crane and the mobile crane - Google Patents
Method and apparatus for operating a mobile crane and the mobile crane Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP3134344B2 EP3134344B2 EP15717490.5A EP15717490A EP3134344B2 EP 3134344 B2 EP3134344 B2 EP 3134344B2 EP 15717490 A EP15717490 A EP 15717490A EP 3134344 B2 EP3134344 B2 EP 3134344B2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- load
- boom
- maximum permissible
- positions
- determined
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 19
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000004040 coloring Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 12
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 7
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000004088 simulation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000007 visual effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001364 causal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004069 differentiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003550 marker Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66C—CRANES; LOAD-ENGAGING ELEMENTS OR DEVICES FOR CRANES, CAPSTANS, WINCHES, OR TACKLES
- B66C23/00—Cranes comprising essentially a beam, boom, or triangular structure acting as a cantilever and mounted for translatory of swinging movements in vertical or horizontal planes or a combination of such movements, e.g. jib-cranes, derricks, tower cranes
- B66C23/88—Safety gear
- B66C23/90—Devices for indicating or limiting lifting moment
- B66C23/905—Devices for indicating or limiting lifting moment electrical
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66C—CRANES; LOAD-ENGAGING ELEMENTS OR DEVICES FOR CRANES, CAPSTANS, WINCHES, OR TACKLES
- B66C13/00—Other constructional features or details
- B66C13/16—Applications of indicating, registering, or weighing devices
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66C—CRANES; LOAD-ENGAGING ELEMENTS OR DEVICES FOR CRANES, CAPSTANS, WINCHES, OR TACKLES
- B66C13/00—Other constructional features or details
- B66C13/18—Control systems or devices
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66C—CRANES; LOAD-ENGAGING ELEMENTS OR DEVICES FOR CRANES, CAPSTANS, WINCHES, OR TACKLES
- B66C23/00—Cranes comprising essentially a beam, boom, or triangular structure acting as a cantilever and mounted for translatory of swinging movements in vertical or horizontal planes or a combination of such movements, e.g. jib-cranes, derricks, tower cranes
- B66C23/18—Cranes comprising essentially a beam, boom, or triangular structure acting as a cantilever and mounted for translatory of swinging movements in vertical or horizontal planes or a combination of such movements, e.g. jib-cranes, derricks, tower cranes specially adapted for use in particular purposes
- B66C23/36—Cranes comprising essentially a beam, boom, or triangular structure acting as a cantilever and mounted for translatory of swinging movements in vertical or horizontal planes or a combination of such movements, e.g. jib-cranes, derricks, tower cranes specially adapted for use in particular purposes mounted on road or rail vehicles; Manually-movable jib-cranes for use in workshops; Floating cranes
Definitions
- the invention relates to mobile cranes, in particular mobile cranes with variable support geometries.
- the present invention also relates to methods for determining a maximum load capacity, measures for ensuring the stability of the mobile crane and means for displaying safe working positions.
- Mobile cranes are usually fitted with a support device to improve stability or increase the load-bearing capacity.
- a support device comprises support beams that protrude from the side of the mobile crane and on which support cylinders are provided.
- the support cylinders can be used to support a protruding end on a base of the mobile crane, thereby increasing the effective base area.
- the increased effective base area can improve the load-bearing capacity, i.e. the maximum permissible load of the mobile crane.
- load tables are provided to determine the load capacity, i.e. the maximum permissible load on the boom, in which the maximum permissible load is specified for the respective configuration of the mobile crane based on possible degrees of freedom.
- the load tables take into account the length or configuration, as well as, for example, the angle of rotation of the boom (usually 0-360°).
- the characteristic map-based determination of the maximum permissible load based on the load tables can also be supplemented by function-based models that take other parameters into account, for example, the load capacity of the load rope.
- the maximum load capacities are usually shown depending on various parameters, in particular the load radius, as well as depending on the respective configuration.
- a crane operator can thus determine the crane operation in advance, in particular the configuration and possible lifting distances of a load to be lifted.
- the publication EP1 444 162 B1 A mobile crane is known in which a working field can be graphically represented on a display in an electronic control device based on one of the parameters load and load radius as well as the size of a counterweight and counterweight radius.
- a mobile crane is known in which individual limit curves or limit values are stored for various parameters of the crane, which may not be exceeded or may only be exceeded by issuing an alarm signal in order to ensure the safety of the crane operation.
- the mobile crane also has means for ensuring crane safety, which are designed in such a way that they monitor the individual limit curves or limit values of the various parameters for exceedance.
- One of the limit curves represents the dependency of the boom strength on the geometric degrees of freedom of the boom or is based on this dependency.
- the publication EP 2 674 384 A1 discloses a method for monitoring the crane safety of a crane with a variable support base and a monitoring unit.
- Several safety criteria are monitored during crane operation by calculating a permissible specific limit value during crane operation for each criterion that depends on at least one parameter relating to the crane configuration or crane movement during crane operation and monitoring compliance.
- the publication DE 20 2010 014 309 U1 discloses a crane, in particular a crawler or mobile crane, with at least one monitoring and simulation means, by means of which a state of the crane can be monitored and/or simulated, wherein the monitoring and simulation means has at least one input means and at least one output means and wherein by means of the monitoring and simulation means the state progression, in particular the load curve of the crane, can be displayed at any time, in particular also when the crane and/or the boom of the crane is moving and/or a possible state and/or possible state progression of the crane, in particular the The crane’s load curve can be simulated and/or displayed.
- EP0539207A1 discloses a safety device for a construction vehicle with a boom to which a load can be attached.
- a load factor can be determined from the attached load and a nominal load dependent on the boom position.
- a safety operation is carried out depending on the load factor.
- the publication WO2012135882A1 discloses a method for monitoring at least one stability parameter of a loading crane mounted on a vehicle, wherein the vehicle is supported on the ground during crane operation via wheels and via support elements separate from the wheels, characterized in that both contributions of the wheels and contributions of the support elements to a value of the stability parameter are recorded and this value is compared with at least one predetermined limit value.
- One idea behind the above method is to consider several possible positions of the boom in the specified position range when planning or operating a mobile crane, as independently as possible of the current direction of movement of the boom and the maximum permissible loads applicable to them. This enables safer operation of the mobile crane and better planning of operations with the best possible use of the load-bearing range, i.e. with optimal use of the load-bearing capacity at every load position in the working area, up to the load-bearing limits determined by the maximum permissible loads.
- the above method enables the recognition of those boom positions in which a local load-bearing limit is reached or exceeded for the currently attached load.
- the maximum permissible loads for the multiple positions in the specified position range of the boom can be determined using a boom strength table and based on a support geometry of support devices.
- respective load limits can be determined by the boom strength table, which specifies boom strength-relevant load restrictions, and the support geometry for each of the multiple positions of the boom.
- the maximum permissible loads can then be determined by determining the minimum of the load limits determined by the boom strength table and the support geometry.
- the load limits determined by the support geometry for the multiple positions of the boom in the specified position range can be determined using a moment balance around one or more tipping lines determined by the support geometry.
- the maximum permissible loads for different positions in the specified position range of the boom can be determined using load limits that are determined by one or more map-based or function-based load capacity models, in particular those dependent on one or more other parameters.
- the several other parameters can represent limiting criteria, such as the maximum load on the support cylinders, the slewing ring, the luffing cylinder and other crane parts located in the force flow of the boom and its displacement on the crane superstructure. From the aforementioned causal relationships, the limiting criteria are derived directly or indirectly from the respective support geometry in a manner known per se.
- the various positions of the boom in a specific geometrical environment of the current position of the boom can be taken into account in order to determine the maximum permissible To determine load capacities, whereby an adjustment speed of the boom is selected, set and limited depending on a load limit curve determined thereby in the specified position range of the boom.
- the adjustment speeds of the boom can be set in all directions of movement depending on a distance from the current load position and a load limit.
- the load limit corresponds to the positions of the load at which the suspended load reaches the maximum permissible load when it is moved in an adjustment direction.
- the adjustment speed can be set depending on a gradient of the course of the maximum permissible load with respect to the adjustment direction.
- the maximum permissible load can be shown on a display for the specified position range of the boom as an absolute value or as a relative value that indicates the ratio of the suspended load to the maximum permissible load. This can provide the crane operator with information about the extent to which he can move a specified load from a specified safe starting position in a non-critical direction to at least a second, safe target position.
- the environmental representation makes it possible to instantly and visually identify a position of the suspended load and a progression of other positions of the load in the vicinity of the position of the suspended load at which the maximum permissible load is or will be exceeded. In this way, a crane operator can be given the opportunity to immediately identify possible remaining degrees of freedom of movement of the boom with the suspended load by looking at the environmental representation on the display and accordingly to place the boom in other positions up to a safe operating limit.
- the absolute value or the relative value of the maximum permissible loads can be shown on the display in a visually distinguishable manner, in particular by means of a respective assigned color and/or brightness and/or shading.
- This type of display facilitates the intuitive understanding of the load progression in the entire working area or in the immediate vicinity of the current load position.
- the load ranges can indicate those positions of the boom or those load positions at which the ratio of the suspended load to the maximum permissible load is within a specified range.
- the display device can be designed to display the load-bearing areas as visually distinguishable areas, in particular as areas distinguishable by color and/or structure and/or by their brightness
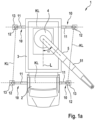
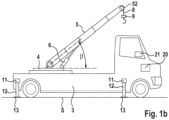
- FIGS. 1a and 1b schematic views of a mobile crane 1 are shown in a top view and a side view.
- the mobile crane 1 has a driver's cab 2 and a crane superstructure 3, on which a slewing ring 4 which can rotate in a horizontal plane and has a boom 5 attached thereto is arranged.
- the slewing ring 4 allows a 360° swivel of the boom 5 attached thereto.
- An angle of rotation ⁇ of the boom 5 can be set as desired within the entire range of rotation of the boom 5.
- a counterweight can be attached to the slewing ring 4 on the crane superstructure 3 (not shown here), which is arranged on a side opposite the boom 5.
- a hydraulic luffing cylinder 6 is arranged on the slewing ring 4, by means of which it is possible to adjust the boom 5 at a luffing angle ⁇ , i.e. a vertical angle perpendicular to the horizontal.
- the boom 5 can be provided with boom segments (boom boxes) 51, which can be telescopically moved into one another in order to adjust or specify the length of the boom 5 by retracting or extending the boom boxes 51, depending on the desired boom configuration.
- boom segments (boom boxes) 51 At the upper end of the boom 5, a circulating roller 52 is provided for a load rope 8, at the end of which a load hook 9 is provided, to which a load can be attached.
