EP2889537A1 - Trocknungsanlage sowie Verbrennungsanlage - Google Patents
Trocknungsanlage sowie Verbrennungsanlage Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2889537A1 EP2889537A1 EP14405092.9A EP14405092A EP2889537A1 EP 2889537 A1 EP2889537 A1 EP 2889537A1 EP 14405092 A EP14405092 A EP 14405092A EP 2889537 A1 EP2889537 A1 EP 2889537A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- hot gas
- dryer
- drying plant
- drying
- plant
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 46
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 title claims description 10
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 40
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 34
- 239000003546 flue gas Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 21
- UGFAIRIUMAVXCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon monoxide Chemical compound [O+]#[C-] UGFAIRIUMAVXCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 20
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000010304 firing Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 abstract description 7
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 abstract description 2
- 239000000428 dust Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000002023 wood Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000009833 condensation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000005494 condensation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000002028 Biomass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000032258 transport Effects 0.000 description 2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011109 contamination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008020 evaporation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008236 heating water Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000008188 pellet Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23K—FEEDING FUEL TO COMBUSTION APPARATUS
- F23K1/00—Preparation of lump or pulverulent fuel in readiness for delivery to combustion apparatus
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F26—DRYING
- F26B—DRYING SOLID MATERIALS OR OBJECTS BY REMOVING LIQUID THEREFROM
- F26B23/00—Heating arrangements
- F26B23/02—Heating arrangements using combustion heating
- F26B23/028—Heating arrangements using combustion heating using solid fuel; burning the dried product
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23K—FEEDING FUEL TO COMBUSTION APPARATUS
- F23K2201/00—Pretreatment of solid fuel
- F23K2201/20—Drying
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F26—DRYING
- F26B—DRYING SOLID MATERIALS OR OBJECTS BY REMOVING LIQUID THEREFROM
- F26B2200/00—Drying processes and machines for solid materials characterised by the specific requirements of the drying good
- F26B2200/24—Wood particles, e.g. shavings, cuttings, saw dust
Definitions
- the invention relates to a drying plant for drying moist material, especially biomass such as wood, especially in the form of wood chips, sawdust or crushed wood bark. It also relates to a combustion plant comprising such a drying plant.
- the invention is based on the object to improve generic drying equipment with respect to the adjustment of the moisture content of the dried material, in a manner which allows energy-saving operation. This task will solved by the invention as characterized in the claims.
- the material is predried in the belt dryer and then finish-dried to the desired moisture content in a rotor dryer in which the degree of drying is easily controllable.
- the lower temperatures in the belt dryer make it possible to continue to use hot gas, usually flue gas or hot air, which has already been used in the rotor dryer, in the belt dryer.
- hot gas usually flue gas or hot air, which has already been used in the rotor dryer, in the belt dryer.
- the energy saving is particularly pronounced when the drying plant is part of a combustion plant and the flue gases produced during combustion are used in the drying plant.
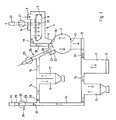
- Fig. 1 shows an inventive incineration plant, which comprises a drying plant according to the invention.
- the incinerator accordingly has a furnace 1 with boilers in which the heat of combustion for heating water or thermal oil eg for heating purposes is being used.
- a discharge 2 is arranged at the lower end of the furnace 1.
- a material feed 3 is followed immediately by a material feed of a subsequent drying plant 4, which comprises a belt dryer 5, a following in the material flow direction on this following Vorsilo 6 and a subsequent rotor dryer 7.
- a closed screen belt 8 is arranged with an upper run and a lower run, which run over several rollers. Its right end is below the material task 3, its left end above the Vorsilos 6.
- a heater 9 is also attached.
- the Vorsilo 6 is closed in the region of its lower end by a designed as a flap 10 separating device, i. separable from the subsequent rotor dryer 7.
- a flap 11 separating device At the lower end of the rotor dryer 7 is also closed by a designed as a flap 11 separating device, so that it can be separated from a bottom subsequent drying silo 12.
- the dry silo 12 is conveyed by a conveyor 13, e.g. Screw conveyor, chain conveyor or a moving floor, connected to the furnace 1. If the drying plant is not used for drying fuel or is not used in an incinerator, by contrast a discharge for dried material is arranged below the drying hopper, which can then be reused, e.g. as starting material for the production of pellets.
- a flue gas line 14 goes out, at the successive in terms of flow direction, a pre-separator 15 and, combined in a single unit, a precooler 16 and a Spark detection path 17 with a common dust collecting vessel are arranged.
