EP2496728B1 - Device for coating a metal strip and method therefor - Google Patents
Device for coating a metal strip and method therefor Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2496728B1 EP2496728B1 EP10774210.8A EP10774210A EP2496728B1 EP 2496728 B1 EP2496728 B1 EP 2496728B1 EP 10774210 A EP10774210 A EP 10774210A EP 2496728 B1 EP2496728 B1 EP 2496728B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- magnets
- strip
- coating
- stripping nozzle
- nozzle
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 title claims description 46
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 title claims description 46
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 13
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 title claims description 9
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 30
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 16
- 230000000087 stabilizing effect Effects 0.000 claims description 15
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000001939 inductive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000006641 stabilisation Effects 0.000 description 32
- 238000011105 stabilization Methods 0.000 description 32
- 238000003618 dip coating Methods 0.000 description 7
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000005246 galvanizing Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000005244 galvannealing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000013178 mathematical model Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007790 scraping Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011982 device technology Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910001338 liquidmetal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000704 physical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C2/00—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor
- C23C2/003—Apparatus
- C23C2/0034—Details related to elements immersed in bath
- C23C2/00342—Moving elements, e.g. pumps or mixers
- C23C2/00344—Means for moving substrates, e.g. immersed rollers or immersed bearings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C2/00—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor
- C23C2/34—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor characterised by the shape of the material to be treated
- C23C2/36—Elongated material
- C23C2/40—Plates; Strips
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C2/00—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor
- C23C2/02—Pretreatment of the material to be coated, e.g. for coating on selected surface areas
- C23C2/022—Pretreatment of the material to be coated, e.g. for coating on selected surface areas by heating
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C2/00—Hot-dipping or immersion processes for applying the coating material in the molten state without affecting the shape; Apparatus therefor
- C23C2/50—Controlling or regulating the coating processes
- C23C2/52—Controlling or regulating the coating processes with means for measuring or sensing
- C23C2/524—Position of the substrate
Definitions
- the invention relates to a device for coating a metallic strip with a coating material comprising a coating container filled with a liquid coating material through which or from which the coated strip is discharged vertically upwards, wherein above the coating container, a scraper for stripping still liquid coating material is arranged from the strip surface, wherein above the wiping nozzle, an electromagnetic device for stabilizing the position of the tape is arranged in a central position, wherein the device comprises at least two magnets arranged on both sides of the metal strip at the same height. Furthermore, the invention relates to a method for coating a metallic strip with a coating material.
- a device for strip edge stabilization of a belt which has at least one sensor for detecting the position of the at least one band edge and at least one adjusting device is provided, with which a means for band edge stabilization can be positioned transversely to the band depending on the band edge position.
- the DE 10 2008 039 244 A1 shows a device for hot dip coating, in which the metal strip is passed through the coating bath and discharged from this vertically upwards.
- a wiping nozzle Above the coating container, a wiping nozzle is arranged, with the excess coating material is blown off the belt surface.
- a band stabilization Above the wiping nozzle, a band stabilization is arranged at a defined distance, with which the band is to be held centrally in the center plane of the plant.
- a stable central belt run in systems with and without downstream heating inductors is of great importance for the strip cooling devices following the wiping nozzle, in order to achieve a uniform cooling effect. Again, it is important to avoid damage to the system and the belt surface.
- the belt position normal to the belt surface is measured in the belt stabilization system by means of displacement sensors and regulated in a closed loop.
- further measuring devices can be used within the downstream devices as additional signals for the band position control.
- the position of the belt stabilization is defined by design and concentrated in the previously known solutions mostly on a spatial proximity to the scraper. Thus arises dependent from design a distance of the belt stabilization magnets from the nozzle lip of the wiper (air outlet from the nozzle).
- the invention is in the light of these disadvantages, the object of developing a device for coating a metallic strip with a coating material and a corresponding method so that it can be responded to the different demands on the tape guide in an improved and simpler manner. Accordingly, the quality of the hot dip coating, in particular the hot dip galvanizing, should be increased.
- the means for adjusting the vertical distance may include at least one hydraulic or pneumatic actuator; they may also comprise at least one mechanical actuator, in particular a spindle-nut system.
- the means for adjusting the vertical distance may comprise at least one lifting element, which is directly or indirectly connected to the wiper.
- the wiping nozzle can have a frame structure or be connected to such, on which the at least one lifting element is arranged.
- a heating element for heating the strip can be arranged above the wiping nozzle in order to be able to carry out a so-called galvannealing process.
- the heating element is preferably formed as an inductive element.
- the means for adjusting the vertical position are preferably formed for adjusting the vertical distance of the magnets in the entire region of the height extension between the wiper and the heating element.
- a cooling section can furthermore be arranged. Between the heating element and the cooling section, a holding furnace can be arranged.
- the object of the invention is procedurally achieved by the method according to claim 10.
- the claimed method of coating a metallic strip with a coating material wherein the strip is passed through liquid coating material contained in a coating container and then discharged vertically upwardly from the coating container, wherein above the coating container still liquid coating material is removed by a wiping nozzle of the Strip surface is stripped and wherein above the wiping the tape by means of an electromagnetic device stabilized to stabilize the position of the tape in a central position, wherein the device comprises two magnets disposed on both sides of the belt at the same height, according to the invention is characterized in that the vertical distance of the magnets is adjusted by the wiper according to a predetermined value, wherein Setting the distance means for adjusting the vertical distance to be operated by a controller.
- the magnets are preferably kept centered in the center position when setting the vertical distance.
- the essence of the invention thus depends on the fact that the position of the belt stabilization magnets is not stationary, but can be adapted to the respective requirements by means of a suitable lifting device.
- the aligned (centered) and optimized position of the belt stabilization magnets to the continuous steel belt - in the direction normal to the belt - by mechanical coupling of the belt stabilization magnets with the wiper remains always exist.
- the belt stabilization system must be positioned as close as possible to the respective device or effective point for optimum function and thus for the purpose of reducing the belt movements (principle of St. Vernant). This is, for example, for optimizing the coating with liquid metal a position as close as possible to the wiping, wherein for a central and quiet tape within the Nacher stiirmungs adopted the position of the non-contact tape stabilization should be selected as close to this device.
- a suitable auxiliary device both positions (once close to the scraper and once near the heating device) without loss of stabilization function.
- other positions can be approached, which allow influencing both parts of the system (scraper and heating device) with the belt stabilization.