- the support devices 10 are provided in the area of the front and rear corners of the mobile crane 1.
- the support devices 10 each have an extendable support beam 11, which can be extended and retracted telescopically using several cylinders that can be moved into one another.
- the support beams 11 can be extended in a plane that is defined by wheel axles (not shown) or that can extend parallel to the support surface S.
- a support cylinder 12 which can be extended in the direction of a support surface S of the mobile crane 1.
- a support plate 13 which is placed on the support surface S so that the support device 10 supports the mobile crane 1 there on the ground.
- boom strength tables which specify a load limit with regard to the boom strength depending on a configuration, i.e. the selected length of the boom 5 and the extended boom segments 51 and depending on the load radius.
- the boom strength tables therefore define map-based limits for the suspended load, which may not be exceeded or may only be exceeded with the output of a warning signal.
- the boom strength tables can therefore be used to determine whether the suspended load is smaller, equal to or larger than the maximum permissible load determined by the boom strength.
- the support beams 11 may not be able to be fully extended. This means that the greatest possible load that would be achieved with the support beams 11 in the maximum extended position cannot be achieved.
- the maximum permissible load of the mobile crane 1 is therefore regularly determined not only on the basis of the boom strength determined by the boom strength table and restrictions with regard to other parameters, but also largely on the basis of a load limitation that is determined by the support geometry of the support positions defined by the support cylinders 12.
- one or more additional parameters in particular the maximum permissible cylinder pressure of the luffing cylinder 6 and/or the support cylinder 12, the load capacity of the load rope 8, the load capacity of the slewing ring 4 and the like, can cause or specify respective load limitations as limits for the permissible load to be suspended by means of function-based load calculations. This may require By forming the minimum of the determined load limits, the maximum permissible total load can be limited to a value which can be smaller than the value of the load limit defined only by the boom strength.
- a significant, reducing influence on the maximum permissible load can arise from outriggers 11 of the outrigger device 10 that are not fully extended.
- the respective degree of extension of the outriggers 11 defines the four (or possibly only three) support positions of the outrigger cylinders 12, on which the entire weight of the mobile crane 1, including the attached load, usually rests.
- the connection of the outrigger positions to one another forms a so-called support geometry, which should be defined by tipping lines KL.
- the tipping lines KL represent the straight connections between two adjacent support positions of the outriggers 10 and thus determine possible axes around which the mobile crane 1 can tip in the event of an overload. The smaller the distance of the center of gravity of the mobile crane 1 from the tipping line KL, the lower the maximum permissible load, which is largely determined by the support geometry.
- a load limitation i.e. a maximum permissible load for a specific load position, can be determined depending on the tilting lines KL determined by the support geometry and the respective boom position (defined by angle of rotation ⁇ and luffing angle ⁇ ).
- This calculation can provide for determining a moment balance around the tipping line KL for various load positions.
- the distance of the load position under consideration which corresponds to a projection of the three-dimensional spatial position of the suspended load onto the essentially horizontal footprint S of the mobile crane 1, to the relevant tipping line KL or the relevant tipping lines KL is determined.
- the relevant tipping lines are determined by the fact that the suspended load causes an outward-acting moment around the relevant tipping line (with respect to the area enclosed by the tipping lines KL).
- the distance between the projected load position and the tipping line can be calculated in a known manner using trigonometric functions.
- a load tipping moment can be determined in a known manner using the suspended load and the distance of the projected load position on the essentially horizontal footprint S to the critical tipping line KL.
- an amount of a static moment determined by the dead weight of the mobile crane 1 is determined with respect to the tipping lines KL defined by the support positions or calculated in the mobile crane 1.
- the distance of the center of mass of the mobile crane 1 from the relevant tipping lines KL can also be determined using known functions, for example trigonometric functions, so that the static moment can be determined from a product of the weight of the mobile crane 1 and the distance of the center of mass from the relevant tipping line KL of the support geometry.
- the difference between the load tipping moment and the static moment determines the stability of the mobile crane 1.
- the load limitations of the mobile crane 1, which are essentially defined by the boom position and the support geometry, for a specific position (at least defined by the angle of rotation and the luffing angle) of the boom 5, are determined by the difference between the load tipping moment and the static moment being zero for a specific support geometry or corresponding to a specific specified value if a specified tolerance is provided.
- a course of the load limitation which can be determined by an existing support geometry and by an existing configuration of the mobile crane 1, can be determined for positions of the boom 5 depending on the angle of rotation ⁇ and the luffing angle ⁇ .
- the maximum permissible load can be determined by minimizing the load limits thus individually determined for the relevant position of the boom 5.
- monitoring can also be carried out in such a way that a movement of the boom 5 is slowed down or prevented at least in a critical direction (with a reducing maximum permissible load). and/or a warning signal is issued as soon as the load on the boom reaches, exceeds or approaches a critical limit of the maximum permissible load.
- a control unit 20 is provided on the mobile crane to carry out the monitoring function and the described determination of the maximum permissible loads based on the individually determined load limits.
- This control unit 20 can be implemented in the general crane control or designed as an independent control unit.
- control unit 20 is coupled to various sensors (not shown) in order to obtain the actual position of the support cylinders 12 based on the extension length of the support beams 11, the angle of rotation ⁇ of the boom 5, the tilt angle ⁇ of the boom 5 and the weight of the attached load. Based on these details and on geometric specifications, such as the position of the center of gravity of the unloaded mobile crane 1 and the current configuration, in particular the boom configuration, the control unit 20 can carry out the calculations to determine the maximum permissible load.
- the control unit 20 carries out calculations in calculation cycles of a few milliseconds.
- the respective maximum permissible loads for positions of the boom 5 in a specified position range are determined cyclically for several positions of the boom 5 according to the above calculation scheme.
- the resulting load limits (with regard to boom strength, support geometry and with regard to one or more of the other and/or limiting parameters) dependent on the respective position of the boom 5 are determined and linked to one another by forming a minimum in order to obtain the total maximum permissible loads for the respective positions of the boom 5.
- the monitoring function of the control unit 20 can now be carried out based on the current position of the boom 5 (or the current load position), the attached load and the maximum permissible loads for the positions of the boom 5 in the specified position range.
- the local course of a load limit corresponds to those positions of the boom 5 or those positions of the load at which the currently attached load is equal to the maximum permissible load.
- the monitoring can provide for slowing down, limiting, allowing or preventing a desired adjustment movement for the boom 5 depending on whether the load is approaching the load limit or moving away from it.
- the control unit 20 is preferably coupled to a display device 21 in order to provide a crane operator with visual information about the maximum permissible load or the course of the load limit via a display 22 for operational planning and for operating the mobile crane 1.
- This visual information can relate to one or more sub-areas of the possible movements or positions of the boom 5.
- the crane operator can be given the respective maximum permissible load in the range of possible load positions as an absolute value for operational planning with a currently set support geometry and a current crane configuration.
- the positions of the respective maximum permissible load can be given as a distance from a boom rotation axis.
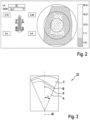
- Figure 2 shows the value of the maximum permissible load for different positions of the suspended load around the boom axis of rotation in different colors, brightness or shading. This allows you to recognize the load capacity for each position of a load, ie the maximum permissible load, based on the graphically displayed color, brightness or shading, so that a crane operator can immediately plan operations in accordance with his lifting plan.
- Figure 3 shows a segment view of the surrounding area around a current load position P as a further display option based on the current load position.
- an angle range of ⁇ 30° of the angle of rotation ⁇ (other angle ranges are also possible) and the entire radius range can be displayed in a segment display.
- the radius range is determined by the effective boom length based on the actual boom length and the possible luffing angles (luffing angle between the minimum and maximum possible luffing angle).
- luffing angles luffing angle between the minimum and maximum possible luffing angle
- Other radius ranges are also conceivable.
- These should preferably include the current load position and the course of the load limit, which is determined by reaching or exceeding the maximum permissible load by the currently attached load.
- the first load range A can, for example, be colored green to indicate the range of load positions in which the currently attached load is below a specified proportion of the maximum permissible load, such as 90% of the maximum permissible load.
- a second (critical) load range B can, for example, be colored yellow to indicate a critical range of load positions in which the attached load almost reaches the maximum permissible load (e.g. between 90% and 100% of the maximum permissible load).
- a subsequent third (impermissible) load range C can, for example, be colored red to indicate the range of load positions in which the currently attached load would exceed the maximum permissible load or the stability of the crane is no longer guaranteed due to its own weight (e.g. rear stability).
- the boundary between the second load range B and the third load range C represents the load limit.
- the control unit 20 calculates the corresponding maximum permissible loads for the respective current load position and for the positions of the boom 5 that correspond to the possible load positions that surround the current load position, and determines the corresponding share that the currently attached load has in this. This share is shown in the segment display in a suitable manner depending on the position by a flat optical design in color, etc.
- any control of the boom 5 that would move the load further in the direction of a load position at which the maximum permissible load would be reduced can be implemented by the control unit 20 at a slower adjustment speed and/or prevented when the load limit is reached.
- controls in adjustment directions of the boom 5 that would bring the load back into the first (non-critical) range of the boom positions can be carried out unchanged by the control unit 20.
- the control unit 20 can therefore set an adjustment speed of the boom depending on the course of the load limit, which indicates the positions of a suspended load at which the maximum permissible load of the mobile crane 1 is exceeded by the suspended load, in the specified position range of the boom 5.
- the adjustment speed of the boom 5 can be set depending on the suspended load and depending on a distance between a load position of the suspended load and a position at which the suspended load reaches the maximum permissible load.
- the adjustment speed can be set depending on a gradient of the course of the maximum permissible load with respect to the adjustment direction.
- the adjustment speed can be reduced depending on the ratio of the load to the maximum permissible load at the current load position.
- the adjustment speed can be reduced compared to the user's wishes or the adjustment speed desired by the user can be limited if the gradient of the course of the maximum permissible load in the direction of the desired adjustment movement is relatively large (e.g. greater than a predetermined threshold value) and a minimum distance to the load limit is not reached.
- Setting the adjustment speed depending on the gradient of the course of the maximum permissible load in the direction of the desired adjustment movement has the advantage that the load limit is approached so slowly that an overshoot of the boom 5 or the attached load beyond the load limit can be avoided.
- FIG. 4 a flow chart is shown to illustrate a method for operating the mobile crane 1.
- step S1 a current position of the boom 5 and the current load position are determined. Based on the current load position, further positions of the boom 5 are defined, which define a surrounding area of possible load positions around the current load position.
- step S2 a respective load limit is determined for the current position of the boom 5 and the other positions of the boom 5, which depends on the support geometry.