- a hot gas guide passes through the rotor dryer 7 and the belt dryer 5 and comprises a parallel to Vorsilo 6 connecting portion 18 between them. The latter opens into an outlet 19 above the right end of the screen belt 8 or laterally thereof.
- a trigger 20 is arranged, which is connected via a fan 21 with a chimney 22. If very low dust levels of the exhaust gas are required, a filter, for example a fabric filter, can be installed in front of the fan 21 for dedusting the exhaust gas.
- a condenser in which the exhaust gas is cooled can be provided in front of the fan 21 and optionally after the filter.
- the condensation heat removed from the exhaust gas can be used.
- a heating register 23 is arranged in the area of the mouth of the hot gas guide in the rotor dryer 7.
- the hot gas guide comprises an air feed 24 with a fan 25.
- the flue gas line 14 opens between the fan 25 and the rotor dryer 7 in the hot gas guide.
- drying plant is not used within the framework of an incineration plant, ie not together with a firing plant, then there is merely an air feed as described, via which air or hot air is usually supplied as hot gas.
- a passage 26 is arranged, which the flue gas line 14 directly to the connecting portion 18th combines.
- a switch designed as a flap 27 closes the passage 26 in a first position, so that the air feed 24 and the flue gas line 14 are connected only via the rotor dryer 7 to the connecting section 18 and further to the belt dryer 5, while in a second position the passage 26 leaves open, but the rotor dryer 7 separates from the connecting portion 18, so that the air supply line 24 and the flue gas line 14 with this and the belt dryer 5 directly, bypassing the rotor dryer 7, are connected.
- a bypass branch 28 from the flue gas line 14 with, a bypass line 29, which leads via a closing device designed as a flap 30 and a fan 31 to a chimney 32.
- a closing device designed as a flap 30 and a fan 31 to a chimney 32.
- Another flap 33 is arranged with respect to the flow direction of the flue gas just behind the junction of the bypass line 29 of the flue gas duct 14 in the latter.
- the material usually wet biomass such as sawdust or woodchips, whose material flow is indicated by solid arrows is introduced through the material task 3 and falls on the belt dryer 5, more precisely on the right end of the upper run of the wire 8, on which it is a uniformly thick Layer forms. From this it is slowly transported to the left end of the said strand, from which it falls into the prefix 6.
- the flap 10 is usually closed, so that the material accumulates in Vorsilo 6 for a while. Then, the flap 10 is opened for a short time and accumulated in Vorsilo 6 material falls into the rotor dryer. 7
- the flap 11 of the rotor dryer 7 is opened and the material falls into the underlying drying silo 12. From there it transports the conveyor 13 into the furnace 1, where it is burned. The flap 11 is closed again and the flap 10 is opened briefly, so that the accumulated in Vorsilo 6 material falls into the rotor dryer 7 and the same is reloaded.
- the flue gas From the furnace 1, the flue gas, whose flow is indicated by long-dashed arrows, first flows into the pre-separator 15, where larger dust and ash particles are separated and discharged and on to the precooler 16 and the spark detection path 17, where any spark is detected and deleted, so that further transport of burning particles into the drying plant 4 is prevented.
- a hot gas By targeted mixture of cooler fresh air (short dashed arrow) or exhaust air from other parts of the drying plant or a mixture of fresh air and exhaust air with the flue gas, a hot gas is produced, the temperature is below a threshold temperature before it is passed into the rotor dryer 7 and on the material hits.
- the limit temperature is set so that evaporation of hydrocarbons from the material, which could lead to undesirable contamination of the hot gas (formation of 'blue haze'), is avoided.
- the limit temperature depends on the type of material. For wood, it is about 120 ° C. If necessary, additional hot air can be introduced into the rotor dryer 7 to increase the dryer output with the heating register 23.
- the hot gas strikes the material and promotes its drying, thereby cooling itself, i. Energy, composed of sensible heat and the condensation of water vapor resulting condensation heat, gives off. It then flows through the connecting section 18 further into the belt dryer 5, where it exits from the outlet 19 in the region lying over the left end of the wire 8. Since at the same time by the fan 21 at the trigger 20, a negative pressure is generated, the flue gas-air mixture flows from top to bottom through die.Schicht of moist material, which lies on the upper run of the screen belt 8 and through said upper strand. In this case, the material, in turn, with cooling of the hot gas, pre-dried before it enters the rotor dryer 7.
