EP2444176B1 - Axial/radial ring rolling system and method of operating such an axial/radial ring rolling system - Google Patents
Axial/radial ring rolling system and method of operating such an axial/radial ring rolling system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2444176B1 EP2444176B1 EP20110008391 EP11008391A EP2444176B1 EP 2444176 B1 EP2444176 B1 EP 2444176B1 EP 20110008391 EP20110008391 EP 20110008391 EP 11008391 A EP11008391 A EP 11008391A EP 2444176 B1 EP2444176 B1 EP 2444176B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- axial
- rolling mill
- ring rolling
- radial ring
- radial
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Revoked
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21H—MAKING PARTICULAR METAL OBJECTS BY ROLLING, e.g. SCREWS, WHEELS, RINGS, BARRELS, BALLS
- B21H1/00—Making articles shaped as bodies of revolution
- B21H1/06—Making articles shaped as bodies of revolution rings of restricted axial length
Definitions
- the invention relates to an axial / Radialringwalzwerk with motor drives and control and / or regulating devices.
- the invention relates to a method for operating such an axial / radial ring rolling mill.
- the invention has for its object, an axial / Radialringwalzwerk according to the assumed genus in such a way that rings of large diameter of one meter to 15 meters, preferably from three meters to eight meters, can be rolled with great accuracy, even if these rings should be profiled.
- the invention has for its object to provide a method for operating such axial / Radialringwalzwerkes.
- the task concerning the axial / radial ring rolling mill is solved by the features of claim 1 .
- the Axialringwalztechnik is directly, that is arranged in the smallest possible spatial distance, in addition to the Radialringwalzwerk such that the machine frame of the Radialringwalztechnikes and thus the longitudinal axis of the Radialringwalztechnikes is arranged at an acute angle to Axialringwalztechnikgerüst and thus to the longitudinal axis of the Axialringwalzwerkes.
- the invention thus differs fundamentally from the prior art by Axialringwalzwerk and Radialringwalzwerk are arranged directly next to each other.
- the machine frame stands at an acute angle of, for example, 20 to 90 degrees to the axial frame.
- the axial frame has a rotary and linear axis.
- the rotation axis automatically moves so that the tapered roller axis always points to the center of the growing ring.
- the linear axis moves so that at the beginning of the intersection of the tapered rollers is in the Dommitte.
- the tapered rollers advance until the ring to be rolled is in the rearward position of the tapered rollers.
- the linear movement of the axial stand can amount to zero to two thousand millimeters, preferably zero to one thousand millimeters.
- a rolling table for receiving the ring blank. If the ring to be rolled is then rolled larger, it is mainly on a roller table or on storage rails, which also serves after rolling to remove the rolled ring. This allows a very short and easy unloading, even for large rings. In addition, eliminates the dangerous and expensive pit between axial and radial scaffolding.
- the main roller can be moved axially and locked in any position. This allows profiled rings to be rolled into a finished profile only in a pre-profile at the end of the rolling process can be. In this case, only the profiled main roller or the inner profiling of the dome, or both, must be moved axially. This succeeds in a forming heat, and the ring can remain lying on the rolling table.
- a directly driving radial piston hydraulic drive can be provided.
- the invention has particular inventive significance for axial / Radialringwalzwerke with motor drives and control and / or regulating devices for controlling the rolling operations, wherein the Axialringwalzwerk is located immediately adjacent to the Radialringwalzwerk, such that the machine frame of the Radialringwalzwerkes and the Axialringwalztechnikgerüst on the same outside of the are arranged to roll ring and the machine frame of the Radialringwalzwerkes and thus dik länpsachse the radialringwalzwerkes at an acute angle to Axialringwalztechnikgerüst and thus laupsachse del axialringwelzwerkesachse is arranged.
- the Axialringwalzwerk is a substantially vertically extending framework, which is associated with a positively guided in the vertical direction of the scaffold on guides slide, the carriage by a motor drive height adjustable and in the particular desired altitude is also locked.
- the carriage is also assigned a transversely / horizontally adjustable carriage, which is also assigned a motor-controllable rotary drive, for example a rotary cylinder, which has an angular tilt T - V of the upper and lower tapered rollers by 20 degrees to 90 degrees , ie, in each case by 10 degrees to 45 degrees, allowed on both sides of a longitudinal center axis of the upper and lower tapered roller, such that the upper tapered roller both in the vertical direction X and Y and transverse thereto A - B, and in the direction T and V, adjustable and controllable and in the desired height and angle position motor is also locked.
- a motor-controllable rotary drive for example a rotary cylinder, which has an angular tilt T - V of the upper and lower tapered rollers by 20 degrees to 90 degrees , ie, in each case by 10 degrees to 45 degrees, allowed on both sides of a longitudinal center axis of the upper and lower tapered roller, such that the upper tapered roller both in the vertical direction
- the upper roll mandrel bearing can be lowered together with the carriage and the drive and that the lowering takes place parallel to the rolling mandrel bearing and the drive.
- Claim 2 describes an advantageous embodiment in which the linear movement of the Axialgerüstes with the tapered roller is zero to two thousand millimeters, preferably zero to one thousand millimeters. This makes it possible, even very large rings with outer diameters of, for example, twelve meters to tolerances to roll.
- the device comprises a rolling table for receiving the ring blank.
- the ring predominantly rests on a roller table or on the support rails, which also serves to remove the rolled ring after the end of rolling.
- the rolling table which may have a weight of 500 to 100,000 kilograms, preferably from 1,000 to 50,000 kilograms, and has a temperature of up to 1250 ° Celsius during hot rolling.
- the rolling mills a conveyor device, for example, a roller table, a lifting beam or other continuous conveyor, assigned, wherein the conveyor device for transport and for loading and unloading of the ring is used.
- a conveyor device for example, a roller table, a lifting beam or other continuous conveyor, assigned, wherein the conveyor device for transport and for loading and unloading of the ring is used.
- rollers of the roller table are driven by a motor. As a result, the removal of the finished rolled ring is facilitated.
- a particularly advantageous embodiment describes claim 6, wherein the main roller is vertically adjustable motor and lockable in the respective position and arranged such that can be rolled in different calibers.
- Claim 7 describes an embodiment in which the radial rolling mill and / or the axial rolling mill are driven by directly driving radial piston motors or geared motors.
- the axial and Radialringwalzwerk two spaced apart roller tables are assigned, in which some or all tubes are driven by a motor.
- this laser measuring device in two, preferably arranged at right angles to each other planes, in particular in the vertical and / or horizontal plane, adjustable and arranged.
- the motor drive for the laser measuring device may be an alternately on both sides by pressure medium pressure, in particular hydraulically acted upon piston-cylinder unit. Such a motor drive operates reliably and precisely and also allows the respective locking of the laser device in the respectively predetermined position - Claim 11.
- the laser measuring device can be lowered by a motor under the level of the roller conveyor.
- the laser measuring device makes it possible to measure the outer and / or inner ring diameter and the ovality of the ring, wherein the values can be forwarded online to a control and / or regulating device.
- the laser measuring device is designed such that it measures the taper and the outer profile of the rings and passes the measured values to the control and / or regulating device, wherein the positions of the mandrel bearings can be corrected on the basis of the measured values ,
- a preferred embodiment of the invention according to claim 15 are preferably arranged on opposite sides in the region of the radial ring rolling mill and the Axialringwalzwerkes ever a motorized centering device with a centering and a centering.
- All control and / or regulating devices of the motor drives of the radial ring rolling mill and the axial ring rolling mill as well as all adjusting devices for these rolling mills and for the laser device can be in a CNC control be included, which has stored to a central control and / or control station in an electronic memory for the different to be rolled ring blanks predetermined signal and guide values with the tolerances and correspondingly the drives of the rolling mills, their positions and the drives of the roller tables and the Laser device, preferably included in a sequence control, controls and / or regulates.
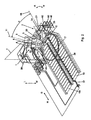
- the reference numeral 1 denotes an axial ring rolling mill and the reference numeral 2 denotes a radial ring rolling mill.
- the Axialringwalzwerk 1 has a substantially vertically extending framework 3, which is associated with a positively guided in the vertical direction, ie in the direction of X or Y on the frame 3 via guides 4 slide 5.
- the carriage 5 is powered by a motor, for.
- a feed cylinder 6, which is designed as a piston-cylinder unit, acted upon by fluid pressure, in particular by a hydraulic medium and thus controlled, whereby then the carriage 5 in the direction of X or Y, for example, by 1000 millimeters in height adjustable and in the respective desired altitude also on the Zustellzylinder 6 or the like can be locked.
- the feed cylinder 6 is supplied via a line 7, a suitable fluid under pressure, for example hydraulic fluid, controlled.
- the carriage 5 is also associated with an adjustable in the direction A or B carriage 8, which is also associated with a motor-controlled rotary drive, for example, a rotary cylinder 9, the pivoting of the upper and lower tapered roller 10 in the direction T or V by an angle from 20 to 90 degrees, that is each allowed by 10 to 45 degrees on both sides of a longitudinal center axis 11 of the upper and lower tapered roller 10.