- a load limit specified by the boom load capacity is determined based on the boom strength table, and in step S4, the one or more function-based load limits are determined based on the other parameters and, if applicable, with respect to other limiting parameters.
- step S5 a maximum permissible load capacity is determined for the current position of the boom 5 and the other positions of the boom 5 by minimizing the load limits.
- step S6 those positions of the boom 5 are determined from the positions of the boom 5 specified above at which the suspended load reaches or exceeds the maximum permissible load. These positions of the boom 5 define the load limit.
- step S7 the load positions that correspond to the specified positions of the boom 5 are assigned to load ranges and graphically displayed as described above.
- the graphical display can include the display of the absolute values of the maximum permissible load for the entire load range and/or the segment display to display the area around the load position with respect to the load limit.
- the load ranges are differentiated from one another by different optical designs so that a user can intuitively recognize permissible crane movements for the attached load.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Jib Cranes (AREA)
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft Mobilkrane, insbesondere Mobilkrane mit variablen Abstützgeometrien. Weiterhin betrifft die vorliegende Erfindung Verfahren zum Ermitteln einer maximalen Traglastfähigkeit, Maßnahmen zur Sicherung der Standsicherheit des Mobilkrans sowie Mittel zur Anzeige von sicheren Arbeitsstellungen.The invention relates to mobile cranes, in particular mobile cranes with variable support geometries. The present invention also relates to methods for determining a maximum load capacity, measures for ensuring the stability of the mobile crane and means for displaying safe working positions.
Mobilkrane werden zur Verbesserung der Standsicherheit bzw. zur Erhöhung der Traglastfähigkeit in der Regel mit einer Abstützeinrichtung versehen. Eine derartige Abstützeinrichtung umfasst seitlich von dem Mobilkran abstehende Abstützholme, an denen Abstützzylinder vorgesehen sind. Mit den Abstützzylindern kann ein abstehendes Ende auf einer Stellfläche des Mobilkrans abgestützt werden und dadurch die effektive Standfläche vergrößert werden. Mit der vergrößerten effektiven Standfläche kann die Traglastfähigkeit, d. h. die maximal zulässige Traglast des Mobilkrans verbessert werden.Mobile cranes are usually fitted with a support device to improve stability or increase the load-bearing capacity. Such a support device comprises support beams that protrude from the side of the mobile crane and on which support cylinders are provided. The support cylinders can be used to support a protruding end on a base of the mobile crane, thereby increasing the effective base area. The increased effective base area can improve the load-bearing capacity, i.e. the maximum permissible load of the mobile crane.
Weiterhin sind zur Bestimmung der Tragfähigkeit, d. h. der maximal zulässigen Traglast an dem Ausleger, Traglasttabellen vorgesehen, in denen für die jeweilige Konfiguration des Mobilkrans die maximal zulässige Traglast basierend auf möglichen Freiheitsgraden angegeben wird. Insbesondere berücksichtigen die Traglasttabellen die Länge bzw. die Konfiguration, sowie z.B. den Drehwinkel des Auslegers (in der Regel 0-360°). Die auf den Traglasttabellen beruhende kennfeldbasierte Ermittlung der maximal zulässigen Traglast kann weiterhin durch funktionsbasierte, weitere Parameter berücksichtigende Modelle ergänzt werden, die z. B. die Tragfähigkeit des Lastseils in Betracht ziehen.Furthermore, load tables are provided to determine the load capacity, i.e. the maximum permissible load on the boom, in which the maximum permissible load is specified for the respective configuration of the mobile crane based on possible degrees of freedom. In particular, the load tables take into account the length or configuration, as well as, for example, the angle of rotation of the boom (usually 0-360°). The characteristic map-based determination of the maximum permissible load based on the load tables can also be supplemented by function-based models that take other parameters into account, for example, the load capacity of the load rope.
Insbesondere beim Einsatz der Mobilkrane auf einer beengten Stellfläche kann es vorkommen, dass die Abstützholme für den Einsatz des Mobilkrans nicht vollständig ausgefahren werden können, so dass sich durch die resultierenden Abstützpositionen eine unsymmetrische Abstützgeometrie ergibt. Bei Mobilkranen mit von vornherein festgelegter Abstützgeometrie, insbesondere im Einsatz mit vollständig ausgefahrenen Abstützholmen, kann die Bestimmung der maximal zulässigen Traglast mit herkömmlichen Traglasttabellen in bekannter Weise erfolgen und ausreichend sein. Jedoch ist es bei Mobilkranen mit variabler Abstützgeometrie bei einer Bestimmung der maximal zulässigen Traglast zusätzlich notwendig, die tatsächlichen Abstützpositionen des Mobilkrans zu berücksichtigen.Particularly when using mobile cranes in a confined space, it may happen that the outriggers cannot be fully extended for the use of the mobile crane, so that the resulting outrigger positions result in an asymmetrical outrigger geometry. For mobile cranes with a predetermined outrigger geometry, particularly when used with fully extended outriggers, the maximum permissible load can be determined using conventional load tables in the usual way and this should be sufficient. However, for mobile cranes with variable outrigger geometry, it is also necessary to take the actual outrigger positions of the mobile crane into account when determining the maximum permissible load.
Für die Einsatzplanung werden in der Regel die maximalen Tragfähigkeiten abhängig von verschiedenen Parametern, insbesondere des Lastradius, sowie abhängig von der jeweiligen Konfiguration dargestellt. Ein Kranführer kann so im Vorfeld den Kranbetrieb, insbesondere Konfiguration und mögliche Hubwege einer zu hebenden Last, bestimmen. Beispielsweise ist aus der Druckschrift
Aus der Druckschrift
Aus der Druckschrift
Die Druckschrift
Die Druckschrift
Die Druckschrift
Die Druckschrift
Es ist Aufgabe der vorliegenden Erfindung, ein Verfahren und eine Vorrichtung zur Verfügung zu stellen, die es ermöglichen, einem Kranführer sowohl zur Einsatzplanung als auch während des Kranbetriebs noch verbleibende Freiheitsgrade und geometrische Beschränkungen der Auslegerbewegung anzugeben und diese in einer einfach verständlichen Art grafisch anzuzeigen.It is an object of the present invention to provide a method and a device which make it possible to indicate to a crane operator the remaining degrees of freedom and geometric restrictions of the boom movement both for operational planning and during crane operation and to display these graphically in an easily understandable manner.
Diese Aufgabe wird durch das Verfahren zum Betreiben eines Mobilkrans mit einem Ausleger gemäß Anspruch 1 sowie durch die Steuereinheit und das System gemäß den nebengeordneten Ansprüchen gelöst.This object is achieved by the method for operating a mobile crane with a boom according to
Weitere Ausgestaltungen sind in den abhängigen Ansprüchen angegeben.Further embodiments are specified in the dependent claims.
Gemäß einem ersten Aspekt ist ein Verfahren zum Betreiben eines Mobilkrans mit einem Ausleger vorgesehen, das die folgenden Schritte umfasst:
- Ermitteln von maximal zulässigen Traglasten für mehrere Stellungen in einem vorgegebenen Stellungsbereich des Auslegers;
- Ermitteln einer insbesondere örtlichen Traglastgrenze und/oder eines oder mehrerer insbesondere örtlicher Traglastbereiche basierend auf einer angehängten Last und auf den maximal zulässigen Traglasten für die mehreren Stellungen des vorgegebenen Stellungsbereichs des Auslegers; und
- Betreiben des Mobilkrans abhängig von der Traglastgrenze und/oder von dem einem oder den mehreren Traglastbereichen.
- Determination of maximum permissible loads for several positions in a given position range of the boom;
- Determining a particular local load limit and/or one or more particular local load ranges based on a suspended load and on the maximum permissible loads for the multiple positions of the specified position range of the boom; and
- Operating the mobile crane depending on the load limit and/or one or more load ranges.
Eine Idee des obigen Verfahrens besteht darin, bei der Einsatzplanung oder beim Betrieb eines Mobilkrans mehrere mögliche Stellungen des Auslegers in dem vorgegebenen Stellungsbereich, möglichst unabhängig von einer aktuellen Bewegungsrichtung des Auslegers und die dafür geltenden maximal zulässigen Traglasten zu berücksichtigen. Dies ermöglicht ein sichereres Bedienen des Mobilkrans und bessere Einsatzplanung unter bestmöglicher Ausnutzung des Lasttragbereiches, d.h. unter optimaler Ausnutzung der Tragfähigkeit an jeder Lastposition im Arbeitsbereich, bis hin zu den durch die maximal zulässigen Traglasten bestimmten Traglastgrenzen. Insbesondere ermöglicht das obige Verfahren das Erkennen derjenigen Auslegerstellungen, bei denen bei der aktuell angehängten Traglast eine örtliche Traglastgrenze erreicht bzw. überschritten wird.One idea behind the above method is to consider several possible positions of the boom in the specified position range when planning or operating a mobile crane, as independently as possible of the current direction of movement of the boom and the maximum permissible loads applicable to them. This enables safer operation of the mobile crane and better planning of operations with the best possible use of the load-bearing range, i.e. with optimal use of the load-bearing capacity at every load position in the working area, up to the load-bearing limits determined by the maximum permissible loads. In particular, the above method enables the recognition of those boom positions in which a local load-bearing limit is reached or exceeded for the currently attached load.
Weiterhin können die maximal zulässigen Traglasten für die mehreren Stellungen in dem vorgegebenen Stellungsbereich des Auslegers mithilfe einer Auslegerfestigkeitstabelle sowie basierend auf einer Abstützgeometrie von Abstützeinrichtungen ermittelt werden. Insbesondere können jeweilige Lastbegrenzungen durch die Auslegerfestigkeitstabelle, die auslegerfestigkeitsrelevante Traglastbeschränkungen angibt, und die Abstützgeometrie für jede der mehreren Stellungen des Auslegers bestimmt werden. Die maximal zulässigen Traglasten können dann durch eine Bestimmung des Minimums der durch die Auslegerfestigkeitstabelle und durch die Abstützgeometrie bestimmten Traglastgrenzen ermittelt werden.Furthermore, the maximum permissible loads for the multiple positions in the specified position range of the boom can be determined using a boom strength table and based on a support geometry of support devices. In particular, respective load limits can be determined by the boom strength table, which specifies boom strength-relevant load restrictions, and the support geometry for each of the multiple positions of the boom. The maximum permissible loads can then be determined by determining the minimum of the load limits determined by the boom strength table and the support geometry.