- the hot gas is filtered by flowing through the layer of material.
- small dust and ash particles are deposited. Therefore, the hot gas usually meets the legal requirements, which set the usual upper limits for the dust content and can be blown off without exhaustive cleaning measures as exhaust gas through the chimney 22 into the open.
- the chimney may be preceded by a filter or a condenser or both.
- the drying of the material can be supported by the heating register 9. While the flap 27 is usually in the in Fig. 1 shown, so that the hot gas flows through the rotor dryer 7, it is held during the unloading and reloading of the rotor dryer 7 in the second position in which the flue gas-air mixture directly, bypassing the rotor dryer 7, from the Flue gas duct 14 flows into the connecting portion 18 and further into the belt dryer 5.
- the bypass branch 28 allows it to be used in emergencies, e.g. in case of a fault in the drying plant 4, the passage of the flue gas through the same to interrupt.
- the precooler is not essential, since sufficient cooling can be achieved by fresh air alone.
- the heating registers can also often be omitted.
- the drying plant can also be used independently of a furnace and instead of flue gas or a flue gas-air mixture, for example. Only hot air can be used as hot gas.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Sustainable Development (AREA)
- Drying Of Solid Materials (AREA)
- Muffle Furnaces And Rotary Kilns (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- Die Erfindung betrifft eine Trocknungsanlage zur Trocknung von feuchtem Material, vor allem Biomasse wie Holz, insbesondere in der Form von Holzschnitzeln, Sägespänen oder zerkleinerter Holzrinde. Ausserdem betrifft sie eine Verbrennungsanlage, welche eine derartige Trocknungsanlage umfasst.
- Gattungsgemässe im wesentlichen aus einem Bandtrockner bestehende Anlagen zur Trocknung von feuchtem Material sind bekannt. Der Feuchtigkeitsgehalt des getrockneten Materials ist bei solchen Anlagen jedoch schlecht einstellbar und schwankt meist stark, sodass bei seiner weiteren Verwendung oft Schwierigkeiten auftreten oder zur Einstellung eines erwünschten Feuchtigkeitsgehalts energetisch ungünstige oder sonstige den Aufwand erhöhende Massnahmen erforderlich sind wie Mischung mit trockenem Material oder auch Zumischung von Wasser.
- Der Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zu Grunde, gattungsgemässe Trocknungsanlagen bezüglich der Einstellung des Feuchtigkeitsgehalts des getrockneten Materials zu verbessern, und zwar auf eine Weise, welche einen energiesparenden Betrieb ermöglicht. Diese Aufgabe wird durch die Erfindung, wie sie in den Ansprüchen gekennzeichnet ist, gelöst.
- Bei erfindungsgemässen Anlagen wird das Material im Bandtrockner vorgetrocknet und dann in einem Rotortrockner, in dem der Trocknungsgrad gut steuerbar ist, bis zum erwünschten Feuchtigkeitsgehalt fertiggetrocknet. Die tieferen Temperaturen im Bandtrockner erlauben dabei, Heissgas, gewöhnlich Rauchgas oder Heissluft, das bereits im Rotortrockner eingesetzt wurde, im Bandtrockner weiterzuverwenden. Dadurch wird eine erhebliche Energieeinsparung erzielt. Besonders ausgeprägt ist die Energieeinsparung, wenn die Trocknungsanlage Teil einer Verbrennungsanlage ist und die bei der Verbrennung entstehenden Rauchgase in der Trocknungsanlage eingesetzt werden.
- Im folgenden wird die Erfindung anhand einer Figur, welche lediglich ein Ausführungsbeispiel darstellt, näher erläutert.
- Fig. 1
- zeigt schematisch den Aufbau einer erfindungsgemässen Verbrennungsanlage.