- the upper tapered roller 10 can be both in the direction of X or Y and in the direction A or B, but also in the direction T and V, adjust and control and in each selected Lock the height and angle position by motor.
- a motor drive z. B.
- a Linearverstellzylinder 12 which is also designed as a piston-cylinder unit and the lines 13 and 14, a suitable fluid under pressure, in particular a hydraulic medium, is controlled fed.
- the rotary cylinder 9 is also a suitable fluid under pressure, preferably a hydraulic medium, for example via the line 15, supplied controlled. From the drawing it can be seen that the longitudinal center axis 11, which also coincides with the longitudinal center axis of the upper tapered roller 10, in the illustrated embodiment at an acute angle of 20 to 90, preferably from 30 to 70, to be rolled to a ring blank 16 (FIG. Fig. 5 ) is adjustable and lockable.
- An already completely or partially rolled ring is designated by the reference numeral 17.
- the ring blank 16 rests on a table 18, while the ring to be rolled 17 is arranged with increasing diameter on two spaced roller tables 19, 19 a. All or some of the roller tables 19, 19a may be motor driven, for example to remove the ring 17 in direction D after it has been finish rolled.
- the upper cone roller opposite roller is designated by the reference numeral 20 and moves except in the XY direction all axes as the upper tapered roller 10th
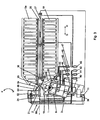
- Reference numeral 21 denotes a main roller cassette in which a shaft 22 is rotatably arranged in bearings on which a main roller 23 of the radial ring rolling mill 2 is rotatably arranged.
- the main roller cassette 21 is positioned in the radial stand.
- the upper roller mandrel bearing 26 and the lower roller mandrel bearing 27 each have a motor drive 28 or 29 assigned.
- These motor drives can also be designed as piston-cylinder units, which alternately on both sides via lines 30 and 31 fluid under pressure, preferably a hydraulic medium, are fed alternately controlled to the rolling mandrel 25 in the direction E or F, preferably in horizontal level, controlled to adjust and also lock in the desired position.
- the upper roller mandrel bearing 26 is lowerable together with the carriage 24 and designed as, for example, cylinder motor drive 28.
- the lowering takes place parallel to the lower roller mandrel bearing 27 and the motor drive, for Example, the cylinder 29.
- the motor drive for the main roller cassette 21 is designated by the reference numeral 32.
- This motor drive 32 may also represent a piston-cylinder unit, which is supplied via a line 33, a fluid under pressure, also preferably a hydraulic medium, alternately controlled on both sides to the main roller cassette 21 in the vertical direction, ie in the direction O or P to adjust and also lock in the respective desired position within the radial roller carriage 24.
- the reference numeral 34 designates a motor drive for the main roll 23.
- This drive can be designed, for example, as a radial piston drive or as a geared motor.
- the two roller tables 19 and 19a are arranged with gap spacing 35 to each other.
- a laser measuring device 36 which via a motor drive 37, in the present case also via a piston-cylinder unit, in direction G or H and optionally via the same motor or a separate motor in the direction L or M, thus orthogonal to the roller tables 19 and 19a, can be driven to the laser measuring device 36th if necessary, lower below the level of the roller tables 19, 19a, but they also in the direction G or H depending on the ring diameter or during rolling with the growth of the ring 17 can adjust.
- the conical shape and the outer profile of the ring 17 can be continuously measured by the laser measuring device 36 and the measured values forwarded to a central control and / or regulating device 38 and the position of the rolling mandrel bearings 26 and 27 corrected on the basis of the measured values.
- the lowering device for driving the laser device in the direction L and M and for locking thereof is designated by the reference numeral 39.
- Reference numerals 40 to 47 designate drive groups with suitable fluid drive devices, for example hydraulic drive devices with valves, reservoirs for fluid, pumps, motors, which through the various lines shown carry all the motors, for example piston-cylinder units, and drives Drive energy, in particular with hydraulic pressure medium supply.
- suitable fluid drive devices for example hydraulic drive devices with valves, reservoirs for fluid, pumps, motors, which through the various lines shown carry all the motors, for example piston-cylinder units, and drives Drive energy, in particular with hydraulic pressure medium supply.
- the control or regulating device 38 may be located in case of need, a suitable electronic memory in which are stored for the various rings, materials, profiles or the like suitable parameters, on the basis of which the various drives on the Control or regulating device 38 are controlled or controlled as part of a sequence control to produce rings 17 in the respectively desired manner.
- the pumps and / or motors of the drive groups 40 to 47 may be adjustable, in particular adjustable, by the control and / or regulating device 38 in terms of their delivery rate.
- hydrostatic pumps may come into consideration, which are control tube or control-controlled by a control valve to change the flow rate of the respective pump.
- control valve to change the flow rate of the respective pump.
- the various drive groups 40 to 47 can also be associated with multi-way valves, not shown, for example, solenoid valves, which are also influenced by the control or regulating device 38 in order to influence the respective pressure medium in the various lines.
- the entire control or regulating device may be formed numerically (NC).
- the centering arms 48 and 49 are each actuated by a motor drive 52 and 53, respectively.
- These motor drives 52 and 53 may also be formed as a piston-cylinder units, the above Lines with a suitable pressurized fluid, in particular with a hydraulic medium alternately be acted upon on both sides.
- Each of the centering arms 48, 49 is each associated with a centering roller 54 and 55, which is rotatably disposed on the respective centering arm 48 and 49 and scans the outer diameter of the ring to be rolled 17.
- the measured values are forwarded to the control or regulating device 38, wherein each centering arm 48 or 49 can be positioned by the motor drive 52 or 53.
- the rotational signals of the centering rollers 54 and 55 are forwarded in the form of control or regulating signals via the control and regulating device 38 to the corresponding motor drives of Axialringwalztechnikes 1 in order to influence its speed accordingly, for example, when the ring to be rolled in 17 its outer shape, for example, should deviate from its predetermined diameter tolerances, for example, assumes an oval shape, so that one or the other role of the outer diameter of the ring 17 would stand out.
- the control or regulation of the speed of the Axialringwalztechnikes 1 is then influenced so that the ring 17 retains its shape within predetermined tolerances or reached again.
- the laser measuring device 36 is lowered and transported away by driving all or more of the roller tables 19 and 19a in the direction D.
- the longitudinal axes 11 of the Axialringwalzwerkes 1 on the one hand and 56 of the Radialringwalztechnikes 2 on the other hand an acute angle ⁇ to each other, which in the illustrated embodiment about 20 to 90 degrees, preferably about 30 to 70 degrees.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Control Of Metal Rolling (AREA)
- Rolls And Other Rotary Bodies (AREA)
- Rolling Contact Bearings (AREA)
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft ein Axial-/Radialringwalzwerk mit motorischen Antrieben und Steuer- und/oder Regelvorrichtungen.The invention relates to an axial / Radialringwalzwerk with motor drives and control and / or regulating devices.
Des weiteren betrifft die Erfindung ein Verfahren zum Betreiben eines derartigen Axial-/Radialringwalzwerkes.Furthermore, the invention relates to a method for operating such an axial / radial ring rolling mill.
Bei bekannt gewordenen Axial-/Radialringwalzwerken sind das Axialwalzwerk und Radialwalzwerk im größeren Abstand zueinander und zwar um 180° versetzt angeordnet, das bedeutet, dass das Axialringwalzwerk und das Radialringwalzwerk diametral einander gegenüberliegend angeordnet sind.In known axial / Radialringwalzwerken the axial rolling and radial rolling mill at a greater distance from one another and that are offset by 180 °, that is, the Axialringwalzwerk and the Radialringwalzwerk are arranged diametrically opposite each other.
Diese Anordnung der Walzwerke zueinander macht das Be- und Entladen, besonders bei großen zu walzenden Ringen, problematisch.This arrangement of the rolling mills to each other makes loading and unloading, especially for large rings to be rolled, problematic.
Darüber hinaus erreicht man beim Walzen großer Ringe regelungstechnische Grenzen. Da das Walzgerüst große Wege zurücklegen muss, werden lange Hydraulikzylinder benötigt, die die Verstellbewegungen ausführen müssen. Dies führt zwangsläufig zu regelungstechnischen Problemen wegen zu geringer Steifigkeit. Um die dabei auftretenden Schwingungen zu minimieren, muss man große Schleppfehler akzeptieren. Die Lage des zu walzenden Ringes im Axialkaliber bestimmt jedoch auch die Kegelwalzendrehzahl. Die regelungstechnischen Anlagen und die Ringlagerregelung von Zentrierarmen gewährleisten es kaum, den zu walzenden Ring stabil zu halten. Dies kann zu Ausschuss oder zu kostspieligen Nacharbeiten führen.In addition, when it comes to rolling large rings control technical limits. Since the rolling mill has to travel long distances, long hydraulic cylinders are required, which must carry out the adjustment movements. This inevitably leads to control engineering problems due to low rigidity. To minimize the vibrations that occur, you have to accept large following errors. However, the position of the ring to be rolled in the axial caliber also determines the taper roller speed. The control systems and the ring bearing control of centering arms hardly ensure that the ring to be rolled is stable. This can lead to rejects or costly rework.