Insbesondere können die durch die Abstützgeometrie bestimmten Lastbegrenzungen für die mehreren Stellungen des Auslegers in dem vorgegebenen Stellungsbereich mithilfe einer Momentenbilanz um eine oder mehrere durch die Abstützgeometrie bestimmten Kipplinien ermittelt werden.In particular, the load limits determined by the support geometry for the multiple positions of the boom in the specified position range can be determined using a moment balance around one or more tipping lines determined by the support geometry.
Zusätzlich können die maximal zulässigen Traglasten für unterschiedliche Stellungen in dem vorgegebenen Stellungsbereich des Auslegers mithilfe von Lastbegrenzungen ermittelt werden, die durch ein oder mehrere, insbesondere von einem oder mehreren weiteren Parametern abhängigen, kennfeldbasierten oder funktionsbasierten Tragfähigkeitsmodelle bestimmt werden. Insbesondere können die mehreren weiteren Parameter begrenzende Kriterien darstellen, wie z.B. die maximale Belastung der Stützzylinder, des Drehkranzes, des Wippzylinders und anderer im Kraftfluss des Auslegers und seiner Verlagerung auf dem Kranoberwagen befindlicher Kranteile. Aus vorgenannten Wirkungszusammenhängen leiten sich die begrenzenden Kriterien in direkter oder indirekter Weise von der jeweiligen Abstützgeometrie in an sich bekannter Weise ab.In addition, the maximum permissible loads for different positions in the specified position range of the boom can be determined using load limits that are determined by one or more map-based or function-based load capacity models, in particular those dependent on one or more other parameters. In particular, the several other parameters can represent limiting criteria, such as the maximum load on the support cylinders, the slewing ring, the luffing cylinder and other crane parts located in the force flow of the boom and its displacement on the crane superstructure. From the aforementioned causal relationships, the limiting criteria are derived directly or indirectly from the respective support geometry in a manner known per se.
Es können beim Betreiben des Mobilkrans die mehreren Stellungen des Auslegers in einem bestimmten geometrischen Umfeld der momentanen Stellung des Auslegers in Betracht gezogen werden, um die maximal zulässigen Traglasten zu ermitteln, wobei eine Verstellgeschwindigkeit des Auslegers abhängig von einem dadurch ermittelten Verlauf einer Traglastgrenze im vorgegebenen Stellungsbereich des Auslegers gewählt, eingestellt und begrenzt wird.When operating the mobile crane, the various positions of the boom in a specific geometrical environment of the current position of the boom can be taken into account in order to determine the maximum permissible To determine load capacities, whereby an adjustment speed of the boom is selected, set and limited depending on a load limit curve determined thereby in the specified position range of the boom.
Insbesondere können die Verstellgeschwindigkeiten des Auslegers in alle Bewegungsrichtungen abhängig von einem Abstand der aktuellen Lastposition und einer Traglastgrenze eingestellt werden. Die Traglastgrenze entspricht den Positionen der Last, an der die angehängte Last die maximal zulässige Traglast erreicht, wenn diese in einer Verstellrichtung bewegt wird. Insbesondere kann die Verstellgeschwindigkeit insbesondere abhängig von einem Gradienten des Verlaufs der maximal zulässigen Traglast bezüglich der Verstellrichtung eingestellt werden.In particular, the adjustment speeds of the boom can be set in all directions of movement depending on a distance from the current load position and a load limit. The load limit corresponds to the positions of the load at which the suspended load reaches the maximum permissible load when it is moved in an adjustment direction. In particular, the adjustment speed can be set depending on a gradient of the course of the maximum permissible load with respect to the adjustment direction.
Weiterhin kann für den vorgegebenen Stellungsbereich des Auslegers die maximal zulässige Traglast als absolute Wertangabe oder als relative Wertangabe, die das Verhältnis der angehängten Last zur maximal zulässigen Traglast angibt, im vorgegebenen Stellungsbereich auf einer Anzeige dargestellt werden. Dadurch kann dem Kranführer eine Angabe darüber bereitgestellt werden, in wieweit er eine vorgegebene Last an einer vorgegebenen sicheren Startposition heraus, in eine unkritische Richtung gehend in eine zumindest zweite, sichere Zielposition bewegen kann.Furthermore, the maximum permissible load can be shown on a display for the specified position range of the boom as an absolute value or as a relative value that indicates the ratio of the suspended load to the maximum permissible load. This can provide the crane operator with information about the extent to which he can move a specified load from a specified safe starting position in a non-critical direction to at least a second, safe target position.
Dadurch kann eine Bewegungsraumanzeige erzeugt werden, die ausgehend von der momentanen Stellung des Auslegers (zumindest definiert durch Drehwinkel und Lastradius) eine Umfelddarstellung des Hubfalls dem Kranführer bereitstellt. Die Umfelddarstellung ermöglicht es, instantan und visuell eine Position der angehängten Last und einen Verlauf von weiteren Positionen der Last, an denen die maximal zulässige Traglast überschritten ist bzw. wird, in der Umgebung der Position der angehängten Last zu erkennen. Auf diese Weise kann einem Kranführer eine Möglichkeit gegeben werden, mögliche verbleibende Freiheitsgrade der Bewegungen des Auslegers mit der angehängten Last sofort durch Betrachten der Umfelddarstellung auf der Anzeige zu erkennen und demgemäß den Ausleger in weitere Positionen bis hin zu einer sicheren Betriebsgrenze zu stellen.This makes it possible to generate a movement space display that provides the crane operator with an environmental representation of the lifting case based on the current position of the boom (at least defined by the angle of rotation and load radius). The environmental representation makes it possible to instantly and visually identify a position of the suspended load and a progression of other positions of the load in the vicinity of the position of the suspended load at which the maximum permissible load is or will be exceeded. In this way, a crane operator can be given the opportunity to immediately identify possible remaining degrees of freedom of movement of the boom with the suspended load by looking at the environmental representation on the display and accordingly to place the boom in other positions up to a safe operating limit.
Gemäß einer Ausführungsform kann die absolute Wertangabe oder die relative Wertangabe der maximal zulässigen Traglasten visuell unterscheidbar, insbesondere durch eine jeweils zugeordnete Färbung und/oder Helligkeit und/oder Schattierung, auf der Anzeige dargestellt werden. Diese Art der Darstellung erleichtert das intuitive Erfassen des Traglastverlaufes im gesamten Arbeitsbereich bzw. im unmittelbaren Umfeld der aktuellen Lastposition.According to one embodiment, the absolute value or the relative value of the maximum permissible loads can be shown on the display in a visually distinguishable manner, in particular by means of a respective assigned color and/or brightness and/or shading. This type of display facilitates the intuitive understanding of the load progression in the entire working area or in the immediate vicinity of the current load position.
Insbesondere können die Traglastbereiche diejenigen Stellungen des Auslegers bzw. diejenigen Lastpositionen angeben, an denen ein Verhältnis der angehängten Last zu der maximal zulässigen Traglast innerhalb eines vorgegebenen Bereichs liegt.In particular, the load ranges can indicate those positions of the boom or those load positions at which the ratio of the suspended load to the maximum permissible load is within a specified range.
Gemäß einem weiteren Aspekt ist eine Steuereinheit zum Betreiben eines Mobilkrans mit einem Ausleger vorgesehen, wobei die Steuereinheit ausgebildet ist, um:
- maximal zulässige Traglasten für mehrere Stellungen in einem vorgegebenen Stellungsbereich des Auslegers zu ermitteln;
- eine Traglastgrenze und/oder eines oder mehrerer Traglastbereiche basierend auf einer angehängten Last und auf den maximal zulässigen Traglasten für die mehreren Stellungen des vorgegebenen Stellungsbereichs des Auslegers zu ermitteln; und
- den Mobilkran abhängig von der Traglastgrenze und/oder von dem einen oder den mehreren Traglastbereichen zu betreiben.
- to determine maximum permissible loads for several positions within a given position range of the boom;
- to determine a load limit and/or one or more load ranges based on a suspended load and on the maximum permissible loads for the several positions of the specified boom position range; and
- to operate the mobile crane depending on the load limit and/or one or more load ranges.
Gemäß einem weiteren Aspekt ist ein System für einen Mobilkran vorgesehen, umfassend:
- die obige Steuereinheit; und
- eine Anzeigeeinrichtung zur visuellen Darstellung einer Anzeige, um im vorgegebenen Stellungsbereich des Auslegers maximal zulässige Traglasten als absolute Wertangabe oder als relative Wertangabe für die mehreren Stellungen des Auslegers im vorgegebenen Stellungsbereich darzustellen, wobei das Verhältnis der angehängten Last zur bei einer Stellung des Auslegers bestehenden maximal zulässigen Traglast angegeben wird.
- the above control unit; and
- a display device for the visual representation of a display in order to show maximum permissible loads in the specified position range of the boom as an absolute value or as a relative value for the several positions of the boom in the specified position range, wherein the ratio of the suspended load to the maximum permissible load existing in one position of the boom is indicated.
Gemäß einem weiteren Aspekt ist ein System für einen Mobilkran vorgesehen, umfassend
- die obige Steuereinheit; und
- eine Anzeigeeinrichtung zur visuellen Darstellung einer Anzeige, um für den vorgegebenen Stellungsbereich die Traglastbereiche um eine momentane Lastposition, die einer momentanen Stellung des Auslegers entspricht, visuell darzustellen.
- the above control unit; and
- a display device for visually displaying a display to visually display the load ranges for the specified position range around a current load position which corresponds to a current position of the boom.
Insbesondere kann die Anzeigeeinrichtung ausgebildet sein, um die Traglastbereiche flächig als visuell voneinander unterscheidbare Bereiche, insbesondere als farblich und/oder strukturell und/oder durch ihre Helligkeiten unterscheidbare Bereiche darzustellenIn particular, the display device can be designed to display the load-bearing areas as visually distinguishable areas, in particular as areas distinguishable by color and/or structure and/or by their brightness
Ausführungsformen werden nachfolgend anhand der beigefügten Zeichnungen näher erläutert. Es zeigen:
- Figuren 1a und 1b
- eine schematische Draufsicht und eine Seitenansicht eines Mobilkrans mit variabler Abstützbasis;
- Figur 2
- eine graphische Darstellung der maximal zulässigen Traglasten eines Auslegers im gesamten Umgebungsbereich des Mobilkrans; und
Figur 3- eine Darstellung eines ausschnittsweisen Umgebungsbereichs der Position der an den Ausleger angehängten Last sowie der unkritischen, kritischen und unzulässigen Traglastbereiche in dem Umgebungsbereich.
- Figur 4
- ein Flussdiagramm zur Veranschaulichung eines Verfahrens zur Ermittlung der maximal zulässigen Traglast, der Traglastgrenze und zur Ausgabe einer Darstellung der die momentane Lastposition umgebenden Traglastbereiche.