-
Fig. 1 zeigt eine erfindungsgemässe Verbrennungsanlage, welche eine erfindungsgemässe Trocknungsanlage umfasst. Die Verbrennungsanlage weist demgemäss eine Feuerungsanlage 1 mit Kesseln auf, in welchen die Verbrennungswärme zum Aufheizen von Wasser oder Thermoöl z.B. für Heizzwecke genutzt wird. Am unteren Ende der Feuerungsanlage 1 ist ein Austrag 2 angeordnet. - Auf eine Materialaufgabe 3 folgt unmittelbar ein Materialeintrag einer anschliessenden Trocknungsanlage 4, welche einen Bandtrockner 5, einen in Materialflussrichtung auf diesen folgenden Vorsilo 6 und einen anschliessenden Rotortrockner 7 umfasst. Im Bandtrockner 5 ist ein geschlossenes Siebband 8 mit einem oberen Trum und einem unteren Trum angeordnet, die über mehrere Rollen laufen. Sein rechtes Ende liegt unterhalb der Materialaufgabe 3, sein linkes Ende oberhalb des Vorsilos 6. Im Deckenbereich ist ausserdem ein Heizregister 9 angebracht. Das Vorsilo 6 ist im Bereich seines unteren Endes durch eine als Klappe 10 ausgebildete Trennvorrichtung verschliessbar, d.h. vom anschliessenden Rotortrockner 7 trennbar.
- Am unteren Ende ist der Rotortrockner 7 ebenfalls durch eine als Klappe 11 ausgebildete Trennvorrichtung verschliessbar, sodass er von einem unten anschliessenden Trockensilo 12 getrennt werden kann. Der Trockensilo 12 ist durch eine Förderanlage 13, z.B. Förderschnecken, Kettenförderer oder ein Schubboden, mit der Feuerungsanlage 1 verbunden. Falls die Trocknungsanlage nicht der Trocknung von Brennmaterial dient oder gar nicht im Rahmen einer Verbrennungsanlage eingesetzt wird, so ist dagegen unterhalb des Trockehsilos ein Austrag für getrocknetes Material angeordnet, das dann auch anders weiterverwendet werden kann, z.B. als Ausgangsmaterial für die Herstellung von Pellets.
- Von der Feuerungsanlage 1 geht eine Rauchgasleitung 14 aus, an der hinsichtlich der Strömungsrichtung aufeinanderfolgend ein Vorabscheider 15 sowie, in einer Baueinheit zusammengefasst, ein Vorkühler 16 und eine Funkenerkennungsstrecke 17 mit einem gemeinsamen Staubsammelgefäss, angeordnet sind. Eine Heissgasführung führt durch den Rotortrockner 7 und den Bandtrockner 5 und umfasst einen zum Vorsilo 6 parallelen Verbindungsabschnitt 18 zwischen denselben. Letzterer mündet in einen Auslass 19 oberhalb des rechten Endes des Siebbandes 8 oder seitlich davon. Unterhalb des oberen Trums des Siebbandes 8 ist ein Abzug 20 angeordnet, der über einen Ventilator 21 mit einem Kamin 22 verbunden ist. Falls sehr niedrige Staubwerte des Abgases gefordert werden, kann vor dem Ventilator 21 ein Filter, z.B. ein Gewebefilter, zur Entstaubung des Abgases eingebaut sein. Vor dem Ventilator 21 und gegebenenfalls nach dem Filter kann ausserdem ein Kondensator vorgesehen sein, in dem das Abgas gekühlt wird. Die dem Abgas entzogene Kondensationswärme kann genutzt werden. Im Bereich der Mündung der Heissgasführung in den Rotortrockner 7 ist ein Heizregister 23 angeordnet.
- Die Heissgasführung umfasst eine Luftzuführung 24 mit einem Ventilator 25. Die Rauchgasleitung 14 mündet zwischen dem Ventilator 25 und dem Rotortrockner 7 in die Heissgasführung. So kann aus dem Rauchgas und aus Frischluft oder auch Abluft aus anderen Teilen der Verbrennungsanlage ein Rauchgas-Luft-Gemisch als Heissgas hergestellt werden.
- Wird die Trocknungsanlage nicht im Rahmen einer Verbrennungsanlage, also nicht zusammen mit einer Feuerungsanlage eingesetzt, so ist lediglich eine Luftzuführung wie beschrieben vorhanden, über die gewöhnlich Luft oder Heissluft als Heissgas zugeführt wird.
- Im Bereich der Mündung der Heissgasführung in den Rotortrockner 7 ist ein Durchlass 26 angeordnet, der die Rauchgasleitung 14 direkt mit dem Verbindungsabschnitt 18 verbindet. Eine als Klappe 27 ausgebildete Weiche verschliesst in einer ersten Stellung den Durchlass 26, sodass die Luftzuführung 24 und die Rauchgasleitung 14 nur über den Rotortrockner 7 mit dem Verbindungsabschnitt 18 und weiter mit dem Bandtrockner 5 verbunden sind, während sie in einer zweiten Stellung den Durchlass 26 offen lässt, aber den Rotortrockner 7 vom Verbindungsabschnitt 18 trennt, sodass die Luftzuführung 24 und die Rauchgasleitung 14 mit diesem und dem Bandtrockner 5 direkt, unter Umgehung des Rotortrockners 7, verbunden sind.