Aus der deutschen Auslegeschrift 1 019 635 ist ein Axial-/Radialwalzwerk vorbekannt, bei welchem das Radialwalzwerk mit seiner Zustellvorrichtung in einem stumpfen Winkel diametral gegenüberliegend zu einer Walze angeordnet ist. Hierdurch wird der für den Ring zur Verfügung stehende Raum ungünstig eingeengt. Außerdem ist es fraglich, wie ein sehr kleiner Ring durch ein derartiges Walzwerk gewalzt werden könnte, zumal die Walze bei der vorbekannten Bauart nur verschwenkbar ist. Das bedeutet, dass bei sehr kleinen Ringen die Walze den Ring gar nicht oder unvollständig walzen kann. Ein derartiges Walzwerk scheint kaum industriell einsetzbar zu sein.From the
Aus der
Der Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, ein Axial-/Radialringwalzwerk gemäß der vorausgesetzten Gattung so auszugestalten, dass auch Ringe großen Durchmessers von ein Meter bis 15 Meter, vorzugsweise von drei Metern bis acht Metern, mit großer Genauigkeit gewalzt werden können, auch dann, wenn diese Ringe profiliert werden sollen.The invention has for its object, an axial / Radialringwalzwerk according to the assumed genus in such a way that rings of large diameter of one meter to 15 meters, preferably from three meters to eight meters, can be rolled with great accuracy, even if these rings should be profiled.
Des weiteren liegt der Erfindung die Aufgabe zugrunde, ein Verfahren zum Betreiben eines derartigen Axial-/Radialringwalzwerkes zu schaffen.Furthermore, the invention has for its object to provide a method for operating such axial / Radialringwalzwerkes.
Die Aufgabe betreffend das Axial-/Radialringwalzwerk wird durch die Merkmale des Patentanspruches 1 gelöst. Hierbei ist das Axialringwalzwerk unmittelbar, das heißt im geringstmöglichen räumlichen Abstand, neben dem Radialringwalzwerk angeordnet, derart, dass das Maschinengerüst des Radialringwalzwerkes und damit die Längsachse des Radialringwalzwerkes in einem spitzen Winkel zum Axialringwalzwerkgerüst und damit zur Längsachse des Axialringwalzwerkes angeordnet ist.The task concerning the axial / radial ring rolling mill is solved by the features of
Die Erfindung weicht somit grundsätzlich vom Stand der Technik ab, indem Axialringwalzwerk und Radialringwalzwerk unmittelbar nebeneinander angeordnet sind. Das Maschinengerüst steht damit je nach Maschinengröße zum Axialgerüst in einem spitzen Winkel von zum Beispiel 20 bis 90 Grad. Das Axialgerüst hat eine Dreh- und Linearachse. Die Drehachse fährt automatisch so, dass immer die Kegelwalzenachse auf die Mitte des wachsenden Ringes zeigt. Die Linearachse fährt so, dass zu Beginn der Schnittpunkt der Kegelwalzen in der Dommitte liegt. Mit steigendem Ringdurchmesser fahren die Kegelwalzen soweit vor, bis sich der zu walzende Ring in der hinteren Position der Kegelwalzen befindet. Die Linearbewegung des Axialgerüstes kann je nach Maschinengröße Null bis zweitausend Millimeter, vorzugsweise Null bis eintausend Millimeter, betragen.The invention thus differs fundamentally from the prior art by Axialringwalzwerk and Radialringwalzwerk are arranged directly next to each other. Depending on the machine size, the machine frame stands at an acute angle of, for example, 20 to 90 degrees to the axial frame. The axial frame has a rotary and linear axis. The rotation axis automatically moves so that the tapered roller axis always points to the center of the growing ring. The linear axis moves so that at the beginning of the intersection of the tapered rollers is in the Dommitte. As the ring diameter increases, the tapered rollers advance until the ring to be rolled is in the rearward position of the tapered rollers. Depending on the size of the machine, the linear movement of the axial stand can amount to zero to two thousand millimeters, preferably zero to one thousand millimeters.
Am Hauptwalzengerüst befindet sich ein Walztisch zur Aufnahme des Ringrohlings. Wenn der zu walzende Ring dann größer gewalzt ist, liegt er überwiegend auf einem Rollgang oder auf Ablageschienen auf, der auch nach Walzende zum Abtransport des gewalzten Ringes dient. Dies erlaubt ein sehr kurzes und einfaches Entladen, auch für große Ringe. Darüber hinaus entfällt die gefährliche und teure Grube zwischen Axial- und Radialgerüst. Die Hauptwalze kann axial verschoben und in jeder Position arretiert werden. Dieses erlaubt, dass profilierte Ringe erst in einem Vorprofil zum Ende des Walzens zu einem Fertigprofil gewalzt werden können. Dabei muss lediglich die profilierte Hauptwalze oder beim Innenprofilieren der Dom, oder beides, axial verschoben werden. Dies gelingt in einer Umformhitze, und der Ring kann auf dem Walztisch liegen bleiben. Um ein einfaches Verschieben zu ermöglichen, kann statt der bisherigen Motor-Getriebe-Kupplungs-Kombination ein direkt treibender Radialkolbenhydroantrieb vorgesehen werden.On the main roll stand is a rolling table for receiving the ring blank. If the ring to be rolled is then rolled larger, it is mainly on a roller table or on storage rails, which also serves after rolling to remove the rolled ring. This allows a very short and easy unloading, even for large rings. In addition, eliminates the dangerous and expensive pit between axial and radial scaffolding. The main roller can be moved axially and locked in any position. This allows profiled rings to be rolled into a finished profile only in a pre-profile at the end of the rolling process can be. In this case, only the profiled main roller or the inner profiling of the dome, or both, must be moved axially. This succeeds in a forming heat, and the ring can remain lying on the rolling table. In order to enable easy shifting, instead of the previous engine-gearbox-clutch combination, a directly driving radial piston hydraulic drive can be provided.
Alles in allem ist es somit möglich, die beim Stand der Technik vorhandenen Nachteile restlos zu beseitigen und ein kompaktes Axial-/Radialringwalzwerk vorzuschlagen, mit dem sich auch sehr große Ringe von zum Beispiel zwölf Metern genau walzen und sicher abtransportieren lassen.All in all, it is thus possible to eliminate the disadvantages existing in the prior art completely and to propose a compact axial / radial ring rolling, with which even very large rings of, for example, twelve meters to roll exactly and can be safely removed.
Die Erfindung hat besondere erfinderische Bedeutung für Axial-/Radialringwalzwerke mit motorischen Antrieben und Steuer- und/oder Regelvorrichtungen zum Kontrollieren der Walzvorgänge, wobei das Axialringwalzwerk unmittelbar neben dem Radialringwalzwerk angeordnet ist, derart, dass das Maschinengerüst des Radialringwalzwerkes und das Axialringwalzwerkgerüst auf derselben Außenseite des zu walzenden Ringes angeordnet sind und das Maschinengerüst des Radialringwalzwerkes und damit dik länpsachse des radialringwalzwerkes in einem spitzen Winkel zum Axialringwalzwerkgerüst und damit zur laupsachse del axialringwelzwerkesachse angeordnet ist.The invention has particular inventive significance for axial / Radialringwalzwerke with motor drives and control and / or regulating devices for controlling the rolling operations, wherein the Axialringwalzwerk is located immediately adjacent to the Radialringwalzwerk, such that the machine frame of the Radialringwalzwerkes and the Axialringwalzwerkgerüst on the same outside of the are arranged to roll ring and the machine frame of the Radialringwalzwerkes and thus dik länpsachse the radialringwalzwerkes at an acute angle to Axialringwalzwerkgerüst and thus laupsachse del axialringwelzwerkesachse is arranged.
Das Axialringwalzwerk ist ein sich im Wesentlichen vertikal erstreckendes Gerüst, dem ein in vertikaler Richtung an dem Gerüst über Führungen zwangsgeführter Schlitten zugeordnet ist, wobei der Schlitten durch einen motorischen Antrieb höhenverstellbar und in der jeweils gewünschten Höhenlage auch arretierbar ist.The Axialringwalzwerk is a substantially vertically extending framework, which is associated with a positively guided in the vertical direction of the scaffold on guides slide, the carriage by a motor drive height adjustable and in the particular desired altitude is also locked.