- Figures 1a and 1b
- a schematic top view and a side view of a mobile crane with variable support base;
- Figure 2
- a graphical representation of the maximum permissible loads of a boom in the entire surrounding area of the mobile crane; and
- Figure 3
- a representation of a partial surrounding area of the position of the load attached to the boom as well as the non-critical, critical and impermissible load areas in the surrounding area.
- Figure 4
- a flow chart illustrating a procedure for determining the maximum permissible load, the load limit and for outputting a representation of the load ranges surrounding the current load position.
In den
Weiterhin ist auf dem Drehkranz 4 ein hydraulischer Wippzylinder 6 angeordnet, durch den es möglich ist, den Ausleger 5 in einem Wippwinkel β, d. h. einem vertikalen Winkel senkrecht zur Horizontalen, zu verstellen.Furthermore, a hydraulic luffing cylinder 6 is arranged on the slewing ring 4, by means of which it is possible to adjust the
Zudem kann der Ausleger 5 mit Auslegersegmenten (Auslegerkästen) 51 versehen sein, die teleskopartig ineinander verschiebbar sein können, um je nach gewünschter Auslegerkonfiguration die Länge des Auslegers 5 durch Einfahren oder Ausfahren der Auslegerkästen 51 einzustellen bzw. vorzugeben. Am oberen Ende des Auslegers 5 ist eine Umlaufrolle 52 für ein Lastseil 8 vorgesehen, an dessen Ende ein Lasthaken 9 vorgesehen ist, an den eine Last angehängt werden kann.In addition, the
Im Bereich der vorderen und hinteren Ecken des Mobilkrans 1 sind (vier) Abstützeinrichtungen 10 vorgesehen. Die Abstützeinrichtungen 10 weisen jeweils einen ausfahrbaren Abstützholm 11 auf, der mit mehreren ineinander verschiebbaren Zylindern teleskopartig aus- und eingefahren werden kann. Die Abstützholme 11 sind dabei in einer Ebene ausfahrbar, die durch (nicht gezeigte) Radachsen definiert ist bzw. die sich parallel zur Stellfläche S erstrecken kann.(Four)
An dem vom Mobilkran 1 abstehenden Ende der Abstützholme 11 befindet sich jeweils ein Abstützzylinder 12, der in Richtung einer Stellfläche S des Mobilkrans 1 ausgefahren werden kann. Am Ende der Abstützzylinder 12 befindet sich jeweils eine Abstützplatte 13, die auf die Stellfläche S aufgesetzt wird, so dass die Abstützeinrichtung 10 den Mobilkran 1 dort bodenseitig abstützt.At the end of the support beams 11 protruding from the
Zur Bestimmung der maximalen zulässigen Traglast des Mobilkrans 1 werden Auslegerfestigkeitstabellen verwendet, die abhängig von einer Konfiguration, d. h. der gewählten Länge des Auslegers 5 und der ausgefahrenen Auslegersegmente 51 und abhängig vom Lastradius eine Lastbegrenzung bezüglich der Auslegerfestigkeit angeben. Die Auslegerfestigkeitstabellen definieren dadurch kennfeldbasierte Grenzen für die angehängte Traglast, die nicht oder nur unter Ausgabe eines Warnsignals überschritten werden dürfen. Mithilfe der Auslegerfestigkeitstabellen kann daher ermittelt werden, ob die angehängte Last kleiner, gleich oder größer als die durch die Auslegerfestigkeit bestimmte maximal zulässige Traglast ist.To determine the maximum permissible load of the
Bei beengten Platzverhältnissen zum Abstellen des Mobilkrans 1 können unter Umständen die Abstützholme 11 nicht vollständig ausgefahren werden. Dies führt dazu, dass die größtmögliche Traglast, die bei der maximalen Ausfahrposition der Abstützholme 11 erreicht werden würde, nicht erreicht werden kann. So wird regelmäßig die maximal zulässige Traglast des Mobilkrans 1 nicht nur anhand der durch die Auslegerfestigkeitstabelle bestimmten Auslegerfestigkeit und Beschränkungen hinsichtlich sonstiger Parameter bestimmt, sondern auch maßgeblich anhand einer Lastbegrenzung, die durch die Abstützgeometrie der durch die Abstützzylinder 12 definierten Abstützpositionen bestimmt ist.If there is limited space for parking the
Zusätzlich zur Auslegerfestigkeit können ein oder mehrere zusätzliche Parameter, insbesondere der maximal zulässige Zylinderdruck des Wippzylinders 6 und/oder der Abstützzylinder 12, die Belastbarkeit des Lastseils 8, die Belastbarkeit des Drehkranzes 4 und dergleichen, durch funktionsbasierte Traglastberechnungen jeweilige Lastbegrenzungen als Begrenzungen für die erlaubte anzuhängende Traglast bewirken bzw. vorgeben. Dadurch muss ggf. durch die Bildung des Minimums der ermittelten Lastbegrenzungen die maximal zulässige Traglast insgesamt auf einen Wert begrenzt werden, der kleiner sein kann als der nur durch die Auslegerfestigkeit definierte Wert der Lastbegrenzung.In addition to the boom strength, one or more additional parameters, in particular the maximum permissible cylinder pressure of the luffing cylinder 6 and/or the
Ein erheblicher, reduzierender Einfluss auf die maximal zulässige Traglast kann von nicht vollständig ausgefahrenen Abstützholmen 11 der Abstützeinrichtung 10 ausgehen. Der jeweilige Grad des Ausfahrens der Abstützholme 11 definiert die vier (oder u.U. nur drei) Abstützpositionen der Abstützzylinder 12, auf denen in der Regel das gesamte Gewicht des Mobilkrans 1 einschließlich der angehängten Last ruht. Die Verbindung der Abstützpositionen untereinander bildet eine sogenannte Abstützgeometrie, die durch Kipplinien KL definiert sein soll. Die Kipplinien KL stellen die geradlinigen Verbindungen zwischen zwei benachbarten Abstützpositionen der Abstützeinrichtungen 10 dar und bestimmen dadurch mögliche Achsen, um die der Mobilkran 1 im Überlastfall kippen kann. Je geringer der Abstand des Massenschwerpunkts des Mobilkrans 1 von der Kipplinie KL ist, desto geringer ist die durch die Abstützgeometrie maßgeblich bestimmte maximal zulässige Traglast.A significant, reducing influence on the maximum permissible load can arise from
Ausgehend von der vorgegebenen Ausleger-Traglastfähigkeit, die durch die Auslegerfestigkeitstabelle definiert ist, sowie den kennfeld- oder funktionsbasierten Lastbegrenzungen für weitere Parameter, wie z.B. die Belastbarkeit des Wippzylinders 6, die Belastbarkeit der Abstützzylinder 12, die Belastbarkeit des Drehkranzes usw., kann abhängig von den durch die Abstützgeometrie bestimmten Kipplinien KL und der jeweiligen Auslegerstellung (definiert durch Drehwinkel α und Wippwinkel β) eine Lastbegrenzung, d. h. eine maximal zulässige Traglast für eine bestimmte Lastposition ermittelt werden.Based on the specified boom load capacity, which is defined by the boom strength table, as well as the map- or function-based load limitations for other parameters, such as the load capacity of the luffing cylinder 6, the load capacity of the
Diese Berechnung kann vorsehen, für verschiedene Lastpositionen eine Momentenbilanz um die Kipplinie KL zu ermitteln. Im Detail wird der Abstand der betrachteten Lastposition, die einer Projektion der dreidimensionalen räumlichen Position der angehängten Last auf die im Wesentlichen horizontale Stellfläche S des Mobilkrans 1 entspricht, zu der relevanten Kipplinie KL bzw. den relevanten Kipplinien KL bestimmt. Die relevanten Kipplinien sind dadurch bestimmt, dass durch die angehängte Last ein (bezüglich der von den Kipplinien KL umschlossenen Fläche) nach außen wirkendes Moment um die betreffende Kipplinie bewirkt wird. Die Berechnung des Abstands zwischen der projizierten Lastposition und der Kipplinie kann in bekannter Weise mithilfe von trigonometrischen Funktionen durchgeführt werden. Durch die angehängte Last und den Abstand der projizierten Lastposition auf der im Wesentlichen horizontalen Stellfläche S zur kritischen Kipplinie KL lässt sich in bekannter Weise ein Last-Kippmoment bestimmen.This calculation can provide for determining a moment balance around the tipping line KL for various load positions. In detail, the distance of the load position under consideration, which corresponds to a projection of the three-dimensional spatial position of the suspended load onto the essentially horizontal footprint S of the
Weiterhin wird ein Betrag eines durch das Eigengewicht des Mobilkrans 1 bestimmten Standmoments bezüglich der durch die Abstützpositionen definierten oder im Mobilkran 1 berechneten Kipplinien KL bestimmt. Auch der Abstand des Massenschwerpunktes des Mobilkrans 1 von den betreffenden Kipplinien KL kann mithilfe bekannter, beispielsweise trigonometrischer Funktionen bestimmt werden, so dass das Standmoment aus einem Produkt des Gewichts des Mobilkrans 1 und des Abstands des Massenschwerpunkts von der betreffenden Kipplinie KL der Abstützgeometrie ermittelbar ist.Furthermore, an amount of a static moment determined by the dead weight of the
Insbesondere bestimmt die Differenz zwischen dem Last-Kippmoment und dem Standmoment die Standfestigkeit des Mobilkrans 1. Die im Wesentlichen durch die Auslegerposition und die Abstützgeometrie definierten Lastbegrenzungen des Mobilkrans 1 bei einer bestimmten Stellung (zumindest definiert durch Drehwinkel und Wippwinkel) des Auslegers 5 wird dadurch bestimmt, dass die Differenz zwischen dem Last-Kippmoment und dem Standmoment bei einer bestimmten Abstützgeometrie Null oder bei Vorsehen einer vorgegebenen Toleranz einem bestimmten vorgegebenen Wert entspricht. Somit kann ein Verlauf der Lastbegrenzung, die jeweils durch eine bestehende Abstützgeometrie und durch eine bestehende Konfiguration des Mobilkrans 1 bestimmt sein kann, für Stellungen des Auslegers 5 abhängig von dem Drehwinkel α und dem Wippwinkel β ermittelt werden.In particular, the difference between the load tipping moment and the static moment determines the stability of the
Insgesamt kann die maximal zulässige Traglast bestimmt sein durch:
- die von der Abstützgeometrie abhängige Lastbegrenzung,
- die durch die Ausleger-Traglastfähigkeit angegebene Lastbegrenzung basierend auf der Auslegerfestigkeitstabelle, sowie
- die eine oder die mehreren funktionsbasierten Lastbegrenzungen basierend auf den weiteren Parametern und gegebenenfalls bezüglich weiterer begrenzender Parameter, wie z.B. die Belastbarkeit des Wippzylinders, die Belastbarkeit der Abstützzylinder 12 in Abhängigkeit der jeweiligen Abstützgeometrie, die Belastbarkeit des Drehkranzes und dergleichen.