- Zwischen dem Vorabscheider 15 und dem Vorkühler 16 zweigt ein Umgehungszweig 28 von der Rauchgasleitung 14 ab, mit, einer Umgehungsleitung 29, welche über eine als Klappe 30 ausgebildete Schliessvorrichtung und einen Ventilator 31 zu einem Kamin 32 führt. Eine weitere Klappe 33 ist hinsichtlich der Strömungsrichtung des Rauchgases knapp hinter der Abzweigung der Umgehungsleitung 29 von der Rauchgasleitung 14 in der letzteren angeordnet.
- Das Material, gewöhnlich feuchte Biomasse wie Sägespäne oder Hackschnitzel, dessen Materialfluss durch durchgezogene Pfeile angedeutet ist, wird über die Materialaufgabe 3 eingeführt und fällt auf den Bandtrockner 5, genauer auf den rechten Endbereich des oberen Trums des Siebbandes 8, auf dem es eine gleichmässig dicke Schicht bildet. Von diesem wird es langsam zum linken Ende des besagten Trums transportiert, von dem es in das Vorsilo 6 fällt. Die klappe 10 ist gewöhnlich geschlossen, sodass sich das Material im Vorsilo 6 eine Zeit lang ansammelt. Dann wird die Klappe 10 kurzzeitig geöffnet und das im Vorsilo 6 angesammelte Material fällt in den Rotortrockner 7.
- Nach einer vorgegebenen Trocknungszeit oder wenn es einen vorbestimmten Feuchtigkeitsgehalt unterschreitet, wird die Klappe 11 des Rotortrockners 7 geöffnet und das Material fällt in den darunterliegenden Trockensilo 12. Von dort transportiert es die Förderanlage 13 in die Feuerungsanlage 1, wo es verbrannt wird. Die Klappe 11 wird wieder geschlossen und die Klappe 10 kurz geöffnet, sodass das im Vorsilo 6 angesammelte Material in den Rotortrockner 7 fällt und derselbe neu beladen wird.
- Von der Feuerungsanlage 1 strömt das Rauchgas, dessen Strömung durch langgestrichelte Pfeile abgedeutet ist, zuerst in den Vorabscheider 15, wo grössere Staub- und Aschepartikel abgeschieden und ausgebracht werden und weiter zum Vorkühler 16 und zur Funkenerkennungsstrecke 17, wo allfälliger Funkenflug erkannt und gelöscht wird, sodass ein Weitertransport von brennenden Partikeln in die Trocknungsanlage 4 verhindert wird. Durch gezielte Mischung von kühlerer Frischluft (kurzgestrichelter Pfeil) oder auch Abluft aus anderen Teilen der Trocknungsanlage oder einer Mischung von Frischluft und Abluft mit dem Rauchgas wird ein Heissgas hergestellt, dessen Temperatur unter einer Grenztemperatur liegt, bevor es in den Rotortrockner 7 geleitet wird und auf das Material trifft. Die Grenztemperatur ist dabei so festgelegt, dass ein Ausdampfen von Kohlenwasserstoffen aus dem Material, das zu einer unerwünschten Verunreinigung des Heissgases (Bildung von 'blue haze') führen könnte, vermieden wird. Die Grenztemperatur hängt von der Art des Materials ab. Bei Holz beträgt sie ca. 120°C. Wenn nötig kann zur Erhöhung der Trocknerleistung mit dem Heizregister 23 zusätzliche Warmluft in den Rotortrockner 7 eingeleitet werden.
- Im Rotortrockner 7 trifft das Heissgas auf das Material und fördert dessen Trocknung, wobei es sich selbst abkühlt, d.h. Energie, zusammengesetzt aus fühlbarer Wärme und beim Auskondensieren von Wasserdampf entstehender Kondensationswärme, abgibt. Es strömt dann durch den Verbindungsabschnitt 18 weiter in den Bandtrockner 5, wo es aus dem Auslass 19 in den über dem linken Ende des Siebbandes 8 liegenden Bereich austritt. Da zugleich durch den Ventilator 21 am Abzug 20 ein Unterdruck erzeugt wird, strömt das Rauchgas-Luft-Gemisch von oben nach unten durch die.Schicht von feuchtem Material, die auf dem oberen Trum des Siebbandes 8 liegt und durch das besagte obere Trum. Dabei wird das Material, wiederum unter Abkühlung des Heissgases, vorgetrocknet, bevor es in den Rotortrockner 7 gelangt.