- the vertical position of the belt stabilizing magnets which are part of a belt stabilizing unit, can be flexibly adjusted to a desired value. This is done depending on the operating state or the desired non-contact Bandlagenbeeinlung.
- the positioning preferably takes place between the wiping nozzle and the downstream in the conveying direction of the belt heating inductors for galvannealing operation or a downstream strip cooling.
- the actuating means for the height adjustment of the magnets always remain centered to the scraper, since they are mechanically coupled thereto.
- the invention enables a variable, selectively adjustable position of the belt stabilizing magnets above the scraper in a hot-dip galvanizing plant.
- the vertical adjustment of the belt stabilizing magnets relative to the scraper nozzle allows any position to obtain optimum operation between the extreme positions directly on the scraper nozzle and directly in front of the downstream heating elements or before the belt cooling.
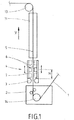
- Fig. 1 is sketched a hot-dip coating plant, which serves for coating a strip 1 with a coating metal.
- the tape 1 is introduced in the embodiment in a known manner in a coating container 2, in which liquid coating material is contained.
- a deflection of the belt 1 in the vertical direction V by means of a deflection roller 14 is made.
- the CVGL method can also be used in the same way, in which the band 1 enters the coating container 2 vertically from below and the bottom opening is sealed by means of an electromagnetic shutter.
- a wiping nozzle 3 Above the wiping nozzle 3 there is a device 4 for stabilizing the band 1.
- This device 4 has as its core two electro-magnets 6 arranged on both sides of the belt 1. With these devices it is achieved that the belt is deliberately subjected to magnetic forces such that it is held in a symmetrical center position 5 of the device.
- means 7 are provided with which the vertical distance H of the magnets 6 can be set by the wiper 3 targeted. This is indicated in Fig. 1 with the double arrows next to the magnets 6 and in that the magnets 6 are sketched once (in a middle position) with solid lines and in two further alternative positions with dashed lines, namely in a lower position near the wiping nozzle 3 and in an upper position at the upper end of the movement, which can be accomplished with the means 7.
- the distance of the magnets 6 from the upper end of the wiper 3 is indicated by H and indicates how far the magnets 6 are lifted by the means 7.
- a cooling section 11 is provided for the band 1.
- the band 1 is deflected by a deflection roller 13 in the horizontal.
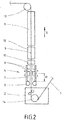
- Fig. 2 is an alternative solution outlined here compared with Fig. 1 an inductive heating device 10 is provided above the belt stabilization 4, with a Galvannealing process can be performed in a conventional manner. Between the heating element 10 and the cooling section 11 is still a holding furnace 12th
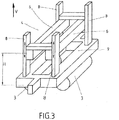
- Fig. 3 An idea of the structural design of the proposed device goes out Fig. 3 out.
- the wiping nozzle 3 is arranged on a frame structure 9, on which four lifting elements 8 are fastened, with which the magnets 6 can be raised or lowered relative to the wiping nozzle 3.
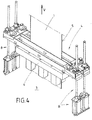
- FIG. 4 Further details of the structural design go out Fig. 4 out.
- four lifting elements 8 - in the present case designed as mechanical actuators in the form of spindle-nut systems - are used to the Move magnets 6 in the vertical direction V or adjust.
- the wiping nozzles 3 are not shown here; they are in the lower part of the illustration according to Fig. 4 ,
- the position of the strip stabilization is also tracked by the mechanical coupling of the strip stabilization magnets.
- the effect of band stabilization in the region of the wiper nozzle 3 is reduced in this case, but it does not go away because of the optimal position calculation by a mathematical model used here.
- the magnets 6 are positioned closer to the heating elements 10 (GA inductors) than to the wiping nozzle 3, but taking into account the physical action in both directions.
- the focus of the stabilizing effect is on minimizing tape movement within the wiping die 3.
- the position of the magnets 6 of the belt stabilization in the region of the wiping nozzle 3 is selected.
- the guide rollers in front of the heating element which are used in previously known systems to stabilize the belt, are no longer necessary, since now the stabilizing effect can be influenced in a targeted manner in the entire height range between the wiper and the heating element.
- the means 7 also advantageously allow a manual cleaning of the wiper 3 during operation.
- the belt stabilization or the magnets 6 are moved to an elevated position, but without losing the stabilizing effect. This is not possible with previously known systems.
- the maintenance personnel obtains free access to the scraper nozzle 3 and therefore can clean the nozzle lips manually. This requirement is met with every hot dip galvanizing line.
- the positioning of the belt stabilizing magnets 6 is as explained with a device which may have two guides, holders and corresponding clamping devices which cause the tensioning of the system and thus the parallel alignment of the belt stabilization (the magnets 6) to the belt or wiper support system.
- This band-stabilizing position changing device is fixedly mounted on the scraping nozzle 3, which includes a frame structure with alignment members.
- the principle is thus a frame construction, which in turn is firmly connected to the basic frame construction of the wiper nozzle 3. This is done with the alignment of the wiper 3 to the band 1 also always a synchronous alignment of the magnets 6 of the band stabilization to the band. 1
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Coating With Molten Metal (AREA)
- Coating Apparatus (AREA)
- Application Of Or Painting With Fluid Materials (AREA)
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft eine Vorrichtung zum Beschichten eines metallischen Bandes mit einem Beschichtungsmaterial, die einen mit einem flüssigen Beschichtungsmaterial gefüllten Beschichtungsbehälter aufweist, durch den oder aus dem das beschichtete Band vertikal nach oben ausgeleitet wird, wobei oberhalb des Beschichtungsbehälters eine Abstreifdüse zum Abstreifen von noch flüssigem Beschichtungsmaterial von der Bandoberfläche angeordnet ist, wobei oberhalb der Abstreifdüse eine elektromagnetische Einrichtung zur Stabilisierung der Lage des Bandes in einer Mittenlage angeordnet ist, wobei die Einrichtung mindestens zwei beidseitig des Metallbandes auf derselben Höhe angeordnete Magnete umfasst. Des weiteren betrifft die Erfindung ein Verfahren zum Beschichten eines metallischen Bandes mit einem Beschichtungsmaterial.The invention relates to a device for coating a metallic strip with a coating material comprising a coating container filled with a liquid coating material through which or from which the coated strip is discharged vertically upwards, wherein above the coating container, a scraper for stripping still liquid coating material is arranged from the strip surface, wherein above the wiping nozzle, an electromagnetic device for stabilizing the position of the tape is arranged in a central position, wherein the device comprises at least two magnets arranged on both sides of the metal strip at the same height. Furthermore, the invention relates to a method for coating a metallic strip with a coating material.