- the load limitation dependent on the support geometry,
- the load limit indicated by the boom load capacity based on the boom strength table, and
- the one or more function-based load limitations based on the further parameters and, if applicable, with respect to further limiting parameters, such as the load capacity of the luffing cylinder, the load capacity of the
support cylinders 12 depending on the respective support geometry, the load capacity of the slewing ring and the like.
Die maximal zulässige Traglast kann durch Minimumbildung der so einzeln ermittelten Lastbegrenzungen für die betreffende Stellung des Auslegers 5 bestimmt werden.The maximum permissible load can be determined by minimizing the load limits thus individually determined for the relevant position of the
Anhand der durch Bestimmung des Minimums ermittelten gesamten maximal zulässigen Traglast wird beim Kranbetrieb überwacht, ob die momentan angehängte Last bei der momentanen Auslegerstellung die ermittelte gesamte maximal zulässige Traglast überschreitet.Based on the total maximum permissible load determined by determining the minimum, it is monitored during crane operation whether the currently suspended load at the current boom position exceeds the determined total maximum permissible load.
Durch Ermittlung der maximal zulässigen Traglast für mehrere Lastpositionen im geometrischen Umfeld der aktuellen Lastposition kann darüber hinaus eine Überwachung derart erfolgen, dass eine Bewegung des Auslegers 5 zumindest in eine kritische Richtung (bei sich reduzierender maximal zulässiger Traglast) verlangsamt oder unterbunden wird und/oder eine Ausgabe eines Warnsignal erfolgt, sobald die Last am Ausleger eine kritische Grenze der maximal zulässigen Traglast erreicht, überschreitet oder sich dieser annähert.By determining the maximum permissible load for several load positions in the geometric environment of the current load position, monitoring can also be carried out in such a way that a movement of the
Auf dem Mobilkran ist eine Steuereinheit 20 vorgesehen, um die Überwachungsfunktion und die beschriebene Ermittlung der maximal zulässigen Traglasten, basierend auf den einzeln ermittelten Lastbegrenzungen durchzuführen. Diese Steuereinheit 20 kann in der generellen Kransteuerung implementiert sein oder als eigenständige Steuereinheit ausgeführt sein.A
Zur Durchführung der Berechnung ist die Steuereinheit 20 mit diversen (nicht gezeigten) Sensoren gekoppelt, um die tatsächliche Position der Abstützzylinder 12 basierend auf der Ausfahrlänge der Abstützholme 11, den Drehwinkel α des Auslegers 5, den Kippwinkel β des Auslegers 5 und das Gewicht der angehängten Last zu erhalten. Basierend auf diesen Angaben und auf geometrischen Vorgaben, wie beispielsweise der Position des Massenschwerpunkts des unbelasteten Mobilkrans 1 und der momentanen Konfiguration, insbesondere der Auslegerkonfiguration, kann die Steuereinheit 20 die Berechnungen zur Ermittlung der maximalen zulässigen Traglast durchführen.To carry out the calculation, the
Die Steuereinheit 20 führt Berechnungen in Berechnungszyklen von wenigen Millisekunden durch. Dabei werden für die Überwachung zyklisch für mehrere Stellungen des Auslegers 5 die jeweiligen maximal zulässigen Traglasten für Stellungen des Auslegers in einem vorgegebenen Stellungsbereich gemäß obigem Berechnungsschema ermittelt. Für jede der zu betrachteten Stellungen des Auslegers 5 werden die von der jeweiligen Stellung des Auslegers 5 abhängigen, resultierenden Lastbegrenzungen (bezüglich Auslegerfestigkeit, Abstützgeometrie und bezüglich eines oder mehrerer der weiteren und/oder begrenzenden Parameter) ermittelt und durch Minimumbildung miteinander verknüpft, um für die jeweiligen Stellungen des Auslegers 5 die gesamten maximal zulässigen Traglasten zu erhalten.The
Die Überwachungsfunktion der Steuereinheit 20 kann nun basierend auf der momentanen Stellung des Auslegers 5 (bzw. der momentanen Lastposition), der angehängten Last und den maximal zulässigen Traglasten für die Stellungen des Auslegers 5 in dem vorgegebenen Stellungsbereich durchgeführt werden. Der örtliche Verlauf einer Traglastgrenze entspricht denjenigen Stellungen des Auslegers 5 bzw. denjenigen Positionen der Last, an denen die aktuell angehängte Last gleich der maximal zulässigen Traglast ist. Beispielsweise kann die Überwachung vorsehen, eine gewünschte Verstellbewegung für den Ausleger 5 abhängig davon zu verlangsamen, zu begrenzen, zuzulassen oder zu unterbinden, ob sich die Last an die Traglastgrenze annähert oder sich davon wegbewegt.The monitoring function of the
Die Steuereinheit 20 ist vorzugsweise mit einer Anzeigeeinrichtung 21 gekoppelt, um einem Kranführer zur Einsatzplanung und zum Betrieb des Mobilkrans 1 über eine Anzeige 22 visuelle Informationen über die maximal zulässige Traglast bzw. den Verlauf der Traglastgrenze zur Verfügung zu stellen. Diese visuelle Information kann einen oder mehrere Teilbereiche der möglichen Bewegungen bzw. Stellungen des Auslegers 5 betreffen. Dabei kann dem Kranführer zur Einsatzplanung bei einer momentan eingestellten Abstützgeometrie und bei einer momentanen Krankonfiguration die jeweilige maximal zulässige Traglast in dem Bereich möglicher Lastpositionen als absoluter Wert angegeben werden. Insbesondere können die Positionen der jeweiligen maximal zulässigen Traglast als Abstand von einer Auslegerdrehachse angegeben werden.The
Eine Vermittlung des Verlaufs der maximal zulässigen Traglasten kann beispielsweise durch eine Darstellung erfolgen, wie sie in der Anzeige 22 der
Die Segmentdarstellung zeigt auf einer Mittenachse M die momentane Lastposition P als Markierung an und durch farbliche Unterscheidung verschiedene Traglastbereiche, die die möglichen Lastpositionen in der geometrischen Umgebung der momentanen Lastposition P abbilden. In der dargestellten Ausführungsform sind drei Traglastbereiche gezeigt:
- ein erster Traglastbereich A, in dem die angehängte Last deutlich kleiner ist als die maximal zulässige Traglast,
- ein zweiter Traglastbereich B, in dem die angehängte Last annähernd der maximal zulässigen Traglast entspricht, und
- ein dritter Traglastbereich C, in dem die angehängte Last gleich oder größer ist als die maximal zulässige Traglast.
- a first load range A, in which the suspended load is significantly smaller than the maximum permissible load,
- a second load range B, in which the suspended load approximately corresponds to the maximum permissible load, and
- a third load range C, in which the suspended load is equal to or greater than the maximum permissible load.
Der erste Traglastbereich A kann beispielsweise durch eine grüne Färbung den Bereich der Lastpositionen angeben, in dem die momentan angehängte Last unterhalb eines vorgegebenen Anteils der maximal zulässigen Traglast, wie z. B. 90% der maximal zulässigen Traglast, liegt. So kann ein zweiter (kritischer) Traglastbereich B beispielsweise durch eine gelbe Färbung einen kritischen Bereich von Lastpositionen, in dem die angehängte Last die maximal zulässige Traglast annähernd erreicht (z.B. zwischen 90% und 100% der maximal zulässigen Traglast liegt. Ein sich daran anschließender dritter (unzulässiger) Traglastbereich C kann beispielsweise durch eine rote Färbung den Bereich der Lastpositionen angeben, in dem die momentan angehängte Last die maximal zulässige Traglast überschreiten würde bzw. die Standsicherheit des Krans aufgrund seines Eigengewichts nicht mehr gewährleistet ist (z.B. rückwärtige Standsicherheit). Die Grenze zwischen dem zweiten Traglastbereich B und dem dritten Traglastbereich C stellt die Traglastgrenze dar.The first load range A can, for example, be colored green to indicate the range of load positions in which the currently attached load is below a specified proportion of the maximum permissible load, such as 90% of the maximum permissible load. A second (critical) load range B can, for example, be colored yellow to indicate a critical range of load positions in which the attached load almost reaches the maximum permissible load (e.g. between 90% and 100% of the maximum permissible load). A subsequent third (impermissible) load range C can, for example, be colored red to indicate the range of load positions in which the currently attached load would exceed the maximum permissible load or the stability of the crane is no longer guaranteed due to its own weight (e.g. rear stability). The boundary between the second load range B and the third load range C represents the load limit.