- Zugleich wird das Heissgas, indem es durch die Materialschicht strömt, gefiltert. Insbesondere werden kleine Staub- und Aschepartikel abgeschieden. Das Heissgas genügt deshalb gewöhnlich den gesetzlichen Bestimmungen, welche übliche Obergrenzen für den Staubgehalt festlegen und kann ohne weitere Reinigungsmassnahmen als Abgas durch den Kamin 22 ins Freie abgeblasen werden. Bei besonders hohen Anforderungen kann wie erwähnt dem Kamin ein Filter oder ein Kondensator oder beides vorgeordnet sein.
- Die Trocknung des Materials kann durch das Heizregister 9 unterstützt werden. Während die Klappe 27 gewöhnlich in der in
Fig. 1 dargestellten ersten Stellung ist, sodass das Heissgas durch den Rotortrockner 7 strömt, wird sie während des Entladens und Neubeladens des Rotortrockners 7 in der zweiten Stellung festgehalten, in der das Rauchgas-Luft-Gemisch direkt, unter Umgehung des Rotortrockners 7, aus der Rauchgasleitung 14 in den Verbindungsabschnitt 18 und weiter in den Bandtrockner 5 strömt. - Bei der beschriebenen Betriebsweise, bei der das aus Rauchgas und Luft zusammengemischte Heissgas meist sowohl durch den Rotortrockner 7 als auch durch den Bandtrockner 5 geleitet wird, wird die Wärme des Rauchgases so weit wie möglich ausgenützt und die Trocknung optimiert.
- Der Umgehungszweig 28'erlaubt es, in Notfällen, z.B. bei einer Störung in der Trocknungsanlage 4, die Durchleitung des Rauchgases durch die dieselbe zu unterbrechen.
- Es sind verschiedene Abwandlungen des oben'beschriebenen Ausführungsbeispiels möglich, ohne dass der Bereich der Erfindung verlassen würde. So ist insbesondere der Vorkühler nicht unbedingt erforderlich, da eine ausreichende Kühlung auch durch Frischluftzufuhr allein erzielt werden kann. Die Heizregister können ebenfalls oft entfallen.
- Wie erwähnt kann die Trocknungsanlage auch unabhängig von einer Feuerungsanlage eingesetzt werden und statt Rauchgas oder einem Rauchgas-Luft-Gemisch z.B. ausschliesslich Heissluft als Heissgas eingesetzt werden.
-
- 1
- Feuerungsanlage
- 2
- Austrag
- 3
- Materialaufgabe
- 4
- Trocknungsanlage
- 5
- Bandtrockner
- 6
- Vorsilo
- 7
- Rotortrockner
- 8
- Siebband
- 9
- Heizregister
- 10
- Klappe
- 11
- Klappe
- 12
- Trockensilo
- 13
- Förderanlage
- 14
- Rauchgasleitung
- 15
- Vorabscheider
- 16
- Vorkühler
- 17
- Funkenerkennungsstrecke
- 18
- Verbindungsabschnitt
- 19
- Auslass
- 20
- Abzug
- 21
- Ventilator
- 22
- Kamin
- 23
- Heizregister
- 24
- Luftzuführung
- 25
- Ventilator
- 26
- Durchlass
- 27
- Klappe
- 28
- Umgehungszweig
- 29
- Umgehungsleitung
- 30
- Klappe
- 31
- Ventilator
- 32
- Kamin
- 33
- Klappe
Claims (10)
- Trocknungsanlage (4) zur Trocknung von feuchtem Material, mit einem Materialeintrag sowie mit einem Bandtrockner (5) mit einem Siebband (8) und mit einer Heissgasführung mit einem Auslass (19) und einem Abzug (20), welche derart angeordnet sind, dass die Heissgasströmung das obere Trum des Siebbandes (8) kreuzt und das Heissgas das darauf befindliche Material durchströmt, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Trockungsanlage (4) einen dem Bandtrockner (5) hinsichtlich des Materialflusses nachgeordneten Rotortrockner (7) umfasst und die Heissgasführung hinsichtlich der Strömungsrichtung des Heissgases vor dem Bandtrockner (5) durch den Rotortrockner (7) führt.