Erfinderisch ist es auch, dass dem Schlitten außerdem ein quer/horizontal verstellbarer Schlitten zugeordnet ist, dem auch ein motorisch steuerbarer Drehantrieb, zum Beispiel ein Drehzylinder, zugeordnet ist, der eine Winkelverschwenkung T - V der oberen und unteren Kegelwalze um 20 Grad bis 90 Grad, also jeweils um 10 Grad bis 45 Grad, zu beiden Seiten einer Längsmittenachse der oberen und unteren Kegelwalze gestattet, derart, dass die obere Kegelwalze sowohl in vertikaler Richtung X bzw. Y als auch quer dazu A - B, und in Richtung T bzw. V, verstellbar und steuerbar und in der jeweils gewünschten Höhen- und Winkelstellung motorisch ebenfalls arretierbar ist.It is also inventive that the carriage is also assigned a transversely / horizontally adjustable carriage, which is also assigned a motor-controllable rotary drive, for example a rotary cylinder, which has an angular tilt T - V of the upper and lower tapered rollers by 20 degrees to 90 degrees , ie, in each case by 10 degrees to 45 degrees, allowed on both sides of a longitudinal center axis of the upper and lower tapered roller, such that the upper tapered roller both in the vertical direction X and Y and transverse thereto A - B, and in the direction T and V, adjustable and controllable and in the desired height and angle position motor is also locked.
Im Rahmen des Erfindungsgedankens liegen auch Axial-/Radialringwalzwerke, bei denen die der oberen Kegelwalze gegenüberliegende Unterwalze außer in Richtung X bzw. Y in allen Achsen wie die obere Kegelwalze verstellbar ist.Within the scope of the inventive concept are also axial / radial ring rolling mills, in which the upper roller roller opposite lower roller is adjustable except in the direction X or Y in all axes as the upper tapered roller.
Des Weiteren ist erfinderisch, dass das obere Walzdornlager zusammen mit dem Schlitten und dem Antrieb absenkbar ist und dass das Absenken parallel zum Walzdornlager und dem Antrieb erfolgt.Furthermore, it is inventive that the upper roll mandrel bearing can be lowered together with the carriage and the drive and that the lowering takes place parallel to the rolling mandrel bearing and the drive.
Weitere erfinderische Ausgestaltungen sind in den Patentansprüchen 2 bis 15 beschrieben.Further inventive embodiments are described in the
Patentanspruch 2 beschreibt eine vorteilhafte Ausführungsform, bei welcher die Linearbewegung des Axialgerüstes mit der Kegelwalze Null bis zweitausend Millimeter, vorzugsweise Null bis eintausend Millimeter, beträgt. Dadurch ist es möglich, auch sehr große Ringe mit Außendurchmessern von zum Beispiel zwölf Metern toleranzgenau zu walzen.
In Patentanspruch 3 ist eine Ausführungsform beschrieben, bei der die Vorrichtung einen Walztisch zur Aufnahme des Ringrohlings aufweist. Bei zunehmendem Durchmesser liegt der Ring überwiegend allerdings auf einem Rollgang bzw. den Auflageschienen auf, der auch nach Walzende zum Abtransport des gewalzten Ringes dient. Beim Beginn des Walzens wird durch den Walztisch eine sichere Unterstützung und Führung des Ringrohlings erreicht, der immerhin ein Gewicht 500 bis 100000 Kilogramm, vorzugsweise von 1000 bis 50000 Kilogramm, aufweisen kann und beim Warmwalzen eine Temperatur von bis zu 1250° Celsius aufweist.In
Vorteilhafterweise ist gemäß Patentanspruch 4 den Walzwerken eine Fördervorrichtung, zum Beispiel ein Rollgang, ein Hubbalken oder ein sonstiges stetiges Fördermittel, zugeordnet, wobei die Fördervorrichtung zum Transport sowie zum Be- und Entladen des Ringes dient. Dies erlaubt ein sehr kurzes und einfaches Entladen, auch für große Ringe von bis zu 12000 Millimetern Außendurchmesser und einem Gewicht von bis zu 50000 kg. Auch die bereits erwähnte teure und gefährliche Grube zwischen Axial und Radialgerüst ist hierbei nicht mehr erforderlich.Advantageously, according to claim 4 the rolling mills, a conveyor device, for example, a roller table, a lifting beam or other continuous conveyor, assigned, wherein the conveyor device for transport and for loading and unloading of the ring is used. This allows a very short and easy unloading, even for large rings of up to 12000 millimeters outside diameter and a weight of up to 50000 kg. The already mentioned expensive and dangerous pit between Axial and Radial framework is no longer necessary.
Bei der Ausführungsform nach Patentanspruch 5 sind alle oder einige der Rollen des Rollganges motorisch angetrieben. Dadurch wird der Abtransport des fertig gewalzten Ringes erleichtert.In the embodiment according to claim 5 all or some of the rollers of the roller table are driven by a motor. As a result, the removal of the finished rolled ring is facilitated.
Eine besonders vorteilhafte Ausführungsform beschreibt Patentanspruch 6, bei welchem die Hauptwalze vertikal motorisch verstellbar und in der jeweiligen Position arretierbar und derart ausgebildet angeordnet ist, dass in verschiedenen Kalibern gewalzt werden kann.A particularly advantageous embodiment describes
Patentanspruch 7 beschreibt eine Ausführungsform, bei welcher das Radialwalzwerk und/oder das Axialwalzwerk durch direkt antreibende Radialkolbenmotoren oder Getriebemotoren antreibbar sind.
Wird eine Ausführungsform nach Patentanspruch 8 gewählt, so sind dem Axial- und Radialringwalzwerk zwei mit Abstand zueinander angeordnete Rollgänge zugeordnet, bei denen einige oder alle Rohre motorisch angetrieben sind.If an embodiment is selected according to claim 8 , the axial and Radialringwalzwerk two spaced apart roller tables are assigned, in which some or all tubes are driven by a motor.
Dies ermöglicht gemäß Patentanspruch 9 die Anordnung einer Lasermessvorrichtung zwischen den beiden Rollgängen.This allows according to claim 9, the arrangement of a laser measuring device between the two roller tables.
Bei der Ausführungsform nach Patentanspruch 10 ist diese Lasermessvorrichtung in zwei, vorzugsweise rechtwinklig zueinander angeordneten Ebenen, insbesondere in vertikaler und/oder horizontaler Ebene, verstellbar ausgebildet und angeordnet.In the embodiment according to
Der motorische Antrieb für die Lasermessvorrichtung kann eine abwechselnd beidseitig durch Druckmitteldruck, insbesondere hydraulisch zu beaufschlagende Kolben-Zylinder-Einheit sein. Ein derartiger motorischer Antrieb arbeitet zuverlässig und präzise und ermöglicht auch die jeweilige Arretierung der Laservorrichtung in der jeweils vorbestimmten Position - Patentanspruch 11. The motor drive for the laser measuring device may be an alternately on both sides by pressure medium pressure, in particular hydraulically acted upon piston-cylinder unit. Such a motor drive operates reliably and precisely and also allows the respective locking of the laser device in the respectively predetermined position -
Besonders vorteilhaft ist es, wenn gemäß Patentanspruch 12 die Lasermessvorrichtung motorisch unter das Niveau des Rollenganges absenkbar ist.It is particularly advantageous if, according to
Wird eine Ausführungsform nach Patentanspruch 13 gewählt, so ermöglicht die Lasermessvorrichtung das Messen des Außen- und/oder Innenringdurchmessers und die Ovalität des Ringes, wobei die Werte an eine Steuer- und/oder Regelvorrichtung online weiterleitbar sind.If an embodiment according to
Besonders vorteilhaft ist eine Ausführungsform nach Patentanspruch 14, bei welcher die Lasermessvorrichtung derart ausgebildet ist, dass sie die Konizität und das Außenprofil der Ringe misst und die Messwerte an die Steuer- und/oder Regelvorrichtung weitergibt, wobei die Positionen der Dornlager anhand der Messwerte korrigierbar sind.Particularly advantageous is an embodiment according to
Bei einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform der Erfindung sind gemäß Patentanspruch 15 vorzugsweise auf gegenüberliegenden Seiten im Bereich des Radialringwalzwerkes und des Axialringwalzwerkes je eine motorisch verstellbare Zentriervorrichtung mit einem Zentrierarm und einer Zentrierrolle angeordnet. Diese Zentrierrollen, und dazu geeignet, die äußere Peripherie der zu walzenden zu berühren Ringe, wobei die dadurch hervorgerufenen Drehsignale an eine Steuer- und/oder Regelvorrichtung der motorischen Antriebe des Axialwalzwerkes weiterleitbar und die Drehzahl entsprechend zu beeinflussen ist.In a preferred embodiment of the invention according to claim 15 are preferably arranged on opposite sides in the region of the radial ring rolling mill and the Axialringwalzwerkes ever a motorized centering device with a centering and a centering. These centering rollers, and adapted to the outer periphery of the rings to be rolled to touch rings, wherein the rotational signals caused thereby to a control and / or regulating device of the motor drives of the axial rolling passed and the speed is to be influenced accordingly.