Die Steuereinheit 20 berechnet für die jeweilige momentane Lastposition und für die Stellungen des Auslegers 5, die den möglichen Lastpositionen entsprechen, die die momentane Lastposition umgeben, die entsprechenden maximal zulässigen Traglasten und ermittelt den entsprechenden Anteil, den die momentan angehängte Traglast daran hat. Dieser Anteil wird in der Segmentdarstellung positionsabhängig in geeigneter Weise durch eine flächige optische Gestaltung farblich usw. dargestellt.The
Dadurch kann der Kranführer zu jedem Zeitpunkt in jedem aktuellen Zustand des Mobilkrans 1 erkennen, welchen Abstand die momentane Lastposition von einer durch die maximal zulässigen Traglasten definierten Grenze (d.h. Grenze, die durch Erreichen bzw. Überschreiten der maximal zulässigen Traglast durch die angehängte Last) aufweist, so dass er beurteilen kann, welche Bewegungen des Auslegers 5 zulässig sind und welche eine kritische Annäherung an eine Lastposition bewirken, an der die angehängte Last der maximal zulässigen Traglast entspricht.This allows the crane operator to see at any time in any current state of the
Befindet sich z. B. die Position der angehängten Last im zweiten (kritischen) Traglastbereich B, so kann jede Ansteuerung des Auslegers 5, die die Last weiter in Richtung einer Lastposition bringen würde, bei der die maximal zulässige Traglast verringert wäre, durch die Steuereinheit 20 mit verlangsamter Verstellgeschwindigkeit umgesetzt und/oder bei Erreichen der Traglastgrenze unterbunden werden. Dagegen dürfen Ansteuerungen in Verstellrichtungen des Auslegers 5, die die Traglast wieder zurück in den ersten (unkritischen) Bereich der Auslegerstellungen bringen würden, durch die Steuereinheit 20 unverändert ausgeführt werden.If, for example, the position of the suspended load is in the second (critical) load range B, any control of the
Allgemein kann die Steuereinheit 20 also eine Verstellgeschwindigkeit des Auslegers abhängig von dem Verlauf der Traglastgrenze, die die Positionen einer angehängten Last angibt, bei der die maximal zulässige Traglast des Mobilkrans 1 durch die angehängte Last überschritten wird, im vorgegebenen Stellungsbereich des Auslegers 5 einstellen. Insbesondere kann die Verstellgeschwindigkeit des Auslegers 5 abhängig von der angehängten Last und abhängig von einem Abstand zwischen einer Lastposition der angehängten Last und einer Position, an der die angehängte Last die maximal zulässige Traglast erreicht, eingestellt werden. Alternativ oder zusätzlich kann die Verstellgeschwindigkeit abhängig von einem Gradienten des Verlaufs der maximal zulässigen Traglast bezüglich der Verstellrichtung eingestellt werden. Zusätzlich kann eine Reduzierung der Verstellgeschwindigkeit abhängig von dem Verhältnis der Last zu der maximal zulässigen Traglast an der momentanen Lastposition erfolgen.In general, the
Insbesondere kann die Verstellgeschwindigkeit gegenüber dem Wunsch des Benutzers reduziert werden bzw. die vom Benutzer gewünschte Verstellgeschwindigkeit begrenzt werden, wenn der Gradient des Verlaufs der maximal zulässigen Traglast in Richtung der gewünschten Verstellbewegung relativ groß (z.B. größer als ein vorgegebener Schwellenwert) ist und ein Mindestabstand zu der Traglastgrenze unterschritten ist. Das Einstellen der Verstellgeschwindigkeit abhängig von dem Gradienten des Verlaufs der maximal zulässigen Traglast in Richtung der gewünschten Verstellbewegung hat den Vorteil, dass eine Annäherung an die Traglastgrenze so langsam ausgeführt wird, dass ein Überschwingen des Auslegers 5 bzw. der angehängten Last über die Tragfähigkeitsgrenze hinaus vermieden werden kann.In particular, the adjustment speed can be reduced compared to the user's wishes or the adjustment speed desired by the user can be limited if the gradient of the course of the maximum permissible load in the direction of the desired adjustment movement is relatively large (e.g. greater than a predetermined threshold value) and a minimum distance to the load limit is not reached. Setting the adjustment speed depending on the gradient of the course of the maximum permissible load in the direction of the desired adjustment movement has the advantage that the load limit is approached so slowly that an overshoot of the
In
In Schritt S1 wird eine momentane Stellung des Auslegers 5 und die momentane Lastposition ermittelt. Ausgehend von der momentanen Lastposition werden weitere Stellungen des Auslegers 5 definiert, die einen Umgebungsbereich von möglichen Lastpositionen um die momentane Lastposition definieren.In step S1, a current position of the
In Schritt S2 werden für die momentane Stellung des Auslegers 5 und die weiteren Stellungen des Auslegers 5 eine jeweilige Lastbegrenzung ermittelt, die von der Abstützgeometrie abhängt.In step S2, a respective load limit is determined for the current position of the
In einem nachfolgenden Schritt S3 werden für die momentane Stellung des Auslegers 5 und die weiteren Stellungen des Auslegers 5 jeweils eine durch die Ausleger-Traglastfähigkeit angegebene Lastbegrenzung basierend auf der Auslegerfestigkeitstabelle und in Schritt S4 jeweils die eine oder die mehreren funktionsbasierten Lastbegrenzungen basierend auf den weiteren Parametern und gegebenenfalls bezüglich weiterer begrenzender Parameter bestimmt.In a subsequent step S3, for the current position of the
In Schritt S5 wird für die momentane Stellung des Auslegers 5 und die weiteren Stellungen des Auslegers 5 jeweils eine maximal zulässige Tragfähigkeit durch Minimumbildung der Lastbegrenzungen bestimmt.In step S5, a maximum permissible load capacity is determined for the current position of the
In Schritt S6 werden diejenigen Stellungen des Auslegers 5 aus den oben vorgegebenen Stellungen des Auslegers 5 bestimmt, an denen die angehängte Last die maximal zulässige Traglast erreicht oder überschreitet. Diese Stellungen des Auslegers 5 definieren die Traglastgrenze.In step S6, those positions of the
In Schritt S7 werden die Lastpositionen, die den vorgegebenen Stellungen des Auslegers 5 entsprechen, Traglastbereichen zugeordnet und wie oben beschrieben grafisch dargestellt. Die grafische Darstellung kann die Darstellung der Absolutwerte der maximal zulässigen Traglast für den gesamten Traglastbereich umfassen und/oder die Segmentdarstellung zur Darstellung des Umfeldes der Lastposition bezüglich der Traglastgrenze. Insbesondere werden bei der Segmentdarstellung die Traglastbereiche durch unterschiedliche optische Gestaltung voneinander unterschieden, so dass ein Benutzer intuitiv zulässige Kranbewegungen für die angehängte Last erkennen kann.In step S7, the load positions that correspond to the specified positions of the
Claims (12)
- A method of operating a mobile crane (1) with a boom (5), comprising the steps of:- determining maximum permissible loads for a plurality of positions in predetermined position range of the boom (5);- determining a local curve of local load limits and / or one or more local load ranges based on a suspended load and on the maximum permissible loads for the plurality of positions of the predetermined position range of the boom (5); wherein the local curve of the load limit indicate those positions of the boom or those load positions, respectively, where the suspended load equals the maximum permissible load, wherein the load ranges indicate those positions of the boom or those load positions, respectively, where a ratio of the suspended load and the maximum permissible load is within a specified range, and- operating the mobile crane (1), depending on the local curve of the determined load limits and/or the one or more determined load ranges.
- The method of claim 1, wherein the maximum permissible loads for the plurality of positions in the predetermined position range of the boom (5) are determined using a boom strength table and based on a support geometry of support means (10), wherein, in particular, respective load limitations are determined by the boom strength table and by the support geometry for each of the plurality of positions of the boom (5), wherein the maximum permissible loads are then determined by a minimum operation applied on the load limits determined by the boom strength table and by the support geometry.
- The method of claim 2, wherein load limitations determined by the support geometry for the plurality of positions of the boom (5) in the predetermined position range are determined using a torque balance around one or more tilting lines (KL) defined by the support geometry.
- A method according to claim 2 or 3, wherein the maximum permissible loads for different positions in the predetermined position range of the boom (5) are determined by means of load limitations determined by one or more load rating models which are map-based or function-based and depending on one or more further parameters or determined by one or more limiting parameters.
- Method according to one of claims 1 to 4, wherein in operation of the mobile crane (1), the plurality of positions of the boom (5) in a given geometric surrounding of the current position of the boom (5) is considered in order to determine the maximum permissible loads, wherein an adjustment speed of the boom (5) is selected depending on the curve of a load limit in the predetermined position range of the boom (5).
- The method of claim 5, wherein the adjustment speed of the boom (5) is controlled depending on a suspended load and on a distance between the current load position and a load limit, wherein the load limit corresponds to the positions of the load at which the suspended load reaches the maximum permissible load if it is moved in an adjustment direction, wherein the adjustment speed may be controlled depending on a gradient of the curve of the maximum permissible load with respect to the adjustment direction.
- A method according to any one of claims 1 to 6, wherein the maximum permissible loads for the predetermined position range of the boom are displayed on a display for the predetermined position range as an absolute value indication or a relative value indication that indicates the ratio of the suspended load to the maximum permissible load.
- The method of claim 7, wherein the absolute value indication or the relative value indication of the maximum permissible loads are displayed on the display in a visually distinguishable manner, in particular by a respectively assigned coloring, brightness or shading.
- A control unit (20) for operating a mobile crane (1) is provided with a boom (5), wherein the control unit (20) is configured to:- determine maximum permissible loads for a plurality of positions in a predetermined position range of the boom (5);- determine a local curve of load limits and / or one or more load ranges based on a suspended load and on the maximum permissible load for the plurality of positions of the predetermined position range of the boom (5), wherein the local curve of the load limits indicate those positions of the boom or those load positions, respectively, where the suspended load equals the maximum permissible load, wherein the load ranges indicate those positions of the boom or those load positions, respectively, where a ratio of the suspended load and the maximum permissible load is within a specified range; and- operate the mobile crane (1) depending on the local curve of the determined load limits and / or the one or more determined load ranges.
- System for a mobile crane (1) comprising:- the control unit (20) according to claim 9; and- a display means (21) for visually presenting a display (22) to present maximum permissible loads in the predetermined position range of the boom (5) as an absolute value indication or as a relative value indication for the plurality of positions of the boom (5) in the predetermined position range, wherein the relative value indication defines a ratio of the suspended load to the maximum permissible load at a position of the boom.
- System for a mobile crane (1) comprising:- a control unit (20) according to claim 9; and- a display means (21) for visually presenting a display (22) to present, for the predetermined position range, the load ranges in the vicinity of a current load position corresponding to a current position of the boom.