- Trocknungsanlage (4) nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass der Rotortrockner (7) unterhalb eines Austragendes des Bandtrockners (5) angeordnet und durch einen mit einer Trennvorrichtung versehenen Vorsilo (6) mit demselben verbunden ist.
- Trocknungsanlage (4) nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass am Austragende des Rotortrockner (7) eine Trennvorrichtung angeordnet ist.
- Trocknungsanlage (4) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Heissgasführung eine hinsichtlich der Strömungsrichtung des Heissgases vor der Trocknungsanlage (4) liegende Luftzuführung (24) umfasst.
- Trocknungsanlage (4) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 4, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass sie eine im Bereich der Mündung der Heissgasführung in den Rotortrockner (7) angeordnete Weiche umfasst, welche zwischen einer ersten Stellung, in der der besagte Bereich über den Rotortrockner (7) mit dem Bandtrockner (5) verbunden ist und einer zweiten Stellung, in der er unter Umgehung des Rotortrockners (7) mit dem Bandtrockner (5) verbunden ist, umstellbar ist.
- Trocknungsanlage (4) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 5, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Heissgasführung ein Heizregister (23) umfasst, welches hinsichtlich der Strömungsrichtung des Heissgases der Trocknungsanlage (4) vorgeordnet ist.
- Trocknungsanlage (4) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 6, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass im Bandtrockner (5) ein Heizregister (9) angeordnet ist.
- Trocknungsanlage (4) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 7, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Heissgasführung einen Filter umfasst, der hinsichtlich der Strömungsrichtung des Heissgases der Trocknungsanlage (4) nachgeordnet ist.
- Verbrennungsanlage mit einer Trocknungsanlage (4) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 8, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass sie eine Feuerungsanlage (1) umfasst sowie eine von der Feuerungsanlage (1) ausgehende Rauchgasleitung (14), welche hinsichtlich der Strömungsrichtung des Heissgases vor.dem Rotortrockner (7) in die Heissgasführung mündet.
- Verbrennungsanlage nach Anspruch 9, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Austragseite des Rotortrockners (7) mit der Feuerungsanlage (1) verbunden ist.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH02007/13A CH708975B1 (de) | 2013-12-04 | 2013-12-04 | Verbrennungsanlage. |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2889537A1 true EP2889537A1 (de) | 2015-07-01 |
| EP2889537B1 EP2889537B1 (de) | 2018-03-07 |
Family
ID=52146400
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP14405092.9A Not-in-force EP2889537B1 (de) | 2013-12-04 | 2014-11-28 | Verbrennungsanlage mit einer Trocknungsanlage |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2889537B1 (de) |
| CH (1) | CH708975B1 (de) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3351885A1 (de) | 2017-01-23 | 2018-07-25 | Rupert Kaindl | Verfahren zum betrieb einer trocknungsanlage für feuchtes holz und trocknungsanlage |
| EP4185827A4 (de) * | 2020-07-24 | 2024-11-06 | Triple Green Products Inc. | Verwendung eines biomasseofens zur direkten lufttrocknung von getreide und anderen teilchen |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115949964A (zh) * | 2023-02-28 | 2023-04-11 | 广西一炉科技集团有限公司 | 一种燃烧高水分树皮锅炉 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0714006A1 (de) * | 1994-11-24 | 1996-05-29 | W. Kunz AG | Verfahren zum Trocknen einer Substanz, insbesondere von Holzspänen |
| US5749160A (en) * | 1995-02-14 | 1998-05-12 | George Koch Sons, Inc. | Multi-zone method for controlling voc and nox emissions in a flatline conveyor wafer drying system |
| US20110030235A1 (en) * | 2008-01-10 | 2011-02-10 | Zdenek Brancuzsky | Method for continuously drying bulk goods, in particular wood fibers and/or wood chips |
| DE102011015769A1 (de) * | 2011-04-01 | 2012-10-04 | Christian Wenner | Vorrichtung zur Trocknung |
-
2013
- 2013-12-04 CH CH02007/13A patent/CH708975B1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
-
2014
- 2014-11-28 EP EP14405092.9A patent/EP2889537B1/de not_active Not-in-force
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0714006A1 (de) * | 1994-11-24 | 1996-05-29 | W. Kunz AG | Verfahren zum Trocknen einer Substanz, insbesondere von Holzspänen |
| US5749160A (en) * | 1995-02-14 | 1998-05-12 | George Koch Sons, Inc. | Multi-zone method for controlling voc and nox emissions in a flatline conveyor wafer drying system |
| US20110030235A1 (en) * | 2008-01-10 | 2011-02-10 | Zdenek Brancuzsky | Method for continuously drying bulk goods, in particular wood fibers and/or wood chips |
| DE102011015769A1 (de) * | 2011-04-01 | 2012-10-04 | Christian Wenner | Vorrichtung zur Trocknung |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3351885A1 (de) | 2017-01-23 | 2018-07-25 | Rupert Kaindl | Verfahren zum betrieb einer trocknungsanlage für feuchtes holz und trocknungsanlage |