Aus der Druckschrift
Vorrichtungen zum Stabilisieren des Laufes eines Metallbandes sind auch aus den Druckschriften
Eine Vorrichtung dieser Art sowie ein entsprechendes Verfahren sind bekannt. Die
Eine ähnliche Lösung ist aus der
In Schmelztauchbeschichtungsanlagen, insbesondere in Feuerverzinkungsanlagen, werden unterschiedliche Anforderungen an die Bandlage und den Band lauf gestellt. Besonders im Bereich der Abstreifdüsen sollen mit berührungslos wirkenden Systemen, den sog. elektromagnetischen Bandstabilisierungssystemen, Bandschwingungen reduziert und die Bandform beeinflusst werden.In hot-dip coating plants, especially in hot-dip galvanizing plants, different requirements are imposed on the strip layer and the strip run. Particularly in the area of wiping nozzles, non-contact systems, the so-called electromagnetic band stabilization systems, are intended to reduce band vibrations and influence the band shape.
In Anlagen mit einem der Abstreifdüse nachgeschalteten induktiven Erwärmungssystem (Galvannealer) werden zusätzlich oberhalb der Abstreifdüse vor der Erwärmungseinrichtung Führungsrollen eingesetzt, die einen ruhigen Bandlauf zwischen den Erwärmungsspulen gewährleisten und Defekte sowohl an der Anlage als auch auf dem Band durch Kontakt des Bandes mit diesen vermeiden sollen.In systems with a stripper nozzle downstream inductive heating system (Galvannealer) guide rollers are additionally used above the wiper prior to the heating device, which ensure a smooth tape between the heating coils and to avoid defects both on the system and on the tape by contact of the tape with these ,
Ebenso ist ein stabiler mittiger Bandlauf in Anlagen mit und ohne nachgeschalteten Erwärmungsinduktoren für die der Abstreifdüse nachfolgenden Bandkühleinrichtungen von großer Bedeutung, um eine gleichmäßige Kühlwirkung zu erzielen. Auch hier gilt es, Beschädigungen der Anlage und der Bandoberfläche zu vermeiden.Likewise, a stable central belt run in systems with and without downstream heating inductors is of great importance for the strip cooling devices following the wiping nozzle, in order to achieve a uniform cooling effect. Again, it is important to avoid damage to the system and the belt surface.
Es sind verschiedene Systeme bekannt geworden, die berührungslos, nämlich elektromagnetisch, Zusatzkräfte auf das Stahlband ausüben, um Bandbewegungen in Form von Schwingungen zu minimieren. Weiterhin kann mit diesen Systemen die Bandform quer zur Transportrichtung beeinflusst werden.Various systems have become known which exert additional forces on the steel strip without contact, namely electromagnetically, in order to minimize band movements in the form of vibrations. Furthermore, with these systems, the band shape can be influenced transversely to the transport direction.
Die Bandposition normal zur Bandoberfläche wird im Bandstabilisierungssystem mittels Wegsensoren gemessen und in einem geschlossenen Regelkreis geregelt. Dabei können auch weitere Messeinrichtungen innerhalb der nachgeschalteten Einrichtungen als Zusatzsignale für die Bandpositionsregelung verwendet werden.The belt position normal to the belt surface is measured in the belt stabilization system by means of displacement sensors and regulated in a closed loop. In this case, further measuring devices can be used within the downstream devices as additional signals for the band position control.
Als nachteilig hat sich folgendes erwiesen: Die Position der Bandstabilisierung ist bauartbedingt definiert und konzentriert sich bei den vorbekannten Lösungen zumeist auf eine räumliche Nähe zur Abstreifdüse. Somit ergibt sich abhängig von der Konzeption ein Abstand der Bandstabilisierungs-Magnete von der Düsenlippe der Abstreifdüse (Luftaustritt aus der Düse).As a disadvantage, the following has been found: The position of the belt stabilization is defined by design and concentrated in the previously known solutions mostly on a spatial proximity to the scraper. Thus arises dependent from design a distance of the belt stabilization magnets from the nozzle lip of the wiper (air outlet from the nozzle).
Dadurch ist der Abstand zu den nachgeschalteten Einrichtungen, wie z. B. zu den Erwärmungsinduktoren oder zu der nachgeschalteten Bandkühlung, sehr groß. Hierdurch ergibt sich keine oder nur eine minimale Wirkung der Bandstabilisierungs-Magnete auf die dortige Bandbewegung und folglich keine Beeinflussungsmöglichkeit der Bandstabilität im von der Abstreifdüse beabstandeten Bereich.As a result, the distance to the downstream facilities, such. B. to the heating inductors or to the downstream strip cooling, very large. This results in no or only a minimal effect of the belt stabilization magnets on the local belt movement and consequently no possibility of influencing the belt stability in the region spaced from the wiper.
Werden die Bandstabilisierung-Magnete indes direkt vor dem Erwärmungsinduktor oder der Bandkühlung installiert, ergibt sich entsprechend eine deutlich verringerte Wirkung auf die Bandzentrierung im Bereich der Abstreifdüse.However, if the belt stabilization magnets are installed directly in front of the heating inductor or the belt cooling, a significantly reduced effect on the belt centering in the area of the scraping nozzle results accordingly.
Bei den vorbekannten Anlagen ergibt sich daher immer nur eine ausgewählte Position, die meist auf die Wirkung im Bereich der Abstreifdüse abgestimmt ist, d. h. die Bandstabilisierungs-Magnete werden meist im Bereich der Abstreifdüse angeordnet.In the case of the previously known systems, therefore, there is always only one selected position, which is usually matched to the effect in the area of the wiping nozzle, ie. H. The band-stabilizing magnets are usually arranged in the region of the wiping nozzle.
Damit lassen sich allerdings die Anforderungen an eine moderne Bandverzinkungsanlage nicht bzw. nur eingeschränkt erfüllen.However, this means that the requirements for a modern strip galvanizing line can not be met or only partially met.