Sämtliche Steuer- und/oder Regelvorrichtungen der motorischen Antriebe des Radialringwalzwerkes und des Axialringwalzwerkes sowie sämtliche Verstellvorrichtungen für diese Walzwerke und für die Laservorrichtung können in eine CNC-Steuerung einbezogen sein, die an einen zentralen Steuer- und/oder Regelstand in einem elektronischen Speicher für die verschieden zu walzenden Ringrohlinge vorgegebene Signal- und Richtwerte mit den Toleranzen abgespeichert aufweist und entsprechend die Antriebe der Walzwerke, deren Positionen und auch die Antriebe der Rollgänge sowie der Laservorrichtung, vorzugsweise in einer Folgesteuerung einbezogen, steuert und/oder regelt.All control and / or regulating devices of the motor drives of the radial ring rolling mill and the axial ring rolling mill as well as all adjusting devices for these rolling mills and for the laser device can be in a CNC control be included, which has stored to a central control and / or control station in an electronic memory for the different to be rolled ring blanks predetermined signal and guide values with the tolerances and correspondingly the drives of the rolling mills, their positions and the drives of the roller tables and the Laser device, preferably included in a sequence control, controls and / or regulates.
Die Aufgabe betreffend das Verfahren wird durch die Merkmale des Verfahrensanspruches 16 gelöst. Hierbei weist die Drehachse des Axialringwalzwerkes durch die Steuer- und Regelungsvorrichtung mit der Kegelwalzenachse immer auf die Mitte des wachsenden Ringes, wobei bei steigendem Ringdurchmesser das Axialringwalzwerk linear auf die Ringmitte fährt, bis der gewalzte Ring in der horizontalen Position der Kegelwalze angeordnet ist.The object concerning the method is solved by the features of
In der Zeichnung ist die Erfindung - teils schematisch - beispielsweise veranschaulicht. Es zeigen:
- Fig. 1
- ein Axial-/Radialringwalzwerk in perspektivischer Darstellung;
- Fig. 2
- das aus
Fig. 1 ersichtliche Axial-/Radialringwalzwerk mit einem bereits teilweise gewalzten Ring; - Fig. 3
- eine Draufsicht auf das aus
Fig. 1 ersichtliche Axial- /Radialringwalzwerk; - Fig. 4
- eine Draufsicht zu
Fig. 2 ; - Fig. 5
- eine Einzelheit aus den
Fig. 1 mit einer Lasermessvorrichtung, teils im Schnitt, undbis 4 - Fig. 6
- eine ähnliche Darstellung wie
Fig. 5 , allerdings mit einem bereits teilweise gewalzten Ring, aufliegend auf einem Rollgang.
- Fig. 1
- an axial / Radialringwalzwerk in perspective view;
- Fig. 2
- the end
Fig. 1 apparent axial / Radialringwalzwerk with an already partially rolled ring; - Fig. 3
- a plan view of the
Fig. 1 apparent axial / radial ring rolling mill; - Fig. 4
- a plan view too
Fig. 2 ; - Fig. 5
- a detail from the
Fig. 1 to 4 with a laser measuring device, partly in section, and - Fig. 6
- a similar representation as
Fig. 5 , but with an already partially rolled ring, resting on a roller table.
In der Zeichnung ist mit dem Bezugszeichen 1 ein Axialringwalzwerk und mit dem Bezugszeichen 2 ein Radialringwalzwerk bezeichnet. Das Axialringwalzwerk 1 weist ein sich im wesentlichen vertikal erstreckendes Gerüst 3 auf, dem ein in vertikaler Richtung, also in Richtung X bzw. Y an dem Gerüst 3 über Führungen 4 zwangsgeführter Schlitten 5 zugeordnet ist. Der Schlitten 5 wird durch einen motorischen Antrieb, z. B. einen Zustellzylinder 6, der als Kolben-Zylinder-Einheit ausgebildet ist, durch Fluiddruck, insbesondere durch ein hydraulisches Medium beaufschlagt und damit gesteuert, wodurch dann der Schlitten 5 in Richtung X bzw. Y zum Beispiel um 1000 Millimeter höhenverstellbar und in der jeweils gewünschten Höhenlage auch über den Zustellzylinder 6 oder dergleichen arretierbar ist. Dem Zustellzylinder 6 wird über eine Leitung 7 ein geeignetes Fluid unter Druck, zum Beispiel Hydraulikflüssigkeit, gesteuert zugeführt.In the drawing, the
Dem Schlitten 5 ist außerdem ein in Richtung A bzw. B verstellbarer Schlitten 8 zugeordnet, dem auch ein motorisch steuerbarer Drehantrieb, zum Beispiel ein Drehzylinder 9 zugeordnet ist, der eine Verschwenkung der oberen und unteren Kegelwalze 10 in Richtung T bzw. V um ein Winkelmaß von 20 bis 90 Grad, also jeweils um 10 bis 45 Grad zu beiden Seiten einer Längsmittenachse 11 der oberen und unteren Kegelwalze 10 gestattet. Auf diese Weise lässt sich die obere Kegelwalze 10 sowohl in Richtung X oder Y als auch in Richtung A oder B, aber auch in Richtung T bzw. V, verstellen und steuern und in der jeweils gewählten Höhen- und Winkelstellung motorisch ebenfalls arretieren. Zur Verstellung in Richtung A bzw. B dient ein motorischer Antrieb, z. B. ein Linearverstellzylinder 12, der ebenfalls als Kolben-Zylinder-Einheit ausgebildet ist und dem über Leitungen 13 bzw. 14 ein geeignetes Fluid unter Druck, insbesondere ein hydraulisches Medium, gesteuert zuführbar ist.The
Dem Drehzylinder 9 wird ebenfalls ein geeignetes Fluid unter Druck, vorzugsweise ein hydraulisches Medium, zum Beispiel über die Leitung 15, gesteuert zugeführt. Aus der Zeichnung ist ersichtlich, dass die Längsmittenachse 11, die ebenfalls mit der Längsmittenachse der oberen Kegelwalze 10 zusammenfällt, bei der dargestellten Ausführungsform unter einem spitzen Winkel von 20 bis 90, vorzugsweise von 30 bis 70, zu einem zu walzenden Ringrohling 16 (
Die der oberen Kegelwalze gegenüberliegende Walze ist mit dem Bezugszeichen 20 bezeichnet und fährt außer in X-Y Richtung alle Achsen wie die obere Kegelwalze 10.The upper cone roller opposite roller is designated by the
Mit dem Bezugszeichen 21 ist eine Hauptwalzenkassette bezeichnet, in der eine Welle 22 in Lagern drehbar angeordnet ist, auf der eine Hauptwalze 23 des Radialringwalzwerkes 2 drehbar angeordnet ist. Die Hauptwalzenkassette 21 ist im Radialgerüst positioniert.