| EP4185827A4 (de) * | 2020-07-24 | 2024-11-06 | Triple Green Products Inc. | Verwendung eines biomasseofens zur direkten lufttrocknung von getreide und anderen teilchen |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2889537B1 (de) | 2018-03-07 |
| CH708975B1 (de) | 2016-07-15 |
| CH708975A2 (de) | 2015-06-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE69115084T2 (de) | Verbrennungs-Schmelzanlage zur Stadt-Müllbeseitigung. | |
| EP2388542B1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur kontinuierlichen Trocknung von Schüttgut, insbesondere von Holzfasern und/oder Holzspänen | |
| EP2771302B1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum aufarbeiten von nassen, organische komponenten enthaltenden abfallstoffen | |
| DE3118931A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum betrieb einer kokereianlage | |
| EP0950855A2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Verbrennung von partikelförmigen Feststoffen | |
| DE2556046A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur waermebehandlung von material | |
| DE3010909A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum brennen von feinkoernigen gut und zur erzeugung von kohlenstaub | |
| AT401420B (de) | Einrichtung zur verfeuerung von biomasse | |
| EP2889537B1 (de) | Verbrennungsanlage mit einer Trocknungsanlage | |
| CH628972A5 (en) | Tunnel furnace with direct firing | |
| DE102010014479B4 (de) | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zur Heißgaserzeugung mit integrierter Erhitzung eines Wärmeträgermediums | |
| DE102015003856A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Temperierung von Gegenständen | |
| DE2256034C3 (de) | Einrichtung zur Wärmebehandlung von Gut auf einem Wanderrost | |
| EP0058892B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Trocknung von Körnerfrüchten mit Warmluft und Anlage zur Durchführung des Verfahrens | |
| EP0030376A2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Trocknen und Erhitzen von feuchter Kohle | |
| EP0501944B1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Verbrennen von stückigen, biogenen Brennstoffen | |
| EP0170304B1 (de) | Klinkerkühler mit Entstaubungsvorrichtung in einem Verfahren zur Zementherstellung | |
| EP1085283A2 (de) | Einrichtung zur Reinigung und Verbrennung von Schachtofenabgasen | |
| DE69614245T2 (de) | Russbehandlungsvorrichtung mit einem Staubsammler | |
| DE102010023391A1 (de) | Biomassetrocknung mittels Rauchgasabwärme | |
| DE1758143B2 (de) | Mehrstufige anlage zum vorwaermen von zementrohmehl oder aehnlichem feinkoernigem material | |
| CH651644A5 (de) | Gekuehlter verbrennungsraum mit einer wirbelschichtfeuerung und verfahren zum betrieb desselben. | |
| DE942679C (de) | Kalk- oder Zenentschachtofen mit angeschlossener, mit Filterflaechen arbeitender Entstaubungsanlage | |
| DE467028C (de) | Abgasbeheizte Trockenanlage | |
| DE1163295B (de) | Verfahren zur Verbesserung der Elektroentstaubung der Abgase von OEfen zur Behandlung trockenen Aufgabegutes |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20141128 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| R17P | Request for examination filed (corrected) |
Effective date: 20151217 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: F23K 1/00 20060101AFI20170912BHEP |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20171020 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 976973 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20180315 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502014007520 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20180307 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180607 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180608 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180607 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502014007520 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180709 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20181210 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 502014007520 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20181128 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20181128 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20181130 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20190520 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20181128 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190601 Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20181130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20181130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20181128 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180307 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180307 Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20141128 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20191130 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20191130 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180707 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 976973 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20191128 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20191128 |