Der Erfindung liegt im Lichte dieser Nachteile die Aufgabe zugrunde, eine Vorrichtung zum Beschichten eines metallischen Bandes mit einem Beschichtungsmaterial sowie ein entsprechendes Verfahren so fortzubilden, dass in verbesserter und einfacherer Weise auf die unterschiedlichen Anforderungen an die Bandführung reagiert werden kann. Demgemäß soll sich die Qualität der Schmelztauchbeschichtung, insbesondere der Feuerverzinkung, erhöhen lassen.The invention is in the light of these disadvantages, the object of developing a device for coating a metallic strip with a coating material and a corresponding method so that it can be responded to the different demands on the tape guide in an improved and simpler manner. Accordingly, the quality of the hot dip coating, in particular the hot dip galvanizing, should be increased.
Diese Aufgabe der Erfindung wird vorrichtungstechnisch gelöst durch den Gegenstand des Patentanspruchs 1.This object of the invention is achieved by the device technology by the subject of
Die Mittel zur Einstellung des vertikalen Abstands können mindestens einen hydraulischen oder pneumatischen Aktuator umfassen; sie können auch mindestens einen mechanischen Aktuator umfassen, insbesondere ein Spindel-Mutter-System.The means for adjusting the vertical distance may include at least one hydraulic or pneumatic actuator; they may also comprise at least one mechanical actuator, in particular a spindle-nut system.
Gemäß einem ersten Ausführungsbeispiel der Erfindung können die Mittel zur Einstellung des vertikalen Abstands mindestens ein Hubelement umfassen, das direkt oder indirekt mit der Abstreifdüse verbunden ist. Die Abstreifdüse kann dabei eine Rahmenstruktur aufweisen bzw. mit einer solchen verbunden sein, auf der das mindestens eine Hubelement angeordnet ist.According to a first embodiment of the invention, the means for adjusting the vertical distance may comprise at least one lifting element, which is directly or indirectly connected to the wiper. The wiping nozzle can have a frame structure or be connected to such, on which the at least one lifting element is arranged.
Oberhalb der Abstreifdüse kann ein Heizelement zur Erhitzung des Bandes angeordnet sein, um einen sog. Galvannealing-Prozess durchführen zu können. Das Heizelement ist dabei bevorzugt als induktives Element ausgebildet. Die Mittel zur Einstellung der vertikalen Lage sind dabei bevorzugt ausgebildet zur Einstellung des vertikalen Abstands der Magnete im gesamten Bereich der Höhenerstreckung zwischen der Abstreifdüse und dem Heizelement.A heating element for heating the strip can be arranged above the wiping nozzle in order to be able to carry out a so-called galvannealing process. The heating element is preferably formed as an inductive element. The means for adjusting the vertical position are preferably formed for adjusting the vertical distance of the magnets in the entire region of the height extension between the wiper and the heating element.
Oberhalb des Heizelements kann weiterhin eine Kühlstrecke angeordnet sein Zwischen Heizelement und Kühlstrecke kann ein Halteofen angeordnet sein.Above the heating element, a cooling section can furthermore be arranged. Between the heating element and the cooling section, a holding furnace can be arranged.
Die Aufgabe der Erfindung wird verfahrenstechnisch gelöst durch das Verfahren gemäß Patentanspruch 10.The object of the invention is procedurally achieved by the method according to
Das beanspruchte Verfahren zum Beschichten eines metallischen Bandes mit einem Beschichtungsmaterial, bei dem das Band durch flüssiges Beschichtungsmaterial das sich in einem Beschichtungsbehälter befindet, hindurchgeführt und dann vertikal nach oben aus dem Beschichtungsbehälter ausgeleitet wird, wobei oberhalb des Beschichtungsbehälters noch flüssiges Beschichtungsmaterial durch eine Abstreifdüse von der Bandoberfläche abgestreift wird und wobei oberhalb der Abstreifdüse das Band mittels einer elektromagnetischen Einrichtung zur Stabilisierung der Lage des Bandes in einer Mittenlage stabilisiert wird, wobei die Einrichtung zwei beidseitig des Bandes auf derselben Höhe angeordnete Magnete umfasst, zeichnet sich erfindungsgemäß dadurch aus, dass der vertikale Abstand der Magnete von der Abstreifdüse gemäß einem vorgegebenen Wert eingestellt wird, wobei zur Einstellung des Abstands Mittel zur Einstellung des vertikalen Abstands von einer Steuerung betätigt werden.The claimed method of coating a metallic strip with a coating material wherein the strip is passed through liquid coating material contained in a coating container and then discharged vertically upwardly from the coating container, wherein above the coating container still liquid coating material is removed by a wiping nozzle of the Strip surface is stripped and wherein above the wiping the tape by means of an electromagnetic device stabilized to stabilize the position of the tape in a central position, wherein the device comprises two magnets disposed on both sides of the belt at the same height, according to the invention is characterized in that the vertical distance of the magnets is adjusted by the wiper according to a predetermined value, wherein Setting the distance means for adjusting the vertical distance to be operated by a controller.
Die Magnete werden dabei bevorzugt bei der Einstellung des vertikalen Abstands stets zentriert in der Mittenlage gehalten.The magnets are preferably kept centered in the center position when setting the vertical distance.
Der Kern der Erfindung stellt also darauf ab, dass die Position der Bandstabilisierungs-Magnete nicht ortsfest ist, sondern mittels einer geeigneten Hebevorrichtung den jeweiligen Erfordernissen angepasst werden kann. Dabei bleibt die ausgerichtete (zentrierte) und optimierte Position der Bandstabilisierungs-Magnete zum durchlaufenden Stahlband - in Richtung normal auf das Band - durch eine mechanische Kopplung der Bandstabilisierungs-Magnete mit der Abstreifdüse stets bestehen.The essence of the invention thus depends on the fact that the position of the belt stabilization magnets is not stationary, but can be adapted to the respective requirements by means of a suitable lifting device. In this case, the aligned (centered) and optimized position of the belt stabilization magnets to the continuous steel belt - in the direction normal to the belt - by mechanical coupling of the belt stabilization magnets with the wiper remains always exist.