- The system of claim 11, wherein the display means (21) is configured to present the load ranges as visually distinguishable areas, particularly as areas which can be distinguished by their colors and / or by their brightnesses.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102014105618.3A DE102014105618A1 (en) | 2014-04-22 | 2014-04-22 | Method and device for operating a mobile crane and mobile crane |
| PCT/EP2015/058525 WO2015162096A1 (en) | 2014-04-22 | 2015-04-20 | Method and device for operating a mobile crane, and mobile crane |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP3134344A1 EP3134344A1 (en) | 2017-03-01 |
| EP3134344B1 EP3134344B1 (en) | 2018-09-12 |
| EP3134344B2 true EP3134344B2 (en) | 2024-04-17 |
Family
ID=52991734
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP15717490.5A Active EP3134344B2 (en) | 2014-04-22 | 2015-04-20 | Method and apparatus for operating a mobile crane and the mobile crane |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10144621B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP3134344B2 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2017513784A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN106715317B (en) |
| DE (1) | DE102014105618A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2015162096A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6309847B2 (en) * | 2014-07-14 | 2018-04-11 | ファナック株式会社 | Robot controller capable of transporting workpieces exceeding the rated workpiece parameters |
| ES2758128T3 (en) * | 2015-10-16 | 2020-05-04 | Palfinger Ag | Arrangement of a control device and a mobile control module |
| DE102016104358B4 (en) | 2016-03-10 | 2019-11-07 | Manitowoc Crane Group France Sas | Method for determining the carrying capacity of a crane and crane |
| DE102016003566A1 (en) * | 2016-03-23 | 2017-09-28 | Liebherr-Werk Biberach Gmbh | Method for monitoring a work machine |
| US10676328B2 (en) * | 2016-08-24 | 2020-06-09 | Manitowoc Crane Companies, Llc | Crane function performance enhancement for non-symmetrical outrigger arrangements |
| WO2018049475A1 (en) * | 2016-09-15 | 2018-03-22 | Terex Australia Pty Ltd | Crane counterweight and suspension |
| US10549970B2 (en) * | 2017-08-02 | 2020-02-04 | Jlg Industries, Inc. | Telehandler with cantilever boom mounting |
| JP6620798B2 (en) * | 2017-08-08 | 2019-12-18 | 株式会社タダノ | Overload prevention device |
| US11142438B2 (en) * | 2017-08-28 | 2021-10-12 | Manitowoc Crane Companies, Llc | Graphical working range diagrams for displaying allowable and projected loads |
| IT201700115700A1 (en) * | 2017-10-13 | 2019-04-13 | Hyva Holding Bv | A PREDICTIVE STABILITY CONTROL METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SELF-PROPELLED WORK MACHINES |
| IT201800001688A1 (en) | 2018-01-23 | 2019-07-23 | Effer S P A | TOWER CRANE |
| DE102018129352A1 (en) * | 2018-11-21 | 2020-05-28 | Liebherr-Werk Biberach Gmbh | Crane and method for monitoring the operation of such a crane |
| EP3722512B1 (en) * | 2019-04-08 | 2022-06-08 | BAUER Maschinen GmbH | Excavation device and method for operating same |
| JP7416065B2 (en) * | 2019-06-20 | 2024-01-17 | 株式会社タダノ | Crane with movement range display system and movement range display system |
| DE102019118902A1 (en) * | 2019-07-12 | 2021-01-14 | Putzmeister Engineering Gmbh | Mobile concrete pump |
| DE102019121628B3 (en) * | 2019-08-12 | 2020-08-20 | Franka Emika Gmbh | Method for operating a robot manipulator with an increased mass of a load |
| AU2020366286A1 (en) * | 2019-10-17 | 2022-04-14 | Terex Australia Pty Ltd | Mobile crane operation control |
| JP2021123436A (en) * | 2020-02-03 | 2021-08-30 | Ihi運搬機械株式会社 | Control device of jib crane |
| IT202000006757A1 (en) | 2020-03-31 | 2021-10-01 | Manitou Italia Srl | Telehandler simulator. |
| FI131037B1 (en) * | 2020-06-03 | 2024-08-08 | Ponsse Oyj | Controlling boom of work machine |
| IT202100023042A1 (en) * | 2021-09-07 | 2023-03-07 | Magni Real Estate S R L | PROCEDURE FOR GENERATION OF LOAD DIAGRAMS FOR TELEHANDLER |
| CA3175122A1 (en) * | 2021-09-28 | 2023-03-28 | Industries N.R.C. Inc | Lifting chart for tow vehicle |
| CN114044452B (en) * | 2021-10-27 | 2023-06-23 | 浙江三一装备有限公司 | Work machine work control method and device and work machine |
Family Cites Families (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5730305A (en) | 1988-12-27 | 1998-03-24 | Kato Works Co., Ltd. | Crane safety apparatus |
| JPH03130291U (en) * | 1990-04-10 | 1991-12-27 | ||
| JP2564060B2 (en) * | 1991-10-24 | 1996-12-18 | 株式会社神戸製鋼所 | Safety equipment for construction machinery |
| JPH07125987A (en) * | 1993-11-08 | 1995-05-16 | Komatsu Mec Corp | Suspension load/overturning moment detecting device for mobile crane |
| EP0857687A4 (en) | 1995-03-03 | 1999-12-29 | Komatsu Mfg Co Ltd | Device for indicating movable range of mobile crane vehicle |
| US6028354A (en) | 1997-10-14 | 2000-02-22 | Amkor Technology, Inc. | Microelectronic device package having a heat sink structure for increasing the thermal conductivity of the package |
| JP2000034093A (en) * | 1998-07-21 | 2000-02-02 | Kobe Steel Ltd | Slewing type working machinery and its safety working area and setting method of rated load |
| JP2002250055A (en) * | 2001-02-23 | 2002-09-06 | Komatsu Ltd | Construction equipment vehicle and its display device |
| DE10155006B4 (en) | 2001-11-06 | 2004-12-16 | Terex-Demag Gmbh & Co. Kg | Mobile crane with super lift device |
| DE202006017730U1 (en) | 2006-11-21 | 2008-04-03 | Liebherr-Werk Ehingen Gmbh | mobile crane |
| DE102010025022A1 (en) * | 2010-06-24 | 2011-12-29 | Hirschmann Automation And Control Gmbh | Method for load moment limitation of a work vehicle with a boom |
| DE202010014310U1 (en) * | 2010-10-14 | 2012-01-18 | Liebherr-Werk Ehingen Gmbh | Crane, in particular caterpillar or mobile crane |
| DE202010014309U1 (en) * | 2010-10-14 | 2012-01-18 | Liebherr-Werk Ehingen Gmbh | Crane, in particular caterpillar or mobile crane |
| AT511234B1 (en) * | 2011-04-08 | 2013-05-15 | Palfinger Ag | STAND SAFETY MONITORING OF A LOADING CRANE MOUNTED ON A VEHICLE |
| DE102012011726C5 (en) * | 2012-06-13 | 2024-06-13 | Liebherr-Werk Ehingen Gmbh | Method for operating a crane with monitoring unit and crane |
| US9446935B2 (en) | 2012-06-13 | 2016-09-20 | Liebherr-Werk Ehingen Gmbh | Method for monitoring crane safety and crane |
-
2014
- 2014-04-22 DE DE102014105618.3A patent/DE102014105618A1/en active Pending
-
2015
- 2015-04-20 WO PCT/EP2015/058525 patent/WO2015162096A1/en active Application Filing
- 2015-04-20 EP EP15717490.5A patent/EP3134344B2/en active Active
- 2015-04-20 JP JP2016564080A patent/JP2017513784A/en active Pending
- 2015-04-20 CN CN201580027113.3A patent/CN106715317B/en active Active
-
2016
- 2016-10-24 US US15/332,359 patent/US10144621B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3134344A1 (en) | 2017-03-01 |
| CN106715317B (en) | 2019-10-18 |
| DE102014105618A1 (en) | 2015-10-22 |
| WO2015162096A1 (en) | 2015-10-29 |
| JP2017513784A (en) | 2017-06-01 |
| US10144621B2 (en) | 2018-12-04 |
| US20170036894A1 (en) | 2017-02-09 |
| CN106715317A (en) | 2017-05-24 |
| EP3134344B1 (en) | 2018-09-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3134344B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for operating a mobile crane and the mobile crane | |
| DE10155006B4 (en) | Mobile crane with super lift device | |
| EP1925585B1 (en) | Mobile crane | |
| EP3219662B1 (en) | Method for determining the load bearing capacity of a crane and crane | |
| EP3470362B1 (en) | Method and device for monitoring the stability of a loading crane mounted on a vehicle | |
| EP2135834B1 (en) | Crane, preferably mobile or caterpillar crane | |
| EP2113481A1 (en) | Mobile crane with crane monitoring system | |
| EP2799386B1 (en) | Device and method for determination and monitoring a counterweight which is fitted to a crane | |
| EP3362399B2 (en) | Arrangement of a control device and a mobile control module | |
| DE102006040782A1 (en) | Safety and control procedures for cranes | |
| WO2016128577A1 (en) | Device for discharging liquids, and method for controlling the movement of at least two extension arms of an agricultural field sprayer | |
| EP3856673B1 (en) | Crane and method for monitoring the operation of such a crane | |
| DE19931302B4 (en) | Continuously adjustable crane | |
| DE3711239A1 (en) | Device for securing movable loading devices (chargers) | |
| AT524349A2 (en) | Crane, in particular mobile crane | |
| EP3287412B1 (en) | Industrial truck and method for controlling an industrial truck | |
| WO1997045358A1 (en) | Method and arrangement for preventing load collisions in a suspended load movement apparatus | |
| WO2014173609A1 (en) | Sensor-based monitoring of wind direction and thermal radiation for a mobile work appliance | |
| DE102021128317A1 (en) | Method and system for planning an operation to lift a load with a crane | |
| DE202019105397U1 (en) | Safety device for construction machines and the like | |
| WO2024217734A1 (en) | Method, system, and computer program for moving a load by means of a plurality of cranes | |
| DE102023109701A1 (en) | Method, system and computer program product for moving a load by means of a plurality of cranes | |
| DE102021133477A1 (en) | truck-mounted concrete pump | |
| DE102014112900A1 (en) | Display device for an industrial truck | |
| DE102023123236A1 (en) | LIFTING POWER SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR LIFTING MACHINES |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE INTERNATIONAL PUBLICATION HAS BEEN MADE |
|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20161121 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| DAV | Request for validation of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: B66C 13/18 20060101ALI20180321BHEP Ipc: B66C 23/90 20060101AFI20180321BHEP Ipc: B66C 13/16 20060101ALI20180321BHEP Ipc: B66C 23/36 20060101ALI20180321BHEP |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20180425 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502015005836 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 1040320 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20181015 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: FP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20181212 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20181212 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20181213 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190112 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190112 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R026 Ref document number: 502015005836 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PLAX | Notice of opposition and request to file observation + time limit sent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS2 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: MANITOWOC CRANE GROUP GERMANY GMBH Effective date: 20190612 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 |
|
| PLBB | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition received |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS3 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190420 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190430 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190430 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190420 |
|
| RAP2 | Party data changed (patent owner data changed or rights of a patent transferred) |
Owner name: TADANO DEMAG GMBH |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 1040320 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20200420 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20150420 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200420 |
|
| APAH | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNO |
|
| APBM | Appeal reference recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNREFNO |
|
| APBP | Date of receipt of notice of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA2O |
|
| APBQ | Date of receipt of statement of grounds of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA3O |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180912 |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230530 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20230420 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| APBU | Appeal procedure closed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA9O |
|
| PUAH | Patent maintained in amended form |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009272 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT MAINTAINED AS AMENDED |
|
| 27A | Patent maintained in amended form |
Effective date: 20240417 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B2 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R102 Ref document number: 502015005836 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20240418 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20240419 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: FP |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20240424 Year of fee payment: 10 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20240425 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20240418 Year of fee payment: 10 |