Mit 25 ist ein Walzdorn des Radialringwalzwerkes 2 bezeichnet, der im wesentlichen vertikal angeordnet ist und in einem oberen Walzdornlager 26 und einem unteren Walzdornlager 27 angeordnet ist und durch eine mittige Durchbrechung des Ringrohlings 16 (
Dem oberen Walzdornlager 26 und dem unteren Walzdornlager 27 ist je ein motorischer Antrieb 28 bzw. 29 zugeordnet. Diese motorischen Antriebe können ebenfalls als Kolben-Zylinder-Einheiten ausgebildet sein, denen abwechselnd beidseitig über Leitungen 30 bzw. 31 Fluid unter Druck, bevorzugt ein hydraulisches Medium, abwechselnd gesteuert zuführbar sind, um den Walzdorn 25 in Richtung E bzw. F, bevorzugt in horizontaler Ebene, gesteuert zu verstellen und in der jeweils gewünschten Stellung auch zu arretieren.The upper roller mandrel bearing 26 and the lower roller mandrel bearing 27 each have a
Das obere Walzdornlager 26 ist zusammen mit dem Schlitten 24 und dem als zum Beispiel Zylinder ausgebildeten motorischen Antrieb 28 absenkbar. Das Absenken erfolgt parallel zum unteren Walzdornlager 27 und dem motorischen Antrieb, zum Beispiel dem Zylinder 29. Mit dieser Option ist es möglich, mit einem kürzeren Walzdorn 25 zu arbeiten, ohne dass durch das Verschieben des oberen Walzdornlagers zusätzliche Momente auf die Maschine und damit auf die Führungen ausgeübt werden. Das hat zur Folge, dass der Walzdorn entsprechend kleiner ausgeführt werden kann. Dies ist von großem Vorteil beim Walzen von Superlegierungen.The upper roller mandrel bearing 26 is lowerable together with the
Der motorische Antrieb für die Hauptwalzenkassette 21 ist mit dem Bezugszeichen 32 bezeichnet. Dieser motorische Antrieb 32 kann ebenfalls eine Kolben-Zylinder-Einheit darstellen, dem über eine Leitung 33 ein Fluid unter Druck, ebenfalls bevorzugt ein hydraulisches Medium, abwechselnd beidseitig gesteuert zugeführt wird, um die Hauptwalzenkassette 21 in vertikaler Richtung, also in Richtung O bzw. P zu verstellen und in der jeweils gewünschten Stellung innerhalb des Radialwalzenschlittens 24 auch zu arretieren.The motor drive for the
Das Bezugszeichen 34 bezeichnet einen motorischen Antrieb für die Hauptwalze 23. Dieser Antrieb kann zum Beispiel als Radialkolbenantrieb oder als Getriebemotor ausgebildet sein.The
Wie man aus der Zeichnung entnehmen kann, sind die beiden Rollgänge 19 und 19a mit Spaltabstand 35 zueinander angeordnet. In diesem Spaltabstand 35 befindet sich eine Lasermessvorrichtung 36, die über einen motorischen Antrieb 37, vorliegend ebenfalls über eine Kolben-Zylinder-Einheit, in Richtung G bzw. H und gegebenenfalls über den gleichen Motor oder einen separaten Motor in Richtung L bzw. M, mithin orthogonal zu den Rollgängen 19 und 19a, angetrieben werden kann, um die Lasermessvorrichtung 36 im Bedarfsfalle unter das Niveau der Rollgänge 19, 19a absenken, aber sie auch in Richtung G bzw. H je nach Ringdurchmesser oder beim Walzvorgang mit dem Wachsen des Ringes 17 verstellen zu können. Über die Lasermessvorrichtung 36 lässt sich die Konizität und das Außenprofil des Ringes 17 kontinuierlich messen und die Messwerte an eine zentrale Steuer- und/oder Regelvorrichtung 38 weiterleiten und die Position der Walzdornlager 26 und 27 anhand der Messwerte korrigieren. Die Absenkvorrichtung für den Antrieb der Laservorrichtung in Richtung L bzw. M und zu deren Arretierung ist mit dem Bezugszeichen 39 bezeichnet.As can be seen from the drawing, the two roller tables 19 and 19a are arranged with gap spacing 35 to each other. In this
Mit den Bezugszeichen 40 bis 47 sind Antriebsgruppen mit geeigneten Fluidantriebsvorrichtungen, zum Beispiel hydraulische Antriebsvorrichtungen mit Ventilen, Vorratsbehältern für Fluid, Pumpen, Motoren, bezeichnet, die durch die verschiedenen dargestellten Leitungen sämtliche Motoren, zum Beispiel Kolben-Zylinder-Einheiten, und Antriebe, mit Antriebsenergie, insbesondere mit hydraulischem Druckmittel, versorgen. In der Steuer- oder Regelvorrichtung 38 kann sich im Bedarfsfalle auch ein geeigneter elektronischer Speicher befinden, in dem für die verschiedenen Ringe, Materialien, Profilierungen oder dergleichen geeignete Parameter abgespeichert sind, anhand derer die verschiedenen Antriebe über die Steuer- oder Regelvorrichtung 38 im Rahmen einer Folgesteuerung gesteuert bzw. geregelt werden, um Ringe 17 in der jeweils gewünschten Art und Weise zu produzieren.
Die Pumpen und/oder Motoren der Antriebsgruppen 40 bis 47 können durch die Steuer- und/oder Regelvorrichtung 38 in ihrer Förderleistung verstellbar, insbesondere regelbar ausgebildet sein. Hierzu können zum Beispiel hydrostatische Pumpen in Betracht kommen, die steuerrohr- oder steuerspiegelgesteuert sind, um die Fördermenge der jeweiligen Pumpe zu ändern. Es ist aber auch möglich, die Drehzahl von Pumpen zu steuern bzw. zu regeln, um die jeweiligen motorischen Antriebe entsprechend mit Energie zu versorgen. Den verschiedenen Antriebsgruppen 40 bis 47 können auch nicht dargestellte Mehrwegeventile, zum Beispiel Magnetventile, zugeordnet sein, die ebenfalls durch die Steuer- oder Regelvorrichtung 38 beeinflusst werden, um das jeweilige Druckmedium in den verschiedenen Leitungen zu beeinflussen. Die gesamte Steuer- oder Regelvorrichtung kann numerisch (NC) ausgebildet sein.The pumps and / or motors of the
Mit den Bezugszeichen 48 und 49 ist je ein Zentrierarm zugeordnet, der um je eine Achse 50 bzw. 51 in Richtung K bzw. N um ein begrenztes Winkelmaß schwenkbeweglich ist. Die Zentrierarme 48 und 49 werden jeweils durch einen motorischen Antrieb 52 bzw. 53 betätigt. Diese motorischen Antriebe 52 und 53 können ebenfalls als Kolben-Zylinder-Einheiten ausgebildet sein, die über dargestellte Leitungen mit einem geeignetem unter Druck stehendem Fluid, insbesondere mit einem hydraulischen Medium abwechselnd beidseitig beaufschlagbar sind.With the
Jedem der Zentrierarme 48, 49 ist je eine Zentrierrolle 54 bzw. 55 zugeordnet, die drehbar an dem betreffenden Zentrierarm 48 bzw. 49 angeordnet ist und den Außendurchmesser des zu walzenden Rings 17 abtastet. Die Messwerte werden an die Steuer- oder Regelvorrichtung 38 weitergeleitet, wobei jeder Zentrierarm 48 bzw. 49 durch den motorischen Antrieb 52 bzw. 53 positionierbar ist. Die Drehsignale der Zentrierrollen 54 und 55 werden in Form von Steuer- oder Regelsignalen über die Steuer- und Regelungsvorrichtung 38 an die entsprechenden motorischen Antriebe des Axialringwalzwerkes 1 weitergeleitet, um dessen Drehzahl entsprechend zu beeinflussen, zum Beispiel dann, wenn der zu walzende Ring 17 in seiner äußereren Gestalt, zum Beispiel von seinen vorgegebenen Durchmessertoleranzen abweichen sollte, zum Beispiel eine Ovalform annimmt, so dass die eine oder andere Rolle vom äußeren Durchmesser des Ringes 17 abheben würde. Die Steuerung oder Regelung der Drehzahl des Axialringwalzwerkes 1 wird dann so beeinflusst, dass der Ring 17 innerhalb vorgegebener Toleranzen seine Form beibehält oder wieder erreicht.Each of the centering
Soll der fertig gewalzte Ring 17 in Richtung D abtransportiert werden, wird die Lasermessvorrichtung 36 abgesenkt und durch Antrieb aller oder mehrerer der Rollgänge 19 und 19a in Richtung D abtransportiert.If the finished rolled
Wie man aus der Zeichnung erkennt, bilden die Längsachsen 11 des Axialringwalzwerkes 1 einerseits und 56 des Radialringwalzwerkes 2 andererseits einen spitzen Winkel α zueinander, der bei der dargestellten Ausführungsform etwa 20 bis 90 Grad, vorzugsweise etwa 30 bis 70 Grad, beträgt.As can be seen from the drawing, the
- 11
- AxialringwalzwerkAxialringwalzwerk
- 22
- RadialringwalzwerkRadial ring rolling mill
- 33
- Gerüstframework
- 44
- Führungenguides
- 55
- Schlittencarriage
- 66
- Zustellzylinder, motorischer AntriebInfeed cylinder, motorized drive
- 77
- Leitungmanagement
- 88th
- Schlittencarriage
- 99
- Drehzylinder, Drehantrieb, motorischerRotary cylinder, rotary drive, motorized
- 1010
- Kegelwalze, obereTapered roller, upper
- 1111
- LängsmittenachseLongitudinal central axis
- 1212
- Linearverstellzylinder, Antrieb, motorischerLinearverstellzylinder, drive, motor
- 1313
- Leitungmanagement
- 1414
- Leitungmanagement
- 1515
- Leitungmanagement
- 1616
- Ringrohlingring blank
- 1717
- Ringring
- 1818
- Tisch, WalztischTable, rolling table
- 1919
- Rollgangroller table
- 19a19a
- Rollgangroller table
- 00
- Walzeroller
- 2121
- HauptwalzenkassetteMain roll cassette
- 2222
- Wellewave
- 2323
- Hauptwalzemain roll
- 2424
- RadialwalzenschlittenRadial roller carriage
- 2525
- Walzdornrolling mandrel
- 2626
- Walzdornlager, oberesRolling mandrel bearing, upper
- 2727
- Walzdornlager, unteresRolling mandrel bearing, lower one
- 2828
- Antrieb, motorischerDrive, motor
- 2929
- Antrieb, motorischerDrive, motor
- 00
- Leitungmanagement
- 3131
- Leitungmanagement
- 22
- Antrieb, motorischer, Kolben-Zylinder-EinheitDrive, motor, piston-cylinder unit