Aus physikalischen Überlegungen ergibt sich, dass das Bandstabilisierungssystem für eine optimale Funktion und damit zwecks Reduzierung der Bandbewegungen möglichst nahe an der jeweiligen Einrichtung bzw. Wirkstelle positioniert werden müssen (Prinzip von St. Vernant). Dies ist beispielsweise für eine Optimierung der Beschichtung mit flüssigem Metall eine Position möglichst nahe an den Abstreifdüsen, wobei für einen mittigen und ruhigen Bandlauf innerhalb der Nacherwärmungseinrichtung die Position der berührungslosen Bandstabilisierung möglichst nahe an dieser Einrichtung gewählt werden sollte. Somit ist es sinnvoll, mittels einer geeigneten Hilfseinrichtung beide Positionen (einmal nahe an der Abstreifdüse und einmal nahe der Erwärmungseinrichtung) ohne Verlust der Stabilisierungsfunktion anfahren zu können. Ferner können auch weitere Positionen angefahren werden, die eine Beeinflussung beider Anlagenteile (Abstreifdüse und Erwärmungseinrichtung) mit der Bandstabilisierung ermöglichen.From physical considerations it follows that the belt stabilization system must be positioned as close as possible to the respective device or effective point for optimum function and thus for the purpose of reducing the belt movements (principle of St. Vernant). This is, for example, for optimizing the coating with liquid metal a position as close as possible to the wiping, wherein for a central and quiet tape within the Nacherwärmungseinrichtung the position of the non-contact tape stabilization should be selected as close to this device. Thus, it makes sense to be able to approach by means of a suitable auxiliary device both positions (once close to the scraper and once near the heating device) without loss of stabilization function. Furthermore, other positions can be approached, which allow influencing both parts of the system (scraper and heating device) with the belt stabilization.
Mittels einer Hubvorrichtung kann also erfindungsgemäß die vertikale Position der Bandstabilisierungs-Magnete, die Bestandteil einer Bandstabilisierungseinheit sind, auf einen gewünschten Wert flexibel eingestellt werden. Dies erfolgt abhängig vom Betriebszustand bzw. der gewünschten berührungslosen Bandlagenbeeinflussung. Die Positionierung erfolgt vorzugsweise zwischen der Abstreifdüse und der in Förderrichtung des Bandes nachgeschalteten Erwärmungsinduktoren für den Galvannealing-Betrieb bzw. einer nachgeschalteten Bandkühlung.By means of a lifting device according to the invention, therefore, the vertical position of the belt stabilizing magnets, which are part of a belt stabilizing unit, can be flexibly adjusted to a desired value. This is done depending on the operating state or the desired non-contact Bandlagenbeeinflussung. The positioning preferably takes place between the wiping nozzle and the downstream in the conveying direction of the belt heating inductors for galvannealing operation or a downstream strip cooling.
Die Betätigungsmittel für die Höheneinstellung der Magnete bleiben dabei stets zentriert zur Abstreifdüse, da sie mechanisch mit dieser gekoppelt sind.The actuating means for the height adjustment of the magnets always remain centered to the scraper, since they are mechanically coupled thereto.
Die Erfindung ermöglicht also eine veränderliche, gezielt einstellbare Position der Bandstabilisierungs-Magnete oberhalb der Abstreifdüse in einer Feuerverzinkungsanlage.Thus, the invention enables a variable, selectively adjustable position of the belt stabilizing magnets above the scraper in a hot-dip galvanizing plant.
Demgemäß erlaubt die vertikale Einstellmöglichkeit der Bandstabilisierungs-Magnete relativ zur Abstreifdüse jede Position zur Erlangung einer optimalen Betriebsweise zwischen den Extremstellen direkt an der Abstreifdüse und direkt vor den nachgeschalteten Heizelementen bzw. vor der Bandkühlung.Accordingly, the vertical adjustment of the belt stabilizing magnets relative to the scraper nozzle allows any position to obtain optimum operation between the extreme positions directly on the scraper nozzle and directly in front of the downstream heating elements or before the belt cooling.
Bei kombinierten Anwendungen, bei denen sowohl die Bandpositionsbeeinflussung in der Abstreifdüse als auch die in den nachgeschalteten Einrichtungen wichtig ist, werden mittels eines mathematischen Modells unter Berücksichtigung der Spannungsverteilung im Band die Auswirkungen auf die jeweiligen Einrichtungen bestimmt; demgemäß wird eine vertikale Position der Bandstabilisierungsmagnete eingestellt, die für den Anwendungsfall optimiert ist.In combined applications, where both tape position control in the wiper nozzle and in the downstream equipment is important, the effects on the respective equipment are determined by means of a mathematical model taking into account the stress distribution in the tape; Accordingly, a vertical position of the belt stabilization magnets is set, which is optimized for the application.
In der Zeichnung sind Ausführungsbeispiele der Erfindung dargestellt. Es zeigen:
- Fig. 1
- schematisch eine Schmelztauchbeschichtungsanlage gemäß einer ersten Ausführungsform der Erfindung,
- Fig. 2
- in der Darstellung von
Fig. 1 eine alternative Ausführungsform der Erfindung, - Fig. 3
- in perspektivischer Darstellung einen Halterahmen für die Abstreifdüse der Schmelztauchbeschichtungsanlage, auf dem Magnete für die Bandstabilisierung höhenveränderlich angeordnet sind, und
- Fig. 4
- in perspektivischer Darstellung die Magnete für die Bandstabilisierung, angeordnet an einer Höhenverstelleinrichtung.
- Fig. 1
- 1 is a schematic representation of a hot-dip coating installation according to a first embodiment of the invention,
- Fig. 2
- in the presentation of
Fig. 1 an alternative embodiment of the invention, - Fig. 3
- a perspective view of a support frame for the Abstreifdüse the hot dip coating system, are arranged on the magnets for the belt stabilization height, and
- Fig. 4
- in a perspective view, the magnets for the belt stabilization, arranged on a height adjustment.
In
Nachdem das beschichtete Band 1 vertikal nach oben aus dem Beschichtungsbehälter 2 ausgetreten ist, wird überschüssiges Beschichtungsmetall durch eine Abstreifdüse 3 abgeblasen. Oberhalb der Abstreifdüse 3 ist eine Einrichtung 4 zum Stabilisieren des Bandes 1 vorhanden. Diese Einrichtung 4 hat als Kernstück zwei beidseits des Bandes 1 angeordnete Elektro-Magnete 6. Mit diesen wird erreicht, dass das Band gezielt so mit magnetischen Kräften beaufschlagt wird, dass es in einer symmetrischen Mittenlage 5 der Vorrichtung gehalten wird.After the
Wesentlich ist, dass Mittel 7 vorhanden sind, mit denen der vertikale Abstand H der Magnete 6 von der Abstreifdüse 3 gezielt eingestellt werden kann. Angedeutet ist dies in
Der Abstand der Magnete 6 vom oberen Ende der Abstreifdüse 3 ist mit H bezeichnet und gibt an, wie weit die Magnete 6 durch die Mittel 7 angehoben sind.The distance of the
Oberhalb der Einrichtung 4 zur Stabilisierung ist in
In
Eine Vorstellung vom konstruktiven Aufbau der vorgeschlagenen Vorrichtung geht aus
Weitere Details des konstruktiven Aufbaus gehen aus
Liegen Bandlagenänderungen vor, die zu einer Nachjustierung der Abstreifdüse führen, wird die Position der Bandstabilisierung durch die mechanische Kopplung der Bandstabilisierungs-Magnete ebenfalls nachgeführt.If strip layer changes occur which lead to a readjustment of the stripper nozzle, the position of the strip stabilization is also tracked by the mechanical coupling of the strip stabilization magnets.
Die stufenlose Höheneinstellung der Magnete 6 der Bandstabilisierung ermöglicht folgendes Vorgehen:
- Für den optimalen Galvannealing-Betrieb (GA-Betrieb) wird die
Bandstabilisierung 4 und namentlich dieMagnete 6 mittels der Mittel 7 (Hebevorrichtung) direkt unterhalb der induktiven Heizelemente 10 positioniert. Da die Beschichtungsdicke für GA-Produkte sehr dünn ist (maximal 90 g/m2) und daher durch die Bandstabilisierungswirkung nur geringe Verbesserungen im Schichtaufbau erzielt werden können, wird der Schwerpunkt der Stabilisierungswirkung auf den Bandlauf im Heizelement 10 (GA-Induktor) und damit auf die Qualität der GA-Beschichtung gelegt. Durch die mechanische Kopplung zur Abstreifdüse 3 stehen dieAbstreifdüse 3 und dieMagnete 6 der Bandstabilisierung jederzeit zentriert zumBand 1.
- For optimum galvannealing operation (GA operation), the
belt stabilizer 4 and, in particular, themagnets 6 are positioned directly below theinductive heating elements 10 by means 7 (lifting device). Since the coating thickness for GA products is very thin (maximum 90 g / m 2 ) and therefore only slight improvements in the layer structure can be achieved by the band stabilization effect, the focus of the stabilizing effect on the tape run in the heating element 10 (GA inductor) and thus placed on the quality of the GA coating. Due to the mechanical coupling to the wipingnozzle 3, the wipingnozzle 3 and themagnets 6 of the belt stabilization are always centered to thebelt 1.
Die Wirkung der Bandstabilisierung in den Bereich der Abstreifdüse 3 hinein ist in diesem Fall reduziert, fällt jedoch aufgrund der optimalen Positionsberechnung durch ein mathematisches Modell, das hierbei eingesetzt wird, nicht weg. Die Magnete 6 werden näher an den Heizelementen 10 (GA-Induktoren) als an der Abstreifdüse 3 positioniert, jedoch unter Berücksichtigung der physikalischen Wirkung in beide Richtungen.The effect of band stabilization in the region of the
Bei anderen Beschichtungsprodukten liegt der Schwerpunkt der Stabilisierungswirkung auf der Minimierung der Bandbewegung innerhalb der Abstreifdüse 3. Hierfür wird die Position der Magnete 6 der Bandstabilisierung im Bereich der Abstreifdüse 3 gewählt.For other coating products, the focus of the stabilizing effect is on minimizing tape movement within the wiping die 3. For this purpose, the position of the
Die Führungsrollen vor dem Heizelement, die bei bisher bekannten Anlagen eingesetzt werden, um das Band zu stabilisieren, sind nicht mehr erforderlich, da nunmehr die Stabilisierungswirkung gezielt im gesamten Höhenbereich zwischen der Abstreifdüse und dem Heizelement beeinflusst werden kann.The guide rollers in front of the heating element, which are used in previously known systems to stabilize the belt, are no longer necessary, since now the stabilizing effect can be influenced in a targeted manner in the entire height range between the wiper and the heating element.
Die Mittel 7 (Hubvorrichtung) ermöglichen ebenfalls in vorteilhafter Weise ein manuelles Reinigen der Abstreifdüse 3 während des Betriebs. Die Bandstabilisierung bzw. die Magnete 6 werden in eine erhöhte Position gefahren, ohne jedoch die Stabilisierungswirkung zu verlieren. Bei vorbekannten Systemen ist dies nicht möglich. Damit erlangt das Wartungspersonal einen freien Zugang zur Abstreifdüse 3 und kann daher die Düsenlippen manuell reinigen. Diese Anforderung ist bei jeder Feuerverzinkungsanlage gegeben.The means 7 (lifting device) also advantageously allow a manual cleaning of the
Die Positionierung der Magnete 6 der Bandstabilisierung erfolgt wie erläutert mit einer Vorrichtung, die zwei Führungen, Halterungen und entsprechende Klemmvorrichtungen aufweisen kann, die die Verspannung des Systems und somit die parallele Ausrichtung der Bandstabilisierung (der Magnete 6) zum Band bzw. zum Abstreifdüsenträgersystem bewirken. Diese Vorrichtung zur Veränderung der Bandstabilisierungsposition ist auf der Abstreifdüse 3, die eine Rahmenkonstruktion mit Stellelementen zur Ausrichtung enthält, fest montiert.The positioning of the
Das Prinzip ist also eine Rahmenkonstruktion, die wiederum fest mit der Grundrahmenkonstruktion der Abstreifdüse 3 verbunden ist. Damit erfolgt mit der Ausrichtung der Abstreifdüse 3 zum Band 1 ebenfalls immer eine synchrone Ausrichtung der Magnete 6 der Bandstabilisierung zum Band 1.The principle is thus a frame construction, which in turn is firmly connected to the basic frame construction of the
- 11
- Bandtape
- 22
- Beschichtungsbehältercoating tank
- 33
- Abstreifdüsewiping
- 44
- Einrichtung zur StabilisierungDevice for stabilization
- 55
- MittenlageSymmetry
- 66
- Magnetmagnet
- 77
- Mittel zur Einstellung der vertikalen LageMeans for adjusting the vertical position
- 88th
- Hubelementlifting
- 99
- Rahmenstrukturframe structure
- 1010
- Heizelementheating element
- 1111
- Kühlstreckecooling section
- 1212
- Halteofenholding furnace
- 1313
- Umlenkrolleidler pulley
- 1414
- Umlenkrolleidler pulley
- VV
- vertikale Richtungvertical direction
- HH
- Abstanddistance
Claims (11)
- A device for coating a metal strip (1) with a coating material which has a coating vessel (2) filled with a liquid coating material, through which or from which the coated strip (1) is discharged vertically (V) upwards, wherein a stripping nozzle (3) for wiping coating material that is still wet from the strip surface is arranged above the coating vessel (2), wherein an electromagnetic device (4) for stabilizing the position of the strip (1) in a central position (5) is arranged above the stripping nozzle (3) and wherein the mechanism (4) comprises at least two magnets (6) arranged at the same height on both sides of the metal strip (1) and a control mechanism for positioning the magnets (6),
characterized by
means (7) for the flexible adjustment of the vertical distance (H) of the magnets (6) from the stripping nozzle (3), wherein the means (7) comprise at least one hydraulic, pneumatic or mechanical actuator; and a control mechanism for actuating the means (7). - The device according to claim 1,
characterized in that
the means (7) for adjusting the vertical distance (H) comprise at least one lifting element (8) which is connected directly or indirectly to the stripping nozzle (3). - The device according to claim 2,
characterized in that
that the stripping nozzle (3) has a frame structure (9) on which the at least one lifting element (8) is arranged. - The device according to one of claims 1 to 3,
characterized in that
a heating element (10) for heating the strip (1) is arranged above the stripping nozzle (3). - The device according to claim 4,
characterized in that