- 3333
- Leitungmanagement
- 3434
- Antrieb, motorischer, Kolben-Zylinder-EinheitDrive, motor, piston-cylinder unit
- 3535
- Spaltabstandgap distance
- 3636
- LasermessvorrichtungLaser measuring device
- 3737
- Antrieb, motorischer, Kolben-Zylinder-EinheitDrive, motor, piston-cylinder unit
- 3838
- Steuer-/RegelvorrichtungControl / regulating device
- 3939
- Absenkvorrichtunglowering
- 4040
- Antriebsgruppedrive group
- 4141
- Antriebsgruppedrive group
- 4242
- Antriebsgruppedrive group
- 4343
- Antriebsgruppedrive group
- 4444
- Antriebsgruppedrive group
- 4545
- Antriebsgruppedrive group
- 4646
- Antriebsgruppedrive group
- 4747
- Antriebsgruppedrive group
- 4848
- Zentrierarmcentering
- 4949
- Zentrierarmcentering
- 5050
- Achseaxis
- 5151
- Achseaxis
- 5252
-
Antrieb, motorischer, Kolben-Zylinder-Einheit, des Zentrierarmes 48Drive, motor, piston-cylinder unit, centering
arm 48 - 5353
-
Antrieb, motorischer, Kolben-Zylinder-Einheit, des Zentrierarmes 49Drive, motor, piston-cylinder unit, centering
arm 49 - 5454
- Zentrierrolleflipper
- 5555
- Zentrierrolleflipper
- 5656
-
Längsachse des Radialringwalzwerkes 2Longitudinal axis of the radial
ring rolling mill 2 - αα
- Winkel zwischen den Längsachsen des Radial- und AxialringwalzwerkesAngle between the longitudinal axes of the radial and Axialringwalzwerkes
- AA
-
Hubrichtung des Schlittens 5 in Achsrichtung der Kegelwalze 10Lifting direction of the
carriage 5 in the axial direction of the tapered roller 10th - BB
-
Hubrichtung des Schlittens 5 in Achsrichtung der Kegelwalze 10Lifting direction of the
carriage 5 in the axial direction of the tapered roller 10th - DD
-
Abtransportrichtung des Ringes 17Abtransportrichtung of the
ring 17 - Ee
-
Hubrichtung des Walzdornlagers 26Lifting direction of the rolling
mandrel bearing 26 - FF
-
Hubrichtung des Walzdornlagers 26Lifting direction of the rolling
mandrel bearing 26 - GG
-
Hubrichtung des motorischen Antriebs 37 für Lasermessvorrichtungen 36Lifting direction of the
motor drive 37 forlaser measuring devices 36 - HH
-
Hubrichtung des motorischen Antriebs 37 für Lasermessvorrichtungen 36Lifting direction of the
motor drive 37 forlaser measuring devices 36 - KK
-
Schwenkrichtung des Zentrierarms 48, 49Pivoting direction of the centering
arm - LL
-
Hubrichtung der Lasermessvorrichtung 36 orthogonal zu den Rollgängen 19, 19aLifting direction of the
laser measuring device 36 orthogonal to the roller tables 19, 19a - MM
-
Hubrichtung der Lasermessvorrichtung 36 orthogonal zu den Rollgängen 19, 19aLifting direction of the
laser measuring device 36 orthogonal to the roller tables 19, 19a - NN
-
Schwenkrichtung des Zentrierarmes 48, 49Pivoting direction of the centering
arm - OO
-
Hubrichtung der Hauptwalzenkassette 21Lifting direction of the
main roller cassette 21 - PP
-
Hubrichtung der Hauptwalzenkassette 21Lifting direction of the
main roller cassette 21 - TT
- Hubrichtungstroke direction
- VV
- Hubrichtungstroke direction
- XX
-
Hubrichtung des Schlittens 5 des Axialringwalzwerkes 1Lifting direction of the
carriage 5 of the Axialringwalzwerkes. 1 - YY
-
Hubrichtung des Schlittens 5 des Axialringwalzwerkes 1Lifting direction of the
carriage 5 of the Axialringwalzwerkes. 1
-
DE 10 19 635 B DE 10 19 635 B -
DE 960 264DE 960 264 -
DE 17 52 887 A1 DE 17 52 887 A1 -
DE 22 22 607 A1 DE 22 22 607 A1 -
DE 29 17 369 A1 DE 29 17 369 A1 -
DE 29 23 001 A1 DE 29 23 001 A1 -
DE 326 925DE 326 925 -
DE 305 929DE 305 929 -
FR 1 009 653 FR 1 009 653 -
US 2,268,330US 2,268,330
Claims (16)
- Motor-driven axial-radial ring rolling mill (1, 2) with control and/or regulating devices for controlling the rolling operations, where the axial ring rolling mill (1) is arranged directly adjacent to the radial ring rolling mill (2) in such a way that the machine stand of the radial ring rolling mill (2) and therefore the longitudinal axis (56) of the radial ring rolling mill (2), are arranged at an acute angle (α) to the axial ring rolling mill (1) and therefore to the longitudinal axis (11) of the axial ring rolling mill (1).
- Axial-radial ring rolling mill according to claim 1 characterised in that the linear motion (A or B) of the axial stand (3) with the tapered rollers (10) is between 0 and 2000 millimetres or, preferably, between 0 and 1000 mm.
- Axial-radial ring rolling mill according to claim 1 or claim 2, characterised in that the device has a rolling table (18) to receive the ring blank (16).
- Axial-radial ring rolling mill according to claim 1 or either of the subsequent claims, characterised in that a conveying device (19, 19a) e.g. a roller table, a walking beam conveyor or other means of continuous transport is assigned to the rolling mills (1, 2), where the conveying device (19, 19a) serves to load and unload the ring (17) before and after rolling.
- Axial-radial ring rolling mill according to claim 4 characterised in that all or some of the rollers of the roller table (19, 19a) are motor-driven.
- Axial-radial ring rolling mill according to claim 1 or any of the claims 2 to 5, characterised in that the main roll is vertically adjustable by motor and lockable in the desired position and is formed and arranged in such a way that rolling can be carried out at varying passes.
- Axial-radial ring rolling mill according to claim 1 or any of the claims 2 to 6, characterised in that the radial ring rolling mill (2) and/or the axial ring rolling mill (1) can be driven by directly driving radial-piston motors or geared motors.
- Axial-radial ring rolling mill according to claim 1 or any of the subsequent claims, characterised in that two roller tables (19, 19a) arranged at a distance from one another are assigned to the axial-radial ring rolling mill (1, 2), of which all or some of the rollers are motor-driven.
- Axial-radial ring rolling mill according to claim 8, characterised in that a laser measuring device (36) is arranged between the two roller tables (19, 19a).
- Axial-radial ring rolling mill according to claim 9, characterised in that the laser measuring device (36) is formed in such a way that it can be adjusted to and locked in two planes preferably arranged at right angles to one another, in particular in the vertical and horizontal planes.
- Axial-radial ring rolling mill according to claim 10, characterised in that the motorised drive system of the laser measuring device (36) is a piston-cylinder unit which can be pressurised, preferably by hydraulic pressure, alternately on either side.
- Axial-radial ring rolling mill according to claim 9 or claim 10, characterised in that the laser measuring device (36) can be lowered by motor below the level of the roller table (19, 19a).
- Axial-radial ring rolling mill according to claim 8 or any of the subsequent claims, characterised in that the laser measuring device (36) is formed in such a way that it measures the outer and inner diameter and the ovality of the ring (17) and transmits the readings online to the control and regulating device (38).
- Axial-radial ring rolling mill according to claim 13, characterised in that the laser measuring device (36) is formed in such a way that it measures the conicity and the outer profile of the rings (17) and that the readings can be transmitted to the control and regulating device (38) and that the position of the expanding mandrel bearing (26, 27) can be adjusted according to the readings.
- Axial-radial ring rolling mill according to claim 1 or any of the claims 2 to 14, characterised in that a motor-adjustable centring device with a centring arm (48, 49) and a centring roll (54, 55) is arranged on at least one side, preferably on each of the opposing sides in the area of the radial ring rolling mill (2) and the axial ring rolling mill (1), which is suitable for touching, guiding or scanning the outer periphery of the ring (17) being rolled, where the centring arm (48, 49) can be positioned by motor power, e.g. by a piston-cylinder unit (52, 53) pressurised alternately by a pressure medium, preferably hydraulic, on either side, where the rotation signals produced by each of the centring rolls (54, 55) can be transmitted to the control and/or regulating device (38) of the motor drive units e.g. of the radial ring rolling mill (2) and/or the axial ring rolling mill (1), and regulate or control the speed.
- Process for operating an axial-radial ring rolling mill according to claim 1 or any of the claims 2 to 15, characterised in that the control and regulating device (38) always causes the axis of rotation of the axial ring rolling mill (1) and the axis of the tapered rollers to point to the centre of the growing ring (17), where, as the diameter of the ring increases, the axial rolling stand moves linearly towards the centre of the ring until the rolled ring (17) is located at the rearmost position of the tapered rollers (10).