the heating element (10) is designed as an inductive element. - The device according to claim 4 or 5,
characterized in that
the means (7) are designed to adjust the vertical distance (H) of the magnets (6) over the entire region of the height extent between the stripping nozzle (3) and the heating element (10). - The device according to one of claims 4 to 6,
characterized in that
a cooling section (11) is arranged above the heating element (10). - The device according to claim 7,
characterized in that
a holding furnace (12) is arranged between the heating element (10) and cooling section (11). - The device according to one of claims 1 to 8,
characterized in that
the mechanical actuator is configured in the form of a spindle-nut system. - A method for coating a metal strip (1) with a coating material in which the strip (1) is passed through liquid coating material which is located in a coating vessel (2) and then discharged vertically (V) upwards out of the coating vessel (2), wherein coating material that is still wet is wiped from the strip surface above the coating vessel (2) by a stripping nozzle (3) and wherein the strip (1) is stabilized above the stripping nozzle (3) by means of an electromagnetic mechanism (4) for stabilizing the position of the strip (1) in a central position (5), wherein the mechanism comprises at least two magnets (6) arranged on both sides of the strip (1) at the same height and
the vertical distance (H) of the magnets (6) from the stripping nozzle (3) is set according to a predefined value,
characterized in that
the means (7) comprising a hydraulic, pneumatic or mechanical actuator for the flexible adjustment of the vertical distance (H) of the magnets (6) from the stripping nozzle (3) are actuated by a control mechanism. - The method according to claim 10,
characterized in that
the magnets (6) are constantly held centred in the central position (5) during adjustment of the vertical height (H).
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PL10774210T PL2496728T3 (en) | 2009-11-04 | 2010-11-04 | Device for coating a metal strip and method therefor |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102009051932A DE102009051932A1 (en) | 2009-11-04 | 2009-11-04 | Apparatus for coating a metallic strip and method therefor |
| PCT/EP2010/066810 WO2011054902A1 (en) | 2009-11-04 | 2010-11-04 | Device for coating a metal strip and method therefor |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2496728A1 EP2496728A1 (en) | 2012-09-12 |
| EP2496728B1 true EP2496728B1 (en) | 2018-01-03 |
Family
ID=43334557
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP10774210.8A Active EP2496728B1 (en) | 2009-11-04 | 2010-11-04 | Device for coating a metal strip and method therefor |
Country Status (11)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2496728B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP5663763B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR101421981B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN102597295B (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2794925C (en) |
| DE (1) | DE102009051932A1 (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2660746T3 (en) |
| HU (1) | HUE038462T2 (en) |
| PL (1) | PL2496728T3 (en) |
| TR (1) | TR201802499T4 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2011054902A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO2786187T3 (en) | 2014-11-21 | 2018-07-28 | ||
| DE102014225516B3 (en) | 2014-11-21 | 2016-03-31 | Fontaine Engineering Und Maschinen Gmbh | Method and device for coating a metal strip |
| DE102015216721B3 (en) * | 2015-09-01 | 2016-11-24 | Fontaine Engineering Und Maschinen Gmbh | Apparatus for treating a metal strip |
| DE102016222230A1 (en) | 2016-08-26 | 2018-03-01 | Sms Group Gmbh | Method and coating device for coating a metal strip |
| DE102017109559B3 (en) | 2017-05-04 | 2018-07-26 | Fontaine Engineering Und Maschinen Gmbh | Apparatus for treating a metal strip |
| DE102018215100A1 (en) * | 2018-05-28 | 2019-11-28 | Sms Group Gmbh | Vacuum coating apparatus, and method for coating a belt-shaped material |
| DE102018219134B3 (en) * | 2018-11-09 | 2020-01-30 | Thyssenkrupp Ag | Device and method for the thermal treatment of a surface of a moving metal strip |
| CN109526081A (en) * | 2018-12-27 | 2019-03-26 | 邵阳高华工贸实业有限公司 | A kind of induction heating equipment and method for reinforcing bar production |
| IT201900023484A1 (en) * | 2019-12-10 | 2021-06-10 | Danieli Off Mecc | STABILIZATION APPARATUS |
Family Cites Families (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0681093A (en) * | 1992-08-31 | 1994-03-22 | Kawasaki Steel Corp | Hot dip metal coating equipment for strip |
| DE4344939C1 (en) | 1993-12-23 | 1995-02-09 | Mannesmann Ag | Method for the control, suitable for the process, of an installation for coating strip-shaped material |
| DE19535854C2 (en) | 1995-09-18 | 1997-12-11 | Mannesmann Ag | Process for strip stabilization in a plant for coating strip-like material |
| KR100207710B1 (en) * | 1996-12-27 | 1999-07-15 | 윤종용 | Printing apparatus for pda and method therefor |
| JPH116046A (en) | 1997-06-18 | 1999-01-12 | Nippon Steel Corp | Method for removing dross in continuous hot-dipping metal coating line and device therefor |
| FR2797277A1 (en) | 1999-08-05 | 2001-02-09 | Lorraine Laminage | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR THE CONTINUOUS PRODUCTION OF A METAL SURFACE COATING ON A SLIP |
| JP2001150015A (en) * | 1999-11-30 | 2001-06-05 | Shinko Electric Co Ltd | Position and vibratory control apparatus for steel plate |
| SE0002889L (en) | 2000-08-11 | 2002-02-12 | Abb Ab | An apparatus and method for controlling the thickness of a coating on a metallic article |
| JP4547818B2 (en) * | 2001-03-16 | 2010-09-22 | Jfeスチール株式会社 | Method for controlling the coating amount of hot dip galvanized steel sheet |
| JP4450662B2 (en) * | 2004-04-05 | 2010-04-14 | 三菱日立製鉄機械株式会社 | Steel plate damping device |
| SE527507C2 (en) * | 2004-07-13 | 2006-03-28 | Abb Ab | An apparatus and method for stabilizing a metallic article as well as a use of the apparatus |
| DE102005060058B4 (en) * | 2005-12-15 | 2016-01-28 | Emg Automation Gmbh | Method and device for stabilizing a band |
| DE102006052000A1 (en) * | 2006-11-03 | 2008-05-08 | Emg Automation Gmbh | Device for stabilizing the run of a metal strip |
| BRPI0815633B1 (en) * | 2007-08-22 | 2018-10-23 | Sms Group Gmbh | melt dip treatment process and installation for tape stabilization of a tape provided with a coating, guided between scraping nozzles of the melt dip installation |
| DE102007045202A1 (en) * | 2007-09-21 | 2009-04-02 | Sms Demag Ag | Device for strip edge stabilization |
| KR100899550B1 (en) * | 2007-11-01 | 2009-05-26 | 현대하이스코 주식회사 | Manufacturing process of galvannealed hot dip coated steel sheet |
-
2009
- 2009-11-04 DE DE102009051932A patent/DE102009051932A1/en not_active Withdrawn
-
2010
- 2010-11-04 CN CN201080050673.8A patent/CN102597295B/en active Active
- 2010-11-04 ES ES10774210.8T patent/ES2660746T3/en active Active
- 2010-11-04 PL PL10774210T patent/PL2496728T3/en unknown
- 2010-11-04 EP EP10774210.8A patent/EP2496728B1/en active Active
- 2010-11-04 KR KR1020127011678A patent/KR101421981B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2010-11-04 TR TR2018/02499T patent/TR201802499T4/en unknown
- 2010-11-04 CA CA2794925A patent/CA2794925C/en active Active
- 2010-11-04 JP JP2012537399A patent/JP5663763B2/en active Active
- 2010-11-04 WO PCT/EP2010/066810 patent/WO2011054902A1/en active Application Filing
- 2010-11-04 HU HUE10774210A patent/HUE038462T2/en unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2496728A1 (en) | 2012-09-12 |
| JP2013510236A (en) | 2013-03-21 |
| KR20120063550A (en) | 2012-06-15 |
| KR101421981B1 (en) | 2014-08-13 |
| WO2011054902A1 (en) | 2011-05-12 |
| CN102597295A (en) | 2012-07-18 |
| DE102009051932A1 (en) | 2011-05-05 |
| JP5663763B2 (en) | 2015-02-04 |
| PL2496728T3 (en) | 2018-06-29 |
| CN102597295B (en) | 2015-04-22 |
| ES2660746T3 (en) | 2018-03-26 |
| CA2794925A1 (en) | 2011-05-12 |
| CA2794925C (en) | 2014-08-19 |
| TR201802499T4 (en) | 2018-03-21 |
| HUE038462T2 (en) | 2018-10-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2496728B1 (en) | Device for coating a metal strip and method therefor | |
| DE69707257T2 (en) | Device and method for hot dip coating | |
| EP2188403B1 (en) | Process and hot-dip coating system for stabilizing a strip guided between stripping dies of the hot-dip coating system and provided with a coating | |
| EP3234204B1 (en) | Device and method for continous treatment of a metal strip | |
| EP3221486B1 (en) | Method and device for coating a metal strip with a coating material which is at first still liquid | |
| EP2344287B1 (en) | Method and device for cooling a leader or band of a metal strand in a hot-rolling mill | |
| EP2445664A1 (en) | Device and method for horizontal casting of a metal band | |
| EP2203265B1 (en) | Device and method for stabilising strip edges | |
| WO2009030388A1 (en) | Device and method for strip position control | |
| DE2656524B2 (en) | Process for one-sided coating of a metal strip with molten metal | |
| EP0721813A1 (en) | Device for guiding hot-rolled strip through an inductor | |
| EP3619333B1 (en) | Device for treating a metal strip | |
| DE69426357T2 (en) | Device and method for checking the coating weight of a metal coating by means of blowing nozzles | |
| EP1563113B1 (en) | Method and device for hot-dip coating a metal bar | |
| DE1508451A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for quenching | |
| EP0614714A1 (en) | Continuous casting machine for the production of thin steel slabs | |
| WO2009068232A1 (en) | Method and device for equalizing the solidification process of a fusible metal, particularly produced by means of strand or strip casting | |
| DE69611144T2 (en) | Method and device for producing a metal broadband | |
| DE10215057B4 (en) | Apparatus for hot-dip coating of metal strands and method therefor | |
| DE19953915A1 (en) | Processing hot strip on path of hot strip mill connected directly to coiler for winding strip, comprises smoothing the still hot strip by mechanical deformation | |
| EP1897636A1 (en) | Continuous casting machine and method | |
| DE10330656A1 (en) | Device for the hot dip coating of a metal strand | |
| DE102013212952A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for supporting a strand during continuous casting | |
| AT410408B (en) | METHOD FOR CONTINUOUSLY casting METAL MELTS | |
| WO2023134904A1 (en) | Stabilization device and sensor construction for continuously moving metal strips |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20120423 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: FONTAINE ENGINEERING UND MASCHINEN GMBH |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20170413 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20170628 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 960341 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20180115 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502010014536 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2660746 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20180326 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: TRGR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: FP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180403 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SK Ref legal event code: T3 Ref document number: E 27075 Country of ref document: SK |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180403 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180503 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180404 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502010014536 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HU Ref legal event code: AG4A Ref document number: E038462 Country of ref document: HU |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20181005 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20181130 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20181130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20181104 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180103 |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230517 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20231120 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: LU Payment date: 20231120 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SK Payment date: 20231031 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20231123 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Payment date: 20231102 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20231120 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20231124 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: HU Payment date: 20231122 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20231120 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: FI Payment date: 20231121 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20231121 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20231121 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Payment date: 20231026 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20231120 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20240126 Year of fee payment: 14 |