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE202010014708U DE202010014708U1 (en) | 2010-10-25 | 2010-10-25 | Axial / radial ring rolling mill |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2444176A1 EP2444176A1 (en) | 2012-04-25 |
| EP2444176B1 true EP2444176B1 (en) | 2012-10-31 |
Family
ID=43495836
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP20110008391 Revoked EP2444176B1 (en) | 2010-10-25 | 2011-10-19 | Axial/radial ring rolling system and method of operating such an axial/radial ring rolling system |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2444176B1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE202010014708U1 (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2398208T3 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102014005332A1 (en) * | 2014-04-11 | 2015-10-15 | Sms Meer Gmbh | Forming machine, in particular ring rolling machine |
| US10065234B2 (en) | 2014-04-11 | 2018-09-04 | Sms Group Gmbh | Forming machine and method for control of a forming machine |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102011108113A1 (en) | 2011-07-21 | 2013-01-24 | Siempelkamp Maschinen- Und Anlagenbau Gmbh & Co. Kg | Roller for a ring rolling mill |
| CN103894524A (en) * | 2014-04-11 | 2014-07-02 | 安徽理工大学 | Fully-automatic ring piece forming machine |
| CN103962482A (en) * | 2014-04-14 | 2014-08-06 | 太原科技大学 | Rolling technology of large wind power flange |
| ES2773635T3 (en) * | 2014-08-08 | 2020-07-13 | Muraro S R L | Machine and method for forming ring elements, such as a rolling machine and a method for ring elements of circular rolling |
| GB201503825D0 (en) * | 2015-03-06 | 2015-04-22 | Cambridge Entpr Ltd | Ring rolling process and apparatus for ring rolling |
| EP3300814A1 (en) * | 2016-09-30 | 2018-04-04 | Forge Pat GmbH | Ring rolling mill with conformation rolls and process for controlling the position of a roll of such a rolling mill |
| DE102017008449A1 (en) * | 2017-09-08 | 2019-03-14 | Schuler Pressen Gmbh | Radial-axial ring rolling mill for rolling a ring |
| CN112792269B (en) * | 2021-01-14 | 2023-04-14 | 重庆大学 | Method for ensuring ring rigidity in rolling process of rectangular ring |
| CN114558964A (en) * | 2022-02-21 | 2022-05-31 | 中国重型机械研究院股份公司 | System and method for controlling axial conical roller position of radial-axial ring rolling mill |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE326925C (en) | 1920-10-05 | Martin Hosse | Tire rolling mill for rough and finish rolling of wheel tires | |
| DE305929C (en) | ||||
| US2268330A (en) | 1938-06-24 | 1941-12-30 | Motor Wheel Corp | Rim rolling machine |
| FR1009653A (en) | 1948-06-12 | 1952-06-03 | Process for manufacturing large-sized rings, in particular bicycle rims | |
| DE960264C (en) | 1952-11-13 | 1957-03-21 | Kronprinz Ag | Method and device for rolling out disc-shaped workpieces |
| DE1019635B (en) | 1956-08-08 | 1957-11-21 | Wagner & Co Werkzeugmaschinenf | Ring rolling mill |
| DE1752887C3 (en) * | 1968-07-31 | 1974-06-06 | J. Banning Ag, 4700 Hamm | Four-roll ring rolling mill |
| DE2222607A1 (en) * | 1972-05-09 | 1973-11-22 | Rheinstahl Ag | RING ROLLING MILL |
| DE2917369A1 (en) * | 1979-04-28 | 1980-11-27 | Thyssen Industrie | MULTI-SPIN RING ROLLING MACHINE |
| DE2923001A1 (en) * | 1979-06-07 | 1981-01-22 | Thyssen Industrie | RING ROLLING MACHINE WITH MANDREL ROLLER TURRETHEAD |
-
2010
- 2010-10-25 DE DE202010014708U patent/DE202010014708U1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2011
- 2011-10-19 ES ES11008391T patent/ES2398208T3/en active Active
- 2011-10-19 EP EP20110008391 patent/EP2444176B1/en not_active Revoked
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102014005332A1 (en) * | 2014-04-11 | 2015-10-15 | Sms Meer Gmbh | Forming machine, in particular ring rolling machine |
| EP2937158A1 (en) | 2014-04-11 | 2015-10-28 | SMS Meer GmbH | Forming machine, in particular ring milling machine |
| US10065234B2 (en) | 2014-04-11 | 2018-09-04 | Sms Group Gmbh | Forming machine and method for control of a forming machine |
| US10507502B2 (en) | 2014-04-11 | 2019-12-17 | Sms Group Gmbh | Forming machine, particularly ring-rolling machine |
| EP2937158B1 (en) * | 2014-04-11 | 2021-06-09 | SMS group GmbH | Ring rolling machine |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ES2398208T3 (en) | 2013-03-14 |
| EP2444176A1 (en) | 2012-04-25 |
| DE202010014708U1 (en) | 2011-01-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2444176B1 (en) | Axial/radial ring rolling system and method of operating such an axial/radial ring rolling system | |
| EP1648646B1 (en) | Device for cutting or welding tubular workpieces or the like | |
| EP3429771A1 (en) | Device and method for descaling a workpiece | |
| DE112017006957B4 (en) | Arrangement and welding plant for longitudinally welded pipes | |
| WO2011038724A2 (en) | Cutting tool, in particular paring tool, drill head, solid drill head or boring head, and cutting machine and method | |
| EP1782896B1 (en) | Method for forming a workpiece and rolling machine | |
| EP2414134B1 (en) | Device and method for water-jet cutting | |
| DE212008000083U1 (en) | Büchsenaufweitvorrichtung | |
| DE3931747C2 (en) | Machine for machining a wheel set | |
| EP3807023A1 (en) | Cold rolling machine and method for producing a profile on a workpiece | |
| DE1402965A1 (en) | Removable device for turning, hole enlarging, milling, drilling and the like. of workpieces of larger dimensions | |
| DE2731494A1 (en) | ROLLER STAND | |
| EP4025359B1 (en) | Cross-rolling unit and method for setting the roll pass of a cross-rolling unit | |
| AT410977B (en) | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR DETERMINING THE CURVING OF LONG GOODS | |
| DE10237375A1 (en) | Pipe geometrical measurement arrangement comprises a rotating drive and contactless measurement system with which the pipe can be rotated around its own axis, while the measurement system is moved along the axis | |
| DE2021820B2 (en) | UNDERGROUND WHEEL SET LATHE | |
| EP2397244B1 (en) | Charging device for a bush widening device for perforated socket blanks made out of steel, for example, and method of forging perforated socket blanks | |
| DE102008028348B4 (en) | Device for guiding rotating mandrel bars and hollow blocks in the area of cross rolling mills | |
| DE4026898C1 (en) | ||
| DE102005018549B3 (en) | Production method for metallic guide element involves implementation of milling operation by position-controlled mill-cutting body with cutting disk of large diameter and flow of material inside high-speed milling cutter system | |
| DE10303215B4 (en) | Method and honing machine for honing workpieces | |
| DE2227388C3 (en) | Device for processing pipe ends | |
| EP3784423B1 (en) | Cross-rolling mill with hydraulic roller actuator | |
| DE2700175C3 (en) | Device to compensate for displacements of the free end of a support sleeve | |
| DE2303268A1 (en) | DEVICE FOR HOT ROLLING RING BODIES |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20111102 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: B21H 1/06 20060101AFI20120614BHEP |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 581698 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20121115 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502011000171 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20121227 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2398208 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20130314 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: VDEP Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130228 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130228 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130201 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130131 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: SMS MEER GMBH Effective date: 20130729 |
|
| PLAX | Notice of opposition and request to file observation + time limit sent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS2 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R026 Ref document number: 502011000171 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20130729 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| PLBB | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition received |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS3 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: C. GROENE CONSULTING, UNIP LDA Effective date: 20131031 |
|
| RAP2 | Party data changed (patent owner data changed or rights of a patent transferred) |
Owner name: SCHULER SMG GMBH & CO. KG |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| RAP2 | Party data changed (patent owner data changed or rights of a patent transferred) |
Owner name: SCHULER PRESSEN GMBH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20131031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20131019 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20141027 Year of fee payment: 4 Ref country code: TR Payment date: 20141013 Year of fee payment: 4 Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20141024 Year of fee payment: 4 Ref country code: CZ Payment date: 20141009 Year of fee payment: 4 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20141021 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20141031 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R103 Ref document number: 502011000171 Country of ref document: DE Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R064 Ref document number: 502011000171 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| RDAF | Communication despatched that patent is revoked |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNREV1 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141031 Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20111019 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20131019 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| RDAG | Patent revoked |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009271 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT REVOKED |
|
| 27W | Patent revoked |
Effective date: 20150428 |
|
| GBPR | Gb: patent revoked under art. 102 of the ep convention designating the uk as contracting state |
Effective date: 20150428 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MA03 Ref document number: 581698 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20150428 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |